
2nd Generation Intel® Core™ Processor Family Desktop
Specification Update
January 2011
Reference Number: 324643-001

Legal Lines and Disclaimers
INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY
ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PRO PERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN
INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEV ER, AND INTEL DISCLAIMS
ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES
RELATING T O FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life saving, life sust aining, critical control or safety systems, or
in nuclear facility applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked “reserved” or “un defined.” Intel reserves these for
future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
The processor may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Current
characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distri butor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Intel processor numbers are not a measure of performance. Processor numbers differentiat e features within each processor family, not across
different processor families. See http://www.intel.com/products/processor_number for details. Over time processor numbers will increment based on
changes in clock, speed, cache, or other features, an d increment s are not inte nded to r epresent pro portional or quantit ative increases in a ny particular
feature. Current roadmap processor number progression is not necessarily representative of future roadmaps. See www.intel.com/products/
processor_number for details.
®
Active Management Technology requires the computer system to have an Intel(R) AMT-enabled chipset, network hardware and software, as
Intel
well as connection with a power source and a corporate network connection . Setu p req uires configu rat ion b y the purchaser and may require scripting
with the management console or further integration into existing security frameworks to enable certain functionality . I t may also require modifications
of implementation of new business processes. With regard to notebooks, Intel AMT may not be available or certain capabilities may be limited over a
host OS-based VPN or when connecting wirelessly, on battery power, sleeping, hibernating or powered off. For more information, see www.intel.com/
technology/platform-technology/intel-amt/
®
Trusted Execution Technology (Intel® TXT) requires a computer system with Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® Virtualization Technology
Intel
®
VT-x) and Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (Intel® VT-d)), a Intel TXT-enabled processor, chipset, BIOS, Authenticated Code
(Intel
Modules and an Intel TXT-compatible measured launched environment (MLE). The MLE could consist of a virtual machine monitor, an OS or an
application. In addition, Intel TXT requires the system to contain a TPM v1.2, as defined by the Trusted Computing Group and specific software for
some uses. For more information, see http://www.intel.com/technology/security
®
Virtualization Technology requires a computer system with an enabled Intel® processor, BIOS, virtual machine monitor (VMM) and, for some
Intel
uses, certain computer system software enabled for it. Functionality, performance or other benefits will vary depending on hardware and software
configurations and may require a BIOS update. Software applications may not be compatible with all operating systems. Please check with your
application vendor.
®
* Intel
Turbo Boost Technology requires a PC with a processor with Intel Turbo Boost Technology capability. Intel Turbo Boost Technology
performance varies depending on hardware, software and overall system configuration. Check with your PC manufacturer on whether your system
delivers Intel Turbo Boost Technology. For more information, see http://www.intel.com/technology/turboboost
®
Intel
Hyper-threading Technology requires a computer system with a processor supporting HT Technology and an HT Technology-enabled chipset,
BIOS, and operating system. Performance will vary depending on the specific hardware and software you use. For more information including details
on which processors support HT Technology, see http://www.intel.com/info/hyperthreading.
64-bit computing on Intel architecture requires a computer system with a processor, chipset, BIOS, operating system, device drivers and applications
enabled for Intel
for more information.
®
64 architecture. Performance will vary depending on your hardware and software confi gurations. Consult with your system vendor
Copies of documents which have an order number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature may be obtained by visiting Intel's
website at http://www.intel.com.
Intel, Intel Core, Celeron, Pentium, Intel Xeon, Intel Atom, Intel SpeedStep, and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel
Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2011, Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
2
Specification Update

Contents
Contents
Revision History...............................................................................................................5
Preface ..............................................................................................................................6
Summary Tables of Changes..........................................................................................8
Identification Information..............................................................................................12
Errata...............................................................................................................................14
Specification Changes...................................................................................................37
Specification Clarifications...........................................................................................38
Documentation Changes...............................................................................................39
§
Specification Update
3

Contents
4
Specification Update
Revision History
Revision Description Date
-001 Initial Release January 2011
Specification Update 5
Preface
This document is an update to the specifications contained in the Affected Documents
table below. This document is a compilation of device and documentation errata,
specification clarifications and changes. It is intended for hardware system
manufacturers and software developers of applications, operating systems, or tools.
