Page 1

Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV
with Intel
®
E7520 Chipset and Intel®
6300ESB ICH Development Kit
User’s Manual
April 2007
Order Number: 311 274-009
Page 2

Lega l Li nes and Discl a imers
INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL® PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY ESTOPPEL OR
OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS
OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHAT SOEVER, AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELA TING
TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE,
MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. Intel products are not intended for
use in medical, life saving, life sustaining, critical control or safety systems, or in nuclear facility applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Intel Corporation may have patents or pending patent applications, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property rights that relate to the
present e d subject matter. The furn i shi ng o f do c um ent s and other mate rial s and information do es not pr ovi d e a n y lic e n se , e xp res s o r impli ed, by es topp el
or otherwise, to any such patents, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property rights.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked “reserved” or “undefined.” Intel reserves these for
future definition and shall have no responsibility w h atsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
Intel processor numbers are not a measure of performance. Processor numbers differentiate featur es within each processor family, not across different
processor families. See http://www.intel.com/products/processor_number for details.
The Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH may contain design defects or errors known as errata
which may cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are availab l e on request.
Hyper-Threading Technology requires a computer system with an Intel® Pentium® 4 processor supporting HT Technology and a HT Technology enabled
chipset, BIOS and operating system. Performance will vary depending on the specific hardware and software you use. See http://www.intel.com/
products/ht/Hyperthreading_more.htm for additional information.
This User’s Manual as well as the software descr ibed in it is furnished under licens e and may only be used or copied in accordance with the terms of the
license. The information in this manual is furnished for informational use only, is subject to change without notice, and should not be construed as a
commitment by In tel C orpor atio n. Intel Cor por atio n assum es no r esponsib ilit y o r l iabili ty f or a ny err ors or in a ccur ac ies that may appear in thi s document
or any software that may be provided in association with this document.
Except as permitted by such license, no part of this document may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any
means without the exp ress written consent of Intel Corporation.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Copies of documents w hich have an order number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature may be obtained by calling
1-800-548-4725 or by visiting Intel's website at http://www.intel.com.
Celeron, Intel, Intel Centrino, Intel logo, Intel NetBurst, Intel NetStructure, Intel Xeon, Intel XScale, Pentium, Pentium II Xeon, Pentium III Xe on and
VTune ar e trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
*Other na m es and bra nds may be claimed as t he pro perty of othe rs.
Copyright © 2007, Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
User’s Manual April 2007
2 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Page 3

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Contents
1.0 About This Ma nual .....................................................................................................7
1.1 Content Overview.......................... ......................................................................7
1.2 Text Conventions ................................................................................... .............7
1.3 Technical Support................................................................................................9
1.3.1 Electronic Support Systems .......................................................................9
1.3.2 Online Documents....................................................................................9
1.3.3 Additional Technical Support......................................................................9
1.4 Product Literature .............................................................................................10
1.5 Related Documents ...........................................................................................10
2.0 Getting Started ........................................................................................................11
2.1 Overview .........................................................................................................11
2.2 Evaluation Board Features..................................................................................12
2.3 Included Hardware ............................................................................................12
2.4 Software Key Features.......................................................................................12
2.4.1 AMIBIOS* for the Development Kit...........................................................13
2.5 Before You Begin...............................................................................................13
2.6 Setting up the Evaluation Board .......................................................................... 13
2.6.1 Safety ..................................................................................................14
2.6.2 Package Contents................................................................................... 14
2.6.3 Installed Hardware.................................................................................15
2.6.4 Installing the Heatsinks for CPU(s) and MCH ..............................................15
2.6.5 CPU Heatsink I nstallation ........................................................................16
2.6.6 MCH Heatsink Installation........................................................................20
2.6.7 Installing Memory ..................................................................................22
2.6.8 Installing Storage Devices....................................................................... 22
2.6.9 Connect the Video Card and Monitor.........................................................23
2.6.10 Connect the Keyboard and Mouse.............................................................24
2.6.11 Connect the Power Supply.......................................................................24
2.6.12 Power up the System......................................................... .....................24
2.7 Configuring the BIOS.........................................................................................24
3.0 Theory of Operati on.................................................................................................25
3.1 Block Diagram ..................................................................................................25
3.2 Thermal Management ........................................................................................25
3.3 System Features ...............................................................................................26
3.3.1 Dual-Core Intel
3.3.2 Intel
®
E7520 MCH and Intel® 6300ESB ICH Chipset ...................................27
3.3.3 Memory Subsystem................................................................................28
3.3.4 Supported DIMM Module Types ................................................................28
3.3.5 Memory Population Rules and Configurations .............................................28
3.3.6 Intel
®
82802AC Firmware Hub (FWH).......................................................29
3.3.7 Boot ROM..............................................................................................29
3.3.8 In-Target Probe (ITP) .............................................................................29
3.3.9 Power Diagram......................................................................................30
3.3.10 Clock Generation....................................................................................31
3.3.11 Platform Resets......................................................................................32
3.3.12 SMBus..................................................................................................33
3.3.13 Platform IRQ Routing..............................................................................34
3.3.14 VRD VID Headers...................................................................................35
3.4 Battery Requirements........................................................................................36
4.0 Platform Management .............................................................................................37
®
Xeon® processor LV.......................................................27
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 3
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 4

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
4.1 Power Button....................................................................................................37
4.2 Sleep States Supported......................................................................................37
4.2.1 S0 State................................................................................................37
4.2.2 S1 State................................................................................................37
4.2.3 S2 State................................................................................................37
4.2.4 S3 State................................................................................................37
4.2.5 S4 State................................................................................................38
4.2.6 S5 State................................................................................................38
4.2.7 Wake-Up Events.....................................................................................38
4.2.8 Wake from S1 Sleep State .......................................................................38
4.2.9 Wake from S3 State................................................................................38
4.2.10 Wake from S5 State................................................................................39
4.3 PCI PM Support.................................................................................................39
4.4 Platform Management ........................................................................................39
4.4.1 Processor Thermal Management ...............................................................39
4.5 System Fan Operation........................................................................................39
5.0 Driver and OS Support .............................................................................................40
6.0 Hardware Reference ................................................................................................41
6.1 Chipset Components ..........................................................................................42
6.2 Expansion Slots and Sockets...............................................................................42
6.2.1 PCI Express* Connector...........................................................................42
6.2.2 32-Bit PCI Connector...............................................................................44
6.2.3 PCI-X Connector.....................................................................................45
6.2.4 Processor Sockets...................................................................................48
6.2.5 Firmware Hub (FWH) BIOS Socket............................................................48
6.2.6 Battery..................................................................................................48
6.3 On-Board Connectors.........................................................................................48
6.3.1 SATA Connector .....................................................................................49
6.3.2 IDE Connector........................................................................................49
6.3.3 Floppy Drive Connector ...........................................................................50
6.3.4 Front Panel Connector.............................................................................50
6.4 Jumpers...........................................................................................................51
6.5 SMBUS Headers................................................................................................. 53
6.6 Back Panel Connectors .......................................................................................53
6.6.1 PS/2-Style Mouse and Keyboard Connectors...............................................53
6.6.2 Parallel Port...........................................................................................53
6.6.3 Serial Ports............................................................................................54
6.6.4 Dual Stacked USB Connectors ..................................................................54
6.6.5 Video Port..............................................................................................55
7.0 Board Setup Checklist..............................................................................................56
8.0 Debug Proce d ure .....................................................................................................57
8.1 Level 1 Debug (Port80/BIOS) ..............................................................................57
8.2 Level 2 Debug (Power Sequence).........................................................................57
8.3 Level 3 Debug (Voltage References).....................................................................58
Figures
1 Board before Installing Additional Hardware.................................................................14
2 Location for the CPU and MCH for Heatsink Installation..................................................16
3 CPU Heatsink Top and Bottom View ............................................................................17
4 Processor in Socket and Package Secured....................................................................17
5 Clean Top of Processor Die ........................................................................................18
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
4 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 5

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
6 Back Plate i n Place...................................................................................................19
7 Heatsink Mounted on CPU ......................................................................................... 19
8 Screw Tightening Order ............................................................................................20
9 MCH Heatsink Top View ............................................................................................20
10 Clean Top of MCH Die...............................................................................................21
11 Hook Heatsink Clip to First Anchor................... ........................................................... 21
12 Hook Heatsink Clip to Second Anchor.......................................................................... 22
13 Block Diagram of Layout...........................................................................................25
14 DDR2-400 Memory—DIMM Ordering...........................................................................29
15 ITP location.............................................................................................................30
16 Power Distribution Block Diagram...............................................................................31
17 Clock Block Diagram.................................................................................................32
18 Platform Reset Diagram......................................................... ...................................33
19 SMBus Block Diagram...............................................................................................34
20 IRQ Routing Diagram................................................................................................35
21 Evaluation Board......................................................................................................41
22 Jumper Locations.....................................................................................................52
23 Back Panel Connectors..............................................................................................53
Tables
1 Related Documents ..................................................................................................10
2 Additional Hardware................................................................................................. 13
3 Heatsink Information................................................................................................15
4 Supported DIMM Module Types..................................................................................28
5 Processor VRD Settings.............................................................................................36
6 Chipset Components................................................................................................. 42
7 Expansion Slots and Socket....................................................................... ................42
8 PCI Express* Connector Pinout ..................................................................................42
9 32-Bit 5 V PCI Connector Pinout................................................................................. 44
10 PCI-X Connector Pinout.............................................................................................45
11 On-Board Connector.................................................................................................48
12 SATA Connector Pinout.............................................................................................49
13 IDE Connector Pinout ...............................................................................................49
14 Floppy Drive Connector Pinout...................................................................................50
15 Front Panel Connector Pinout.....................................................................................50
16 Jumpers and Jumper Functions..................................................................................51
17 SMBUS 3.3 V STBY Pinout.........................................................................................53
18 PS/2-Style Mouse and Keyboard Pinout.......................................................................53
19 Parallel Port Connector Pinout....................................................................................54
20 Serial Port Connector Pinout......................................................................................54
21 USB Connector Pinout...............................................................................................54
22 Video Port Connector Pinout......................................................................................55
23 Level 1 Debug (Port80/BIOS) ....................................................................................57
24 Level 2 Debug (Power Sequence) ...............................................................................57
25 Level 3 Debug (Voltage Reference).............................................................................58
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 5
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 6

