HP LaserJet Pro Color MFP M476 Repair Manual and Troubleshooting Manual

HP LaserJet Pro Color MFP M476
Troubleshooting Manual
M476dn
M476dw
M476nw
www.hp.com/support/colorljMFPM476
www.hp.com/support

HP LaserJet Pro Color MFP M476 Printer
Troubleshooting Manual

Conventions used in this guide
TIP: Tips provide helpful hints or shortcuts.
NOTE: Notes provide important information to explain a concept or to complete a task.
CAUTION: Cautions indicate procedures that you should follow to avoid losing data or damaging the
product.
WARNING! Warnings alert you to specific procedures that you should follow to avoid personal injury,
catastrophic loss of data, or extensive damage to the product.
ENWW iii

Table of contents
1 Theory of operation ....................................................................................................................................... 1
Basic operation ...................................................................................................................................................... 2
Major systems ..................................................................................................................................... 2
Product components ........................................................................................................................... 2
Sequence of operation ........................................................................................................................ 3
Formatter-control system ..................................................................................................................................... 4
Sleep Delay .......................................................................................................................................... 4
Input/output ........................................................................................................................................ 4
USB .................................................................................................................................... 4
10/100 networking ........................................................................................................... 4
Fax ..................................................................................................................................... 4
USB hosts .......................................................................................................................... 5
Memory ................................................................................................................................................ 5
Flash memory ................................................................................................................... 5
Random access memory ................................................................................................... 5
Nonvolatile memory ......................................................................................................... 5
Memory Enhancement technology ................................................................................... 5
Wireless radio ...................................................................................................................................... 5
PJL overview ........................................................................................................................................ 5
LEDM overview .................................................................................................................................... 6
ACL overview ....................................................................................................................................... 6
PML ...................................................................................................................................................... 6
Control panel ....................................................................................................................................... 6
NFC ....................................................................................................................................................... 6
Engine control system ........................................................................................................................................... 7
DC controller ........................................................................................................................................ 8
Power supply ....................................................................................................................................... 9
Protective function ........................................................................................................... 9
Power saving ................................................................................................................... 10
Fuser control ................................................................................................................... 10
Fuser control circuit ...................................................................................... 11
Fuser protective function ............................................................................. 12
ENWW v

Fuser failure detection ................................................................................. 13
High-voltage power supply ............................................................................................ 14
Laser/scanner system ......................................................................................................................................... 15
Laser failure detection ...................................................................................................................... 15
Image-formation system .................................................................................................................................... 16
Image-formation process ................................................................................................................. 16
Overview ......................................................................................................................... 16
Latent-image formation stage ....................................................................................... 17
Step 1: primary charging .............................................................................. 17
Step 2: laser-beam exposure ....................................................................... 18
Developing stage ............................................................................................................ 18
Step 3: development .................................................................................... 18
Transfer stage ................................................................................................................. 19
Step 4: primary transfer ............................................................................... 19
Step 5: secondary transfer ........................................................................... 19
Step 6: separation from the drum ............................................................... 20
Fusing stage .................................................................................................................... 20
Step 7: fusing ................................................................................................ 20
ITB cleaning stage ........................................................................................................... 21
Step 8: ITB cleaning ...................................................................................... 21
Drum cleaning stage ....................................................................................................... 22
Step 9: drum cleaning .................................................................................. 22
Developing roller engagement/disengagement control ............................ 22
Pickup-and-feed system ..................................................................................................................................... 23
Jam detection .................................................................................................................................... 25
Pad transfer ....................................................................................................................................... 25
Multiple-feed prevention .................................................................................................................. 26
Scanning and image capture system .................................................................................................................. 27
Scanner power-on sequence of events ............................................................................................ 27
Copy or scan sequence of events ...................................................................................................... 28
Scanner operation ............................................................................................................................. 28
ADF operation ...................................................................................................................................................... 30
ADF duplex operation ........................................................................................................................ 30
ADF paper path and ADF sensors ...................................................................................................... 30
ADF jam detection ............................................................................................................................. 31
ADF jam clearance ............................................................................................................................. 32
Fax functions and operation ............................................................................................................................... 33
Computer and network security features ........................................................................................ 33
PSTN operation ................................................................................................................................. 33
Receive faxes when you hear fax tones ........................................................................................... 33
Distinctive ring function .................................................................................................................... 34
vi ENWW

Fax by using Voice over IP services ................................................................................................... 34
The fax subsystem ............................................................................................................................ 35
Fax card in the fax subsystem .......................................................................................................... 35
Safety isolation ............................................................................................................... 35
Safety-protection circuitry ............................................................................................. 35
Data path ......................................................................................................................... 35
Hook state ....................................................................................................................... 36
Downstream current detection ...................................................................................... 36
Hook switch control ........................................................................................................ 36
Ring detect ...................................................................................................................... 36
Line current control ........................................................................................................ 36
Billing- (metering-) tone filters ...................................................................................... 37
Fax page storage in flash memory ................................................................................................... 37
Stored fax pages ............................................................................................................. 37
Advantages of flash memory storage ............................................................................ 37
USB flash drive ..................................................................................................................................................... 38
2 Solve problems ........................................................................................................................................... 39
Solve problems checklist ..................................................................................................................................... 40
Menu structure .................................................................................................................................................... 42
Configuration report ............................................................................................................................................ 43
Troubleshooting process .................................................................................................................................... 44
Determine the problem source ......................................................................................................... 44
Power subsystem .............................................................................................................................. 45
Power-on checks ............................................................................................................ 45
Control-panel checks ........................................................................................................................ 45
Tools for troubleshooting ................................................................................................................................... 46
Individual component diagnostics .................................................................................................... 46
Tools for troubleshooting: LED diagnostics ................................................................... 46
Network LEDs ............................................................................................... 46
Control panel LEDs ....................................................................................... 46
Tools for troubleshooting: Engine diagnostics .............................................................. 47
Engine-test button ....................................................................................... 47
Drum rotational check ................................................................................. 47
Half self-test functional check ..................................................................... 48
Diagrams ........................................................................................................................................... 49
Diagrams: Formatter connections .................................................................................. 49
Diagrams: Location of major components ..................................................................... 50
Major components ........................................................................................ 50
Motors and fans ............................................................................................ 52
Rollers ........................................................................................................... 53
ENWW vii

PCAs .............................................................................................................. 54
Optional 250-sheet cassette ....................................................................... 55
Diagrams: General timing chart ...................................................................................... 56
Diagrams: Circuit diagram .............................................................................................. 57
Diagrams: CPU/ASIC diagrams ........................................................................................ 58
Diagrams: HVT/Toner EMP diagram ............................................................................... 60
Diagrams: Driver PCA diagram ....................................................................................... 61
Diagrams: Duplexer PCA diagram .................................................................................. 62
Diagrams: FSR diagram .................................................................................................. 63
Print-quality troubleshooting tools ................................................................................................. 64
Print-quality troubleshooting tools: Repetitive defects ruler ....................................... 64
Tools for troubleshooting: Control panel menus ............................................................................. 65
Setup menu ..................................................................................................................... 65
HP Web Services menu ................................................................................. 65
Reports menu ............................................................................................... 66
Self Diagnostics menu .................................................................................. 66
Fax Setup menu ............................................................................................ 67
System Setup menu ..................................................................................... 69
Service menu ................................................................................................ 72
Network Setup menu .................................................................................... 74
Quick Forms menu ........................................................................................ 75
Fax Menu ......................................................................................................................... 75
Copy Menu ....................................................................................................................... 77
Tools for troubleshooting: Interpret control panel messages ........................................................ 78
Control panel message types ......................................................................................... 78
Control panel messages ................................................................................................. 79
10.100X Supply Memory Error ..................................................................... 79
30.XXXX Scanner Error ................................................................................. 80
49 Error, Turn off then on ............................................................................ 80
50.XXXX Fuser Error ..................................................................................... 81
51.XX and 52.XX Error To continue turn off then on ................................... 82
54.0100 — 54.1599 Error ............................................................................ 82
55.1 DC controller Memory Error ................................................................. 83
57 Fan Error, Turn off then on ..................................................................... 83
58.04 Error Turn off then on ........................................................................ 83
59.XXXX Error Turn off then on ................................................................... 84
60.XXXX Error Turn off then on ................................................................... 85
79 Error Turn off then on ............................................................................. 85
Device is busy. Try again later. ..................................................................... 86
Document feeder mispick. Reload. .............................................................. 86
Document feeder jam. Clear and reload. ..................................................... 87
viii ENWW

