Page 1

LASERJET PRO 400 MFP
Troubleshooting Manual
M425
Page 2

Page 3

HP LaserJet Pro 400 MFP M425 Series
Troubleshooting Manual
Page 4

Copyright and License
Trademark Credits
© 2012 Copyright Hewlett-Packard
Development Company, L.P.
Reproduction, adaptation, or translation
without prior written permission is
prohibited, except as allowed under the
copyright laws.
The information contained herein is subject
to change without notice.
The only warranties for HP products and
services are set forth in the express warranty
statements accompanying such products and
services. Nothing herein should be
construed as constituting an additional
warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical
or editorial errors or omissions contained
herein.
Part number: CF286-91012
Edition 1, 4/2012
Microsoft®, Windows®, Windows® XP,
and Windows Vista® are U.S. registered
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Page 5

Conventions used in this guide
TIP: Tips provide helpful hints or shortcuts.
NOTE: Notes provide important information to explain a concept or to complete a task.
CAUTION: Cautions indicate procedures that you should follow to avoid losing data or damaging
the product.
WARNING! Warnings alert you to specific procedures that you should follow to avoid personal
injury, catastrophic loss of data, or extensive damage to the product.
ENWW iii
Page 6

iv Conventions used in this guide ENWW
Page 7

Table of contents
1 Theory of operation .......................................................................................................... 1
Basic operation ........................................................................................................................ 2
Major product systems ............................................................................................... 2
Product components .................................................................................................. 3
Sequence of operation ............................................................................................... 4
Engine control system ............................................................................................................... 6
DC controller ............................................................................................................ 7
Motor control ............................................................................................................ 9
Fan control ............................................................................................................. 10
High-voltage power supply ....................................................................................... 11
Fuser control circuit .................................................................................. 12
Fuser temperature control ........................................................... 13
Fuser protection function ............................................................ 14
Fuser failure detection ................................................................ 14
Low-voltage power supply ........................................................................................ 16
Protective function .................................................................................... 16
Safety ..................................................................................................... 17
Low-voltage power supply unit failure detection ............................................ 17
Laser scanner system .............................................................................................................. 18
Laser failure detection .............................................................................................. 19
Image-formation system ........................................................................................................... 20
Image-formation process .......................................................................................... 21
Latent-image formation stage .................................................................................... 22
Step 1: Primary charging .......................................................................... 22
Step 2: Laser-beam exposure ..................................................................... 23
Developing stage .................................................................................................... 23
Step 3: Development ................................................................................ 23
Transfer stage ......................................................................................................... 24
Step 4: Transfer ....................................................................................... 24
Step 5: Separation ................................................................................... 24
Fusing stage ........................................................................................................... 25
Step 6: Fusing ......................................................................................... 25
ENWW v
Page 8

Drum cleaning stage ................................................................................................ 26
Step 7: Drum cleaning .............................................................................. 26
Pickup and feed system ........................................................................................................... 27
Jam detection ......................................................................................................... 30
Paper feeder (optional Tray 3) ................................................................................................. 32
Paper feeder operation ............................................................................................ 34
Jam detection ......................................................................................................... 35
Scanner system ...................................................................................................................... 37
Scanner power-on sequence of events ....................................................................... 37
Copy or scan sequence of events .............................................................................. 38
Fax functions and operation .................................................................................................... 39
Computer and network security features ..................................................................... 39
PSTN operation ...................................................................................................... 39
Receive faxes when you hear fax tones ...................................................................... 39
Distinctive ring function ............................................................................................ 40
Use fax with voice over IP services ............................................................................ 40
The fax subsystem ................................................................................................... 41
Fax card in the fax subsystem ................................................................................... 41
Safety isolation ........................................................................................ 41
Safety-protection circuitry .......................................................................... 41
Data path ................................................................................................ 42
Hook state ............................................................................................... 42
Downstream device detection .................................................................... 43
Hook switch control .................................................................................. 43
Ring detect .............................................................................................. 43
Line current control ................................................................................... 43
Billing- (metering-) tone filters ..................................................................... 43
Fax page storage in flash memory ............................................................................ 43
Stored fax pages ...................................................................................... 44
Advantages of flash memory storage .......................................................... 44
USB flash drive ...................................................................................................................... 45
2 Solve problems ............................................................................................................... 47
Solve problems checklist ......................................................................................................... 48
Menu map ............................................................................................................................ 50
Troubleshooting process .......................................................................................................... 51
Pre-troubleshooting checklist ..................................................................................... 51
Determine the problem source ................................................................................... 53
Power subsystem ..................................................................................................... 54
Power-on checks ...................................................................................... 54
Control-panel checks ............................................................................................... 54
vi ENWW
Page 9

Tools for troubleshooting ......................................................................................................... 55
Component diagnostics ............................................................................................ 55
LED diagnostics ........................................................................................ 55
Network LEDs ........................................................................... 55
Control panel LEDs .................................................................... 55
Engine diagnostics ................................................................................... 56
Engine test ................................................................................ 56
Diagrams ............................................................................................................... 57
Plug/jack locations ................................................................................... 57
Locations of major components .................................................................. 58
General timing chart ................................................................................. 60
General circuit diagrams ........................................................................... 61
Use HP Device Toolbox (Windows) ........................................................................... 64
Internal print-quality test pages .................................................................................. 65
Clean the paper path ............................................................................... 65
Print the configuration page ....................................................................... 65
Print-quality troubleshooting tools .............................................................................. 65
Repetitive image defect ruler ...................................................................... 65
Control panel menus ................................................................................................ 67
HP Web Services menu ............................................................................. 67
Reports menu ........................................................................................... 67
Quick Forms menu ................................................................................... 68
USB Flash Drive menu ............................................................................... 69
System Setup menu ................................................................................... 69
Service menu ........................................................................................... 72
Network Setup menu ................................................................................ 75
Interpret control-panel messages ............................................................................... 77
Control panel message types ..................................................................... 77
Control panel messages ............................................................................ 77
49 Error, Turn off then on ........................................................... 77
50.x Fuser Error ........................................................................ 77
51.XX Error .............................................................................. 77
54.XX Error .............................................................................. 78
55.X Error ................................................................................ 78
57 Fan Error, Turn off then on ..................................................... 78
59.X Error ................................................................................ 79
79 Error Turn off then on ............................................................ 79
79 Service error ........................................................................ 79
Black cartridge low ................................................................... 79
Black cartridge very low ............................................................. 80
Cleaning .................................................................................. 80
ENWW vii
Page 10

Communication error. ................................................................ 80
Device error, press OK .............................................................. 81
Document feeder door is open. Canceled fax. .............................. 81
Door open ................................................................................ 81
Fax is busy. Canceled send. ....................................................... 81
Fax is busy. Redial pending. ....................................................... 82
Fax receive error. ...................................................................... 82
Fax Send error. ......................................................................... 83
Fax storage is full. Canceling the fax receive. ............................... 83
Fax storage is full. Canceling the fax receive. ............................... 83
Fax storage is full. Canceling the fax send. ................................... 84
Genuine HP supply installed ....................................................... 84
Incompatible black .................................................................... 84
Install black cartridge ................................................................. 84
Invalid driver Press [OK] ............................................................ 84
Jam in Tray 1, Clear jam and then press OK ................................ 85
Load Tray 1 <TYPE> <SIZE>, Press OK to use available media ....... 85
Load Tray 1, <PLAIN> <SIZE> / Cleaning mode, OK to start ......... 85
Load tray <X> Press [OK] for available media .............................. 85
Load tray <X> <TYPE> <SIZE> .................................................... 85
Manual Duplex Load Tray 1, Press OK ........................................ 86
Manual feed <SIZE> <TYPE>, Press OK to use available media ...... 86
Memory is low. Press OK. .......................................................... 86
Misprint, Press OK ..................................................................... 86
No dial tone. ............................................................................ 87
No fax answer. Canceled send. .................................................. 87
No fax answer. Redial pending. ................................................. 87
No fax detected. ....................................................................... 88
Print failure, press OK. If error repeats, turn off then on. ................. 88
Rear door open ......................................................................... 88
Remove shipping material from toner cartridge ............................. 89
Replace black cartridge ............................................................. 89
Unexpected size in tray <X> Load <size> Press [OK] ..................... 89
Unsupported black cartridge Press [OK] to continue ...................... 89
Used black cartridge is installed Press [OK] to continue ................. 90
Event-log messages ................................................................................................. 91
Print the event log ..................................................................................... 91
Show an event log ................................................................................... 91
Event log messages .................................................................................. 91
Clear jams ............................................................................................................................ 94
Jam locations .......................................................................................................... 94
viii ENWW
Page 11

Clear jams from the document feeder ........................................................................ 95
Clear a jam in Tray 1 .............................................................................................. 96
Clear a jam in Tray 2 .............................................................................................. 98
Clear a jam in optional Tray 3 ................................................................................ 100
Clear jams from the output bin ................................................................................ 101
Clear a jam in the duplexer area ............................................................................ 101
Clear a jam in the fuser area .................................................................................. 102
Solve paper-handling problems .............................................................................................. 104
The product picks up multiple sheets of paper ........................................................... 104
The product does not pick up paper ........................................................................ 104
Solve image quality problems ................................................................................................ 105
Print quality examples ............................................................................................ 105
Clean the product ................................................................................................................ 110
Clean the pickup and separation rollers ................................................................... 110
Clean the paper path ............................................................................................ 110
Clean the scanner glass strip and platen .................................................................. 110
Clean the document feeder pickup rollers and separation pad .................................... 111
Clean the touchscreen ........................................................................................... 112
Solve performance problems ................................................................................................. 113
Factors affecting print performance ......................................................................... 113
Print speeds ........................................................................................... 114
The product does not print or it prints slowly ............................................................. 114
The product does not print ....................................................................... 114
The product prints slowly ......................................................................... 115
Solve connectivity problems ................................................................................................... 116
Solve direct-connect problems ................................................................................. 116
Solve network problems ......................................................................................... 116
Poor physical connection ......................................................................... 116
The computer is using the incorrect IP address for the product ...................... 116
The computer is unable to communicate with the product ............................ 117
The product is using incorrect link and duplex settings for the network .......... 117
New software programs might be causing compatibility problems ................ 117
The computer or workstation might be set up incorrectly .............................. 117
The product is disabled, or other network settings are incorrect .................... 117
Solve wireless network problems ............................................................................. 118
Wireless connectivity checklist ................................................................. 118
The control panel displays the message: The wireless feature on this product
has been turned off ................................................................................ 119
The product does not print after the wireless configuration completes ............ 119
The product does not print, and the computer has a third-party firewall
installed ................................................................................................ 119
ENWW ix
Page 12

The wireless connection does not work after moving the wireless router or
product ................................................................................................. 119
Cannot connect more computers to the wireless product .............................. 119
The wireless product loses communication when connected to a VPN ........... 120
The network does not appear in the wireless networks list ........................... 120
The wireless network is not functioning ...................................................... 120
Service mode functions ......................................................................................................... 121
Service menu ........................................................................................................ 121
Service menu settings .............................................................................. 121
Restore the factory-set defaults ................................................................. 121
Secondary service menu ........................................................................................ 121
Open the secondary service menu ............................................................ 122
Secondary service menu structure ............................................................. 122
Product resets ....................................................................................................... 123
NVRAM initialization .............................................................................. 123
Super NVRAM initialization ..................................................................... 123
Solve fax problems ............................................................................................................... 124
Fax troubleshooting checklist .................................................................................. 124
Solve problems receiving faxes ............................................................................... 126
The fax does not respond ........................................................................ 126
The fax has a dedicated phone line ........................................... 126
An answering machine is connected to the product ..................... 126
A telephone handset is connected to the product ......................... 127
The Answer Mode setting is set to the Manual setting ................... 127
Voice mail is available on the fax line ........................................ 127
The product is connected to a DSL phone service ........................ 128
The product uses a fax over IP or VoIP phone service ................... 128
An error message displays on the control panel ......................................... 129
The No fax detected. message displays ..................................... 129
The Communication error. message displays .............................. 129
The Fax storage is full. message displays ................................... 130
The Fax is busy. message displays ............................................ 130
A fax is received but does not print .......................................................... 131
The Private Receive feature is on ............................................... 131
Sender receives a busy signal .................................................................. 131
A handset is connected to the product ........................................ 131
A phone line splitter is being used ............................................. 131
No dial tone .......................................................................................... 131
Fax cuts off or prints on two pages ........................................................... 132
Solve problems sending faxes ................................................................................. 132
An error message displays on the control panel ......................................... 133
x ENWW
Page 13

The Communication error. message displays .............................. 133
No dial tone. .......................................................................... 133
The Fax is busy. message displays ............................................ 134
The No fax answer. message displays ....................................... 134
Document feeder paper jam ..................................................... 135
The Fax storage is full. message displays ................................... 135
Scanner error ......................................................................... 135
The control panel displays a Ready message with no attempt to send the fax . 136
The control panel displays the message "Storing page 1" and does not
progress beyond that message ................................................................. 136
Faxes can be received, but not sent .......................................................... 136
Unable to use fax functions from the control panel ...................................... 137
Unable to use speed dials ....................................................................... 137
Unable to use group dials ....................................................................... 137
Receive a recorded error message from the phone company when trying to
send a fax ............................................................................................. 138
Unable to send a fax when a phone is connected to the product .................. 138
Solve fax performance problems ............................................................................. 139
Faxes are sending slowly ........................................................................ 139
Fax quality is poor ................................................................................. 140
Solve DSL problems ............................................................................................... 140
Cannot send or receive a fax on a PBX line ............................................... 140
Manually update the firmware ............................................................................................... 141
Appendix A Service and support ..................................................................................... 143
Hewlett-Packard limited warranty statement ............................................................................. 144
HP's Premium Protection Warranty: LaserJet toner cartridge limited warranty statement ................. 146
HP policy on non-HP supplies ................................................................................................ 147
HP anticounterfeit Web site ................................................................................................... 148
Data stored on the toner cartridge .......................................................................................... 149
End User License Agreement .................................................................................................. 150
OpenSSL ............................................................................................................................. 153
Customer support ................................................................................................................. 154
Repack the product .............................................................................................................. 155
Appendix B Product specifications ................................................................................... 157
Physical specifications .......................................................................................................... 158
Power consumption, electrical specifications, and acoustic emissions .......................................... 158
Environmental specifications .................................................................................................. 158
ENWW xi
Page 14