Information types defined in Nomenclature are consolidated into the specification
update and are no longer published in other documents.
This document may also contain information that was not previously published.
Affected Documents
nd
Generation Intel® Core™ Processor Family Desktop Datasheet, Volume 1 324641-001
2
nd
2
Generation Intel® Core™ Processor Family Desktop Datasheet, Volume 2 324642-001
Related Documents
AP-485, Intel® Processor Identification and the CPUID Instruction http://www.intel.com/
®
Intel
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual,
Volume 1: Basic Architecture
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual,
Intel
Volume 2A: Instruction Set Reference Manual A-M
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual,
Intel
Volume 2B: Instruction Se t Reference Manual N-Z
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual,
Intel
Volume 3A: System Programming Guide
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual,
Intel
Volume 3B: System Programming Guide
®
64 and IA-32 Intel Architecture Optimization Reference
Intel
Manual
®
Intel
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual
Documentation Changes
ACPI Specifications www.acpi.info
Document Title
Document Title
Document
Number
Document Number/
Location
design/processor/
applnots/241618.htm
http://www.intel.com/
products/processor/
manuals/index.htm
http://www.intel.com/
design/processor/
specupdt/252046.htm
6 Specification Update

Nomenclature
Errata are design defects or errors. These may cause the processor behavior to
deviate from published specifications. Hardware and software designed to be used with
any given stepping must assume that all errata documented for that stepping are
present on all devices.
S-Spec Number is a five-digit code used to identify products. Products are
differentiated by their unique characteristics such as, core speed, L2 cache size,
package type, etc. as described in the processor identification information table. Read
all notes associated with each S-Spec number.
Specification Changes are modifications to the current published specifications.
These changes will be incorporated in any new release of the specification.
Specification Clarifications describe a specification in greater detail or further
