Hyundai HD-65, HD-72, HD-78 Wiring Diagram
INTRODUCTION E103F6A0
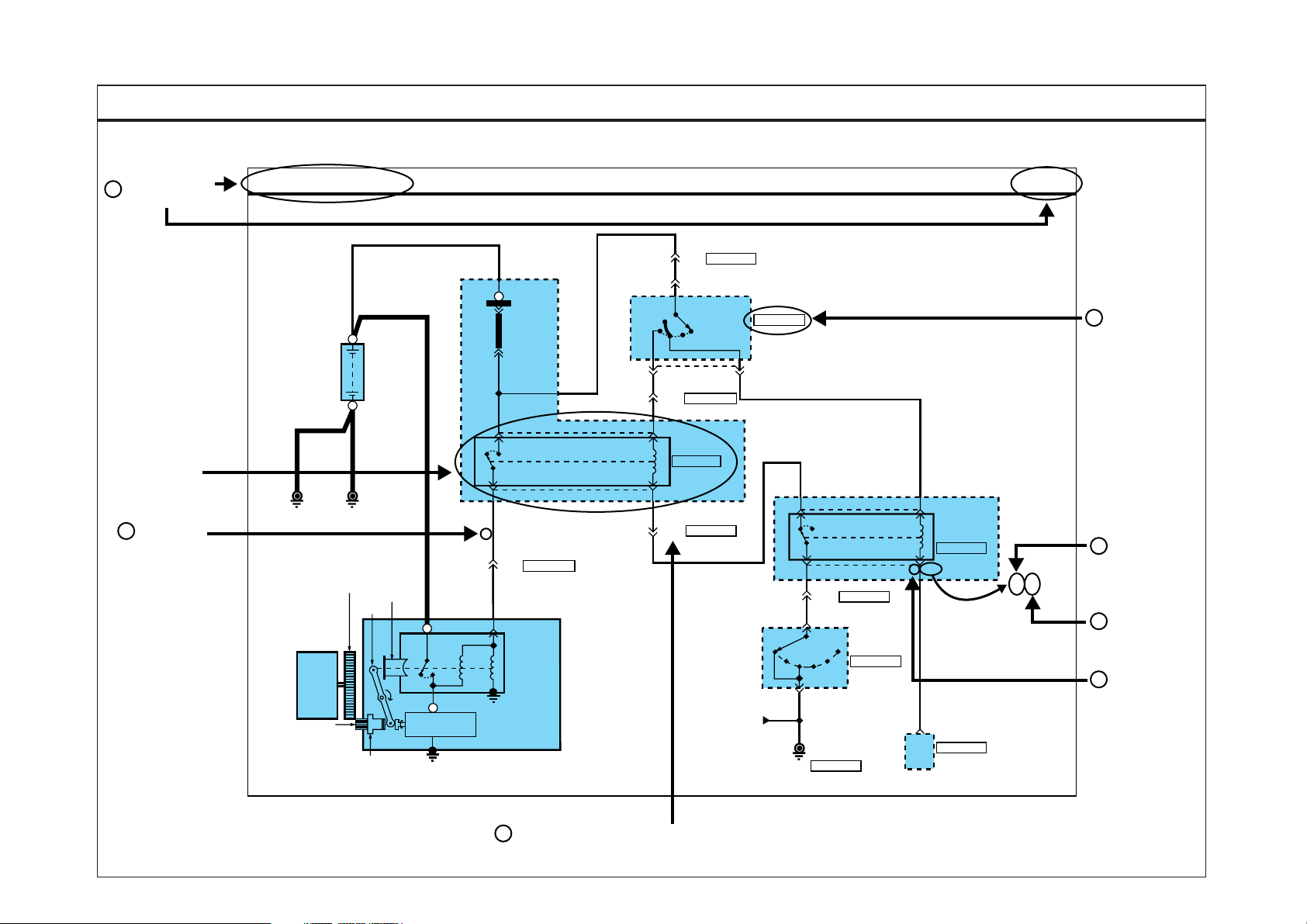
STARTING SYSTEM
System name/
1
System code
Component
symbol
Wire color
6
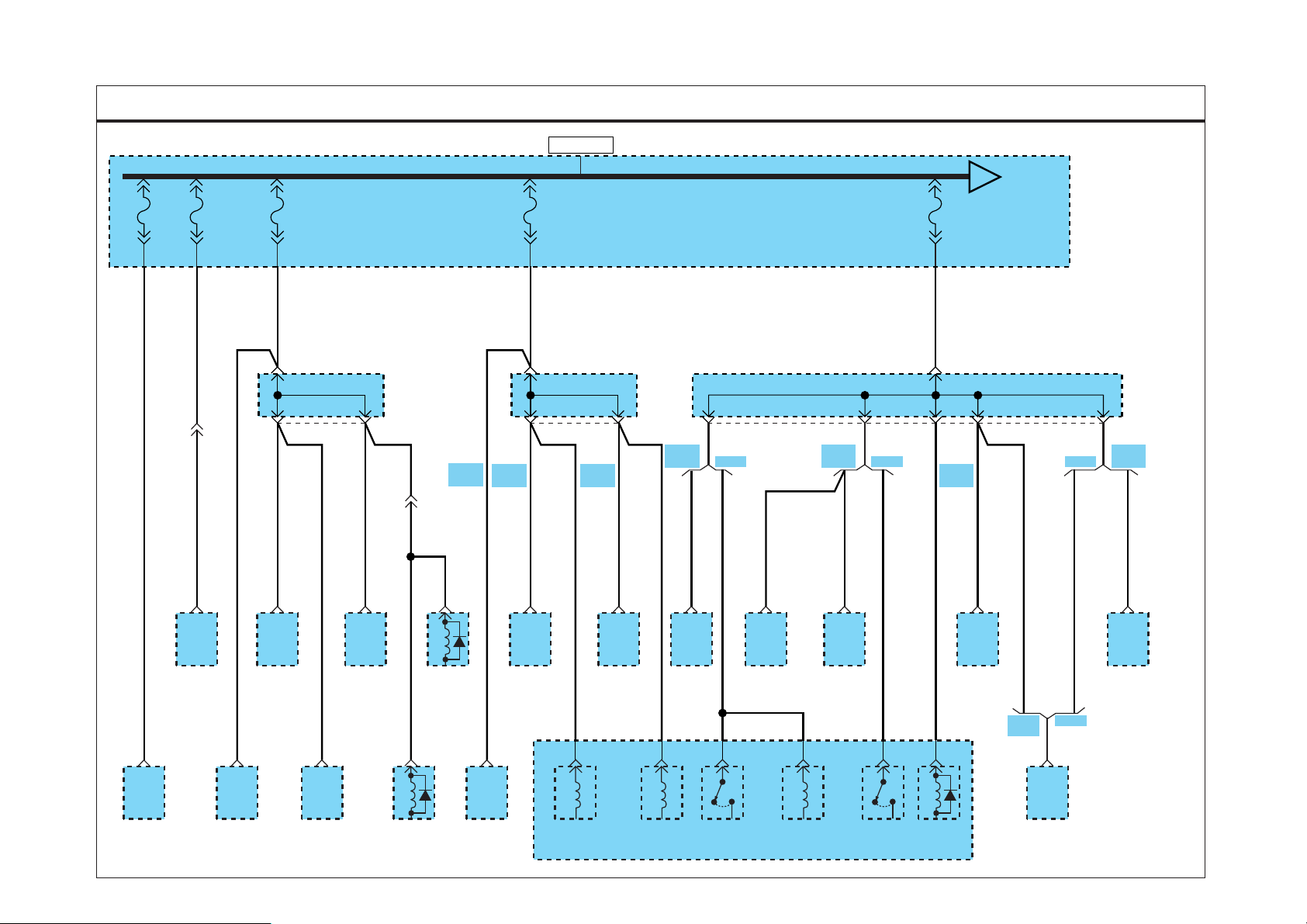
STARTING SYSTEM (1)
BATTERY
GROUND
ENGINE
PINION
GEAR
B
BODY
GROUND
FLYWHEEL
LEVER
OVERRUNNING
CLUTCH
BATTERY
MAGNETIC
WBB
MOTOR
B/Y
R
R
1
2
L
1
FUSIBLE
LINK(IGN)
30A
EE01
PHOTO 07
START
SOLENOID
START
MOTOR
5
W
1
W
P
P
ST
5
3
ON
EM01
E27
E27
EM025
R
1
R
6
EM03
M11
AM
LOCK
ACC
PHOTO 08
START
RELAY
PHOTO 02
PHOTO 08
PHOTO 08
4
G
See
Ground
Distribution
IGNITION
SWITCH
PHOTO 01
M11
E/R
RELAY &
FUSE
BOX
P
R
Gr
Gr
7
B
B
G10
4
8
N
C34
MC027
PHOTO 09
C34
L
2
D
PHOTO 05
TRANSAXLE
RANGE
SWITCH
PHOTO 04
51
3
W
6
M19
BURGLAR
ALARM
RELAY
PHOTO 03
M19
M70-1
ETACM
PHOTO 06
SD360-1
I/P
JUNCTION
BOX
M19
Picture number
4
for component
locations
Harness
7
classification
Connector
classification
8
number
Connector
5
terminal
number
GI-1INTRODUCTION (1)
3
Distinguish harness from harness connection connector
E2RG360A
EVT GI70001L
INTRODUCTION
STARTING SYSTEM
STARTING SYSTEM (2)
M05
GI-2INTRODUCTION (2)
SD360-2
M06 M11 M13
Connector
2
configurations
(components)
Explanation of
connector code
234
KET_090II_04F_W KET_090II_10M_W
AMP_PLM2_02F_B KET_090II_06M_W
Unused
pin
*
12
12
56 8910
*
M81M67
12
3456
4
*
M05
1
234
KET_090II_04F_W
a
b
cde
1234
KUM_AR_04F_W KET_090II_10F_W
BLANK BLANK
a : Connector manufacturer
b : Terminal series number
c : The number of connector terminals
d : Connector distinguishing
B (Black)
Br (Brown)
e : Connector color
abbreviations
G (Green)
Gr (Gray)
L (Blue)
R (Red)
W (White)
Y (Yellow)
Female Pin : F
Male Pin : M
134
*
**
5678
E2RG360B
EVT GI70002L
INTRODUCTION
1
Pages by system/ Name of Schematic diagram
Each page is consisted of circuits by system. This schematic
diagram includes the path of electricity flow, connection condition
for each switch, and the function of other relevant circuits at once.
It is applicable to real service work.
It is very important to understand relevant circuits exactly before
troubleshooting diagnosis.
Circuits by system depends upon part number and are indicated
on schematic diagram index.
2
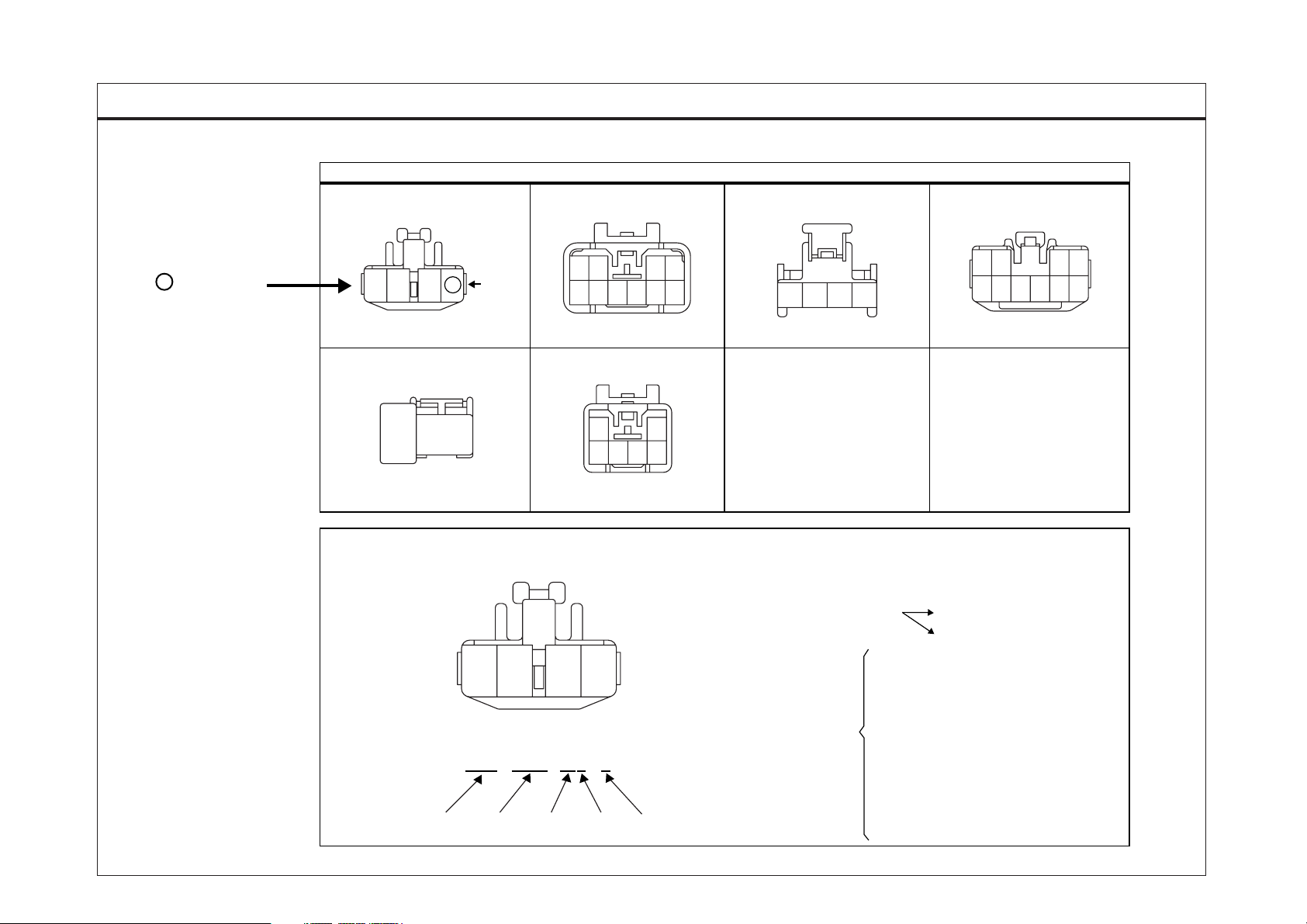
Connector configuration (components)
The connector figure of components in the schematic diagram
by system is indicated on the last page of schematic diagram.
It shows the front of the connector on the harness side when not
to the harness connector. The terminal number on each connector
can be obtained by following the pattern used in 5 connector view
and numbering order. Unused terminals are marked with an asterisk ( ).
3
Connector configurations (connection between harnesses)
When connecting the harness with connector between harnesses,
it shows female and male connectors and indicates them on the
connector configurations group.
EM02
GI-3INTRODUCTION (3)
5
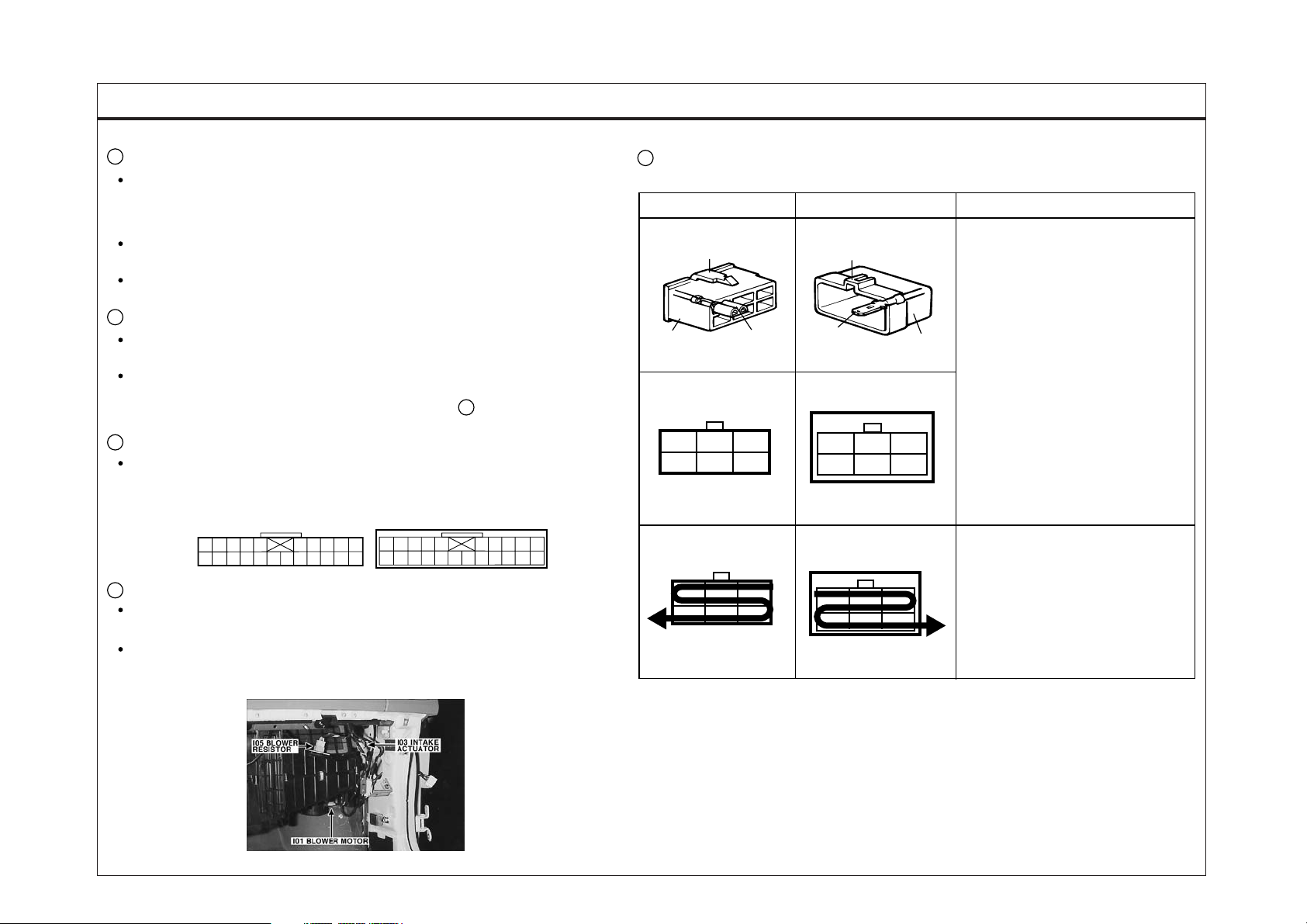
CONNECTOR VIEW AND NUMBERING ORDER
Female
Locking point
Housing Pin
*
321
654
Male
Locking point
Pin
123
456
Housing
Remarks
It is not the shape of the connector
housing, but the connector pin
that distinguishes between male
or female connectors.
When numbering female and male
connectors, refer to the numbering
order in the following table.
Some connectors may not follow this
method of numbering order.
For individual detailed numbering,
refer to the CONNECTOR
CONFIGURATIONS.
10 9 8 7
4
Component locations
6543
2122
1718192016 15
2
1314 12 11
2
1
1
13 141211
6
543
17 18 19
16
15
20
10987
21 22
To find the components easily, a component locations diagram is
indicated with "PHOTO NO" on the lower portion of the component name.
To make it easy to distinguish connectors, the connector in the
picture is indicated being installed in the vehicle.
PHOTO 03
Numbered in order from upper
right to lower left
321
654
123
456
Numbered in order from upper
left to lower right
NOTE
UNLESS OTHERWISE STATED, ALL CONNECTOR VIEWS ARE FROM
THE TERMINAL SIDE OF THE CONNECTOR.
