Page 1

ISS Technology Update
Volume 6, Number 9
Keeping you informed of the latest ISS technology
I/O configuration for the HP ProLiant xw460c Blade Workstation............................................................1
Future of PCI-X slots in ProLiant servers...................................................................................................3
Port monitoring in Virtual Connect for the c-Class BladeSystem................................................................4
Licensing ports on the Brocade 4/12 SAN Switch for HP c-Class BladeSystem ..........................................6
Frequently asked questions regarding the adoption of HP VDI................................................................. 8
ProLiant management tip of the month..................................................................................................11
Recently published industry standard server technology communications ..............................................14
Contact us .............................................................................................................................................14
I/O configuration for the HP ProLiant xw460c Blade Workstation
About the workstation
The HP ProLiant xw460c Blade Workstation (Figure 1-1) is a data center workstation that offers data center security,
manageability, and remote multi-location access flexibility—all with a workstation-class user experience. With dual-core and
quad-core Intel
combines power-efficient, high-density computing with expanded memory for maximum performance.
Figure 1-1. HP ProLiant xw460c Blade Workstation
®
Xeon™ processors and features similar to desktop workstations, the dual-processor-capable HP ProLiant xw460c
Page 2
ISS Technology Update Volume 6, Number 9
Graphics traffic to remote workstations
The question has been asked, how is graphics data transmitted from the HP ProLiant xw460 Blade Workstation to remote
workstations? Users may assume that since it is in a mezzanine slot, the graphics data goes to interconnect bays 3 and 4.
However, there is no connection between the graphics mezzanine card and the interconnect slots; all output of the graphics
card is captured by Remote Graphics Software (RGS) and sent over the network. The integrated NICs are routed to interconnect
bays 1 and 2, the same as with the BL460c and BL465c half-height server blades.
Graphics output also depends on the remote console mode:
• Setup mode — Both the NVIDIA controller and embedded ATI controller are enabled, but the ATI is primary. In this mode,
graphical console redirection through the iLO is possible.
NOTE
On initial boot, one must access BIOS under system options to set the remote console to
Setup mode. To do so, reboot, press F9 into BIOS, and then select System Settings -> Remote
Console Mode -> Setup.
• Admin mode — Only the ATI controller is enabled, and the NVIDIA is disabled. In this mode, graphical console redirection
through iLO is possible.
• User mode (normal use) — The NVIDIA controller is enabled and the embedded ATI controller is disabled. In this mode,
graphical console redirection through iLO is NOT possible. A blinking cursor at the left top corner is the only thing visible
from the system console and iLO console redirection is rendered unavailable due to a dependence on the ATI controller.
At this point, the Workstation blade needs to be connected with an RGS receiver through the network. The graphics content is
compressed and sent to the receiver over this network connection. One receiver can connect to multiple senders, or one
sender can send to many receivers for session sharing.
Mixed configuration
The most common configuration question is this: can the HP ProLiant xw460 Blade Workstation be implemented with other
devices (such as an InfiniBand or Fibre channel device in mezzanine 2)? The Workstation blade is designed for both flexibility
and compatibility; it will work in harmony with all other HP BladeSystem products. Furthermore, Workstation blades, server
blade, and storage blades can be housed in the same chassis without impacting operability of the server or storage blade.
NOTE
At this time, the Workstation blade does not support the entire ProLiant BladeSystem family.
Further testing is required.
Future plans
There are future plans for the HP ProLiant xw460c Blade Workstation to support SB40c, PCI blades, tape blades, and shared
storage blades. With the release of RGS 5.0, support of Insight Control Environment for BladeSystems has been added to the
Blade Workstation’s capabilities.
