Page 1
User Guide
p
s
XB1 COM Express™ Module
Document No. 4162 • Edition 5
2007-05
COM
Ex
res
Page 2

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Contents
About this Manual ........................................................... 4
Edition History......................................................... 4
Related Documents ..................................................... 5
Nomenclature ......................................................... 5
Trade Marks .......................................................... 5
Legal Disclaimer - Liability Exclusion ......................................... 5
XB1 COM Express Module Features .............................................. 6
Feature Summary ...................................................... 6
Short Description XB1 COM Express Module .................................. 8
Block Diagram XB1 COM Express Module ................................... 10
Assembly Drawing XB1 COM Express Module ................................ 11
Strapping Headers ..................................................... 12
Connectors & Sockets .................................................. 12
Indicators ........................................................... 12
Microprocessor ....................................................... 13
Thermal Considerations ................................................. 14
Main Memory ........................................................ 15
LAN Subsystem ....................................................... 15
Serial ATA Interface (SATA) .............................................. 16
Enhanced IDE Interface (PATA) ........................................... 16
Graphics Subsystem ................................................... 17
Real-Time Clock ....................................................... 18
Universal Serial Bus (USB) ............................................... 18
LPC Super-I/O Interface ................................................. 18
Firmware Hub (Flash BIOS) .............................................. 18
Watchdog/Reset ...................................................... 19
PG (Power Good) LED .................................................. 19
GP (General Purpose) LED ............................................... 19
Installing and Replacing Components ............................................ 20
Before You Begin...................................................... 20
Installing the Board .................................................... 21
Removing the Board ................................................... 22
EMC Recommendations................................................. 23
Installing or Replacing the Memory Modules ................................. 24
Replacement of the Battery .............................................. 24
Technical Reference ......................................................... 25
Local PCI Devices ...................................................... 25
Local SMB Devices ..................................................... 26
Hardware Monitor LM87 ................................................ 26
GPIO Usage .......................................................... 27
GPIO Usage ICH6 ................................................ 27
GPIO Usage FWH ................................................ 28
GPIO Usage SIO ................................................. 29
Configuration Jumpers ................................................. 30
Reset Jumper BIOS CMOS RAM Values (J-GP) ........................... 30
Reset Jumper ICH6 RTC Core (J-RTC) .................................. 30
©EKF -2- ekf.com
Page 3

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Connectors .......................................................... 31
PLD Programming Header ISPCON ................................... 31
J-COM ........................................................ 32
Processor Debug Header PITP ....................................... 36
P-SIO ......................................................... 37
Board Dimensions ..................................................... 38
Top View, Bottom View................................................. 39
Literature ........................................................... 40
©EKF -3- ekf.com
Page 4
User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
About this Manual
This manual describes the technical aspects of the XB1 COM Express Module, required for installation
and system integration. It is intended for the experienced user only.
Edition History
Ed.
Contents/Changes
1 User Manual XB1 COM Express Module, English, initial edition (Text #4162,
File: xb1_uge.wpd)
2 Table J-COM modified (PCIe Lane #3) jj 1 August 2006
3 Illustration 'Assembly Drawing' jj 31 August
4 Added XB1 photographs jj 16 November
5 Added XB1-060 jj 2 May 2007
Author Date
jj 27 April 2006
2006
2006
©EKF -4- ekf.com
Page 5

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Related Documents
For ordering information refer to document XB1 COM Express Module Product Information, available
at http://www.ekf.com/x/xb1/xb1_pie.pdf.
Nomenclature
Signal names used herein with an attached '#' designate active low lines.
Trade Marks
Some terms used herein are property of their respective owners, e.g.
< Intel, Pentium, Celeron, SpeedStep: ® Intel
< PCI Express: ® PCI-SIG
< COM Express:™ PICMG
< CompactPCI, CompactPCI Express, PICMG: ® PICMG
< Windows (2000, XP, Vista etc): ® Microsoft
< EKF, ekf system: ® EKF
EKF does not claim this list to be complete.
Legal Disclaimer - Liability Exclusion
This manual has been edited as carefully as possible. We apologize for any potential mistake.
Information provided herein is designated exclusively to the proficient user (system integrator,
engineer). EKF can accept no responsibility for any damage caused by the use of this manual.
©EKF -5- ekf.com
Page 6

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
XB1 COM Express Module Features
Feature Summary
Feature Summary XB1
Form Factor PICMG COM Express R1.0 (COM.0), Basic Module form factor (125x95mm2),
Pin-out Type 2
Processor Designed for Intel® Pentium® M Micro FC-BGA 479 processors (90nm
Dothan), maximum junction temperature 100°C
< XB1-060: 600MHz ULV Celeron® M (Banias 130nm), 400MHz FSB, 512KB
L2 cache, 7W
< XB1-100: 1.0GHz ULV Celeron® M (Dothan 373), 400MHz FSB,
512KB L2 cache, 5W
< XB1-140: 1.4GHz LV Pentium® M (Dothan 738), 400MHz FSB, 2MB
L2 cache, 10W
< XB1-200: 2.0GHz Pentium® M (Dothan 760), 533MHz FSB, 2MB L2
cache, 27W
Chipset Intel® i915 embedded systems chipset (Alviso) consisting of:
< 82915GM Graphics/Memory Controller Hub (GMCH) with Intel®
Graphics Media Accelerator (GMA) 900
< 82801FB I/O Controller Hub (ICH6)
< 82802 Compatible Firmware Hub (FWH)
Memory Dual 200-pin SO-DIMM socket, DDR2 533 SDRAM, 2 x 1GB maximum,
symmetric dual channel capable
Video Up to 2048x1536 pixel 16M colours @75Hz refresh rate (analog), up to
1600 x 1200 pixel 16M colours @60Hz (digital), dual screen support
< Dual SDVO
< Analog VGA
< Dual LVDS
< TV Out
< PEG PCI Express x 16 external graphics interface, multiplexed with
SDVO
USB 8 x USB2.0
Ethernet PCIe to Gigabit Ethernet controller 10/100/1000Mbps
PATA (IDE) ICH6 integrated Ultra ATA/100 I/F
SATA 4 x SATA-150
GPIO 8 GPIO lines
Sound System AC '97 or HD Audio Azalia (external Codec)
PCI ICH6 integrated 32-bit PCI bridge, 133MBps CPCI master
PCI Express 3-Lane PCIe if PCIe Gigabit Ethernet controller is stuffed
4-Lane PCIe (x 4 Link) w/o PCIe Gigabit Ethernet controller (stuffing option)
BIOS Phoenix BIOS
©EKF -6- ekf.com
Page 7
User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Feature Summary XB1
Drivers < Intel graphics drivers
< Intel networking drivers
Power
Requirements
Environmental
Conditions
MTBF tbd
EC Regulations • EN55022, EN55024, EN60950-1 (UL60950-1/IEC60950-1)
Performance
Rating
Measured with
PCMark2005
+12V ±0.5V, tbd A max. @2.0GHz (tbd A WinXP idle mode)
< Operating temperature: 0°C ... +70°C (CPU dependent)
< Storage temperature: -40°C ... +85°C, max. gradient 5°C/min
< Humidity 5% ... 95% RH non condensing
< Altitude -300m ... +3000m
< Shock 15g 0.33ms, 6g 6ms
< Vibration 1g 5-2000Hz
• 2002/95/EC (RoHS)
Board Processor CPU/MEM
XB1-060
XB1-100
XB1-140
600MHz ULV Celeron® M (Banias) tbd
1.0GHz ULV Celeron® M (Dothan 373) tbd
1.4GHz LV Pentium® M (Dothan 738) tbd
Score
XB1-201
2.0GHz Pentium® M (Dothan 760) tbd
Subject to technical changes
XB1 COM Express Module with Heatspreader
©EKF -7- ekf.com
Page 8
User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Short Description XB1 COM Express Module
COM Express™ (also known as ETXexpress™) is
an open PICMG® standard for Computer-OnModules, comprising of latest technologies such
as PCI Express, Serial ATA, Gigabit Ethernet and
SDVO. While designing the carrier board only
once, users profit from upgrading or scaling
their application by simply changing the CPU
module.
Alternatively equipped with the Intel series of
(LV) Pentium® M and ULV Celeron® M
processors and up to 2GB RAM, the EKF
XB1 is
a versatile COM Express basic form factor
module, designed especially for systems which
require high performance at low power
consumption.
technology and has integrated a powerful dual
screen graphics accelerator. The SDVO and VGA
video interfaces allow for attachment of digital flat
panel displays and analog monitors.
The chipset is based on PCI Express
The XB1 is provided with a Gigabit Ethernet
controller, and eight USB 2.0 ports for high speed
communication. Four Serial ATA channels are
available in addition to the legacy PATA I/F. The dual
slot DIMM socket is suitable to address up to 2GB
interleaved (symmetric) dual channel memory.
Typically, the XB1 will be combined with a custom
specific carrier board. As a basic development tool,
EKF can supply a third party evaluation carrier board.
In addition, EKF offers their design services to create
a turn-key ready customer solution.
The XB1 COM Express module is the perfect choice
for embedded applications that require a low power
standard processor at the centre of their design.
OEMs can significantly improve their flexibility and
reduce their total cost by adopting the open
standards based architecture of COM Express.
XB1 COM Express Module
©EKF -8- ekf.com
Page 9