EVT GI70003L
INTRODUCTION
6
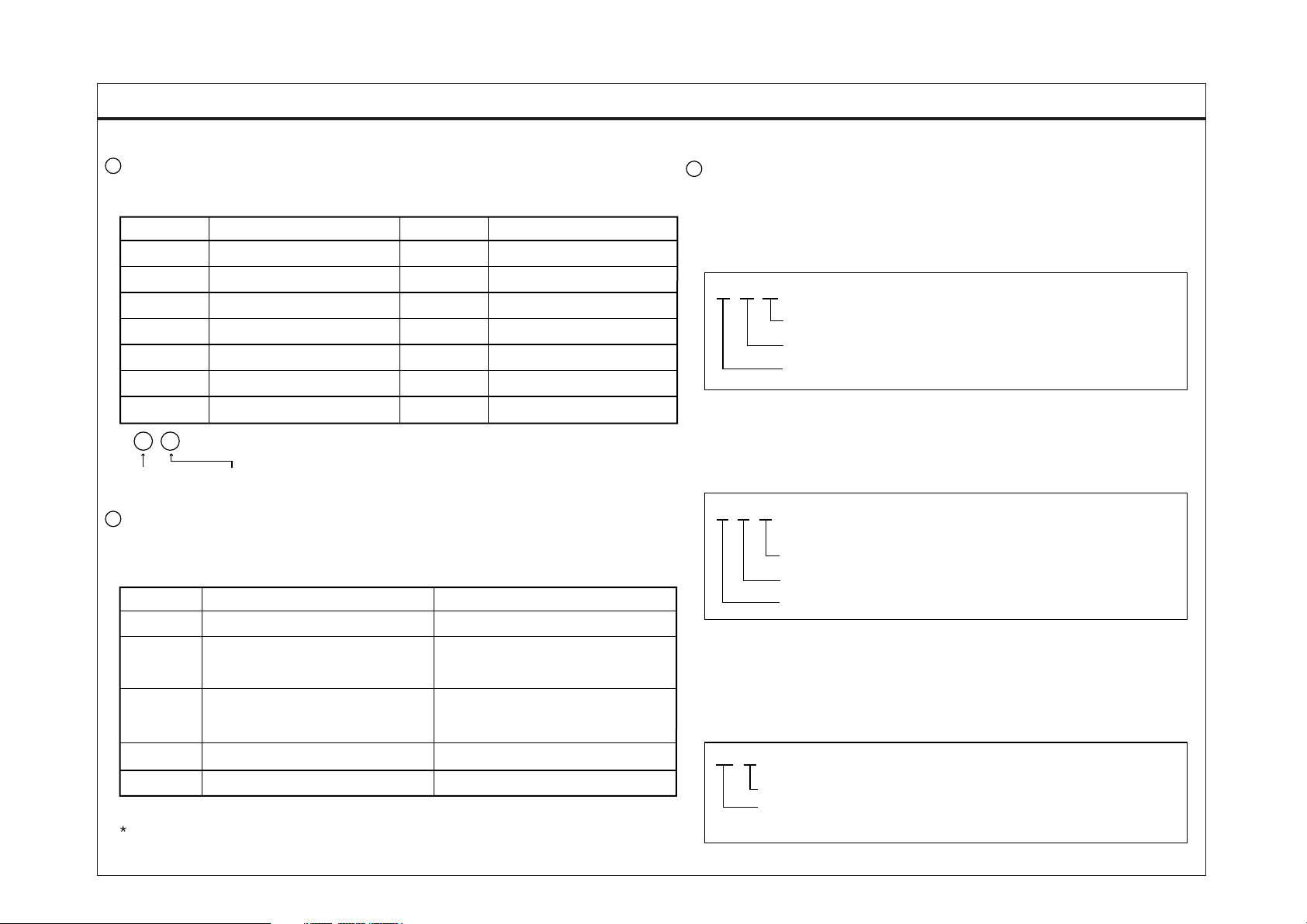
WIRE COLOR ABBREVIATIONS
The following abbreviations are used to identify wire colors in the
circuit schematics.
Symbol Color of wire Symbol Color of wire
B
Br
G
Gr
L
Lg
T
/ B : Black stripe with yellow ground (2 colors)
Y
*
the color of
background
7
HARNESS CLASSIFICATION
Electrical wiring connectors are classified according to the wiring parts in the
Harness Layouts.
E
M
C
Engine harness
Main, Floor, Floor center,
Roof harness
Chassis, Side marker,
EXH M/V harness
Black
Brown
Green
Gray
Blue
Light Green
Tan
the color of
stripe
O
P
R
W
Y
Pp
LI
LocationHarness nameSymbol
Engine compartment
Passenger compartment,
Floor, Roof
Chassis compartment
Orange
Pink
Red
White
Yellow
Purple
Light Blue
GI-4INTRODUCTION (4)
8
CONNECTOR IDENTIFICATION
A connector identification symbol consists of a wiring harness location
classification symbol corresponding to a wiring harness location and
number corresponding to the connector.
These connector locations can be found in the HARNESS LAYOUTS.
For example:
E 10 -1
Number corresponding to sub-connector (Serial Number)
Number corresponding to main connector (Serial Number)
Symbol indicating wiring harness (Engine wiring harness)
NOTE
Connectors which connect each wiring harness are represented by
the following symbols.
For example:
M R 01
Number corresponding to main connector (Serial Number)
Rear wiring harness
Main wiring harness
JUNCTION BLOCK IDENTIFICATION
A junction block identification symbol consists of a wiring harness
location classification symbol corresponding to a wiring harness location
and number corresponding to the connector in the junction block.
For example:
A
D
It depends on vehicles, it is necessary to check the harness name symbol
on the harness layouts for detailed symbol.
Air con, A.B.S harness
Door harness
Under crash pad and Floor
Door
I/P- A
Connector name
Abbreviation of the word
"Passenger compartment junction block"
EVT GI70004L
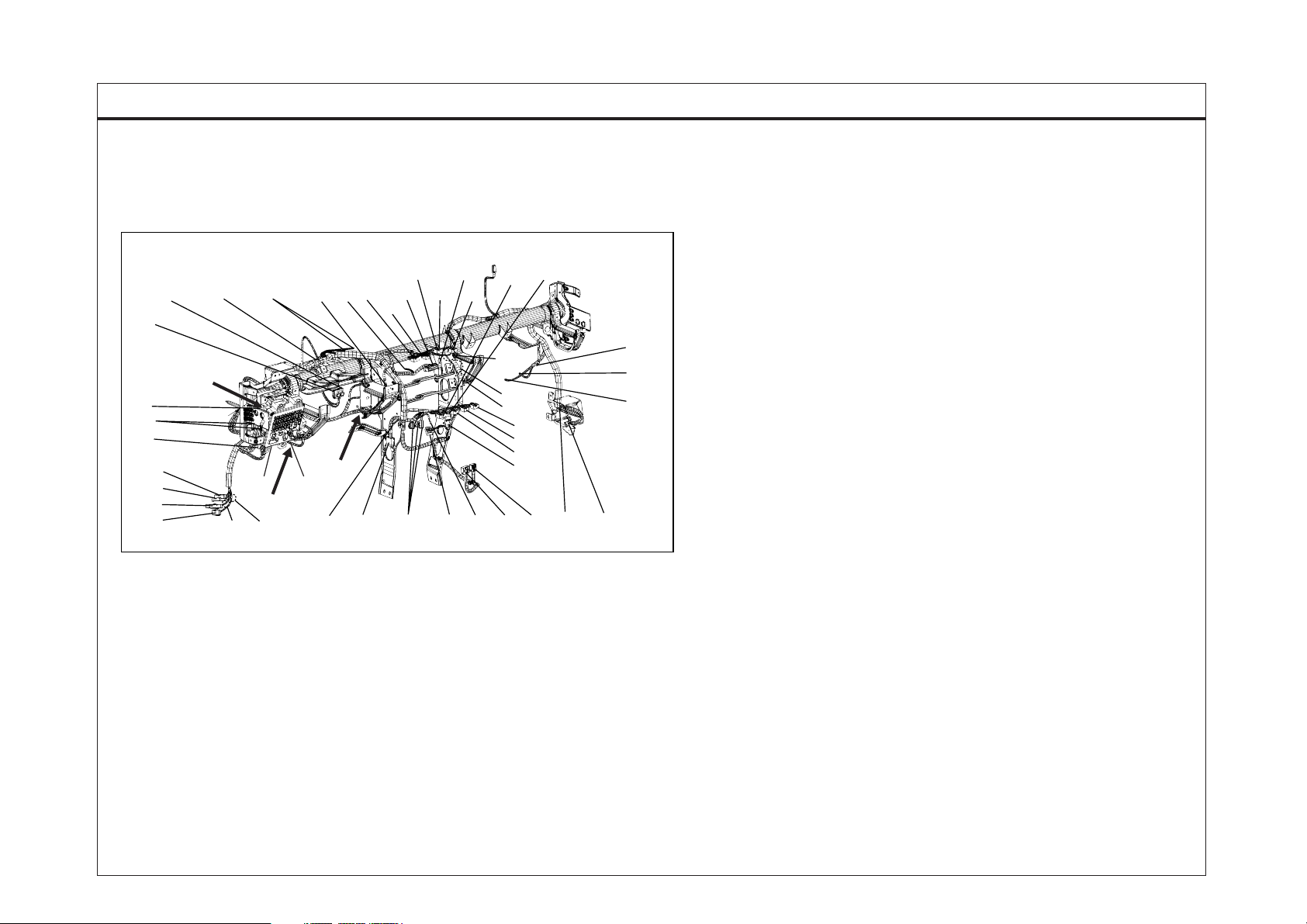
INTRODUCTION
HARNESS LAYOUTS
Harness layouts show the routing of the major wiring harnesses,
the in-line connectors and the splices between the major harnesses.
These layouts will make electrical troubleshooting easier.
M37
G11
M29
M30
Passenger
Compartment
Junction Block
(I/P-E,F,G,H,J)
Z02
MI01
M41
MM04
MM03
MM01
MM02
M09-3 M09-1,2
M33
VIEW 'B'
SM01 SM02
M13
MC06
Z03
VIEW 'A'
M36
G14 G12 M26 M31 M34
M15
M16 Z01
M14
M25-1,2,3
M19-2
M11
SM06
SM07
SM08
M23
M21
M22
M32
M35
M20
MC05 MC04
M02
M03-1,2
MI04
MI06
MI03
MI05
GI-5INTRODUCTION (5)
EVT GI70005L
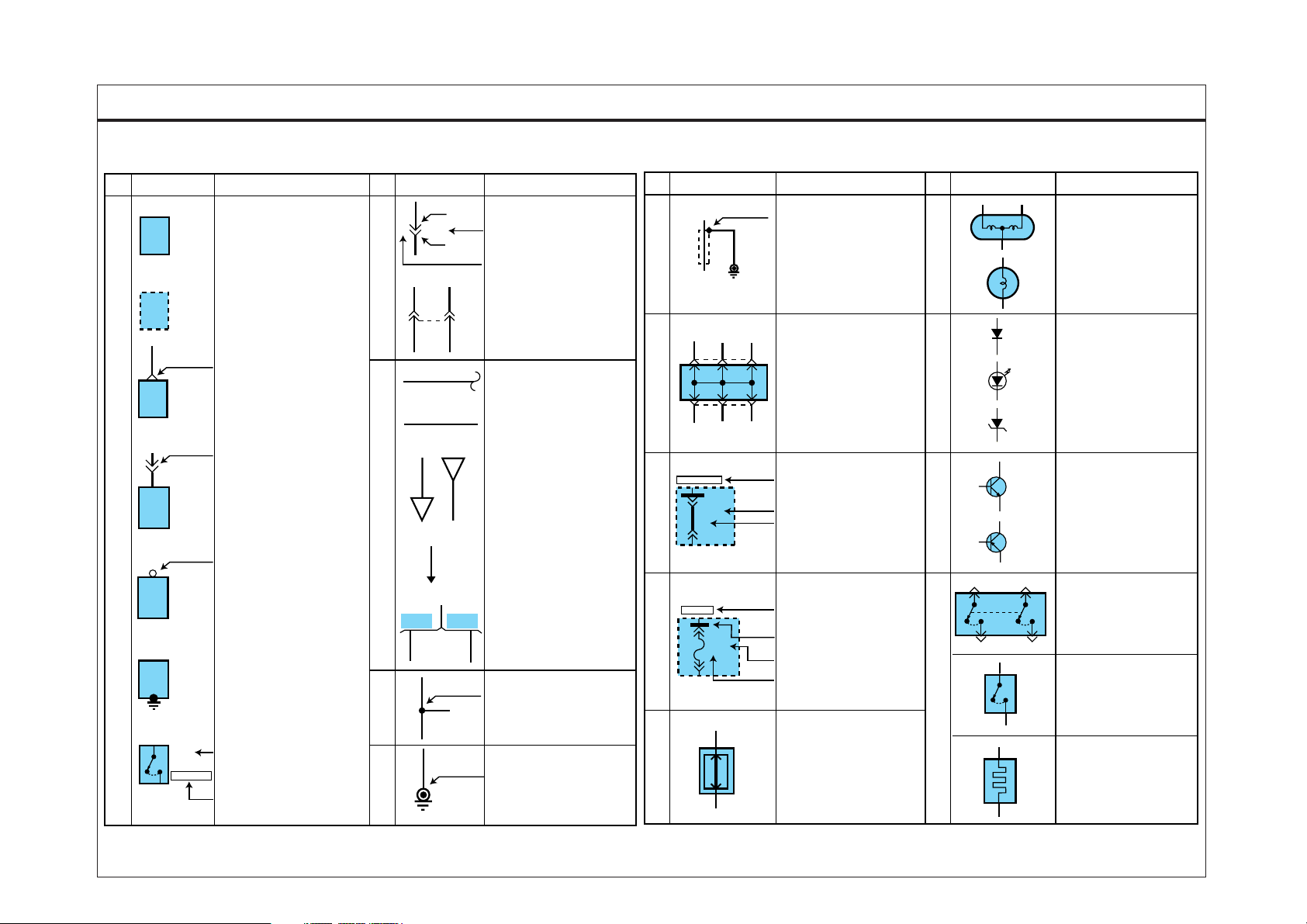
SYMBOLS EBB531CD
GI-6SYMBOLS (1)
Section
C
O
M
P
O
N
E
N
T
Symbol
STOP
LAMP
SWITCH
PHOTO 03
Meaning Symbol Meaning Symbol Meaning Symbol Meaning
A solid line means the entire
component is shown.
A broken line indicates only
part of the component is
shown.
This means the connector
connects directly to the
component.
This indicates the connector
connects to a lead (pigtail),
wired directly to the component.
This indicates a screw terminal
on the component.
This ground symbol (dot and
3 lines overlapping the component) means the housing
of the component is attached
to a metal part of the vehicle.
The name of the component
appears next to its upper right
corner.
Shows the number of pictures
for component location.
Section
Male
10
C
O
N
N
E
C
T
O
R
W
I
R
E
Name of Circuit
S
P
L
I
C
E
S
G
R
O
U
N
D
connector
M05-2
Female
connector
R
Y/L
13
R Y/L
B
Y/R
From C52
A
A
To MC02
R
Automatic
Manual
G
Transaxle
Transaxle
GG
L
L
G06
Shows the name of each connector
on the component location index
for reference.
Indicates the number of
corresponding terminal.
(Only relevant terminal on the
corresponding schematic diagram).
The dashed-line means each of
E35
two wires connect with same
connector(E35)
A wavy line means the
wire is broken but
is to be continued.
Wire insulation is yellow
with a red strip.
Current path is continued on
the same page or another
page.The arrow shows the
direction of current flow.
You should look for the "A"
in the marked position.
A wire connects to another
circuit. The wire is shown
again on that circuit which
the arrow is pointing.
Wire choices for options or
different models are labeled
and shown with a "choice"
bracket like this.
Splices are numbered and
shown as a dot with circle.
The exact location and connection of these splices may
vary among vehicles.
This symbol means the end
of the wire is attached to a
metal part of the vehicle.
Section
S
H
E
L
D
W
R
E
J
O
N
T
C
O
N
N
E
C
T
O
R
S
L
O
W
B
L
O
W
F
U
S
E
P
O
W
E
R
I
I
I
C
O
N
N
E
C
T
O
R
HOT AT ALL TIMES
F/FOG
FUSE
15A
HOT IN ON
FUSE 10
10A
G06
E/R FUSE &
RELAY
BOX
DASH
FUSE
BOX
This represents RFI (Radio
Frequency Interference)
Shielding around a wire.
The shielding is always
connected to ground.
This is a connector showing
the joining wires.
Power supplied at all times.
Name
Capacity
This means power is supplied
with the ignition on position.
This means the short bar
connects to other fuses.
Identification
Current rating
Control battery power at all times
Section
L
A
M
P
D
O
D
E
TR
G
E
N
E
R
A
L
C
O
M
P
O
N
E
N
T
S
Y
M
B
O
L
Double filament
Single filament
Diode
I
Led diode
Zener diode
C
B
B
NPN
E
C
PNP
E
NPN
PNP
These switches move
together:
a dashed line shows a
mechanical connection
between them.
Switch (1 contact point)
Heater
EVT GI70006L
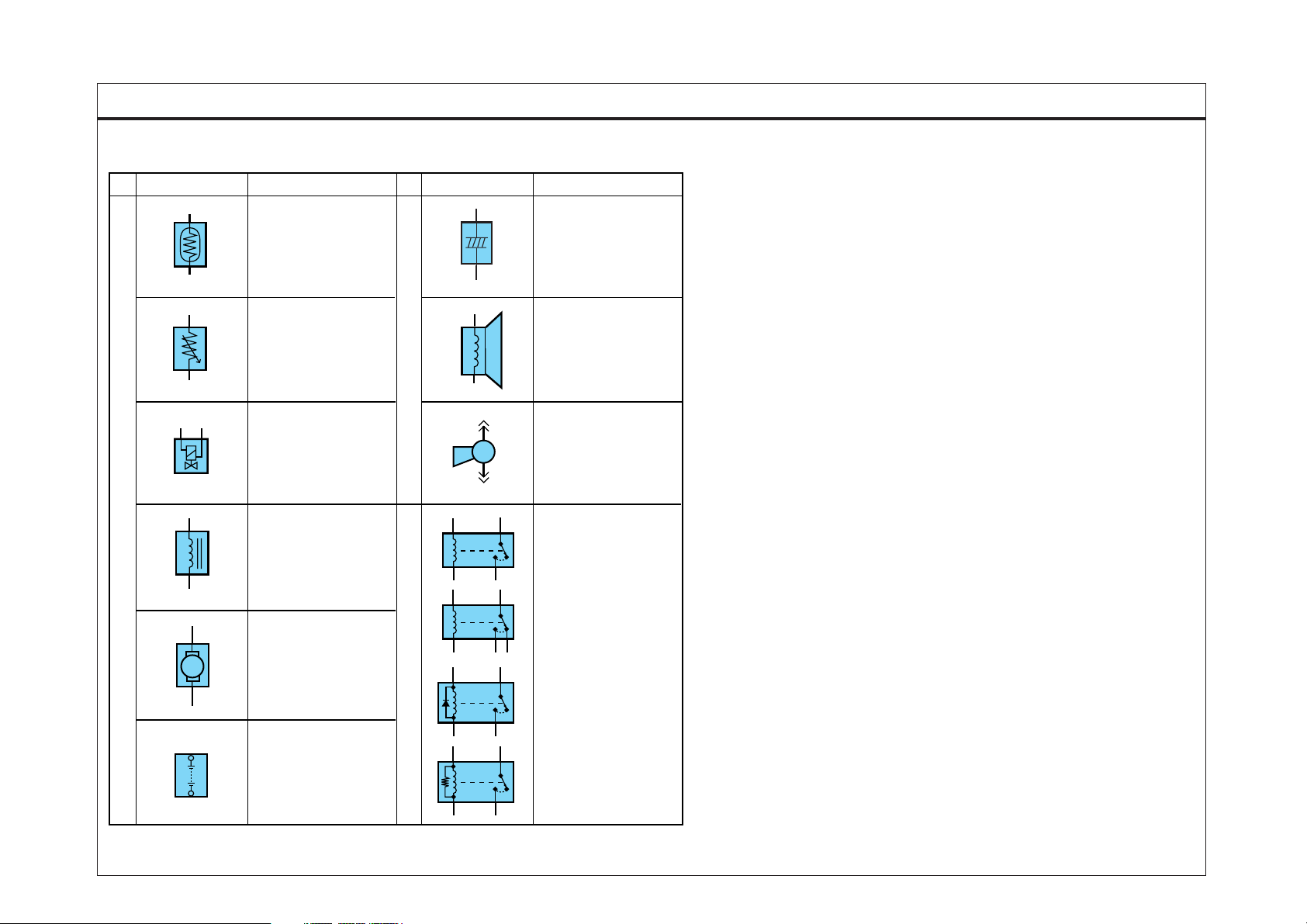
SYMBOLS
GI-7SYMBOLS (2)
Section
G
E
N
E
R
A
L
C
O
M
P
O
N
E
N
T
S
S
Y
M
B
O
L
Symbol Meaning Symbol Meaning
Sensor
Sender
Injector
Solenoid
M
Motor
Section
G
E
N
E
R
A
L
C
O
M
P
O
N
E
N
T
S
S
Y
M
B
O
L
R
E
L
A
Y
Condenser
Speaker
Horn, Buzzer, Siren,
Chime Bell
Normally open contact
This is a relay shown with no
current flowing through its coil.
