Page 1

Distributed by:
Jameco Part Number 875940
www.Jameco.com ✦ 1-800-831-4242
The content and copyrights of the attached
material are the property of its owner.
Page 2

82546GB Dual Port Gigabit Ethernet
Controller
Networking Silicon
Datasheet
Product Features
■ PCI/PCI-X
—PCI-X Revision 1.0a support for
frequencies up to 133 MHz
—Multi-function PCI device
—PCI Revision 2.3 su pport for 3 2-bit wide
or 64-bit wide interface at 33 MHz and
66 MHz
■ MAC
—IEEE 802.3x compliant flow control
support with software controllable pause
times and threshold values
—Programmable host memory receive
buffers (256 Bytes to 16 Kbytes) and
cache line size (16 Bytes to 256 Bytes)
—Wide, optimized internal data path
architecture (128 bits)
—Dual 64 Kbytes configurable Transmit
and Receive FIFO buffers
—Optimized descriptor fetching and write-
back mechanisms
■ PHY
—Integrated PHY for 10/100/1000 Mbps
full and half duplex operation
—IEEE 802.3ab Auto-Negotiation support
—IEEE 802.3ab PHY compliance and
compatibility
—PHY ability to automatically detect
polarity and cable lengths and MDI
versus MDI-X cable at all speeds
■ Host Offloading
—Transmit and receive IP, TCP and UDP
checksum off-loading capabilities
—Transmit TCP segmentation
—IEEE 802.1q VLAN support with
VLAN tag insertion, stripping and
packet filtering for up to 4096 VLAN
tags
—Advanced packet filtering
■ Manageability
—Manageability features on both ports:
SMB port, ASF 1.0, ACPI, Wake on
LAN, and PXE
—Compliance with PCI Power
Management 1.1 and ACPI 2.0 register
set compliant
■ T wo complete gigabit Ethernet connections
in a single device
■ Eight activity and link indication outputs
that directly drive LEDs
■ Lead-free
a
364-pin Ba ll Grid Array (BGA).
Devices that are lead-free are marked with
a circled “e1” and have the product code:
NHxxxxxx.
a. This device is lead-free. That is, lead has not been intentionally added, but lead may still exist as an impurity at <1000 ppm.
The Material Declaration Data Sheet, which includes lead impurity levels and the concentration of other Restriction on Hazardous Substances (RoHS)-banned materials, is available at:
ftp://download.intel.com/design/packtech/material_content_IC_Package.pdf#pagemode=bookmarks
In addition, this device has been tested and conforms to the same parametric specifications as previous versions of the de-
vice. For more information regarding lead-free products from Intel Corporation, contact your Intel Field Sales representative.
Revision 1.7
October 2005
Page 3
Revision History
Revision Date Description
1.7 Oct 2005
1.6 June 2005
1.5 April 2005
1.4 Sept 2004
1.3 Dec 2003 Added an I/O Characteristics table in Section 4.3, “DC Characteristics.”
1.2 Nov 2003
1.1 Sept 2003 Declassified document from confidential status.
1.0 July 2003 Initial release.
Corrected the nominal impedance values for the I/O cells from 50 KΩ to a
nominal impedance value of 120 KΩ, with a minimum of 90 KΩ and a
maximum of 190 KΩ.
Corrected typing error of “q” to “θ” in Section 6.3, “Thermal Specifications,” on
page 38.
• Changed interrupt signals INTA# and INTB# symbol types from TS (tristate) to OD (open drain).
• Added a more detailed AUX_PWR pin description.
• Added tristate and XOR non-JTAG test modes description.
• Added lead-free product and ordering information.
• Added major product features to cover page.
• Added text stating that the TTL inputs on the Ethernet controller are not 5V
tolerant.
• Updated thermal specifications.
Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products. No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual
property rights is granted by this document. Except as provided in Intel's Terms and Conditions of Sale for such products, Intel assumes no liability
whatsoever, and Intel disclaims any express or implied warranty , relating to sale and/or use of Intel products including liability or warranties relating to
fitness for a particular purpose, merchantability, or infringement of any patent, copyright or other intellectual property right. Intel products are not
intended for use in medical, life saving, or life sustaining applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked "reserved" or "undefined." Intel reserves these for
future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
The 82546GB Gigabit Ethernet controller may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from
published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order .
Copies of documents which have an ordering number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature may be obtained by calling 1-800-
548-4725 or by visiting Intel's website at http://www.intel.com.
Copyright © 2005, Intel Corporation.
®
Intel
is a trademark or registered trademark of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
*Third-party brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
ii Datasheet
Page 4

Networking Silicon — 82546GB
Contents
1.0 Introduction.........................................................................................................................1
1.1 Document Scope...................................................................................................2
1.2 Reference Documents . ....... ...... .......................................................... ....... ...... ......2
1.3 Product Codes.......................................................................................................3
2.0 Additional 82546GB Features............................................................................................5
2.1 PCI ........................................................................................................................5
2.2 MAC ......................................................................................................................5
2.3 PHY.......................................................................................................................5
2.4 Host Offloading...... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ...... ....... ...... .............................................6
2.5 Manageability ........................................................................................................6
2.6 Device ...................................................................................................................7
2.7 Technology............................................................................................................7
3.0 Signal Descriptions.............................................................................................................8
3.1 Signal Type Definitions..........................................................................................8
3.2 PCI Bus Interface ..................................................................................................8
3.2.1 PCI Address, Data and Control Signals ...................................................9
3.2.2 Arbitration Signals ..................................................................................10
3.2.3 Interrupt Signals .....................................................................................10
3.2.4 System Signals.......................................................................................11
3.2.5 Error Reporting Signals..........................................................................11
3.2.6 Power Management Signals ..................................................................11
3.2.7 Impedance Compensation Signals.........................................................12
3.2.8 SMB Signals...........................................................................................12
3.3 EEPROM Interface Signals.................................................................................12
3.4 Flash Interface Signals........................................................................................13
3.5 Miscellaneous Signals.........................................................................................13
3.5.1 LED Signals............................................................................................13
3.5.2 Software Definable Signals....................................................................13
3.6 PHY Signals ................ ....... ...... ....... ...... ...... ....... .................................................14
3.6.1 Crystal Signals .......................................................................................14
3.6.2 PHY Analog Signals.................................... ....... ...... ....... .......................14
3.7 Serializer / Deserializer Signals...........................................................................15
3.8 JTAG Test Interface Signals ...............................................................................16
3.9 Power Supply Connections .................................................................................16
3.9.1 Power Support Signals...........................................................................16
3.9.2 Digital Supplies.......................................................................................16
3.9.3 Analog Supplies ................. .......................................................... ...... ....1 6
3.9.4 Ground and No Connects.......................................................................17
4.0 Test Port Functionality......................................................................................................18
4.1 XOR Testing........................................................................................................18
4.1.1 XOR Tree Control and Operation...........................................................18
4.1.2 Pins Tested ............................................................................................19
4.2 Tristate Mode ......................................................................................................20
4.2.1 Tristate Mode Control and Operation.....................................................20
Datasheet iii
Page 5

82546GB — Networking Silicon
4.2.2 Tristate Mode Using JTAG (TAP)...........................................................20
5.0 Voltage, Temperature, and Timing Specifications ...........................................................21
5.1 Targeted Absolute Maximum Ratings.................................................................21
5.2 Recommended Operating Conditions.................................................................21
5.3 DC Specifications................................................................................................22
5.4 AC Characteristics ..............................................................................................25
5.5 Serial Interface Specifica tio ns............ ...... ...... ....... ...... ........................................26
5.6 Timing Specifications ............................... ...... .....................................................27
5.6.1 PCI/PCI-X Bus Interface ........................................................................27
5.6.1.1 PCI/PCI-X Bus Interface Clock..................................................27
5.6.1.2 PCI/PCI-X Bus Interface Timing................................................28
5.6.2 Link Interface Timing..............................................................................30
5.6.2.1 Link Interface Rise and Fall Time..............................................30
5.6.2.2 Link Interface Transmit Timing..................................................31
5.6.2.3 Link Interface Receive Timing..... ...... ........................................32
5.6.3 Flash Interface .......................................................................................33
5.6.4 EEPROM Interface ... ...... .......................................................... ....... ...... .34
6.0 Package and Pinout Information......................................................................................35
6.1 Device Identification ...........................................................................................35
6.2 Package Information ...........................................................................................36
6.3 Thermal Specifications........................................................................................38
6.4 Ball Mapping Diagram.........................................................................................39
6.5 Pinout Information...............................................................................................40
Figures
Tables
1 Gigabit Ethernet Controller Block Diagram ...........................................................2
2 XOR Tree Concept..............................................................................................18
3 AC Test Loads for General Output Pins..............................................................26
4 PCI/PCI-X Clock Timing......................................................................................27
5 PCI Bus Interface Output Timing Measurement .................................................29
6 PCI Bus Interface Input Timing Measurement Conditions..................................29
7 TVAL (max) Rising Edge Test Load....................................................................29
8 TVAL (max) Falling Edge Test Load...................................................................30
9 Link Interface Rise/Fall Timing............................................................................31
10 Transmit Interface Timing ..... ...... ....... ...... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... .31
11 Receive Interface Timing ....................................................................................32
12 Flash Read Timing..............................................................................................33
13 Flash Write Timing ..............................................................................................33
14 82546GB Device Identification Markings ............................................................35
15 82546GB 364-Lead BGA Ball Pad Dimensions..................................................36
16 82546GB Mechanical Spec ifi catio ns.................................. ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... .37
1 Tested Pins Included in XOR Tree......................................................................19
2 Absolute Maximum Ratings ................................................................................21
3 Recommended Operating Conditions.................................................................21
4 DC Characteristics ..............................................................................................22
5 Power Supply Characteristics.............................................................................22
iv Datasheet
Page 6

Networking Silicon — 82546GB
6 I/O Characteristics...............................................................................................24
7 AC Characteristics: 3.3 V Interfacing ..................................................................25
8 25 MHz Clock Input Requirements......................................................................25
9 Link Interface Clock Requirements .....................................................................25
10 EEPROM Interface Clock Requirements ............................................................26
11 AC Test Loads for General Output Pins..............................................................26
12 Driver Characteristics..........................................................................................26
13 Receiver Characteristics .....................................................................................27
14 PCI/PCI-X Bus Interface Clock Parameters........................................................27
15 PCI/PCI-X Bus Interface Timing Parameters......................................................28
13 PCI Bus Interface Timing Measurement Conditions ...........................................28
16 Rise and Fall Times.............................................................................................30
17 Transmit Interface Timing....................................................................................31
18 Receive Interface Timing.....................................................................................32
19 Flash Read Operation Timing .............................................................................33
20 Flash Write Operation Timing..............................................................................34
21 Link Interface Clock Requirements .....................................................................34
22 Link Interface Clock Requirements .....................................................................34
23 Thermal Characteristics ......................................................................................38
24 PCI Address, Data, and Control Signals.............................................................40
25 PCI Arbitration Signals........................................................................................40
26 Interrupt Signals ..................................................................................................41
27 System Signals....................................................................................................41
28 Error Reporting Signals.......................................................................................41
29 Power Management Signals ...............................................................................41
30 Impedance Compensation Signals......................................................................41
31 SMB Signals........................................................................................................41
32 EEPROM Interface Signals.................................................................................41
33 Flash Interface Signals........................................................................................42
34 LED Signals.........................................................................................................42
35 Software Definable Signals.................................................................................42
36 Crystal Signals ....................................................................................................42
37 PHY Signals ................ ....... ...... ....... .......................................................... ...... ....4 2
38 Serializer / Deserializer Signals...........................................................................43
39 JTAG Test Interface Signals ...............................................................................43
40 Power Support Signals........................................................................................43
41 Digital Power Signals ..........................................................................................44
42 Analog Power Signals . ....... .......................................................... ...... ....... ...... ....44
43 Grounds and No Connect Signals.......................................................................45
44 Reserved Signals ................................................................................................46
Datasheet v
Page 7

82546GB — Networking Silicon
Note: This page is intentionally left blank.
vi Datasheet
Page 8

