Page 1

HP ProLiant 100-series Intel-based G6 server
technology
Technology brief, 3
rd
edition
Abstract.............................................................................................................................................. 3
Introduction......................................................................................................................................... 3
Intel Xeon 5500 Series processor technology .......................................................................................... 3
Multi-level caches............................................................................................................................. 4
QuickPath Interconnect controller ....................................................................................................... 4
Hyper Threading.............................................................................................................................. 5
Turbo Boost technology..................................................................................................................... 5
Intel Xeon 3400 Series processor technology .......................................................................................... 6
Memory.............................................................................................................................................. 8
DDR-3............................................................................................................................................. 8
DIMM Choices............................................................................................................................. 8
Memory Mirroring with DDR-3 .....................................................................................................10
Memory channel interleaving....................................................................................................... 10
Lockstep memory mode ............................................................................................................... 10
I/O technologies ............................................................................................................................... 11
PCI Express technology................................................................................................................... 11
HP Smart Array and SAS/SATA technology ...................................................................................... 11
SAS-2 standard.......................................................................................................................... 12
New generation HP Smart Array controllers .................................................................................. 12
Battery backed write cache ......................................................................................................... 13
Zero Memory RAID..................................................................................................................... 13
Software RAID ........................................................................................................................... 13
Smart Array Advanced Pack........................................................................................................ 13
Networking technologies ................................................................................................................ 14
Power and thermal technologies .......................................................................................................... 14
Efficient power delivery................................................................................................................... 14
Common Slot power supplies....................................................................................................... 15
Redundant power operation ........................................................................................................ 16
Voltage regulation...................................................................................................................... 16
Improved thermal sensors and fan control ......................................................................................... 16
Phase shedding ............................................................................................................................. 16
Memory phase shedding............................................................................................................. 16
Dynamic CPU phase shedding..................................................................................................... 17
Managing processor technologies.................................................................................................... 17
QuickPath Interconnect power...................................................................................................... 17
Disabling processor cores............................................................................................................ 17
C-state package limit setting ........................................................................................................ 17
Managing memory technologies ...................................................................................................... 17
Memory channel interleaving....................................................................................................... 17
Maximum memory data rates.......................................................................................................17
Managing I/O technologies............................................................................................................ 18
Page 2

Disable PCIe 2.0........................................................................................................................ 18
Power Efficiency Mode ................................................................................................................... 18
Power Performance Benchmarks .......................................................................................................... 18
Security ............................................................................................................................................ 18
Trusted Platform Module.................................................................................................................. 18
BitLocker Drive Encryption ............................................................................................................... 19
Server management and deployment ................................................................................................... 19
Systems management and monitoring...............................................................................................19
Insight Management Agents......................................................................................................... 19
Remote management and control ..................................................................................................... 20
HP Lights-Out 100i ..................................................................................................................... 20
LO100i shared and dedicated networks ....................................................................................... 21
IPMI 2.0 and DCMI 1.0.................................................................................................................. 23
Server deployment ......................................................................................................................... 23
HP ProLiant Easy Set-up CDs ........................................................................................................ 23
OS support ....................................................................................................................................... 23
DL1000 Multi Node server design for scale out computing ..................................................................... 24
Chassis design............................................................................................................................... 24
Shared power............................................................................................................................ 25
Riser options .............................................................................................................................. 25
Fans and fan control....................................................................................................................... 25
Power supply support ..................................................................................................................... 26
Advanced Power Management........................................................................................................ 26
Power Interface Controller ........................................................................................................... 26
Summary .......................................................................................................................................... 27
For more information.......................................................................................................................... 28
Call to action .................................................................................................................................... 29
Page 3

Abstract
This technology brief describes the key technologies implemented in Intel-based HP ProLiant 100-series
G6 servers. The 100-series family includes the ProLiant DL100-series, the ML100-series, and the
DL1000 Multi Node architecture. As of this writing, the Intel-based 100-series G6 servers include the
ProLiant DL120, DL160, DL180, ML110, ML150, DL170h, DL2x170h, and DL4x170h. Links to the
QuickSpecs for each of these servers are listed in the “For more information” section at the end of this
technology brief.
Introduction
HP ProLiant G6 servers have been the focus of extensive engineering and development.