When a current flows through
coil, contact will toggle.
Diode interior relay
+
Battery
-
Resistance interior relay
EVT GI70007L
TROUBLESHOOTING INSTRUCTIONS E 69D8CAB
TROUBLESHOOTING INSTRUCTIONS
TROUBLESHOOTING PROCEDURES TROUBLESHOOTING EQUIPMENT
GI-8TROUBLESHOOTING INSTRUCTIONS (1)
The following five-step troubleshooting procedure is recommended.
1. Verify the customer's complaints
Turn on all the components in the problem circuit to check the accuracy of the
customer's complaints. Note the symptoms.
Do not begin disassembly or testing until you have narrowed down the probable
causes.
2. Read and analyze the schematic diagram
Locate the schematic for the problem circuit. Determine how the circuit is
supposed to work by tracing the current paths from the power source through
the system components to ground. If you do not understand how the circuit
should work, read the circuit operation text. Also check other circuits that share
with the problem circuit. The name of circuits that share the same fuse, ground,
or switch, for example, are referred to on each diagram. Try to operate any
shared circuits you did not check in step 1. If the shared circuit works, the
shared wiring is okay, and the cause must be within the wiring used only by the
problem circuit.
If several circuits fail at the same time, the fuse or ground is a likely cause.
3. Inspect the circuit/ component with the problem isolated
Make a circuit test to check the diagnosis you made in step 2. Remember that a
logical, simple procedure is the key to efficient troubleshooting. Narrow down the
probable causes using the troubleshooting hints and system diagnosis charts.
Test for the most likely cause of failure first.
Try to make tests at points that are easily accessible.
VOLTMETER AND TEST LAMP
Use a test lamp or a voltmeter on circuits without solidstate units and use a test
lamp to check for voltage. A test lamp is made up of a 12-volt light bulb with a
pair of leads attached. After grounding one lead, touch the other lead to various
points along the circuit where voltage should be present.
When the bulb goes on, there is voltage at the point being tested.
CAUTION
A number of circuits include solid-state modules, such as the Engine
Control Module(ECM), used with computer command control injection.
Voltage in these circuits should be tested only with a 10-megaohm or
higher impedance digital multimeter. Never use a test lamp on circuits
that contain solid state modules. Damage to the modules may result.
A voltmeter can be used in place of a test lamp. While a test lamp shows
whether the voltage is present or not, a voltmeter indicates how much voltage
is present.
TEST LAMP
4. Repair the problem
Once the problem is found, make the necessary repairs.
5. Make sure the circuit works
Repeat the system check to be sure you have repaired the problem. If the
problem was a blown fuse, be sure to test all of the circuits on that fuse.
SELF-POWERED TEST LAMP AND OHMMETER
Use a self-powered test lamp or an ohmmeter to check for continuity.
The ohmmeter shows how much resistance there is between two points along
a circuit. Low resistance means good continuity.
EVT GI70008L
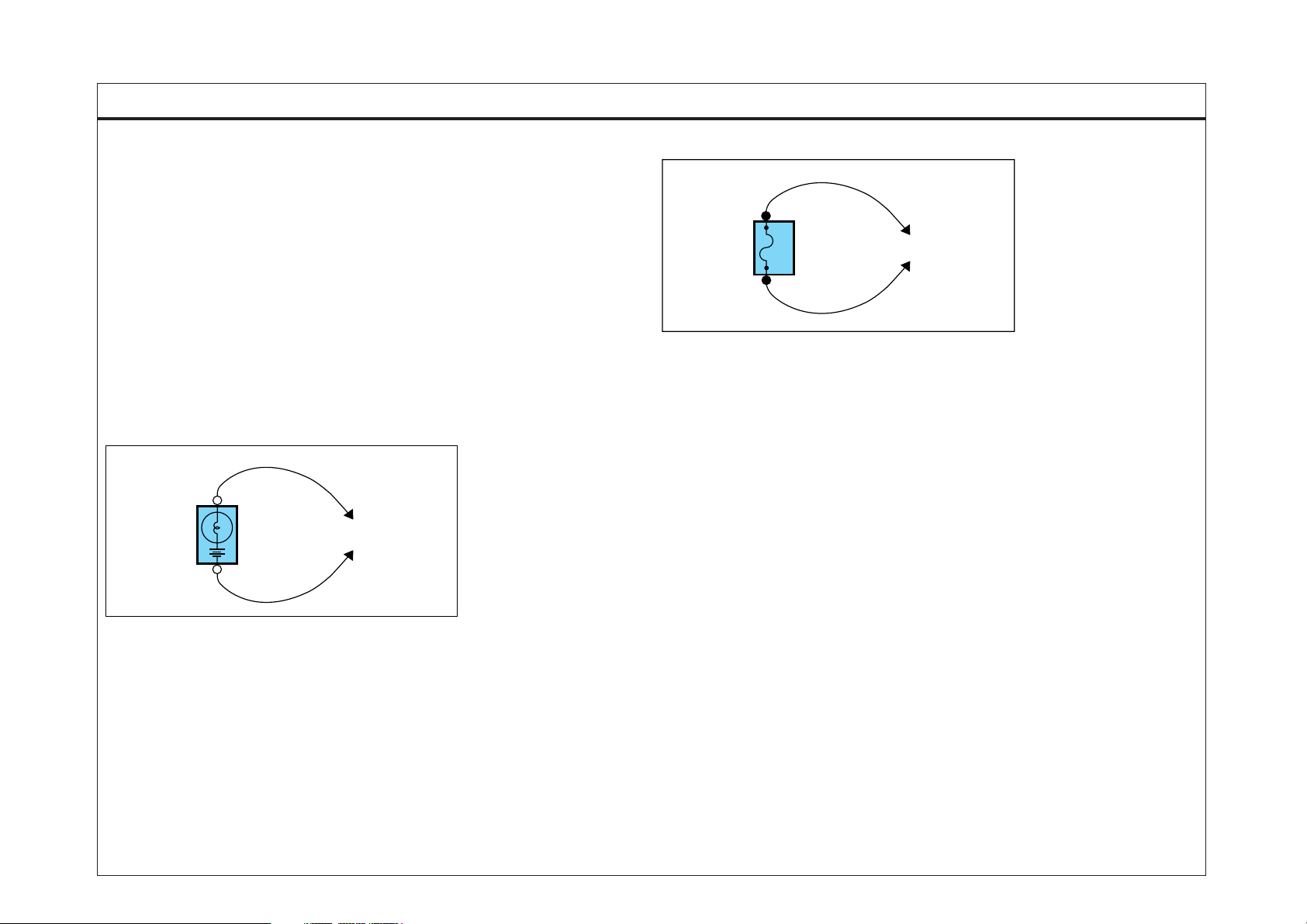
TROUBLESHOOTING INSTRUCTIONS
CAUTION
Never use a self-powered test lamp on circuits that contain solid state
modules. Damage to these modules may result.
GI-9TROUBLESHOOTING INSTRUCTIONS (2)
An ohmmeter can be used in place of a self-powered test lamp.
The ohmmeter shows how much resistance there is between two points along a
circuit. Low resistance means good continuity.
Circuits which include any solid-state devices should be tested only with a
10-megaohm or higher impedance digital multimeter. When measuring
resistance with a digital multimeter, the battery negative terminal should be
disconnected. Otherwise, there may be incorrect readings. Diodes and
solid-state devices in a circuit can make an ohmmeter give a false reading.
To find out if a component is affecting a measurement, take one reading,
reverse the leads and take a second reading.
If different the solid-state device is affecting the measurement.
SELFPOWERED
TEST LAMP
JUMPER WIRE WITH FUSE
Use a jumper wire with a fuse to by-pass an open circuit.
A jumper wire is made up of an in-line fuse holder connected to a set of test leads.
This tool is available with small clamp connectors providing adaption to most connectors without damage.
CAUTION
5A
SHORT FINDER
A short finder is available to locate a short to ground. The short finder creates a
pulsing magnetic field in the shorted circuit and shows you the location of the
short through body trim or sheet metal.
TROUBLESHOOTING TEST
1. TESTING FOR VOLTAGE
This test measures voltage in a circuit. When testing for voltage at a connector, you do not have to separate the two halves of the connector. lnstead,
probe the connector from the back(backprobe). Always check both sides of
the connector because dirt and corrosion between its contact surfaces can
cause electrical problems.
A. Connect one lead of a test lamp or voltmeter to a ground. If you are using
a voltmeter, be sure it is the voltmeter's negative test lead you have con nected to ground.
B. Connect the other lead of the test lamp or voltmeter to a selected test
point(connector or terminal).
C. If the test lamp glows, there is voltage present. If you are using a
voltmeter, note the voltage reading. A loss of more than 1 volt from
specification indicates a problem.
Do not use a fuse with a higher rating than the specified fuse that protects the
circuit being tested. Do not use this tool in any situation to substitute an input
or output at the solid-state control module, such as ECM, TCM, etc.
EVT GI70009L
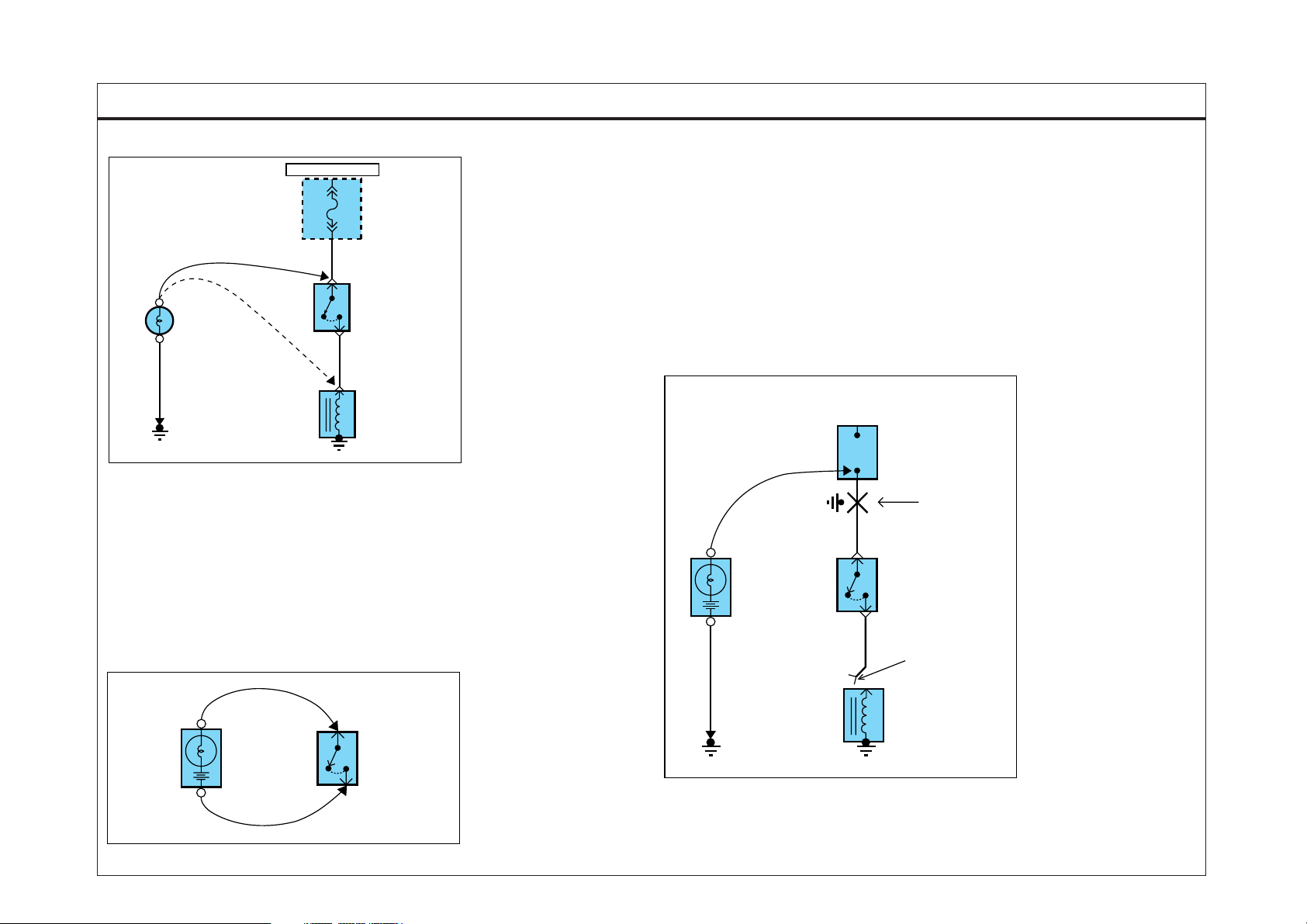
TROUBLESHOOTING INSTRUCTIONS
GI-10TROUBLESHOOTING INSTRUCTIONS (3)
ON
TEST LAMP
OR
VOLTMETER
HOT AT ALL TIMES
OFF
R
4
G
DASH
FUSE
BOX
SWITCH
M11
SOLENOID
2. TESTING FOR CONTINUITY
A. Disconnect the battery negative terminal.
B. Connect one lead of a self-powered test lamp or ohmmeter to one end of
the part of the circuit you wish to test. If you are using an ohmmeter, hold
the leads together and adjust the ohmmeter to read zero ohms.
C. Connect the other lead to the other end.
D. If the self-power test lamp glows, there is continuity. If you are using an
ohmmeter, low or zero resistance means good continuity.
3. TESTING FOR SHORT TO GROUND
A. Disconnect the battery negative terminal.
B. Connect one lead of a self-powered test lamp or an ohmmeter to the fuse
terminal on the load side.
C. Connect the other lead to a ground.
D. Beginning near the fuse block move the harness from side to side.
Continue this proceedure(about six inches apart) while watching the
self-powered test lamp or ohmmeter.
E. When the self-powered test lamp glows, or ohmmeter registers, there is a
short to a ground in the wiring near that point.
Battery
disconnected
FUSE BOX
(Fuse removed)
Short to ground
R
1
SELF-POWERED
TEST LAMP
OR
VOLTMETER
M11
4
G
SWITCH
M11
SOLENOID
Load
disconnected
SELFPOWERED
TEST LAMP
OR
OHMMETER
STOP
LAMP
SWITCH
EVT GI70010L
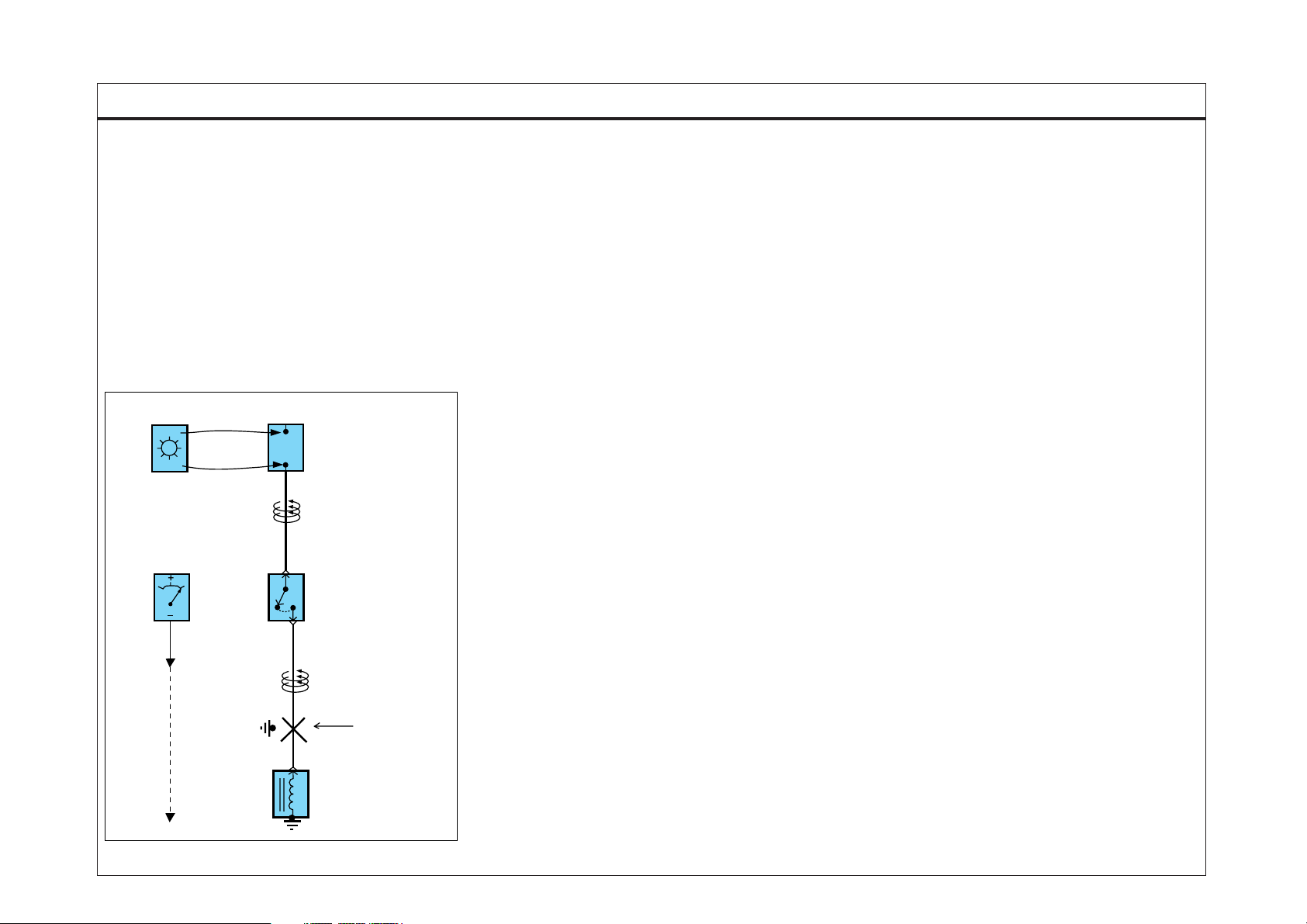
TROUBLESHOOTING INSTRUCTIONS
4. TESTING FOR A SHORT WITH A SHORT FINDER
A. Remove the blown fuse. Leave the battery connected.
B. Connect the short finder across the fuse terminals.
C. Close all switches in series in the circuit that is being testing.
D. Turn on the short circuit locator. It sends pulses of current to the short.
This creates a pulsing magnetic field around the wiring between the fuse
box and the short.
