Hyundai HD78 User Manual
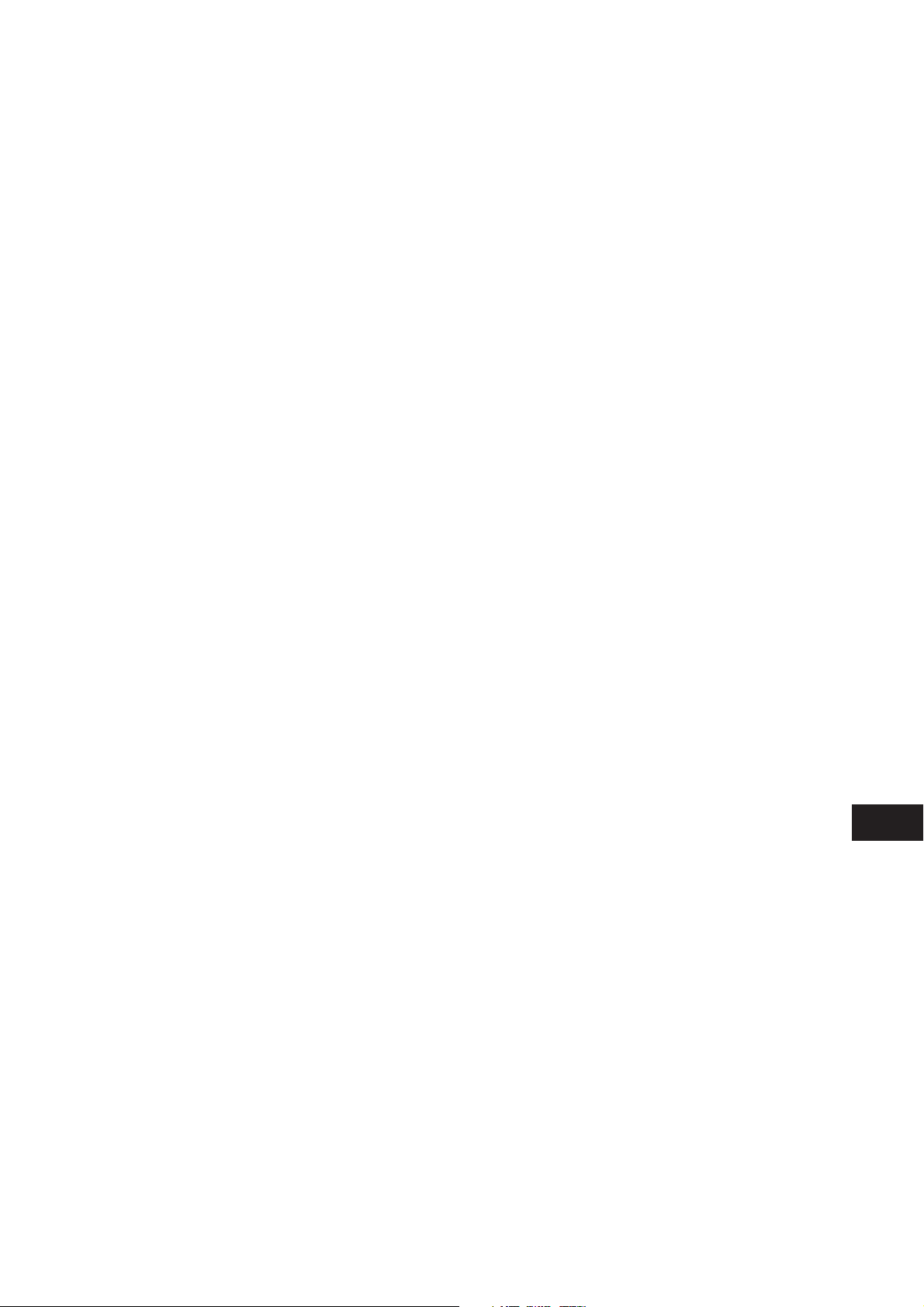
Brake System
(WABCO ABS)
General
Description.................................................... BR -3
Components ................................................. BR -14
Dignosis ........................................................ BR -16
On-Vehicle Inspection And Adjustment ....... BR -20
Specifications ............................................... BR -22
Vacuum Assisted Hydraulic Brake
Brake Pedal
Components............................................ BR -27
Removal .................................................. BR -28
Installation ............................................... BR -28
Adjustment .............................................. BR -28
Brake Booster
Component ............................................. BR -30
Removal .................................................. BR -31
Installation ............................................... BR -32
Inspection ................................................ BR -33
Brake Master Cylinder
Components............................................ BR -36
Removal .................................................. BR -37
Installation ............................................... BR -38
Load Sensing Proportioning Valve(LSPV)
Components............................................ BR -39
Removal .................................................. BR -40
Inspection ................................................ BR -40
Front Brake Assembly
Disc Brake
Components............................................ BR -41
Removal .................................................. BR -42
Installation ............................................... BR -43
Disassembly............................................ BR -44
Reassembly ............................................ BR -45
Inspection ................................................ BR -46
Drum Brake
Components............................................ BR -48
Removal .................................................. BR -49
Replacement ........................................... BR -50
Installation ............................................... BR -51
Parking Brake System
Components ................................................. BR -52
Removal ....................................................... BR -53
Installation .................................................... BR -54
Adjustment .................................................... BR -56
Rear Brake Assembly
Drum Brake
Components............................................ BR -57
Removal .................................................. BR -58
Replacement........................................... BR -59
Installation ............................................... BR -61
Exhaust Brake
Component Location .............................. BR -62
Components............................................ BR -63
Replacement........................................... BR -67
Disassembly............................................ BR -68
Reassembly ............................................ BR -68
Inspection ................................................ BR -70
ABS(Anti-Lock Brake System)
Specifications ............................................... BR -72
Description.................................................... BR -72
Using Blink Code Diagnostics ..................... BR -76
DTC Troubleshooting ................................... BR -83
Repair Instruction ......................................... BR -88
Connector Configurations ............................ BR -90
Full Circuit Diagram ..................................... BR -91
Inspection ..................................................... BR -91
Adjustment .................................................... BR -92
ABS Modulator
Removal .................................................. BR -94
Installation ............................................... BR -94
Wheel Speed Sensor
Description .............................................. BR -95
Replacement........................................... BR -95
ABS Control Module
Removal .................................................. BR -97
Installation ............................................... BR -98
Schematic Diagrams .............................. BR -99
DTC Chart ............................................... BR -104
0000 ........................................................ BR -107
0001 ........................................................ BR -110
0002 ........................................................ BR -113
0003 ........................................................ BR -116
0004 ........................................................ BR -119
0009 ........................................................ BR -122
000A ........................................................ BR -125
000B ........................................................ BR -128
000C ........................................................ BR -131
000D ........................................................ BR -134
000E ........................................................ BR -137

000F ........................................................ BR -140
0010 ........................................................ BR -143
0011 ........................................................ BR -146
0017 ........................................................ BR -149
0018 ........................................................ BR -152
0019 ........................................................ BR -155
001A ........................................................ BR -158
001B ........................................................ BR -161
001C ........................................................ BR -164
001D ........................................................ BR -167
001E ........................................................ BR -170
001F ........................................................ BR -173
0020 ........................................................ BR -176
0021 ........................................................ BR -179
0022 ........................................................ BR -182
0023 ........................................................ BR -185
0024 ........................................................ BR -188
0029 ........................................................ BR -191
002A ........................................................ BR -194
002B ........................................................ BR -197
002C ........................................................ BR -200
002D ........................................................ BR -203
002E ........................................................ BR -206
002F ........................................................ BR -209
0030 ........................................................ BR -212
0032 ........................................................ BR -215
0033 ........................................................ BR -218
0037 ........................................................ BR -221
0038 ........................................................ BR -223
0039 ........................................................ BR -225
003B ........................................................ BR -227
003C ........................................................ BR -230
003D ........................................................ BR -233
003F ........................................................ BR -235
0040 ........................................................ BR -237
0041 ........................................................ BR -240
0042 ........................................................ BR -243
0043 ........................................................ BR -246
0044 ........................................................ BR -249
0045 ........................................................ BR -252
0046 ........................................................ BR -255
0047 ........................................................ BR -257
0049 ........................................................ BR -260
004A ........................................................ BR -263
004B ........................................................ BR -266
004C ........................................................ BR -269
004D ........................................................ BR -272
004E ........................................................ BR -275
004F ........................................................ BR -278
0050 ........................................................ BR -281
0051 ........................................................ BR -284
0052 ........................................................ BR -287
0053 ........................................................ BR -290
0054 ........................................................ BR -293
0055 ........................................................ BR -296
0056 ........................................................ BR -299
0057 ........................................................ BR -302
0058 ........................................................ BR -305
0059 ........................................................ BR -308
005A ........................................................ BR -311
005B ........................................................ BR -314
005C ........................................................ BR -317
005D ........................................................ BR -320
General
DESCRIPTION
BRAKE SYSTEM
The service brakes are internally expanding type
hydraulic brakes acting on all w h e els. The brakes for the
front wheels are 2-leading type and those for the rear
wheels are duo-servo or dual 2-leading type.
The brake booster gives faster hydraulic pressure
buildup. Tandem type brake master cylinder also
contributes to safety. The brake pedal, which is
easy-to-operate pendant type, transmits depression force
via operating rod, etc. to the BRAKE BOOSTER, which
boosts it and drives the master cylinder.
The BRAKE BOOSTER vacuum line is equipped with a
vacuum tank which minimizes negative pressure change
even in the case of repeated and frequent braking
operation.
Brake Booster
1. When not in Operation
When not in operation, no force acts on the operating
rod and hence the valve plunger is seated on the
poppet to open the negative pressure valve and to
close the atmospheric valve.
Negative pressure generated by the engine draws out
air from the chamber on the left side of the
diaphragm plate. And as the chamber on the right
side of the diaphragm plate is also evacuated via the
vacuum channel and the negative pressure valve that
is opened. As a result, the diaphragm plate is
pressed tightly onto the rear shell surface by the
diaphragm plate return spring. Atmosphere goes
through the air filter into space around the operating
rod but does not flow further as the atmospheric
valve of the valve plunger is closed.
2. When in Operation
When the brake pedal depression force overcomes
the valve return spring force, the operating rod, valve
plunger and poppet now move to the left and the
poppet is pressed tightly onto the valve plunger seat
by the poppet spring, closing the negative pressure
valve. When the brake pedal is further depressed
following closure of this valve, the valve plunger
clears the poppet to open the atmospheric valve and
atmosphere now flows through the channel into the
chamber on the right side of the diaphragm.
This flow of atmosphere produces the pressure
difference across the diaphragm and the force
resulting from such pressure difference overcomes
the piston return spring force. As a result, the
diaphragm pushes the push rod as it moves from
right to left. The push rod thus pushes the master
cylinder piston, generating high fluid pressure from
low pedal depression force.
SUDBR9016L
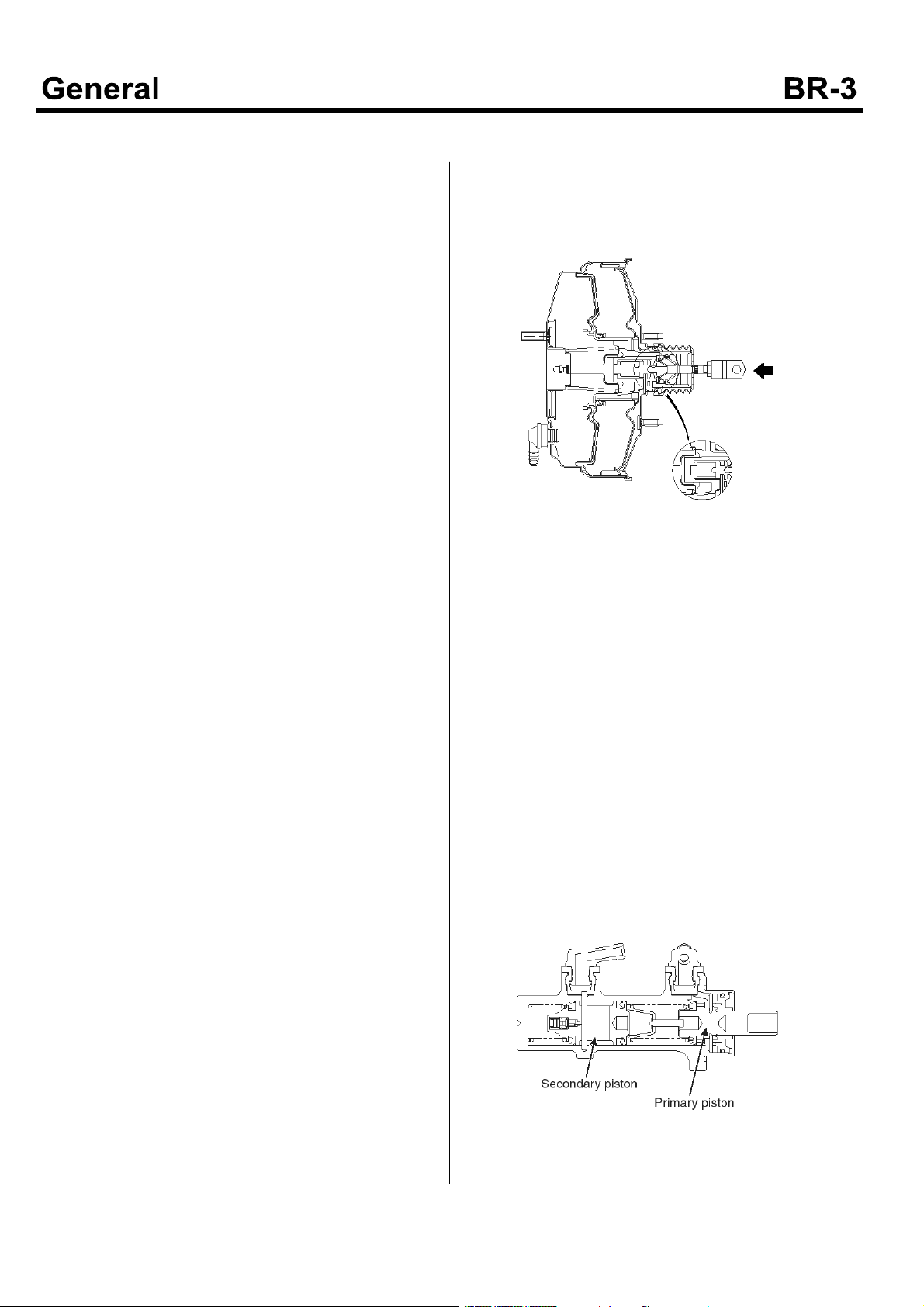
Brake Master Cylinder
1. Normal Operation
The tandem type brake master cylinder has
independent hydraulic systems for front and rear
brakes.
Should one of the two hydraulic systems fail, braking
by survived system (front or rear wheels) ensures
safety. When the brake pedal is depressed, the
primary piston is pushed to left, developing hydraulic
pressure in the pressure chamber on the primary
side. This pressure directly acts on the secondary
piston to push the secondary piston to left,
developing hydraulic pressure also in the pressure
chamber on the secondary side. As a result, each
piston pressurizes brake fluid to generate hydraulic
pressure in both front and rear brake systems.
SUDBR9017L
2. When fluid leaks are caused in front brake system
In this case, depression of the brake pedal to push
the push rod does not develop hydraulic pressure as
the brake fluid leaks from the front brake system.