Fax is busy. Canceled send. .......................................................................... 87
Fax receive error. .......................................................................................... 87
Fax Send error. ............................................................................................. 88
Fax storage is full. Canceling the fax send/receive. .................................... 88
Front door open. ........................................................................................... 89
Jam in Tray 1, Clear jam and then press OK ................................................. 89
Jam in Tray 2, Clear jam and then press OK ................................................. 89
Jam in Tray 3, Clear jam and then press OK ................................................. 90
Load paper .................................................................................................... 90
Load Tray 1 <TYPE> <SIZE>, Press OK to use available media ................... 90
Load Tray 1, <PLAIN> <SIZE> / Cleaning mode, OK to start ........................ 90
Load tray <X> Press [OK] for available media ............................................. 90
No dial tone. .................................................................................................. 91
No fax detected. ........................................................................................... 91
The product is unable to calibrate. Close the lid and remove paper
from the document feeder. .......................................................................... 91
Unexpected size in tray # Load <size> Press [OK] ...................................... 92
Tools for troubleshooting: Event-log messages ............................................................................. 92
Print the event log .......................................................................................................... 92
Event log messages ........................................................................................................ 92
Clear jams ............................................................................................................................................................ 95
Jam locations .................................................................................................................................... 95
Experiencing frequent or recurring paper jams? .............................................................................. 95
Clear jams in the document feeder ................................................................................................... 97
Clear jams in Tray 1 ........................................................................................................................... 98
Clear jams in Tray 2 ......................................................................................................................... 100
Clear jams in Tray 3 (accessory) ..................................................................................................... 101
Clear jams in the duplexer .............................................................................................................. 103
Clear jams in the output bin ............................................................................................................ 105
Paper feeds incorrectly or becomes jammed ................................................................................................... 106
The product does not pick up paper ............................................................................................... 106
The product picks up multiple sheets of paper .............................................................................. 106
Solve image-quality problems .......................................................................................................................... 107
Solve image quality problems: Image defects table ...................................................................... 107
Improve print quality ...................................................................................................................... 112
Print from a different software program ..................................................................... 113
Check the paper-type setting for the print job ............................................................ 113
Check the paper type setting (Windows) ................................................... 113
Check the paper type setting (Mac OS X) ................................................... 113
Check toner-cartridge status ....................................................................................... 113
Print and interpret the print quality page .................................................................... 114
ENWW ix

Clean the product ......................................................................................................... 115
Print a cleaning page .................................................................................. 115
Check the scanner glass for dirt and smudges .......................................... 115
Visually inspect the toner cartridge ............................................................................. 116
Check paper and the printing environment ................................................................. 116
Step one: Use paper that meets HP specifications .................................... 116
Step two: Check the environment .............................................................. 116
Calibrate the product to align the colors ..................................................................... 117
Check other print job settings ...................................................................................... 117
Check the EconoMode settings .................................................................. 117
Adjust color settings (Windows) ................................................................ 118
Try a different print driver ............................................................................................ 119
General print-quality issues ........................................................................................................... 120
Solve paper-handling problems ....................................................................................................................... 125
Product feeds incorrect page size .................................................................................................. 125
Product pulls from incorrect tray ................................................................................................... 125
Paper does not feed automatically ................................................................................................ 125
Paper does not feed from Tray 2 or 3 ............................................................................................. 126
Output is curled or wrinkled ........................................................................................................... 126
Product will not duplex or duplexes incorrectly ............................................................................ 127
Clean the product .............................................................................................................................................. 128
Clean the pickup and separation rollers ......................................................................................... 128
Clean the paper path ....................................................................................................................... 128
Clean the scanner glass strip and platen ....................................................................................... 128
Clean the document feeder pickup rollers and separation pad ..................................................... 129
Clean the touchscreen .................................................................................................................... 130
Solve performance problems ............................................................................................................................ 131
Factors affecting print performance .............................................................................................. 131
Print speeds .................................................................................................................. 131
The product does not print or it prints slowly ................................................................................ 132
The product does not print ........................................................................................... 132
The product prints slowly ............................................................................................. 133
Solve connectivity problems ............................................................................................................................. 134
Solve USB connection problems ..................................................................................................... 134
Solve wired network problems ....................................................................................................... 134
Poor physical connection ............................................................................................. 134
The computer is using the incorrect IP address for the product ................................. 134
The computer is unable to communicate with the product ........................................ 135
The product is using incorrect link and duplex settings for the network ................... 135
New software programs might be causing compatibility problems ........................... 135
The computer or workstation might be set up incorrectly .......................................... 135
x ENWW

The product is disabled, or other network settings are incorrect ............................... 135
Solve wireless network problems .................................................................................................. 135
Wireless connectivity checklist .................................................................................... 136
The product does not print after the wireless configuration completes .................... 136
The product does not print, and the computer has a third-party firewall installed ... 137
The wireless connection does not work after moving the wireless router or
product .......................................................................................................................... 137
Cannot connect more computers to the wireless product .......................................... 137
The wireless product loses communication when connected to a VPN ...................... 137
The network does not appear in the wireless networks list ....................................... 137
The wireless network is not functioning ...................................................................... 137
Perform a wireless network diagnostic test ................................................................ 138
Reduce interference on a wireless network ................................................................ 138
Solve fax problems ............................................................................................................................................ 139
Checklist for solving fax problems ................................................................................................. 139
Perform a fax diagnostic test ......................................................................................................... 140
Solve general fax problems ............................................................................................................ 140
Faxes are sending slowly ............................................................................................. 140
Fax quality is poor ........................................................................................................ 141
Fax cuts off or prints on two pages .............................................................................. 142
Solve problems receiving faxes ...................................................................................................... 142
The fax does not respond ............................................................................................. 143
The fax has a dedicated phone line ........................................................... 143
An answering machine is connected to the product ................................. 143
The Answer Mode setting is set to the Manual setting ............................. 144
Voice mail is available on the fax line ........................................................ 144
The product is connected to a DSL phone service ..................................... 144
The product uses a fax over IP or VoIP phone service ............................... 144
An error message displays on the control panel ......................................................... 145
The No Fax Detected message displays .................................................... 145
The Communication Error message appears ............................................ 145
The Fax storage is full. message appears ................................................. 146
The Fax is busy. message appears ............................................................ 146
A fax is received but does not print .............................................................................. 147
The Private Receive feature is on .............................................................. 147
Sender receives a busy signal ...................................................................................... 147
A handset is connected to the product ...................................................... 147
A phone line splitter is being used ............................................................. 147
No dial tone ................................................................................................................... 147
Cannot send or receive a fax on a PBX line .................................................................. 147
Solve problems sending faxes ........................................................................................................ 147
ENWW xi

An error message displays on the control panel ......................................................... 148
The Communication Error message appears ............................................ 148
No dial tone. ............................................................................................... 149
The Fax is busy. message appears ............................................................ 149
The No fax answer. message appears ....................................................... 149
Document feeder paper jam ...................................................................... 150
The Fax storage is full. message appears ................................................. 150
Scanner error .............................................................................................. 150
The control panel displays a Ready message with no attempt to send the fax ......... 150
The control panel displays the message "Storing page 1" and does not progress
beyond that message ................................................................................................... 151
Faxes can be received, but not sent ............................................................................. 151
Product is password protected .................................................................................... 151
Unable to use fax functions from the control panel .................................................... 152
Unable to use speed dials ............................................................................................. 152
Unable to use group dials ............................................................................................. 152
Receive a recorded error message from the phone company when trying to send
a fax .............................................................................................................................. 152
Unable to send a fax when a phone is connected to the product ................................ 153
Fax trace report ............................................................................................................................... 154
Fax error report printing ................................................................................................................. 154
Print all fax reports ....................................................................................................... 154
Print individual fax reports ........................................................................................... 154
Set the fax error report ................................................................................................ 155
Set the fax-error-correction mode ................................................................................................. 155
Change the fax speed ...................................................................................................................... 155
Solve email problems ........................................................................................................................................ 156
Cannot connect to the email server ................................................................................................ 156
The email failed ............................................................................................................................... 156
Unable to scan ................................................................................................................................. 156
Validate LDAP gateway ..................................................................................................................................... 157
Access control for LaserJet Pro devices ......................................................................................... 157
Product resets ................................................................................................................................................... 158
Restore the factory-set defaults .................................................................................................... 158
NVRAM initialization ........................................................................................................................ 158
Super NVRAM initialization ............................................................................................................. 158
Firmware upgrades ........................................................................................................................................... 159
Appendix A Product specifications ................................................................................................................. 161
Product dimensions ........................................................................................................................................... 162
Power consumption, electrical specifications, and acoustic emissions .......................................................... 162
xii ENWW