2
Page 3

ISS Technology Update Volume 6, Number 9
Additional resources
For additional information on the topics discussed in this article, visit the following links:
Resource URL
HP ProLiant xw460c Blade
Workstation QuickSpecs
HP ProLiant xw460c Blade
Workstation - Business Support
Center
http://h18000.www1.hp.com/products/quickspecs/12680_na/12680_na.PDF
http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bizsupport/TechSupport/Home.jsp?lang=en&cc=us&prodCl
assId=-1&prodTypeId=12454&prodSeriesId=3355016
Future of PCI-X slots in ProLiant servers
PCI Express (PCIe) is now becoming the predominant I/O bus for new server platforms. HP will continue, however, to provide
legacy support for the different levels of PCI, including PCI-X. HP has introduced PCIe technology into ProLiant servers to coexist
with PCI-X 133, allowing ProLiant server customers to install new higher bandwidth cards (for example, dual 4-Gb Fibre
Channel, x4 InfiniBand, and 10-Gb Ethernet) using PCIe technology. At the same time, the continued commitment from HP to
PCI-X allows ProLiant server customers to connect to their existing I/O cards.
Current ProLiant ML servers have a mix of PCI-X and PCIe slots, while ProLiant DL servers have optional riser boards to provide
different combinations of PCI-X and PCIe slots. Table 2-1 shows the current ProLiant server models and their support for PCI-X.
Next generation ProLiant servers will no longer feature PCI-X slots as standard offerings. However, PCI-X will continue to be
supported on these servers through the use of the appropriate optional riser boards.
For the latest information, go to
Table 2-1. Number of PCI-X slots in ProLiant DL and ML servers
www.hp.com/go/proliant and check the QuickSpecs for a specific server.
Server series Server model Standard Optional Total
ML 300 ML 310 G4
ML 350 G5
ML 370 G5
ML 500 ML 570 G4 4 0 4
DL 140 G3 0 2 3 DL 100
DL 145 G3 0 1 1
DL 300 DL 320 G5
DL 380 G5
DL 385 G2
DL 500
DL 580 G5
DL 580 G4
DL 585 G2
2
3
2
0
0
0
0
1
2
0
2
0
1
2
2
3
2
0
2
5
2
1
2
2
3
3
2
Customers requiring peripheral bandwidth in excess of 1 GB/s will most likely find those peripherals implemented with PCIe
technology. It is expected that most device manufacturers will use PCIe technology for higher bandwidth peripheral devices
such as 10-Gb Ethernet. For peripherals that require bandwidth less than 1 GB/s, PCI and PCI-X remain viable technologies
3
Page 4
ISS Technology Update Volume 6, Number 9
and continue to provide backward compatibility, although it is expected that almost all future discrete I/O devices, regardless
of their bandwidth requirements, will be developed to the PCIe standard.
HP has been a leader in the development and implementation of industry-standard I/O technology and continues to be a core
member of the PCI Special Interest Group. HP is committed to delivering industry-leading products that meet customer
requirements for flexibility, performance, and investment protection.
Port monitoring in Virtual Connect for the c-Class BladeSystem
The ability to monitor Ethernet settings (port monitoring) is available in a free Virtual Connect (VC) firmware update. This feature
is available to users with server and network administrator privileges. All other users will have read-only access. To use port
monitoring, all modules within the domain must be using Virtual Connect Manager 1.20a
There are two steps to monitoring an Ethernet port.
1. Configure Virtual Connect to mirror to the desired server NIC traffic to an “analyzer” port (available in 1.20a and higher)
2. Connect a network sniffer or analyzer to the analyzer port
Port monitoring allows an administrator to duplicate the network traffic over a set of server ports and send it to an unused uplink
port for the purpose of monitoring or debugging network traffic.
• Any unused port on a VC-Ethernet module can be specified as the port monitoring port (one per enclosure).
• Any server Network Interface card’s ingress or egress (or both) traffic can be mirrored to that port.
1
or higher.