highlight a specification’s impact to a complex design situation. These clarifications will
be incorporated in any new release of the specification.
Documentation Changes include typos, errors, or omissions from the current
published specifications. These will be incorporated in any new release of the
specification.
Note: Errata remain in the specification update throughout the product’s lifecycle, or until a
particular stepping is no longer commercially available. Under these circumstances,
errata removed from the specification update are archived and available upon request.
Specification changes, specification clarifications and documentation changes are
removed from the specification update when the appropriate changes are made to the
appropriate product specification or user documentation (datasheets, manuals, etc.).
Specification Update 7
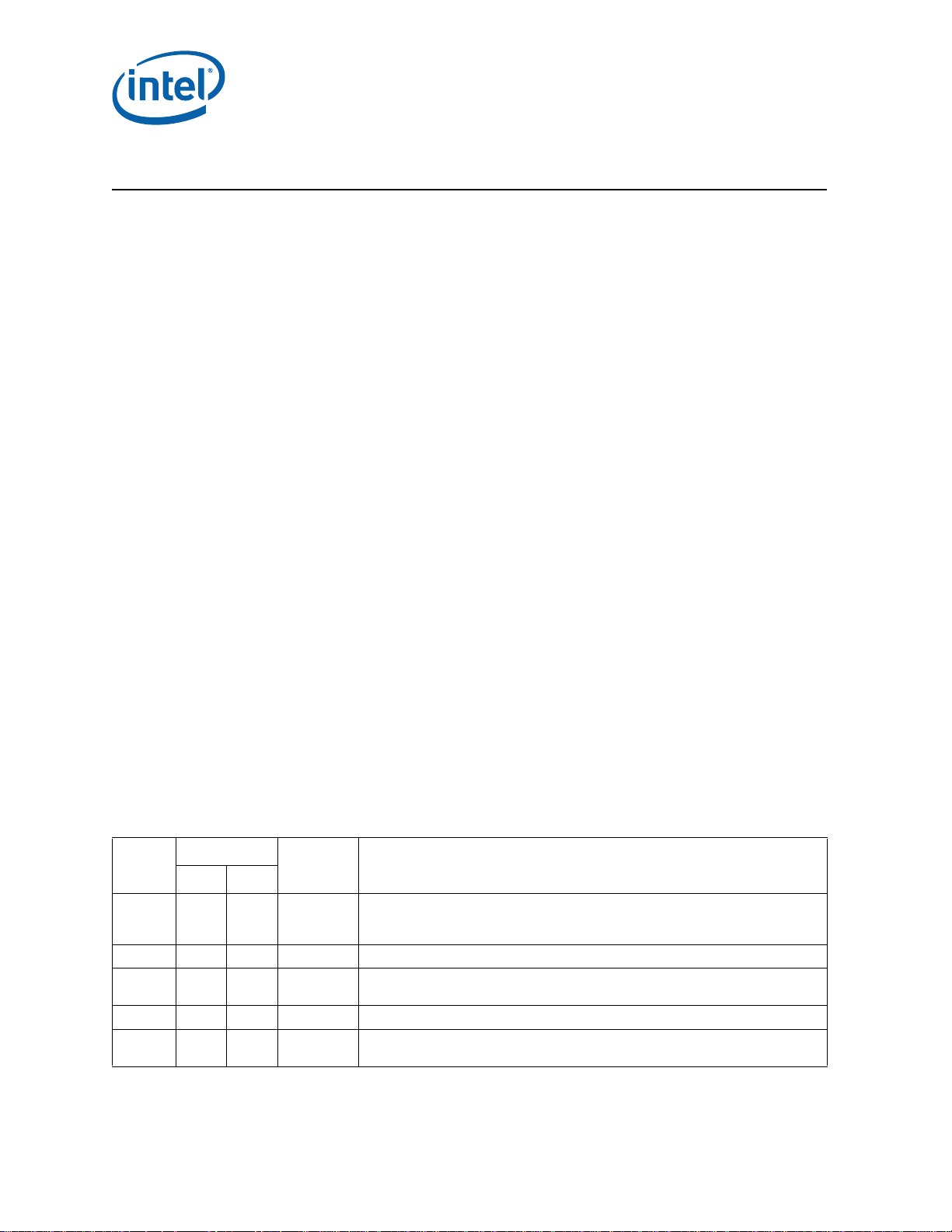
Summary Tables of Changes
The following tables indicate the errata, specification changes, specification
clarifications, or documentation changes which apply to the processor. Intel may fix
some of the errata in a future stepping of the component, and account for the other
outstanding issues through documentation or specification changes as noted. These
tables uses the following notations:
Codes Used in Summary Tables
Stepping
X: Errata exists in the stepping indicated. Specification Change or
(No mark)
or (Blank box): This erratum is fixed in listed stepping or specification change
Page
(Page): Page location of item in this document.
Status
Doc: Document change or update will be implemented.
Plan Fix: This erratum may be fixed in a future stepping of the product.
Fixed: This erratum has been previously fixed.
No Fix: There are no plans to fix this erratum.
Row
Change bar to left of a table row indicates this erratum is either new or modified from
the previous version of the document.
Errata (Sheet 1 of 4)
Number
BJ1
BJ2
BJ3
BJ4
BJ5
Steppings
Status ERRATA
D-2 Q-0
XXNo Fix
XXNo FixAPIC Error “Received Illegal Vector” May be Lost
XXNo Fix
XXNo FixB0-B3 Bits in DR6 For Non-Enabled Breakpoints May be Incorrectly Set
XXNo Fix
Clarification that applies to this stepping.
does not apply to listed stepping.
