
Four Character 5.0 mm
(0.2 inch) Smart
5 x 7 Alphanumeric Displays
Technical Data
HDLX-2416 Series
Features
• Enhanced Drop-in Replacement to HPDL-2416
• Smart Alphanumeric
Display
Built-in RAM, ASCII Decoder,
and LED Drive Circuitry
• CMOS IC for Low Power
Consumption
• Software Controlled
Dimming Levels and Blank
• 128 ASCII Character Set
• End-Stackable
• Categorized for Luminous
Intensity; Yellow and
Green Categorized for
Color
• Low Power and Sunlight
Viewable AlGaAs Versions
• Wide Operating
Temperature Range
-40°C to +85°C
• Excellent ESD Protection
• Wave Solderable
• Wide Viewing Angle
(50° typ)
Description
These are 5.0 mm (0.2 inch) four
character 5 x 7 dot matrix
displays driven by an on-board
CMOS IC. These displays are pin
for pin compatible with the
HPDL-2416. The IC stores and
decodes 7 bit ASCII data and
displays it using a 5 x 7 font.
Multiplexing circuitry, and
drivers are also part of the IC.
The IC has fast setup and hold
times which makes it easy to
interface to a microprocessor.
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Supply Voltage, V
Input Voltage, Any Pin to Ground.......................... -0.5 V to VDD + 0.5 V
Free Air Operating Temperature Range, T
Storage Temperature, T
CMOS IC Junction Temperature, TJ (IC) ................................... +150°C
Relative Humidity (non-condensing) at 65°C................................... 85%
Maximum Solder Temperature, 1.59 mm
(0.063 in.) below Seating Plane, t < 5 sec. ............................... 260°C
ESD Protection, R = 1.5 kΩ, C = 100 pF ............. VZ = 2 kV (each pin)
Note:
1. Maximum Voltage is with no LEDs illuminated.
to Ground
DD
[1]
..................................... -0.5 V to 7.0 V
................ -40°C to +85°C
........................................ -40°C to 100°C
S
A
Devices:
Standard Red AlGaAs Red High Efficiency Red Orange Yellow Green
HDLR-2416 HDLS-2416 HDLO-2416 HDLA-2416 HDLY-2416 HDLG-2416
HDLU-2416
ESD WARNING: STANDARD CMOS HANDLING PRECAUTIONS SHOULD BE OBSERVED WITH
THE HDLX-2416

2
The address and data inputs can
be directly connected to the
microprocessor address and data
buses.
The HDLX-2416 has several
enhancements over the HPDL-
2416. These features include an
expanded character set, internal 8
level dimming control, external
dimming capability, and individual digit blanking. Finally, the
extended functions can be
Package Dimensions
disabled which allows the HDLX2416 to operate exactly like an
HPDL-2416 by disabling all of the
enhancements except the expanded character set.
The difference between the
sunlight viewable HDLS-2416 and
the low power HDLU-2416 occurs
at power-on or at the default
brightness level. Following power
up, the HDLS-2416 operates at
the 100% brightness level, while
the HDLU-2416 operates at the
27% brightness level. Power on
sets the internal brightness
control (bits 3-5) in the control
register to binary code (000). For
the HDLS-2416 binary code (000)
corresponds to a 100% brightness
level, and for the HDLU-2416
binary code (000) corresponds to
a 27% brightness level. The other
seven brightness levels are
identical for both parts.
Notes:
1. Unless otherwise specified, the tolerance
on all dimensions is ± 0.254 mm (± 0.010")