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Revision History
Date Revision Description
Section 2.6.9 updated to clarify that video card is not included in the kit.
April 2007 009
March 2007 008 Updates to Chap ter 2.0, “Getting Started” to include safety warnings.
February 2007 007 Minor updates.
December 2006 006 Update for Intel® Celeron® 1.83 GHz processor launch.
December 2006 005 Update for Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV 2.16 GHz (dual-processor capable) launch.
October 2006 004 Update for product launch.
May 2006 003 Chapter 6: changed jumper descriptions/comments
March 2006 001 Initial public release.
Section 2.3 updated to remove the reference to the Blue stand and add the standoffs.
Section 2.6.11 added safety warning.
Section 3 updated with correct part number for CPU heat sink fan.
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
6 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 7

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
1.0 About This Manual
This manual describes how to set up and use the evaluation board and other
components included in your Dual-Core Intel
Chipset and Intel
®
6300ESB ICH Development Kit.
1.1 Content Overvie w
Chapter 1.0, “Ab out Thi s Manual ” – Des cript io n of con v enti ons used in this manua l and
instructions for obtaining literature and contacting customer support.
Chapter 2.0, “Getting Started” – Complete instructions on how to configure the
evaluation board and processor assembly by setting jumpers, connecting peripherals,
providing power, and configuring the BIOS.
Chapter 3.0, “Theory of Operation” – Information on the system design.
Chapter 4.0, “Platform Management” – Description of jumper settings and functions,
and pinout information for each connector.
Chapter 5.0, “Driver and OS Support” – List of supported drivers and operating
systems.
Chapter 6.0, “Hardware Reference” – Re ference information on the hardw are, including
locations of evaluation board components, co nnector pinout information, and jumper
settings.
Chapter 7.0, “Board Setup Checklist” – Checklist of items to ensure proper functionality
of the evaluation board.
Chapt er 8.0, “Debu g Pr oced ur e” – Debu g pro cedu re t o det erm in e base li ne fu nct iona l ity
for the Development Kit.
®
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520
1.2 Tex t Convent ion s
The following notations may be used throughout this manual:
# - The pound symbol (#) appended to a signal name indicates that the signal is active
low.
Variables - Variables are shown in italics. Variables must be replaced with correct
values.
Instructions - Instruction mnemonics are shown in uppercase. When you are
programming, instructions are not case-sensiti ve. You may use either upper- or
lowercase.
Numbers - Hexadecimal numbers are represented by a string of hexadecimal digits
followed by the character “h”. A zero prefix is added to numbers that begin with A
through F. For example, FF is shown as 0FFh. Decimal and binary numbers are
represented by their customary notations. That is, 255 is a decimal number and 1111
1111 is a binary number. In some cases, the character “b” is added for clarity.
Signal Names - Signal names are shown in uppercase. When several signals share a
common name, an individual signal is represented by the signal name followed by a
number, while the group is represented by the signal name followed by a variable (n).
For example, the lower chip-select signals are named CS0#, CS1#, CS2#, and so on;
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 7
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 8

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
they are collectively called CSn#. A pound symbol (#) appended to a signal name
identifies an active-low signal. Port pins are represented by the port abbreviation, a
period, and the pin number (e.g., P1.0).
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
8 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 9

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Units of Measure The following abbreviations are used to represent units of measure:
A amps, amperes
GB GByte, gigabytes
GHz gigahertz
KB KByte, kilobytes
ΚΩ kilo-ohms
mA milliamps, milliamperes
MB MByte, megabytes
MHz megahertz
ms milliseconds
mW milliwatts
ns nanoseconds
pF picofarads
W watts
V volts
μA microamps, microamperes
μF microfarads
μs microseconds
μW microwatts
1.3 Technical Support
Support Services for your hardware and software are provided through the secure
®
Intel
Premier Support Web site at https://premier.intel.com. After you log on, you can
obtain technical support, review “What’s New,” and download any items required to
maintain the platform.
1.3.1 Electronic Support Systems
Intel’s site on the World Wide Web (http://www.intel.com/) provides up-to-date
technical information and product support.
1.3.2 Online Document s
Product documentation is provided online in a variety of web-friendly formats at:
http://www.intel.com/hardwaredesign/solutions/index.htm
1.3.3 Additional Technical Support
If you require additional technical support, please contact your field sales
representative or local distributor.
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 9
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 10
1.4 Product Literature
You can order product literature from the following Intel literature centers.
U.S. and Canada 1-800-548-4725
U.S. (f rom overseas) 708-296-9333
Europe (U.K.) 44(0)1793-43 1155
Germany 44(0)1793-421333
France 44(0)1793-421777
Japan (fax only) 81(0)120-47-88-32
1.5 Related Documents
Table 1 is a partial list of the available collateral. For the full lists, contact your local
Intel representative.
Table 1. Related Documents
Document Document Number
®
Intel
6300ESB I/O Controll er Hub (ICH) Datasheet
Intel® E7520 Me mory Controller Hub (M CH) Datasheet
®
Dual-Core Intel
Intel® E7520 Memory Controller Hub (MCH) Specification
Intel® E7520 Memory Controller Hub (MCH) Specifications Addendum
®
E7520 Memory Controller Hub (MCH) Specifications Embedded
Intel
Addendum
Embedded Voltage Regulator-D own (EmVRD) 11 .0
Xeon® Processor LV and ULV Datasheet
Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Contact your Intel field
representative for access .
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
10 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 11

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
2.0 Getting Started
This chapter identifies the Dual-Core Intel® Xeo n® processor LV with Intel® E7520
Chipset and Intel
®
6300ESB ICH Development Kit’s key components , features and
specifications. It also describes how to set up the board for operation.
Note: This manual assumes you are familiar with basic concepts involved with installing and
configuring hardware for a PC or server system.
2.1 Overview
The Development Kit contains a baseboard with two Dual-Core Intel Xeon processors
LV, Intel
connectors. Various software and documentation are also included in the kit.
In addition to the included Dual-Core Intel
the following processors are also supported with this Development Kit:
• Dual-Core In tel
• Dual-Core In tel
• Celeron
• Celeron
If you wish to use one of these options instead of the included processors, please
contact y our In te l s ale s re pr esen tat iv e. You will be sent new p roc es so r(s) and w ill ne ed
to download the latest microcode updates and BIOS revision specific to your new
processor(s). There are currently two versions of BIOS. One version supports the LV
and ULV versions, while the other version supports Celeron version.
®
E7520 MCH, 6300ESB, and other system board components and peripheral
®
Xeon® processors LV 2.0 GHz processors,
®
Xeon® processor LV 1.66 GHz (dual-processor capable)
®
Xeon® processor ULV 1.66 GHz (dual-processor capable)
®
processor 1.66 GHz (uni-processor only)
®
processor 1.83 GHz (uni-processor only)
Note: The evaluation board is shipped as an open system with standoffs allowing for
maximum flexibility in changing hardware configuration and peripherals in a lab
environment. Since the board is not in a protective chassis, the user is required to
observe extra precautions when handling and operating the system. Some assembly is
required before use.
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 11
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 12

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
2.2 Evalua ti on Bo ard Feat u re s
The evaluation board features are summarized below:
•CPU
— Two Dual-Core Intel Xeon processors LV capable of 667 MHz Front Side Bus
— On-board processor voltage regulators compatible with EmVRM11 Design Guide
®
•Intel
•System I/O
• ITP-XDP debug port
• Port 80 7-segment LEDs
• Board Form Factor - 13.3” x 14” for benchtop use
E7520 MCH and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
— Supports three PCI Express x8 slots
— Four DDR2–400 DIMMs on two channels (8 slots total)
— From 6300ESB
1 PCI 2.2 32/33 Slot
2 PCI-X 66 MHz slots
1 IDE connector
2 Serial ATA connectors
2 Serial ports
4 USB 2.0 po rt s
— Super I/O via LPC bus from the 6300ESB
1 Flopp y po rt
1 Parallel port
1 Serial port
1 PS/2 por t
2.3 Included Hardware
The following hardware is included in the Development Kit:
• Two Dual-Core Intel Xeon processors LV capable of 667 MHz Front Side Bus
• Two CPU heatsinks (pre-installed)
•One ATX Power Supply
• Pre -inst alled jum per s
• Two 512 Mbytes DDR2-400 DIMMs
• Unformatted SATA Hard Drive
•SATA cable
• Intel Network Interface Card
• Standoffs for board
• FWH mounted and flashed with the BIOS
2.4 Software Key Features
The software in the Development Kit was chosen to facilitate development of real-time
applicati ons base d on th e com pone nts use d in the ev a lu ation boar d. The so ftwa re tools
included are described in this section.
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
12 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 13

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Drivers included:
Windows
Chipset INF Install Utility version 7.0.0.1019
Optional Intel 6300ESB ICH chipset driver updates
Linux Driver Packages
RedHat* Enterprise Linux 3.0 Server driver updates
Note: Software in the kit is provided free by the vendor and is only licensed for evaluation
purposes.
Refer to the documentation in your Development Kit for further details on any terms
and conditions that may be applicable to the granted licenses. Customers using tools
that work with other third party products must have licensed those products. Any
targets created by those tools should also have appropriate licenses. Software included
in the kit is subject to change.
Refer to http://developer.intel.com/design/intarch/devkits for details on additional
software from other third party vendors.
2.4.1 AMIBIOS* for the Development Kit
The evaluation board is pre-installed and licensed with a copy of AMIBIOS* from
American Megatrends*.
2.5 Before You Begin
Table 2 presents the additional hardware you may need for your Development Kit.
Warning: Do not install the power supply until all other installation steps have been completed.
Table 2. Additional Hardware
VGA Card and Monitor You can use any st and ar d VGA or greater reso luti on monitor us ing a VGA card.
Keyboard You can use a keyboard with a PS/2 style connector or adapter as well as USB.
Mouse You can use a mouse with a PS/2 style connector or adapter as well as USB.
Hard Drives You can connect up to two IDE and two SATA devices to the evaluation board.
Floppy Drive
(optional)
Other Devices and
Adapters
You can connect a floppy drive to the connector on the evaluation board. No floppy
drives or cables are included in the Development Kit.
The evaluation board behaves much like a standard PC motherboard. Many PCcompatible peripherals can be attached and configured to work with the evaluation
board. For example, you may want to install a sound card or additional network
adapters. You are responsible for procuring and installing any drivers required for
additional devices.
2.6 Setting up the Evaluation Board
Once you have gathered the hardware described in Section 2.5, follow the steps below
to set up your Development Kit. This manual assumes you are familiar with basic
concepts involved with installing and configuring hardware for a PC or server system.
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 13
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 14

