Page 1

Intel® Express 530T
Intel
®
Express 530T Switch User Guide
Switch
User Guide
Page 2

Year 2000 Capable
An Intel® product, when used in accordance with its associated documentation, is "Year 2000 Capable" when, upon
installation, it accurately stores, displays, processes, provides, and/or receives date data from, into, and between 1999
and 2000, and the twentieth and twenty-first centuries, including leap year calculations, provided that all other
technology used in combination with said product properly exchanges date data with it. Intel makes no representation
about individual components within the product should they be used independently from the product as a whole.
Copyright © 2000, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
Intel Corporation, 5200 NE Elam Young Parkway, Hillsboro OR 97124-6497
Intel Corporation assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions in this manual. Nor does Intel make any commitment to update the
information contained herein.
* Other product and corporate names may be trademarks of other companies and are used only for explanation and
to the owners’ benefit, without intent to infringe.
First Edition September 2000 A30581-001
Page 3

Contents
1.0 Setting up the Intel® Express 530T Switch 1
Management .............................................................................. 1
Switch Features ......................................................................... 2
Status LED ................................................................................3
Port LEDs ........................ ........................................................ .3
Modules .................................................................................... 4
Installing a Module ................................................................... 5
Module LEDs ............................................................................ 6
Configuring Modules ................................................................ 6
Media Requirements ............................................... .................. 7
Straight-through vs. Crossover Cable .......................................8
Stacking .................................................................................... 9
2.0 Using the Intel® Express 530T Switch 11
What is a Switch? ..................................................................... 12
Sample Configurations ............................................................. 13
Flow Control ............................................................................. 14
Spanning Tree Protocol ............................................................ 14
Tagged Frames .............................................................. ............ 15
Priority ...................................................................................... 15
Link Aggregation ......................................................................16
Virtual LANs ............................................................................ 17
GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) .......................... 2 0
Internet Group Multicast Protocol ............................................20
3.0 Using Intel® Device View 2.1 21
Installing Intel Device View ..................................................... 22
Starting Intel Device View .......................................................23
Installing a New Device ............................................................ 24
Using the Device Tree .............................................................. 25
Managing a Switch .................................................................... 27
Viewing RMON Information .................................................... 28
i
Page 4

CONTENTS Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
4.0 Using the Web Device Manager 29
Accessing the Web Device Manager ........................................ 30
Navigating the Web Device Manager ....................................... 31
Using Management Screens ...................................................... 32
Configuring the Switch’s IP Settings ........................................ 33
Configuring a Port .................................................................... 34
Managing User Accounts ........................................ .................. 35
Configuring VLANs ................................................................. 37
Link Aggregation ......................................................................42
Static MAC Addresses ................................. ...... ....................... 43
Configuring Community Strings and Trap Receivers ..............44
Monitoring Switch Activity ...................................................... 45
Viewing/Changing Switch Information .................................... 46
Updating Switch Firmware ....................................................... 47
Saving Configuration Changes and Logging Out ..................... 49
5.0 Using Local Management 51
Accessing Management ............................................................ 51
Logon Screen ............................................................................ 52
Navigation ................................................................................. 53
Main Menu (Top Screen) .................................................... ..... .54
Configure Stack ................................................. ....................... 55
IP Settings ................................................................................. 56
Port Settings ........................................... ................................... 57
Configure Optional Module ................... ...... ............................. 58
Stack Settings ............................................................................ 59
View Stack Information ............................................................ 60
Configure Advanced Switch Settings ....................................... 61
Configure Spanning Tree Protocol ........................................... 62
Configure Spanning Tree for Ports ...........................................64
Forwarding and Filtering .......................................................... 65
Configure IGMP Snooping .......................... ...... ....................... 66
Configure Static MAC Addresses ....................................... ...... 67
Configure Port Security ..................................... ..... .................. 68
ii
Page 5

CONTENTS Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
Configure MAC Address Filter Table .......................................69
Configure Ethernet Multicast Filtering ......................................70
Ethernet Multicast Filtering (Ports) ...........................................71
Port Mirroring ...................... ...... ..... ...........................................72
Link Aggregation .......................................................................73
Broadcast Storm Control ...........................................................74
Configure Management .......................................................... ...75
Community Strings and Trap Receivers ....................................76
User Accounts ............................................................................77
How to Manage User Accounts .................................................78
Update Firmware and Configuration Files ................................80
Reset and Console Options ........................................................81
Configure VLAN Operation Mode ......................................... ...82
Configure Port-based VLANs ...................................................83
Add a Port-based VLAN ...........................................................84
Edit/Delete a Port-based VLAN ................................................85
Edit VLAN Membership (Port-based) ........................ ..............86
Configure IEEE 802.1Q VLAN ................................................87
Add an IEEE 802.1Q VLAN (Configure Port Membership) ....88
Add an IEEE 802.1Q VLAN (Configure Port Tagging) ...........89
How to Configure 802.1Q VLAN ............................................. 90
Edit/Delete an IEEE 802.1Q VLAN........................................... 92
Edit an IEEE 802.1Q VLAN (Configure Port Membership) ....93
Edit an IEEE 802.1Q VLAN (Configure Port Tagging) ..........94
Configure VLAN ID for Untagged Traffic ...............................95
GVRP and Ingress Filtering Settings .........................................96
Monitoring (Network Statistics) ................................................97
Switch Stack Overview .............................................................98
Port Traffic Statistics .................................. ..... ..........................99
Port Error Statistics ........................................................... ...... ...101
Packet Analysis ..........................................................................103
IGMP Snooping Status ..............................................................104
Browse Address Table ...............................................................105
VLAN and GVRP Status ...........................................................107
Tools ..........................................................................................108
iii
Page 6

CONTENTS Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
Switch Event Log ...................................................................... 109
Ping a Device .......................................................... ...... ...... ...... 110
Upload Configuration Image File ............................................. 111
Appendix: Technical Info 113
About Configuration Files ........................................................113
Sample Configuration File ........................................................ 114
BOOT Menu .......................................... ...... ............................. 116
List of Factory Defaults ............................................................ 117
Troubleshooting/FAQs ............................................................. 118
Locating MIB files .................................................................... 120
Regulatory Information .............................................................121
Warnings ................................................................................... 121
Limited Hardware Warranty ..................................................... 124
Limited Hardware Warranty (Europe only) .............................. 125
Limitaition de garantie du materiel (Europe).....................126
Garanzia limitata sull’hardware (valida solo in Europa).... 127
Beschrankte Hardwaregarantie (Nur fur Europa).............. 128
Garantia limitada de hardware (solo para Europa)............. 129
Index 131
Intel Customer Support Last Page
iv
Page 7
Setting up the Intel
®
1
Express 530T Switch
Overview
This guide provides information on configuring and managing the Intel
Express 530T Switch and is organized into these chapters:
• Chapter 1 - Information on the switch hardware and optional
modules
• Chapter 2 - Information on using the switch in a LAN and advanced
features such as link aggregation and Virtual LANs (VLANs)
• Chapter 3 - How to use Intel Device View
• Chapter 4 - How to use Web Device Manager
• Chapter 5 - Overview of Local Management
Management
Through the switch’s built-in management you can configure the device
and monitor network health. There are several methods for managing this
switch; you can use one method or any combination.
®
• SNMP management applications such as Intel
LANDesk
Intel products and show a graphical representation of the device
(with the use of the proper MIB).
• Onboard management allows control ov er the de vice without
using an SNMP application. The Web Device Manager provides a
graphical interface; Local Management is a menu-driven interface.
• Other SNMP-compliant applications can manage 530T switches
if you compile the switch’s MIB files into that application.
® Network Manager, or HP OpenView* are tailored for
Device View,
®
Page 8
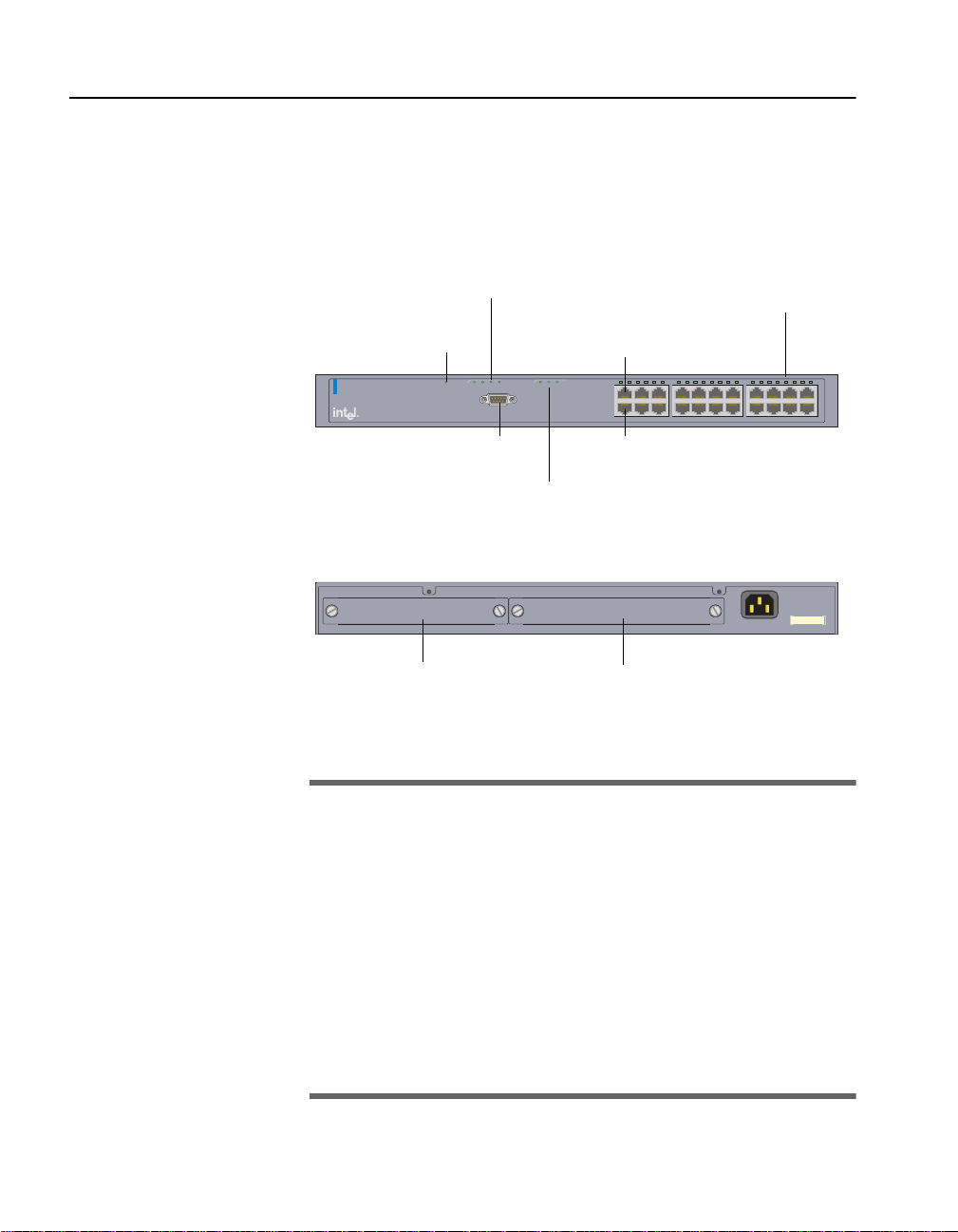
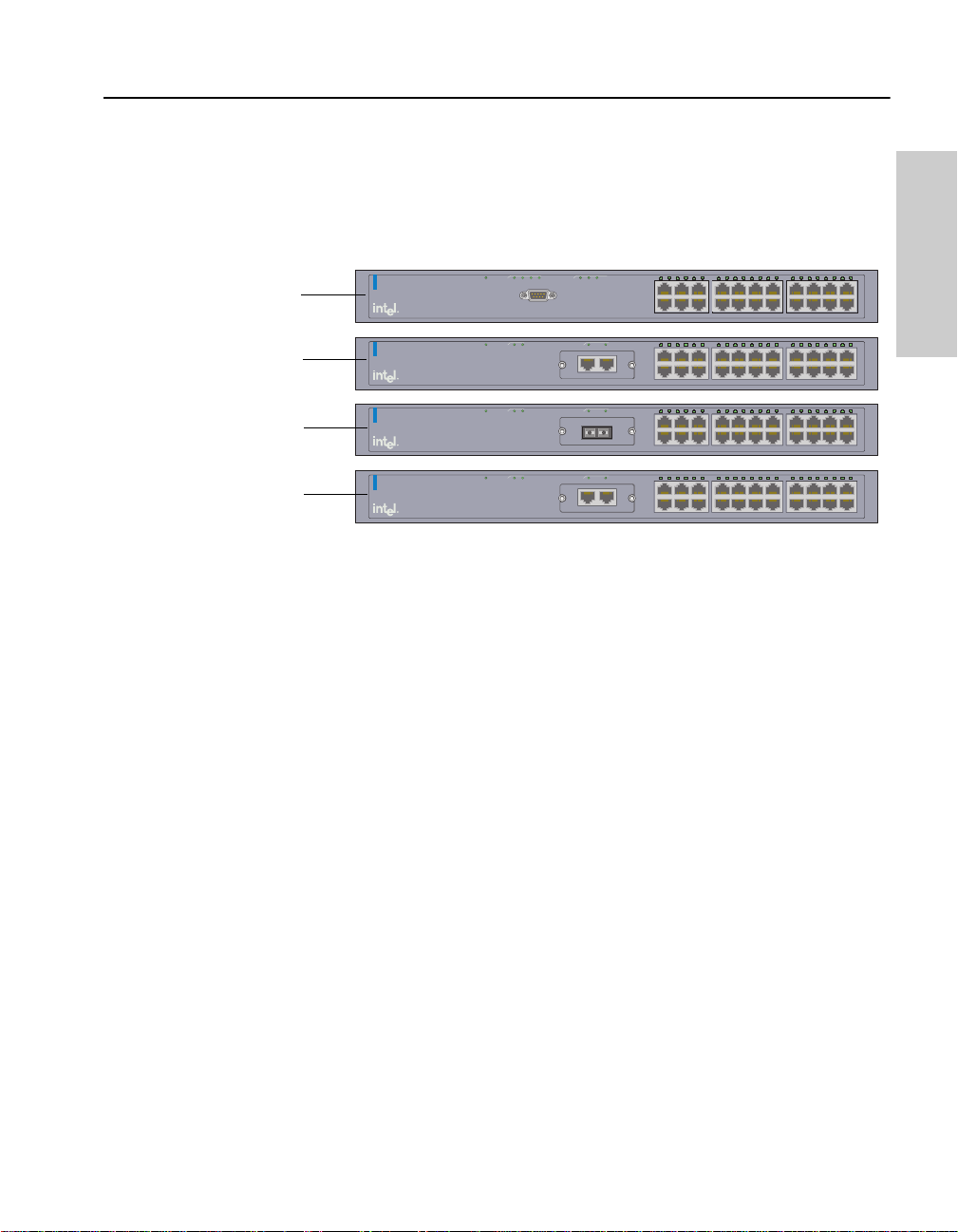
C H A P T E R 1 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
Switch Features
These are the major features of the 530T switch.
Stack Matrix Module LEDs
(Status, SW1, SW2, SW3)
Port Status LEDs
Switch status
Intel® Express 530T Switch
Local management
Matrix
Switch
Module
Status
Management
Status Sw1 Sw2 Sw3
Local
(EIA 232)
Module A
(Gigabit)
Console: 9600-8-N-1
FlowCtrl=None
StatusPort 1
Link/
Act
Port 2
Link/
Act
Port 1
246 8
135 79
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
123456789101112131415161718192021
Port 2
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
13 15 17 19 21
11
22
Module A (Gigabit) LEDs
(Status, Port 1, Port 2)
AC Input
100-240 VAC
50Hz-60Hz
1.5A max
009027390008
MAC Address
Module A
Matrix ModuleModule A (Gigabit)
Matrix Module
• Auto-negotiates speed, duplex, and flow control—10Mbps or
100Mbps per port.
• Half- and full-duplex flo w cont ro l.
• Two-port expansion slot fo r t he optional 100 0Base-SX, 1000BaseLX, or 100/1000Base-T module.
• Can be stacked with up to three 535T (member) switches.
• Port settings can be configured manually through management.
• Access menu-driven Local Management through the serial port or a
Telnet session.
• Access the graphic, Web-based, Web Device Manager through a
Web browser.
2
Page 9

C H A P T E R 1 Seting up the Intel® Express 530T Switch
t
c
NOTE
When the switch is first
powered on the Status LED is
red for a couple of seconds
before the diagnostic mode
starts, then it turns orange.
1
Status LED
The Status LED is located to the left of the Matrix Module LEDs.
Status LED
l® Express 530T Switch
Switch
Status
Matrix
Module
Local
Management
(EIA 232)
Status Sw1 Sw2 Sw3
Module A
(Gigabit)
Status Port 1
Console: 9600-8-N-1
FlowCtrl=None
LED Status Meaning
Status Orange Switch is performing diagnosti cs.
Green Diagnostics have passed, the switch is ready.
Red Diagnostics have failed.
Port LEDs
The LEDs above each port indicate port status and port activity.
Express 530T Setup
Por
Lin
Link/
A
Act
s Port 1
-1
Port 1 LED
Port 2
Link/
Link/
Act
Act
Port 1
Link\Activity
Port 2
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
Port 2 LED
246 8
135 79
12345
78910111213
6
LED Status Meaning
Left (Upper port) Solid green Device linked.
Blinking green Receiving traffic on that port.
Off No link detec ted.
Right (Bottom port) Solid green Device linked.
Blinking green Receiving traffic on that port.
Off No link detec ted.
10 12
11
13
3
Page 10

