Page 1

HP Mini
User Guide
Page 2

© Copyright 2009 Hewlett-Packard
Development Company, L.P.
Bluetooth is a trademark owned by its
proprietor and used by Hewlett-Packard
Company under license. Microsoft and
Windows are U.S. registered trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation. SD Logo is a
trademark of its proprietor.
The information contained herein is subject
to change without notice. The only
warranties for HP products and services are
set forth in the express warranty statements
accompanying such products and services.
Nothing herein should be construed as
constituting an additional warranty. HP shall
not be liable for technical or editorial errors
or omissions contained herein.
First Edition: July 2009
Document Part Number: 537596-001
Product notice
This user guide describes features that are
common to most models. Some features
may not be available on your computer.
Page 3

Safety warning notice
WARNING! To reduce the possibility of heat-related injuries or of overheating the computer, do not
place the computer directly on your lap or obstruct the computer air vents. Use the computer only on a
hard, flat surface. Do not allow another hard surface, such as an adjoining optional printer, or a soft
surface, such as pillows or rugs or clothing, to block airflow. Also, do not allow the AC adapter to contact
the skin or a soft surface, such as pillows or rugs or clothing, during operation. The computer and the
AC adapter comply with the user-accessible surface temperature limits defined by the International
Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment (IEC 60950).
iii
Page 4

iv Safety warning notice
Page 5

Table of contents
1 Features
Identifying the hardware ....................................................................................................................... 1
Top components .................................................................................................................. 1
TouchPad ............................................................................................................ 1
Lights ................................................................................................................... 3
Buttons ................................................................................................................ 4
Keys .................................................................................................................... 5
Front components ................................................................................................................ 5
Right-side components ........................................................................................................ 6
Left-side components .......................................................................................................... 7
Display components ........................................................................................................... 8
Bottom components ............................................................................................................. 8
Wireless antennas ............................................................................................................... 9
Additional hardware components ...................................................................................... 10
Identifying the labels ........................................................................................................................... 10
2 Power management
Setting power options ......................................................................................................................... 12
Using power-saving states ................................................................................................. 12
Using the battery meter ..................................................................................................... 13
Using power plans ............................................................................................................. 13
Setting password protection on wakeup ............................................................................ 14
Using external AC power .................................................................................................................... 14
Connecting the AC adapter ............................................................................................... 15
Using battery power ........................................................................................................................... 16
Finding battery information in Help and Support ............................................................... 16
Using Battery Check .......................................................................................................... 16
Displaying the remaining battery charge ........................................................................... 17
Inserting or removing the battery ....................................................................................... 17
Charging a battery ............................................................................................................. 18
Maximizing battery discharge time .................................................................................... 19
Managing low battery levels .............................................................................................. 19
Initiating and exiting Sleep ................................................................................ 12
Initiating and exiting Hibernation ....................................................................... 13
Viewing the current power plan ......................................................................... 14
Selecting a different power plan ........................................................................ 14
Customizing power plans .................................................................................. 14
Identifying low battery levels ............................................................................. 19
Resolving a low battery level ............................................................................. 19
v
Page 6

3 Wireless
Resolving a low battery level when external power is available ....... 19
Resolving a low battery level when a charged battery is
available ........................................................................................... 19
Resolving a low battery level when no power source is
available ........................................................................................... 20
Resolving a low battery level when the computer cannot exit
Hibernation ....................................................................................... 20
Calibrating a battery ........................................................................................................... 20
Step 1: Fully charge the battery ........................................................................ 20
Step 2: Disable Hibernation and Sleep ............................................................. 20
Step 3: Discharge the battery ............................................................................ 21
Step 4: Fully recharge the battery ..................................................................... 22
Step 5: Reenable Hibernation and Sleep .......................................................... 22
Conserving battery power .................................................................................................. 22
Storing a battery ................................................................................................................ 22
Disposing of a used battery ............................................................................................... 23
Replacing the battery ........................................................................................................ 23
Testing an AC adapter ....................................................................................................................... 24
Shutting down the computer ............................................................................................................... 24
Using wireless devices (select models only) ...................................................................................... 25
Identifying wireless and network icons .............................................................................. 25
Using the wireless controls ................................................................................................ 26
Using the wireless switch ................................................................................................... 26
Using operating system controls ........................................................................................ 26
Using a WLAN .................................................................................................................................... 27
Setting up a WLAN ............................................................................................................ 27
Protecting your WLAN ....................................................................................................... 27
Connecting to a WLAN ...................................................................................................... 29
Roaming to another network .............................................................................................. 29
Using HP Mobile Broadband (select models only) ............................................................................. 30
Inserting a SIM ................................................................................................................... 30
Removing a SIM ................................................................................................................ 31
Using Bluetooth wireless devices (select models only) ...................................................................... 33
Bluetooth and Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) ............................................................. 33
4 Multimedia
Multimedia features ............................................................................................................................ 34
Multimedia software ........................................................................................................................... 36
Audio .................................................................................................................................................. 38
Video .................................................................................................................................................. 40
Optical drive (select models only) ...................................................................................................... 41
vi
Identifying your multimedia components ........................................................................... 34
Adjusting the volume ......................................................................................................... 35
Using preinstalled multimedia software ............................................................................. 37
Installing multimedia software from a disc ......................................................................... 37
Connecting external audio devices .................................................................................... 38
Checking your audio functions ........................................................................................... 38
Connecting an external monitor or projector ...................................................................... 40
Page 7

5 Security
Identifying the external optical drive .................................................................................. 41
Using optical discs ............................................................................................................. 41
Selecting the right disc ....................................................................................................... 41
CD-R discs ........................................................................................................ 42
CD-RW discs ..................................................................................................... 42
DVD±R discs ..................................................................................................... 42
DVD±RW discs ................................................................................................. 42
Playing music ..................................................................................................................... 42
Watching a movie .............................................................................................................. 43
Changing DVD region settings .......................................................................................... 44
Creating or “burning” a CD or DVD .................................................................................... 45
Removing an optical disc (CD or DVD) ............................................................................. 45
Webcam ............................................................................................................................................. 47
Adjusting webcam properties ............................................................................................. 47
Protecting the computer ..................................................................................................................... 48
Using passwords ................................................................................................................................ 49
Setting passwords in Windows .......................................................................................... 49
Setting passwords in Computer Setup .............................................................................. 49
Setup password ................................................................................................................. 50
Managing a setup password ............................................................................. 51
Entering a setup password ................................................................................ 52
Power-on password ........................................................................................................... 52
Managing a power-on password ....................................................................... 53
Entering a power-on password ......................................................................... 54
Requiring a power-on password at restart ........................................................ 55
Using Computer Setup DriveLock ..................................................................................... 55
Setting a DriveLock password ........................................................................... 56
Entering a DriveLock password ........................................................................ 57
Changing a DriveLock password ...................................................................... 58
Removing DriveLock protection ........................................................................ 59
Using Computer Setup security features ............................................................................................ 60
Securing system devices ................................................................................................... 60
Using Computer Setup stringent security .......................................................................... 60
Setting stringent security ................................................................................... 61
Removing stringent security .............................................................................. 62
Viewing Computer Setup System Information ................................................................... 62
Using antivirus software ..................................................................................................................... 63
Using firewall software ....................................................................................................................... 64
Installing critical updates .................................................................................................................... 65
Installing a security cable ................................................................................................................... 66
6 External devices
Using a USB device ........................................................................................................................... 67
Using external drives .......................................................................................................................... 69
Connecting a USB device .................................................................................................. 67
Stopping and removing a USB device ............................................................................... 67
Using USB legacy support ................................................................................................. 68
Using optional external devices ......................................................................................... 69
vii
Page 8

Using an optional external MultiBay II ............................................................................... 69
Using an optional external optical drive (select models only) ............................................................. 70
Inserting an optical disc (CD or DVD) ................................................................................ 70
Removing an optical disc (CD or DVD) ............................................................................. 71
When the disc tray opens .................................................................................. 71
When the disc tray does not open ..................................................................... 72
7 External media cards
Using SD Card Reader cards ............................................................................................................. 73
Inserting a digital card ........................................................................................................ 73
Stopping and removing a digital card ................................................................................ 74
8 Pointing devices and keyboard
Using pointing devices ....................................................................................................................... 75
Setting pointing device preferences ................................................................................... 75
Using the TouchPad .......................................................................................................... 75
Connecting an external mouse .......................................................................................... 75
Using the keyboard function keys ...................................................................................................... 76
Switching the screen image (f2) ........................................................................................ 77
Decreasing screen brightness (f3) ..................................................................................... 77
Increasing screen brightness (f4) ...................................................................................... 77
Initiating Sleep (f5) ............................................................................................................. 77
Initiating QuickLock (f6) ..................................................................................................... 77
Muting speaker sound (f8) ................................................................................................. 78
Decreasing speaker sound (f10) ........................................................................................ 78
Increasing speaker sound (f11) ......................................................................................... 78
Using keypads .................................................................................................................................... 78
Using the embedded numeric keypad ............................................................................... 78
Enabling and disabling the embedded numeric keypad .................................... 79
Switching key functions on the embedded numeric keypad ............................. 79
Using an optional external numeric keypad ....................................................................... 79
Cleaning the TouchPad and keyboard ............................................................................................... 80
9 Drives
Identifying installed drives .................................................................................................................. 81
Handling drives ................................................................................................................................... 81
Improving hard drive performance ..................................................................................................... 83
Using HP 3D DriveGuard (select models only) .................................................................................. 84
Replacing a hard drive ....................................................................................................................... 86
10 Memory modules
11 Computer Setup
Starting Computer Setup .................................................................................................................... 93
viii
Using Disk Defragmenter ................................................................................................... 83
Using Disk Cleanup ........................................................................................................... 83
Identifying HP 3D DriveGuard status ................................................................................. 84
Using HP 3D DriveGuard software .................................................................................... 84
Page 9

Using Computer Setup ....................................................................................................................... 93
Navigating and selecting in Computer Setup ..................................................................... 93
Restoring factory settings in Computer Setup ................................................................... 94
Computer Setup menus ..................................................................................................................... 94
File menu ........................................................................................................................... 94
Security menu .................................................................................................................... 95
Diagnostics menu .............................................................................................................. 95
System Configuration menu .............................................................................................. 96
12 Backing up and recovering
Backing up .......................................................................................................................................... 99
Recovering ....................................................................................................................................... 100
Index ................................................................................................................................................................. 101
ix
Page 10

x
Page 11
1 Features
Identifying the hardware
Components included with the computer may vary by region and model. The illustrations in this chapter
identify the standard features on most computer models.
To see a list of hardware installed in the computer, follow these steps:
1. Select Start > Computer > System properties.
2. In the left pane, click Device Manager.
You can also add hardware or modify device configurations using Device Manager.
NOTE: Windows® includes the User Account Control feature to improve the security of your computer.
You may be prompted for your permission or password for tasks such as installing applications, running
utilities, or changing Windows settings. Refer to Help and Support for more information.
Top components
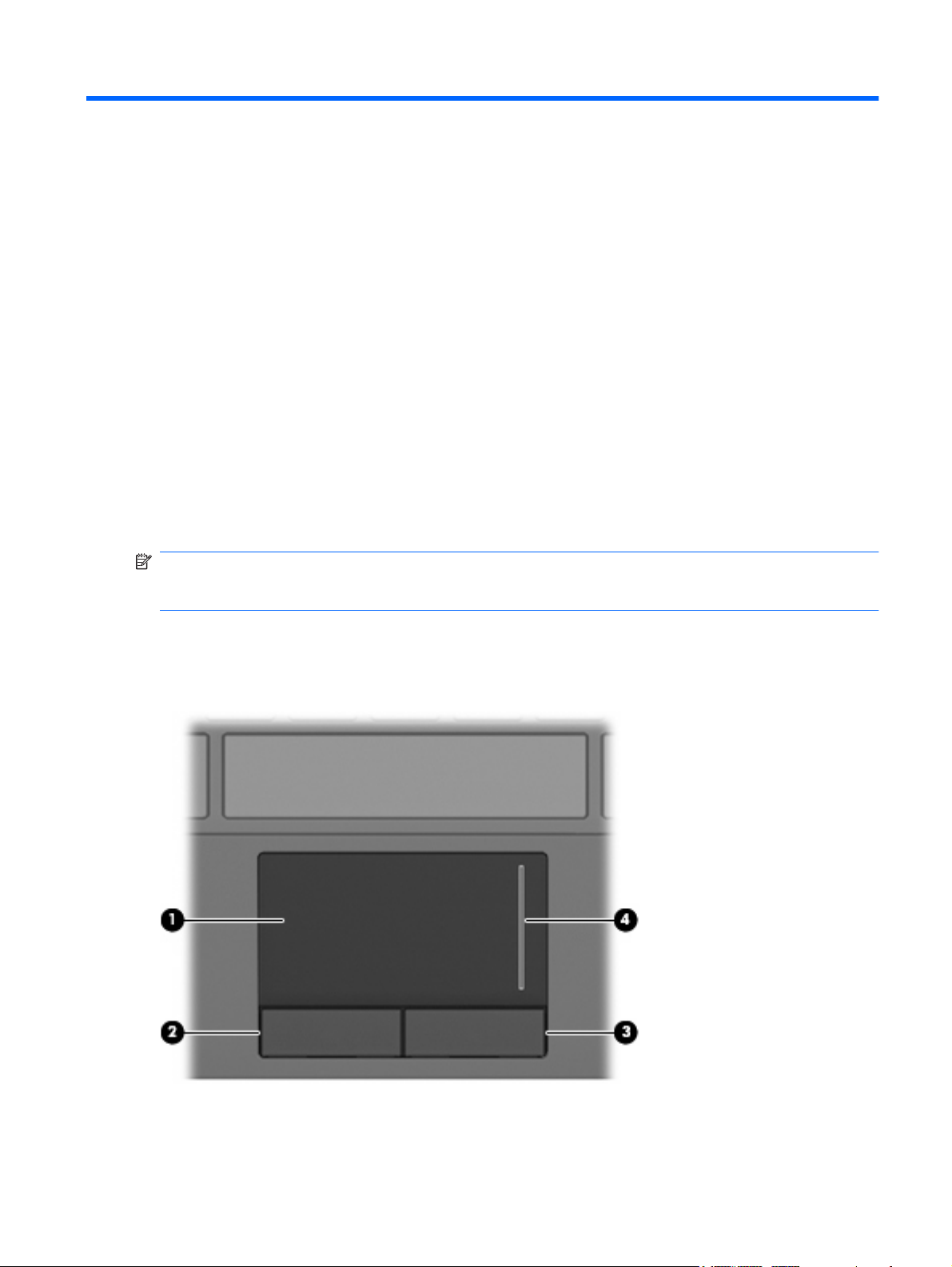
TouchPad
Identifying the hardware 1
Page 12

Component Description
(1) TouchPad* Moves the pointer and selects or activates items on the screen.
(2) Left TouchPad button* Functions like the left button on an external mouse.
(3) Right TouchPad button* Functions like the right button on an external mouse.
(4) TouchPad scroll zone Scrolls up or down.
*This table describes factory settings. To view or change pointing device preferences, select Start > Control Panel > Hardware
and Sound > Mouse.
2 Chapter 1 Features
Page 13