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Figure 1. Board before Installing Additional Hardware
2.6.1 Safety
Ensure a safe wor k envi r on ment. Make sure you are in a static-free environment
before removing any components from their anti-static packaging. The evaluation
board is susceptible to electrostatic discharge, which may cause product failure or
unpredictable operation.
Caution: Connecting the wrong cable or reversing a cable may damage the evaluation board and
may damage the device being connected. Since the board is not in a protective chassis,
use caution when connecting cables to this product.
Note: Review the document provided with the Development Kit titled “Important Safety and
Regul atory In formati on”. This document contains a dditi on safet y warnin gs and ca utions
that must be observed when using this development kit.
2.6.2 Packag e Contents
Verify kit contents. Inspect the c ontents of y our kit, and ensure that everyt hing li sted
in Section 2.3 is included. Check for damage that may have occurred during shipment.
Contact your sales representative if any items are missing or damaged.
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
14 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 15

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Check jumper settings. Verify that the jumpers are set in their default state. Refer to
Section 6.4 for detailed descriptions of all jumpers and their default settings indicated
in bold.
2.6.3 Instal led Hardware
Verify installed hardware. Make sure the following hardware is populated on your
evaluation board:
• Two Dual-Core Intel Xeon processors LV with heatsinks
•BIOS FWH
• Battery in holder
Note: The CPU sockets have a screw locking mechanism. The socket has an indication to
show if the CPU is locked in place.
Caution: The above hardware should have been correctly installed at the factory. If components
are not installed correctly, DO NOT power on the board. Correctly re-install the
components before proceeding. If you suspect that any of the kit components have
been damaged, contact your Intel field sales representative or local distributor for
assistance.
2.6.4 Installing the Heatsinks for CPU(s) and MCH
Heatsink Installation: In order for t h e bo ar d t o o pe r at e pro p er l y, a he atsink must b e
installed o n th e pr oce ssor s and on the E7 520 M CH. DO NOT powe r on bo ar d wi t h out a
CPU thermal solution. Heatsinks may already come pre-installed on both CPU(s) and
MCH. Please refer to this section if you need to remove or re-install the heatsinks.
Tools Needed: Flat head screwdriver and Phillips head screwdriver
Consumable Items Needed: Dispos ab le tow els and iso p ropy l alco h ol
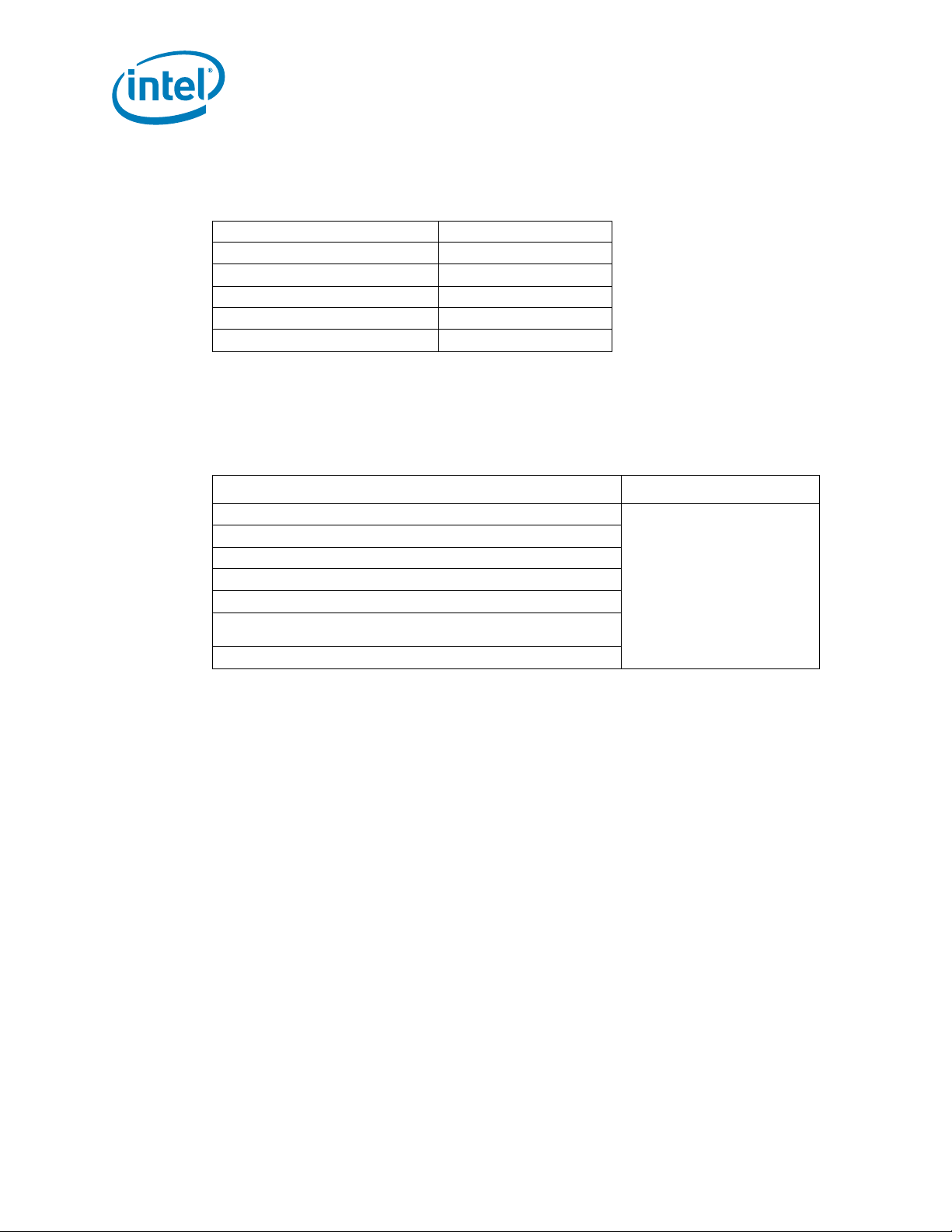
Note: CPU heatsinks may be silver or copper in color.
Table 3. H eatsink Information
Component
®
Dual-Core Intel
®
Xeon
processor LV
E7520 MCH 1 Co o ler Master ECB-000208-0 1 Active heats ink
Quantity Per
Board
2 Cooler Master* P/N EEP-N41CS-I1-GP
Heatsink
Manufacturer
Part Number Comments
Active heatsink +
back plate
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 15
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 16

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Figure 2. Location for the CPU and MC H for He atsink Installation
Caution: Applying excess pressure may cause damage to the CPU.
Note: Do not turn power on until the CPU thermal solution has been installed.
2.6.5 CPU Heatsink Installation
This section details how to install the CPU heatsink. This section may not apply if the
CPU heatsink is pre-installed on the board.
Note: If the Thermal Interface Material (TIM) is scratched, scrape it off and replace with new
material. If a replacement is needed, use a TIM with high thermal conductivity such as
thermal grease or a phase change material. The gasket ensures the heatsink is sitting
flat on the package.
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
16 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 17
Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Figure 3. CPU Heatsi n k To p an d Bo tto m V i ew
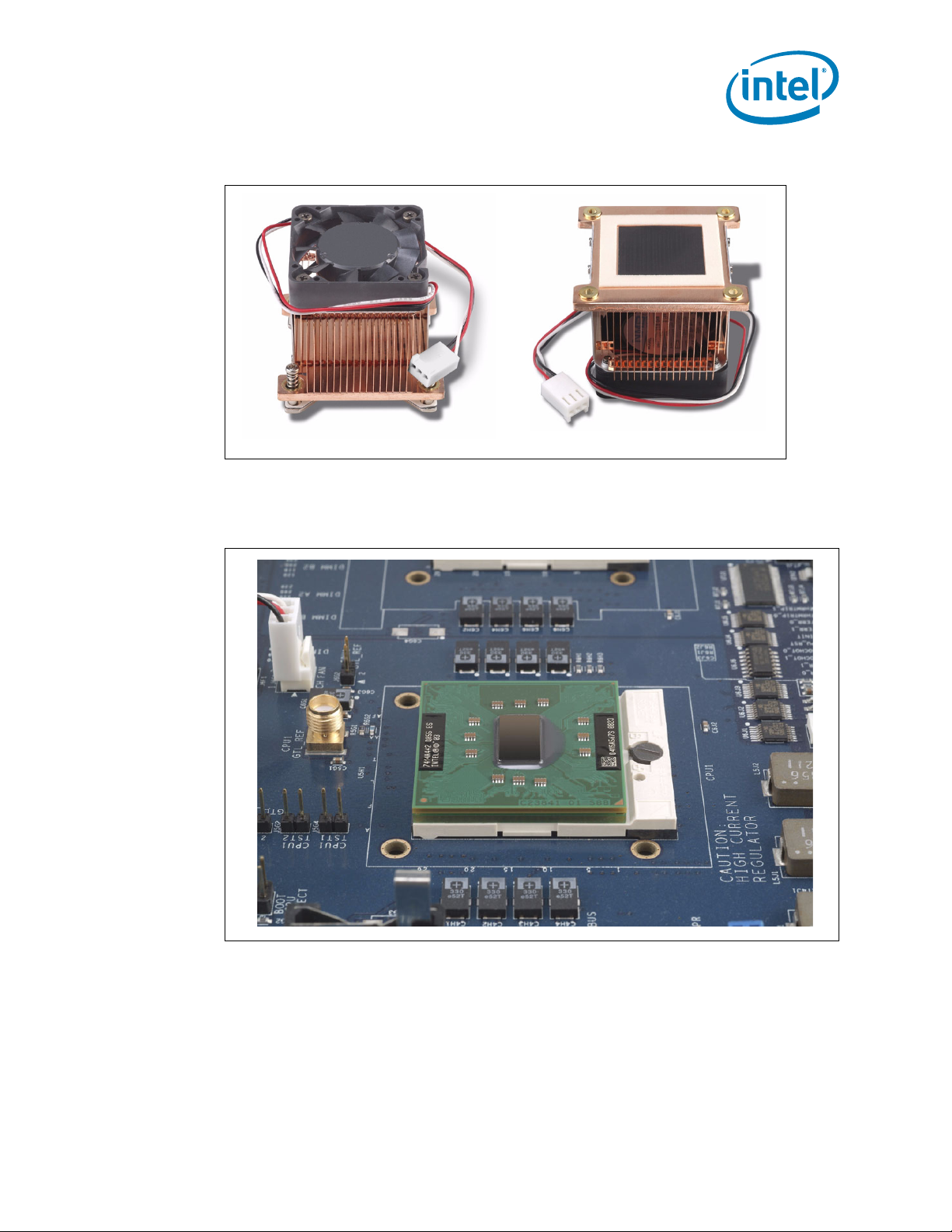
1. Make certain that the processor is firmly seated in the socket, and the package is
secured using a flathead screwdriver. Note: This shows CPU1 populated. However
for single CPU operation socket 0 should be populated.
Figure 4. Processor in Socket and Package Secured
z
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 17
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 18