Appendix C Regulatory information ................................................................................. 159
FCC regulations ................................................................................................................... 160
Environmental product stewardship program ........................................................................... 161
Protecting the environment ...................................................................................... 161
Ozone production ................................................................................................. 161
Power consumption ............................................................................................... 161
Toner consumption ................................................................................................ 161
Paper use ............................................................................................................. 161
Plastics ................................................................................................................. 161
HP LaserJet print supplies ....................................................................................... 162
Return and recycling instructions ............................................................................. 162
United States and Puerto Rico .................................................................. 162
Multiple returns (more than one cartridge) .................................. 162
Single returns .......................................................................... 162
Shipping ................................................................................ 162
Non-U.S. returns .................................................................................... 163
Paper .................................................................................................................. 163
Material restrictions ............................................................................................... 163
Disposal of waste equipment by users ...................................................................... 164
Electronic hardware recycling ................................................................................. 164
Chemical substances ............................................................................................. 164
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) ......................................................................... 164
For more information ............................................................................................. 164
Declaration of conformity ...................................................................................................... 166
Declaration of conformity ...................................................................................................... 168
Safety statements ................................................................................................................. 170
Laser safety .......................................................................................................... 170
Canadian DOC regulations .................................................................................... 170
VCCI statement (Japan) .......................................................................................... 170
Power cord instructions .......................................................................................... 170
Power cord statement (Japan) ................................................................................. 170
EMC statement (Korea) .......................................................................................... 171
Laser statement for Finland ..................................................................................... 171
GS statement (Germany) ........................................................................................ 172
Substances Table (China) ....................................................................................... 172
Restriction on Hazardous Substances statement (Turkey) ............................................. 172
Restriction on Hazardous Substances statement (Ukraine) ........................................... 172
Additional statements for telecom (fax) products ....................................................................... 173
EU Statement for Telecom Operation ....................................................................... 173
New Zealand Telecom Statements ........................................................................... 173
Additional FCC statement for telecom products (US) .................................................. 173
xii ENWW
Page 15

Telephone Consumer Protection Act (US) .................................................................. 174
Industry Canada CS-03 requirements ...................................................................... 174
Vietnam Telecom wired/wireless marking for ICTQC Type approved products ............. 175
Additional statements for wireless products .............................................................................. 176
FCC compliance statement—United States ................................................................ 176
Australia statement ................................................................................................ 176
Brazil ANATEL statement ........................................................................................ 176
Canadian statements ............................................................................................. 176
European Union regulatory notice ........................................................................... 176
Notice for use in France ......................................................................................... 177
Notice for use in Russia ......................................................................................... 177
Mexico statement .................................................................................................. 177
Korean statement .................................................................................................. 177
Taiwan statement .................................................................................................. 178
Vietnam Telecom wired/wireless marking for ICTQC Type approved products ............. 178
Index ............................................................................................................................... 179
ENWW xiii
Page 16

xiv ENWW
Page 17

List of tables
Table 1-1 Product components ................................................................................................................ 3
Table 1-2 Sequence of operation ............................................................................................................ 5
Table 1-3 DC controller electrical components .......................................................................................... 7
Table 1-4 Motor control components ....................................................................................................... 9
Table 1-5 Fan control components ........................................................................................................ 10
Table 1-6 Fuser control circuit components ............................................................................................. 12
Table 1-7 Pickup and feed system electrical components .......................................................................... 28
Table 1-8 Paper feeder components ...................................................................................................... 33
Table 2-1 Plug/jack locations ............................................................................................................... 57
Table 2-2 Major components (1 of 2) .................................................................................................... 58
Table 2-3 Major components (2 of 2) .................................................................................................... 59
Table 2-4 Repetitive defects .................................................................................................................. 66
Table 2-5 Event-log messages ............................................................................................................... 91
Table 2-6 Event-log-only messages ........................................................................................................ 92
Table 2-7 Secondary Service menu ..................................................................................................... 122
Table B-1 Physical specifications ......................................................................................................... 158
Table B-2 Operating-environment specifications .................................................................................... 158
ENWW xv
Page 18

xvi ENWW
Page 19

List of figures
Figure 1-1 Product systems ..................................................................................................................... 2
Figure 1-2 Product components ............................................................................................................... 3
Figure 1-3 Optional Tray 3 components .................................................................................................. 4
Figure 1-4 Engine control system components ........................................................................................... 6
Figure 1-5 DC controller ........................................................................................................................ 7
Figure 1-6 Main motor .......................................................................................................................... 9
Figure 1-7 Fan control ......................................................................................................................... 10
Figure 1-8 High-voltage power supply ................................................................................................... 11
Figure 1-9 Fuser control circuit .............................................................................................................. 12
Figure 1-10 Fuser temperature control ................................................................................................... 13
Figure 1-11 Low-voltage power supply .................................................................................................. 16
Figure 1-12 Laser scanner system .......................................................................................................... 18
Figure 1-13 Image-formation system ...................................................................................................... 21
Figure 1-14 Image-formation process .................................................................................................... 22
Figure 1-15 Primary charging process ................................................................................................... 22
Figure 1-16 Laser-beam exposure ......................................................................................................... 23
Figure 1-17 Development process ......................................................................................................... 23
Figure 1-18 Transfer process ................................................................................................................ 24
Figure 1-19 Separation from the drum ................................................................................................... 24
Figure 1-20 Fusing .............................................................................................................................. 25
Figure 1-21 Drum cleaning .................................................................................................................. 26
Figure 1-22 Pickup and feed system paper path ..................................................................................... 27
Figure 1-23 Pickup and feed system electrical components ....................................................................... 28
Figure 1-24 Jam detection sensors ........................................................................................................ 30
Figure 1-25 Paper-feeder paper path .................................................................................................... 32
Figure 1-26 Paper feeder signal flow .................................................................................................... 33
Figure 1-27 Paper feeder electrical components ..................................................................................... 34
Figure 1-28
Figure 2-1 Major components (1 of 2) ................................................................................................... 58
Figure 2-2 Major components (2 of 2) ................................................................................................... 59
Figure 2-3 Timing diagram ................................................................................................................... 60
Figure 2-4 Circuit diagram — main unit (1 of 2) ..................................................................................... 61
Jam detection sensors ........................................................................................................ 35
ENWW xvii
Page 20

Figure 2-5 Circuit diagram — main unit (2 of 2) ..................................................................................... 62
Figure 2-6 Circuit diagram — optional Tray 3 ........................................................................................ 63
xviii ENWW
Page 21

1 Theory of operation
Basic operation
●
Engine control system
●
Laser scanner system
●
Image-formation system
●
Pickup and feed system
●
Paper feeder (optional Tray 3)
●
Scanner system
●
Fax functions and operation
●
USB flash drive
●
ENWW 1
Page 22
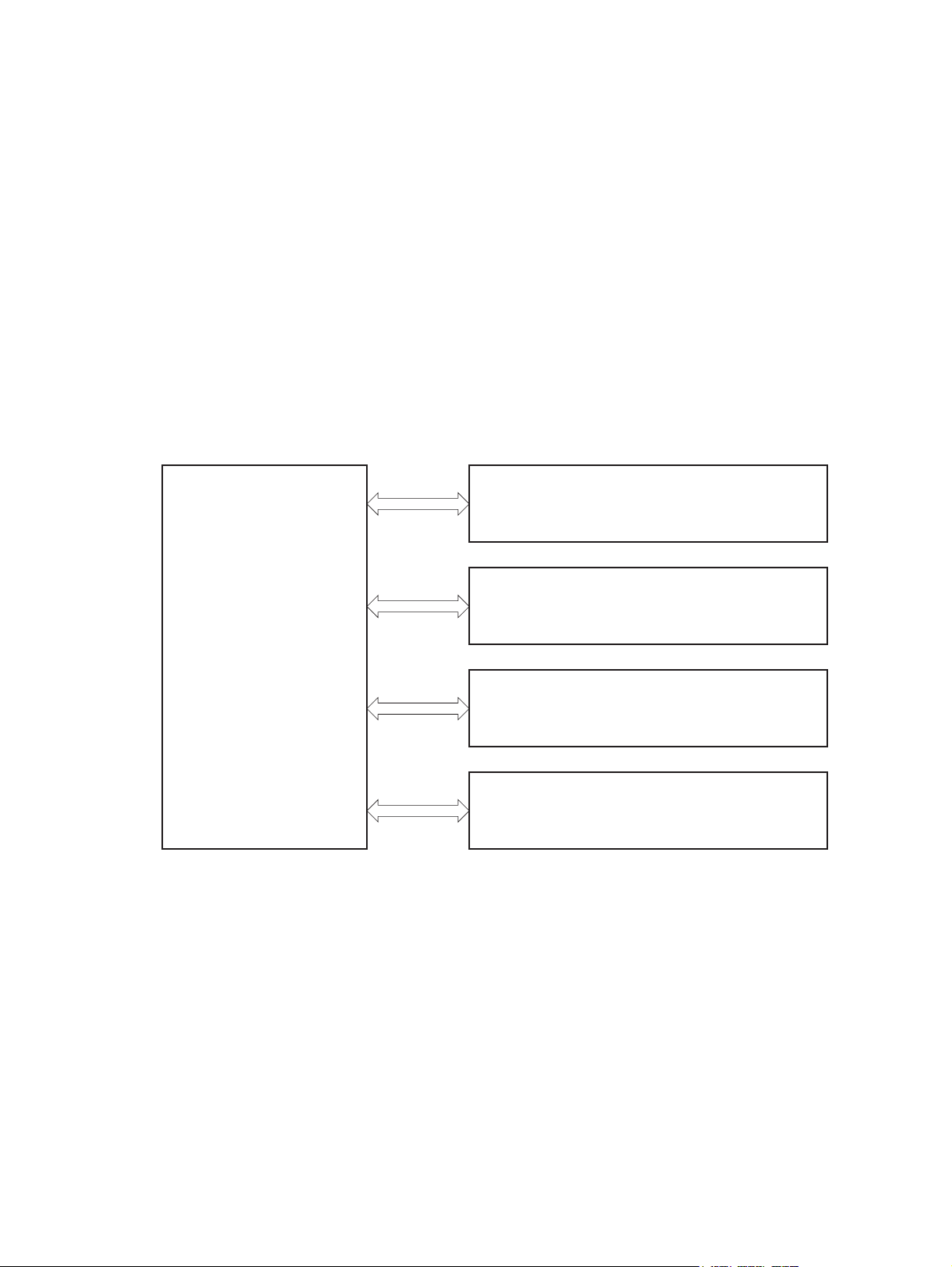
Basic operation
Major product systems
The product includes the following systems:
Engine control system
●
Laser scanner system
●
Image-formation system
●
Pickup and feed system
●
Accessory
●
Figure 1-1 Product systems
LASER SCANNER SYSTEM
ENGINE CONTROL
SYSTEM
IMAGE-FORMATION SYSTEM
PICKUP, FEED AND DELIVERY SYSTEM
ACCESSORY
2 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 23
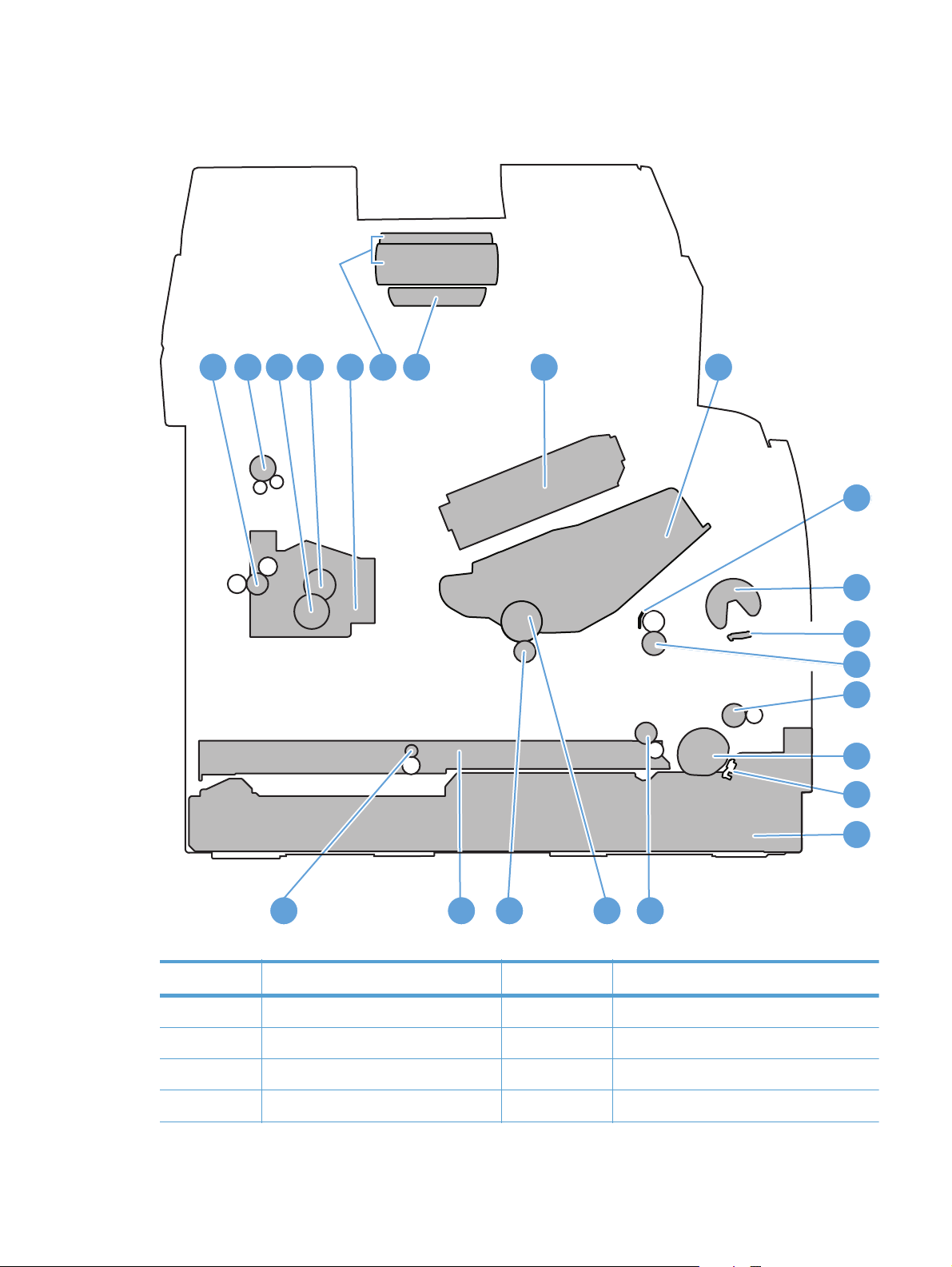
Product components
Figure 1-2 Product components
1
2 8 9
4 5 73 6
1010
182122 1920
Table 1-1 Product components
Item Description Item Description
1 Fuser delivery roller 12 Multipurpose tray (Tray 1) separation pad
2 Face-down delivery roller 13 Registration roller
11
12
13
13
14
15
16
17
ENWW
3 Pressure roller 14 Feed roller
4 Fuser film assembly 15 Tray 2 cassette pickup roller
Basic operation
3
Page 24
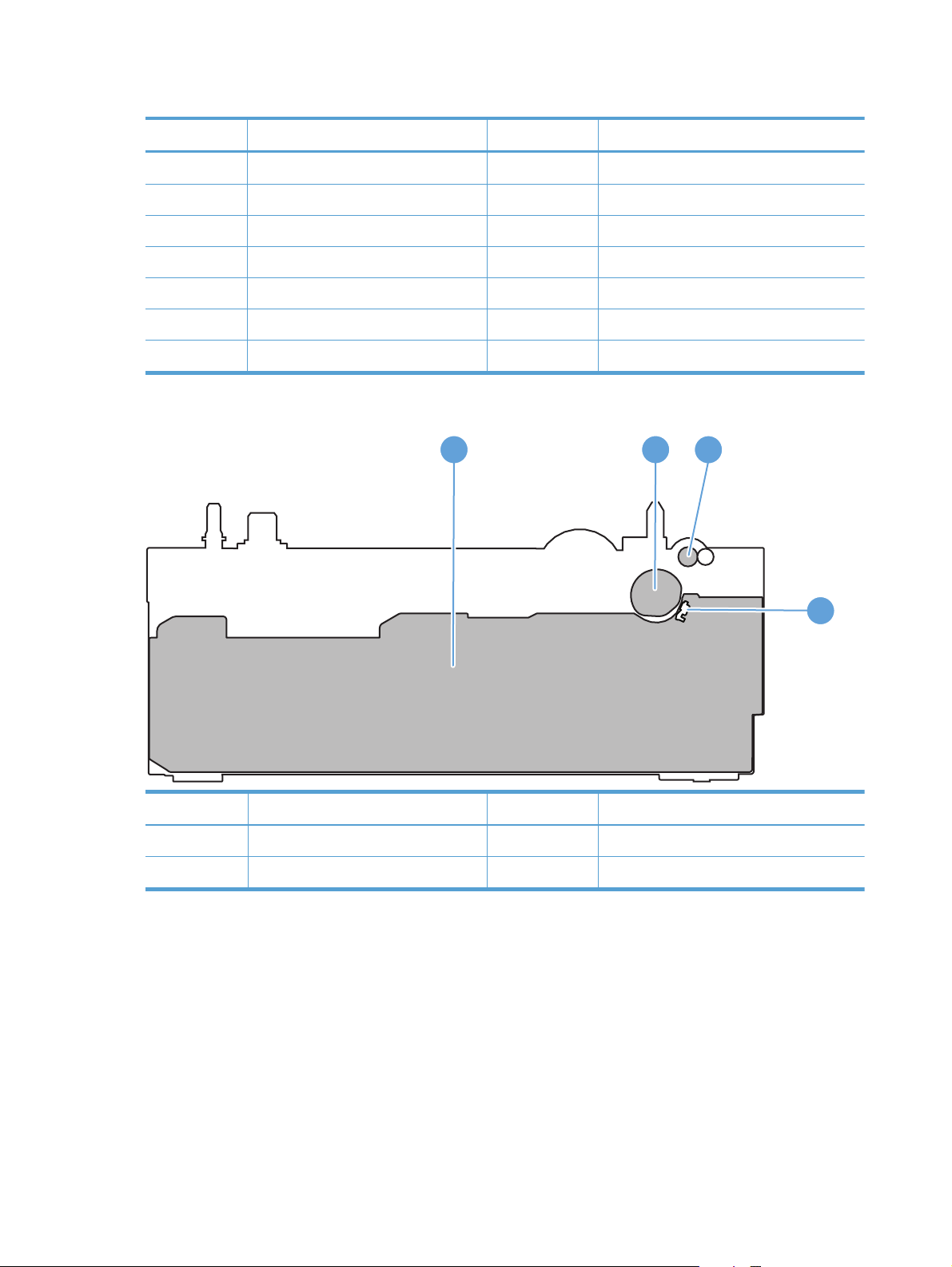
Table 1-1 Product components (continued)
Item Description Item Description
5 Fuser 16 Tray 2 cassette separation pad
6 Document feeder pickup rollers 17 Tray 2 cassette
7 Document feeder separation pad 18 Duplex re-pickup roller
8 Laser scanner 19 Photosensitive drum
9 Toner cartridge 20 Transfer roller
10 Registration shutter 21 Duplex feed assembly
11 Multipurpose tray (Tray 1) pickup roller 22 Duplex feed roller
Figure 1-3 Optional Tray 3 components
1 2
Item Description Item Description
1 Tray 3 cassette 3 Tray 3 feed roller
2 Tray 3 pickup roller 4 Tray 3 separation pad
3
4
Sequence of operation
The product operational sequence is controlled by the DC controller that is on the engine control
system. The following table describes each period of a print operation from when the product is turned
on until the motor stops rotating.
4 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 25