Lights
Component Description
(1) Caps lock light On: Caps lock is on.
(2) Quick Launch Web light On: The default Internet browser is being launched.
(3) Quick Launch Mail light On: The default mail application is being launched.
(4) Power light
On: The computer is on.
●
Blinking: The computer is in the Sleep state.
●
Off: The computer is off or in Hibernation.
●
Identifying the hardware 3
Page 14
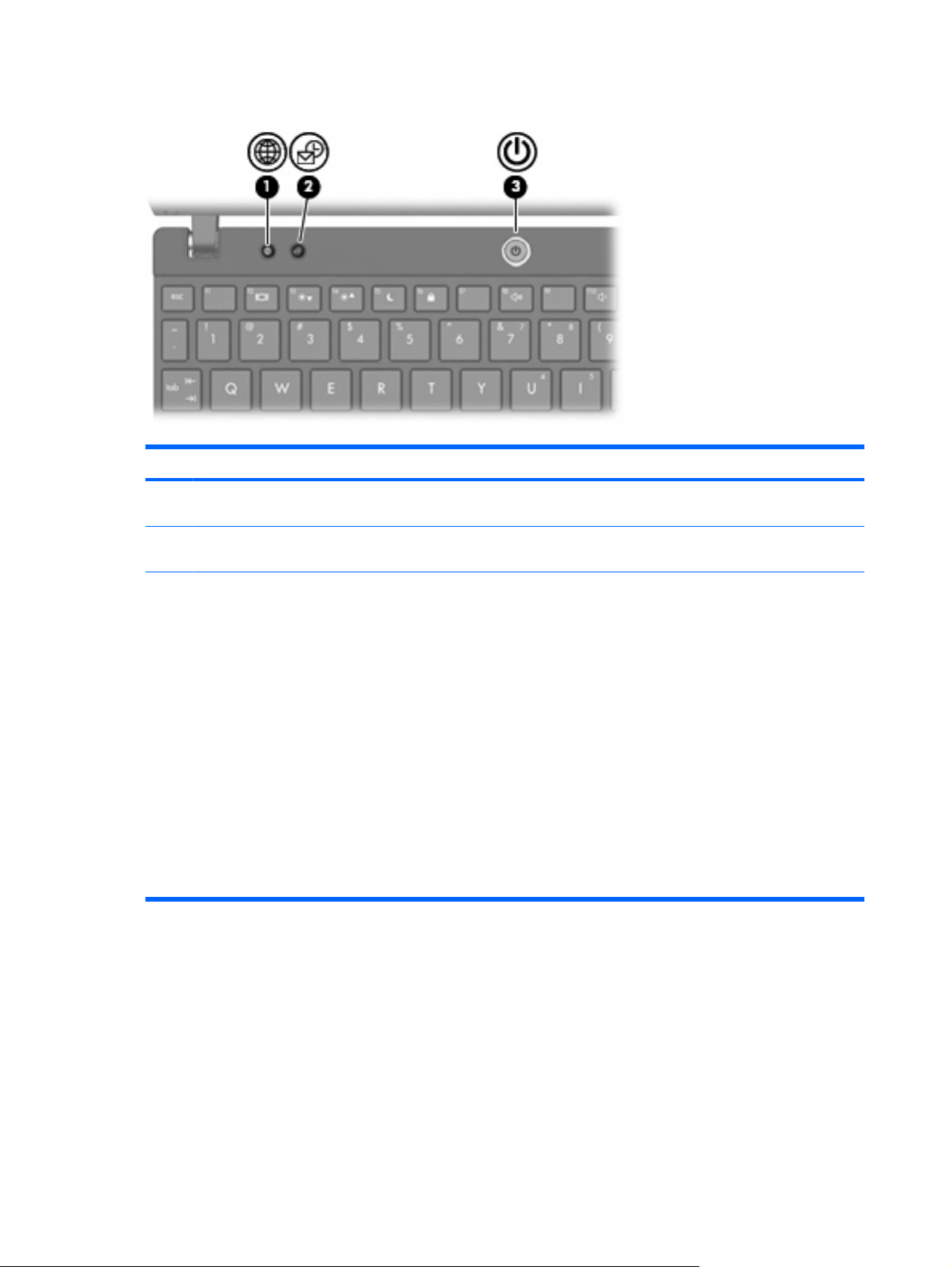
Buttons
Component Description
(1) Quick Launch Web button Opens the default Internet browser when the computer is
on.
(2) Quick Launch Mail button Opens the default mail application when the computer is
(3) Power button
on.
When the computer is off, press the button to turn on
●
the computer.
When the computer is on, press the button to shut
●
down the computer.
When the computer is in the Sleep state, press the
●
button briefly to exit Sleep.
When the computer is in Hibernation, press the
●
button briefly to exit Hibernation.
If the computer has stopped responding and Windows
shutdown procedures are ineffective, press and hold the
power button for at least 5 seconds to turn off the
computer.
To learn more about your power settings, select Start >
Control Panel > System and Maintenance > Power
Options.
4 Chapter 1 Features
Page 15
Keys
Component Description
(1) esc key Displays system information when pressed in combination with the
(2) fn key Displays system information when pressed in combination with the
(3) Windows logo key Displays the Windows Start menu.
(4) Windows applications key Displays a shortcut menu for items beneath the pointer.
(5) Embedded numeric keypad keys Can be used like the keys on an external numeric keypad.
(6) Function keys Execute the action represented by the icon on the key.
Front components
Component Description
fn key.
esc key.
(1) Drive light Blinking: The hard drive is being accessed.
Identifying the hardware 5
Page 16

Component Description
(2) Wireless light
(3) Wireless switch Turns the wireless feature on or off, but does not create a wireless
(4) Speakers (2) Produce sound.
Right-side components
Blue: An integrated wireless device, such as a wireless local
●
area network (WLAN) device and/or a Bluetooth® device, is
on.
Amber: All wireless devices are off.
●
NOTE: The wireless light turns amber when the computer turns
on and all wireless devices are off.
connection.
NOTE: To establish a wireless connection, a wireless network
must already be set up.
Component Description
(1) SD Card Reader Supports the following optional digital card formats:
MultiMediaCard (MMC)
●
Secure Digital (SD) Memory Card
●
(2) Audio-out (headphone) jack Produces sound when connected to optional powered stereo
speakers, headphones, ear buds, a headset, or television audio.
NOTE: When a device is connected to the headphone jack, the
computer speakers are disabled.
(3) Audio-in (microphone) jack Connects an optional computer headset microphone, stereo array
microphone, or monaural microphone.
(4) Powered USB port Provides power to a USB device, such as an optional external
optical drive, if used with a powered USB cable.
(5) RJ-45 (network) jack Connects a network cable.
(6) Security cable slot Attaches an optional security cable to the computer.
NOTE: The security cable is designed to act as a deterrent, but
it may not prevent the computer from being mishandled or stolen.
6 Chapter 1 Features
Page 17

Left-side components
Component Description
(1) Power light
(2) Power connector Connects an AC adapter.
(3) External monitor port Connects an external VGA monitor or projector.
(4) Vent Enables airflow to cool internal components.
(5) USB ports (2) Connect optional USB devices.
Blue: The computer is on.
●
Blinking: The computer is in the Sleep state.
●
Off: The computer is off or in Hibernation.
●
NOTE: The computer fan starts up automatically to cool internal
components and prevent overheating. It is normal for the internal
fan to cycle on and off during routine operation.
Identifying the hardware 7
Page 18
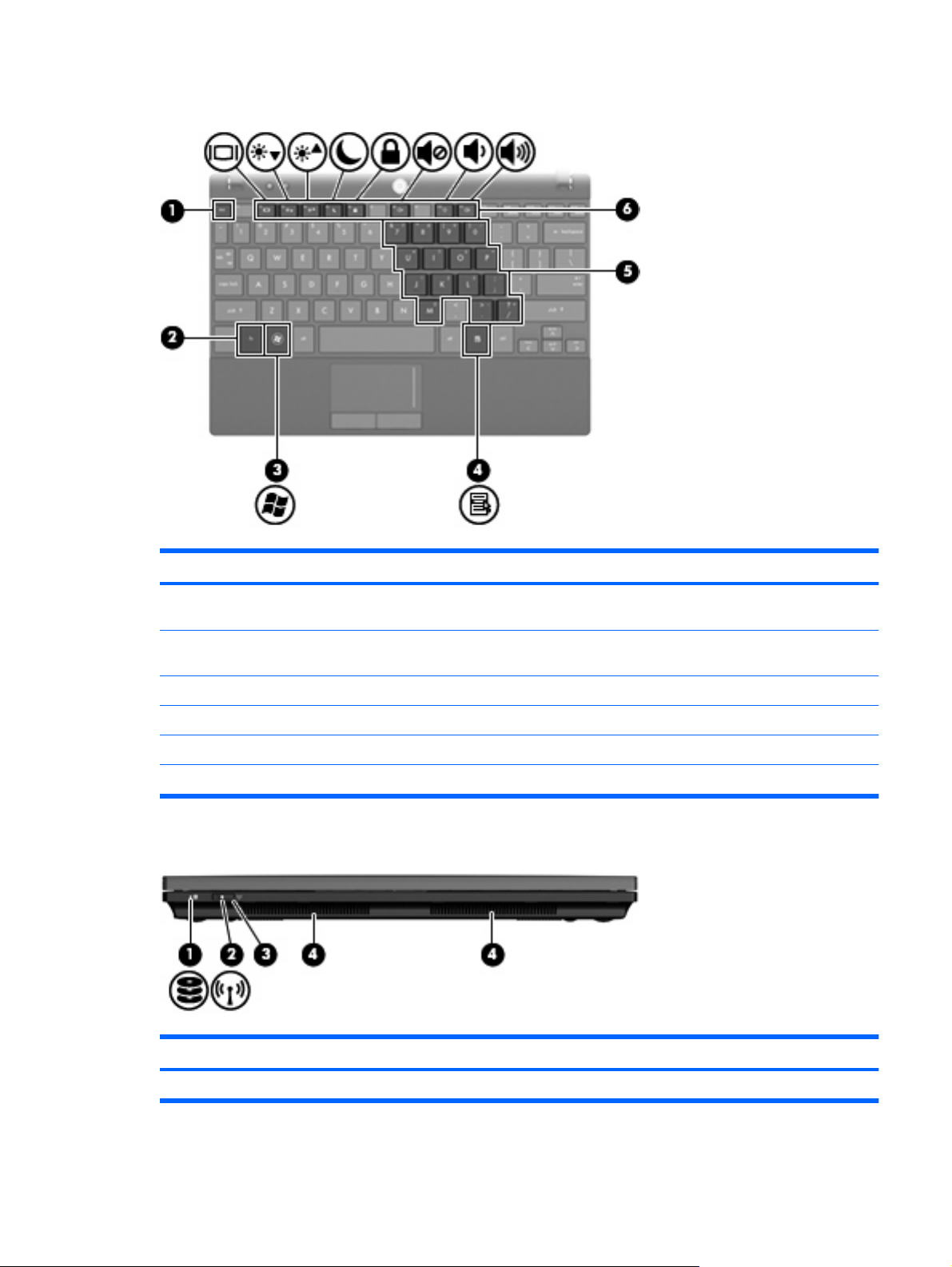
Display components
Component Description
(1) Webcam light On: The webcam is in use.
(2) Webcam Records audio and video and captures still photographs.
(3) Internal microphones (2) Record sound.
(4) Speakers (2) Produce sound.
Bottom components
NOTE: If there is a microphone icon next to each microphone
opening, your computer has internal microphones.
8 Chapter 1 Features
Page 19

Component Description
(1) Battery bay Holds the battery.
(2) Battery release latches (2) Release the battery from the battery bay.
(3) Service tag Provides the product brand and series name, serial number (s/n),
(4) Memory module compartment Contains the memory module slot.
(5) Vents (2) Enable airflow to cool internal components.
Wireless antennas
On select computer models, at least 2 antennas send and receive signals from one or more wireless
devices. These antennas are not visible from the outside of the computer.
and product number (p/n) of your computer. Have this information
available when you contact technical support.
NOTE: The computer fan starts up automatically to cool internal
components and prevent overheating. It is normal for the internal
fan to cycle on and off during routine operation.
NOTE: For optimal transmission, keep the areas immediately around the WLAN and WWAN antennas
free from obstructions.
To see wireless regulatory notices, refer to the section of the Regulatory, Safety and Environmental
Notices that applies to your country or region. These notices are located in Help and Support.
Identifying the hardware 9
Page 20
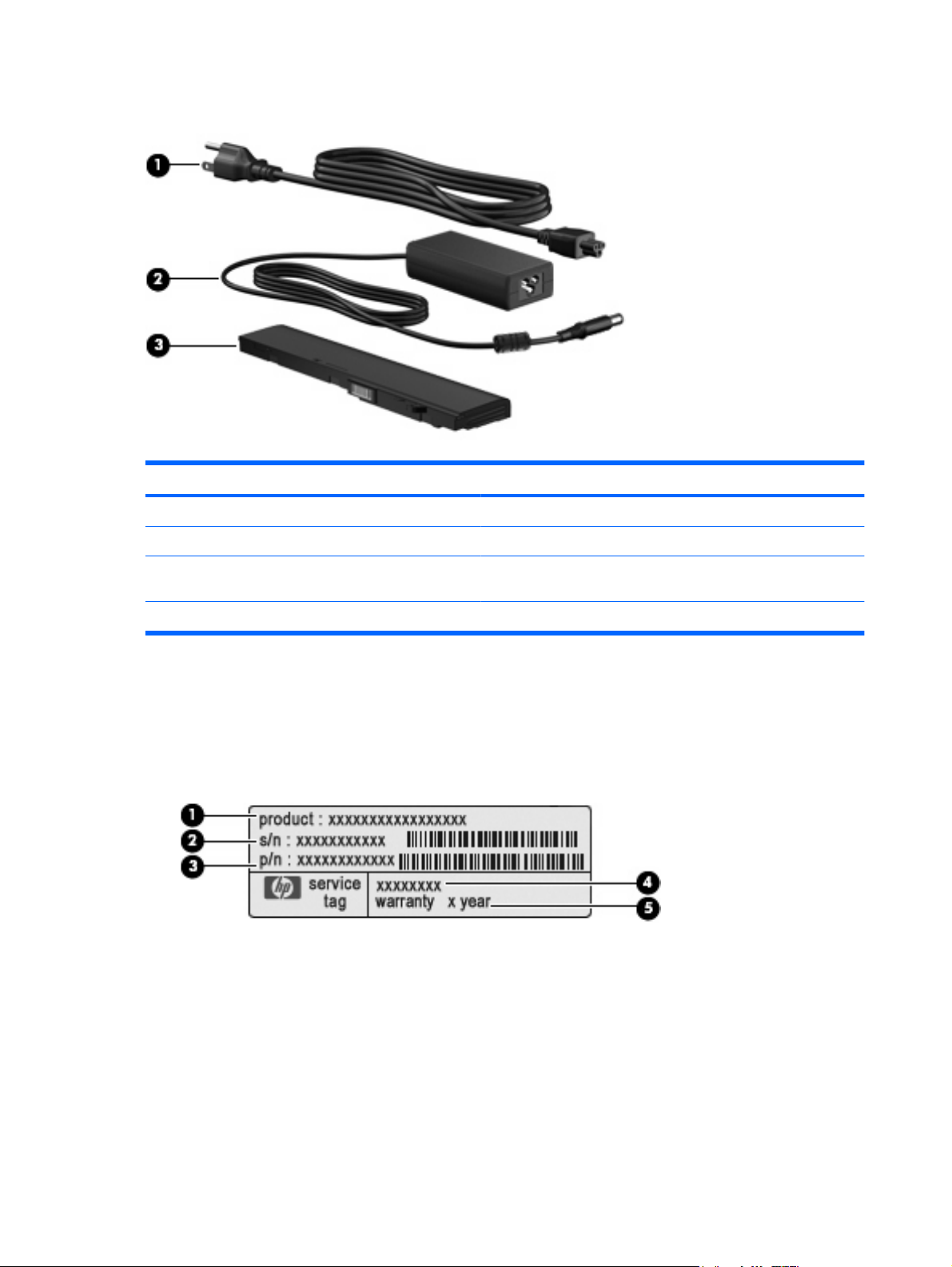
Additional hardware components
Component Description
(1) Power cord* Connects an AC adapter to an AC outlet.
(2) AC adapter Converts AC power to DC power.
(3) Battery* Powers the computer when the computer is not plugged into
external power.
*Batteries and power cords vary in appearance by region and country.
Identifying the labels
The labels affixed to the computer provide information you may need when you troubleshoot system
problems or travel internationally with the computer.
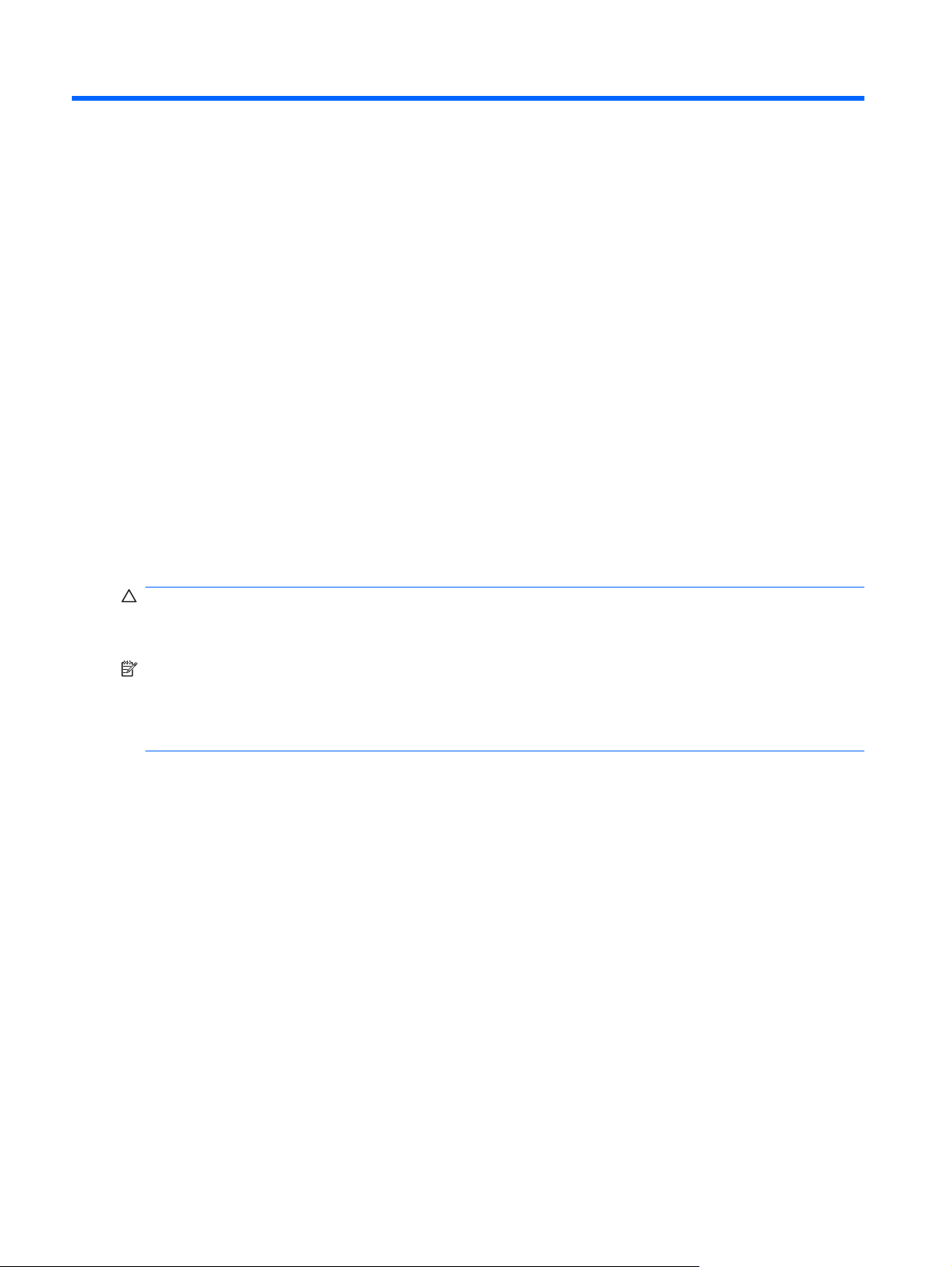
Service tag—Provides important information including:
●
Product Name (1). This is the product name affixed to the front of your computer.
◦
Serial Number (s/n) (2). This is an alphanumeric identifier that is unique to each product.
◦
Part Number/Product Number (p/n) (3). This number provides specific information about the
◦
product's hardware components. The part number helps a service technician to determine
what components and parts are needed.
10 Chapter 1 Features
Page 21

