Page 1

iSeries
iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map
Version 5
SA41-5155-05
Page 2

Page 3

iSeries
iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map
Version 5
SA41-5155-05
Page 4
Note
Before using this information and the product it supports, be sure to read the information in
“Appendix D. Notices” on page 45.
Sixth Edition (May 2001)
This edition replaces SA41-5155-04. This edition applies only to reduced instruction set computer (RISC) systems.
© Copyright International Business Machines Corporation 1997, 2001. All rights reserved.
US Government Users Restricted Rights – Use, duplication or disclosure restricted by GSA ADP Schedule Contract
with IBM Corp.
Page 5

Contents
iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map,
SA41–5155–05 ............v
Who Should Read This Book .........v
Conventions and Terminology Used in This Book . . v
Prerequisite and related information ......vii
OperationsNavigator..........viii
How to send your comments ........viii
Chapter 1. Overview of RISC-to-RISC
Upgrades and Data Migrations .....1
What is in this Road Map? .........1
Why Upgrade from one AS/400 or iSeries 400 Server
to Another iSeries 400 Server? ........2
What is an Upgrade? ...........2
Upgrade process flow ..........2
Hardware Investment for Upgrading ......3
How Long will the Upgrade Take? .......3
WhatisaDataMigration?..........3
Data migration process flow ........4
How Long will the Data Migration Take?.....5
Books to Use for Software Release Upgrades . . . 5
Chapter 2. Planning Your Order for
Upgrading or Data Migration ......7
Determining Your Upgrade Needs .......7
Performance Tools for Capacity Planning and
Performance Analysis ..........7
How to Gather Configuration Information . . . 8
How to Gather Performance Information ....8
Prerequisites Before Placing an Order ......9
Version 4 Software Items .........9
Other Software Related Items ........9
HardwareConsiderations.........9
System Configuration Considerations.....10
Services and Other Assistance .......10
Model-specific Considerations for Placing an Order 11
Upgrading from a 4xx, 5xx, Sxx, or 6xx to a 7xx 12
Migratingfroma5xxtoan8xx........13
Upgrading from a 6xx or 7xx to an 8xx .....14
Placing the Upgrade Order .........14
Who is Responsible for Ordering the Upgrade? 14
HowtoGetHelpwiththeOrder......15
SendingtheOrdertoIBM........15
Sending the Order to a Software Service Provider
Other Than IBM ............15
Preparing the Current System ........18
Preparing for System Assurance prior to
hardware upgrade ...........20
System Assurance Checkpoint .......23
Installing the Hardware for the RISC-to-RISC
Upgrade ...............24
Managing your new system I/O resources ....24
Performing a new system backup .......28
Chapter 4. Procedure for a Data
Migration (RISC-to-RISC) .......31
Prerequisites for data migration (RISC to RISC) . . 31
Preparing the source system for the migration . . . 31
Datamigration(RISC-to-RISC)........32
Appendix A. AS/400 Global Services . . 35
iSeries and AS/400 Data Migration Services . . . 35
LPAR Planning and Implementation Services . . . 35
iSeries Planning and Migration Services .....35
System Migration Services .........35
Related Support Services ..........36
AS/400 Solution Services ..........36
Installation Services ..........36
Performance Examinations ........36
Consulting Services...........36
Midrange Enhanced Software Service (MRESS) 37
Appendix B. Considerations and
Solutions..............39
IBM HTTP Server for AS/400 ........39
Operations Console............40
OptiConnect ..............40
Integrated Netfinity Server .........40
Clustering and Logical Partitions .......40
Lotus Notes Enhanced Integration .......40
OnDemand ..............40
SRC A900 2000 Recovery ..........40
How to Move Files That Have Been Saved with
Storage Free Specified ...........41
How to Move Freed Database Files without New
Members..............41
Appendix C. Obtain the Latest
Preventive Service Planning
Information .............43
Chapter 3. Procedure for an Upgrade
(RISC-to-RISC) ...........17
Who is Responsible for Upgrading the System. . . 17
What to Do When the Hardware Arrives ....18
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1997, 2001 iii
Appendix D. Notices .........45
Trademarks..............46
Index ...............49
Page 6

iv iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 7

iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map, SA41–5155–05
Use this book as a guide for planning and conducting an upgrade or data
migration, from one iSeries 400 or AS/400 reduced instruction set computer (RISC),
to another RISC model.
For information on supported releases, see
http://as400service.ibm.com/supporthome.nsf/document/17623433
See “Prerequisite and related information” on page vii for a list of other required
and recommended publications.
Who Should Read This Book
This road map is for anyone who is considering an upgrade for an iSeries server or
is involved in migrating data from one RISC model to another RISC model. This
audience includes:
v Customers
v Hardware services personnel
v Software services personnel
v Business partners
v Marketing representatives
Everyone involved in the model upgrade or data migration needs to know all of
the information in this book.
Each customer should have a Customer Account Team Leader. This team leader
can be a Hardware Service Representative, Software Service Representative,
Business Partner, or Marketing Representative. The Availability Center usually
assigns a Customer Account Team Leader.
Conventions and Terminology Used in This Book
This road map identifies activities, programs, tools, and references that you can use
to upgrade the model.
As you read this book, you should be aware of the following terms:
v The terms source system and target system are used throughout this manual.
The source system is the system you are upgrading from. The target system is
the system you are upgrading to.
v The term Marketing Representative can mean either an IBM Marketing
Representative,aBusiness Partner,oraServices Specialist.
v The term 1xx includes Model 150 or 170.
v The term 2xx includes Model 250 or 270.
v The term 4xx includes Model 400, 40S, or 436.
v The term 5xx includes Model 50x, 50S, 510, or 530.
v The term Sxx includes Model S10, S20, S30, S40, SB1, SB2, or SB3.
v The term 6xx includes Model 600, 620, 640, or 650.
v The term 7xx includes Model 720, 730, or 740.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1997, 2001 v
Page 8

v The term 8xx includes Model 820, 830, or 840.
v The term iSeries or iSeries 400 as used in this document refers to the new
generation of (previously AS/400) systems and servers positioned for e-business:
e-systems and e-servers, for example Model 170.
v The term iSeries server as used in this document refers to:
– iSeries system- Models 40x, 5x0, 150 and 6x0.
– iSeries server- Models 40S, 5xS, Sxx, 170, 2xx, 7xx and 8xx.
v The term System Products Division (SPD) book-type adapter cards includes all
adapter cards that are not Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) adapter
cards.
In this publication, the version, release, and modification levels are shown in a
shortened form:
V4R4M0 Version 4 Release 4 Modification 0
V4R5M0 Version 4 Release 5 Modification 0
V5R1M0 Version 5 Release 1 Modification 0
V4R4 Version 4 Release 4 Modification (any)
V4R5 Version 4 Release 5 Modification (any)
V5R1 Version 5 Release 1 Modification (any)
Version 5 Any version 5 release, such as, V5R1M0.
Version 4 Any version 4 release, such as, V4R1M0, V4R2M0 or V4R3M0.
Attention:
Is used in this book to indicate that a step, or process may cause loss of data.
Namely: Installing incorrect versions of the operating system.
CAUTION:
Is used in this book to indicate possible damage to the system.
Namely: Static damage to component.
DANGER
Is used in this book to indicate possible damage to the users and equipment.
Namely: Electrical shock.
In any position that contains numerals, an x = any supported value, for example
SFxxxxx,orVxRxMx.
Examples of displays might contain only pertinent information to a topic. So, some
display examples do not show all text and lines, especially blank lines.
vi iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 9

Prerequisite and related information
Use the iSeries Information Center as your starting point for looking up iSeries and
AS/400e technical information. You can access the Information Center two ways:
v From the following Web site:
http://www.ibm.com/eserver/iseries/infocenter
v From CD-ROMs that ship with your Operating System/400 order:
iSeries Information Center, SK3T-4091-00. This package also includes the PDF
versions of iSeries manuals, iSeries Information Center: Supplemental Manuals,
SK3T-4092-00, which replaces the Softcopy Library CD-ROM.
The iSeries Information Center contains advisors and important topics such as CL
commands, system application programming interfaces (APIs), logical partitions,
clustering, Java, TCP/IP, Web serving, and secured networks. It also includes links
to related IBM Redbooks and Internet links to other IBM Web sites such as the
Technical Studio and the IBM home page.
With every new hardware order, you receive the following CD-ROM information:
v iSeries 400 Installation and Service Library, SK3T-4096-00. This CD-ROM contains
PDF manuals needed for installation and system maintenance of an IBM ~
iSeries 400 server.
v iSeries 400 Setup and Operations CD-ROM, SK3T-4098-00. This CD-ROM contains
IBM iSeries Client Access Express for Windows and the EZ-Setup wizard. Client
Access Express offers a powerful set of client and server capabilities for
connecting PCs to iSeries servers. The EZ-Setup wizard automates many of the
iSeries setup tasks.
Your RISC-to-RISC upgrade or data migration requires the following publications:
v This book. The online version of this book is on the iSeries Information Center
http://www.ibm.com/eserver/iseries/infocenter
under the System Planning and Installation topic.
v iSeries Information Center, SK3T-4091-00 is required for logical partition
information along with many other topics.
v Software Installation, SC41-5120-05 is required for the software upgrade. A PDF
version of this manual is available from the iSeries Information Center under
System planning and installation -> Hardware and software -> Software and
licensed programs -> Install software
v Physical Planning in the iSeries Information Center under Getting Started with
iSeries -> Planning ->Physical planning for your new system.
http://www.ibm.com/eserver/iseries/infocenter
v Getting started with iSeries topic under System planning and installation in the
Information Center.
v The Backup and Recovery manual is available in PDF format from the iSeries
Information Center (under Systems Management -> Backup, recovery, and
availability -> Manuals and Redbooks) and is shipped with your order.
v iSeries Model 270, 8xx, SB2, and SB3 System Installation and Upgrade, SY44-5966-01.
v iSeries 400 Model 830, 840, SB2 and SB3 Problem Analysis, Repair and Parts,
SY44-5969.
v iSeries 400 Model 270 and 820 Problem Analysis, Repair and Parts, SY44-5967.
v Operations Console Setup, SC41-5508-02.
iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map, SA41–5155–05 vii
Page 10

For information about Logical Partitioning, see the LPAR web site at:
www.as400.ibm.com/LPAR
For information about working with PTFs, see the Managing fixes topic in the
Information Center under System planning and installation -> Getting started
with iSeries -> Managing system operations.
For information about other AS/400 publications (except Advanced 36), see the
following:
v Prior to V4R4, the Publications Reference, SC41-5003, in the AS/400 Softcopy
Library.
v The AS/400 Information Directory is a unique, multimedia interface to a
searchable database. It contains descriptions of titles available from IBM or from
other selected publishers. It comes with the OS/400 operating system at no extra
charge.
v iSeries Information Center: Supplemental Manuals, SK3T-4092-00.
An upgrade might require the use the following publications:
v Operations Console Setup, SC41-5508-02
v BEST/1 Capacity Planning Tool, SC41-5341-01
v LPS: OnDemand for AS/400, GC41-5079-01
v OptiConnect for OS/400, SC41-5414-02
Operations Navigator
IBM Operations Navigator is a powerful graphical interface for managing your
iSeries 400 servers. Operations Navigator functionality includes system navigation,
configuration, planning capabilities, and online help to guide you through your
tasks. Operations Navigator makes operation and administration of the server
easier and more productive and is the only user interface to the new, advanced
features of the OS/400 operating system. It also includes Management Central for
managing multiple servers from a central server.
For more information on Operations Navigator, see the iSeries Information Center.
How to send your comments
Your feedback is important in helping to provide the most accurate and
high-quality information. If you have any comments about this book or any other
iSeries documentation, fill out the readers’ comment form at the back of this book.
v If you prefer to send comments by mail, use the readers’ comment form with the
address that is printed on the back. If you are mailing a readers’ comment form
from a country other than the United States, you can give the form to the local
IBM branch office or IBM representative for postage-paid mailing.
v If you prefer to send comments by FAX, use either of the following numbers:
– United States, Canada, and Puerto Rico: 1-800-937-3430
– Other countries: 1-507-253-5192
v If you prefer to send comments electronically, use one of these e-mail addresses:
– Comments on books:
RCHCLERK@us.ibm.com
– Comments on the iSeries Information Center:
RCHINFOC@us.ibm.com
viii iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 11

