Page 1

HP 37718A
OmniBER 718
User’s Guide
DSn/SONET
Operation
Page 2

Copyright HewlettPackard Ltd.1998
All rights reserved.
Reproduction,
adaption, or
translation without
prior written
permission is
prohibited, except as
allowed under the
copyright laws.
HP Part No.
37718-90022
First edition, 09/98
Second Edition, 12/98
Printed in U.K.
Warranty
The information
contained in this
document is subject to
change without notice.
Hewlett-Packardmakes
no warranty of any
kindwithregardto this
material, including,
but not limited to, the
implied warranties or
merchantability and
fitness for a particular
purpose.
Hewlett-Packard shall
not be liable for errors
contained herein or for
incidental or
consequentialdamages
in connection with the
furnishing,
performance, or use of
this material.
WARNING
WarningSymbols Used
on the Product
!
The product is marked
with this symbol when
the usershould refer to
the instruction manual
in order to protect the
apparatus against
damage.
The product is marked
with this symbol to
indicate that
hazardous voltages are
present
The product is marked
with this symbol to
indicate that a laser is
fitted. The user should
refer tothe laser safety
information in the
Calibration Manual.
Hewlett-Packard Limited
Telecommunications Networks Test Division
South Queensferry
West Lothian, Scotland EH30 9TG
Page 3

User’s Guide DSn/SONET Operation
HP 37718A
OmniBER 718
Page 4

About This Book
This book tells you how to select the features that you want to use for your test.
The selections available are presented in the following groups:
• Transmit and receive interfaces
• Testfeatures,forexample,theaddition oferrors andalarmsto thetest
signal
• Measurements including test timing
• Storing, logging and printing results with general printer information
• Using instrument and disk storage
• Using the “Other” features.
The selections available will depend on the options fitted to your
instrument. The examples given in this book cover all options and
therefore may include selections which are not available on your
instrument.
iv
Page 5

Contents
1 Setting the Interfaces
Setting DSn Transmit Interface 2
Setting SONET Transmit Interface 4
Setting Jitter Transmit Interface 7
Setting Wander Transmit Interface 9
Setting SONET THRU Mode 11
Using Smart Test 13
Setting DSn Receive Interface 15
Setting SONET Receive Interface 17
Setting Jitter Receive Interface 18
Setting Extended Jitter Receive Interface 19
Setting Wander Receive Interface 20
2 Selecting Test Features
Using Transmit Overhead Setup 22
Using Receive Overhead Monitor 24
Setting Overhead Trace Messages 26
Generating Overhead Sequences 27
Using Receive Overhead Capture 29
Adding Frequency Offset to SONET Signal 31
Adding Frequency Offset to the DSn Signal 33
Setting up Signaling Bits 34
Setting Transmit Structured Payload/Test Signal 37
Setting Receive Structured Payload/Test Signal 39
Setting Transmit N x 64 kb/s/N x 56 kb/s
Structured Payload/Test Signal 40
Setting Receive N x 64 kb/s/N x 56 kb/s
Structured Payload/Test Signal 42
v
Page 6

Contents
Inserting an External DSn Payload/Test Signal 43
Dropping an External Payload/Test Signal 46
Adding Errors & Alarms at the SONET Interface 49
Adding Errors & Alarms to the DSn Interface/DSn Payload 50
Using FEAC Codes 51
Setting DSn Spare Bits 53
Adding Pointer Adjustments 54
Using Pointer Graph Test Function 61
Stressing Optical Clock Recovery Circuits 63
Generating Automatic Protection Switch Messages 64
Inserting & Dropping Data Communications Channel 65
3 Making Measurements
Using Overhead BER Test Function 68
Test Timing 69
Making SONET Analysis Measurements 70
Making DSn Analysis Measurements 71
Measuring Frequency 72
Measuring Optical Power 73
Measuring Round Trip Delay 74
Monitoring Signaling Bits 76
Measuring Service Disruption Time 77
Performing a SONET Tributary Scan 80
Performing an SONET Alarm Scan 82
Performing a DSn Alarm Scan 83
Measuring Jitter 84
Measuring Extended Jitter 86
Measuring Wander 87
Measuring Jitter Tolerance 89
vi
Page 7

Contents
Measuring Jitter Transfer 92
4 Storing, Logging and Printing
Saving Graphics Results to Instrument Store 98
Recalling Stored Graph Results 99
Viewing the Bar Graph Display 101
Viewing the Graphics Error and Alarm Summaries 103
Logging Graph Displays 105
Logging Results 107
Logging on Demand 110
Logging Jitter Tolerance Results 112
Logging Jitter Transfer Results 114
Logging Results to Parallel (Centronics) Printer 116
Logging Results to HP-IB Printer 117
Logging Results to Internal Printer 118
Logging Results to RS-232-C Printer 119
Printing Results from Disk 120
Connecting an HP 850C DeskJet Printer to a Parallel Port 121
Changing Internal Printer Paper 122
Cleaning Internal Printer Print Head 125
5 Using Instrument and Disk Storage
Storing Configurations in Instrument Store 128
Titling Configuration in Instrument Store 129
Recalling Configurations from Instrument Store 130
Formatting a Disk 131
vii
Page 8

Contents
Labeling a Disk 132
Managing Files and Directories on Disk 133
Saving Graphics Results to Disk 140
Saving Data Logging to Disk 142
Saving Configurations to Disk 143
Recalling Configuration from Disk 144
Recalling Graphics Results from Disk 145
Copying Configuration from Instrument Store to Disk 146
Copying Configuration from Disk to Instrument Store 148
Copying Graphics Results from Instrument Store to Disk 150
6 Selecting and Using "Other" Features
Coupling Transmit and Receive Settings 154
Setting Time & Date 155
Enabling Keyboard Lock 156
Enabling Beep on Received Error 157
Suspending Test on Signal Loss 158
Setting Error Threshold Indication 159
Setting Screen Brightness and Color 160
Dumping Display to Disk 161
Running Self Test 163
viii
Page 9

Contents
7 STS-1 SPE Background Patterns
8 ETSI/ANSI Terminology
ETSI/ANSI Conversion and Equivalent Terms 170
ix
Page 10

Contents
x
Page 11

1
1 Setting the Interfaces
This chapter tells you how to set the instrument
interfaces to match the network being tested.
Page 12

Setting the Interfaces
Setting DSn Transmit Interface
Description DSn transmit interface settings should match network equipment
settings of Rate, Termination and Line Code and determine the Payload
to be tested.
TIP: To set the Transmitter and Receiver to the same interface settings
choose .
OTHER
SETTINGS CONTROL COUPLED
HOW TO: 1 Choose the required SIGNAL rate.
Rates of DS1, DS3, 2 Mb/s and 34 Mb/s are available.
2 If you have chosen 2 Mb/s as the SIGNAL rate, choose the required
CLOCK SYNC source - internally generated or recovered from the
received DSn signal.
If Jitter,Option 204, 205 or206,is fitted andSIGNAL is chosen
a choice is added to the menu. This allows you to choose the
2M REF
synchronization source for the 2 Mb/s reference. The synchronization
source is supplied from theSONETClockmodule. It can be internally
generated, derived from an external clock or recovered from the
SONET received signal.
2
2 Mb/s
Page 13
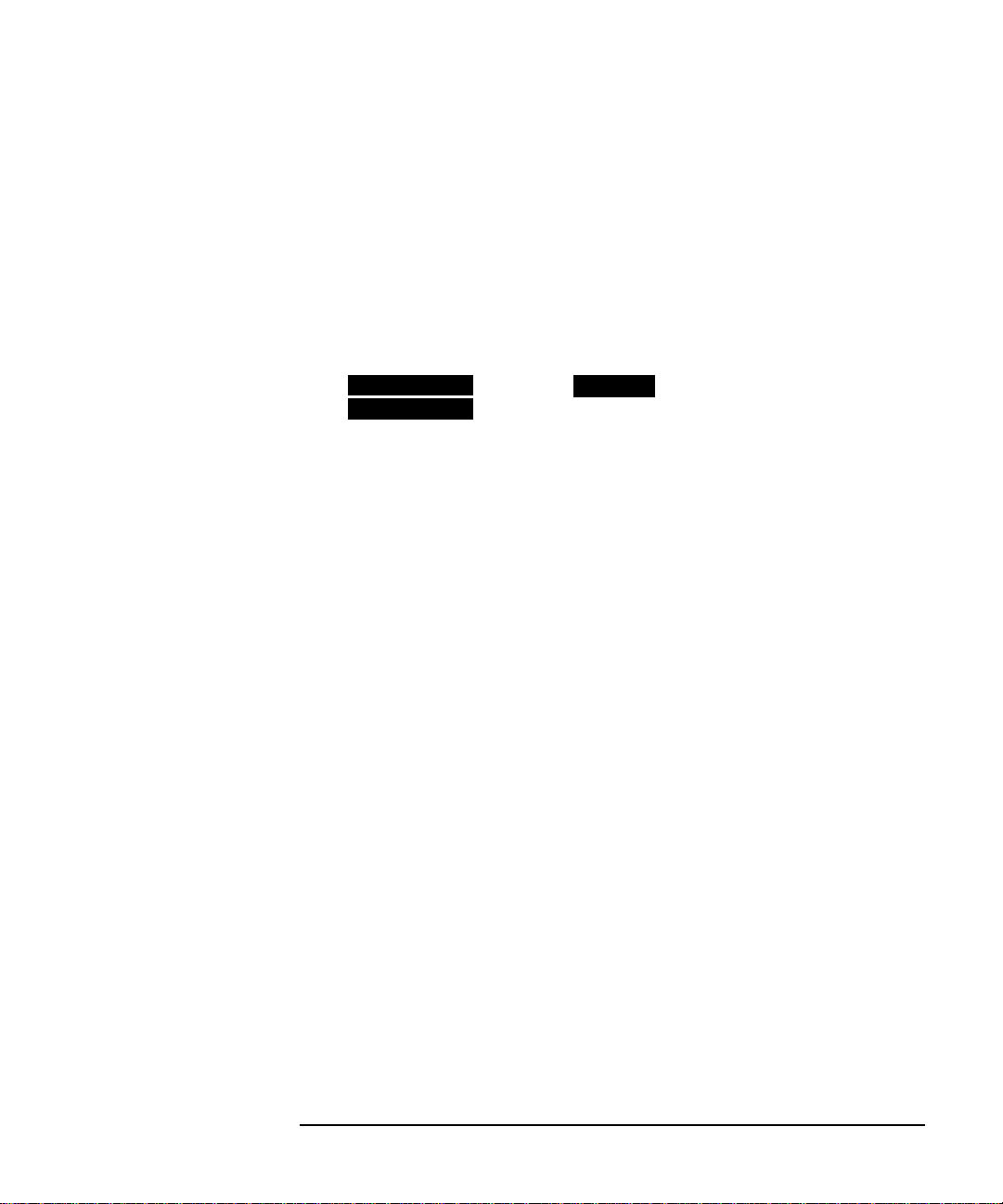
Setting the Interfaces
Setting DSn Transmit Interface
3 If DS1 or DS3 is chosen, choose the required OUTPUT LEVEL.
4 If you have chosen 2 Mb/s as the SIGNAL rate, choose the required
TERMINATION. (At all other signal rates the impedance is fixed).
5 If you have chosen 2 Mb/s or DS1 as the SIGNAL rate, choose the
required LINE CODE. (At 34 Mb/s and DS3 coding is fixed).
6 If required, choose the FREQUENCY OFFSET value.
See “Adding Frequency Offset to the DSn Signal” page 33.
7 Choose the required PAYLOAD TYPE.
If is required must be chosen.
STRUCTURED
If is chosen the DSn test signal must be set up. See
STRUCTURED
FRAMED
“Setting Transmit Structured Payload/Test Signal” page 37.
If you have chosen 2 Mb/s, DS1 or DS3 as the DSn signal rate, the
Framed choice is expanded to provide a menu of framing types.
8 Choose the PATTERN type and the PRBS POLARITY.
3
Page 14
Setting the Interfaces
Setting SONET Transmit Interface
Setting SONET Transmit Interface
Description SONET transmit interface settings should match the network
equipment settings of Rate, Wavelength and Mapping, determine the
payload to be tested and set background conditions to prevent alarms
while testing.
TIP: If you wish to set the HP 37718A transmitter and receiver to the same
interface settings choose .
OTHER
SETTINGS CONTROL COUPLED
HOW TO: 1 Make your choice of SIGNAL rate.
If Option106, Dual Wavelengthopticalmodule, isfittedand an optical
rate is chosen, choose the required wavelength (1550) or (1310).
If STS-1 is chosen, choose the required interface level.
Choose unless isrequired.If is
chosen, see "Setting SONET THRU Mode " page 11.
2 Make your choice of CLOCK synchronization source. The RECEIVE
clocksynchronizationchoice dependsonthe SONET ReceiveInterface
choice.
EXTERNAL
3 If required choose the FREQUENCY OFFSET value. See “Adding
Frequency Offset to SONET Signal” page 31.
4
INTERNAL THRU MODE THRU MODE
allows a choice of MTS, BITS or 10 MHz clocks.
Page 15