C H A P T E R 1 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
About the 530T Switch
General
• The 530T switch is capable of auto-negotiating port speed and can
operate at 10Mbps or 100Mbps per port. The switch matches t he
highest possible speed of an attached device.
• The 530T switch is capable of auto-negotiating port duplex and can
operate at half- or full-duplex.
Cabling
• Use Category 5 or greater unshielded twisted-pair (CAT 5 UTP)
cable when connecting 100Mbps devices to the switch.
• Use Category 3, 4, or 5 unshielded twisted-pair (CAT 3, 4, or 5
UTP) cable when connecting 10Mbps devices to the switch.
• Limit the cable length between devices to 100 meters (328 feet).
• Use a straight-through cable to connect the switch to a server or
workstation. For more information on cabling, see pages 7 and 8.
Modules
The 530T switch accepts a Stack Matrix Module to connect with up to
three member switches and an uplink module (Module A) to provide an
additional two Gigabit ports.
The four modules supported by the 530T are:
• Stack Matrix Module (Connects to a maximum of three 535T
[member] switches.) (ES530MSM)
• 1000Base-SX (ES530MSX)
• 1000Base-LX (ES530MLX)
• 100/1000Base-T (ES530MT)
4
Page 11
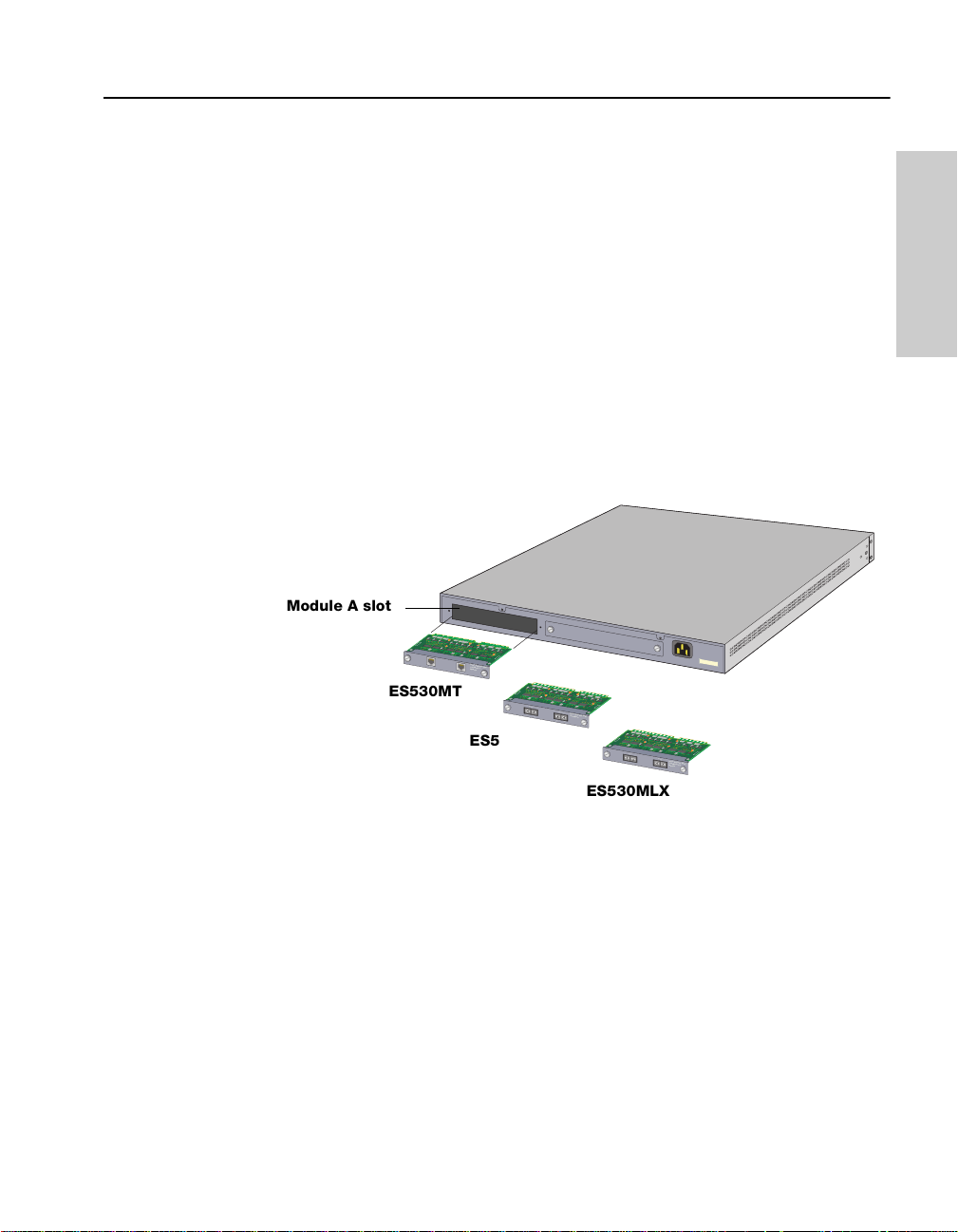
C H A P T E R 1 Seting up the Intel® Express 530T Switch
NOTE
Install the Stac k Matrix Module
in the slot labeled Matrix
Module.
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
Installing a Module
You can install only gigabit modules in the Module A slot located at the
back of the 530T switch. Use the LEDs on the fro nt of the switch to check
the module’s status.
Install the module in the switch
1 Un plug the power cord from the switch. Remove the panel from the
expansion slot labeled Module A.
2 Align the module with the card guides inside the switch and slide the
module into the slot. Press firmly to connect the module and secure
it with the retaining screws.
3 Plug in the power cord.
Module A slot
A
C
In
p
u
t
1
0
0
2
4
0
V
A
C
5
0
H
z
6
0
H
z
1
.5
A
m
a
x
009027
390008
M
A
C
A
d
d
r
e
s
s
P
o
r
t
2
In
®
t
e
l
E
x
p
r
e
s
s
1
5
0
3
0
0
0
T
B
a
s
e
L
X
M
o
d
u
l
e
T
x
R
x
P
o
r
t
1
ES530MT
M
o
d
u
l
e
A
(G
ig
a
b
it)
I
n
®
t
e
l
E
x
p
r
e
s
s
1
5
0
3
0
0
0
T
B
a
s
e
T
M
o
d
u
l
e
P
o
r
t
2
ES530MSX
M
a
t
rix
M
o
d
u
le
P
o
r
t
1
P
o
r
t
2
In
®
t
e
l
E
x
T
p
x
r
e
s
s
1
5
0
3
R
0
0
x
0
T
B
a
s
e
S
X
M
o
d
u
l
e
T
x
R
x
P
o
r
t
1
T
x
R
x
ES530MLX
Express 530T Setup
5
Page 12

C H A P T E R 1 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
NOTE
The 1000SX and 1000LX
modules connect at only
1000Mbps and full-duplex.
Module LEDs
Stack Matrix Module LEDs
Matrix
Module
itch
Switch
Status
Status Sw1 Sw2 Sw3
Local
Management
Module A LEDs
Module A
(Gigabit)
Status Port 1
Link/
Console: 9600-8-N-1
Act
Port 2
Link/
Act
Stack Matrix Module LEDs
LED Status Meaning
Status Off No module present.
Solid green Module present.
SW1, SW2, SW3 Off No link detected.
Solid green Switch connected to stack.
Module A (Gigabit) LEDs
LED Status Meaning
Status Off No module present.
Solid green Module present.
Ports 1, 2 Off No link detected.
2
1
6
Solid green Device linked.
Blinking green Link with traffic.
Configuring Modules
Normally you do not need to make any changes to the optional modules
because they are designed to configure them selves automatically for the
attached device. However, you might need to configure the modules in
order to communicate with older devices. You can use the Local
Management or Web Device Manager to configure the 1000SX,
1000LX, or 1000T modules.
Page 13

C H A P T E R 1 Seting up the Intel® Express 530T Switch
NOTE
100 meters = 328 feet
200 meters = 656 feet
500 meters = 1640 feet
2 km = 2000 meters = 6560 feet
5 km = 5000 meters = 16400 feet
Media Requirements
Incorrect cabling is often the cause of network performance problems.
Read the next two pages to make sure your cabling is correct.
10Base-T
The 10Base-T Ethernet specification allows you to use CAT 3, CAT 4,
or CAT 5 UTP cabling. The limit is 100 meters between any two devices.
100Base-TX
The 100Base-TX Fast Ethernet specification requires that you use CAT
5 UTP cabling to operate at 100Mbps. If you use lower grade cabling
(CAT 3 or CAT 4) you may get a connection, but also experience data
loss or slow performance. You ’re limited to 100 meters between any two
devices.
1000Base-T
The 1000Base-T Gigabit specification requires that y ou use CAT 5 UTP
cabling to operate at 1000Mbps. If you use a lower grade cabling you will
experience either no connection or extreme data loss. The maximum
distance between any two devices is 100 meters.
1000Base-SX/1000Base-LX
Express 530T Setup
The optional 1000Base-SX and -LX Gigabit Modules provide a highspeed connection to another device up to 5 km away. The maximum
distance depends on the type of cable used. Refer to the following table
for a list of cable types and maximum distances. Use cables with an SCtype fiber optic connector.
Selecting the right cable
Media Type Cabling Used Maximum Distance
1000/100Base-T (Gigabit)
Module
1000Base-SX
(Gigabit) Module
1000Base-LX
(Gigabit) Module
Category 5 (CAT 5)
unshielded twisted pair
cable
50/125
62.4/125
50/125
62.4/125
9/125
µm multimode
µm multimode
µm multimode
µm multimode
µm singlemode
100m
550m
260m
550m
550m
5,000m
7
Page 14
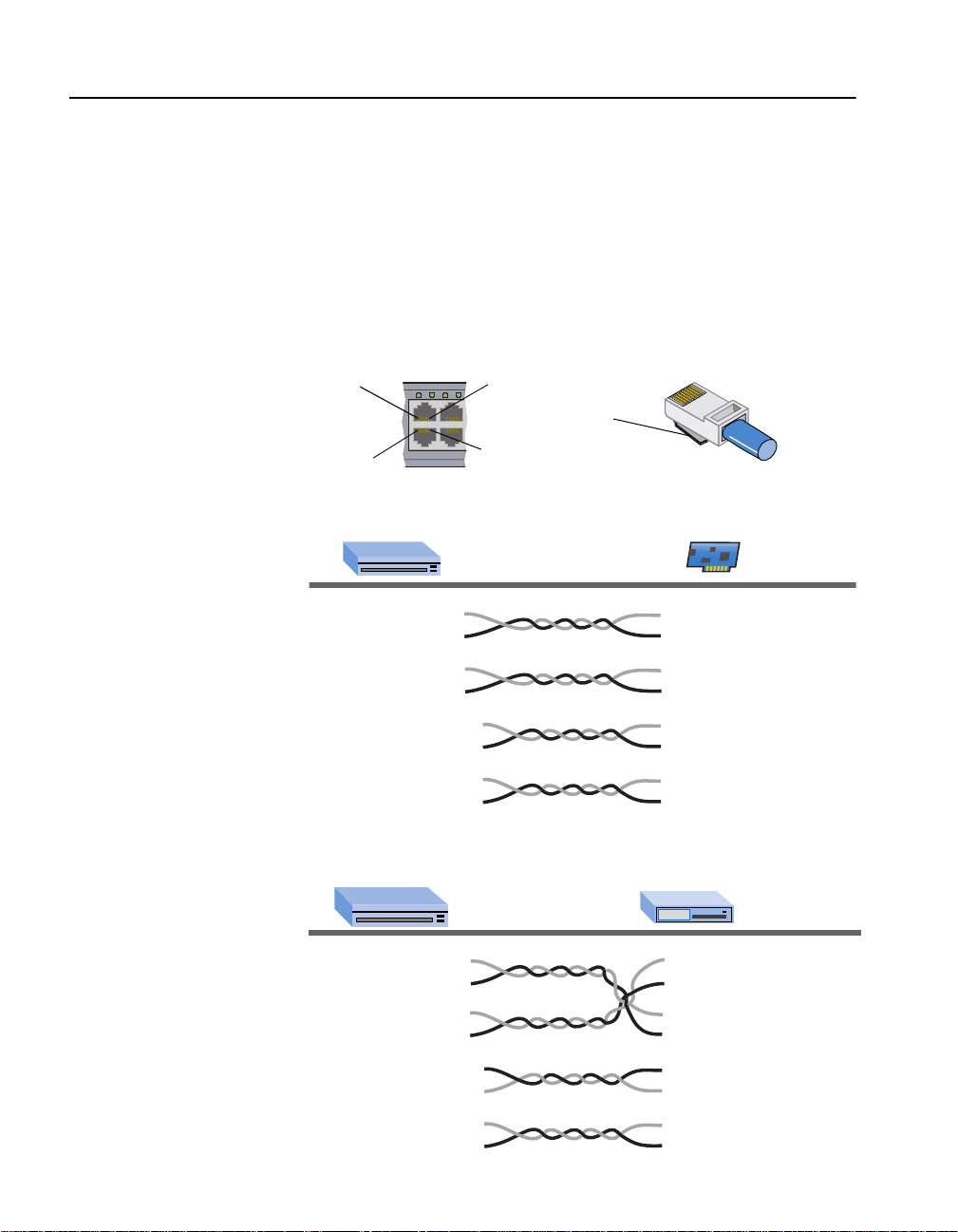
C H A P T E R 1 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
13
24
123
4
NOTE
Pairs 4/5 and 7/8 are RX/TX
when operating at 1000Mbps.
Straight-through vs. Crossover
Cable
Switch ports are wired MDI-X, so use a straight-through cable to connect
to a workstation or server (network adapter cards are wired MDI). To
connect to another MDI-X port, use a crossover cable. Here are the pin
arrangements for the switch’s Ethernet port and the typical RJ-45
connector.
Ethernet port RJ-45 connector
Pin 8
Pin 1
Clip
8
1
Pin 1
Pin 8
Straight-through UTP cable (for 100Base-TX)
Switch (MDI-X) Adapter (MDI)
1 (RX+) 1 (TX+)
2 (RX-) 2 (TX-)
3 (TX+) 3 (RX+)
6 (TX-) 6 (RX-)
4 Not used 4 Not used
5 Not used 5 Not used
7 Not used 7 Not used
8 Not used 8 Not used
Crossover UTP cable (for 100Base-TX)
Switch (MDI-X) Hub (MDI-X)
10/100
1 (RX+) 1 (RX+)
2 (RX-) 2 (RX-)
8
3 (TX+) 3 (TX+)
6 (TX-) 6 (TX-)
4 Not used 4 Not used
5 Not used 5 Not used
7 Not used 7 Not used
8 Not used 8 Not used
Page 15
C H A P T E R 1 Seting up the Intel® Express 530T Switch
Control (530T)
Member 2 (535T)
Member 3 (535T)
Member 4 (535T)
Stacking
The 530T switch can be stacked with up to three 535T switches. Stacking
allows for a single point of management for all switches.
Matrix
Module
Intel® Express 530T Switch
Intel® Express 535T Switch
Intel® Express 535T Switch
Intel® Express 535T Switch
Switch
Status
Management
Stacking
Module
Switch
Status
Stacking
Module
Switch
Status
Stacking
Module
Switch
Status
About a stack
• There can be only one 530T switch in a stack.
• The 530T switch requires the installation of a Stack Matrix Module
to stack it with a 535T . (Only one Stack Matrix Module is needed for
the entire stack.)
• The 530T can be stacked only with 535T switches.
• You can stack up to three 535T switches with a 530T.
• In a stack, the 530T is the control switch and the 535Ts are the
member switches.
• The member switches are all managed through the control switch’s
management interface.
• There is only one IP address for the entire stack of switches (the
control switch’s IP address).
• There can be only one instance of Spanning Tree, regardless of the
number of switches in the stack.
• Ports from any switch can be members of any VLAN.
• For link aggregation, the anchor ports are 1, 7, 15 for both the
control and member switches. You can also link aggregate the
module ports on the control switch (530T).
• You can only link aggregate ports on the same switch.
Local
(EIA 232)
Status Sw1 Sw2 Sw3
Status Link
Status Link
Status Link
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
Module A
(Gigabit)
Console: 9600-8-N-1
FlowCtrl=None
Module A
Module A
Module A
StatusPort 1
Link/
Act
Port 1 Port 2
10/100Base-T Module
Port 1 Port 2
Port 1 Port 2
100Base-FX - SC Module
Tx Rx
Port 1 Port 2
10/100Base-T Module
Port 1 Port 2
246 8
Port 2
Link/
Act
Module A
Port 1
Module A
Module A
135 79
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
123456789101112131415161718192021
246 8
135 79
123456789101112131415161718192021
246 8
135 79
123456789101112131415161718192021
246 8
135 79
123456789101112131415161718192021
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
13 15 17 19 21
11
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
13 15 17 19 21
11
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
13 15 17 19 21
11
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
13 15 17 19 21
11
22
22
22
22
Express 530T Setup
9
Page 16

C H A P T E R 1 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
NOTE
When setting up a stack, stack
the 535T switches in the order in
which they are connected to the
Matrix Module.
The 535T connected to the
Switch 1 port of the Matrix
Module would be the switch
directly under the control switch,
the 535T connected to the Switch
2 port would be underneath that,
etc.
This makes it easier to determine
which switch is which when
managing them.
Assemble a stack
To stack a 530T with 535Ts, you need to purchase a Stack Matrix
Module.
1 Insert the Stack Matrix Module into the slot in the back of the 530T,
labeled Matrix Module, and tighten the screws.
Stack Matrix Module
Control switch
Member 2 (connected
to the Switch 1 port)
Member 3 (connected
to the Switch 2 port)
Member 4 (connected
to the Switch 3 port)
AC Input
100-240 VAC
Intel® Express 530T Matrix Module
Switch 1 Switch 2 Switch 3
Matrix ModuleModule A (Gigabit)
Connect to Matrix Module
Stack Interface Module
Connect to Matrix Module
Stack Interface Module
Connect to Matrix Module
Stack Interface Module
50Hz-60Hz
1.5A max
AC Input
100-240 VAC
50Hz-60Hz
1.5A max
AC Input
100-240 VAC
50Hz-60Hz
1.5A max
AC Input
100-240 VAC
50Hz-60Hz
1.5A max
009027390008
MAC Address
Stack Interface Module
2 Run a cable from the slot in the back of the 535T, labeled Stack
Interface Module, to the control switch’s Stack Matrix Module,
where it reads “Switch 1.” This connection makes this 535T switch
Member 2 in the stack.
3 Rep eat step 2 until you have added all member switches (535Ts) to
the stack. You can add a total of three member switches.
4 Power on the control switch.
Which switch is which in a stack
In a stack of switches, the 530T is the control switch and the 535Ts are
member switches.
The switch that you connect to the port labeled Switch 1 in the 530T’s
Stack Matrix Module is referred to in the Web Device Manager and
Local Management as Member 2. The switch connected to the port
labeled Switch 2, is Member 3. And the switch connected to the port
labeled Switch 3, is Member 4.
10
Page 17