Be sure to include the following:
v The name of the book or iSeries Information Center topic.
v The publication number of a book.
v The page number or topic of a book to which your comment applies.
iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map, SA41–5155–05 ix
Page 12

x iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 13

Chapter 1. Overview of RISC-to-RISC Upgrades and Data Migrations
The road map lists important considerations and activities that are critical to the
successful model upgrade of a system. Although this road map is not designed to
be an all inclusive how-to source for activities relating to upgrading your system, it
covers the essentials by guiding you to the proper source. Follow all the steps in
the order presented and notify your IBM
into difficulties.
This road map also covers how to perform a model to model data migration. A
data migration can be performed from almost any iSeries 400 model to any model.
The source model must be at the same release as the new model to correctly
complete the data migration. Data migration involves a new system with a new
serial number.
For an overview of the RISC-to-RISC upgrades and data migration, refer to
“Upgrade process flow” on page 2 and the “Data migration process flow” on
page 4.
What is in this Road Map?
This road map covers the following RISC-to-RISC upgrades:
®
representative for assistance if you run
Note: The current system may require hardware upgrades or configuration
changes to satisfy capacity and compatibility requirements of new software
and hardware.
v IBM AS/400 Model 170 to IBM AS/400 Model 170
There are no upgrades into or out of a Model 170. The Data Migration section of
this book covers the procedure used to perform a data move from the source
system to the new iSeries model.
v IBM ~ iSeries Model 270 to IBM ~ iSeries Model 270
There are no upgrades into or out of a Model 270. The Data Migration section of
this book covers the procedure used to perform a data move from the source
system to the new iSeries model.
v IBM AS/400 Models 5xx to IBM AS/400 Models 7xx
v IBM AS/400 Models 6xx to IBM AS/400 Models 7xx
v IBM AS/400 Models 7xx to IBM AS/400 Models 7xx
v IBM AS/400 Models Sxx or IBM AS/400 Models 5xx to IBM ~ iSeries
Models 8xx
There are no model upgrades into a Model 8xx from a Model 5xx, 6xx, Sxx, or
SBx. However, some hardware may be moved from the 5xx into a migration I
expansion unit (I/O and disk unit). The Data Migration section of this book
covers the procedure used to perform a data move from the source system to the
new iSeries 400 model.
v IBM AS/400 Models 6xx to IBM ~ iSeries Models 8xx
v IBM AS/400 Models 7xx to IBM ~ iSeries Models 8xx
v IBM ~ iSeries Models 8xx to IBM ~ iSeries Models 8xx
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1997, 2001 1
Page 14
Contact your local IBM representative or authorized dealer for additional
information on permitted upgrades.
For servers that do not have an upgrade path, use the data migration section of
this book. This would include scenarios such as an AS/400
iSeries 400 Model 270.
®
Model 540 to an
Why Upgrade from one AS/400 or iSeries 400 Server to Another iSeries 400 Server?
You might ask yourself why IBM is doing this and why upgrade your server now?
Most customers need to increase performance and add capacity.
What is an Upgrade?
In this book, an upgrade is any improvement made to the software or the
hardware of an iSeries 400 or AS/400 model that retains the serial number of the
iSeries 400 or AS/400 model. This includes moving the compatible hardware, the
Licensed Internal Code, operating system, and the licensed programs to a new
target system for better performance and reliability.
A data migration is the process of moving only the data from one iSeries 400 or
AS/400 model to a new iSeries 400 model, with a new serial number.
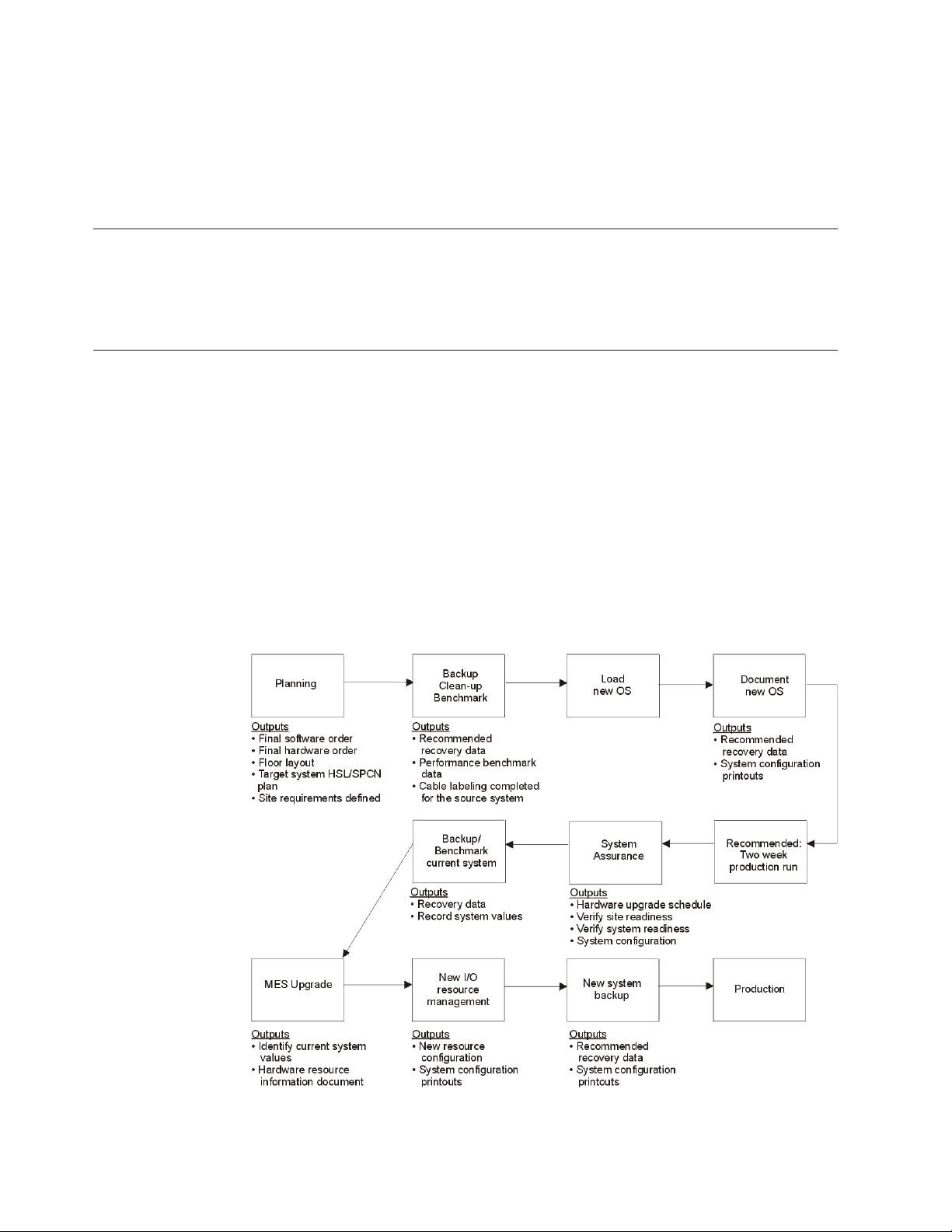
Upgrade process flow
The following flow chart describes each step of an MES upgrade and lists the
required outputs for each stage.
2 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 15
Hardware Investment for Upgrading
You may choose to upgrade your existing RISC system processor, or replace it with
a new iSeries 400 model. In either case, you may keep most of the current system.
The process of either an upgrade of your existing system or moving parts from an
existing system to a new system, are called miscellaneous equipment specification
(MES). MES denotes the process steps of an upgrade. The type of MES depends on
several factors:
v Your current processor model
v Costs
v Your system availability requirements
The information in this book will help to determine the right path to an upgrade.
This is based on the current model and the goals of the process.
How Long will the Upgrade Take?
The upgrade process includes planning, ordering, shipping, installing and testing
the system. The following table shows approximately how long an upgrade might
take.
Note: You should plan at least one additional hour of down time to load the
operating system for systems not preloaded.
Order Planning - 5 to 15
Days
See “Prerequisite and
related information” on
page vii for required
publications.
System Requirements Solution Assurance Upgrade Software Verify System
Performance Hardware and Software
Determine Services
Needed
Place Order
Installation Planning and Preparation - 10 to 30 days Phase II Installation - Weekend
(1 to 3 days)
Save System
See “Prerequisite and
related information” on
page vii for required
publications.
Preparation
Physical Planning (Site
Preparation)
Phase I Installation - 5 to
20 Days
Save System Upgrade Hardware
Check History and Clean
Up Messages
Save System
What is a Data Migration?
A data migration is the process of moving the OS/400®and the data from one
model iSeries 400 or AS/400 to a new model iSeries 400 AS/400.
The source system must be at the same release level as the target server. This
includes OS/400, all objects, and all licensed programs.
For customers ordering a new RISC iSeries 400 server with V4R4 or V4R5 to
replace an existing RISC iSeries 400 or AS/400 model (″source″) and needing to
migrate their data from the ″source″ model to the new server, a new feature code
Feature Code (F/C) #0205, is now available. This new feature code should be
ordered against the new RISC iSeries 400 server. It is valid on orders for all new
servers except the Models 150 and SB1.
Chapter 1. Overview of RISC-to-RISC Upgrades and Data Migrations 3
Page 16

For Feature Code #0205, the customer must have purchased a new server with
enough hardware and disk unit to hold all of the data from the ″source″ model as
well as any new data including any required IBM software (OS/400 and so forth).
Additionally, the RISC-to-RISC Data Migration process requires that the ″source″
model must be at the same version/release of OS/400 and Licensed Program
Products (LPPs) as that of the ″new″ server which has been ordered/received.
Customers with Version 3 (V3R7) on their ″source″ model must upgrade to Version
4. It is recommended that they purchase Software Subscription for AS/400. They
must then order and upgrade to match the new server (V4R4 or V4R5) in order to
proceed with their data migration. V3R7 cannot be directly upgraded to V4R4 or
V4R5 therefore, to do this the source system will need to be upgraded to V4R2 or
V4R3 before upgrading to V4R4 or V4R5. Customers with Version 4 must obtain
new server release of OS/400 licenses of the LPPs, either through new orders or
via Software Subscription for AS/400.
A License Addendum will be provided to allow the customer to install and use the
copy of OS/400 (received with the newly ordered server) on their source model for
up to 70 days. This Addendum authorizes the customers to use the new Version
and Release on the source system for the sole purpose of migrating their data. The
previous Version and Release must be reinstalled after the migration is completed.
The V4R4 or V4R5 licenses of OS/400 and the LPPs will only allow the products to
be run on one system at a time. Model 150 customers who are not at the new
server release of OS/400 must purchase the BasePak Upgrade (5649-EP5 for V4R4)
in addition to any upgrades for installed Optional Products in order to proceed
with their data migration. Feature Code #0205 provides for minimal pre loading of
the new server, inclusion of a special License Addendum.
Feature Code #0205 differs from Feature Code #0203. Feature Code #0203 SHOULD
NOT be ordered for iSeries 400 or AS/400 RISC-to-RISC data migrations as it is
designed exclusively for AS/400 CISC-to-RISC data migrations.
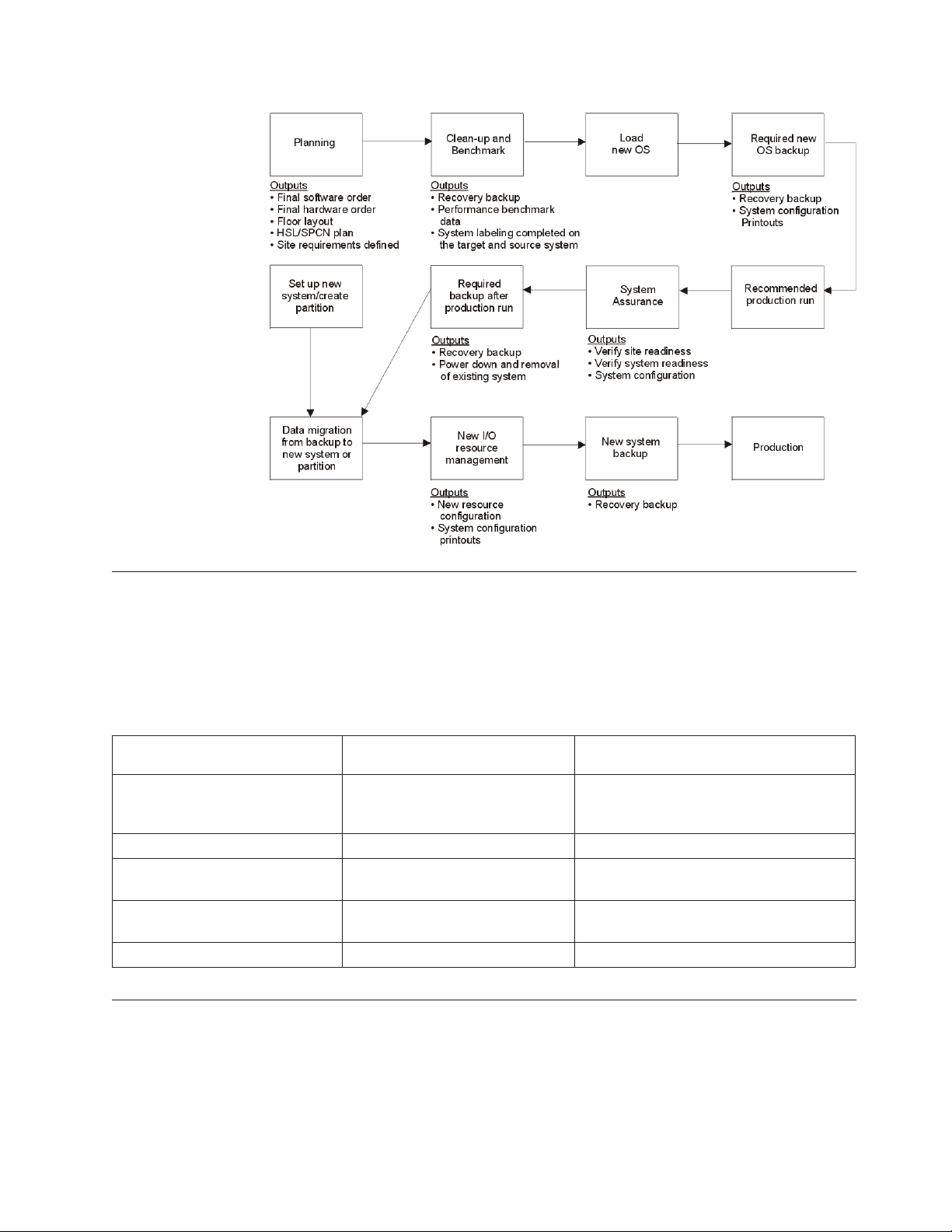
Data migration process flow
The following flow chart describes each step of a data migration and lists the
required outputs for each stage.
4 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 17
How Long will the Data Migration Take?
The data migration process includes planning, ordering, shipping, installing and
testing the system. The following table shows approximately how long a data
migration might take.
Note: You should plan at least one additional hour of down time to upgrade the
operating system for source systems not at the new server release level.
Order Planning - 5 to 15 Days Installation Planning and
Preparation - 10 to 30 days
See “Prerequisite and related
information” on page vii for
required publications.
System Requirements Solution Assurance Verify System
Performance Physical Planning (Site
Determine Services Needed Software Preparation (Upgrade
Place Order Save System
See “Prerequisite and related
information” on page vii for
required publications.
Preparation)
Source System Software)
Phase II Installation - Weekend (1 to 3
days)
Migrate Data
Check History and Clean Up Messages
Save System
Books to Use for Software Release Upgrades
The following table lists software release considerations, and which book to use for
upgrading the operating system and licensed programs.
Chapter 1. Overview of RISC-to-RISC Upgrades and Data Migrations 5
Page 18

OS/400 Release Currently Installed Book To Use For Upgrade and Software Installation
V5R1
V4R5
V4R4
If you have one of these releases installed on your system, your system
already runs on the RISC architecture. Use this manual, iSeries 940x
RISC-to-RISC Road Map, SA41-5155-05, for the upgrade. Use the manual
Software Installation, SC41-5120-05, to replace the installed operating system
and licensed programs. A PDF version of this manual is available from the
iSeries Information Center under System planning and installation ->
Hardware and software -> Software and licensed programs -> Install
software. Use the manual Backup and Recovery, SC41-5304-05, for the save
and restore requirements of these procedures. A PDF version of this manual
is available from the Information Center under Systems Management ->
Backup, recovery, and availability -> Manuals and Redbooks.
Note: V4R4 introduced logical partitions. Go to the iSeries Information
Center for help with setting up, upgrades to, and maintaining logical
partitions.
See the Software Installation manual for other software requirements and
limitations prior to the OS/400 upgrade.
6 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 19