Setting the Interfaces
Setting SONET Transmit Interface
4 Choose FOREGROUND , BACKGROUND
B/G MAPPING
MAPPING and type of payload.
F/G MAPPING
Mapping may beselectedfroma pictorial display by moving the cursor to
MAPPING and pressing .
SET
Use and to move betweenSTSLayer choice, VTLayerchoice and
Payload Layer choice. Use and to choose the mapping.
SET
Use to confirm your choice and return to the
MAIN SETTINGS
display.
SONET
5 If VT-6 mapping is chosen, VT CONCATENATION selection is
enabled, choose or the tributary at which the concatenation
OFF
begins, VT6-2C through VT6-6C.
The BACKGROUND, PATTERN IN OTHER VT-6’s is fixed at
NUMBERED, that is, each VT-6 contains a unique number to allow
identification in case of routing problems.
6 If required, choose DS1/2M/34M/DS3 OFFSET value. See “Adding
Frequency Offset to SONET Signal” page 31
7 If FULL SPE, VT-6, VT-2orVT-1.5mapping is chosen, choose the test
tributary CHANNEL,including the STS-3foran OC-12/OC-48 signal.
8 Choose the payloadframingunder PAYLOAD TYPE or VTPAYLOAD.
If is required must be chosen.
STRUCTURED
If is chosen, thePayloadtestsignal must besetup. See
STRUCTURED
FRAMED
“Setting Transmit Structured Payload/Test Signal” page 37.
If is chosen, see “Inserting an External DSn Payload/Test
INSERT
Signal” page 43.
5
Page 16
Setting the Interfaces
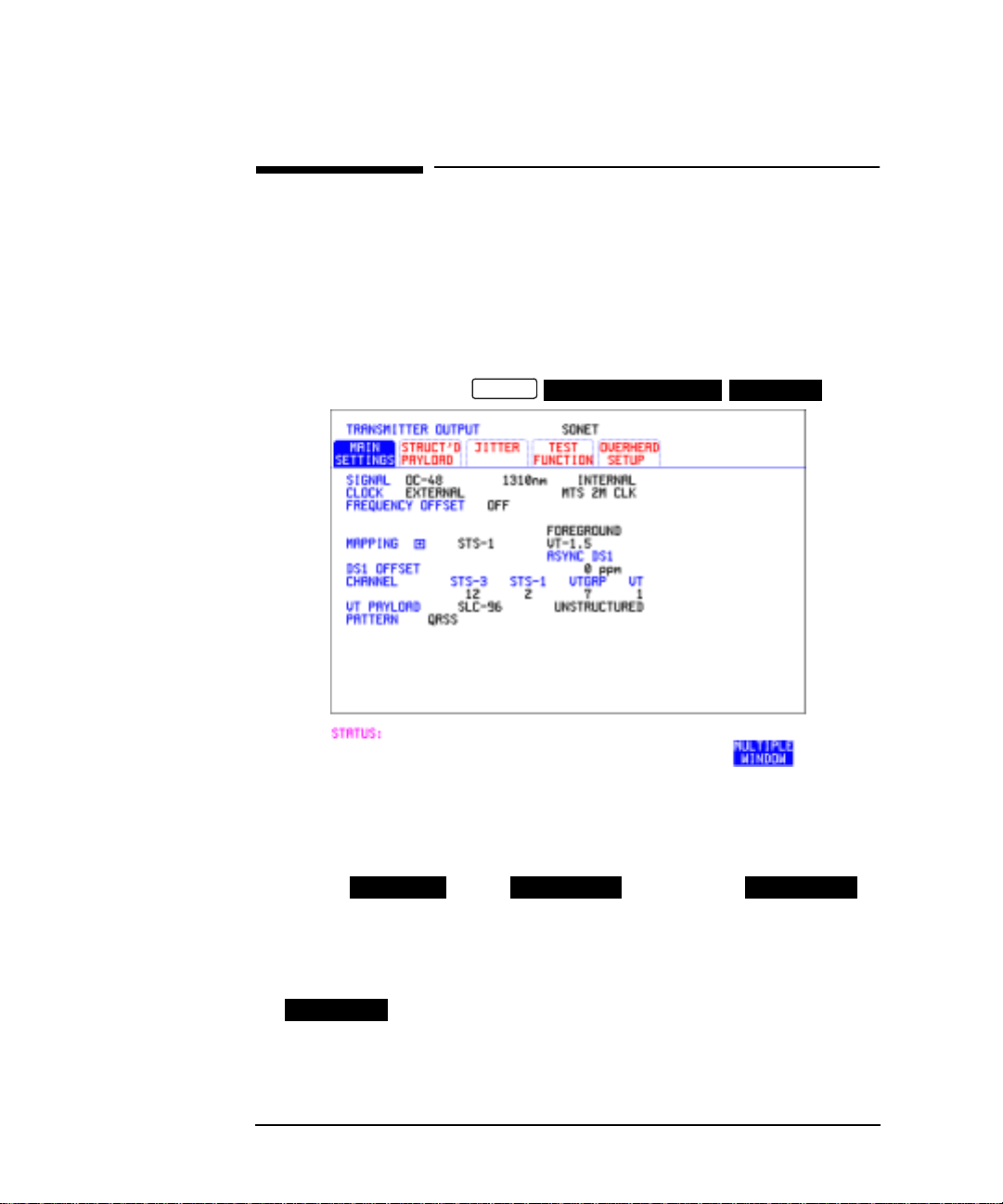
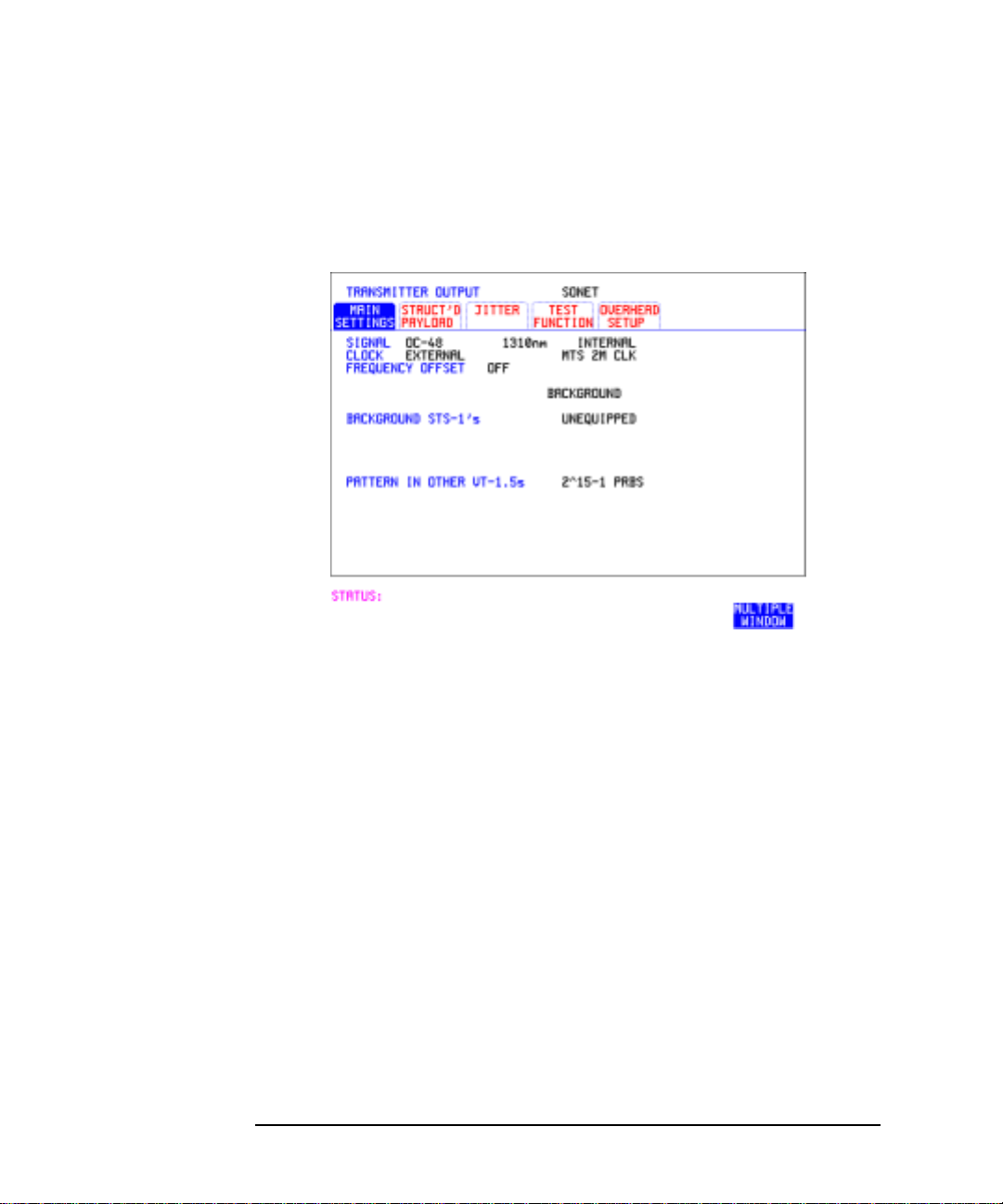
Setting SONET Transmit Interface
If you have chosen 2 Mb/s, DS1 or DS3 under Mapping, the Framed
choice is expanded to provide a menu of framing types.
9 Choose the PATTERN type and PRBS polarity.
10 Choose the mapping required in the background (non-test) STS’s.
11 If VT mapping is chosen for the test STS, choose the PATTERN IN
OTHER VT’s.
6
Page 17

Setting the Interfaces
Setting Jitter Transmit Interface
Setting Jitter Transmit Interface
Description: You can add jitter to the transmitted DSn or SONET signal at 2 Mb/s,
34 Mb/s, STS-3, OC-3, OC-12, and OC-48. You can source the jitter
modulation internally or from an external source.
HOW TO: 1 If you are adding jitter to the DSn signal, set up the DSn transmit
interface. See Chapter “Setting DSn Transmit Interface”.
2 If you are adding jitter to the SONET signal, set up the SONET
transmit interface. See “Setting SONET Transmit Interface” page 4.
3 Choose JITTER/WANDER .
If you wish to add wander to the DSn or SONET signal, See “Setting
Wander Transmit Interface” page 9.
4 Choose JITTER .
If you wish to perform a Jitter Tolerance measurement, choose
AUTO TOLERANCE
If you wish to perform a Jitter Transfer measurement choose
TRANSFER FUNCTION
ON
. See “Measuring Jitter Tolerance” page 89.
JITTER
. See “Measuring Jitter Transfer” page 92.
7
Page 18

Setting the Interfaces
Setting Jitter Transmit Interface
5 Choose the modulation source.
If adding jitter to the DSn signal and is chosen, connect
EXTERNAL
the external source to the MOD IN port of the DSn Jitter TX module.
Up to 10 UI ofexternaljittermodulation can be added at the MOD IN
port.
If adding jitter to the SDH signal and is chosen, connect
EXTERNAL
the external source to the MOD IN port of the SONET Clock module.
Up to 20 UI ofexternaljittermodulation can be added at the MOD IN
port.
6 Choose the JITTER MASK setting required.
You can choose the jitter range, jitter modulating frequency and jitter
amplitude if is chosen.
If youchoose ,the HP 37718A will "sweep"throughthe ITU-T
OFF
SWEPT
jitter mask (G.823 for DSn, G.958, G.825 or G.253 for SONET)
adjusting the jitter amplitude according to the jitter frequency.
If you choose , you can choose the "spot" jitter frequency. The
SPOT
jitter amplitude is adjusted and controlled according to your jitter
frequency choice.
TIP: If, when using the SWEPT MASK capability, a problem occurs around a
certain frequency, this may require closer examination. Stop the sweep
at that point by choosing . You can then control the "spot" jitter
SPOT
frequency to make closer examination of the problem.
8
Page 19

Setting the Interfaces
Setting Wander Transmit Interface
Setting Wander Transmit Interface
Description: You can add Wander to the 2 Mb/s DSn signal and the STS-3, OC-3,
OC-12 or OC-48 SONET signal.
HOW TO: DSn Wander (2 Mb/s)
1 ConnectREFOUT on theSONET Clockmoduleto REF INon the DSn
Jitter TX module (this provides the Wander Reference).
2 Setupthe DSntransmitinterface, chooseCLOCK SYNC and
select the SOURCE required from the menu. See “Setting DSn
Transmit Interface” page 2.
3 Choose JITTER/WANDER .
Ifyouwish toadd jitter tothe DSnsignal,See “SettingJitter Transmit
Interface” page 7.
4 Choose WANDER .
5 Choose the modulation source.
If is chosen, connect the external source to the MOD IN
EXTERNAL
port of the DSn Jitter TX module. Up to 10 UI of external wander
modulation can be added.
2M REF
WANDER
ON
9
Page 20

Setting the Interfaces
Setting Wander Transmit Interface
6 Choose the WANDER MASK setting required.
You can choose the wander modulating frequency and wander
amplitude if is chosen.
If you choose ,youcanchoosethe"spot"wander frequency. The
OFF
SPOT
wanderamplitude isadjustedand controlledaccordingto yourwander
frequency choice.
SONET Wander (STS-3, OC-3, OC-12, OC-48)
7 Set up the SONET transmit interface. See “Setting SONET Transmit
Interface” page 4.
8 Choose JITTER/WANDER .
WANDER
If you wish to add jitter to the SONET signal, see "Setting Jitter
Transmit Interface " page 7.
9 Choose WANDER .
ON
10 Choose the WANDER MASK setting required.
You can choose the wander modulating frequency and wander
amplitude if is chosen.
If you choose ,youcanchoosethe"spot"wander frequency. The
OFF
SPOT
wanderamplitude isadjustedand controlledaccordingto yourwander
frequency choice.
10
Page 21

Setting the Interfaces
Setting SONET THRU Mode
Setting SONET THRU Mode
Description THRU mode is used to non-intrusively monitor SONET lines where no
protected monitor points are available.
As THRU mode locks some user settings, you must set SIGNAL RATE,
STS rate, STS-1 SPE CHANNEL (if appropriate) before selecting THRU
mode.
The entire frame can be errorred at a user defined rate if PAYLOAD
OVERWRITE and TOH+POH CHANNEL OVERWRITE are both set to
. If eitheroverwriteisenabled the ENTIRE FRAME ERROR RATE
OFF
function is disabled.
OC-1/STS-1, OC-3/STS-3
You can substituteanewpayload, Section and Line Overhead (TOH) and
Path overhead (POH) in the received OC-1/STS-1 or OC-3/STS-3 signal
for testing.
OC-12, OC-48
The overhead and payload may be overwritten for STS-3c SPE and AU3.
PAYLOAD OVERWRITE is not available for STS-12C or STS-48C.
TOH+POH CHANNEL overwrite is available for STS-12C and STS-48C.
HOW TO:
1 Make the required SIGNAL RATE, MAPPING and CHANNEL
choices on the SONET and displays, See
"Setting SONET Transmit Interface " page 4 and "Setting SONET
Receive Interface " page 17.
TRANSMIT
RECEIVE
11
Page 22

Setting the Interfaces
Setting SONET THRU Mode
2 Make the PAYLOAD OVERWRITE choice required.
If STS-3cSPE, STS-1 SPE,VT-6,VT-2or VT-1.5ischosen, the Section,
Line and Path CVs are recalculated before transmission and the
Mapping, Selected VT, VT Payload, Pattern, Tributary Offset and
Pattern in other VT’s settings are displayed. To choose the settings in
these, See "Setting SONET Transmit Interface " page 4, steps 4
through 10.
3 Make the TOH+POH CHANNEL OVERWRITE choice required.
You canonlymodify those overhead bytes available under
SONET TEST FUNCTION SONET
: Errors & Alarms, Sequences,
TRANSMIT
Overhead BER, APS Messages and DCC Insert.
The Section, Line and Path CVs are recalculated before transmission.
4 Ifyouwish toadd jitterto theSTS-3,OC-3, OC-12or OC-48signal, See
“Setting Jitter Transmit Interface” page 7.
12
Page 23