An Enabled Debug Breakpoint or Single Step Trap May Be Taken after MOV SS/
POP SS Instruction if it is Followed by an Instruction That Signals a Floating Point
Exception
An Uncorrectable Error Logged in IA32_CR_MC2_STATUS May also Result in a
System Hang
Changing the Memory Type for an In-Use Page Translation May Lead to MemoryOrdering Violations
8 Specification Update
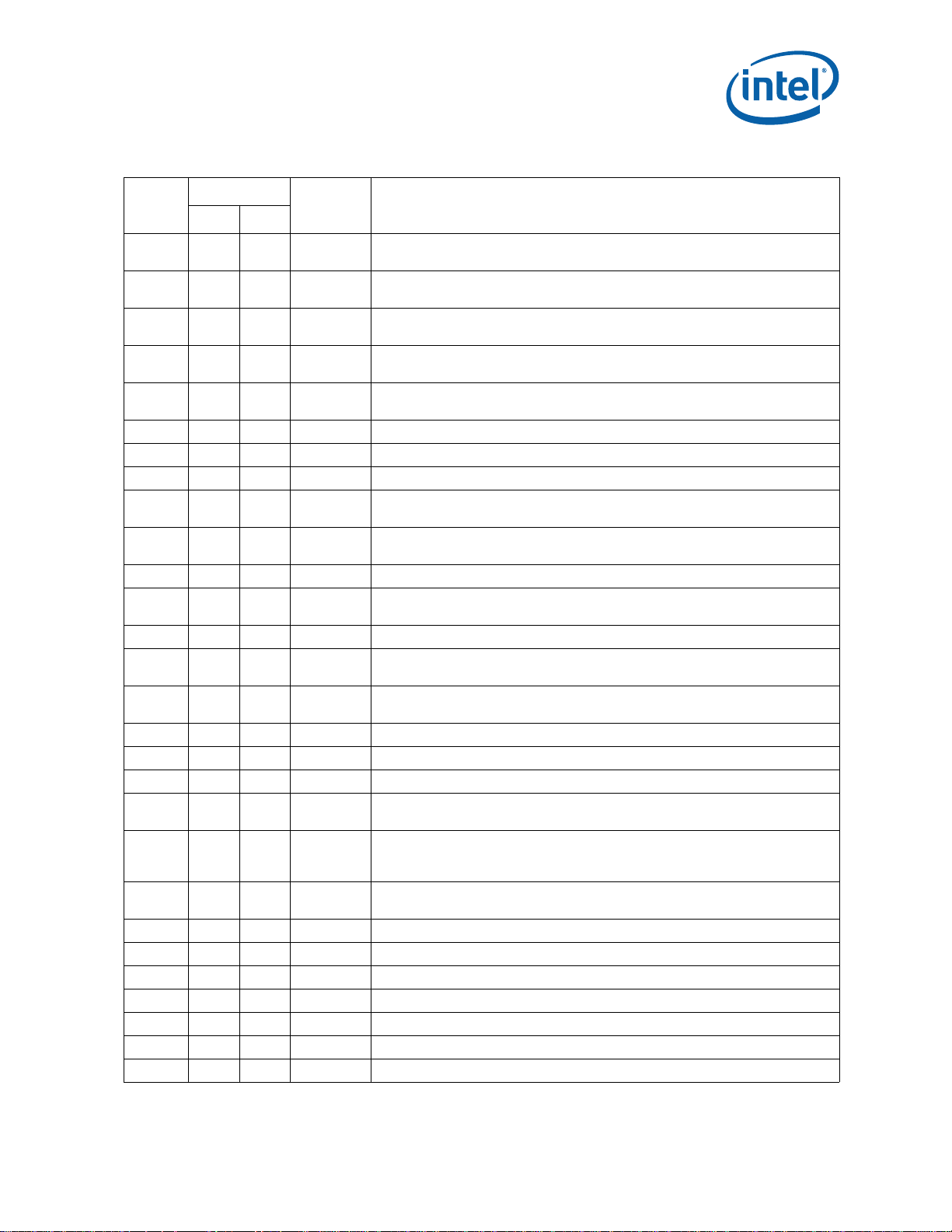
Errata (Sheet 2 of 4)
Number
BJ6
BJ7
BJ8
BJ9
BJ10
BJ11
BJ12
BJ13
BJ14
BJ15
BJ16
BJ17
BJ18
BJ19
BJ20
BJ21
BJ22
BJ23
BJ24
BJ25
BJ26
BJ27
BJ28
BJ29
BJ30
BJ31
BJ32
BJ33
Steppings
D-2 Q-0
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
Status ERRATA
Code Segment Limit/Canonical Faults on RSM May be Serviced before Higher
Priority Interrupts/Exceptions and May Push the Wrong Address Onto the Stack
Corruption of CS Segment Register During RSM While Transitioning From Real
Mode to Protected Mode
Debug Exception Flags DR6.B0-B3 Flags May be Incorrect for Disabled
Breakpoints
DR6.B0-B3 May Not Report All Breakpoints Matched When a MOV/POP SS is
Followed by a Store or an MMX Instruction
EFLAGS Discrepancy on Page Faults and on EPT-Induced VM Exits after a
Translation Change
XXNo FixFault on ENTER Instruction May Result in Unexpected Values on Stack Frame
XXNo FixFaulting MMX Instruction May Incorrectly Update x87 FPU Tag Word
XXNo FixFREEZE_WHILE_SMM Does Not Prevent Event From Pending PEBS During SMM
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
General Protection Fault (#GP) for Instructions Greater than 15 Bytes May be
Preempted
#GP on Segment Selector Descriptor that Straddles Canonical Boundary May Not
Provide Correct Exception Error Code
XXNo FixIO_SMI Indication in SMRAM State Save Area May be Set Incorrectly
XXNo Fix
IRET under Certain Conditions May Cause an Unexpected Alignment Check
Exception
XXNo FixLER MSRs May Be Unreliable
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
LBR, BTS, BTM May Report a Wrong Address when an Exception/Interrupt Occurs
in 64-bit Mode
MCi_Status Overflow Bit May Be Incorrectly Set on a Single Instance of a DTLB
Error
XXNo FixMONITOR or CLFLUSH on the Local XAPIC's Address Space Results in Hang
XXNo FixMOV To/From Debug Registers Causes Debug Exception
XXNo FixPEBS Record not Updated when in Probe Mode
XXNo Fix
Performance Monitoring Event FP_MMX_TRANS_TO_MMX May Not Count Some
Transitions
REP MOVS/STOS Executing with Fast Strings Enabled and Crossing Page
XXNo Fix
Boundaries with Inconsistent Memory Types may use an Incorrect Data Size or
Lead to Memory-Ordering Violations
XXNo Fix
Reported Memory Type May Not Be Used to Access the VMCS and Referenced
Data Structures