Using the Intel®
2
Express 530T Switch
Overview
This section provides an overview for using the Intel® Express 530T
Switch within a network. The chapter covers the basic differences
between a switch and hub, basic switching features, such as flow control
and Spanning Tree, and a discuss ion of the more advan ced features such
as link aggregation and the types of VLANs available on the switch.
If you are already familiar with switching technology you can skip ahead
to a particular section within the chapter. Following is a basic overview
of the chapter and the pages where you can find a particular topic.
• Sample Configurations page 13
• Flow Control page 14
• Spanning Tree Protocol page 14
• Tagged Frames page 15
• Priority page 15
• Link Aggregation page 16
• VLANs page 17
• GVRP page 20
• Internet Group Multicast Protocol page 20
Page 18
C H A P T E R 2 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
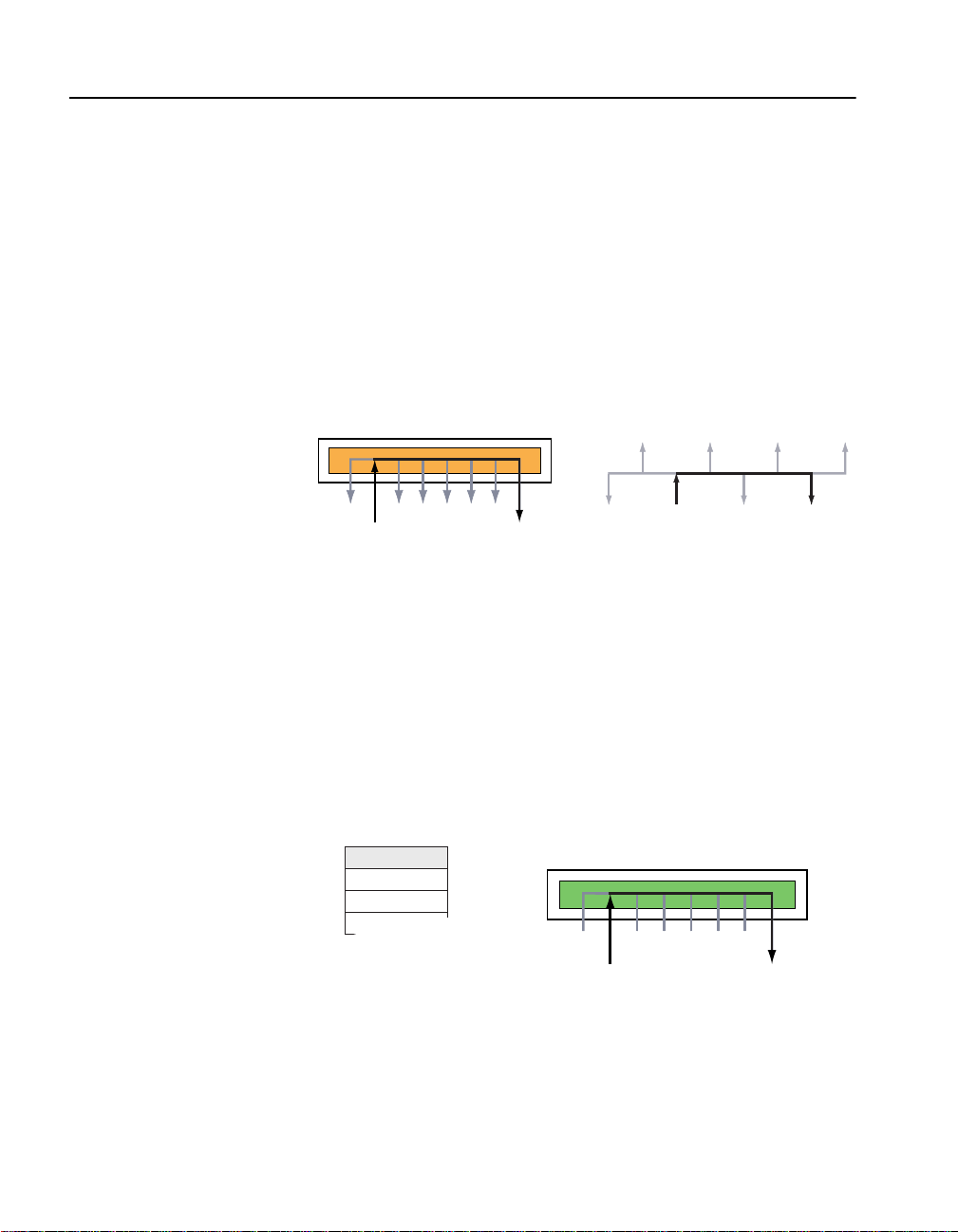
What is a Switch?
A switch segments traffic, providing each port its own collision domain.
This is different than a hub where all ports belong to the same collision
domain.
Segments and hubs
Hubs combine multiple wires so all attached devices behave as though
they are on the same wire. Since the devices share the same segment, data
sent by one device is retransmitted to all devices on the same hub. This
is equivalent to having all devices connected in a bus topology as
illustrated below.
Client A sends
signal to Client B
Signal sent to all ports
Client B
receives signal
Client A Client B
The disadvantage is all devices must share the total available bandwidth.
The more devices that are attached to the hub results in less bandwidth
for each user. Also, network performance suffers since all devices
receive traffic and collisions from other users because the hub
retransmits data across all ports.
Switches
Switches send traffic only to specific ports, rather than transmit data
across all ports. This means that each device attached to the switch
receives fewer collisions and the entire bandwidth is available to the
device.
MAC Address Port
006011FB34DB 2
00A027D36FAA 8
The signal is not
Client A sends
signal to Client B
The switch maintains a table that associates a device’s MAC address to
a port on the switch. When Client A communicates with Client B, the
switch looks in the table to determine which port Client B is attached to
and then forwards the traffic to that port. If a device sends traffic to an
address that is not in the table (or sends broadcast or multicast traffic) the
switch sends the traffic out to all ports on the switch. When the switch
receives a response it updates the table with the new address.
sent to all ports
Client B
receives signal
12
Page 19
C H A P T E R 2 Using the Intel® Express 530T Switch
Module A (Gigabit)
Tx Rx Tx Rx
Port 1 Port 2
Intel® Express 530T
1000Base-SX
Module
Module A (Gigabit)
Port 1 Port 2
Intel® Express 530T
1000Base-T
Module
Module A (Gigabit)
Tx Rx Tx Rx
Port 1 Port 2
Intel® Express 530T
1000Base-LX
Module
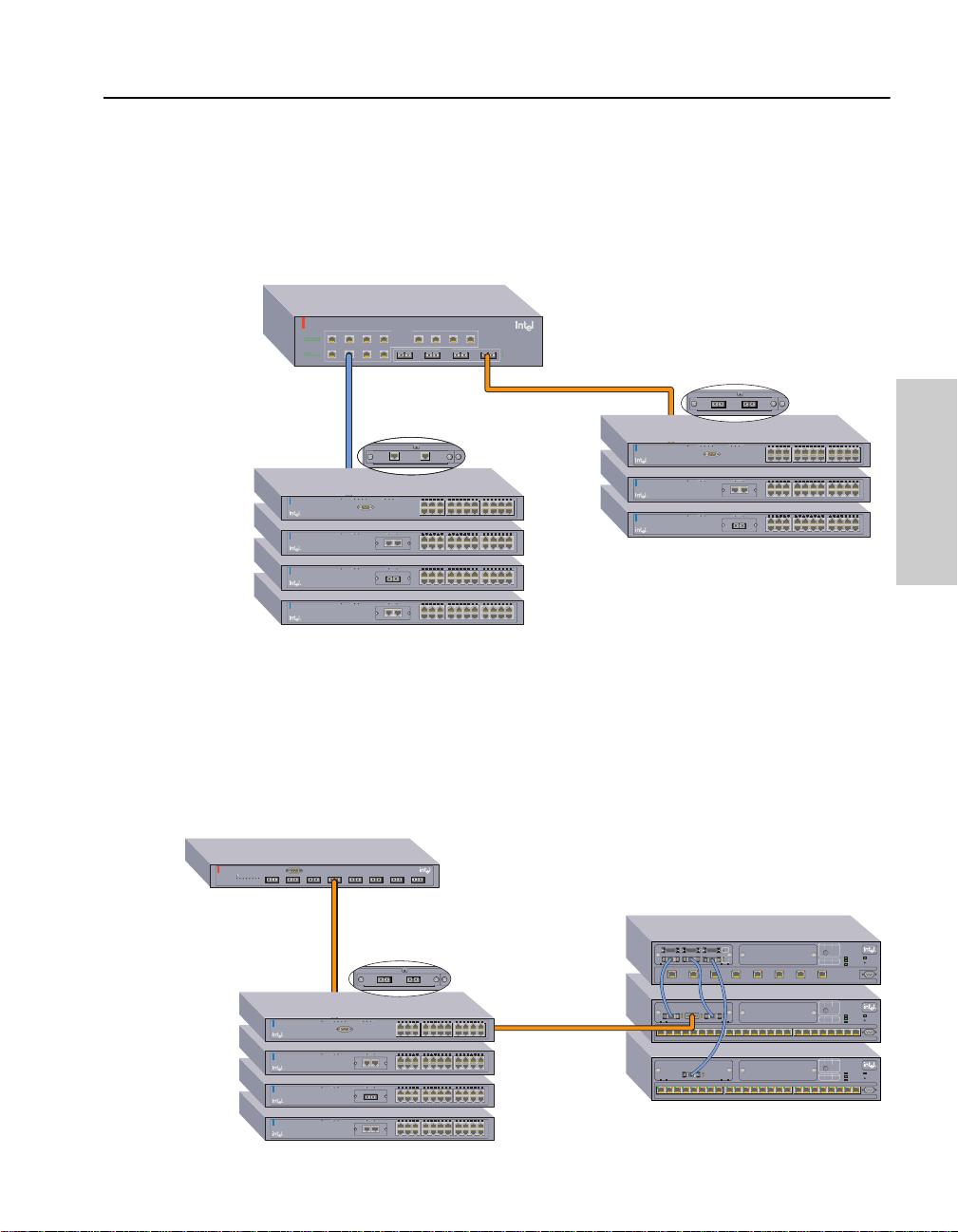
Sample Configurations
The following examples illustrate how the 530T switch can be used in a
network.
®
Intel
NetStructure™ 480T Switch
™
Intel® NetStructure
480T Routing Switch
1234 5678
Speed
12345678
Link\Act
Speed : Solid Green = 1000Mbps
Off = 100Mbps
Link\Activity : Solid Green = Link
9101112
Blinking Orange = Activity
Blinking Green = Disabled
Speed
910111213141516
Link\Act
100BASE-TX/1000BASE-T
1000BASE-X
13 14 15 16
Tx Rx Tx Rx Tx Rx Tx Rx
Power Supply 1
Power Supply 2
Management
Intel
Stack of 530T and
535T switches
1000T
connection
Matrix
Switch
StatusSw1 Sw2 Sw3
Module
Status
Intel® Express 530T Switch
Local
Management
(EIA 232)
Stacking
Switch
StatusLink
Module
Status
Intel® Express 535T Switch
Intel® Express 535T Switch
Intel® Express 535T Switch
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
Stacking
Switch
StatusLink
Module
Status
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
Stacking
Switch
StatusLink
Module
Status
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
Stack of 530T and 535T switches
The example below shows how a stack of 530/535 switches connects
with a stack of 550/510 switches (they cannot be in the same stack). This
example also demonstrates the 530T’s gigabit uplink by connecting it to
a 470F switch.
®
NetStructure™ 470F Switch
Local
Intel® NetStructure™ 470F Switch
Status
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
12345678
Activity = Blinking Green
Console: 9600-8-N-1
Management
Flow Ctrl=None
(EIA 232)
12345678
Link\Act
TX RX TX RX TX RX TX RX TX RX TX RX TX RX TX RX
1000SX
connection
Matrix
Module A
Switch
StatusSw1 Sw2 Sw3
StatusPort 1
Module
(Gigabit)
Status
Intel® Express 530T Switch
Local
Console: 9600-8-N-1
Management
FlowCtrl=None
(EIA 232)
Stacking
Module A
Switch
StatusLink
Module
Status
Intel® Express 535T Switch
Intel® Express 535T Switch
Intel® Express 535T Switch
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
Stacking
Module A
Switch
StatusLink
Module
Status
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
Stacking
Module A
Switch
StatusLink
Module
Status
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
Module A
StatusPort 1
Port 2
(Gigabit)
Link/
Link/
Act
Act
Console: 9600-8-N-1
FlowCtrl=None
Module A
Port 1 Port 2
10/100Base-T Module
Port 1 Port 2
Module A
Module A
Port 1 Port 2
100Base-FX - SC Module
Port 1
Tx Rx
Module A
Module A
Port 1 Port 2
10/100Base-T Module
Port 1 Port 2
Module A
Port 2
Link/
Link/
Act
Act
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
Port 1 Port 2
10/100Base-T Module
Port 1 Port 2
Module A
Port 1 Port 2
100Base-FX - SC Module
Port 1
Tx Rx
Module A
Port 1 Port 2
10/100Base-T Module
Port 1 Port 2
Module A
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
246 8
135 79
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
246 8
135 79
123456789101112131415161718192021
246 8
135 79
123456789101112131415161718192021
246 8
135 79
123456789101112131415161718192021
246 8
135 79
123456789101112131415161718192021
11
123456789101112131415161718192021
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
246 8
135 79
11
123456789101112131415161718192021
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
246 8
135 79
11
123456789101112131415161718192021
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
246 8
135 79
11
123456789101112131415161718192021
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
13 15 17 19 21
11
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
13 15 17 19 21
11
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
13 15 17 19 21
11
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
13 15 17 19 21
11
13 15 17 19 21
13 15 17 19 21
13 15 17 19 21
13 15 17 19 21
22
22
22
22
1000LX connection
22
22
22
22
1000SX
connection
Matrix
Intel® Express 530T Switch
Intel® Express 535T Switch
Intel® Express 535T Switch
Module A
Switch
StatusSw1 Sw2 Sw3
StatusPort 1
Port 2
Module
(Gigabit)
Status
Link/
Link/
Act
Act
Local
Console: 9600-8-N-1
Management
FlowCtrl=None
(EIA 232)
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
Stacking
Module A
Switch
StatusLink
Port 1 Port 2
Module
Status
10/100Base-T Module
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Port 1 Port 2
Activity = Blinking Green
Module A
Stacking
Module A
Switch
StatusLink
Port 1 Port 2
Module
Status
100Base-FX - SC Module
Port 1
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Tx Rx
Activity = Blinking Green
Module A
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
246 8
135 79
13 15 17 19 21
11
123456789101112131415161718192021
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
246 8
135 79
13 15 17 19 21
11
123456789101112131415161718192021
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
246 8
135 79
13 15 17 19 21
11
123456789101112131415161718192021
Stack of 530T and 535T switches
®
Intel
Express 550T Routing Switch
®
Express 510T Switches
and Intel
Slot BSlot A
LEDs Green Orange
526
4
Module
Status
Matrix Module for 500 Series Switches
Link
Status
Rear Port
1
3
12345678
Gigabit Stacking Module for 500 Series Switches
2
1
3
TX RX
4
3
12
StackInterfaceModule for500SeriesSwitches
3
12
5
4
5
12
876
11
10
9
13
12
876
11
10
9
13
Off
Solid
LEDs Green Orange
Solid
Blink
Slot BSlot A
LEDs Green Orange
Off
Solid
LEDs Green Orange
Solid
Blink
20
17
18
16
14
15
Slot BSlot A
LEDs Green Orange
Off
Solid
LEDs Green Orange
Solid
Blink
20
17
18
16
14
15
Using the 530T
22
22
22
10 Mbps
Half duplex
Intel Express
100 Mbps
Full duplex
550T Routing
Port Status
Switch
Power
Status
Temperature
Link
Disabled
Reset
Activity
Collision
RPS
Console
9600-8-N-1
10 Mbps
Half duplex
Intel® Express
100 Mbps
Full duplex
510T Switch
Port Status
Power
Status
Temperature
Link
Disabled
Reset
Activity
Collision
RPS
Console
21
24232219
9600-8-N-1
10 Mbps
Half duplex
Intel® Express
100 Mbps
Full duplex
510T Switch
Port Status
Power
Status
Temperature
Link
Disabled
Reset
Activity
Collision
RPS
Console
21
24232219
9600-8-N-1
13
Page 20
C H A P T E R 2 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
Flow Control
During times of heavy network activity, the switch’s port buffers can
receive too much traffic and fill up faster than the switch can send the
information. In cases like this, the switch tells the transmitting device to
wait so the information in the buffer can be sent. This traffic control
mechanism is called flow control.
The method of flow control depends on whether the port is set to full- or
half-duplex. If a port is operating at half-duplex, the switch sends a
collision (also called backpressure) which causes the transmitting device
to wait. If the port operates at full-duplex, the switch sends out an IEEE
802.3x PAUSE frame. You can enable or disable flow control for each
port on the Express 530T switch.
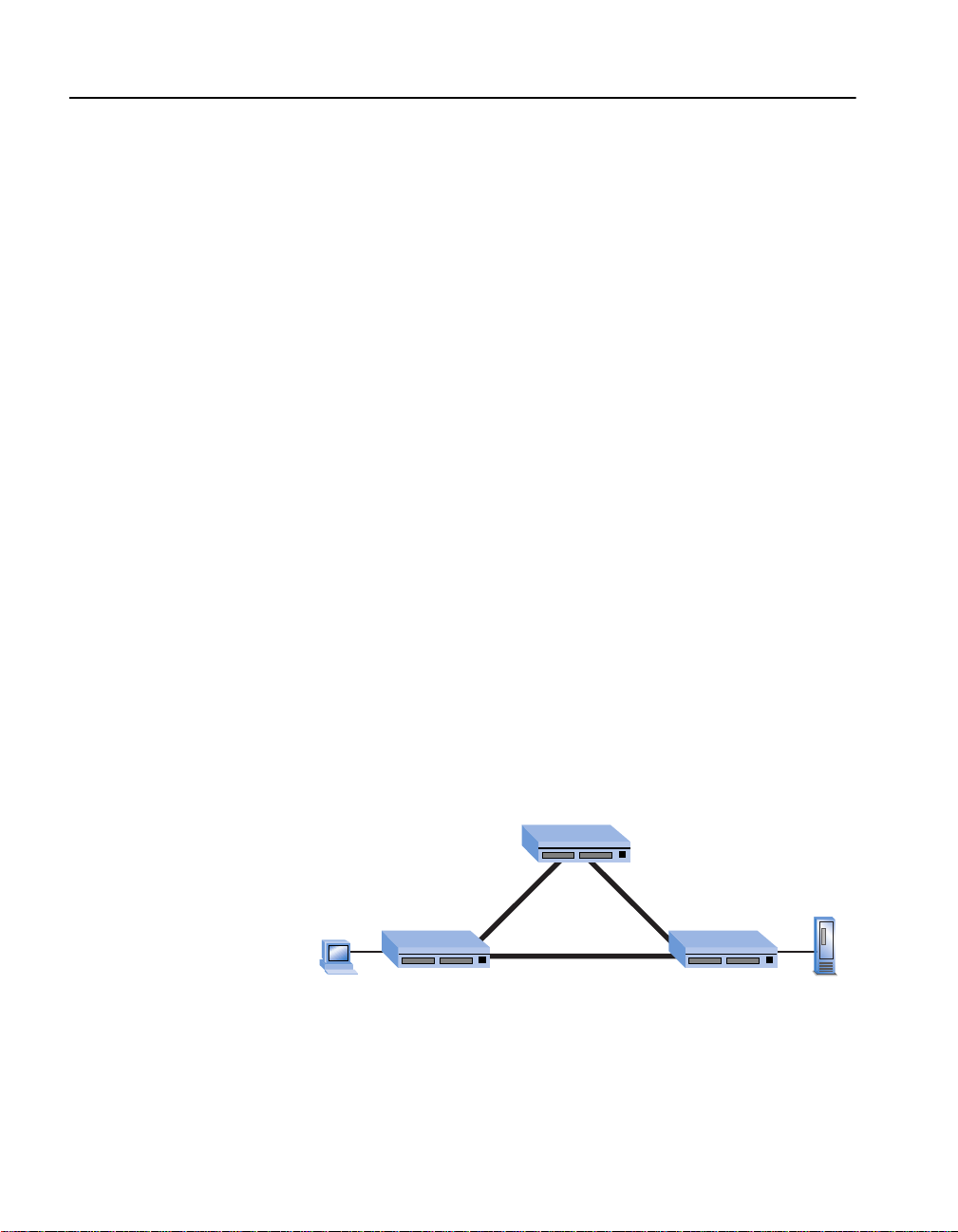
Spanning Tree Protocol
Spanning Tree helps to prevent any loops within the network topology.
A loop can occur if there is more than one path for information to travel
between devices. The Spanning Tree Protocol works by determining the
“cost” of a connection. For example, if two devices are connected b y two
links, Spanning Tree uses the conn ection with the lowest cost and b locks
the second connection from working.
Spanning Tree prevents loops by allowing only one active path between
any two network devices at a time. However, you can also use this
behavior to establish redundant links between devices which can take
over in the event the primary link fails.
The 530T supports one instance of Spanning Tree per switch (or per
stack of switches).
14
Switch B
Path: 2
Cost: 200
Switch C
Server B
PC Client A
Switch A
Path: 3
Cost: 100
Path: 1
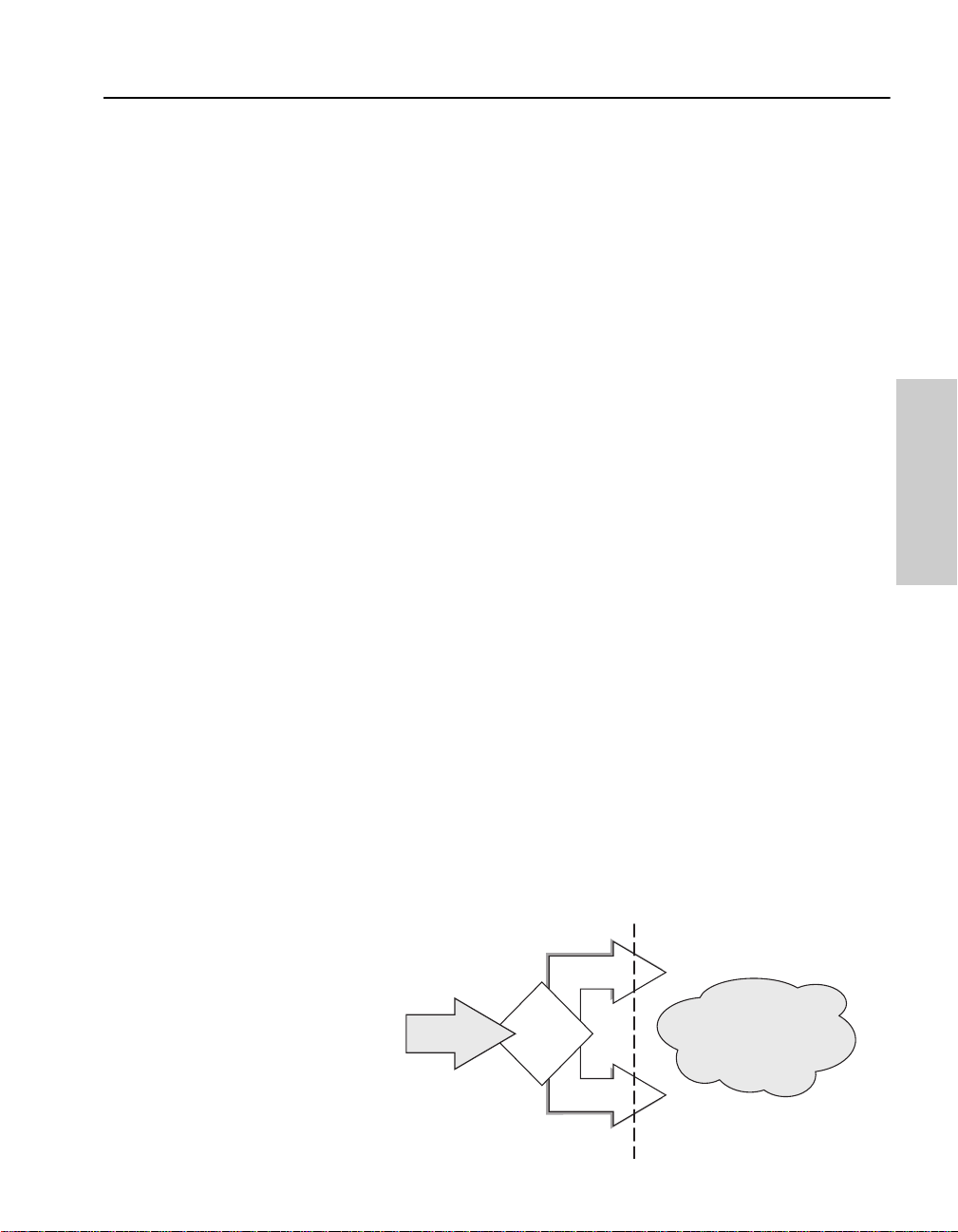
Cost: 100
In this example, Client A can communicate with Server B over two
different paths. The primary path is Path 1 because the cost of the
connection between switches A and C is lower than the cost between
switches A, B and C. If the primary path fails, traffic is sent over the
backup path automatically.
Page 21
C H A P T E R 2 Using the Intel® Express 530T Switch
Tagged Frames
The 802.1D (1998 Edition) and 802.1Q specifications published by the
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers) extends Ethernet
functionality to add tag information to Ethernet frames and propagate
these tagged frames between bridges (for examp le, a switch). The tag can
carry priority information, VLAN information, or both and allows
bridges to intelligently direct traffic across the network.
For outgoing (egress) packets you can specify whether you want the
packets to be tagged or untagged. For incoming (ingress) packets you
can set the ingress filtering so that packets are forwarded to a specific
port as long as that port is a member of the VLAN. You can set a Port
VLAN Identifier (PVID) so that if untagged traffic goes to that port, the
packet inherits the VLAN Identifier (VID) of the port.
Priority
The IEEE 802.1D (1998 Edition) specification incorporates IEEE 802. 1p
and defines information in the frame tag to indicate a priority level.
When these tagged packets are sent out on the network, the higher
priority packets are transferred first. Priority packet tagging (also known
as Traffic Class Expediting) is usually set on the LAN adapter in a PC
and works with other elements of the network (switches, routers) to
deliver priority packets firs t. The priority level can rang e from 0 (low) to
7 (high).
The 530T switch can read the priority tags and forward traffic on a perport basis. The switch uses two priority queues per port and routes traffic
to a queue depending on the packet’s tag. For example, when a packet
comes into the switch with a high priority tag, the switch routes the
packet to its high-priority queue.
Even though there are eight priority levels, the 530T switch can route a
packet into only one of the two queues. The switch maps levels 0-3 to the
low queue (the default) and levels 4-7 to the high queue. If a packet is
untagged, the switch determines the best way to send the packet.
Express 530T
7
HIGH
6
5
4
Incoming
packet
Transmit
queue
for the
port
3
2
1
LOW
0
Using the 530T
Network
15
Page 22
C H A P T E R 2 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
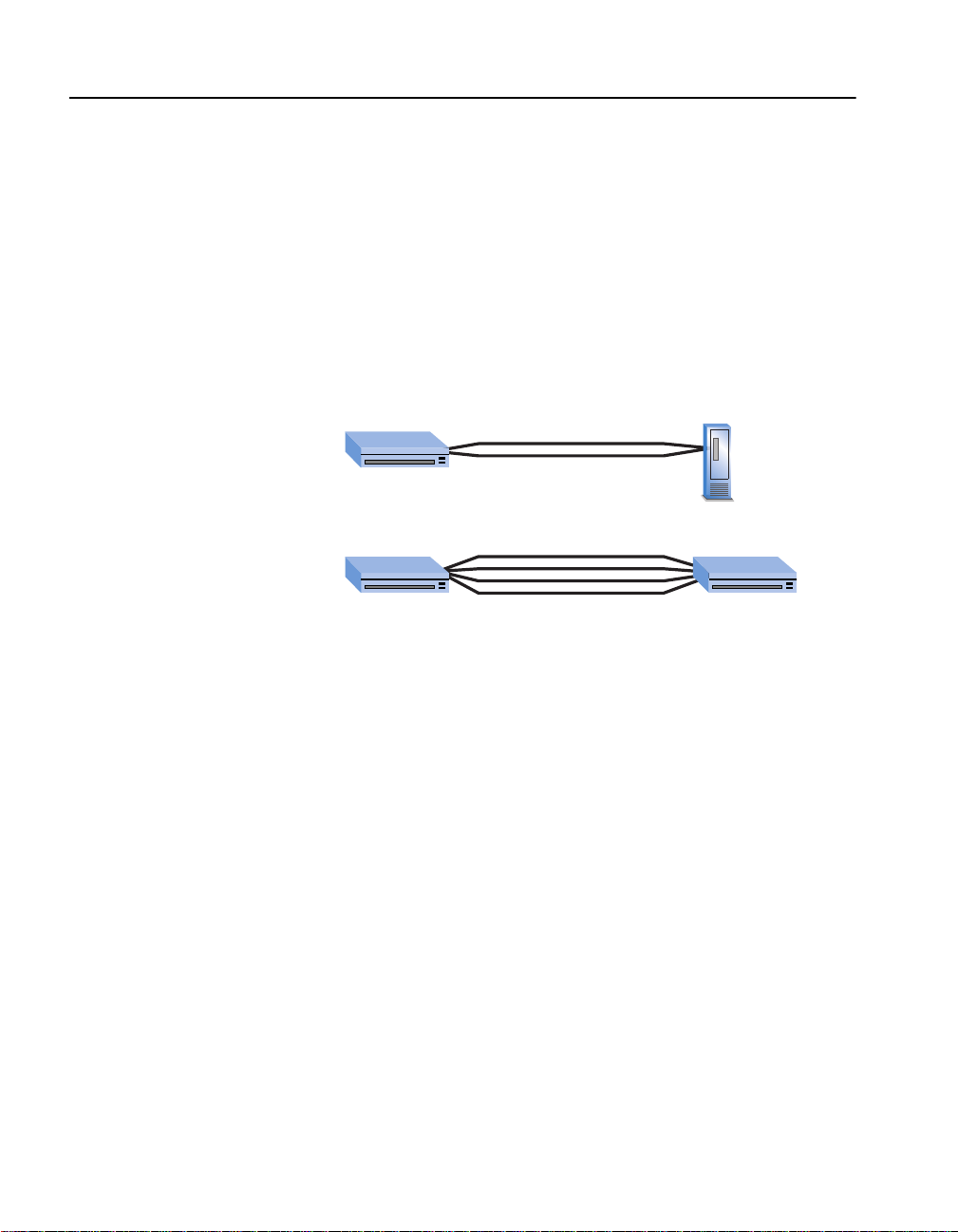
Link Aggregation
Link aggregation allows you to combine from 2 to 8 (adjacent) ports so
that they function as a single high-speed link. For example, link
aggregation is useful when making connections between switches or to
connect servers to the switch.
Link aggregation, sometimes known as port trunking, can be used to
increase the bandwidth to some devices. Link aggregation can also
provide a redundant link for faul t tolerance. If one link in the agg regation
fails, the switch balances the traffic among the remaining links.
2 ports aggregated x 100Mbps = 200Mbps link
4 ports aggregated x 100Mbps = 400Mbps link
16
To aggregate ports, you must link an “anchor” port with an adjacent port.
The 530T switch supports up to four link aggregation groups (anchor
ports 1, 7, 15) This includes one link aggregation group for the two
module ports.
Guidelines
• The switch treats aggregated links as a single port. This includes
Spanning Tree and VLANs.
• All ports share the same settings as the anchor port. You can change
anchor port settings, but you cannot configure other ports in the link.
• When a port is configured as a member of an aggregated link, it
immediately adopts the characteristics of the anchor port. When a
port is no longer a member of an aggregated link, the characteristics
are reset to the default settings (autonegotiate speed/duplex, flow
control enabled).
• If a port is part of an aggregated link, it cannot be configured as the
target port for a port mirror. However, a port in an aggregated link
can serve as the source port for a port mirror.
• When a 530T is stacked with one or more 535T switches, you
cannot aggregate ports that belong to separate switches. The 530T
supports up to four link aggregatio n groups, and each 535T suppo rts
up to three.
Page 23
C H A P T E R 2 Using the Intel® Express 530T Switch
Virtual LANs
A Virtual LAN is a logical network grouping that allows you to isolate
network traffic so members of the VLAN receive traffic only from o ther
members. Creating a VLAN is the physical equivalent of moving a group
of devices to a separate switch (creating a Layer 2 broadcast domain).
The advantage of VLANs is that you can reduce broadcast traffic for the
entire switch and increase security, withou t chan ging the wiring of y our
network.
The Express 530T switch supports two types of VLANs:
• Port-based
• IEEE 802.1Q (tag) -based
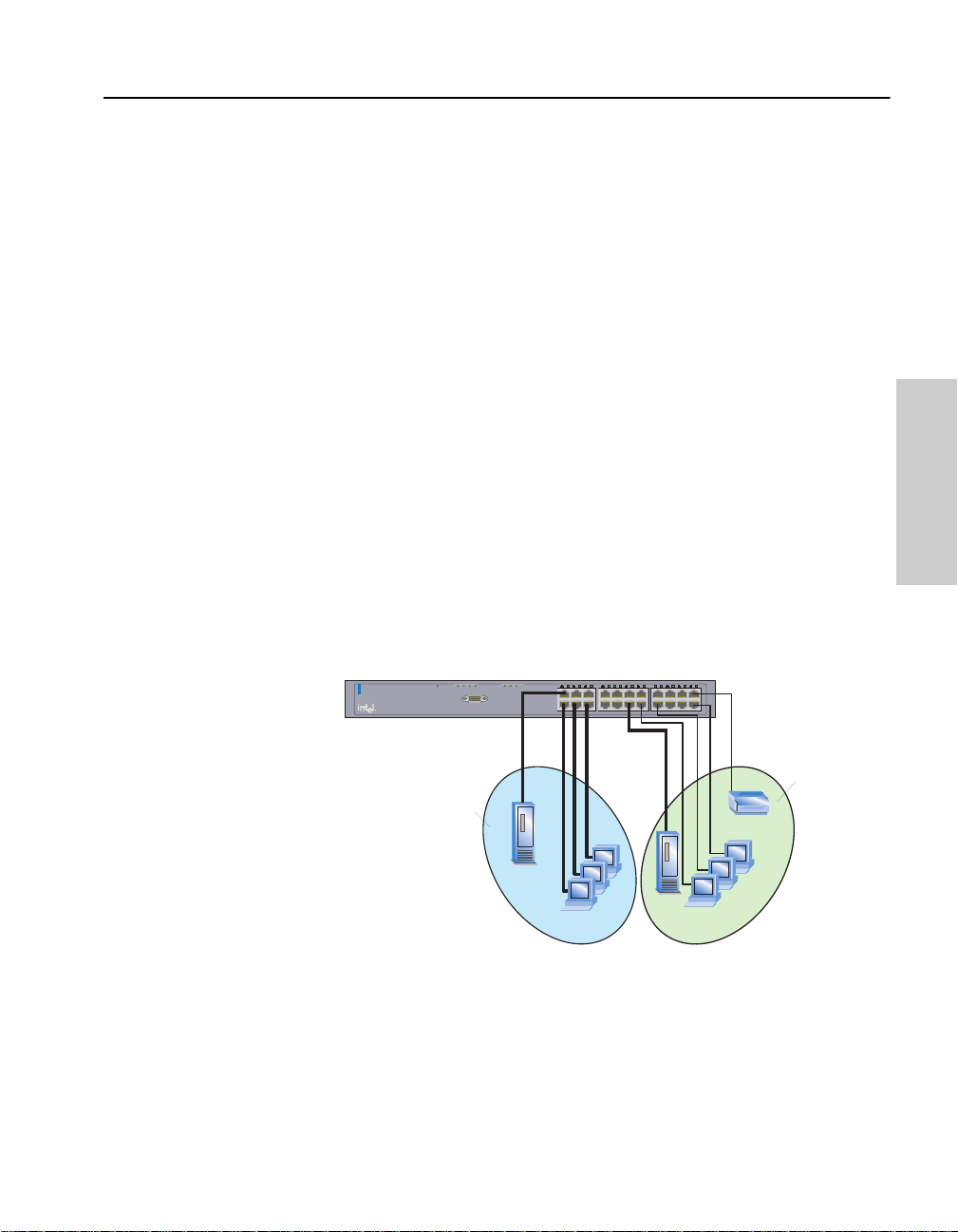
Port-based VLANs
This is the simplest and most common form of VLAN. In a port-based
VLAN, the system administrator assigns the switch’s ports to a specific
VLAN. For example, the system administrator can designate ports 2, 4,
6, and 9 as part of the engineering VLA N and ports 17, 1 9, 21, and 22 as
part of the marketing VLAN. The advantage of port-based VLANs is that
they are easy to configure and all changes happen at the switch so they
are transparent to the users. The 530T supports a maximum of 24 portbased VLANs. A port can belong to only one VLAN at a time.
Matrix
Intel® Express 530T Switch
Module A
Switch
Status Sw1 Sw2 Sw3
StatusPort 1
Module
(Gigabit)
Status
Local
Console: 9600-8-N-1
Management
FlowCtrl=None
(EIA 232)
135 79
Port 2
Link/
Link/
Act
Act
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
123456789101112131415161718192021
246 8
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
13 15 17 19 21
11
Using the 530T
22
These devices
are members
of VLAN 1
VLAN 1:
Engineering
These devices
are members
of VLAN 2
VLAN 2:
Marketing
If a user changes location, the system administra tor reassigns the port to
the new VLAN. Another advantage is if a hub is connected to a port that
is part of a VLAN, all devices connected to the hub are also part of the
VLAN. The disadvantage is that there is no way to exclude an individual
device on that hub from becoming part of the VLAN.
When a 530T switch is stacked with one or more 535T switches, ports
from any of the switches can be members of a port-based VLAN.
17
Page 24
C H A P T E R 2 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
NOTE
When a 530T is stacked with
one or more 535T switches,
ports from any/all of the
switches can be members of
each VLAN.
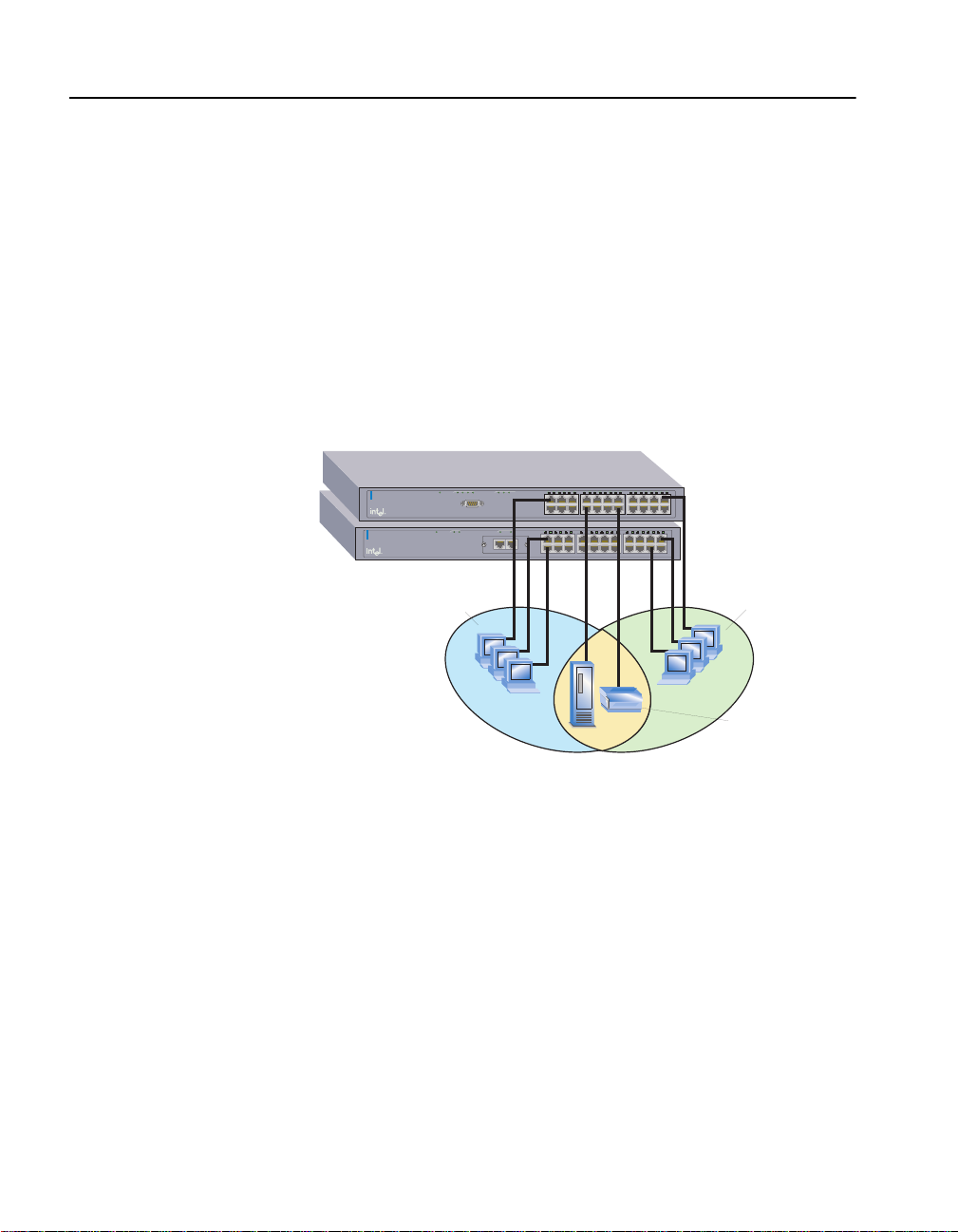
IEEE 802.1Q (tag)-based VLANs
The second type of V LAN supp orted b y th e 530T switch is base d on the
IEEE 802.1Q specification. Th e specification provides a uniform way for
creating VLANs within a network and allows the creation of a VLAN
that can also span across the network. Until recently, VLAN
implementation was vendor specific so it was not possible to create a
VLAN across devices from di fferent vendors.
The 802.1Q VLAN works by using a tag added to the Ethernet frames.
The tag contains a VLAN Identifier (VID) that identifies the frame as
belonging to a specific VLAN. These tags allow switches that support the
802.1Q specification to segregate traffic between devices and
communicate a device’s VLAN association across switches.
Matrix
Intel® Express 530T Switch
Intel® Express 535T Switch
Module A
Switch
Status Sw1 Sw2 Sw3
StatusPort 1
Local
(EIA 232)
Status Link
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
Console: 9600-8-N-1
Port 2
(Gigabit)
Link/
Link/
Act
Act
FlowCtrl=None
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
Module A
Port 1 Port 2
10/100Base-T Module
Port 1 Port 2
Module A
Module
Status
Management
Stacking
Switch
Module
Status
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
246 8
135 79
123456789101112131415161718192021
246 8
135 79
123456789101112131415161718192021
13 15 17 19 21
11
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
13 15 17 19 21
11
530T
22
535T
22
VLAN 1:
Engineering
VLAN 1 computers
can't see VLAN 2
computers
VLAN 2:
Manufacturing
Server and printer
are members of both
VLANs
There are multiple advantages to implementing 802.1Q VLANs. First, it
helps to contain broadcast and multicast traffic across the switch thus
improving performance. Second, ports can belong to more than one
VLAN. Third, VLANs can span multiple switches that support the
802.1Q specification. Finally, it can provide security and improve
performance by logically isolating users and grouping them together.
The 530T switch supports up to 2047 tag-based VLANs.
A logical grouping can be mapped to a work g roup. For example, you can
create a VLAN that groups all the users from the engineering department
into one VLAN. A benefit of this logical grouping is that it can improve
performance by cutting down traffic that belongs to a different logical
group (for example, mark eting), improv e security (engineer ing can’t see
marketing), and ease moves since the user doesn’t have to be physically
located in the same group to participate in the VLAN.
When a 530T switch is stacked with one or more 535T switches, ports
from any/all of the switches can be members of a tag-based VLAN.
18
Page 25
C H A P T E R 2 Using the Intel® Express 530T Switch
On the 530T switch, overlapping VLANs can be supported through the
use of 802.1Q-capable devices. However, for non-802.1Q-capable
devices, overlapping VLANs can be supported by implementing an
asymmetric VLAN on the switch (see references below for more
information). An asymmetric VLAN is a type of 802.1Q configuration
where endstations send traffic on one VLAN and receive traffic on
another VLAN. The 530T switch can support asymmetric VLANs.
To learn more about asymmetric VLANs, see
http://support.intel.com/support or refer to IEEE 802.1Q Specification
Annex B.1.3.
Spanning Tree and VLANs
The 530T supports the Spanning Tree Protocol across the entire switch
(or stack of switches), not per VLAN. If a lo op occurs in a VLAN the port
is disabled and all VLAN traffic over that port is blocked.
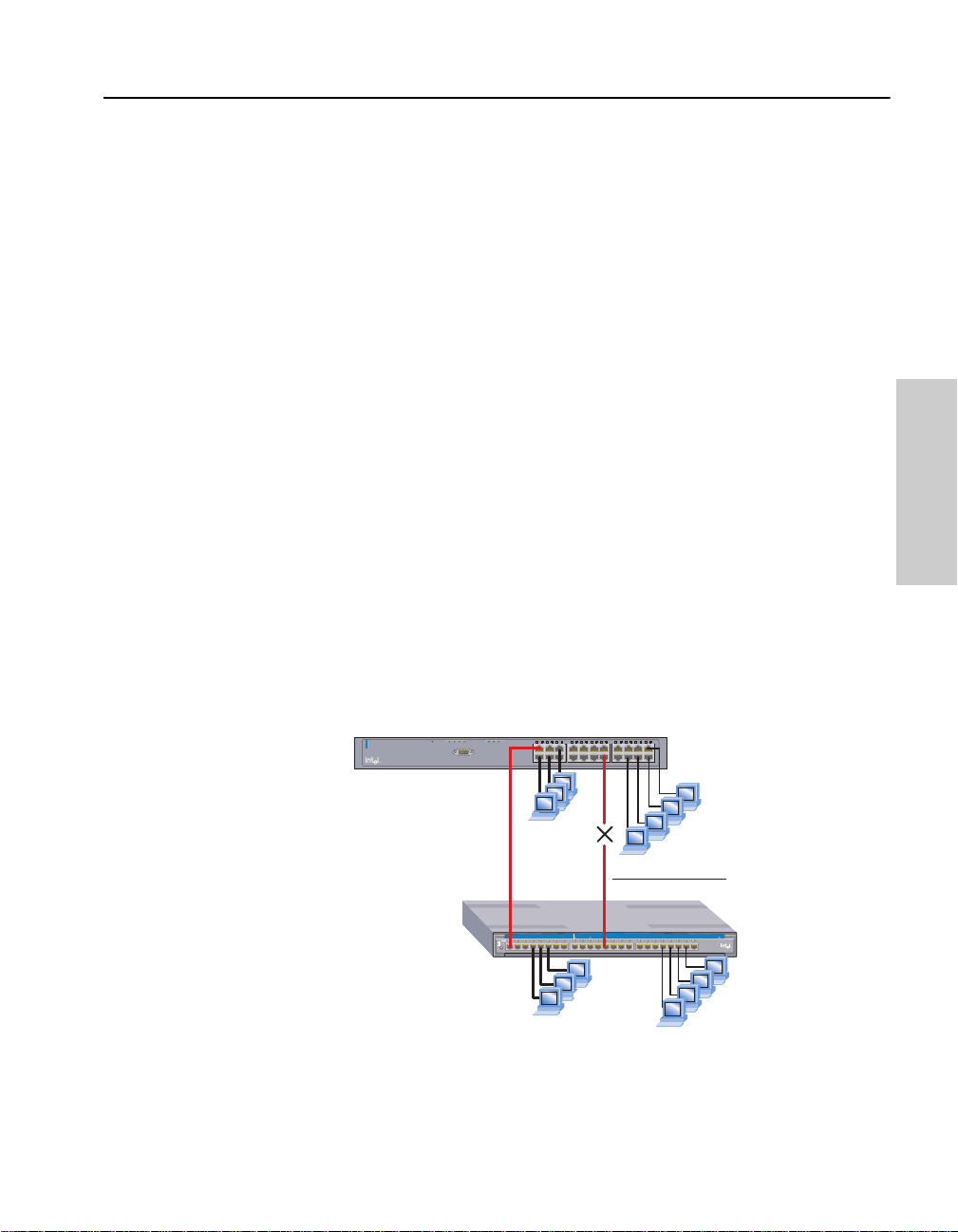
A good example of this can be seen below. Both Switch 1 and Switch 2
have two port-based VLANs configured. Crossover cables connect the
ENG_VLAN on Switch 1 to ENG_VLAN on and Switch 2. Crossover
cables also connect the MRKT_VLAN on Switch 1 to the
MRKT_VLAN on Switch 2. When Spanning Tree is enabled, the
redundant link between the MRKT_VLANs is blocked and th ose
VLANs can no longer communicate.
When the switch is running 802.1Q VLANs, Spanning Tree is required
for GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) to work properly.
Matrix
Switch
StatusSw1 Sw2 Sw3
Intel® Express 530T Switch
Module
Status
Local
Management
(EIA 232)
Switch 1
Crossover connecting
ENG_VLANs
Switch 2
Module A
(Gigabit)
Console: 9600-8-N-1
FlowCtrl=None
StatusPort 1
Port 2
Link/
Link/
Act
Act
Link\Activity
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
Intel® Express 460T Standalone Switch
MDI
12345678
MDI-X
ENG_VLAN
ports 1-8
10 12 14 16 18 20 22
246 8
135 79
123456789101112131415161718192021
13 15 17 19 21
11
Module A
Port 1 Port 2
Link\Act\Coll
Link\Act\Coll
Status
910111213141516 1718192021222324
22
MKT_VLAN
ports 15-22
Spanning Tree disables
the redundant crossover,
breaking the connection
between the MKT_VLANs.
Status
Left
Link = Solid Green
Activity = Blinking Green
Collision = Blinking Orange
Right
10Mbps = Solid Orange
100Mbps = Off
Using the 530T
ENG_VLAN
ports 1-8
MKT_VLAN
ports 17-24
19
Page 26