Setting the Interfaces
Using Smart Test
Using Smart Test
Description The SmartTest functioncanhelp speed-up configuring the instrument in
two ways.
1 A Smartsetup feature that will attempt to configure the instrument
to receive the incoming signal.
2 A series of “links” that provide quick access to some of the most
frequently used features of the instrument. Note that these tests are
run with the instrument in its current configuration, no attempt is
made to set the instrument to the requirements of the test.
Smartsetup can help the user by attempting to identify the incoming
signal structure and detect mixed payload signal structures.
HOW TO USE
SMARTSETUP:
1 Connect the HP 37718A to the network and choose if necessary the
SET
RECEIVE
SELECT
required SONET interface on the HP 37718A (Smartsetup
will select DSn or SONET/SDH, but can not select between SONET
and SDH).
2 Press .
The display will show the Smart Test menu above.
3 Press either or .
SMART TEST
13
Page 24

Setting the Interfaces
Using Smart Test
4 In SONET mode the incoming signal will be identified on the top line
of the display, and under this the payload mappings, the J1Traceand
C2 byte indicators are displayed on the bottom lines.
5 Use the and keys to display the J1 Trace informationforeach
STS SPE. When the STS SPE of interest has been identified choose
either or .
VIEW PAYLOAD PRBS SEARCH
6 Choosing will identify and display the payload
VIEW PAYLOAD
mapping of the TUG structured signal, as shown below.
Choose the required tributary using and .
7 There are four choices available at this point:
SETUP RX
TROUBLE SCAN
tributary, exitstothe displayandstarts
which sets the receiver to receive the selected tributary.
which sets the receiver to receive the selected
RESULTS
TROUBLE SCAN
gating.
VIEW LABELS
which displaystheC2/V5/J1/J2 trace information for
the selected tributary.
TOP LEVEL
which returns the display to the STS SPE selection
window.
8 Choosing at Step 5 will prompt you for additional
PRBS SEARCH
information about patterns and which mapping to search. When the
required data has been entered press .
GO
9 When the search is complete a tributary display appears, with any
tributariescontainingthe required PRBSindicated with a“P”. Choose
the required tributary using and .
14
Page 25

Setting the Interfaces
Setting DSn Receive Interface
Setting DSn Receive Interface
Description DSn Receive interface settings should match the network equipment
settings of Rate, Termination and Line Code and determine the Payload
to be tested.
TIP: To set the transmitter and receiver to the same interface settings choose
OTHER
SETTINGS CONTROL COUPLED
.
HOW TO: 1 Choose the required SIGNAL rate.
2 If you have chosen 2 Mb/s as the SIGNAL rate, choose the required
TERMINATION. (At all other rates the impedance is fixed.)
3 If you have chosen 2 Mb/s or DS1 as the SIGNAL rate, choose the
required LINE CODE. (At 34Mb/s and DS3 coding is fixed.)
4 If you are measuring at the networkequipmentmonitorpoint,set the
LEVEL field to . In this case the received signal will be 20
to 30 dB below the normal level.
Choose the GAIN required to return the received signal to normal.
Choose EQUALIZATION to compensate for cable losses if
required.
MONITOR
ON
15
Page 26
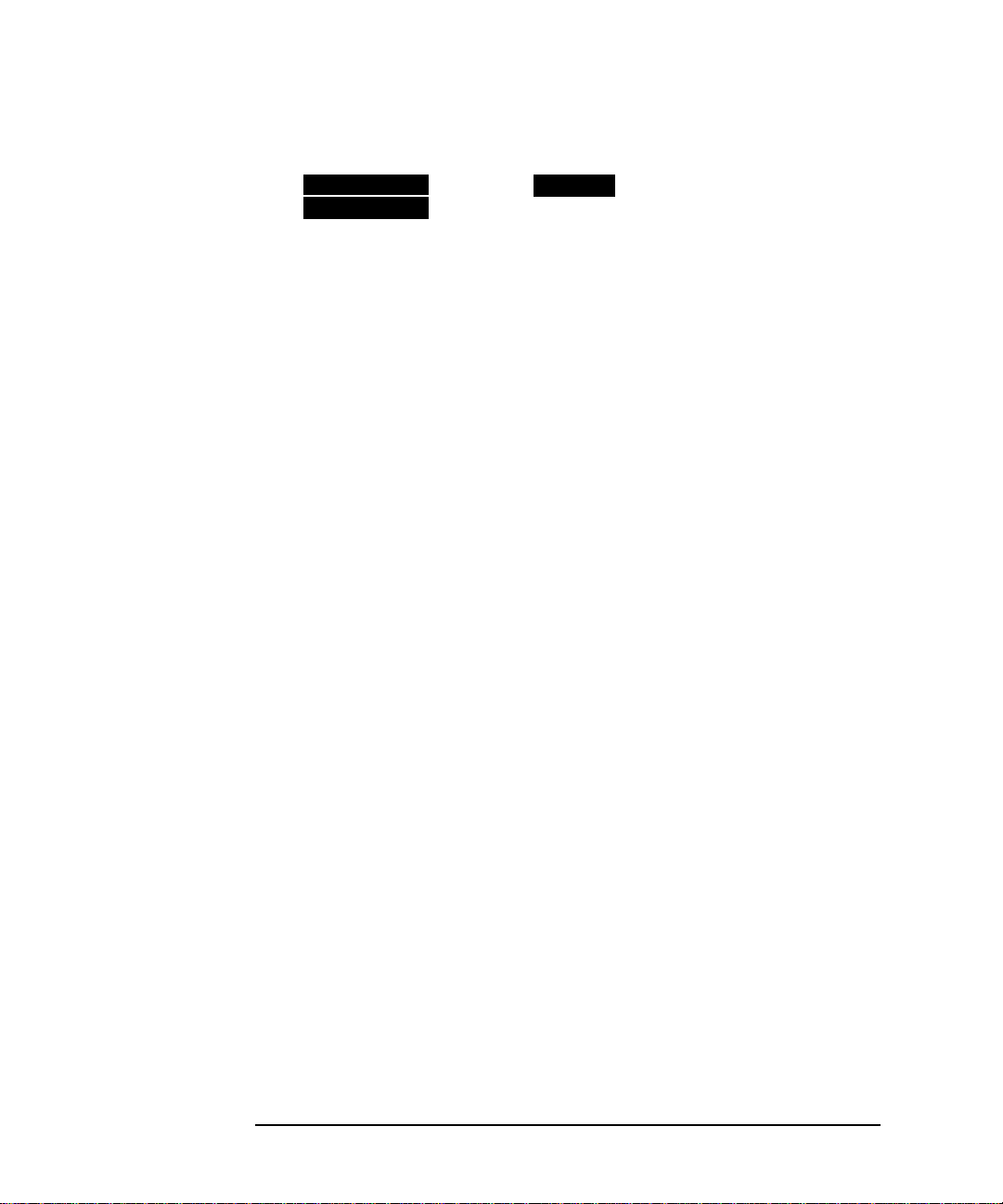
Setting the Interfaces
Setting DSn Receive Interface
5 Choose the PAYLOAD TYPE.
If is required must be chosen.
STRUCTURED
If is chosen, the DSn test signal must be set up. See
STRUCTURED
FRAMED
“Setting Transmit Structured Payload/Test Signal” page 37.
If you chose 2 Mb/s, DS1 or DS3 as the PDH/DSn SIGNAL rate, the
FRAMED choice is expanded to provide a menu of framing types.
6 Choose the PATTERN type and the PRBS POLARITY required.
16
Page 27
Setting the Interfaces
Setting SONET Receive Interface
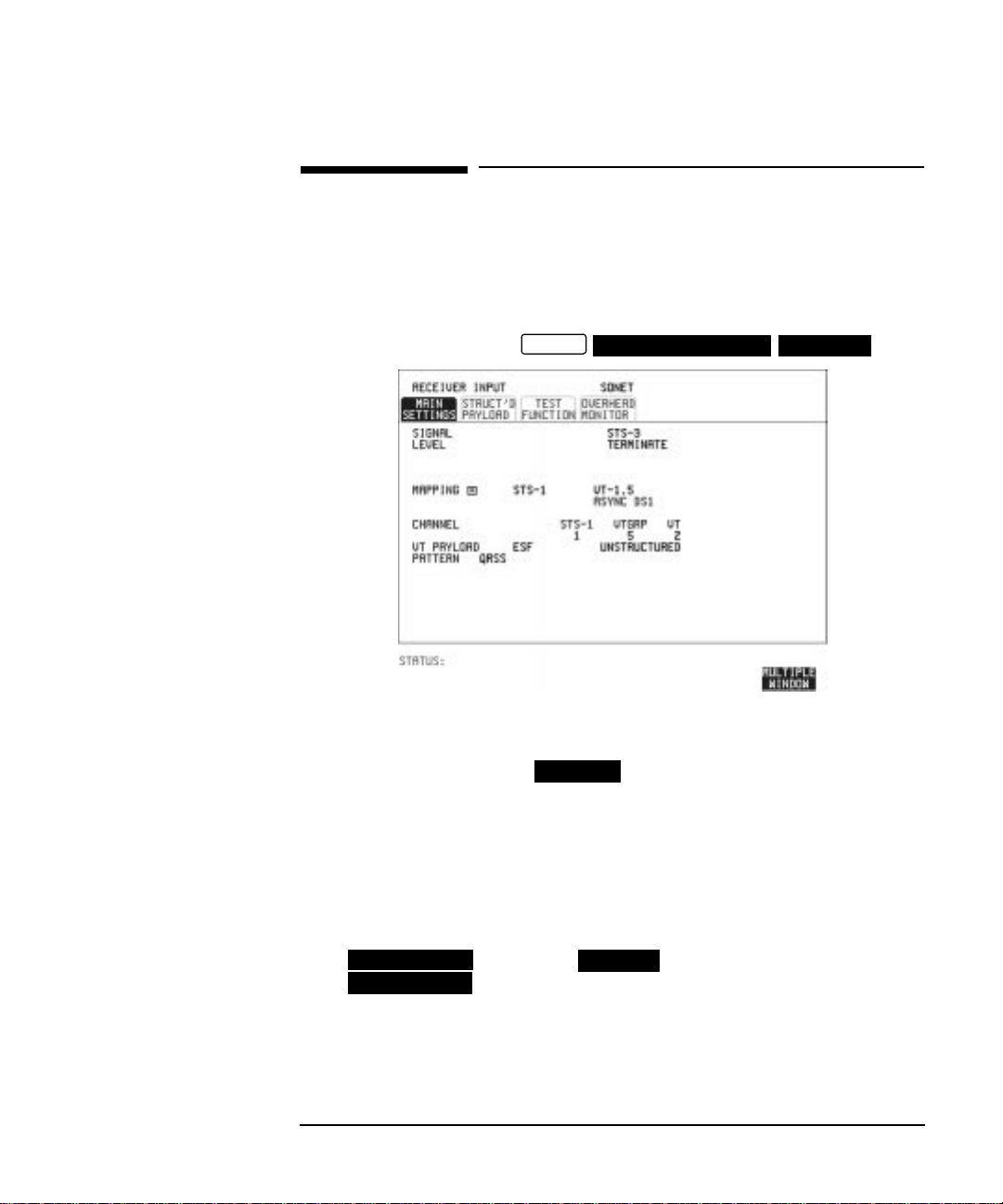
Setting SONET Receive Interface
Description SONET Receive interface settings should match the network equipment
settings of Rate and Mapping, and determine the payload to be tested.
TIP: If you wish to set the HP 37718A transmitter and receiver to the same
interface settings, choose .
OTHER
SETTINGS CONTROL COUPLED
HOW TO: 1 Choose the required SIGNAL source.
If STS-1 or STS-3 is chosen, choose the required LEVEL.
If the LEVEL chosen is choose the required GAIN.
MONITOR
2 Choose mapping and type of payload.
3 If VT-6 mapping is chosen,and CONCATENATIONisenabled, choose
the tributary at which the concatenation begins.
If VT-6, VT-2 or VT-1.5 mapping is chosen, choose the test tributary
under CHANNEL.
4 Choose the payloadframingunder PAYLOAD TYPE or VTPAYLOAD.
If is required must be chosen.
STRUCTURED
If is chosen the Payload test signal must besetup. See
STRUCTURED
FRAMED
“Setting Receive Structured Payload/Test Signal” page 39.
If DROP is chosen, see “Dropping an External Payload/Test Signal”
page 46.
5 Choose the PATTERN type and PRBS polarity.
17
Page 28
Setting the Interfaces
Setting Jitter Receive Interface
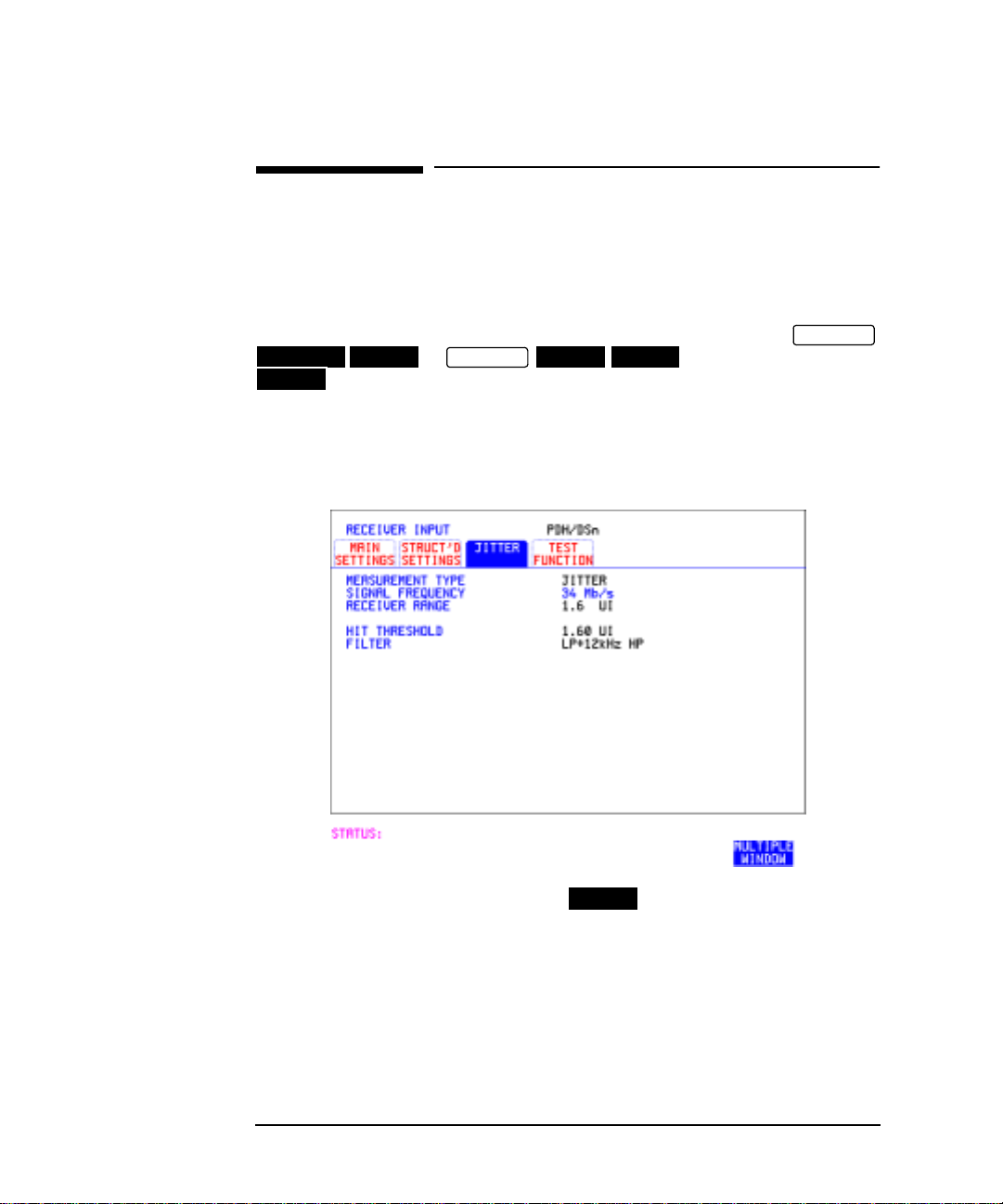
Setting Jitter Receive Interface
Description: Jitter and error measurements are made simultaneously when a jitter
option is fitted. The measurements are made on the normal input to the
DSn or SONET receiver and the interface selections are the normal
Receiver selections. Thejitterreceiveinterfaceis selected with
PDH/DSn JITTER
JITTER
.
or MEASUREMENT TYPE
RECEIVE
SONET
JITTER
The choices made on the jitter receive interface determine the jitter
measurement range, the threshold level for determining a jitter hit and
which filters are used in the jitter measurement.
RECEIVE
HOW TO: 1 Choose MEASUREMENT TYPE .
JITTER
2 Choose the RECEIVER RANGE - the jitter measurement range.
3 Choose the HIT THRESHOLD level - if the received jitter exceeds the
value chosen a jitter hit is recorded.
4 Choose the FILTER you wish to include in the peak to peak and RMS
jitter measurement.
18
Page 29