Characterized by increased performance, better power efficiency, and more powerful management
tools, the servers include these new technologies:
• The Intel® Xeon® Processor 5500 Series
• The Intel Xeon Processor 3400 Series
• Double Data Rate-3 (DDR-3) memory DIMMs
• Thermal sensors incorporated throughout the ProLiant100-series G6 servers
• ProLiant Onboard Administrator Powered by Lights-Out 100i (LO 100i)
• I/O technologies such as PCIe generation 2 (PCIe 2.0) and faster Smart Array controllers that
incorporate common form factor components
• ”Right Size” Common Slot power supplies in multiple sizes to provide the required amount of power
and improve power efficiency
• Management options accessed from the BIOS setup utility that can reduce power and thermal use
by power supplies, I/O, processors, and memory
The technologies discussed in this paper are implemented in all Intel-based ProLiant 100-series G6
servers. Exceptions are noted where different levels of technology implementation or service exist
among individual ProLiant 100-series G6 platforms.
For complete specifications of all ProLiant 100-series servers, see the HP website:
www.hp.com/products/servers/platforms
.
Intel Xeon 5500 Series processor technology
Some ProLiant Intel-based 100-series G6 servers contain the Xeon 5500 Series processors. The
processors include an integrated memory controller and Intel QuickPath technology to boost
bandwidth between processors, memory, and I/O subsystems. Three memory channels from each
integrated memory controller to its dedicated memory provide a total bandwidth of 32 gigabytes per
second.
The Xeon 5500 Series microarchitecture is built on hafnium-based, 45 nanometer high-k metal gate
silicon technology to reduce electrical leakage. These small, energy-efficient, high-performance
processors support distributed shared memory, Intel Hyper-Threading technology, and Intel Turbo
Boost Technology with Intelligent Power Technology.
1