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Benefits of the XB1 COM Express Module
< PICMG COM.0 Compliant Module Type 2
< Pentium® M 2GHz (FSB 533MHz)
< PCI Express Chipset for Embedded Applications
< 2 x 1GB DDR2 Memory (Dual Channel Mode Capable)
< Dual-Screen Graphics Controller
< Video I/F SDVO, PEG, LVDS, VGA, TV
< Gigabit Ethernet Controller
< 4 x SATA I/F
< 8 x USB 2.0 Channels
< RoHS Compliant
XB1 from Bottom
©EKF -9- ekf.com
Page 10
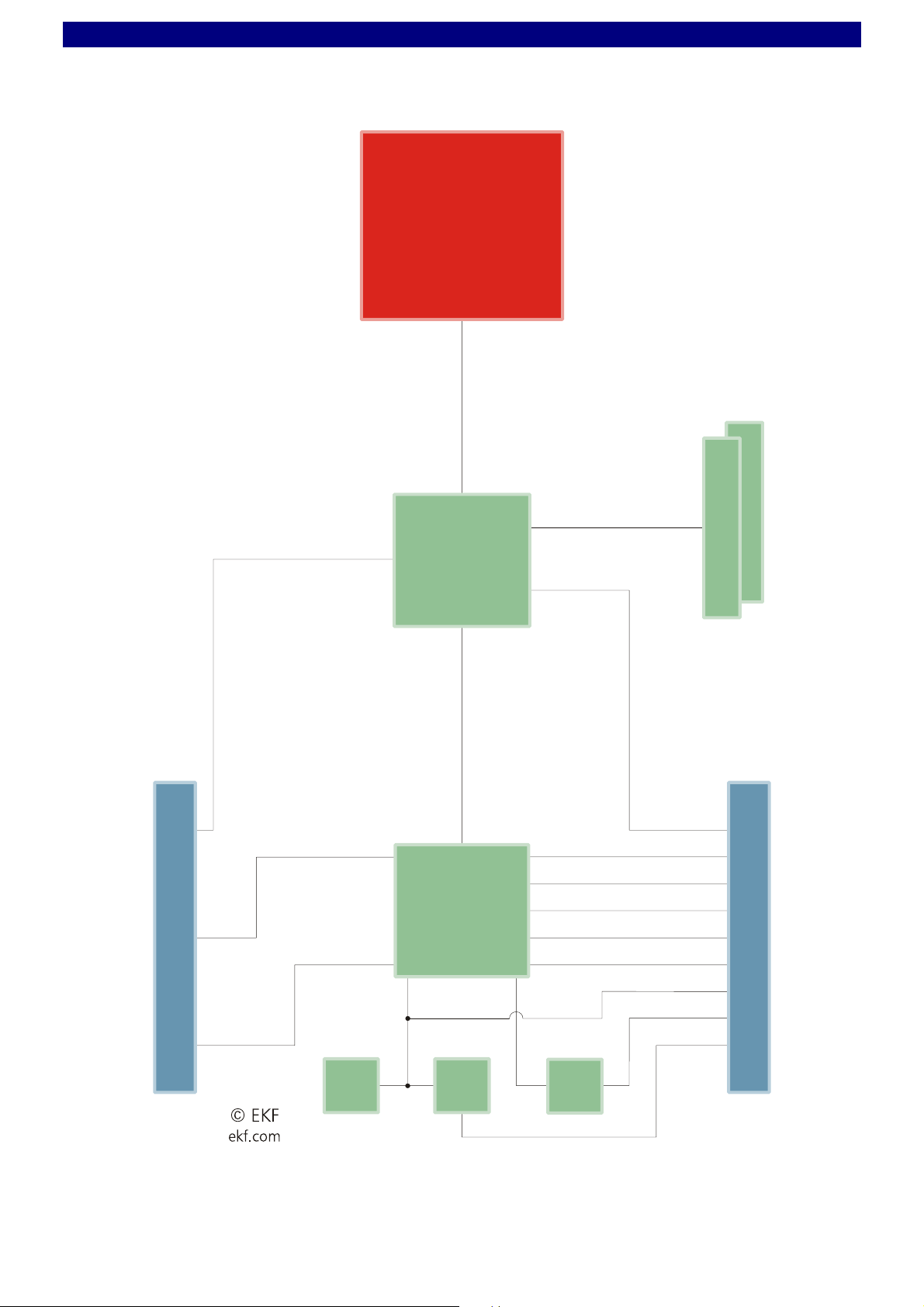
User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Block Diagram XB1 COM Express Module
Simplified
Block Diagram
X
B1
COM Express
Module
SDVO
PEG
Pentium® M
760
2.0GHz
FSB 533MHz
GMCH
82915
GM
VGA
LVDS/TV
Alternative CPU:
• Pentium® M 745 1.8GHz
• LV Pentium® M 738 1.4GHz
• Celeron® M 370 1.5GHz
• ULV Celeron® M 373 1.0GHz
DDR2 533
512MB-2GB
Dual
Channel
SO-DIMM 200
SO-DIMM 200
C-D
SDVO
PEG
IDE
PCI
BIOS
82
802
DMI x 4
ICH6
82801
SIO
87
61
VGA
8 x USB
4 x SATA
3 x PCIe
AC '97
SMB
PCIeLPC
G-ETH
LPC
GBE
GPIO
A-B
82
573
©EKF -10- ekf.com
Page 11
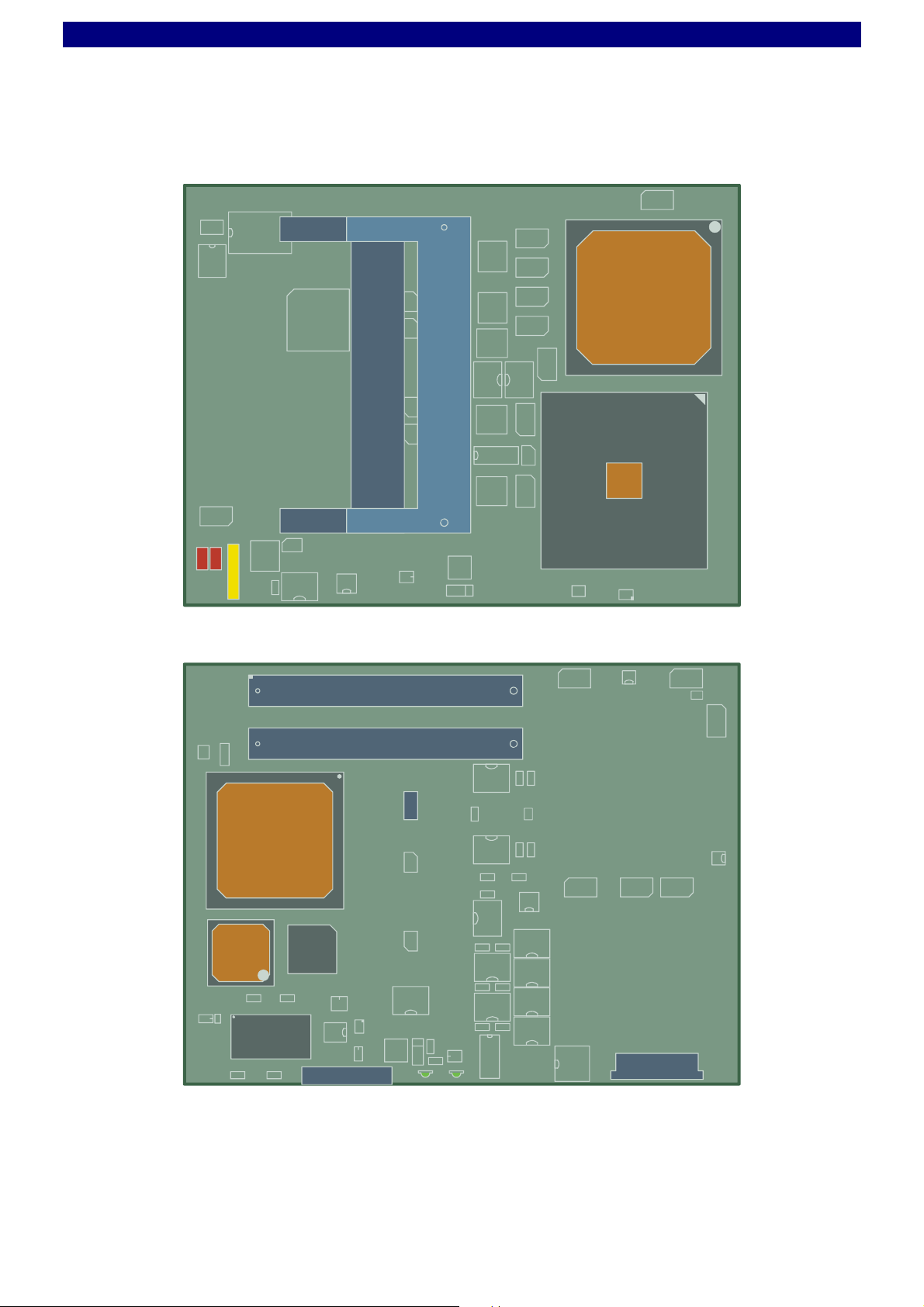
User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Assembly Drawing XB1 COM Express Module
DDR2 SODIMM
isp
DDR2 SODIMM
CPU
GAL
X
B1
Top
© EKF
ekf.com
BAT
+
J-GP
J-RTC
© EKF • B1 COM Express Module • ekf.com
A1
B1
COM Express Module Connector
C1
D1
X
J-COM A-B
J-COM C-D
1
P-SIO
GMCH
X
B1
Bottom
© EKF
ekf.com
ICH
NIC
SIO
FWH
1
1
ISPCON
©EKF -11- ekf.com
GP
LED
PG
P-ITP
Page 12