2. All dimensions are in mm/inches.
3. For yellow and green displays only.
Pin Pin
No. Function No. Function
1CE
2CE
3 CLR Clear 12 D
4 CUE Cursor Enable 13 D
5 CU Cursor Select 14 D
6 WR Write 15 D
7A
8A
9V
Chip Enable 10 GND
1
Chip Enable 11 D0 Data Input
2
Address Input 16 D5 Data Input
1
Address Input 17 D4 Data Input
0
DD
18 BL Display Blank
Data Input
1
Data Input
2
Data Input
3
Data Input
6

Character Set
3
NOTES: 1 = HIGH LEVEL
0 = LOW LEVEL

4
Recommended Operating Conditions
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Supply Voltage V
DD
4.5 5.0 5.5 V
Electrical Characteristics over Operating Temperature Range
4.5 < V
All Devices
I
DD
Input Current I
< 5.5 V (unless otherwise specified)
DD
25°C
[1]
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Max. Units Test Conditions
Blank I
(blnk) 1.0 4.0 mA All Digits Blanked
DD
I
-40 10 µAV
= 0 V to V
IN
VDD = 5.0 V
DD
Input Voltage High V
Input Voltage Low V
IH
IL
2.0 V
DD
GND 0.8 V
V
HDLO/HDLA/HDLY/HDLG-2416
25°C
[1]
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Max. Units Test Conditions
IDD 4 digits IDD(#) 110 130 160 mA "#" ON in all four
20 dots/character
[2, 3]
locations
IDD Cursor all IDD (CU) 92 110 135 mA Cursor ON in all
dots ON @ 50% four locations
HDLS/HDLU-2416
25°C
[1]
Part Number Parameter Symbol Typ. Max. Max. Units Test Conditions
HDLS-2416 I
4 digits I
DD
20 dots/character
[2,3]
(#) 125 146 180 mA Four "#" ON in
DD
all four locations
HDLU-2416 34 42 52
HDLS-2416 IDD Cursor all dots IDD(CU) 105 124 154 mA Four cursors ON
ON @ 50% in all four locations
HDLU-2416 29 36 45
HDLR-2416
25°C
[1]
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Max. Units Test Conditions
I
4 digits I
DD
20 dots/character
[2,3]
(#) 125 146 180 mA "#" ON in all four
DD
locations
IDD Cursor IDD(CU) 105 124 154 mA Cursor ON in all
all dots ON @ 50% four locations
Notes:
1. V
= 5.0 V
DD
2. Average IDD measured at full brightness. Peak I
3. IDD(#) max. = 130 mA for HDLO/HDLA/HDLY/HDLG-2416, 146 mA for HDLR/HDLS-2416, and 42 mA for HDLU-2416 at default
brightness, 150°C IC junction temperature and VDD = 5.5 V.
= 28/15 x Average IDD(#).
DD
5
Optical Characteristics at 25°C
[1]
VDD = 5.0 V at Full Brightness
HDLR-2416
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Units Test Conditions
Average Luminous I
Intensity per digit, 19 dots ON
V
Character Average
Peak Wavelength λ
Dominant Wavelength
[2]
PEAK
λ
d
HDLS/HDLU-2416
Part Number Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Units Test Conditions
HDLS-2416 Average Luminous I
Intensity per digit, four digits, 19 dots ON
HDLU-2416 Character Average 1.2 3.1 mcd per digit.
All Peak Wavelength λ
Dominant Wavelength
HDLO-2416
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Units Test Conditions
Average Luminous I
Intensity per digit, 19 dots ON
V
Character Average
Peak Wavelength λ
Dominant Wavelength
[2]
λ
PEAK
d
0.5 1.1 mcd ''*'' illuminated in all four digits.
655 nm
640 nm
V
PEAK
[2]
λ
d
4.0 12.7 mcd ''*'' illuminated in all
645 nm
637 nm
1.2 3.5 mcd ''*'' illuminated in all four digits.
635 nm
626 nm
HDLA-2416
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Units Test Conditions
Average Luminous I
Intensity per digit, 19 dots ON
V
1.2 3.5 mcd ''*'' illuminated in all four digits.
Character Average
Peak Wavelength λ
Dominant Wavelength
[2]
λ
PEAK
d
600 nm
602 nm
HDLY-2416
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Units Test Conditions
Average Luminous I
Intensity per digit, 19 dots ON
V
1.2 3.7 mcd ''*'' illuminated in all four digits.
Character Average
Peak Wavelength λ
Dominant Wavelength
[2]
λ
PEAK
d
583 nm
585 nm

HDLG-2416
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Units Test Conditions
6
Average Luminous I
V
1.2 5.6 mcd ''*'' illuminated in all four digits.
Intensity per digit, 19 dots ON
Character Average
Peak Wavelength λ
Dominant Wavelength
Notes:
1. Refers to the initial case temperature of the device immediately prior to the light measurement.
2. Dominant wavelength, λd, is derived from the CIE chromaticity diagram, and represents the single wavelength which defines
the color of the device.