2. Clean the top surface of the processor die with a clean towel and isopropyl alcohol
(IPA).
Figure 5. Clean Top of Processor Die
Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
18 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 19

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
3. Install the back plate to the bottom side of the PCB at the CPU location. Align the
standoffs to the four mounting holes in the board.
Note: There is a non-electrically conductive tape to hold the back plate in place until the
heatsink is completely installed.
Figure 6. Back Plate in Place
4. Mount the heatsink to the CPU. Ensure the TIM and die have contact.
Figure 7. Heat s ink Moun t ed on CPU
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 19
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 20

5. Align the screws (4x at corners) to the threaded holes of the standoffs on the back
plate. Using the Phillips head screwdriver, tighten the four screws in a diagonal
manner (as shown in the diagram). Tighten each screw half of the screw length for
A to B and follow by ¼ for C to D. Then tighten A to B until the screw hard stops
and repeat for C to D. The screws are designed to compress the springs a
predetermined amount.
Figure 8. Screw Tighten ing Order
Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
6. Plug the fan connector to the fan pin header on the board.
7. Repeat steps 1-6 for the second CPU heatsink (if applicable).
Note: The heatsink removal process is the reverse of the installation procedure.
2.6.6 MCH Heatsink Installation
This section may not apply if the MCH heatsink is pre-installed on the board. However,
you may want to briefly look over the procedure to verify that the heatsink is properly
installed and it has not been damaged in the packaging.
Note: If the Thermal Interface Material (TIM) is scratched, scrape it off and replace with new
Figure 9. MCH Heatsink Top View
material. Use a TIM with high thermal conductivity, such as thermal grease or phase
change material.
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
20 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 21

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
1. Clean the top surf ace of the MCH die with a cl ean tow el and is oprop yl alc oho l (IP A ).
Figure 10. Clean Top of MCH Die
2. Hook one end of the heatsink clip to one of the anchors located near the corner of
the MCH. Securely hold the other end of the heatsink clip.
Figure 11. Hook Heatsink Clip to First Anchor
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 21
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 22

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
3. Hold the clip firmly to the anchor to prevent the heatsink from moving. Attach the
other end of the clip to the other anchor. Ensure that the heatsink is level with the
MCH package.
Figure 12. Hook Heatsink Clip to Second Anchor
4. Plug the fan connector to the fan pin header on the board.
Note: The heatsink removal process is the reverse of the installation procedure.
2.6.7 Installi ng M emory
Your kit includes two 512 MByte registered ECC DIMMs. To install, ensure the tabs on
the slot are open, or rotated outward from the slot. Line up the DIMM above the slot
(the DIMM is keyed so that it only fits in the slot in one orientation). Firmly but carefully
insert the DIMM into the slot until the tabs close. Repeat for all other DIMM and slots.
Note: When populating both channels, always place identical DIMMs in sockets that have the
same position on channel A and channel B (i.e., DIMM A2 should be identical to DIMM
B2).
Note: Populate DIMMs starting with the sockets farthest away from the MCH (DIMM slots A4
and B4).
Caution: Do NOT bend the board when installing memory. There are a large number of
components near the memory slots and excessive board flex can lead to solder joint
failure.
Note: Refer to Section 3.3.3.
2.6.8 Install i ng Storage De vi c es
There is one IDE connector on the evaluation board, which supports an IDE device. For
a correct boot-up of the system, ensure that a hard drive is installed as the primary
master . (Master/slave settings are determined by a jumper on each IDE device. Consult
the device label/documentation to verify that the jumper is set correctly for any
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
22 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 23

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
configuration you choose.) A CD-ROM drive or additional hard drive may be installed as
a primary slave device. Follow this procedure to install a hard drive on the evaluation
board:
1. Verify that the jumper on the hard drive is set correctly for single or master,
depending on your configuration.
2. Install the hard drive. This can be done using either the IDE or SATA.
IDE Installation:
a. Connect the short end of the IDE cable to the IDE connector J1K2 on the board.
Ensure that the red line (pin one on the cable) is aligned with pin one of the
connector indicated by an arrow.
b. Connect the middle connector of the cable to the hard drive. Again, ensure that
the red line, pin one on the cable, is aligned with pin one on the hard drive.
Note: Failure to properly align the IDE cable may damage the evaluation board and/or the
hard drive.
SATA Installation:
a. Connect one end of the SATA cable to the hard drive connection. Connect the
other end to the SATA1 or S ATA2 connect or (J1F4 or J1G1, r esp e ctiv el y) on th e
board.
3. Connect a power connector from the power supply to the hard drive. The power
connector on the SAT A drive may have a plastic cover that will need to be removed.
(Old style power connector is supported.)
4. Install the CD-ROM drive (optional). A CD-ROM drive is not included in the kit and
is not required, but you may find it useful in loading additional software. To install it
on the evaluation board :
a. Verify that the jumper on the CD-ROM drive is set for slave.
b. Connec t the un used end of the IDE c able to th e CD-R OM dr ive. Ensu re th at the
red line, pin one on the cable, is aligned with pin one of the CD-ROM drive
connector, indicated by an arrow.
c. Connect a large 4-pin power connector from the power supply to the CD-ROM
drive.
5. Install the floppy drive (optional). A floppy disk drive is not included in your kit and
is not required, but you may find it useful in loading additional software. To install a
floppy drive on the evaluation board:
a. Connect the flop p y cabl e to the fl oppy con necto r J1K 1. Ens ure that the red line
(pin one on the cable) is aligned with pin one of the connector, indicated by an
arrow.
b. Connect the other end of the floppy cable to the floppy drive.
c. Connect a power cable to the floppy drive. Ensure that the red line (pin one on
the cable) is aligned with pin one on the floppy drive.
2.6.9 Connec t the Video Car d and Monitor
Insert a video card into the appropriate slot. Connect the monitor cable and power to
the video card port.
Note: Monitor and video card are not included in this Development Kit.
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 23
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 24

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
2.6.10 Connect the Keyb oard and M ou s e
Connect a PS/2 mouse and keyboard to the stacked PS/2 connector on the evaluation
board. The bottom connector, often purple, is the keyboard connector and the top,
often g reen, i s the m ous e con ne cto r. Al ter nati v ely, you ma y pl ug a U SB ke yboar d an d a
USB mouse into the USB connectors on the evaluation board.
Note: Keyboard and mouse are not included in this Development Kit.
2.6.11 Connect the Power Supply
Caution: Measures mus t be ta ke n to prot ec t the un us ed DC con necto r s of th e p ower s up ply f ro m
accidental contact to objects in the work area.
Make sure the power supply is turned off and unplugged. Connect the two ATX power
supply cables to connectors J2K2 and J6K2 on the evaluation board. Next, plug the
power cord into the power supply and the wall. Then turn on the switch on the back of
the powe r supp ly.
2.6.12 Power up the System
Turn on the monitor and then turn on the evaluation board.
Note: Do not turn power on until both CPU thermal solutions have been installed.
Caution: Ensure that fan heatsink on the both processors are operational. If not, turn off the
power immediately and verify that both fan heatsinks are connected to the board
correctly (see Section 2.6.4). If the fan heatsink is not operating, contact your Intel
field sales representative or local distributor.
2.7 Configuring the BIOS
An AMI* BIOS is pre-loaded on the evaluation board. You may need to make changes
to the BIOS to enable hard disks, floppy disks and other supported features. You may
use the setup program to modify BIOS settings and control the special features of the
system. Setup options ar e configured through a menu-driven user interface.
On first boot-up of the system, you may want to use the BIOS setup program to verify
the date/time and boot device. BIOS updates may periodically be posted to the Intel
Developer web site at http://developer. int el.com/design/intarch. Pressing the Delete
key during boot causes the system to enter into the BIOS setup program.
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
24 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 25

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
rt
Intel®
Two S
ATA
Four
USB (
2.0) Ports
SIO
PCI-X 66 MHz
PCI 32/33
Two
IDE
TPM
}A
X8 PCI
e
X8 PCIe
X8 PCIe
3.0 Theory of Operation
3.1 Block Diagram
Figure 13. Block Diagram of Layout
DDuuaall--CCoorree
®
®
l
XXeeoonn®®
IInntteel
pprroocceessssoorr LLV
167 MHz/667 MT/s
C
B
E7520
6300ESB
LPC Bus
FWH
V
(MCH)
HL 1.5 Interface
Intel®
DDuuaall--CCoorree
IInntteel
®
®
l
XXeeoon
®
®
n
pprroocceessssoorr LLVV
VGA
DDR2 400
Single or dual
channel suppo
R
R
R
3.2 Thermal Management
The objective of thermal management is to ensure that the temperature of each
component is maintained within specified functional limits. The functional temperature
limit is the range within which the electrical circuits may be expected to meet their
specified performance requirements. Operation outside the functional limit may
degrade system per forma n ce and cau s e reliab ili ty problem s. The Develo pm en t Kit is
shipped with heatsink thermal solutions to be installed on the processor. This thermal
solution has been tested in an open air environment at room temperature and is
sufficient for evaluation purposes. The designer must ensure that adequate thermal
management is provided for any customer-derived designs.
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 25
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 26

3.3 System Features
Processor
• Supports two Dual-Core Intel Xeon processors LV
• On-board processor voltage regulators compatible with EmVRD11 Design Guide.
Chipset
•Intel
•Intel
Clocking
• CK409B clock synthesizer that generates all host clock and the PCI Express
• DB800 generates the PCI Express differential pair clocks to the onboard PCI
Memory
• Registered ECC DDR2-400 DIMMs
• Each of the tw o memor y c hanne ls on the I ntel
• 3.2 Gbytes/s bus per channel bandwidth with DDR2-400
®
E7520 MCH
®
6300ESB ICH
interface clock for the MCH PHY layer
Express components and the dedicated PCI Express slots
maximum of four DDR2-400 DIMMs per chann el
Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
®
E7520 MCH o n th is C RB s upp orts a
Graphics
• ATI Sapphire PCI Radeon* 700 64 MB graphics card
I/O
•From Intel
®
6300ESB ICH
— One PCI 2.2 32/33 Slot
— Two PCI-X 66 MHz slots
— One IDE connector
— Two Serial ATA connectors
— Two Serial ports
— Four USB 2.0 ports
Two on rear panel I/O
Two on front panel header
— Super I/O via LPC bus from the 6300ESB
One Floppy port
One Parallel port
One Serial port (10-pin header)
Two PS2 port
Low Pin Count Bus
• National LPC 47M172 Super I/O residing on LPC bus
•Firmware hub
Board Form Factor
• 13.3” x 14” for bench top use
• Common ATX 12V Power supply
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
26 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 27