Setting the Interfaces
Setting Extended Jitter Receive Interface
Setting Extended Jitter Receive
Interface
Description: Extended Jitter measurements are made in a jitter bandwidth of 0.1 Hz
to 25 kHz. These measurements are made at the upper end of the
standard wander frequency range and the lower end of the standard
jitter frequency range. The extended jitter receive interface is selected
with or
RECEIVE
MEASUREMENT TYPE .
The choices made on the jitter receive interface determine the threshold
level for determining a jitter hit. The measurement Range and the
Filters are not selectable.
PDH/DSn JITTER
EXTENDED
RECEIVE
SONET
JITTER
HOW TO: 1 Choose MEASUREMENT TYPE .
2 Choose the HIT THRESHOLD level - if the received jitter exceeds the
value chosen a jitter hit is recorded.
EXTENDED
19
Page 30
Setting the Interfaces
Setting Wander Receive Interface
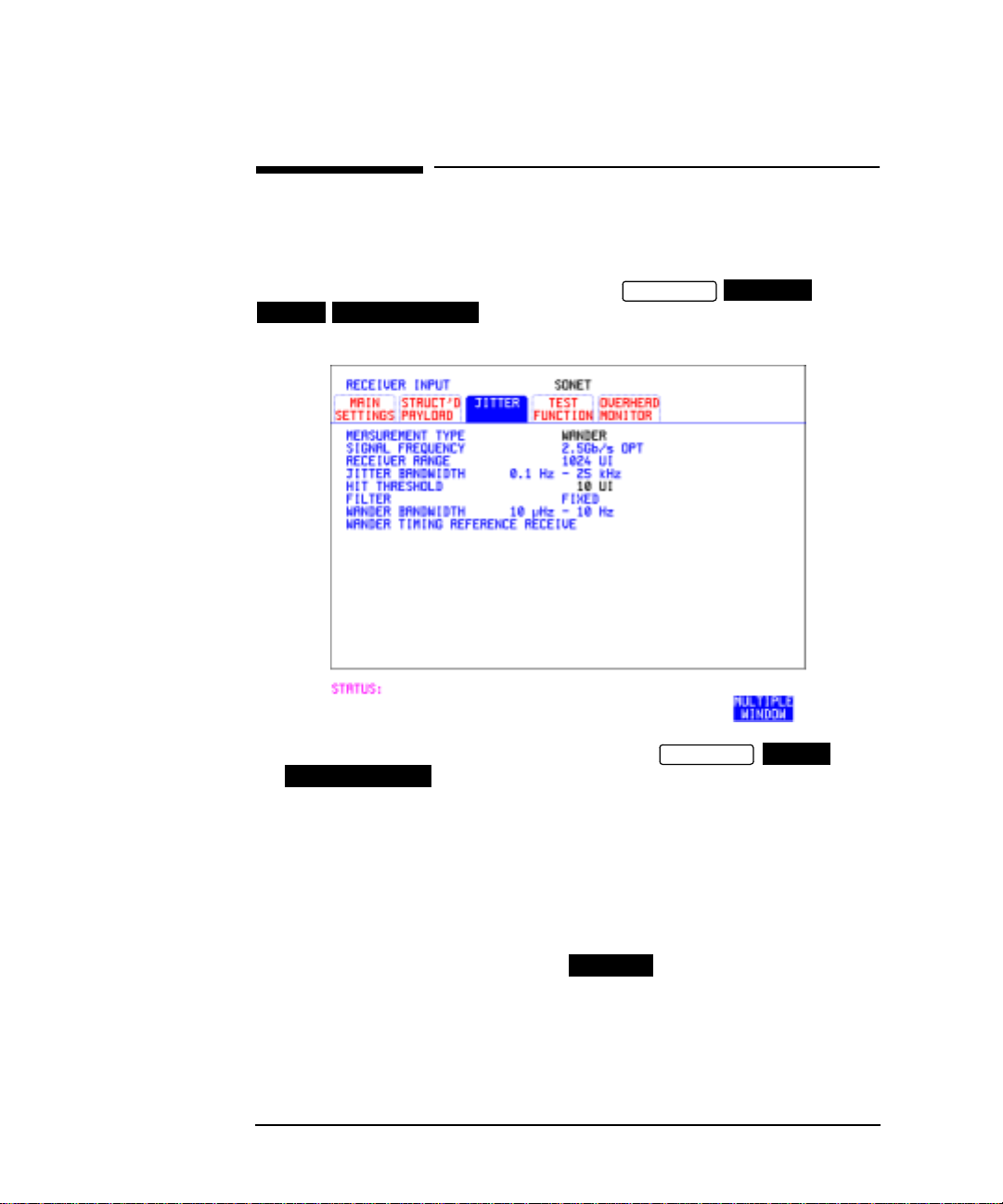
Setting Wander Receive Interface
Description: You can measure Wander at all DSn and SONET rates. An external
timing reference should be selected on the or
SONET MAIN SETTINGS
display to ensure accurate Wander results.
TRANSMIT
PDH/DSn
HOW TO: 1 Choose an external timing reference on the
MAIN SETTINGS
display. See, “Setting SONET Transmit Interface”
page 4.
2 If you intend to measure wander on a DSn signal, set up the DSn
receive interface. See, “Setting DSn Receive Interface” page 15.
3 If you intend to measure wander on a SONET signal, set up the
SONET receive interface. See, “Setting SONET Receive Interface”
page 17.
4 Choose MEASUREMENT TYPE .
WANDER
5 Choose the wander HIT THRESHOLD - if the received wander
exceeds the value chosen a wander hit is recorded.
20
TRANSMIT
SONET
Page 31

2
2 Selecting Test Features
Page 32

Selecting Test Features
Using Transmit Overhead Setup
Description You can set an overhead byte to a known static state to aid
troubleshooting, for example to quickly check for "stuck bits" in path
overhead bytes. Transport Overhead, Path Overhead, Trace Messages
and Labels can be set using this feature.
HOW TO: 1 Set up the SONET transmit interface and payload required. See
"Setting SONET Transmit Interface " page 4.
2 Choose the type of overhead to SETUP.
If OC-12 or OC-48 is chosen as the SONET interface, choose the STS3# and STS-1# you wish to set up.
If STS-3 is chosen as the SONET interface, choose the STS-1# you
wish to set up.
DEFAULT - Use to set all overhead bytes to the standard values
defined by ITU-T.
If a test function is active then the overhead byte value is determined
by the choices made in the Test Function. If APS Messages is chosen,
for example, K1K2 value is set by the APS Messages setup.
22
Page 33

Selecting Test Features
Using Transmit Overhead Setup
If (Transport Overhead) is chosen, choose the STS-1 to be
TOH
displayed.Manybytes in and areunlabeledas the
STS-1# 2 STS-1#3
other overhead functions have not yet been defined.
If is chosen, the hexadecimal value of all 81 bytes of the
STS-1# 1,2,3
STS-3 section & line overhead selected are displayed (all 324 bytes of
an OC-12 or 1,296 bytes ofanOC-48are displayed 81 bytes at a time
by selecting each STS-3 in turn). The value of the bytes can be set
using .
DECREASE DIGIT INCREASE DIGIT
If BYTE NAMES is chosen, the labels for the overhead
STS-1# 1,2,3
bytes are displayed.
3 If POH (Path Overhead) is chosen, choose the TYPE of overhead
within STS-1 under test to be setup.
J1 and J2 bytes can be set under Path Overhead or Trace Messages.
H4 byte has a choice of sequences for VT-2, VT-1.5 and VT-6 mapping:
Full Sequence - 48 byte binary sequence.
Reduced Sequence - Binary count sequence of 0 to 3 i.e. 111111(00
to 11).
COC1 Sequence - Binary count sequence of 0 to 3 i.e. 110000(00 to
11).
H4 byte is transmitted as all zero’s for 34 Mb/s and DS3.
4 If TRACE MESSAGES is chosen, see "Setting Overhead Trace
Messages " page 26.
NOTE Any bit of an overhead byte which is displayed as x or s cannot be set at
any time. All other bits can be set to 0 or 1.
TIP: You can set all overhead bytes to the default state by selecting SETUP
DEFAULT
.
You can set all overhead bytes and test functions to the default state by
recalling Stored Settings [0] on the display.
OTHER
23
Page 34

Selecting Test Features
Using Receive Overhead Monitor
Using Receive Overhead Monitor
Description When first connecting to a SONET network, a start up confidence check
can be made by viewing the behavior of all the overhead bytes. If the
SONET network shows alarm indications,somediagnosisoftheproblem
may be gained from viewing all the overhead bytes.The OVERHEAD
MONITOR display is updated once per second (once per 8000 frames)
approximately.
TIP: A snapshot of the received overhead can be logged to the chosen logging
device. See "Logging on Demand " page 110.
HOW TO: 1 Set up the receive SONET interface and payload as required. See
“Setting SONET Receive Interface” page 17.
2 Choose the type of overhead to MONITOR.
3 If (Transport Overhead) is chosen, choose the STS-3 # and
TOH
STS-1# to be displayed.
Manybytes in and areunlabeled becausethe other
overhead functions have not yet been defined.
If is chosen, the hexadecimal value of all 81 bytes of
STS-1# 1,2,3
section overhead isdisplayed(all 324 bytes of anOC-12or1,296 bytes
of an OC-48 are displayed 81 bytes at a time by selecting eachSTS-3
in turn).The value of the bytes can be set using
INCREASE DIGIT
24
STS-1# 2 STS-1#3
DECREASE DIGIT
.
Page 35

Selecting Test Features
Using Receive Overhead Monitor
If BYTE NAMES is chosen, the labels for the overhead
STS-1# 1,2,3
bytes are displayed.
4 If POH (Path Overhead) is chosen, choose the source of the overhead,
SPE or VTSPE.
J1 and J2 bytes can be monitored under Path Overhead or Trace
Messages
5 If TRACE MESSAGES is chosen, you can monitor a data message to
verify portions of the network.
If the 16 byte CRC7 message structure is detected, the 15 characters
within the message are displayed.
If the CRC7 structure is not detected in J1, the 64 byte message
format is assumed and displayed.
If the CRC7 structure is not detected for J0 or J2, all 16 bytes are
displayed.
6 If LABELS is chosen, the S1 sync status, STS path label (C2) and the
VT Path label (V5) are monitored.
7 If APS MESSAGES is chosen, choose the TOPOLOGY, (GR-
253) or (GR-1230). The K1 and K2 bits are monitored.
RING
LINEAR
TIP: If any abnormal behavior is observed on a particular path or section
overhead byte, or an associated group of bytes (3XA1,3XA2; D1 - D3), the
RECEIVE
TEST FUNCTION
display of can be
OVERHEAD CAPTURE
used to "Zoom" in on the suspect byte or bytes on a frame by frame basis.
See "Using Receive Overhead Capture " page 29.
25
Page 36

Selecting Test Features
Setting Overhead Trace Messages
Setting Overhead Trace Messages
Description You can insert a data message to verify portions of the network:
J0 verifies the section overhead.
J1 verifies the STS-1 SPE or STS-3c SPE path connection.
J2 verifies the VT SPE path connection.
HOW TO: 1 Choose the message for insertion in the chosen trace channel.
ChoosingLABELSin TRACE MESSAGESallows the settingof the S1
SYNC STATUS, STS PATH LABEL (C2) and VT PATH LABEL (V5).
26
Page 37