Table 1-2 Sequence of operation
Period Duration Purpose Remarks
WAIT From the time the power is
turned on or the door is
closed until the drum-phase
adjustment is complete
STBY (Standby period) From end of the WAIT or
LSTR period until either the
print command is received
from the formatter or the
power is turned off
INTR (Initial rotation) From the time the print
command is received until the
fuser temperature reaches its
target temperature
PRINT From the end of INTR period
until the fuser paper sensor
detects the trailing edge of
paper
LSTR (Last rotation) From the end of the PRINT
period until the delivery motor
stops rotating
Brings the product to the
ready state
Maintains the product in
readiness for a print
command
Prepares the high-voltage
biases, laser scanner, and
fuser for printing
Forms the images on the
photosensitive drum and
transfers the toner image to
the print media
Moves the printed sheet out
of the product, and stops the
output from the laser scanner
and high-voltage biases
The product detects the toner
level, cartridge presence, and
environment.
The product enters sleep
mode when the formatter
sends a sleep command.
The product enters the INTR
period as soon as the
formatter sends another print
command.
ENWW
Basic operation
5
Page 26
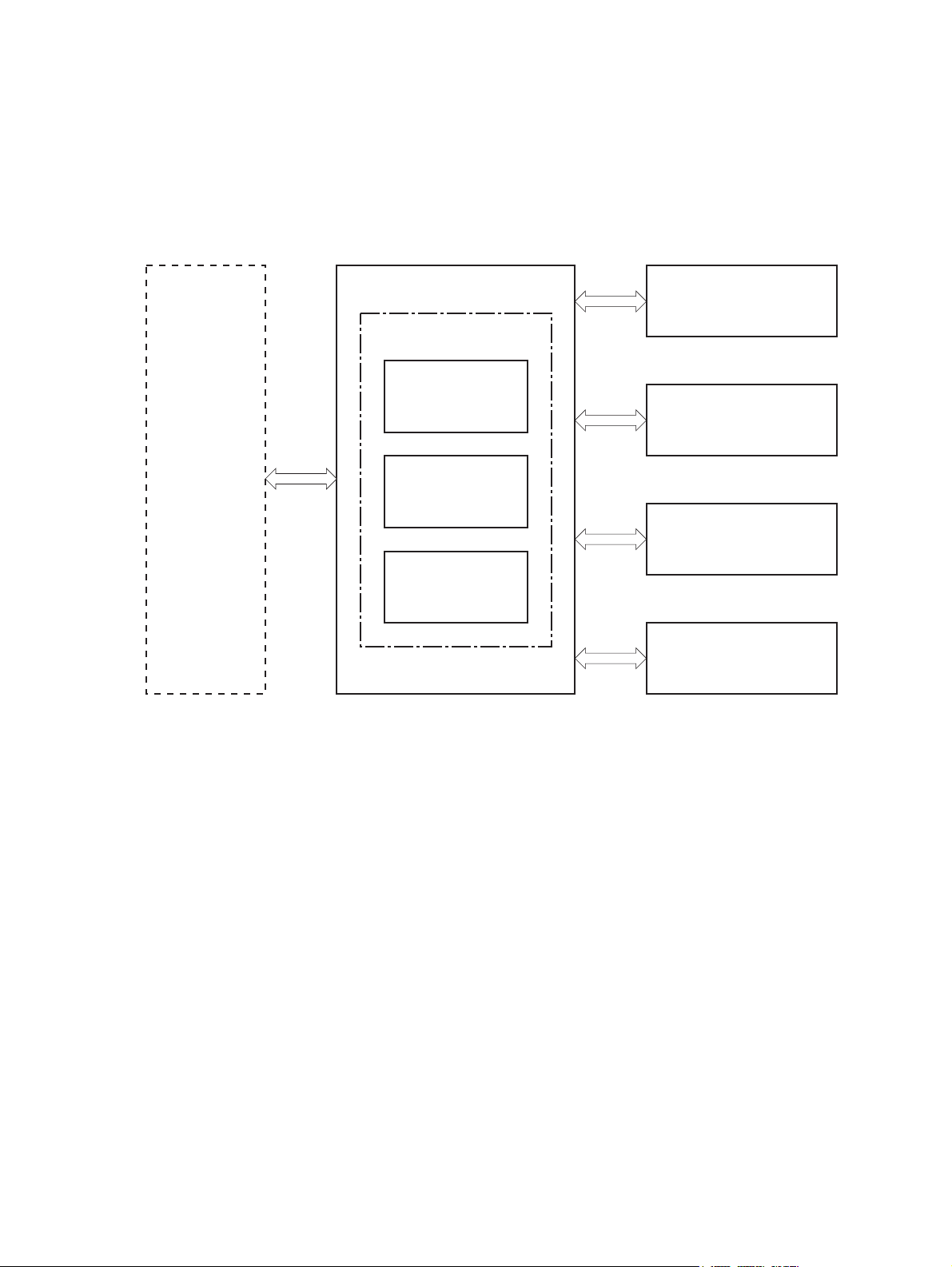
Engine control system
The engine control system coordinates all product functions and drives the other three systems.
The engine control system contains the DC controller, high-voltage power supply PCA, and low-voltage
power supply.
Figure 1-4 Engine control system components
Formatter
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
LASER SCANNER SYSTEM
Engine controller
DC controller
IMAGE-FORMATION SYSTEM
Low-voltage
power supply
PICKUP, FEED AND
DELIVERY SYSTEM
High-voltage
power supply
ACCESSORY
6 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 27
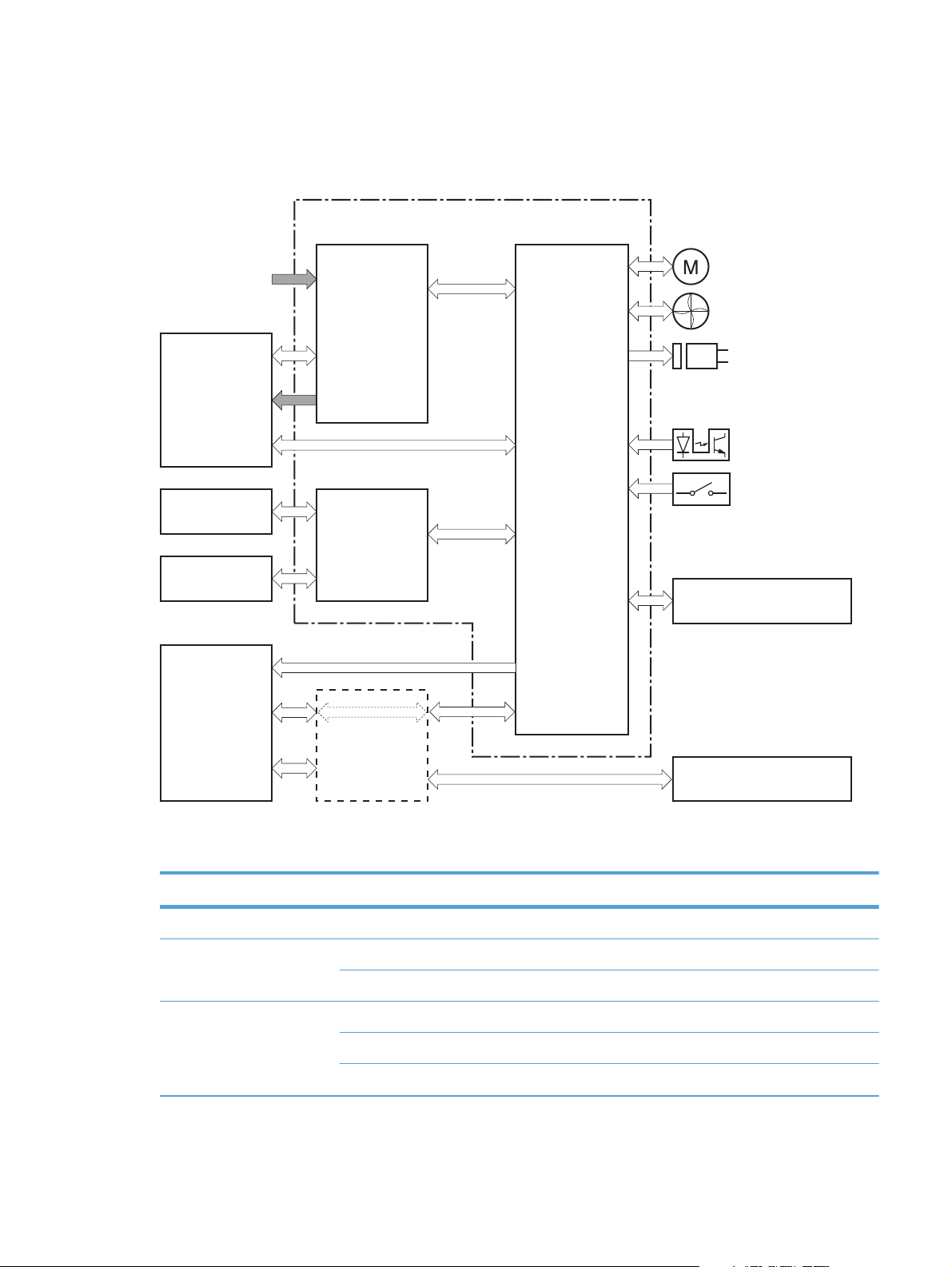
DC controller
The DC controller controls the product operational sequence.
Figure 1-5 DC controller
Engine controller
AC input
Fuser
Transfer roller
Cartridge
Laser scanner
assembly
Motor
Fan
Low-voltage
power supply
Solenoid
Photointerrupter
Switch
DC controller
High-voltage
power supply
Accessory
Formatter
ENWW
Table 1-3 DC controller electrical components
Component type Symbol Description
Fan FM1 Main fan
Motor M1 Main motor
M2 Scanner motor
Solenoid SL1 Multipurpose tray pickup solenoid
SL2 Cassette pickup solenoid
SL3 Duplex reverse solenoid
Engine control system
Control panel
7
Page 28