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
3.3.1 Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV
• 667 MHz FSB
3.3.2 Intel® E7520 MCH and Intel® 6300ESB ICH Chipset
The features of the chipsets are detailed below.
3.3.2.1 Intel
®
E7520 MCH Memory Controller Hub (MCH)
The architecture of the MCH provides the performance and feature set required for dual
processor-based volume to performance servers. Configuration options facilitate
optimization of the platform for workloads characteristic of communication,
presentation, storage, performance computation, or database applications. Coverage
includes the MCH interface units (system bus, system memory, PCI Express, Hub
Interface (HI), SMBus, power management, MCH clocking, MCH system reset and
power sequencing) as well as RASUM (Reliability, Availability, Serviceability, Usability,
and Manage abi lit y) fe atu res.
Features:
• Registered ECC DIMM support
• Integrated four-channel DMA engine with IOxAPIC functionality
• High speed seri al PC I Express interfa ce
• Hub interface to 6300ESB ICH
3.3.2.2 Intel® 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub (ICH)
The Intel® 6300ESB ICH is designed for a variety of processors/memory controller
hubs. The 6300ESB provides the data buffering and interface arbitration required to
ensure that system interfaces operate efficiently and provide the bandwidth necessary
to enable the system to obtain peak performance.
Features:
• Upstream HI for access to the MCH
• Two port Serial ATA controllers
•IDE connector
• PCI-X 1.0 Interface
•PCI 2.2 Interface
• Two serial I/O ports
• Two-stage WDT (Watch Dog Timer)
•LPC Interface
• EPLD for Port 80 decode and display
•FWH Interface
• SMBus 2.0 controller
•I/O APIC
• Four USB 2.0 Ports
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 27
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 28

3.3.3 Memory Subsystem
Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
The memory subsystem is designed to support Double Data Rate 2 (DDR2)
Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory (SDRAM) using the Intel
®
E7520 MCH.
The MCH provides two independent DDR channels, which support DDR2-400 DIMMs.
The peak bandwidth of each DDR2 branch channel is 3.2 GByte/s (8 bytes x 400 MT/s)
with DDR2-400. The two DDR2 channels from the MCH operate in lock step; the
effective overall peak bandwidth of the DDR2 memory subsystem is 6.4 GByte/s for
DDR2-400.
3.3.4 Supported DIMM Module Types
Table 4 shows all DIMM technology validated by Intel on the CRB.
Table 4. Supported DIM M Modu l e Types
A1
A2
A3
A4
B1
B2
B3
B4
Size 512M 512M 2G 4G 4G 4G 5G 6G 8G 8G 8G 16G 16G
Channels Single Single Dual Dual Single Dual Dual Dual Dual Dual Dual Dual Dual
Note: SR = Single Rank; DR = Dual Rank
512MSR512M
DR
1G
SR
1G
SR
1G
SR
1G
SR
1G
SR
1G
SR
512M
SR
512M
SR
512M
SR
512MSR512MDR1GSR2GDR2GSR1GSR4GDR2G
1GSR512M
1GSR512M
1GSR512M
1GSR512MSR512MDR1GSR2GDR2GSR1GSR4GDR2G
SR
SR
SR
1GSR1G
SR
1GSR1GSR2GDR2GSR1GSR4GDR2G
1GSR1G
SR
1GSR1G
SR
2GDR2GSR1GSR4GDR2G
1G
SR
1G
SR
1G
SR
1G
SR
2G
SR
2G
SR
SR
SR
2G
SR
2G
SR
SR
SR
3.3.5 Memory Population Rules and Configurations
The system supports four DDR2-400 DIMM slots for Channel A and four DDR2-400
DIMM slots for Channel B. The eight slots are interleaved and placed in a row in the
following order: A1, B1, A2, B2, A3, B3, A4, B4 with A1 being closest to the MCH. This
design supports only registered ECC-enabled DIMMs.
When populating both channels, always place identical DIMMs in sockets that have the
same position on Channel A and Channel B (i.e., DIMM A2 should be identical to DIMM
B2).
In addition, single-rank DIMMs should be populated furthest from the MCH when a
combination of single-rank and double-rank DIMMs are used. This recommendation is
based on the signal integrity requirements of the DDR2 interface.
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
28 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 29

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Figure 14. DDR2-400 Memory—DIMM Ordering
3.3.6 Intel
®
82802AC Firmware Hub (FWH)
A socketed FLASH device is used to store system BIOS as well as an Intel
Number Generator (RNG). A bootblock locking jumper is provided to allow a mechanical
means of protecting the bootblock BIOS firmware. All BIOS programming is controlled
via software.
FWH Features:
• 32-pin PLCC package
• Symmetrically-blocked flash memory array (64 Kbyte)
• Pin and register-based block locking
• Integrated hardware RNG
• Single-byte read/write
•Five GPIs
3.3.7 Boot ROM
The system boot ROM is installed on the Intel 82802AC FWH device. The FWH is
addressable on the LPC bus off the Intel
3.3.8 In-Target Probe (ITP)
The evaluation board contains an in-target probe (ITP) connector for an ITP-XDP
connector. You must use an ITPFlex specific to the Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV.
Other ITPs will not work and if installed, could damage the platform and/or the ITP.
Figure 15 shows the ITP connector which is located between the DIMM B4 connector
and the edge of the board. For more information refer to ITP700 Debug Port Design
Guide (http://www.intel.com/design/Xeon/guides/249679.htm ).
®
6300ESB ICH.
®
Random
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 29
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 30

Figure 15. ITP location
3.3.9 Power Diagram
Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Figure 16 shows the power distribution for the CRB. Refer to the CRB schematics for
details on the power distribution logic (contact your Intel field sales representative to
obtain the schematics).
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
30 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 31

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
VR
M 11
0 . 8375 - 1 . 6000 V 50 A
VCCP
1 . 05 V 6 . 0 A
0 . 8375 - 1 . 6000 V 50 A
DDR
1 . 8 V 50 A
13 A
3 . 3 AUX
1 . 7 A
3 A
DDR
S 3
Switch
S 3 _
5 . 0
50 A
18 A
- 5 . 0 V
Figure 16. Power Distribution Block Diagram
12 V
- 12 V
1 A
5 . 0 V
0 . 5 A
VSTBY
2 . 5 A
3 . 3 V
28 A
VCCP 0
1 . 5 V
VCCP 1
1 . 8 VDDRSB
3 . 3 VSTBY
3 . 0 A
1 . 5 VSTBY
0 . 8 A
DIMMS
CNTRL
450 W ATX
3.3.10 Clock Generation
The CRB uses one CK409B Clock Synthesizer to generate the host differential pair
clocks and the 100MHz differential clock to the DB800. The DB800 then generates the
100 MHz differential pair clock for the PCI Express devices. Figure 17 shows the CRB
clock configuration.
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 31
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 32

Figure 17. Clock Block Diagram
Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
CPU0_BCLK
CPU1_BCLK
ITP_BCLK
MCH_BCLK
MCH_66MHZ_CLK
ICH_USB_48MHZ_CLK
SMA
14.318 MHz
CK-409B
LPC_14MHZ_CLK
ICH_33MHZ_CLK
ICH_HI66MHZ_CLK
ICH_PX66MHZ_CLK
SIO_33MHZ_CLK
LPC_14MHZ_CLK
LAI_HI66MHZ_CLK
DB800_SRC_100MHZ_CLK
VIDEO_33MHZ_CLK
FWH_33MHZ_CLK
PORT80_33MHZ_CLK
PCI_SLOT6_33MHZ_CLK
TPM_33MHZ_CLK
CPU0
CPU1
ITP
MCH
HI LAI
ICH
32.786 kHz
SIO
29.499 MHz
DDRA_CMDCLK[0..3]
DDRB_CMDCLK[0.3]
ICH_PX_PCLK0[0..1]
Video
FWH
Port 80
PCI 2.2
TPM
DDRA
DDRB
MCH_SRC_100MHZ_CLK
PCI-X
ICH_SRC_100MHZ_CLK
ICH_SUSCLK
MIDBUS_100MHZ_CLK
EXP_SLOT3_100MHZ_CLK
EXP_SLOT4_100MHZ_CLK
EXP_SLOT5_100MHZ_CLK
DB800
PCI Ex p ress
Midbus Probe
PCI Express
Slot
PCI Express
Slot
PCI Express
Slot
3.3.11 Platform Resets
Figure 18 depicts the reset logic for the CRB. The 6300ESB provides most of the reset,
following assertion of power good and system reset.
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
32 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 33

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Figure 18. Platform Reset Diagram
3.3.12 SMBus
SYS_RESET#
VRM_PWRGD
IDE
IDERST#
LPC
Debug
ICH
SYS_PWRGD_3V3
PCIRST2#
SIO
PCIRST_N
FWH
PCIRST1#
TPM
VGA Port 80
MCH
PCI-E
PCI-E
Slots
PCI 32
PCI-X
PCI-X
CPURST#
PCI-E
CPU 0
CPU 1
ITP
Figure 19 below illustrates the routing of the SMBus signal among the components.
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 33
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 34

Figure 19. SMBus Block Di a gram
Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
ITP XDP
SMBus
Master Only
Intel® E7520-
PF
CK409B
DB800
Allagash SMBus
SMBus
Repeater
0-ohm
3.3VSBY
3.3V
MCH_SMB
ICH_SMB
SMBus
Repeater
ICH-S
HECETA
7
SMBus
Repeater
SMBus
Repeater
3.3V
0-ohm
0-ohm
3.3VSBY
TPM
ID
EEPROM
DIMM #A1
Addr 0xA0
DIMM #A2
Addr 0xA2
DIMM #A3
Addr 0xA4
DIMM #A4
Addr 0xA6
SMBALERT_N
PCI Express Slot
(Slot # 3)
PCI Express Slot
(Slot # 4)
PCI Express Slot
DIMM #B1
Addr 0xA8
DIMM #B2
Addr 0xAA
DIMM #B3
Addr 0xAC
DIMM #B 4
Addr 0xAE
(Slot #5)
PCI 32-bit/ 33 M H z
(Slot #6)
PCI-X 66MHz Slot
(Slot #7)
PCI-X 66MHz Slot
(Slot #8)
DDR CH A DDR CH B
3.3.13 Platform IRQ Rou t i ng
Figure 20 shows how the 6300ESB uses these segments:
• IRQ 14 for IDE segment
• SERIRQ for SIOPIXRQ segment
•PCRIRQ for the PCI-X segment
• PIRQ for the PCI 32/33 segment
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
34 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 35