1.0 Introduction
The Intel® 82546GB Dual Port Gigabit Ethernet Controller is a single, compact component with
two full integrated Gigabit Ethernet Media Access Control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY)
functions. The Intel
area and can be used for desktop and workstation PC network designs as well as backplane
applications with critical space constraints.
The Intel
®
82546GB integrates Intel’s fourth generation gigabit MAC and PHY to provide a
standard IEEE 802.3 Ethernet interface for 1000BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, and 10BASE-T
applications (802.3, 802.3u, and 802.3ab). The controller is capable of transmitting and receiving
two channels of data at rat es o f 1000 Mbps, 10 0 Mbps , or 1 0 Mbps. In addi tion, it provi des a 64- bit
wide direct Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) 2.3 and PCI-X 1.0a compliant interface
capable of operating at frequencies up to 133 MHz. The 82546GB also delivers a dual port PCI-X
solution without added bridge lat ency.
The Intel
®
82546GB on-board System Management Bus (SMB) port enables network
manageability implementations required by information technology personnel for remote con trol
and alerting through the LAN. Using the SMB, management packets can be routed to or from a
management processor. The SMB port enables industry standards, such as Intelligent Platform
Management Interface (IPMI) and Alert Standard Format (ASF), to be implemented using the
82546GB. In addition, on chip ASF 1.0 circuitry provides alerting and remote control capabilities
with standardized interfaces.
®
82546GB enables dual port Gi gabit Eth ernet i mplement ations in a ver y small
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
The 82546GB Dual Port Gigabit Ethernet Controller architecture is designed to deliver high
performance and PCI/PCI-X bus efficiency. Wide internal data paths eliminate performance
bottlenecks by efficiently handling large address and data words. Combining a parallel and pipelined logic architecture optimized for Gigabit Ethernet and independent transmit and receive
queues, the 82546GB controller efficiently handles packets with minimum latency. The 82546GB
controller includes advanced interrupt handling features to limit PCI bus traf fic and a PCI interface
that maximizes the use of bursts for efficient bus usage. The 82546GB is able to cache up to 64
packet descriptors in a single burst for efficient PCI bandwidth use. A large 64 Kbyte on-chip
packet buffer maintains superior performance as available PCI bandwidth changes. By using
hardware acceleration, the controller is able to offload tasks, such as checksum calculations and
TCP segmentation, from the host processor.
Datasheet 1
Page 9
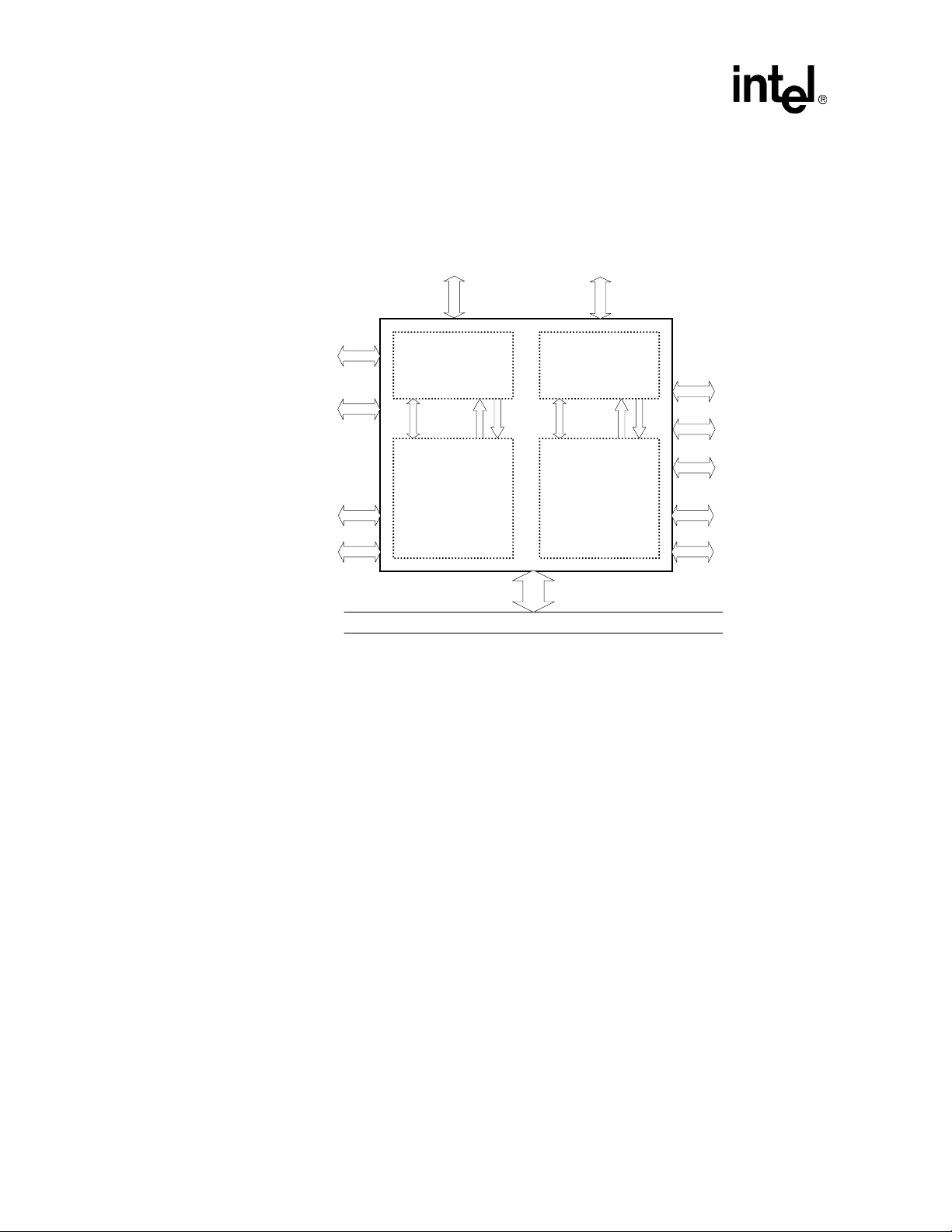
82546GB — Networking Silicon
PCI (64 bit,33/66MHz); PCI
S/W Defined
Pins MDI
Interface A
Design For Test
Interface
LED's
EEPROM
Interface
e
SM Bus
Interface
PHY
MDIO
MII
PHY
MDIO
MII S/W Defined
Pins LED's
External
TBI Interface
MDI Interface B
The 82546GBis packaged in a 21 mm x 21 mm 364-ball grid array and footprint compatible with
the Intel
Controller.
Figure 1. Gigabit Ethernet Controller Block Diagram
®
82544GC Gigabit Ethernet Controller and 82546EB Dual Port Gigabit Ethernet
1000Base-T PHY Interfaces
10/100/1000
GMII/
Device Funct. #0
MAC/Controller
(LAN A)
10/100/1000
GMII/
Device Funct. #1
MAC/Controlle r
(LAN B)
Flash Interfac
1.1 Document Scope
This document contains datasheet specifications for the 82546GB Dual Port Gigabit Ethernet
Controller, which includes sign al des cri pti on s, DC and AC parameters, packaging d at a, an d p in ou t
information.
1.2 Refe r ence Documents
It is assumed that the designer is acquainted with high-speed design and board layout techniques.
Document that may provide additional information are:
• PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 2.3, PCI Special Interest Group.
• PCI-X Specification, Revision 1.0a, PCI Special Interest Group.
• PCI Bus Power Management Interface Specification, Rev. 1.1, PCI Special Interest Group.
• IEEE Standard 802.3, 1996 Edition, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
• IEEE Standard 802.3u, 1995 Edition, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
• IEEE Standard 802.3x, 1997 Edition, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
• IEEE Standard 802.3z, 1998 Edition, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
-X (133MHz)
2 Datasheet
Page 10

• IEEE Standard 802.3ab, 1999 Edition, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
(IEEE).
®
• Intel
Ethernet Controllers Timing Device Selection Guide, AP-419. Intel Corporation.
1.3 Product Codes
The product ordering code for the 82546GB is: FW82546GB.
The lead-free product ordering code for the 82546GB is: NH82546GB.
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
Datasheet 3
Page 11

82546GB — Networking Silicon
Note: This page intentionally left blank.
4 Datasheet
Page 12
2.0 Additional 82546GB Features
2.1 PCI
Feature Benefits
Algorithms that optimally use advanced PCI, MWI,
MRM, and MRL commands as well as PCI-X MRD,
MRB, and MWB commands
2.2 MAC
Features Benefits
Low-latency transmit and receive queues
Caches up to 64 packet descriptors in a single burst • Efficient use of PCI bandwidth
Descriptor ring management hardware for transmit
and receive
Mechanism available for reducing interrupts
generated by transmit and receive operations
Support for transmission and reception of packets up
to 16 Kbytes
• Efficient bus operations
• Network packets handled without waiting or buffer
overflow.
• Simple software programming model
• Maximizes system performance and throughput
• Enables jumbo frames
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
2.3 PHY
Feature Benefits
State-of-the-art DSP architecture implements digital
adaptive equalization, echo cancellation, and crosstalk cancellation
Datasheet 5
• Robust performance in noisy environments
• Tolerance of common electrical signal
impairments
Page 13
82546GB — Networking Silicon
2.4 Host Offloading
Features Benefits
Descriptor ring management hardware for transmit
and receive
16-Kbyte jumbo frame support
Interrupt coalescing (multiple packets per interrupt)
2.5 Manageability
Features Benefits
On-board SMB port
Preboot eXecution Environment (PXE) Flash
interface support (32-bit and 64-bit)
Compliance with PCI Power Management 1.1 and
ACPI 2.0 register set compliant including:
• D0 and D3 power states
• Network Device Class Power Management
Specification 1.1
• PCI Specification 2.3
SNMP and RMON statistic counters
SDG 3.0, WfM 2.0, and PC2001 compliance
Wake on LAN support
IPMI MAC Address Read capability
2
IPMI I
C Addressing capability • Enables device addressing over the I2C bus
• Optimized fetching and write-back mechanisms for
efficient system memory and PCI bandwidth
usage
• High throughput for large data transfers on
networks supporting jumbo frames
• Increased throughput by reducing interrupts
generated by transmit and receive operations
• Enables IPMI and ASF implementations
• Allows packets routing to and from either LAN port
and a server management processor
• Local Flash interface for PXE image
• PCI power management capability requirements
for PC and embedded applications
• Easy system monitoring with industry standard
consoles
• Remote network management capabilities through
DMI 2.0 and SNMP software
• Packet recognition and wake-up for NIC and LOM
applications without software configuration
• Allows MAC address read to be read by remote
users through IMPI
6 Datasheet
Page 14
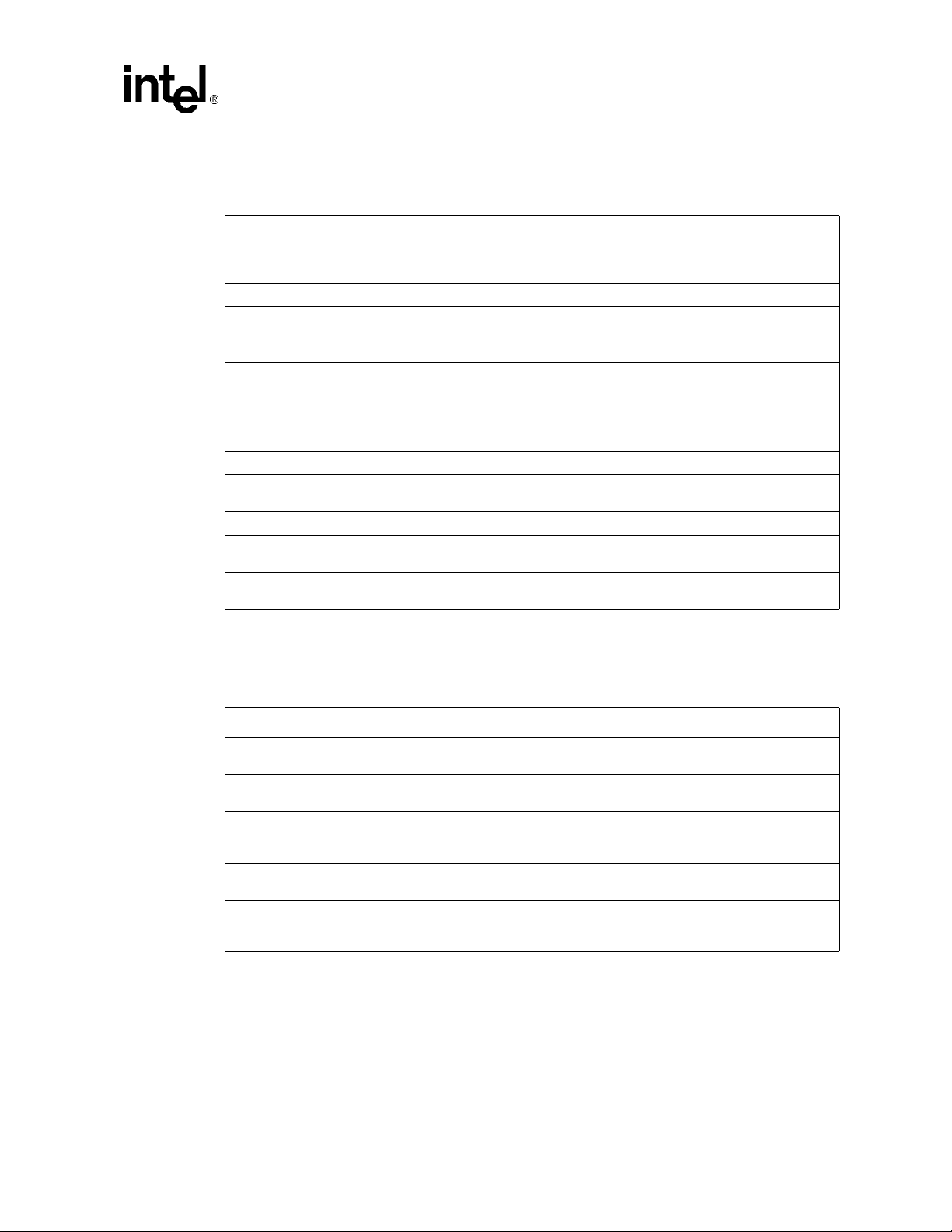
2.6 Device
Internal PLL for clock generation (use either a 25 MHz
crystal or a 25 MHz oscillator)
JTAG (IEEE 1149.1) Test Access Port built in silicon • Simplified testing using boundary scan
On-chip power control circuitry
Eight software definable pins
Supports little endian byte ordering for both 32 and 64
bit systems and big endian byte ordering for 64 bit
systems
Provides loopback capabilities • Validates silicon integrity
Single-pin LAN disable function
VLAN Management Filtering • Allows VLAN-based management packet filtering
Full 2/3 Wire Downshift capability
PICMIG 3.1 Compliant SERDES Interface
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
Features Benefits
• Lower component count and system cost
• Reduced number of on-board power supply
regulators
• Simplified power supply design
• Additional flexibility for LEDs or other low speed
I/O devices
• Portable across application architectures
• Allows LAN port enabling and disabling through
BIOS control (OS not required) for both ports
• Allows silicon to downshift speed to two or three
wire install and still achieve valid link
• Enables interface connections with PICMIG 3.1
compliant devices
2.7 Technology
364-pin Ball Grid Array (BGA) package
Footprint compatible with the 82544GC/EI and
82545GM/EM single port gigabit Ethernet controllers
Implemented in 0.15µ CMOS process
3.3 V PCI signaling with an average power dissipation
of 3.5 W
Operating temperature: 0° C to 55° C (with or without
thermal management, maximum); 0° C to 70° C (with
increased thermal management, maximum)
Features Benefits
• 21 mm x 21 mm component makes LOM designs
easier
• Single port or dual port implementation on the
same board with minor option changes.
• Offers lowest geometry to minimize power and
size while maintaining Intel quality reliability
standards
• Lower power requirements
• Extended temperature attainable with thermal
management device for more demanding systems
requiring a wider temperature range.
Datasheet 7
Page 15