Therefore, the primary piston compresses the
primary return spring and the retainer pushes the
secondary piston, which then pressurizes brake fluid
in space between the secondary piston and cylinder
body, thus generating hydraulic pressure in the rear
brake system only.
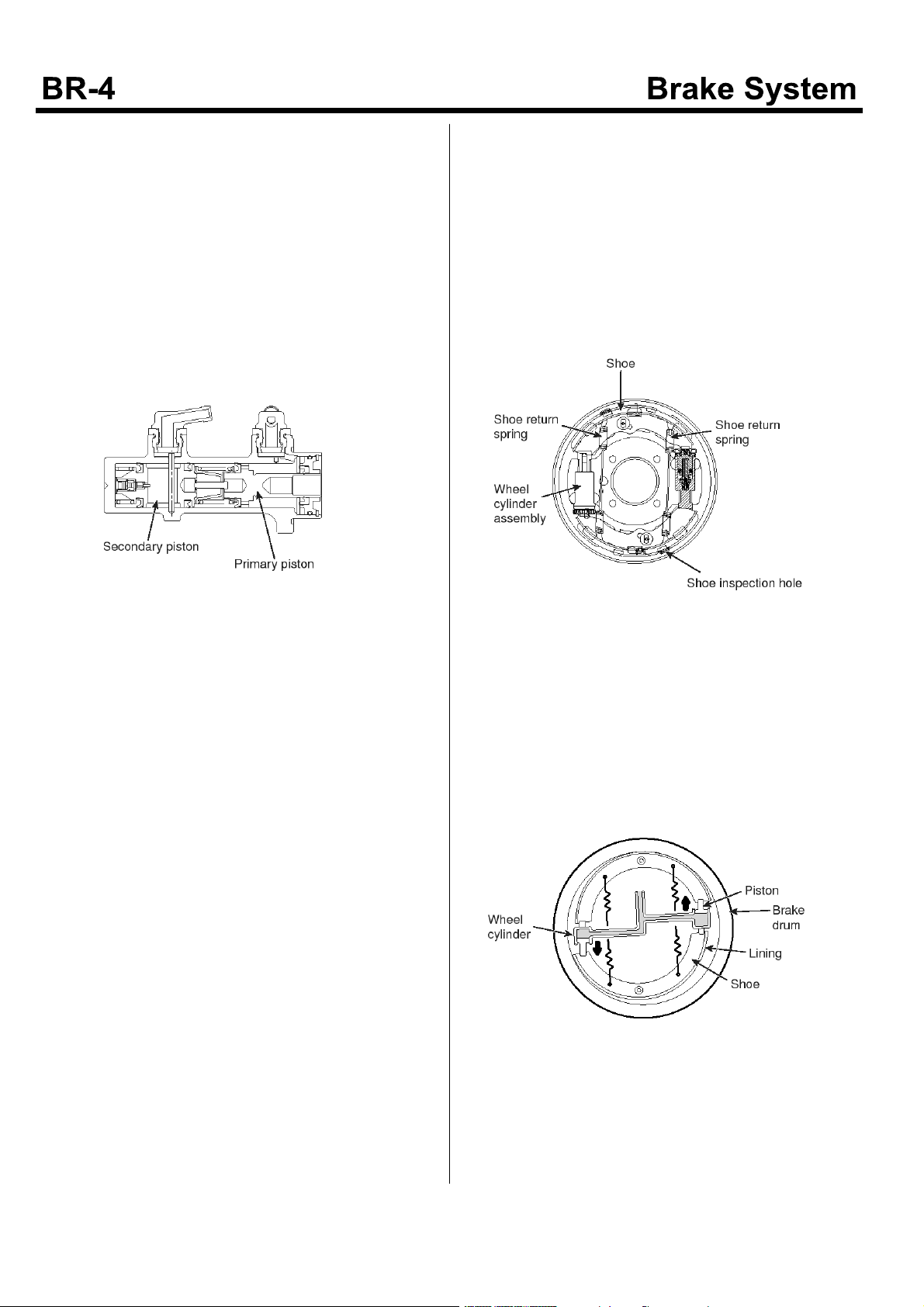
Front And Rear Wheel Brakes
Front wheel Brakes
The wheel cylinder is so constructed that the piston
extends in one direction only to push the shoes which are
held down to the backing plate by the shoe hold down
pin. The return springs mounted on the shoe fixed and
moving sides cause contraction of the shoe and wheel
cylinder piston when the brake is released.
When the vehicle is running forward, both shoes work as
leading shoes.
SUDBR9018L
3. When fluid leaks are caused in rear brake system
In this case, when the brake pedal is depressed to
push out the push rod, the secondary piston end
comes into contact with the cylinder body since brake
fluid in the rear brake system leaks. When the push
rod is further pushed, the primary piston pressurizes
brakefluidinthespacebetweentheprimaryand
secondary pistons, generating hydraulic pressure in
the front brake system only.
EMTBR5004A
When the pedal is depressed, brake fluid supplied under
pressure from the master cylinder enters the wheel
cylinder, of which piston moves the shoe moving side so
thattheliningispressedagainstthedruminside.
Resultant friction between the lining and drum causes the
shoe to try to turn with the drum, thus boosting the
braking force.
EMTBR5005A
Rear Wheel Brake
Dual 2-leading Brake
The wheel cylinders are installed at front and rear and
the pistons extend in both upward and downward
directions to push the shoes from both directions. The
shoes are held down to the backing plate by shoe hold
down pins and the return springs mounted on the shoes
causing contraction of the shoe and wheel cylinder piston
when the brake is released. During both forward and
reverse operation of the vehicle, the shoes work as
leading shoes.
EMTBR5004A
When the pedal is depressed, brake fluid supplied under
pressure from the master cylinder enters the wheel
cylinder, of which piston causes the shoe to expand in
both directions to press the lining against the drum
inside. Resultant friction between the lining and drum
causes the shoe to try to turn with the drum, thus
boosting the braking force.
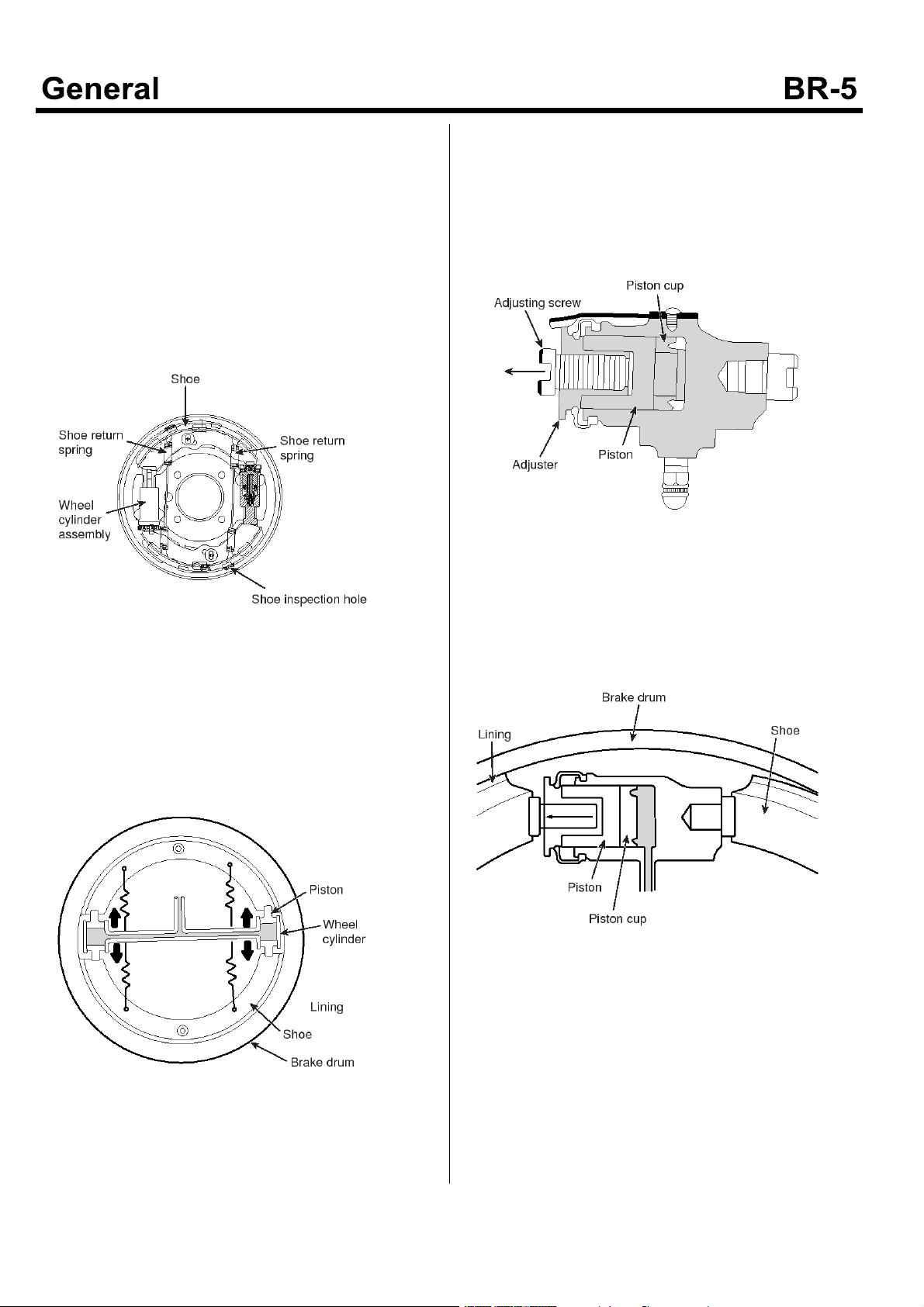
Wheel Cylinder
The wheel cylinder driven by hydraulic pressure
generated by the brake master cylinder presses the shoe
(lining) against the brake drum.
There are following two types of wheel cylinder according
to the method of pushing the shoe.
EMTBR5007A
1. 2-leading type : Front brake
In pedaling brake, oil pressure rising is master
cylinder goes into wheel cylinder and pushes piston.
Shoe contacting with the end of piston sticks to brake
drum and generates frictional force.
EMTBR5006A
EMTBR5008A
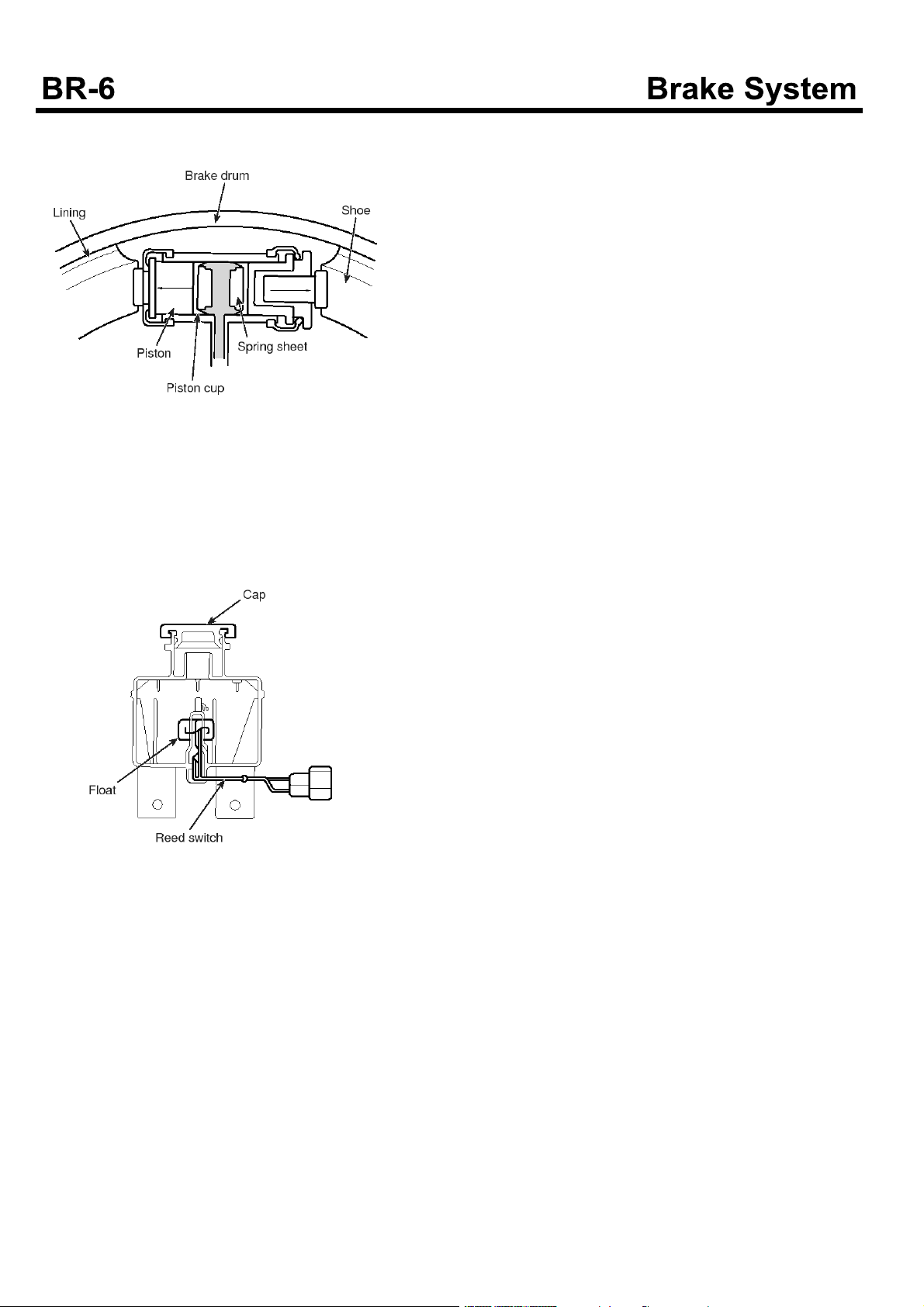
2. Dual 2-leading type : rear brake
EMTBR5009A
Brake Fluid Level Sensor
The brake fluid level sensor installed in the brake fluid
tank senses the brake fluid level in the tank. When the
fluid level drops to a preset level, the sensor operates to
turn on the warning lamp in the cluster to warn low brake
fluid level.