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Figure 20. IRQ Routing Diagram
CPU0
CPU0
PCI-E
8x
MSI
PCI-E
MSIMSI
SMI NMI
FSB
MCH
SMI
NMI
FSB
MSI
MSI
HI PCI-E
MSI MSI
IDE
PCI-E
8x
MSI
PCI-E
HI
IRQ14/15
MSI
SMI NMI
NMISMI
ICH
SERIRQ
A
B
C
D
E
PIRQPXIRQ
F
G
H
A
B
C
D
PCI-E
8x
MSI
PCI-E
PCI Slot
REQ/GNT: 0
IDSEL: AD16
A B C D A
PCI-X 64/66 PCI 32/33
Video
REQ/GNT: 1
IDSEL: AD17
PCI-X Slot
REQ/GNT: 0
IDSEL: AD17
A B C D
PCI-X Slot
REQ/GNT: 1
IDSEL: AD18
A B C D
SIO
3.3.14 VRD VID Head ers
VID headers provide for manual control of the processor core voltage regulator output
level(s). Normally, the processor should be run at its default VID (voltage
identifica tion) v alue as set d uring manuf actur ing. Howev er, in the event th e user need s
to set a different VID value from the default value, it can be accomplished through a
jumper block found on the board.
Note: These headers are not populated by default. EmVRD11 Controller VID input 0 and 7 are
tied low. Initial boards will not have the VID Header populated, CPU1 must have VID
override enab led fo r the initial Dual- Cor e Intel Xeon process o r LV samples. The, VID
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 35
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 36

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
override enable, jumper controls whether or not the VID header jumpers control the
VID to the regulator or not.
Table 5. Processor VRD Settings
VR6 VR5 VR4 VR3 VR2 VR1 Vccmax VR6VR5VR4VR3VR2VR1Vccmax
0000011.60000
0000101.58750
0000111.575001001001.16250
0001001.562501001011.15000
0001011.55000
0001101.537501001111.12500
0001111.525001010001.11250
0010001.51250
0010011.500001010101.08750
0010101.487501010111.07500
0010111.47500
0011001.462501011011.05000
0011011.450001011101.03750
0011101.43750
0011111.425001100001.01250
0100001.412501100011.00000
0100011.40000
0100101.387501100110.97500
0100111.375001101000.96250
0101001.36250
0101011.350001101100.93750
0101101.337501101110.92500
0101111.32500
0110001.312501110010.90000
0110011.300001110100.88750
0110101.28750
0110111.275001111000.86250
0111001.262501111010.85000
0111011.25000
0111101.237501111110.82500
0111111.22500
1000001.21250
1000011.20000
1
1000101.18750
1000111.17500
1001101.13750
1010011.10000
1011001.06250
1011111.02500
1100100.98750
1101010.95000
1110000.91250
1110110.87500
1111100.83750
3.4 Battery Require m ents
A type 2032 3 V lithium coin cell battery is required and included in the evaluation
board kit.
1. For the table above 1 means the jumper is installed.
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
36 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 37

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
4.0 Platform Management
The following sections describe how the system power management operates, and how
the different ACPI states are implemented. Platform management involves:
• ACPI implementation-specific details
• System mon itoring, cont rol , an d r esp o ns e to therm a l, vo ltage, and intr us ion events
• B IO S se cu rit y
4.1 Power Button
The system power button is connected to the I/O controller component. When the
button is pressed, the I/O controller receives the signal and transitions the system to
the proper sleep state as determined by the operating system and software. If the
power button is pressed and held for four seconds, the system powers off (S5 state).
This feature is called power button override and is particularly helpful in case of system
hang and sy stem loc k. T h e po wer b utto n i s lo ca ted n ext to the S ATA connec tors on the
board.
4.2 Sleep States Supported
The I/O controller controls the system sleep states. States S0, S1, S3, and S5 are
supported. The platform enters sleep states in response to BIOS, operating system, or
user actions. Norm all y the oper at ing syst em determ ines which sle ep state to tra nsiti on
into. However, a four second power button override event places the system
immediately into S5. When transitioning into a software-invoked sleep state, the I/O
controller attempts to gracefully put the system to sleep by first going into the
processor C2 state.
4.2.1 S0 State
This is the normal operating state, even though there are some power savings modes
in this state using processor Halt and Stop Clock (processor C1 and C2 states). S0
affords the fastest wake-up response time of any sleep state because the system
remains fully powered and memory is intact.
4.2.2 S1 State
This state is entered via a processor Sleep signal from the I/O controller (processor C3
state). The system remains fully powered with memory contents intact but the
processors enter their lowest power state. The operating system disables bus masters
for uniprocessor configurations while flushing and invalidating caches before entering
this state in multiprocessor configurations. Wake-up latency is slightly longer in this
state than in S0; however, power savings are improved from S0.
4.2.3 S2 State
This state is not sup po r ted.
4.2.4 S3 State
This state is called Suspend to RAM (STR). The system context is maintained in system
DRAM, but power is shut off to non-critical circuits. Memory is retained, and refreshes
continue. All clocks stop except the RTC. S3 is entered when the I/O controller asserts
the SLP_S3# signal to downstream circuitry to control 1.8 V power plane switching.
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 37
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 38

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Power must be switched from the normal 1.8 V rail to standby 1.8 V, because the ATX
12v 450 W po wer sup ply d oe s no t di re ct ly su ppl y a st and b y 1 .8 V r a il . T he seq ue nc e to
enter Suspen d to RAM is as follow s:
1. The OS and BIOS prepare for S3 sleep state.
2. The OS sets the appropriate sleep bits in the I/O controller.
3. The I/O controller drives STPCLK to the processors.
4. The processors respond with a Stop-Grant cycle, passed over hub interface by
MCH.
5. The I/O controller indicates an S3 (STR) sleep mode to the MCH via Hub Interface
A.
6. The MCH puts DDR memory into the self-refresh mode.
7. The MCH drives DDR CMDCLK differential pairs and all DDR outputs low.
8. The MCH drives a completion message via Hub Interface A to the I/O controller.
9. The I/O controller turns off all voltage rails (except Standby 5V) from the main
power supply by asserting the SLP_S3_N signal.
When in the S3 state, only the standby 5 V rail is available from the power supply. The
board uses this standby source to generate 1.8 V standby rail to power the DIMMs.
The asserted SLP_S3_N signal also controls the logic to switch the DIMM power source
from main 1.8 V to standby 1.8 V.
4.2.5 S4 State
This state is not supported.
4.2.6 S5 State
This state is the normal off state whether entered through the power button or soft off.
All power is shut off except for the logic required to restart. The system remains in the
S5 state only while the power supply is plugged into the electrical outlet. If the power
supply is unplugged, this is considered a mechanical off or G3.
4.2.7 Wake-Up Ev ents
The types of wake-up events and wake-up latencies are related to the actual power
rails available to the system in a particular sleep state, as well as to the location in
which the system context is stored. Regardless of the sleep state, wake on the power
button is always supported except in a mechanical off situation. When in a sleep state,
the system complies with the PCI specification by supplying the optional 3.3 V standby
voltage to each PCI slot as well as the PME# signal. This enables any compliant PCI
card to wake up the system from any supported sleep state except mechanical off.
4.2.8 Wake from S1 Sleep Stat e
During S1 the system is fully powered, permitting support for PCI Express Wake and
Wake on PCI PME#.
4.2.9 Wake from S3 State
Keyboard press or mouse movement is used to wake from S3.
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
38 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 39

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
4.2.10 Wake from S5 State
The power button is used to wake from S5.
4.3 PCI PM Support
This design holds the system reset signal low when in a sleep state. The system
supports the PCI PME# signal and provides 3.3 V standby to the PCI and PCI Express
slots. This support allows any compliant PCI or PCI Express card to wake up the system
from any sleep state except mechanical off. Because of the limited amount of power
available on 3.3 V standby, the user and the operating system must configure the
system carefully following the PCI power management interface specification.
4.4 Platform Management
The LM 93 monitors the majority of the system voltages. The VID signals from the
processors are also monitored by LM 93. All voltage lev els can be read via the SMBus.
4.4.1 Processor Ther mal Management
Each processor monitors its own core temperature and thermally manages itself when
it reaches a certain temperature. The system also uses the internal processor diode to
monitor the die temperature. The diode pins are routed to the diode input pins in the
LM 93. The LM 93 can be programmed to force the processor fans to full speed
operation when it senses the processor core temperature exceeding a specific value. In
addition, the LM 93 has an on-chip thermal monitor which allows it to monitor the
incoming ambi ent tempe rature. Addition al proce ssor therm al manageme nt requi res the
system to communicate to the processors when the VRD reaches a critical
temperature. The VR thermal monitor asserts FORCEPR_N signal to the processor.
4.5 System Fan Operation
The system use s bo th th e LM 93 an d SMSC LPC47M172 to monitor and control the fan s
in the system.T he LM93 us es puls e wid th modul a ted (PWM ) outputs that ca n modula te
the voltage across the fans, providing a variable duty cycle to effect a reduced DC
voltage from nominal 12V DC.
By default, the CPU fans are jumpered to run at full speed all the time. The fan
headers are the standard 12 V, three-pin type used in previous servers, which support
tachometer out. The LM 93 also has four tachometer inputs that it can use to monitor
the fans it controls. All fan tachometer data can be extracted from the controllers via
the SMBus. The system fan speed control circuit does not control the power supply fan.
Each PWM output has a bypass jumper that causes all fans to run at full speed and
ignore the PWM control. Each processor fan has its own dedicated PWM output and
tachometer input, so each fan is controlled and monitored independently, depending on
the core temperature.
The LM 93 is dedicated to processor fan speed control and monitor, and can be
programmed with temperature limit values that allow it to speed up or idle the
processor fans, depending upon the input temperature.
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 39
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 40

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
5.0 Driver and OS Support
The CRB supports the following operating systems:
•Red Hat* EL 3.0 AS and WS
• QNX Neutrino*
• Windows* Server 2003
• Microsoft* Windows XP and embedded XP
Note: Operating systems are not included in the Development Kit.
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
40 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 41

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
6.0 Hardware Reference
This section provides reference information on the hardware, including locations of
evaluation board components, connector pinout information, and jumper settings.
Figure 21 shows the evaluation board.
Figure 21. Evaluation Board
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 41
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 42