Selecting Test Features
Generating Overhead Sequences
Generating Overhead Sequences
Description You may insert a pattern into a functional group of overhead bytes for
testing or troubleshooting purposes.
HOW TO: 1 Set up the SONET transmit interface and payload required. See
“Setting SONET Transmit Interface” page 4.
2 Choose the type of sequence required.
SINGLE RUN - runs the sequence once and then stops.
REPEAT RUN - runs the sequence repeatedly until STOPPED is
chosen.
3 Choose the overhead type as required.
SOH- Section Overhead
LOH- Line Overhead
POH - Path Overhead
4 Choose the byte or bytes of overhead required.
5 Set up the required number of data patterns and the number of
frames in which each data pattern should appear.
Yoursequence isderivedfrom upto 5blocksof hexadecimaldata. Each
block can be transmitted in up to 64,000 frames.
The data and the number of frames are set using
INCREASE DIGIT
.
DECREASE DIGIT
27
Page 38

Selecting Test Features
Generating Overhead Sequences
6 Start the sequence by choosing .
START
NOTE When youstart the sequenceillustrated,one Out ofFramealarm andone
Loss of Frame alarm should occur every eight seconds.
28
Page 39

Selecting Test Features
Using Receive Overhead Capture
Using Receive Overhead Capture
Description Section, Line and Path overhead provide network support functions,
responding dynamically to network conditions and needs. It is therefore
useful to capture overhead activity on a frame by frame basis.
TIP: The Overhead Capture display can be logged to the chosen logging
device. See "Logging on Demand " page 110.
HOW TO: 1 Set up the receive SONET interface and payload as required. See
“Setting SONET Receive Interface” page 17.
2 Choose the overhead type as required.
SOH- Section Overhead
LOH- Line Overhead
POH- Path Overhead
3 Choose the Byte or bytes of overhead to be captured.
Choose the TRIGGER to determine the start point of the capture.
- starts immediately the capture is initiated. Can be used to
OFF
provide a frame by frame monitor of the chosen byte or bytes.
-captures activity after your specified overhead state has occurred.
ON
Can be used for transient detection from a specified expected state.
29
Page 40

Selecting Test Features
Using Receive Overhead Capture
ON NOT
- captures activityafterthe first occurrence of adeviationfrom
your specified overhead state. Can be used for transient detection from a
specified expected state.
4 Up to 16 records of overhead state are provided. Each record will
represent between 1 and 64,000 frames. A capture is started by
pressing CAPTURE and terminates when up to 16 records
START
havebeen captured.Thecapture canbe terminatedearlierby pressing
CAPTURE .
STOP
30
Page 41

Selecting Test Features
Adding Frequency Offset to SONET Signal
Adding Frequency Offset to SONET Signal
Description Frequency offset can be added to the SONET interface rate signal and to
the payload signal.
HOW TO: SONET Line Rate Offset
1 Choose the amount of frequency offset required.
You can set the Frequency Offset in the range -999 ppm to +999 ppm
in1ppm stepsusing and .
The amount of applied Frequency Offset can be varied while
measurements are taking place.
If the value of the SONET line rate offset chosen is sufficient to cause
the maximum stuff rate to be exceeded, the asynchronous payload is
offset to prevent bit errors occurring and the maximum stuff rate is
maintained. WhenFloatingByte 2 Mb/sischosen, in conjunction with
SONET line rate offset, the chosen tributary will be offset as the line
rate is offset. (No pointer movements).
DECREASE DIGIT INCREASE DIGIT
31
Page 42

Selecting Test Features
Adding Frequency Offset to SONET Signal
Tributary Offset ±100 ppm
1 Choose the amount of tributary offset required.
You can set the Offset in the range -100 ppm to +100 ppm in 1 ppm
steps using and .
DECREASE DIGIT INCREASE DIGIT
The amount of applied Frequency Offset can be varied while
measurements are taking place.
Tributary offset affects the stuff rate but does not cause pointer
movements and can be used to test mapping jitter. If the combined
valueofSONETlinerate offsetand tributaryoffset chosenis sufficient
to causethe maximum stuff ratetobe exceeded thepayloadis offset to
prevent bit errors occurring and the maximum stuff rate is
maintained.
32
Page 43

Selecting Test Features
Adding Frequency Offset to the DSn Signal
Adding Frequency Offset to the DSn Signal
Description You can add frequency offset to the interface DSn SIGNAL at all rates.
Frequency Offset can be added at preset ITU values or as User defined
values in the range ±100 ppm. The preset values change with the
SIGNAL rate chosen as shown:
DS-1 (1.544 Mb/s) + 32 ppm −32 ppm
2 Mb/s (E1) + 50 ppm −50 ppm
34 Mb/s (E3) + 20 ppm −20 ppm
DS-3 (44.736 Mb/s) + 20 ppm −20 ppm
HOW TO: 1 Choose the FREQUENCY OFFSET required.
2 If you choose USER OFFSET, you can set the frequency offset to be
between -100 ppm and +100 ppm in 1 ppm steps.
Select the field immediately below USER OFFSET and use
DECREASE DIGIT INCREASE DIGIT
frequency offset.(The amount of frequency offset can be varied while
measurements are taking place.)
, , and to set the
33
Page 44

Selecting Test Features
Setting up Signaling Bits
Setting up Signaling Bits
Description When transmitting 2.048 Mb/s signals with timeslot-16 CAS (PCM30 or
PCM30CRC) multiframing the state of A,B,C,D signaling bits can be set.
The signaling bits of all timeslots are set to the user-defined 4 bit value.
When transmitting a DS1 framed, structured signal the values of the
A,B signaling bits for D4 and SLC-96 payloads, and A,B,C,D signaling
bits for ESF payloads can be defined.
HOW TO Transmit a 2 Mb/s signal with user-defined signaling bits
DSn Operation
1 Choose on the display.
2 Choose SIGNAL and PAYLOAD TYPE or
PCM30CRC
PDH/DSn
2 Mb/s PCM30
on the display.
TRANSMIT
MAIN SETTINGS
3 If UNSTRUCTURED is chosen set the 2M CAS ABCD bits value on
the display.
MAIN SETTINGS
If STRUCTURED is chosen set the 2M CAS ABCD bits value on the
STRUCTURED SETTINGS
display.
34
Page 45

Selecting Test Features
Setting up Signaling Bits
SONET Operation
1 Choose on the display
SONET
2 Choose MAPPING or and VT
PAYLOAD or on the display.
PCM30 PCM30CRC
TRANSMIT
ASYNC 2Mb/s FL BYTE 2Mb/s
MAIN SETTINGS
3 If UNSTRUCTURED is chosen set the 2M CAS ABCD bits value on
the display.
MAIN SETTINGS
If STRUCTURED is chosen set the 2M CAS ABCD bits value on the
STRUCTURED SETTINGS
display.
HOW TO Transmit a DS1 payload signal with user-defined signaling bits
DSn Operation
1 Choose on the display.
PDH/DSn
TRANSMIT
35
Page 46

Selecting Test Features
Setting up Signaling Bits
2 Choose SIGNAL or , and PAYLOAD TYPE
on the display
MAIN SETTINGS
3 Choose TEST SIGNAL or on the
SETTINGS
DS1 DS3
56 kb/s Nx56 kb/s
display.
STRUCTURED
STRUCTURED
4 Set the A,B bits (for D4 and SLC-96) and A,B,C,D bits (for ESF) as
required.
SONET Operation
1 Choose on the display.
SONET
2 Choose MAPPING or and VT PAYLOAD
STRUCTURED MAIN SETTINGS
on the display
3 Choose TEST SIGNAL or on the
SETTINGS
display .
TRANSMIT
ASYNC DS1
56 kb/s Nx56 kb/s
DS3
STRUCTURED
4 Set the A,B bits (for D4 and SLC-96) and A,B,C,D bits (for ESF) as
required.
36
Page 47

Selecting Test Features
Setting Transmit Structured Payload/Test Signal
Setting Transmit Structured Payload/Test Signal
Description Structured DSn Payload/Test Signal settings determine the SONET
payload or the DSn test signal to be tested and set any background (non
test) conditions to prevent alarms while testing.
TIP: If you wish to set the HP 37718A transmitter and receiver to the same
Payload settings, choose .
OTHER
SETTINGS CONTROL COUPLED
HOW TO: 1 Choose the required TEST SIGNAL rate. If Nx64 kb/s or N X 56 kb/s
is chosen, see "Setting Transmit N x 64 kb/s/N x 56 kb/s Structured
Payload/Test Signal " page 40.
2 Choose the PAYLOAD framing pattern.
If TEST SIGNAL 2Mb/s is chosen is added to the
PAYLOAD menu.See "Insertingan External DSnPayload/TestSignal
" page 43.
If TEST SIGNAL DS1 is chosen is added to the menu.
See "Inserting an External DSn Payload/Test Signal " page 43.
3 Choosethetest tributaryin the structuredpayload, under34Mb, 8Mb,
2Mb, 64 kb/s or DS2, DS1, 56 kb/s.
4 Choose the PATTERN type and PRBS POLARITY.
INSERT 2 Mb/s
INSERT DS1
37
Page 48

Selecting Test Features
Setting Transmit Structured Payload/Test Signal
5 Choose the B/G PATTERN.
The B/G PATTERN in the non test 56/64 kb/s timeslots is fixed as
NUMBERED,that is,each timeslotcontains auniquenumber toallow
identification in case of routing problems.
Signaling
6 If a 2 Mb/s PAYLOAD with PCM30 or PCM30CRC framing,or 56 kb/s
or Nx56kb/s Test Signal is chosen. See, "Setting up Signaling Bits "
page 34.
38
Page 49

Selecting Test Features
Setting Receive Structured Payload/Test Signal
Setting Receive StructuredPayload/Test Signal
Description Structured DSn Payload/Test Signal settings determine the SONET
payload or the DSn test signal to be tested.
TIP: If you wish to set the HP 37718A transmitter and receiver to the same
Payload settings, choose .
OTHER
STORED SETTINGS COUPLED
HOW TO: 1 Choose the required Test Signal rate. If N x 64 kb/s or N x 56 kb/s is
chosen, see "Setting Receive N x 64 kb/s/N x 56 kb/s Structured
Payload/Test Signal " page 42.
2 Choose the Framing pattern of the PAYLOAD.
If TEST SIGNAL 2 Mb/s is chosen, is added to the
menu. See "Dropping an External Payload/Test Signal " page 46.
If TEST SIGNAL DS1 is chosen, is added to the menu.
See "Dropping an External Payload/Test Signal " page 46.
3 Choose the test tributary within the structured payload,under34Mb,
8Mb, 2Mb, 64 kb or DS2, DS1, 56 kb/s.
4 Choose the PATTERN type and PRBS polarity.
DROP 2 Mb/s
DROP DS1
39
Page 50

Selecting Test Features
Setting TransmitNx64kb/s/N x 56 kb/s Structured Payload/Test Signal
Setting Transmit N x 64 kb/s/N x 56 kb/s
Structured Payload/Test Signal
Description Wideband services such as high speed data links and LAN
interconnection require a bandwidth greater than 56/64 kb/s but less
than DS1/2 Mb/s for example 112 kb/s or 336 kb/s. These wideband
signals are sent in a DS1/2 Mb/s frame by sharing the signal between
multiple timeslots.
N x 64kb/s/N x 56 kb/s structured payload allows a test pattern to be
inserted across a number of timeslots even if the chosen timeslots are
non-contiguous.
HOW TO: 1 Choose the required Test Signal rate.
2 Choose the Framing pattern of the 2M or DS1 PAYLOAD.
3 Choose the test timeslots within the structured payload using
DESELECT ALL DESELECT SELECT
timeslot is selected, an * marks the chosen timeslot. In the example
above Timeslots 3, 5, 9, 21, 22, 23 are selected for test.
4 Choose the PATTERN type and PRBS polarity.
5 Choose the B/G PATTERN.
40
and softkeys. As each
Page 51

Selecting Test Features
Setting TransmitNx64kb/s/N x 56 kb/s Structured Payload/Test Signal
6 The B/G PATTERN in the non-test 56/64 kb/s timeslots is fixed as
NUMBERED, that is, each timeslot contains a unique identification
number.
Signaling
7 If a 2 Mb/s PAYLOAD with PCM30 or PCM30CRC framing,or 56 kb/s
or Nx56kb/s Test Signal is chosen. See, "Setting up Signaling Bits "
page 34.
41
Page 52

Selecting Test Features
Setting Receive N x 64 kb/s/N x 56 kb/s Structured Payload/Test Signal
Setting Receive N x 64 kb/s/N x 56 kb/s
Structured Payload/Test Signal
Description Wideband services such as high speed data links and LAN
interconnection require a bandwidth greater than 56/64 kb/s but less
than DS1/2 Mb/s e.g. 112 kb/s or 336 kb/s. These wideband signals are
sent in a DS1/2 Mb/s frame by sharing the signal between multiple
timeslots.
N x 64kb/s andNx56kb/s structured payload/test signal allows the test
Timeslots to be chosen for error measurement even when the Timeslots
are non contiguous.
HOW TO: 1 Choose the required Test Signal rate.
2 Choose the Framing pattern of the 2M or DS1 PAYLOAD.
3 Choose the test timeslots within the structured payload using
DESELECT ALL DESELECT SELECT
timeslot is chosen an * marks the chosen timeslot. In the example
above Timeslots 3, 5, 9, 21, 22, 23 are chosen for test.
4 Choose the PATTERN type and PRBS polarity.
42
and softkeys. As each
Page 53

Selecting Test Features
Inserting an External DSn Payload/Test Signal
Inserting an External DSn Payload/Test Signal
Description You can insert a DSn signal from external equipment into the SONET
signal, or you can insert2Mb/sor DS1 into the structured DSn signal, as
shown in the table below. DS3 and 34 Mb/s can only be inserted if
SONET is chosen as the receive interface. 2 Mb/s or DS1 can be inserted
from a structured or non-structured SONET payload and from a
structured DSn signal.
RATE Availability Option
DS3 SONET 011 Only
34Mb/s SONET 010 and 011
2Mb/s DSn & SONET 010 and 011
DS1 DSn & SONET 011 Only
HOW TO: Insert 34 Mb/s & DS3
1 Connect the external payload to the 75Ω IN port of the PDH/DSn
receive module.
2 Set up the required transmit SONET interface, and choose VT
PAYLOAD or as required.
INSERT 34 Mb/s
INSERT DS3
43
Page 54