For additional information about Intel processors, see the HP technology brief titled “The Intel processor
roadmap for industry-standard servers”:
http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs
/support/SupportManual/c00164255/c00164255.pdf.
1
3
Page 4
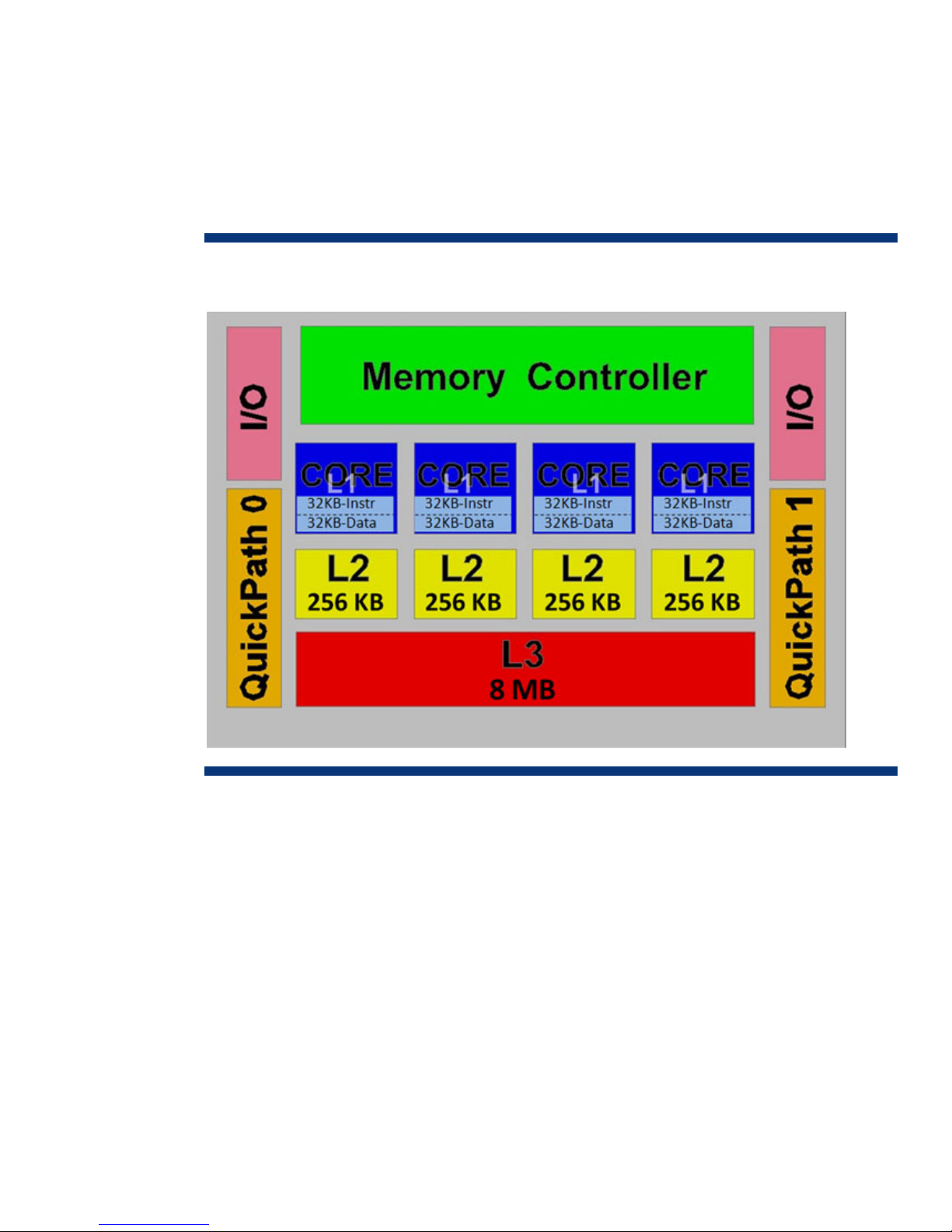
Multi-level caches
Xeon 5500 Series processors have a three-level cache hierarchy (Figure 1):
• An on-core, 64-kilobyte, Level 1 cache, split into two 32 kilobyte caches: one for data and one for
instructions
• 256-kilobyte, Level 2 cache for each core to reduce latency
• A Level 3 cache of up to 8 megabytes shared by all cores
Figure 1. Blo
ck diagram of three-level cache hierarchy for Intel Xeon 5500 Series processors
The Level 3 cache is shared and inclusive, which means that it du
1 and Level 2 caches of each core. This guarantees that data is stored outside the cores and
minimizes latency by eliminating unnecessary core snoops to the Level 1 and Level 2 caches. Flags in
the Level 3 cache track which core’s cache supplied the original data. Therefore, if one core modifies
another core’s data in Level 3 cache, the Level 1 and Level 2 caches are updated as well. This
eliminates excessive inter-core traffic and ensures multi-level cache coherency.
plicates the data stored in the Level
QuickPath Interconnect controller
Xeon 5500 Series processors attain their performance potential through the Intel QuickPath
Architecture (Figure 2); high-speed, point-to-point interconnects directly connect the processors with
each other. The Intel QuickPath architecture also connects each processor to distributed shared
memory and to the I/O chipset.
Each QuickPath Interconnect consists of two unidirectional links that operate simultaneously in each
direction using differential signaling. Unlike a typical serial bus, the QuickPath interconnects transmit
data packets in parallel across multiple lanes and packets are broken into multiple parallel transfers.