82546GB — Networking Silicon
3.0 Signal Descriptions
Note: The targeted signal names are subject to change without notice. Verify with your local Intel sales
office that you have the latest information before finalizing a design.
3.1 Signal Type Definitions
The signals of the 82546GB controller are electrically defined as follows:
Name Definition
I Input. Standard input only digital signal.
O Output. S t andard output only digital signal.
TS Tri-state. Bi-directional three-state digital input/output signal.
Sustained Tri-state. Sustained digital three-state signal driven by one agent at a time.
STS
OD
A Analog. PHY analog data signal.
P Power. Power connection, voltage reference, or other reference connection.
R Reserved.
An agent driving the STS pin low must actively drive it high for at least one clock before letting it
float. The next agent of the signal cannot drive the pin earlier than one clock after it has been
released by the previous agent.
Open Drain. Wired-OR with other agents.
The signaling agent asserts the OD signal, but the signal is returned to the inactive state by a
weak pull-up resistor. The pull-up resistor may require two or three clock periods to fully restore
the signal to the de-asserted state.
Note: The TTL inputs on the Ethernet controller are not 5V tolerant. If these inputs are connected to 5V,
then damage to the Ethernet controller is likely to occur. TTL inputs include the JTAG interface
pins, the FLASH interface pins, the EEPROM interface pins, the LED pins, the software definable
pins, and the LAN_PWR_GOOD pin.
3.2 PCI Bus Interface
When the Reset signal (RST#) is asserted, the 82546GB will not drive any PCI outpu t or bidirectional pins except the Power Management Event signal (PME#).
8 Datasheet
Page 16
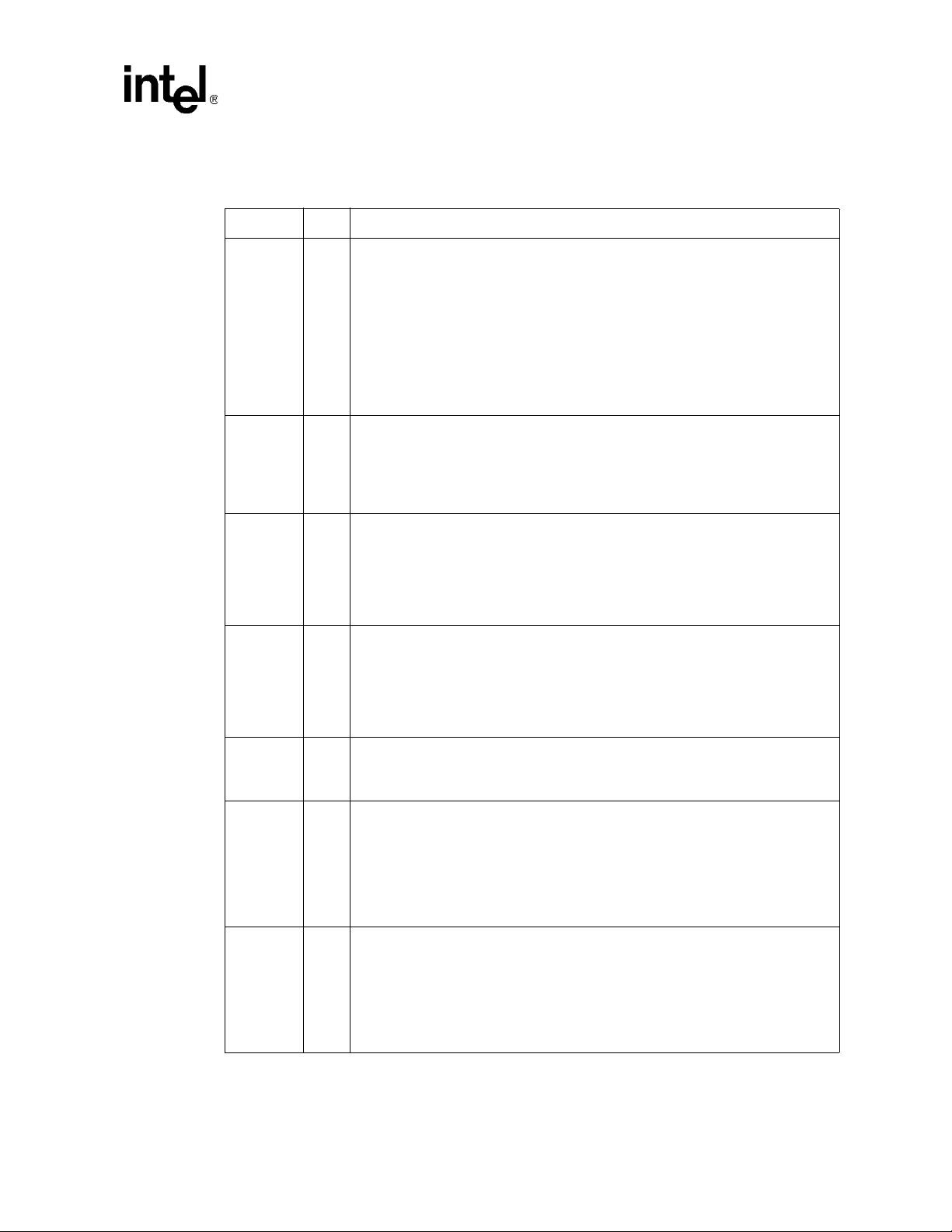
3.2.1 PCI Address, Data and Control Signals
Symbol Type Name and Function
Address and Data. Address and data signals are multiplexed on the same PCI pins. A
bus transaction includes an address phase followed by one or more data phases.
The address phase is the clock cycle when the Frame signal (FRAME#) is asserted
low. During the address phase AD[63:0] contain a physical address (64 bits). For I/O,
this is a byte address, and for configuration and memory, a DWORD address. The
AD[63:0] TS
CBE[7:0]# TS
PAR TS
PAR64 TS
FRAME# STS
IRDY# STS
TRDY# STS
82546GB device uses little endian byte ordering.
During data phases, AD[7:0] contain the least significant byte (LSB) and AD[63:56]
contain the most significant byte (MSB).
The 82546GBcontroller may optionally be connected to a 32-bit PCI bus. On the 32-bit
bus, AD[63:32] and other signals corresponding to the high order byte lanes do not
participate in the bus cycle.
Bus Command and Byte Enables. Bus command and byte enable signals are
multiplexed on the same PCI pins. During the address phase of a transaction,
CBE[7:0]# define the bus command. In the data phase, CBE[7:0]# are used as byte
enables. The byte enables are valid for the entire data phase and determine which byte
lanes contain meaningful data.
CBE0# applies to byte 0 (LSB) and CBE7# applies to byte 7 (MSB).
Parity. The Parity signal is issued to implement even parity across AD[31:0] and
CBE[3:0]#. PAR is stable and valid one clock after the address phase. During data
phases, PAR is stable and valid one clock after either IRDY# is asserted on a write
transaction or TRDY# is asserted after a read transaction. Once PAR is valid, it remains
valid until one clock after the completion of the current data phase.
When the 82546GB controller is a bus master, it drives P AR for address and write data
phases, and as a slave device, drives PAR for read data phases.
Parity 64. The Parity 64 signal is issued to implement even parity across AD[63:32] and
CBE[7:4]#. PAR64 is stable and valid one clock after the address phase. During data
phases, PAR64 is stable and valid one clock after either IRDY# is asserted on a write
transaction or TRDY# is asserted after a read transaction. Once PAR64 is valid, it
remains valid until one clock after the completion of the current data phase.
When the 82546GB controller is a bus master, it drives PA R64 for address and write
data phases, and as a slave device, drives PAR64 for read data phases.
Cycle Frame.
beginning and length of an access and indicate the beginning of a bus transaction.
While FRAME# is asserted, data transfers continue. FRAME# is de-asserted when the
transaction is in the final data phas
Initiator Ready. Initiator Ready indicates the ability of the 82546GB controller (as bus
master device) to complete the current data phase of the transaction. IRDY# is used in
conjunction with the Target Ready signal (TRDY#). The data phase is completed on any
clock when both IRDY# and TRDY# are asserted.
During the write cycle, IRDY# indicates that valid data is present on AD[63:0]. For a
read cycle, it indicates the master is ready to accept data. Wait cycles are inserted until
both IRDY# and TRDY# are asserted together. The 82546GB controller drives IRDY#
when acting as a master and samples it when acting as a slave.
Target Ready. The Target Ready signal indicates the ability of the 82546GB controller
(as a selected device) to complete the current data phase of the transaction. TRDY# is
used in conjunction with the Initiator Ready signal (IRDY#). A data phase is completed
on any clock when both TRDY# and IRDY# are sampled asserted.
During a read cycle, TRDY# indicates that valid data is present on AD[63:0]. For a write
cycle, it indicates the target is ready to accept data. Wait cycles are inserted until both
IRDY# and TRDY# are asserted together. The 82546GB device drives TRDY# when
acting as a slave and samples it when acting as a master.
The Frame signal is driven by the 82546GB device to indicate the
e.
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
Datasheet 9
Page 17
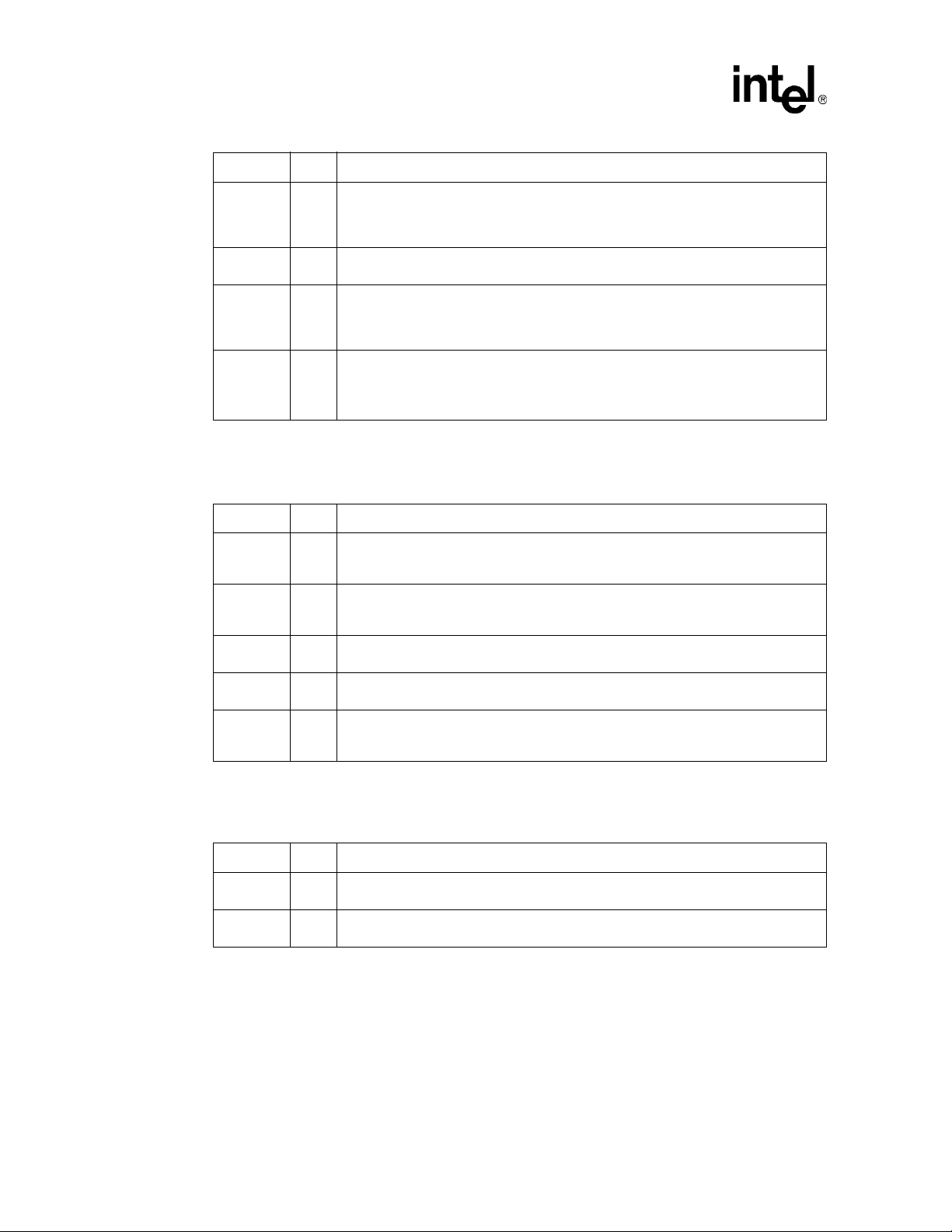
82546GB — Networking Silicon
Symbol Type Name and Function
Stop. The Stop signal indicates the current target is requesting the master to stop the
STOP# STS
IDSEL# I
DEVSEL# STS
VIO P
current transaction. As a slave, the 82546GB controller drives STOP# to request the
bus master to stop the transaction. As a master, the 82546GB controller receives
STOP# from the slave to stop the current transaction.
Initialization Dev ic e Se lect. The Initialization Device Select signal is used by the
82546GB as a chip select signal during configuration read and write transactions.
Device Select. When the Device Select signal is actively driven by the 82546GB, it
signals notifies the bus master that it has decoded its address as the target of the
current access. As an input, DEVSEL# indicates whether any device on the bus has
been selected.
VIO. The VIO signal is a voltage reference for the PCI interface (3.3 V or 5 V PCI
signaling environment). It is used as the clamping voltage.
Note: An external resistor is required between the voltage reference and the VIO pin.
The target resistor value is 100 KΩ
3.2.2 Arbitration Signals
Symbol Type Name and Function
REQ64# TS
ACK64# TS
REQ# TS
GNT# I
LOCK# I
Request Transfer. The Request Transfer signal is generated by the current initiator
indicating its desire to perform a 64-bit transfer. REQ64# has the same timing as the
Frame signal.
Acknowledge Transfer. The Acknowledge Transfer signal is generated by the currently
addressed target in response to the REQ64# assertion by the initiator. ACK64# has the
same timing as the Device Select signal.
Request Bus. The Request Bus signal is used to request control of the bus from the
arbiter. This signal is point-to-point.
Grant Bus. The Grant Bus signal notifies the 82546GB that bus access has been
granted. This is a point-to-point signal.
Lock Bus. The Lock Bus signal is asserted by an initiator to require sole access to a
target memory device during two or more separate transfers. The 82546GB device
does not implement bus locking.
3.2.3 Interrupt Signals
Symbol Type Name and Function
INTA# OD
INTB# OD
Interrupt A. Interrupt A is used to request an interrupt by port 1 of the 82546GB. It is
an active low, level-triggered interrupt signal.
Interrupt B. Interrupt B is used to request an interrupt by port 2 of the 82546GB. It is
an active low, level-triggered interrupt signal.
10 Datasheet
Page 18