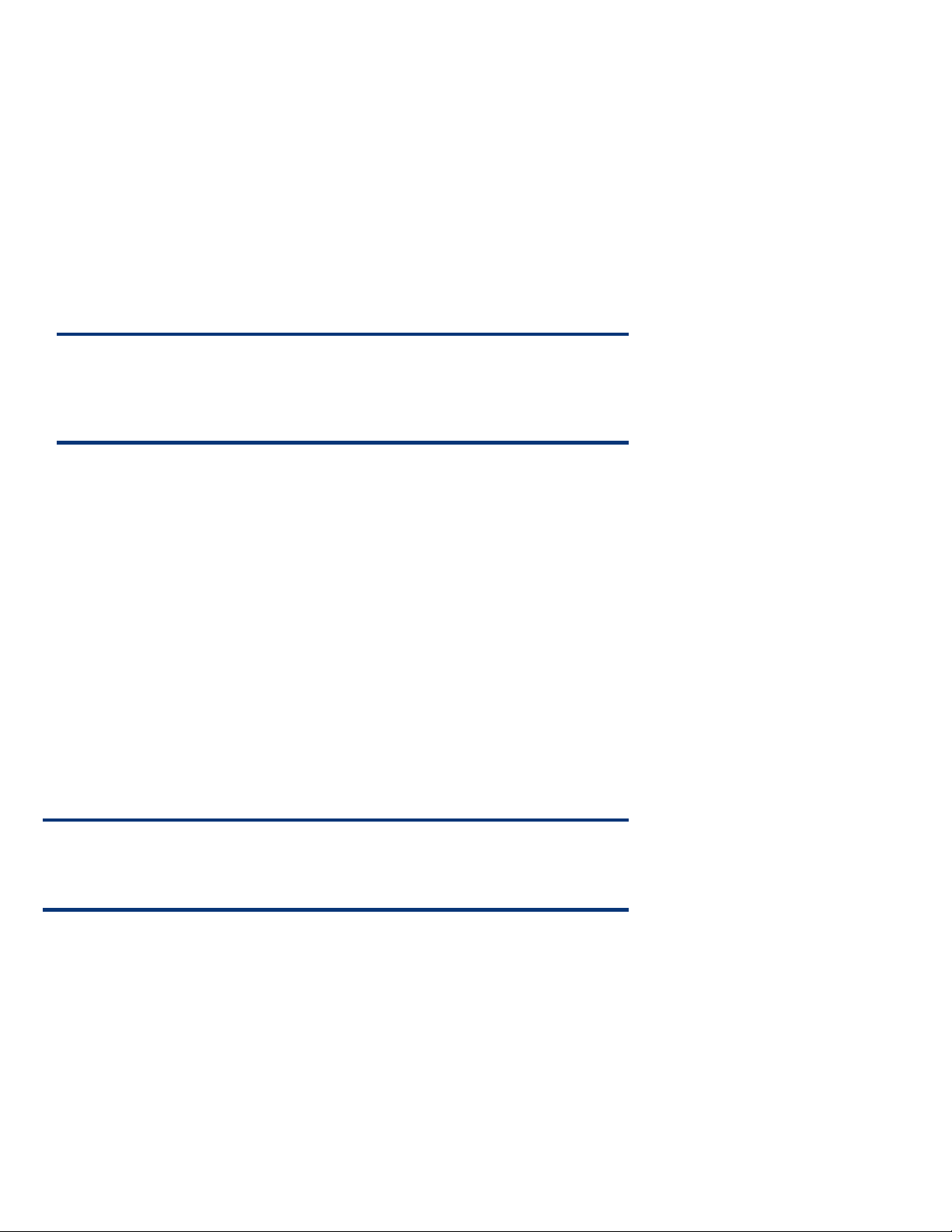
Administrators can access port monitoring through the Virtual Connect Manager over the same Ethernet connection used to
access the HP Onboard Administrator and iLO connections (Figure 3-1).
Figure 3-1. Virtual Connect Manager screen for Ethernet settings
1
Version 1.20a is available for download from
http://h18023.www1.hp.com/support/files/server/us/download/28035.html?jumpid=reg_R1002_USEN.
4
Page 5
ISS Technology Update Volume 6, Number 9
When port monitoring is enabled, a warning icon appears on the Virtual Connect Manager page, as shown in Figure 3-1.
If port monitoring is configured and enabled within the Virtual Connect domain, Ethernet data from the monitored ports is
replicated on the network analyzer port, for that reason it is important to verify the Network Analyzer is set up properly to
avoid passing traffic back onto the network.