Model Description (4). This is the alphanumeric identifier you need to locate documents,
◦
drivers, and support for your computer.
Warranty period (5). This number describes the duration (in years) of the warranty period for
◦
this computer.
Have this information available when you contact technical support. The service tag label is affixed
to the bottom of the computer.
Microsoft® Certificate of Authenticity—Contains the Windows Product Key. You may need the
●
Product Key to update or troubleshoot the operating system. This certificate is affixed to the bottom
of the computer.
Regulatory label—Provides regulatory information about the computer. The regulatory label is
●
affixed to the bottom of the computer.
Wireless certification label(s) (select models only)—Provide information about optional wireless
●
devices and the approval markings of some of the countries or regions in which the devices have
been approved for use. An optional device may be a wireless local area network (WLAN) device
or an optional Bluetooth® device. If your computer model includes one or more wireless devices,
one or more certification labels are included with your computer. You may need this information
when traveling internationally. Wireless certification labels are affixed inside the battery bay.
Identifying the labels 11
Page 22
2 Power management
Setting power options
Using power-saving states
The computer has two power-saving states enabled at the factory: Sleep and Hibernation.
When Sleep is initiated, the power light blinks and the screen clears. Your work is saved to memory,
letting you exit Sleep faster than exiting Hibernation. If the computer is in the Sleep state for an extended
period or if the battery reaches a critical battery level while in the Sleep state, the computer initiates
Hibernation.
When Hibernation is initiated, your work is saved to a hibernation file on the hard drive and the computer
turns off.
CAUTION: To prevent possible audio and video degradation, loss of audio or video playback
functionality, or loss of information, do not initiate Sleep or Hibernation while reading from or writing to
a disc or an external media card.
NOTE: You cannot initiate any type of networking connection or perform any computer functions while
the computer is in the Sleep state or in Hibernation.
NOTE: When HP 3D DriveGuard has parked a drive, the computer will not initiate Sleep or Hibernation,
and the display will be turned off.
Initiating and exiting Sleep
The system is set at the factory to initiate Sleep after 15 minutes of inactivity when running on battery
power and 30 minutes of inactivity when running on external power.
Power settings and timeouts can be changed using Power Options in Windows® Control Panel.
With the computer on, you can initiate Sleep in any of the following ways:
Press f5.
●
Click Start, and then click the Power button.
●
Click Start, click the arrow next to the Lock button, and then click Sleep.
●
To exit Sleep:
Briefly press the power button.
▲
When the computer exits Sleep, the power lights turn on and your work returns to the screen where
you stopped working.
12 Chapter 2 Power management
Page 23

NOTE: If you have set a password to be required when the computer exits Sleep, you must enter your
Windows password before your work will return to the screen.
Initiating and exiting Hibernation
The system is set at the factory to initiate Hibernation after 1080 minutes of inactivity when running on
battery power, 1080 minutes (18 hours) of inactivity when running on external power, or when the battery
reaches a critical battery level.
Power settings and timeouts can be changed using Power Options in Windows Control Panel.
To initiate Hibernation:
1. Click Start, and then click the arrow next to the Lock button.
2. Click Hibernate.
To exit Hibernation:
Briefly press the power button.
▲
The power lights turn on and your work returns to the screen where you stopped working.
NOTE: If you have set a password to be required when the computer exits Hibernation, you must enter
your Windows password before your work will return to the screen.
Using the battery meter
The battery meter is located in the notification area, at the far right of the taskbar. The battery meter
allows you to quickly access power settings, view remaining battery charge, and select a different power
plan.
To display the percentage of remaining battery charge and the current power plan, move the pointer
●
over the battery meter icon.
To access Power Options, or to change the power plan, click the battery meter icon and select an
●
item from the list.
Different battery meter icons indicate whether the computer is running on battery or external power. The
icon also displays a message if the battery has reached a critical battery level.
To hide or display the battery meter icon:
1. Right-click the taskbar, and then click Properties.
2. Click the Notification Area tab.
3. Under System icons, clear the Power check box to hide the battery meter icon, or select the
Power check box to display the battery meter icon.
4. Click OK.
Using power plans
A power plan is a collection of system settings that manages how the computer uses power. Power
plans can help you conserve power or maximize performance.
You can change power plan settings or create your own power plan.
Setting power options 13
Page 24

Viewing the current power plan
Move the pointer over the battery meter icon in the notification area, at the far right of the taskbar.
▲
– or –
Select Start > Control Panel > System and Maintenance > Power Options.
Selecting a different power plan
Click the battery meter icon in the notification area, and then select a power plan from the list.
▲
– or –
Select Start > Control Panel > System and Maintenance > Power Options, and then select a
power plan from the list.
Customizing power plans
1. Click the battery meter icon in the notification area and then click More power options.
– or –
Select Start > Control Panel > System and Maintenance > Power Options.
2. Select a power plan, and then click Change plan settings.
3. Change the Turn off the display and Put the computer to sleep timeout settings, as needed.
4. To change additional settings, click Change advanced power settings and make your changes.
Setting password protection on wakeup
To set the computer to prompt for a password when the computer exits Sleep or Hibernation, follow
these steps:
1. Select Start > Control Panel > System and Maintenance > Power Options.
2. In the left pane, click Require a password on wakeup.
3. Click Change Settings that are currently unavailable.
4. Click Require a password (recommended).
5. Click Save changes.
Using external AC power
External AC power is supplied through one of the following devices:
WARNING! To reduce potential safety issues, use only the AC adapter provided with the computer,
a replacement AC adapter provided by HP, or a compatible AC adapter purchased from HP.
Approved AC adapter
●
Optional docking device or optional expansion product
●
Connect the computer to external AC power under any of the following conditions:
14 Chapter 2 Power management
Page 25

WARNING! Do not charge the computer battery while you are onboard aircraft.
When you are charging or calibrating a battery
●
When you are installing or modifying system software
●
When you are writing information to a CD or DVD
●
When you connect the computer to external AC power, the following events occur:
The battery begins to charge.
●
If the computer is turned on, the battery meter icon in the notification area changes appearance.
●
When you disconnect external AC power, the following events occur:
The computer switches to battery power.
●
The display brightness is automatically decreased to save battery life. To increase display
●
brightness, press the f4 key or reconnect the AC adapter.
Connecting the AC adapter
WARNING! To reduce the risk of electric shock or damage to the equipment:
Plug the power cord into an AC outlet that is easily accessible at all times.
Disconnect power from the computer by unplugging the power cord from the AC outlet (not by
unplugging the power cord from the computer).
If provided with a 3-pin attachment plug on the power cord, plug the cord into a grounded (earthed) 3pin outlet. Do not disable the power cord grounding pin, for example, by attaching a 2-pin adapter. The
grounding pin is an important safety feature.
To connect the computer to external AC power, follow these steps:
1. Plug the AC adapter into the power connector (1) on the computer.
2. Plug the power cord into the AC adapter (2).
3. Plug the other end of the power cord into an AC outlet (3).
Using external AC power 15
Page 26

Using battery power
When a charged battery is in the computer and the computer is not plugged into external power, the
computer runs on battery power. When the computer is plugged into external AC power, the computer
runs on AC power.
If the computer contains a charged battery and is running on external AC power supplied through the
AC adapter, the computer switches to battery power if the AC adapter is disconnected from the
computer.
NOTE: The display brightness is decreased to save battery life when you disconnect AC power. To
increase display brightness, use the f4 key or reconnect the AC adapter.
You can keep a battery in the computer or in storage, depending on how you work. Keeping the battery
in the computer whenever the computer is plugged into AC power charges the battery and also protects
your work in case of a power outage. However, a battery in the computer slowly discharges when the
computer is off and unplugged from external power.
WARNING! To reduce potential safety issues, use only the battery provided with the computer, a
replacement battery provided by HP, or a compatible battery purchased from HP.
Computer battery life varies, depending on power management settings, programs running on the
computer, display brightness, external devices connected to the computer, and other factors.
Finding battery information in Help and Support
The “Battery information” section of the Help and Support Learning Center provides the following tools
and information:
Battery Check tool to test battery performance
●
Information on calibration, power management, and proper care and storage to maximize battery
●
life
Information on battery types, specifications, life cycles, and capacity
●
To access battery information:
▲
Select Start > Help and Support > Learning Center > HP Power and Battery Learning
Center.
Using Battery Check
Battery Check, a part of the Total Care Advisor, provides information on the status of the battery installed
in the computer.
To run Battery Check:
1. Connect the AC adapter to the computer.
NOTE: The computer must be connected to external power for Battery Check to function properly.
2. Select Start > Help and Support > Troubleshooting tools > Battery Check.
Battery Check examines the battery and its cells to see if they are functioning properly, and then reports
the results of the examination.
16 Chapter 2 Power management
Page 27