Chapter 2. Planning Your Order for Upgrading or Data Migration
Review this chapter as you identify a solution and again after a decision is made
to verify the accuracy and completeness of the order. After you finish reviewing
this chapter, you should have the following:
v Final software order
v Final hardware order
v Floor layout
v High-speed link (HSL) and system power control network (SPCN) plan
v Cable labelling of source system
v Site requirements defined
Refer to the “Upgrade process flow” on page 2 or “Data migration process flow”
on page 4, depending on your situation, to identify where Planning is in the
overall process.
Determining Your Upgrade Needs
To help determine the upgrade needs, please consider the following:
v What problems does this upgrade need to address?
v What additional applications or growth do you expect or plan for in the future?
v What new technology do you want as part of the upgrade?
v What are the requirements for the following:
– Capacity
– Capability
– Performance
– Availability
v What are your expectations for the following:
– Impact on business operations
– Cost
– Performance
v What are the financial considerations to keep in mind? For example:
– Government discounts
– Capital planning cycles
– Tax implications
– Budget
Performance Tools for Capacity Planning and Performance Analysis
The licensed program Performance Tools/400 (Program 57xx-PT1) and QSIZE400
on the iSeries 400 configurator can be used for capacity planning and performance
analysis.
The BEST**/1 Capacity Planning function of the Performance Tools licensed
program provides the capability to analyze how a different AS/400 or iSeries 400
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1997, 2001 7
Page 20

configuration will perform with your current workload. The program temporary
fixes (PTFs) are now available that include capacity planning information for the
PowerPC processor models of the system. You can use Performance Tools to help
you determine the proper configuration of the processor main storage, and disk
resources that will meet your performance requirements.
Performance Tools are the best source of information for determining what
configuration meets your performance requirements. You should order the PTF
that updates your version of Performance Tools with the PowerPC AS processor
models.
Note: If you do not have Performance Tools on your system, you should obtain
modeling information in another way, such as by using consulting services.
Modeling the characteristics of your target configuration helps ensure that
the configuration meets your needs.
The latest PTFs for AS/400 BEST/1 Capacity Planner are required. You can order
or download these PTFs from the following Web site:
http://as400service.ibm.com
You need to register at this site. Do the following to go to the Internet PTF Facility:
1. Click Fixes, Downloads and Updates
2. Click Internet PTF Downloads (iPTF)
How to Gather Configuration Information
You and your marketing representative use the MRPD (Machine Reported Product
Data) and the IBM Configurator for e-business. This process compares your current
configuration with your desired configuration and creates the MES order
automatically. This simplifies the work that you and the marketing representative
have to do and ensures a correct MES order.
Machine Reported Product Data (MRPD)
The hardware and software inventory of a system can be transmitted to IBM and
stored in databases there. Once the information has been captured, it can be
accessed by the marketing representative to establish a starting point for a system
upgrade. The data may also be used for problem determination by hardware and
software support centers.
The data can be sent to IBM with these tools:
v Manually, with the WRKORDINF command. The WRKORDINF command sends
the information once through the Electronic Customer Support line.
v Automatically, with Service Agent and Management Central. Service Agent can
be customized to automatically transmit the data regularly on a monthly basis.
How to Gather Performance Information
Gathering performance data before installing a release gives you a base with which
to compare your system’s performance after the installation is complete.
Performance data is also useful when determining the correct hardware
configuration for your upgrade.
To gather performance information before you install a release, see the Prepare for
software installation topic in the Information Center under System planning
and installation -> Hardware and software -> Software and licensed programs.
8 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 21

Prerequisites Before Placing an Order
This section will cover the prerequisites of placing an order to upgrade the system.
These include software-related items, hardware considerations, system
configuration considerations, and available services that everyone should know
before placing an order.
You may also need information about logical partitioning. Refer to the web site:
www.as400.ibm.com/LPAR
Version 4 Software Items
See the table on supported releases for software upgrades in the book Software
Installation, SC41-5120-05, to find what versions may be upgraded from and to. For
example, you must be at V4R4 to upgrade to V4R5 or V5R1.
The ″Preparing Program Temporary Fixes Required Before Installing V4R5M0
Software″ section in the Software Installation book describes how to apply PTFs.
Other Software Related Items
v Determine whether there are any additional software charges that are associated
with the processor group change. Two passes must be run on the iSeries 400
configuration program to determine these changes.
v Determine whether there are any additional usage changes because of the
user-based pricing that is associated with the software products on the system.
v Verify with the software service representative, or the business partner, that any
third party software that you use was tested on the software release level
ordered.
v Contact the software service representative for any software considerations and
restrictions that might apply to the model upgrade.
Notes:
1. If you have tape management software, ensure that it uses support that is
available on your target system. Do the following:
a. Type DSPOBJD OBJ(QSYS/QUSTAPEX) OBJTYPE(*PGM)
b. If you receive the message Object QUSTAPEX in library QSYS type *PGM
not found, you do not have this potential problem with tape management
software.
c. If you see the Display Object Description display for the QUSTAPEX
program, press F12 (Cancel). Contact the vendor who supplies your tape
management software to determine how the vendor will provide equivalent
support for your target release.
You may need to order an OS/400 feature called MSE (Media and Storage
Extensions).
2. For other software related questions, see Technical Studio and the book Software
Installation, SC41-5120-05.
Hardware Considerations
v Ensure that a PC has been properly configured as an Operations Console.
v Determine the prerequisite engineering changes and program temporary fixes
(PTFs) that are needed to upgrade the system.
v Determine the attached input-output devices and the operating system.
Chapter 2. Planning Your Order for Upgrading or Data Migration 9
Page 22

v Verify with the original equipment manufacturer vendor that any non-IBM
devices are compatible with the model upgrade and the new software release.
Note: The customer should request written confirmation of this compatibility
from the original equipment manufacturer vendor.
v The target system may have different power requirements than the source
system. Appropriate planning and preparation by the customer is very
important. Determine whether you need additional space and power
requirements for any additional system units or system racks. For more
information, see Technical Studio at
http://www.iseries.ibm.com/tstudio/planning/plngstrt.htm.
v Verify that the target system has a tape drive compatible with the tape format
used to save information on the source system.
v Ensure that your marketing representative or IBM business partner is aware of
the number of ports on your current twinaxial workstation controllers and the
number of ports you will need on your new model. This will help to ensure that
the proper model and features get ordered for your upgrade.
v Ensure that you label the cables of your current system before the upgrade. To
do this, see the Physical Planning guide in the iSeries Information Center under
Getting Started with iSeries -> Planning ->Physical planning for your new
system.
http://www.ibm.com/eserver/iseries/infocenter
System Configuration Considerations
v When implementing changes to the auxiliary storage pool (ASP) configuration,
do it either before or after the upgrade, but never during the upgrade.
v If you use mirroring, make sure to specify the correct level.
v A current system configuration list should be available for the hardware service
representative. The configuration list provides details of your current system
configuration.
To print the System Configuration List, do the following:
1. On the OS/400 Main Menu command line, type STRSST. Then, press the
Enter key.
2. Type QSECOFR on the System Service Tool Sign on display and press Enter.
3. On the STRSST display, select Start a service tool option. Press the Enter key.
4. On the Start a Service Tool display, select Hardware service manager. Press
the Enter key.
5. From the Hardware Service Manager display, press F6 (print configuration).
6. To return to the OS/400 Main Menu, Press F3 (Exit) twice, and then press the
Enter key.
7. Keep the printed list - the service representative will need it.
Services and Other Assistance
v Determine whether you need on-site support or services. “Appendix A. AS/400
Global Services” on page 35 has information about the following:
– IBM Global Services
– iSeries 400 and AS/400 Data Migration Services
– LPAR Planning and Implementation Services
– iSeries Planning and Migration Services
– AS/400 System Migration Services
10 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 23

– Related support services
– iSeries 400 and AS/400 solution services
v Determine the responsibilities for all upgrade activities. These responsibilities
include:
– Outline the model upgrade activities and the person responsible for each
activity, as described in Table 4 on page 17.
– Develop an installation plan, a schedule of activities, and a checklist. See the
SA Advisor in the Expert menu Application on HONE.
Your IBM Representative may visit the Solutions Assurance Web site:
http://w3.ibm.com/support/assure
Your IBM representative can use marketing tools to get more information:
- Only your IBM representative can access MKTTOOLS at this Web site:
http://w3-1.ibm.com/sales/systems/ibmsm.nsf
- Or on a Virtual Machine (VM) system, the representative types:
TOOLS SENDTO LEXVMIC1 TOOLS SAPRDOC GET SA95008 SCRIPT *
TOOLS SENDTO LEXVMIC1 TOOLS SAPRDOC GET SA95008 LIST3820 *
v Order any optional hardware and software publications by using PUBORDER or
the System Library Subscription Service (SLSS).
v Determine whether you have any education needs.
Model-specific Considerations for Placing an Order
There are unique model-specific considerations when upgrading from one RISC
model to another RISC model. Before placing an order, everyone involved in the
upgrade process should review these upgrade considerations:
v The prerequisite for migrating SPD book-type adapter cards is an Model S20, S30,
S40, SB1, 620, 640, 650, 720, 730, or 740.
v There is concurrent disk unit maintenance.
v You can use the alternate IPL device function for any installation or recovery
that requires replacing Licensed Internal Code or other licensed programs. Some
models might require an alternate installation device. You can use this device
for installing distribution tapes that were created by a central site, or for
recovery, using a SAVSYS tape. The Appendix about alternate installation
devices of the Software Installation manual describes the alternate installation
device function and identifies situations in which older tape devices may require
its use. The Appendix also describes how to set up, enable, or disable an
alternate installation device. A PDF version of this manual is available from the
iSeries Information Center under System planning and installation ->
Hardware and software -> Software and licensed programs -> Install software
Note: In Models S10, S20, 600, 620 and 720, the input-output processor (IOP) to
which certain older tape devices connect, require an expansion unit in
order to use the devices. The following tape devices are affected: 2440,
3422, 3430, 3480, 9347, 7208-002, and some models of 3490. Other 7208
models and 3490 models Exx, C11, and C22 are supported without an
expansion unit. Models 3490 C1A and C2A can be converted to Small
Computer Systems Interface (SCSI) format, which is supported without an
expansion unit. If you use older tape devices as alternate installation
devices, on Models S10, S20, 600,620 and 720, you need the expansion
unit. You need to set up the devices as alternate installation devices.
v Models Sxx and 6xx have a new internal-external SCSI input-output adapter.
Chapter 2. Planning Your Order for Upgrading or Data Migration 11
Page 24

v Be aware that upgrades to an AS/400 or iSeries server may require wiring
changes to a building. For more information, see Technical Studio at
http://www.iseries.ibm.com/tstudio/planning/plngstrt.htm.
The customer should work with the marketing representative to schedule a
system assurance meeting to review all of the following activities.
Note: This meeting should include the customer, IBM marketing representative,
hardware service representative, software service representative, and any
non-IBM software service representative.
v Review memory considerations as follows:
– Net-priced main storage feature exchanges are not available when upgrading
to another AS/400 PowerPC AS model. In addition, you cannot exchange
AS/400 or iSeries 400 memory cards for credit toward the purchase of newer
or larger AS/400 or iSeries 400 memory cards. To reduce the necessity for
future memory exchanges, the customer should order sufficient memory card
sizes for future growth requirements.
®
– Main storage for AS/400 Models 400
each other.
– Main storage for AS/400 Models 40S, 50S, and 53S is not compatible with
each other.
– You must plug in main storage cards in equally-sized pairs for the Model 500
Feature Processor 2142. Therefore, it might not be possible to reuse all of the
main storage cards from the previous feature processor (2140 or 2141).
– You must plug in main storage cards in equally-sized pairs for the AS/400
Models 510 and 530 and the AS/400 Models 50S and 53S.
v Ensure that you know how to accomplish RAID protection on a migrated
internal disk unit. You must have an attachment to a Feature Code for a high
availability DASD controller (for example, 6502, 6512, 6532, 2726,or2740).
, 500, and 530 is not compatible with
Note: In order to avoid additional charges for the IBM service representative’s
time, perform ASP management after completion of the hardware
upgrade.
v Be prepared to delete the old device description and create a new one, if the
type of console changes.
v Review and confirm the hardware and software order.
v Some systems have a mix of unsupported disk unit devices. If the system has
such a mix, consider one of the following:
– Purchase additional supported disk unit devices in order to enable the
removal of all unsupported devices before the model upgrade.
– Purchase AS/400 Data Migration Services.
Upgrading from a 4xx, 5xx, Sxx, or 6xx to a 7xx
Many installed AS/400 Models 4xx, 5xx, 6xx, and Sxx (except SB1) can be
upgraded to an AS/400 Model 7xx.
All system units and expansion units have locations for features including
processors, main storage, power, expansion units, disk units, tape drives, CD-ROM
drive, and IOPs. Some restrictions may apply to certain combinations of features.
The configurator contains the rules and performance considerations for placement
12 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 25