E. Beginning at the fuse box, slowly move the short finder along the circuit
wiring. The meter will show current pulses through sheet metal and body
trim. As long as the meter is between the fuse and the short, the needle
will move with each current pulse. Once the meter is moved past the point
of the short, the needle will stop moving. Check around this area to locate
the cause of the short circuit.
Battery
disconnected
FUSE BOX
(Fuse removed)
SHORT
FINDER
METER
Pulsing
magnetic
field
R
M111
SWITCH
GI-11TROUBLESHOOTING INSTRUCTIONS (4)
Move meter
along wire
Needle stops
moving here
4 M11
G
Pulsing
magnetic
field
SOLENOID
Short to ground
EVT GI70011L
FUSE & REL AY INFORMATION EBF7DCCF
FUSE BOX
SD100-1FUSE & RELAY INFORMATION (1)
<D4DD>
FUSE 1
15A
FUSE 25
10A
FUSE 1
15A
FUSE 13
20A
FUSE 25AFUSE 3
10A
FUSE 14
FUSE 26
FUSE 25AFUSE 3
FUSE 14
15A
10A
10A
FUSE 15
10A
FUSE 27
10A
10A
FUSE 15
10A
FUSE 4
10A
FUSE 16
20A
FUSE 28
10A
FUSE 4
10A
FUSE 16
10A
FUSE 5
15A
FUSE 17
10A
FUSE 29
10A
FUSE 5
15A
FUSE 17
10A
FUSE 65AFUSE 75AFUSE 8
FUSE 18
FUSE 30
15A
10A
FUSE 19
10A
FUSE 31
10A
FUSE 20
FUSE 325AFUSE 33
<D4AF/D4AL>
FUSE 65AFUSE 7
5A
FUSE 18
15A
FUSE 19
15A
10A
20A
FUSE 9
10A
FUSE 21
20A
20A
FUSE 9
15A
FUSE 10
15A
FUSE 34
15A
FUSE 11
10A
FUSE 23
10A
FUSE 35
10A
FUSE 11
10A
FUSE 23
10A
FUSE 12
10A
FUSE 24
15A
FUSE 36
15A
FUSE 12
10A
FUSE 24
15A
FUSE 25
10A
FUSE 26
10A
FUSE 27
10A
FUSE 28
10A
FUSE 29
10A
FUSE 30
10A
FUSE 31
10A
FUSE 33
USE THE DESIGNATED FUSE ONLY
15A
FUSE 34
15A
FUSE 36
15A
EVT SD7100AL
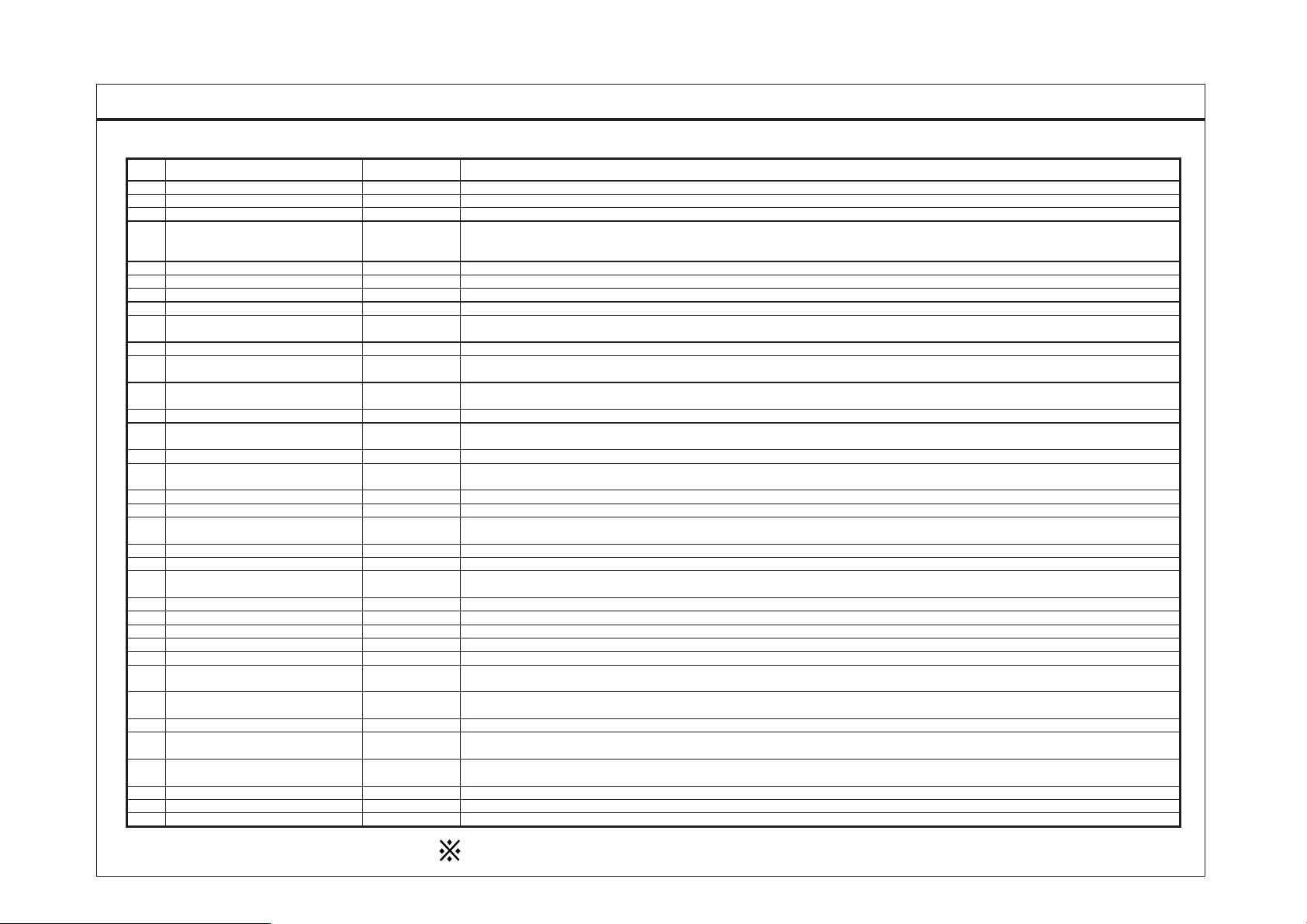
FUSE & REL AY INFORMATION
CIRCUIT
Fuse Description (A) Circuit protected
1
2
3
4
D4DD(TACHOGRAPH, GLOW, ABS),
5
6
7
8
9
10
13
15
17
18
D4DD(STOP LP, HORN, DIAG CONN)
20
21
24
25
26
27
28
29 TAIL LP (LH) 10A
30 TAIL LP (RH) 10A
31
32 D4DD(ENG ECU) 5A(D4DD)
34
35
36
WORKING LAMP
HEAD LP (RELAY)
A/CON
D4AF/D4AL(COLD START),
EXH. BRAKE
WIPER WASHER
A. B. S (ECU)
P. T. O (OPT)
D4DD(ENG ECU)
D4AF/D4AL(SUB START),
D4DD(ENG ECU, EXH BRAKE)
D4DD(SUB START)
D4AF/D4AL(OVERHEAT BZ),
REVERSE LP, SPD SENSOR
D4AF/D4AL(ALTR (R)),
CLUSTER, ETACS
D4AF/D4AL(P/WINDOW)
D4AF/D4AL(STOP LP, HORN)
D4DD(HEAT'G MIRROR)
HAZARD, T/SIG LP, CAB TILT'G
D4AF/D4AL(RR FOG LAMP)
D4DD(P/WINDOW)
C/DOOR LOCK
A. B. S (VALVE)
D4AF/D4AL(HEAT'G MIRROR)
D4DD(ENG ECU)
D4DD(FUEL HEATER)
D4DD(ETACS, TACHOGRAPH),
AUDIO, ROOM LP, CLOCK
START MOTOR
HEAD LP (DIM. LH)
HEAD LP (DIM. RH)
HEAD LP (MAIN. LH)
HEAD LP (MAIN. RH)
FOG LAMP
D4AF/D4AL(CONDENSER FAN)
D4DD(A/C COMP, CONDENSER)
HEATER BLOWER
D4DD(ETACS)
CIGAR, AUDIO, CLOCK
15A
5A
10A
10A
15A
5A
5A
10A(D4DD)
15A(D4AF/D4AL)
10A(D4DD)
15A(D4DD)
10A
10A
20A
10A(D4AF/D4AL)
15A(D4DD)
10A
10A(D4AF/D4AL)
20A(D4DD)
10A
15A
15A(D4AF/D4AL)
10A(D4DD)
20A(D4DD)
20A(D4DD)
10A
15A
10A
10A
10A
10A
10A
15A(D4AF/D4AL)
20A(D4DD)
15A
10A(D4DD)
15A
Working lamp switch
Head lamp leveling actuator(D4AF/D4AL), Head lamp leveling switch(D4AF/D4AL), Head lamp relay(High/Low)
Mode switch, Intake switch, A/C switch, Evaporator sensor, Blower relay, Condenser fan relay
Cold start switch(D4AF/D4AL), Exhaust brake clutch pedal position switch(D4AF/D4AL), Tachograph, High speed warning device(D4AF/D4AL),
High speed warning buzzer(D4AF/D4AL), Glow relay(D4DD), Fuel heater relay(D4DD), Exhaust brake relay(D4DD), ABS relay
Wiper motor, Washer motor, Wiper relay(High/Low)
ABS control module
PTO relay, Dump relay, PTO control switch
Main ECM(D4DD)
Neutral switch(D4AF/D4AL), Main ECM(D4DD), Exhaust brake relay(D4DD)
Neutral switch(D4DD)
Overheat buzzer relay(D4AF/D4AL), Vehicle speed sensor, Back-up lamp switch, Water separator sensor(D4DD), Generator(D4DD)11
Instrument cluster(Indicator), ETACM, Generator(D4AF/D4AL)12
Power window relay(D4AF/D4AL)
Data link connector(D4AF/D4AL), Stop lamp switch(D4AF/D4AL), Horn(D4AF/D4AL), Outside mirror defogger relay(D4DD)14
Cab tilting switch, Flasher unit
Rear fog lamp relay(D4AF/D4AL), Rear fog indicator relay(D4AF/D4AL), Power window relay(D4DD)16
Power door lock relay, Power door unlock relay
ABS relay box(Fail safe relay)
Outside mirror defogger relay(D4AF/D4AL), Data link connector(D4DD), Stop lamp switch(D4DD), Horn(D4DD), Horn relay(D4DD)19
Engine ECM relay(D4DD), Main ECM(D4DD)
Fuel heater relay(D4DD)
Instrument cluster(Clock), ETACM, Audio, Front room lamp, Rear room lamp, Tachograph23
ETACM(D4AF/D4AL), Start solenoid, Sub start switch, Main ECM(D4DD)
Head lamp LH(Lo)
Head lamp RH(Lo)
Head lamp LH(Hi), Instrument cluster(High-beam indicator)
Head lamp RH(Hi)
Hazard switch, Defogger switch, A/C switch, Front fog lamp switch, License lamp, Rear combination lamp LH, Rear fog lamp switch(D4AF/D4AL),