Displaying the remaining battery charge
Move the pointer over the battery meter icon in the notification area, at the far right of the taskbar.
▲
– or –
View the estimated number of minutes of battery charge remaining in Windows Mobility Center:
Click the battery meter icon, and then click Windows Mobility Center.
▲
– or –
Select Start > Control Panel > Mobile PC > Windows Mobility Center.
The time shown indicates the approximate running time remaining on the battery if the battery
continues to provide power at the current level. For example, the time remaining will decrease
when a DVD is playing and will increase when a DVD stops playing.
Inserting or removing the battery
CAUTION: Removing a battery that is the sole power source can cause loss of information. To prevent
loss of information, initiate Hibernation or shut down the computer through Windows before removing
the battery.
To insert the battery:
1. Turn the computer upside down on a flat surface, with the battery bay toward you.
2. Insert the battery into the battery bay (1) and push in until it is seated.
The battery release latches (2) automatically lock the battery into place.
To remove the battery:
1. Turn the computer upside down on a flat surface, with the battery bay toward you.
2. Slide the battery release latches (1) to release the battery.
Using battery power 17
Page 28
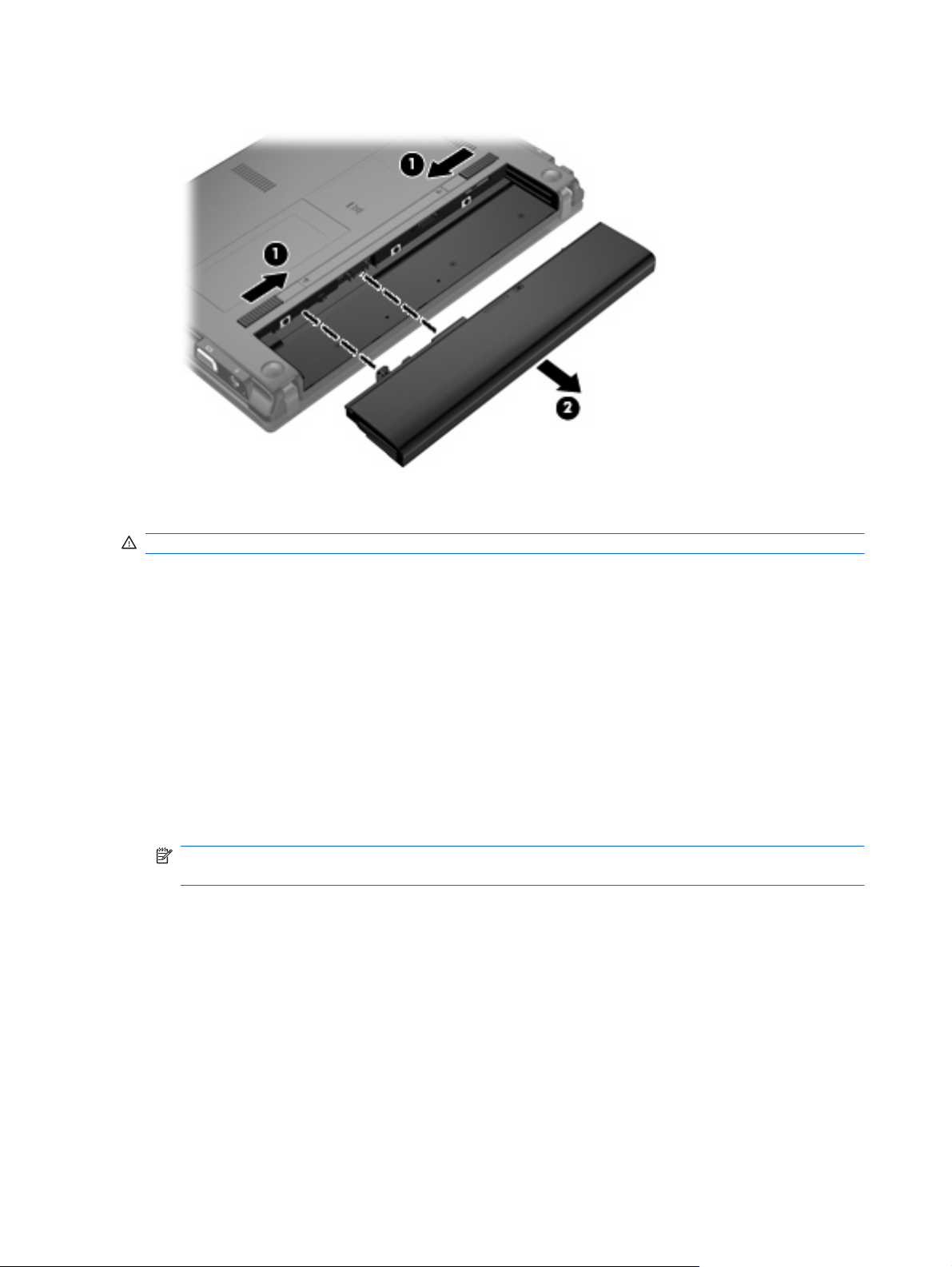
3. Remove the battery (2) from the computer.
Charging a battery
WARNING! Do not charge the computer battery while you are onboard aircraft.
The battery charges whenever the computer is plugged into external power through an AC adapter, an
optional power adapter, an optional expansion product, or an optional docking device.
The battery charges whether the computer is off or in use, but it charges faster when the computer is
off.
Charging may take longer if a battery is new, has been unused for 2 weeks or more, or is much warmer
or cooler than room temperature.
To prolong battery life and optimize the accuracy of battery charge displays, follow these
recommendations:
If you are charging a new battery, charge it fully before turning on the computer.
●
Charge the battery until the battery light turns off.
●
NOTE: If the computer is on while the battery is charging, the battery meter in the notification
area may show 100 percent charge before the battery is fully charged.
Allow the battery to discharge below 5 percent of a full charge through normal use before charging
●
it.
If the battery has been unused for one month or more, calibrate the battery instead of simply
●
charging it.
The battery light displays charge status:
On: The battery is charging.
●
Blinking: The battery has reached a low battery level or critical battery level and is not charging.
●
Off: The battery is fully charged, in use, or not installed.
●
18 Chapter 2 Power management
Page 29

Maximizing battery discharge time
Battery discharge time varies, depending on the features you use while on battery power. Maximum
discharge time gradually shortens as the battery storage capacity naturally degrades.
Tips for maximizing battery discharge time:
Lower the brightness on the display.
●
Select the Power saver setting in Power Options.
●
Remove the battery from the computer when it is not being used or charged.
●
Store the battery in a cool, dry location.
●
Managing low battery levels
The information in this section describes the alerts and system responses set at the factory. Some low
battery alerts and system responses can be changed using Power Options in Windows Control Panel.
Preferences set using Power Options do not affect lights.
Identifying low battery levels
When a battery that is the sole power source for the computer reaches a low battery level, the battery
light blinks.
If a low battery level is not resolved, the computer enters a critical battery level, and the battery light
continues to blink.
The computer takes the following actions for a critical battery level:
If Hibernation is enabled and the computer is on or in the Sleep state, the computer initiates
●
Hibernation.
If Hibernation is disabled and the computer is on or in the Sleep state, the computer remains briefly
●
in the Sleep state, and then shuts down and loses any unsaved information.
Resolving a low battery level
CAUTION: To reduce the risk of losing information when the computer reaches a critical battery level
and has initiated Hibernation, do not restore power until the power lights turn off.
Resolving a low battery level when external power is available
Connect one of the following devices:
▲
AC adapter
●
Optional expansion product or docking device
●
Optional power adapter
●
Resolving a low battery level when a charged battery is available
1. Turn off the computer or initiate Hibernation.
2. Remove the discharged battery, and then insert a charged battery.
3. Turn on the computer.
Using battery power 19
Page 30
Resolving a low battery level when no power source is available
Initiate Hibernation.
▲
– or –
Save your work and shut down the computer.
Resolving a low battery level when the computer cannot exit Hibernation
When the computer lacks sufficient power to exit Hibernation, follow these steps:
1. Insert a charged battery or plug the computer into external power.
2. Exit Hibernation by briefly pressing the power button.
Calibrating a battery
Calibrate a battery under the following conditions:
When battery charge displays seem inaccurate
●
When you observe a significant change in battery run time
●
Even if a battery is heavily used, it should not need to be calibrated more than once a month. It is also
not necessary to calibrate a new battery.
Step 1: Fully charge the battery
WARNING! Do not charge the computer battery while you are onboard aircraft.
NOTE: The battery charges whether the computer is off or in use, but it charges faster when the
computer is off.
To fully charge the battery:
1. Insert the battery into the computer.
2. Connect the computer to an AC adapter, optional power adapter, optional expansion product, or
optional docking device, and then plug the adapter or device into external power.
The battery light on the computer turns on.
3. Leave the computer plugged into external power until the battery is fully charged.
The battery light on the computer turns off.
Step 2: Disable Hibernation and Sleep
1. Click the battery meter icon in the notification area, and then click More power options.
– or –
Select Start > Control Panel > System and Maintenance > Power Options.
2. Under the current power plan, click Change plan settings.
3. Record the Turn off the display and Put the computer to sleep settings listed in the On
battery column so that you can reset them after the calibration.
20 Chapter 2 Power management
Page 31

4. Change the Turn off the display and Put the computer to sleep settings to Never.
5. Click Change advanced power settings.
6. Click the plus sign next to Sleep, and then click the plus sign next to Hibernate after.
7. Record the On battery setting under Hibernate after so that you can reset it after the calibration.
8. Change the On battery setting to Never.
9. Click OK.
10. Click Save changes.
Step 3: Discharge the battery
The computer must remain on while the battery is being discharged. The battery can discharge whether
or not you are using the computer, but the battery will discharge faster while you are using it.
If you plan to leave the computer unattended during the discharge, save your information before
●
beginning the discharge procedure.
If you use the computer occasionally during the discharge procedure and have set energy-saving
●
timeouts, expect the following performance from the system during the discharge process:
The monitor will not turn off automatically.
◦
Hard drive speed will not decrease automatically when the computer is idle.
◦
System-initiated Hibernation will not occur.
◦
To discharge a battery:
1. Unplug the computer from its external power source, but do not turn off the computer.
2. Run the computer on battery power until the battery is discharged. The battery light begins to blink
when the battery has discharged to a low battery level. When the battery is discharged, the battery
light turns off and the computer shuts down.
Using battery power 21
Page 32

Step 4: Fully recharge the battery
To recharge the battery:
1. Plug the computer into external power and maintain external power until the battery is fully
recharged. When the battery is recharged, the battery light on the computer turns off.
You can use the computer while the battery is recharging, but the battery will charge faster if the
computer is off.
2. If the computer is off, turn it on when the battery is fully charged and the battery light has turned
off.
Step 5: Reenable Hibernation and Sleep
CAUTION: Failure to reenable Hibernation after calibration may result in a full battery discharge and
information loss if the computer reaches a critical battery level.
1. Click the battery meter icon in the notification area, and then click More power options.
– or –
Select Start > Control Panel > System and Maintenance > Power Options.
2. Under the current power plan, click Change plan settings.
3. Reenter the settings that you recorded for the items in the On battery column.
4. Click Change advanced power settings.
5. Click the plus sign next to Sleep, and then click the plus sign next to Hibernate after.
6. Reenter the setting that you recorded for On battery.
7. Click OK.
8. Click Save changes.
Conserving battery power
Select low power-use settings through Power Options in Windows Control Panel.
●
Turn off wireless and local area network (LAN) connections and exit modem applications when you
●
are not using them.
Disconnect external devices that are not plugged into an external power source, when you are not
●
using them.
Stop, disable, or remove any external media cards that you are not using.
●
Use the f3 and f4 keys to adjust screen brightness as needed.
●
If you leave your work, initiate Sleep or Hibernation, or shut down the computer.
●
Storing a battery
CAUTION: To prevent damage to a battery, do not expose it to high temperatures for extended periods
of time.
22 Chapter 2 Power management
Page 33

If a computer will be unused and unplugged from external power for more than 2 weeks, remove the
battery and store it separately.
To prolong the charge of a stored battery, place it in a cool, dry place.
NOTE: A stored battery should be checked every 6 months. If the capacity is less than 50 percent,
recharge the battery before returning it to storage.
Calibrate a battery before using it if it has been stored for one month or more.
Disposing of a used battery
WARNING! To reduce the risk of fire or burns, do not disassemble, crush, or puncture; do not short
external contacts; do not dispose of in fire or water.
Refer to the Regulatory, Safety and Environmental Notices for battery disposal information.
Replacing the battery
Computer battery life varies, depending on the power management settings, programs running on the
computer, display brightness, external devices connected to the computer, and other factors.
Battery Check notifies you to replace the battery when an internal cell is not charging properly, or when
the battery storage capacity has reached a “weak” condition. A message refers you to the HP Web site
for more information about ordering a replacement battery. If the battery is possibly covered by an HP
warranty, instructions include a warranty ID.
NOTE: To ensure that you always have battery power when you need it, HP recommends purchasing
a new battery when the storage capacity indicator turns green-yellow.
Using battery power 23
Page 34

Testing an AC adapter
Test the AC adapter if the computer exhibits any of the following symptoms:
The computer will not turn on when connected to the AC adapter.
●
The display does not turn on when the computer is connected to the AC adapter.
●
The power light is off when the computer is connected to the AC adapter.
●
To test the AC adapter:
1. Remove the battery from the computer.
2. Connect the AC adapter.
3. Turn on the computer.
If the power light turns on, the AC adapter is functioning properly.
●
If the power light remains off, the AC adapter is not functioning and should be replaced.
●
Contact technical support for information on obtaining a replacement AC power adapter by
selecting Start > Help and Support > Contact support.
Shutting down the computer
CAUTION: Unsaved information will be lost when the computer is shut down.
The Shut Down command closes all open programs, including the operating system, and then turns off
the display and computer.
Shut down the computer under any of the following conditions:
When you need to replace the battery or access components inside the computer
●
When you are connecting an external hardware device that does not connect to a USB port
●
When the computer will be unused and disconnected from external power for an extended period
●
To shut down the computer, follow these steps:
NOTE: If the computer is in the Sleep state or in Hibernation, you must first exit Sleep or Hibernation
before shutdown is possible.
1. Save your work and close all open programs.
2. Click Start, and then click the arrow next to the Lock button.
3. Click Shut Down.
If the computer is unresponsive and you are unable to use the preceding shutdown procedures, try the
following emergency procedures in the sequence provided:
Press ctrl+alt+delete, and then click the power button.
●
Press and hold the power button for at least 5 seconds.
●
Disconnect the computer from external power and remove the battery.
●
24 Chapter 2 Power management
Page 35

3Wireless
Using wireless devices (select models only)
Wireless technology transfers data across radio waves instead of wires. Your computer may be
equipped with one or more of the following wireless devices:
Wireless local area network (WLAN) device—Connects the computer to wireless local area
●
networks (commonly referred to as Wi-Fi networks, wireless LANs, or WLANs) in corporate offices,
your home, and public places such as airports, restaurants, coffee shops, hotels, and universities.
In a WLAN, each mobile wireless device communicates with a wireless router or a wireless access
point.
Bluetooth® device—Creates a personal area network (PAN) to connect to other Bluetooth-enabled
●
devices such as computers, phones, printers, headsets, speakers, and cameras. In a PAN, each
device communicates directly with other devices, and devices must be relatively close together—
typically within 10 meters (approximately 33 feet) of each other.
Computers with WLAN devices support one or more of the following IEEE industry standards:
802.11b, the first popular standard, supports data rates of up to 11 Mbps and operates at a
●
frequency of 2.4 GHz.
802.11g supports data rates of up to 54 Mbps and operates at a frequency of 2.4 GHz. An 802.11g
●
WLAN device is backward compatible with 802.11b devices, so they can operate on the same
network.
802.11a supports data rates of up to 54 Mbps and operates at a frequency of 5 GHz.
●
NOTE: 802.11a is not compatible with 802.11b and 802.11g.
Wi-Fi CERTIFIED 802.11n draft 2.0 supports data rates of up to 300 Mbps and may operate at 2.4
●
GHz or 5 GHz, making it backward compatible with 802.11a, b, and g.
NOTE: The specifications for the 802.11n WLAN are draft specifications and are not final. If the
final specifications differ from the draft specifications, it may affect the ability of the computer to
communicate with other 802.11n WLAN devices.
For more information on wireless technology, refer to the information and Web site links provided in
Help and Support.
Identifying wireless and network icons
Icon Name Description
Using wireless devices (select models only) 25
Page 36

Wireless (connected) Identifies the location of the wireless light and the wireless switch on
the computer.
Wireless
(disconnected)
Network status
(connected)
Network status
(disconnected)
Using the wireless controls
You can control the wireless devices in your computer using these features:
Wireless switch
●
Operating system controls
●
Using the wireless switch
Indicates that all of the wireless devices are off.
Indicates that one or more of your network drivers are installed and one
or more network devices are connected to the network.
Indicates that one or more of your network drivers are installed but no
network devices are connected to the network.
The computer has a wireless switch, one or more wireless devices, and one or two wireless lights,
depending on the model. All of the wireless devices on your computer are enabled at the factory, so the
wireless light is on (blue) when you turn on the computer.
The wireless light indicates the overall power state of your wireless devices, not the status of individual
devices. If the wireless light is blue, at least one wireless device is on. If the wireless light is amber, all
wireless devices are off.
Because the wireless devices are enabled at the factory, you can use the wireless switch to turn on or
turn off the wireless devices simultaneously. Individual wireless devices can be controlled through
Computer Setup.
NOTE: If the wireless devices are disabled by Computer Setup, the wireless switch will not work until
you reenable your devices.
Using operating system controls
Some operating systems also offer a way to manage integrated wireless devices and the wireless
connection. For more information, refer to the operating system documentation.
26 Chapter 3 Wireless
Page 37

Using a WLAN
With a WLAN device, you can access a wireless local area network (WLAN), which is composed of other
computers and accessories that are linked by a wireless router or a wireless access point.
NOTE: The terms wireless router and wireless access point are often used interchangeably.
A large-scale WLAN, such as a corporate or public WLAN, typically uses wireless access points
●
that can accommodate a large number of computers and accessories and can separate critical
network functions.
A home or small office WLAN typically uses a wireless router, which allows several wireless and
●
wired computers to share an Internet connection, a printer, and files without requiring additional
pieces of hardware or software.
NOTE: To use the WLAN device in your computer, you must connect to a WLAN infrastructure
(provided through a service provider or a public or corporate network).
Setting up a WLAN
To set up a WLAN and connect to the Internet, you need the following equipment:
A broadband modem (either DSL or cable) (1) and high-speed Internet service purchased from an
●
Internet service provider (ISP)
A wireless router (purchased separately) (2)
●
The wireless computer (3)
●
The illustration below shows an example of a wireless network installation that is connected to the
Internet.
As your network grows, additional wireless and wired computers can be connected to the network to
access the Internet.
For help in setting up your WLAN, refer to the information provided by your router manufacturer or your
ISP.
Protecting your WLAN
Because the WLAN standard was designed with only limited security capabilities—basically to foil casual
eavesdropping rather than more powerful forms of attack—it is essential to understand that WLANs are
vulnerable to well-known and well-documented security weaknesses.
WLANs in public areas, or “hotspots,” like coffee shops and airports may not provide any security. New
technologies are being developed by wireless manufacturers and hotspot service providers that make
the public environment more secure and anonymous. If you are concerned about the security of your
computer in a hotspot, limit your network activities to noncritical e-mail and basic Internet surfing.
Using a WLAN 27
Page 38