Selecting Test Features
Inserting an External DSn Payload/Test Signal
Insert 2 Mb/s or DS1 (Unstructured SONET Payload)
1 Connect the external payload to the MUX port of the PDH/DSn
Transmit module.
If 2 Mb/s connect to 75ΩMUX port. If DS1 connect to 100Ω MUX port.
2 Set up the required transmit SONET interface, and choose VT-2 or
VT-1.5 MAPPING and VT PAYLOAD or .
INSERT 2 Mb/s
INSERT DS1
Insert 2 Mb/s or DS1 (Structured SONET Payload or Structured DSn)
1 Connect the external payload to the MUX port of the DSn Transmit
module.
If 2 Mb/s connect to 75ΩMUX port. If DS1 connect to 100Ω MUX port.
44
Page 55

Selecting Test Features
Inserting an External DSn Payload/Test Signal
Structured SONET Payload
2 Set up the required transmit SONET interface. See "Setting SONET
Transmit Interface " page 4.
3 Set up the SONET structured payload. See "Setting Transmit
Structured Payload/Test Signal " page 37.
4 Choose 2M PAYLOAD/DS1 PAYLOAD or
INSERT DS1
.
INSERT 2 Mb/s
5 Choose the LINE CODE.
Structured DSn
6 Set up, the required transmit DSn interface, See "Setting DSn
Transmit Interface " page 2.
7 Set up the DSn Test Signal interface. See "Setting Transmit
Structured Payload/Test Signal " page 37
8 Choose 2M PAYLOAD/DS1 PAYLOAD or
INSERT DS1
.
INSERT 2 Mb/s
9 Choose the LINE CODE.
45
Page 56

Selecting Test Features
Dropping an External Payload/Test Signal
Dropping an External Payload/Test Signal
Description You can drop a DSn signal from the received payload or drop 2 Mb/s or
DS1 from the structured DSn signal to external equipment as shown in
the table below. DS3 and 34 Mb/s can only be dropped if SONET is
chosen as the receive interface. 2 Mb/s or DS1 can be dropped from a
structured ornon-structuredSONETpayload and from astructuredDSn
signal.
RATE Availability Option
DS3 SONET 011 Only
34Mb/s SONET 010 and 011
2Mb/s DSn & SONET 010 and 011
DS1 DSn & SONET 011 Only
HOW TO: Drop 34 Mb/s & DS3
1 Connect the 75Ω OUT port of the DSn Transmit module to the
external equipment.
2 Set up the receive SONET interface, and choose VT PAYLOAD ,
DROP 34 Mb/s
If is chosen, choose the DS3 output level.
DROP DS3
46
or .
DROP DS3
Page 57

Selecting Test Features
Dropping an External Payload/Test Signal
Drop 2 Mb/s /DS1 (Unstructured SONET Payload)
1 Connect the DEMUX port of the DSn module to the external
equipment.
2 Set up the required receive SONET interface, and choose VT-2 or
VT-1.5 MAPPING and VT PAYLOAD or .
DROP 2 Mb/s
DROP DS1
3 Choose the required LINE CODE.
Drop 2 Mb/s/DS1 (Structured SONET Payload or Structured DSn
1 Connect the DEMUX port of the Receive DSn module to the external
equipment.
If 2 Mb/s connect to 75Ω DEMUX port. If DS1 connect to 100Ω
DEMUX port.
47
Page 58

Selecting Test Features
Dropping an External Payload/Test Signal
Structured SONET Payload
2 Set up the required receive SONET interface. See "Setting SONET
Receive Interface " page 17.
3 Set up the SONET structured payload. See "Setting Receive
Structured Payload/Test Signal " page 39.
4 Choose 2M PAYLOAD or DS1 PAYLOAD .
DROP 2 Mb/s
DROP DS1
5 Choose the LINE CODE.
Structured DSn
6 Set up, the required receive DSn interface, See "Setting DSn Receive
Interface " page 15.
7 Set upthe DSn TestSignal interface.See "Setting ReceiveStructured
Payload/Test Signal " page 39
8 Choose 2M PAYLOAD or DS1 PAYLOAD .
DROP 2 Mb/s
DROP DS1
9 Choose the LINE CODE.
48
Page 59

Selecting Test Features
Adding Errors & Alarms at the SONET Interface
Adding Errors & Alarms at the SONET
Interface
Description Errors and alarms can be added to the SONET interface signal during
testing.
HOW TO: 1 Set up the SONET transmit interface and payload required. See
"Setting SONET Transmit Interface " page 4.
2 Choose the ERROR ADD TYPE and RATE required.
Errors can be added at preset rates and at USER programmable rate.
With theexceptionof ENTIRE FRAME and A1A2FRAME,errors can
be added at ERROR ALL rate.
If CV-L errors are chosen errors can be added to trigger an APS
THRESHOLD.This takes the form ofN errors in T timeperiod. N and
T are both selectable.
3 Choose the ALARM TYPE
Errors and Alarms can be added at the same time.
49
Page 60

Selecting Test Features
Adding Errors & Alarms to the DSn Interface/DSn Payload
Adding Errors & Alarms to the DSn Interface/
DSn Payload
Description Errors and alarms can be added to the DSn interface/payload signal
during testing.
HOW TO: 1 If SONET interface is chosen, set up the SONET transmit interface
and payload required. See “Setting SONET Transmit Interface”
page 4.
If DSn interface is chosen, set up the DSn interface and payload
required. See “Setting DSn Transmit Interface” page 2.
2 Choose the ERROR ADD TYPE and RATE on the Transmitter
TEST FUNCTION
The RATEcan be selected from afixedvalue or is userprogrammable.
If you select USER PROGRAM you can select the error rate before
enabling the errors. This feature is useful for error threshold testing.
3 Choose the ALARM TYPE.
Errors and Alarms can be added at the same time.
50
display.
Page 61

Selecting Test Features
Using FEAC Codes
Using FEAC Codes
Description The third C-Bit in subframe 1 is used as a FEAC channel, where alarm
or status information from the far-end terminal can be sent back to the
near-end terminal. The channel is also used to initiate DS3 and DS1 line
loopbacks at the far-end terminal from the near-end terminal.
The codes are six digits long and are embedded in a 16 bit code word; the
format is 0XXXXXX011111111.
There are two types of code, Loopback and Alarm Status.
Loopback provides a choice of two DS1 messages and two DS3 Messages.
The DS1 Messages can be sent in ALL DS1 channels or in a SINGLE
channel. The message can be repeated up to 15 times.
Alarm Status provides 13 preset codes and a USER programmable code
function. These codes can be transmitted continuously or in bursts.
The new code is transmitted by choosing or .
HOW TO: Transmit an FEAC code
1 Choose SIGNAL and PAYLOAD TYPE on the
MAIN SETTINGS
2 Choose and ALARM TYPE .
TRANSMIT
DS3 CBIT
display.
TEST FUNCTION DS3 FEAC
When a FEAC code is not being transmitted, an all ones pattern is
transmitted.
BURST ON
TRANSMIT
51
Page 62

Selecting Test Features
Using FEAC Codes
3 Choose the FEAC CODE TYPE.
4 Choose the MESSAGE from the choices displayed.
If you chose a DS1 message an additional field to the right of the DS1
MESSAGE is displayed. Position the cursor on this field and choose
or .
ALL
If youchoose use theEDIT keys toselecta channel
from 1 to 28. Press when finished.
5 If is chosen, choose the REPEAT (TIMES) LOOP and
LOOPBACK
SINGLE CHANNEL
SINGLE CHANNEL
END EDIT
MESS, in the range 1 to 15.
6 If is chosen, choose the BURST LENGTH (TIMES).
ALARM/ STATUS
7 Choose TRANSMIT NEW CODE or to transmit the
selected FEAC message.
TIP: To View FEAC Messages
The received FEAC message can be viewed on the display.
BURST
ON
RESULTS
52
Page 63

Selecting Test Features
Setting DSn Spare Bits
Setting DSn Spare Bits
Description Certain Spare Bits will cause the occurrence of a minor alarm when
received as a logical "0".:
8 Mb/s & 34 Mb/s - FAS Bit 12
2 Mb/s - NFAS Timeslot (timeslot 0 of NFAS frame) Bit 0
HOW TO: 1 If SONET interface is chosen, set up the SONET transmit interface
and payload required. See "Setting SONET Transmit Interface "
page 4.
If DSn interface is chosen, set up the DSn transmit interface and
payload required. See "Setting DSn Transmit Interface " page 2.
2 Set the value of the spare bits required for testing.
If a BIT SEQUENCE is required, choose SEND SEQUENCE to
transmit the sequence.
ON
53
Page 64

Selecting Test Features
Adding Pointer Adjustments
Adding Pointer Adjustments
Description The transmitted SPE or VT pointer value can be adjusted for testing
purposes.
HOW TO: 1 Set up the SONET transmit interface and payload required. See
"Setting SONET Transmit Interface " page 4.
2 Choose the POINTER TYPE.
3 Choose the ADJUSTMENT TYPE required.
BURST - You determine the size of the burst by the number of
PLACES chosen. If, for example, you choose 5 PLACES the pointer
value will be stepped 5 times in unit steps e.g. 0 (start value), 1, 2, 3,
4, 5 (final value). The interval between steps is as follows:
For AU and TU-3, the minimum spacing between adjustments is
500 us. For VT the minimum spacing between adjustments is 2 ms.
Choose ADJUST POINTER [ON] to add the chosen burst.
NEW POINTER- Youcanchoose apointer value inthe range 0to 782
with or without a New Data Flag.
The current pointer value is displayed for information purposes.
Choose ADJUST POINTER [ON] to transmit the new pointer value.
54
Page 65

Selecting Test Features
Adding Pointer Adjustments
OFFSET - You can frequency offset the line rate or the SPE/VT rate,
relative toeachother,thus producing pointer movements.If you offset
the SPE pointer, an 87:3 sequence of pointer movements is generated.
The available configurations are listed in the following table.
If you are currently adding Frequency Offset to the SONET interface
or payload, pointer OFFSET is not available.
Pointer Type Line Rate SPE Rate VT Rate
SPE Constant Offset Tracks AU Payload
SPE Offset Constant Constant
VT Constant Constant Offset
VT Offset Tracks Line Rate Constant
T1.105/GR-253 - Provides pointer movements according to T1.105 and
GR-253:
4 Choose the T1.105/GR-253 ADJUSTMENT TYPE.
5 ChoosethePOLARITY,INTERVAL andPATTERN (whereapplicable)
for the selected sequence.
6 Choose POINTERSEQUENCES to generate the selected
G.783 sequence and to stop the pointer sequences.
STOP INIT
START INIT
T1.105/GR-253 Pointer Sequences Explained
In addition to the BURST, NEW POINTER and OFFSET pointer
movements described, the HP 37718A can also generate pointer
sequences (pointer movements) according to T1.105.03 and GR-253.
Before running a pointer sequence you can elect to run an initialization
sequence, followed by a cool down period, and then run the chosen
sequence. This is selected using the START INIT softkey shown in the
display on the previous page. Initialized pointer sequences are made up
of three periods: the Initialization Period, the Cool Down Period, and the
Sequence (Measurement) Period, an example is given in the following
figure:
55
Page 66

Selecting Test Features
Adding Pointer Adjustments
Non Periodic Sequence
Periodic Sequence
Initialization Sequence
Initialization
No Pointer Activity
Continuous Sequence
Cool Down
Sequence
Time
Measurement
Period
Note: SINGLE (A1), BURST (A2) and PHASE TRANSIENT(A3) are Non
Periodic Sequences.
Initialization Period
ForSINGLEA1,BURSTA2and PHASE TRANSIENT A3 sequences the
initialization sequence consists of 60 seconds of pointer adjustments
applied at a rate of 2 adjustments per second and in the same direction
as the specified pointer sequence.
Cool Down Period
A period following the initialization periodwhichforSINGLE e), BURST
f) and PHASE TRANSIENT sequences is 30 seconds long when no
pointer activity is present.
Sequence (Measurement) Period
The period following the Cool Down period where the specified pointer
sequence runs continuously.
Periodic Test Sequences
For periodic test sequences (for example PERIODIC ADD) both the 60
second initialization and 30 second cool down periods consist of the same
sequence as used for the subsequent measurement sequence. If the
product of the period T and the selected Optional background pattern
(87+3 or 26+1) exceeds 60 seconds then the longer period is used for the
initialization. For example, if T is set for 10 seconds then the
initialization period may be extended to 900 seconds.
The HP 37718A displays a message indicating which phase
(initialization, cool down or measurement) the transmitter is currently
generating.
56
Page 67

Selecting Test Features
Adding Pointer Adjustments
NOTE The following conditions apply for pointer sequence generation:
The sequences can onlybeappliedto the SPE pointer when the SPE does
not contain a VT structure, otherwise it is applied to the VT pointer.
Pointer sequence generation is not available when a frequency offset is
being applied to the Line Rate.
The following figure gives an example of a T1.105/GR-253, 87-3 Pointer
Sequence.
T1.105 A4 and A5, 87-3 Pattern
No Pointer
Adjustment
Pointer Adjustment
Start of Next
87-3 Pattern
Pointer Sequence
T1.105 A1 SINGLE
GR-253 5-29
T1.105 A2 BURST OF 3
GR-253 5-30
87
3
An Example of a Pointer Sequence
Description
Periodic Single adjustments, all of the same polarity which is
selectable. Separation between pointer adjustments is fixed at
approximately 30 seconds.
Periodic bursts of 3 adjustments, all of the same polarity which is
selectable. The interval between bursts is fixed at approximately 30
seconds. The interval between adjustments within a burst is set to
the minimum.
57
Page 68