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
6.1 Chipset Components
Table 6 lists the chipset and other major components on the evaluation board.
Table 6. Chipset Components
Component Designator Component Description
U5E1 Intel
U3F1 Intel® 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub (ICH)
U1H1 Intel
®
E7520 Memory Controller Hub (MCH)
®
82802AC Firmware Hub (FWH)
6.2 Expansi on Slots and Sockets
Table 7 lists the expansion slots and sockets on the evaluation board.
Table 7. Expansion Slots and Socket
Slot/Socket Reference Designator Slot/Socket Description
J2B2 PCI Express Port A
J3B2 PCI Express Port B
J3B1 PCI Express Port C
J2B1 PCI Slot
J1B1 PCI-X Slot 1
J1B2 PCI-X Slot 2
U5H1 CPU1
U7H1 CPU0
U1H1 Firmware H ub ( FWH ) BIO S Socket
XB4G1 Battery
6.2.1 PCI Expr ess * C onnector
Table 8 lists the signals assigned to the PCI Express* port A, B, and C slot connectors
found at J2B2, J3B2, and J3B1 respectively.
Table 8. PCI Express* Connector Pinout (Sheet 1 of 2)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
A1 PRSNT1# B1 12 V
A2 12 V B2 12 V
A3 12 V B3 12 V
A4 GND B4 GND
A5 JTAG2 B5 SMCLK
A6 JTAG3 B6 SMDAT
A7 JTAG4 B7 GND
A8 JTAG5 B8 3.3 V
A9 3.3 V B9 JTAG1
A10 3.3 V B10 3.3 V
A11 PWRGD B11 WAKE#
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
42 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
AUX
Page 43

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Table 8. PCI Express* Connector Pinout (Sheet 2 of 2)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
A12 GND B12 Reserved
A13 Refclk+ B13 GND
A14 Re fclk - B14 HSOP_0
A15 GND B15 HSON_0
A16 HSIP_0 B16 GND
A17 HSIN_0 B17 PRSNT2_1#
A18 GND B18 GND
A19 Reserved B19 HSOP_1
A20 GND B20 HSON_1
A21 HSIP_1 B21 GND
A22 HSIN_1 B22 GND
A23 GND B23 HSOP_2
A24 GND B24 HSON_2
A25 HSIP_2 B25 GND
A26 HSIN_2 B26 GND
A27 GND B27 HSOP_3
A28 GND B28 HSON_3
A29 HSIP_3 B29 GND
A30 HSIN_3 B30 Reserved
A31 GND B31 PRSNT2_2#
A32 Reserved B32 Reserved
A33 Reserved B33 HSOP_4
A34 GND B34 HSON_4
A35 HSIP_4 B35 GND
A36 HSIN_4 B36 GND
A37 GND B37 HSOP_5
A38 GND B38 HSON_5
A39 HSIP_5 B39 GND
A40 HSIN_5 B40 GND
A41 GND B41 HSOP_6
A42 GND B42 HSON_6
A43 HSIP_6 B43 GND
A44 HSIN_6 B44 GND
A45 GND B45 HSOP_7
A46 GND B46 HSON_7
A47 HSIP_7 B47 GND
A48 HSIN_7 B48 PRSNT2_3#
A49 GND B49 GND
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 43
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 44

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
6.2.2 32 -Bit PCI Connector
Table 9 presents the signals assigned to the 32-bit PCI slot connector found at J2B1.
Table 9. 32-Bit 5 V PCI Connector Pinout (Sheet 1 of 2)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
A1 TRST# B1 -12 V
A2 +12 V B2 TCK
A3 TMS B3 GND
A4 TDI B4 TDO
A5 5 V B5 5 V
A6 INTA# B6 5 V
A7 INTC# B7 INTB#
A8 5 V B8 INTD#
A9 RSVD1 B9 PRSNT1#
A10 5 V B10 Reserved
A11 RSVD3 B11 PRSNT2#
A12 GND B12 GND
A13 GND B13 GND
A14 3.3 V
A15 RST# B15 GND
A16 5 V B16 CLK
A17 GNT# B17 GND
A18 GND B18 REQ#
A19 PME# B19 5 V
A20 AD30 B20 AD31
A21 3.3 V B21 AD29
A22 AD28 B22 GND
A23 AD26 B23 AD27
A24 GND B24 AD25
A25 AD24 B25 3.3 V
A26 IDSEL B26 C/BE3#
A27 3.3 V B27 AD23
A28 AD22 B28 GND
A29 AD20 B29 AD21
A30 GND B30 AD19
A31 AD18 B31 3.3 V
A32 AD16 B32 AD17
A33 3.3 V B33 C/BE 2#
A34 FRAME# B34 GND
A35 GND B35 IRDY#
A36 TRDY# B36 3.3 V
A37 GND B37 DEVSEL#
AUX
B14 Reserved
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
44 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 45

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Table 9. 32-Bit 5 V PCI Connector Pinout (Sheet 2 of 2)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
A38 STOP# B38 GND
A39 3.3 V B39 LOCK#
A40 SDONE B40 PERR#
A41 SBO# B41 3.3 V
A42 GND B42 SERR#
A43 PAR B43 3.3 V
A44 AD15 B44 C/BE1#
A45 3.3 V B45 AD14
A46 AD13 B46 GND
A47 AD11 B47 AD12
A48 GND B48 AD10
A49 AD9 B49 GND
A50 KEY B50 KEY
A51 KEY B51 KEY
A52 CBEO# B52 AD8
A53 3.3 V B53 AD7
A54 AD6 B54 3.3 V
A55 AD4 B55 AD5
A56 GND B56 AD3
A57 AD2 B57 GND
A58 AD0 B58 AD1
A59 5 V B59 5 V
A60 REQ64# B60 ACK64#
A61 5 V B61 5 V
A62 5 V B62 5 V
6.2.3 PCI-X Connector
Table 10 presents the PCI-X connector pinout for J1B1 and J1B2.
Table 10. PCI-X Connector Pinout (Sheet 1 of 4)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
A1 TRST# B1 -12 V
A2 +12 V B2 TCK
A3 TMS B3 GND
A4 TDI B4 TDO
A5 5 V B5 5 V
A6 INTA# B6 5 V
A7 INTC# B7 INTB#
A8 5 V B8 INTD#
A9 Reserved B9 PRSNT1#
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 45
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 46

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Table 10. PCI-X Connector Pinout (Sheet 2 of 4 )
Pin Signal Pin Signal
A10 3.3 V B10 Reserved
A11 Reserved B11 PRSNT2#
A12 KEY B12 KEY
A13 KEY B13 KEY
A14 3.3 V
AUX
A15 RST# B15 GND
A16 3.3 V B16 CLK
A17 GNT# B17 GND
A18 GND B18 REQ#
A19 PME# B19 3.3 V
A20 AD30 B20 AD31
A21 3.3 V B21 AD29
A22 AD28 B22 GND
A23 AD26 B23 AD27
A24 GND B24 AD25
A25 AD24 B25 3.3 V
A26 IDSEL B26 C/BE3#
A27 3.3 V B27 AD23
A28 AD22 B28 GND
A29 AD20 B29 AD21
A30 GND B30 AD19
A31 AD18 B31 3.3 V
A32 AD16 B32 AD17
A33 3.3 V B33 C/BE2#
A34 FRAME# B34 GND
A35 GND B35 IRDY#
A36 TRDY# B36 3.3 V
A37 GND B37 DEVSEL#
A38 STOP# B38 PCIXCAP
A39 3.3 V B39 LOCK#
A40 SDONE B40 PERR#
A41 SBO# B41 3.3 V
A42 GND B42 SERR#
A43 PAR B43 3.3 V
A44 AD15 B44 CBE1#
A45 3.3 V B45 AD14
A46 AD13 B46 GND
A47 AD11 B47 AD12
A48 GND B48 AD10
A49 AD9 B49 M66EN
B14 Reserved
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
46 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Page 47

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Table 10. PCI-X Connector Pinout (Sheet 3 of 4)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
A50 GND B50 GND
A51 GND B51 GND
A52 CBEO# B52 AD8
A53 3.3 V B53 AD7
A54 AD6 B54 3.3 V
A55 AD4 B55 AD5
A56 GND B56 AD3
A57 AD2 B57 GND
A58 AD0 B58 AD1
A59 3.3 V B59 3.3 V
A60 REQ64# B60 ACK64#
A61 5 V B61 5 V
A62 5 V B62 5 V
A63 GND B63 Reserved
A64 C/BE7# B64 GND
A65 C/BE5# B65 C/BE6#
A66 3.3 V B66 C/BE4#
A67 PAR64 B67 GND
A68 AD62 B68 AD63
A69 GND B69 AD61
A70 AD60 B70 3.3 V
A71 AD58 B71 AD59
A72 GND B72 AD57
A73 AD56 B73 GND
A74 AD54 B74 AD55
A75 3.3 V B75 AD53
A76 AD52 B76 GND
A77 AD50 B77 AD51
A78 GND B78 AD49
A79 AD48 B79 3.3 V
A80 AD46 B80 AD47
A81 GND B81 AD45
A82 AD44 B82 GND
A83 AD42 B83 AD43
A84 3.3 V B84 AD41
A85 AD40 B85 GND
A86 AD38 B86 AD39
A87 GND B87 AD37
A88 AD36 B88 3.3V
A89 AD34 B89 AD35
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 47
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 48

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Table 10. PCI-X Connector Pinout (Sheet 4 of 4 )
Pin Signal Pin Signal
A90 GND B90 AD33
A91 AD32 B91 GND
A92 Reserved B92 Reserved
A93 GND B93 Reserved
A94 Reserved B94 GND
6.2.4 Process or Sockets
The processor is keyed so that it fits into the socket in one particular orientation.
6.2.5 Firmware Hub ( F WH) BIOS Sock et
The system boot ROM is installed on the Intel® 82802AC Firmware Hub. The FWH is
addressable on the LPC bus off the Intel
The FWH or BIOS flash memory fits into the 32-pin socket U1H1, giving you the option
to remove and reprogram it without the use of soldering equipment. There is also a
flash uti lit y tha t is supp lie d wi th the BI OS that can be u sed to pr ogram the FWH. This is
the recommende d way to program the FWH.
There is only one correct orientation for the FWH to be placed into its socket. Line up
the circular marking on the FWH, denoting pin one, with the arrow marking on the
evaluation board socket.
6.2.6 Battery
A type 2032, 3 V lithium coin cell battery is used in socket XB4G1 on the evaluation
board. The battery is held in place by a metal arm. To remove the battery, gently push
the metal arm and remove the battery.
6.3 On-Board Connectors
Table 11. On-Board Connecto r
Connector Reference Designator Connector Description
J1G1, J1F4 SATA Connector
J1K2 IDE Connector
JJ1K1 Floppy Connector
J9F4 ITP Connector
J2G1 Front Panel Connector
®
6300ESB ICH.
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
48 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 49