EMTBR5010A
Exhaust Brake
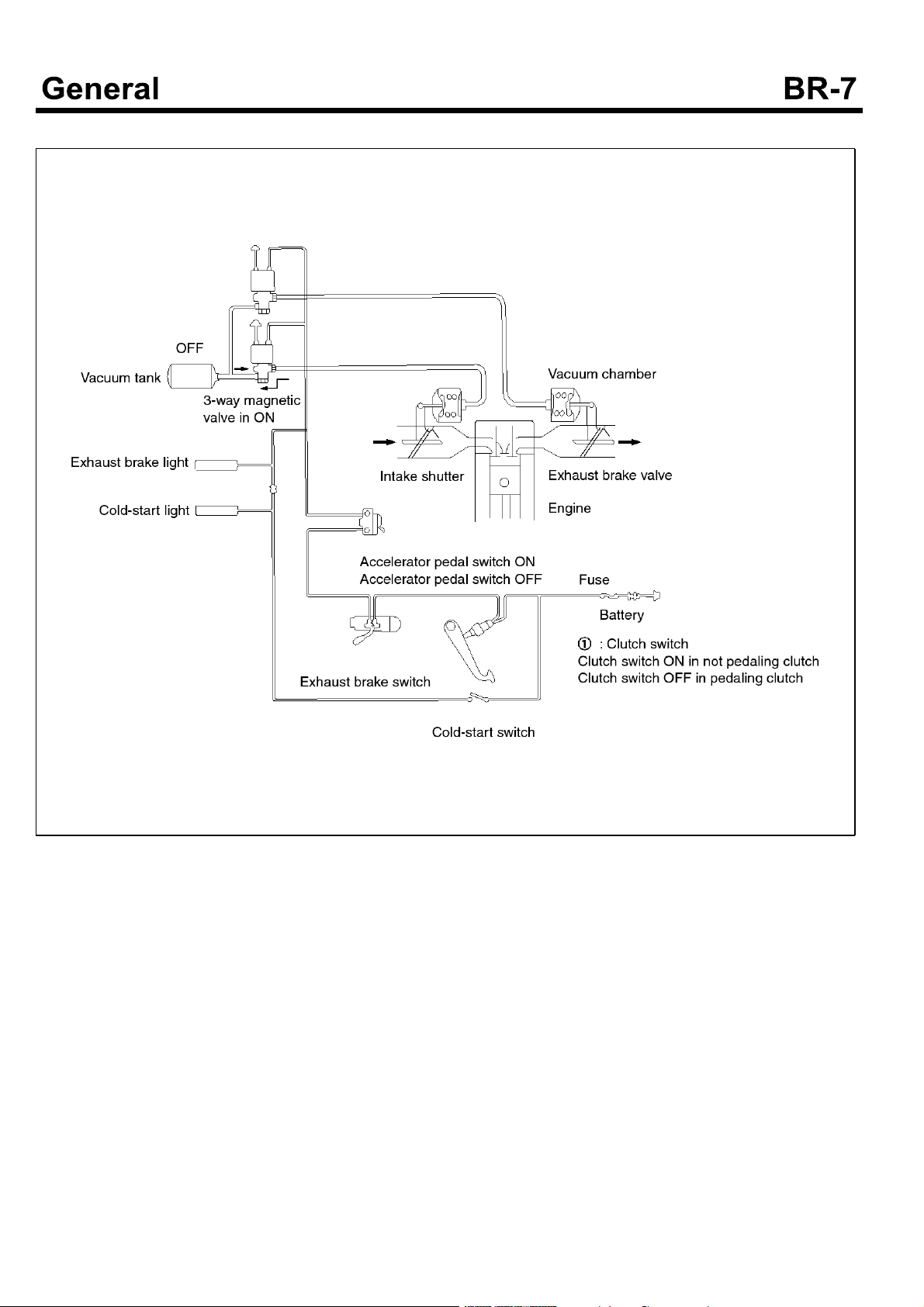
The exhaust brake system, as an assistant function of
the service brake, comprises of the exhaust brake device
installed at the middle portion of the exhaust pipe and the
intake shutter installed at the intake manipulate to reduce
the intake air noise.
When the exhaust brake device close the butterfly valve,
the pressure inside of the pipe increases. This increased
pressure influences to the piston to get the braking force.
At that time, the intake shutter is also closed. When the
clutch pedal, the accelerator pedal or the exhaust brake
switch is released, the electric circuit is OFF and the
exhaust brake is released.
The exhaust brake is the vacuum type assistant device
which uses the negative pressure.
SUDBRA015L
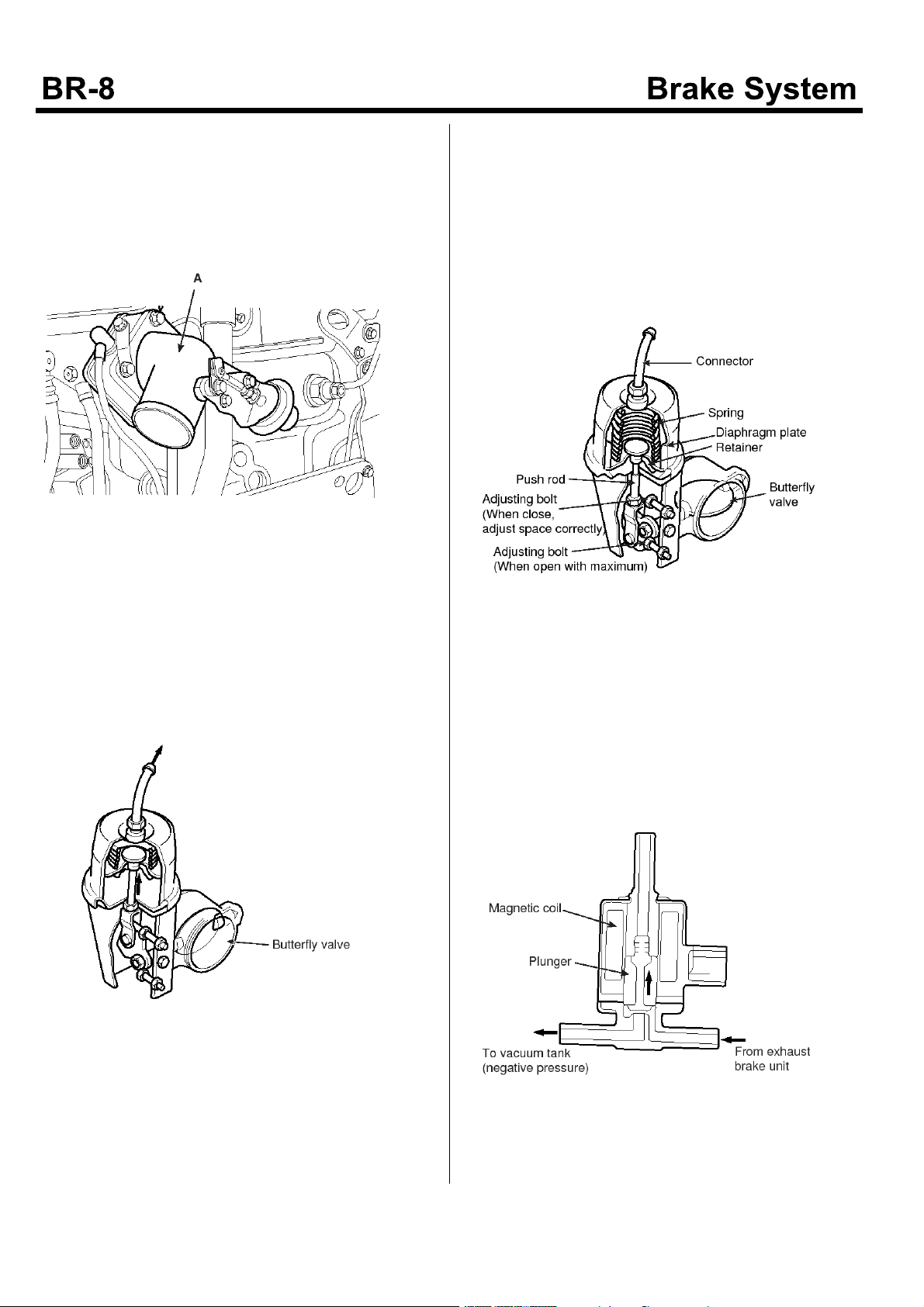
Intake Shutter
When the exhaust brake is operating, the intake
shutter(A) reduces the amount of the intake air through
the intake manipulate so as that the exhaust pressure is
operated to the piston effectively. As a result, the noise
will be reduced and the brake will be more effective.
KMTBR5513A
Exhaust Brake Unit
1. At Working
If the exhaust brake switch is ON, the three-way
magnetic valve is opened. The vacuum pressure of
the vacuum tank is applied to the exhaust brake unit
so as to pull the piston.
Asaresult,thebutterflyvalvelinkedtothepushrod
is closed so that the exhaust brake is working.
2. At releasing
If the exhaust brake switch, the clutch switch and the
accelerator switch are OFF, the 3-way magnetic
valve closes the circuit to the vacuum tank and opens
the atmosphere circuit.
Therefore, the atmospheric pressure is applied to the
exhaust brake unit. Due to the spring tension, the
butterfly valve is opened. The exhaust brake is
released.
EMTBR5013A
The 3-way Magnetic Valve
1. At working
If the exhaust brake switch is ON, an electric current
will flow through the coil and then a magnetic field is
formed. The magnetic force pulls the plunge to
upward. At that time, the valve seat at the plunger
closes the way to the atmosphere pressure while it
opens the way linking the vacuum tank and the brake
chamber.
EMTBR5012A
EMTBR5014A
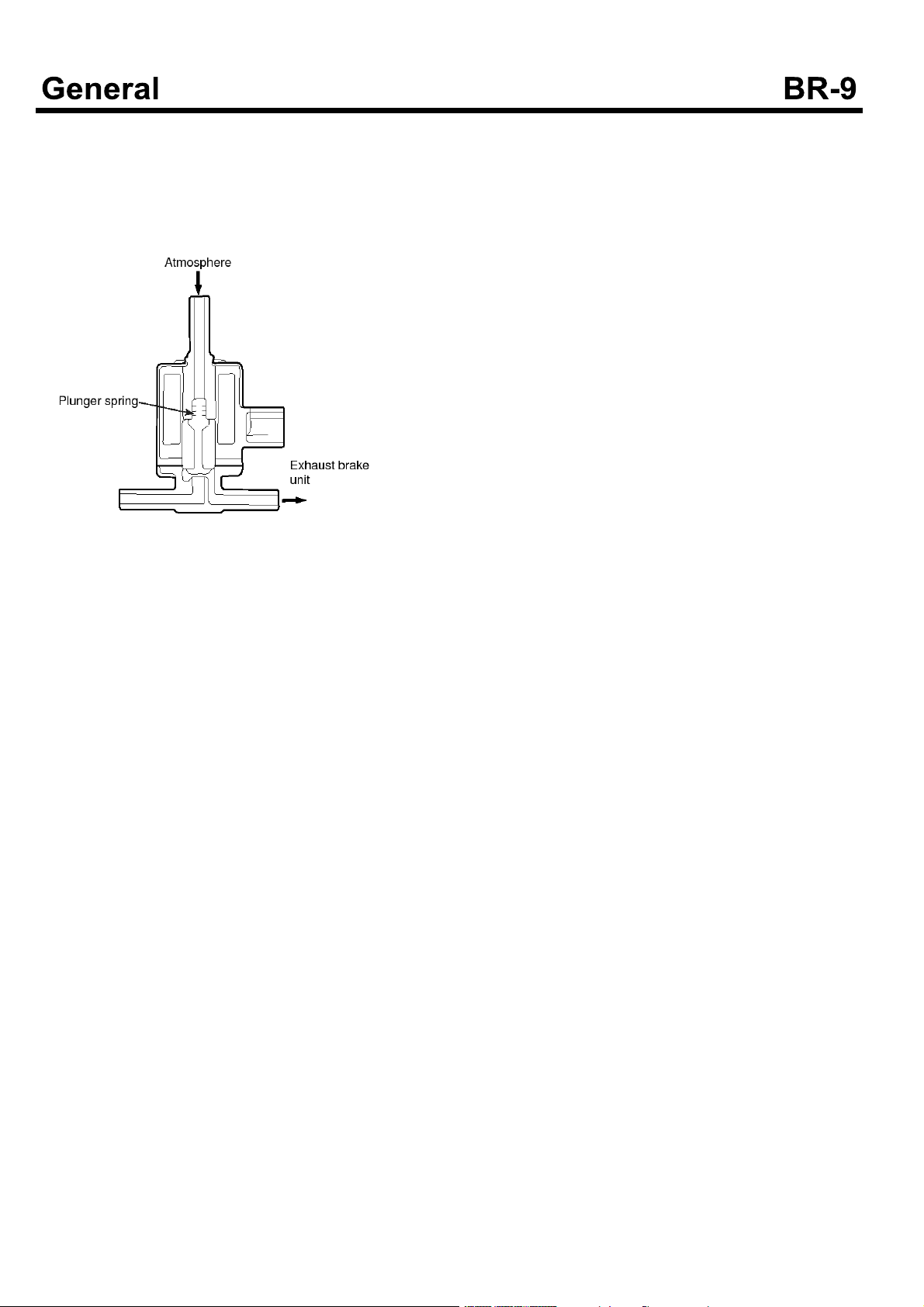
2. At releasing
If the exhaust brake switch is OFF, the electric
current flowing through the coil is shut down. Due to
the spring tension, the plunger will be pushed so as
to close the way to vacuum tank while the way to the
atmosphere pressure and the brake chamber.
EMTBR5060A
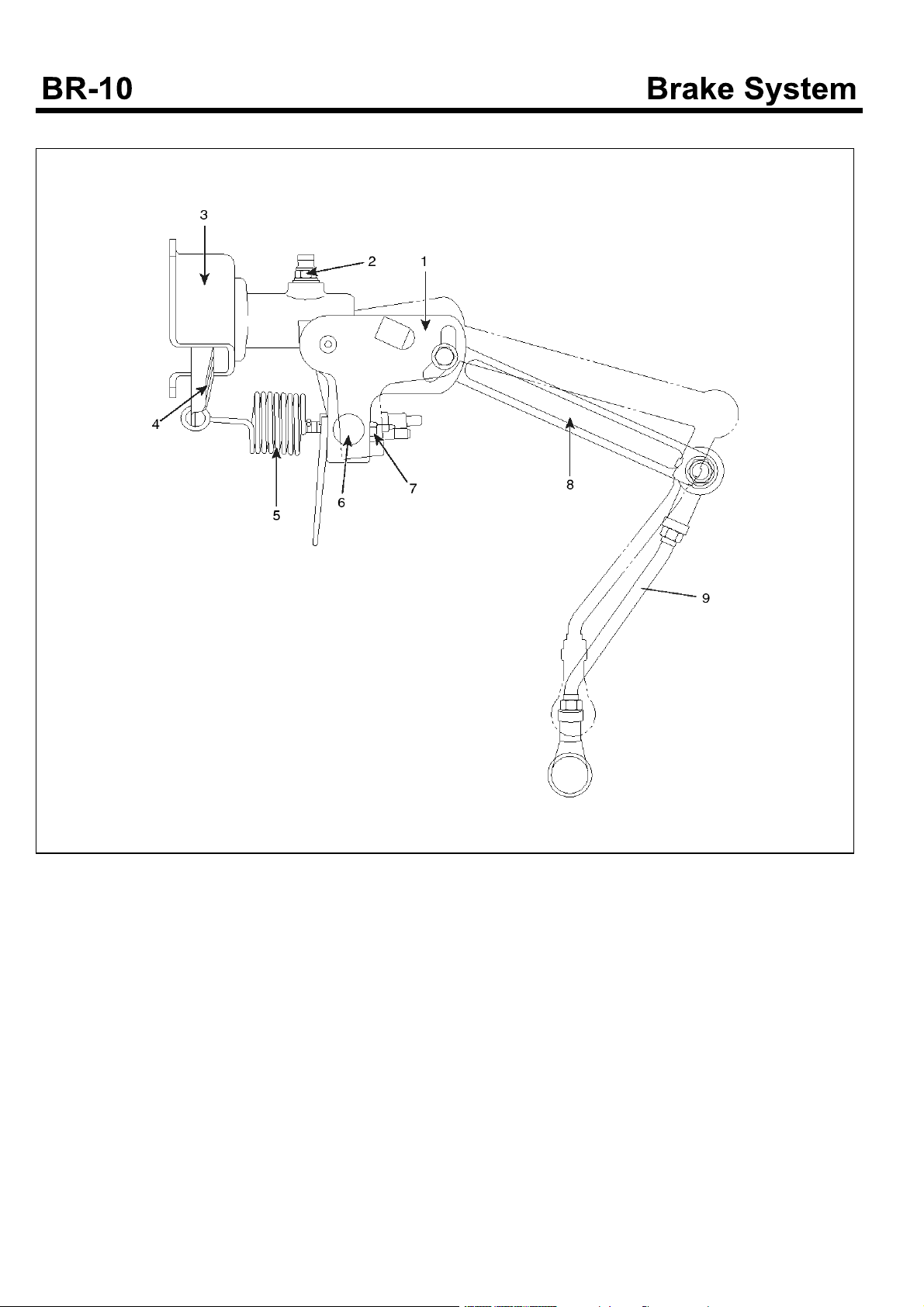
LOAD SENSING PROPORTIONING VALVE
1. LSPV assembly
2. Bleeder screw
3. Bracket
4. Lever assembly
5. Sensor spring
6. Spring guide
SUDBRA021L
7. Adjusting nut
8. Operating lever
9. Connecting link assembly
Construction
LSPV is consist of sensor part and pressure controller
part.