When you set up a WLAN or access an existing WLAN, always enable security features to protect your
network from unauthorized access. The common security levels are Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) and
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP). Because wireless radio signals travel outside the network, other WLAN
devices can pick up unprotected signals and either connect to your network (uninvited) or capture
information being sent across it. However, you can take precautions to protect your WLAN:
Use a wireless transmitter with built-in security
●
Many wireless base stations, gateways, and routers provide built-in security features such as
wireless security protocols and firewalls. With the correct wireless transmitter, you can protect your
network from the most common wireless security risks.
Work behind a firewall
●
A firewall is a barrier that checks both data and requests for data that are sent to your network and
then discards any suspicious items. Firewalls are available in many varieties, both software and
hardware. Some networks use a combination of both types.
Use wireless encryption
●
A variety of sophisticated encryption protocols is available for your WLAN. Find the solution that
works best for your network security:
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a wireless security protocol that uses a WEP key to
◦
encode or encrypt all network data before it is transmitted. Usually, you can allow the network
to assign the WEP key. Alternatively, you can set up your own key, generate a different key,
or choose other advanced options. Without the correct key, others will not be able to use the
WLAN.
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access), like WEP, uses security settings to encrypt and decrypt data
◦
that is transmitted over the network. However, instead of using one static security key for
encryptions as WEP does, WPA uses temporal key integrity protocol (TKIP) to dynamically
generate a new key for every packet. It also generates different sets of keys for each computer
on the network.
Close your network
●
If possible, prevent your network name (SSID) from being broadcast by the wireless transmitter.
Most networks initially broadcast the name, telling any computer nearby that your network is
available. By closing the network, other computers are less likely to know that your network exists.
NOTE: If your network is closed and the SSID is not broadcast, you will need to know or remember
the SSID to connect new devices to the network. Write down the SSID and store it in a secure
place before closing the network.
28 Chapter 3 Wireless
Page 39

Connecting to a WLAN
To connect to the WLAN, follow these steps:
1. Be sure that the WLAN device is on. If it is on, the wireless light is on. If the wireless light is amber,
slide the wireless switch.
2. Select Start > Connect To.
3. Select your WLAN from the list, and then type the network security key, if required.
If the network is unsecured, meaning that anyone can access the network, a warning is
●
displayed. Click Connect Anyway to accept the warning and complete the connection.
If the network is a security-enabled WLAN, you are prompted to enter a network security key,
●
which is a security code. Type the code, and then click Connect to complete the connection.
NOTE: If no WLANs are listed, you are out of range of a wireless router or access point.
NOTE: If you do not see the network you want to connect to, click Show all connections. A list
of options will appear that includes creating a new network connection, as well as troubleshooting
connection issues.
After the connection is made, place the mouse pointer over the network status icon in the notification
area, at the far right of the taskbar, to verify the name and status of the connection.
NOTE: The functional range (how far your wireless signals travel) depends on WLAN implementation,
router manufacturer, and interference from other electronic devices or structural barriers such as walls
and floors.
More information about using a WLAN is available through the following resources:
Information from your ISP and the manufacturer's instructions included with your wireless router
●
and other WLAN equipment
Information and Web site links provided in Help and Support
●
For a list of public WLANs near you, contact your ISP or search the Web. Web sites that list public
WLANs include Cisco Internet Mobile Office Wireless Locations, Hotspotlist, and Geektools. Check with
each public WLAN location for cost and connection requirements.
For additional information on connecting your computer to a corporate WLAN, contact your network
administrator or IT department.
Roaming to another network
When you move your computer within range of another WLAN, Windows attempts to connect to that
network. If the attempt is successful, your computer is automatically connected to the new network. If
Windows does not recognize the new network, follow the same procedure you used initially to connect
to your WLAN.
Using a WLAN 29
Page 40

Using HP Mobile Broadband (select models only)
HP Mobile Broadband enables your computer to use wireless wide area networks (WWANs) to access
the Internet from more places and over larger areas than it can by using WLANs. Using HP Mobile
Broadband requires a network service provider (called a mobile network operator), which in most cases
is a mobile phone network operator. Coverage for HP Mobile Broadband is similar to mobile phone voice
coverage.
When used with mobile network operator service, HP Mobile Broadband gives you the freedom to stay
connected to the Internet, send e-mail, or connect to your corporate network whether you are on the
road or outside the range of Wi-Fi hotspots.
HP supports the following technologies:
HSPA (High Speed Packet Access), which provides access to networks based on the Global
●
System for Mobile Communications (GSM) telecommunications standard.
EV-DO (Evolution Data Optimized), which provides access to networks based on the code division
●
multiple access (CDMA) telecommunications standard.
You may need the HP Mobile Broadband Module serial number to activate mobile broadband service.
The serial number is printed on a label inside the battery bay of your computer.
Some mobile network operators require the use of a subscriber identity module (SIM). A SIM contains
basic information about you, such as a PIN (personal identification number), as well as network
information. Some computers include a SIM that is preinstalled in the battery bay. If the SIM is not
preinstalled, it may be provided in the HP Mobile Broadband information provided with your computer
or the mobile network operator may provide it separately from the computer.
For information on inserting and removing the SIM, refer to the “Inserting a SIM” and “Removing a SIM”
sections in this chapter.
For information on HP Mobile Broadband and how to activate service with a preferred mobile network
operator, refer to the mobile broadband information included with your computer. For additional
information, see the HP Web site at
Inserting a SIM
CAUTION: To prevent damage to the connectors, use minimal force when inserting a SIM.
To insert a SIM:
1. Shut down the computer. If you are not sure whether the computer is off or in Hibernation, turn the
computer on by pressing the power button. Then shut down the computer through the operating
system.
2. Close the display.
3. Disconnect all external devices connected to the computer.
4. Unplug the power cord from the AC outlet.
5. Turn the computer upside down on a flat surface, with the battery bay toward you.
6. Remove the battery.
http://www.hp.com/go/mobilebroadband (US only).
30 Chapter 3 Wireless
Page 41

7. Insert the SIM into the SIM slot, and gently push the SIM into the slot until it is firmly seated.
8. Replace the battery.
NOTE: HP Mobile Broadband will be disabled if the battery is not replaced.
9. Reconnect external power.
10. Reconnect external devices.
11. Turn on the computer.
Removing a SIM
To remove a SIM:
1. Shut down the computer. If you are not sure whether the computer is off or in Hibernation, turn the
computer on by pressing the power button. Then shut down the computer through the operating
system.
2. Close the display.
3. Disconnect all external devices connected to the computer.
4. Unplug the power cord from the AC outlet.
5. Turn the computer upside down on a flat surface, with the battery bay toward you.
6. Remove the battery.
Using HP Mobile Broadband (select models only) 31
Page 42

7. Press in on the SIM (1), and then remove it from the slot (2).
8. Replace the battery.
9. Reconnect external power.
10. Reconnect external devices.
11. Turn on the computer.
32 Chapter 3 Wireless
Page 43

Using Bluetooth wireless devices (select models only)
A Bluetooth device provides short-range wireless communications that replace the physical cable
connections that traditionally link electronic devices such as the following:
Computers (desktop, notebook, PDA)
●
Phones (cellular, cordless, smart phone)
●
Imaging devices (printer, camera)
●
Audio devices (headset, speakers)
●
Bluetooth devices provide peer-to-peer capability that allows you to set up a personal area network
(PAN) of Bluetooth devices. For information on configuring and using Bluetooth devices, refer to the
Bluetooth software Help.
Bluetooth and Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)
HP does not recommend setting up one computer with Bluetooth as a host and using it as a gateway
through which other computers may connect to the Internet. When two or more computers are connected
using Bluetooth, and Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) is enabled on one of the computers, the other
computers may not be able to connect to the Internet using the Bluetooth network.
The strength of Bluetooth is in synchronizing information transfers between your computer and wireless
devices including cellular phones, printers, cameras, and PDAs. The inability to consistently connect
two or more computers to share the Internet through Bluetooth is a limitation of Bluetooth and the
Windows operating system.
Using Bluetooth wireless devices (select models only) 33
Page 44

4 Multimedia
Multimedia features
Your computer includes multimedia features that allow you to listen to music and view pictures. Your
computer may include the following multimedia components:
Integrated speakers for listening to music
●
Integrated microphones for recording your own audio
●
Integrated webcam that allows you to capture and share video
●
Preinstalled multimedia software that allows you to play and manage your music, movies, and
●
pictures
Function keys that provide fast access to volume control
●
NOTE: Your computer may not include all of the components listed.
The following sections explain how to identify and use the multimedia components included with your
computer.
Identifying your multimedia components
The following illustration and table describe the multimedia features of the computer.
34 Chapter 4 Multimedia
Page 45

Component Description
(1) Webcam light On: The webcam is in use.
(2) Webcam Records audio and video and captures still photographs.
(3) Internal microphones (2) Record sound.
(4) Audio-in (microphone) jack Connects an optional computer headset microphone, stereo array
microphone, or monaural microphone.
(5) Audio-out (headphone) jack Produces sound when connected to optional powered stereo
(6) Speakers (2) Produce sound.
Adjusting the volume
You can adjust the volume using the following controls:
Computer volume function keys—Either the f8 (2), f10 (3), or f11 (4) function key:
●
To mute or restore volume, press f8.
◦
To decrease volume, press f10.
◦
speakers, headphones, ear buds, or a headset.
WARNING! To reduce the risk of personal injury, adjust the
volume before putting on headphones, earbuds, or a headset. For
additional safety information, refer to the Regulatory, Safety and
Environmental Notices.
NOTE: When a device is connected to the headphone jack, the
computer speakers are disabled.
Multimedia features 35
Page 46

To increase volume, press f11.
◦
Windows volume control:
●
a. Click the Volume icon in the notification area, at the far right of the taskbar.
b. Increase or decrease the volume by moving the slider up or down. Click the Mute icon to mute
the volume.
– or –
a. Right-click the Volume icon in the notification area, and then click Open Volume Mixer.
b. Increase or decrease the volume by moving the slider up or down. You can also mute the
volume by clicking the Mute icon.
If the Volume icon is not displayed in the notification area, follow these steps to add it:
a. Right-click in the notification area, and then click Properties.
b. Click the Notification Area tab.
c. Under System icons, select the Volume check box.
d. Click OK.
Program volume control:
●
Volume can also be adjusted within some programs.
Multimedia software
Your computer includes preinstalled multimedia software that allows you to play music and view pictures.
The following sections provide details about preinstalled multimedia software and installing multimedia
software from a disc.
36 Chapter 4 Multimedia
Page 47

Using preinstalled multimedia software
To locate preinstalled multimedia software:
Select Start > All Programs, and then open the multimedia program you want to use.
▲
NOTE: Some programs may be located in subfolders.
Installing multimedia software from a disc
NOTE: To install multimedia software from a disc, you must have an external optical drive connected
to the computer. The computer provides one powered USB port on the left side of the computer. This
port provides power to the external optical drive when used with a powered USB cable. An external
optical drive connected to the other USB port on the computer must be connected to AC power.
To install any multimedia software from a CD or DVD, follow these steps:
1. Insert the disc into a connected external optical drive.
2. When the installation wizard opens, follow the on-screen instructions.
3. Restart the computer if prompted to do so.
NOTE: For details about using software included with the computer, refer to the software
manufacturer’s instructions, which may be provided with the software, on disc, or on the
manufacturer’s Web site.
Multimedia software 37
Page 48

Audio
Your computer enables you to use a variety of audio features:
Play music using your computer speakers and/or connected external speakers
●
Record sound using the internal microphones or connect an external microphone
●
Download music from the Internet
●
Create multimedia presentations using audio and images
●
Transmit sound and images with instant messaging programs
●
Stream radio programs (select models only) or receive FM radio signals
●
Create or “burn” audio CDs using an external optical drive
●
Connecting external audio devices
WARNING! To reduce the risk of personal injury, adjust the volume before putting on headphones,
earbuds, or a headset. For additional safety information, refer to the Regulatory, Safety and
Environmental Notices.
To connect external devices such as external speakers, headphone, or a microphone, refer to the
information provided with the device. For best results, remember the following tips:
Be sure that the device cable is securely connected to the correct jack on your computer. (Cable
●
connectors are normally color-coded to match the corresponding jacks on the computer.)
Be sure to install any drivers required by the external device.
●
NOTE: A driver is a required program that acts like a translator between the device and the
programs that use the device.
Checking your audio functions
To check the system sound on your computer, follow these steps:
1. Select Start > Control Panel.
2. Click Hardware and Sound.
3. Click Sound.
4. When the Sound window opens, click the Sounds tab. Under Program, select any sound event,
such as a beep or alarm, and click the Test button.
You should hear sound through the speakers or through connected headphones.
To check the record functions of the computer, follow these steps:
1. Select Start > All Programs > Accessories > Sound Recorder.
2. Click Start Recording and speak into the microphone. Save the file to the desktop.
3. Open Windows Media Player and play back the sound.
38 Chapter 4 Multimedia
Page 49

NOTE: For best results when recording, speak directly into the microphone and record sound in a
setting free of background noise.
To confirm or change the audio settings on your computer, right-click the Sound icon on the
▲
taskbar, or select Start > Control Panel > Audio.
Audio 39
Page 50

Video
Your computer enables you to use a variety of video features:
Play games over the Internet
●
Edit pictures and video to create presentations
●
Connect external video devices
●
Connecting an external monitor or projector
The external monitor port connects an external display device such as an external monitor or a projector
to the computer.
To connect a display device, connect the device cable to the external monitor port.
▲
NOTE: If a properly connected external display device does not display an image, press f2 to transfer
the image to the device. Repeatedly pressing f2 alternates the screen image between the computer
display and the device.
40 Chapter 4 Multimedia
Page 51

Optical drive (select models only)
Your computer may come with an external optical drive that expands the functionality of the computer.
The external optical drive allows you to read data discs, play music, and watch movies.
Identifying the external optical drive
Select Start > Computer.
▲
You will see a list of all the devices installed on your computer, including the connected external optical
drive. You may have one of the following types of drives:
DVD-ROM Drive
●
DVD/CD-RW Combo Drive
●
DVD±RW/R and CD-RW Combo Drive with Double-Layer (DL) support
●
NOTE: Some of the drives listed above may not be supported by your computer.
Using optical discs
An optical drive, such as a DVD-ROM drive, supports optical discs (CDs and DVDs). These discs store
information, such as music, photos, and movies. DVDs have a higher storage capacity than CDs.
The external optical drive can read standard CD and DVD discs.
NOTE: Some of the optical drives listed may not be supported by your computer. The listed drives are
not necessarily all of the supported optical drives.
Some optical drives can also write to optical discs as described in the following table.
Optical drive type Read from CD and
DVD-ROM media
DVD-ROM Drive Yes No No No
DVD/CD-RW Combo
Drive
DVD±RW/CD-RW
Combo Drive
Yes Yes No No
Yes Yes Yes No
CAUTION: To prevent possible audio and video degradation, loss of information, or loss of audio or
video playback functionality, do not initiate Sleep or Hibernation while reading or writing to a CD or DVD.
Selecting the right disc
An optical drive supports optical discs (CDs and DVDs). CDs, used to store digital data, are also used
for commercial audio recordings and are convenient for your personal storage needs. DVDs are used
primarily for movies, software, and data backup purposes. DVDs are the same form factor as CDs but
have 6 to 7 times the storage capacity.
Write to CD-R/RW
media
Write to DVD (includes
DVD+R DL, DVD±RW/
R, and DVD-ROM
media)
Write label to
LightScribe CD or
DVD
NOTE: The external optical drive connected to your computer may not support all the types of optical
discs discussed in this section.
Optical drive (select models only) 41
Page 52