C H A P T E R 2 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
NOTE
The 530T supports a
maximum of 24 IGMP
sessions, with a maximum of
32 multicast groups per
session. These parameters are
the same whether the 530T is
standalone or in a stack.
GARP VLAN Registration Protocol
(GVRP)
Since IEEE 802.1Q VLANs can span networks, it poses a challenge for
network administrators to manage changes to the VLAN. The GARP
(Generic Attribute Registration Protocol) VLAN Registration Protocol
(GVRP) provides a dynamic mechanism for switches to share topology
information and manage changes with other switches. This alleviates the
network administrator from manually propag ating VLAN configur ation
information across switches.
GARP is defined by the IEEE 802.1D (1998 Edition) specification and
is the mechanism used by switches and end nodes to propagate VLAN
configurations across the network domain. GVRP uses GARP as a
foundation to propagate VLAN configurations to other switches.
Devices that support GVRP transmit their updates to a known multicast
address that all GVRP-capable devices monitor for infor mation u pdates.
Sending GVRP messages between switches accomplishes these tasks:
• Dynamically adds or removes a port from participating in a VLAN
• Sends updates about the switch’s own VLAN configuration to
neighboring GVRP-capable devices
• Integrates dynamic and static VLAN configurations within the same
switch. Static VLAN configurations are created by the user on the
switch for devices that don’t support GVRP
Dynamically created VLANs are not saved in the switch’s memory.
When the device that is sending out the GVRP updates is disabled or
rebooted the dynamic VLAN is removed.
20
Internet Group Multicast Protocol
Under normal circumstances, multicast traffic is bro adcast by the switch
to all ports. For multicast traffic based on the IGMP (Internet Group
Multicast Protocol), the switch can optimize the broadcasting of
multicast traffic by forwarding multicast traffic to only the ports that
require it.
IGMP snooping is a feature that allows the switch to forward multicast
traffic intelligently. The switch “snoops” the IGMP query and report
messages and forwards traffic to on ly the ports th at request the multicast
traffic. This prevents the switch from broadcasting the traffic to all ports
and possibly affecting network performance.
IGMP requires a router that records the presence of multicast group s on
its subnets and keeps track of group membership. It is important to
remember that multicasting is not connection oriented, so data is
delivered to the requesting hosts on a best-effort level of service.
Page 27
Using Intel® Device
3
View 2.1
Overview
Intel Device View allows you to manage the Intel® Express 530T Switch
and other supported Intel networking devices on your network.
Intel Device View provides these features:
• The ability to configure new network devices
• Graphical device manager for Intel switches, hubs, and routers
• Autodiscovery, which finds supported Intel devices on the network
• The Device Tree, which shows all the supported devices detected on
your network
• Remote Network Monitoring (RMON)
• Web or Windows* platform
• Plug-in to HP OpenView*, IBM Tivoli NetView*, and Intel
LANDesk
• Other useful tools such as a TFTP server
®
Network Manager
Page 28