[2]
PEAK
λ
d
568 nm
574 nm
AC Timing Characteristics over Operating
Temperature Range at VDD = 4.5 V
Parameter Symbol Min Units
Address Setup t
Address Hold t
Data Setup t
Data Hold t
Chip Enable Setup t
Chip Enable Hold t
Write Time t
Clear t
Clear Disable t
AS
AH
DS
DH
CES
CEH
W
CLR
CLRD
10 ns
40 ns
50 ns
40 ns
0ns
0ns
75 ns
10 µs
1 µs
Timing Diagram Enlarged Character Font
Notes:
1. Unless otherwise specified the
tolerance on all dimensions is ± 0.254
mm (0.010")
2. Dimensions are in mm (inches).

7
Electrical Description
Pin Function Description
Chip Enable CE1 and CE2 must be a logic 0 to write to the
(CE1 and CE2, display.
pins 1 and 2)
Clear When CLR is a logic 0 the ASCII RAM is reset
(CLR, pin 3) to 20hex (space) and the Control Register/
Attribute RAM is reset to 00hex.
Cursor Enable CUE determines whether the IC displays the
(CUE pin 4) ASCII or the Cursor memory. (1 = Cursor,
0 = ASCII).
Cursor Select CU determines whether data is stored in the
(CU, pin 5) ASCII RAM or the Attribute RAM/Control
Register. (1 = ASCII, 0 = Attribute
RAM/Control Register).
Write WR must be a logic 0 to store data in the
(WR, pin 6) display.
Address A0-A1 selects a specific location in the display
Inputs memory. Address 00 accesses the far right
(A1 and A0, display location. Address 11 accesses the far
pins 8 and 7) left location.
Data Inputs D0-D6 are used to specify the input data for the
(D0-D6, display.
pins 11-17)
V
DD
(pin 9)
GND GND is the display ground.
(pin 10)
Blanking BL is used to flash the display, blank the
Input display or to dim the display.
(BL, pin 18)
VDD is the positive power supply input.
Display Internal Block Diagram
Figure 1 shows the HDLX-2416
display internal block diagram.
The CMOS IC consists of a 4 x 7
Character RAM, a 2 x 4 Attribute
RAM, a 5 bit Control Register, a
128 character ASCII decoder and
the refresh circuitry necessary to
synchronize the decoding and
driving of four 5 x 7 dot matrix
displays.
Four 7 bit ASCII words are stored
in the Character RAM. The IC
reads the ASCII data and decodes
it via the 128 character ASCII
decoder. The ASCII decoder
includes the 64 character set of
the HPDL-2416, 32 lower case
ASCII symbols, and 32 foreign
language symbols.
A 5 bit word is stored in the
Control Register. Three fields
within the Control Register
provide an 8 level brightness
control, master blank, and extended functions disable.
For each display digit location,
two bits are stored in the Attribute
RAM. One bit is used to enable a
cursor character at each digit
location. A second bit is used to
individually disable the blanking
features at each digit location.
The display is blanked and
dimmed through an internal
blanking input on the row drivers.
Logic within the IC allows the user
to dim the display either through
the BL input or through the
brightness control in the control
register. Similarly the display can
be blanked through the BL input,
the Master Blank in the Control
Register, or the Digit Blank
Disable in the Attribute RAM.

8
Figure 1. Internal Block Diagram

9
Display Clear
Data stored in the Character
RAM, Control Register, and
Attribute RAM will be cleared if
the clear (CLR) is held low for a
minimum of 10 µs. Note that the
display will be cleared regardless
of the state of the chip enables
(CE1, CE2). After the display is
cleared, the ASCII code for a
space (20hex) is loaded into all
character RAM locations and
00hex is loaded into all Attribute
RAM/Control Register memory
locations.
Data Entry
Figure 2 shows a truth table for
the HDLX-2416 display. Setting
the chip enables (CE1, CE2) to
logic 0 and the cursor select (CU)
to logic 1 will enable ASCII data
loading. When cursor select (CU)
is set to logic 0, data will be
loaded into the Control Register
and Attribute RAM. Address
inputs A0-A1 are used to select the
digit location in the display. Data
inputs D0-D6 are used to load
information into the display. Data
will be latched into the display on
the rising edge of the WR signal.
D0-D6, A0-A1, CE1, CE2, and CU
must be held stable during the
write cycle to ensure that correct
data is stored into the display.
Data can be loaded into the
display in any order. Note that
when A0 and A1 are logic 0, data is
stored in the right most display
location.
Cursor
When cursor enable (CUE) is a
logic 1, a cursor will be displayed
in all digit locations where a logic
1 has been stored in the Digit
Cursor memory in the Attribute
RAM. The cursor consists of all
35 dots ON at half brightness. A
flashing cursor can be displayed
by pulsing CUE. When CUE is a
logic 0, the ASCII data stored in
the Character RAM will be displayed regardless of the Digit
Cursor bits.