1. Sensor part
It consists of spring, operating lever, link. It senses
the height of vehicle with varying according to the
amount loads
2. Pressure controller part
It consists of valve stem mechanism for proportioning
control of sensor force.
SUDBR9036L
Service and Inspection of the LSPV
Check the LSPV as below when replace the sensor
spring, valve body assembly or reinstall the rear axle,
rear spring.
EMTBR5016A
Operating Principle
LSPV body is mounted in the frame and the end of the
link is mounted in the rear axle. With varying of amount
of vehicle load changes the relative position of frame and
rear axle, so sensor spring force varies to the valve stem.
It controls the rear axle brake fluid pressure.
1. Unloaded status
The sensor spring presses the valve stem slightly, so
the brake fluid pressure is set weakly.
2. Loaded status
The sensor spring presses the valve stem strongly,
sothebrakefluidpressureissethighly.
NOTICE
Don't loose or don't retighten the adjusting nut
crimping.
Symptom
Braking force is i nsufficient.
Rear brake is locktoofast.
Probable Cause Remedy
Insufficient air bl-
Air bleeding
eeding
Maladjusted sen-
Readjust
sor spring
Sensor spring broken
Oil leakage in the
brake fluid line or
LSPV assembly
Maladjusted sen-
Replace valve assembly
Tighten brake fluid line or replace
LSPV assembly
Readjust
sor spring
Inner fault the LSPV
Replace LSPV assembly
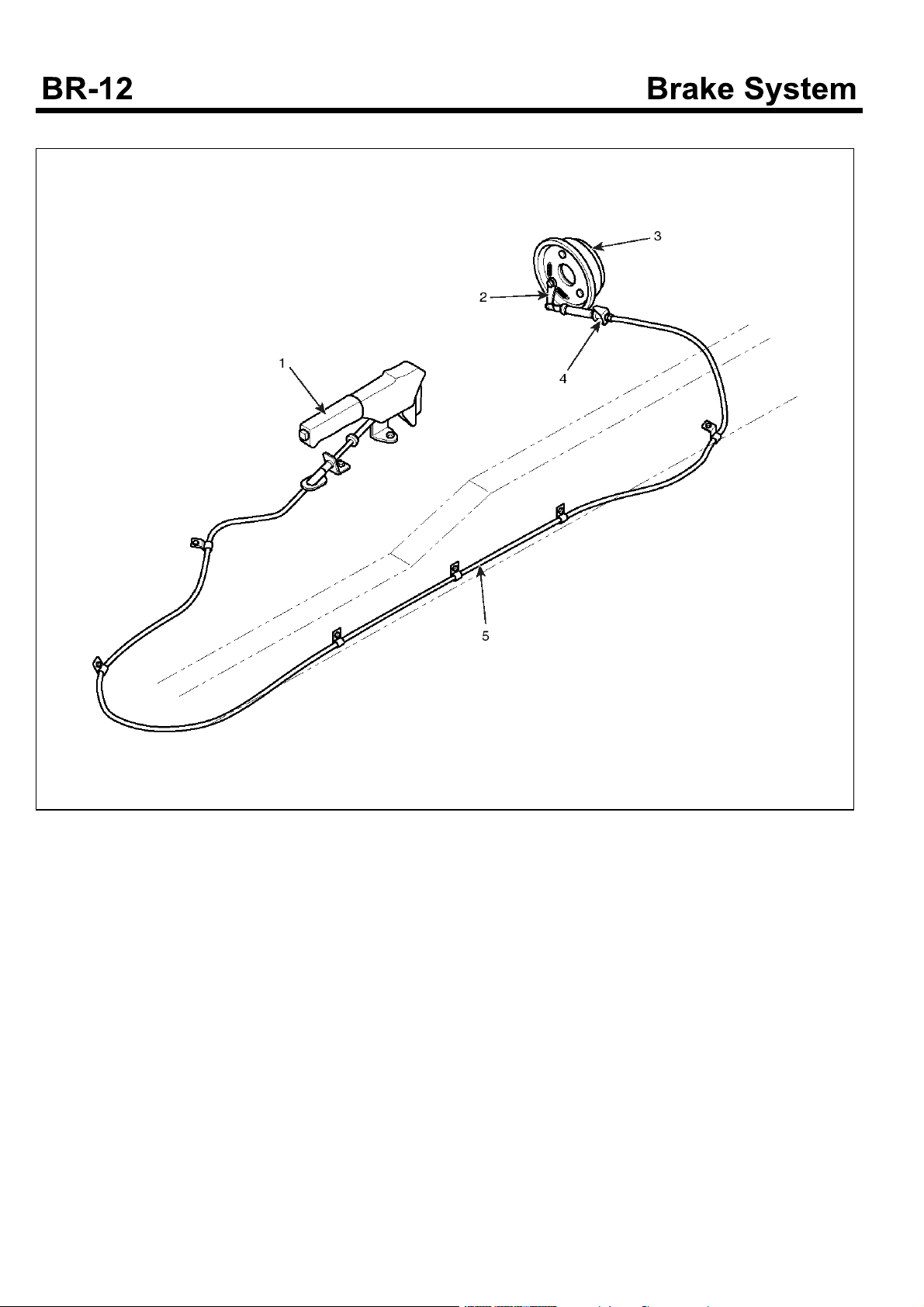
PARKING BRAKE GENERAL
1. Parking brake lever assembly
2. Cam lever
3. Parking brake drum
4. Adjusting nut
5. Parking brake cable
The parking brake installed behind the transmission is an
internal expansion type acting on the propeller shaft.
It controls propeller shaft rotation to work as a parking
brake.
The control is wire mechanical type; brake shoes are
pressedviaawiretocontrolthepropellershaft.
SUDBRA022L

Parking Brake Proper
When the lever at the driver's seat is pulled, the cam
lever is actuated via a wire cable and resultant cam
rotation causes the brake shoes to expand and be forced
against the brake drum. The braking force is thus
obtained by friction between the shoes and drum. When
the lever is released, the cam lever returns to the initial
position and the braking force is released by the brake
shoe return springs.
EMTBR5019A
COMPONENTS(LHD)
1. Vacuum tank
2. Vacuum hose
3. Brake booster
4. Master cylinder
5. Reservoir tank
6. A.B.S modulator
SUDBRA001L
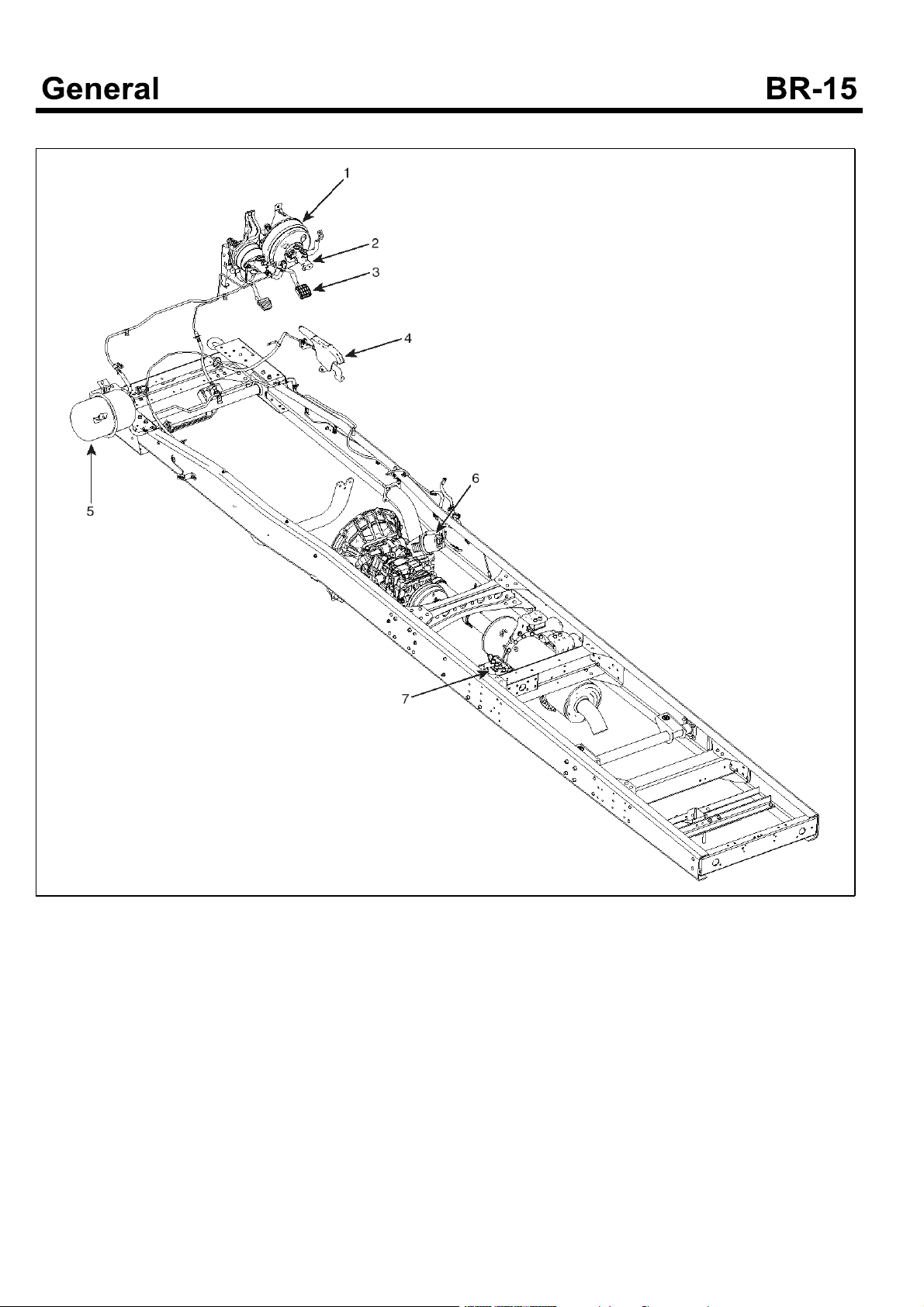
COMPONENTS(RHD)
1. Brake booster
2. Master cylinder
3. Brake pedal
4. Parking brake lever
5. Vacuum tank
6. Exhaust brake
7. ABS HECU(Hydraulic Electrical Control Unit)
SUDBRA002L
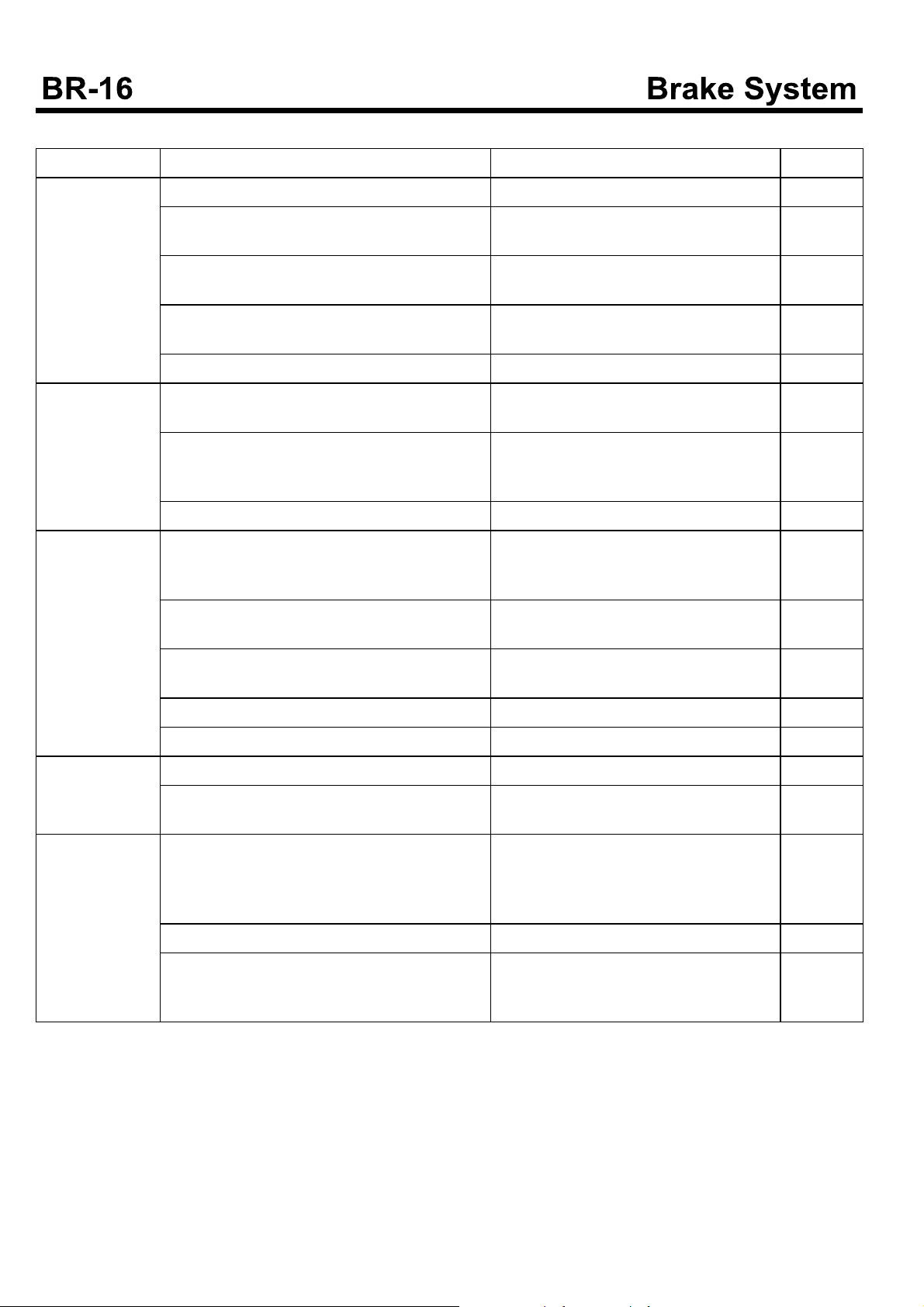
Diagnosis
Symptom Causes Remedy Remark
Irregular Braking
Force
After releasing the brake pedal,
the braking force
is release too late.