of these features. It should be used to ensure a valid configuration. The use of
performance tools may also help in optimizing a configuration to match a specific
set of requirements.
Note: When ordering a model upgrade from a mixed-mode server (S20, S30, S40)
to AS/400 7xx servers, an Interactive Specify code must be on the model Sxx
inventory record prior to ordering the model upgrade. The configurator will
generate a Record Purpose Only (RPO) order to add a zero-priced
Interactive Specify code to the installed mixed-mode server prior to the
upgrade. This is a required step.
Sxx Interactive Specify codes that the configurator will add:
v Model S20 Interactive Specify codes
– 1490
– 1492
v Model S30 Interactive Specify codes
– 1492
– 1493
– 1494
v Model S40 Interactive Specify codes
– 1495
– 1496
Migrating from a 5xx to an 8xx
When migrating SPD expansion units from an AS/400 Model 5xx or from any
unsupported path to an iSeries Model 8xx, the order must have a migration
expansion unit included.
IBM does not provide a pre-planned or pre-programmed upgrade from a Model
5xx to a Model 8xx. The user who wants to move I/O to 8xx hardware will have
to analyze their current configuration and determine what will and will not move
and plan the sequence of actions to make it happen. Here are some general
considerations:
v SPD I/O expansion unit can not be directly attached to an 8xx. A migration
expansion unit with SPD capability is required. If you have a Model 830 or 840
and do not have a migration expansion unit yet, a migration expansion unit
(migration expansion unit II), FC #5077 (and perhaps an FC #5057 expansion
unit), should be ordered. IBM does not offer an option to order a migration
expansion unit (migration expansion unit I) which could attach to an 820.
v SPD IOPs can not be inserted into an 8xx except via SPD slots in a migration
expansion unit or in SPD I/O expansion unit attached via a migration expansion
unit.
v Not all I/O is supported by V4R5 or V5R1 on an 8xx. There were several older
disk units, tape drives, IOPs, and so forth, which were no longer supported as of
V4R1.
v The I/O expansion unit, on a Model 500 or 510 only has a 266 Mbps Optical bus
Adapter which is too slow for the migration expansion unit to support. Using
the S40388 RPQ, the expansion unit can be converted to a faster I/O expansion
unit with a 1063 Mbps Optical Bus Adapter.
v Since V4R5, the only type of PC console that an 8xx system supports is
Operations Console.
Chapter 2. Planning Your Order for Upgrading or Data Migration 13
Page 26

v Planning assistance from IBM Global Services or from an IBM Business Partner
may be very helpful if this is an unfamiliar area to the customer.
Upgrading from a 6xx or 7xx to an 8xx
Many installed AS/400 Models 6xx and 7xx, except SB1, can be upgraded to an
iSeries 400 Model 8xx. 8xx models require V4R5 or later versions of OS/400
depending on the hardware function required.
All system units and expansion units have locations for features including
processors, main storage, power, expansion units, disk units, tape drives, CD-ROM
drive, and IOPs. Some restrictions may apply to certain combinations of features.
The configurator is used by your marketing representative or business partner. It
contains the rules and performance considerations for placement of these features.
It should be used to ensure a valid configuration. The use of performance tools
may also help in optimizing a configuration to match a specific set of
requirements.
Placing the Upgrade Order
After you have identified what is necessary for the upgrade, continue with the
following sections:
Who is Responsible for Ordering the Upgrade?
The following tables show a check-off sequence for tasks during the ordering
process.
Note: IBM Services personnel may perform the customer activities for a fee.
Table 1. Tasks and Responsibilities for Ordering
Checkoff Tasks and Responsibilities for Ordering Person Responsible
Understand objectives and needs Marketing Representative
Know existing system. Print system
configuration list.
Use the AS/400 Configurator Marketing Representative, Business Partner
Determine prerequisites Marketing Representative, Business Partner,
Determine current running release Marketing Representative, Business Partner,
Determine release-level requirements before
model upgrade
Determine responsibilities Customer Account Team Leader
Determine documentation and education
needs
Determine physical needs Customer, Business Partner
Determine special needs (for example,
mirroring)
Determine upgrade path Marketing Representative, Business Partner,
Marketing Representative, Customer
Software Service Representative
Customer
Marketing Representative, Business Partner
Marketing Representative, Business Partner
Marketing Representative, Business Partner,
Customer
Customer
14 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 27
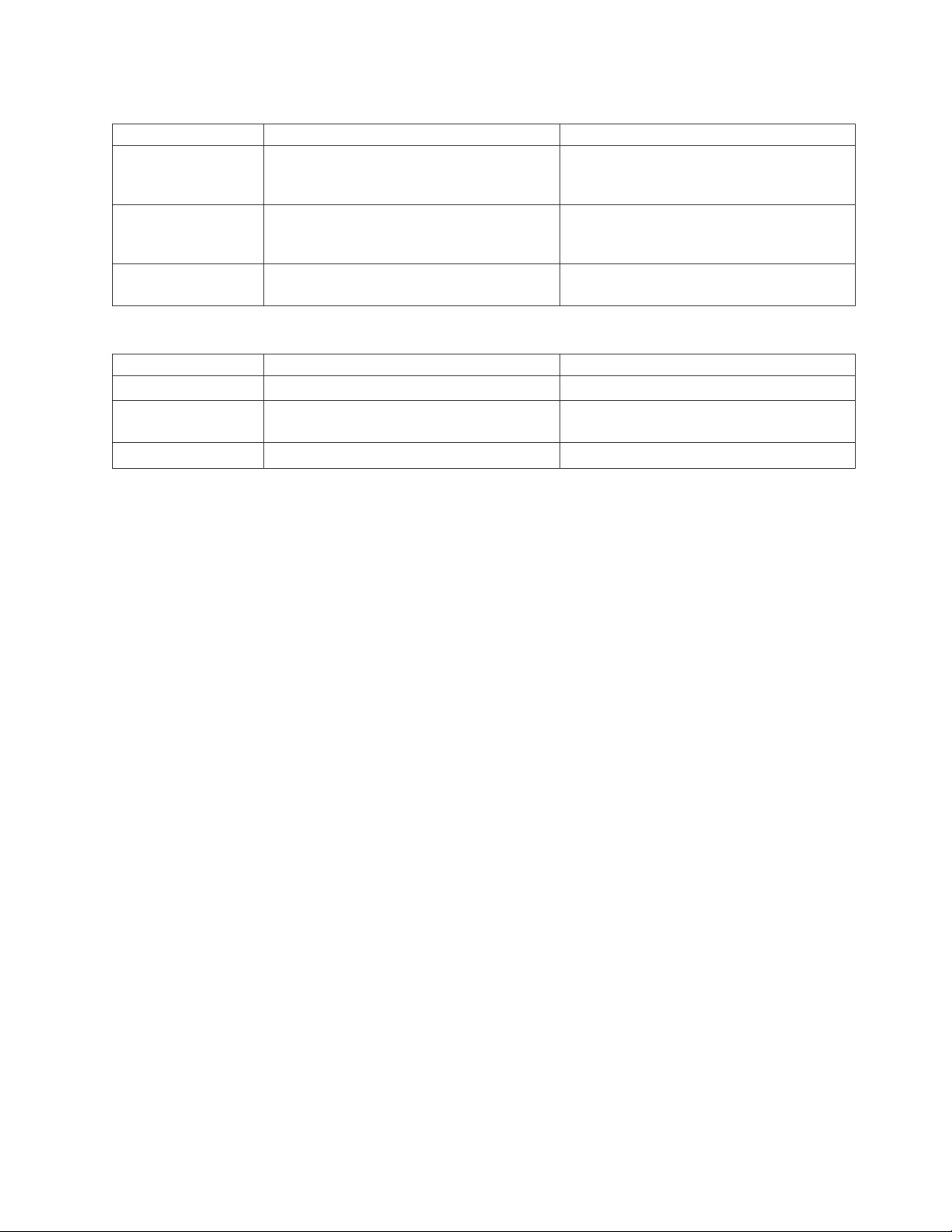
Table 2. Tasks and Responsibilities for Ordering Software
Checkoff Tasks and Responsibilities for Ordering Person Responsible
Order software release Customer, who may need assistance from a
Marketing Representative or Business
Partner
Order program temporary fixes (PTFs) Customer, who may need assistance from a
Marketing Representative or Business
Partner
Order publications Customer, Marketing Representative,
Business Partner
Table 3. Tasks and Responsibilities for Ordering Hardware
Checkoff Tasks and Responsibilities for Ordering Person Responsible
Order engineering changes Marketing Representative, Business Partner
Run the iSeries 400 or AS/400 configurator
to place the order
Order publications Marketing Representative, Business Partner
Marketing Representative, Business Partner
Contact your local IBM representative or authorized dealer to place the order or
for further assistance.
How to Get Help with the Order
Ordering assistance is available from IBM. When you type GO ORDER on the
command line and press the Enter key, the Request Order Assistance display
appears.
Note: If you need assistance when trying to place an order, you can also use the
Request Order Assistance (RQSORDAST) command to request assistance
from IBM.
Use the Request Order Assistance display as follows:
v Type in your telephone number and your name.
v Verify the accuracy of other contact information.
v Press the Enter key.
v Type a short description of your needs.
v Press F10 (send) to send the file to IBM.
Sending the Order to IBM
The RQSORDAST command can send a list which contains your current iSeries
400 or AS/400 system configuration, with your order. IBM uses this list to assess
your ordering needs.
Sending the Order to a Software Service Provider Other Than IBM
You can send your order request to IBM or to a provider other than IBM. When
you send your order request to a provider other than IBM, you can use the
RQSORDAST command to communicate with the provider. The provider can send
Chapter 2. Planning Your Order for Upgrading or Data Migration 15
Page 28

you a response electronically. You can use the WRKORDRQS command to view the
response and manage the order request. The provider will fill your order or
forward your request to IBM.
16 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 29
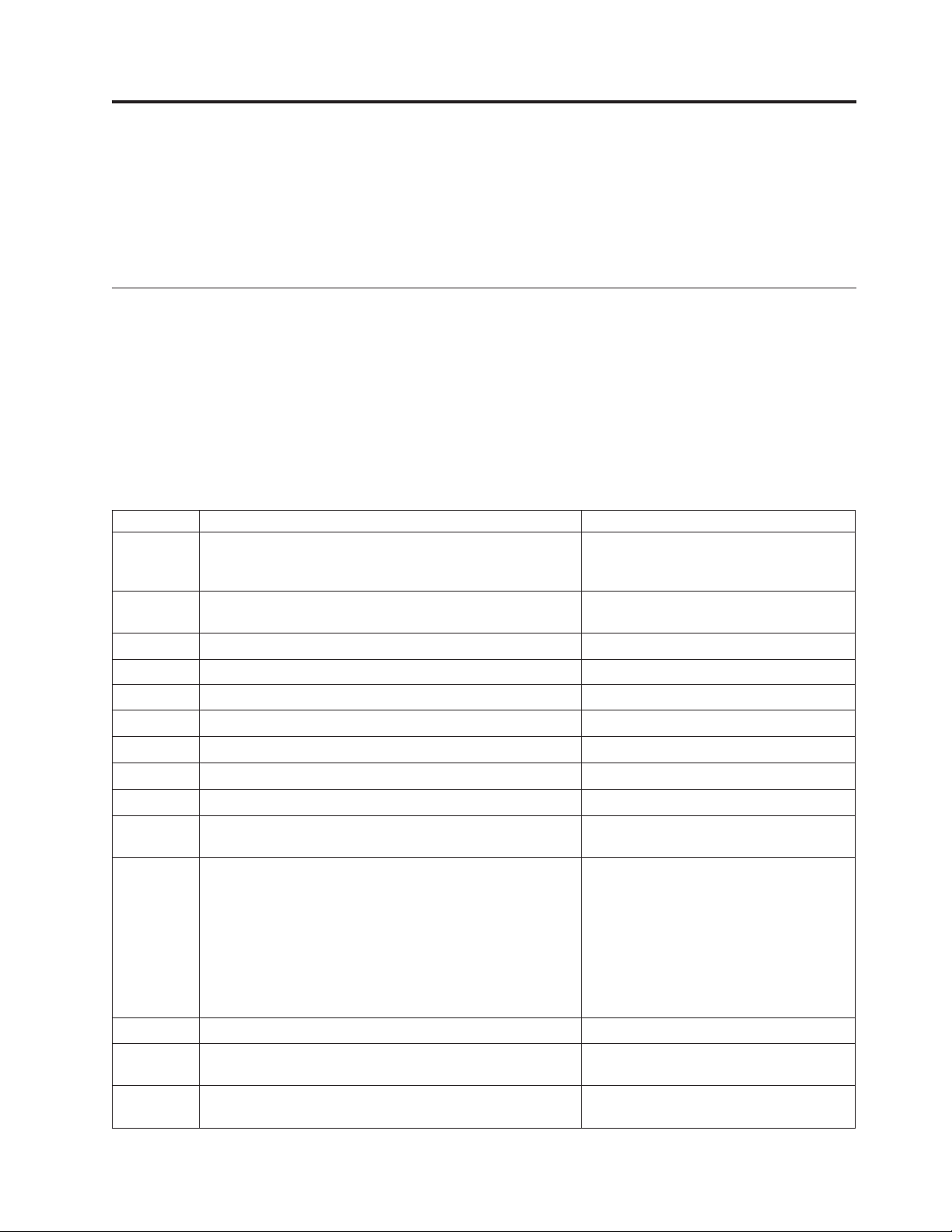
Chapter 3. Procedure for an Upgrade (RISC-to-RISC)
After you finish reviewing this chapter, you should have performed the upgrade
tasks and obtained the outputs outlined in the “Upgrade process flow” on page 2
(except for the planning tasks and outputs already covered in “Chapter 2. Planning
Your Order for Upgrading or Data Migration” on page 7).
Who is Responsible for Upgrading the System
The following table establishes a check-off list for task responsibilities in
preparation for and during the upgrade. The list is arranged in the sequence the
tasks should be done.
IBM Services can be provided for additional cost to assist customers.
For customer install systems and servers such as Model 170, follow the instructions
that came with the system.
Table 4. Tasks and Responsibilities for the Upgrade Path
Checkoff Task Person Responsible
Consider needs for installation Customer, Business Partner, Software
Service Representative, Hardware Service
Representative
Establish tentative installation date Customer and their authorized
representative
Read preventive service planning (PSP) information Customer
Save the system, full save Customer
Install Target Software Release and appropriate PTFs Customer
Verify that all applications are running Customer
Record performance and evaluate Customer
Complete physical planning Customer
Save the system, full save Customer
Contact customer Hardware Service Representative and
schedule the upgrade after the order arrives
System Assurance
Customer
Hardware Service Representative
Verify the following:
v Prerequisite Engineering Changes are installed
v Customer has installed all required PTFs
v Correct operating system level
v Customer has backed up the system, including all
customer data
Inventory parts received from IBM as part of the upgrade Hardware Service Representative
Run Work with Hardware Products (WRKHDWPRD)
command option 4
Upgrade hardware using parts shipped from IBM and the
CUII
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1997, 2001 17
Hardware Service Representative
Hardware Service Representative
Page 30