XXNo FixSingle Step Interrupts with Floating Point Exception Pending May Be Mishandled
XXNo FixStorage of PEBS Record Delayed Following Execution of MOV SS or STI
XXNo FixThe Processor May Report a #TS Instead of a #GP Fault
XXNo FixVM Exits Due to “NMI-Window Exiting” May Be Delayed by One Instruction
XXNo FixPending x87 FPU Exceptions (#MF) May be Signaled Earlier Than Expected
XXNo FixValues for LBR/BTS/BTM Will be Incorrect after an Exit from SMM
XXNo FixUnsupported PCIe Upstream Access May Complete with an Incorrect Byte Count
Specification Update 9
Errata (Sheet 3 of 4)
Number
BJ34
BJ35
BJ36
BJ37
BJ38
BJ39
BJ40
BJ41
BJ42
BJ43
BJ44
BJ45
BJ46
BJ47
BJ48
BJ49
BJ50
BJ51
BJ52
BJ53
BJ54
BJ55
BJ56
BJ57
BJ58
BJ59
Steppings
D-2 Q-0
XXNo Fix
Status ERRATA
Malformed PCIe Transactions May be Treated as Unsupported Requests Instead of
as Critical Errors
XXNo FixPCIe Root Port May Not Initiate Link Speed Change
XXNo Fix
Incorrect Address Computed For Last Byte of FXSAVE/FXRSTOR or XSAVE/
XRSTOR Image Leads to Partial Memory Update
XXNo FixPerformance Monitor SSE Retired Instructions May Return Incorrect Values
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
FP Data Operand Pointer May Be Incorrectly Calculated After an FP Access Which
Wraps a 4-Gbyte Boundary in Code That Uses 32-Bit Address Size in 64-bit Mode
FP Data Operand Pointer May Be Incorrectly Calculated After an FP Access Which
Wraps a 64-Kbyte Boundary in 16-Bit Code
XXNo FixSpurious Interrupts May be Generated From the Intel® VT-d Remap Engine
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
Fault Not Reported When Setting Reserved Bits of Intel® VT-d Queued Invalidation
Descriptors
VPHMINPOSUW Instruction in Vex Format Does Not Signal #UD When vex.vvvv
!=1111b
LBR, BTM or BTS Records May have Incorrect Branch From Information After an
EIST/T-state/S-state/C1E Transition or Adaptive Thermal Throttling
VMREAD/VMWRITE Instruction May Not Fail When Accessing an Unsupported
Field in VMCS
XXNo FixClock Modulation Duty Cycle Cannot be Programmed to 6.25%
XXNo Fix
Execution of VAESIMC or VAESKEYGENASSIST With An Illegal Value for
VEX.vvvv May Produce a #NM Exception
XXNo FixMemory Aliasing of Code Pages May Cause Unpredictable System Behavior
XXNo Fix
PCI Express Graphics Receiver Error Reported When Receiver With L0s Enabled
and Link Retrain Performed
XXNo FixUnexpected #UD on VZEROALL/VZEROUPPER
XXNo FixPerfmon Event LD_BLOCKS.STORE_FORWARD May Overcount
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
Conflict Between Processor Graphics Internal Message Cycles And Graphics
Reads From Certain Physical Memory Ranges May Cause a System Hang