Selecting Test Features
Adding Pointer Adjustments
Pointer Sequence
T1.105 A3 PHASE
TRANSIENT
GR-253 5031
T1.105 A4 PERIODIC
NORMAL (87-3 Pattern)
GR-253 5-33(b)
T1.105 A4 PERIODIC
NORMAL (Continuous
Pattern) GR-253 5-34(b)
GR-253 5-32(b)
PERIODIC NORMAL (26-1
Pattern)
T1.105 A5 PERIODIC ADD
(87-3 Pattern)
GR-253 5-33(c)
Phase transient pointer adjustment burst test sequence. All
adjustments are of the same polarity, which is selectable. The
interval between bursts is fixed at 30 seconds. Each burst consists
of 7 pointer movement. The first 3 in each burst are 0.25 s apart,
and the interval between the 3 and 4 movement, and each
remaining movement 0.5 seconds.
An 87-3 pattern is selected. The sequence pattern is 87 pointer
movements followed by 3 missing pointer movements. Pointer
polarity is selectable and the time interval between pointer
adjustments settable.
Provides a continuous sequence of pointer adjustments. The
polarity of the adjustments is selectable, and the time interval
between adjustments can be set (see Note 1).
This selection is only available if you have selected VT1.5 mapping.
The sequence pattern is 26 pointer movements followed by 1
missing pointer movement. Pointer polarity is selectable and the
time interval between pointer adjustments programmable to 200
ms, 500 ms, 1 s, 2 s, 5 s or 10 seconds.
An 87-3 pattern is selected. The sequence pattern is 87 pointer
movements followedby3missing pointer movements with anadded
pointer movement after the 43rd pointer. The spacing between the
added adjustment and the previous adjustment is set to the
minimum. Pointerpolarity is selectable. Thetimeinterval between
pointer adjustments can be set (see Note 1). Added adjustments
occur every 30 seconds or every repeat of the 87-3 pattern,
whichever is longer.
Description
T1.105 A5 PERIODIC ADD
(Continuous Pattern)
GR-253 5-34(c)
Periodic Single adjustments, with selectable polarity and added
adjustment (1 extra). The spacing between the added adjustment
and the previous adjustment is set to the minimum, (see Note 2).
The time interval between pointer adjustments can be set (see Note
1). Added adjustments occur every 30 seconds or every repeat of the
87-3 pattern, whichever is longer.
58
Page 69

Selecting Test Features
Adding Pointer Adjustments
Pointer Sequence
GR-253 5-32(c)
PERIODIC ADD (26-1
Pattern)
T1.105 A5 PERIODIC
CANCEL (87-3 pattern)
GR-253 5-33(d)
T1.105 A5 PERIODIC
CANCEL (Continuous
Pattern)
GR-253 5-34(d)
GR-253 5-32(d)
PERIODIC CANCEL (26-1
pattern)
This selection is only available if you have selected VT1.5 mapping.
The sequence pattern is 26 pointer movements followed by 1
missing pointer movement. Theaddedadjustmentoccurs 2 ms after
the 13th pointer adjustment. Pointer polarity is selectable and the
time interval between pointer adjustments programmable to 200
ms, 500 ms, 1 s, 2 s, 5 s or 10 s. Added adjustments occur every 30
seconds or every repeat of the 26-1 pattern, whichever is longer.
An 87-3 pattern is selected. The sequence pattern is 87 pointer
movements followed by 3 missing pointer movements with a
cancelled pointer movement at the 87th pointer. Pointer polarity is
selectable, and the time interval between pointer adjustments can
be set (see Note1).Cancelledadjustments occur every 30 seconds or
every repeat of the 87-3 pattern, whichever is longer.
Periodic Single adjustments, with selectable polarity and cancelled
adjustment (1 less). The time interval between pointer adjustments
can be set (see Note 1). Cancelled adjustments occur every 30
seconds or every repeat of the 87-3 pattern, whichever is longer.
This selection is only available if you have selected VT1.5 mapping.
The sequence pattern is 26 pointer movements followed by 1
missing pointer movement. The cancelled adjustment is the 26th
pointer adjustment, that is the one before the regular gap of 1.
Pointer polarity is selectable and the time interval between pointer
adjustments programmable to 200 ms, 500 ms, 1 s, 2 s, 5 s or 10s.
Cancelled adjustments occur every30secondsor every repeat of the
26-1 pattern, whichever is longer.
Description
NOTE For SPE pointers the sequence interval is selectable from 7.5 ms, 10, 20,
30, 34 ms; 40 to 100 ms in 10 ms steps, 100 to 1000 ms in 100 ms steps
1, 2, 5, 10 seconds.
ForVTpointers the sequence interval is selectable from: 200 ms, 500 ms,
1, 2, 5 and 10 seconds.
ForSPEpointerstheminimumspacingbetweenadjustmentsis500us.
For VT pointers the minimum spacing between adjustments is 2 ms.
59
Page 70

Selecting Test Features
Adding Pointer Adjustments
Table 1 Pointer Sequences Available with Selected Mapping
MAPPING
POINTER SEQUENCE
A1 SINGLE
A2 BURST OF 3
A3 PHASE TRANSIENT
A4 PERIODIC NORMAL(87-3)
A4 PERIODIC NORMAL (Continuous)
PERIODIC NORMAL (26-1)
A5 PERIODIC ADD (87-3)
A5 PERIODIC ADD (Continuous)
PERIODIC ADD (26-1)
A5 PERIODIC CANCEL (g) 87-3
A5 PERIODIC CANCEL (Continuous)
PERIODIC CANCEL 26-1
SPE VT6, VT2 VT1.5
✓✓✓
✓✓✓
✓✓✓
✓
✓✓✓
✓
✓
✓✓✓
✓
✓
✓✓✓
✓
60
Page 71

Selecting Test Features
Using Pointer Graph Test Function
Using Pointer Graph Test Function
Pointer Graph shows the relative offset during the measurement period.
This allows the time relationship of SPE or VT pointer movements to be
observed. Up to4days of storage allows long termeffectssuchas Wander
to be observed. If an alarm occursduringthemeasurementperiod, a new
graph starts at the centre of the display (offset zero) after recovery from
the alarm.
TIP: The Pointer Graph display can be logged to the chosen logging device.
See "Logging on Demand " page 110.
TIP: The graph can also beviewedonthe display
at the end of the measurement.
HOW TO: 1 Set up the receive SONET interface and payload as required. See
“Setting SONET Receive Interface” page 17.
2 Choose the CAPTURE INTERVAL required.
The capture interval determines the time between captures. Low
values of capture interval should be chosen when a high degree of
pointer movements is expected.
High values ofcaptureinterval should be chosen when alowdegree of
pointer movements is expected, for example Wander over 1 day, use 5
MINS and Wander over 4 days, use 20 MINS.
RESULTS
SONET RESULTS
61
Page 72

Selecting Test Features
Using Pointer Graph Test Function
If, during a long term measurement (4 days), an event occurs at a
particular time each day, a short term measurement can be made at
the identified time to gain more detail of the event.
3 Choose the POINTER UNDER TEST type.
4 Press to start the measurement.
RUN/STOP
TIP: If the event occurs outside normal working hours, a Timed Start
measurement can be made.
1 SEC - display window of approximately 5 minutes.
5 SECS - display window of approximately 25 minutes.
20 SECS - display window of approximately 1 hour 40 minutes.
1 MIN - display window of approximately 5 hours.
5 MIN - display window of approximately 1 day.
20 MIN - display window of approximately 4 days.
62
Page 73

Selecting Test Features
Stressing Optical Clock Recovery Circuits
Stressing Optical Clock Recovery
Circuits
Description Ideally clock recovery circuits in the network equipment optical
interfaces should recover the clock even in the presence of long strings of
0’s. You can check the performance of your optical clock recovery circuits
using the STRESS TEST test function.
The stress test is available at all optical rates.
HOW TO: 1 Set up the SONET transmit interface and payload required. See
"Setting SONET Transmit Interface " page 4.
Choose the required STRESSING PATTERN.
The G.958 test pattern consists of 7 consecutive blocks of data as
follows:
the first row of section overhead bytes, ALL ONES, a PRBS, the first
row of section overhead bytes,ALL ZEROS, a PRBS and the first row
of section overhead bytes.
2 If you choose ALL ONES or ALL ZEROS as the stressing pattern,
choose the number of bytes in the BLOCK LENGTH.
63
Page 74

Selecting Test Features
Generating Automatic Protection Switch Messages
Generating Automatic Protection
Switch Messages
Description You can program the K1 and K2 bytes to exercise the APS functions for
Both LINEAR (ITU-T G.783) and RING (ITU-T G.841) topologies.
HOW TO: 1 Set up the SONET transmit interface and payload required. See
"Setting SONET Transmit Interface " page 4.
2 Choose the ITU-T TOPOLOGY required.
3 Choose the message to be transmitted.
If LINEAR topology is chosen, choose the CHANNEL, the BRIDGED
CHANNEL NO., the ARCHITECTURE and the RESERVED bits you
require.
If RING topology is chosen, choosetheDESTINATIONNODE ID, the
SOURCE NODE ID, the type of PATH and the status code (K2 Bits 6>8)
The currentTXand RX, K1 and K2,valuesare displayed for reference
only.
4 Choose to transmit the new K1/K2 values.
64
DOWNLOAD
Page 75

Selecting Test Features
Inserting & Dropping Data Communications Channel
Inserting & Dropping Data
Communications Channel
Description The Data Communications Channel (DCC) of the regenerator and
multiplexer section overhead can be verified by protocol testing. The
Insert and Drop capability provides access to the DCC via the RS-449
connector on the front panel of the Multirate Analyser module.
DCC INSERT is available on the , ,
display.
DCC DROP is available on the
display.
HOW TO: 1 Connect the Protocol Analyzer to the DCC port on the Multirate
Analyzer module.
2 Choose the required DCC.
TRANSMIT
RECEIVE
SONET TEST FUNCTION
SONET TEST FUNCTION
65
Page 76

Selecting Test Features
Inserting & Dropping Data Communications Channel
66
Page 77

3
3 Making Measurements
Page 78

Making Measurements
Using Overhead BER Test Function
Using Overhead BER Test Function
Description You can perform a Bit Error Rate test on chosen bytes of the section, line
and path overhead bytes.
You can access the transmit Overhead BER on the
TEST FUNCTION
display.
TRANSMIT
SONET
HOW TO: 1 Set up the SONET transmit interface and payload required. See
"Setting SONET Transmit Interface " page 4.
2 Set up the receive SONET interface and payload as required. See
"Setting SONET Receive Interface " page 17.
3 Choose the overhead byte to be tested on the
TEST FUNCTION
display.
RECEIVE
SONET
4 Choose the overhead byte to be tested on the
TEST FUNCTION
5 Press to start the test.
RUN/STOP
display.
6 The PRBS pattern can be errored by pressing .
TRANSMIT
SINGLE
68
SONET
Page 79

Making Measurements
Test Timing
Test Timing
Description There are two aspects to test timing:
• Error results may be displayed as short term or cumulative over the
measurement period.If short term error measurements are required,
the short term period may be selected.
• The period of the test may be defined or controlled manually.
HOW TO: 1 Choose on the display.
TIMING CONTROL
RESULTS
2 Choose the SHORT TERM PERIOD to the timing required for short
term results.
3 Choose the type of TEST TIMING required:
For manual control with choose .
RUN/STOP
MANUAL
For a single timed measurement period started with ,
choose and choose the Test duration.
SINGLE
Fora timed period starting at a specified time, choose , choose
the Test duration and the test START date and time.
RUN/STOP
TIMED
69
Page 80

Making Measurements
Making SONET Analysis Measurements
MakingSONETAnalysisMeasurements
Description G.826, M.2101, M.2110 and M.2120 analysis results are provided for all
relevant SONET error sources.
In addition the following results are provided:
Cumulative error count and error ratio
Short Term error count and error ratio
Alarm Seconds
Frequency
Pointer Values
Pointer Graph
HOW TO: 1 Set up the receive SONET interface and payload required. See
"Setting SONET Receive Interface " page 17.
2 If required set up the SONET transmit interface and payload. See
"Setting SONET Transmit Interface " page 4.
3 Press to start the measurement.
4 You can view the analysis results on the
TIP: The measurement will not be affected if you switchbetweenthedifferent
results provided.
70
RUN/STOP
ANALYSIS
display.
RESULTS
SONET
Page 81

Making Measurements
Making DSn Analysis Measurements
Making DSn Analysis Measurements
Description G.821, G.826, M.2100, M.2110 and M.2120 analysis results are provided
for all relevant DSn and DSn Payload error sources.
In addition the following results are provided:
Cumulative error count and error ratio
Short Term error count and error ratio
Alarm Seconds
SIG/BIT Monitor. See "Monitoring Signaling Bits " page 76.
HOW TO: 1 If SONET is chosen as the interface, set up the Receive Interface and
Payloadrequired. See "Setting SONETReceive Interface" page 17. If
required set up the Transmit Interface and Payload. See "Setting
SONET Transmit Interface " page 4.
2 If DSn ischosenas the interface, set up the DSnreceiveinterface. See
"Setting DSn Receive Interface " page 15. If required set up the DSn
transmit interface. See "Setting DSn Transmit Interface " page 2.
3 Press to start the measurement.
RUN/STOP
4 If SONET is chosenasthe interface, you can view the analysis results
on the display
RESULTS
DSn PAYLOAD
ERROR ANALYSIS
If DSn is chosen as the interface, you can view the analysis results on
the display.
RESULTS
DSn ERROR ANALYSIS
71
Page 82

Making Measurements
Measuring Frequency
Measuring Frequency
Description The signal frequencyandthe amount of offset from thestandardrate can
be measured to give an indication of probability of errors.
HOW TO: 1 Connect the signal to be measured to the IN port of the DSN Receive
module or the IN port of the Multirate Analyzer module (SONET
electrical) or the IN port of the Optical Interface module (SONET
optical).
NOTE Frequency measurement is always available even if test timing is off.
72
Page 83

Making Measurements
Measuring Optical Power
Measuring Optical Power
Description Optical power measurement can be performed on the SONET signal
connected to the Optical module IN port.
HOW TO: 1 Connect the SONET optical signal to the IN port of the Optical
Interface module.
2 Choose the received input signal rate on the
display.
NOTE Optical power measurement is always available even if test timing is off.
RECEIVE
SONET
73
Page 84

Making Measurements
Measuring Round Trip Delay
Measuring Round Trip Delay
Description: The time taken for voice traffic to pass through the network is very
important. Excessive delay can make speech difficult to understand.
The Round Trip Delay feature of the HP 37718A measures the delay in a
64 kb/s timeslot.
A test pattern is transmitted in the 64 kb/s timeslot and a timer is set
running. A loopback is applied to the network equipment to return the
test signal. The received pattern stops the timer and the Round Trip
Delay is calculated.
NOTE You can only measure Round Trip Delayona64kb/stestsignalobtained
from a 34 Mb/s or 2 Mb/s DSn interface or DSn payload signal.
HOW TO: 1 If measuringonan SONET interface, set uptheSONET transmit and
receive interfaces and payloads required. See "Setting SONET
Transmit Interface " page 4 and “Setting SONET Receive Interface”
page 17.
2 If measuring on a DSn interface, set up the DSn transmit and receive
interfaces and payloads required. See “Setting DSn Transmit
Interface” page 2 and “Setting DSn Receive Interface” page 15.
3 Connect a loopback to the network equipment.
74
Page 85