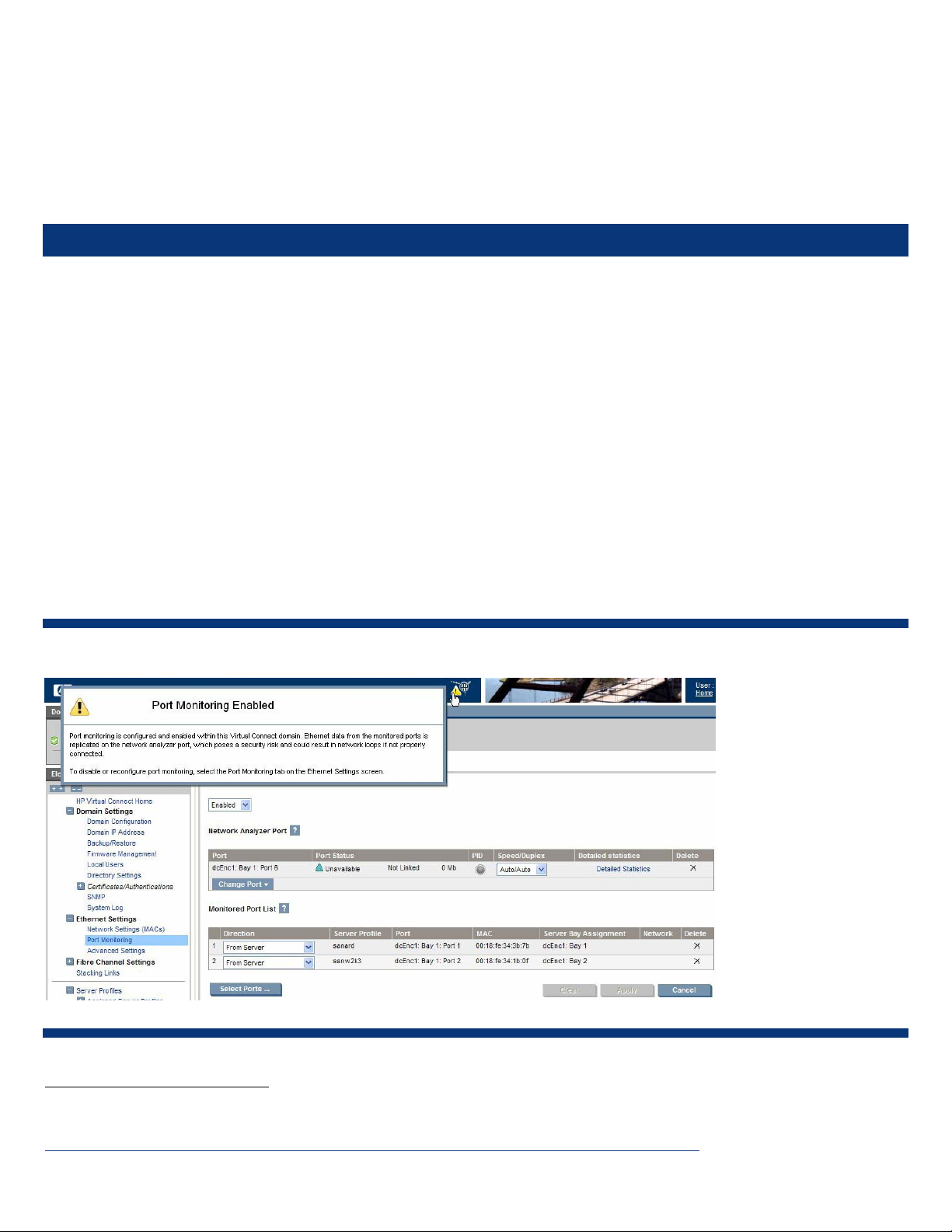
Up to 16 ports can be monitored, which are chosen from the Select Monitored Ports screen in Virtual Connect, as shown in
Figure 3-2.