Strapping Headers
J-GP Jumper to reset BIOS CMOS RAM values
J-RTC Jumper to reset RTC core of ICH6, not stuffed
Connectors & Sockets
ISPCON PLD programming connector, not stuffed
J-COM A-B COM Express connector rows A and B (VGA, LVDS, TV, PCIe, SATA,
J-COM C-D COM Express connector rows C and D (Dual SDVO / PEG, IDE, PCI)
P-ITP CPU debug port
User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Ethernet, USB, AC'97, SMB, LPC)
P-SIO I/O connector for debugging (not stuffed), comprises PS/2
SODIMM1
SODIMM2
Indicators
GP General Purpose LED
PG LED indicating Power Good / Board Healthy
mouse/keyboard signals, UART (TTL)
200-pin DDR2 SDRAM PC2-3200/4200 (DDR400/533) 1.8V memory
module sockets
©EKF -12- ekf.com
Page 13

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Microprocessor
The XB1 COM Express Module is designed for use with Pentium® M and Celeron® M processors
manufactured in 90nm technology (Dothan). These include also the Ultra Low-Voltage (ULV)
Celeron® M and the Low-Voltage (LV) Pentium® M processors as listed below. The processors are
housed in a Micro FC-BGA package for direct soldering to the PCB, i.e. the CPU chip cannot be
removed or changed by the user.
The processors supported by the XB1 COM Express Module are running at FSB clock speeds of
400MHz and 533MHz. The internal Pentium M processor speed is achieved by multiplying the host
bus frequency by a variable value. The multiplier is chosen by currently required performance and the
actual core temperature. This technology is called Enhanced Intel SpeedStep®.
Power is applied across the COM Express connectors J-COM (+12V). The processor core voltage is
generated by a switched voltage regulator. The processor signals its required core voltage by 6
dedicated pins according to Intels IMVP-IV voltage regulator specification.
90nm (Dothan) Processors Supported
Processor Speed
min/max
[GHz]
2)
2)
1) 2)
1.0/1.0 400 0.5 5 0-100 06D8h C-0 SL8LW
2)
0.6/1.4 400 2 10 0-100 06D6h
0.6/1.8 400 2 21 0-100 06D6h
0.8/2.0 533 2 27 0-100 06D8h C-0 SL869
ULV Celeron M 373
LV Pentium M 738
Pentium M 745
Pentium M 760
1)
This processor does not support SpeedStep® technology, instead it runs at a fixed core speed
2)
Following the Intel Embedded Roadmap, this processor is recommended for long time availability
Host Bus
[MHz]
L2 Cache
[MB]
TDP
[W]
Die Temp
[°C]
CPU ID Stepping sSpec
06D8h
06D8h
B-1
C-0
B-0
C-0
SL7P9
SL89N
SL7Q6
SL8U8
©EKF -13- ekf.com
Page 14

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Thermal Considerations
In order to avoid malfunctioning of the XB1 COM Express Module, take care of appropriate cooling
of the processor and system, e.g. by a cooling fan suitable to the maximum power consumption of
the CPU chip actually in use. Please note, that the processors temperature is steadily measured by a
special controller (LM87), attached to the onboard SMBus® (System Management Bus). A second
temperature sensor internal to the LM87 allows for acquisition of the boards surface temperature.
Beside this the LM87 also monitors most of the supply voltages. A suitable software to display both,
the temperatures as well as the supply voltages, is MBM (Motherboard Monitor), which can be
downloaded from the web. After installation, both temperatures and voltages can be observed
permanently from the Windows taskbar.
The XB1 COM Express Module is equipped with a passive heatsink (heat-spreader). In addition, a
forced airflow through the system enclosure by a suitable fan unit is highly recommended (>15m3/h
or 200LFM around the CPU module). As an exception, the XB1-100 (ULV Celeron M 1GHz) can be
operated with natural convection only. Be sure to thoroughly discuss your actual cooling needs with
EKF. Generally, the faster the CPU speed the higher its power consumption. For higher ambient
temperatures, consider increasing the forced airflow to 400 or 600LFM.
The table showing the supported processors above give also the maximum power consumption (TDP
= Thermal Design Power) of a particular processor. Fortunately, the power consumption is by far
lower when executing typical Windows or Linux tasks. The heat dissipation may increase considerably
when e.g. rendering software such as the Acrobat Distiller is executed.
The Pentium M processors support Intel's Enhanced SpeedStep® technology. This enables dynamic
switching between multiple core voltages and frequencies depending on core temperature and
currently required performance. The processors are able to reduce their core speed and core voltage
in up to 8 steps down to 600MHz. This leads to an obvious reduction of power consumption (max.
7.5W @600MHz) resulting in less heating. This mode of lowering the processor core temperature is
called TM2 (TM=Thermal Monitor). Note, that TM2 is not supported by Celeron M processors.
Another way to reduce power consumption is to modulate the processor clock. This mode (TM1) is
supported also by the Celeron M processors and is achieved by actuating the 'Stop Clock' input of the
CPU. A throttling of 50% e.g. means a duty cycle of 50% on the stop clock input. However, while
saving considerable power consumption, the data throughput of the processor is also reduced. The
processor works at full speed until the core temperature reaches a critical value. Then the processor
is throttled by 50%. As soon as the high temperature situation disappears the throttling will be
disabled and the processors runs at full speed again.
A similar feature is embedded within the Graphics and Memory Controller (GMCH) i915GM. An ondie temperature sensor is used to protect the GMCH from exceeding its maximum junction
temperature (T
=105°C) by reducing the memory bandwidth.
J,max
These features are controllable by BIOS menu entries. By default the BIOS of the XB1 COM Express
Module enables mode TM2 which is the most efficient.
©EKF -14- ekf.com
Page 15