C H A P T E R 3 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
Installing Intel Device View
Before you install Intel Device View, make sure your PC meets the
system requirements in the Intel Device View User Guide, which is
included on the Intel Device View CD-ROM.
To install Intel Device View
1 Insert the Intel Device View CD-R OM in your computer’s CD-ROM
drive. The Intel De vice V i ew ins tallation screen appears. If it doesn’t
appear, run autoplay.exe from the CD-ROM.
22
2 Ch oose the version of Intel Device View you want to install.
• Click Install for Windows to install Intel Device View for use
on this PC only.
• Click Install for Web to install Intel Device View on a Web
server. You will be able to access the Device View server from
any PC on your network with Internet Explorer* 4.0x or later.
• Click Install as Plug-in to install Intel network device support
for HP OpenView, IBM Tivoli NetView, or Intel LANDesk
Network Manager. This option is not available if you don’t have
OpenView, Net View, or LANDesk Network Manager installed
on the PC.
3 Follow the on-screen instructions in the installation program.
Page 29
C H A P T E R 3 Intel® Device View 2.1
NOTE
These are the requirements if
you want to use the Web
version of Device View:
Web browser
Internet Explorer 4.0 or
newer
Web server
Internet Information Server
(IIS) 2.0 or newer
Peer Web Services*
Netscape Enterprise* Web
server 3.01 or later.
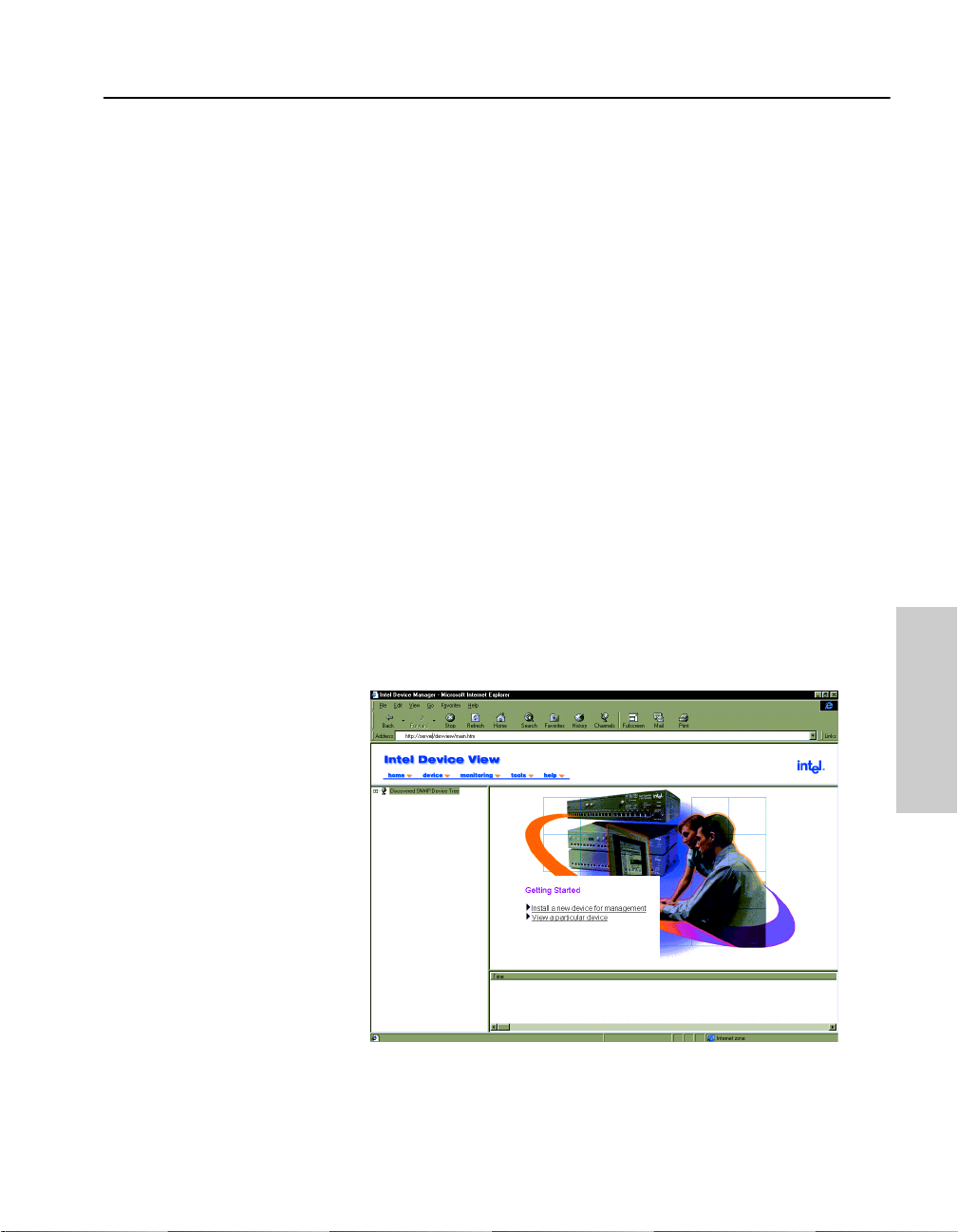
Starting Intel Device View
Install either the Windows or Web version of Intel Device View.
Windows version
From your desktop, click Start and then point to Programs > Intel Device
View > Intel Device View - Windows. Intel Device View’s main scr ee n
appears.
Web version
• From your desktop, click Start and then point to Programs > Intel
Device View > Intel Device View - Web. Intel Device View’s main
screen appears.
• To view In tel Device View from another PC on your network, type
the following URL. In the example shown below, the URL is entered
into the Address field for Internet Explorer.
http://servername/devview/main.htm
where servername is the IP address or name of the server where
Intel Device View is installed.
Intel Device View’s main screen appears.
Device View 2.1
23
Page 30
C H A P T E R 3 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
NOTE
The 530T sends BootP
requests for several minutes;
after that time, if no IP has
been entered, the switch stops
sending the request and
continues to boot.
In a stack of switches, only one
MAC address (the control
switch’s MAC address) is
discovered.
Installing a New Device
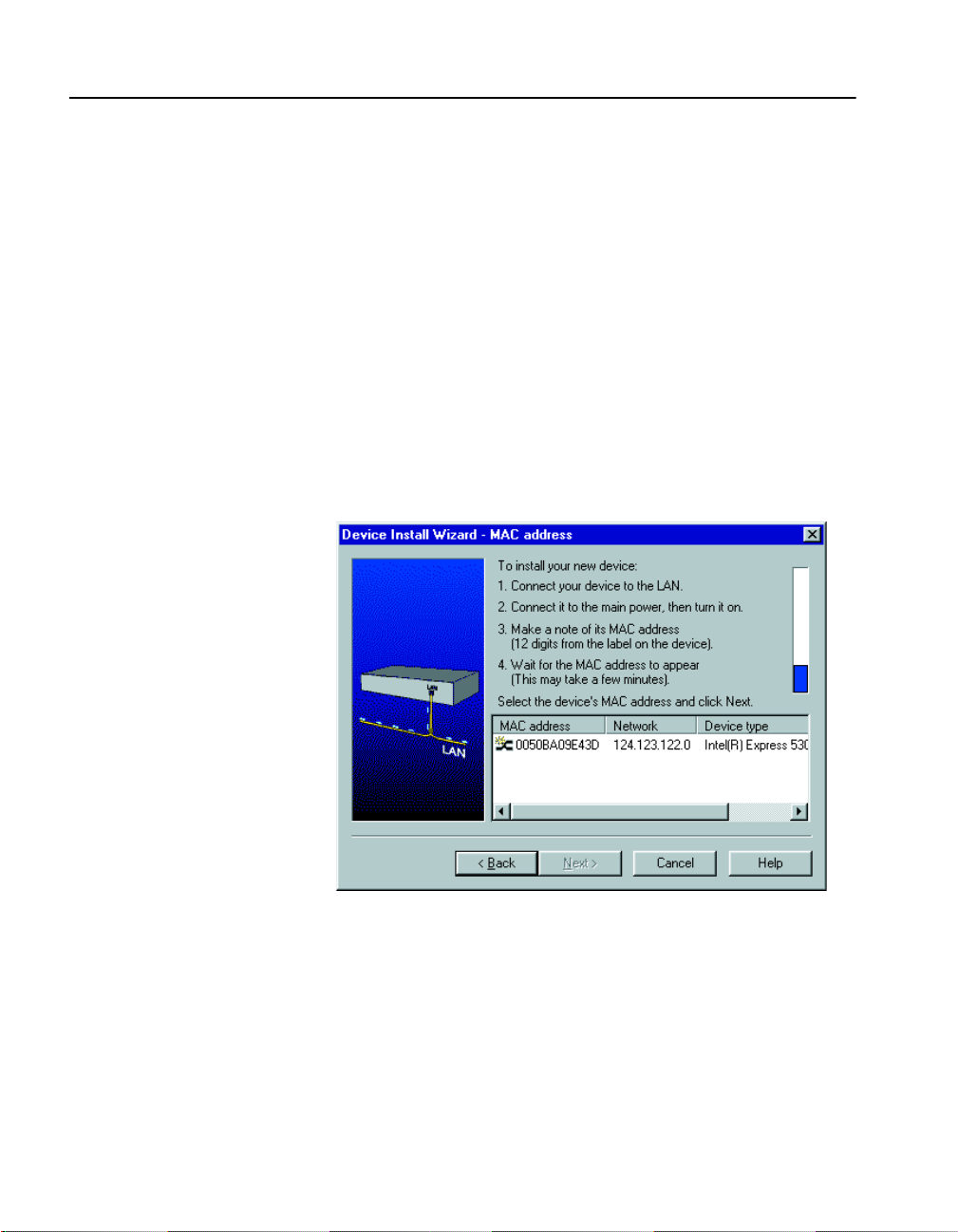
After you’ve installed a new switch on your network, you can use Intel
Device View’s Device Install Wizard to configure it for management.
To install and configure a new switch for
management
1 Start Intel Device View. The Device Install Wizard appears. If it
doesn’t appear, click Install from the Device menu or double-click
the appropriate MAC address in the Device Tree under Unconfigured Devices. (The MAC address is located on the rear of the
switch.)
2 On the Device Install Wizard - Start screen, click Next.
3 On the Device Install Wizard - MAC Address screen, click the MA C
address of the new switch and then click Next.
24
4 Follow the instructions in the wizard to assign an IP address and a
name to the switch (or stack of switches).
Page 31

C H A P T E R 3 Intel® Device View 2.1
Using the Device Tree
When you start Intel Device View, the Device Discovery service begins
searching for supported Intel network devices on your network. As it
discovers devices, the Device Discovery service adds an icon for each
device to the Device Tree on the left side of the screen.
Different states of the 530T switch are represented b y unique icons in the
Device Tree.
Device Tree icons
Device Tree root
Subnet
Intel Express Switch (if non-responding the icon is red)
Unconfigured Intel Express Switch
Group of Intel Express Switches
Intel Express Router
Intel Express Switch (Layer 3 capable)
Intel Express Stackable Hub
The Device Tree works much like Windows Explorer. To expand the
root or a subnet, click the (+) next to the icon. To collapse the view, click
the (-) next to the icon. Double-click a device icon to view the device
image.
Device View 2.1
25
Page 32

C H A P T E R 3 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
To add a device to the Device Tree
Use this procedure if the device does not automatically appear after
installation.
1 Right-click anywhere on the Device Tree.
2 On the menu that appears click Add Device.
3 In the Add Device dialog box, type the IP address of the switch you
want to add.
4 Fill in the other fields, as appropriate.
5 Cl ick OK.
The new switch’s icon appears in the Device Tree.
To refresh the Device Tree
1 Right-click anywhere on the Device Tree.
2 On the menu that appears click Refresh.
Refreshing the Device Tree updates it to show any newly discovered
devices and changes in device status.
To delete a device from the Device Tree
1 Right-click the device you want to remove from the Device Tree.
2 On the menu that appears click Delete.
Deleting a device from the Device Tree does not affect the actual device.
26
To find a device in the Device Tree
1 Right-click anywhere on the Device Tree.
2 On the menu that appears click Find.
3 In the Find Device dialog box, type the IP address of the device you
want to find in the tree.
4 Cl ick OK.
The device’s icon is highlighted in the Device Tree.
Losing contact with a device
If Intel Device View loses contact with a switch, it replaces the switch
icon with the non-responding switch icon, which is red.
Page 33

C H A P T E R 3 Intel® Device View 2.1
If the non-responding switch icon appears, you will not be able to
manage the device in Intel Device View. If you’re unable to ping the
device or start a Telnet session, try accessing the switch’s Local
Management.
Managing a Switch
To manage the 530T switch, double-click the switch icon in the Device
Tree. In the example shown below, the switch has been assigned an IP
address of 124.123.122.3.
The 530T Web Device Manager appears in the Intel Device View
window. For information on using the Web Device Manager, see
Chapter 4.
For more information on using Intel Dev ice View, refer to th e program’s
online help or see the User Guide on the Intel Device View installation
CD-ROM.
Device View 2.1
27
Page 34