CD-R discs
Use CD-R (write-once) discs to create permanent archives and to share files with virtually anyone.
Typical uses include the following:
●
●
●
●
●
After data is recorded, it cannot be erased or written over.
CD-RW discs
Use a CD-RW disc (a rewritable version of a CD) to store large projects that must be updated frequently.
Typical uses include the following:
●
●
●
Distributing large presentations
Sharing scanned and digital photos, video clips, and written data
Making your own music CDs
Keeping permanent archives of computer files and scanned home records
Offloading files from your hard drive to free up disk space
Developing and maintaining large documents and project files
Transporting work files
Making weekly backups of hard drive files
Updating photos, video, audio, and data continuously
●
DVD±R discs
Use blank DVD±R discs to permanently store large amounts of information. After data is recorded, it
cannot be erased or written over.
DVD±RW discs
Use DVD±RW discs if you want to be able to erase or write over data that you saved earlier. This type
of disc is ideal for testing audio or video recordings before you burn them to a CD or DVD that cannot
be changed.
Playing music
NOTE: Be sure that the external optical drive is connected to your computer before beginning these
steps.
1. Turn on the computer.
2. Press the release button (1) on the external optical drive bezel to release the disc tray.
3. Pull out the tray (2).
4. Hold the disc by the edges and position the disc label-side up over the tray spindle.
NOTE: If the tray is not fully accessible, tilt the disc carefully to position it over the spindle.
42 Chapter 4 Multimedia
Page 53

5. Gently press the disc (3) down onto the tray spindle until the disc snaps into place.
6. Close the disc tray.
7. If you have not yet configured AutoPlay, the AutoPlay dialog box opens and asks how you want to
use the media content. Choose Windows Media Player, which is preinstalled on your computer.
NOTE: After you insert a disc, a short pause is normal.
If Sleep or Hibernation is accidentally initiated during playback of a disc:
Your playback may be interrupted.
●
You may see a warning message asking if you want to continue. If this message is displayed, click
●
No.
You may need to restart the CD or DVD to resume playback.
●
Watching a movie
To play a movie from the external optical drive, software must be obtained separately (not included).
NOTE: Be sure that the external optical drive is connected to your computer before beginning these
steps.
1. Turn on the computer.
2. Press the release button (1) on the external optical drive bezel to release the disc tray.
3. Pull out the tray (2).
4. Hold the disc by the edges and position the disc label-side up over the tray spindle.
NOTE: If the tray is not fully accessible, tilt the disc carefully to position it over the spindle.
Optical drive (select models only) 43
Page 54

5. Gently press the disc (3) down onto the tray spindle until the disc snaps into place.
6. Close the disc tray.
NOTE: After you insert a disc, a short pause is normal.
Changing DVD region settings
Most DVDs that contain copyrighted files also contain region codes. The region codes help protect
copyrights internationally.
You can play a DVD containing a region code only if the region code on the DVD matches the region
setting on your DVD drive.
CAUTION: The region settings on your DVD drive can be changed only 5 times.
The region setting you select the fifth time becomes the permanent region setting on the DVD drive.
The number of region changes remaining is displayed on the DVD Region tab.
To change settings through the operating system:
1. Select Start > Computer > System properties.
2. In the left pane, click Device Manager.
NOTE: Windows includes the User Account Control feature to improve the security of your
computer. You may be prompted for your permission or password for tasks such as installing
applications, running utilities, or changing Windows settings. Refer to Windows Help and Support
for more information.
3. Click the "+" sign next to DVD/CD-ROM drives.
4. Right-click the DVD drive for which you want to change region settings, and then click
Properties.
5. Make the desired changes on the DVD Region tab.
6. Click OK.
44 Chapter 4 Multimedia
Page 55

Creating or “burning” a CD or DVD
If your external optical drive is a CD-RW, DVD-RW, or DVD±RW optical drive, you can use software
such as Windows Media Player to burn data and audio files, including MP3 and WAV music files. To
burn video files to a CD or DVD, use MyDVD.
Observe the following guidelines when burning a CD or DVD:
Before burning a disc, save and close any open files and close all programs.
●
A CD-R or DVD-R is usually best for burning audio files because after the information is copied, it
●
cannot be changed.
Because some home and car stereos will not play CD-RWs, use CD-Rs to burn music CDs.
●
A CD-RW or DVD-RW is generally best for burning data files or for testing audio or video recordings
●
before you burn them to a CD or DVD that cannot be changed.
DVD players used in home systems usually do not support all DVD formats. Refer to the user guide
●
that came with your DVD player for a list of supported formats.
An MP3 file uses less space than other music file formats, and the process for creating an MP3
●
disc is the same as the process for creating a data file. MP3 files can be played only on MP3 players
or on computers with MP3 software installed.
To burn a CD or DVD, follow these steps:
1. Download or copy the source files into a folder on your hard drive.
2. Insert a blank CD or DVD into the external optical drive.
3. Select Start > All Programs and the name of the software you want to use.
4. Select the kind of CD or DVD you want to create—data, audio, or video.
5. Right-click Start, click Explore, and navigate to the folder where the source files are stored.
6. Open the folder, and then drag the files to the drive that contains the blank optical disc.
7. Initiate the burning process as directed by the program you have selected.
For specific instructions, refer to the software manufacturer's instructions, which may be provided with
the software, on disc, or on the manufacturer's Web site.
CAUTION: Observe the copyright warning. It is a criminal offense, under applicable copyright laws,
to make unauthorized copies of copyright-protected material, including computer programs, films,
broadcasts, and sound recordings. Do not use this computer for such purposes.
Removing an optical disc (CD or DVD)
1. Press the release button (1) on the drive bezel to release the disc tray, and then gently pull out the
tray (2) until it stops.
Optical drive (select models only) 45
Page 56

2. Remove the disc (3) from the tray by gently pressing down on the spindle while lifting the outer
edges of the disc. Hold the disc by the edges and avoid touching the flat surfaces.
NOTE: If the tray is not fully accessible, tilt the disc carefully as you remove it.
3. Close the disc tray and place the disc in a protective case.
46 Chapter 4 Multimedia
Page 57

Webcam
Your computer model includes an integrated webcam, located at the top of the display. The webcam
can be used with a variety of software for the following functions:
●
●
●
NOTE: Be sure that you have installed software that is designed for use with the integrated webcam.
NOTE: For information about using software designed for use with the integrated webcam, refer to
the online Help for that software.
For optimum performance, observe the following guidelines while using the integrated webcam:
●
●
Capturing video
Streaming video with instant message software
Taking still photos
Be sure that you have the latest version of an instant message program before attempting a video
conversation.
The webcam may not work properly across some network firewalls.
NOTE: If you are having trouble viewing or sending multimedia files to someone on another LAN
or outside your network firewall, temporarily disable the firewall, perform the task you want to
perform, and then reenable the firewall. To permanently resolve the problem, reconfigure the
firewall as necessary, and adjust the policies and settings of other intrusion detection systems. For
additional information, contact your network administrator or IT department.
Whenever possible, place bright light sources behind the webcam and out of the picture area.
●
Adjusting webcam properties
You can adjust webcam properties using the Properties dialog box, which is accessible from various
programs that use the integrated webcam, usually from a configuration, settings, or properties menu:
Brightness—Controls the amount of light that is incorporated into the image. A higher brightness
●
setting creates a brighter image; a lower brightness setting creates a darker image.
Contrast—Controls the difference between lighter and darker areas on the image. A higher
●
contrast setting intensifies the image; a lower contrast setting maintains more of the original
information’s dynamic range but leads to a flatter image.
Hue—Controls the aspect of color that distinguishes it from another color (what makes a color red,
●
green, or blue). Hue is distinct from saturation, which measures the intensity of the hue.
Saturation—Controls the strength of color in the final image. A higher saturation setting creates a
●
bolder image; a lower saturation setting creates a more subtle image.
Sharpness—Controls the definition of edges in an image. A higher sharpness setting creates a
●
more defined image; a lower sharpness setting creates a softer image.
Gamma—Controls the contrast affecting the mid-level grays or midtones of an image. Adjusting
●
the gamma of an image allows you to change the brightness values of the middle range of gray
tones without dramatically altering the shadows and highlights. A lower gamma setting makes
grays look black, and makes dark colors even darker.
For information about using the webcam, select Start > Help and Support.
Webcam 47
Page 58

5Security
Protecting the computer
NOTE: Security solutions are designed to act as deterrents. These deterrents may not prevent a
product from being mishandled or stolen.
NOTE: In some countries or regions, the computer supports CompuTrace, which is an online-security-
based tracking and recovery service. If the computer is stolen, CompuTrace can track the computer if
the unauthorized user accesses the Internet. You must purchase the software and subscribe to the
service in order to use CompuTrace. For information about ordering the CompuTrace software, see the
HP Web site at
Security features provided with your computer can protect the computer, personal information, and data
from a variety of risks. The way you use your computer will determine which security features you need
to use.
http://www.hpshopping.com.
The Windows operating system offers certain security features. Additional security features are listed
in the following table. Most of these additional security features can be configured in the Computer Setup
utility.
To protect against Use this security feature
Unauthorized use of the computer Power-on authentication using passwords or smart cards
Unauthorized access to Computer Setup (f10) Setup password in Computer Setup*
Unauthorized access to the contents of a hard drive DriveLock password in Computer Setup*
Unauthorized reset of Computer Setup (f10) passwords Stringent security feature in Computer Setup*
Unauthorized startup from an optical drive, diskette drive, or
internal network adapter
Unauthorized access to data
Unauthorized access to Computer Setup settings and other
system identification information
Unauthorized removal of the computer Security cable slot (used with an optional security cable)
*Computer Setup is a non-Windows utility accessed by pressing f10 when the computer is turned on or restarted. When using
Computer Setup, you must use the keys on your computer to navigate and make selections.
Boot options feature in Computer Setup*
Firewall software
●
Windows updates
●
Setup password in Computer Setup*
48 Chapter 5 Security
Page 59

Using passwords
A password is a group of characters that you choose to secure your computer information. Several types
of passwords can be set, depending on how you want to control access to your information. Passwords
can be set in Windows or in the non-Windows Computer Setup utility that is preinstalled on the computer.
CAUTION: To prevent being locked out of the computer, record each password you set. Because
most passwords are not displayed as they are set, changed, or deleted, it is essential to record each
password immediately and store it in a secure place.
You can use the same password for a Computer Setup feature and for a Windows security feature. You
can also use the same password for more than one Computer Setup feature.
Use the following guidelines when setting a password in Computer Setup:
A password can be any combination of up to 8 letters and numbers and is case sensitive.
●
A password set in Computer Setup must be entered at a Computer Setup prompt. A password set
●
in Windows must be entered at a Windows prompt.
Use the following tips for creating and saving passwords:
When creating passwords, follow requirements set by the program.
●
Write down your passwords and store them in a secure place away from the computer.
●
Do not store passwords in a file on the computer.
●
Do not use your name or other personal information that could be easily discovered by an outsider.
●
The following sections list Windows and Computer Setup passwords and describe their functions. For
additional information about Windows passwords, such as screen-saver passwords, select Start > Help
and Support.
Setting passwords in Windows
Windows passwords Function
Administrator password* Protects access to a Windows administrator-level account.
User password* Protects access to a Windows user account.
*For information about setting a Windows administrator password or a Windows user password, select Start > Help and
Support.
Setting passwords in Computer Setup
Computer Setup passwords Function
Setup password Protects access to Computer Setup.
Power-on password Protects access to the computer contents when the computer
turns on, restarts, or exits Hibernation.
Using passwords 49
Page 60

Computer Setup passwords Function
DriveLock master password Protects access to the internal hard drive that is protected by
DriveLock user password Protects access to the internal hard drive that is protected by
Setup password
The Computer Setup setup password protects the configuration settings and system identification
information in Computer Setup. After this password is set, it must be entered to access Computer Setup
and to make changes using Computer Setup.
Note the following characteristics of the setup password:
It is not interchangeable with a Windows administrator password, although both passwords can be
●
identical.
It is not displayed as it is set, entered, changed, or deleted.
●
It must be set and entered with the same keys. For example, a setup password set with keyboard
●
number keys will not be recognized if you enter it thereafter with embedded numeric keypad number
keys.
DriveLock. It is also used to remove DriveLock protection. This
password is set under DriveLock Passwords during the enable
process.
DriveLock, and is set under DriveLock Passwords during the
enable process.
It can include any combination of up to 32 letters and numbers and is not case sensitive.
●
50 Chapter 5 Security
Page 61

Managing a setup password
A setup password is set, changed, and deleted in Computer Setup.
To manage, set, change, or delete this password, follow these steps:
1. Open Computer Setup by turning on or restarting the computer, and then pressing f10 while the
“F10 = ROM Based Setup” message is displayed in the lower-left corner of the screen.
2. Use the arrow keys to select Security > Setup Password, and then press enter.
To set a setup password, type your password in the New password and Verify new
●
password fields, and then press f10.
To change a setup password, type your current password in the Old password field, type a
●
new password in the New password and Verify new password fields, and then press f10.
To delete a setup password, type your current password in the Old password field, and then
●
press f10.
3. To save your preferences, use the arrow keys to select File > Save changes and exit. Then follow
the instructions on the screen.
Your preferences go into effect when the computer restarts.
Using passwords 51
Page 62

Entering a setup password
At the Setup password prompt, type your setup password (using the same kind of keys you used to
set the password), and then press enter. After 3 unsuccessful attempts to enter the setup password,
you must restart the computer and try again.
Power-on password
The Computer Setup power-on password prevents unauthorized use of the computer. After this
password is set, it must be entered each time the computer is turned on.
Note the following characteristics of a power-on password:
It is not displayed as it is set, entered, changed, or deleted.
●
It must be set and entered with the same keys. For example, a power-on password set with
●
keyboard number keys will not be recognized if you enter it thereafter with embedded numeric
keypad number keys.
It can include any combination of up to 32 letters and numbers and is not case sensitive.
●
52 Chapter 5 Security
Page 63

Managing a power-on password
A power-on password is set, changed, and deleted in Computer Setup.
To manage, set, change, or delete this password, follow these steps:
1. Open Computer Setup by turning on or restarting the computer, and then pressing f10 while the
“F10 = ROM Based Setup” message is displayed in the lower-left corner of the screen.
2. Use the arrow keys to select Security > Power-On password, and then press enter.
To set a power-on password, type the password in the New password and Verify new
●
password fields, and then press f10.
To change a power-on password, type the current password in the Old password field, type
●
the new password in the New password and Verify new password fields, and then press
f10.
To delete a power-on password, type the current password in the Old password field, and
●
then press f10.
3. To save your preferences, use the arrow keys to select File > Save changes and exit. Then follow
the instructions on the screen.
Your preferences go into effect when the computer restarts.
Using passwords 53
Page 64

Entering a power-on password
At the Power-on Password prompt, type your password (using the same kind of keys you used to set
the password), and then press enter. After 3 unsuccessful attempts to enter the password, you must
turn off the computer, turn it back on, and then try again.
54 Chapter 5 Security
Page 65