Rear marker lamp LH(D4AF/D4AL), Front outside marker lamp(D4AF/D4AL), Cigarette lighter(D4DD)
Position lamp RH, Front room lamp, Endout marker lamp, Rear combination lamp RH, Rear marker lamp RH(D4AF/D4AL),
Rear outside marker lamp(D4AF/D4AL)
Front fog lamp relay
Engine PTO cab in switch(D4DD), Accelerator pedal sensor(D4DD), Exhaust brake clutch pedal position switch(D4DD), Stop lamp switch(D4DD),
Multifunction switch(Exhaust brake switch)(D4DD), Idle up/down switch(D4DD)
Condenser fan relay, A/C relay33
Blower relay
Not used(D4DD)
Cigarette lighter, Audio, Instrument cluster(Clock)
SD100-2FUSE & RELAY INFORMATION (2)
USE THE DESIGNATED FUSE ONLY
EVT SD7100BL
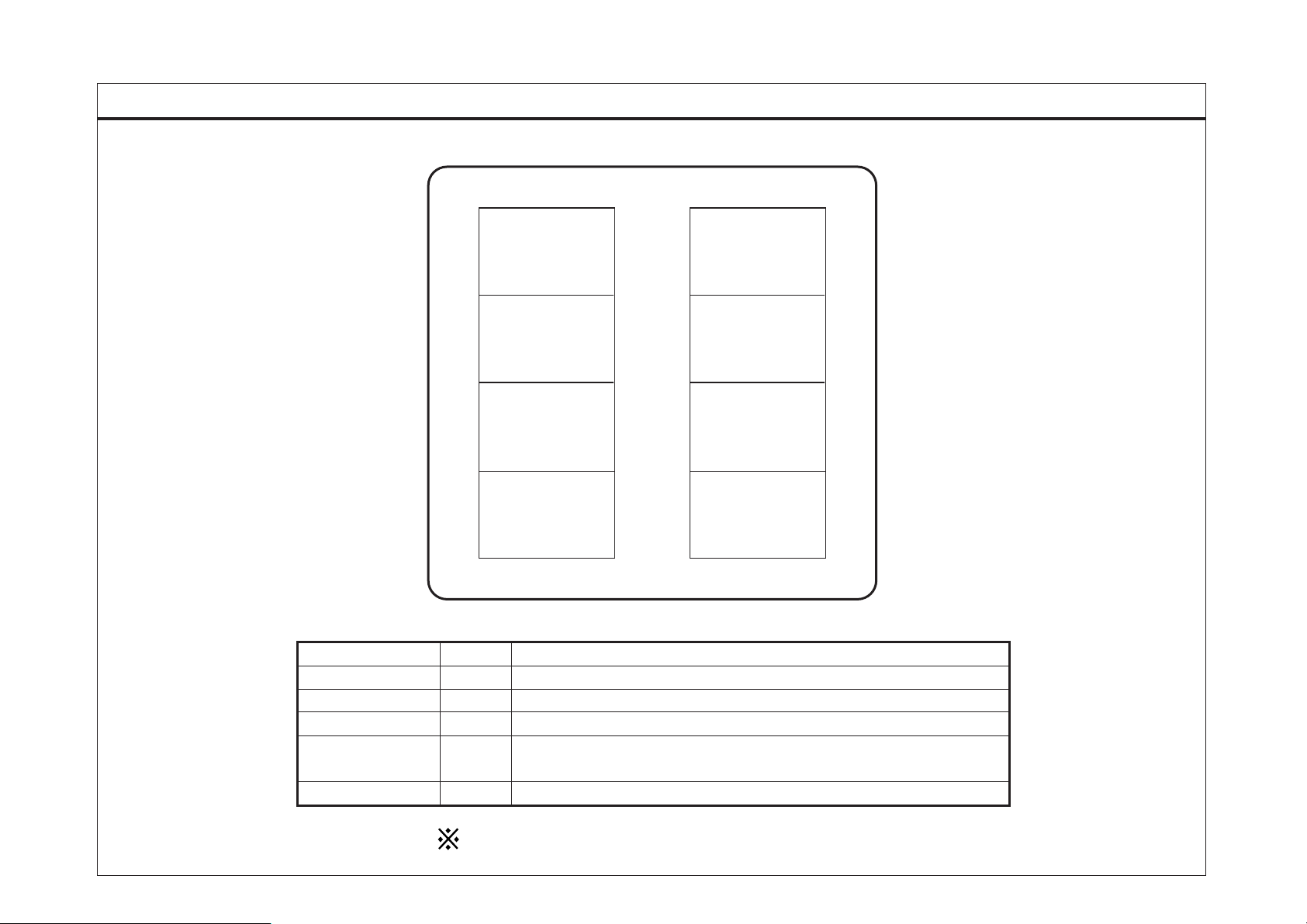
FUSE & REL AY INFORMATION
SD100-3FUSE & RELAY INFORMATION (3)
FUSIBLE LINK BOX
ABS
30A
A/CON
30A
IGN SW
30A
CIRCUIT
Description (A) Circuit protected
ABS
A/CON
IGN SW
ALTERNATOR
30A
30A
30A
40ABODY
60A
ABS relay box(Pump motor relay)
Fuse box(Fuse 33, Fuse 34)
Ignition switch
Relay box(Head lamp relay (High/Low), Tail lamp relay),
Fuse box(D4AF/D4AL(Fuse 13~19), D4DD(Fuse 15~21), Fuse 31)
Generator
BODY
40A
ALTERNATOR
60A
USE THE DESIGNATED FUSE ONLY
EVTSD7100CL
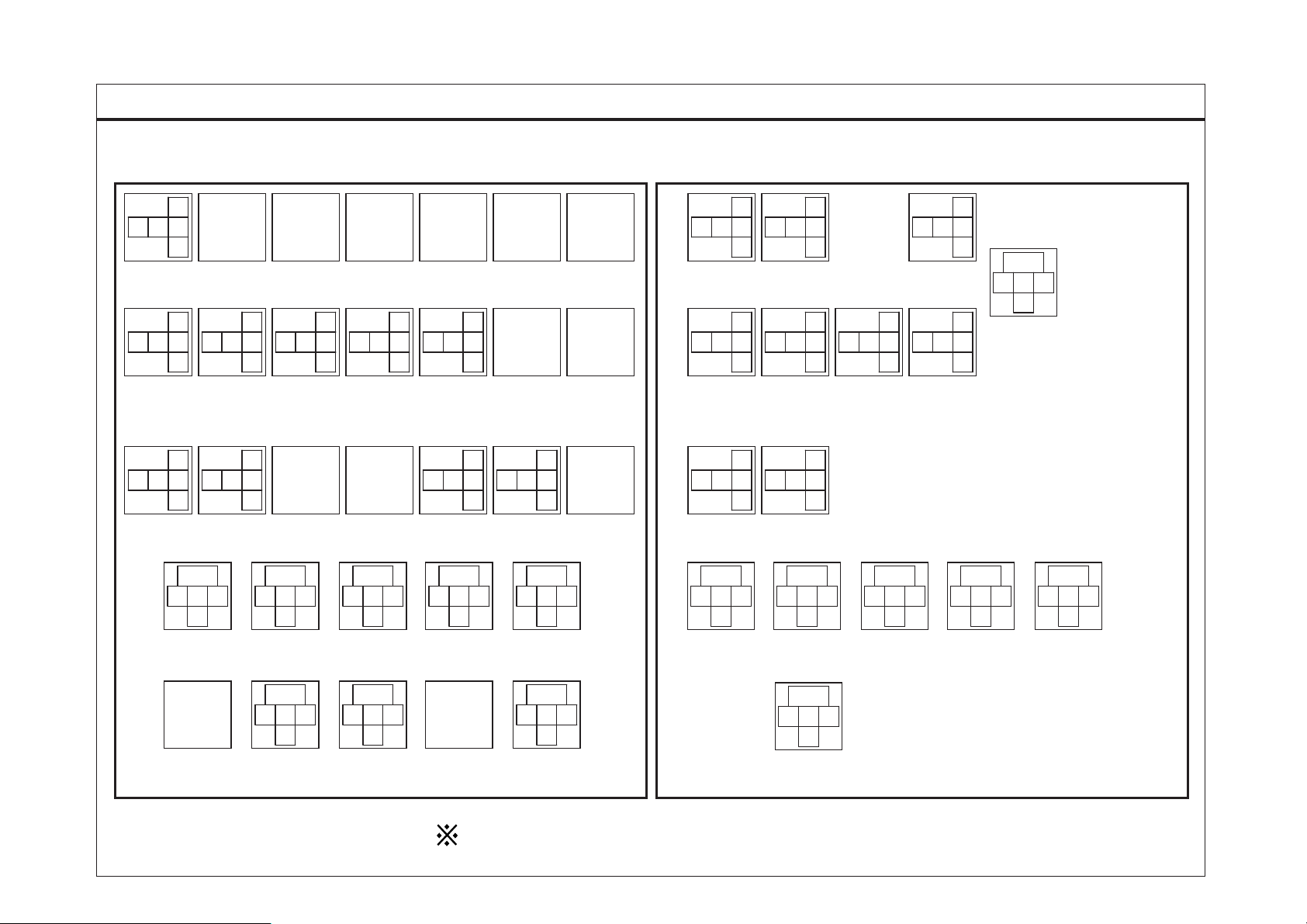
FUSE & REL AY INFORMATION
SD100-4FUSE & RELAY INFORMATION (4)
3
12
*
5
M01
FRONT FOG
LAMP RELAY
3
14
*
5
M15
ABS
RELAY
3
14
*
5
M08
PTO
RELAY
RELAY (HIGH)
124
POWER
DOOR
LOCK
RELAY
14
DUMP
RELAY
1
234
5
M11
WIPER
M05
*
M09
3
5
3
5
124
M06
POWER
DOOR
UNLOCK
RELAY
1
234
5
M12
WIPER
RELAY (LOW)
<D4DD> <D4AF/D4AL>
3
5
DEFOGGER
HEAD LAMP
RELAY (HIGH)
12
M07
OUTSIDE
MIRROR
RELAY
1
24
*
5
M13
3
12
*
5
RELAY
12
EXHAUST
BRAKE RELAY
HEAD LAMP
RELAY (LOW)
M88
HORN
M93
1
*
5
M14
3
*
5
3
12
*
5
24
WINDOW RELAY
M94
GLOW
RELAY
POWER
3
*
5
1
*
5
M04
RELAY BOX
24
3
12
*
5
M01
FRONT FOG
LAMP RELAY
3
14
*
5
M15
ABS
RELAY
3
124
5
M08
PTO
RELAY
1
234
5
M11
WIPER
RELAY (HIGH)
3
12
*
5
M16
REAR FOG
LAMP RELAY
3
124
5
M05
POWER
DOOR
LOCK
RELAY
3
14
*
5
M09
DUMP
RELAY
1
5
M12
WIPER
RELAY (LOW)
124
POWER
UNLOCK
RELAY
234
BUZZER RELAY
3
5
M06
DOOR
1
*
5
M13
HEAD LAMP
RELAY (HIGH)
14
OVERHEAT
12
OUTSIDE
MIRROR
DEFOGGER
RELAY
24
3
*
5
M97
3
*
5
M07
M14
HEAD LAMP
RELAY (LOW)
TAIL LAMP
1
24
*
5
1
24
*
5
M02
RELAY
M04
POWER
WINDOW RELAY
1
24
*
5
1
24
*
5
M90
FUEL HEATER
RELAY
1
24
*
5
M91
ENGINE
ECM RELAY
1
*
5
M02
TAIL LAMP
RELAY
24
1
24
*
5
M86
REAR FOG
INDICATOR RELAY
USE THE DESIGNATED FUSE ONLY
EVTSD7100DL

POWER DISTRIBUTION E A007534
SD110-1POWER DISTRIBUTION (1)
8.0W
1
C13
+
-
+
BATTERY
BATTERY
3.0Y
1
ABS
FUSIBLE
LINK
30A
CC03
2
8.0L
8.0L
2
ALTERNATOR
FUSIBLE
LINK
60A
CC01
5.0W
EC03
1
3.0G
3.0G
1
1
A/CON
FUSIBLE
LINK
30A
2.0R
BODY
FUSIBLE
LINK
40A
CC02
2
3.0R
3
2.0L 2.0L
3.0R
5
3.0R
1.25G
1
A
M14
M14
HEAD
LAMP
RELAY
(LOW)
To IGN SW
Fusible Link 30A
(SD110-2)
M13
5
M13
1
1.25O
FUSIBLE
LINK
BOX
HEAD
LAMP
RELAY
(HIGH)
3.0L3.0R
MC03
6
3.0L
2.0L 0.5L
5
1
See Tail, Parking
& License Lamps
(SD928-1)(SD928-2)
1.25G/O
RELAY
BOX
M02
2
TAIL
LAMP
RELAY
M02
4
3.0L
FUSE BOX
-
BATTERY
GROUND
START
MOTOR
FUSE 33
8.0W
C34-2
1
ABS
RELAY
BOX
8.0L
E17
1
GENERATOR
15A(D4AF/D4AL)
20A(D4DD)
See Passenger
Compartment Fuse Details
(SD120-7)
FUSE
FUSE
16
15
20A
10A
FUSE 34
15A
Compartment Fuse Details
D4DD D4AF/D4AL
FUSE
FUSE
17
18
10A
15A
FUSE 23
10A
See Passenger
(SD120-5)
FUSE
19
10A
FUSE
FUSE
20
21
20A
20A
See Passenger
Compartment Fuse Details
(SD120-3)(SD120-4)
FUSE
FUSE
26
25
10A
10A
See Passenger
Compartment Fuse Details
(SD120-5)(SD120-6)
FUSE
FUSE
13
14
20A
10A
FUSE
27
10A
FUSE
15
10A
FUSE
28
10A
FUSE
16
10A
FUSE
29
10A
FUSE
17
10A
FUSE
30
10A
FUSE
FUSE
18
19
15A
15A
See Passenger
Compartment Fuse Details
(SD120-7)
FUSE
31
10A
EVT SD7110AL
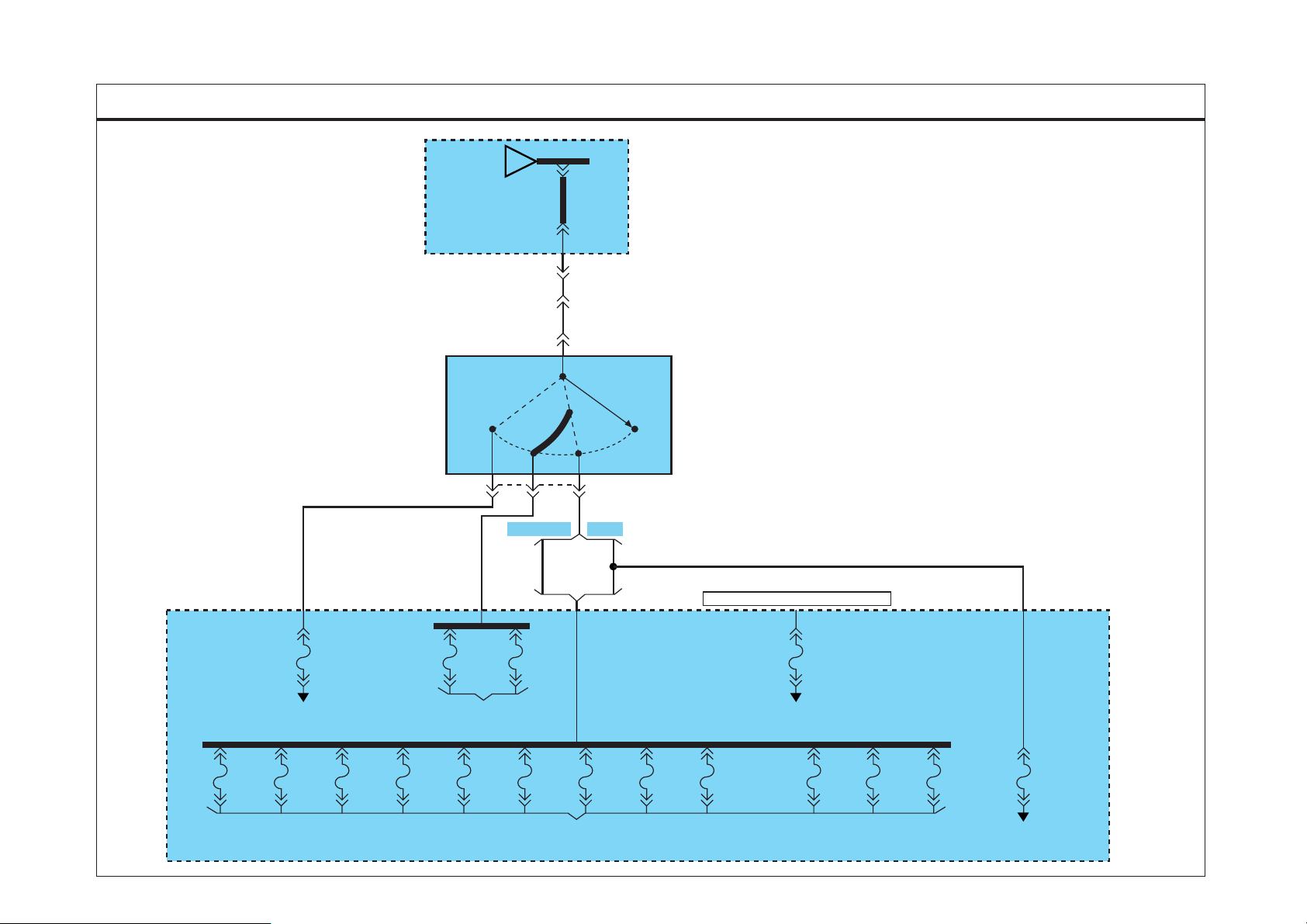
POWER DISTRIBUTION
SD110-2POWER DISTRIBUTION (2)
Battery Power
(SD110-1)
START
2.0G 2.0L
From
A
1
3.0W
5
3.0W
6
AM
ACC ON
2 4 3
D4AF/D4AL D4DD
3.0O
FUSIBLE
LINK
BOX
IGN SW
FUSIBLE
LINK
30A
CC01
MC03
M42
IGNITION
SWITCH
LOCK
M42
3.0O
3.0O 3.0O
HOT WITH ENGINE ECM RELAY ON
FUSE
BOX
FUSE 24
15A
See Passenger
Compartment Fuse Details
(SD120-5)
FUSE 1
15A
FUSE 2
5A
FUSE 3
10A
FUSE 35
10A
See Passenger
Compartment Fuse Details
(SD120-7)
FUSE 4
10A
FUSE 5
15A
Compartment Fuse Details
FUSE 36
15A
FUSE 65AFUSE 75AFUSE 8
See Passenger
(SD120-1)(SD120-2)
10A
FUSE 32
5A
See Passenger
Compartment Fuse Details
(SD120-7)
FUSE 9
15A(D4AF/D4AL)
10A(D4DD)
FUSE 10
15A
FUSE 11
10A
FUSE 12
10A
See Passenger
Compartment Fuse Details
FUSE 14
15A
(SD120-3)
EVT SD7110BL
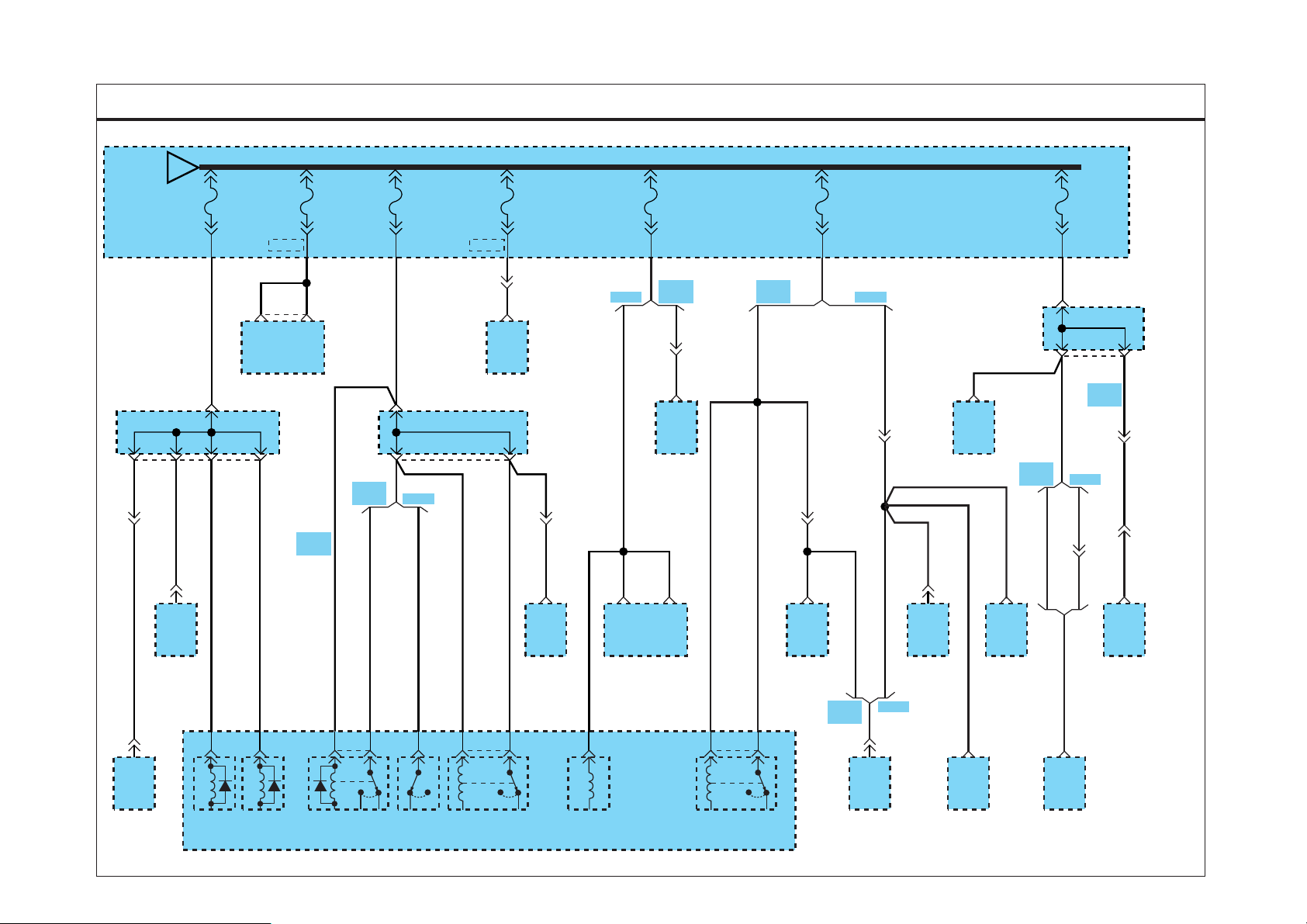