Blanking
Blanking of the display is controlled through the BL input, the
Control Register and Attribute
RAM. The user can achieve a
variety of functions by using these
controls in different combinations,
such as full hardware display
blank, software blank, blanking of
individual characters, and synchronized flashing of individual
characters or entire display (by
CUE BL CLR CE1CE2WR CU A1A
011 Display ASCII
111 Display Stored Cursor
XX0 Reset RAMs
X01 RAMS and Control Register
X X 1 0 0 0 1 = 100 = 17% 1 = Digit Digit from being blanked.
XX1 000 Write to Character RAM
X X 1 X 1 X X X X X X X X X X X No Change
0 = Logic 0; 1 = Logic 1; X = Do Not Care; * 000 = 27% for HDLU-2416
XX XXXX X XXX X X X
0 0 0 Functions Control Blank Blank Cursor and Control Register
0 0 1 Enable 001 = 60% Display Blank Cursor blanked
0 1 0 Disable 101 = 10% Display Blank Cursor
0 1 1 Always Blank Cursor DC
1 0 0 Digit 0 ASCII Data (Right Most Character)
1 0 1 Digit 1 ASCII Data
1 1 0 Digit 2 ASCII Data
1 1 1 Digit 3 ASCII Data (Left Most Character)
1X X
XX 1
D
0
Extended Intensity Master Digit Digit Write to Attribute RAM
Disable Disable 0 0
D1-D
D1-D
Enabled Disable 3 3 Digit n
D5D4D
6
0 = 000 = 100%* 0 = Digit Digit DBD
010 = 40% ON Disable 1 1
5
011 = 27% DBDn = 1 Prevents Digit n
110 = 7% Blanked Disable 2 2 DCn = 0 Removes cursor from
5
D
111 = 3% Digit n
0
D
3
2
D
1
Digiit Digit
D
Function
0
Blank Display but do not reset
= 0, Allows Digit n to be
n
= 1 Stores cursor at
n
Figure 2. Display Truth Table

10
strobing the blank input). All of
these blanking modes affect only
the output drivers, maintaining the
contents and write capability of
the internal RAMs and Control
Register, so that normal loading of
RAMs and Control Register can
take place even with the display
blanked.
Figure 3 shows how the Extended
Function Disable (bit D6 of the
Control Register), Master Blank
(bit D2 of the Control Register),
Digit Blank Disable (bit D1 of the
Attribute RAM), and BL input can
be used to blank the display.
When the Extended Function
Disable is a logic 1, the display
can be blanked only with the BL
input. When the Extended
Function Disable is a logic 0, the
display can be blanked through
the BL input, the Master Blank,
and the Digit Blank Disable. The
entire display will be blanked if
either the BL input is logic 0 or
the Master Blank is logic 1,
providing all Digit Blank Disable
bits are logic 0. Those digits with
Digit Blank Disable bits a logic 1
will ignore both blank signals and
remain ON. The Digit Blank
Disable bits allow individual
characters to be blanked or
flashed in synchronization with the
BL input.
EFD MB DBDnBL
0 0 0 0 Display Blanked by BL
0 0 X 1 Display ON
0X 1 0
0 1 0 X Display Blanked by MB
0111
1 X X 0 Display Blanked by BL
1 X X 1 Display ON
Figure 3. Display Blanking Truth Table
Display Blanked by BL. Individual characters
"ON" based on "1" being stored in DBD
Display Blanked by MB. Individual characters
"ON" based on "1" being stored in DBD
Dimming
Dimming of the display is controlled through either the BL input
or the Control Register. A pulse
width modulated signal can be
applied to the BL input to dim the
display. A three bit word in the
Control Register generates an
internal pulse width modulated
signal to dim the display. The
internal dimming feature is
enabled only if the Extended
Function Disable is a logic 0.
n
n
Bits 3-5 in the Control Register
provide internal brightness
control. These bits are interpreted
as a three bit binary code, with
code (000) corresponding to the
maximum brightness and code
(111) to the minimum brightness.
In addition to varying the display
brightness, bits 3-5 also vary the
average value of IDD. IDD can be
specified at any brightness level as
shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Current Requirements at Different Brightness Levels
Symbol D5D4D
Brightness 25°C Typ. 25°C Max. Max. over Temp. Units
3
IDD(#) 0 0 0 100% 110 130 160 mA
0 0 1 60% 66 79 98 mA
0 1 0 40% 45 53 66 mA
0 1 1 27% 30 37 46 mA
1 0 0 17% 20 24 31 mA
1 0 1 10% 12 15 20 mA
1 1 0 7% 9 11 15 mA
11 1 3% 4 6 9 mA

11
Figure 4. Intensity Modulation Control
Using an Astable Multivibrator
(reprinted with permission from
Electronics magazine, Sept. 19, 1974,
VNU Business pub. Inc.)