C H A P T E R 3 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
Viewing RMON Information
The remote monitoring (RMON) specification extends Simple Network
Management Protocol (SNMP) functionality to look at traffic patterns on
the network instead of merely looking at the traffic for an individual
device. The following RMON groups are supported:
• Group 1 (Stat istics): Monitors utilization and error statistics for
each network segment (10Mbps or 100Mbps).
• Group 2 (History): Records periodic statistical sam ples from
variables available in the statistics group.
• Group 3 (Alarms): Allows you to set a sampling interval and alarm
thresholds for statistics. When a threshold is pa ssed, the switch
creates an event. For example, you might set an alarm if switch
utilization exceeds 30%.
• Group 9 (Events): Provides notification and tells the switch what to
do when an event occurs on the netw ork . Ev en ts can send a trap to a
receiving station or place an entry in the log table, or both. For
example, when the switch experiences an RMON Ev ent, it send s out
an Alarm.
The switch also keeps a log that shows a list of the RMON Events and
RMON Alarms that have occurred on the switch.
28
To view RMON statistics
1 Right-click the switch’s icon in the Device Tree, then point to
RMON.
2 Click the RMON option you want to view:
You can also access RMON features by using LANDesk Network
Manager, or an SNMP application that supports RMON such as
OpenView. For more information about using RMON to monitor the
switch, refer to the Intel Device View Help.
Page 35

Using the Web
4
Device Manager
Overview
The Web Device Manager, built into the Intel® Express 530T Switch,
lets you use a Web browser to manage and monitor the switch. For
example, you can use the Web Device Manager to configure the switch
or individual ports, or to monitor traffic statistics and utilization.
This chapter covers the major management functions of the 530T. For
additional information about using this interface, see the Web Device
Manager Help.
Page 36

C H A P T E R 4 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
NOTE
The default IP address
assigned to the switch is
192.0.2.1. To access the
switch with the default IP
address, your workstation
must be on the 192.0.2.0
subnet.
Alternatively, you can connect
to the switch using Local
Management and set an IP
address that is on your
network. Then you can access
the Web Device Manager using
the new IP address.
Accessing the Web Device Manager
1 In the Location or Address field of your Web browser type the IP
address of the switch. For example, to use the default IP address of
the switch, type 192.0.2.1 in the Location or Address field and then
press Enter.
2 When prompted, type your user nam e and password. By default, no
user name or password is assigned. If you set a user name and
password using Local Management, type those here.
3 Click OK. The Web Device Manager screen appears in your Web
browser.
30
Page 37

C H A P T E R 4 Using the Web Device Manager
Navigating the Web Device
Manager
Navigate between switches
On the switch stack graphic at the top of the page, click the switch you
want to configure. The “active” switch is highlighted in green.
Click a switch in the
stack to view or
configure its settings.
Navigate between menus
1 On the left side of the Web Device Manager window, click a menu
item (such as Configure Stack) to show the available options.
2 Click an option in the menu. The corresponding screen appears on
the right side of your Web browser window.
3 To hide the options, click the menu item again.
Click a menu to view
available options.
Web Device Manager
31
Page 38

C H A P T E R 4 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
Using Management Screens
After you select an option from the navigation menu, the corresponding
screen appears in the right side of the Web browser.
Switch faceplate graphic
A graphical representation of the switch’s faceplate appears at the top of
the screen.
If the option you’re working with allows you to configure or monitor a
specific port, you can change to another port by clicking it on the
faceplate graphic.
Port color on the faceplate graphic indicates the status of the port.
Port Color Meaning
Green Port has a link at 100Mbps.
Green with “10” Port has a link at 10Mbps.
32
Magenta outline Ports are in a link aggregation.
Orange Port is disabled.
Gray No link.
Buttons
Configuration screens include four buttons on the b ottom of each screen.
Button Function
Submit App lies the configuration settings on the current screen.
Note: If you do not save the settings to the switch’s memory
your changes will be lost when the switch is rebooted.
Reset Clears any changes you made on the current screen and
restores the currently applied settings.
Default Applies factory defaults for this screen’s settings. W hen you
log out, you can permanently save the new settings to the
switch. Otherwise, they are lost upon the next reboot.
Help Displays help for the current screen.
Page 39

C H A P T E R 4 Using the Web Device Manager
NOTE
Each stack of switches has one
IP address.
Configuring the Switch’s IP Settings
Note: You must select Manual in the IP Assignment Method box before
you can change the IP settings.
1 Click the Configure Stack menu and then click IP Settings. The IP
Settings screen appears on the right side of the Web Device Manager
window.
Web Device Manager
2 To manually configure the IP settings, select Manual in the IP
Assignment Method box. In the Change box, type the new IP
address, subnet mask, and default gateway. If you have set up tagbased VLANs on the switch, you can specify the VID (VLAN ID) of
the VLAN where the switch’s SNMP management agent will reside.
3 To apply the changes, click Submit.
4 Click Save and Reboot for the new settings to take effect. Rebooting
the switch temporarily interrupts network connectivity to the switch.
Click Reboot Later if you want to reboot the switch later. The new IP
settings do not take effect until the switch reboots.
33
Page 40

C H A P T E R 4 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
NOTE
If you change the flow control
or IP settings, you must reboot
the switch before the new
settings can take effect.
Configuring a Port
You can use the Web Device Manager to enable or disable a port, and to
change its speed, duplex, flow control, and priority settings.
To change port settings
1 Click the Configure Stack menu and then click Port Settings. To
access the Port Settings screen for each port, click the port you want
to configure on the faceplate graphic.
34
2 Click the options you want to change.
• Port State: Enable or disable the port.
• Speed/Duplex: Set port speed to Auto-Negotiate, 10Mbps,or
100Mbps.
• Flow Control: Enable or disable flow control.
• Priority Queue: Set the priority queue for packets sent or
received on this port.
3 Click Submit.
Page 41

C H A P T E R 4 Using the Web Device Manager
NOTE
The accounts and passwords
you create with the Web
Device Manager are the same
accounts and passwords used
to access Local Management.
Managing User Accounts
Create user accounts to give specific users read or write access to the
switch through the Web Device Manager and Local Management. You
can create a maximum of three accounts on the switch.
To create a user account
1 Click the Configure Management menu and then click User
Accounts. The first account you create must be an administrator.
2 Click Add.
Web Device Manager
3 Type a user name in the User Name box. Th e us ername can be u p to
fifteen characters long and is case-sensitive.
4 The password can be up to fifteen characters long and is case-
sensitive. Asterisks (*) appear on the screen as you type the
password.
5 I n the Confirm Password box, type the same password.
6 In the Access Level box click an access level. An administrator can
view all settings and make configuration changes. A user can only
view settings.
7 Click Submit.
35
Page 42

C H A P T E R 4 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
To delete a user account
1 Click the Configure Management menu and then click User
Accounts.
2 In the User Accounts screen, click the account you want to delete.
3 Click Delete.
If you delete the account you used to log in for this session, you can still
use that account until you log out. If you delete the only user account on
the switch, you can log in again using the defaul t of no user name and no
password.
36
Page 43

C H A P T E R 4 Using the Web Device Manager
NOTE
You can have only one
operation mode (either portor tag-based) active on the
switch at a time.
Configuring VLANs
Virtual LANs, or VLANs, provide a way to create a logical network
grouping without regard to physical location of the network nodes.
For more information about VLANs, refer to “Virtual LANs” in
Chapter 2.
There are two main steps to set up a VLAN with the Web Device
Manager:
• Set the switch’s VLAN operation mode.
• Configure the type of VLAN you selected.
To set the switch’s VLAN operation mode
1 Click the Configure VLAN menu and then click VLAN Operation
Mode.
2 Fr o m the Current VLAN mode box, click the type of VLAN to set
up.
You can set the 530T switch to use port-based or tag-based VLANs.
See “V irtual LANs” in Chapter 2 for more information about VLAN
types.
3 Click Submit.
4 The switch w ill au tomatically reboot. The 530T must be rebooted
whenever you change its VLAN operation mode.
After the switch restarts, you can configure the type of VLAN that you
selected.
37
Web Device Manager
Page 44

C H A P T E R 4 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
NOTE
When the 530T is in a stack
with 535T switches, the 530T
is the control switch. The other
switches are numbered in the
management interface
according to how they are
plugged into the Stack Matrix
Module.
Member Switch 2 = Plugged
into switch port 1
Member Switch 3 = Plugged
into switch port 2
Member Switch 4 = Plugged
into switch port 3
Port-based VLAN
You configure a port-based VLAN by first creating the VLAN and then
adding participating ports. The switch can support up to 24 port-based
VLANs. A port can be a member of only one VLAN; port-based VLANs
cannot overlap.
To configure a port-based VLAN
1 Click the Configure VLAN menu and then click Port-based VLAN.
2 Click Add to create a new VLAN, or select a VLAN and click Edit
to change its configuration.
38
3 If you are creating a new VLAN, type a name in the VLAN Name
box.
4 I n the Switch Unit box, select a switch whose ports you want to add
to the VLAN. You can include ports from any/all switches in a port-
based VLAN.
5 In the Available ports box, select a port to add to the VLAN and
click Add. Continue adding ports from each switch as necessary.
6 When you have finished ad ding ports, click Submit.
Page 45

C H A P T E R 4 Using the Web Device Manager
Ta g - ba s e d V L A N
You configure a tag-based VLAN by configuring port membership and
ingress/egress rules. It is important to note whether the devices in your
VLAN support 802.1Q VLAN tags. If some of your devices don’t
support tagging, additional configuration may be necessary.
To configure a tag-based (IEEE 802.1Q) VLAN
1 Create a VLAN and assign member ports.
• Click the Configure VLAN menu and then click Tag-based
(IEEE 802.1Q) VLAN.
• From the main T ag-based VLAN page, click Add to create a ne w
VLAN. T o modify an existing VLAN, click the VLAN name and
click Edit.
• If you are creating a new VLAN, type a name and VID (from 2
to 4094) to identify it.
• In the Switch Unit box, select a switch whose ports you want to
include in the VLAN. You can include ports from any/all
switches in a tag-based VLAN.
• To add a port to the VLAN, click the port in the Available ports
box and click Add. To remove a port, click the port in the
Member ports box and click Remove.
• The switch supports a maximum of 24 IGMP (Internet Group
Multicast Protocol) Snooping sessions to manage broadcast
traffic. If you want the VLAN to be part of an IGMP Snooping
session, select the Enable IGMP Snooping check box.
• When you have finished adding ports, click Next.
39
Web Device Manager
Page 46

C H A P T E R 4 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
NOTE
Select “Tag” when devices
connected to the port support
802.1Q VLANs. Select “Untag”
when devices connected to the
port do not support 802.1Q
VLANs.
2 Configure ports for egress (outbound) tagging.
• Ensure that the VLAN Name field displays the name of the
VLAN you are configuring.
• Select Tag or Untag for each of the VLAN’s ports, to determine
whether the switch removes (untags) tags before sending traffic
out of each port.
If the VLAN members are from more than one switch, scroll
down the screen to configure tagging for those ports.
• Click Submit.
40
Page 47

C H A P T E R 4 Using the Web Device Manager
3 Configure ports for handling untagged traffic.
• From the main Tag-based VLAN page, cli ck Port Settings.
• On the Port Settings screen, you can set port-specific behaviors
for processing VLAN traff ic. To configure a specific port, click it
in the faceplate graphic. To configure the same setting across all
ports, click Configure All Ports and Module.
Options include:
• Default Port VID: (This option is only available when you click
Configure All Ports and Module. Sets the port VID (PVID) that
is assigned to untagged traffic on a given port. For example, if
port 10's default PVID is 100, a ll untagged packets on port 10
belong to VLAN 100. The default setting for all ports is VID 1.
• GVRP (GARP VLAN Registration Protocol): Allows
automatic VLAN configuration between the switch and nodes.
• Ingress filtering: Allows incoming frames belonging to a
specific VLAN to be forwarded if the port belongs to the same
VLAN. Disabling this setting causes all frames to be forwarded,
regardless of the port's VLAN membership.
Click Submit after you have changed the settings.
Web Device Manager
41
Page 48

C H A P T E R 4 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
NOTE
When configuring link
aggregation between two 530T
switches, you must connect
anchor port to anchor port,
and member port to member
port.
When a 530T is stacked with
one or more 535T switches,
you cannot aggregate ports
that belong to different
switches. The 530T supports
up to four link aggregation
groups (which includes the
module ports), and each 535T
in the stack supports up to
three groups.
NOTE
Connectivity is momentarily
interrupted when you apply
changes.
Link Aggregation
Link aggregation lets you group up to eight consecutive ports into a
single dedicated connection. This f eature can expand bandwidth between
devices on the network, such as another switch or a server.
The anchor port is the base port in a link aggregation; it is the only port
with configurable settings in the aggregation. All member ports in an
aggregation take on the settings of the anchor port, this includes settings
relating to VLANs and Spanning Tree.
Only consecutive ports, starting fro m the ancho r port, can be g rouped in
a link aggregation. For example, ports 1, 2, and 3 are a valid link
aggregation; ports 2, 4, and 7 are not.
On the Web Device Manager’s switch faceplate graphic, a link
aggregation is shown with its ports outlined in magenta (pink).
To create a link aggregation
1 Click the Configure Stack menu, then click Link Aggregation.
42
2 Choose the switch for which you want to configure link aggregation.
3 Choose the anchor port. Anchor ports are listed by number in the left
column.
4 From the Port Width box, click the total number of ports (including
the anchor port) to include in the link aggregation.
5 Type a name for the aggregation group.
6 Click Enable to make the group active.
7 Click Submit.
Page 49

C H A P T E R 4 Using the Web Device Manager
NOTE
To view the switch’s address
table, click the Monitor menu,
click Advanced, the n click MAC
Address Table.
Static MAC Addresses
The MAC address table stores all the MAC addresses that the switch
records. The switch uses this table for forwarding traffic to specific
devices, so it does not rely solely on broadcasting traffic to every port for
communication.
There are two ways to add addresses to the MAC address table:
1 The switch can record addresses and add them dynamically.
Dynamic entries remain in the table only while the associated node
is active, and the y are deleted if the node is inactive for longer than a
specified period of time (age-out time; the default is 300 seconds).
2 You can manually add MAC addresses to the table. These are called
static addresses because they remain in the table until you remove
them, even if the ass ociated node is inacti v e or tak en of f the networ k.
To add a static MAC address to the address
table
1 Click the Configure Stack menu, then click Forwarding and
Filtering.
2 Click Static MAC Addresses.
3 Click Add.
NOTE
If you want to associate a MAC
address with multiple VLANs,
you must use tag-based
VLANs.
Web Device Manager
4 In the MAC Address box, type the MAC address of a device on the
network. Do not include hyphens.
5 If port-based or tag-based (IEEE 802.1Q) VLANs are set up on the
switch, static MAC addresses are associated with specific VLANs.
Type the VLAN name (port-based VLANs) or VID (tag-based
VLANs) to associate with the MAC address.
6 I n the Switch box , select th e switch to whose ports you want to
apply the filter.
7 In the Port number box, click a port number.
For the LX and SX optional modules, the port number is MP1.
8 Click Add.
43
Page 50

C H A P T E R 4 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
NOTE
These traps are supported by the
switch:
• Power to the switch
was cycled or reset.
• Link, speed, or other
status changes on a
port.
• Spanning Tree topology
changes.
• A port is partitioned.
• Authentication failure.
Configuring Community Strings and
Trap Receivers
A trap receiver is a computer on the network that is running an SNMP
management application and receives messages sent by the switch. For
example, the switch can send a trap to the trap receiver when it detects a
change in port speed.
To specify a trap receiver
1 Click the Configure Management menu and then click Community
Strings and Traps.
44
2 In the IP Address box, type the IP address of the computer you want
to use as a trap receiver. You can specify up to four trap receivers.
3 From the Status box, click Enabled.
4 In the Community Strings box, type the trap receiver’s SNMP
application community strings. (The defaults are “public” for the
Read Community String and “private” for the Write Community
String.
5 Click Submit.
Page 51

C H A P T E R 4 Using the Web Device Manager
Monitoring Switch Activity
The Web Device Manager lets you view traffic, utilization, and error
statistics for the switch and for individual ports. For more information on
statistics, see “Port Traffic Statistics,” “Port Error Statistics,” and
“Packet Analysis” in Chapter 5.
To view port statistics
1 Click the Monitor menu, and then click Port Statistics.
2 Fr om the row of options below the page heading, click the option
you want to view:
• Traffic
• Utilization Graph
• Errors
• Packet Analysis
45
Web Device Manager
Page 52

C H A P T E R 4 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
Viewing/Changing Switch
Information
You can view general information about the switch, such as its MAC
address, firmware version, name, location, and contact person. Some of
the fields can be updated; others are read-only.
1 Click the Configure Stack menu, and then click Stack Settings.
46
2 The Switch Name, Location, and Contact fields allow you to pr ovide
additional information about the switch. You can type up to 40
characters in each field. After modifying the settings, click Submit.
Page 53

C H A P T E R 4 Using the Web Device Manager
NOTE
If you don’t have a TFTP server
application, one is provided
with Intel Device View (for
Windows) and LANDesk®
Network Manager.
Updating Switch Firmware
The Update Firmware screen sets up the switch to update its firmware
from a TFTP server. The actual firmware update occurs while the switch
is rebooting.
To update the switch’s firmware
1 Click the Reset and Update menu, and then click Update Firmware.
2 Select a mode from the Update Mode box.
• If the switch uses a network connection for do wnloading the ne w
firmware file, click Network.
• If the switch uses a SLIP connection for downloading the new
firmware file, click SLIP.
3 Type the IP address of the server that hosts the file in the TFTP
Server Address box.
4 Click Enabled from the Firmware Update box.
5 In the File Nam e box , type the nam e of the firmware file.
6 Click Submit.
The next time the switch reboots it downloads and installs the new
firmware during the boot process. If you want to view this process, you
must use a terminal program and be connected to the switch thr ough the
console port.
47
Web Device Manager
Page 54

C H A P T E R 4 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
To update the switch’s configuration file
The configuration file contains information and configuration settings
specified by the network administrator. For more information on using
configuration files, see “Upload Configuration Image File” in Chapter 5.
1 Click the Reset and Update menu and then click Change
Configuration File.
48
2 Select a mode from the Update Mode box.
• If the switch uses a network connection for do wnloading the ne w
configuration file, click Network.
• If the switch uses a SLIP out-of-band connection (for example,
via a serial port) for downloading the new configuration file,
click SLIP.
3 Type the IP address of the server that hosts the file in the TFTP
Server Address box.
4 Click Enabled from the File Download box.
5 I n the File Nam e box, type the name of the configuration file.
6 Click Submit.
The new configuration settings are applied to the switch upon the next
reboot.
Page 55

C H A P T E R 4 Using the Web Device Manager
Saving Configuration Changes and
Logging Out
Each time you make configuration changes using the Web Device
Manager, the switch immediately uses the new settings. However, when
you log out of the Web Device Manager, you are prompted to
permanently save the current configuration settings.
If you do not save the current configuration settings to the switch’s
permanent memory, the settings are lost upon the next switch reboot.
To save changes and log out
1 Click Log Out from the menu.
2 Click Save Now to save the current configuration settings. The Web
browser window closes and you are successfully logged off of the
Web Device Manager.
If you click Do Not Save, all current configuration settings are lost
the next time the switch is rebooted.
49
Web Device Manager
Page 56

C H A P T E R 4 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
50
Page 57

Using Local
NOTE
When running HyperTerminal
on Windows 2000, use the
T and b keys rather
than the arrow keys to move
between fields.
NOTE
You use the same user name
and password to log into Web
Device Manager and Local
Management.
5
Management
Overview
Another way to configure the switch is through the Local Management
interface. Local Management provides the same functionality as the Web
Device Manager using a text-based interface.
Accessing Management
You can access Local Management two di fferent ways: co nnect directly
to the switch’s serial port, or through a Telnet session (using either an IP
address you assign or the default IP address of 192.0.2.1).
Using the serial port
1 Use the enclosed null modem cable to connect the serial port of your
PC to the serial port of the switch.
2 Start a terminal emulation program (such as HyperTerminal* in
Windows* 2000). Use these communication parameters:
• 9600 baud • 1 stop bit
• 8 data bits • No flow control
• No parity
Press E to connect to the Local Management.
3 Log on to Local Management. By default, no password or user name
is assigned. To assign them, see the section titled User Accounts in
this chapter.
Page 58