4
Page 5
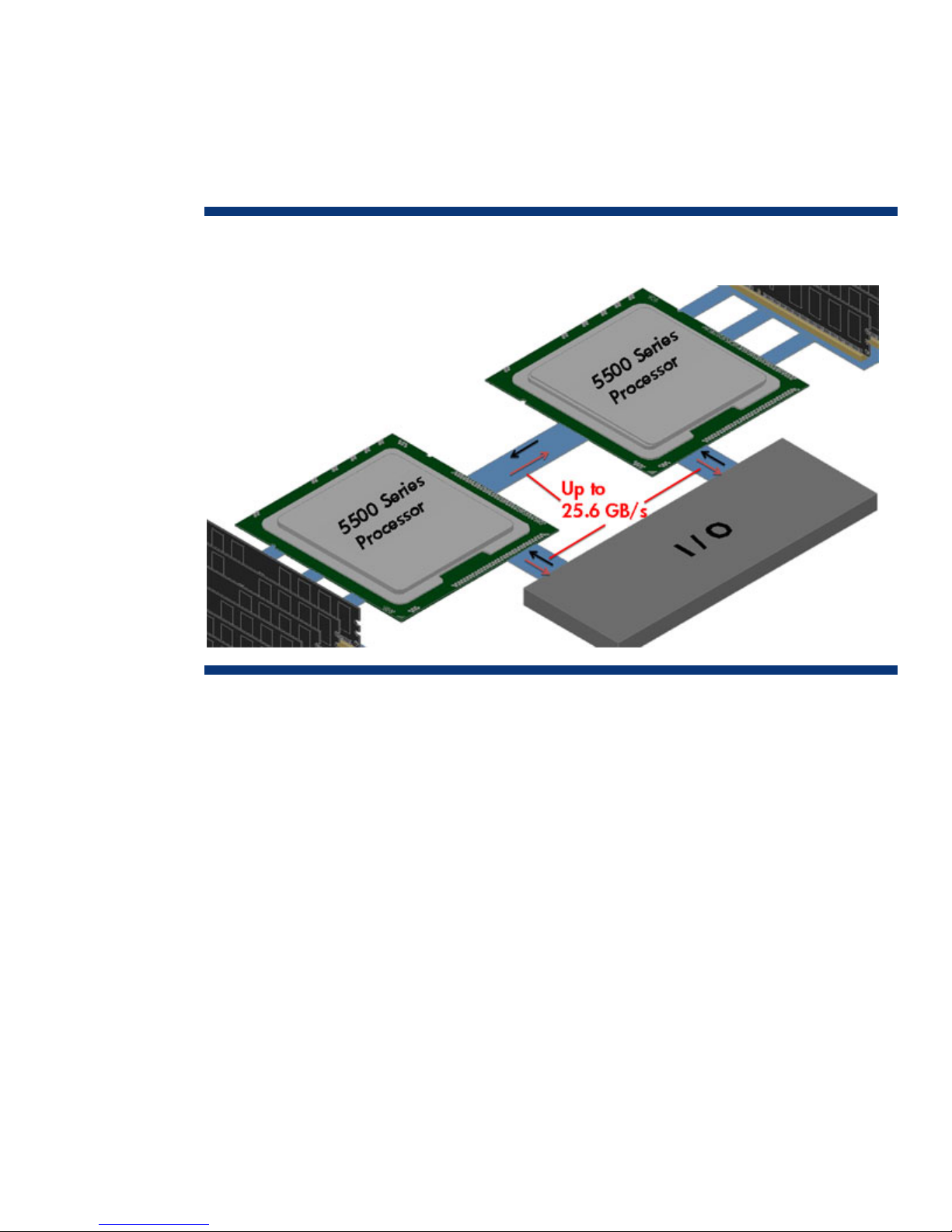
Each link is comprised of 20, one-bit lanes. A maximum of 16 bits are used to transfer data; the
remaining 4 bits are used for the protocol and error correction. The interconnect performs a maximum
of 6.4 gigatransfers per second and has a bandwidth of 12.8-gigabytes per second in each
direction, for a total bandwidth of 25.6 gigabytes per second.
If an application requests data from the memory of another processor, the QuickPath interconnect
uses high-bandwidth inter-processor communication to retrieve the data.
Figure 2. Bloc
k diagram of QuickPath architecture
Hyper Threading
Simultaneous Multi-threading Technology, or SMT, is an enhanced version of Intel’s Hyper-Threading
technology. SMT lets each core execute two computational threads at the same time. A single
processor can execute up to eight threads simultaneously. In addition, the high-bandwidth memory
subsystem supplies data faster to the two computational processes than traditional front side buses,
and the low-latency cache hierarchy allows more instructions to be processed simultaneously. HyperThreading improves performance per watt, allowing Intel-based ProLiant G6 servers to accomplish
more using the same, or less, power than servers based on previous-generation Intel processors.
Turbo Boost technology
Intel’s Turbo Boost technology complements SMT by increasing the performance of both multithreaded and single-threaded workloads. For workloads and applications that do not benefit from
multi-threading, Turbo Boost technology can provide better performance. Turbo Boost is engaged by
default and automatically increases the clock frequency of active cores operating below power and
thermal design points determined by the processor. The maximum frequency depends on the number
of active cores and varies based on the specific configuration on a per-processor-number basis. Turbo
Boost technology is OS independent, and Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI)
-aware operating systems require no changes to support Turbo Boost technology.