Requiring a power-on password at restart
In addition to requiring that a power-on password be entered each time the computer is turned on, you
can also require that a power-on password be entered each time the computer is restarted.
To enable and disable this feature in Computer Setup, follow these steps:
1. Open Computer Setup by turning on or restarting the computer, and then pressing f10 while the
“F10 = ROM Based Setup” message is displayed in the lower-left corner of the screen.
2. Use the arrow keys to select Security > Password options, and then press enter.
3. Use the arrow keys to select Enable or Disable in the Require password on restart field, and
then press f10.
4. To save your preferences, use the arrow keys to select File > Save changes and exit. Then follow
the instructions on the screen.
Using Computer Setup DriveLock
CAUTION: To prevent the DriveLock-protected hard drive from becoming permanently unusable,
record the DriveLock user password and the DriveLock master password in a safe place away from your
computer. If you forget both DriveLock passwords, the hard drive will be permanently locked and can
no longer be used.
DriveLock protection prevents unauthorized access to the contents of a hard drive. DriveLock can be
applied only to the internal hard drive(s) of the computer. After DriveLock protection is applied to a drive,
a password must be entered to access the drive. The drive must be inserted into the computer, not into
an optional docking device or external MultiBay, in order for it to be accessed by the DriveLock
passwords.
To apply DriveLock protection to an internal hard drive, a user password and a master password must
be set in Computer Setup. Note the following considerations about using DriveLock protection:
After DriveLock protection is applied to a hard drive, the hard drive can be accessed only by entering
●
either the user password or the master password.
The owner of the user password should be the day-to-day user of the protected hard drive. The
●
owner of the master password may be either a system administrator or the day-to-day user.
The user password and the master password can be identical.
●
You can delete a user password or master password only by removing DriveLock protection from
●
the drive. DriveLock protection can be removed from the drive only with the master password.
NOTE: When your power-on password and DriveLock user password are identical, you will be
prompted to enter only a power-on password instead of both a power-on password and a DriveLock
user password.
Using passwords 55
Page 66

Setting a DriveLock password
To access the DriveLock settings in Computer Setup, follow these steps:
1. Open Computer Setup by turning on or restarting the computer, and then pressing f10 while the
“F10 = ROM Based Setup” message is displayed in the lower-left corner of the screen.
2. Use the arrow keys to select Security > DriveLock passwords, and then press enter.
3. Select the location of the hard drive you want to protect, and then press f10.
4. Use the arrow keys to select Enable in the Protection field, and then press f10.
5. Read the warning. To continue, press f10.
6. Type your user password in the New password and Verify new password fields, and then press
f10.
7. Type your master password in the New password and Verify new password fields, and then
press f10.
8. To confirm DriveLock protection on the drive you have selected, type DriveLock in the
confirmation field, and then press f10.
9. To exit DriveLock settings, use the arrow keys to select Esc.
10. To save your preferences, use the arrow keys to select File > Save changes and exit. Then follow
the instructions on the screen.
Your preferences go into effect when the computer restarts.
56 Chapter 5 Security
Page 67

Entering a DriveLock password
Be sure that the hard drive is inserted into the computer (not into an optional docking device or external
MultiBay).
At the DriveLock Password prompt, type your user or master password (using the same kind of keys
you used to set the password), and then press enter.
After 2 incorrect attempts to enter the password, you must shut down the computer and try again.
Using passwords 57
Page 68

Changing a DriveLock password
To access the DriveLock settings in Computer Setup, follow these steps:
1. Open Computer Setup by turning on or restarting the computer, and then pressing f10 while the
“F10 = ROM Based Setup” message is displayed in the lower-left corner of the screen.
2. Use the arrow keys to select Security > DriveLock passwords, and then press enter.
3. Use the arrow keys to select the location of the internal hard drive, and then press f10.
4. Use the arrow keys to select the field for the password you want to change. Type your current
password in the Old password field, and then type the new password in the New password field
and in the Verify new password field. Then press f10.
5. To save your preferences, use the arrow keys to select File > Save changes and exit. Then follow
the instructions on the screen.
Your preferences go into effect when the computer restarts.
58 Chapter 5 Security
Page 69

Removing DriveLock protection
To access the DriveLock settings in Computer Setup, follow these steps:
1. Open Computer Setup by turning on or restarting the computer, and then pressing f10 while the
“F10 = ROM Based Setup” message is displayed in the lower-left corner of the screen.
2. Use the arrow keys to select Security > DriveLock passwords, and then press enter.
3. Use the arrow keys to select the location of the internal hard drive, and then press f10.
4. Use the arrow keys to select Disable in the Protection field, and then press f10.
5. Type your master password in the Old password field. Then press f10.
6. To save your preferences, use the arrow keys to select File > Save changes and exit. Then follow
the instructions on the screen.
Your preferences go into effect when the computer restarts.
Using passwords 59
Page 70

Using Computer Setup security features
Securing system devices
From the Boot options menu or the Port options menu in Computer Setup, you can disable or enable
system devices.
To disable or reenable system devices in Computer Setup, follow these steps:
1. Open Computer Setup by turning on or restarting the computer, and then pressing f10 while the
“F10 = ROM Based Setup” message is displayed in the lower-left corner of the screen.
2. Use the arrow keys to select System Configuration > Boot options or System Configuration
> Port options. Then press enter and use the arrow keys to select the options you want.
3. To confirm your preferences, press f10.
4. To save your preferences, use the arrow keys to select File > Save changes and exit. Then follow
the instructions on the screen.
Your preferences go into effect when the computer restarts.
Using Computer Setup stringent security
CAUTION: To prevent the computer from becoming permanently unusable, record your configured
setup password, power-on password, or smart card PIN in a safe place away from your computer.
Without these passwords or PIN, the computer cannot be unlocked.
The stringent security feature enhances power-on security by forcing user authentication with your
configured setup password, power-on password, or smart card PIN before granting access to the
system.
60 Chapter 5 Security
Page 71

Setting stringent security
To enable stringent security in Computer Setup, follow these steps:
1. Open Computer Setup by turning on or restarting the computer, and then pressing f10 while the
“F10 = ROM Based Setup” message is displayed in the lower-left corner of the screen.
2. Use the arrow keys to select Security > Password options, and then press enter.
3. Use the arrow keys to select Enable in the Stringent security field.
4. Read the warning. To continue, press f10.
5. To enable the feature each time the computer is turned on, press f10.
6. To save your preferences, use the arrow keys to select File > Save changes and exit. Then follow
the instructions on the screen.
Your preferences go into effect when the computer restarts.
Using Computer Setup security features 61
Page 72

Removing stringent security
To remove stringent security in Computer Setup, follow these steps:
1. Open Computer Setup by turning on or restarting the computer, and then pressing f10 while the
“F10 = ROM Based Setup” message is displayed in the lower-left corner of the screen.
2. Use the arrow keys to select Security > Password options and then press enter.
3. Use the arrow keys to select Disable in the Stringent security field, and then press f10.
4. To save your preferences, use the arrow keys to select File > Save changes and exit. Then follow
the instructions on the screen.
Your preferences go into effect when the computer restarts.
Viewing Computer Setup System Information
The System Information feature in Computer Setup provides 2 types of system information:
Identification information about the computer model.
●
Specification information for the processor, cache and memory size, and system ROM.
●
To view this general system information, follow these steps:
1. Open Computer Setup by turning on or restarting the computer, and then pressing f10 while the
“F10 = ROM Based Setup” message is displayed in the lower-left corner of the screen.
2. Use the arrow keys to select File > System Information, and then press enter.
NOTE: To prevent unauthorized access to this information, you must create a setup password in
Computer Setup.
62 Chapter 5 Security
Page 73

Using antivirus software
When you use the computer to access e-mail, a network, or the Internet, you expose the computer to
computer viruses. Computer viruses can disable the operating system, applications, or utilities, or cause
them to function abnormally.
Antivirus software can detect most viruses, destroy them, and in most cases, repair any damage they
have caused. To provide ongoing protection against newly discovered viruses, antivirus software must
be updated.
For more information about computer viruses, type viruses in the Search box in Help and Support.
Using antivirus software 63
Page 74

Using firewall software
When you use the computer to access e-mail, a network, or the Internet, unauthorized persons may be
able to gain access to information about you, the computer, and your personal files. Use the firewall
software preinstalled on the computer to protect your privacy.
Firewall features include information on logging and reporting, and automatic alarms to monitor all
incoming and outgoing traffic. Refer to the firewall documentation or contact your firewall manufacturer
for more information.
NOTE: Under some circumstances a firewall can block access to Internet games, interfere with printer
or file sharing on a network, or block authorized e-mail attachments. To temporarily solve the problem,
disable the firewall, perform the task that you want to perform, and then reenable the firewall. To
permanently resolve the problem, reconfigure the firewall.
64 Chapter 5 Security
Page 75

Installing critical updates
CAUTION: To protect the computer from security breaches and computer viruses, install the online
critical updates from Microsoft as soon as you receive an alert.
Updates to the operating system and other software may have become available after the computer
was shipped. To be sure that all available updates are installed on the computer, observe these
guidelines:
Run Windows Update monthly to install the latest software from Microsoft.
●
Obtain updates, as they are released, from the Microsoft Web site and through the updates link in
●
Help and Support.
Installing critical updates 65
Page 76

Installing a security cable
NOTE: The security cable is designed to act as a deterrent, but it may not prevent the computer from
being mishandled or stolen.
1. Loop the security cable around a secured object.
2. Insert the key (1) into the cable lock (2).
3. Insert the cable lock into the security cable slot on the computer (3), and then lock the cable lock
with the key.
66 Chapter 5 Security
Page 77

6 External devices
Using a USB device
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is a hardware interface that can be used to connect an optional external
device, such as a USB keyboard, mouse, drive, printer, scanner, or hub.
Some USB devices may require additional support software, which is usually included with the device.
For more information about device-specific software, refer to the manufacturer's instructions.
Your computer model has 2 USB ports, which support USB 1.0, USB 1.1, and USB 2.0 devices. A USB
hub provides additional USB ports that can be used with the computer.
Connecting a USB device
CAUTION: To prevent damage to a USB connector, use minimal force to connect a USB device.
To connect a USB device to the computer, connect the USB cable for the device to the USB
▲
port.
You will hear a sound when the device has been detected.
NOTE: The first time you connect a USB device, a message is displayed in the notification area to let
you know the device is recognized by the computer.
Stopping and removing a USB device
CAUTION: To prevent loss of information or an unresponsive system, stop a USB device before
removing it.
Using a USB device 67
Page 78

CAUTION: To prevent damage to a USB connector, do not pull on the cable to remove the USB device.
To stop and remove a USB device:
1. Double-click the Safely Remove Hardware icon in the notification area, at the far right of the
taskbar.
NOTE: To display the Safely Remove Hardware icon, click the Show Hidden Icons icon (< or
<<) in the notification area.
2. Click the name of the device in the list.
NOTE: If the USB device is not listed, you do not have to stop the device before you remove it.
3. Click Stop, and then click OK.
4. Remove the device.
Using USB legacy support
USB legacy support (enabled by default) permits the following actions:
Using a USB keyboard, mouse, or hub connected to a USB port on the computer during startup or
●
in an MS-DOS-based program or utility
Starting or restarting from an optional external MultiBay or an optional USB bootable device
●
USB legacy support is enabled at the factory. To disable or enable USB legacy support:
1. Open Computer Setup by turning on or restarting the computer, and then pressing f10 while the
“F10 = ROM Based Setup” message is displayed in the lower-left corner of the screen.
2. Use the arrow keys to select System Configuration > Device configurations, and then press
enter.
3. Use the arrow keys to enable or disable USB legacy support, and then press f10.
4. To save your preferences and exit Computer Setup, use the arrow keys to select File > Save
changes and exit. Then follow the instructions on the screen.
Your preferences go into effect when the computer restarts.
68 Chapter 6 External devices
Page 79

Using external drives
Removable external drives expand your options for storing and accessing information. A USB drive can
be added by connecting the drive to a USB port on the computer.
NOTE: HP external USB optical drives should be connected to the powered USB port on the left side
of the computer.
USB drives include the following types:
1.44-megabyte diskette drive
●
Hard drive module (a hard drive with an adapter attached)
●
DVD-ROM Drive
●
DVD/CD-RW Combo Drive
●
DVD+RW and CD-RW Combo Drive
●
DVD±RW/CD-RW Combo Drive
●
MultiBay device
●
Using optional external devices
NOTE: For more information about required software and drivers, or to learn which computer port to
use, refer to the manufacturer's instructions.
To connect an external device to the computer:
CAUTION: To reduce the risk of damage to the equipment when connecting a powered device, be
sure that the device is turned off and the AC power cord is unplugged.
1. Connect the device to the computer.
2. If you are connecting a powered device, plug the device power cord into a grounded AC outlet.
3. Turn on the device.
To disconnect an unpowered external device, turn off the device, and then disconnect it from the
computer. To disconnect a powered external device, turn off the device, disconnect it from the computer,
and then unplug the AC power cord.
Using an optional external MultiBay II
An external MultiBay II connects to a USB port on the computer and enables you to use MultiBay II
devices. The computer provides one powered USB port on the left side of the computer. This port
provides power to the external MultiBay when used with a powered USB cable. An external MultiBay
connected to the other USB port on the computer must be connected to AC power.
For more information about the external MultiBay II, refer to the user guide that is included with the
device.
Using external drives 69
Page 80

Using an optional external optical drive (select models only)
An external optical drive connects to a USB port on the computer and enables you to use optical discs
(CDs and DVDs). The computer provides one powered USB port on the left side of the computer. This
port provides power to the external optical drive when used with a powered USB cable. An external
optical drive connected to the other USB port on the computer must be connected to AC power.
An external optical drive, such as a DVD-ROM drive, supports optical discs (CDs and DVDs). These
discs store or transport information and play music and movies. DVDs have a higher storage capacity
than CDs.
All optical drives can read from optical discs and some drives can also write to optical discs as described
in the following table.
Optical drive type Read from CD and
DVD-ROM media
DVD-ROM Drive Yes No No No
DVD/CD-RW Combo
Drive
DVD±RW/CD-RW
Combo Drive
NOTE: Some of the optical drives listed may not be supported by your computer. The listed drives are not necessarily all of
the supported optical drives.
Yes Yes No No
Yes Yes Yes No
Write to CD-R/RW
media
Write to DVD
(includes DVD+R DL,
DVD±RW/R, and DVDRAM media)
Write label to
LightScribe CD or
DVD
CAUTION: To prevent possible audio and video degradation, or loss of audio or video playback
functionality, do not initiate Sleep or Hibernation while reading from or writing to a CD or DVD.
To prevent loss of information, do not initiate Sleep or Hibernation when writing to a CD or DVD.
If Sleep or Hibernation is initiated during playback of a disc, you may experience the following behaviors:
Your playback may be interrupted.
●
You may see a warning message asking if you want to continue. If this message is displayed, click
●
No.
You may need to restart the CD or DVD to resume audio and video playback.
●
Inserting an optical disc (CD or DVD)
1. Turn on the computer.
2. Press the release button (1) on the drive bezel to release the disc tray.
3. Pull out the tray (2).
4. Hold the disc by the edges to avoid touching the flat surfaces and position the disc label-side up
over the tray spindle.
NOTE: If the tray is not fully accessible, tilt the disc carefully to position it over the spindle.
70 Chapter 6 External devices
Page 81

5. Gently press the disc (3) down onto the tray spindle until the disc snaps into place.
6. Close the disc tray.
Removing an optical disc (CD or DVD)
There are 2 ways to remove a disc, depending on whether the disc tray opens normally or not.
When the disc tray opens
1. Press the release button (1) on the drive bezel to release the disc tray, and then gently pull out the
tray (2) until it stops.
2. Remove the disc (3) from the tray by gently pressing down on the spindle while lifting the outer
edges of the disc. Hold the disc by the edges and avoid touching the flat surfaces.
NOTE: If the tray is not fully accessible, tilt the disc carefully as you remove it.
3. Close the disc tray and place the disc in a protective case.
Using an optional external optical drive (select models only) 71
Page 82