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
Using Telnet
NOTE
Your workstation must be in
the same subnet as the switch
to Telnet to the switch.
1 Open a Telnet application. In Windows 98 or Windows NT*, select
Run from the Start Menu and then type: telnet E.
2 From the Terminal menu, select Preferences. Make sure the
emulation type is VT-100/ANSI and that VT100 arrows are enabled.
3 From the Connect menu, select Remote System. Enter the IP address
of the switch and click Connect. (The default IP address is
192.0.2.1.)
4 Log on to Local Management. By default, no password or user name
is assigned.
Logon Screen
52
Description
By default, no user name or password is assigned to the switch. Press
E twice to log on to the Local Manager. User names and passwords
can consist of any characters and can be up to fifteen characters in length.
Remember that user names and passwords are also case-sen sitive.
Page 59

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
NOTE
When running HyperTerminal
on Windows 2000, use the Tab
key rather than the arrow keys
to move between fields.
Help text at the bottom of the
screen provides information
on the selected item.
Navigation
The console menus provide a basic interface for configuring switch
options. The text below the data provides navigation tips.
Screen legend
Use the W Z A S keys or the T and b keys to move between
screen fields.
<Manual> Angle brackets indicate a toggle field. Use the z to
toggle selections within the field. In this example, the options change
between Manual, BOOTP (Boot Prom), and DHCP (Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol).
[255.255.255.0] Brackets indicate an input field. Select the field with the
arrow keys and type the required information. By default, Local
Management is in overstrike mode, which means it replaces existing
characters as you type.
SUBMIT Any word in all caps is a button. Use the T key or the W
Z A S keys to select the button, and press E to activate it.
Local Management
53
Page 60

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
Main Menu (Top Screen)
Description
LOCATION
To return to the Main Menu at
any time, press c T.
The Main Menu is the starting point for all other Local Management
screens. Use the W Z arrow keys to choose an option and p ress E
to display the screen.
Configure stack: Accesses menus to assign an IP address to the stack,
change port settings, or configure advanced switch settings.
Configure management: Allows you to set S NMP tr aps and tr ap
monitoring stations, administer user accounts, or update the switch’s
firmware.
Configure VLAN: Set up and administer VLANs on the switch.
Monitoring: Accesses menus to monitor traffic and activity at the port
or switch level. They also provide information on network errors and
collisions.
Tools: View the switch Trap/Event log, ping devices to check
connectivity, save the current switch configuration to an image file on a
server.
SAVE SETTINGS: Saves configuration changes to the switch’s flash
memory. Any changes not saved to memory are lost on the next reboot.
LOGOUT: Returns to the logon screen.
54
Page 61

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
Configure Stack
Description
IP settings: Configures the switch’s (stack’s) IP address.
Port settings: Configures port speed, enables and disables ports, and
displays link status.
Optional module settings: Configures the module’s speed and duplex
settings, enables and disables ports, and displays link status.
Stack settings: Sets stack’s identification, displays detailed information
about the switch hardware and firmware, an d configures some ad vanced
switch settings.
Spanning Tree Protocol: Configures Spanning Tree for the entire
switch or individual ports.
Forwarding and filtering: Adds, removes, or locks the switch’s address
table, enables IGMP snooping, and sets filters for specific MAC
addresses.
Port mirroring: Sends a copy of data from one port to another for
monitoring and troubleshooting purposes.
Link aggregation: Combine ports on the switch to increase bandwidth.
Broadcast storm control: Configures ports to drop excessive bro adcast
traffic before it floods the network.
Local Management
55
Page 62

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
IP Settings
NOTE
The default IP address for the
switch is 192.0.2.1
If the 530T is in a stack of
switches, there is only one IP
address.
Default VLAN for SNMP agent:
Port-based: DEFAULT_VLAN
802.1q-based: VID=1
56
IP Settings
Description
Switch MAC address: The unique hardware address assigned by Intel.
Current settings: The switch’s current IP configuration.
New settings: Assign a new IP configuration to the switch.
• Assign IP: Indicates if the switch will use a BOOTP or DHCP
server to obtain an IP address dynamically, or if you will assign
an address manually.
• IP address: The IP configuration used by the switch. Use the IP
address shown here to access the switch through Telnet or a ping
test.
• Subnet mask: Should match the mask for other devices on the
network.
• Default gateway: The IP address of the device that routes to
different networks—typically, a router or routing server. Set this
option to manage the switch remotely.
• VLAN or VLAN ID (port-based or tag-based VLANs only):
Specify a VLAN where the switch’s SNMP management agent
will reside. This option appears only when port-based and IEEE
802.1Q VLANs are active on the switch.
SUBMIT: Submits the changes and returns you to the Conf igure Device
screen. You must save the changes to the switch’s flash memory and
reboot the switch for the new IP settings to take effect.
Page 63

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
Port Settings
Port Settings
Description
Select switch: Press the z to select a switch to configure.
Configure ports: Press the z to select a range of ports to
configure.
State: Press the z to toggle the field and disable or enable ports.
Speed/Duplex: Press the z to toggle the fiel d ’s options and
change the speed and duplex of the port. You can set the port to autonegotiate speed, or to 10Mbps or 100Mbps at half- or full-duplex.
Flow Ctrl (Control): Press the z to enable or disable flow
control.
Priority: Press the z to change the settings. The <Frame> setting
reads the packet’s 802.1p priority tag and handles it accordingly. The
<Low> or <High > settings force the packet into one of two priority
queues. Forcing a packet into a queue does not retag the packet.
Link: Indicates the port’s current link status:
• -- : No device link or port is disabled.
• 10M/100M: The port’s speed, either 10Mbps or 100Mbps.
• Full/Half: A device is connected at full- or half-duplex.
• IEEE/BackP: The type of flow control, either IEEE PAUSE
frames or backpressure.
• Partitioned: Port was disabled due to a partition error.
• Source mirror/Target mirror: The port being mirrored and
where the data is being sent.
57
Local Management
Page 64

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
Optional Module...
NOTE
This screen is for Module A’s
settings; the Matrix Module is
not configurable.
This screen also allows you to
configure the Module A ports
for any 535T switches in the
stack.
1000SX and 1000LX modules
connect at 1000Mbps, fullduplex only.
58
Configure Optional Module
Description
Select switch: Press the z to select a switch.
Module A: Displays the type of module installed.
State: Press the z to toggle the field and disable or enable ports.
Speed/Duplex: Press the z to toggle the field’s options and
change the speed and duplex of the port. You can set the port to autonegotiate speed or force to 100Mbps at half- or full-duplex (535T
modules only).
Flow control: Press the z to enable or disable flow control.
Priority: Press the z to change the settings. The <Frame> setting
reads the packet’s 802.1 priority tag and handles it accordingly. The
<Low> or <High > settings force the packet into one of two priority
queues. Forcing a packet into a queue does not retag the packet.
Link: Indicates the port’s current link status:
• --: Indicates no device link or port is disabled.
• 10M/100M/1000M: Th e port’s speed, either 10Mbps, 100Mbps,
or 1000Mbps (535T modul es only; 53 0T modules are 1000Mbps
only).
• Full/Half: A device is connected at full- or half-duplex.
• IEEE/BackP: The type of flow control, either IEEE PAUSE
frames or backpressure.
• Partitioned: Port was disabled due to a partition error.
• Source mirror/Target mirror: The port being mirrored and
where the data is being sent.
Page 65

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
Stack Settings
NOTE
It’s a good idea to write down
both the firmware version and
Boot PROM version, in case
you need to contact Intel
Customer Support.
Stack Settings
Description
Name: The name of the switch, up to 40 characters long.
Location: The location of the switch, up to 40 characters long.
Contact: The contact person or phone number for the switch, up to 40
characters long.
MAC address: The unique hardware address assigned by Intel.
Boot PROM version: The version of the switch’s boot code.
Firmware version: The version of the firmware installed on the switch.
You can update this software through the Update firmware and
configuration files screen.
Serial number: The hardware serial number for the switch.
VIEW STACK INFORMATION: Use this to view information about
the control switch (530T) and any member switches (535Ts) in the stack.
CONFIGURE ADVANCED SETTINGS: Advanced switch settings
such as port auto-partition and Head of Line blocking.
Local Management
59
Page 66

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
Stack Settings
View Stack...
NOTE
When the 530T is in a stack
with 535T switches, the 530T
is the control switch. The other
ports are numbered according
to how they are plugged into
the Matrix Module.
Member Switch 2 = Switch 1
Member Switch 3 = Switch 2
Member Switch 4 = Switch 3
View Stack Information
Description
The View Stack Information screen displays information about the
control switch (535T) and any member switches (530T) that are in the
stack.
Control switch: The name of the control switch. This is always Intel
Express 530T Switch.
Module A: The type of module installed.
Stack Matrix Module: A message indicating whether or n ot the Matrix
Module is installed.
Hardware version: The hardware version installed on each switch.
Member X switch: The module and hardware version for each member
switch in the stack.
60
Page 67

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
Stack Settings
Configure Advanced...
Configure Advanced Switch
Settings
Description
Auto-partition capability on all ports: If this option is enabl ed, the
switch partitions the port when more than 61 collisions occur
consecutively while receiving data. The first time the switch receives a
good packet it then unpartitions the port. If a port is partitioned the switch
can transmit data over this port, but not receive data.
Head of Line (HOL) blocking prevention: If this option is enabled it
prevents the forwarding of data to a port that is blocked. Norm ally, when
the switch sends traffic to a port it goes to the port’s transmit queue and
then is sent out. If the port’s transmit queue is already busy trying to send
out data, then the switch will place the waiting traffic in the buffer
memory until the port is ready to send it out.
However, if the port’s transmit queue remains full, the switch fills up
more of the buffer with traffic waiting to be sent on that port. HOL
blocking works on the assumption that it is better to drop the traffic
waiting in the buffer than to continue using more memory and impacting
performance across all the ports.
High-priority packet service ratio: This option lets you determine how
many high-priority packets are sent out by the switch before sending a
low-priority packet. For example, a ratio of 8 high:1 low means that the
switch will send out eight high-priority packets before sending out one
low-priority packet.
Local Management
61
Page 68

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
Spanning Tree Protocol
NOTE
Only once instance of
Spanning Tree is supported
per switch (or per stack).
62
Configure Spanning Tree Protocol
Description
The IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol specification prevents loops
in a network by allowing only one acti ve path bet ween any two netw ork
devices at a time.
Spanning Tree status: Use the z to enable or disable support fo r
the Spanning Tree Protocol, where the entire switch is a bridge for which
you can set spanning tree parameters. (Note: If you are running 802.1Q
VLANs, spanning tree must be enabled and will be turned on
automatically by the switch.)
Topology changes: The number of times the sp anning tree has ch anged
its configuration.
Time since change: The elapsed time (since the last switch reboot) since
the spanning tree last changed its topology (the paths used to get through
the network).
Root MAC address, Root path cost, Root port: Information used by
the root bridge in the same spanning tree as the switch.
Switch priority: Accepts a number from 0 to 65535 (default is 32768).
The device with the lowest number becomes the root device (starting
point for the spanning tree).
Hello time: Accepts a number from 1 to 10 seconds (default is 2
seconds). This is the time between transmissions of configuration
BPDUs (Bridge Protocol Data Units) when the switch is, or is attempting
to become, the root in the spanning tree.
Page 69

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
Max age: Type a number from 6 to 40 seconds (default is 20 seconds).
This is the maximum time that information from a configuration BPDU
is used by the switch before it is discarded.
Forward delay: Type a number from 4 to 30 seconds (default is 15
seconds). This is the amount of time between port states when the
spanning tree is changing its status from blocking to forwarding.
CONFIGURE SPANNING TREE FOR PORTS: Takes you to the
screen where you can set spanning tree values for individual ports.
Local Management
63
Page 70

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
Spanning Tree Protocol
Configure STP for...
Configure Spanning Tree for Ports
Description
Select switch: The switch you want to configure for spanning tree.
STP State: Use the z to enable or disable each port to be active
in the spanning tree.
Cost: Accepts a number from 1 to 65535 (default is 10). This value is
used by the Spanning Tree Protocol to determine alternate routes in the
network to forward traffic. The higher the cost of a port, the lower the
chance of this port being used to forward traffic. When possible, assign
a port a low cost if it is connected to a fast network segment.
Priority: Accepts a number from 0 to 255 (default is 128) to set the
port’s priority in the spanning tree. The higher the value, the lower the
chance of this port being used as the root port. If two por ts on the switch
have the same priority value, the spanning tree uses the port with the
lowest number. For example, the spanning tree would choos e port 1 over
port 4 if they both had the same priority setting.
64
Page 71

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
Forwarding and Filtering
Forwarding and Filtering
Description
Lock address table: Use the z to toggle field values. <Yes>
prevents the switch from learning new MAC addresses. Any existing
addresses that the switch has learned remain in the address table.
MAC address aging: Sets the time interval at which the switch scans its
MAC address table to determine the age of entries.
Configure IGMP snooping: Sets Internet Group Management
Protocols (IGMP) options for multimedia applications, such as desktop
video conferencing, that use IP multicast addresses.
Configure static MAC addresses (forwarding): Allows permanent
mapping between a network device and a port.
Configure port security: Configures the switch to allow the
transmission of authorized traffic only over a particular port.
Configure MAC address filtering: Allows the switch to drop traffic
from a specific source.
Configure Ethernet multicast filtering: Blocks or forwards traffic over
each port for Ethernet (MAC-based) multicast groups.
Local Management
65
Page 72

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
Forwarding and Filtering
IGMP Snooping
NOTE
If tag-based (IEEE 802.1Q) or
port-based VLANs are
currently running and you
want to enable IGMP snooping
for any of the VLANs, you must
enable IGMP snooping for
each VLAN separately. The
switch supports a maximum of
24 VLAN IGMP snooping
sessions.
66
Configure IGMP Snooping
Description
IGMP Snooping (Internet Group Management Protocol) is a feature that
allows the switch to forward multicast traffic intelligently. The switch
“snoops” the IGMP query and report messages and forwards traff ic only
to the ports that request the multicast traffic. This prevents the switch
from broadcasting the traffic to all ports and possibly affecting network
performance.
IGMP requires a router that learns about the presence of multicast groups
on its subnets and keeps track of group membership. Multicasting is not
connection oriented, so data is delivered to the requesting hosts on a besteffort level of service.
VLAN name (when port-based or ta g- based VLANs are running):
The VLAN for which IGMP snooping is enabled. You can also enable
IGMP snooping for a VLAN in the Configure VLAN section.
IGMP snooping state: Use the z to enable or disable IGMP
Snooping.
IGMP snooping age-out timer: Specify the acceptable time (in
seconds) between IGMP queries since the switch last received an IGMP
query from the multicast server. The default time is 300 seconds. A query
allows the server to determine which network hosts are (or want to be)
part of the IP multicast group, and are configured and ready to receive
traffic for the given application.
Page 73

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
Forwarding and Filtering
Configure Static MAC...
NOTE
If tag-based or port-based
VLANs are currently running,
you must assign each static
MAC address to a specific
VLAN.
Configure Static MAC Addresses
Description
Static MAC addresses are MAC addresses that remain in the switch’s
address table, whether the device is physically connected to the switch.
After you define a static MAC address, it remains in the switch’s address
table until you remove it.
Enter MAC: Type the MAC address you want to permanently add to the
address table.
VLAN or VLAN ID (when port-based or tag-based VLANs are
running): When VLANs are active on the switch you can define static
MAC addresses for each VLAN. If port-based VLANs are active press
the z to select a VLAN. If tag-based VLANs are active type the
VLAN ID that the static MAC address will be assigned to.
Select switch: Use the z to select the switch you want to
configure.
Select port: Use the z to select a port on the switch where the
switch forwards traffic.
ADD/DELETE: Use these buttons to add or remove a MAC address
from the switch’s table.
Local Management
67
Page 74

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
Forwarding and Filtering
Configure Port...
NOTE
You must first configure port
security and then configure a
static MAC address.
Configure Port Security
Description
Port security prevents unauthorized access of a port by “securing” a list
of specific MAC addresses to a port. If the switch sees a MAC address
that is not on the secured list, it discards the traffic.
68
To set port security from Local Management
1 Fr o m the Configure Device screen, select Forwarding and Filtering.
2 From the menu select Configure Port Security.
3 Press the z to select the switch you want to configure.
4 Select a port you want to secure. Press z in the Lear ning f ield
to disable the port’s ability to learn new MAC addresses.
5 Press q to move up a level and select the Configure Static MAC
Addresses screen.
6 Define a list of MAC addresses and as sign them to th e same port you
secured in the Port Security screen.
To turn off port security
1 Fr o m the Configure Device screen, select Forwarding and Filtering.
Select Configure Port Security from this menu.
2 Press the z to select the switch you want to configure.
3 Select the port on which you want to disable security. Press the
z in the Learning field to disable security and allow the port
to learn new MAC addresses.
Page 75

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
Forwarding and Filtering
Configure MAC...
NOTE
If tag-based (IEEE 802.1Q) or
port-based VLANs are
currently running, you must
assign each MAC address filter
to a specific VLAN.
Configure MAC Address Filter Table
Description
MAC address filtering allows the switch to drop unwanted traffic. The
switch will drop any traffic when it sees the specified MAC address in
either the source address or destination address of the incoming packet.
For example, if your network is congested because of high utilization
from a specific MAC address, you can filter all traffic transmitted from
that address and restore network flow, while you troubleshoo t the
problem.
Enter MAC: Type the MAC address you want to filter.
VLAN/VLAN ID (when port-based or tag-based VLANs are
running): If VLANs are active on the switch you can set MAC address
filtering on a per VLAN basis. For port-based VLANs, press the z
to select the name of VLAN. For tag-based VLANs, type in the VLAN
ID where the MAC address belongs.
ADD: Press e to activate the filter and add the MAC address to the
list.
DELETE: Press e to remove the filter for the specified MAC
address.
Local Management
69
Page 76

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
Forwarding and Filtering
Ethernet Multicast...
NOTE
If tag-based (IEEE 802.1Q) or
port-based VLANs are
currently running, you must
assign each multicast filter to a
specific VLAN.
Configure Ethernet Multicast
Filtering
Description
Ethernet multicast filters allow you to define which ports can receive
ethernet multicast traffic from a specific multicast MAC address. This is
similar to IGMP snooping, except you define everything manu ally.
Multicast address: Type the MAC address to which you want to apply
a filter.
VLAN/VLAN ID: If VLANs are active on the switch you can set
Ethernet Multicast filtering on a per-VLAN basis. For port-based
VLANs, press the z to select the name of VLAN. For tag-based
VLANs, type in the VLAN ID where the multicast address belongs.
ADD: Press e to activate the filter and add the address to the list.
DELETE: Press e to remove the filter for the specified address.
70
Adding/Deleting a multicast filter
1 In the Multicast address field, type a multicast address.
2 If the switch is running tag-based or port-based VLANs, select a
VLAN to locate the filter.
3 Select ADD using the arrow keys and press e.
4 To remove a filter, type in the MAC address in the Multicast field,
select DELETE, and press e.
Page 77

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
Forwarding and Filtering
Ethernet Multicast...
Multicast Filters...
Ethernet Multicast Filtering (Ports)
Description
Select switch: Press the z to select a switch to configure.
Multicast address: Displays the multicast address you want to filter.
Action: Use the z to select whether to block or forward traffic to
the selected port.
APPLY CHANGES: Applies the changes to the multicast filter once
you have configured the ports.
Local Management
Modifying a multicast filter
1 Under the Configure Ethernet Multicast Filter screen use the arrow
keys to select an address from the list on the right s ide of the scr een.
Press e.
2 Decide which ports should receive the multicast traffic by using the
z to set Forward or Block for each port.
3 Select APPLY CHANGES and press e. This activates the
changes to the multicast filter and returns you to the previous screen.
71
Page 78

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
Port Mirroring
CAUTION
Do not mirror traffic to a target
port that is connected to
network devices other than a
protocol analyzer. Their
behavior may be
unpredictable.
If a port is part of an
aggregated link, it cannot be
configured as the target port
for a port mirror. However, a
port in an aggregated link can
serve as the source port for a
port mirror.
Port Mirroring
Description
Port mirroring is a useful diagnostic tool because it allows you to send a
copy of the good Ethernet frames transmitted or received on one port to
another port. On the second port you can attach a protocol analyzer to
capture and analyze the data without interfering with the client on the
original port.
Source switch: Use the z to select the switch you want to
configure.
Source port: Use the z to select the port whose traffic you want
to mirror.
Target switch: Use the z to select the switch you want to receive
mirrored traffic.
Target port: Use the z to select a port to receive the mirrored
traffic. This is a port to which you have connected a protocol analyzer.
State: Use the z to enable or disable the port’s mirror.
72
Page 79