3.2.4 System Signals
Symbol Type Name and Function
PCI Clock. The PCI Clock signal provides timing for all transactions on the PCI bus
CLK I
M66EN I
RST# I
LAN_
PWR_
GOOD
and is an input to the 82546GB device. All other PCI signals, except the Interrupt A
(INTA#) and PCI Reset signal (RST#), are sampled on the rising edge of CLK. All other
timing parameters are defined with respect to this edge.
66 MHz Enable.
system bus is capable of supporting an operating frequency of 66 MHz.
PCI Reset. When the PCI Reset signal is asserted, all PCI output signals, except the
Power Management Event signal (PME#), are floated and all input signals are ignored.
The PME# context is preserved, depending on power management settings.
Most of the internal state of the 82546GB is reset on the de-assertion (rising edge) of
RST#.
Power Good (Power-on Reset). The Power Good signal is used to indicate that stable
I
power is available for the 82546GB. When the signal is low, the 82546GB holds itself in
reset state and floats all PCI signals.
3.2.5 Error Reporting Signals
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
The 66 MHz Enable signal is used to indicate whether or not the
Symbol Type Name and Function
SERR# OD
PERR# STS
System Error. The System Error signal is used by the 82546GB controller to report
address parity errors. SERR# is open drain and is actively driven for a single PCI clock
when reporting the error.
Parity Error. The Parity Error signal is used by the 82546GB controller to report data
parity errors during all PCI transactions except by a Special Cycle. PERR# is sustained
tri-state and must be driven active by the 82546GB controller two data clocks after a
data parity error is detected. The minimum duration of PERR# is one clock for each
data phase a data parity error is present.
3.2.6 Power Management Signals
Symbol Type Name and Function
Power Management Event. The 82546GB device drives this signal low when it
PME# OD
AUX_PWR I
receives a wake-up event and either the PME Enable bit in the Power Management
Control/Status Register or the Advanced Power Management Enable (APME) bit of the
Wake-up Control Register (WUC) is 1b.
Auxiliary Power. If the Auxiliary Power signal is high, then auxiliary power is available
and the 82546GB device should support the D3cold power state.
Note that AUX_PWR is not a supply input, but is an indication of whether AUX_PWR is
available to the 82546GB and/or subsystem. Setting AUX_PWR to 1b enables
advertising D3cold Wake Up support and changes the reset function of PME_En and
PME_Status. AUX_PWR is level sensitive, and any changes are immediately reflected
in the D3cold Wake Up advertisements and the PME_En and PME_Status behavior on
PCI reset.
Datasheet 11
Page 19

82546GB — Networking Silicon
3.2.7 Impedance Compensa ti on Signa ls
Symbol Type Name and Function
N Device Impedance Compensation. This signal should be connected to an external
precision resistor (to VDD) that is indicative of the PCI/PCI-X trace load. This cell is
ZN_COMP I/O
ZP_COMP I/O
used to dynamically determine the drive strength required on the N-channel transistors
in the PCI/PCI-X I/O cells.
The internal pull-up impedance is nominally 120 KΩ with a minimum of 90 KΩ and a
maximum of 190 KΩ.
P Device Impedance Compensation. This signal should be connected to an external
precision resistor (to VSS) that is indicative of the PCI/PCI-X trace load. This cell is
used to dynamically determine the drive strength required on the P-channel transistors
in the PCI/PCI-X I/O cells.
The internal pull-up impedance is nominally 120 KΩ with a minimum of 90 KΩ and a
maximum of 190 KΩ.
3.2.8 SMB Signals
Note: A pull-up resistor with a recommended value of 4.7 KΩ should be placed along the SMB. A
precise value may be calculated from the SMB specification.
Symbol Type Name and Function
SMBCLK I/O SMB Clock. The SMB Clock signal is an open drain signal for serial SMB interface.
SMBDATA I/O SMB Data. The SMB Data signal is an open drain signal for serial SMB interface.
SMBALRT# O SM B A lert. The SMB Alert signal is open drain for serial SMB interface.
3.3 EEPROM Interface Signals
Symbol Type Name and Function
EE_DI O
EE_DO I
EE_CS O EEPROM Chip Select. The EEPROM Chip Select signal is used to enable the device.
EE_SK O
EEPROM Data Input. The EEPROM Data Input pin is used for output to the memory
device.
EEPROM Data Output. The EEPROM Data Output pin is used for input from the
memory device. The EE_DO includes an internal pull-up resistor.
EEPROM Serial Clock. The EEPROM Shift Clock provides the clock rate for the
EEPROM interface, which is approximately 1 MHz.
12 Datasheet
Page 20