Table 4. Tasks and Responsibilities for the Upgrade Path (continued)
Checkoff Task Person Responsible
Save the system, just a system save Customer
Run WRKHDWPRD command option 5 if OS/400 is on
the target system at the completion of the upgrade
Configure extra devices (DASD, for example) Customer
Tune performance Customer
Perform Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID)
and mirroring steps
Save the system, full save Customer
Hold post-installation meeting Customer Account Team Leader
Ensure IBM systems are accurate and updated Marketing Representative
Customer
Customer
What to Do When the Hardware Arrives
When the hardware arrives, the customer should notify the hardware service
representative and schedule a time for system assurance checkpoint prior to the
hardware installation (MES upgrade).
Notes:
1. For customer install systems follow the instructions that came with your server
to get set up. If you are replacing an existing system while preserving the
original serial number, use the data migration section of this book.
2. The customer must have at least 64MB of memory or arrange to have
additional memory installed before the upgrade can proceed. For more
information on prerequisites prior to an upgrade, see the manual Software
Installation, SC41-5120-05. A PDF version of this manual is available from the
iSeries Information Center under System planning and installation ->
Hardware and software -> Software and licensed programs -> Install
software.
Preparing the Current System
In this section, you will be asked to save your system several times. IBM strongly
recommends that you save your system when instructed to do so. Saving your
system allows you to have recovery data in case of disaster.
Approximately two weeks before the hardware service representative arrives, the
customer should do the following:
__ 1. Acquire the preventive service planning information (see “Appendix C.
Obtain the Latest Preventive Service Planning Information” on page 43)
from electronic customer support, if available, or from the software service
representative.
__ 2. For information pertaining to logical partitions, see the Logical Partitions
topic under Systems Management in the iSeries Information Center. There
are some specific steps to perform for upgrading a server with primary
and secondary partitions installed.
__ 3. For considerations when upgrading to 5769-RD1 OnDemand, see
“Appendix B. Considerations and Solutions” on page 39 for information on
OnDemand.
18 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 31
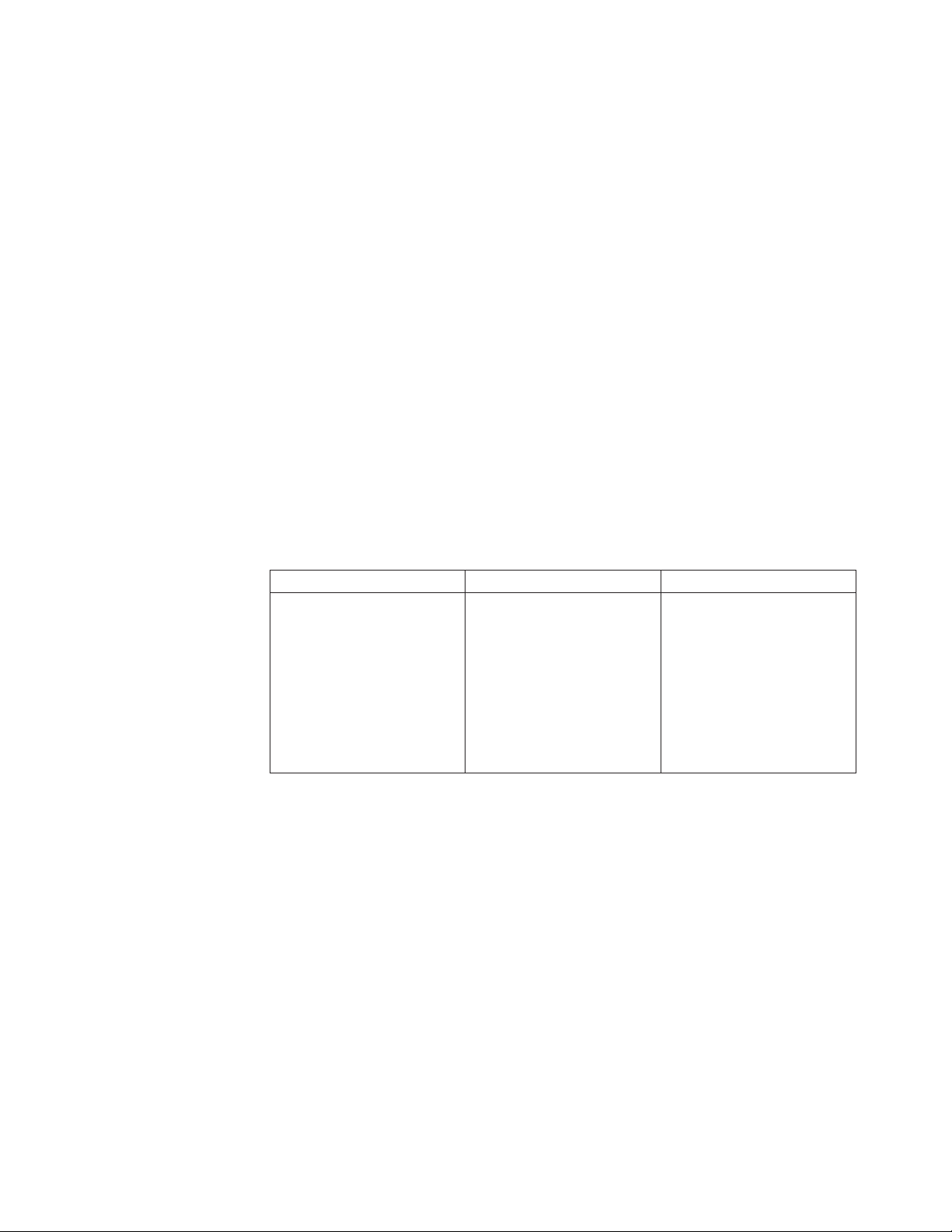
__ 4. For considerations when upgrading an AS/400 or iSeries 400 server with
OptiConnect installed, see the book OptiConnect for OS/400, SC41-5414-02.
__ 5. For considerations when upgrading an AS/400 or iSeries 400 server with
Integrated Netfinity
®
Server installed, see the book Getting Started with
Integrated Netfinity Server, SC41-5123-01.
__ 6. Refer to “How to Gather Performance Information” on page 8 in order to
record the performance of your system.
This is where you load the new operating system.
__ 7. See the manual Software Installation, SC41-5120-05 to install software (for
example, Licensed Internal Code, operating system, PTFs, etc.). Install
software for the required and desired partitions. A PDF version of this
manual is available from the iSeries Information Center under System
planning and installation -> Hardware and software -> Software and
licensed programs -> Install software.
Important: If you are using logical partitions, update all your partitions to
V5R1, if needed.
__ 8. Delete any unused device configuration descriptions (delete unused line,
line descriptions, and non-reporting resources).
Important: To delete line and device and descriptions, use the WRKLIND and
WRKDEVD commands and verify that all the descriptions listed are in use. If
you are sure one is not, you should delete it. If you are not sure, you
should leave it.
Table 5. Clear non-reporting resources on each LPAR Partition.
No LPAR LPAR Primary LPAR Secondary
Use the Hardware Service
Manager service option to
remove non-reporting
resources that no longer are
associated with existing
hardware.
Use the Hardware Service
Manager service option to
remove non-reporting
resources that no longer are
associated with existing
hardware.
Use the same procedure as
described for the LPAR
Primary for each Secondary
Partition that is configured.
Attention: Ensure all I/O
resources are assigned to a
partition.
__ 9. Before proceeding with the next step, make that sure during step 7, you
obtained or performed the following:
a. OS/400 is current (You determined whether you needed to replace
software and replaced Licensed Internal Code, operating system, and
licensed programs if needed.)
b. PTFs are current
c. Saved your current system (recommended as recovery data in case of
disaster)
__ 10. If you do not have a current system backup that allows you to recover in
case of disaster, save the entire system on each partition. Make sure that
you save the system and data on a tape unit that is compatible with the
tape unit on the target system. To save the system, use option 21 on the
Save menu. For more information about saving the entire system using
option 21, refer to any of the following:
v The chapter on saving your iSeries server in the manual Backup and
Recovery, SC41-5304-05. A PDF version of this manual is available from
Chapter 3. Procedure for an Upgrade (RISC-to-RISC) 19
Page 32

the Information Center under Systems Management -> Backup,
recovery, and availability -> Manuals and Redbooks.
v The Backup, recovery, and availability topic under Systems
Management in the Information Center:
http://www.ibm.com/eserver/iseries/infocenter
To find the procedure for saving the entire system (using option 21) in
the Information Center, do the following:
a. Click Systems Management
b. Click Backup, recovery, and availability
c. Click Backing up your server
d. Click Saving your server with the GO SAVE command
e. Click Saving your whole server with GO SAVE: Option 21
__ 11. Resume normal system operations and processing.
__ 12. To verify that all your applications are running properly, use the system
with the new software release until you feel comfortable with the new
production environment. For example, many customers use the system
for 2 weeks or longer.
Preparing for System Assurance prior to hardware upgrade
Before the hardware upgrade is to take place, the customer should do the
following:
__ 1. Ensure that the currently installed machine and LPAR partitions are
documented.
No LPAR or LPAR Primary Partition Secondary LPAR Partitions
Before proceeding with the MES Installation,
where possible, use (A) or (B) to document
the installed iSeries server. Use an
appropriate method:
(A) - If your country supports the
WRKORDINF command and if the installed
iSeries server is capable of using Electronic
Customer Support (ECS), use this method:
On the command line, type ″WRKORDINF″,
then press Enter.
On the next screen, enter Option 1 in the
Option field next to QMAnnnnn
Note: nnnnn is the serial number of the
machine, press enter. Write ″ECS″ on the top
oftheRMERform.
(B) - Use this method if the installed iSeries
server is not ECS capable, or you cannot use
’A’ for another reason: On the command line
type ″DSPSFWRSC *PRINT″, press enter.
Retrieve hard copy listing from the system
printer. Attach the listing to the RMER. If no
RMER form is present, then ignore this step.
Use the same procedure as described for the
primary partition for each secondary
partition that is configured.
20 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 33

__ 2. Print Disk Configuration Status of the installed system.
No LPAR or LPAR Primary Partition Secondary LPAR Partitions
Find disk configuration information using
the System Service Tools (SST).
a. Ensure you sign on to the system with
the user profile (such as QSRV).
b. Enter the command, STRSST, to start SST.
c. Select option to Work with Disk Units.
d. Select option to Display Disk
Configuration.
e. At the Display Disk Configuration Status
display, print the entire disk
configuration by using the print screen
function. Ensure all the disk
configuration information is printed.
Note: If you have trouble getting your
printed output, systems with OS/400
installed can use AS/400 Operational
Assistant.
a. Enter the command GO ASSIST, to get to
the AS/400 Operational Assistant Menu.
b. Select the option to Work with Printer
Output.
Use the same procedure as described for the
primary partition for each secondary
partition that is configured. Record the S/N
of the load source disk unit for each
partition on the system.
__ 3. Print Parity Set Configuration and Status of the Installed system.
No LPAR or LPAR Primary Partition Secondary LPAR Partitions
a. Enter the command, STRSST, to start SST.
b. Type QSECOFR on the System Service Tool
Sign on display and press Enter.
c. Select option to Work with Disk Units.
d. Select Display Disk Configuration.
e. Select Display Device Parity Status.
f. At the Display Disk Parity Set Status
display, print the entire Parity Set
configurations using the print screen
function.
DASD MES Notes:
Attention: Parity Sets can only be moved
when the protection status shows Active.
ASP management tasks, such as
re-configuring RAID arrays or significant
protection changes, are generally billable to
the customer.
Ensure this is discussed before the upgrade.
Use the same procedure as described for the
Primary Partition for each Secondary
Partition that is configured.
__ 4. If you do not have a current system backup that allows you to recover in
case of disaster, save the entire system on each partition just before the
hardware upgrade is to be started. Make sure that you save the system and
data on a tape unit that is compatible with the tape unit on the target
Chapter 3. Procedure for an Upgrade (RISC-to-RISC) 21
Page 34

system. To save the system, use option 21 on the Save menu. For more
information about saving the entire system using option 21, refer to any of
the following:
v The chapter on saving your iSeries 400 server in the manual Backup and
Recovery, SC41-5304-05. A PDF version of this manual is available from the
Information Center under Systems Management -> Backup, recovery,
and availability -> Manuals and Redbooks.
v The Backup, recovery, and availability topic under Systems
Management in the Information Center:
http://www.ibm.com/eserver/iseries/infocenter
To find the procedure for saving the entire system (using option 21) in the
Information Center, do the following:
a. Click Systems Management
b. Click Backup, recovery, and availability
c. Click Backing up your server
d. Click Saving your server with the GO SAVE command
e. Click Saving your whole server with GO SAVE: Option 21
__ 5. Enter the command WRKDSKSTS OUTPUT (*PRINT) to get disk
configuration and protection information. Use this printout to help analyze the
disk unit configuration and protection.
If you want a different configuration after the upgrade, use this printout to
plan for the desired configuration. Before you power down the system to
perform the hardware upgrade, you must logically remove any disk unit
that you will move during the upgrade.
__ 6. Use the Retrieve Configuration Source (RTVCFGSRC) command for the
existing line, controller, and device descriptions. The configuration source is
needed if any configuration objects must be manually changed or re-created.
The RTVCFGSRC command builds a source file member for specified
configuration objects. This source file can be converted later to a control
language program. Keep updated records of all hardware and configuration
objects. Before and after every upgrade, you can generate a report of your
hardware and configuration objects. (From each partition) type the following
commands:
DSPHDWRSC TYPE(*LWS) OUTPUT(*PRINT)
DSPHDWRSC TYPE(*STG) OUTPUT(*PRINT)
DSPHDWRSC TYPE(*CMN) OUTPUT(*PRINT)
DSPHDWRSC TYPE(*PRC) OUTPUT(*PRINT)
Make certain that the printouts are marked as to which partition they
represent.
__ 7. Run the WRKHDWPRD command, option 4 to display and verify the
information. Use F17 to print the information for the service representative.
__ 8. Print the LPAR configuration
No LPAR LPAR Primary Partition LPAR Secondary Partition
No action required, skip to
the next numbered step.
22 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
On the Primary Partition,
Use the Work with Logical
Partition utility under SST to
Print the Logical Partition
Configuration.
No action required on
Secondary Partitions.
Page 35