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Main Memory
The XB1 COM Express Module is equipped with two sockets for installing 200-pin SO-DIMM modules
(module height = 1.25 inch). Supported are unbuffered DDR2 SO-DIMMs (VCC=1.8V) without ECC
featuring on-die termination (ODT), according the PC2-3200 or PC2-4200 specification. Minimum
memory size is 128MB; maximum memory size is 2GB. Due to the video requirements of the i915GM
chipset (some of the system memory is dedicated to the graphics controller), a minimum of 2x256MB
memory is recommended for the operating systems Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000 or Windows XP.
The contents of the SPD EEPROM on the SO-DIMMs are read during POST (Power-on Self Test) to
program the memory controller within the chipset.
The i915GM chipset supports symmetric and asymmetric memory organization. The maximum
memory performance can be obtained by using the symmetric mode. To achieve this mode, two
SO-DIMMs of equal capacity must be installed in the memory sockets. In asymmetric mode different
memory modules may be used with the drawback of less bandwidth. A special case of asymmetric
mode is to populate only one memory module (i.e. one socket may be left empty).
LAN Subsystem
The Ethernet LAN subsystem is comprised of the Intel 82573 Gigabit Ethernet controller, which
provides also legacy 10Base-T and 100Base-TX connectivity.
< Single PCI Express lane linkage
< 1000Base-Tx (Gigabit Ethernet), 100Base-TX (Fast Ethernet) and 10Base-T (Classic Ethernet)
capability
< Half- or full-duplex operation
< IEEE 802.3u Auto-Negotiation for the fastest available connection
< Jumperless configuration (completely software-configurable)
The NIC (Networking Interface Controller) is connected by a single PCI Express lane to the chipset
southbridge (ICH6). Its MAC address (unique hardware number) is stored in a dedicated EEPROM. The
Intel Ethernet software and drivers for the 82573 is available from Intel's World Wide Web site for
download (link provided on the EKF website).
By specification, the XB1 COM Express Module does not provide any I/O connector. Instead, the
carrier board must provide the RJ45 receptacle with integrated magnetics for copper twisted pair
Ethernet. All MDI (Media Dependent Interface) signals of the Ethernet PHY are routed to the
connector J-COM A-B.
The 82573 controller is connected to the PCI Express lane #3. As an alternate stuffing option, this
lane is available across the J-COM connector instead, for carrier board applications which require 4
PCIe lanes (typically configured as PCIe x 4 link). If this stuffing option had been ordered, no Ethernet
connectivity is provided on the XB1 itself, but may be replicated on the carrier board.
©EKF -15- ekf.com
Page 16

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Serial ATA Interface (SATA)
The XB1 COM Express Module provides four serial ATA (SATA) ports, each capable of transferring
150MB/s. Integrated within the ICH6, the SATA controller features different modes to support also
legacy operating systems. The SATA channels are available to the carrier board across the J-COM A-B
connector.
Available for download from Intel are drivers for popular operating systems, e.g. Windows® 2000,
Windows® XP and Linux.
Enhanced IDE Interface (PATA)
The parallel ATA (PATA, also known as IDE) interface is provided for attachment of legacy peripheral
devices such as hard disks, ATA CompactFlash cards and CD-ROM drives. The interface supports:
C Up to two ATA devices
C PIO Mode 3/4, Ultra ATA/33, Ultra ATA/66, Ultra ATA/100
The PATA port is available to the carrier board across the J-COM C-D connector. The IDE controller is
integrated into the ICH6. Ultra ATA IDE drivers can be downloaded from the Intel website.
©EKF -16- ekf.com
Page 17

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Graphics Subsystem
The graphics subsystem is part of the versatile Intel i915GM Graphics/Memory Controller Hub
(GMCH), and is also known as Intel Graphics Media Accelerator (GMA) 900. As an alternative, PCI
Express based graphics is supported (requires discrete PEG controller present on the carrier board).
The main features of the GMA900 are:
< Dual Serial Digital Video Output (SDVO) - allows for two independent DVI connectors
< RGB output - suitable for a VGA style connector
< TV out (HDTV resolution)
< LVDS wide panel support
For legacy CRT style monitors, the XB1 COM Express Module is provided with RGB signals on the
J-COM A-B connector, suitable for a VGA D-Sub accommodated on the carrier board. Also the TV out
and the LCD panel signals (LVDS port) are routed to the J-COM A-B connector.
The GMCH multiplexes a PCI Express Graphics interface with two Intel SDVO ports. The SDVO ports
can each support a single-channel SDVO device. If both ports are active in single-channel mode, they
can have different display timing and data. Alternatively the SDVO ports can be combined to support
dual channel devices, enabling higher resolutions and refresh rates. On the XB1 COM Express Module,
the SDVO/PEG signals are routed to the connector J-COM C-D. Typically, one or two discrete display
transmitter chips located on the carrier board are used to convert Intels proprietary, PCI express based
SDVO interfaces to the differential DVI signals required for attachment of modern flat panel monitors.
E.g., the SiI1362 (Silicon Image) transmitter uses PanelLink® Digital technology to support displays
ranging from VGA to UXGA resolutions (25 - 165Mpps) in a single link interface. With two DVI
connectors on the carrier board, independent dual screen operation is available (this also applies for
one DVI and one D-Sub connector).
The GMCH supports several video resolutions and refresh rates. A partial list is contained in the table
below. Please note, that flat-panel displays should be operated with their native (maximum) resolution
at 60Hz refresh rate (some models also accept 75Hz). 16-bit high colour mode is recommended.
Partial List of i915GM GMCH Video Modes (analog / digital)
Resolution 60Hz 70Hz 72Hz 75Hz 85Hz
640x480 T / TT / TT / TT / TT / T
800x600 T / TT / TT / TT / TT / T
1024x768 T / T
1280x1024 T / T
1600x1200 T / T1)
1)
1)
2)
T / TT / TT / TT / T
T / TT / TT / TT / T
T / - T / - T / - T / -
2048x1536 T / - T / - T / - T / - - / -
1)
This video mode is suitable for popular flat-panel displays
2)
In dual screen mode 2 x 1600x1200, 32-bit true colours are not available for both outputs simultaneously
Graphics drivers for the i915GM can be downloaded from the Intel website.
©EKF -17- ekf.com
Page 18

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Real-Time Clock
The XB1 COM Express Module has a time-of-day clock and 100-year calendar, integrated into the
ICH6.
A battery on the board keeps the clock current when the computer is turned off. The XB1 uses a
Vanadium-Pentoxide-Lithium rechargeable battery, giving an autonomy of more than 50 days when
fully loaded after 24 hours. The cell is free of memory effects and withstands deep discharging. Under
normal conditions, replacement should be superfluous during lifetime of the board. Custom specific
versions of the XB1 may not provide the accumulator.
In addition, VCC_RTC is also redundantly derived from the carrier board (if supported). The time
keeping autonomy period is then defined by the battery capacity accommodated on the carrier.
Universal Serial Bus (USB)
The XB1 COM Express Module is provided with eight USB ports, all of them are USB 2.0 capable. Four
active-low over-current sensing inputs are available in addition, suitable for attachment of electronic
switches such as the LM3526-L on the carrier board. The USB controllers are integrated into the ICH6.
LPC Super-I/O Interface
In a modern system, legacy ports as PS/2 keyboard/mouse, COM1/2 and LPT have been replaced by
USB and Ethernet connectivity. The 1.4MB floppy disk drive has been swapped against CD/DVD-RW
drives or USB memory sticks. Hence, the XB1 COM Express Module is virtually provided with all
necessary I/O functionality. However, for BIOS and OS software compatibility, the XB1 is additionally
equipped with a simple Super-I/O chip. The Super-I/O controller resides on the local LPC bus (LPC =
Low Pin Count interface standard), which is a serialized ISA bus replacement. For debug only, a
connector P-SIO may be stuffed on the XB1, with KB/MS signals derived from the SIO and also a
rudimentary serial I/F (TTL-level Tx/Rx RTS/CTS).
The SIO provides a rich set of GPIO lines. Four channels are used as GPI0..3, and another 4 channels
as GPO0..3, all routed to the connector J-COM A-B, for use on the carrier board.
Firmware Hub (Flash BIOS)
The BIOS is stored in an 8Mbit Firmware Hub attached to the LPC bus. The firmware hub contains a
nonvolatile memory core based on flash technology, allowing the BIOS to be upgraded. The XB1
firmware hub may be deselected by the carrier board from use as primary BIOS source, by activating
the signal BIOS_DISABLE# on J-COM A-B. This allows a potential secondary firmware hub residing on
the carrier board to be used as alternative BIOS source.
The FWH can be reprogrammed (if suitable) by a DOS based tool. This program and the latest XB1
COM Express Module BIOS are available from the EKF website. Read carefully the enclosed
instructions. If the programming procedure fails e.g. caused by a power interruption, the XB1 COM
Express Module may no more be operable. In this case you would have to send in the board, because
the BIOS is directly soldered to the PCB and cannot be changed by the user.
©EKF -18- ekf.com
Page 19