Making Measurements
Measuring Round Trip Delay
4 Choose ACTION to start the measurement.
ON
If measuring on an SONET interface, the results are available on the
RESULTS
DSn PAYLOAD
display.
If measuring on a DSn interface, the results are available on the
display.
RESULTS
DSn
The Round Trip delay measurement range is up to 2 seconds. The
resolution varies with the received interface signal rate:
2 Mb/s 1 microsecond
34 Mb/s 110 microseconds
STS-1,STS-3 0.5 milliseconds
OC-12, OC-48 0.5 milliseconds
75
Page 86

Making Measurements
Monitoring Signaling Bits
Monitoring Signaling Bits
Description The HP 37718A receiver can be used to monitor the state of signaling
bits in received 2 Mb/s signals with timeslot-16 CAS multiframing
(PCM30 or PCM30CRC) and DS1 structured signals.
2.048 Mb/s
Results
DS1 Results D4 and SLC-96 payloads
For 2 Mb/s signals with timeslot-16 CAS multiframing a table showing
the values of A,B,C,D signaling bits in all 30 channels is given.
A table simultaneously showing the state of the A and B signaling bits in
the 6th and 12th frames of a superframe is given. Each frame contains
24 timeslots. In SLC-96 mode A and B choices are 0, 1 or alternating. If
you set bit A or B to alternate, the displayed bit changes to an A, to
indicate that the bit is alternating from 1 to 0. The same signaling is
transmitted in all channels.
ESF Payloads
A table simultaneously showing the state of the A, B, C and D signaling
bits in the 6th, 12th, 18th and 24th frames of a superframe is given.
Each frame contains 24 timeslots.
76
Page 87

Making Measurements
Measuring Service Disruption Time
Measuring Service Disruption Time
Description: Protection switching ensures that data integrity is maintained and
revenue protectedwhenequipment failure occurs. The speedofoperation
of the protection switch can be measured.
The sequence of events involved in measuring the switching time is:
• Pattern Synchronization (no errors) is achieved.
• The protection switch is invoked - Pattern Synchronization is lost.
• The standby line is in place - Pattern Synchronization is regained.
The time interval between pattern sync loss and pattern sync gain is a
measure of the disruption of service due to protection switching.
Service Disruption is chosen on the page except for the
following configuration:
• If you choose a DSn or SONET interface and an ANSI (DS1, DS3)
framed, unstructured payload you must select Service Disruption on
the Transmitter and Receiver display.
RESULTS
TEST FUNCTION
77
Page 88

Making Measurements
Measuring Service Disruption Time
NOTE At DS1 and DS3 Service Disruption results are only available for
Unstructured payloads.
Error Burst Definition
Error bursts start and finish with an error. Bursts of less than 10 us are
ignored.
Bursts are assumed to have completed when >2000ms elapses without
any errors being received.
The longest burst detected is 2 seconds.
Accuracy
300 us for DS1, 2Mb/s and 34Mb/s signals.
60 us for DS3 signals.
HOW TO: 1 If interfacing at SONET set up the SONET transmit and receive
interfaces and payloads required. See "Setting SONET Transmit
Interface " page 4 and "Setting SONET Receive Interface " page 17.
2 If interfacing at DSn set up the DSn transmit and receive interfaces
and payloads as required. See "Setting DSn Transmit Interface "
page 2 and "Setting DSn Receive Interface " page 15.
3 If you choose a DS1 or DS3 framed unstructured payload, choose
SERVICE DISRUPT
on the and
TRANSMIT
RECEIVE
TEST FUNCTION
displays.
78
Page 89

Making Measurements
Measuring Service Disruption Time
4 Press to start the measurement.
RUN/STOP
5 Invoke the protection switch.
6 View the results on the display.
RESULTS
SRVC DISRUPT
Results Displayed
LONGEST - Longest burst of errors during measurement.
SHORTEST - Shortest burst of errors during measurement.
LAST - Length of last burst of errors detected during measurement.
79
Page 90

Making Measurements
Performing a SONET Tributary Scan
Performing a SONET Tributary Scan
Description Tributary Scan tests each tributary for error free operation and no
occurrence of Pattern Loss. A failure is indicated by highlighting the
tributary in which the failure occurred. The
MAIN SETTINGS
, mapping setup determines the tributary structure.
TRANSMIT
The HP 37718A will configure the Transmitter to the Receiver and the
PATTERN is forced to the payload it will fill.
TIP: The SONET Tributary Scan display can be logged to the chosen logging
device. See "Logging on Demand " page 110.
SONET
HOW TO: 1 Set up the transmit and receive SONET interfaces and payload as
required. See "Setting SONET Transmit Interface " page 4 and
"Setting SONET Receive Interface " page 17.
2 Choose the required BIT ERROR THRESHOLD.
This determines the error rate above which a failure is declared.
3 Choose the required TEST TIMING.
The valueyouchoose is the testtimefor each individual tributary and
not the total test time.
For example, 28 VT-1.5 tributaries in an STS-1 SPE - the time taken
to complete the Tributary Scan will be 28 X TEST TIMING choice.
80
Page 91

Making Measurements
Performing a SONET Tributary Scan
4 The Tributary Scan results can be viewed on the
SONET TRIBSCAN
The Scancanbe started on the
display or the display by choosing START.
If the Scan is started on the
display, the HP 37718A changes to the display.
display.
RESULTS
TRANSMIT
TRANSMIT
SONET TEST FUNCTION
RESULTS
If a single path, for example, MAPPING is chosen, then
Tributary Scan is disabled.
NOTE The keyboard is locked during tributary scan.
RESULTS
SONET TEST FUNCTION
STS-3c SPE
81
Page 92

Making Measurements
Performing an SONET Alarm Scan
Performing an SONET Alarm Scan
Description SONET Alarm Scan tests each channel for alarm free operation and
identifies and indicates any Unequipped channels.
You can configure the Scan to check for the occurrence of any Path layer
CV errors above a chosen threshold.
The channel in which an alarm occurred is highlighted if any of the
following alarms occur:
STS SPE: LOP-P, RDI-P, AIS-P,
VT-1.5: LOP-P, AIS-P, RDI-P, H4 LOM, LOP-V, AIS-V, RDI-V
TIP: The SONET Alarm Scan display can be logged to the chosen logging
device. See "Logging on Demand " page 110.
HOW TO: 1 Set up the receive SONET interface and payload as required. See
“Setting SONET Receive Interface” page 17.
2 Choose on the display.
SONET ALM SCAN
RESULTS
3 Choose AUTO or RX SETTINGS.
RX SETTINGS: The scan checks the structure set on the
SONET
display.
RECEIVE
AUTO: The scan checks the structure being received. This can be
particularly useful when receiving mixed payloads.
4 Choose the CV error threshold.
5 Choose to start the Alarm Scan.
START
82
Page 93

Making Measurements
Performing a DSn Alarm Scan
Performing a DSn Alarm Scan
Description DSn Alarm Scan tests each channel for the following alarms:
Frame Loss
RAI
AIS
The channel in which an alarm occurs is highlighted.
HOW TO: 1 Setupthe receiveDSn interfaceasrequired. See“Setting DSnReceive
Interface” page 15.
2 Choose to start the Alarm Scan.
ON
83
Page 94

Making Measurements
Measuring Jitter
Measuring Jitter
Description: Jitter and error measurements are made simultaneously when a jitter
option is fitted. The measurements are made on the normal input to the
DSn or SONET receiver and the interface selections are the normal DSn
or SONET Receiver selections.
Cumulative and Short Term results of Jitter Amplitude and Jitter Hits
are provided on the display.
Graph and Text results for Jitter Transfer and Jitter Tolerance are also
provided.
RESULTS
JITTER
HOW TO: 1 If measuring Jitter on a DSn signal, set up the receive DSn interface
and the receive Jitter interface. See “Setting DSn Receive Interface”
page 15 and “Setting Jitter Receive Interface” page 18.
2 If measuring Jitter on an SONET signal, set up the receive SONET
interfaceandthe receiveJitterinterface. See“Setting SONET Receive
Interface” page 17 and “Setting Jitter Receive Interface” page 18.
84
Page 95

Making Measurements
Measuring Jitter
3 If performing a Jitter Tolerance measurement, See “Measuring Jitter
Tolerance” page 89.
If performing a Jitter Transfer measurement, See “Measuring Jitter
Transfer” page 92.
4 Press to start the measurement.
RUN/STOP
5 You can view the Jitter hits and Amplitude results on the
JITTER
display.
RESULTS
85
Page 96

Making Measurements
Measuring Extended Jitter
Measuring Extended Jitter
Description: Extended jitter measurements are made in a jitter bandwidth of 0.1 Hz
to 25 kHz. These measurements are made at the upper end of the
standard wander frequency range and the lower end of the standard
jitter frequency range.
When is chosen Jitter results are provided. Cumulative and
Short Term results of Jitter Amplitude and Jitter Hits are provided on
the display.
HOW TO: 1 If measuring Extended Jitter on a DSn signal, set up the receive DSn
EXTENDED
RESULTS
interface and the receive Jitter interface. See “Setting DSn Receive
Interface” page 15 and "Setting Extended Jitter Receive Interface "
page 19.
JITTER
2 If measuring Extended Jitter on an SONET signal, set up the receive
SONETinterfaceand thereceive Jitterinterface. See“Setting SONET
Receive Interface” page 17 and "Setting Extended Jitter Receive
Interface " page 19.
3 Press to start the measurement.
86
RUN/STOP
Page 97

Making Measurements
Measuring Wander
Measuring Wander
Description: Accurate Wander measurements require a Wander reference derived
from the SONET Clock module. Wander results are displayed in UI and
nanoseconds and Jitter Amplitude and Jitter Hits results are available.
When wander is measured at 2 Mb/s, Estimated Bit and Frame slips are
calculated and a Bar Graph shows the cumulative Wander over the
measurement period.
HOW TO: Make the Measurement
1 To obtain the Wander reference from the DSn transmitter connect
REF OUT on the SONET Clock module to REF IN on the DSn Jitter
TX module. Choose SIGNAL on the
MAIN SETTINGS
display, choose CLOCK SYNC and
choose the SOURCE required from the menu. See “Setting DSn
Transmit Interface” page 2.
2 To obtain the Wander reference from the SONET transmitter choose
the required reference from the CLOCK menu on the
MAIN SETTINGS
display. See, “Setting SONET Transmit Interface” page 4.
3 If measuring wander at a DSn rate set up the DSn receive interface.
See, “Setting DSn Receive Interface” page 15.
2 Mb/s
TRANSMIT
WANDER REF IN
TRANSMIT
PDH/DSn
SONET
87
Page 98

Making Measurements
Measuring Wander
4 If measuring wander at a SONET rate set up the SONET receive
interface. See, “Setting SONET Receive Interface” page 17.
5 Choose MEASUREMENT TYPE .
6 ChoosetheWANDERHIT THRESHOLDlevel- ifthe receivedwander
exceeds the value chosen a wander hit is recorded.
7 Press to start the measurement.
RUN/STOP
HOW TO: View the Results
1 Choose on the display and choose thedisplay units
WANDER
required:
TIME displays the wander results in nanoseconds.
UI displays the wander results in Unit Intervals
If you are measuring wander at 2 Mb/s Estimated Bit slips and
Estimated Frame slip results are provided and a choice is
added to the menu.
If is chosen the cumulative wander results are displayed in
GRAPH
graphical form. The Graphs are additive and in the example shown
above the Wander is -76.5 BITS.
WANDER
RESULTS
GRAPH
NOTE Estimated Bit Slips signify the slippage from the start of the
measurement.
One Estimated Frame Slip corresponds to 256 Bit Slips.
Implied Frequency Offset is calculated from the Wander results.
88
Page 99

Making Measurements
Measuring Jitter Tolerance
Measuring Jitter Tolerance
Description: The jitter auto tolerance feature provides jitter tolerance measurements
within the relevant ITU-T mask, G.823 for DSn, G.958, G.825 and
Bellcore GR-253 for SONET.
Jitter is generated at a range of frequencies within the mask and an
error measurement is made. If no errors occur (PASS), the jitter
amplitude at that frequency point is increased until errors occur (FAIL)
or the maximum jitter amplitude is reached. The highest jitter
amplitude at which PASS occurs is plotted on the graph as the Jitter
Tolerance for that jitter frequency.
TIP: The transmitter and receiver can be set to different rates to allowtesting
across multiplexers,for example transmitter set toSTS-3with embedded
DS-3 and receiver set to DS-3.
HOW TO: Make the Measurement
1 Ifyouareperformingjitter toleranceon theDSn signal,setup theDSn
transmitandreceiveinterfaces.See“SettingDSn TransmitInterface”
page 2 and “Setting DSn Receive Interface” page 15.
89
Page 100

Making Measurements
Measuring Jitter Tolerance
2 If you are performing jitter toleranceontheSONET signal, set up the
SONET transmit and receive interfaces. See “Setting SONET
Transmit Interface” page 4 and “Setting SONET Receive Interface”
page 17.
3 If SONET is chosen as the interface, choose the SONET MASK.
TYPE A masks as per ITU-T G.958havegood jitter tolerance and the
mask corner points are modified to compensate.
TYPE B masks as per ITU-T G.958 have poorer jitter tolerance but a
narrower jitter transfer function and the mask corner points are
modified to compensate.
4 Choose the required test PATTERN.
5 Choose the NUMBER OF POINTSatwhichjitter is transmitted (3 to
55)
6 Choose the DWELL TIME - the time jitter is generated at each jitter
frequency point (1 to 99.9 seconds).
7 Choose the DELAY TIME - the time delay between the jitter
frequency/amplitude being applied and the error measurement being
made. This allows the network equipment to settle as jitter frequency
is changed. (0 to 99.9 seconds).
8 Choose the ERROR THRESHOLD.
If ANY ERRORS is chosen, any BIP or BIT error will result in a FAIL.
If BIT ERRORS is chosen, choose a value between 1 and 1,000,000 to
determine the bit error threshold for the jitter tolerance PASS/FAIL
decision.
BER>= shows the bit error ratio calculated from the bit error
threshold choice and the dwell time choice.
9 Press to start the jitter auto tolerance measurement.
The measurements progress can be monitored on the
RUN/STOP
TRANSMIT
display. At the end of the test the results can be viewed on the
or displays. The display is cleared
TRANSMIT
when is pressed but the results remain on the
TRANSMIT
RESULTS
TRANSMIT
RESULTS
display until the next jitter tolerance measurement is made.
90
 Loading...
Loading...