Environmental specifications ............................................................................................................................ 162
Certificate of Volatility ...................................................................................................................................... 163
Index ........................................................................................................................................................... 165
ENWW xiii

List of tables
Table 1-1 Sequence of operation ......................................................................................................................................... 3
Table 2-1 Basic problem solving ........................................................................................................................................ 40
Table 2-2 Major components ............................................................................................................................................. 50
Table 2-3 Solenoid, sensors, and motors .......................................................................................................................... 52
Table 2-4 Rollers ................................................................................................................................................................ 53
Table 2-5 PCAs .................................................................................................................................................................... 54
Table 2-6 Optional 250-sheet cassette ............................................................................................................................. 55
Table 2-7 Repetitive defects .............................................................................................................................................. 64
Table 2-8 HP Web Services menu ....................................................................................................................................... 65
Table 2-9 Reports menu ..................................................................................................................................................... 66
Table 2-10 Self Diagnostics menu ..................................................................................................................................... 66
Table 2-11 Fax Setup menu ............................................................................................................................................... 67
Table 2-12 System Setup menu ......................................................................................................................................... 69
Table 2-13 Service menu .................................................................................................................................................... 72
Table 2-14 Network Setup menu ....................................................................................................................................... 74
Table 2-15 Quick Forms Menu ............................................................................................................................................ 75
Table 2-16 Fax Menu .......................................................................................................................................................... 75
Table 2-17 Copy Menu ........................................................................................................................................................ 77
Table 2-18 Event-log messages ........................................................................................................................................ 92
Table 2-19 Event-log-only messages ................................................................................................................................ 94
Table 2-20 Image defects table ....................................................................................................................................... 107
Table 2-21 General print-quality issues .......................................................................................................................... 120
Table 2-22 Factors affecting print performance ............................................................................................................. 131
Table A-1 Physical specifications ..................................................................................................................................... 162
Table A-2 Operating-environment specifications ........................................................................................................... 162
ENWW xv

List of figures
Figure 1-1 Product components ........................................................................................................................................... 2
Figure 1-2 Engine control system components ................................................................................................................... 7
Figure 1-3 DC controller circuit diagram .............................................................................................................................. 8
Figure 1-4 Low-voltage power supply ................................................................................................................................. 9
Figure 1-5 Fuser block diagram ......................................................................................................................................... 10
Figure 1-6 Fuser control circuit .......................................................................................................................................... 11
Figure 1-7 High-voltage power supply .............................................................................................................................. 14
Figure 1-8 Laser/scanner system ...................................................................................................................................... 15
Figure 1-9 Image-formation system .................................................................................................................................. 16
Figure 1-10 Image-formation process ............................................................................................................................... 17
Figure 1-11 Primary charging ............................................................................................................................................ 17
Figure 1-12 Laser-beam exposure ..................................................................................................................................... 18
Figure 1-13 Development .................................................................................................................................................. 18
Figure 1-14 Primary transfer ............................................................................................................................................. 19
Figure 1-15 Secondary transfer ......................................................................................................................................... 19
Figure 1-16 Separation from the drum .............................................................................................................................. 20
Figure 1-17 Fusing .............................................................................................................................................................. 20
Figure 1-18 ITB cleaning ..................................................................................................................................................... 21
Figure 1-19 Drum cleaning ................................................................................................................................................. 22
Figure 1-20 Pickup-and-feed system ................................................................................................................................ 23
Figure 1-21 Multiple-feed prevention ................................................................................................................................ 26
Figure 1-22 ADF paper path ............................................................................................................................................... 31
Figure 1-23 ADF jam clearance ........................................................................................................................................... 32
Figure 2-1 Control-panel 2ndary Service test access buttons .......................................................................................... 45
Figure 2-2 Engine test button access ................................................................................................................................. 47
Figure 2-3 Major components ............................................................................................................................................ 50
Figure 2-4 Motors and fans ................................................................................................................................................ 52
Figure 2-5 Rollers ............................................................................................................................................................... 53
Figure 2-6 PCAs ................................................................................................................................................................... 54
Figure 2-7 Optional 250-sheet cassette ............................................................................................................................ 55
Figure 2-8 Timing diagram ................................................................................................................................................. 56
Figure 2-9 Circuit diagram .................................................................................................................................................. 57
ENWW xvii

Figure 2-10 CPU diagram ................................................................................................................................................... 58
Figure 2-11 ASIC diagram ................................................................................................................................................... 59
Figure 2-12 HVT/Toner EMP diagram ................................................................................................................................ 60
Figure 2-13 Driver PCA diagram ......................................................................................................................................... 61
Figure 2-14 Duplexer PCA diagram .................................................................................................................................... 62
Figure 2-15 FSR diagram .................................................................................................................................................... 63
Figure A-1 Certificate of Volatility (1 of 2) ....................................................................................................................... 163
Figure A-2 Certificate of Volatility (2 of 2) ....................................................................................................................... 164
xviii ENWW
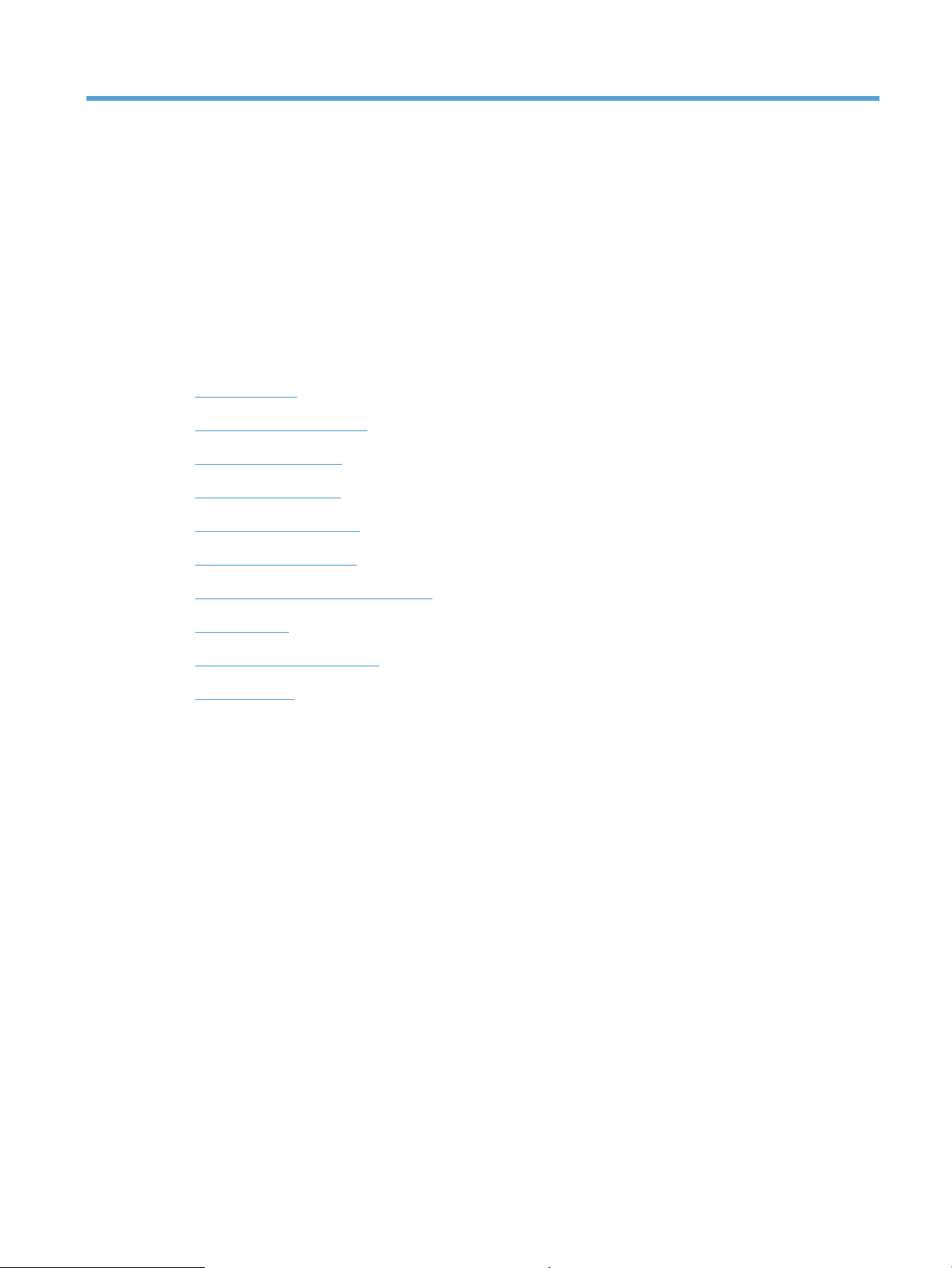
1 Theory of operation
This chapter presents an overview of the major components of the product, and includes a detailed
discussion of the image-formation system.
●
Basic operation
●
Formatter-control system
●
Engine control system
●
Laser/scanner system
●
Image-formation system
●
Pickup-and-feed system
●
Scanning and image capture system
●
ADF operation
●
Fax functions and operation
●
USB flash drive
ENWW 1
Basic operation
1 2 3 4 5
13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6
Major systems
The product includes the following systems:
●
Engine control system
●
Laser/scanner system
●
Image-formation system
●
Pickup-and-feed system
●
Document feeder system
Product components
Figure 1-1 Product components
Item Description Item Description
1 Fuser unit 8 Pickup roller
2 Delivery roller 9 Separation roller
3 Print cartridge 10 Registration roller
4 Laser/scanner unit 11 Secondary transfer roller
5 Photosensitive drum 12 Fusing film
2 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW

Item Description Item Description
6 Primary transfer pad 13 Pressure roller
7 Intermediate transfer belt (ITB)
Sequence of operation
Table 1-1 Sequence of operation
Period Duration Purpose Remarks
WAIT From the time the power is
turned on or the door is closed
until the drum-phase
adjustment is complete
STBY (Standby period) From end of the WAIT or LSTR
period until either the print
command is received from the
formatter or the power is
turned off
INTR (Initial rotation) From the time the print
command is received until the
media is picked up
PRINT From the end of INTR period
until the fuser paper sensor
detects the trailing edge of
paper
LSTR (Last rotation) From the end of the PRINT
period until the delivery motor
stops rotating
Clears the potential from the
drum surface, adjusts the drum
phase, and cleans the ETB
Maintains the product in
readiness for a print command
Prepares the photosensitive
drum for printing
Forms the images on the
photosensitive drum and
transfers the toner image to
the print media
Moves the printed sheet out of
the product
Detects the toner level,
cartridge presence, and
environment; completes any
required calibration (color
registration control and image
stability)
The product enters sleep mode
when the formatter sends a
sleep command, and performs
color registration and the
image stability control when
the formatter sends those
commands
Performs image stabilization at
a specified print interval or at
specified times
The product enters the INTR
period as soon as the formatter
sends another print command
ENWW Basic operation 3

Formatter-control system
The formatter is involved in the following procedures.
●
Controlling the Sleep Delay function
●
Receiving and processing print data from the various product inputs
●
Monitoring control-panel functions and relaying product status information (through the control panel
and the bidirectional input/output)
●
Developing and coordinating data placement and timing with the DC controller PCA
●
Storing font information
●
Communicating with the host computer through the bidirectional interface
The formatter receives a print job from the bidirectional interface and separates it into image information
and instructions that control the printing process. The dc controller PCA synchronizes the image-formation
system with the paper-input and -output systems, and then signals the formatter to send the print-image
data.
Sleep Delay
When the product is in Sleep Delay, the control-panel backlight is turned off, but the product retains all
product settings, downloaded fonts, and macros. The default setting is a 15-minute idle time. Sleep Delay
can be turned off from the System Setup menu on the control panel.
The product exits Sleep Delay and enters the warm-up cycle when any of the following occurs.
●
A print job, valid data, or a PML or PJL command is received at the serial port.
●
The control panel is touched.
●
A document is loaded in the document feeder or the scanner lid is opened.
●
A tray is opened.
●
The engine-test button is pressed.
TIP: Error messages override the Sleep Delay message. The product enters Sleep mode at the appropriate
time, but the error message continues to appear.
Input/output
The following sections discuss the input and output features of the product.
USB
The product includes a universal serial bus (USB) 2.0 connection.
10/100 networking
The product includes a 10/100 network connection.
Fax
The product includes a fax phone line connection.
4 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW

USB hosts
The product includes USB hosts for USB flash drive and wireless communication control.
Memory
If the product encounters a problem when managing available memory, a clearable warning message
appears on the control panel.
Flash memory
NOR: Stores microprocessor control programs and internal character sets (fonts).
NAND: Stores fax memory and driver installation software.
Random access memory
All models come with 192 MB of memory installed. The formatter has 256MB NAND Flash.
Nonvolatile memory
The product uses nonvolatile memory (NVRAM) to store I/O and information about the print environment
configuration. The contents of NVRAM are retained when the product is turned off or disconnected.
Memory Enhancement technology
The HP Memory Enhancement technology (MEt) effectively doubles the standard memory through a variety
of font- and data-compression methods.
NOTE: The MEt is available only in PCL mode; it is not functional when printing in PS mode.
Wireless radio
Wireless products contain a wireless card to enable 802.11b/g/n wireless communication.
PJL overview
Printer job language (PJL) is an integral part of configuration, in addition to the standard printer command
language (PCL). With standard cabling, use PJL to perform a variety of functions.
●
Dynamic I/O switching. The product can be configured with a host on each I/O by using dynamic I/O
switching. Even when the product is offline, it can receive data from more than oneI/O simultaneously,
until the I/O buffer is full.
●
Context-sensitive switching. The product can automatically recognize the personality (PS or PCL) of
each job and configure itself in that personality.
●
Isolation of print environment settings from one print job to the next. For example, if a print job is sent
to the product in landscape mode, the subsequent print jobs are printed in landscape mode only if they
are formatted for it.
ENWW Formatter-control system 5