5
Page 6
Intel Xeon 3400 Series processor technology
The Intel Xeon 3400 Series are four core processors used with the Intel 5 series 3400 and 3420
chipsets. The Intel Xeon 3400 series microarchitecture is based on 45 nanometer core technology
with an integrated memory controller and PCI Express graphics interface. Xeon 3400 series
processors are used in the ProLiant ML110 and DL120 G6 servers.
The Xeon 3400 Series processors and chipsets can accommodate up to three DIMMs per channel
with registered DIMMs and up to two DIMMs per channel with unbuffered DIMMs. Figure 3 shows the
features available with the Intel 3400 chipset.
Figure 3. Intel X
6 SATA ports
6 SATA ports
12 USB 2.0 ports
12 USB 2.0 ports
eon processor 3400 series and Intel 3400 series chipset architecture
Dual channel DDR3
memory
3 GB/s each
680 Mb/s
PCI 32/33PCI 32/33
Intel Xeon
3400 Series
processor
2 GB/s
Intel Xeon
Intel Xeon
3400 Series
3400 Series
Chipset
Chipset
PCI Express X1
8 GB/s
8 GB/s
bi-directional
bi-directional
8 GB/s
8 GB/s
bi-directional
bi-directional
2 GB/s
2 GB/s
bi-directional
bi-directional
500 MB/s
500 MB/s
500 MB/s
bi-directional
bi-directional
bi-directional
Integrated 10/100/1000 MAC
Integrated 10/100/1000 MAC
8X PCI Express
8X PCI Express
8X PCI Express
8X PCI Express
PCI Express X4 ports
PCI Express X4 ports
2 PCI Express X1 ports
2 PCI Express X1 ports
2 PCI Express X1 ports
2 PCI Express X1 ports
Gigabit
Gigabit
Ethernet
Ethernet
controller
controller
Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet
LAN connection
LAN connection
6
Page 7

The ProLiant ML110 and DL120 G6 servers are single-processor platforms which means that the Xeon
3400 Series processors used in these servers do not support the QuickPath architecture found in the
Xeon 5500 Series processors. Otherwise, the Xeon 3400 processors support the same architecture
found in the Xeon 5500 processors, including distributed shared memory, Intel Hyper-Threading
technology, and Intel Turbo Boost technology with Intelligent Power technology. Table 1 shows the
ML110 G6 and DL120 G6 servers’ implementation of Hyper-Threading and Turbo Boost technologies
for the various processor frequencies. All processors in the 3400 Series family are quad core, have
8 MB L3 caches, and operate at 95W.
Table 1. Processor technologies supported on the ML110 G6 and DL120 G6 servers
Intel Xeon
Processor
Processor 3430 2.40
Processor 3440 2.53
Processor 3450 2.66
Processor 3460 2.80
Processor 3470 2.93
CPU
Frequency
GHz
GHz
GHz
GHz
GHz
Supported ML and
DL G6 platforms
ML110 No n=1 n=1 n=2 n=3
DL120 No n=1 n=1 n=2 n=3
ML110 Yes n=1 n=1 n=2 n=3
DL120 Yes n=1 n=1 n=2 n=3
ML110 Yes n=1 n=1 n=4 n=4
DL120 Yes n=1 n=1 n=4 n=4
ML110 Yes n=1 n=1 n=4 n=5
DL120 Yes n=1 n=1 n=4 n=5
ML110
(3470 not supported)
Intel HT
Technology
NA NA NA NA NA
Max Turbo Boost frequency
increment (n)*
Active cores
4 3 2 1
DL120 Yes n=1 n=1 n=4 n=5
*“n” indicates the multiplier used to calculate the maximum potential frequency increment supported by Intel Turbo Boost
technology for each processor model and given number of active cores. This number (n) is multiplied by bus clock frequency
(BCLK) to get the actual frequency. The standard bus clock frequency is 133.33 MHz.
7
Page 8

Memory
Xeon 3400 and 5500 Series processors connect directly to memory rather than through a chipset.
They support only DDR-3 dual inline memory modules (DIMMs). In the ProLiant 100-series G6 servers,
HP manages all processor functionality options, including memory mirroring and memory channel
interleaving, through the G6 server BIOS and BIOS Setup Utility (BSU).