Unbalance at therightandleft
braking force
The air pressures of tire are different. Adjust the air pressure of tire.
The sizes of the right and left tires are different
.
The adjustment of the wheel bearing is defective.
The sizes of the right and left wheel bases are
different.
The wheel alignment is defective. Adjust
The vertical surface of the back plate is rough.
The operation of the wheel cylinder is defective.Check the contacting, the piston cup and
The return spring is damaged. Replace the spring.
The surface of the lining is contaminated by the oil, grease or water.
The lining is defective or The material of lining
is improper.
Replace the tire.
Adjust (Check the wheel bearing)
Check and adjust the loosening the U-bolt or damages on center bolt.
Replace the back plate or check the lining.
wearing status. If needed, replace it. Check the lining.
If it is contaminated by oil or grease, thenreplaceit.Ifitiscontaminatedbywater
,dryit.
Replace or adjust.
Unstable brakingforce
Improper Lock
Point
The wear is irregular. The surface is rough. Replace the lining. Check the inside of t-
he drum, if needed, replace it.
The lining contact is defective. Adjust the lining with being installed.
The brake drum is worn irregularly. Adjust or replace it.
The brake drum is deformed. Replace
The back plate is deformed or loosened. The
vertical surface of it is rough.
The drum is worn. Adjust or Replace Drum limit
The lining is worn irregularly. Adjust
The lining contact is defective. Adjust with being installed.
If it is loosened, tighten with specified torque. Otherwise, replace it.
STD
:Dia+2mm
(Temperature of lining should be less than 100°C)
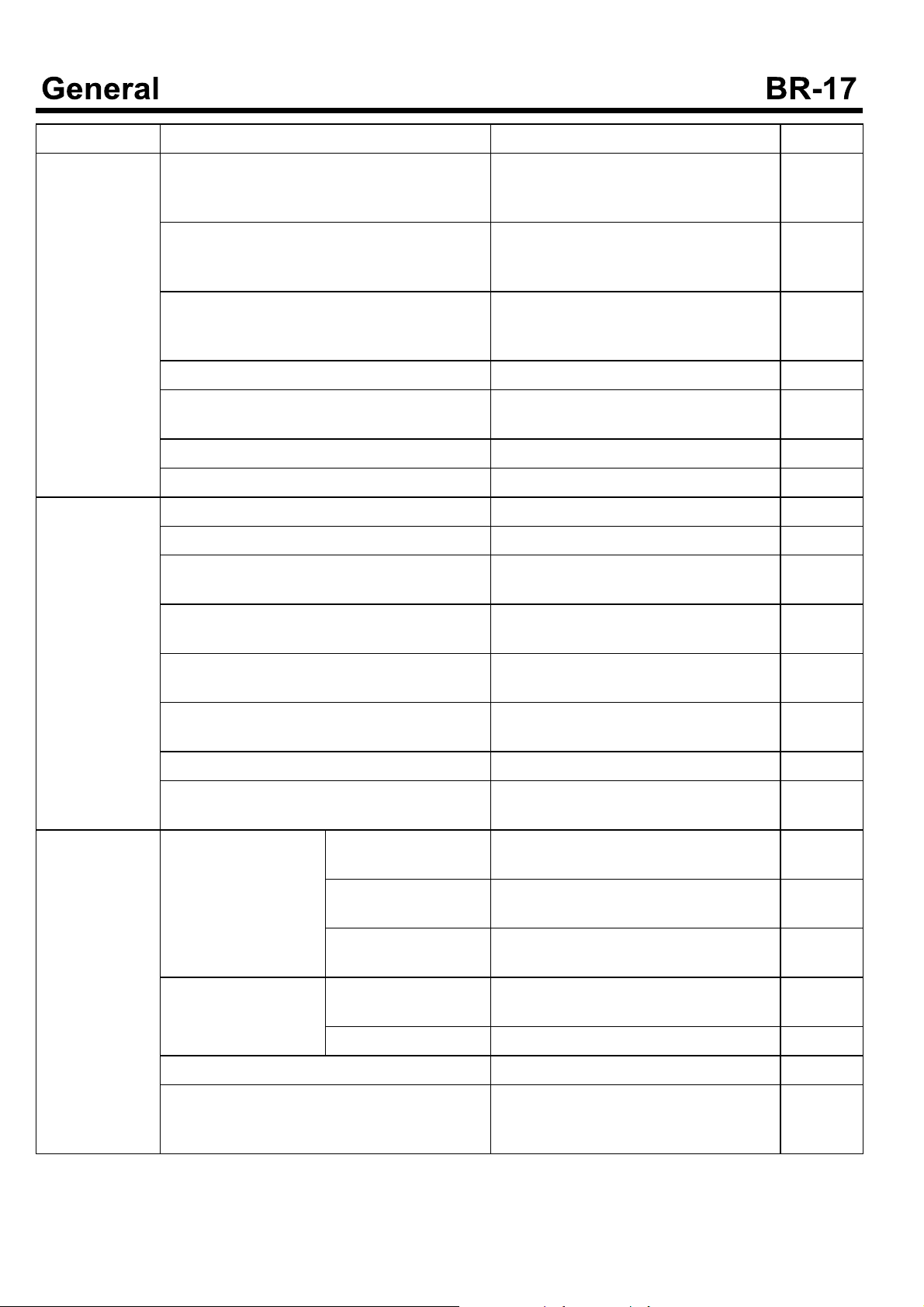
Symptom Causes Remedy Remark
Low Braking Force
The clearance between the pedal and the floor is too narrow.
The clearance between the brake pedal and floor is 45mm or more. (at Pressure-600mmHg,
Pressure 50kg)
Refer to the item for decreasing the clearance between the brake pedal and floor.
The lining contact is defective. Adjust with being installed not being dis-
assembled. (Temperature should be 100
°
Corless)
The surface of the lining is contaminated by the oil, grease or water.
The lining is deteriorated.
If it is contaminated by oil or grease, thenreplaceit.Ifitiscontaminatedbywater
,dryit.
The vacuum force is too low. Replace the lining.
The drum surface is rough. Check the pipe or the vacuum pump. If
needed, replace.
The brake booster is defective. Adjust or Replace
The brake oil level is too low. Adjust or Replace
The air intrudes. Refill
Vapor lock Air Exhausting
The adjustment on pedal is defective.
The clearance is too large.
Referring to the brake drawn item, adjust
or replace. And then exhaust the air.
During braking,
the noise and shock are made
abnormally.
The shoe clearance is too large.
Adjust the pedal clearance. Check the total stroke.
The cup of the master cylinder is defective. Adjust the shoe clearance.
If the wear exceeds the limit, replace.
The brake shoe is deformed or damaged. If the tightening does not satisfy the spe-
cifications, replace the kit.
The brake booster is defective. Replace
When the wheel is rotating with being lifted by
jack, there are some noises.
During braking (at low
speed), noise is made
continually.
Foreign materials in drum
Return spring is damaged.
Hold down cup is damaged.
The grease is deficiency in sliding parts.
Improper adjustment
on wheel bearing
Replace
Check that the brake is damaged. Remove the foreign materials.
Check that the parts are damaged by broken parts. If needed, replace.
Check that the parts are damaged by broken parts. If needed, replace.
Check the rotating surface. Adjust
The lining is worn. Replace
The drum inside surface is rough. Apply the grease.
Modify the inner surface with sand paper
The drum is cracked.
.
Replace
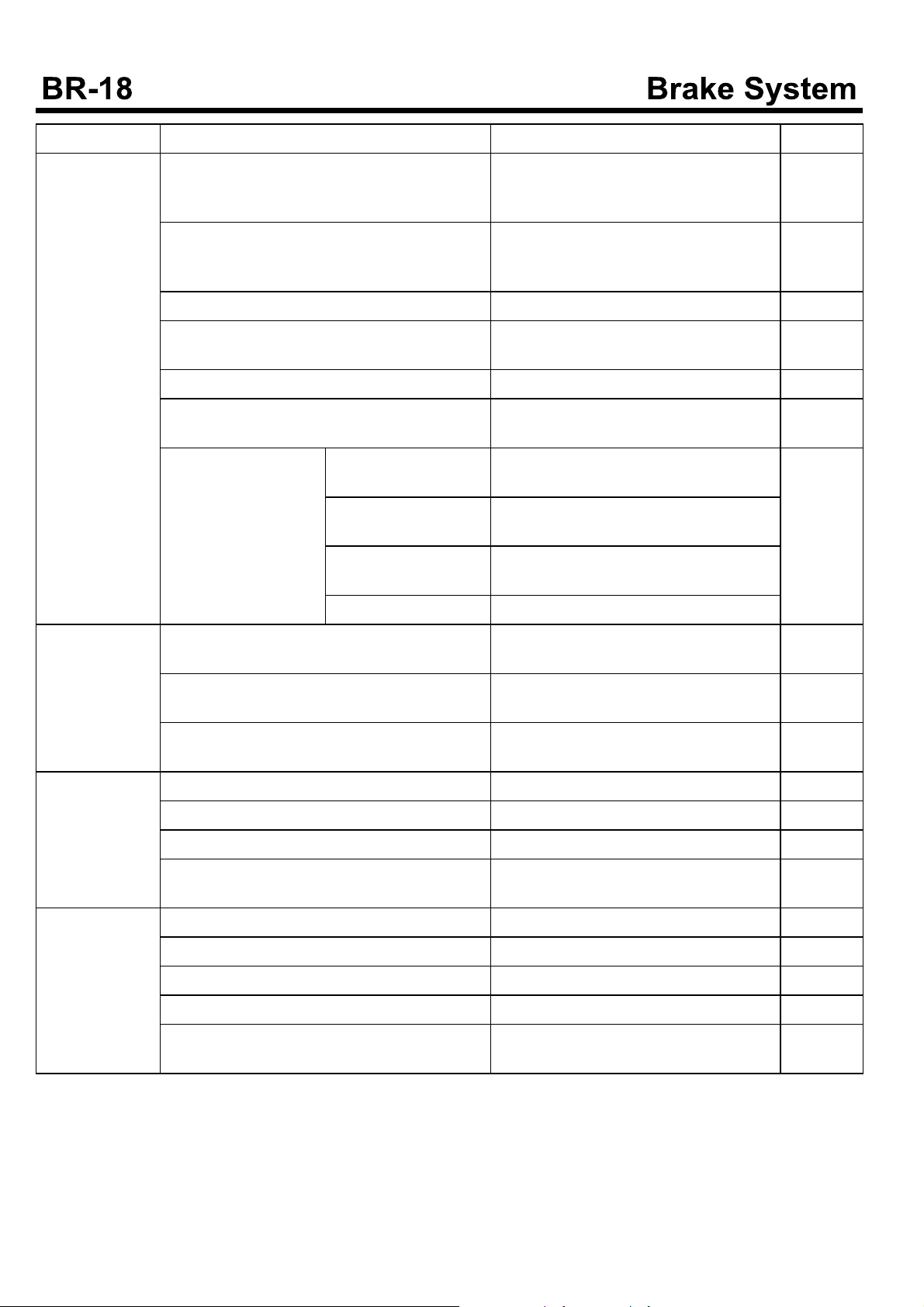
Symptom Causes Remedy Remark
The drum is overheated.
The outlet of the brake master cylinder is clogged.
If the booster operating rod is not properly adjusted, adjust the pedal clearance of
the rod clevis to 10~15mm.
The brake does not return. Check the burst of the return spring, the
bearing lubricant, the stop lamp switch adjustment. If needed, adjust.
The booster is defective. Replace
The vertical surface of the back plate is scratched.
If the surface is too rough, replace.
If it is too dry, apply the grease.
The wheel cylinder piston cup is defective. Replace
The oil return has problems due to the over tight of the brake pipe nut.
When the wheel is rotating with being lifted
by jack, the wheel is hardtorotate.
The wheel bearing clearance is too large.
Shoe clearance is improper.
Return spring is defective.
Check the connector hole diameter. If it
is reduced, replace.
Replace bearing or adjust.
Adjust
Check the part damages due to the spring over working. If needed replace.
Brake shoe is worn. Replace
Specific
wheel is overheated.
The pedal returning is defective.
The pedal linkage is rusted or deformed.
It is bursting due to the defectives on the pedal
return spring.
The booster operating rod is pushed.
Disassemble. Adjust or replace. Oil the
grease.
Replace
Adjust the pedal clearance with 10~15
mm.
Brake is vibratin-g.The drum is eccentrically centered. Replace
The drum is deformed. Replace
The king pin bushing is worn. Replace the bushing
The hub bearing is worn.
Adjust (Check the rolling surface) or repl ace.
Brake is drawn. The pedal clearance is too narrow. Adjust the booster working rod.
The shoe clearance is improper. Adjust
The back plate vertical surface is rough. Replace the back plate.
Theshoespringisburst. Replace
The master cylinder or wheel cylinder piston cup is deteriorated and swelled.
Replace
Symptom Causes Remedy Remark
Brake makes noises.
Exhaust brake
does not work.
Brake shoe contacting is defective. Adjust the lining with being installed not
being disassembled (Temperature should be 100°Corless)
Lining is deformed. Replace the lining. Replace the drum if it
has hardened surface.
Drum has hardened surface. Replace.
Shoe is deformed. Replace.
Back plate is deformed or installed improperly. Replace or adjust
Front bearing is loosened. Adjust (Check the rolling surface)
Powder from the wear of the lining is adhered. Clear
Lining is worn. Replace.
Vacuum pressure is improper.
Check the vacuum pump or piping. If needed repair.
Electric circuit is defective. Check the clutch switch, the micro switch
and the exhaust brake circuit. If needed,
repair.
Vacuum pipe is damaged. Replace.
3-way magnetic valve does not work. Replace.
Exhaust brake can not be released.
Exhaust brake valve does not work. Replace.
Exhaust brake valve shaft is adhered. Replace.
Power chamber is defective. Disassemble and check.
3-way magnetic valve does not work. Replace.
Exhaust brake valve does not work. Replace.
Exhaust brake valve shaft is adhered. Replace.
Electric circuit is defective. Check the clutch switch, the micro switch
and the exhaust brake circuit. If needed,
repair.
Diagnosis (Parking brake)
Symptom Causes Remedy Remark
Parking brake does not work.
Parking brake can not be released.
Operating
mechanismhasaproblem.
Parking brake is defective.
Operating
mechanismhasaproblem.
When pulling the parking brake with 30kg, there is no lever stroke clearance and shoe clearance.
The locking status between the lever lock latch and Ratchet pull is improper.
Wire is broken or elongated. Replace the cable.
Tolerance between the shoe clearance and the brake lever pulling is
too large.
Drum inner surface is deformed or
twisted.
Lining is irregularly worn. Drum inner surface is contacted irregularly
.
The oil of drum and lining is contaminated.
Return spring is damaged. The tension of the return spring is inferior
.
The inner cable does not move smoothly.
Adjust the shoe clearance and cable.
Adjust the Ratchet pull lock status. Replace it
Adjust the shoe clearance.
Repair the drum inner surface. Replace
the lining.
Replace the lining.