3.4 Flash Interface Signals
Symbol Type Name and Function
FL_ADDR
[18:0]
FL_CS# O
FL_OE# O
FL_WE# O
FL_DATA
[7:2]
FL_DATA
[1:0]/
LAN_DISA
BLE#
Flash Address Output. The Flash Address Output signals are used for a Flash or Boot
O
ROM device.
Flash Chip Select. The Flash Chip Select signal is used to enable the Flash or Boot
ROM device.
Flash Output Enable. The Flash Output Enable signal is used to enable the Flash
buffers.
Flash Write Enable Output. The Flash Write ENable Output signals are used for write
cycles.
Flash Data I/O. The Flash Data I/O signals are bi-directional and used for Flash data.
TS
These signals include internal pull-up devices.
Flash Data I/O [1:0] / LAN Port Disable. These pins are inputs from the Flash
memory. Alternatively, they can be used to disable the LAN A or LAN B port from a
system Super I/O General (GP) port. (FL_DATA[1] corresponds to LAN B, and
FL_DATA[0], to LAN A.) They have internal pull-up devices. If the 82546GB is not using
TS
Flash functionality, these pins should be connected to external pull-up resistors.
If the pins are used as LAN_DISABLE#, the device transitions to a low power state, and
the corresponding LAN port is disabled when its pin is sampled low on the rising edge
of PCI reset.
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
3.5 Miscellaneous Signals
3.5.1 LED Signals
Symbol Type Name and Function
LED1/ACT# O
LED0/LINK# O Link. Programmable LED indication. Defaults to indicate link connectivity.
LED2/LINK100# O Link100. Programmable LED indication. Defaults to indicate link at 100 Mbps.
LED3/LINK1000# O Link1000. Programmable LED indication. Defaults to indicate link at 1000 Mbps.
3.5.2 Software Definable Signals
Symbol Type Name and Function
SDP[7:6]
SDP[1:0]
TS
Activity. Programmable LED indication. Defaults to flash to indicate transmit or
receive activity.
Software Defi ne d Pin. The Software Defined Pins are reserved and programmable
with respect to input and output capability. These default to input signals upon power-up
but may be configured differently by the EEPROM. The upper four bits may be mapped
to the General Purpose Interrupt bits if they are configured as input signals.
Note: SDP5 is not included in the group of Software Defined Pins.
Datasheet 13
Page 21

82546GB — Networking Silicon
3.6 PHY Signals
3.6.1 Crystal Signals
Symbol Type Name and Function
XTAL1 I
XTAL2 O
Crystal One. The Crystal One pin is a 25 MHz +/- 30 ppm input signal. It can be
connected to either an oscillator or crystal. If a crystal is used, Crystal Two (XTAL2)
must also be connected.
Crystal Two . Crystal Two is the output of an internal oscillator circuit used to drive a
crystal into oscillation. If an external oscillator is used in the design, XTAL2 must be
disconnected.
3.6.2 PHY Analog Signals
Symbol Type Name and Function
REF_A P
MDIA[0]+/- A
MDIA[1]+/- A
MDIA[2]+/- A
MDIA[3]+/- A
REF_B P
Reference A. This Reference signal should be connected to VSS through an external
2.49 KΩ resistor.
Media Dependent Interface A [0].
1000BASE-T: In MDI configuration, MDIA[0]+/- corresponds to BI_DA+/-, and in MDI-X
configuration, MDIA[0]+/- corresponds to BI_DB+/-.
100BASE-TX: In MDI configuration, MDIA[0]+/- is used for the transmit pair, and in MDI-
X configuration, MDIA[0]+/- is used for the receive pair.
10BASE-T: In MDI configuration, MDIA[0]+/- is used for the transmit pair, and in MDI-X
configuration, MDIA[0]+/- is used for the receive pair.
Media Dependent Interface A [1].
1000BASE-T: In MDI configuration, MDIA[1]+/- corresponds to BI_DB+/-, and in MDI-X
configuration, MDIA[1]+/- corresponds to BI_DA+/-.
100BASE-TX: In MDI configuration, MDIA[1]+/- is used for the receive pair, and in MDI-X
configuration, MDIA[1]+/- is used for the transit pair.
10BASE-T: In MDI configuration, MDIA[1]+/- is used for the receive pair, and in MDI-X
configuration, MDIA[1]+/- is used for the transit pair.
Media Dependent Interface A [2].
1000BASE-T: In MDI configuration, MDIA[2]+/- corresponds to BI_DC+/-, and in MDI-X
configuration, MDIA[2]+/- corresponds to BI_DD+/-.
100BASE-TX: Unused.
10BASE-T: Unused.
Media Dependent Interface A [3].
1000BASE-T: In MDI configuration, MDIA[3]+/- corresponds to BI_DD+/-, and in MDI-X
configuration, MDIA[3]+/- corresponds to BI_DC+/-.
100BASE-TX: Unused.
10BASE-T: Unused.
Reference B. This Reference signal should be connected to VSS through an external
2.49 KΩ resistor.
14 Datasheet
Page 22

Networking Silicon — 82546GB
Symbol Type Name and Function
Media Dependent Interface B [0].
1000BASE-T: In MDI configuration, MDIB[0]+/- corresponds to BI_DA+/-, and in MDI-X
configuration, MDIB[0]+/- corresponds to BI_DB+/-.
MDIB[0]+/- A
MDIB[1]+/- A
MDIB[2]+/- A
MDIB[3]+/- A
100BASE-TX: In MDI configuration, MDIB[0]+/- is used for the transmit pair, and in MDI-
X configuration, MDIB[0]+/- is used for the receive pair.
10BASE-T: In MDI configuration, MDIB[0]+/- is used for the transmit pair, and in MDI-X
configuration, MDIB[0]+/- is used for the receive pair.
Media Dependent Interface B [1].
1000BASE-T: In MDI configuration, MDIB[1]+/- corresponds to BI_DB+/-, and in MDI-X
configuration, MDIB[1]+/- corresponds to BI_DA+/-.
100BASE-TX: In MDI configuration, MDIB[1]+/- is used for the receive pair , and in MDI-X
configuration, MDIB[1]+/- is used for the transit pair.
10BASE-T: In MDI configuration, MDIB[1]+/- is used for the receive pair, and in MDI-X
configuration, MDIB[1]+/- is used for the transit pair.
Media Dependent Interface B [2].
1000BASE-T: In MDI configuration, MDIB[2]+/- corresponds to BI_DC+/-, and in MDI-X
configuration, MDIB[2]+/- corresponds to BI_DD+/-.
100BASE-TX: Unused.
10BASE-T: Unused.
Media Dependent Interface B [3].
1000BASE-T: In MDI configuration, MDIB[3]+/- corresponds to BI_DD+/-, and in MDI-X
configuration, MDIB[3]+/- corresponds to BI_DC+/-.
100BASE-TX: Unused.
10BASE-T: Unused.
3.7 Serializer / Deserializer Signals
Symbol Type Name and Function
RXA+/RXB +/-
TXA+/TXB +/-
SIG_
DETECT
(A and B)
SERDES Receive Pairs A and B. These signals make the differential receive pair for
I
the 1.25 GHz serial interface. If the SERDES interface is not used, these pins should
not be connected.
SERDES Transmit Pairs A and B. These signals make the differential transmit pair for
O
the 1.25 GHz serial interface. If the SERDES interface is not used, these pins should
not be connected.
Signal Detects A and B. These pins indicate whether the SERDES signals
(connected to the 1.25 GHz serial interface) have been detected by the optical
I
transceivers. If the SERDES interface is not used, the SIG_DETECT inputs should be
connected to ground using pull-down resistors.
Datasheet 15
Page 23

82546GB — Networking Silicon
3.8 JTAG Test Interface Signals
Symbol Type Name and Function
JTAG_TCK I JTAG Clock.
JTAG_TDI I JTAG TDI.
JTAG_TDO O JTAG TDO.
JTAG_TMS I JTAG TMS.
JTAG_
TRST#
CLK_VIEW O
TEST# I
JTAG Reset. This is an active low reset signal for JTAG. This signal should be
I
terminated using a pull-down resistor to ground. It must not be left unconnected.
Clock View. The Clock View signal is an output of clock signals required for IEEE
testing.
Factory Test Pin. This is an active low input and has an internal pull-up resistor. For
normal operation, TEST# should be left unconnected.
3.9 Power Supply Connections
3.9.1 Power Support Signals
Symbol Type Name and Function
CTRL_15 O
CTRL_25A O
CTRL_25B O
1.5 V Control. The 1.5 V Control signal is an output to an external power transistor. If
regulators are used, it should be left unconnected.
2.5 V Control. The 2.5 V Control signal is an output to an external power transistor. If
regulators are used, it should be left unconnected.
2.5 V Control. The 2.5 V Control signal is an output to an external power transistor. If
regulators are used, it should be left unconnected.
3.9.2 Digital Supplies
Symbol Type Name and Function
VDDO P 3.3 V I/O Power Supply.
DVDD P 1.5 V Digital Core Power Supply.
3.9.3 Analog Supplies
Symbol Type Name and Function
AVDDH P 3.3 V Analog Power Supply.
AVDDLA P 2.5 V Analog Power Supply to Port A.
AVDDLB P 2.5 V Analog Power Supply to Port B.
16 Datasheet
Page 24

3.9.4 Ground and No Connects
Symbol Type Name and Function
GND P Ground.
NC P
Reserved R
No Connect. Do not connect any circuitry to these pins. Pull-up or pull-down resistors
should not be connected to these pins.
Reserved. These pins are reserved for factory purposes and should be left
unconnected. (However, the following pins should be pulled down to ground: A20, B18,
and M5. In addition, the following pins should be pulled down to ground through a 1 KΩ
pull-down resistor: A6, E7 and R1.)
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
Datasheet 17
Page 25

82546GB — Networking Silicon
4.0 Test Port Functionality
4.1 XOR Testing
A common board or system-level manufacturing test for proper electrical continuity between a
silicon component and the board is some type of cascaded-XOR or NAND tree test. The 82546GB
implements an XOR tree spanning most I/O signals. The component XOR tree consists of a series
of cascaded XOR logic gates, each stage feeding in the electrical value from a unique pin. The
output of the final stage of the tree is visible on an output pin from the component.
Figure 2. XOR Tree Concept
By connecting to a set of test-points or bed-of-nails fixture, a manufacturing test fixture can test
connectivity to each of the component pins included in the tree by sequentially testing each pin,
testing each pin when driven both high and low, and observing the output of the tree for the
expected signal value and/or change.
4.1.1 XOR Tree Control and Operation
The following signals are required to place the 82546GB in XOR tree test mode:
Test
Function/
Mode
XOR Tree
Test
Pin Name TEST_DM_N EWRAP CLK_BYP_N CLK_VIEW SDP_B[7]
Dual-Mode
Name
00000
TEST_
MODE[3]
TEST_
MODE[2]
TEST_
MODE[1]
TEST_
MODE[0]
18 Datasheet
Page 26

I/O pins wit h dual-mode func tion for XOR test:
Pin Name Dual-Mode Name Pin Function
FLSH_CE_N XOR_OUT Output of XOR tree.
When XOR tree test is selected, the following pin behavior(s) occur:
• Output drivers for the pins listed as tested are all placed in high-impedance (tri-state) state to
ensure that the board/system test fixture can drive the tested inputs without contention
• The output driver for the XOR tree output on pin FLSH_CE_N is explicitly enabled.
4.1.2 Pins Tested
When performing XOR test, those pins tested by the XOR tree all function as inputs, regardless of
the normal directionality of the pin. The following table(s) cites the pins tested and not-testable as
inputs to the XOR tree. Table entries do not reflect the natural order of input into the XOR tree
itself (nor need to, as the output of a multi-input XOR function is order-independent).
Pins included in XOR test tree are listed in Table 1:
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
T a ble 1. Tested Pins Included in XOR Tree
Pin Name Pin Name Pin Name
PCI_AD[63:0] M66EN RX_DATA[7:0]
PCI_CBE_N[7:0] PCI_RST_N RBC0/RX_CLK
PCI_PAR LAN_PWR_GOOD RBC1/MTX_CLK
PCI_PAR64 PCI_SERR_N EE_DI
PCI_FRAME_N PCI_PERR_N EE_DO
PCI_IRDY_N PCI_PME_N EE_CS
PCI_TRDY_N AUX_PWR EE_SK
PCI_STOP_N SMBCLK FLSH_ADDR[18:0]
PCI_IDSEL SMBDAT FLSH_OE_N
PCI_DEVSEL_N TX_DATA[9]/TX_ER FLSH_WE_N
PCI_REQ64_N TX_DATA[8]/TX_EN FLSH_DATA[7:0]
PCI_ACK64_N TX_DATA[7:0] LED_A[3:0]
PCI_REQ_N GTX_CLK LED_B[3:0]
PCI_GNT_N COL SDP_A[7,6,1,0]
PCI_LOCK_N CRS SDP_B[6,1,0]
PCI_INTA_N LINK/LOS ALTCLK_125
PCI_INTB_N RX_DATA[9]/RX_ER
PCI_CLK RX_DATA[8]/RX_DV
Datasheet 19
Page 27