LEDM overview
The low-end data model (LEDM) provides one consistent data representation method and defines the
dynamic and capabilities tickets shared between clients and devices, as well as the access protocol, event,
security, and discovery methods.
ACL overview
The advanced control language (ACL) is a language that supports product control and firmware downloads in
printers that support both PJL/PCL and host-based printing. Each sequence of ACL commands must be
preceded by a unified exit command (UEL) and an @PJL ENTER LANGUAGE=ACL command. The ACL sequence
is always followed by a UEL. Any number of commands can be placed between the UELs. The only exception
to these rules is the download command. If a firmware download is done, the download command must be
the last command in the sequence. It will not be followed by a UEL.
The firmware searches for the UEL sequence when parsing commands. However, while downloading binary
data such as host-based code or NVRAM data the firmware suspends UEL parsing. To handle hosts that
“disappear” during binary sequences, the firmware times out all ACL command sessions. If a timeout occurs
during a non-download command sequence, it is treated as the receipt of a UEL. If a timeout occurs during
firmware download the product resets.
PML
The printer management language (PML) allows remote configuration and status monitoring through the I/O
ports.
Control panel
The formatter sends and receives product status and command data to and from a touch-screen control
panel.
NFC
(Wireless bundles only) This product supports near field communication (NFC) capabilities. NFC enables an
easy one-to-one HP wireless direct print connection using a simple device-to-device touch. Mobile device
users can quickly connect to the printer and print documents and images from a mobile device, such as a
smartphone or tablet, by touching the device to the NFC icon on the bottom of the control panel.
6 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
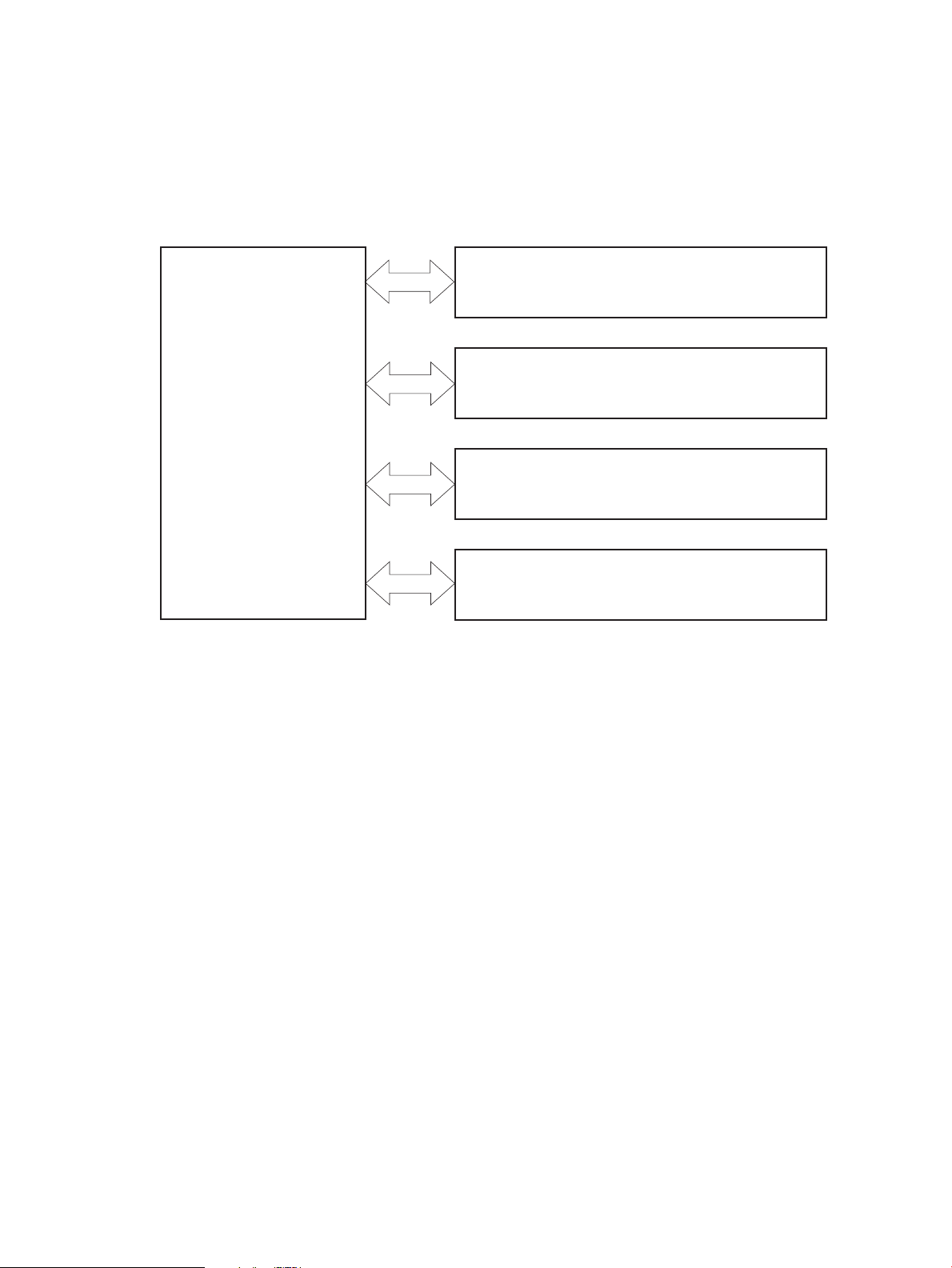
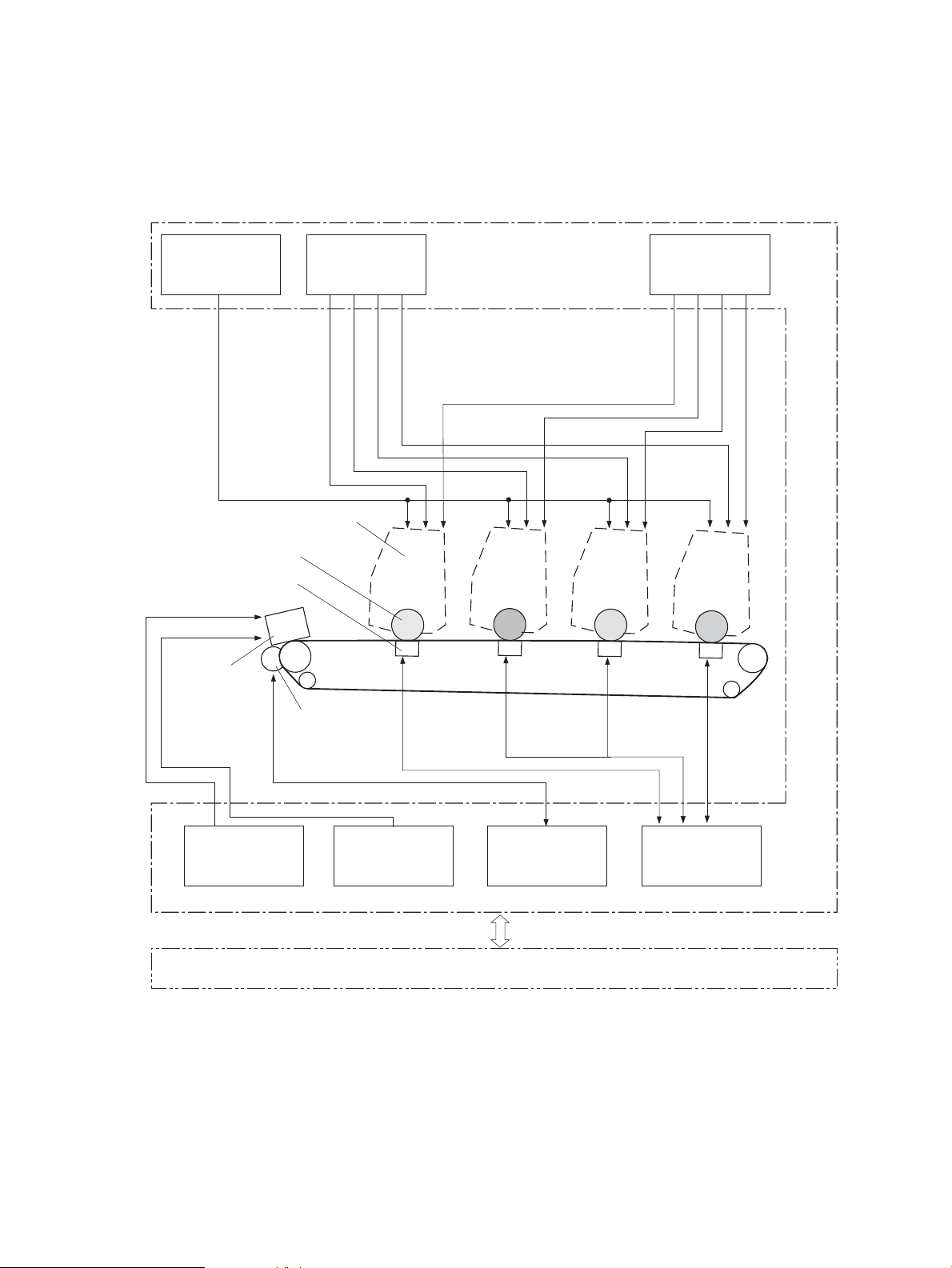
Engine control system
PICKUP-AND-FEED SYSTEM
LASER/SCANNER SYSTEM
ENGINE CONTROL
SYSTEM
IMAGE-FORMA TION SYSTEM
DOCUMENT FEEDER SYSTEM
The engine control system coordinates all product functions and drives the other three systems.
The engine control system contains the DC controller, high-voltage power supply PCA, and low-voltage
power supply/fuser power supply unit.
Figure 1-2 Engine control system components
ENWW Engine control system 7
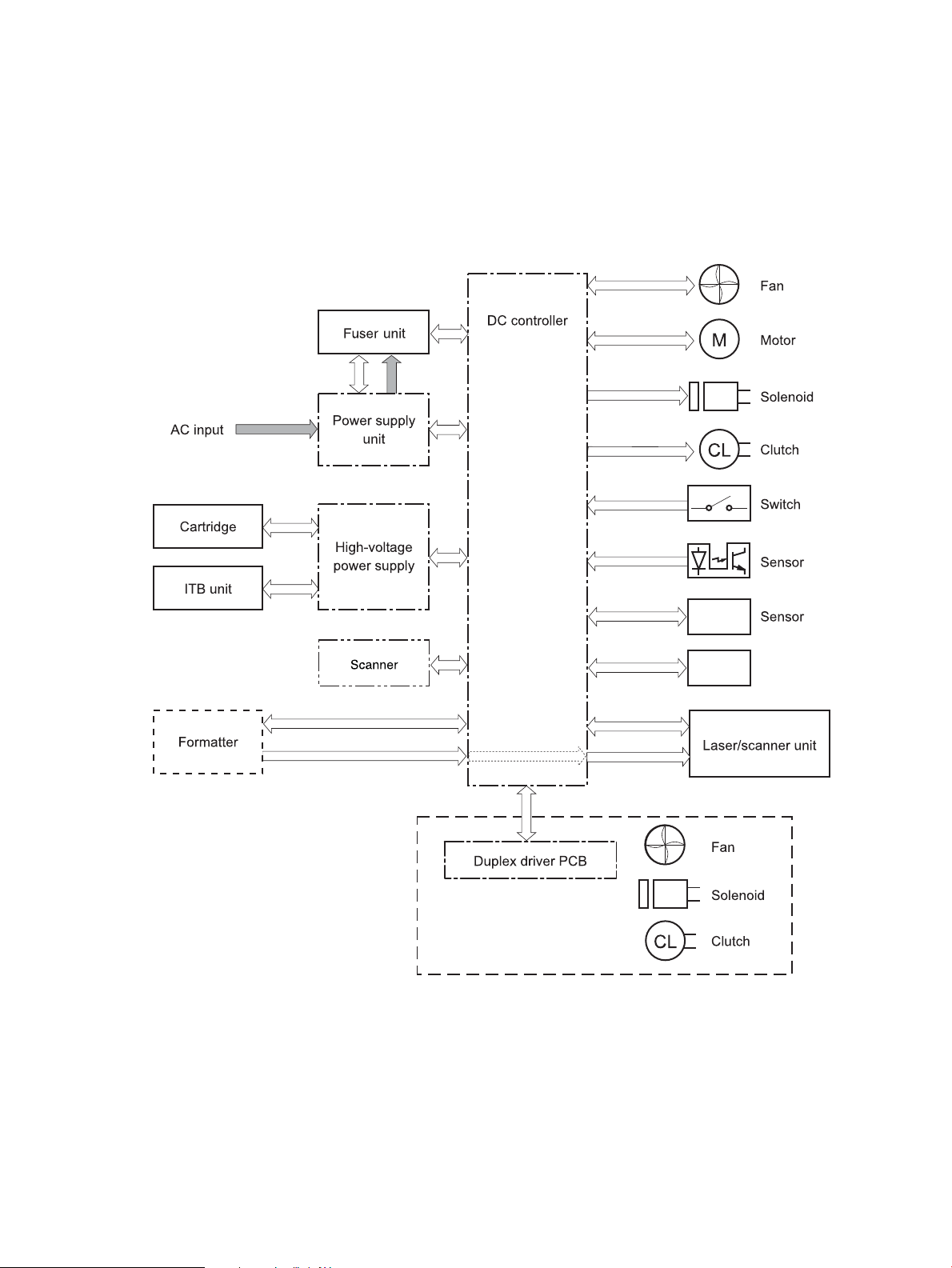
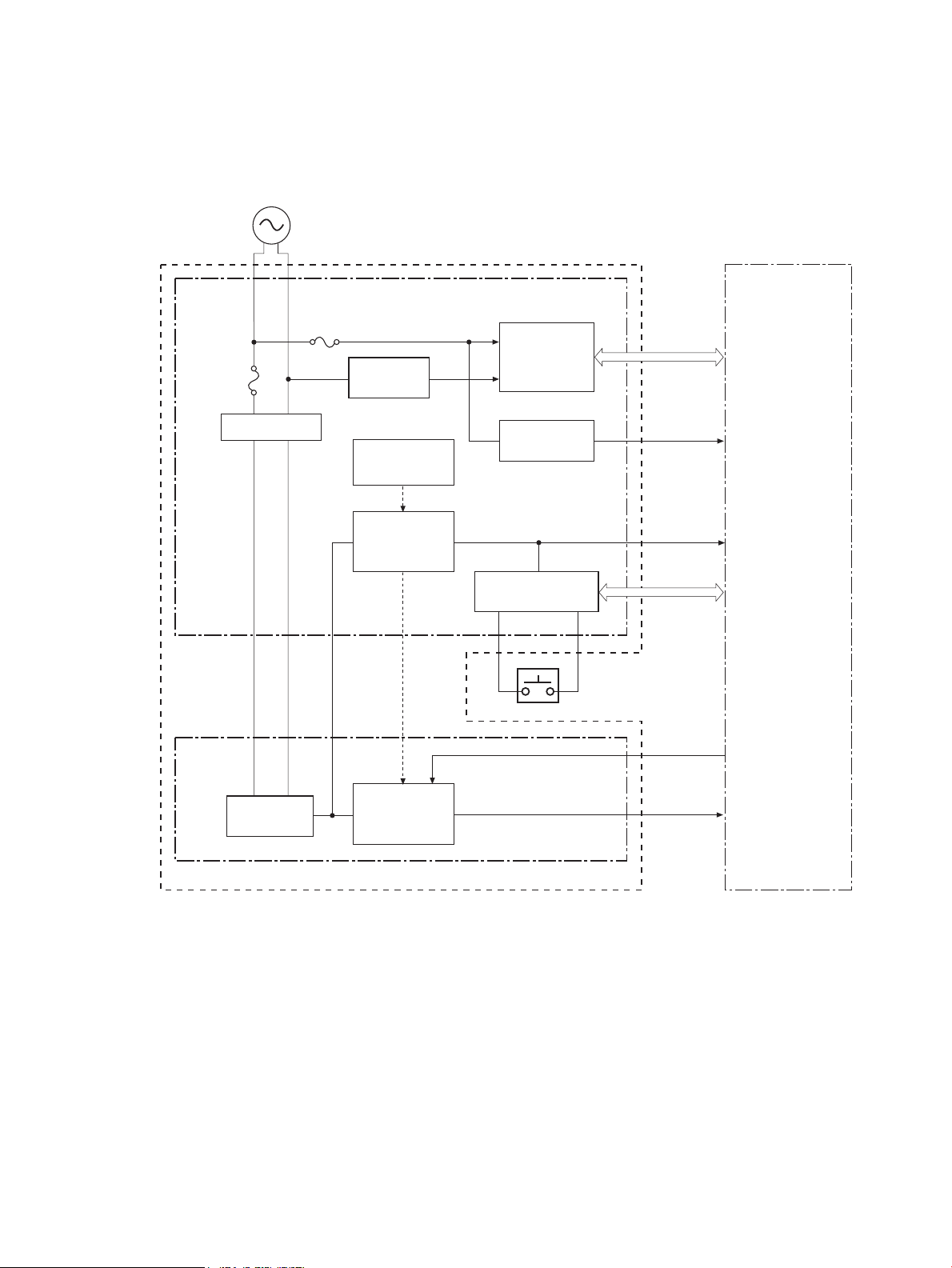
DC controller
Walk up USB
The DC controller PCA controls the operation of the product and its components. The DC controller PCA starts
product operation when the power is turned on and the power supply sends DC voltage to the DC controller
PCA. After the product enters the standby sequence, the DC controller PCA sends out various signals to
operate motors, solenoids, and other components based on the print command and image data that the host
computer sends.
Figure 1-3 DC controller circuit diagram
8 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Power supply
+3.3V
Protection circuit
Rectifying
circuit
Zero crossing
circuit
+24V
ZEROX
PSREM24V
Low-voltage power supply
Power switch
SW3001
AC input
+24V generation
circuit
Noise filter
Fuse
FU2801