PASSENGER COMPARTMENT FUSE DETAILS EC996EE F
SD120-1PASSENGER COMPARTMENT FUSE DETAILS (1)
1.25W
FUSE 1
15A
1.25Br
1.25Br
1
1
FUSE 6
5A
MA01
0.5O
A01
0.85O
13
0.5O
12
1
FUSE 3
10A
M80
0.5O
M28
11
0.85O
M80
0.5L/B
M21
5
JOINT
CONNECTOR
0.5O
MA02
4
0.5R
0.5R
4
D4AF/
D4AL
0.85Br
A15
0.5Br
10
D4AF/
D4AL
0.85Br
9
1
HOT IN ON
FUSE 2
5A
M54
0.5Br
M60
D4AF/
D4AL
0.5Br
8
4
JOINT
CONNECTOR
M54
0.5Br
M44
D4AF/
D4AL
0.5L
3
1
D4AF/
0.5L
D4AL
4
M73
D4DD D4DD
0.5L
0.5L
M47
M24
3
4
0.5L
0.5L
0.5L
6
FUSE 4
10A
M78
D4AF/
D4AL
0.5L
25
1
A
M22
To FUSE 5
15A
(SD120-2)
0.5L
0.5L
FUSE
BOX
D4DD
3
M78
0.5L
D4AF/
D4AL
1
JOINT
CONNECTOR
M49
M75
1
WORKING
LAMP
SWITCH
ABS
CONTROL
MODULE
ACTUATOR
2
MODE
SWITCH
M33
INTAKE
EVAPORATOR
M64
1
A/C
SWITCH
SENSOR
BLOWER
RELAY
A16
4
CONDENSER
FAN RELAY
HEAD LAMP
LEVELING
ACTUATOR RH
M53
1
HEAD LAMP
LEVELING
ACTUATOR LH
HEAD LAMP
LEVELING
SWITCH
M13
2
HEAD
LAMP RELAY
(HIGH)
COLD
START
SWITCH
M14
2
HEAD
LAMP RELAY
(LOW)
TACHOGRAPH
(ELECTRONIC)
0.5L 0.5L
M94
1
GLOW
RELAY
HEATER
RELAY
HIGH SPEED
WARNING
2 M90
FUEL
DEVICE
M93
1
EXHAUST
BRAKE
RELAY
HIGH SPEED
M15
5
ABS
RELAY
WARNING
BUZZER
RELAY
BOX
PEDAL POSITION
D4AF/
TACHOGRAPH
(CASSETTE TYPE)
D4AL
D4DD
M45
8
EXHAUST
BRAKE CLUTCH
SWITCH
EVT SD7120AL
PASSENGER COMPARTMENT FUSE DETAILS
SD120-2PASSENGER COMPARTMENT FUSE DETAILS (2)
From
HOT IN ON
(SD120-1)
0.85L 0.5R
7
0.85L
97
MM02
1.25L
5
A
FUSE 5
15A
1.25L
M80
10
0.85L 0.85L
M31
D4DD
22
MAIN ECM
M80
58
FUSE 8
10A
0.5R
0.5R0.5R
M99-2
12
JOINT
CONNECTOR
D4AF/
D4AL
0.5R
0.5R
M54
17
15
D4AF/
D4AL
0.5R 0.5R
FUSE 7
5A
D4DD
0.5R
D4DD
1.25R
11
0.85R
1
NEUTRAL
SWITCH
16
0.5R
FUSE 10
15A
MC06
C11
JOINT
CONNECTOR
M54
0.85R
MC01
5
(D4AF/D4AL)
MC05(D4DD)
4
C14
2
FUSE
BOX
FUSE 9
15A(D4AF/D4AL)
10A(D4DD)
D4AF/
D4AL
0.85Br/O1.25Y
0.85Br/O
0.85Br/O
0.85Br/O
7
D4AF/
D4AL
2.0R
2
2.0R
2
NEUTRAL
SWITCH
0.85Br/O 0.85Br/O
1.25Y
M99-3
1
MC01
C11
M99-2
D4DD
1.25Y0.85Y
11
MC01
0.85Br/O
C57
3
FUSE 11
10A
D4DD
0.85Br/O
0.85Br/O
0.85Br/O
2
MC05
0.5Br/O
0.5O
INSTRUMENT
0.85Br/O
C45
1
M36-3
2
CLUSTER
0.85Br/O
D4AF/
D4AL
C39
1
0.85O
14
16
0.5O
0.5O
FUSE 12
10A
M78
D4DD
100.5O
D4AF/
D4AL
0.85O
0.85O
MM07
0.5R
JOINT
CONNECTOR
M78
15
MC01
16
EC02
1
E10
1
M107
2
WASHER
MOTOR
WIPER
MOTOR
M12
2
WIPER
RELAY
(LOW)
M11
2
WIPER
RELAY
(HIGH)
5
PTO
RELAY
PTO
CONTROL
SWITCH
M08
1
RELAY
1
PTO
M08
5
DUMP
RELAY
M09
1
EXHAUST
BRAKE
RELAY
5
M93
MAIN ECM
5
OVERHEAT
BUZZER
RELAY
1
M97
VEHICLE
SPEED
SENSOR
RELAY
BOX
D4AF/
D4AL
BACK-UP
SWITCH
2
LAMP
WATER
SEPARATOR
SENSOR
D4DD
C12
GENERATOR
C57
1
VEHICLE
SPEED
SENSOR
M56-2
6
ETACM
GENERATOR
EVT SD7120BL
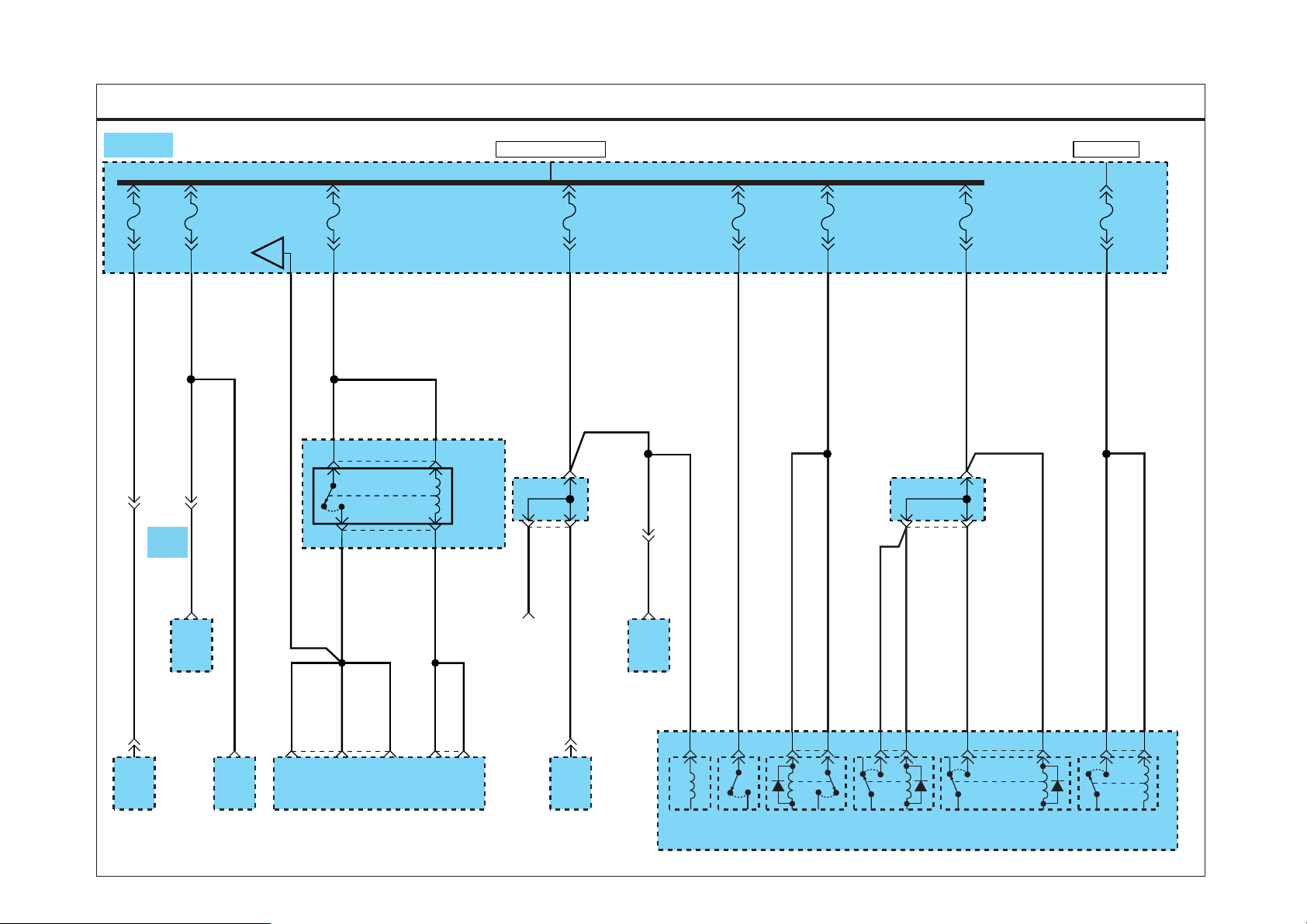
PASSENGER COMPARTMENT FUSE DETAILS
SD120-3PASSENGER COMPARTMENT FUSE DETAILS (3)
D4DD
1.25R
9
1.25R
FUSE 18
15A
0.85O
0.5O
MC05
W/O
Double
Cab
0.85O
8
2
FUSE 15
10A
To FUSE
32 5A
(SD120-7)
MM01
0.85O
M104
B
0.85L/G
2.0R/O
1.25G/O
5
FUSE 20
20A
HOT AT ALL TIMES
FUSE 19
10A
0.85Y
0.85R/O2.0R/O
M78
JOINT
CONNECTOR
M78
0.85Y
0.85Y
0.85Y
MC06
6
0.85Y
C18
2
0.5L
2
41
M91
M91
ENGINE
ECM
RELAY
RELAY
BOX
12
0.5Y
0.85Y
M72
9
DATA LINK
CONNECTOR
13
11
1.25W
FUSE 21
20A
1.25Y/O
0.5Y/O 1.25
Y/O
FUSE 16
20A
0.85L 0.5L
0.85L
6
0.85L 0.5L
7
5
FUSE 17
10A
M54
JOINT
CONNECTOR
M54
HOT IN ON
FUSE 14
15A
0.85P
0.85P 0.5P
FUSE
BOX
2
ABS
RELAY
BOX
C34-2
CAB
TILTING
SWITCH
1.25G/O 1.25G/O1.25G/O
M10
6
FLASHER
UNIT
65
MAIN ECM
7
M99-1
0.5L0.5L
M99-3
65
M41
2
STOP
LAMP
SWITCH
HORN
M88
5
HORN
RELAY
M90
5
FUEL
HEATER
RELAY
25
WINDOW
M04
POWER
RELAY
M05
25
POWER DOOR
LOCK RELAY
RELAY BOX
25
POWER DOOR
UNLOCK RELAY
M06
1
OUTSIDE MIRROR
DEFOGGER RELAY
M07
5
EVTSD7120CL
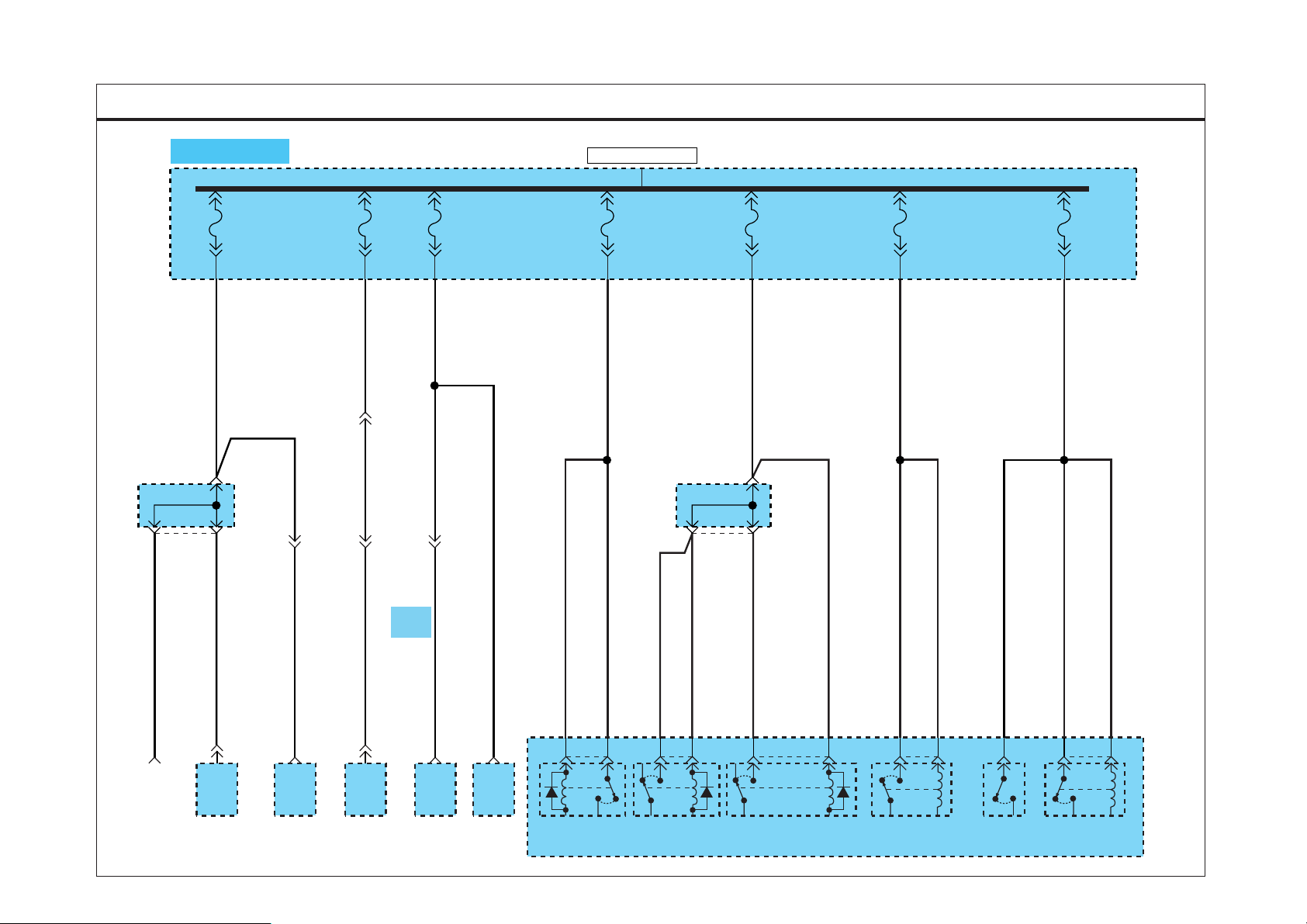
PASSENGER COMPARTMENT FUSE DETAILS
SD120-4PASSENGER COMPARTMENT FUSE DETAILS (4)
D4AF/D4AL
12
0.5Y
0.85Y
13
0.85Y
11
FUSE 14
10A
M78
JOINT
CONNECTOR
M78
0.85Y
0.85Y
HOT AT ALL TIMES
FUSE
BOX
FUSE 18
15A
1.25R
MA01
4
1.25R
1.25R
CA01
6
Double
MC02
5
0.85O
0.5O
0.85O
W/O
Cab
8
FUSE 15
10A
MM01
0.85O
1.25Y/O
0.5Y/O 1.25Y/O
FUSE 13
20A
0.85L 0.5L
0.85L
6
0.85L 0.5L
7
M54
5
FUSE 17
10A
M54
JOINT
CONNECTOR
FUSE 19
15A
0.85P
0.85P 0.5P
0.5R
FUSE 16
10A
0.85R
0.85R 0.5R
M72
9
DATA LINK
CONNECTOR
2
STOP
LAMP
SWITCH
M41
C18
2
HORN
2
ABS
RELAY
BOX
C34-2
M104
2
CAB
TILTING
SWITCH
M10
6
FLASHER
UNIT
25
POWER
WINDOW
M04
RELAY
M05
25
POWER DOOR
LOCK RELAY
25
POWER DOOR
UNLOCK RELAY
M06
OUTSIDE MIRROR
DEFOGGER RELAY
5
M07
M86
5
REAR FOG
INDICATOR
RELAY
1
REAR FOG
LAMP RELAY
1
5
M16
RELAY
BOX
EVTSD7120DL
PASSENGER COMPARTMENT FUSE DETAILS
SD120-5PASSENGER COMPARTMENT FUSE DETAILS (5)
HOT AT ALL TIMES
FUSE 23
10A
0.85Gr 2.0B/O
M77
20
0.5Gr
16
D4AF/
D4AL
0.5Gr
18 19 17
D4AF/
D4AL
0.5Gr
0.5Gr
0.5Gr
D4AF/