Execution of Opcode 9BH with the VEX Opcode Extension May Produce a #NM
Exception
Executing The GETSEC Instruction While Throttling May Result in a Processor
Hang
A Write to the IA32_FIXED_CTR1 MSR May Result in Incorrect Value in Certain
Conditions
Instruction Fetch May Cause Machine Check if Page Size and Memory Type Was
Changed Without Invalidation
Reception of Certain Malformed Transactions May Cause PCIe Port to Hang
Rather Than Reporting an Error
XXNo FixPCIe LTR Incorrectly Reported as Being Supported
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
PerfMon Overflow Status Can Not be Cleared After Certain Conditions Have
Occurred
XSAVE Executed During Paging-Structure Modification May Cause Unexpected
Processor Behavior
10 Specification Update
Errata (Sheet 4 of 4)
Number
BJ60
BJ61
BJ62
BJ63
BJ64
BJ65
BJ66
BJ67
BJ68
BJ69
BJ70
BJ71
BJ72
BJ73
BJ74
BJ75
BJ76
BJ77
Steppings
D-2 Q-0
Status ERRATA
XXNo FixC-state Exit Latencies May be Higher Than Expected
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
MSR_T emperature_Target May Have an Incorrect V alue in the Temperature Control
Offset Field
Intel® VT-d Interrupt Remapping Will Not Report a Fault if Interrupt Index Exceeds
FFFFH
XXNo FixPCIe Link Speed May Not Change From 5.0 GT/s to 2.5 GT/s
XXNo FixL1 Data Cache Errors May be Logged With Level Set to 1 Instead of 0
XXNo Fix
An Unexpected Page Fault or EPT Violation May Occur After Another Logical
Processor Creates a Valid Translation for a Page
XXNo FixTSC Deadline Not Armed While in APIC Legacy Mode
XXNo FixPCIe Upstream TCfgWr May Cause Unpredictable System Behavior
XXNo FixProcessor May Fail to Acknowledge a TLP Request
XXNo Fix
Executing The GETSEC Instruction While Throttling May Result in a Processor
Hang
XXNo FixPerfMon Event LOAD_HIT_PRE.SW_PREFETCH May Overcount
XXNo Fix
Execution of FXSAVE or FXRSTOR With the VEX Prefix May Produce a #NM
Exception
XXNo FixUnexpected #UD on VPEXTRD/VPINSRD
XXNo Fix
Restrictions on ECC_Inject_Count Update When Disabling and Enabling Error
Injection
XXNo FixSuccessive Fixed Counter Overflows May be Discarded
XXNo Fix
#GP May be Signaled When Invalid VEX Prefix Precedes Conditional Branch
Instructions
XXNo FixA Read from The APIC-Timer CCR May Disarm The TSC_Deadline Counter
XXNo FixAn Unexpected PMI May Occur After Writing a Large Value to IA32_FIXED_CTR2
Specification Changes
Number SPECIFICATION CHANGES
None for this revision of this specification update.
Specification Clarifications
Number SPECIFICATION CLARIFICATIONS
None for this revision of this specification update.
Documentation Changes
Number DOCUMENTATION CHANGES
None for this revision of this specification update.