__ 9. Print the status of all PTFs on the system (each system partition if LPAR)
after installing the V5R1 software and before the hardware upgrade. Type
the following command:
DSPPTF LICPGM(*ALL) OUTPUT(*PRINT)
System Assurance Checkpoint
The customer needs to ensure that the following is completed before the
hardware service representative arrives:
1. Verify that the physical planning items were completed:
v High Speed Link cable diagram
v Floor plan, system layout diagram
v Cable labelling
To complete the items, see the Physical Planning in the iSeries Information
Center under Getting Started with iSeries -> Planning ->Physical planning
for your new system.
http://www.ibm.com/eserver/iseries/infocenter
2. Ensure that you have installed the latest V5R1 cumulative PTF package and
specific software release PTFs on all partitions. Refer to step 7 on page 19.
3. Verify that you have the latest full system backup (Save option 21) tapes on
hand and labeled. Refer to step 4 on page 21.
4. Verify the availability of a compatible alternate IPL device (CD-ROM or tape
unit attached to the system bus 1). If the system uses an alternate installation
device (CD-ROM, DVD, or tape unit attached to a bus other than the system
bus 1) for installation or restore operations, ensure the availability of the
location information for that device.
Note: If a tape unit is attached to a bus other than the system bus 1, record the
following information about the tape unit location:
v Type and model
v System bus
v System card
This information is necessary to set up and enable the tape unit as an
alternate installation device. For more information about alternate
installation devices, go to the Software Installation manual. A PDF version
of this manual is available from the iSeries Information Center under
System planning and installation -> Hardware and software ->
Software and licensed programs -> Install software.
5. Ensure that the console device is available and ready. For information about
setting up and configuring Operations Console, see the manual Operations
Console Setup, SC41-5508-02. A PDF version of this manual is available from the
iSeries Information Center under Client Access Express -> Manuals and
Redbooks.
6. Verify that you have the following printouts on hand (refer to step 1 on page 20
through step 9):
v Latest system configuration list
v Latest device descriptions printout on hand
v Latest controller descriptions printout on hand
v Latest PTF level printout on hand
v Latest complete and accurate label location chart or worksheet on hand
Chapter 3. Procedure for an Upgrade (RISC-to-RISC) 23
Page 36

7. Verify that prerequisite hardware changes are installed or are available to install
on all system components and input or output devices.
8. Document the IPL status for all your partitions. Then, set the IPL System Action
for each Secondary Partition:
No LPAR LPAR Primary Partition LPAR Secondary Partition
No action Required, skip to
the next numbered step.
Under the Primary Partition,
Use the Work with System
Partitions utility to select
each Secondary Partition and
set each IPL System Action
to HOLD.
No action required.
9. As appropriate, confirm the schedule for the hardware upgrade.
10. If you do not have a current system backup that allows you to recover in case
of disaster, save the entire system on each partition just before the hardware
upgrade is to be started. Make sure that you save the system and data on a
tape unit that is compatible with the tape unit on the target system. To save
the system, use option 21 on the Save menu. For more information about
saving the entire system using option 21, refer to any of the following:
v The chapter on saving your iSeries server in the manual Backup and
Recovery, SC41-5304-05. A PDF version of this manual is available from the
Information Center under Systems Management -> Backup, recovery, and
availability -> Manuals and Redbooks.
v The Backup, recovery, and availability topic under Systems Management
in the Information Center:
http://www.ibm.com/eserver/iseries/infocenter
To find the procedure for saving the entire system (using option 21) in the
Information Center, do the following:
a. Click Systems Management
b. Click Backup, recovery, and availability
c. Click Backing up your server
d. Click Saving your server with the GO SAVE command
e. Click Saving your whole server with GO SAVE: Option 21
Installing the Hardware for the RISC-to-RISC Upgrade
The hardware service representative should do the following:
1. Participate in the system assurance checkpoint (refer to “System Assurance
Checkpoint” on page 23).
2. Perform the model upgrade.
3. Prepare any parts that need to be sent to IBM.
4. Perform any contracted relocation or rearrangement services prior to returning
the system to the customer for their use.
5. Perform normal cleanup and housekeeping tasks. This includes proper
reporting of time and activities, including any fee-based services delivered.
6. Provide the customer with critical resource documentation.
Managing your new system I/O resources
After the hardware is installed, the customer should do the following:
24 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 37

In the next few steps the customer will be required to use the information from the
service representative to finish the resource management on the new server. The
goal of these steps is to ensure the server is set up and running to the customer’s
needs. You will be asked to save your system. IBM strongly recommends that you
save your system when instructed to do so. Saving your system allows you to
have recovery data in case of disaster.
__ 1. Ensure that you received the source system’s label locations printout from
the hardware service representative (refer to step 7 on page 22). This is
used to get the hardware resources correctly assigned to resource names.
__ 2. Continue the initial program load (IPL) by selecting option 1 from the IPL
or Install the System screen.
Notes:
a. You might see a disk unit format optimize warning message. IBM
suggests that you handle this disk optimization and protection later. See
step 8 on page 30.
b. If the Add All Disk Units to the System ASP screen appears, IBM
recommends that you wait and add the disk units at step 3 on page 29.
Note:
Changing the QIPLTYPE system value may result in receiving the system
reference code (SRC) A900 2000.
SRC A900 2000
You might see the SRC A900 2000 on the control panel display of the
system unit. Or, you might receive message CPF0975 Console did not
vary on on the console display. This SRC and message appear if there
is no device description for the console display. They might also
appear if the QIPLTYPE system value is set to 2.
This SRC and message are normal during the upgrade procedure. The
SRC will disappear when you perform a normal IPL later in the
upgrade procedure.
If no workstation on your system is operational when you receive
SRC A900 2000, continue with “SRC A900 2000 Recovery” on page 40.
Note: The System reference codes and primary partitions topic, located in
the Information Center under System planning and installation ->
Getting started with iSeries -> Managing system operations ->
Starting and stopping the iSeries, describes other SRCs that you
might see during a manual IPL.
__ 3. Sign on to the system as the security officer using the QSECOFR user
profile.
__ 4. At the IPL Options screen verify the date and time. Verify that the following
items are set as follows. If any of these items are not correct, change them
now as shown in the example below.
Start print writers = N
Start to system to restricted state = Y
Define or change system at IPL = Y
__ 5. After the IPL completes, use the Work with Configuration Status
(WRKCFGSTS) *LIN *ALL command to ensure that all communications
lines are varied off.
Chapter 3. Procedure for an Upgrade (RISC-to-RISC) 25
Page 38

__ 6. Vary off all devices, except the display station in use as the console. Use
the WRKCFGSTS *DEV command to display a list of devices. Note that the
console is assigned to the QCTL controller.
__ 7. Use the WRKCFGSTS *CTL *ALL command to ensure that all controllers
are varied off.
__ 8. Use the label location worksheet to assist you with the upgrade process.
On it, the service representative should have indicated controllers (and
devices) that are in different locations than they were on your source
system. You must correct resource names to be able to access the devices
on your system.
__ 9. Run the WRKHDWPRD command to determine whether devices are in
different locations than they were on the source system.
a. On the command line, type WRKHDWPRD and press the Enter key.
b. On the Work with hardware products display, select the Change description
label locations option. Press the Enter key.
c. Read the information on the Using Change Label Locations display and
press the Enter key.
d. Compare the label information on the display with the source system’s
label locations. The source system’s label locations should have been
written down before the hardware upgrade took place (see step 7 on
page 22). Label information matches if the Label column on the display
matches what the source system had. Label information does not match
if any one of the following is true:
v The display has label information, but the source system did not
have label information in that location.
v The source system label information does not match the information
found in the Label column on the display.
v *NONE appears in the Label column on the display, and there is label
information for the source system.
Note: When *NONE appears in the Label column for a controller or
device that was added or upgraded, select option 2. Then
select the correct label description from the list provided. If
any problems arise from this, call your service provider.
v *INCORRECT or *INVALID appears in the Label column.
This means that the type and model number of the hardware
resource information does not match the type and model of the
configuration description that is currently associated with that
resource. The system cannot vary on the configuration description.
v *INCORRECT — where the physical location is also ’**’.
This identifies a controller or device description that no longer has a
valid resource on the system.
e. Do you have any locations that do not match the label information on
the system?
Note: It is normal for the resource names to change during the upgrade
process. Do not use the resource name information from other
displays to match the labels.
YES - Go to step 9f on page 27.
26 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 39

NO - The system label information is the same as the (physical) label.
Go to step 10.
f. On the Change Description Label Locations display, type 2 in the Opt
column for each location that requires a label change. Press the Enter
key.
Note: You may make more than one selection at a time, but if More...
appears on the bottom of the display, do not press the Enter key.
Page forward to select the remaining labels.
g. The Change Description Label display appears.
A list of possible label names is shown. To select the label name (on the
display) that matches the label that was on the source system, perform
the following:
v Type 1 in the Opt column for each location that you want to change.
v Press the Enter key.
Note: If you cannot find the label (on the display) that matches the
label on the source system, contact your hardware service
representative.
h. If you chose to change more than one item, the Change Description Label
display appears for the next label. A message at the bottom of the
display indicates whether the previous change was successful.
i. For all the labels that need a change, repeat the previous three steps.
j. After you change the last label, the Change Description Label Locations
display appears with the updated information. A message at the bottom
of the display indicates whether the last change was successful. If
More... appears on the bottom of the display, scroll forward to view
more information.
k. Press the F17 key on the Change Description Label display to request a
printout of the new information for your records.
Note: The printout will be in the default output queue for your
workstation. You can print it later when you vary on your printer
devices and start printer writers.
l. Verify that the labels on the printout match the labels in the Label
column on your source system. If you find any errors, go back to step 9f
and repeat the steps.
Attention: Do not exchange cards for problem analysis purposes. Card
and device serial numbers are tied to the system configuration.
__ 10. The Change Description Label Locations display appears. Determine whether
the new target system has more storage or communications lines than the
source had. If that is the case, check the work management objects. To do
this, see the Work management topic under Systems Management in the
Information Center.
Chapter 3. Procedure for an Upgrade (RISC-to-RISC) 27
Page 40

Performing a new system backup
__ 1. Perform a normal IPL:
No LPAR LPAR Primary Partition LPAR Secondary Partition
Perform the following:
a. Make sure that the
system is set to B and
Normal (N) mode before
performing the power
down and subsequent
IPL of the system.
b. Once the system is set to
B and Normal mode,
follow these steps:
1) Type PWRDWNSYS on
the command line
and prompt on the
command (Press F4).
2) Make sure that you
select these options
for the PWRDWNSYS
command:
v For How to end,
*CNTRLD
v For Delay time, if
*CNTRLD, 3600
(use the default
value, in seconds,
or the value that
you consider
appropriate given
your software and
system settings)
v For Restart after
power down, *YES
v For IPL Source,
*PANEL
Perform the steps in the No
LPAR column after verifying
that all secondary partitions
are powered down.
For information about
powering down a system,
see the Powering down a
system with logical
partitions topic in the
Information Center under
Systems Management ->
Logical partitions ->
Managing logical partitions
-> Restarting and powering
down a system with logical
partitions.
Perform the steps in the No
LPAR column (set partitions
to B Normal mode, and then
power down and perform an
IPL on the partitions), using
appropriate LPAR service
tool steps, only after
successfully performing a
normal IPL of the primary
partition.
For instructions on setting
the IPL mode, powering
down, and performing an
IPL on secondary partitions,
see the Restarting and
powering down a system
with logical partitions
topic in the Information
Center under Systems
Management -> Logical
partitions -> Managing
logical partitions.
SRC A900 2000 should not appear on the control panel when the IPL
completes. If SRC A900 2000 does appear and you are using Operations
Console, you must perform an IPL in Manual mode (M) on the system to
arrive at the Dedicated Service Tools (DST). Then, in DST, set the console
mode system value to Operations Console, and continue the IPL to sign on.
To set the system to manual mode, do the following:
v For systems without logical partitions, see the Changing operating modes
and IPL types topic in the Information Center under System hardware ->
Restarting the system (IPL) -> IPL type.
v For systems with logical partitions, see the Changing operating mode for
a logical partition topic in the Information Center under Systems
Management -> Logical partitions -> Managing logical partitions ->
Restarting and powering down a system with logical partitions.
28 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 41

To set the console mode to Operations Console at DST, do the following
starting at the DST main menu:
a. Select Work with DST environment.
b. Select System devices.
c. Select Console mode.
d. Depending on your Operations Console configuration, select either
Operations Console (LAN) or Operations Console (Direct).
e. Exit Dedicated Service Tools.
A normal IPL after this process should clear SRC A900 2000.
__ 2. If you want to start device parity on any non-configured units, do it now.
For more information, see the manual Backup and Recovery, SC41-5304-05.A
PDF version of this manual is available from the Information Center under
Systems Management -> Backup, recovery, and availability -> Manuals
and Redbooks.
__ 3. Perform disk unit management (for example, manage disk protection and
disk configuration). To do this, you can use the Work with Disk Units option
from the Dedicated Service Tools display. For more information, see the
manual Backup and Recovery, SC41-5304-05. A PDF version of this manual is
available from the Information Center under Systems Management ->
Backup, recovery, and availability -> Manuals and Redbooks.
__ 4. Save the entire system just after the hardware upgrade is done. Use option
21 on the Save menu. For more information about saving the entire system
using option 21, refer to any of the following:
v The chapter on saving your iSeries server in the manual Backup and
Recovery, SC41-5304-05. A PDF version of this manual is available from the
Information Center under Systems Management -> Backup, recovery,
and availability -> Manuals and Redbooks.
v The Backup, recovery, and availability topic under Systems
Management in the Information Center:
http://www.ibm.com/eserver/iseries/infocenter
To find the procedure for saving the entire system (using option 21) in the
Information Center, do the following:
a. Click Systems Management
b. Click Backup, recovery, and availability
c. Click Backing up your server
d. Click Saving your server with the GO SAVE command
e. Click Saving your whole server with GO SAVE: Option 21
__ 5. Generate reports of the hardware and configuration objects (for each
partition) by issuing the following commands:
DSPHDWRSC TYPE(*LWS) OUTPUT(*PRINT)
DSPHDWRSC TYPE(*STG) OUTPUT(*PRINT)
DSPHDWRSC TYPE(*CMN) OUTPUT(*PRINT)
DSPHDWRSC TYPE(*PRC) OUTPUT(*PRINT)
DSPPTF LICPGM(*ALL) OUTPUT(*PRINT)
__ 6. Print a new system configuration list using Start a service tool option.
a. Do the following on the OS/400 Main menu command line:
Type Start System Service Tools (STRSST).
Press the Enter key.
Chapter 3. Procedure for an Upgrade (RISC-to-RISC) 29
Page 42

b. Type QSECOFR on the System Service Tool Sign on display and press
Enter.
c. Select Start a service tool option. Press the Enter key.
d. On the Start a Service Tool display, select Hardware service manager. Press
the Enter key.
e. From the Hardware Service Manager display, press F6 (print configuration).
f. To return to the AS/400 Main menu, press F3 (Exit) twice. Then, press the
Enter key.
g. Keep the list for future reference.
__ 7. For LPAR systems:
No LPAR LPAR Primary Partition LPAR Secondary Partition
No action Required, skip to
the next numbered step.
Go to the Information Center
(CD-ROM or online) and
follow the procedures on
how to restore an LPAR
system after an upgrade.
After the primary is
configured properly, follow
the steps to recover the
secondary partition
configurations. After
recovering the original
secondary partitions, more
secondary partitions may be
added.
__ 8. If you receive the disk unit format warning screen during the first IPL (IPL
started at step 2 on page 25), then the disk unit format might need to be
optimized. For more information, see the manual Backup and Recovery,
SC41-5304-05. A PDF version of this manual is available from the
Information Center under Systems Management -> Backup, recovery, and
availability -> Manuals and Redbooks.
__ 9. Resume normal operations and verify that all your applications run
properly. IBM recommends that you tune the system performance. There are
billable services available that can do this for you. You can find information
about performance tuning in the Work Management manual. A PDF version
of this manual is available from the iSeries Information Center under
Systems Management -> Work management-> Work Management
Manuals.
30 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 43