0.5Gr
D4AL
M77
D4DD
0.5Gr
1
JOINT
CONNECTOR
Double Cab
0.5G/B
MM07
0.5Gr
W/O
2
MM03
With
Double Cab
0.5R
0.5R 0.5R
0.5B/O
10
2.0B/O
2.0B/O
D4AF/
D4AL
MC01
2.0B/O
HOT IN START
FUSE 24
15A
1.25B/O
D4DD
1.25B/O
1.25B/O
MC05
1
2.0B/O 0.5L/R
2.0B/O
HOT WITH HEAD LAMP
RELAY (LOW) ON
FUSE 25
10A
1.25G
1.25G
HOT WITH HEAD LAMP
RELAY (HIGH) ON
FUSE 26
10A
1.25B/O
1.25B/O
FUSE 27
10A
0.85B/O
1.25Gr
FUSE 28
10A
FUSE
BOX
M56-1
4
ETACM
M26
10
AUDIO
INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER
M45
7
TACHOGRAPH
(CASSETTE TYPE)
M36-3
4
ETACM
M24
1
TACHOGRAPH
(ELECTRONIC)
1
M56-2
0.5Gr
0.5Gr
4
0.5Gr
M56-1
ETACM
FRONT
ROOM
M56-2
1
3
LAMP
M110
M110
3
FRONT
ROOM
LAMP
M114
3
REAR
ROOM
LAMP
M56-2
7
ETACM
C44
1
START
SOLENOID
D4AF/
D4AL
SWITCH
2
SUB
START
D4DD
C01
C44
1
START
SOLENOID
14
MAIN
ECM
1
Low
HEAD
LAMP LH
M99-2
M50
M57
1
Low
HEAD
LAMP RH
M50
3
Hi
HEAD
LAMP LH
HEAD
LAMP RH
M36-1
8
INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER
M57
3
Hi
EVT SD7120EL
PASSENGER COMPARTMENT FUSE DETAILS
REAR
A/C
SWITCH
DEFOGGER
SWITCH
CIGARETTE
LIGHTER
FOG LAMP
SWITCH
HAZARD
SWITCH
FUSE 29
10A
HOT WITH TAIL LAMP RELAY ON
FUSE 30
10A
FUSE
BOX
SD120-6PASSENGER COMPARTMENT FUSE DETAILS (6)
M64
2
0.5G/O
14
15
See Illuminations
(SD941-1)
EUROPE EUROPE
C05
C05-1
1
(EUROPE)
1
0.5G/O
0.85G/W
C52
M65
2
0.85G/O1.25G/O
0.85G/O
0.85G/O
0.85G/W0.85G/O0.85G/O
0.85G/W
C70
1
M68
1
0.5G/O
13
12
D4AF/D4AL D4DD
MC02
1
CC04
1
0.85G/O
D4AF/D4AL D4DD
C72
1
M67
2
0.5G/O
D4AF/D4ALD4DD
M84
0.85G/O
0.85G/O
0.85G/O 0.85G/W
MC05
18
C07
3
M62
2
0.5G/O 1.25G/O
11
0.5G/O
C05
1
2
M84
0.5R/B
M63
JOINT
CONNECTOR
With
Double Cab
0.5G/W
M110
2
0.85G
M112
2
12
1
MM03
W/O
Double Cab
0.85G/W
M113
2
0.5G/W
2
0.5G/W0.85G/W
M120
13
0.85G
1
POSITION
LAMP RH
M121
2
M58
0.5G/W
2
0.85G
M122
17
0.85G
14
M54
M5411
0.85G
MC05
17
0.85G
0.85G0.85G
3
JOINT
CONNECTOR
D4AF/D4ALD4DD
MC01
0.85G
EUROPE
C08
EUROPE
0.85G
1
0.85G/W
0.85G/W 0.85G/W
C53
1
1
CC05
C73
C74
1
LICENSE
LAMP
REAR
MARKER
LAMP LH
FRONT
OUTSIDE
MARKER
LAMP LH
FRONT
OUTSIDE
MARKER
LAMP RH
REAR
COMBINATION
LAMP LH
LICENSE
LAMP
FRONT
FOG LAMP
SWITCH
FRONT
ROOM
LAMP
ENDOUT
MARKER
LAMP 'A'
ENDOUT
MARKER
LAMP 'B'
ENDOUT
MARKER
LAMP 'C'
ENDOUT
MARKER
LAMP 'D'
ENDOUT
MARKER
LAMP 'E'
REAR
COMBINATION
LAMP RH
REAR
MARKER
LAMP RH
REAR
OUTSIDE
MARKER
LAMP LH
REAR
OUTSIDE
MARKER
LAMP RH
EVTSD7120FL
PASSENGER COMPARTMENT FUSE DETAILS
SD120-7PASSENGER COMPARTMENT FUSE DETAILS (7)
0.85W
FUSE 31
10A
0.5L/O
0.85L/O
HOT AT ALL TIMESHOT AT ALL TIMES
From Engine
ECM Relay
(SD120-3)
MC04
8
D4DD
B
0.85L/O
0.5L/O0.85L/O0.5L/O 0.85L/O
FUSE 32
5A
0.5L/O
0.85L/O
FUSE 33
15A(D4AF/D4AL)
20A(D4DD)
0.85G
93
2.0G
0.85G/W2.0G
2.0P
FUSE 34
15A
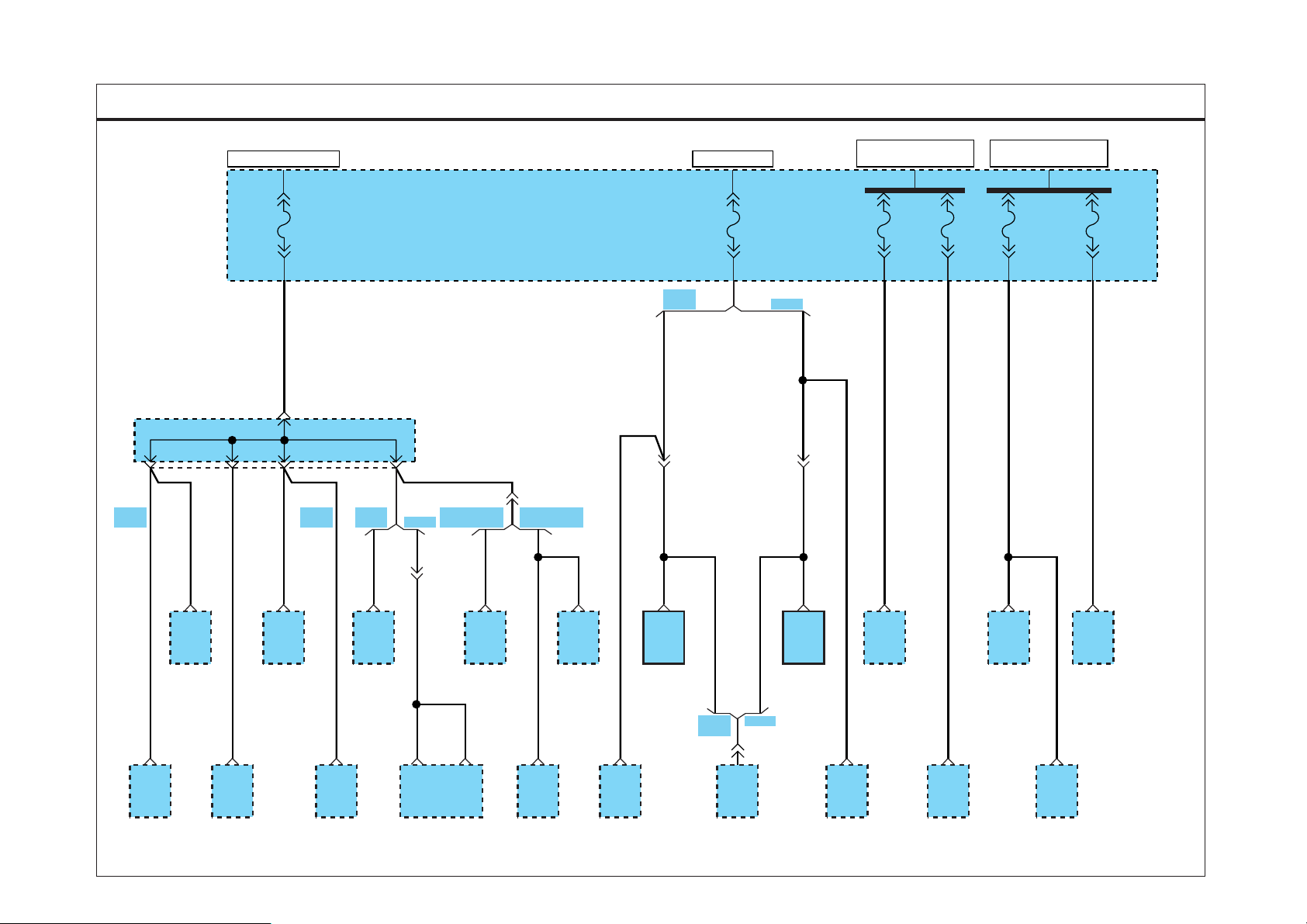
D4DD
MA02
HOT IN ACC OR ON
FUSE 35
10A
MM06
16
Not used
FUSE
BOX
FUSE 36
15A
0.85L/O0.5L0.85P
0.85L/O 0.5L/O0.85L/O
M01
1
FRONT
FOG LAMP
RELAY
RELAY
BOX
1
PTO
EC04
M39
5
ENGINE
PTO CAB
IN SWITCH
M32
4
ACCELERATOR
PEDAL
SENSOR
M41
4
STOP
LAMP
SWITCH
M43-1
2
MULTIFUNCTION
SWITCH
M17
3
IDLE
UP/DOWN
SWITCH
M49
2
EXHAUST
BRAKE CLUTCH
PEDAL POSITION
SWITCH
A16
3
CONDENSER
FAN
RELAY
A17
3
A/C
RELAY
A15
1
BLOWER
RELAY
M68
3
LIGHTER
M36-3
5
INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER
M26
11
AUDIOCIGARETTE
EVTSD7120GL

PASSENGER COMPARTMENT FUSE DETAILS
MEMO
SD120-8PASSENGER COMPARTMENT FUSE DETAILS (8)
EVTSD7120HL
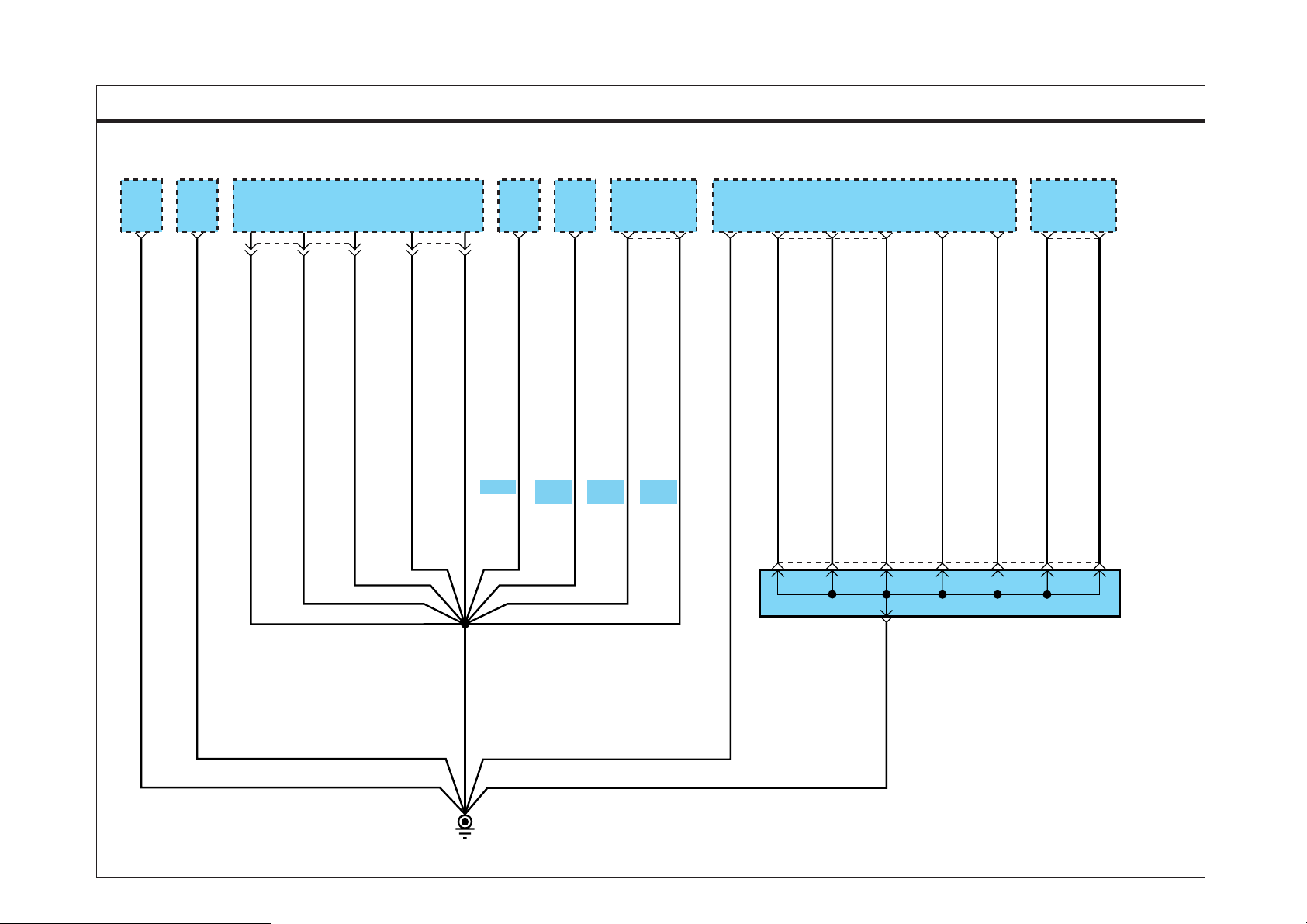
GROUND DIST RIBUTION E C2E9F76
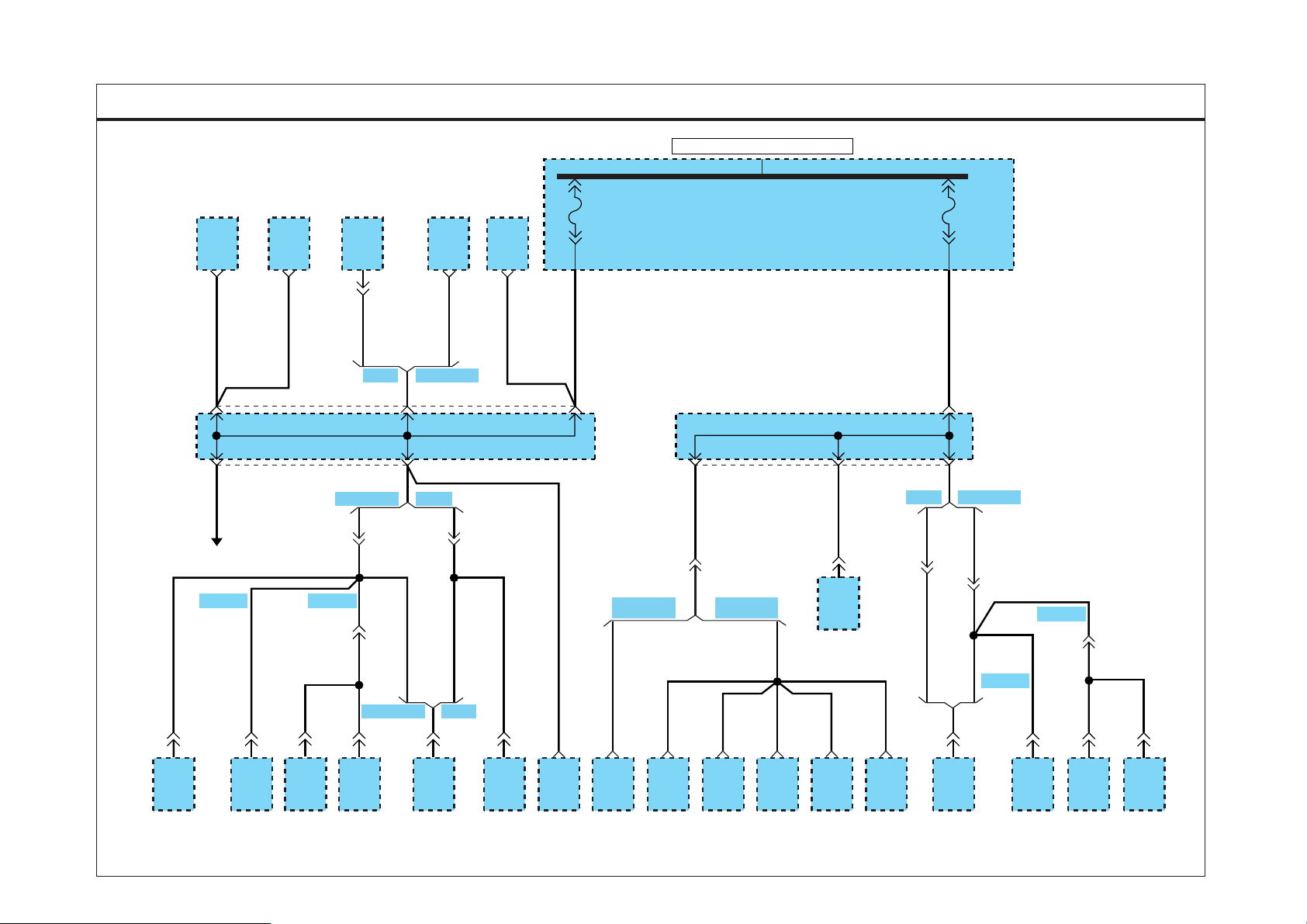
SD130-1GROUND DISTRIBUTION (1)
BLOWER
SWITCH
3
1.25B
M27
AUDIO
0.5B
MULTIFUNCTION SWITCH INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
M26
7
8
0.5B 0.5B 0.5B 0.5B 0.5B
12
M43-1
14 2 8
UP/DOWN
M43-2
D4DD
IDLE
SWITCH
M17
1
SWITCH
0.5B0.5B
D4AF/
D4AL
COLD
START
M47
1
HEAD LAMP
LEVELING
SWITCH
3
0.5B 0.5B
D4AF/
D4AL
D4AF/
D4AL
PTO SWITCH
M36-2 M36-1
13
10 1
0.5B
M36-1
1
2
0.5B 0.5B 0.5B 0.5B 0.5B 0.5B 0.5B
8
M44
5
M36-4
M37
6
3
7 M762 3 4 81 6
JOINT
CONNECTOR
0.5B
G01(MAIN)
0.5B
M76
5
EVT SD7130AL
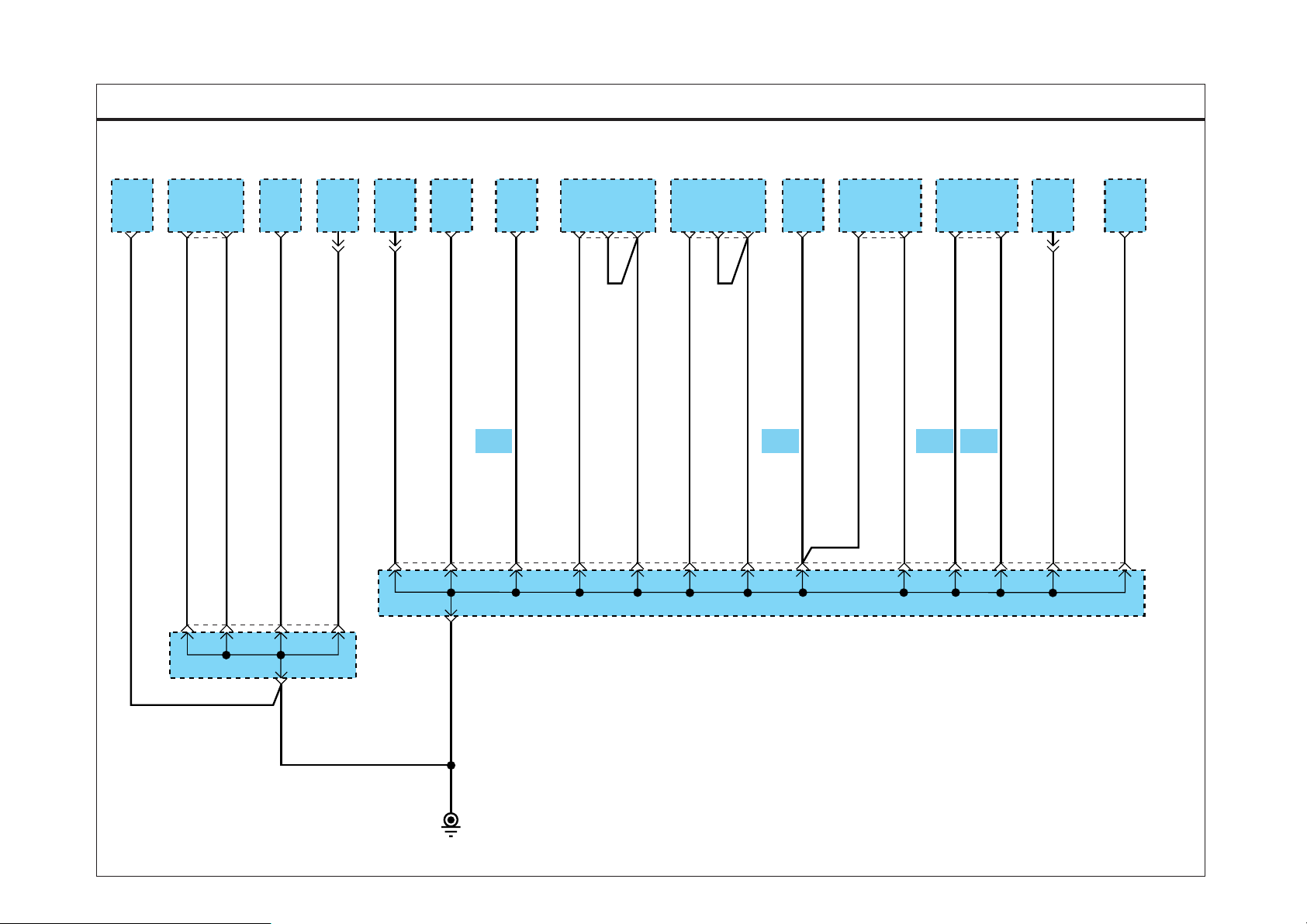
GROUND DIST RIBUTION
SD130-2GROUND DISTRIBUTION (2)
MODE
SWITCH
M29
6
M28
2
MODE
ACTUATOR
INTAKE
SWITCH
3
12 13 14
WIPER
CIGARETTE
MOTOR
M33
1
15
M31
2
M77
LIGHTER
M68
2
0.85B
4
JOINT
CONNECTOR
SWITCH
0.5B
10
A/C
6
M64
M84
HEAD LAMP
LEVELING
ACTUATOR RH
M60
3
0.85B
D4AF/
D4AL
1
DEFOGGER
SWITCH
3 5
0.5B
0.5B 0.5B
M65
6
FRONT
FOG LAMP
SWITCH
3 5
0.5B
0.5B 0.5B
6 18
6
M63
D4AF/
D4AL
REAR
FOG LAMP
SWITCH
M67
6
0.5B
9
HAZARD
SWITCH
6
0.85B 0.5B
M62
5
7
TACHOGRAPH
(ELECTRONIC)
5
0.5B 0.5B
D4AF/
D4AF/
D4AL
D4AL
ASHTRAY
M24
4
20
2
0.5B0.5B 0.5B 0.5B 0.85B0.5B
165
TACHOGRAPH
ILL.