Table 1-3 DC controller electrical components (continued)
Component type Symbol Description
Switch SW1001 Power switch
SW301 Door-open detection switch
Photointerrupter PS912 Top sensor
PS913 Paper width sensor
PS914 Cassette media out sensor
PS914 Left paper width sensor
PS915 Multipurpose tray media out sensor
PS915 Right paper width sensor
PS916 Fuser output sensor
PS916 Output-bin paper-full sensor
8 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 29
Motor control
The product has one motor for media feed and image formation.
Figure 1-6 Main motor
ENWW
Table 1-4 Motor control components
Symbol Name Driving part Failure detection
M1 Main motor Rollers in the product an
rollers in the paper feeder
Yes
Engine control system
9
Page 30
Fan control
The product has one fan for preventing the product from overheating.
Figure 1-7 Fan control
Table 1-5 Fan control components
Symbol Name Cooling area Type Speed
FM1 Fan Inside the product Intake Full
10 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 31

High-voltage power supply
The DC controller controls the high-voltage power supply to generate high-voltage biases. The highvoltage power supply generates the high-voltage biases that are applied to the primary charging roller,
developing roller, transfer roller, and fuser film.
Figure 1-8 High-voltage power supply
Engine controller
DC controller
High-voltage power supply
Fuser
Fuser film
Pressure roller
Primary
charging
bias circuit
Developing
bias circuit
Transfer
bias circuit
FB
PR
DV
TR
Cartridge
Primary charging roller
Developing roller
Photosensitive drum
Transfer roller
ENWW
Engine control system
11
Page 32

Fuser control circuit
The fuser control circuit controls the fuser temperature. The product uses an on-demand fusing method.
Figure 1-9 Fuser control circuit
H1
TP1
TH1
FUSER HEATER CONTROL signal
Fuser film
Pressure roller
FUSER TEMPERATURE signal
Fuser heater
safety circuit
DC controller
Fuser heater
control circuit
Fuser control circuit
Low-voltage power supply
Engine controller
Table 1-6 Fuser control circuit components
Symbol Name Description
H1 Fuser heater Heats the fuser film
TH1 Thermistor Detects fuser temperature (contact type)
TP1 Thermoswitch Prevents an abnormal temperature rise
of the fuser heater (contact type)
These temperature controls in the fuser are performed by the fuser heater control circuit and the fuser
heater safety. They are controlled by the DC controller.
12 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 33

Fuser temperature control
The fuser temperature control maintains the fuser heater at its targeted temperature.
Figure 1-10 Fuser temperature control
Engine controller
Low-voltage power supply
Fuser control circuit
+24V
Relay control
circuit
Fuser heater
safety circuit
Fuser heater
control circuit
RL101
Frequency
detection circuit
DC controller
FREQSNS
FSRD
RLYD
FSRTH
Fuser film assembly
ENWW
TH1
Pressure roller
TP1
H1
H1: Fuser heater
TP1: Thermoswitch
TH1: Thermistor
Fuser
The DC controller monitors the fuser temperature (FSRTH) signal and sends the fuser heater control
(FSRD) signal according to the detected temperature. The fuser heater control circuit controls the fuser
heater depending on the signal so that the heater remains at the target temperature.
Engine control system
13
Page 34

Fuser protection function
When the protective function detects an abnormal temperature rise in the fuser, it interrupts the power
supply to the fuser heater. The following components prevent an abnormal temperature rise of the fuser
heater:
DC controller: The DC controller monitors the detected temperature of the thermistor. The DC
●
controller makes the fuser heater control signal inactive and releases the relay to interrupt power
supply to the fuser heater when it detects that the thermistor temperature is 240° C (464° F) or
higher.
Fuser heater safety circuit: The fuser heater safety circuit monitors the detected temperature of
●
the thermistor. The fuser heater safety circuit releases the relay control circuit to interrupt power
supply to the fuser heater when it detects that the thermistor temperature is 265° C (509° F) or
higher.
Thermoswitch: The contact of the thermoswitch is broken to interrupt power supply to the fuser
●
heater when it detects that the temperature fuse is 230° C (446° F) or higher
Fuser failure detection
The DC controller determines a fuser failure, makes the fuser heater control signal inactive, releases the
relay to interrupt power supply to the fuser heater, and notifies the formatter of a failure state when it
encounters the following conditions.
Start-up failure
●
If the detected temperature of the thermistor is kept at a specified temperature or higher for a
◦
specified period of heater start-up during the wait period.
If the detected temperature of the thermistor is kept at a specified temperature or lower for a
◦
specified period under the heater temperature control during the initial rotation period.
If the detected temperature of the thermistor is kept at a specified temperature or lower for a
◦
specified period under the heater temperature control during the print period.
If the detected temperature of the thermistor does not reach its targeted temperature within a
◦
specified period under the heater temperature control during the initial rotation period.
Abnormal low temperature
●
If the detected temperature of the thermistor is kept at a specified temperature or lower for a
◦
specified period under the heater temperature control.
14 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 35

Abnormal high temperature
●
If the detected temperature of the main thermistor is kept at a specified temperature or higher
◦
for a specified period.
Drive circuit failure
●
If a specified frequency of the frequency signal is not detected within a specified period after
◦
the product is turned on.
If an out of specified frequency of the frequency signal is detected after the product is turned
◦
on.
ENWW
Engine control system
15
Page 36

Low-voltage power supply
The low-voltage power supply converts AC power from the power receptacle into DC power to cover
the DC loads.
Figure 1-11 Low-voltage power supply
Low-voltage power supply
Engine controller
Noise
filter
Protection
circuit
Fuse
(FU101)
Fuse
(FU102)
+24V generation
circuit
Noise
filter
+3.3V generation
circuit
Fusing
control circuit
PSAVE
+3.3V
+24V
High-voltage power supply
DOORSNS
DC controller
FET
+24U
Door switch
PSW
Power switch
(SW1001)
Fuser
+24P1
(SW301)
Protective function
The low-voltage power supply has a protective function against overcurrent and overvoltage conditions
to prevent failures in the power supply circuit. If an overcurrent or overvoltage event occurs, the system
automatically cuts off the output voltage.
If the DC power is not being supplied from the low-voltage power supply, the protective function might
have activated. In this case, turn off the power switch, and then unplug the power cord. Do not plug in
the power cord or turn the power switch on again until the root cause is found.
16 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 37

In addition, two fuses in the low-voltage power supply protect against an overcurrent event. If an
overcurrent event occurs in the AC line, the fuse blows and cuts off the power distribution.
Safety
For safety purposes, the product has a function to interrupt the 24V power supply to the fuser and the
high-voltage power supply. The door switch is turned off and 24V power stops if the cartridge door is
opened (SW301 is turned off).
The product has the power switch on the DC line, so if the AC power flows, even the power switch is
turned off. Be sure to unplug the power cord before disassembling the product.
Low-voltage power supply unit failure detection
The DC controller determines a low-voltage power supply failure, stops 24V output and notifies the
formatter when it detects that the 24V output is higher than the specified voltage.
ENWW
Engine control system
17
Page 38

Laser scanner system
The laser scanner system forms a latent image on the photosensitive drum according to the video
signals sent from the formatter.
The main components of the laser scanner are the laser assembly and the scanner motor assembly,
which are controlled by the signals sent from the DC controller.
Figure 1-12 Laser scanner system
Engine controller
DC controller
Formatter
VIDEO signal
BD INPUT signal
LASER CONTROL signal
SCANNER MOTOR SPEED CONTROL signal
Scanner mirror
BD sensor
Scanner motor assembly
Photosensitive drum
Laser assembly
18 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 39

Laser failure detection
The optical unit failure detection sensor manages the laser scanner unit failure-detection functions. The
DC controller identifies the laser scanner unit failure and notifies the formatter if the laser scanner unit
encounters the following conditions:
Scanner motor failure
●
BD failure
●
ENWW
Laser scanner system
19
Page 40

Image-formation system
The image-formation system forms a toner image on the paper. The image-formation system includes the
following components:
Toner cartridge
●
Transfer roller
●
Fuser
●
Laser scanner
●
20 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 41

The DC controller controls the laser scanner and high-voltage power supply to form the toner image on
the photosensitive drum. The image is transferred to the paper and fused.
Figure 1-13 Image-formation system
Laser scanner
Laser beam
Fuser film
Fuser
Pressure roller
Image-formation process
Laser printing requires the interaction of several different technologies including electronics, optics, and
electrographics to provide a printed page. Each process functions independently and must be
coordinated with the other processes. Image formation consists of the following processes:
Cartridge
Photosensitive drum
Transfer roller
Engine controller
High-voltage power supply
DC controller
ENWW
Latent-image formation
●
Development
●
Image-formation system
21
Page 42

Transfer
●
Fuser
●
Drum cleaning
●
These processes are divided into seven steps, which are shown below and described in the following
sections.
Figure 1-14 Image-formation process
Paper path
Direction of the drum rotation
Block
Step
Latent image formation
2. Laser-beam exposure
1. Primary charging
Developing
3. Developing
Drum cleaning
Delivery
6. Fusing
Fusing
Latent-image formation stage
During the steps that comprise this stage, a latent image is formed by applying a negative charge to
the photosensitive drum. You cannot see this image on the drum.
Step 1: Primary charging
To prepare for latent image formation, the surface of the photosensitive drum is charged with a uniform
negative charge. The primary charging roller receives the primary charging bias, and then the roller
charges the drum directly.
Figure 1-15 Primary charging process
Primary charging roller
7. Drum cleaning
5. Separation
Transfer
4. Transfer
Pickup
Primary charging bias
Photosensitive drum
22 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 43

Step 2: Laser-beam exposure
The laser beam scans the photosensitive drum to neutralize the negative charge on portions of the drum
surface. An electrostatic latent image forms where the negative charge was neutralized.
Figure 1-16 Laser-beam exposure
Unexposed area Exposed area
Developing stage
The developing roller contacts the photosensitive drum and deposits toner on the electrostatic latent
image, which becomes visible.
Laser beam
Step 3: Development
Toner acquires a negative charge as a result of the friction from the developing roller rotating against
the developing blade. When the negatively charged toner comes in contact with the drum, it adheres to
the electrostatic latent image. When the toner is on the drum, the image becomes visible. The
developing bias is applied to the developing roller.
Figure 1-17 Development process
Blade
Exposed area
Unexposed area
Developing roller
Photosensitive drum
Unexposed area
Exposed area
Developing bias
ENWW
Image-formation system
23
Page 44

Transfer stage
During the transfer stage, the photosensitive drum transfers a toner image to the paper.
Step 4: Transfer
The transfer bias is applied to the transfer roller to give the paper a positive charge. The positively
charged paper attracts the negatively charged toner from the photosensitive drum surface.
Figure 1-18 Transfer process
Transfer roller
Photosensitive
drum
Paper
Transfer bias
Step 5: Separation
The elasticity of the paper and the curvature of the photosensitive drum cause the paper to separate
from the drum surface. The static charge eliminator reduces back side static discharge of the paper for
stable paper feeding and image quality.
Figure 1-19 Separation from the drum
Static charge eliminator
Photosensitive
drum
Paper
Transfer roller
24 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 45

Fusing stage
Until the fusing stage is complete, the image is not permanently affixed to the print media. The toner
can be easily smudged until the heat and pressure of the fusing process fix the image to the sheet.
Step 6: Fusing
The product uses an on-demand fusing method to fuse the toner image onto the media. The toner image
is permanently affixed to the print media by the heat and pressure. The fusing bias is applied to the
pressure roller to improve image quality.
Figure 1-20 Fusing
Fuser heater
Fusing bias
Fuser film
Toner
Paper
Pressure roller
ENWW
Image-formation system
25
Page 46

Drum cleaning stage
Not all of the toner is removed from the photosensitive drum during the transfer stage. During the
cleaning stage, the residual, or waste, toner is cleared from the drum surface to prepare the surface for
the next latent-image formation.
Step 7: Drum cleaning
The cleaning blade scrapes the residual toner off the surface of the photosensitive drum and deposits it
in the toner collection box. The drum is now clear and ready for the next image-formation process.
Figure 1-21 Drum cleaning
Cleaning blade
Toner collection box
Photosensitive
drum
26 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 47