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
Link Aggregation
NOTE
All custom settings for a port
(including VLAN membership)
are lost when you add that port
to a link aggregation.
You cannot link aggregate
ports from different switches
in the stack.
Link Aggregation
Description
Link aggregation is a way of combining ports on the switch to increase
the available bandwidth and provide redundancy. All ports in the
aggregated link take on the characteristics of the anchor por t. This means
that if you set the anchor port to 100Mbps full duplex, all the ports
aggregated to that anchor port will share the same setting.
Select switch: Use the z to set the switch you want to configure.
Anchor Port: This shows the first port in the link aggregation.
Width: Use the z to set the total number of (consecutive) member
ports in the aggregated link. The minimum number of ports for an
aggregated link is two, and the maximum is eight. The link aggregation
width includes the anchor port.
Group Name: Assigns a name to the aggregated links for management
or identification purposes.
Status: Use the z to enable or disable the aggregated link.
Local Management
73
Page 80

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Stack
Broadcast Storm Control
Broadcast Storm Control
Description
This feature allows you to filter out broadcasts from faulty devices and
prevent them from degrading network performance.
Select switch: Use the z to select the switch to configure.
Setting: Use the z to enable or disable broad cast storm control on
this port.
Upper Threshold: Accepts a value from 1-20%. The default value is
20%. This control lets you set the threshold of broadcast traffic on a port
(shown as a percentage of the port’s total bandwidth) that will activate
broadcast storm control. When the amount of broadcast traffic on the port
exceeds the upper threshold, the port drops all broadcast traffic. When
broadcast traffic falls down below the threshold the switch will
automatically start forwarding broadcast traffic again.
74
Page 81

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Management
Configure Management
Description
Configure community strings and trap receivers: Sets the switch’s
community strings and specify trap monitoring stations.
Administer user accounts: Use this menu to configure user accounts.
You can add or delete users, update passwords, and change a user’s
access rights.
Update firmware and configuration files: Configures the switch’s
internal software and to specify the location of configuration files.
Reset and console options: Reboots the switch or changes the settings
on the serial port. You can also use this menu to set the switch back to its
factory defaults.
Local Management
75
Page 82

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Management
Community Strings and...
NOTE
The switch supports these
traps:
• Power to the switch
was cycled or reset.
• Link, speed, or other
status changes on a
port.
• Spanning Tree topology
changes.
• A port is partitioned.
• Authentication failure.
Community Strings and Trap
Receivers
Description
76
Use this screen to send alerts to PCs with SNMP management
applications (such as OpenView*) installed.
• Current read community: Sets a password for viewing (not
changing) the switch configuration. The string you define here
must match the read community string defined in an SNMP
application. The default read community string is “public.”
• Current write community: Sets a password for viewing and
changing the switch configuration. The string you define here
must match the write community string defined in an SNMP
application. The default write community string is “private.”
Trap Receiving Stations: When an event occurs, the switch
automatically alerts the SNMP management application by sending a
trap to the SNMP management stations (for ex ample, PCs) defined here.
• Station IP Address: The IP addresses of PCs with SNMP
applications (such as Intel
®
Device View or LANDesk Network
Manager) installed.
• Community string: Type a string for the trap that matches the
community string defined in the SNMP management application.
If you don’t define one, the default is “public.”
• State: Enables or disables sending of traps to the specified trap
receiver.
Page 83

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Management
Administer User Accounts
User Accounts
Description
Add Users/Change Passwords
• Username: By default, no username is assigned. Usernames can
consist of any character and can be up to fifteen characters long.
You can define three usernames.
• Old password: Used when changing the password of a current
user. If this is a new account, you can skip over to the New
password field. By default, no password is assigned.
• New password: Sets a new password for accessing Local
Management. The one you specify here is used the next time you
reset the switch or log out and log in on Local Management.
Passwords are case-sensitive and can be up to fifteen characters
long.
• Confirm password: Verifies the entry in the New password
field.
• Access level: Use the z to determine a user’s access
rights. Administrators can make any changes to Local
Management. All other users (categorized under Normal user)
can view information but cannot make changes. To change a
user’s access rights, see Modify User Accounts.
• APPLY CHANGES: Select this button to save changes when
adding users or changing passwords.
Local Management
77
Page 84

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
Modify User Accounts
Access level: Use the z to change access rights for the user.
Delete: The default value is <No>. To delete an account, use the
z to change the value to <Yes>.
APPLY CHANGES: Saves changes when modifying or deleting user
accounts.
How to Manage User Accounts
System Administrators can create up to three user accounts for managing
the switch. You can also change the access rights for current users and
delete user accounts. Make sure you always set up at least one
Administrator account.
To create a user account
1 Fr o m the Main Menu, select Configure Management. Under this
menu select Administer User Accounts and press E.
2 On the User Accounts screen, type the name of the new user in the
Username field and press E.
3 Since this is a new user, press T to skip the Old password field
and go to the New password field.
4 Type the password for the new user and press E. Passwords
are case-sensitive and can be up to eight characters long.
5 To confirm the new password, retype it in the Confirm new password
field. Press E.
6 To select the access rights for the new use, press the z.
7 To save the information, press T to select SAVE CHANGES
(below the Confirm ne w pass word f ield) and press E. The new
account appears in the list under Modify User Accounts.
78
Page 85

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
To change a password
1 From the Main Menu, select Configure Manag ement, press E.
Under this screen, select Administer User Accounts and press
E.
2 In the Username field, type the username of the account for which
you want to change the password. Press E.
3 Type the current password in the Old password field and press
E.
4 Type the new password in the New password field and press
E.
5 To confirm the passwo rd and retype it in the Confirm new password
field, press E.
6 To save the new password, press T to select SAVE CHANGES
(below the Confirm new password field) and press E.
To modify a user’s access level
1 From the Main Menu, select Configure Manag ement, press E.
Under this screen select Administer User Accounts and press
E.
2 Press T to select the account to be modified under Access
Level.
3 Press the z to change the user’s access rights. Users with
Administrator access can make changes to the management
configuration; users with Normal User access can view the
configuration but cannot make changes.
4 To save changes, press T to select SAVE CHANGES at the
bottom of the screen and press E.
Local Management
To delete a user account
1 From the Main Menu, select Configure Manag ement, press E.
Under this screen, select Administer User Accounts and press
E.
2 Select the account to be removed under Delete.
3 Press the z to toggle the field from <No> to <Yes >.
4 To remove the user account, press T to select SA VE CHANGES
at the bottom of the screen and press E.
79
Page 86

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Management
Update Firmware and...
NOTE
Check Intel’s Customer
Support Web site for firmware
updates to the 530T switch.
Update Firmware and Configuration
Files
Description
80
Software update mode: Use the z to select whether to update the
switch’s firmware over the network or through a SLIP connection.
TFTP server address: IP address of the server used as the TFTP server.
Update Management Module Firmware
• Firmware update: Use the z to enable or disable the
firmware update. When enabled, the switch searches for the
TFTP server specified at the top of the screen and attempts to
update the firmware.
• Firmware file name: Path and filename of the firmware located
on the server.
Change Configuration File
• Config file download: Use the z to enable or disable the
ability to download a configuration file. When this field is
enabled, the switch searches the TFTP server specified at the top
of the screen.
• Config file name: Path and filename of the configuration file
located on the server.
Last TFTP server address: The IP address of the last TFTP server
accessed by the switch.
REBOOT TO START UPDATE: Starts the update process. The switch
reboots and downloads the specified file.
Page 87

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure Management
Reset and Console Options
Reset and Console Options
Description
Reset Option
• Reboot stack: Resets the stack. If you changed the IP
configuration or login setting, the new settings take effect after
you select this option.
• Reset stack settings to factory defaults: This clears any IP
address or current changes and resets the stack back to its factory
defaults. All counters are cleared and the switch starts sending
BOOTP requests.
Serial Port Settings
• Port setting: Con figures the swit ch’s serial port for out-of-band
(SLIP) management. Press the z to toggle the field from
<Console> to <SLIP>. Settings take effect on the next reboot.
• Console timeout: Logs out a user after a period of inactivity.
Settings are from 0-90 minutes in 15-minute increments. A
setting of <0 mins> means no timeout. The default is 60 minutes.
Local Management
81
Page 88

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure VLAN
(if switch is in Default Mode)
Configure VLAN Operation Mode
Description
This screen allows you to activate or change the type of VLAN operating
on the switch. If there are no VLANs active on the switch, this is the first
screen displayed when you select Configure VLAN from the Main
Menu. By default, VLANs are not active on the Express 530T switch so
they must be turned on before you can start configuring them.
The Express 530T supports only a single type of VLAN operating at a
time. However, you can have multiple VLANs of the same type.
Select the type of VLAN: Press z to change the type of VLAN
on the switch. The 530T switch supports two types of VLANs: portbased and IEEE 802.1Q (tag-based) VLANs.
APPLY: Makes the changes to the VLAN active and reboo ts the switch.
Note: To change between VLAN types the switch must be rebooted.
1 Select C onfigure VLAN from the Main Menu.
2 Fro m the Configure VLAN menu, select VLAN Operation Mode.
3 Press z to change the type of VLAN on the switch. Press
e.
4 Select the APPLY button and press e. This reboots the switch
and changes the VLAN mode.
82
Page 89

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure VLAN
NOTE
You can have a maximum of
24 port-based VLANs on the
switch.
VLAN membership can span
between the switches in a
stack. (Ports from any switch
in a stack can be members of a
VLAN.)
Configure Port-based VLANs
Description
A port-based VLAN allows you to create multiple VLANs each with its
own broadcast domain and member ports. For example, if port 5 is in
VLAN_1 and port 10 is in VLAN_2 the two ports cannot communicate
with each other even though they are part of the same switch. Ports can
be members of only a single port-based VLAN. Any port that is not a
member of a user-defined VLAN is a member of the DEFAULT_VLAN.
VLAN operation mode: Changes the type of VLAN operating on the
switch, or disables VLANs entirely.
Add a port-based VLAN: Creates a port-based VLAN and adds ports
to the VLAN.
Edit/Delete a port-based VLAN: Selects a VLAN to change port
membership in the VLAN, or removes a VLAN from the switch.
Local Management
83
Page 90

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure VLAN
Add a Port-based VLAN
Add a Port-based VLAN
Description
VLAN name: This field allows you to assign a name to the VLAN.
Names can consist of any character (no spaces) and be up to 12
characters long. After a VLAN is created the name cannot be changed. If
you want to change the name you need to delete the VLAN, create a new
one, and assign the ports to the new VLAN.
Select switch: Press the z to select a switch to configure.
Member: Determines which ports will participate in the VLAN being
created. Ports can be members of only one port-based VLAN. Press the
z to toggle the field for the following options:
• <Yes>: The port will be a member of the VLAN
• <No >: The port will not be a member of the VLAN.
• – : The port is part of an aggregated link.
• N/A : The port is already participating in another VLAN. Ports
can belong to only one VLAN.
APPLY: Select this button and press e to create the VLAN and
activate the settings.
84
Page 91

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
NOTE
Ports from any switch in the
stack can be members of the
VLAN; follow this procedure to
add ports from each switch, on
switch at a time.
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure VLAN
Edit/Delete a Port-based..
Edit VLAN
To create a port-based VLAN
1 Select C onfigure VLAN from the Main Menu.
Note: Make sure the switch’s current VLAN operation mode is set
to port-based VLAN. If another type of VLAN is running, refer to
“Configure VLAN Operation Mode” in Chapter 5 to change the
VLAN operation mode.
2 Select Add a Port-based VLAN and press e.
3 Type a name for the new VLAN and press e.
4 Select the switch whose ports you want to be members of the
VLAN, using the z to toggle between switches.
5 Select p orts to add to the VLAN by using the z to toggle the
Member field to Yes.
6 Select the APPLY button and press e.
Edit/Delete a Port-based VLAN
Local Management
Description
Action: Delete a VLAN or change its port membership. Press the
z to toggle Edit or Delete and then use the T or S keys to
select a VLAN and press e. The DEFAULT_VLAN cannot be
deleted from the switch.
VLAN Name: The names of existing port-based VLANs.
Ports: Total number of member ports in the specified VLAN.
85
Page 92

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure VLAN
Edit/Delete a Port-based...
Edit VLAN Membership (Port-based)
Description
This screen is very similar to the VLAN creation screen. You can change
the membership status of ports within the VLAN but y ou canno t change
the name of the VLAN.
VLAN name: The name of the VLAN you are editing.
Select switch: Press the z to select a switch to configure.
Member: Determines which ports will participate in the current VLAN.
Ports can be members of only one port-based VLAN. Press the z
to toggle the field for the following options:
• <Yes>: The port will be a member of the VLAN.
• <No >: The port will not be a member of the VLAN.
• – : The port is part of an aggregated link.
• N/A : If this is displayed it means the port is already
participating in another VLAN. Ports can belong to only one
VLAN.
APPLY: Select this button and press e to activate the settings.
86
Page 93

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure VLAN
Configure IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
Description
VLAN operation mode: Changes the type of VLAN operating on the
switch, or to disable VLANs entirely.
Create an IEEE 802.1Q VLAN: Creates a new 802.1Q VLAN and add
ports to the VLAN.
Edit/Delete an IEEE 802.1Q VLAN: Changes port membership of an
existing VLAN, or you can remove a VLAN from the switch.
Configure port VLAN ID (PVID) for untagged and priority-tagged
traffic: Assigns a VLAN to incoming packets without a VID.
GVRP and ingress filtering settings: Sets port-level options for
dynamic VLAN creation and packet filtering by VLAN.
Local Management
87
Page 94

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure VLAN
Create an 802.1Q VLAN
NOTE
Devices on the network must
have the same VID as the
VLAN to be on the VLAN and
be able to communicate.
NOTE
A ‘+’ next to the Member
toggle indicates that the port is
a member of more than one
VLAN.
Add an IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
(Configure Port Membership)
Description
VLAN name: This field allows you to assign a name to the VLAN. The
name can consist of any character (no spaces) and be up to 12 charac ters
long. Once a VLAN is created the name cannot be changed.
VLAN ID: Assign a unique ID number to the VLAN. This number will
be used to identify all packets belonging to that VLAN. Type in a number
from 2 to 4094. The DEFAULT_VLAN (created when you select a
VLAN operation mode) is assigned a VID of 1.
Allow IGMP snooping: Press the z to determine if the switch
will perform IGMP snooping on this VLAN. There are a maximum of 24
IGMP snooping sessions allowed.
Select switch: Press the z to select a switch to configure.
Member: Identifies which ports will participate in the VLAN being
created. Press the z to toggle the field for the following options:
• <Yes>: The port is a member of the VLAN
• <No >: The port is not a member of the VLAN.
• – : The port is part of an aggregated link.
NEXT: Select this button and press e to access the Add an IEEE
802.1Q VLAN (Configure Port Tagging) scre en.
88
Page 95

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure VLAN
Create an 802.1Q VLAN
Add an 802.1Q VLAN...
Add an IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
(Configure Port Tagging)
Description
VLAN name: Displays the VLAN name assigned on the Add an IEEE
802.1Q VLAN (Configure Port Membership) screen.
VLAN ID: Displays the VLAN ID assigned on the Add an IEEE 802.1Q
VLAN (Configure Port Membership) screen.
Select switch: Displays the switch that is being configured.
Action: Indicates whether the device connected to this port supports
tagging (press z).
PREV: Returns to the Add an IEEE 802.1Q VLAN (Configure Port
Membership) screen.
APPLY: Returns to the Configure IEEE 802.1Q VLANs screen.
Local Management
89
Page 96

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
NOTE
Determine which devices on
your network support tagbased VLANs and which do
not, before you start this
procedure.
How to Configure 802.1Q VLAN
Setting up a 802.1Q VLAN is a two-step process. The first step is to
create a VLAN on the switch and assign member p orts. The seco nd step
requires you to make sure that tagging is set up properly for your attached
devices. For devices that don’t support tagging an extra configuration
step is required.
Step 1: Create an 802.1Q VLAN and add ports
1 From the Main Menu, select Configure VLAN.
Note: Make sure the switch’s cur rent VLAN operation mode is set to
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN. Refer to “Configure VLAN Operation Mode”
in Chapter 5 to change the VLAN operation mode.
2 Select Create an IEEE 802.1Q VLAN and press E.
3 Type a name for the new VLAN (no spaces) and press E.
4 Type a VLAN ID and press E. The ID number can be any
number from 2 to 4094.
5 Determine if you want to allow IGMP Snooping on this VLAN. This
is important since the switch can support more 8 02.1Q VLANs th an
the maximum of 24 IGMP snooping sessions available.
6 Press the z to display the switch you want to configure.
7 Select ports to add to the VLAN. Use z to toggle the Member
field to Yes.
8 Select the NEXT button and press E.
90
Step 2: Configure tagging for member ports
If the device on a particular port does not support tags , configure that port
as untagged. This ensures that the switch removes tags from packets
before they leave the switch for the device. If you configure a port as
untagged, proceed to step 3 (Configure VLAN for untagged devices)
when you are finished with step 2.
1 Press z to select Tag or Untag for each port that is a member
of the VLAN.
2 Select the APPLY button and press E.
If you configured any o f the po rts in the VLAN as Untagg ed, pro ceed to
step 3 to configure ports for untagged devices and associate those ports
with a PVID (port VLAN ID).
Page 97

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
Step 3: Configure VLAN for untagged devices
Even if the device attached to the switch doesn’t support 802.1Q tags it
is still possible for the device to participate in the VLAN. When
communicating with untagged devices the switch performs two
functions:
First, the switch determines how to forward untagged traffic. Fo r
untagged traffic, the switch assigns a default VID to the incoming traffic
from the untagged device. Normally, all untagged traffic receiv ed on the
switch is assigned a VLAN ID=1 or the DEFAULT_VLAN. You can
change this PVID to the VID of the VLAN you want the port to use.
Next, the switch strips 802.1Q tags before sending traffic to the
untagged device. When the switch needs to send traffic from a port to an
untagged device, it strips the 802.1Q tag, otherwise the un tagged device
may not understand how to process the VID tag.
Use the following steps to add an untagged device to an 802.1Q VLAN.
1 Ensure that the port is a member of the VLAN. Refer to the proce-
dure in ste p 1 (previous page) t o add a port to an 802.1Q VLAN.
2 Fro m the Configure VLAN menu, select Configure VLAN ID for
untagged and priority-tagged traffic and press E.
3 Press the z to display the switch you want to configure.
4 Select the port where the untagged device is connected. For
example, port 7.
5 Type the VID of the VLAN you want the port to belong to and press
E. This is the same ID number you entered in step 1.
By specifying a VID you set the switch to assign a particular VID to any
incoming traffic it receives on that port.
Local Management
91
Page 98

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure VLAN
Edit/Delete an 802.1Q...
Edit/Delete an IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
Description
Use this screen to select a VLAN to edit the port membership in the
VLAN or delete the VLAN entirely from the switch.
Action: Press the z to toggle between <Edit> and <Delete>, then
select a VLAN from the list and press E.
VLAN name: The name of the VLAN you are configuring.
VLAN ID: A unique number assigned to identify an 802.1Q VLAN.
92
Page 99

C H A P T E R 5 Using Local Management
LOCATION
Main Menu
Configure VLAN
Edit IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
NOTE
A ‘+’ next to the Member
toggle indicates that the port is
a member of more than one
VLAN.
Edit an IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
(Configure Port Membership)
Description
VLAN name: Name of the VLAN you are editing or deleting.
VLAN ID: Assigns a unique ID number to the VLAN. This number will
be used to identify all packets belonging to that VLAN. Type in a number
from 2 to 4094.
Allow IGMP snooping: Press the z to determine if the switch
will perform IGMP snooping on this VLAN. There are a maximum of 24
IGMP snooping sessions allowed.
Select switch: Press the z to select a switch to configure.
Member: Determines which ports are part of the VLAN being created.
Press the z to toggle the field for the following options:
• <Yes>: The port will be a member of the VLAN.
• <No >: The port will not be a member of the VLAN.
• – : The port is part of an aggregated link.
NEXT: Select this button and press e to access the Edit an IEEE
802.1Q VLAN (Configure Port Tagging) scre en.
Local Management
93
Page 100

C H A P T E R 5 Intel® Express 530T Switch Users Guide
Edit an IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
(Configure Port Tagging)
Description
94
This screen allows the switch to manage outgoing packets that do not
contain IEEE 802.1Q VLAN tags.
VLAN name: Displays the name of the VLAN you are editing or
deleting.
VLAN ID: Displays the ID number of the VLAN. This number identifies
all packets belonging to that VLAN.
Select switch: Press the z to select a switch to configure.
Action: Determines whether outgoing traffic from that port is untagged
by the switch.
PREV: Returns you to the Edit an IEEE 802.1Q VLAN screen.
APPLY: Returns you to the Configure VLAN (IEEE 802.1Q) screen.
 Loading...
Loading...