Figure 4 shows a circuit designed
to dim the display from 98% to 2%
by pulse width modulating the BL
input. A logarithmic or a linear
potentiometer may be used to
adjust the display intensity.
However, a logarithmic potentiometer matches the response of
the human eye and therefore
provides better resolution at low
intensities. The circuit frequency
should be designed to operate at
10 kHz or higher. Lower frequencies may cause the display to
flicker.
Extended Function Disable
Extended Function Disable (bit D
of the Control Register) disables
the extended blanking and dimming functions in the HDLX-2416.
If the Extended Function Disable
is a logic 1, the internal brightness
control, Master Blank, and Digit
Blank Disable bits are ignored.
However the BL input and Cursor
control are still active. This allows
downward compatibility to the
HPDL-2416.
Mechanical and Electrical Considerations
The HDLX-2416 is an 18 pin DIP
package that can be stacked
horizontally and vertically to
create arrays of any size. The
HDLX-2416 is designed to operate
continuously from -40°C to + 85°C
for all possible input conditions.
The HDLX-2416 is assembled by
die attaching and wire bonding
140 LEDs and a CMOS IC to a
high temperature printed circuit
board. A polycarbonate lens is
placed over the PC board creating
an air gap environment for the
LED wire bonds. Backfill epoxy
environmentally seals the display
package. This package construction makes the display highly
tolerant to temperature cycling
and allows wave soldering.
The inputs to the CMOS IC are
protected against static discharge
and input current latchup. However, for best results standard
CMOS handling precautions
should be used. Prior to use, the
HDLX-2416 should be stored in
anti-static tubes or conductive
material. During assembly a
grounded conductive work area
should be used, and assembly
personnel should wear conductive
wrist straps. Lab coats made of
synthetic material should be
avoided since they are prone to
6
static charge build-up.
Input current latchup is caused
when the CMOS inputs are subjected either to a voltage below
ground (Vin < ground) or to a
voltage higher than VDD (V
VDD) and when a high current is
forced into the input. To prevent
input current latchup and ESD
damage, unused inputs should be
in
>
connected either to ground or to
VDD. Voltages should not be
applied to the inputs until V
been applied to the display.
Transient input voltages should be
eliminated.
DD
has
Soldering and Post
Solder Cleaning
Instructions for the
HDLX-2416
The HDLX-2416 may be hand
soldered or wave soldered with
SN63 solder. When hand soldering
it is recommended that an electronically temperature controlled
and securely grounded soldering
iron be used. For best results, the
iron tip temperature should be set
at 315°C (600°F). For wave
soldering, a rosin-based RMA flux
can be used. The solder wave
temperature should be set at
245°C ± 5°C (473°F ±9°F), and
dwell in the wave should be set
between 1 1/2 to 3 seconds for
optimum soldering. The preheat
temperature should not exceed
110°C (230°F) as measured on the
solder side of the PC board.
For further information on soldering and post solder cleaning, see
Application Note 1027, Soldering
LED Components.
Contrast Enhancement
The objective of contrast enhancement is to provide good readability in the end user’s ambient
lighting conditions. The concept is
to employ both luminance and
chrominance contrast techniques.
These enhance readability by
having the OFF-dots blend into the
display background and the ONdots vividly stand out against the
same background. For additional
information on contrast enhancement, see Application Note 1015.