Pickup and feed system
The system picks up and feeds the print media. It consists of several types of feed rollers. The duplex
feed assembly reverses and re-sends the paper to print on second side of paper.
Figure 1-22 Pickup and feed system paper path
Face-down delivery roller
Fuser film
Photosensitive drum
Pressure roller
Fuser delivery roller
: Simplex media path
: Duplex media path
Duplex feed roller
Transfer roller
Duplex re-pickup roller
Registration roller
Cassette pickup roller
The pickup and feed system includes the following electrical components.
MP tray pickup roller
MP tray separation pad
Cassette separation pad
ENWW
Pickup and feed system
27
Page 48

Figure 1-23 Pickup and feed system electrical components
SL3
PS918
M1
SL1
PS916
PS913
PS914
PS915
PS912
PS914
SL2
Table 1-7 Pickup and feed system electrical components
Number Description Signal
M1 Main motor Main motor control signal
SL1 Cassette pickup solenoid Cassette pickup solenoid control signal
SL2 Multipurpose tray pickup solenoid MP tray pickup solenoid control signal
SL3 Duplex reverse solenoid Duplex reverse solenoid control signal
PS915
PS912 Top-of-page sensor Top signal
PS913 Paper width sensor Media width signal
PS914 Cassette paper out sensor Cassette media out signal
28 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 49

Table 1-7 Pickup and feed system electrical components (continued)
Number Description Signal
PS914 Left paper width sensor Media width signal
PS915 Multipurpose tray media out sensor MP tray media out signal
PS915 Right paper width sensor Media width signal
PS916 Fuser output sensor Fuser output signal
PS918 Output-bin full sensor Output-bin media-full signal
Document Loaded Sensor Paper present signal
Top of Form Sensor Top-of-page signal
ENWW
Pickup and feed system
29
Page 50

Jam detection
The product uses the following sensors to detect the presence of paper and to check whether the paper
is being fed correctly or has jammed.
Figure 1-24 Jam detection sensors
PS916
: Simplex media path
: Duplex media path
PS913
PS914
PS915
PS912
Number Description
PS912 Top-of-page sensor
PS913 Paper-width sensor
30 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 51

Number Description
PS914 Left paper-width sensor
PS915 Right paper-width sensor
PS916 Fuser output sensor
Document loaded sensor
Top of Form Sensorr
The product detects the following jams:
Pickup delay jam
●
Pickup stationary jam
●
Delivery delay jam
●
Delivery stationary jam
●
Fuser wrapping jam
●
Door open jam
●
Residual paper jam
●
Duplex reverse jam 1
●
Duplex reverse jam 2
●
Document feeder mispick
●
Document feeder long document jam
●
Document feeder stall jam
●
ENWW
Pickup and feed system
31
Page 52

Paper feeder (optional Tray 3)
The paper feeder is optionally installed at bottom of the product. It picks up and feeds the paper to the
product. The product DC controller controls the paper feeder operational sequence.
Figure 1-25 Paper-feeder paper path
: Simplex media path
: Duplex media path
PF feed roller
PF pickup roller
PF separation pad
The next figure shows the paper feeder controller signal flow.
32 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 53

Figure 1-26 Paper feeder signal flow
Paper feeder
+24V
DC controller
Table 1-8 Paper feeder components
Name Symbol Description
Solenoid SL4 Paper-feed pickup solenoid
Photointerrupter PS1201 Paper-feeder-cassette paper-out sensor
Paper feeder
connector PCA
Solenoid
Photointerrupter
ENWW
Paper feeder (optional Tray 3)
33
Page 54

Paper feeder operation
The paper feeder picks up the paper from the cassette and feeds it to the product.
Figure 1-27 Paper feeder electrical components
M1
SL4
PS1201
Number Description Signal
SL4 Tray 3 cassette pickup solenoid Tray 3 cassette pickup solenoid control signal
PS1201 Tray 3 cassette paper presence sensor Tray 3 cassette paper presence signal
34 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 55

Jam detection
The product uses the following sensors to detect the presence of paper and to check whether the paper
is being fed correctly or has jammed.
Figure 1-28 Jam detection sensors
PS916
: Simplex media path
: Duplex media path
PS913
PS914
PS915
PS912
ENWW
Number Description
PS912 Top-of-page sensor
Paper feeder (optional Tray 3)
35
Page 56

Number Description
PS913 Paper-width sensor
PS914 Left paper-width sensor
PS915 Right paper-width sensor
PS916 Fuser output sensor
Paper jam events in the paper feeder are detected by the DC controller. The product detects the
following jams:
Pickup delay jam
●
Pickup stationary jam
●
Delivery delay jam
●
Delivery stationary jam
●
Fuser wrapping jam
●
Door open jam
●
Residual paper jam
●
Duplex reverse jam 1
●
Duplex reverse jam 2
●
36 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 57

Scanner system
The flatbed image scanner captures an electronic image of the document on the glass. The scanner
does this by illuminating the document with LEDs (red, green, and blue) and capturing the image in the
image sensor to create an electronic format of the document. The flatbed scanner consists of three main
elements.
CIS scanner. The CIS (contact image sensor) scanner captures an image using the product's
●
optical path. Red, green, and blue LEDs sequentially illuminate a small strip of the document (often
called a raster line), and the optical system captures each color in a single row of CCD sensors
that cover the entire page width. Because only one color is captured for each line per exposure,
the three colors are recombined electronically to create the full color image. For monochromatic
scans or copies, all three LEDs are illuminated to create a white light for the scan so the raster line
can be captured in one exposure.
Mechanical carriage drive. The carriage drive moves the CIS scan head along the document
●
length to create the image. In this product, a small DC motor with an optical encoder creates this
motion. The speed of the carriage drive is proportional to the scan resolution (300 ppi is much
faster than 1200 ppi) and also proportional to the type of scan (color scans are three-times slower
than monochromatic scans). A 1200 ppi color scan moves so slowly that the product may appear
to not be working, whereas a monochromatic copy scan moves at 50 times that speed and will be
a little noisy.
Image processing system (formatter). The formatter processes the scanner data into either
●
a copy or a scan to the computer. For copies, the image data is sent directly to the product
without being transmitted to the computer. Depending on user selections for the copy settings, the
formatter enhances the scanner data significantly before sending it to the product. Image data is
captured at 300 ppi for copies and is user selectable for scans to the computer. Each pixel is
represented by 8 bits for each of the three colors (256 levels for each color), for a total of 24 bits
per pixel (24-bit color).
Scanner power-on sequence of events
When the product is turned on, it performs the following tests:
Motor test. The product moves the motor left and right to confirm operation. It reports a scanner
●
error 12 if no motion is detected in the motor encoder system.
Wall find. The scan carriage moves slowly to the left while watching an encoder on the carriage
●
motor to determine when the carriage has found the side wall or stop. This enables the product to
identify the document origin (position of the original). If the document origin cannot be located, a
default position is used instead.
LED check. The product moves the carriage to the white calibration label under the left side of
●
the flatbed image scanner, and it verifies that the minimum and maximum response is acceptable.
It reports a scanner error 14 if the response is unacceptable.
Home find. The scan carriage uses the optical scanner to find physical reference features that
●
relate to the document origin at the left side of the image glass. This process ensures accurate
location of the first document pixels so that the user documents will have an accurate placement of
ENWW
Scanner system
37
Page 58

the image on scans and copies. It reports a scanner error 6 message if the reference features are
not found.
Calibration. This test, also known as scanner color calibration, enables the product to identify
●
the black and white on every pixel in the CCD. Calibration occurs in two major processes: a
broad (analog) adjustment of all pixels to bring them into the target output range, and a pixel-bypixel adjustment (digital) to fine tune the actual black and white response. The calibration process
occurs under the left side of flatbed image scanner where there is a special white calibration
label.
Calibration is the most important step in creating a high quality image. Calibration problems can
include color inaccuracies, brightness inaccuracies, and vertical streaks through the image. The
calibration process identifies any bad pixels and enables the image formatter to recreate the lost
information from adjacent pixels. Extreme cases of this problem can appear as large vertical
streaks or image smears. The user has no control over the calibration process itself or this pixelreplacement process.
Copy or scan sequence of events
To create an accurate rendition of a document, the scanner must be calibrated for the requested
operation. If the user selects a scan at 600 ppi color, the flatbed image scanner calibrates for that
specific operational mode. Subsequently, the flatbed image scanner automatically re-calibrates for the
next requested operation. Calibration does not occur for every new copy request.
Normal sequence of operation for a flatbed copy or scan job includes the following.
1. LEDs illuminate.
2. Carriage motion begins moving the CIS scanner toward the right.
3. Image capture continues for the entire page or length requested in a scan operation.
4. Carriage returns to the home position on the left.
38 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 59

Fax functions and operation
Computer and network security features
The product can send and receive fax data over telephone lines that conform to public switch telephone
network (PSTN) standards. The secure fax protocols make it impossible for computer viruses to be
transferred from the telephone line to a computer or network.
The following product features prevent virus transmission:
No direct connection exists between the fax line and any devices that are connected to the USB or
●
Ethernet ports.
The internal firmware cannot be modified through the fax connection.
●
All fax communications go through the fax subsystem, which does not use Internet data-exchange
●
protocols.
PSTN operation
The PSTN operates through a central office (CO) that generates a constant voltage on the TIP and RING
wires (48 V, usually). A device goes on-hook by connecting impedance (such as 600 ohms for the
U.S.) across the TIP and RING so that a line current can flow. The CO can detect this current and can
send impulses like dial tones. The product generates more signaling tones, such as dialing digits, to tell
the CO how to connect the call. The product can also detect tones, such as a busy tone from the CO,
that tell it how to behave.
When the call is finally connected, the CO behaves like a piece of wire connecting the sender and
receiver. This is the period during which all of the fax signaling and data transfer occurs. When a call
is completed, the circuit opens again and the line-current flow ceases, removing the CO connection
from both the sender and the receiver.
On most phone systems, the TIP and RING wires appear on pins 3 and 4 of the RJ-11 modular jack (the
one on the fax card). These two wires do not have to be polarized because all the equipment works
with either TIP or RING on pin 3 and the other wire on pin 4. This means that cables of either polarity
can interconnect and will still work.
These basic functions of PSTN operation are assumed in the design of the fax subsystem. The product
generates and detects the signaling tones, currents, and data signals that are required to transmit and
receive faxes on the PSTN.
Receive faxes when you hear fax tones
In general, incoming faxes to the product are automatically received. However, if other devices are
connected to the same phone line, the product might not be set to answer automatically.
ENWW
Fax functions and operation
39
Page 60

If the product is connected to a phone line that receives both fax and phone calls, and you hear fax
tones when you answer the extension phone, receive the fax in one of two ways:
If you are near the product, touch the Start Fax button on the control panel.
●
Press 1-2-3 in sequence on the extension phone keypad, listen for fax transmission sounds, and
●
then hang up.
NOTE: In order for the 1-2-3 sequence to work, the Extension Phone setting must be set to On in the
Fax Setup menu.
Distinctive ring function
The distinctive ring feature is a service that a telephone company provides. The distinctive ring service
allows three phone numbers to be assigned to one phone line. Each phone number has a distinctive
ring. The first phone number has a single ring, the second phone number has a double ring, and the
third phone number has a triple ring.
NOTE: The product has not been tested with all of the distinctive-ring services that telephone
companies provide in all countries/regions. HP does not guarantee that the distinctive-ring function will
operate correctly in all countries/regions. Contact the local telephone service provider for assistance.
Set up the distinctive ring function
1.
From the Home screen on the product control panel, touch the Setup
2. Open the following menus:
Fax Setup
●
Basic Setup
●
Distinctive Ring
●
3. Use the arrow buttons to select one of the following options:
All Rings (default setting)
●
Single
●
Double
●
Triple
●
Double and Triple
●
Use fax with voice over IP services
Voice over IP (VoIP) services provide normal telephone service, including long distance service through
a broadband Internet connection. These services use packets to break up the voice signal on a
telephone line and transmit it digitally to the receiver, where the packets are reassembled. The VoIP
services are often not compatible with fax machines. The VoIP provider must state the service supports
fax over IP services.
button.
40 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 61

Because the installation process varies, the VoIP service provider will have to assist in installing the
product fax component.
Although a fax might work on a VoIP network, it can fail when the following events occur:
Internet traffic becomes heavy and packets are lost.
●
Latency (the time it takes for a packet to travel from its point of origin to its point of destination)
●
becomes excessive.
If you experience problems using the fax feature on a VoIP network, ensure that all of the product
cables and settings are correct. Configuring the Fax Speed setting to Medium(V.17) or Slow(V.29) can
also improve your ability to send a fax over a VoIP network.
If you continue to have problems faxing, contact your VoIP provider.
The fax subsystem
The formatter, fax card, firmware, and software all contribute to the fax functionality. The designs of the
formatter and fax card, along with parameters in the firmware, determine the majority of the regulatory
requirements for telephony on the product.
The fax subsystem is designed to support V.34 fax transmission, lower speeds (such as V.17 fax), and
older fax machines.
Fax card in the fax subsystem
Two versions of the fax card are used in the product. One is used in the North American, South
American, and Asian countries/regions. The other is used primarily in European countries/regions.
The fax card contains the modem chipset (DSP and CODEC) that controls the basic fax functions of tone
generation and detection, along with channel control for fax transmissions. The CODEC and its
associated circuitry act as the third-generation silicon data access arrangement (DAA) to comply with
worldwide regulatory requirements.
The only difference between the two versions is that each version is compliant with the 2/4-wire phone
jack system from the respective country/region.
Safety isolation
The most important function of the fax card is the safety isolation between the high-voltage, transientprone environment of the telephone network (TNV [telephone network voltage]) and the low-voltage
analog and digital circuitry of the formatter (SELV [secondary extra-low voltage]). This safety isolation
provides both customer safety and product reliability in the telecom environment.
Any signals that cross the isolation barrier do so magnetically. The breakdown voltage rating of barriercritical components is greater than 5 kV.
Safety-protection circuitry
ENWW
In addition to the safety barrier, the fax card protects against overvoltage and overcurrent events.
Fax functions and operation
41
Page 62