DDR-3
DDR-3 has several key enhancements including an 8-bit prefetch buffer for storing data before it is
requested. By comparison, DDR-2 has a 4-bit buffer. For DDR-3, the data signal rate can increase to
1333 Megatransfers per second (MT/s). While this is commonly referred to as having a speed of
1333 MHz, the maximum clock speed for the DIMMs is actually 667 MHz and the signal is doublepumped to achieve the data rate of 1333 MT/s. DDR3-1333 DIMMs can operate at clock speeds of
667 MHz, 533 MHz, and 400 MHz with corresponding data rates of 1333, 1066, and 800 MT/s.
The three memory channels between each processor’s integrated memory controller and its dedicated
DDR-3 memory provide a total bandwidth of 32 gigabytes per second.
HP DDR-3 DIMM modules incorporate an integrated thermal sensor that signals the chipset to throttle
memory traffic to the DIMM if its temperature exceeds a programmable critical trip point. Using the
data from these thermal sensors, ProLiant G6 servers can reduce fan speed when memory is idle,
which reduces power consumption. The BIOS in ProLiant G6 servers verifies the presence of the
thermal DIMM sensor during POST. Some third-party DIMMs may not include this thermal sensor. If it
is absent, a POST message will warn that the DIMM does not have a thermal sensor, and the fans will
be forced to run at higher speeds (requiring more power).
DIMM Choices
DDR
-3 is available as both Unbuffered Dual In-line Memory Modules (UDIMMs) and Registered
(buffered) Dual In-line Memory Modules (RDIMMs). Both RDIMMs and UDIMMs support error
correcting code (ECC).
There are three types of DDR-3 available for ProLiant G6 servers:
• PC3-8500R (RDIMM, ECC compliant) —1066 or 800 MT/s data rate, depending on memory
configuration and processor installed.
• PC3-10600E (UDIMM, ECC compliant) —1333, 1066, or 800 MT/s data rate, depending on
memory configuration and processor installed.
• PC3-10600R (RDIMM, ECC compliant) —1333, 1066, or 800 MT/s data rate, depending on
memory configuration and processor installed.
Administrators can configure ProLiant 100-series G6 servers using either RDIMMs or UDIMMs but
RDIMM and UDIMM memory cannot be mixed within a single server
2
. ProLiant 100-series G6 servers
have up to 18 DIMM slots, allowing larger memory capacities than with platforms that used DDR-2.
ProLiant G6 servers optimize memory performance by operating DDR-3 memory at the maximum rate
possible based on the memory configuration and the processor that is installed.
When choosing memory configurations for ProLiant 100-series G6 systems, the following guidelines
should prove helpful:
• UDIMM configurations are limited to a maximum of two UDIMMs per memory channel because the
memory controller must drive the address and command signals to each DRAM chip on a channel.
This results in a 24 GB maximum configuration in ProLiant 100-series G6 servers. Because they
require fewer components, UDIMMs are typically less expensive than RDIMMs.
2
The ProLiant ML110 G6 server does not support RDIMM memory, only the PC3-10600E UDIMM
8
Page 9

• RDIMM configurations can provide larger memory capacity configuration because the memory
controller only drives the address and command signals to a single register chip, thereby reducing
the electrical load on the memory controller. Users requiring large memory footprints can install
three 8-GB RDIMMs per channel for a total of 144 GB.
• For smaller memory configurations, installing only one or two DIMMs per memory channel can
potentially increase memory performance. In many instances this allows administrators to clock the
memory channel at a higher data rate.
Processor SKU determines the ability of ProLiant G6 servers to run DDR-3 memory at a top speed of
1333 MT/s. The processor SKU also dictates the range of speeds possible in different DIMM per
channel (DPC) configurations. DIMM operating speeds are also subject to memory slot configuration
and to the number of slots (4, 6, 12, 16, or 18). Table 2 displays DIMM speeds possible in 100series G6 servers with a Xeon X5500 (95W), W5500 (130W), or 3400 (95W) processor.