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Watchdog/Reset
The XB1 COM Express Module is provided with two supervisor circuits to monitor the supply voltages
1.8V, 3.3V, 5V, and to generate a clean power-on reset signal. The healthy state of the XB1 COM
Express Module immideately after a reset is signalled by the LED PG (Power Good), indicating that all
power voltages are within their specifications and the reset signal has been deasserted.
An important reliability feature is the watchdog function, which is programmable by software. The
behaviour of the watchdog is defined within the PLD, which activates/deactivates the watchdog and
controls its time-out period. The time-out delay is adjustable in the steps 2, 10, 50 and 255 seconds.
After alerting the WD and programming the time-out value, the related software (e.g. application
program) must trigger the watchdog periodically. All watchdog related functions are made available
by calling service requests within the BIOS.
The watchdog is in a passive state after a system reset. There is no need to trigger it at boot time. The
watchdog is activated on the first trigger request. If the duration between two trigger requests
exceeds the programmed period, the watchdog times out and a system reset will be generated. The
watchdog remains in its active state until the next system reset. There is no way to disable it once it
had been put on alert, whwereas it is possible to reprogram its time-out value at any time.
PG (Power Good) LED
The XB1 COM Express Module offers a software programmable LED located. After system reset, this
LED defaults to signal the board healthy respectively power good. By the first setting of the GPO20 of
the ICH6 this LED changes its function and is then controlled only by the level of the GPO20 pin.
Setting this pin to 1 will switch on the LED. The PG LED remains in the programmable state until the
next system reset.
GP (General Purpose) LED
A second, programmable LED can be also observed from the front panel. The status of the GP LED is
controlled by the GPO18 output of the ICH6. Setting this pin to 1 will switch on the LED. As of
current, the GP LED is not dedicated to any particular hardware or firmware function (this may change
in the future).
©EKF -19- ekf.com
Page 20

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Installing and Replacing Components
Before You Begin
Warnings
The procedures in this chapter assume familiarity with the general terminology associated with
industrial electronics and with safety practices and regulatory compliance required for using and
modifying electronic equipment. Disconnect the system from its power source and from
any telecommunication links, networks or modems before performing any of the
procedures described in this chapter. Failure to disconnect power, or telecommunication
links before you open the system or perform any procedures can result in personal injury
or equipment damage. Some parts of the system can continue to operate even though
the power switch is in its off state.
Caution
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage components. Perform the procedures described in this
chapter only at an ESD workstation. If such a station is not available, you can provide
some ESD protection by wearing an antistatic wrist strap and attaching it to a
metal part of the system chassis or board front panel. Store the board only in its
original ESD protected packaging. Retain the original packaging (antistatic bag and
antistatic box) in case of returning the board to EKF for rapair.
©EKF -20- ekf.com
Page 21

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Installing the Board
Warning
This procedure should be done only by qualified technical personnel. Disconnect the system from its
power source before doing the procedures described here. Failure to disconnect power, or
telecommunication links before you open the system or perform any procedures can result in personal
injury or equipment damage.
Typically you will perform the following steps:
C Switch off the system, remove the AC power cord
C Attach your antistatic wrist strap to a metallic part of the system
C Remove the board packaging, be sure to touch the board only at the heat spreader
C Insert module carefully into the complementary J-COM connectors on the carrier board
C Fix mounting screws
C Retain original packaging in case of return
©EKF -21- ekf.com
Page 22

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Removing the Board
Warning
This procedure should be done only by qualified technical personnel. Disconnect the system from its
power source before doing the procedures described here. Failure to disconnect power, or
telecommunication links before you open the system or perform any procedures can result in personal
injury or equipment damage.
Typically you will perform the following steps:
C Switch off the system, remove the AC power cord
C Attach your antistatic wrist strap to a metallic part of the system
C Identify the board, be sure to touch the board only at the front panel
C Unfasten screws
C Remove the module carefully
C Store board in the original packaging, do not touch any components, hold the board at the
heat spreader only
Warning
Do not expose the card to fire. Battery cells and other components could explode
and cause personal injury.
©EKF -22- ekf.com
Page 23

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
EMC Recommendations
In order to comply with the CE regulations for EMC, it is mandatory to observe the following rules:
C The chassis or rack including other boards in use must comply entirely with CE
C Close all board slots not in use with a blind front panel
C Front panels must be fastened by built-in screws
C Cover any unused front panel mounted connector with a shielding cap
C External communications cable assemblies must be shielded (shield connected only at one end
of the cable)
C Use ferrite beads for cabling wherever appropriate
C External I/O connectors may require additional isolating parts
Reccomended Accessories
Blind CPCI Front
Panels
Ferrit Bead Filters ARP Datacom,
Metal Shielding
Caps
EKF Elektronik Widths currently available
(1HP=5.08mm):
with handle 4HP/8HP
without handle
2HP/4HP/8HP/10HP/12HP
Ordering No.
63115 Dietzenbach
102 820 (cable diameter 6.5mm)
102 821 (cable diameter 10.0mm)
102 822 (cable diameter 13.0mm)
Conec-Polytronic,
59557 Lippstadt
Ordering No.
CDFA 09 165 X 13129 X (DB9)
CDSFA 15 165 X 12979 X (DB15)
CDSFA 25 165 X 12989 X (DB25)
©EKF -23- ekf.com
Page 24

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Installing or Replacing the Memory Modules
Note: If you decide to replace the memory, observe the precautions in 'Before You Begin'
By default, the XB1 COM Express Module comes fully equipped and tested with two DDR2 SDRAM
memory modules. So normally there should be no need to install the memory modules.
The XB1 COM Express Module requires at least one PC2-3200/4200 (400/533MHz) DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM module. For optimum performance two SO-DIMMs of equal capacity are recommended.
Further it is highly recommended that Serial Presence Detect (SPD) SO-DIMMs be used, since this
allows the chipset to accurately configure the memory settings for optimum performance.
A replacement memory module must match the 200-pin SO-DIMM form factor (known from
Notebook PCs), DDR2, VCC=1.8V, PC2-3200/PC2-4200 (400/533MHz), on-die termination (ODT),
unbuffered, non-ECC style. Suitable modules are available up to 1GB each. The i915GM supports
modules of up to a maximum of 14 address lines (A0...A13). Memory modules organized by more
than14 address lines are not suitable.
Replacement of the Battery
When the XB1 is removed from the carrier board, an optional on-board battery maintains the voltage
to run the time-of-day clock and to keep the values in the CMOS RAM over ~30 days. The battery is
rechargeable und should last during the lifetime of the XB1 COM Express Module. For replacement,
the old battery must be desoldered, and the new one soldered. We suggest that you send back the
board to EKF for battery replacement.
Warning
Danger of explosion if the battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the same or
equivalent type. Do not expose a battery to fire.
©EKF -24- ekf.com
Page 25