Figure 3-2. Select Monitored Ports screen in Virtual Connect
To capture Local Area Network (LAN) traffic for a monitored port, a program that monitors data traveling over the network,
typically referred to as a network sniffer (such as WireShark,
every Ethernet frame it sees and displays it on a screen. It is up to an administrator to create filters to look for specific patterns
within that traffic. Instead of using a sniffer program, a network analyzer could be used, which is a piece of hardware
specifically dedicated to this function
Detailed instructions about using Port Monitoring can be found in the “HP Virtual Connect for c-Class BladeSystem User Guide”
at
http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c00865618/c00865618.pdf.
www.wireshark.org) is also required. A network sniffer captures
5
Page 6

ISS Technology Update Volume 6, Number 9
Licensing ports on the Brocade 4/12 SAN Switch for HP c-Class BladeSystem
The Brocade 4/12 SAN Switch for HP c-Class BladeSystem is provided with 12 port licenses, two of which are pre-reserved for
external ports. This article focuses on port licensing as it relates to the many questions that HP representatives encounter at
technical events. Here are two such questions:
• Can more than 8 servers be licensed with each Brocade 4/12 SAN switch (Figure 4-1) at the expense of external ports (for
example, 10 server ports and 2 external ports)?
• Are there any rules determining which bay’s ports get licensed (for example, only servers in bays 1 through 8), or can one
manually assign licenses to any server port in the enclosure, regardless of bay number?
Figure 4-1. Brocade 4GB SAN switch*
* This illustration shows 4 SFPs. However, out-of-the-box the Brocade 4/12 SAN switch has 2 SFPs in the left-most slots.
We’ll share what we know about these licensing questions from both a practical field perspective and a product feature
vantage point.
Quick answers
In addressing the first question, the proposed scenario is permitted. The only requirement is to maintain at least one licensed
external port. However, if the configuration contains two HP c-Class Brocade 4/12 SAN Switches side-by-side in a dual path
configuration, the servers on the top of the enclosure should use Host Bus Adapter (HBA) port 1 and servers on the bottom
should use port 2. This will split the load between the two paths.
As for the second question, licenses are granted on a first-request basis; any of the 16 internal ports can request and be
granted a license. It is possible to turn off dynamic license allocation in the Fabric OS (FOS) and assign licenses manually if
desired, as described in the Command Line Interface (CLI) guide for Brocade FOS. Ultimately, licensing is not dependent on
bay numbers.
NOTE
If more than 11 servers are plugged into the Blade System, all the ports can be automatically
assigned to internal servers with no external connections.
About port management
In the past, Ports On Demand (POD) functionality was static. A preset group of ports was individually enabled per each POD
license. In contrast, the new Dynamic Ports On Demand (DPOD) feature does not require predefined port assignment. Port
assignment is determined by the discovery of active HBA ports, but is limited to the quantity of purchased ports.
6
Page 7

ISS Technology Update Volume 6, Number 9
If DPOD has been turned off, simply use the licensePort command to initiate it.
NOTE
For the Brocade 4Gb SAN switch, DPOD assigns a port license only when a server blade with
HBA installed is inserted in the enclosure. A server blade without an active HBA will not prompt
the switch to assign a port license.
Dynamic licensing
Today, the concept of dynamic licensing is really quite flexible, enabling users to license any port and move licenses around
from port to port. In fact, they can allocate a license to a port, and then later de-allocate that license, putting it back in the pool
of available licenses.
A 12-port switch has 24 physical connections, but a maximum of 12 can be used at any given time. Licenses can be prereserved for any port. Two external ports are pre-reserved as an out-of-box default, leaving 10 available for dynamic port
assignment. Customers are allowed to change this assignment ratio if desired (1:11 or 3:9 for example).
If DPOD is enabled, ports are assigned as activity is detected. Removing a connection does not de-allocate the port⎯this allows
maintenance removal and replacement without the license being given away to another port. As such, license persistence can
sometimes exhaust the pool of licenses. For instance, moving a server with an HBA across four server bays will result in licenses
being allocated to all four of those bays. Users are advised to occasionally review license assignments made by DPOD to free
up unneeded license associations; this will return them to the available license pool.
NOTE
It is possible to upgrade the Brocade 4Gb SAN switch to 24 licensed ports by purchasing
optional licenses. (Refer to “Additional resources” below for links to further information.)