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
6.3.1 SATA Connector
Table 12. SATA Connector Pinout
Pin Connector Description
1GND
2A+
3A4GND
5B6B+
7GND
6.3.2 IDE Connector
The evaluation board has a 40-pin connector for the IDE controller present in the Intel®
6300ESB ICH. Table 13 lists the signals assigned to the IDE connector.
Table 13. IDE Connector Pinout
Pin Connector Description Pin Connector Description
1Reset IDE 21PDDREQ
2GND 22GND
3 Host Data 23 I/O Write #
4 Host Data 24 GN D
5 Host Data 25 I/O Read #
6 Host Data 26 GN D
7 Host Data 27 I/O CH RDY
8 Host Data 28 GN D
9 Host Data 29 DACK#
10 Host Data 30 GND
11 Host Data 31 IRQ 1 4
12 Host Data 32 Reserved
13 Host Data 33 Addr1
14 Host Data 34 Primary IDE Cable Detect
15 Host Data 35 Addr0
16 Host Data 36 Addr2
17 Host Data 37 Chip Select 1#
18 Host Data 38 Chip Select 3#
19 GND 39 Activity
20 Key 40 GND
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 49
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 50

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
6.3.3 Floppy Dr iv e Connecto r
The evaluation board provides one 34-pin floppy connector, which is located at J1K1.
Table 14. Floppy Drive Connector Pinout
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1GND 18DIR#
2Drive Enable 0 19GND
3GND 20STEP#
4Reserved 21GND
5Key 22Write Data#
6Drive Enable 1 23GND
7GND 24Write Gate#
8Index 25GND
9 GND 26 T rack 00#
10 Motor Enable A# 27 GND
11 GND 28 Write Protect#
12 Reserved 29 GND
13 GND 30 Read Data#
14 Drive Select 0# 31 GND
15 GND 32 Side 1 Select#
16 Reserved 33 GND
17 GND 34 Diskette Change#
6.3.4 Front Pa nel Connect or
The development kit is not shipped with a chassis, so the front panel connector is
unused by default. However, if you want to place your evaluation board in a chassis,
refer to Table 15 for the pinout of the front panel connector J2G1.
Table 15. Front Panel Connector Pinout
Pin Connector Description Pin Connector Description
1V
3V
5 GND 6 FP_PWR _BTN_N
7 FP_RST_BTN_N 8 GND
9 GND 10 No Pin
CC
CC
2 HD_ACT_LED_N
4FPNTPNL_PWR_LED
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
50 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 51

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
6.4 Jumpers
The evaluation board has a number of jumpers that control various functions of the
system.
Table 16 presents the descriptions of the jumpers and their settings.
Figure 22 illustrates the location s of the jumper s on the bo ard.
Table 16. Jumpers and Jumper Functions
Jumper Function / Default Setting Comments
J9E2 ITP Mode / 1-2 and 3-4
J7K2 CPU 0 Fan Override / 1-2
J6K1 CPU 1 Fan Override / 1-2
J4G1 Cl ea r CM OS / 1-2
J3K1 CPU1 VIDs / 1.325 V (one jumper on posi tion 5)
J4A1 5 V
J4B1 3. 3 V
J8E1 S3 Enable / 1-2
J4F6 Memory PLL0 / 1-2 Valid for both FSB speeds
J3J1 CPU BSEL 0 / Open
enable / 1-2
AUX
Enable / 1-2
AUX
2-4 = UP
1-2 and 3-4 = DP
1-2 = Normal use
2-3 = Clear CMOS
Open = 667 MT/s
2-3 = 533 MT/ s
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 51
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 52

Figure 22. Jumper Locations
Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
52 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 53

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
6.5 SMBUS Headers
The SMBUS headers are used to connect the SMBUS. Refer to the following tables for
pinout inform at ion .
Table 17 describes the SMBUS 3.3 V STBY pinout.
Table 17. SMBUS 3.3 V STBY Pino ut
Pin Connector Description
1SMBDAT
2GND
3SMB CLK
6.6 Back Pa nel Connectors
The evalua ti on b oar d co ntain s a nu mbe r of c onnec tor s for ex ter nal sy s tem dev ice s a nd
peripherals. Figure 23 shows the peripheral connectors.
The following sections provide pinouts for each connector.
Note: The video connector may not be present.
Figure 23. B ack Panel Connect ors
6.6.1 PS/2-Style Mouse and Keyboard Connectors
Table 18 lists the signals assigned to the PS/2-style keyboard and mouse connectors.
The keyboard port is on the top and the mouse port is on the bottom.
Table 18. PS/2-Style Mouse and Keyboard Pinout
Pin Connector Description
1,7 Data
2,8 Reserved
3,9, 13-17 Ground
4,10 +5 V (fused)
5,11 Clock
6, 12 Reserved
6.6.2 Parallel Port
Table 19 lists the signals assigned to the parallel port connector.
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 53
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 54

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
Table 19. Parallel Port Connector Pinout
Pin Connector Description Pin Connector Description
1 Strobe# 14 Auto Feed#
2 Data Bi t 0 15 Fault#
3 Data Bi t 1 16 INIT#
4 Data Bi t 2 17 SLC IN#
5 Data Bi t 3 18 Ground
6 Data Bi t 4 19 Ground
7 Data Bi t 5 20 Ground
8 Data Bi t 6 21 Ground
9 Data Bi t 7 22 Ground
10 ACK# 23 Ground
11 Busy 24 Ground
12 Paper end 25 Ground
13 SLCT
6.6.3 Serial Po r ts
Table 20 lists the signals assigned to the serial port connector.
Table 20. Serial Port Connector Pinout
Pin Connector Description
1DCD
2 Serial In - RXD
3 Serial Out - TXD
4DTR
5Ground
6DSR
7RTS
8CTS
9RI
6.6.4 Dual Stac ked USB Co nnectors
Table 21 lists the signals assigned to the dual stacked USB connector.
Table 21. USB Connector Pinout
Pin Connector Description
1,5 Power (fused)
2,6 USBP1 # [USBP2#]
3,7 USBP1 [USBP2]
4,8 Ground
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
54 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 55

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
6.6.5 Video Port
Note: This section may not apply if vide o connec tor is not presen t on the board.
Table 22 lists the signals assigned to the video port connector.
Table 22. Video Port Connector Pinout
Pin Connector Description
1VGA Red
2 VGA Green
3VGA Blue
4Monitor ID
5GND
6GND
7GND
8GND
9GND
10 GND
11 Monitor ID
12 DDCDA
13 HSYNC
14 YSYNC
15 DDCLK
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 55
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 56

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
7.0 Board Setup Checklist
The following is a checklist of items to ensure proper functionality of the CRB.
• All cabl es are pro perl y plugg ed in :
—Hard drives
—SATA and/or IDE
— Monitor, keyboard, mouse
— Additional peripherals such as CD, DVD, floppy, etc.
—Power
• Fans are securely in place and plugged into the appropriate jumpers.
• Memory, PCI, and PCI Express cards are secured in slots.
• RTC battery is installed.
• Jumpers are configured correctly (refer to S ec tio n 6.4, “Jumpe rs” on page 51).
• Proper standoffs or mounting for board (if applicable).
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
56 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 57

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
8.0 Debug Procedure
The debug procedure in this section is used to determine baseline functionality for the
Dual-Core Intel
®
Xeo n® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB
ICH Development Kit. This is a cursory set of tests designed to provide a level of
confidence in the platform operation.
8.1 Level 1 Debug (Port80/BIOS)
Refer to the steps in Table 23 when debuggi ng a board that does not boot.
Table 23. Level 1 Debug (Port80/BIOS)
Step Test Pass/Fail Criteria Cause of Failure
1 Verify “SYSTEM PWRGD” LED Green
2 Is “PCI Reset” LED illuminated?
3 Verify CPURST LED is off Off
4 Verify Port 80 posting
5 Verify BIOS settings Latest BIOS installed
6 Verify default jumper settings See default settings Improper jumper settings
Decimal on Port 80 display
RED
Port 80 LEDs are posting
boot codes and stopping
8.2 Level 2 Debug (Power Sequence)
Power sequence failure – go
immediately to Level 2 debug
PCI reset stuck – go to Level 3 debug
CPU reset stuck – go to Level 3
debug
System Hang – Check BIOS go to
level 3 debug. Refer to AMI* BIOS
documentation for details.
Contac t Intel representative for the
latest BIOS image
Table 24. Level 2 Debu g (Pow e r Se quen ce )
Step Test Pass/Fail Criteria Cause of Failure
Measure voltages across:
3.3V
1 Prima ry pow e r sup pl y vol t ages
2 1.8V 1.8V DDR2 power supply failure
3 1.5V 1.5V MCH/ICH core power supply failure
4 1.8V VSBY 1.8V DDR2 standby power supply failure
5 CPU VTT Power Supply 1.05V CPU_VTT p owe r supply failure
6 CPU0 VRD 1.2V – 1.4V CPU0 VRD failure
7 CPU1 VRD 1.2V – 1.4V CPU1 VRD failure
8 Verify “SYSTEM PWRGD” LED Green Power sequence failure
-12V
5V
5V
12V
External power supply failure
April 2007 User’s Manual
Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9 57
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 Chipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
Page 58

Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor LV / E7520 Chipset / 6300ESB ICH
8.3 Level 3 Debug (Voltage References)
Table 25 includes the first items to look at when debugging a board that is not booting.
Table 25. Level 3 Debug (Voltage Reference)
Step Test Pass/Fail Criteria Cause of Failure
1 MCH DDR2 Channel A Vref 0.9 V Vref incorrect: check resistor values
2 MCH DDR2 Channel B Vref 0.9 V Vref incorrect: check resistor values
3 MCH Hublink Vref 0.354V Vref incorrect: check resistor values
4 MCH Hublink Vswing 0.8 04V Vs win g incorrect: check resistor values
5 ICH Hublink Vref 0.347V Vref incorrect: check resistor values
6 ICH Hublink Vswing 0.696V Vswing incorrect: check resistor values
CPU0 VTT Vref
7
(back side of board)
CPU1 VTT Vref
8
(back side of board)
9 MCH VTT Vref 0.775V Vref incorrect: check resisto r values
0.775V Vref incorrect: check resistor values
0.754V Vref incorrect: check resistor values
®
Dual-Core Intel
User’s Manual April 2007
58 Order Nu mber: 311274 - 00 9
Xeon® processor LV with Intel® E7520 C hipset and Intel® 6300ESB ICH
 Loading...
Loading...