Clear the inner surface of the drum. Replace the lining.
Replace the return spring.
Replace the cable.
After the parking brake is released
, the brake is operating.
Parking brake is defective.
Return spring is damaged. The tension of the return spring is inferior
.
The shoe clearance is too narrow.
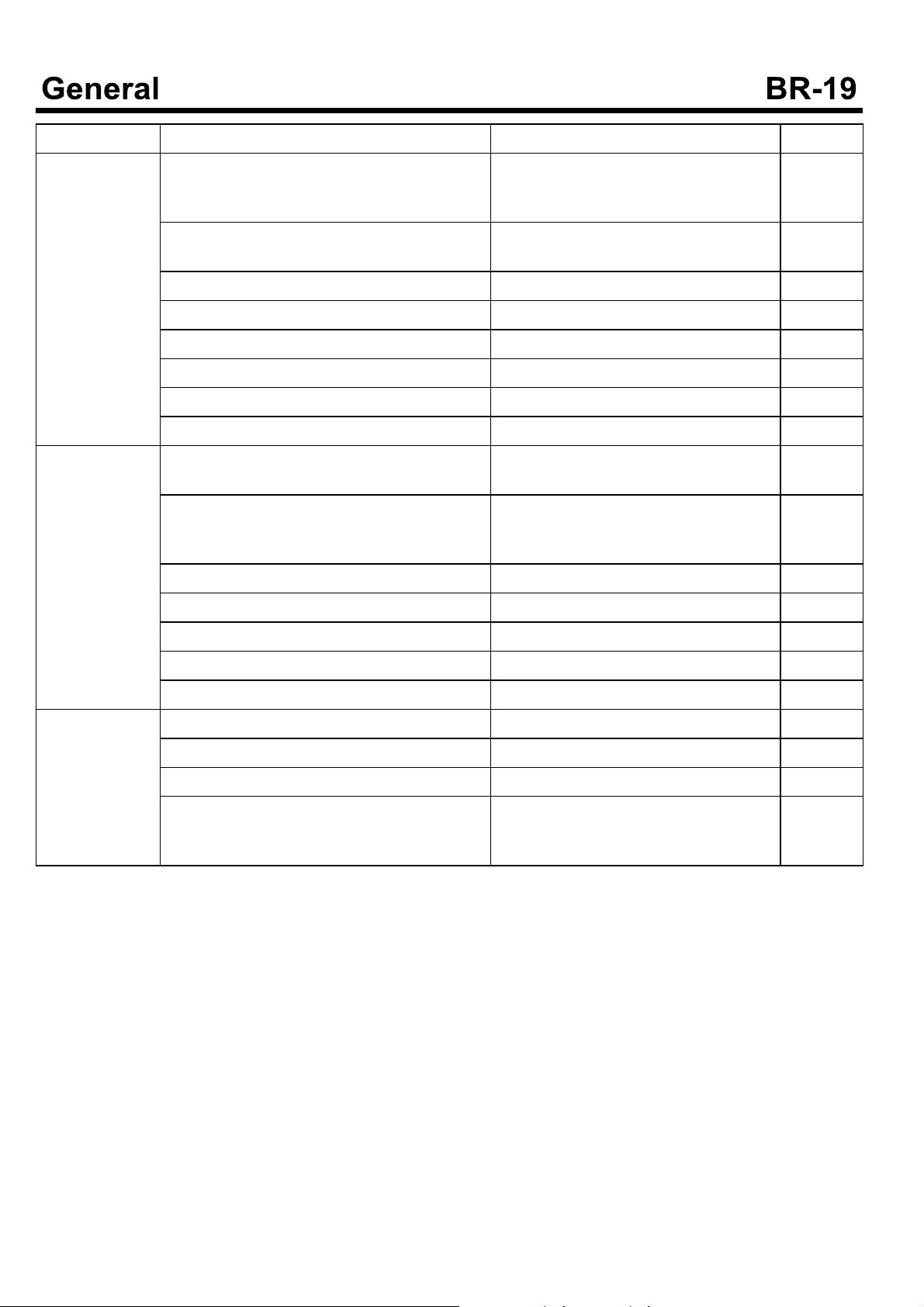
On-Vehicle Inspection and Adjustment
Air bleeding of the Brake
1. Fill up the brake oil tank with the brake oil at the
maximum level. During the air bleeding, if the level is
lowered, refill the brake oil.
CAUTION
Be careful that the brake oil does not drop on the
painted surface. If the brake oil contacts the
painted surface, immediately wash it by water.
2. Connecting an end of transparent vinyl tubes at the
air breather of the front wheel cylinder and the rear
wheel cylinder, put the other end of the tubes into the
transparent container having the brake oil.
Adjust the pulling tolerance limit.
Replace the return spring.
Adjust the shoe clearance.
KMTBR5518A
3. Step on the brake pedal several times. Pressing the
brake pedal at half, loosen the air bleeder screw to
evacuate the air with the brake oil.
And then, pressing the pedal until it reaches to the
floor, tighten the air bleeder screw. Release the
pedal. There procedures should be repeated until any
air bubble is not shown in the brake oil.
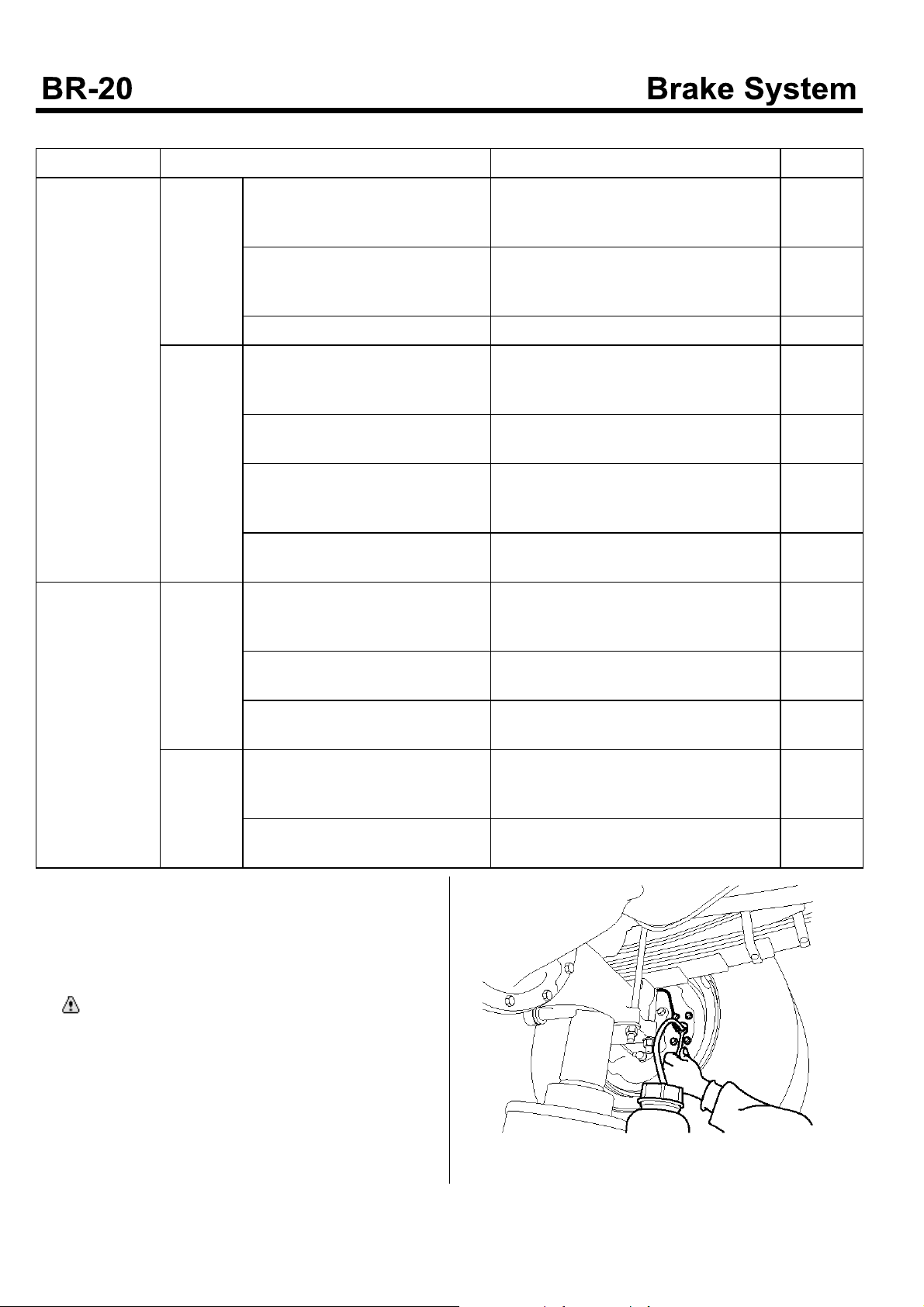
Adjustment of Brake Shoe Gap
1. Using the screw driver(A), turn the wheel cylinder
adjuster(B) to the shoe expansion direction until the
drum is not rotate anymore. Turn the adjuster
reversely with the following notch number. (At that
time, the drag torque between the lining and the drum
should be less than 50kgf.m).
KMTBR5519A
4. Tighten the bleeder screw
Tightening Torque for the bleeder Screw
Front: 6.9~8.8Nm(0.7~0.9kgf.m, 5.1~6.5lb-ft)
Rear : 6.9~8.8Nm(0.7~0.9kgf.m, 5.1~6.5lb-ft)
5. Step on the brake pedal several times. Pressing the
brake pedal at half, loosen the air breather screw to
evacuate the air with the brake oil.
And then, pressing the pedal until it reaches to the
floor, tighten the air breather screw. Release the
pedal. There procedures should be repeated until any
air bubble is not shown in the brake oil.
KMTBR5521A
The Notch Number for reverse rotation of the
Adjuster.
Front Wheel Cylinder
Auto adjuster type 9~11
Manual adjuster type 4~6
Rear Wheel Cylinder Auto adjuster type 9~11
Manual adjuster type 4~6
KMTBR5520A
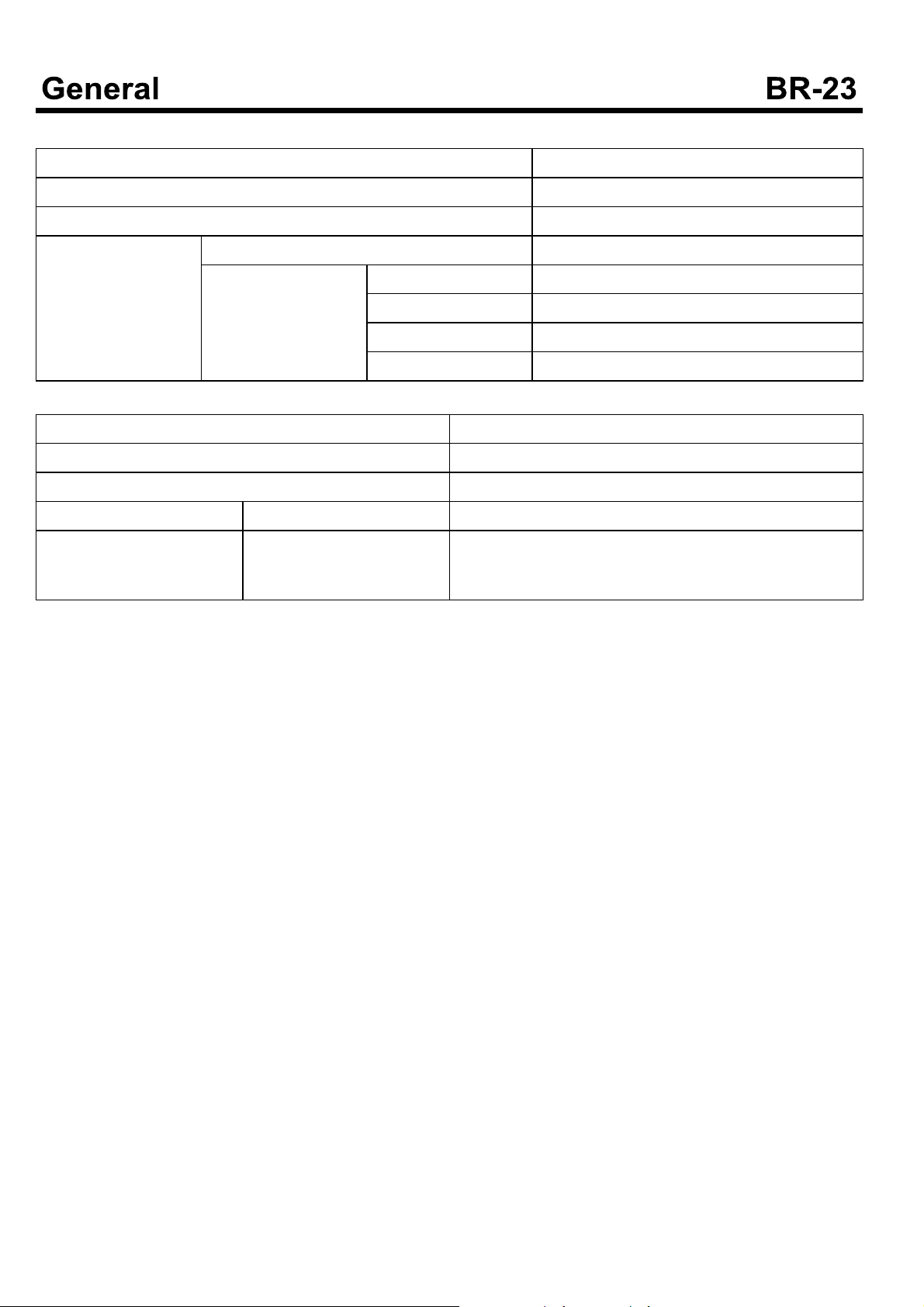
Specifications
Front Wheel Brake (Drum Type)
Item Specifications
Brake type 2-leading Brake
Wheel cylinder Inner diameter 31.75mm
Brake drum Inner diameter 320mm
Brake lining Width x Thickness (mm) 85 x 10(Standard), 110 x 11(Option in case of HD72,78)
Front wheel Brake (Disk Type)
Item Specifications
Cylinder diameter Ø76mm
Effective radius 118 mm
Disk outer diameter Ø304mm
Disk inner diameter Ø164mm
Pad thickness 12.5 mm
Padeffectivethickness 10.5 mm
Rear Wheel Brake
Item Specifications
Brake type 2-leading Brake
Wheel cylinder Inner diameter 28.57mm
Brake drum Inner diameter 320mm
Brake lining Width x Thickness (mm) 85 x 10(Standard), 110 x 11(Option in case of HD72,78)
Brake system
Item Specification
Brake Pedal Total Stroke 140 mm
Booster Total Stroke 31 mm
Master Cylinder Inner Diameter Ø 31.75 mm, Ø 30.15 mm
Stroke Piston 31±1mm
Primary 17±0.5 mm
Secondary 14±0.5 mm
Exhaust Brake
Item Specification
Control System Combination of Electric and Vacuum Type
Exhaust Brake Valve Type Butterfly Valve
Exhaust Brake Chamber
Diaphragm Effective Diameter 76.2mm
With Installing
N(kg)