DC controller
Fuser power supply
Noise filter
Fuser control
circuit
Fuse
FU2901
Power supply unit
+3.3V generation
circuit
Power switch
control circuit
The low-voltage power supply and the fuser power supply convert AC power from the power receptacle into
DC power to cover the DC loads.
Figure 1-4 Low-voltage power supply
Protective function
The power supply unit has a protective function against overcurrent and overvoltage to prevent failures in
the power supply circuit. If an overcurrent or overvoltage instance occurs, the system automatically cuts off
the output voltage.
If the DC voltage is not being supplied from the power supply unit, the protective function might be running.
If that is the case, turn off the power switch and unplug the power cord. Do not plug in the power cord and do
not turn the power switch on again until the root cause is found.
In addition, a fuse protects against overcurrent instances. If an overcurrent instance flows into the AC line,
the fuse deactivates and cuts off the power distribution.
ENWW Engine control system 9
Power saving
TH801
FU1
H120/H220
TH802
TH803
FUSER HEATER
CONTROL signal
Fuser control
circuit
FUSER TEMPERATURE signal
Pressure roller
Fuser sleeve
DC controllerPower supply unit
Fuser heater
safety circuit
The Sleep Delay feature reduces power consumption when the product has been inactive for an extended
period. You can set the length of time before the product enters sleep mode. See Sleep Delay on page 4.
The Auto Power Down feature turns the product off after a certain length of time. You can adjust this time
setting.
Fuser control
The power supply unit controls the temperature in the fuser unit. The product uses an on-demand fusing
method.
Figure 1-5 Fuser block diagram
The fuser is composed of the following components.
●
Heater (100V model: H120—200V model: H220): Heats the fuser sleeve
●
Thermistors
◦
Main thermistor (TH801): Detects the center temperature of the fuser heater (contact type)
◦
Sub thermistor 1 (TH802): Detects the right side temperature of the fuser heater (contact type)
◦
Sub thermistor 2 (TH803): Detects the left side temperature of the fuser heater (contact type)
●
Thermal fuse (FU1): Prevents an abnormal temperature rise of the fuser heater
These fuser temperature controls are performed by the fuser control circuit and the fuser heater safety
circuit, which receive commands from the DC controller.
10 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
Fuser control circuit
FU2901
DC controller
Fuser control circuit
FU1: Thermal fuse
TH801: Main thermistor
TH802: Sub thermistor 1
TH803: Sub thermistor 2
Fuser
heater
(H120/H220)
Pressure
roller
Fuser sleeve
Fuser unit
Fuser heater
safety circuit
Fuser heater
control circuit
Relay
drive
circuit
RL2901
TH801
TH802
TH803
Sub power supply
MAINTH
SUBTH
SUB2TH
RLD-
FSRD
/RLD+
RL1
Zero crossing
circuit
ZEROX
Fuser power supply
The fuser control circuit maintains the temperature of the fuser heater at its targeted temperature.
The DC controller monitors the fuser temperature (MAINTH, SUBTH and SUB2TH) signals and sends the fuser
heater control (FSRD) signal according to the detected temperature. The fuser heater control circuit controls
the fuser heater depending on the signal so that the heater remains at the targeted temperature.
Figure 1-6 Fuser control circuit
ENWW Engine control system 11