Specification Update 11
Identification Information
Component Identification using Programming Interface
The processor stepping can be identified by the following register contents:
1
Extended
2
Model
Reserved
Reserved
31:28 27:20 19:16 15:14 13:12 11:8 7:4 3:0
Note:
1. The Extended Family , bits [27:20] are used in con junction with the F amily Code, specif ied in bits [11:8],
2. The Extended Model, bits [19:16] in conjunction with the Model Number, specified in bits [7:4], are
3. The Processor Type, specified in bits [13:12] indicates whether the processor is an original OEM
4. The Family Code corresponds to bits [11:8] of the EDX register after RESET, bits [11:8] of the EAX
5. The Model Number corresponds to bits [7:4] of the EDX register after RESET, bits [7:4] of the EAX
6. The Stepping ID in bits [3:0] indicates the revision number of that model. See Table 1 for the processor
Extended
Family
00000000b 0010b 00b 0110 1010b xxxxb
to indicate whether the processor belongs to the Intel386, Intel486, Pentium, Pentium Pro, Pentium 4,
®
or Intel
used to identify the model of the processor within the processor’s family.
processor, an OverDrive processor, or a dual processor (capable of being used in a dual processor
system).
register after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 1 in the EAX register, and the generation field of
the Device ID register accessible through Boundary Scan.
register after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 1 in the EAX register, and the model field of the
Device ID register accessible through Boundary Scan.
stepping ID number in the CPUID information.
Core™ processor family.
Processor
3
Type
Family
Code
4
Model
Number
Stepping
5
ID
6
When EAX is initialized to a value of ‘1’, the CPUID instruction returns the Extended
Family, Extended Model, Processor Type, Family C ode, Mode l Number and Step ping ID
value in the EAX register. Note that the EDX processor signature value after reset is
equivalent to the processor signature output value in the EAX register.
Cache and TLB descriptor parameters are provided in the EAX, EBX, ECX and EDX