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Technical Reference
Local PCI Devices
The following table shows the on-board PCI devices and their location within the PCI configuration
space. These devices reside mainly within the i915GM chipset.
Bus
Number
0 0 0 0x8086 0x2590 Host Bridge
0 2 0 0x8086 0x2592 Internal Graphics Device
0 2 1 0x8086 0x2792 Int. Graphics Config. Regs.
0 27 0 0x8086 0x2668 Intel High Definition Audio
0 28 0 0x8086 0x2660 PCI Express Port 1
0 28 1 0x8086 0x2662 PCI Express Port 2
0 28 2 0x8086 0x2664 PCI Express Port 3
0 28 3 0x8086 0x2666 PCI Express Port 4
0 29 0 0x8086 0x2658 USB UHCI Controller #1
0 29 1 0x8086 0x2659 USB UHCI Controller #2
0 29 2 0x8086 0x265A USB UHCI Controller #3
0 29 3 0x8086 0x265B USB UHCI Controller #4
0 29 7 0x8086 0x265C USB 2.0 EHCI Controller
Device
Number
Function
Number
Vendor ID Device ID Description
0 30 0 0x8086 0x244E PCI-to-PCI Bridge
0 30 2 0x8086 0x266E AC'97 Audio Controller
0 30 3 0x8086 0x266D AC'97 Modem Controller
0 31 0 0x8086 0x2640 LPC Bridge
0 31 1 0x8086 0x266F IDE Controller
0 31 2 0x8086 0x2651 SATA Controller
0 31 3 0x8086 0x266A SMB Controller
1)
3
1)
2)
This bus number can vary depending on the PCI enumeration schema implemented in BIOS.
The XB1 COM Express Module is available with a 82573L or 82573E/V Ethernet controller.
0 0 0x8086 0x108B
0x108C
2)
2)
Ethernet Controller NC1
©EKF -25- ekf.com
Page 26

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Local SMB Devices
The XB1 COM Express Module contains a few devices that are attached to the System Management
Bus (SMBus). These are the clock generation chip, the SPD EEPROMs on the SO-DIMM memory
modules, a general purpose serial EEPROM and a supply voltage and CPU temperature controlling
device in particular. Other devices could be connected to the SMB on the carrier board across J-COM
A-B.
Address Description
0x58 Hardware Monitor/CPU Temperature Sensor (LM87)
0xA0 SPD of SODIMM1
0xA2 SPD of SODIMM2
0xAE General Purpose EEPROM
0xD2 Main Clock Generation (CK-410M)
Hardware Monitor LM87
The XB1 COM Express Module is provided with a LM87 hardware monitor attached to the SMB. This
device is capable to observe board and CPU temperatures as well as several supply voltages generated
on the board with a resolution of 8 bit. The following table shows the mapping of the voltage inputs
of the LM87 to the corresponding supply voltages of the XB1 COM Express Module:
Input Source Resolution
Register
[mV]
AIN1 CPU Core Voltage 9.8 0x28
AIN2 +1.05V 9.8 0x29
VCCP1 +1.5V 14.1 0x21
VCCP2/D2- +1.8V 14.1 0x25
+2.5V/D2+ +2.5V 13 0x20
+3.3V +3.3V 17.2 0x22
+5V +5V 26 0x23
+12V +12V 62.5 0x24
Besides the continuous measuring of temperatures and voltages the LM87 may compare these values
against programmable upper and lower boundaries. As soon as a measurement violates the allowed
value range, the LM87 may request an interrupt via the GPI[7] of the ICH6.
©EKF -26- ekf.com
Page 27

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
GPIO Usage
GPIO Usage ICH6
XB1 COM Express Module GPIO Usage ICH6
GPIO Type Tol. Function Description
GPI 0 I 5V EXCD1_CPPE# PCI ExpressCard PCI Express capable card 1 request
GPI 1 I 5V EXCD0_CPPE# PCI ExpressCard PCI Express capable card 0 request
GPI 2 I 5V PG_VR33 Power Good signal from 3.3V voltage regulator
GPI 3 I 5V WAKE1# General purpose wake up signal from carrier board
GPI 4 I 5V PWR_OK Power OK from main power supply
GPI 5 I 5V BATLOW# Indicates that external battery is low
GPI 6 I 3.3V GP_JUMP# BIOS CMOS Values Reset Jumper JGP
GPI 7 I 3.3V HM_INT# Hardware Monitor LM87 Interrupt Line
2
GPI 8 I 3.3V I2C_DAT I
C emulated data signal (input only, see also GPIO 28)
GPI 9 I 3.3V USB_OC45# USB Ports 4 & 5 Overcurrent Detect Line (GPI9/10 joined)
GPI 10 I 3.3V USB_OC45# USB Ports 4 & 5 Overcurrent Detect Line (GPI9/10 joined)
GPI 11 I 3.3V SMB_ALERT# System Management Bus Alert
GPI 12 I 3.3V PEG_ENABLE# If pulled low externally, enables the PCI Express x 16 external
graphics interface and disables internal graphics (internally
pulled up 10k/3.3V)
2
GPI 13 I 3.3V I2C_CK I
C emulated clock signal (input only, see also GPIO 27)
GPI 14 I 3.3V USB_OC67# USB Ports 6 & 7 Overcurrent Detect Line (GPI14/15 joined)
GPI 15 I 3.3V USB_OC67# USB Ports 6 & 7 Overcurrent Detect Line (GPI14/15 joined)
GPO 16 O 3.3V EXCD1_RST# PCI ExpressCard reset card 1
GPO 17 O 3.3V EXCD0_RST# PCI ExpressCard reset card 0
GPO 18 O 3.3V ICH_GPO18 Control output to PLD
GPO 19 O 3.3V ICH_GPO19 Control output to PLD
GPO 20 O 3.3V ICH_GPO20 Control output to PLD
GPO 21 O 3.3V ICH_GPO21 Control output to PLD
GPO 23 O 3.3V not used - open
GPIO 24 I/O 3.3V ICH_GPIO24 for future use as PLD control signal (either input or output)
GPIO 25 O 3.3V not used - open (configured as output by BIOS)
GPI 26 I 3.3V CLK_64HZ 64Hz clock from 4040 binary counter
2
GPIO 27 O 3.3V I2C_CK I
GPIO 28 O 3.3V I2C_DAT I
C emulated clock signal (output only, see also GPI 13)
2
C emulated data signal (output only, see also GPI 8)
GPI 29 I 3.3V BOARD_CFG1 Board configuration options line 1
©EKF -27- ekf.com
Page 28

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
XB1 COM Express Module GPIO Usage ICH6
GPIO Type Tol. Function Description
GPI 30 I 3.3V BOARD_CFG2 Board configuration options line 2
GPI 31 I 3.3V BOARD_CFG3 Board configuration options line 3
GPIO 32 O 3.3V not used - open (configured as output by BIOS)
GPIO 33 O 3.3V NC1_OFF# Enable Ethernet Controller NC1
GPIO 34 I/O 3.3V ICH_GPIO34 for future use as PLD control signal (either input or output)
GPI 40 I 5V PG_VR18 Power Good signal from 1.8V voltage regulator
GPI 41 I 3.3V LPC_DRQCOM# LPC Port DMA request from COM Express carrier board
GPO 48 O 3.3V not used - open
GPO 49 OD 1.05V CPU_PWRGD CPU Power Good signal
italic blue –> signal available on J-COM
GPIO Usage FWH
XB1 COM Express Module GPIO Usage FWH
GPIO Type Tol. Function Description
GPI 0 I 3.3V FWH_ID FWH Identity: Fixed to GND (indicates FWH #1)
GPI 1 I 3.3V IDE_CLBID# IDE 80-pos. Cable Detection Line
GPI 2 I 3.3V WDOGRST Last Hardware Reset caused by watchdog
GPI 3 I 3.3V LSB PCB REV GPI 4 GPI 3 Rev.
0 0 0
0 1 1
GPI 4 I 3.3V MSB PCB REV
1 0 2
1 1 3+
©EKF -28- ekf.com
Page 29