Brocade Access Gateway feature
Users might also wonder if a license is required to enable the Brocade Access Gateway feature. Since this is a feature of the
FOS that is user-enabled through Brocade Web Tools or the Brocade CLI, no additional license is required. The number of port
licenses is still controlled by the switch’s number of DPOD licenses.
Summary
Flexibility is the hallmark of port licensing; it can be assigned automatically or manually. The DPOD feature simplifies port
management:
• Automatically detects HBA connected server ports or cabled ports
• Automatically enables ports
• Automatically assigns port licenses
7
Page 8

ISS Technology Update Volume 6, Number 9
Additional resources
For additional information on the topics discussed in this article, visit the following links:
Resource URL
Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for
HP c-Class BladeSystem – user
guide and other reference
manuals
HP Brocade 4/12 SAN Switch
– QuickSpecs
Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for
HP c-Class BladeSystem
overview & features
–
http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bizsupport/TechSupport/DocumentIndex.jsp?contentType=SupportMa
nual&lang=en&cc=us&docIndexId=64179&taskId=101&prodTypeId=12169&prodSeriesId=3185340
http://h18006.www1.hp.com/products/quickspecs/12480_na/12480_na.html
http://h18004.www1.hp.com/storage/saninfrastructure/switches/b4gbsscblade/index.html?jumpid=
reg_R1002_USEN
Frequently asked questions regarding the adoption of HP VDI
This is the second in a series of several newsletter articles about HP Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI), in which we will
continue to address more of the frequently asked questions (FAQs) that our technical staff receives. It is our goal to share these
answers publicly as the HP knowledge base for VDI environments keeps expanding.
This set of FAQs includes, but is not limited to, the following VDI-related topics:
• What happens if you use sound? (see Question #1)
• A success story to tell your customers or stakeholders (see Question #2)
• The scoop about connection brokers (see Questions #3 and #4)
• Multi-monitor support (see Question #5)
To read the first article in this series that includes a brief introduction to VDI technology, go to
http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c01278462/c01278462.pdf.
FAQs
Question #1________________________________________________________________________________
Q. Is it possible to use sound in a VDI environment?
Yes. You may run sound in a VDI environment. Depending on the display protocol, however, the quality of sound may vary.
A.
For example, with Microsoft Remote Desktop Protocol (MS RDP), the sound is unidirectional, but functional in most
circumstances. You would not want to record audio over the protocol, yet a user could certainly listen to an audio podcast
without resulting in obvious degradation of sound quality.
Question #2________________________________________________________________________________
Q. Are there any VDI success stories available?
Yes. HP has perhaps the biggest success story in the industry regarding the practical application of VDI technology. Collier
A.
County Schools in Collier County, Florida, has a very large implementation based on HP p-Class and c-Class server blades,
and they have been successfully running their VDI environment for over a year. A video of this success story is available at
www.hp.com/go/vdi. You can check this website for regular updates of success stories, demos, and other general
information about VDI.
8
Page 9

ISS Technology Update Volume 6, Number 9
Question #3________________________________________________________________________________
Q. Is it required to use a connection broker in a VDI environment?
No. Many customers implement VDI without using a connection broker. The ability to hand an end user a dedicated
A.
resource may make sense in smaller environments, developer environments, and in Business-to-Business (B2B) connections.
As the environment grows and becomes more complex, the disadvantages may then be more pronounced in a non-brokered
environment. Items such as centralized management are invariably compromised when a connection broker is absent in
large environments. Connection tracking (the ability of a connection broker to decipher whether a discreet connection is
active and functioning) also becomes more critical as the implementation grows. Insuring that an end user always has a
resource is a benefit of connection-brokered environments that is not easy to attain in a non-brokered environment. Finally, a
connection broker provides a “big picture” overview of the utilization of the VDI environment.