Fuser protective function
The protective function detects an abnormal temperature rise of the fuser and interrupts power supply to the
fuser heater. The following protective components prevent an abnormal temperature rise of the fuser
heater.
●
DC controller
The DC controller monitors the detected temperature of the thermistors. It deactivates the fuser heater
control signal and releases the relay to interrupt the power supply to the fuser heater under the
following conditions.
◦
Main thermistor: 253°C (487.4°F) or higher
◦
Sub thermistor 1: 273°C (523.4°F) or higher
◦
Sub thermistor 2: 273°C (523.4°F) or higher
●
Fuser heater safety circuit
The fuser heater safety circuit monitors the detected temperature of the thermistors. It releases the
relay to interrupt the power supply to the fuser heater under the following conditions.
◦
Main thermistor: 320°C (608°F) or higher
◦
Sub thermistor 1: 295°C (563°F) or higher
◦
Sub thermistor 2: 295°C (563°F) or higher
●
Thermal fuse
The thermal fuse blows to interrupt power supply to the fuser heater if the thermal fuse temperature
reaches 228°C (442°F) or higher.
12 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW

Fuser failure detection
The DC controller determines a fuser unit failure, deactivates the fuser heater control signal, releases the
relay to interrupt power supply to the fuser heater, and then notifies the formatter of a failure state when it
encounters the following conditions.
●
Start-up failure conditions
◦
◦
◦
●
Abnormal low temperature conditions
◦
●
Abnormal high temperature conditions
◦
The main thermistor temperature does not reach 50°C (122°F) within a specified period of heater
startup during the wait period.
The main thermistor temperature does not reach the targeted temperature within a specified
period after the temperature once reaches 50°C (122°F) from the heater startup during the wait
period.
The main thermistor temperature does not reach the targeted temperature within a specified
period under the heater temperature control during the initial rotation period.
The main thermistor temperature remains at 100°C (212°F) or lower for a specified period under