82546GB — Networking Silicon
Pins not included in XOR test tree:
• JTAG (TAP) interface: TRST_N, TCK, TDO, TMS, and TDO
• Test mode decode controls TEST_DM_N, EWRAP, CLK_BYP_N, CLK_VIEW, and
SDP_B[7]
• Each internal PHY's analog signals including PHYREF, MDI +/-, and PH Y_HS DACP/N
• PCI Impedance Compensation ZPCOMP and ZNCOMP
• Oscillator signals XTAL1 and XTAL2
• Test signals including PHY_TSTPT and each PHY's HSDACP/N
• Power-control pins CTRL_15, CTRL_25_A, and CTRL_25_B
• SMB_ALERT_N/PCI_PWR_GOOD
4.2 Tristate Mode
The 82546GB's tristate test mode is used to explicitly disable output driv ers and place outputs in
high-impedance (tristate) state. To more readily support XOR or NAND-tree like testing of other
system components, the 82546GB decodes this test mode from the same signal pins used to
exercise XOR tree testing. The 82546GB additionally supports a mechanism to enter tristate mode
via the IEEE 802.3 JTAG (TAP) controller.
4.2.1 Tristate Mode Control and Operation
The following signals are required to place the 82546GB in tristate test mode:
Test
Function/
Mode
Tristate
Mode
Pin Name TEST_DM_N EWRAP CLK_BYP_N CLK_VIEW SDP_B[7]
Dual-Mode
Name
00101
TEST_
MODE[3]
When in tristate test mode:
• All output drivers for all digital signal pins are disabled (with the exception of the TDO pin).
• Analog signals such as MDI+/-, analog test points, and regulator controls are unaffected.
4.2.2 Tristate Mode Using JTAG (TAP)
The 82546GB can also be placed in tristate mode using the JTAG interface and the HIGHZ
instruction.
The HIGHZ instruction is used to place the 82546GB in high-impedance (TRISTATE) mode,
where all digital signal outputs are placed in high-impedance (tri-state) output state.
TEST_
MODE[2]
TEST_
MODE[1]
TEST_
MODE[0]
20 Datasheet
Page 28

Networking Silicon — 82546GB
5.0 Voltage, Temperature, and Timing Specifications
Note: The specification values listed in this section are subject to change without notice. Verify with your
local Intel sales office that you have the latest information before finalizing a design.
5.1 Targeted Absolute Maximum Ratings
Table 2. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit
VDD (3.3)
VDD (2.5)
VDD (1.5)
VDD DC supply voltage VSS - 0.5 4.6 V
VI / VO LVTTL input voltage VSS - 0.5 4.6 V
VI / VO 5 V compatible input voltage VSS - 0.5 6.6 V
IO
TSTG Storage temperature range -40 125 C
a. Maximum ratings are referenced to ground (VSS). Permanent device damage is likely to occur if the ratings in this table are
exceeded. These values should not be used as the limits for normal device operations.
b. The maximum value is the lesser value of 4.6 V or VDD(2.5) + 0.5 V. This specification applies to biasing the device to a steady
state for an indefinite duration. During normal device power-up, explicit power sequencing is not required.
c. The maximum value is the lesser value of 4.6 V or VDD(2.5) + 0.5 V.
DC supply voltage on VDDD or
AVDDH with respect to VSS
DC supply voltage on AVDDL with
respect to VSS
DC supply voltage on DVDD with
respect to VSS
DC output current (by cell type):
IOL = 3 mA
IOL = 6 mA
IOL - 12 mA
ESD per MIL_STD-883 Test
Method 3015, Specification 2001V
Latchup Over/Undershoot: 150
mA, 125 C
a
VSS - 0.5 4. 6 V
VSS - 0.5
VSS - 0.5
4.6 or
VDD (2.5) + 0.5
4.6 or
VDD (1.5) + 0.5
10
20
40
VDD overstress:
VDD(3.3)(7.2 V)
b
c
V
V
mA
V
5.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
Table 3. Recommended Operating Conditions
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit
VDD (3.3)
VDD (2.5) DC supply voltage on AVDDL
VDD (1.5) DC supply voltage on DVDD 1.43 1.57 V
VIO PCI bus voltage reference 3.0 5.25 V
DC supply voltage on VDDD or
b
AVDDH
Datasheet 21
a
3.0 3.6 V
c
2.38 2.62 V
Page 29

82546GB — Networking Silicon
Table 3. Recommended Operating Conditions
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit
tR / tF Input rise/fall time (normal input) 0 200 ns
tr/tf input rise/fall time (Schmitt input) 0 10 ms
TA
TJ Junction temperature ≤125 C
a. Sustained operation of the device at conditions exceeding these values, even if they are within the absolute maximum rating
limits, might result in permanent damage.
b. It is recommended for VDDO to equal AVDDH (VDDO = AVDDH) during power-up and normal operation.
c. It is recommended for both VDDO and AVDDH to be of a value greater than AVDDL, with a value greater than DVDD, during
power-up (VDDO or AVDDH > AVDDL > DVDD). However, voltage sequencing is not a strict requirement if the power supply
ramp must be faster than approximately 200 ms.
d. A higher operating temperature of up to 70 C can be achieved using an appropriate thermal management device.
Operating temperature range
(ambient)
d
5.3 DC Specifications
T able 4. DC Characteristics
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units
VDD (3.3)
VDD (2.5)
VDD (1.5)
DC supply voltage on
VDDO or AVDDH
DC supply voltage on
AVDDL
DC supply voltage on
DVDD
a
055C
3.00 3.3 3.60 V
2.38 2.5 2.62 V
1.43 1.5 1.57 V
Table 5.a Power Supply Characteristics
D0a (both ports)
Unplugged/No Link 10 Mbps Operation 100 Mbps Operation 1000 Mbps Operation
Ty p Icc
(mA)
3.3 V 65 85 100 110 115 120 240 265
2.5 V 60 65 80 80 130 135 310 335
1.5 V 180 190 160 170 200 220 740 840
Total
Device
Power
650 mW 800 mW 1.0 W 2.7 W 3.2 W
Max Icc
(mA)
Typ Icc
(mA)
Max Icc
(mA)
Typ Icc
(mA)
Max Icc
(mA)
Typ Icc
(mA)
Max Icc
(mA)
22 Datasheet
Page 30

T able 5.b
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
T able 5.c
D3cold - Wake Up Enabled (both ports)
Unplugged/No Link 10 Mbps Operation 100 Mbps Operation
Typ Icc
(mA)
3.3 V 65 75 100 110 95 120 65 75
2.5 V 65 70 65 70 125 1140 60 65
1.5 V 50 50 60 70 105 130 20 40
Total
Device
Power
3.3 V 75 80 50 55
2.5 V 100 120 50 60
1.5 V 360 385 20 25
Total
Device
Power
450 mW 600 mW 800 mW 400 mW
D(n) Uninitialized
(LAN PWR GOOD = 0)
Typ Icc
(mA)
1.0 W 325 mW
Max Icc
(mA)
Uninitialized/Disabled
Max Icc
(mA)
Typ Icc
(mA)
Disabled
(via Flash Address)
Typ Icc
(mA)
Max Icc
(mA)
Max Icc
(mA)
Typ Icc
(mA)
Max Icc
(mA)
D3cold - Wake Up
Disabled (both ports)
Typ Icc
(mA)
Max Icc
(mA)
T able 5.d
(including magnetics, LED, and regulator circuits)
D3cold / Wake
disabled
Typ Ic c
(mA)
3.3 V 65 75 110 120 115 140 250 275
2.5 V 60 65 85 90 175 190 500 525
1.5 V 20 40 60 70 105 130 740 840
Subsystem
3.3 V
Current
Max Icc
(mA)
180 mA 280 mA 460 mA 1.65 A
D3cold / Wake enabled
Typ Ic c
(mA)
Complete Subsystem
at 10 Mbps
Max Icc
(mA)
D3cold / Wake enabled
at 100 Mbps
Typ Ic c
(mA)
Max Icc
(mA)
D0 at 1000 Mbps
Typ Ic c
(mA)
Max Icc
(mA)
Datasheet 23
Page 31

82546GB — Networking Silicon
T able 5.e
Component Only
Table 5.f
D0a
(SERDES active)
Ty p Icc
(mA)
Max Icc
(mA)
D3cold
Wake Disabled
(SERDES off)
Typ Icc
(mA)
Max Icc
(mA)
3.3 V 110 135 85 95
2.5 V 120 125 leakage leakage
1.5 V 170 240 15 20
Total
Device
900 mW 1.2 W 300 mW 375 mW
Power
Complete Subsystem (SERDES design)
Including LED and Regulator Cir c uits
(no optics)
D3cold
Wake Disabled
(auxiliary power)
Typ Icc
(mA)
Max Icc
(mA)
D0 SERDES Active
(primary power)
Typ Icc
(mA)
Max Icc
(mA)
3.3 V 85 95 110 135
2.5 ~0 ~0 120 125
1.5 V 15 20 170 240
Subsystem
3.3 V
115 mA 500 mA
Current
T a ble 6. I/O Characteristics
Symbol Parameter Condition Min Typ Max Unit
V
IL
V
IH
V
OL
V
OH
V
SH
Voltage input LOW -0.5 0.8 V
V
Voltage input HIGH 2.0
DD
+0.3
Voltage output LOW 0.4 V
Voltage output HIGH 2.4 V
Schmitt Trigger Hysteresis 0.1 V
V
Output current LOW
12
3
6
mA
mA
mA
a
I
OL
3mA drivers (TTL3)
6mA drivers (TTL6)
12mA drivers (TTL12)
V
OL
V
OL
V
OL
24 Datasheet
Page 32

T able 6. I/O Characteristics
Symbol Parameter Condition Min Typ Max Unit
Output current HIGH
a
I
OH
I
IN
I
OZ
C
IN
C
OUT
C
PUD
a. TTL3 signals include: EE_DI, EE_SK, EE_CS, and JTAG_TDO.
TTL6 signals include: FL_CE#, CLK_VIEW, FL_DATA[7:0], FL_ADDR[18:0], FL_OE#, and FL_WE#.
TTL12 signals include: ACT_A#, ACT_B#, LINK_A#, LINK_B#, LEDA100#, LEDB100#, LEDA1000#, and LEDB1000#.
3mA drivers (TTL3)
6mA drivers (TTL6)
12mA drivers (TTL12)
Inputs with pull-down resistors
TTL inputs with pull-up resistors
3-state output leakage current V
Input capacitance
Output capacitance Any output buffer 2.0 pF
Pull-up/down Resistor value 7.5 20 kΩ
Input Current
TTL inputs
V
OH
V
OH
V
OH
= VDD or V
V
IN
V
= VDD
IN
= V
V
IN
SS
= VDD or V
OH
Any input and bi-
directional buffer
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
-3
-6
-12
-10
SS
150
±1
-150
-10 ±110µA
SS
2.5 pF
10
480
-480
mA
mA
mA
µA
µA
µA
5.4 AC Characteristics
T able 7. AC Characteristics: 3.3 V Interfacing
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
fPCICLK Clock frequency in PCI mode 66 MHz
fPCICLK Clock frequency in PCI-X mode 66 133 MHz
Table 8. 25 MHz Clock Input Requirements
Symbol Parameter
fi_TX_CLK TX_CLK_IN frequency 25 - 50 ppm 25
a. This parameter applies to an oscillator connected to the Crystal One (XTAL1) input. Alternatively, a crystal may be connected
to XTAL1 and XTAL2 as the frequency source for the internal oscillator.
Table 9. Link Interface Clock Requirements
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
a
fGTX
a. GTX_CLK is used externally for test purposes only.
GTX_CLK frequency 125 MHz
a
Min Typ Max Unit
25 + 50
ppm
MHz
Datasheet 25
Page 33