Question #4________________________________________________________________________________
Q. What connection brokers does HP recommend?
Ultimately, HP leaves connection broker selection up to its customers. However, we do have partnerships, and where it
A.
makes sense, HP can offer a broad range of choices based on customer needs. These choices are quickly becoming the
standard in proof-of-concept implementations. Provision Networks, HP Session Allocation Manager (SAM), and VMware’s
upcoming Virtual Desktop Manager are all available from HP for VDI support⎯and in some cases (Provision Networks and
SAM), the same connection brokers also support other technologies, such as Consolidated Client Infrastructure (CCI) and HP
Workstation Blades. For software quotes from third-party vendors, such as Provision Networks, call HP Software and
Licensing Management Solutions toll-free line at 1-800-597-4622, or access one of the URLs listed below in “Additional
resources.”
Question #5________________________________________________________________________________
Q. Does VDI support multi-monitor deployments to the end user?
VDI supports monitor spanning rather than true multi-monitor deployment. The main differences are as follows:
A.
• Multi-monitor capability allows end users to maximize an application in one window while leaving another monitor
completely available for work.
• Monitor spanning allows a single desktop to be spread across two or more physical display devices, with non-
maximized applications displaying separately on each monitor.
VDI using HP Remote Graphics Software PC (RGS-PC) edition supports monitor spanning with a cumulative resolution of
3840x1200. This allows for up to two spanned monitors, as long as the access device supports such a configuration.
Question #6________________________________________________________________________________
Q. How much memory should be installed in a system that will be a VDI host?
Much like consolidation from virtualization, VDI does not have strict rules about how much memory to use; however, there
A.
are excellent guidelines that will greatly increase the chances of a successful deployment. With regards to memory, more is
better only to a point. VMware supports up to 64 GB on a single server and up to 16 GB on a single VM. A better rule of
thumb than loading every system with 64 GB of memory is to follow a ratio of 4 GB of memory for every processing core on
a system when the virtual machines are running Windows XP. An eight-core system, such as a DL585 G2 or BL480c with
quad-core, would be outfitted with 32 GB of RAM; and a DL380 G5 with dual-core processors would be fine with 16 GB
under most circumstances.
9
Page 10

ISS Technology Update Volume 6, Number 9
Question #7________________________________________________________________________________
Q. Where is user data stored in a VDI environment?
A. Administrators actually have a choice of where they can store end-user data in a VDI environment. It is possible, especially in
non-brokered environments, to place user data within the virtual machine itself. This is very much like a traditional desktop
model. For a more robust solution, end-user data should be redirected using Active Directory policies and, potentially,
Roaming Profiles.
Question #8________________________________________________________________________________
Q. How are activities such as virus scans handled in a shared environment?
A. I/O-intensive activities (for example, full-system virus scans) create a huge impact on end users in a VDI environment. To
counteract the effects of hundreds of individual virus scans launching simultaneously, some best practices should be
followed:
• Run real-time virus scanning within the Virtual Machines (VM), but do not require a full-system scan to be done on the
virtual machine itself.
• Redirect user data to Network Attached Storage (NAS) or other lower-cost, centralized storage solution, and run full-
system scans on this device. Active Directory simplifies this process (see Question #7).
• Minimize user-write permissions to the VM. Many security risks operate at the access level of the end user. Reducing
end-user permissions on the local disk drive also reduces the damage potential of a user-level threat.
Question #9________________________________________________________________________________
Q. What operating systems are acceptable for the end user to connect to in a VDI environment?
The buying market points to what is most popular, but operating system choice really depends on the connection broker, the
A.
connection protocol, and the expected return on investment.
• Windows XP Professional is the desired OS for VDI implementations. This operating system is supported on all popular
display protocols (Virtual Network Computing (VNC), RGS-PC, and MS RDP and fulfills recommendations made by
multiple vendors as far as sizing and management. There are few known limitations with Windows XP, and support is
currently available.
• Linux is supported by VNC and some open source protocols. Connection broker support appears to be nominal for
Linux operating systems in a desktop VM as well.
• Windows Vista is supported by the latest versions of MS RDP and has sparked interest in VDI as a tool for desktop OS
migrations from 2000/XP to Vista.
As with all VDI implementations, a proof of concept is recommended before proceeding, with special attention paid to
sizing (scalability) and functionality.