(CASSETTE TYPE)
M30
0.5B
9
819
M45
M842 17
JOINT
CONNECTOR
M77
11
0.85B0.5B
0.85B
G01(MAIN)
EVT SD7130BL
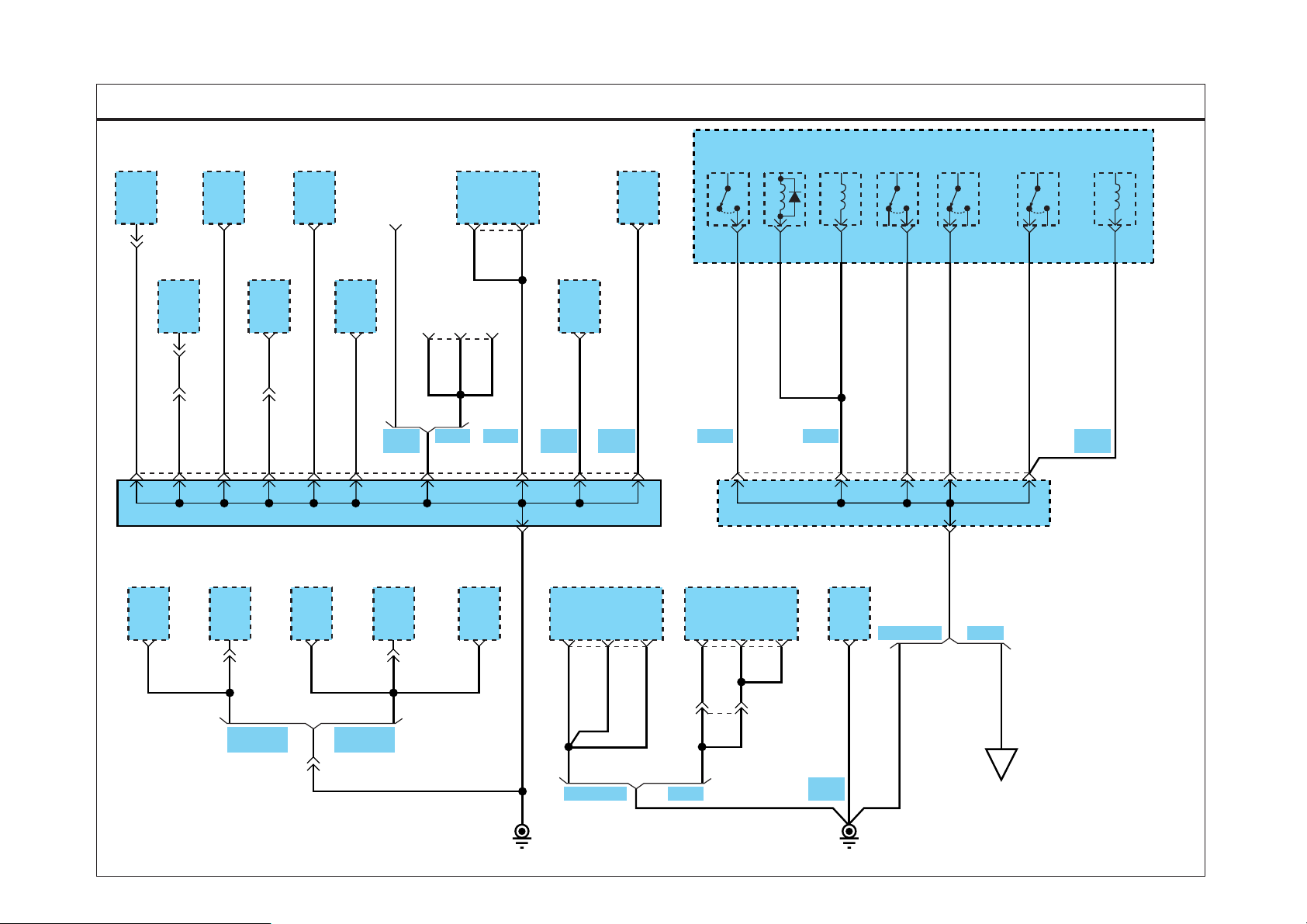
GROUND DIST RIBUTION
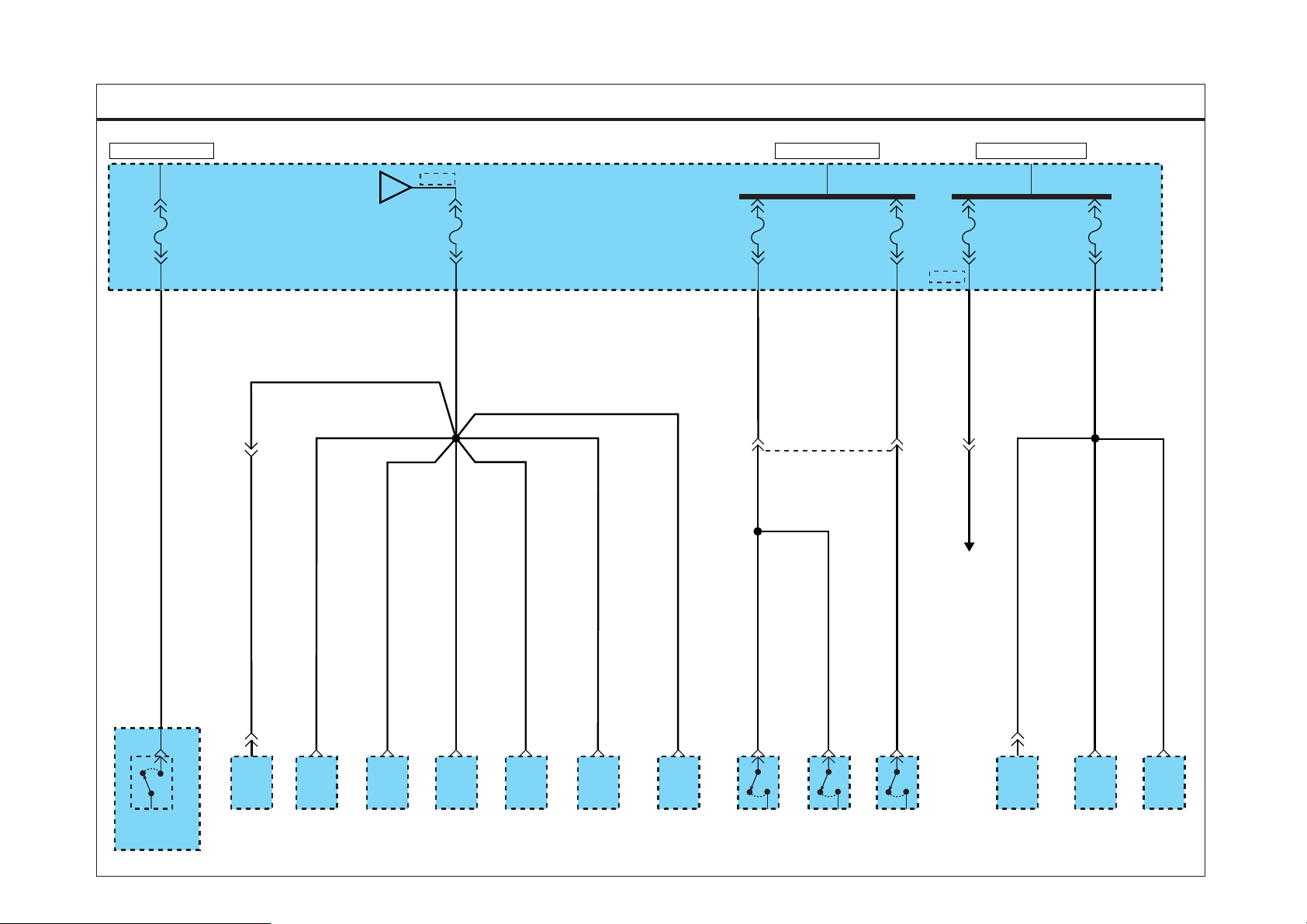
SD130-3GROUND DISTRIBUTION (3)
POSITION
LAMP LH
M51
2
SEAT BELT
SWITCH
0.5B
0.5B0.5B 0.5B 0.85B 0.5B 1.25B 0.5B
1 7 11 14
SIDE
REPEATER
LAMP LH
FRONT
TURN SIGNAL
LAMP LH
M52
2
POWER
DOOR LOCK
ACTUATOR LH
M102
2
0.85B
MM01
9
5
2
OUTSIDE
MIRROR
DEFOGGER LH ETACM
FLUID LEVEL
D06
3
MD02
4
REPEATER
BRAKE
SENSOR
SIDE
LAMP LH
1
M46
LAMP LH
HEAD
2
DATA LINK
CONNECTOR
M72
16
M50
OUTSIDE
MIRROR
DEFOGGER LH
0.5B 0.5B
D4AF/
D4AL
5
6
ENGINE PTO
CAB IN SWITCH
3
DATA LINK
CONNECTOR
16
0.5B
0.5B
D4DD D4DD D4DDD4DD
POWER
WINDOW
MAIN SWITCH
M86
RELAY
BOX
PTO CLUTCH
PEDAL POSITION
SWITCH
M48
M53
D4AF/
ETACM
0.5B
D4AL
2
49
M38
JOINT
CONNECTOR
M39
6
HEAD LAMP
M38
13
LEVELING
ACTUATOR LH
3
0.85B
D4AF/
D4AL
3
0.5B0.5B
M72
4
0.5B
HORN
RELAY
0.85B
PTO
RELAY
M88
3
1
1
M08
GLOW
RELAY
3
0.5B0.5B
0.5B
2
HIGH SPEED
WARNING
DEVICE
WIPER
RELAY
(LOW)
M94
0.85B 0.85B 0.5B
DOOR LOCK
M124M05
1
4 6
POWER
RELAY
5 M79
POWER
DOOR UNLOCK
RELAY
M06
4
0.85B
M79
7
JOINT
CONNECTOR
REAR FOG
INDICATOR
RELAY
4
D4AF/
D4AL
0.85B
1 D04
0.85B
D02
1
W/O Power
Window
0.85B
0.85B
6
With Power
Window
MD01
0.85B
1.25B0.85B
D4DDD4AF/D4AL
D02
1
3 D051 D04
1.25B
1.25B
1.25B
G01(MAIN) G02(MAIN)
0.5B
0.5B
5
0.5B
20 M56-1
19
0.5B
D4DDD4AF/D4AL
0.5B
18
0.5B
0.5B
5
0.5B
0.5B
0.5B
19 M56-1
20
0.5B/O
MM07
11
0.5B
D4AF/
D4AL
M73
2
0.85B
0.85B
A
To Ground
(SD130-4)
EVTSD7130CL
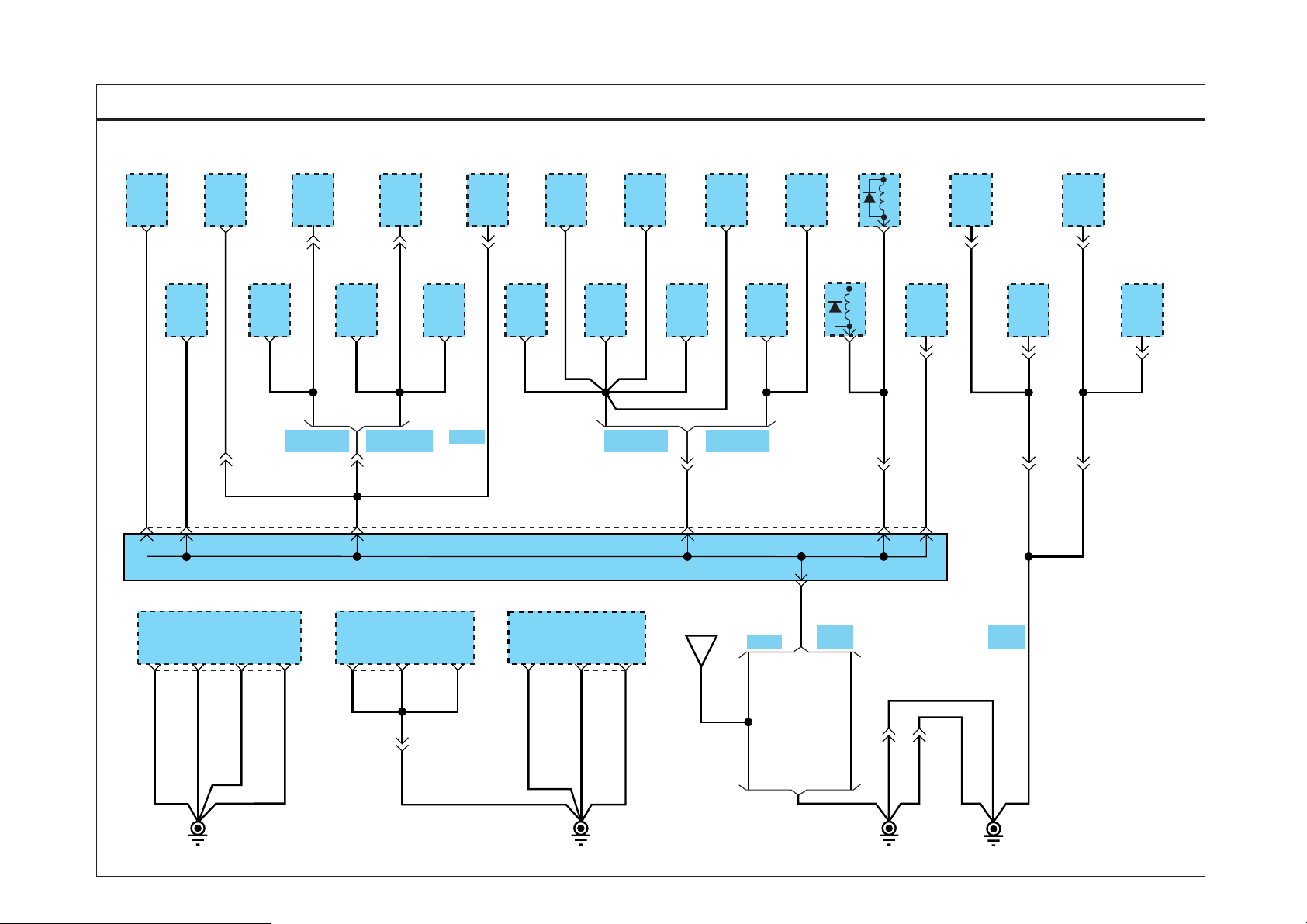
GROUND DIST RIBUTION
SD130-4GROUND DISTRIBUTION (4)
FRONT
TURN SIGNAL
LAMP RH
2 M59
HEAD
LAMP RH
2 M57
0.5B
1.25B
1
2
ABS CONTROL MODULE
POWER
DOOR LOCK
ACTUATOR RH
3 D16
REPEATER
LAMP RH
0.85B
0.85B
MD04
4
OUTSIDE
MIRROR
DEFOGGER RH
D12
1
SIDE
1 D14
REPEATER
0.85B
0.85B
0.85B 1.25B
W/O Power
Window
0.85B0.5B
0.85B
DEFOGGER RH
SIDE
LAMP RH
1 D14
0.85B
With Power
Window
MD03
6
3
OUTSIDE
MIRROR
D12
1
SUB SWITCH
1.25B 0.5B
MAIN ECM
POWER
WINDOW
3 D15
D4DD
VACUUM
SWITCH
M71
2
0.5B
ENDOUT
MARKER
LAMP 'A'
1 M112
ENDOUT
MARKER
LAMP 'B'
1 M113
0.5B
0.85B
0.85B 0.5B
ENGINE ECM
FRONT
ROOM
LAMP
1 M110
Double Cab
ENDOUT
MARKER
LAMP 'C'
1 M120
0.5B
W/O
ENDOUT
MARKER
LAMP 'D'
1 M121
0.5B
4
0.5B
6
Joint Connector
(SD130-3)
ENDOUT
MARKER
LAMP 'E'
0.5B
With
Double Cab
MM03
From
A
1 M122
0.5B
FRONT
ROOM
LAMP
1 M110
D4DD
REAR
ROOM
LAMP
1 M114
0.5B
5
RELAY
0.5B 0.5B
M81
D4AF/
D4AL
A/C
2
A17
BLOWER
RELAY
A15
2
2
0.5B
7
OUTSIDE MARKER
LAMP RH
POSITION
LAMP RH
M58
2
0.85B 0.85B 0.85B 0.85B
0.5B0.5B
MA02
M81
8
REAR
C74
2
OUTSIDE MARKER
LAMP LH
0.85B 0.85B
1.25B
JOINT
CONNECTOR
D4AF/
D4AL
FRONT
OUTSIDE MARKER
LAMP LH
REAR
2
2
2
C73
CC052CC04
0.85B
C70
FRONT
OUTSIDE MARKER
LAMP RH
C72
2
55
30 29 28
0.85B 0.85B 1.25B 0.85B
A01
4 28
1.25B 0.5B
1.25B
1.25B
1.25B
3
MC04
2
M99-1M99-3
1 4
1.25B
1.25B 1.25B
C10-1C10-2
5
0.85B 1.25B
1.25B
1.25B
2 4
3.0B 2.0B
G02(MAIN)G05(CHASSIS/D4DD)G04(A.B.S)
MC03
2.0B 3.0B
G03(CHASSIS)
1.25B
EVTSD7130DL
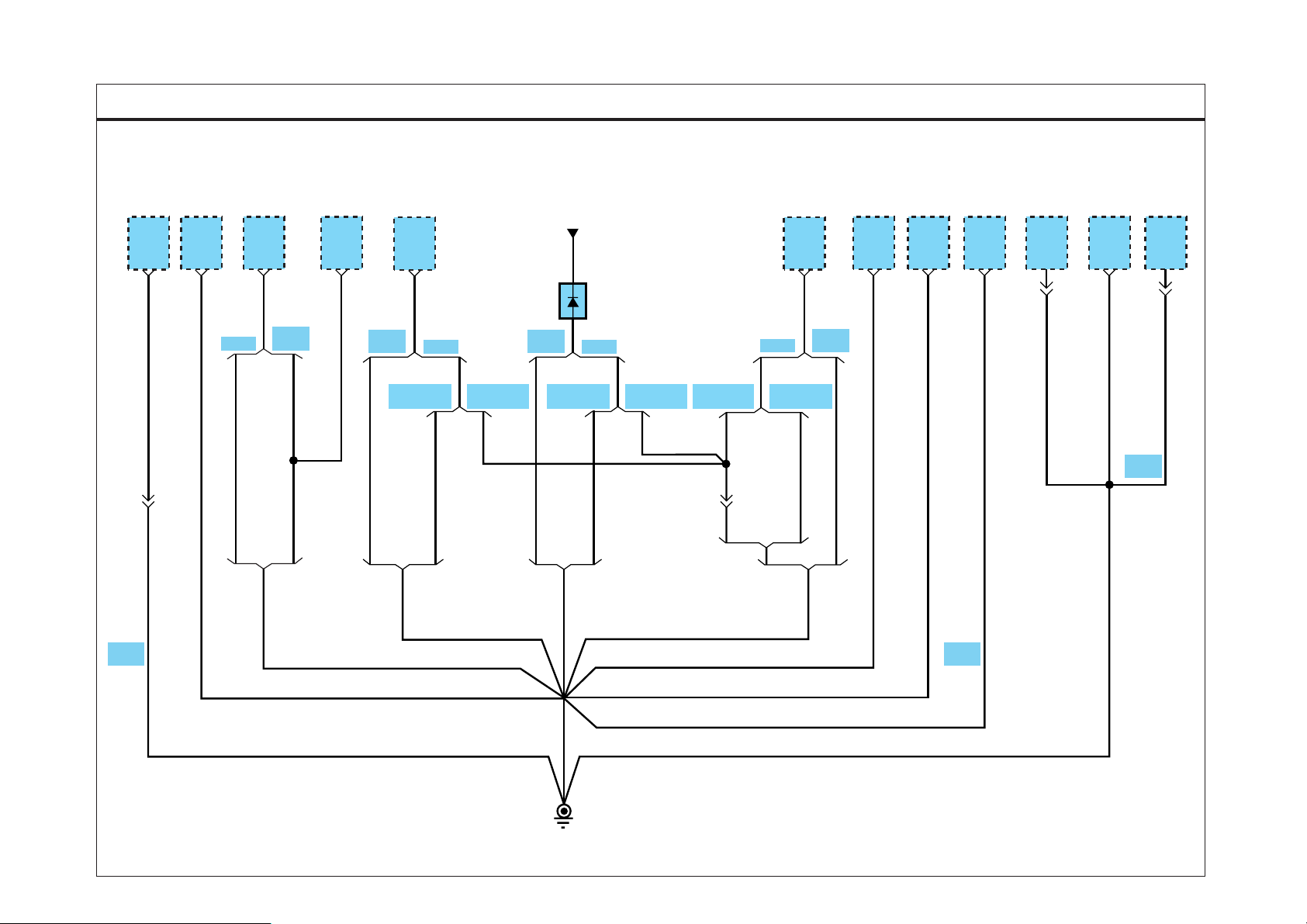
GROUND DIST RIBUTION
SD130-5GROUND DISTRIBUTION (5)
TACHO-
METER
SENSOR
1 E05
0.5B
6
0.85B
1.25B
EC02
FRONT
FOG
LAMP RH
1 C19
CONDENSER
FAN
MOTOR
(TCI)
2 C15(D4DD)
C20(D4AL)
D4DD
1.25B1.25B
D4AF/
D4AL
CONDENSER
FAN MOTOR
(NA)
2 C15(D4AF)
0.85B
0.85B 0.85B
INTAKE
SHUTTER
D4AF/
D4AL
Double Cab
See P.T.O Control System/
VALVE
C25
1
D4DD D4DD
W/O
With
Double Cab
Exhaust Parking Brakes
(SD471-1)(SD471-2)
(SD596-1)(SD596-2)
0.85L/B
D4AF/
D4AL
0.85B
DIODE
Z03
With
Double Cab
0.85B
W/O
Double Cab
0.85B0.85B
W/O
Double Cab
0.85B
0.85B
CC06
1
0.85B
EXHAUST
MAGNETIC
VALVE
1
D4DD
With
Double Cab
C26
D4AF/
D4AL
0.85B 0.85B0.85B
PTO
MAGNETIC
VALVE
C24
1
FRONT
FOG
LAMP LH
1 C17
1.25B
IDLE UP
MAGNETIC
VALVE
1 C40
0.85B
WORKING
LAMP
1.25B
DUMP
WARNING
SWITCH
1 C03
0.85B
1.25B
COMBI-
NATION
LAMP RH
1.25B
D4AF/
D4AL
REAR
4 C081 C02
D4AF/
D4AL
1.25B
G03(CHASSIS)
D4AF/
D4AL
EVT SD7130EL
 Loading...
Loading...