registers after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 2 in the EAX register.
The processor can be identified by the following register contents:
Stepping Vendor ID1Host Device ID
D-2 8086h 0100h
Q-0 8086h 0100h
Notes:
1. The Vendor ID corresponds to bits 15:0 of the Vendor ID Register located at offset 00–01h in the PCI
2. The Host Device ID corresponds to bits 15:0 of the Device ID Register located at Devic e 0 offset 02–03h
3. The Processor Graphics Device ID (DID2) corresponds to bits 15:0 of the Device ID Register located at
4. The Revision Number corresponds to bits 7:0 of the Re vision ID Register located at offset 08h in the PCI
12 Specification Update
function 0 configuration space.
in the PCI function 0 configuration space.
Device 2 offset 02–03h in the PCI function 0 configuration space.
function 0 configuration space.
2
Processor Graphics
Device ID
GT1: 0102h
GT2: 0112h
GT2 (>1.3 GHz Turbo): 122h
GT1: 0102h
GT2: 0112h
GT2 (>1.3 GHz Turbo): 122h
3
Revision ID
09h
09h
4
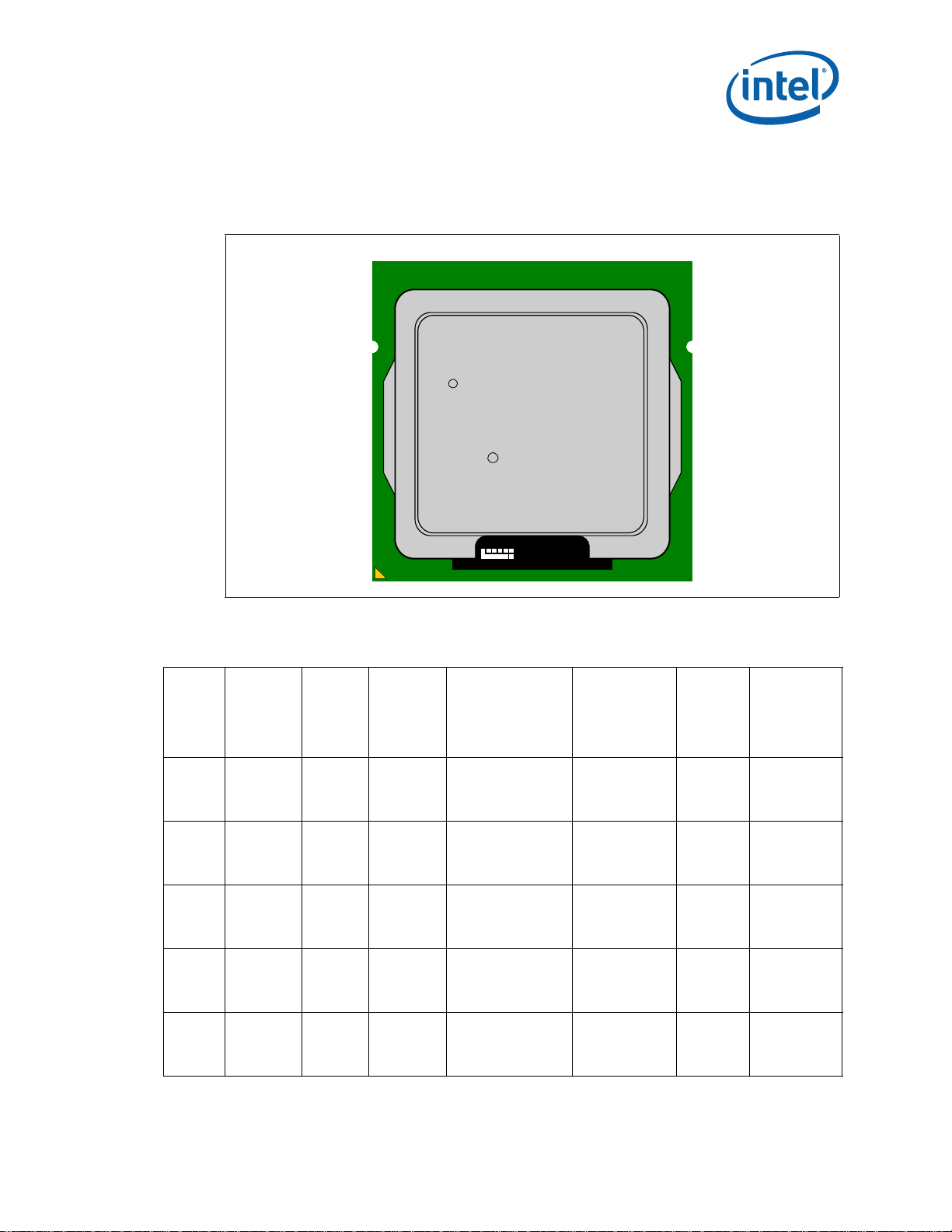
Component Marking Information
LOT NO S/N
i ©'10
BRAND PROC#
SLxxx SPEED
[COO]
[FPO]
M
e4
The processor stepping can be identified by the following component markings.
Figure 1. Processor Production Top-side Markings (Example)
Table 1. Processor Identification (Sheet 1 of 2)
Core Frequency
S-
SpecNu
mber
SR008 i5-2500K D-2 000206a7h 3.3 / 1333 / 850
SR00T i5-2500 D-2 000206a7h 3.3 / 1333 / 850
SR00Q i5-2400 D-2 000206a7h 3.1 / 1333 / 850
SR009 i5-2500S D-2 000206a7h 2.7 / 1333 / 850
SR00S i5-2400S D-2 000206a7h 2.5 / 1333 / 850
Processor
Number
Stepping
Processor
Signature
(GHz) /
DDR3 (MHz) /
Processor
Graphics
Frequency
(GHz)
®
1
Max Intel
Turbo Boost
Technology
2.0 Frequency
4 core: 3.4
3 core: 3.5
2 core: 3.6
1 core: 3.7
4 core: 3.4
3 core: 3.5
2 core: 3.6
1 core: 3.7
4 core: 3.2
3 core: 3.3
2 core: 3.3
1 core: 3.4
4 core: 2.8
3 core: 3.2
2 core: 3.6
1 core: 3.7
4 core: 2.6
3 core: 2.8
2 core: 3.2
1 core: 3.3
Shared
L3 Cache
Size (MB)
64, 6
6 3, 4, 5, 6
6 3, 4, 5, 6
6 3, 4, 5, 6
6 3, 4, 5, 6
Notes
Specification Update 13
 Loading...
Loading...