Chapter 4. Procedure for a Data Migration (RISC-to-RISC)
This chapter guides you through a data migration (RISC to RISC) that moves data
from one iSeries model server to another. It requires two servers with unique serial
numbers. To migrate data from one iSeries 400 server to an upgraded model that
retains the original serial number, refer to “Chapter 3. Procedure for an Upgrade
(RISC-to-RISC)” on page 17.
Prerequisites for data migration (RISC to RISC)
This procedure assumes that:
v The target system is set up and is running, with only SLIC and the base OS
installed (FC 0205) and that the DASD has been configured for ASP 1. For help
with DASD configuration, you may wish to investigate the IBM billable service
DASD management.
v You have completed a clean-up of the source system, and obtained current
performance benchmarks.
Note: Failure to obtain performance benchmarks may make it extremely difficult
to provide support for your iSeries system after moving to the new
model. IBM strongly recommends that you maintain performance
benchmarks of your system before and after a migration.
v Completed a recovery backup of your source system, at the previous release
level.
Preparing the source system for the migration
This procedure assumes that you have:
v _ Loaded the new OS/400 version on your source system, and brought all
existing objects and licensed programs to the new release level. Complete the
procedure “Preparing the Current System” on page 18 through step 14.
v _ Set the system values, and print the current configuration.
v _ Completed a recovery backup of the source system at the new release level,
and printed your latest system configuration information, including:
– Latest system configuration list from hardware service manager
– Latest device descriptions printout of the source system
– Latest controller descriptions printout of the source system
– Latest PTF level printout from the source system
v _ Run your source system at the new release level for two weeks, and
completed a recovery backup. (Recommended)
v _ Have set up your new system, and/or created the new partition, including
Operations Console setup (if selected in system order).
v _ Done your disk unit management (for example, manage disk protection and
disk configuration). To do this, you can use the Work with Disk Units option from
the Dedicated Service Tools display. For more information, see the manual
Backup and Recovery, SC41-5304-05. A PDF version of this manual is available
from the Information Center under Systems Management -> Backup, recovery,
and availability -> Manuals and Redbooks.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1997, 2001 31
Page 44

v _ Verified the availability of a compatible alternate IPL device (tape unit
attached to the system bus 1). If the system uses an alternate installation device
for install or restore operations, ensure the availability of the location
information for that device.
Data migration (RISC-to-RISC)
__ 1. Using the Backup and Recovery book, Chapter 4, checklist 20 steps 1
through 9, perform a recovery after a complete system loss. Include the
following additions before the IPL. The Backup and Recovery manual,
SC41-5304-05, is available in PDF format from the Information Center under
Systems Management -> Backup, recovery, and availability -> Manuals and
Redbooks.
__ 2. Rename or replace the hardware descriptions on the target system.
a. On the command line, type WRKHDWPRD and press the Enter key.
b. Select the Change description label locations option. Press the Enter
key.
c. If a controller or device no longer has a valid resource on the system, the
Using Change Description Label Locations display appears, allowing
you to make corrections.
d. Determine whether the new target system has different communications
lines or storage than the source system. If so, check the work
management objects. For more information, see the Work management
topic under Systems Management in the Information Center.
__ 3. Install any new LPPs or PTFs. For more information, refer to the Software
Installation book.
__ 4. Change the QAUTOCFG, QIPLTYPE, and QPFRADJ system values to the
desired values. For more details, refer to the book Basic System Operation,
Administration, and Problem Handling , SC41-5206-03.
Verify that all objects were restored from the source system. Use the Backup
and Recovery book to fix any discrepancies.
__ 5. Perform an IPL.
__ 6. Print a copy of your system configuration information:
v _ Generate reports of the hardware and configuration objects by issuing
the following command:
PRTSYSINF
v _ Print the spooled file that was generated by the above command.
v _ Print a new system configuration list using Start a service tool option. To
do this complete the following steps on the AS/400 Main menu command
line:
a. Start System Service Tools by entering:
STRSST
b. On the STRSST display, select Start a service tool option. Press the Enter
key.
c. On the Start a Service Tool display, select Hardware service manager. Press
the Enter key.
d. From the Hardware Service Manager display, press F6 (print
configuration).
e. Your system configuration should print. Keep the list for future
reference.
32 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 45

f. Return to the AS/400 Main menu, Press F3 (Exit) twice, and then press
the Enter key.
__ 7. Save the entire system. Use Option 21 on the Save menu. For more
information about saving the entire system using option 21, refer to any of
the following:
v The chapter on saving your iSeries server in the manual Backup and
Recovery, SC41-5304-05.
v The Backup, recovery, and availability topic under Systems
Management in the Information Center:
http://www.ibm.com/eserver/iseries/infocenter
To find the procedure for saving the entire system (using option 21) in the
Information Center, do the following:
a. Click Systems Management
b. Click Backup, recovery, and availability
c. Click Backing up your server
d. Click Saving your server with the GO SAVE command
e. Click Saving your whole server with GO SAVE: Option 21
__ 8. Resume normal operations and verify that all your applications run
properly.
__ 9. IBM recommends that you tune the system performance. There are billable
services available that can do this for you. You can find information about
performance tuning in the Work Management manual. A PDF version of this
manual is available from the iSeries Information Center under Systems
Management -> Work management-> Work Management Manuals.
Chapter 4. Procedure for a Data Migration (RISC-to-RISC) 33
Page 46

34 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 47

Appendix A. AS/400 Global Services
The following appendix describes on-site support or services that are available. For
more information refer to the web site: http://www.as400.ibm.com/services
iSeries and AS/400 Data Migration Services
IBM has a fee-based service called AS/400 Data Migration Services, which moves
customer data migrated from existing disk units to new or replacement disk units.
You can do this without the need for a save and restore with tape. This procedure
decreases the overall time that is needed to perform an upgrade.
Selected hardware service representatives have been trained to deliver this service.
Only an AS/400 Data Migration Services trained hardware service representative
should attempt this procedure. This representative can assess the appropriateness
of this activity.
If you would like more information about AS/400 Data Migration Services, contact
your IBM iSeries 400 and AS/400 hardware service representative. Your IBM
iSeries 400 and AS/400 hardware service representative can perform the procedure
or put you in contact with the closest trained hardware service representative.
LPAR Planning and Implementation Services
It will assist a customer in planning and installing iSeries 400 and AS/400 logical
partitioning on a new or existing n-way server (Models 6xx, Sxx, 7xx, 8xx, or later).
This service will provide a planning session with the customer to ensure that all
known customer requirements are fully discussed with a final hardware and
software configuration and installation schedule provided. The services specialist
can also perform on-site implementation services to install, configure, and
optionally manage the new LPAR configuration.
For more information, contact your local IBM representative or business partner or
see the following Web site:
http://www.as400.ibm.com/lpar
iSeries Planning and Migration Services
It will assist a customer in planning and migrating to the iSeries 400 V4R5 or later
server line. This service will provide a planning session with the customer to
ensure that all known customer requirements are fully discussed with a final
hardware and software configuration and installation plan provided. The services
specialist can also perform on-site services to upgrade the server to V5R1, convert
the CEC and IO using a new migration expansion unit (if required) and provide
additional migration services.
System Migration Services
IBM has a fee-based service offering called AS/400 System Migration Services,
which maximizes productivity when a customer installs a new iSeries server.
AS/400 System Migration Services can move the customer’s data from one system
and restore it to a new system by using tape. The new system may be the same
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1997, 2001 35
Page 48

release level or a different release level. Selected hardware service representatives
have been trained to deliver this service. Only an AS/400 System Migration
Services-trained hardware service representative should attempt this procedure.
This representative can assess whether this activity is appropriate. If you would
like more information about the AS/400 System Migration Services offering,
contact your IBM iSeries 400 and AS/400 hardware service representative. Your
IBM iSeries 400 and AS/400 hardware service representative can perform the
procedure or put you in contact with the closest AS/400 System Migration
Services-trained service representative.
Related Support Services
For related support services, see the AS/400 Technical Support Web site at
http://www.as400service.ibm.com.
Notes:
1. Contact your marketing representative for information about the services that
are available in your area.
2. For information about IBM Global Services, see the following Web site:
http://www.ibm.com/services
AS/400 Solution Services
See: http://www-1.ibm.com/services/its/us/as400.html
Installation Services
With Installation Services, IBM takes over the responsibility of planning and
installing the iSeries 400 hardware and software. This service includes the
following:
v IBM Smooth Start Services for iSeries 400.
v A project manager for installation
v On-site education for both the system operation and the recovery management
v System software loading and enabling
v Installation of Customer Set Up (CSU) or non-IBM equipment
v Comprehensive site planning
Performance Examinations
The IBM iSeries 400 and AS/400 Performance Examination (PERFEX) provides an
in-depth analysis of applications by IBM Performance Consultants at the
customer’s location. This service includes the following:
v High quality graphical and chart representation
v Performance recommendations and conclusions
v A detailed, written summary
v Performance education
Consulting Services
Consulting services provide customized consultation on any iSeries 400 topic that
is important to the customer. This personalized assistance from IBM consultants is
one of the most popular services at IBM. The topics include the following:
v Capacity planning
v Performance analysis
36 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 49

v Application planning to implementation
v Application design review
v Application design
v AS/400 Communications network consulting
v AS/400 unattended operations for communications applications
v Security audit
v Multi-vendor integration services
v Client Access/400
v AS/400 recovery readiness audit
v Multiple implementations
Midrange Enhanced Software Service (MRESS)
The purpose of MRESS is to increase the technical staff of the customers who want
a direct link to an IBM Software Service Representative. The representative
supports iSeries 400 and AS/400 system software, makes PTF recommendations,
and notifies the customer about problems that might affect system operation.
MRESS includes the following:
v Software problem resolution
v PTF consultation
v Pro-active account support
Appendix A. AS/400 Global Services 37
Page 50

38 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 51

Appendix B. Considerations and Solutions
See the AS/400 Homepage, AS/400 Information Center for further information
regarding your concerns.
http://www.as400.ibm.com
http://www.as400.ibm.com/infocenter
http://www.ibm.com/eserver/iseries/infocenter
IBM HTTP Server for AS/400
When migrating your AS/400 system from V3R7 to V4R2, some existing common
gateway interface, CGI programs may not function correctly. The CGI interface in
V4R2 was changed to improve performance.
What was the change?
The AS/400 runtime environment now allows the IBM HTTP Server for AS/400 to
put into effect byte streams for CGI standard in and standard out.
Why was the change made?
Customer requirements caused this change to remove the line length limitations
on, (standard in and standard out).
What problems were detected or flagged?
1. Programs that call QtmhRdStdin multiple times to read the standard in data
are incorrect, and this does not work.
2. All programs that read from (standard in), (QtmhRdSdtin) need to check the
Content-Length environment variable to determine the number of bytes to read.
Programs that do not use the Content-Length environment variable and read
more than the Content-Length will not work.
Why was the change made?
Customer requirements to remove the 250 byte limit on standard in and standard
out, motivated the change.
When was the change made?
The change is available via the following PTFs:
v V4R1 - 5769SS1 SF46810
v 5769TC1 SF47332
v V4R2 - 5769TC1 SF46558
What should the customer do?
The customer should use the Web Programming Guide to ensure that the programs
meet standard guidelines.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1997, 2001 39
Page 52

Operations Console
For information about setting up and configuring Operations Console, see the
manual Operations Console Setup, SC41-5508-02. A PDF version of this manual is
available from the iSeries Information Center under Client Access Express ->
Manuals and Redbooks. If you are setting up a new iSeries server, see the cabling
instructions in the cabling poster.
OptiConnect
For information pertaining to an upgrade, see the book OptiConnect for OS/400,
SC41-5414-02.
Integrated Netfinity Server
See the book Getting Started with Integrated Netfinity Server, SC41-5123-01, for
information on Integrated Netfinity Server.
Clustering and Logical Partitions
IBM representatives can get further information about clustering and logical
partitions from the iSeries Information Center
http://www.ibm.com/eserver/iseries/infocenter
Follow the link to Planning and then Logical Partitions.
Lotus Notes Enhanced Integration
For V4R4M0, OS/400 option 24 (OS/400 Lotus Notes Enhanced Integration) is no
longer supported, and is deleted when upgrading to V4R4M0. A migration of the
data in (OS/400 Lotus Notes Enhanced Integration) must be accomplished before
the upgrade. IBM recommends migrating the data to Lotus Domino. For detailed
migration instructions see the following URL:
http://www.as400.ibm.com/techstudio
OnDemand
Consideration when upgrading to 5769-RD1 OnDemand:
v If your target release is Version 4 Release 2 (or a later release) and your source
system has either of the following features installed:
– 5716-RD1 Option 1 - OnDemand output queue archival feature
– 5716-RD1 Option 2 - OnDemand object archival feature
And you plan to use either of the following features on your target system:
– 5769-RD1 Option 1 - OnDemand output queue archival feature
– 5769-RD1 Option 2 - OnDemand object archival feature
Then:
– For OnDemand migration and upgrade information, see the book LPS:
OnDemand for AS/400, GC41-5079-01.
SRC A900 2000 Recovery
Attention: Use this procedure only if no workstation on your system is
operational:
40 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 53