82546GB — Networking Silicon
L
Table 10. EEPROM Interface Clock Requirements
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
fSK 1MHz
Table 11. AC Test Loads for General Output Pins
Symbol Signal Name Value Units
CL TDO 10 pF
CL APM_WAKEUP, PME#, SDP[7:6], SDP[1:0] 16 pF
CL
CL RX_ACTIVITY, TX_ACTIVITY, LINK_UP 20 pF
EE_DI, EE_SK, FL_ADDR[18:0], FL_CS#, FL_OE#,
FL_WE#, FL_DATA[7:0]
Figure 3. AC Test Loa ds for General Output Pins
18 pF
5.5 Serial Interface Specifications
Table 12. Driver Characteristics
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units
V
OD
V
Output Offset Voltage 1075 1325 mV
OS
Delta V
R
O
I
, ISB
SA
I
SAB
a. T his is th e maxim um insi de dime nsion of th e eye pat tern, m easure d on high and lo w data pa t-
terns with pre-emphasis present. Load = 100 Ω.
b. This is defined as an absolute value of amplitude jitter.
Differential Output
Voltage Swing
Change in V
OD
b
and 1
Differential Output
Impedance
Output Current on Short
to VSS
Output Current when A
and B are Shorted
a
between 0
OD
875 1325
80 120 Ω
C
mV
peak-
peak
25 mV
40 mA
12 mA
26 Datasheet
Page 34

T able 13. Receiver Characteristics
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Un its
V
ID
R
IN
Differential Input Voltage
Swing
Differential Input
Impedance
5.6 Timing Specifications
5.6.1 PCI/PCI-X Bus Interface
5.6.1.1 PCI/PCI-X Bus Interface Clock
T a ble 14. PCI/PCI-X Bus Interface Clock Parameters
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
100 2000
80 120 Ω
peak-
mV
peak
Symbol Parameter
a
TCYCCLK cycle time 7.5201520153030 ns
TH CLK high time 3 6 6 11 ns
TL CLK low time 3 6 6 11 ns
CLK slew rate 1.541.541.54 1 4 V/ns
RST# slew ra te
a. Rise and fall times are specified in terms of the edge rate measured in V/ns. This slew rate must be met across the minimum
peak-to-peak portion of the clock waveform as shown.
b. The minimum RST# slew rate applies only to the rising (de-assertion) edge of the reset signal and ensures that system noise
cannot render a monotonic signal to appear bouncing in the switching range.
b
Figure 4. PCI/PCI-X Clock Timing
3.3 V Clock
0.5 Vcc
0.4 Vcc
0.3 Vcc
PCI-X 133
MHz
PCI-X 66 MHz PCI 66MHz PCI 33 MHz
Units
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
50 50 50 50 mV/ns
Tcyc
Th
0.6 Vcc
0.4 Vcc p-to-p
(minimum)
0.2 Vcc
Tl
Datasheet 27
Page 35

82546GB — Networking Silicon
5.6.1.2 PCI/PCI-X Bus Interface Timing
Table 15. PCI/PCI-X Bus Interface Timing Parameters
PCI-X 133
Symbol Parameter
TVAL
TVAL
(ptp)
TONFloat to active delay0022ns
TOFF Active to float delay 7 7 14 28 ns
TSU
TSU
(ptp)
TH Input hold time from CLK 0.5 0.5 0 0 ns
TRRSU
TRRH
NOTES:
1. Output timing measurements are as shown.
2. REQ# and GNT# signals are point-to-point and have different output valid delay and input setup times than
bussed signals. GNT# has a setup of 10 ns; REQ# has a setup of 12 ns. All other signals are bussed.
3. Input timing measurements are as shown.
CLK to signal valid delay:
bussed signals
CLK to signal valid delay:
point-to-point signals
Input setup time to CLK:
bussed signals
Input setup time to CLK:
point-to-point signals
REQ64# to RST# setup
time
RST# to REQ64# hold
time
MHz
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
0.7 3.8 0.7 3.8 2 6 2 11 ns
0.7 3.8 0.7 3.8 2 6 2 12 ns
1.2 1.7 3 7 ns
1.2 1.7 5
10*
TCYC
0000ns
PCI-X 66 MHz PCI 66MHz PCI 33 MHz
10,
12
10*
TCYC
10*
TCYC
10*
TCYC
Units
ns
ns
Table 13. PCI Bus Interface Timing Measurement Conditions
Symbol Parameter PCI-X
VTH Input measurement test voltage (high) 0.6*VCC 0.6*VCC V
VTL Input measurement test voltage (low) 0.25*VCC 0.2*VCC V
VTEST Output measurement test voltage 0.4*VCC 0.4*VCC V
Input signal slew rate 1.5 1.5 V/ns
PCI 66 MHz
3.3 v
Unit
28 Datasheet
Page 36

Figure 5. PCI Bus Interface Output Timing Measurement
)
t
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
V
TH
PCI_CLK
Output
Delay
V
TEST
output current≤ leakage current
V
V
TEST
STEP
Tri-State
Output
T
ON
T
OFF
Figure 6. PCI Bus Interface Input Timing Measurement Conditions
PCI_CLK
T
SU
V
TH
Input V
V
TL
V
TEST
Input
Valid
V
T
TEST
H
V
(3.3V Signalling
TEST
V
TL
V
TH
V
TL
MAX
Figure 7. TVAL (max) Rising Edge Test Load
Pin
1/2 inch max.
25Ω
10 pF
Test
Poin
Datasheet 29
Page 37

82546GB — Networking Silicon
t
Figure 8. TVAL (max) Fa lling Edge Test Load
Pin
5.6.2 Link In terface Timing
5.6.2.1 Link Interface Rise and Fall Time
Table 16. Rise and Fall Times
Symbol Parameter Condition Min Max Unit
TR Clock rise time 0.8 V to 2.0 V 0.7 ns
TF Clock fall time 2.0 V to 0.8 V 0.7 ns
TR Data rise time 0.8 to 2.0 V 0.7 ns
TF Data fall time 2.0 V to 0.8 V 0.7 ns
1/2 inch max.
10 pF
25Ω
V
Test
Poin
CC
30 Datasheet
Page 38

Figure 9. Link Interface Rise/Fall Timing
V
2.0 V
0.8 V
5.6.2.2 Link Interface Transmit Timing
Figure 10. Transmit Interface Timing
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
T
T
R
F
TX_CLOCK
TX_DATA[9:0] Valid Data
T a ble 17. Transmit Interface Timing
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
TPERIOD
TSETUP Data setup to rising GTX_CLK 2.5 ns
THOLD Data hold from rising GRX_CLK 1.0 ns
TDUTY GTX_CLK duty cycle 40 60 %
a. GTX_CLK should have a 100 ppm tolerance.
GTX_CLK period
TBI mode (1000 Mbps)
1.4
T
SU
T
PERIOD
a
T
H
8ns
Datasheet 31
Page 39

82546GB — Networking Silicon
5.6.2.3 Link Interface Receive Timing
Figure 11. Receive Interface Timing
RBC1
2.0V
RX_DATA[9:0]
0.8V
2.0V
COM_DET
0.8V
RBC0
T a ble 18. Receive Interface Timing
T
SU
COMMA
Code_Group
T
A-B
1.4V
T
H
Valid
Data
T
T
SU
H
1.4V
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
TREQ
TSETUP D ata setup before rising RBC0/RBC1 2.5 ns
THOLD Data hold after rising RBC0/RBC1 1 ns
TDUTY RBC0/RBC1 duty cycle 40 60 %
TA-B RBC0/RBC1 skew 7.5 8.5 ns
RBC0/RBC1 frequency
TBI mode (1000 Mbps)
62.5 MHz
32 Datasheet
Page 40

5.6.3 Flash Inter f ace
0ns
250ns
0ns
250ns
500ns
Figure 12. Flash Read Timing
Flash WE#
Flash Address [18:0]
Table 19. Flash Read Operation Timing
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
Flash CE#
Flash OE#
Flash Data
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
TCE Flash CE# or OE# to read data delay 160 ns
TACC Flash address setup time 160 ns
THOLD Data hold time 0 ns
Figure 13. Flash Write Timing
Flash Address [18:0]
Flash CE#
Flash OE#
Flash WE#
Flash Data
Datasheet 33
Page 41

82546GB — Networking Silicon
T a ble 20. Flash Write Operation Timing
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
TWE Flash write pulse width (WE#) 160 ns
TAH Flash address hold time 0 ns
TDS Flash data setup time 160 ns
5.6.4 EEPROM Interface
T a ble 21. Link Interface Clock Requirements
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
TPW EE_SK pulse width
T a ble 22. Link Interface Clock Requirements
Symbol Parameter
TDOS EE_D O setup time TCYC*2 ns
TDOH EE_DO hold time 0 ns
a. The EE_DO setup and hold time is a function of the CLK cycle time but is referenced to O_EE_SK.
a
TPERIOD*128 ns
Min Typ Max Unit
34 Datasheet
Page 42

6.0 Package and Pinout Information
Intel (C)'ZZ
6.1 Device Identification
Figure 14. 82546GB Device Identification Markings
(R)
FW82546GB
YYWW
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
Tnnnnnnnn
Country
82546GB Product Name
FW82546GB Intel Product Number
(c)’ZZ Copyright Information
YYWW Date Code
Tnnnnnnnn Lot Trace Code
Country Country of Origin Assembly
NOTE: The black mark in the lower left corner indicates the location of pin 1.
Datasheet 35
Page 43

82546GB — Networking Silicon
6.2 Package Information
The 82546GB device is a 364-lead ball grid array (BGA) measuring 21 mm2. The package
dimensions are detailed in the figures below. The nominal ball pitch is 1 mm.
Figure 15. 82546GB 364-Lead BGA Ball Pad Dimensions
0.50 mm +/- 0.05 mm
Solder Mask Opening
0.65 mm +/- 0.05 mm
Pad Size
Detail Area
36 Datasheet
Page 44

Figure 16. 82546GB Mechanical Specifications
0.40
2.03
20.80
0.51
1.12
0.50
20.80
18.80
18.80
BODY EDGE.
BETWEEN THE EDGE OF THE SOLDER BALL AND THE
4. THERE SHALL BE A MINIMUM CLEARANCE OF 0.25 mm
BALL DIAMETER, PARALLEL TO PRIMARY DATUM C.
3. DIMENSION b IS MEASURED AT THE MAXIMUM SOLDER
2. PRIMARY DATUM C AND SEATING PLANE ARE DEFINED
BY THE SPHERICAL CROWNS OF THE SOLDER BALLS.
1. CONTROLLING DIMENSION: MILLIMETER.
E2
E1
D
B
C
B
A
1
-B-
D1
11
10
68
7
9
12
13
3
2
4
5 19
18
20
14
16
15
17
V
N
M
L
K
J
H
G
F
R
PUT
E
W
Y
-A-
e
D
D3
D2
DETAIL A'
A'
A2
O
DETAIL B'
-C-
A1
2
A
NOTE:
ddd
C
C
eee
fff
O
ddd
bbb
aaa
E3
e
E3
E
E2
3
CSC
S
fff
eee
AB
D3
E
E1
D2
D
C
b
A2
D1
A
A1
Symbol
0.7480.740 0.75619.00 19.20
0.25
0.10
0.15
15.00
1.0 BASIC
0.20
0.25
0.004
0.010
0.006
0.039 BASIC
0.010
0.008
0.591
0.819
0.020
0.044
0.020
0.819
0.740
21.00
19.00 BSC
15.00
19.00
21.20
19.20
21.00
19.00 BSC
0.56
0.60
1.17
21.20
0.61
1.22
0.70
0.748 BSC
0.827
0.748
0.591
0.835
0.756
0.748 BSC
0.827
0.022
0.024
0.046
0.835
0.024
0.048
0.028
MIN
0.016
0.080
dimension in inchdimension in mm
0.50
2.23
NOMMIN
0.60
2.43
MAX
0.020
0.088
NOM
0.024
0.096
MAX
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
Datasheet 37
Page 45