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
GPIO Usage SIO
XB1 COM Express Module GPIO Usage SIO
GPIO Type Tol. Function Description
GPIO 10 I/O 5V/16mA
GPIO 11 I/O 5V/16mA
1)
1)
GPIO 12 O LPC_DRQSIO# LPC Port DMA request from SIO
GPIO 13 I/O 5V/8mA
GPIO 14 I/O 5V/8mA
GPIO 15 I/O 5V/8mA
GPIO 16 I/O 5V/24mA
GPIO 17 I/O 5V/24mA
GPIO 20 I 5V
GPIO 21 I 5V
GPIO 22 I 5V
GPIO 23 I 5V
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
MSDAT PS/2 mouse data or custom GPIO
MSCLK PS/2 mouse clock or custom GPIO
not used
not used
not used
not used
not used
GPI0 GPI signal from COM Express module carrier board
GPI1 GPI signal from COM Express module carrier board
GPI2 GPI signal from COM Express module carrier board
GPI3 GPI signal from COM Express module carrier board
GPIO 24 OC 10k/3.3V 24mA GPO0 GPO signal to COM Express module carrier board
GPIO 25 OC 10k/3.3V 24mA GPO1 GPO signal to COM Express module carrier board
GPIO 26 OC 10k/3.3V 24mA GPO2 GPO signal to COM Express module carrier board
GPIO 27 OC 10k/3.3V 24mA GPO3 GPO signal to COM Express module carrier board
1)
These GPIOs have pullup resistors of approx. 50kΩ within the SIO
italic blue –> signal available on J-COM
italic green –> signal available on P-SIO
©EKF -29- ekf.com
Page 30

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Configuration Jumpers
Reset Jumper BIOS CMOS RAM Values (J-GP)
The jumper J-GP is used to reset the contents of the battery backed CMOS RAM to their default state.
The BIOS uses the CMOS to store configuration values, e.g. the order of boot devices. Using this
jumper is appropriate only, if it is not possible to enter the setup screen of the BIOS. To restore the
CMOS RAM, install a short circuit jumper on JGP and perform a system reset. As long as the jumper
is stuffed, the BIOS will use the default CMOS values after any system reset. To get normal operation
again, the jumper has to be removed.
JGP
1
1=GPI6 2=GND
© EKF 240.1.02 ekf.com
JGP Function
Jumper removed
1)
No CMOS reset performed
Jumper set CMOS reset performed
1)
This setting is the factory default
Reset Jumper ICH6 RTC Core (J-RTC)
The jumper J-RTC can be used to reset the battery backed core of the ICH6. This effects some registers
within the ICH6 RTC core that are important before the CPU starts its work after a system reset. Note
that JRTC will neither perform the clearing of the CMOS RAM values nor resets the real time clock.
Normally JRTC is not stuffed on the XB1 COM Express Module. To reset the RTC core, the XB1 COM
Express Module must be removed from the carrier board. It is important to accomplish the RTC reset
while the module has no power applied to it. Short-circuit the JRTC pads for about 1s. After that,
reinstall the module to the carrier and switch on the power.
JRTC
1
1=RTCRST# 2=GND
© EKF 240.1.02 ekf.com
JRTC Function
Jumper OFF
1)
No RTC reset performed
Jumper ON RTC reset performed
1)
This setting is the factory default
©EKF -30- ekf.com
Page 31

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Connectors
Caution
Some of the internal connectors provide operating voltage (3.3V and 5V) to devices inside the system
chassis, such as internal peripherals. Not all of these connectors are overcurrent protected. Do not use
these internal connectors for powering devices external to the computer chassis. A fault in the load
presented by the external devices could cause damage to the board, the interconnecting cable and
the external devices themselves.
PLD Programming Header ISPCON
This pin header is the programming port for the on-board ispLSI2064 programmable glue logic chip.
The ISPCON is normally not stuffed.
ISPCON
1
1=3.3V 2=Serial Out 3=Serial In 4=ispGAL Enable
5=NC 6=Mode 7=GND 8=Clock
240.1.08.I
© EKF
ekf.com
©EKF -31- ekf.com
Page 32

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
J-COM
J-COM is the pair of connectors which serves as interface between the XB1 COM Express Module and
the carrier board. The assembly is composed of two double-row, high speed, 0.5mm pitch plugs.
Each row has 110 leads, i.e. J-COM provides 440 contact positions in total. The COM.0 specification
assigns each row a letter A, B and C, D. For Type 1 COM Express modules, rows A and B are sufficient
(single connector, 220 leads). In addition, rows C and D (dual connector, 440 positions) are required
for extended functionality incorporated into Type 2 modules such as the XB1.
AB#CD
GND GND 1 GND GND
ETH_MX3- 1) ETH_LKACT# 1) 2 IDE_D7 IDE_D5
ETH_MX3+ 1) LPC_FRAME# 3 IDE_D6 IDE_D10
ETH_LK100# 1) LPC_AD0 4 IDE_D3 IDE_D11
ETH_LK1000# 1) LPC_AD1 5 IDE_D15 IDE_D12
ETH_MX2- 1) LPC_AD2 6 IDE_D8 IDE_D4
ETH_MX2+ 1) LPC_AD3 7 IDE_D9 IDE_D0
ETH_LKACT# 1) LPC_DRQCOM# (LPC_DRQ0#) 8 IDE_D2 IDE_DREQ
ETH_MX1- 1) LPC_DRQ1# 9 IDE_D13 IDE_IOW#
ETH_MX1+ 1) CLK_33LPC (LPC_CLK) 10 IDE_D1 IDE_DACK#
GND GND 11 GND GND
ETH_MX0- PWRBTN# 12 IDE_D14 IDE_IRQ
ETH_MX0+ SMB_CLK 13 IDE_IORDY IDE_A0
+2.5V (ETH_CTREF) SMB_DATA 14 IDE_IOR# IDE_A1
ICH_SLP_S3# (SUS_S3#) SMB_ALERT# 15 PCI_PME# IDE_A2
SATA_0TP SATA_1TP 16 PCI_GNT2# IDE_CS1#
SATA_0TN SATA_1TN 17 PCI_REQ2# IDE_CS3#
ICH_SLP_S4# (SUS_S4#) SUS_STAT# 18 PCI_GNT1# IDE_RST#
SATA_0RP SATA_1RP 19 PCI_REQ1# PCI_GNT3#
SATA_0RN SATA_1RN 20 PCI_GNT0# PCI_REQ3#
GND GND 21 GND GND
SATA_2TP SATA_3TP 22 PCI_REQ0# PCI_AD1
SATA_2TN SATA_3TN 23 PCI_RST# PCI_AD3
ICH_SLP_S5# (SUS_S5#) PWR_OK 24 PCI_AD0 PCI_AD5
SATA_2RP SATA_3RP 25 PCI_AD2 PCI_AD7
SATA_2RN SATA_3RN 26 PCI_AD4 PCI_CBE0#
BATLOW# WDOGRST (WDT) 27 PCI_AD6 PCI_AD9
SATA_ACT# AC_SDIN2 28 PCI_AD8 PCI_AD11
AC_SYNC AC_SDIN1 29 PCI_AD10 PCI_AD13
AC_RST# AC_SDIN0 30 PCI_AD12 PCI_AD15
©EKF -32- ekf.com
Page 33

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
AB#CD
GND GND 31 GND GND
AC_BITCLK SPKR 32 PCI_AD14 PCI_PAR
AC_SDOUT I2C_CK 33 PCI_CBE1# PCI_SERR#
BIOS_DISABLE# I2C_DAT 34 PCI_PERR# PCI_STOP#
THRMTRIP# THRM# 35 PCI_LOCK# PCI_TRDY#
USB_6N USB_7N 36 PCI_DEVSEL# PCI_FRAME#
USB_6P USB_7P 37 PCI_IRDY# PCI_AD16
USB_OC67# USB_OC45# 38 PCI_CBE2# PCI_AD18
USB_4N USB_5N 39 PCI_AD17 PCI_AD20
USB_4P USB_5P 40 PCI_AD19 PCI_AD22
GND GND 41 GND GND
USB_2N USB_3N 42 PCI_AD21 PCI_AD24
USB_2P USB_3P 43 PCI_AD23 PCI_AD26
USB_OC23# USB_OC01# 44 PCI_CBE3# PCI_AD28
USB_0N USB_1N 45 PCI_AD25 PCI_AD30
USB_0P USB_1P 46 PCI_AD27 PCI_IRQC#
+VCCRTC EXCD1_RST# 47 PCI_AD29 PCI_IRQD#
EXCD0_RST# EXCD1_CPPE# 48 PCI_AD31 PCI_CLKRUN#
EXCD0_CPPE# SYS_RESET# 49 PCI_IRQA# PCI_M66EN
SERIRQ (LPC_SERIRQ) CB_RESET# 50 PCI_IRQB# CLK_33PCI (PCI_CLK)
GND GND 51 GND GND
PCIE_TX5+ PCIE_RX5+ 52 SDVO_TVCLKIN+ PEG_RX0+ SDVOB_RED0+ PEG_TX0+
PCIE_TX5- PCIE_RX5- 53 SDVO_TVCLKIN- PEG_RX0- SDVOB_RED- PEG_TX0-
GPI0 GPO1 54 TYPE0# (NC) PEG_LANE_RV#
PCIE_TX4+ PCIE_RX4+ 55 SDVOB_INT+ PEG_RX1+ SDVOB_GRN+ PEG_TX1+
PCIE_TX4- PCIE_RX4- 56 SDVOB_INT- PEG_RX1- SDVOB_GRN- PEG_TX1-
GND GPO2 57 TYPE1# (NC) TYPE2# (NC)
PCIE_TX3+ 1) PCIE_RX3+ 1) 58 SDVO_FLDSTALL+ PEG_RX2+ SDVOB_BLU+ PEG_TX2+
PCIE_TX3- 1) PCIE_RX3- 1) 59 SDVO_FLDSTALL- PEG_RX2- SDVOB_BLU- PEG_TX2-
©EKF -33- ekf.com
Page 34