1. Find your copy of the Basic System Operation, Administration, and Problem
Handling book. It describes the procedures for working with the control panel
on your processor unit. Use it for more information on how to perform the
remaining tasks.
2. Use the system control panel to place your system in manual mode.
3. Use the system control panel to force power down on your system.
4. Perform an IPL on your system.
5. Sign on as QSECOFR.
6. On the IPL or Install the System display, select option 1 (perform an IPL).
7. On the IPL Options display, specify Y for the Define or change the system at
IPL prompt.
8. On the Define or Change the System at IPL display, select 3 (System value
commands).
9. On the System Value Commands display, select 3 (Work with System Values).
10. On the Work with System Values display, type QIPLTYPE in the Position to
field.
11. In the Option column for the QIPLTYPE system value, type 2 (Change).
12. On the Change System Value display for the QIPLTYPE system value, type 2
(Attended IPL, console in debug mode).
13. Press the Enter key. You see the Work with System Values display.
14. Press F3 twice to return to the Define or Change Your System display.
15. Press F3 (Exit and continue IPL) to continue your IPL.
How to Move Files That Have Been Saved with Storage Free Specified
If you have saved database files and specified STG(*FREE), you must take special
steps to transfer the descriptive information about those files to your RISC target
system. (All customers must do this, whether or not you have the Media and
Storage Extensions product installed.) When you save a database file and specify
STG(*FREE), the system saves the contents of the file. The system then deletes the
contents from the system copy of the file, so that the contents exist only on the
save media. The file description information, including a list of members, remains
on the system as a type of archival record. To create usable object descriptions for
your RISC target system, use the procedures that follow. If your source system
does not have adequate auxiliary storage to restore the contents of archival files,
you might need to make arrangements to use another system to restore your files
and save them again. Make sure that the system has a tape unit that is compatible
with the tape unit that you will have on your upgraded system.
How to Move Freed Database Files without New Members
Use the procedure below only if both of the following conditions are true:
1. The database file on the source system was previously saved with STG(*FREE).
2. No new members were added to the file after it was saved on the source
system.
If both conditions were true, move freed database files without new members as
follows:
1. For a physical file, use the
RSTOBJ
command or the
Appendix B. Considerations and Solutions 41
Page 54

RSTLIB
command to restore the file. For a logical file, use the
RSTOBJ
command or the
RSTLIB
command to restore the based-on physical files.
2. If you need to save the files separately to make space available on your system,
use the
SAVOBJ or SAVLIB
command. Do not specify STG(*FREE). Make sure that you mark the save
tapes. You can then delete the files or save them again on different tapes with
STG(*FREE).
3. After you have restored the files to your target system, you can save them
again with STG(*FREE). The object description remains on your upgraded
system as an archival record.
If you have a file that has some members with contents and other members that
were saved with STG(*FREE), you must create a version of the file that has a
complete set of members with contents. You do this by restoring the members that
were saved with STG(*FREE). When the complete database file is on the system,
perform again the specific instructions for saving your system. These instructions
are outlined in the upgrade or migration procedure that sent you here.
42 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 55

Appendix C. Obtain the Latest Preventive Service Planning Information
You need the most recent cumulative package of the Preventive Service Planning
Information. The IBM software support center updates this information regularly. It
provides the most current information about conditions that could impede your
software installation process.
There are multiple preventive service planning documents, categorized by topic.
We recommend that you review at least the software installation document and the
general document for the release of the operating system. The general document
lists topics covered in additional preventive service planning information
documents that you might want to order, if they apply to your system.
You can order the preventive service planning documents through electronic
customer support:
PSP Document Command to Order, program temporary fix
(PTF)
General document for the release Send Program Temporary Fix Order
(SNDPTFORD) SF98xxx
V4R4 software installation SNDPTFORD SF98040
V4R4 (System Upgrade Road Map RISC to
RISC)
V4R5 software installation SNDPTFORD SF98050
V4R5 (System Upgrade Road Map RISC to
RISC)
V5R1 software installation SNDPTFORD SF98060
V5R1 (System Upgrade Road Map RISC to
RISC)
SNDPTFORD SF98161
SNDPTFORD SF98163
SNDPTFORD SF98165
For all customers, PTFs can be downloaded from the following Web site:
http://as400service.ibm.com
You need to register at this site. To download a PTF, go to the AS/400 Internet PTF
Facility:
1. Click Fixes, Downloads and Updates.
2. Click Internet PTF Downloads (iPTF).
If you do not have access to electronic customer support, contact your software
support provider to obtain this information. This ensures that you will receive the
required PTF as well. Information about displaying and printing preventive service
planning documents is available in the Ordering fixes topic under System
planning and installation -> Getting started with iSeries -> Managing system
operations -> Managing fixes -> Ordering preventive service packs (PSPs) in the
Information Center.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1997, 2001 43
Page 56

44 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 57

Appendix D. Notices
This information was developed for products and services offered in the U.S.A.
IBM may not offer the products, services, or features discussed in this document in
other countries. Consult your local IBM representative for information on the
products and services currently available in your area. Any reference to an IBM
product, program, or service is not intended to state or imply that only that IBM
product, program, or service may be used. Any functionally equivalent product,
program, or service that does not infringe any IBM intellectual property right may
be used instead. However, it is the user’s responsibility to evaluate and verify the
operation of any non-IBM product, program, or service.
IBM may have patents or pending patent applications covering subject matter
described in this document. The furnishing of this document does not give you
any license to these patents. You can send license inquiries, in writing, to:
IBM Director of Licensing
IBM Corporation
500 Columbus Avenue
Thornwood, NY 10594
U.S.A.
For license inquiries regarding double-byte (double-byte character set (DBCS))
information, contact the IBM Intellectual Property Department in your country or
send inquiries, in writing, to:
IBM World Trade Asia Corporation
Licensing
2-31 Roppongi 3-chome, Minato-ku
Tokyo 106, Japan
The following paragraph does not apply to the United Kingdom or any other
country where such provisions are inconsistent with local law:
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS MACHINES CORPORATION PROVIDES THIS
PUBLICATION “AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Some states do not allow disclaimer of express or
implied warranties in certain transactions, therefore, this statement may not apply
to you.
This information could include technical inaccuracies or typographical errors.
Changes are periodically made to the information herein; these changes will be
incorporated in new editions of the publication. IBM may make improvements
and/or changes in the product(s) and/or the program(s) described in this
publication at any time without notice.
Licensees of this program who wish to have information about it for the purpose
of enabling: (i) the exchange of information between independently created
programs and other programs (including this one) and (ii) the mutual use of the
information which has been exchanged, should contact:
IBM Corporation
Software Interoperability Coordinator
3605 Highway 52 N
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1997, 2001 45
Page 58

Rochester, MN 55901-7829
U.S.A.
Such information may be available, subject to appropriate terms and conditions,
including in some cases, payment of a fee.
The licensed program described in this information and all licensed material
available for it are provided by IBM under terms of the IBM Customer Agreement
or any equivalent agreement between us.
Any performance data contained herein was determined in a controlled
environment. Therefore, the results obtained in other operating environments may
vary significantly. Some measurements may have been made on development-level
systems, and there is no guarantee that these measurements will be the same on
generally available systems. Furthermore, some measurement may have been
estimated through extrapolation. Actual results may vary. Users of this document
should verify the applicable data for their specific environment.
Information concerning non-IBM products was obtained from the suppliers of
those products, their published announcements, or other publicly available sources.
IBM has not tested those products and cannot confirm the accuracy of
performance, compatibility, or any other claims related to non-IBM products.
Questions on the capabilities of non-IBM products should be addressed to the
suppliers of those products.
Trademarks
All statements regarding IBM’s future direction or intent are subject to change or
withdrawal without notice, and represent goals and objectives only.
The information herein is subject to change before the products described become
available.
This information contains examples of data and reports used in daily business
operations. To illustrate them as completely as possible, the examples include the
names of individuals, companies, brands, and products. All of these names are
fictitious and any similarity to the names and addresses used by an actual business
enterprise is entirely coincidental.
If you are viewing this information softcopy, the photographs and color
illustrations might not appear in your view.
The following terms are trademarks of International Business Machines
Corporation in the United States, or other countries, or both:
Advanced 36
Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking (APPN) Performance Edge
Application System/400
APPN
AS/400
AS/400e
Client Access/400
IBM
Integrated Netfinity Server
Operating System/400
OS/400
46 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 59

PowerPC AS
RETAIN
System/36
400
C-bus is a trademark of Corollary, Inc.
Lotus is a trademark of Lotus Development Corporation in the United States, or
other countries, or both.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows NT, the Windows 95 and the Windows 98 logo are
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Java and HotJava are trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and other countries licensed
exclusively through X/Open Company Limited.
PC Direct is a registered trademark of Ziff Communications Company and is used
by IBM Corporation under license.
Other company, product, and service names may be trademarks or service marks
of others.
Appendix D. Notices 47
Page 60

48 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 61

Index
A
A900 2000 SRC
recovery 25
A900 2000 system reference code
(SRC) 25
alternate installation device
installing from
considerations for placing an
order 11
verify availability of hardware 23
AS/400 Data Migration Services 35
AS/400 Solution Services 36
AS/400 System Migration Services 35
auxiliary storage pool (ASP) 10
C
command, CL
Display Hardware Resources
(DSPHDWRSC) 22, 29
DSPHDWRSC (Display Hardware
Resources) 22, 29
Retrieve Configuration Source
(RTVCFGSRC) 22
RTVCFGSRC (Retrieve Configuration
Source) 22
considerations 12, 14
Consulting Services 36
CPF0975 message 25
customer’s upgrade needs
additional applications 7
expectations 7
financial considerations 7
new technology 7
problems 7
requirements 7
customer tasks
after hardware installed 24
before installing hardware 23
before upgrade takes place 20
current system preparation 18
when hardware arrives 18
D
data migration 1
Display Hardware Resources
(DSPHDWRSC) command 22, 29
DSPHDWRSC (Display Hardware
Resources) command 22, 29
F
Files Saved with Storage Free
Specified 41
from models 4xx, 5xx, Sxx or 6xx to a
7xx 12
from models 6xx or 7xx to a 8xx 14
H
hardware investment 3
hardware service representative tasks 24
how long will the data migration take 5
how long will the upgrade take 3
How to Move Files That Have Been
Saved with Storage Free Specified 41
I
information
ordering additional
preventive service planning 43
Installation Services 36
installing
from an alternate installation device
considerations for placing an
order 11
installing the hardware 24
Interactive Specify codes, Sxx 13
iSeries Planning and Migration
Services 35
L
LPAR Planning and Implementation
Services Offering 35
M
MES 3
MES upgrade 1
message
CPF0975 25
Midrange Enhanced Software Service 37
MRESS 37
N
Notices 45
O
ordering assistance 15
ordering prerequisites
hardware considerations 9
software items 9
system configurations
considerations 9
ordering responsibilities 14
ordering specifications 11
ordering tasks
hardware 14
software 14
P
Performance Examinations 36
performing the upgrade
responsibilities 17
tasks 17
placing the order 14
planning your order 7
PowerPC 2, 3
preventive service planning information
ordering 43
product support 35
R
recovery
SRC A900 2000 25
related support services 36
Retrieve Configuration Source
(RTVCFGSRC) command 22
return material equipment report
(RMER) 24
RISC 2, 3
RISC-to- RISC data migration 1
RISC-to-RISC upgrade 1
RTVCFGSRC (Retrieve Configuration
Source) command 22
S
sending the order 15
sending the order to other than IBM 15
services 9
software release to upgrade 5
SRC (system reference code)
A900 2000 25
recovery 25
Sxx Interactive Specify codes 13
system reference code (SRC)
A900 2000 25
recovery 25
U
upgrade overview 1
upgrades covered in this road map
models 170 1
models 2xx 1
models 6xx 1
models 7xx 1
models 8xx 1
models Sxx 1
upgrading
memory considerations 10
W
what is a data migration 3
what is an upgrade 2
why upgrade 2
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1997, 2001
49
Page 62

50 iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map V5R1
Page 63

Readers’ Comments — We’d Like to Hear from You
iSeries
iSeries 940x RISC-to-RISC Road Map
Version 5
Publication No. SA41-5155-05
Overall, how satisfied are you with the information in this book?
Very Satisfied Satisfied Neutral Dissatisfied Very
Dissatisfied
Overall satisfaction hhhhh
How satisfied are you that the information in this book is:
Very Satisfied Satisfied Neutral Dissatisfied Very
Dissatisfied
Accurate hhhhh
Complete hhhhh
Easy to find hhhhh
Easy to understand hhhhh
Well organized hhhhh
Applicable to your tasks hhhhh
Please tell us how we can improve this book:
Thank you for your responses. May we contact you? h Ye s h No
When you send comments to IBM, you grant IBM a nonexclusive right to use or distribute your comments in any
way it believes appropriate without incurring any obligation to you.
Name Address
Company or Organization
Phone No.
Page 64

___________________________________________________________________________________________________
Readers’ Comments — We’d Like to Hear from You
SA41-5155-05
_________________________________________________________________________________________
Fold and Tape Please do not staple Fold and Tape
NO POSTAGE
NECESSARY
IF MAILED IN THE
UNITED STATES
Cut or Fold
Along Line
BUSINESS REPLY MAIL
FIRST-CLASS MAIL PERMIT NO. 40 ARMONK, NEW YORK
POSTAGE WILL BE PAID BY ADDRESSEE
IBM CORPORATION
Attention Department 542
ID CLERK
3605 Highway 52 N
Rochester, MN 55901-7829
_________________________________________________________________________________________
Fold and Tape Please do not staple Fold and Tape
SA41-5155-05
Cut or Fold
Along Line
Page 65

Page 66

Printed in the United States of America
on recycled paper containing 10%
recovered post-consumer fiber.
SA41-5155-05
 Loading...
Loading...