82546GB — Networking Silicon
6.3 Thermal Spe cifications
The 82546GB Gigabit Ethernet controller i s speci fied for operation when the ambient temperature
(TA) is within the range of 0° C to 55° C. The maximum permitted junction temperature is 125° C.
TC (case temperature) is calculated using the equation:
TC = TA + P (θ
TJ (junction temperature) is calculated using the equation:
TJ = TA + P θ
The power consumption (P) is calculated by using the typical ICC and nominal VCC. The thermal
resistances are shown in Table 23 .
T able 23. Thermal Characteristics
JA
JA
- θJC)
Symbol Parameter
θ
JA
θ
JC
Thermal resistance, junction-toambient
Thermal resistance, junction-tocase
Value at specified airflow (m/s)
Units
0123
17.7 15.6 14.8 14.0 C/Watt
6.8 6.8 6.8 6.8 C/Watt
Thermal resistances are determined empirically with test devices mounted on standard thermal test
boards. Real system designs may have dif ferent characteristics due to board thickness, arrangement
of ground planes, and proximity of other components. The case temperature measurements should
be used to assure that the 82546GB Gigabit Ethernet controller is operating under recommended
conditions.
The use of a heat sink device can enhance the overall
θ
of the solution in situations where
JA
tolerance of higher overall ambient air temperatures is desired. Intel does not qualify or
recommend any specific heat sink dev ice for u se with the 8 2546GB Gigabi t Eth ernet cont roller but
can provide a thermal report mod eling a g eneric heat sink d evice and the
θ
that might be achieved
JA
with the use of a heat sink device. Refer to the 82546EB/GB Gigabit Ethernet Controller Thermal
Properties with External Heat Sink Application Note for more information.
38 Datasheet
Page 46

6.4 Ball Mapping Diagram
V
W
Note: The 82546GB device uses five categories of VDD connections: VDDO (3.3 V), AVDDH (Analog
3.3 V), AVDDL (Analog 2.5 V), and DVDD (1.5 V).
1234567891011121314151617181920
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
Y
Datasheet 39
Page 47

82546GB — Networking Silicon
6.5 Pinout Information
Table 24. PCI Address, Data, and Control Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin
PCI_AD[0] T14 PCI_AD[28] Y3 PCI_AD[56] T17
PCI_AD[1] V14 PCI_AD[29] U4 PCI_AD[57] U18
PCI_AD[2] Y15 PCI_AD[30] V3 PCI_AD[58] V18
PCI_AD[3] W14 PCI_AD[31] V1 PCI_AD[59] U16
PCI_AD[4] T13 PCI_AD[32] L16 PCI_AD[60] V17
PCI_AD[5] V13 PCI_AD[33] M20 PCI_AD[61] W18
PCI_AD[6] Y14 PCI_AD[34] M19 PCI_AD[62] Y19
PCI_AD[7] U12 PCI_AD[35] M16 PCI_AD[63] T16
PCI_AD[8] V12 PCI_AD[36] M18 CBE[0]# Y13
PCI_AD[9] T12 PCI_AD[37] M17 CBE[1]# V10
PCI_AD[10] W12 PCI_AD[38] N20 CBE[2]# T8
PCI_AD[11] Y12 PCI_AD[39] N16 CBE[3]# Y4
PCI_AD[12] V11 PCI_AD[40] P20 CBE[4]# V16
PCI_AD[13] T11 PCI_AD[41] N18 CBE[5]# Y18
PCI_AD[14] Y11 PCI_AD[42] P19 CBE[6]# Y17
PCI_AD[15] W10 PCI_AD[43] P16 CBE[7]# T15
PCI_AD[16] U8 PCI_AD[44] R20 PAR U10
PCI_AD[17] Y7 PCI_AD[45] P18 PAR64 V15
PCI_AD[18] Y6 PCI_AD[46] P17 FRAME# V8
PCI_AD[19] V7 PCI_AD[47] T20 IRDY# W8
PCI_AD[20] T7 PCI_AD[48] R16 TRDY# Y8
PCI_AD[21] W 6 PCI_AD[49] U20 STOP# V9
PCI_AD[22] Y5 PCI_AD[50] R18 IDSEL T6
PCI_AD[23] V6 PCI_AD[51] T19 DEVSEL# T9
PCI_AD[24] U6 PCI_AD[52] V20 VIO Y1
PCI_AD[25] V5 PCI_AD[53] T18 VIO Y20
PCI_AD[26] W4 PCI_AD[54] W20
PCI_AD[27] V4 PCI_AD[55] V19
Table 25. PCI Arbitration Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin
REQ64# U14 REQ# W2 LOCK# Y9
ACK64# W16 GNT# T3
40 Datasheet
Page 48

Table 26. Interrupt Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin
INTA# Y2 INTB# T1
T able 27. System Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin
PCICLK U2 PCIRST# T5
M66EN Y16 LAN_PWR_GOOD A17
Table 28. Error Reporting Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin
SERR# T10 PERR# Y10
Table 29. Power Management Signals
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
Signal Pin Signal Pin
PME# T4 AUX_PWR R3
Table 30. Impedance Compensation Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin
ZN_COMP T2 ZP_COMP R5
Table 31. SMB Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin
SMBCLK A14 SMBDATA A15 SMBALRT# A16
T able 32. EEPROM Interface Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin
EE_DI C19 EE_CS C20
EE_DO B20 EE_SK D20
Datasheet 41
Page 49

82546GB — Networking Silicon
T able 33. Flash Interface Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin
FL_ADDR[0] F16 FL_ADDR[10] G17 FL_OE# K18
FL_ADDR[1] E18 FL_ADDR[11] G 16 FL_W E# C17
FL_ADDR[2] E16 FL_ADDR[12] B15
FL_ADDR[3] E15 FL_ADDR[13] D19
FL_ADDR[4] E14 FL_ADDR[14] D18 FL_DATA[2] J16
FL_ADDR[5] E13 FL_ADDR[15] C15 FL_DATA[3] H18
FL_ADDR[6] D15 FL_ADDR[16] D16 FL_DATA[4] J17
FL_ADDR[7] B16 FL_ADDR[17] C18 FL_DATA[5] J18
FL_ADDR[8] F17 FL_ADDR[18] D17 FL_DATA[6] K17
FL_ADDR[9] F18 FL_CS# H20 FL_DATA[7] K16
Table 34. LED Signals
FL_DATA[0] /
LAN_A_DISABLE
FL_DATA[1] /
LAN_B_DISABLE
H16
G18
Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin
ACT_A# N1 LINKA1000# N3 LINKB100# C14
LINK_A# M1 ACT_B# B13 LINKB1000# C13
LINKA100# N4 LINK_B# A13
Table 35. Software Definable Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin
SDPA[0] G4 SDPB[0] D13
SDPA[1] G5 SDPB[1] B12
SDPA[6] E12 SDPB[6] C12
SDPA[7] E11 SDPB[7] D12
Table 36. Crystal Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin
XTAL1 A3 XTAL2 A4
Table 37. PHY Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin
REF_A E3 MDIA2- D1 MDIB1- L1
REF_B L4 MDIA2+ D2 MDIB1+ K1
MDIA0- B1 MDIA3- E1 MDIB2- J2
42 Datasheet
Page 50

Table 37. PHY Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin
MDIA0+ B2 MDIA3+ E2 MDIB2+ J1
MDIA1- C1 MDIB0- L3 MDIB3- H3
MDIA1+ C2 MDIB0+ K3 MDIB3+ J3
Table 38. Serializer / Deserializer Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin
RXA+ G19 TXA+ F19 SIG_DETECT_A E20
RXA- G20 TXA- F20 SIG_DETECT_B L20
RXB+ J19 TXB+ K19
RXB- J20 TXB- K20
T able 39. JTAG Test Interface Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin
JTAG_TCK P1 JTAG_TMS P5 CLK_VIEW P3
JTAG_TDI P4 JTAG_RST# N5 TEST# A8
JTAG_TDO P2
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
Table 40. Power Support Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin
CTRL_15 A18 CTRL_25A F2 CTRL_B H5
Datasheet 43
Page 51

82546GB — Networking Silicon
Table 41. Digital Power Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin
VDDO (3.3V) B8 VDDO (3.3V) U7 DVDD (1.5V) H13
VDDO (3.3V) B14 VDDO (3.3V) - PLL U11 DVDD (1.5V) H14
VDDO (3.3V) B19 VDDO (3.3V) U15 DVDD (1.5V) J7
VDDO (3.3V) C10 VDDO (3.3V) U19 DVDD (1.5V) J14
VDDO (3.3V) C16 VDDO (3.3V) W1 DVDD (1.5V) M7
VDDO (3.3V) D6 VDDO (3.3V) W5 DVDD (1.5V) M14
VDDO (3.3V) D11 VDDO (3.3V) W9 DVDD (1.5V) N7
VDDO (3.3V) E17 VDDO (3.3V) W13 DVDD (1.5V) N 8
VDDO (3.3V) - PHY B H4 VDDO (3. 3V) W17 DVDD (1.5V) N13
VDDO (3.3V) H19 DVDD (1.5V) G7 DVDD (1.5V) N14
VDDO (3.3V) L17 DVDD (1.5V) G8 DVDD (1.5V) P7
VDDO (3.3V) M2 DVDD (1.5V) G9 DVDD (1.5V) P8
VDDO (3.3V) N19 DVDD (1.5V) G12 DVDD (1.5V) P9
VDDO (3.3V) R4 DVDD (1.5V) G13 DVDD (1.5V) P12
VDDO (3.3V) R17 DVDD (1.5V) G14 DVDD (1.5V) P13
VDDO (3.3V) U1 DVDD (1.5V) H7 DVDD (1.5V) P14
VDDO (3.3V) U3 DVDD (1.5V) H8
Table 42. Analog Power Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin
AVDDH (3.3 V) B4 AVDDLA (2.5 V) G1 AVDDLB (2.5 V) L2
AVDDH (3.3 V) - PHY A F1 AVDDLA (2.5 V) G2 AVDDLB (2.5 V) L5
AVDDLA (2.5 V) A19 AVDDLA (2.5 V) G3 AVDDLB (2.5 V) L18
44 Datasheet
Page 52

Table 43. Grounds and No Connect Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin
GND A1 GND K2 GND
GND A2 GND K4 GND
GND A5 GND K5 GND
GND A10 GND K7 GND
GND B3 GND K8 GND
GND B6 GND K9 GND
GND B11 GND K10 GND
GND B17 GND K11 GND
GND C3 GND
GND D3 GND
GND D8 GND
GND D14 GND
GND E19 GND
GND F3 GND
GND G10 GND
GND G11 GND
GND H2 GND
GND H9 GND
GND H10 GND
GND H11 GND
GND H12 GND
GND H17 GND
GND J8 GND
GND J9 GND
GND J10 GND
GND J11 GND
GND J12 GND
GND J13 GND
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
N10
N11
N12
N17
P10
P11
R2
R19
K12 GND U5
K13 GND U9
K14 GND U13
L7 GND U17
L8 GND V2
L9 GND W3
L10 GND W7
L11 GND W11
L12 GND W15
L13 GND W19
L14 NC A11
L19 NC A12
M4 NC F4
M8 NC F5
M9 NC H1
M10 NC J4
M11 NC J5
M12 NC M3
M13 NC N2
N9
Datasheet 45
Page 53

82546GB — Networking Silicon
Table 44. Reserved Signals
Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin
Reserved[0] D4 Reserved[10] E10 Reserved[20] A9
Reserved[1] D5 Reserved[11] B7 Reserved[21] C11
Reserved[2] C4 Reserved[12] A7 Reserved[22] B10
Reserved[3] E4 Reserved[13] C8 Reserved[23] C6
Reserved[4] C5 Reserved[14] E8 Reserved[24] A20
Reserved[5] E5 Reserved[15] E9 Reserved[25] B18
Reserved[6] B5 Reserved[16] D9 Reserved[26] M5
Reserved[7] E6 Reserved[17] C9 Reserved[27] E7
Reserved[8] D7 Reserved[18] B9 Reserved[28] A6
Reserved[9] C7 Reserved[19] D10 Reserved[29] R1
46 Datasheet
Page 54

Note: This page intentionally left blank.
Networking Silicon — 82546GB
Datasheet 47
Page 55

82546GB — Networking Silicon
48 Datasheet
 Loading...
Loading...