When the disc tray does not open
1. Insert the end of a paper clip (1) into the release access in the front bezel of the drive.
2. Press in gently on the paper clip until the tray is released, and then pull out the tray (2) until it stops.
3. Remove the disc (3) from the tray by gently pressing down on the spindle while lifting the outer
edges of the disc. Hold the disc by the edges and avoid touching the flat surfaces.
NOTE: If the tray is not fully accessible, tilt the disc carefully as you remove it.
4. Close the disc tray and place the disc in a protective case.
72 Chapter 6 External devices
Page 83

7 External media cards
Using SD Card Reader cards
Optional digital cards provide secure data storage and convenient data sharing. These cards are often
used with digital media–equipped cameras and PDAs as well as with other computers.
The SD Card Reader supports the following formats:
MultiMediaCard (MMC)
●
Secure Digital (SD) Memory Card
●
Inserting a digital card
CAUTION: To avoid damaging the digital card or the computer, do not insert any type of adapter into
the SD Card Reader.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to the digital card connectors, use minimal force to insert a digital card.
1. Hold the digital card label-side up, with the connectors facing the computer.
2. Insert the card into the SD Card Reader, and then push in on the card until it is firmly seated.
You will hear a sound when the device has been detected, and a menu of available options may
be displayed.
Using SD Card Reader cards 73
Page 84

Stopping and removing a digital card
CAUTION: To prevent loss of data or an unresponsive system, stop a digital card before removing it.
1. Save your information and close all programs associated with the digital card.
NOTE: To stop a data transfer, click Cancel in the operating system Copying window.
2. Stop the digital card:
a. Double-click the Safely Remove Hardware icon in the notification area, at the far right of the
taskbar.
NOTE: To display the Safely Remove Hardware icon, click the Show Hidden Icons icon
(< or <<) in the notification area.
b. Click the name of the digital card in the list.
c. Click Stop, and then click OK.
3. Press in on the digital card (1), and then remove the card from the slot (2).
74 Chapter 7 External media cards
Page 85

8 Pointing devices and keyboard
Using pointing devices
Setting pointing device preferences
Use Mouse Properties in Windows® to customize settings for pointing devices, such as button
configuration, click speed, and pointer options.
To access Mouse Properties, select Start > Control Panel > Hardware and Sound > Mouse.
Using the TouchPad
To move the pointer, slide your finger across the TouchPad surface in the direction you want the pointer
to go. Use the TouchPad buttons like the corresponding buttons on an external mouse. To scroll up and
down using the TouchPad vertical scroll zone, slide your finger up or down over the lines.
NOTE: If you are using the TouchPad to move the pointer, you must lift your finger off the TouchPad
before moving it to the scroll zone. Simply sliding your finger from the TouchPad to the scroll zone will
not activate the scrolling function.
Connecting an external mouse
You can connect an external USB mouse to the computer using one of the USB ports on the computer.
A USB mouse can also be connected to the system using the ports on an optional docking device or
expansion product.
Using pointing devices 75
Page 86

Using the keyboard function keys
The icons on the function keys f2 through f6 and f8, f10, and f11 keys represent the action performed
when a function key is pressed. The following table and sections describe the function keys.
NOTE: Your computer may look slightly different from the illustration in this section.
Function Key
Alternate between computer display and external display. f2
Decrease screen brightness. f3
Increase screen brightness. f4
Initiate Sleep. f5
Initiate QuickLock. f6
Mute or restore computer sound. f8
Decrease computer sound. f10
Increase computer sound. f11
76 Chapter 8 Pointing devices and keyboard
Page 87

Switching the screen image (f2)
Press f2 to switch the screen image among display devices connected to the system. For example, if a
monitor is connected to the computer, pressing f2 alternates the screen image from computer display
to monitor display to simultaneous display on both the computer and the monitor.
Most external monitors receive video information from the computer using the external VGA video
standard. The f2 key can also alternate images among other devices receiving video information from
the computer.
The following video transmission types, with examples of devices that use them, are supported by the
f2key:
LCD (computer display)
●
External VGA (most external monitors)
●
Decreasing screen brightness (f3)
Press f3 to decrease screen brightness. Hold down the key to decrease the brightness level
incrementally.
Increasing screen brightness (f4)
Press f4 to increase screen brightness. Hold down the key to increase the brightness level
incrementally.
Initiating Sleep (f5)
CAUTION: To reduce the risk of information loss, save your work before initiating Sleep.
Press f5 to initiate Sleep.
When Sleep is initiated, your information is stored in system memory, the screen is cleared, and power
is conserved. While the computer is in the Sleep state, the power lights blink.
The computer must be on before you can initiate Sleep.
To exit Sleep, briefly press the power button or press any key on the keyboard.
The function of the f5 key can be changed. For example, you can set the f5 key to initiate Hibernation
instead of Sleep.
Initiating QuickLock (f6)
Press f6 to initiate the QuickLock security feature.
QuickLock protects your information by displaying the operating system Log On window. While the Log
On window is displayed, the computer cannot be accessed until a password is entered.
NOTE: Before you can use QuickLock, you must set a password.
To use QuickLock, press f6 to display the Log On window and lock the computer. Then follow the
instructions on the screen to enter your password and access the computer.
Using the keyboard function keys 77
Page 88

Muting speaker sound (f8)
Press f8 to mute speaker sound. Press the key again to restore speaker sound.
Decreasing speaker sound (f10)
Press f10 to decrease speaker sound. Hold down the key to decrease speaker sound incrementally.
Increasing speaker sound (f11)
Press f11 to increase speaker sound. Hold down the key to increase speaker sound incrementally.
Using keypads
The computer has an embedded numeric keypad and also supports an optional external numeric keypad
or an optional external keyboard that includes a numeric keypad.
Component Description
(1) fn key Alternates the functions of the keys on the embedded numeric
(2) Embedded numeric keypad Can be used like the keys on an external numeric keypad.
(3) num lk key Enables the embedded numeric keypad.
Using the embedded numeric keypad
The 15 keys of the embedded numeric keypad can be used like the keys on an external keypad. When
the embedded numeric keypad is turned on, each key on the keypad performs the function indicated by
the icon in the upper-right corner of the key.
78 Chapter 8 Pointing devices and keyboard
keypad when pressed in combination with a keypad key or the
shift key.
Page 89

Enabling and disabling the embedded numeric keypad
Press fn+num lk to enable the embedded numeric keypad. Press fn+num lk again to return the keys to
their standard keyboard functions.
NOTE: The embedded numeric keypad will not function while an external keyboard or numeric keypad
is connected to the computer, an optional docking device, or an optional expansion product.
Switching key functions on the embedded numeric keypad
You can temporarily alternate the functions of keys on the embedded numeric keypad between their
standard keyboard functions and their keypad functions by using the fn key or the fn+shift key
combination.
To change the function of a keypad key to keypad functions while the keypad is off, press and hold
●
the fn key while pressing the keypad key.
To use the keypad keys temporarily as standard keys while the keypad is on:
●
Press and hold the fn key to type in lowercase.
◦
Press and hold fn+shift to type in uppercase.
◦
Using an optional external numeric keypad
Keys on most external numeric keypads function differently according to whether num lock is on or off.
(Num lock is turned off at the factory.) For example:
When num lock is on, most keypad keys type numbers.
●
When num lock is off, most keypad keys function like the arrow, page up, or page down keys.
●
When num lock on an external keypad is turned on, the num lock light on the computer is turned on.
When num lock on an external keypad is turned off, the num lock light on the computer is turned off.
To turn num lock on or off on an external keypad as you work:
Press the num lk key on the external keypad, not on the computer.
▲
Using keypads 79
Page 90

Cleaning the TouchPad and keyboard
Dirt and grease on the TouchPad can cause the pointer to jump around on the screen. To avoid this,
clean the TouchPad with a damp cloth, and wash your hands frequently when using the computer.
WARNING! To reduce the risk of electric shock or damage to internal components, do not use a
vacuum cleaner attachment to clean the keyboard. A vacuum cleaner can deposit household debris on
the keyboard surface.
Clean the keyboard regularly to prevent keys from sticking and to remove dust, lint, and particles that
can become trapped beneath the keys. A can of compressed air with a straw extension can be used to
blow air around and under the keys to loosen and remove debris.
80 Chapter 8 Pointing devices and keyboard
Page 91

9Drives
Identifying installed drives
To view the drives installed on the computer, select Start > Computer.
On models with a secondary hard drive (drive D), the optical drive becomes drive E. The next drive
added to the system, such as a new USB drive, will be assigned the next available drive letter.
NOTE: Windows includes the User Account Control feature to improve the security of your computer.
You may be prompted for your permission or password for tasks such as installing applications, running
utilities, or changing Windows settings. Refer to Help and Support for more information.
Handling drives
Drives are fragile computer components that must be handled with care. Refer to the following cautions
before handling drives. Additional cautions are included with the procedures to which they apply.
Identifying installed drives 81
Page 92

CAUTION: To reduce the risk of damage to the computer, damage to a drive, or loss of information,
observe these precautions:
Before you move a computer that is connected to an external hard drive, initiate Sleep and allow the
screen to clear, or properly disconnect the external hard drive.
Before handling a drive, discharge static electricity by touching the unpainted metal surface of the drive.
Do not touch the connector pins on a removable drive or on the computer.
Handle a drive carefully; do not drop a drive or place items on it.
Before removing or inserting a drive, shut down the computer. If you are unsure whether the computer
is off, in the Sleep state, or in Hibernation, turn the computer on and then shut it down through the
operating system.
Do not use excessive force when inserting a drive into a drive bay.
Do not type on the keyboard or move the computer while an optional optical drive is writing to a disc.
The write process is sensitive to vibration.
When the battery is the only source of power, be sure that the battery is sufficiently charged before
writing to media.
Avoid exposing a drive to temperature or humidity extremes.
Avoid exposing a drive to liquids. Do not spray the drive with cleaning products.
Remove media from a drive before removing the drive from the drive bay, or traveling with, shipping, or
storing a drive.
If a drive must be mailed, place the drive in a bubble-pack mailer or other suitable protective packaging
and label the package “FRAGILE.”
Avoid exposing a drive to magnetic fields. Security devices with magnetic fields include airport walkthrough devices and security wands. The airport security devices that check carry-on luggage, such as
conveyor belts, use X-rays instead of magnetism and will not damage a drive.
82 Chapter 9 Drives
Page 93

Improving hard drive performance
Using Disk Defragmenter
As you use the computer, files on the hard drive become fragmented. Disk Defragmenter consolidates
the fragmented files and folders on the hard drive so that the system can run more efficiently.
To run Disk Defragmenter:
1. Select Start > All Programs > Accessories > System Tools > Disk Defragmenter.
2. Click Defragment now.
NOTE: Windows includes the User Account Control feature to improve the security of your
computer. You may be prompted for your permission or password for tasks such as installing
applications, running utilities, or changing Windows settings. Refer to Help and Support for more
information.
For additional information, access the Disk Defragmenter software Help.
Using Disk Cleanup
Disk Cleanup searches the hard drive for unnecessary files that you can safely delete to free up disk
space and help the computer to run more efficiently.
To run Disk Cleanup:
1. Select Start > All Programs > Accessories > System Tools > Disk Cleanup.
2. Follow the on-screen instructions.
Improving hard drive performance 83
Page 94

Using HP 3D DriveGuard (select models only)
HP 3D DriveGuard protects the hard drive by parking the drive and halting I/O requests under either of
the following conditions:
You drop the computer.
●
You move the computer with the display closed while the computer is running on battery power.
●
A short time after the end of one of these events, HP 3D DriveGuard returns the hard drive to normal
operation.
NOTE: Hard drives that are in an optional docking device or are connected to a USB port are not
protected by HP 3D DriveGuard.
For more information, refer to the HP 3D DriveGuard software Help.
Identifying HP 3D DriveGuard status
The drive light on the computer changes to an amber color to show that the drive is parked. To determine
whether drives are currently protected or whether a drive is parked, use Mobility Center:
If the software is enabled, a green check mark is superimposed over the hard drive icon.
●
If the software is disabled, a red X is superimposed over the hard drive icon.
●
If the drives are parked, a yellow moon is superimposed over the hard drive icon.
●
If HP 3D DriveGuard has parked the drive, the computer will behave in the following ways:
The computer will not shut down.
●
The computer will not initiate Sleep or Hibernation, except as described in the following Note.
●
NOTE: If the computer is running on battery power and reaches a critical battery level, HP 3D
DriveGuard allows the computer to initiate Hibernation.
The computer will not activate battery alarms set on the Alarms tab in Power Options properties.
●
Before you move the computer, HP recommends that you either shut it down or initiate Sleep or
Hibernation.
Using HP 3D DriveGuard software
The HP 3D DriveGuard software enables you to perform the following tasks:
Enable and disable HP 3D DriveGuard.
●
NOTE: Depending on your user privileges, you may not be able to enable or disable HP 3D
DriveGuard. Additionally, members of an Administrator group can change the privileges for nonAdministrator users.
Determine whether a drive in the system is supported.
●
84 Chapter 9 Drives
Page 95

To open the software and change settings, follow these steps:
1. In Mobility Center, click the hard drive icon to open the HP 3D DriveGuard window.
– or –
Select Start > Control Panel > Hardware and Sound > HP 3D DriveGuard.
2. Click the appropriate button to change settings.
3. Click OK.
Using HP 3D DriveGuard (select models only) 85
Page 96

Replacing a hard drive
CAUTION: To prevent information loss or an unresponsive system:
Shut down the computer before removing the hard drive from the hard drive bay. Do not remove the
hard drive while the computer is on, in the Sleep state, or in Hibernation.
If you are not sure whether the computer is off or in Hibernation, turn the computer on by briefly pressing
the power button. Then shut down the computer through the operating system.
To remove a hard drive:
1. Save your work.
2. Shut down the computer and close the display.
3. Disconnect all external hardware devices connected to the computer.
4. Unplug the power cord from the AC outlet.
5. Turn the computer upside down on a flat surface, with the battery bay toward you.
6. Remove the battery from the computer.
7. Remove the 3 screws from the back edge of the computer.
8. Turn the computer display-side up, with the front toward you, and open the display.
86 Chapter 9 Drives
Page 97

9. Lift the top edge of the keyboard up and remove the keyboard from the computer to expose the
hard drive.
10. Remove the two hard drive screws (1).
11. Loosen the captive hard drive screw (2).
12. Pull the hard drive tab (3) to the right to disconnect the hard drive, and then lift the hard drive out
of the hard drive bay (4).
To install a hard drive:
1. Insert the hard drive into the hard drive bay (1).
2. Pull the hard drive tab (2) to the left to connect the hard drive.
3. Tighten the captive hard drive screw (3).
Replacing a hard drive 87
Page 98

4. Replace the hard drive screws (4).
5. Insert the front edge of the keyboard into the keyboard tray (1), and then press the keyboard into
place (2).
6. Close the computer display and turn the computer upside down on a flat surface.
88 Chapter 9 Drives
Page 99

7. Replace the 3 screws on the back edge of the computer.
8. Replace the battery.
Replacing a hard drive 89
Page 100

10 Memory modules
The computer has one memory module compartment, which is located under the keyboard. The memory
capacity of the computer can be upgraded by replacing the existing memory module in the memory
module slot.
WARNING! To reduce the risk of electric shock and damage to the equipment, unplug the power cord
and remove all batteries before installing a memory module.
CAUTION: Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage electronic components. Before beginning any
procedure, be sure that you are discharged of static electricity by touching a grounded metal object.
To add or replace a memory module:
1. Save your work.
2. Shut down the computer and close the display.
If you are not sure whether the computer is off or in Hibernation, turn the computer on by briefly
pressing the power button. Then shut down the computer through the operating system.
3. Disconnect all external devices connected to the computer.
4. Unplug the power cord from the AC outlet.
5. Turn the computer upside down on a flat surface.
6. Slide the battery latch (1) to release the battery from the computer.
7. Remove the battery from the computer.
8. Slide the battery latch again, and the memory module compartment cover pops open.
90 Chapter 10 Memory modules
 Loading...
Loading...