Telephone overvoltage events can be either differential mode or common mode. The event can be
transient in nature (a lightning-induced surge or ESD) or continuous (a power line crossed with a phone
line). The fax card protection circuitry provides margin against combinations of overvoltage and
overcurrent events.
Common mode protection is provided by the selection of high-voltage-barrier critical components
(transformer and relay). The safety barrier of the fax card printed circuit board traces and the clearance
between the fax card and surrounding components also contribute to common mode protection.
A voltage suppressor (a crowbar-type SIDACTOR) provides differential protection. This product
becomes low impedance at approximately 300 V differential, and crowbars to a low voltage. A series
thermal switch works in conjunction with the crowbar for continuous telephone line events, such as
crossed power lines.
All communications cross the isolation barrier magnetically. The breakdown voltage rating of barriercritical components is greater than 5 kV.
Data path
TIP and RING are the two-wire paths for all signals from the telephone network. All signaling and data
information comes across them, including fax tones and fax data.
The telephone network uses DC current to determine the hook state of the telephone, so line current
must be present during a call. The silicon DAA provides a DC holding circuit to keep the line current
constant during a fax call.
The silicon DAA converts the analog signal to a digital signal for DSP processing, and also converts the
digital signal to an analog signal for transmitting data through a telephone line.
The magnetically coupled signals that cross the isolation barrier go either through a transformer or a
relay.
The DSP in the fax card communicates with the ASIC in the formatter using the high-speed serial
interface.
Hook state
Another magnetically coupled signal is the control signal that disconnects the downstream devices (such
as a telephone or answering machine). A control signal originating on the DSP can change the relay
state, causing the auxiliary jack (downstream jack) to be disconnected from the telephone circuit.
The product takes control of calls that it recognizes as fax calls. If the product does not directly pick up
the call, it monitors incoming calls for the fax tone or for the user to direct it to receive a fax. This idle
mode is also called eavesdropping. This mode is active when the product is on-hook but current exists
in the downstream phone line because another device is off-hook. During eavesdropping, the receive
circuit is enabled but has a different gain from the current that is generated during normal fax
transmissions.
The product does not take control of the line unless it detects a fax tone or the user causes it to connect
manually. This feature allows the user to make voice calls from a phone that is connected to the product
without being cut off if a fax is not being received.
42 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 63

Downstream device detection
The line voltage monitoring module of the silicon DAA can detect the line state as well as the
downstream device. It tells DSP via DIB that an active device (telephone, modem, or answering
machine) is connected to the auxiliary port on the product (the right side of the RJ-11 jack). The DSP
uses the signal to ensure that the product does not go off-hook (and disconnect a downstream call) until
it has been authorized to do so (by a manual fax start or the detection of the appropriate tones).
Hook switch control
In the silicon DAA, the CODEC controls the hook switch directly. The CODEC is activated when it
receives commands from the DSP. When the circuit is drawing DC current from the central office, it is
considered off-hook. When no DC current flows, the state is considered on-hook.
Ring detect
Ring detect is performed by the line voltage monitoring module of the silicon DAA, and is a
combination of voltage levels and cadence (time on and time off). Both must be present to detect a
valid ring. The CODEC works with DSP as well as the firmware to determine if an incoming signal is an
answerable ring.
Line current control
The DC current from the CO needs to have a path to flow from TIP to RING. The DC impedance
emulation line modulator and DC terminations modules in the silicon DAA act as a DC holding circuit,
and works with the firmware to achieve the voltage-current characteristic between TIP and RING. The
impedance (the current-voltage characteristic) changes depending on certain special events, such as
pulse dialing or when the product goes on-hook.
Billing- (metering-) tone filters
Switzerland and Germany provide high-frequency AC signals on the telephone line in order to bill
customers.
A filter in a special fax cable (for certain countries/regions), can filter these signals. Because these
billing signals are not used in the U.S., these filters are not present in the U.S. fax cable.
To obtain a special fax cable, contact your local telephone service provider.
Fax page storage in flash memory
Fax pages are the electronic images of the document page. They can be created in any of three ways:
scanned to be sent to another fax machine, generated to be sent by the computer, or received from a
fax machine to be printed.
The product stores all fax pages in flash memory automatically. After these pages are written into flash
memory, they are stored until the pages are sent to another fax machine, printed on the product,
transmitted to a computer, or erased by the user.
ENWW
These pages are stored in flash memory, which is the nonvolatile memory that can be repeatedly read
from, written to, and erased. The product has 8 MB of flash memory, of which 7.5 MB is available for
Fax functions and operation
43
Page 64

fax storage. The remaining 0.5 MB is used for the file system and reclamation. Adding RAM does not
affect the fax page storage because the product does not use RAM for storing fax pages.
Stored fax pages
The user can reprint stored fax receive pages in case of errors. For a fax send, the product will resend
the fax in case of errors. The product will resend stored fax pages after a busy signal, communication
error, no answer, or power failure. Other fax devices store fax pages in either normal RAM or shortterm RAM. Normal RAM immediately loses its data when power is lost, while short-term RAM loses its
data about 60 minutes after power failure. Flash memory maintains its data for years without any
applied power.
Advantages of flash memory storage
Fax pages that are stored in flash memory are persistent. They are not lost as a result of a power
failure, no matter how long the power is off. Users can reprint faxes in case the print cartridge runs out
of toner or the product experiences other errors while printing faxes.
The product also has scan-ahead functionality that makes use of flash memory. Scan-ahead
automatically scans pages into flash memory before a fax job is sent. This allows the sender to pick up
the original document immediately after it is scanned, eliminating the need to wait until the fax is
transmission is complete.
Because fax pages are stored in flash memory rather than RAM, more RAM is available to handle
larger and more complicated copy and print jobs.
44 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 65

USB flash drive
The product features printing from a USB flash drive. The product prints the following file types from the
USB flash drive.
PDF
●
RGB JPEG
●
When a USB flash drive is inserted into the front of the product, the control panel will display the USB
Flash Drive menu. The files on the USB flash drive can be accessed from the control panel using the
touchscreen. Any RGB JPEG or PDF files on the USB flash drive can be printed directly from the product
control panel.
ENWW
USB flash drive
45
Page 66

46 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Page 67

2 Solve problems
Solve problems checklist
●
Menu map
●
Troubleshooting process
●
Tools for troubleshooting
●
Clear jams
●
Solve paper-handling problems
●
Solve image quality problems
●
Clean the product
●
Solve performance problems
●
Solve connectivity problems
●
Service mode functions
●
Solve fax problems
●
Manually update the firmware
●
ENWW 47
Page 68

Solve problems checklist
1. Make sure that the product is set up correctly.
a. Press the power button to turn on the product or to deactivate the Auto-Off mode.
b. Check the power-cable connections.
c. Make sure that the line voltage is correct for the product power configuration. (See the label
that is on the back of the product for voltage requirements.) If you are using a power strip
and its voltage is not within specifications, plug the product directly into the wall. If it is
already plugged into the wall, try a different outlet.
2. Check the cabling.
a. Check the cable connection between the product and the computer. Make sure that the
connection is secure.
b. Make sure that the cable itself is not faulty by using a different cable, if possible.
c. Check the network connection: Make sure the network light is lit. The network light is next to
the network port on the back of the product.
If the product remains unable to connect to the network, uninstall and then reinstall the
product. If the error persists, contact a network administrator.
3. Check to see if any messages appear on the control panel.
4. Make sure that the paper that you are using meets specifications.
5. Make sure that the paper is loaded correctly in the input tray.
6. Make sure that the product software is installed correctly.
7. Verify that you have installed the printer driver for this product, and that you are selecting this
product from the list of available printers.
8. Print a configuration page.
a. If the page does not print, verify that the input tray contains paper and that the paper is
properly loaded.
b. Make sure that the toner cartridge is installed correctly.
48 Chapter 2 Solve problems ENWW
Page 69

c. If the page jams in the product, clear the jam.
d. If the print quality is unacceptable, complete the following steps:
Verify that the print settings are correct for the paper that you are using.
●
Solve print-quality problems.
●
9. Print a small document from a different program that has worked in the past. If this solution works,
then the problem is with the program you are using. If this solution does not work (the document
does not print), complete these steps:
a. Try printing the job from another computer that has the product software installed.
b. Check the cable connection. Direct the product to the correct port, or reinstall the software,
selecting the connection type that you are using.
ENWW
Solve problems checklist
49
Page 70

Menu map
Use the following procedure to print a control-panel menu layout map.
1.
From the Home screen, touch the Setup
2. Touch the Reports button.
3. Touch the Menu Structure button.
button.
50 Chapter 2 Solve problems ENWW
Page 71

Troubleshooting process
When the product malfunctions or encounters an unexpected situation, the product control panel alerts
you to the situation. This chapter contains information to help diagnose and solve problems.
Use the pre-troubleshooting checklist to evaluate the source of the problem and to reduce the
●
number of steps that are required to fix the problem.
Use the troubleshooting flowchart to pinpoint the root cause of hardware malfunctions. The
●
flowchart guides you to the section of this chapter that contains steps for correcting the
malfunction.
Before beginning any troubleshooting procedure, check the following issues:
Are supply items within their rated life?
●
Does the configuration page reveal any configuration errors?
●
NOTE: The customer is responsible for checking supplies and for using supplies that are in good
condition.
Pre-troubleshooting checklist
The following table includes basic questions to ask the customer to quickly help define the problem(s).
General topic Questions
Environment
Media
Input trays
Is the product installed on a solid, level surface (+/- 1°)?
●
Is the power-supply voltage within ± 10 volts of the specified power source?
●
Is the power-supply plug inserted in the product and the outlet?
●
Is the operating environment within the specified parameters?
●
Is the product exposed to ammonia gas, such as that produced by diazo
●
copiers or office cleaning materials?
NOTE: Diazo copiers produce ammonia gas as part of the copying
processes. Ammonia gas (from cleaning supplies or a diazo copier) can have
an adverse effect on some product components (for example, the toner
cartridge OPC).
Is the product exposed to direct sunlight?
●
Does the customer use only supported media?
●
Is the media in good condition (no curls, folds, or distortion)?
●
Is the media stored correctly and within environmental limits?
●
Is the amount of media in the tray within specifications?
●
Is the media correctly placed in the tray?
●
ENWW
Are the paper guides aligned with the stack?
●
Is the tray correctly installed in the product?
●
Troubleshooting process
51
Page 72

General topic Questions
Toner cartridge
Transfer unit and fuser
Covers
Condensation
Miscellaneous
Is the toner cartridge installed correctly?
●
Are the transfer unit and fuser installed correctly?
●
Is the front cover closed?
●
Does condensation occur following a temperature change (particularly in
●
winter following cold storage)? If so, wipe affected parts dry or leave the
product on for 10 to 20 minutes.
Was a toner cartridge opened soon after being moved from a cold to a warm
●
room? If so, allow the toner cartridge to sit at room temperature for 1 to 2
hours.
Check for and remove any non-HP components (toner cartridges, memory
●
modules, and EIO cards) from the product.
If the hardware or software configuration has not changed or the problem is
●
not associated with any specific software, see the complete service manual for
this product.
Remove the product from the network and ensure that the failure is associated
●
with the product before beginning troubleshooting.
For any print-quality issues, calibrate the product.
●
52 Chapter 2 Solve problems ENWW
Page 73

Determine the problem source
The following table includes basic questions to ask the customer to quickly help define the problem or
problems.
General topic Questions
Environment
Paper
Input tray
Is the product installed on a solid, level surface (± 1°)?
●
Is the power-supply voltage within ± 10 volts of the specified power source?
●
Is the power-supply plug inserted in the product and the outlet?
●
Is the operating environment within the specified parameters?
●
Is the product exposed to ammonia gas, such as that produced by diazo
●
copiers or office cleaning materials?
NOTE: Diazo copiers produce ammonia gas as part of the coping
processes. Ammonia gas (from cleaning supplies or a diazo copier) can have
an adverse affect on some product components (for example, the toner
cartridge imaging drum).
Is the product exposed to direct sunlight?
●
Does the customer use only supported paper?
●
Is the paper in good condition (no curls, folds, or distortion)?
●
Is the paper stored correctly and within environmental limits?
●
Is the amount of paper in the tray within specifications?
●
Is the paper correctly placed in the tray?
●
Are the paper guides aligned with the stack?
●
Supplies
Transfer roller and fuser
Covers
Condensation
Miscellaneous
Is the toner cartridge installed correctly and firmly seated?
●
Has the sealing tape been removed from the toner cartridge?
●
Is the toner cartridge within its estimated life? (Check the supplies status page.)
●
Are the transfer roller and fuser installed correctly?
●
Are the front and rear doors firmly closed?
●
Does condensation occur following a temperature change (particularly in
●
winter following cold storage)? If so, wipe affected parts dry or leave the
product on for 90 to 120 minutes.
Was a toner cartridge opened soon after being moved from a cold to a warm
●
room? If so, allow the toner cartridge to sit at room temperature for 1 to 2
hours.
Check for and remove any non-HP components (for example, a toner
●
cartridge) from the product.
Remove the product from the network and make sure that the failure is with the
●
product before beginning troubleshooting.
ENWW
Troubleshooting process
53
Page 74

Power subsystem
Power-on checks
When you turn on the product, if it does not make any sound or if the control-panel display is blank,
check the following items:
Verify that the product is plugged directly into an active electrical outlet that has the correct
●
voltage. Do not plug the product into a surge protector or power strip.
Verify that the on/off switch is in the on position.
●
Verify that the formatter is seated and operating correctly.
●
Remove any HP Jetdirect accessories or other devices, and then try to turn the product on again.
●
Make sure that the control-panel display is connected.
●
Check the two fuses on the power supply.
●
If necessary, replace the power supply.
●
If necessary, replace the DC controller.
●
Control-panel checks
Use the product control panel to conduct tests on the control panel LEDs, display, or buttons.
1.
From the Home screen on the product control panel, touch the Setup
2. Touch the left arrow button, and then quickly touch the Cancel
to Ready status.
3.
Press the Setup
menu.
4. Touch the 2ndary Service menu, and then scroll to one of the following menu items.
LED Test
●
Display Test
●
Button Test
●
5. Touch the menu item to begin the test.
6. After the test has finished, return the product to the Ready state, and then touch the Cancel
button to remove the 2ndary Service menu from the menu list.
button again to open the menus. The first menu should be the 2ndary Service
button.
button. The display should return
54 Chapter 2 Solve problems ENWW
Page 75