the heater temperature control during the print period.
The main thermistor temperature remains at 235°C (487°F) or higher for a specified period.
◦
The temperature of either one of the sub thermistors remains at 273°C (523°F) or higher for a
specified period.
●
Fuser heater drive circuit failure
◦
The specified count of the zero crossing signal is not detected within a specified period after the
product is turned on.
◦
The frequency is out of the specified range (40 to 70 Hz).
ENWW Engine control system 13
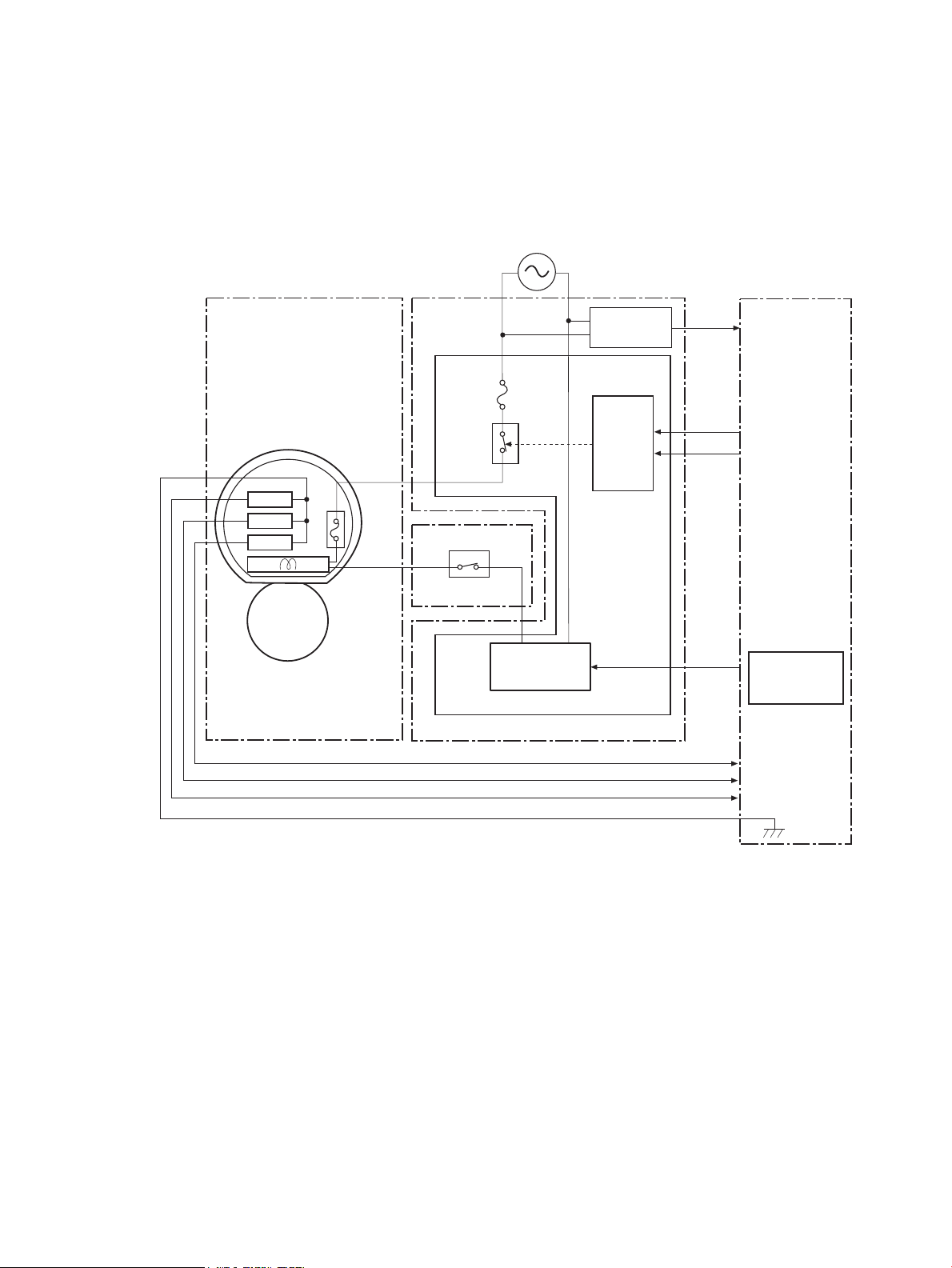
High-voltage power supply
ITB
TR1_1
TR1_23
TR1_23
TR1_4
TR2
ICLB
BLD1
BLD2
BLD3
BLD4
DEV1
DEV2
DEV3
DEV4
PRI
ICLR
Photosensitive drum
Primary transfer pad
DC controller
High-voltage power supply
Primary charging
bias circuit
Developing bias
circuit
Primary transfer
bias circuit
Cartridge
Secondary transfer
bias circuit
ITB cleaning brush
bias circuit
ITB cleaning roller
bias circuit
Blade bias circuit
Secondary
transfer roller
ITB cleaning unit
YKMC
The DC controller controls the high-voltage power supply to generate high-voltage biases. The high-voltage
power supply generates the high-voltage biases that are applied to the primary charging roller, developing
roller, primary transfer pad, secondary transfer roller, and ITB cleaning unit.
Figure 1-7 High-voltage power supply
14 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
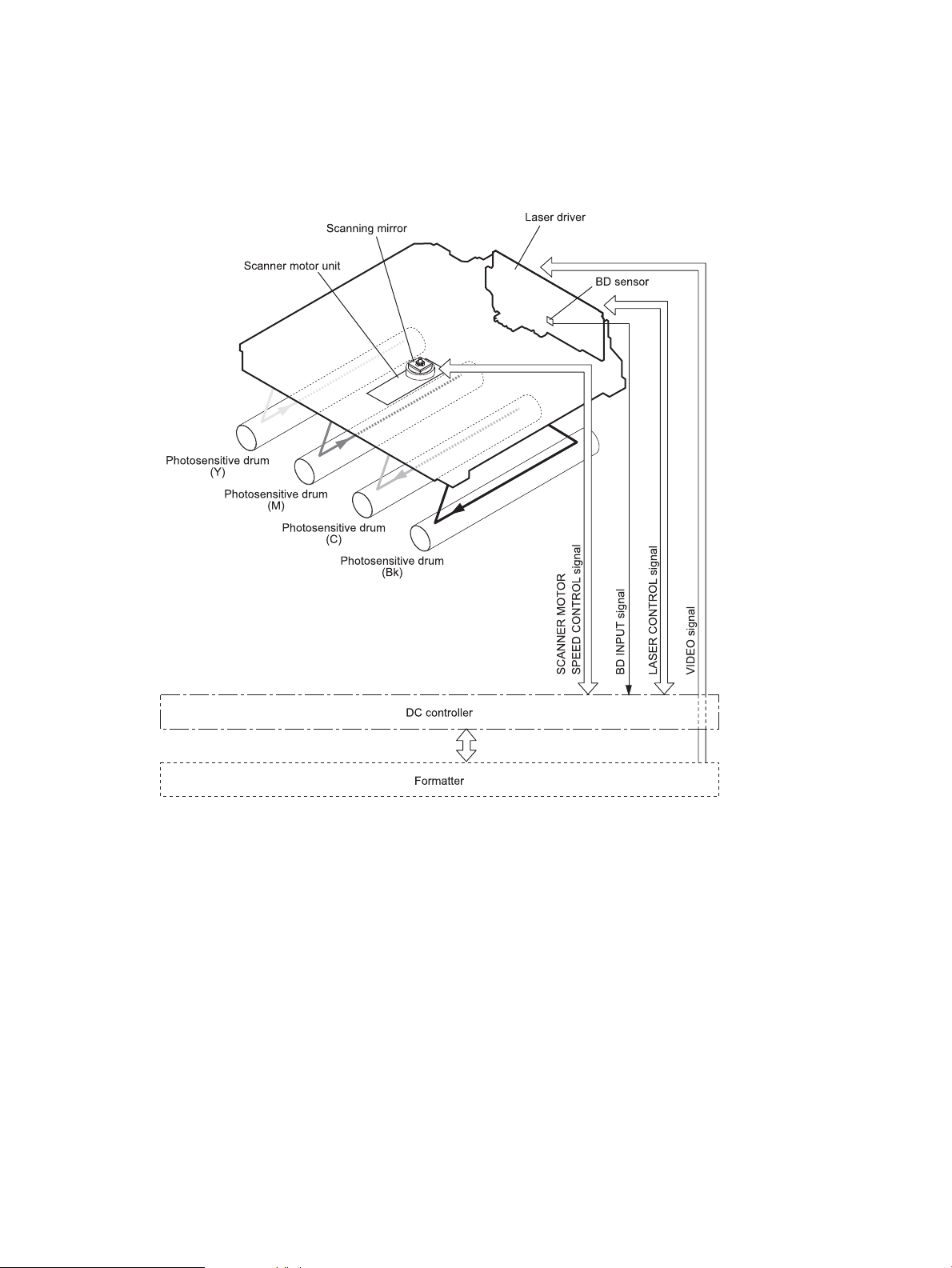
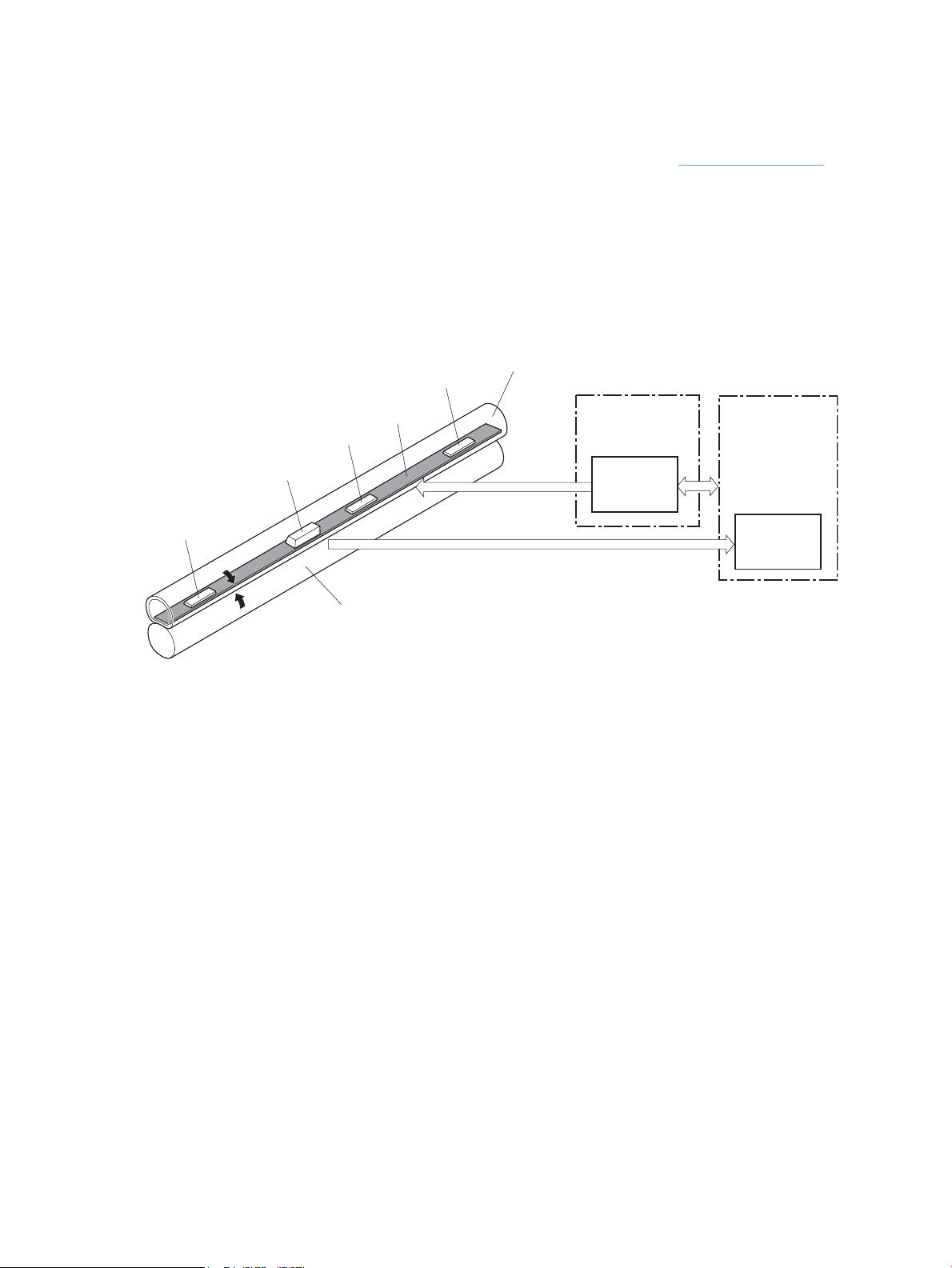
Laser/scanner system
The formatter sends video signals to the DC controller, which controls the laser/scanner. When the laser/
scanner system receives those signals, it converts them to latent images on the photosensitive drum.
Figure 1-8 Laser/scanner system
Laser failure detection
The optical unit failure detection sensor manages the laser/scanner unit failure-detection functions. The DC
controller identifies the laser/scanner unit failure and notifies the formatter if the laser/scanner unit
encounters the following conditions:
●
Scanner motor failure
●
BD failure
ENWW Laser/scanner system 15
 Loading...
Loading...