Spring Tension 90~110 (9.18~11.22)
Rod Tensile Force 142.1(14.5): Vacuum Pressure-400mmHg
Spring Tension 125~153 (12.78~15.62)
Rod Tensile Force 103(10.5) Vacuum Pressure-400mmHg
Parking brake
Item Specification
Type Internalexpansiontypeactingonpropellershaft
Control Mechanical cable
Parking lever Normal stroke 8~9clicks(20kgf)
Parking brake size Drum i.d. x Lining width x Li-
ning thickness
180 x 35 x 5 (T/M : M2S5, M3S5)
190 x 45 x 4 (T/M : M035S5)
230 x 55 x 4 (T/M : T60S5, T60S6)
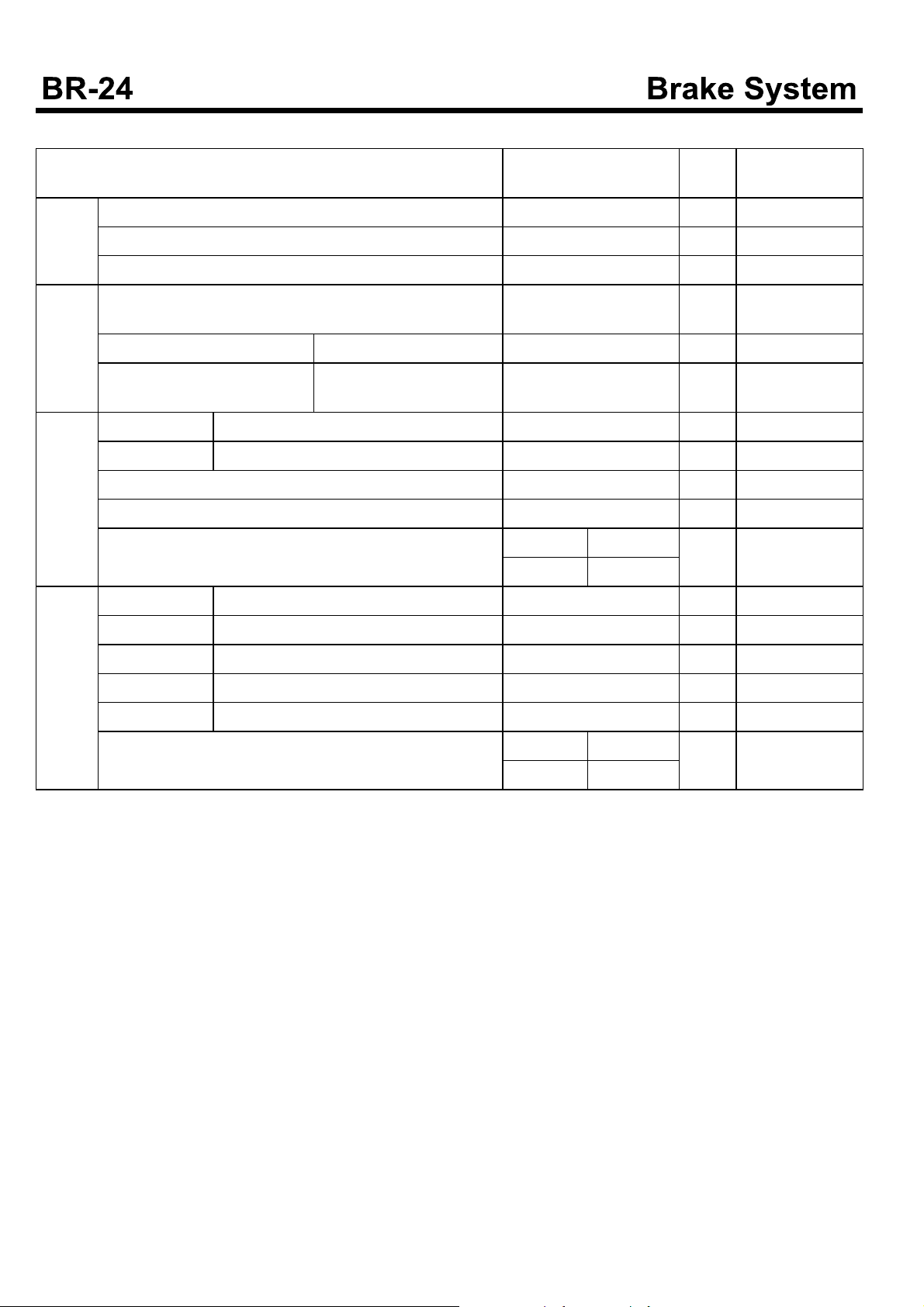
SERVICE STANDARDS
Brake
pedal
Brake
master
cylinder
Front
drum brake
Rear wheel brake
Description
Bushing to collar clearance [16]0.02 to 0.26 0.5 Replace bushing
Brake pedal play 3-8 Adjust
Stop lamp switch installation clearance 0to1 Replace
Primary and secondary piston to cylinder body clearance 0.038~0.145 0.2 Replace
Primary retainer assembly Free length 38.1 Replace
Secondary spring deterioratio-nFree length 37.7 Replace
Brake drum I.D. 320 322 Replace
Brake lining Thickness 10 4 Replace
Return spring 30±3/227 19/227 Replace
Wheel cylinder body to piston clearance [31.75]0.03 to 0.13 0.2 Replace
Brake shoe clearance(No. of notches returned of wheel cylinder adjuster)
Brake drum I.D. 320 322 Replace
Brake lining Thickness 10 4 Replace
Return spring Load N(kgf)/installed length 30±3/227 19/227 Replace
Nominal value, mm
(Basic diameter in [ ])
Auto 9~11 Adjust
Manual 4~6
Limit
(mm)
Correction and
remarks
Wheel cylinder Body to piston clearance 0.02-0.11 0.2 Replace
Brake drum Out of roundness 0.05 - Replace
Brake shoe clearance (number of return notches of wheel
cylinder adjuster)
Auto 9~11 Adjust
Manual 4~6
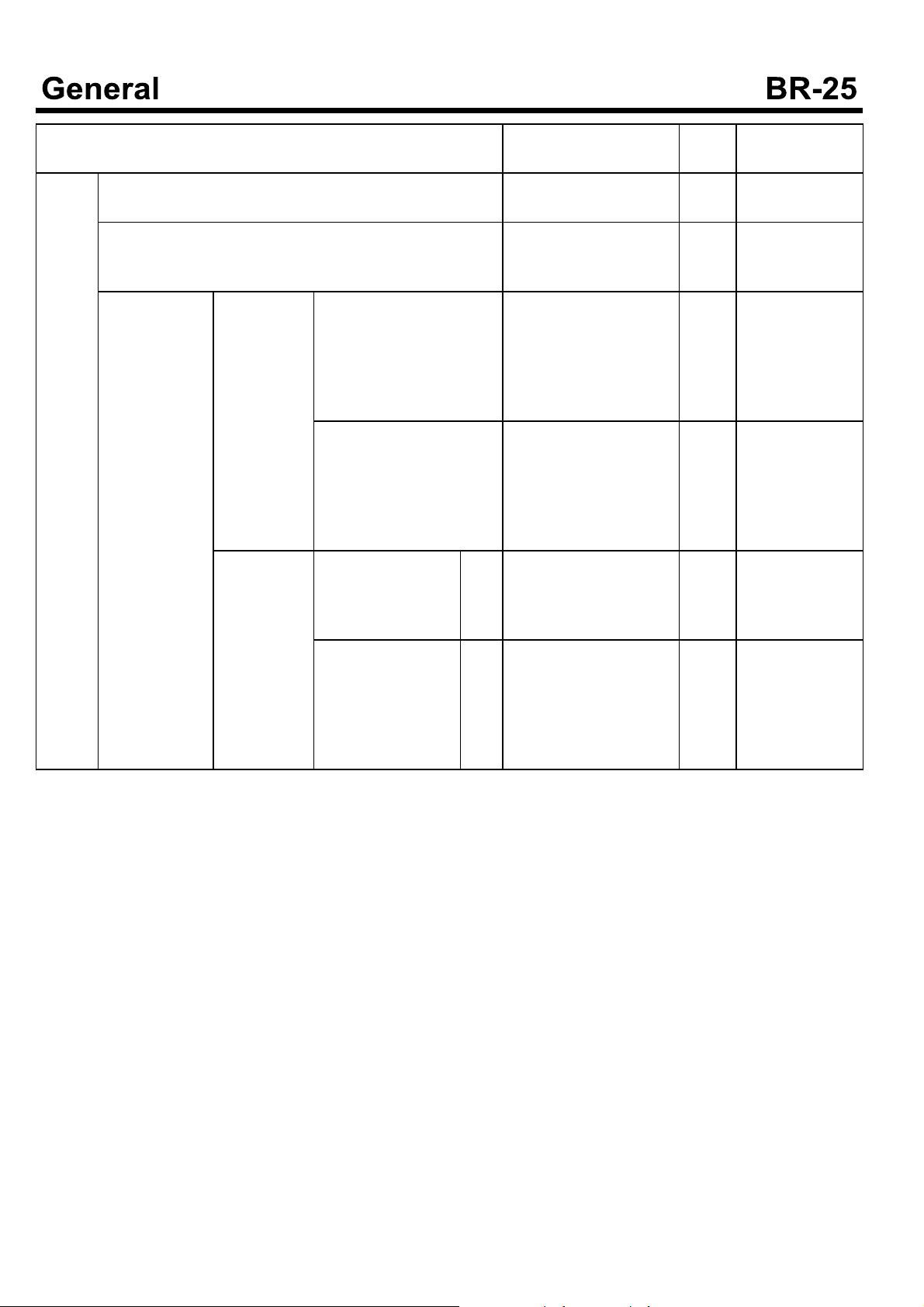
Description
Nominal value, mm
(Basic diameter in [ ])
Limit
(mm)
Correction and
remarks
Exhaust brake
Power chamber air tightness [15 seconds after application of -67 kPa (-500 mmHg) negative pressure]
Valve to body clearance when butterfly valve is fully closed [at power chamber vacuum -87 to -93 kPa(-650 to -70
0 mmHg)
3-way magnet
valve
Air tightness When -100 kPa (-750 m-
mHg) negative pressure is
applied from vacuum tank side to operate valve with exhaust brake unit side
plugged tightly
When 98 kPa (1 kgf/cm²
air pressure is applied fromatmospheresidetooperate valve with exhaust
brake unit side plugged tightly
Minimum operating voltage
When -100 kPa(-75
0 mmHg) negative
pressure is applied
24V
type
unit
to vacuum tank side
-63 kPa (-475 mmHg) or
Replace
more
0.1 to 0.4mm Replace
Noairtobesuckedinf-
Replace
rom atmosphere side
No air to leak from vacu-
Replace
um tank side
22V or less Replace
When 98 kPa (1 kgf
/cm² air pressure is
applied from atmosphere side with exhaust brake unit side
plugged tightly
24V
22V or less Replace
type
unit
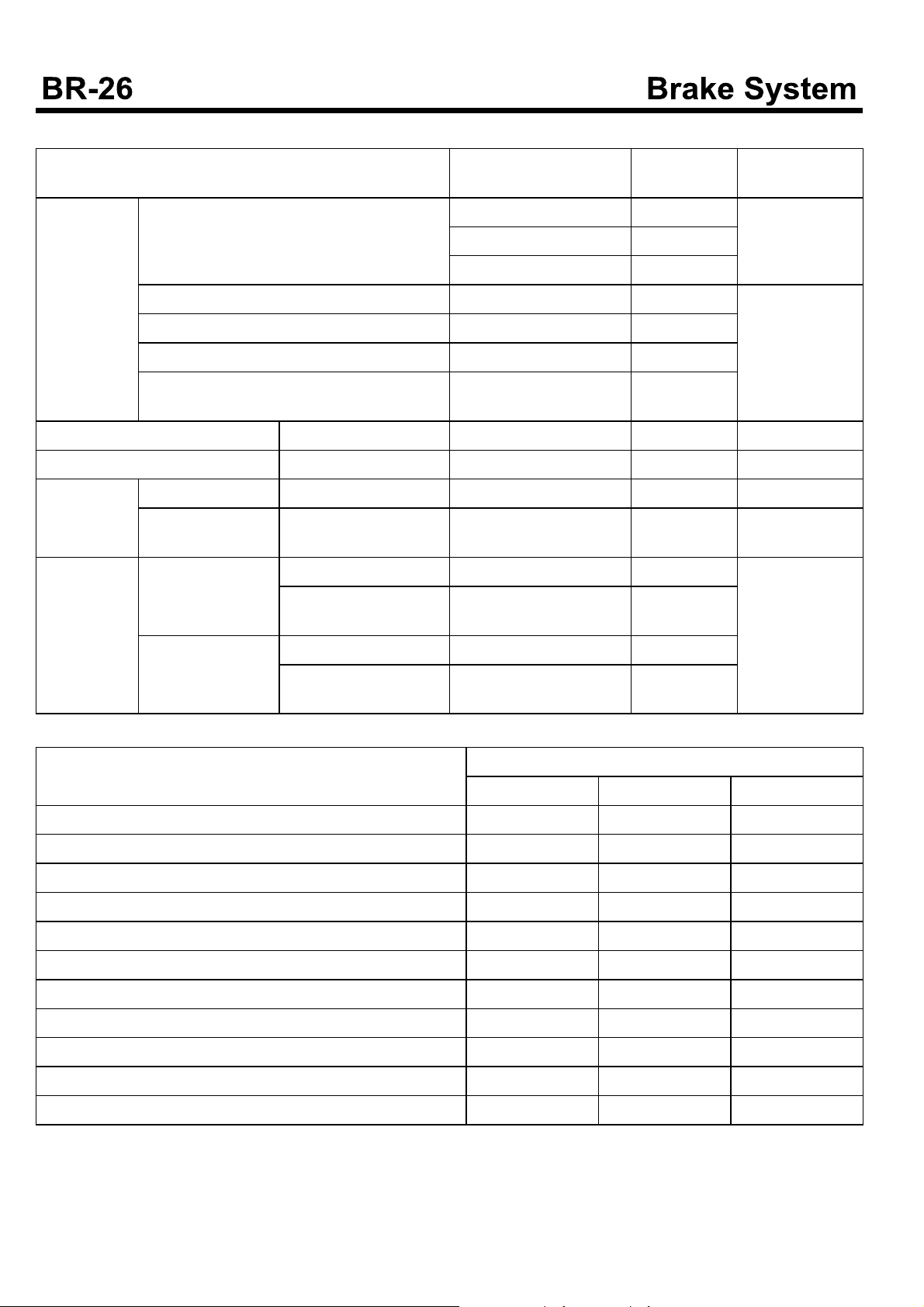
SERVICE STANDARDS (Parking brake)
Description Nominalvalue,mm
(Basic diameter in [ ])
Brake drum I.D. 180 181 Correct to limit,
190 192
230 232
Squareness 0.05 or less Correct or repla-
Concentricity 0.1 or less
Cylindricity 0.1 or less
Static rotation imbalance 0.49 N.cm(50 gf.cm) or l-
ess
Brake lining thickness Model with M2S5 T/M 10~11 4.0 Replace
Brake shoe clearance Model with M2S5 T/M 0.25 to 0.35 Adjust
Brake shoe return spring
Shoe hold down spring
Free length Model with M2S5 T/M 98 -
Load N (kgf)/installed length
Spring A(longer one of free length)
Model with M2S5 T/M 67 to 86 (6.8 to 8.8)/104 104.364
Free length 34.1 Replace
Load N (kgf)/installed length
59 to 69 (6.0 to 7.0)/13.7 59 (6.0)/13.7
Limit
(mm)
(6.5)/104
Correction and
remarks
replace when limit is reached.