Tools for troubleshooting
Component diagnostics
LED diagnostics
Network LEDs
The onboard network solution has two network port LEDs. When the product is connected to a properly
working network through a network cable, the yellow LED indicates network activity, and the green LED
indicates the link status. A blinking yellow LED indicates network traffic. If the green LED is off, a link
has failed.
For link failures, check all of the network cable connections. In addition, you can try to manually
configure the network card link speed setting by using the product control-panel.
Change the Link Speed setting
1.
From the Home screen on the product control panel, touch the Setup
2. Scroll to, and then touch the Network Setup menu.
3. Scroll to, and then touch Link Speed item.
4. Touch the appropriate link speed.
Control panel LEDs
The state of the Ready light and Attention light on the product signal the product status. The following
table outlines the possible control-panel light states.
Product state Ready light state Attention light state
Initializing Blinking Blinking
Ready On Off
Receiving data/processing job or
cancelling job
Error message Off Blinking
Fatal error (49 or 79 error)
1
The product will power off and then power on after one of these errors occurs.
button.
Blinking Off
1
On On
ENWW
Tools for troubleshooting
55
Page 76

Engine diagnostics
Engine test
If the duplex unit is disabled, the engine test produces a single-sided sheet with horizontal lines when
you perform the engine test. If the duplex unit is activated (the default state), the engine test produces a
double-sided sheet with horizontal lines when you perform the engine test.
To perform the test, with the product in the Ready state, open and shut the cartridge door three times. If
the engine is functioning properly, the product will initialize and then print the test page
56 Chapter 2 Solve problems ENWW
Page 77

Diagrams
Plug/jack locations
Table 2-1 Plug/jack locations
Item Description
1 Hi-Speed USB 2.0 port
2 Network port
3 Fax ports
ENWW
Tools for troubleshooting
57
Page 78

Locations of major components
Figure 2-1 Major components (1 of 2)
1 2 3 4
Table 2-2 Major components (1 of 2)
Item Description
1 Registration assembly
2 Fuser assembly
3 Feed drive assembly (simplex models)
Duplex drive assembly (duplex models)
4 Laser scanner assembly
5 Duplex feed assembly
5
58 Chapter 2 Solve problems ENWW
Page 79

Figure 2-2 Major components (2 of 2)
1 2
43
Table 2-3 Major components (2 of 2)
Item Description
1Fan
2 Transfer roller
3 Main motor
4 Sensor assembly
ENWW
Tools for troubleshooting
59
Page 80

General timing chart
12
Fuser heater
12
Fuser heater
The following charts lists the approximate timing for this product, specified in seconds.
Figure 2-3 Timing diagram
STBYRTSLTNIRPRTNIYBTSTIAW
Power ON
Signal
1 TOP sensor (PS912)
4 Scanner motor
2 Fuser output sensor (PS916)
3 Print command (EEC12)
Laser6BD signal (BDO)
5
Primary charging bias (DC)
Primary charging bias (AC)
7 Main motor (M1)
9
8
10 Developing bias
Transfer bias
Cassette pickup solenoid (SL2)
11
13
Main fan (FM1)
14
60 Chapter 2 Solve problems ENWW
Page 81

General circuit diagrams
Figure 2-4 Circuit diagram — main unit (1 of 2)
Connector PCA
FANLOCK
/DUPSOL
/CSTSOL
123456
123456
TAG
COILB
COILA
1234567
J1205
+24P1
+24P1
+24P1
+24P1
J1103
4
GND
/DEC
213
/ACC
1234
J1105
FM1
123
123
GND
321
1234
4213
J802
1234
SL
21
MPSOL
M2
M
12
12
+24V
12345
CNT0
assembly
scanner
Laser
J801
789
VDO2
GND(DCOM)
/VDO2
10
11 13
12
GND(DCOM)
GND(PB)
2345678910
1
+3.3V
/BDI
654 3 2 1
12
13
11
6
VDO1
/VDO1
GND(DCOM)
CNT2
CNT1
J1101
12
12
12
SL
J1104
12
12
1
SL
2
7
7
J1102
1 34567
FANLOCK
2
DUPSOL
CSTSOL
GND
/DEC
/ACC
COR1
J2100
12
+24P1
J207
J581
12
12
TAG1
TAG2
1
J201
1
2
/BDO
WAKEVC
Formatter
234
56789
3456789
WAKEENG
/SCLK
/SC
/RSTO
10
12
14
6
123
45
45612
111315
1011121314
GND
/BDI
+3.3U
15
GND
CNT2
CNT1
CNT0
MPSOL
+24V
3
345612
123456
GND
GND
GND
+3.3C
+3.3C
Engine controller PCA
+24P2
FT2
J216
SW301
21
FT1
+24U
1
J2142
1
J2141
+24V
FULSNS
WDSNS1
/PISNS
WDSNS2
WDSNS3
/CSTSNS
+3.3U
+3.3U
+3.3U
J213
1
J918
PS918
123
123
GND
J203
123456
1234
56
GND
J204
21
GND
321
3
23 123 123
321
PS912
321
1
PS913
321
PS914
62534
321
J912
PS915
321
J914
PS914
21
3
J205
12345671234567
S MODE
21
3456
/TESTP
GND
+3.3U
7
+24P1
J211
+3.3U
/MPSNS
+3.3U
/POSNS
123
GND
J206
123
GND
321123 12
123
J915
J916
PS915
PS916
321
3
21
Fuser assembly
J210
GND
FSRTH
ILMLEDCLK
/ILMLED
+3.3V
5
12345
1234
SW1001
1
LED1001
B
GND
PSW1
345
2
21
J215
1234
12
J1001
5
AC-N
FB
J302
AC-H
J101
32
1
31
2
COR2
FT3
INL101
321
A
+24P1
J202
J1202
12345
154
M1
/MACC
/MDEC
GND
MFG
ACH
ACN
5
1234
45
123
2
3
54321
M
C
TH1
21
12
J102
TSH1
21
12
TP
12
TP1
21
J4
H1
21
D
ENWW
Tools for troubleshooting
61
Page 82

Figure 2-5 Circuit diagram — main unit (2 of 2)
654 3 2 1
Formatter Control panel
242620
22
23
21
25
1234567891011 13 15 17 19 21 23 25
14
1816
17 19
15
12 14 22
8910
12
13
11
4
6
7
5
24 26201816
2
3
1
A
B
C
D
62 Chapter 2 Solve problems ENWW
Page 83

Figure 2-6 Circuit diagram — optional Tray 3
654 3 2 1
PF connector PCA
+3.3U
+24P1
GND
3
1
27
1234567
J1201
+24P1
OPT SOL
+3.3U
OPT SNS
OPT SOL
J1202
12
12
12
SL
J1202
SR1
GND
321
321
OPT SNS
65
231
1234567
321
7162354
S MODE
/TESTP
+3.3U
734562147345621
+24P1
J211
Engine controller PCA
GND
ENWW
A
B
C
D
Tools for troubleshooting
63
Page 84

Use HP Device Toolbox (Windows)
Use the HP Device Toolbox for Windows to view or change product settings from your computer.
This tool opens the HP Embedded Web Server for the product.
NOTE: This tool is available only if you performed a full installation when you installed the product.
The HP Embedded Web Server, however, is still available by opening a Web browser and entering the
product IP address in the browser address box.
1. Click the Start button, and then click the Programs item.
2. Click your HP product group, and then click the HP Device Toolbox item.
Tab or section Description
Home tab
Provides product, status, and
configuration information.
System tab
Provides the ability to configure the
product from your computer.
Device Status: Shows the product status and shows the approximate percent life
●
remaining of HP supplies.
Supplies Status: Shows the approximate percent life remaining of HP supplies.
●
Actual supply life remaining can vary. Consider having a replacement supply
available to install when print quality is no longer acceptable. The supply does not
need to be replaced unless the print quality is no longer acceptable.
Device Configuration: Shows the information found on the product configuration
●
page.
Network Summary: Shows the information found on the product network
●
configuration page.
Reports: Allows you to print the configuration and supplies status pages that the
●
product generates.
Event Log: Shows a list of all product events and errors.
●
Device Information: Provides basic product and company information.
●
Paper Setup: Allows you to change the paper-handling defaults for the product.
●
Print Quality: Allows you to change the print quality defaults for the product,
●
including calibration settings.
Paper Types: Allows you to configure print modes that correspond to the paper
●
types that the product accepts.
System Setup: Allows you to change the system defaults for the product.
●
Service: Allows you to start the cleaning procedure on the product.
●
Product Security: Allows you to set or change the product password.
●
Save and Restore: Save the current settings for the product to a file on the
●
computer. Use this file to load the same settings onto another product or to restore
these settings to this product at a later time.
NOTE: The System tab can be password-protected. If this product is on a network,
always consult with the administrator before changing settings on this tab.
64 Chapter 2 Solve problems ENWW
Page 85

Tab or section Description
Print tab
Provides the ability to change
default print settings from your
computer.
Networking tab
Provides the ability to change
network settings from your
computer.
HP Web Services tab Use this tab to set up and use various Web tools with the product.
HP Smart Install tab Use this tab to download and install the print driver.
Printing: Change the default product print settings, such as number of copies and
●
paper orientation. These are the same options that are available on the control
panel.
PCL5c: View and change the PCL5c settings.
●
PostScript: Turn off or on the Print PS Errors feature.
●
Network administrators can use this tab to control network-related settings for the product
when it is connected to an IP-based network. It also allows the network administrator to
set up wireless direct functionality. This tab does not appear if the product is directly
connected to a computer.
Internal print-quality test pages
Clean the paper path
During the printing process, paper, toner, and dust particles can accumulate inside the product. Over
time, this buildup can cause print-quality problems such as toner specks or smearing. This product has a
cleaning mode that can correct and prevent these types of problems.
1.
From the Home screen on the product control panel, touch the Setup
2. Touch the Service menu.
3. Touch the Cleaning Page button.
4. Load plain letter or A4 paper when you are prompted.
5. Touch the OK button to begin the cleaning process.
Wait until the process is complete. Discard the page that prints.
Print the configuration page
1.
From the Home screen on the product control panel, touch the Setup
2. Touch the Reports menu.
3. Touch the Configuration Report button to print the report.
Print-quality troubleshooting tools
Repetitive image defect ruler
button.
button.
ENWW
Defects on product rollers can cause image defects to appear at regular intervals on the page,
corresponding to the circumference of the roller that is causing the defect. Measure the distance
Tools for troubleshooting
65
Page 86

between defects that recur on a page. Use the following table or the repetitive-defect ruler to determine
which roller is causing the defect. To resolve the problem, try cleaning the roller first. If the roller
remains dirty after cleaning or if it is damaged, replace the part that is indicated in
Table 2-4 Repetitive
defects on page 66.
CAUTION: Do not use solvents or oils to clean rollers. Instead, rub the roller with lint-free paper. If
dirt is difficult to remove, rub the roller with lint-free paper that has been dampened with water.
NOTE: The following table replaces the graphical repetitive defect ruler. You can make your own
ruler by using these measurements. For the most accurate results, use a metric ruler.
Table 2-4 Repetitive defects
Component Distance between defects
Primary charging roller 38 mm (1.5 in)
Transfer roller 39 mm (1.54 in)
Developer roller 42 mm (1.65 in)
Registration roller 43 mm (1.69 in)
Fuser film 57 mm (2.24 in)
Pressure roller 63 mm (2.48 in)
Photosensitive drum 75 mm (2.95 in)
66 Chapter 2 Solve problems ENWW
Page 87

Control panel menus
HP Web Services menu
●
Reports menu
●
Quick Forms menu
●
USB Flash Drive menu
●
System Setup menu
●
Service menu
●
Network Setup menu
●
HP Web Services menu
Use the HP Web Services menu to set up the HP Web Services features.
Menu item Description
Print Information Sheet Prints a report that instructs the user how to set up the HP Web Services features.
Display E-Mail Address Displays the product email address.
Turn ePrint On/Off Enables or disables the product HP ePrint functionality.
Turn Apps On/Off Enables or disables the product HP Web Services applications.
Enable Web Services Enables the HP Web Services features.
Remove Services Removes the HP Web Services features from the product.
Clear Apps History Deletes the stored history of the product HP Web Services applications.
Proxy Settings Allows you to enter proxy server information for the product internet connection.
Reports menu
Use the Reports menu to print reports that provide information about the product.
Menu item Description
Demo Page Prints a sample page that demonstrates print quality.
Menu Structure Prints a map of the control panel-menu layout. The active settings for each menu are
Configuration Report Prints a list of all the product settings. Includes network information when the
listed.
product is connected to a network.
ENWW
Tools for troubleshooting
67
Page 88

Menu item Description
Supplies Status Prints the status for each toner cartridge, including the following information:
Estimated percentage of cartridge life remaining
●
Approximate pages remaining
●
Part numbers for HP toner cartridge
●
Number of pages printed
●
Information about ordering new HP toner cartridges and recycling used HP
●
toner cartridges
Network Summary Prints a list of all product network settings
Usage Page Prints a page that lists PCL pages, PCL 6 pages, PS pages, pages that were jammed
or mispicked in the product, and reports the page count
PCL Font List Prints a list of all the PCL fonts that are installed
PS Font List Prints a list of all the PostScript (PS) fonts that are installed
PCL6 Font List Prints a list of all the PCL6 fonts that are installed
Service Page Provides information on supported paper types, copy settings, and other
miscellaneous settings that are not on the configuration page
Quick Forms menu
Menu item Sub-menu item Description
Notebook Paper Narrow Rule
Graph Paper 1/8 inch
Checklist 1 Column
Music Paper Portrait
Prints pages that have preprinted lines
Wide Rule
Child Rule
Prints pages that have preprinted graph lines
5 mm
Prints pages that have preprinted lines with check boxes
2 Column
Prints pages that have preprinted lines for writing music
Landscape
68 Chapter 2 Solve problems ENWW
Page 89