Summary
Like any emerging technology, VDI presents certain challenges to which there are viable (and often preferred) solutions. The
myriad of support services available from HP, along with website information (including success stories) and third-party-vendor
resources, are meant to help address these issues. Our continuing series of articles on VDI-related FAQs is another source of
useful explanations to common technical difficulties. Watch for the next article to find out more answers.
10
Page 11

ISS Technology Update Volume 6, Number 9
Additional resources
For additional information on the topics discussed in this article, visit the following links:
Resource URL
HP VDI www.hp.com/go/vdi
HP RGS PC trial site
HP RGS PC edition site
HP Software Licensing &
Management Solutions (SLMS)
http://h20293.www2.hp.com/portal/swdepot/displayProductInfo.do?productNumber=GN
038AAT
http://h20293.www2.hp.com/portal/swdepot/displayProductInfo.do?productNumber=GN038AA&j
umpid=reg_R1002_USEN
www.hp.com/software/slms
ProLiant management tip of the month
Troubleshooting HP SIM connections
Frequently troubleshooting why a system is unable to launch a tool or why clicking the hardware status icon does not launch the
System Management Homepage boils down to answering the dual question, ”What services are running on the target? and has
HP SIM discovered them?” Sure, it’s possible to visit each system’s information page in HP SIM, and then expand the ”Product
Description” to look at the protocols, but that can be a time-consuming process for a lot of systems (see Figure 5-1). You may
even have visited the Reports section to see if you can generate a report on each system and the protocols discovered only to
be disappointed.
Figure 5-1. Product description
Well, the good news is that you actually can do what you want, but not in the way you expected. A little known fact about HP
SIM collections is that when you create a collection using attributes specified by you, those attributes become available for
display as columns in the table view. Therefore, if you were to create a new collection and specify “Management Protocol” with
all of the possible options, you would get a collection definition that would look like Figure 5-2.
11
Page 12

ISS Technology Update Volume 6, Number 9
Figure 5-2. Table view
Once you display the collection, you can click the [Customize…] link to the upper right of the table and hide columns that do
not need to be displayed for this purpose such as the non-hardware status columns, system type, and so forth. You will then
have a table that looks like Figure 5-3.
The first thing you might notice is that there are two columns with the simple heading ‘label.’ This is because the entries would
be longer than HP SIM would allow. The first one would correspond to ”WS-Management” and the second to “Systems
Management Home Page.” Other than that, the list is self-explanatory and it provides a truth table of sorts that lets you see
exactly what protocols HP SIM has been able to identify on a target. This can be a very effective tool in fine-tuning your HP SIM
infrastructure and remediating the managed targets.
12
Page 13

ISS Technology Update Volume 6, Number 9
Figure 5-3. Non-hardware status
13
Page 14

ISS Technology Update Volume 6, Number 9
Recently published industry standard server technology communications
Title URL
The AMD processor roadmap for industry-standard
servers – Technology Brief
Critical factors in intra-rack power distribution planning
for high-density systems – Technology Brief Podcast
High-Density Server Deployment Demonstration: Power
and Cooling Considerations – Video
Implementing Microsoft Windows Server Virtualization
CTP release on HP ProLiant servers – Integration Note
Power basics for IT professionals – Technology Brief http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c01234
Technologies for HP ProLiant 300-series servers –
Technology Brief
http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c00428
708/c00428708.pdf
http://h10068.www1.hp.com/blogpost/Podcast/Server_IntraRack.mp3
http://h18004.www1.hp.com/products/servers/technology/whitepapers
/datacenter.html#power
http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c01286
554/c01286554.pdf
421/c01234421.pdf
http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c00502
616/c00502616.pdf
Industry standard server technical communications can be found at www.hp.com/servers/technology.
Contact us
Send comments about this newsletter to TechCom@HP.com.
Legal Notices
© Copyright 2007 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein is subject to
change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty
statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an
additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Intel and Intel Xeon are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the United States and other countries.
Linux is a U.S. registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Microsoft and Windows are US registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
TC071106NL
November 2007
 Loading...
Loading...