ce
Replace
Spring B(shorter one of free length)
Free length 23.6
Load N (kgf)/installed length
59 to 69 (6.0 to 7.0)/10.5 59 (6.0)/10.5
Tightening torque table
Description Tightening torque
Nm Kgf.m Lb-ft
Mounting nut between the master cylinder and booster 17.7~24.5 1.8~2.5 13~18.1
Master cylinder set bolt 12~16 1.2~1.6 8.7~11.6
Brake booster mounting nut 12.7~15.7 1.3~1.6 9.4~11.8
Brake booster clevis lock nut 15.7~21.6 1.6~2.2 11.6~15.9
Master cylinder outlet port nut 12.7~16.8 1.3~1.7 9.4~12.3
LSPV connecting link mounting bolt 22~33 2.2~3.3 15.9~23.9
LSPV flange bolt mounting bolt 22~33 2.2~3.3 15.9~23.9
Front drum brake air bleeding port 6.9~12.7 0.7~1.3 5.1~9.4
Front spindle mounting bolt 98~137 10~14 72~101
Brake hose to union mounting bolt(Front drum brake) 24.5~29.4 2.5~3 18.1~21.7
Exhaust brake to exhaust pipe mounting bolt 44.1~58.8 4.5~6 32.5~43.4

Vacuum Assisted Hydraulic Brake
Brake Pedal
Component
1. Clevis pin
2. Hose connector
3. Grommet
4. Master cylinder
SUDBRA003L
5. Booster
6. Pedal assembly
7. Return spring
Removal
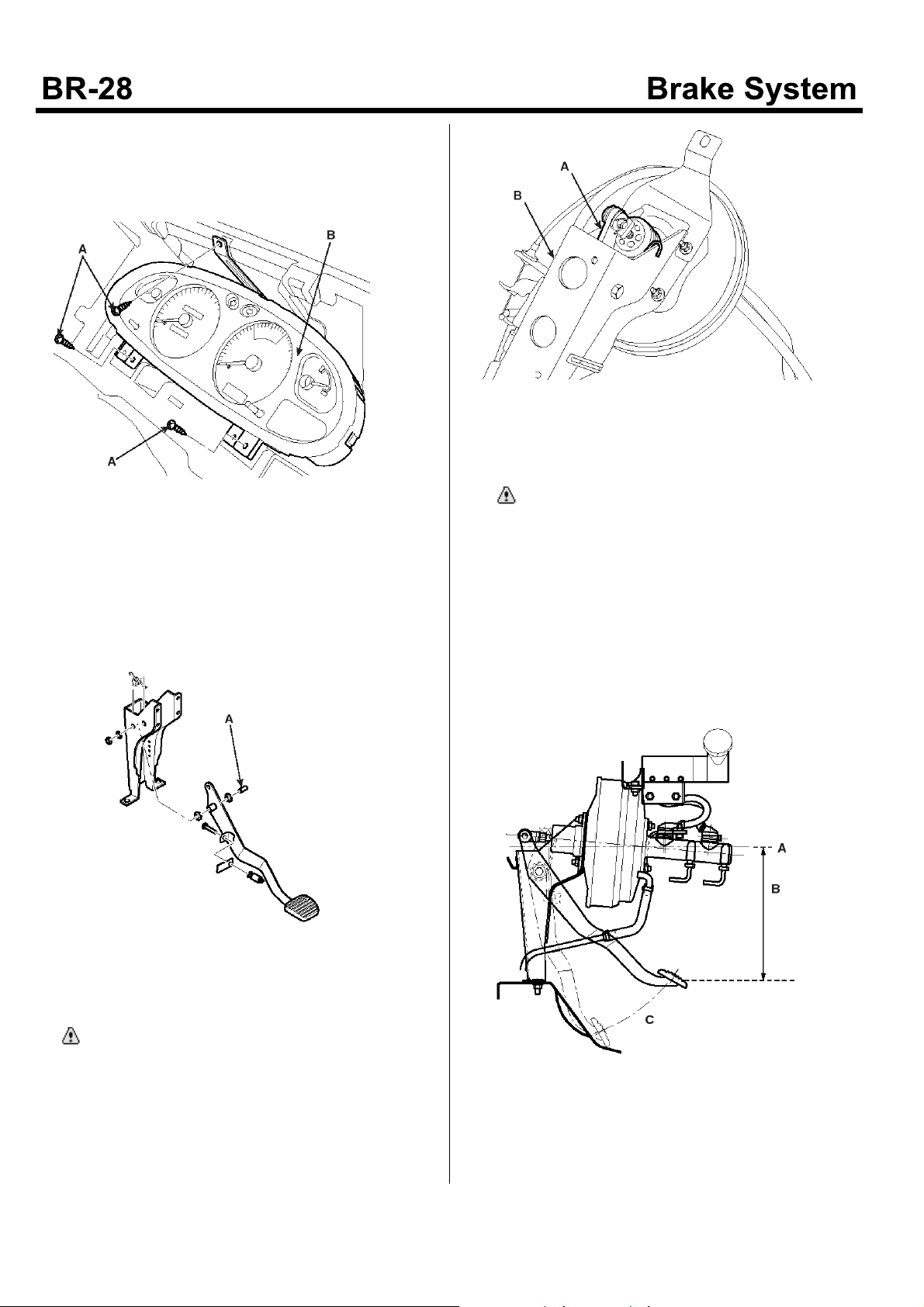
1. Loosen the steering column assembly mounting bolt.
Pull down the steering column.
2. Loosen the bolt(A), Remove the instrument panel(B).
KMTBR5527A
2. Install the brake light switch.
3. Install the booster and the master cylinder.
KMTBR5003A
3. Remove the master cylinder (Refer to the BR-"Master
cylinder")
4. Remove the brake booster (Refer to the
BR-"Booster")
5. Remove the brake light switch.
6. Remove the shaft bolt(A) connected to the bracket.
CAUTION
Apply the grease on the clevis pin and the
washer
Adjustment
Adjust the height of the brake pedal
1. Turn the booster operating rod so that the distance
from the center of the brake pedal pad to the A point
of the instrument panel lower portion is the 'B'. After
adjusting, fix the clevis with the nut. Check that the
maximum stroke of the pedal is more than 'C' (before
filling the brake oil)
KMTBR5040A
Installation
1. Install the brake pedal assembly(A) to the bracket(B).
CAUTION
Before the assembling, apply the grease inside
of the brake pedal assembly pipe.
SUDBRA004L
Engine B(mm) C(mm)
Non A-BSD4DD, D4GA 280±2 140±4
The others 273±3 140±4
ABS D4DD, D4GA 280±2 140±4
The others 273±2 140±4
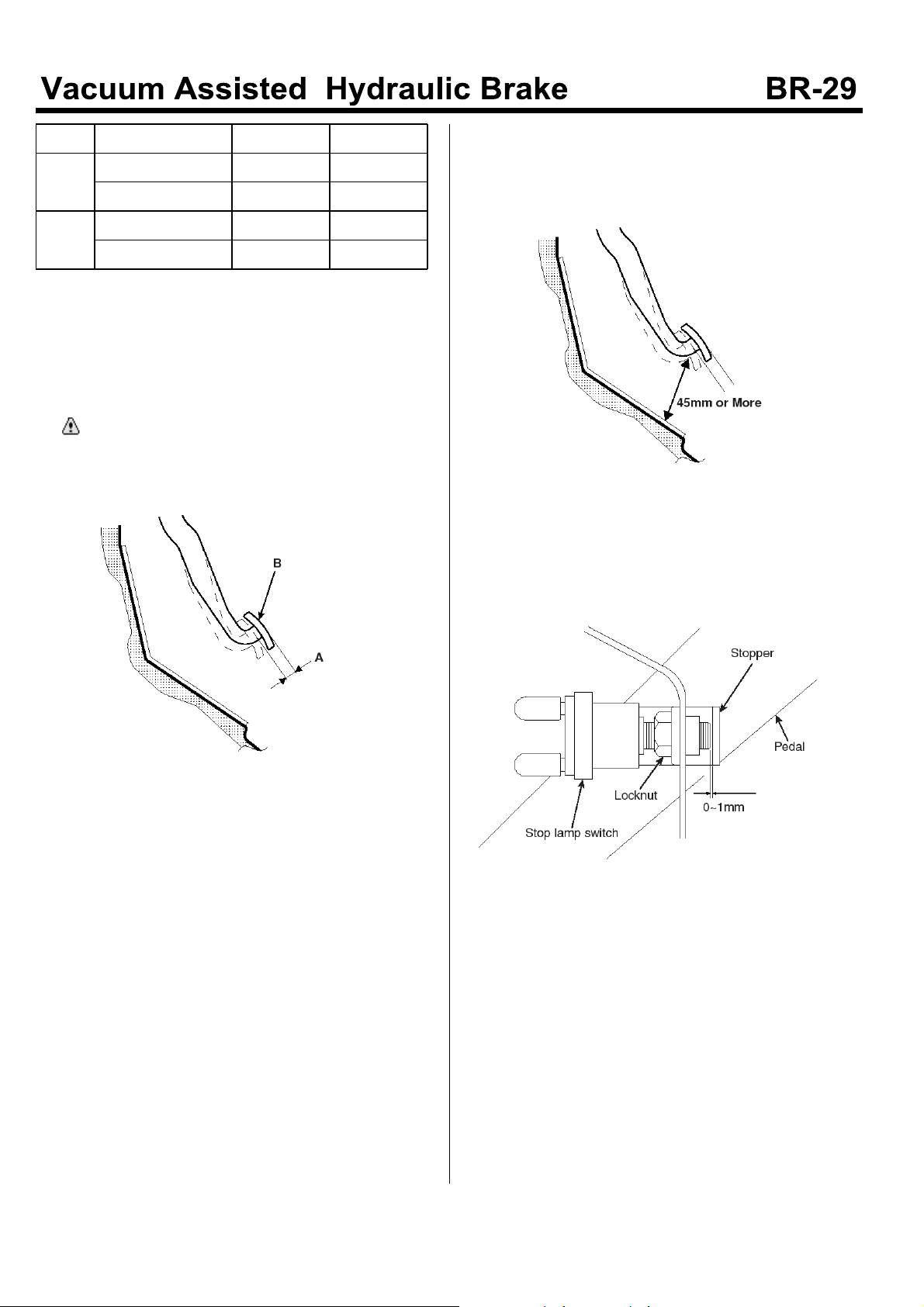
Free play clearance of the Brake pedal
1. Setting the brake pedal to the original position, check
if the free play(B) clearance is 5mm at least by
pressing the pedal(A).
If the clearance excesses the reference, re-adjust the
position of the brake pedal.
CAUTION
When checking the free play clearance of the
brake pedal, the master back negative pressure
should be 0.
Gap between the brake pedal and the floor.
1. After cranking the engine, check if the gap between
the floor and the pedal is more than 45mm by
pressing the pedal with 50kg.
EMTBR5023A
Stop Lamp Switch
1. Adjusting the gap between the end of the brake. Stop
lamp switch screw and the pedal stopper to 0~1mm,
tighten the locknut.
KMTBR5005A
SUDBR9014L
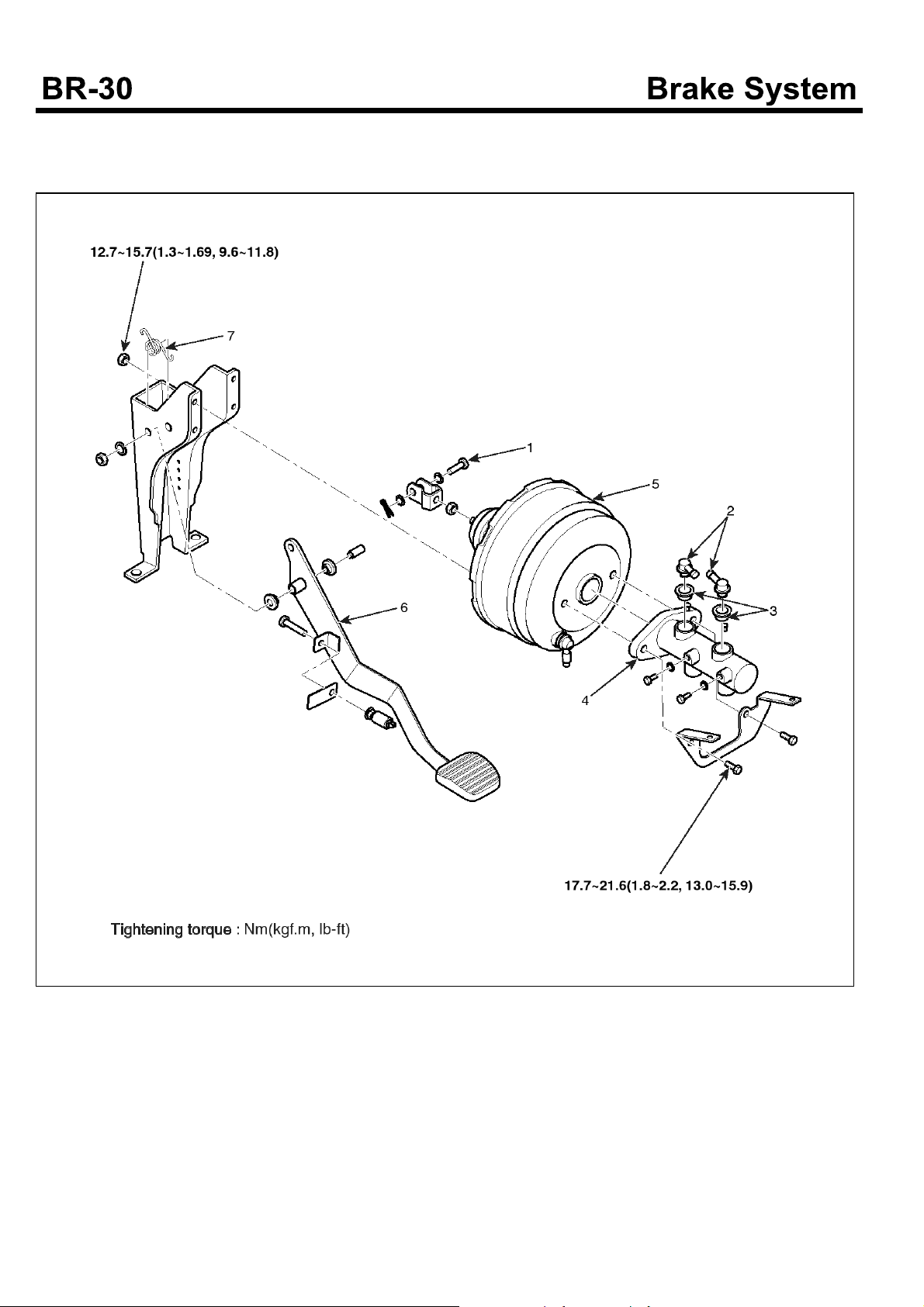
Brake Booster
Components
1. Clevis pin
2. Hose connector
3. Grommet
4. Master cylinder
SUDBRA005L
5. Booster
6. Pedal assembly
7. Return spring
 Loading...
Loading...