USB Flash Drive menu
Print Documents Prints documents stored on the USB drive. Use the arrow
Easy Photo Print Prints photo files directly from the product.
Thumbnail Sheet(s) Prints a page or pages of 30 “thumbnail” graphic images.
View and Print Photos Previews photos on the USB drive. Use the arrow buttons to
buttons to scroll through the documents. Touch the names of
documents that you want to print.
Touch the summary screen to change settings such as the
number of copies, the paper size, or the paper type.
Touch the Print button when you are ready to print the
documents.
NOTE: This menu item is available for LCD control panel
models only.
NOTE: This menu item is available for LCD control panel
models only.
scroll through the photos. Touch the preview image for each
photo that you want to print. You can adjust the settings, and
you can save the changes as the new default settings. When
you are ready to print the photos, touch the Print button.
Scan to USB Drive Scans a document and stores it as a .PDF document or .JPEG
System Setup menu
In the following table, items that have asterisks (*) indicate the factory default setting.
Menu item Sub-menu item Sub-menu item Description
Language Select the language for the
Paper Setup Default Paper Size Letter
Default Paper Type A list of available
A4
Legal
paper types
appears.
image on the USB flash drive.
control panel display messages
and the product reports.
Sets the size for printing internal
reports or any print job that does
not specify a size.
NOTE: The default setting is
determined by the choice of
location during the initial
product setup.
Select the paper type for printing
internal reports or any print job
that does not specify a type.
ENWW
Tray 1 Paper Type
Paper Size
Select the default size and type
for Tray 1 from the list of
available sizes and types.
Tools for troubleshooting
69
Page 90

Menu item Sub-menu item Sub-menu item Description
Tray 2 Paper Type
Paper Size
Paper Out Action Wait forever*
Cancel
Override
Select the default size and type
for Tray 2 from the list of
available sizes and types.
Select how the product should
react when a print job requires a
size or type that is not available
or when a specified tray is
empty.
Select the Wait forever option to
make the product wait until you
load the correct paper and press
the OK button. This is the default
setting.
Select the Override option to
print on a different size or type
after a specified delay.
Select the Cancel option to
automatically cancel the print
job after a specified delay.
If you select either the Override
or Cancel options, the control
panel prompts you to specify the
number of seconds to delay. Use
the arrow buttons to increase (up
to 3600 seconds) or decrease
the time.
Energy Settings Sleep Delay Off
1 Minute
15 Minutes*
30 Minutes
1 Hour
2 Hours
Auto Power Down Power Down Delay Never
Sets how long the product
30 Minutes
1 Hour
2 Hours
4 Hours
8 Hours
24 Hours
remains idle before it enters
sleep mode. The product
automatically exits sleep mode
when you send a print job or
press a control panel button.
Sets the period of time that must
elapse before the product Auto
Power Down feature activates.
70 Chapter 2 Solve problems ENWW
Page 91

Menu item Sub-menu item Sub-menu item Description
Wake Events USB Job
LAN Job
Wireless Job
(wireless models
only)
Button Press
USB Drive Insert
Print Density A range of 1 to 5. Select the print density level. The
Supply Settings Black Cartridge Very Low Setting Stop
Prompt*
Continue
Enables or disables certain
product events (like when a
control panel button is pressed)
that will cause the product to
revert from Auto Power Down
mode to Ready status.
default setting is 3
Set how the product behaves
when the black toner cartridge
reaches the very low threshold.
Stop: The product stops
●
printing until you replace
the toner cartridge.
Prompt: The product stops
●
printing and prompts you to
replace the toner cartridge.
You can acknowledge the
prompt and continue
printing.
Continue: The product
●
alerts you that the toner
cartridge is very low, but it
continues printing.
Low Threshold A percentage range
of 1 to 100.
Administration Product Security Enable product security. If turned
USB Flash Drive On*
Off
Display Contrast Medium*
Darker
Darkest
Lightest
Lighter
Select the level of contrast for the
Enable or disable the walkup
Set the percentage of estimated
life remaining at which the
product alerts you that the toner
cartridge is low.
on, the product prompts you to
set a password. After it is set,
the password will be needed to
change product settings.
USB port.
display.
ENWW
Tools for troubleshooting
71
Page 92

Menu item Sub-menu item Sub-menu item Description
Courier Font Regular*
Quiet Mode Enable or Disable the product
Service menu
Use this menu to restore default settings, clean the product, and activate special modes that affect print
output. Items that have asterisks (*) indicate the factory default setting.
Menu item Sub-menu item Sub-menu item Description
Fax Service Clear Saved Faxes Touch the OK button to clear any
Run Fax Test The product prints a fax test page.
Print T.30 Trace Now
Dark
Selects a version of the Courier
font..
Quiet Mode.
fax messages stored in the product
memory.
Use this menu either to manually
Never*
If Error
print a T30 trace report, or to set
up automatic report printing.
At End of Call
Error Correction On*
Off
Fax Service Log The product prints a fax service
Cleaning Page Use this option to clean the product
Use this menu to enable or disable
the error correction feature for the
product fax accessory.
report.
if you see toner specks or other
marks on the printed output. The
cleaning process removes dust and
excess toner from the paper path.
When you select this item, the
product prompts you to load plain
paper in Tray 1 and then press the
OK button to start the cleaning
process. Wait until the process is
complete. Discard the page that
prints.
72 Chapter 2 Solve problems ENWW
Page 93

Menu item Sub-menu item Sub-menu item Description
USB Speed High*
Full
Less Paper Curl On
Off*
Archive Print On
Off*
Firmware Date Displays the current firmware
Restore Defaults Sets all customized copy settings to
Signature Check Cancel if Invalid*
Prompt if Invalid
Sets the USB speed to High or Full.
For the product to actually operate
at high speed, it must have high
speed enabled and be connected
to an EHCI host controller that is
also operating at high speed. This
menu item also does not reflect the
current operating speed of the
product.
If printed pages are consistently
curled, use this option to set the
product to a mode that reduces
curl.
If you are printing pages that will
be stored for a long time, use this
option to set the product to a mode
that reduces toner smearing and
dusting.
datecode.
the factory default values.
Configures how the product
proceeds when a firmware
upgrade file does not have a valid
signature.
HP Smart Install On*
Off
LaserJet Update Check For Updates Now Prompts the product to search for a
Manage Updates Allow Downgrade Yes*: Allows the firmware upgrade
Check Automatically On*: Allows the product to
Enables or disables the HP Smart
Install functionality.
newer firmware upgrade file and
then upload it.
functionality to upload an older
firmware version.
No: Prevents the product from
loading older firmware files.
automatically search for new
firmware updates.
Off: Prevents the product from
loading new firmware update files.
ENWW
Tools for troubleshooting
73
Page 94

Menu item Sub-menu item Sub-menu item Description
Prompt Before Install Install Automatically: Allows the
product to automatically load a
firmware update file.
Always Prompt*: Causes the
product to display a prompt at the
control panel before the product
can load a firmware update file.
Allow Updates Yes*: Allows the product to load
firmware update files.
No: Prevents the product from
loading firmware update files.
74 Chapter 2 Solve problems ENWW
Page 95

Network Setup menu
Use this menu to establish network configuration settings.
Menu item Sub-menu item Description
Wireless Menu (wireless products
only)
Wireless Setup Wizard
Wi-Fi Protected Setup If your wireless router supports this feature, use this
Run Wireless Test Tests the wireless network and prints a report with
Turn Wireless On/Off Enable or disable the wireless network feature.
TCP/IP Config Automatic*
IPv4 Config Method DHCP
Card Sharing On*
Wireless Direct Settings
method to set up the product on a wireless network.
This is the simplest method.
the results.
Select Automatic to automatically configure all the
TCP/IP settings.
Manual
Select Manual to manually configure the IP address,
subnet mask, and default gateway.
Set the IPv4 configuration method.
BOOTP
Auto IP
Manual
Enable or disable file sharing of a memory card that
has been inserted into the product walkup USB port.
Off
ENWW
Auto Crossover On*
Off
Network Services IPv4
IPv6
Show IP Address No*
Yes
This item is used when you are connecting the
product directly to a personal computer using an
Ethernet cable (you might have to set this to On or
Off depending on the computer being used).
This item is used by the network administrator to limit
the network services available on this product.
On
Off
The default setting is On.
No: The product IP address will not appear on the
control panel display.
Yes: The product IP address will appear on the
control panel display.
Tools for troubleshooting
75
Page 96

Menu item Sub-menu item Description
Link Speed Automatic (Default)
10T Full
10T Half
100TX Full
100TX Half
Security Product Security Enable product security. If turned on, the product
HTTPS Enforcement Enable or disable the HTTPS Enforcement setting.
Firewall Enable, disable, or reset the product firewall.
Access Control List Enable, disable, or reset the network access control
802.1x (wireless models only) Enable or disable the 802.1x wireless authentication
Reset All Security Reset the security settings to the factory-set default
Sets the link speed manually if needed.
After setting the link speed, the product automatically
restarts.
prompts you to set a password. After it is set, the
password will be needed to change product settings.
The default setting is On.
list.
protocol.
values.
Restore Defaults Press the OK button to restore the network
configuration settings to the default values.
USB Flash Drive On
Off
Enable or disable the walkup USB port.
76 Chapter 2 Solve problems ENWW
Page 97

Interpret control-panel messages
Control panel message types
Alert and warning messages appear temporarily and might require you to acknowledge the message
by touching the OK button to resume or by touching the Cancel
certain warnings, the job might not complete or the print quality might be affected. If the alert or
warning message is related to printing and the auto-continue feature is on, the product will attempt to
resume the printing job after the warning has appeared for 10 seconds without acknowledgement.
Critical error messages can indicate some kind of failure. Turning off and then turning on the power
might fix the problem. If a critical error persists, the product might require service.
Control panel messages
49 Error, Turn off then on
Description
The product experienced an internal error.
Recommended action
Turn the product off, wait at least 30 seconds, and then turn the product on and wait for it to initialize.
button to cancel the job. With
If you are using a surge protector, remove it. Plug the product directly into the wall socket. Turn the
product power on.
If the message persists, contact HP support.
50.x Fuser Error
Description
The product has experienced an error with the fuser.
Recommended action
Turn the product power off, wait at least 30 seconds, and then turn the product power on and wait for
it to initialize.
Turn off the product, wait at least 25 minutes, and then turn on the product.
If you are using a surge protector, remove it. Plug the product directly into the wall socket. Turn the
product power on.
If the message persists, contact HP support.
51.XX Error
ENWW
Description
The product has experienced an internal hardware error.
Tools for troubleshooting
77
Page 98

Recommended action
Turn the product power off, wait at least 30 seconds, and then turn the product power on and wait for
it to initialize.
If you are using a surge protector, remove it. Plug the product directly into the wall socket. Turn the
product on.
If the message persists, contact HP support.
54.XX Error
Description
The product has experienced an error with one of the internal sensors.
Recommended action
Turn the product power off, wait at least 30 seconds, and then turn the product power on and wait for
it to initialize.
If you are using a surge protector, remove it. Plug the product directly into the wall socket. Turn the
product power on.
If the message persists, contact HP support.
55.X Error
Description
The product has experienced an internal error.
Recommended action
Turn the product power off, wait at least 30 seconds, and then turn the product power on and wait for
it to initialize.
If you are using a surge protector, remove it. Plug the product directly into the wall socket. Turn the
product power on.
If the message persists, contact HP support.
57 Fan Error, Turn off then on
Description
The product has experienced a problem with its internal fan.
Recommended action
Turn the product power off, wait at least 30 seconds, and then turn the product power on and wait for
it to initialize.
If you are using a surge protector, remove it. Plug the product directly into the wall socket. Turn the
product power on.
78 Chapter 2 Solve problems ENWW
Page 99

If the message persists, contact HP support.
59.X Error
Description
The product has experienced a problem with one of the motors.
Recommended action
Turn the product power off, wait at least 30 seconds, and then turn the product power on and wait for
it to initialize.
If you are using a surge protector, remove it. Plug the product directly into the wall socket. Turn the
product power on.
If the message persists, contact HP support.
79 Error Turn off then on
Description
The product has experienced an internal firmware error.
Recommended action
Turn the product power off, wait at least 30 seconds, and then turn the product power on and wait for
it to initialize.
If you are using a surge protector, remove it. Plug the product directly into the wall socket. Turn the
product power on.
If the message persists, contact HP support.
79 Service error
Description
An incompatible DIMM is installed.
Recommended action
1. Turn the product power off.
2. Install a DIMM that the product supports.
3. Turn the product on.
If the message persists, contact HP support. For a list of supported DIMMs, see the user guide.
Black cartridge low
ENWW
Description
The toner cartridge is nearing the end of its useful life.
Tools for troubleshooting
79
Page 100

Recommended action
Printing can continue, but consider having a replacement toner cartridge on hand.
Black cartridge very low
Description
The toner cartridge is at the end of its useful life. A customer configurable option on this product is
"Prompt to Remind Me in 100 pages, 200 pages, 300 pages, 400 pages, or never." This option is
provided as a customer convenience and is not an indication these pages will have acceptable print
quality.
Recommended action
To ensure optimal print quality, HP recommends replacing the toner cartridge at this point. You can
continue printing until you notice a decrease in print quality. Actual cartridge life may vary.
Once an HP toner cartridge has reached very low, HP's Premium Protection Warranty on that toner
cartridge has ended. All print defects or cartridge failures incurred when an HP toner cartridge is used
in continue at very low mode will not be considered to be defects in materials or workmanship in the
toner cartridge under the HP Print Cartridge Warranty Statement.
Cleaning
Description
The product periodically performs a cleaning procedure to maintain the best print quality.
Recommended action
Wait for the cleaning process to finish.
Communication error.
Description
A fax communication error occurred between the product and the sender or receiver.
Recommended action
Allow the product to retry sending the fax. Unplug the product telephone cord from the wall, plug in a
telephone, and try making a call. Connect the product phone cord into a jack for another phone line.
Try a different phone cord.
Set the Fax Speed option to the Slow(V.29) setting or disable the Fast(V.34) setting.
Turn off the Error Correction feature to prevent automatic error correction.
NOTE: Turning off the Error Correction feature can reduce image quality.
Print the Fax Activity Log report from the control panel to determine if the error occurs with a specific
fax number.
80 Chapter 2 Solve problems ENWW
 Loading...
Loading...