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
AB#CD
GND GND 60 GND GND
PCIE_TX2+ PCIE_RX2+ 61 PEG_RX3+ SDVOB_CLK+ PEG_TX3+
PCIE_TX2- PCIE_RX2- 62 PEG_RX3- SDVOB_CLK- PEG_TX3-
GPI1 GPO3 63 RSVD RSVD
PCIE_TX1+ PCIE_RX1+ 64 RSVD RSVD
PCIE_TX1- PCIE_RX1- 65 PEG_RX4+ SDVOC_RED+ PEG_TX4+
GND PE_WAKE# (WAKE0#) 66 PEG_RX4- SDVOC_RED- PEG_TX4-
GPI2 WAKE1# 67 RSVD GND
PCIE_TX0+ PCIE_RX0+ 68 SDVOC_INT+ PEG_RX5+ SDVOC_GRN+ PEG_TX5+
PCIE_TX0- PCIE_RX0- 69 SDVOC_INT- PEG_RX5- SDVOC_GRN- PEG_TX5-
GND GND 70 GND GND
LVDS_A0+ LVDS_B0+ 71 PEG_RX6+ SDVOC_BLU+ PEG_TX6+
LVDS_A0- LVDS_B0- 72 PEG_RX6- SDVOC_BLU- PEG_TX6-
LVDS_A1+ LVDS_B1+ 73 SDVO_I2C_DATA SDVO_I2C_CLK
LVDS_A1- LVDS_B1- 74 PEG_RX7+ SDVOC_CLK+ PEG_TX7+
LVDS_A2+ LVDS_B2+ 75 PEG_RX7- SDVOC_CLK- PEG_TX7-
LVDS_A2- LVDS_B2- 76 GND GND
LVDS_VDD_EN LVDS_B3+ 77 RSVD IDE_CBLID#
LVDS_A3+ LVDS_B3- 78 PEG_RX8+ PEG_TX8+
LVDS_A3- LVDS_BKLT_EN 79 PEG_RX8- PEG_TX8-
GND GND 80 GND GND
LVDS_A_CK+ LVDS_B_CK+ 81 PEG_RX9+ PEG_TX9+
LVDS_A_CK- LVDS_B_CK- 82 PEG_RX9- PEG_TX9-
LVDS_I2C_CK LVDS_BKLT_CTRL 83 RSVD RSVD
LVDS_I2C_DAT VCC_5V_SBY 84 GND GND
GPI3 VCC_5V_SBY 85 PEG_RX10+ PEG_TX10+
ICH_RCIN# (KBD_RST#) VCC_5V_SBY 86 PEG_RX10- PEG_TX10-
ICH_A20GATE (KBD_A20GATE) VCC_5V_SBY 87 GND GND
CLK_PE_COMP RSVD 88 PEG_RX11+ PEG_TX11+
CLK_PE_COMN VGA_RED 89 PEG_RX11- PEG_TX11-
©EKF -34- ekf.com
Page 35

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
AB#CD
GND GND 90 GND GND
RSVD VGA_GREEN 91 PEG_RX12+ PEG_TX12+
RSVD VGA_BLUE 92 PEG_RX12- PEG_TX12-
GPO0 VGA_HSYNC 93 GND GND
RSVD VGA_VSYNC 94 PEG_RX13+ PEG_TX13+
RSVD VGA_DDCCL (VGA_I2C_CK) 95 PEG_RX13- PEG_TX13-
GND VGA_DDCDAT (VGA_I2C_DAT) 96 GND GND
+12V TV_DAC_A 97 RSVD PEG_ENABLE#
+12V TV_DAC_B 98 PEG_RX14+ PEG_TX14+
+12V TV_DAC_C 99 PEG_RX14- PEG_TX14-
GND GND 100 GND GND
+12V +12V 101 PEG_RX15+ PEG_TX15+
+12V +12V 102 PEG_RX15- PEG_TX15-
+12V +12V 103 GND GND
+12V +12V 104 +12V +12V
+12V +12V 105 +12V +12V
+12V +12V 106 +12V +12V
+12V +12V 107 +12V +12V
+12V +12V 108 +12V +12V
+12V +12V 109 +12V +12V
GND GND 110 GND GND
marked light gray italic - signal not available
marked light green italic - pin position reserved by specification
1) stuffing option: GB Ethernet provided by factory default, PCIe lane #3 via J-COM on request
A1
© EKF 275.50.00.440.00 ekf.com
D1
J-COM (View on Bottom Side of Board)
©EKF -35- ekf.com
Page 36

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Processor Debug Header PITP
This FFC style connector (Molex 52435-2872) can be used to attach an emulator probe to the board.
This is a valuable tool when debugging hardware or tracing software. The connector PITP is situated
at the bottom side of the board.
PITP
1TDI
2TMS
3TRST#
4NC
5TCK
6NC
7TDO
8BCLKN
9BCLKP
10 GND
11 FBO
12 RST#
13 BPM5#
14 GND
15 BPM4#
16 GND
17 BPM3#
18 GND
19 BPM2#
20 GND
21 BPM1#
22 GND
23 BPM0#
24 DBA#
25 DBR#
26 VTAP
27 V
28 V
©EKF -36- ekf.com
TT
TT
Page 37

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
P-SIO
The connector P-SIO is normally not stuffed. The mature PS/2 and UART ports have been overcome by
USB in most applications. For low level debugging however, these interfaces can be very useful (e.g.
the BIOS can communicate across the serial I/O). Please contact EKF before ordering the XB1 COM
Express Module, if the P_SIO connector is required by the user.
P-SIO
21
MS_CLK 1 2 MS_DAT
KB_CLK 3 4 KB_DAT
10
276.53.010.01
1.27mm Socket
267.03.010.01
Mating Stacker
© EKF ekf.com
COM_CTS# (TTL) 5 6 COM_RTS# (TTL)
COM_RXD (TTL) 7 8 COM_TXD (TTL)
GND 9 10 +5V
The UART port does not include RS-232 transceivers (TTL level signals only). If necessary, the user must
provide RS-232 or RS-485 transceivers externally.
©EKF -37- ekf.com
Page 38

Board Dimensions
User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
D1
Top View ( seen through board)connectors
COM Express
Basic Module
© EKF
ekf.com
95.00
18.00 91.00
4.00
A1
16.50
74.20
80.00
121.00
125.00
6.00
4.00
©EKF -38- ekf.com
Page 39

Top View, Bottom View
User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
XB1 Top View
XB1 Bottom View
©EKF -39- ekf.com
Page 40

User Guide XB1 COM Express Module
Literature
Theme Document Title Origin
COM Express
Ethernet IEEE Std 802.3, 2000 Edition standards.ieee.org
PCI Express PCI Express Base Specification 1.1 www.pcisig.com
Serial ATA Serial ATA Revision 2.5 www.serialata.org
USB Universal Serial Bus Specification www.usb.org
PICMG® COM.0
COM Express™ Module Base Specification
Revision 1.0 2005-07
www.picmg.org
EKF Elektronik GmbH
Philipp-Reis-Str. 4
59065 HAMM
Germany
Fax. +49 (0)2381/6890-90
Tel. +49 (0)2381/6890-0
Internet www.ekf.com
E-Mail info@ekf.com
 Loading...
Loading...