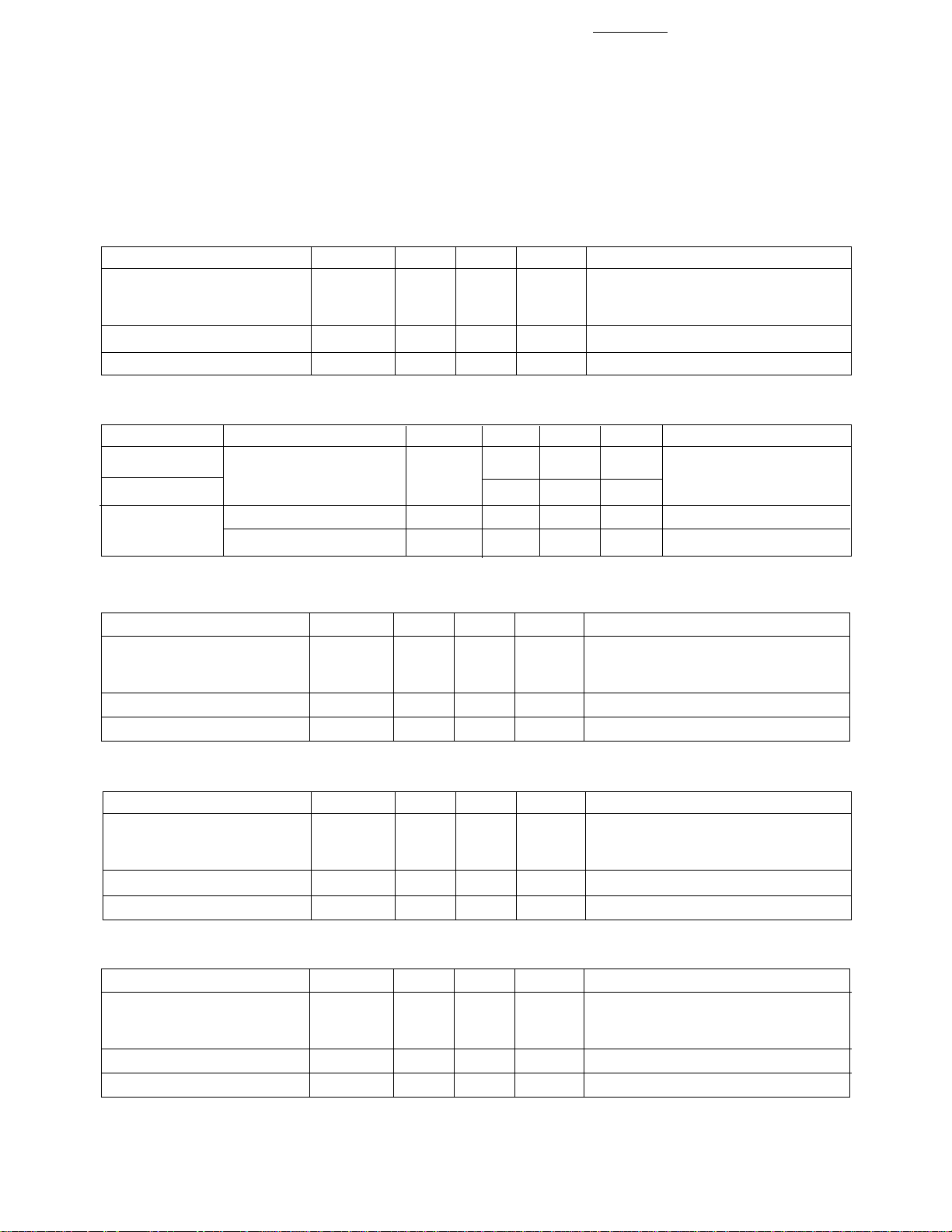
Intensity Bin Limits for HDLR-2416
Intensity Range (mcd)
Bin Min. Max.
A 0.54 0.90
B 0.74 1.31
C 0.93 1.42
D 1.16 1.77
E 1.45 2.21
Note:
Test conditions as specified in Optical Characteristic table.
Intensity Bin Limits for HDLS-2416
Intensity Range (mcd)
Bin Min. Max.
E 3.97 6.79
F 5.55 9.50
G 7.78 13.30
H 10.88 18.62
I 15.24 26.07
J 21.33 36.49
Note:
Test conditions as specified in Optical Characteristic table.
Color Bin Limits
Color Range (nm)
Color Bin Min. Max.
Yellow 3 581.5 585.0
4 584.0 587.5
5 586.5 590.0
6 589.0 592.5
Green 1 576.0 580.0
2 573.0 577.0
3 570.0 574.0
4 567.0 571.5
Note:
Test conditions as specified in Optical Characteristic table.
Intensity Bin Limits for HDLX-2416
Intensity Range (mcd)
Bin Min. Max.
A 1.20 1.77
B 1.25 2.47
C 2.02 3.46
D 2.83 4.85
E 3.97 6.79
F 5.55 9.50
G 7.78 13.30
Note:
Test conditions as specified in Optical Characteristic table.
www.semiconductor.agilent.com
Data subject to change.
Copyright © 2001 Agilent Technologies, Inc.
July 20, 2001
Obsoletes 5964-6380E (11/99)
5988-3269EN
 Loading...
Loading...