Table 2. DDR-3 memory options on 100-series G6 servers supporting Xeon 5500 or 3400 Series processors
running at 95W or 130W
DIMM Type
PC3-8500R RDIMM 4 quad
PC3-8500R RDIMM 8 dual
PC3-
10600R
PC3-
10600R
PC3-
10600R
PC3-
10600E
PC3-
10600E
*
UDIMMs will not run at 1333 MT/s data rates with two DIMMs per channel on systems that support three DIMM sockets per
channel. Support for 1333 MT/s data rate with two DIMMs may require a ROM upgrade.
** Applies to half-width system boards with 16 slots like the G6 DL170h
RDIMM 2 dual
RDIMM 4 dual
RDIMM 8 dual
UDIMM 1 single
UDIMM 2 dual
Capacity
(GB)
1 DPC
Rank
1066
1066
1333
1333
1333
1333
1333
2 DPC in
4 slots
N/A 1066 N/A 800 800 N/A
N/A N/A N/A 1066 1066 800
1333 1333 800 1333 1333 800
1333 1333 800 1333 1333 800
N/A N/A N/A 1333 1333 800
1333 1333 N/A 1066 1333
1333 1333 N/A 1066 1333
Max. data rate in MT/s
DIMMs per channel (DPC)
2 DPC in
6 slots
3 DPC in
6 slots
2 DPC in
16** and
18 slots
2 DPC in
12 slots
*
*
3 DPC in
16** and
18 slots
N/A
N/A
A BIOS setting on select ProLiant 100-series G6 servers allows the PC3-10600R memory modules to
run at 1333 MT/s with two DIMMs per channel. HP design and testing have produced system boards
with signal integrity that can operate at 1333 speeds in this configuration without degradation.
Only HP branded DIMMs have been fully validated to operate at this speed. Therefore, HP does not
recommend configuring the BIOS setting for 1333 MT/s data rates with two DIMMs per channel
when using third-party DIMMs, because they may not meet HP’s stringent design requirements.
Operating the memory at 1333 MT/s is supported only on select 100-series G6 servers using Xeon
3400 or 5500 Series processors operating at 95W or 130W.
For help configuring DDR-3 memory in ProLiant G6 servers, use the DDR-3 Memory Configuration Tool
found at http://h18004.www1.hp.com/products/servers/options/tool/hp_memtool.html
.
9
Page 10

Memory Mirroring with DDR-3
ProLiant 100-series G6 servers using the Xeon 5500 processor support memory mirroring which
protects the system against uncorrectable memory errors that would otherwise result in a system hang
or crash. Mirroring occurs when all data is written to both sets of physical memory in channels one
and two. Administrators can configure memory mirroring through BSU. To implement mirroring with
DDR-3, the two memory channels must be populated identically. The third memory channel must be
empty.
If an uncorrectable error occurs, the system automatically directs the read to the mirrored location to
obtain the correct data. The OS does not revert to Advanced ECC Mode until the DIMM is replaced
and the server rebooted. Since each mirrored DIMM is one of a pair, one DIMM can be protected by
mirroring while another is degraded. As a result, even after mirroring is degraded by a DIMM failure,
the other DIMM in the mirrored pair is still protected by Advanced ECC.
Memory channel interleaving
Xeon 340
0 and 5500 Series processors retrieve data from the memory DIMMs in 64-byte chunks.
With channel interleaving, the system is set up so that each consecutive 64-byte chunk in the memory
map is physically transferred by means of alternate routing through the three available data channels.
The result is that when the memory controller needs to access a block of logically contiguous memory,
the requests are distributed more evenly across the three channels rather than potentially stacking up
in the request queue of a single channel. This alternate routing decreases memory access latency and
increases performance. However, interleaving memory channels increases the probability that more
DIMMs need to be kept in an active state (requiring more power) since the memory controller
alternates between channels and between DIMMs. This is discussed further in the “Power and thermal
technologies” section.
Lockstep memory mode
Lock
-step mode is an advanced memory protection feature supported in ProLiant Intel 100-series G6
servers using the Xeon 5500 Series processor. It uses two of the Xeon 5500 processor's three memory
channels to provide an even higher level of protection than Advanced ECC. In lockstep mode, two
channels operate as a single channel—each write and read operation moves a data word two
channels wide. The cache line is split across both channels to provide 2x 8-bit error detection and 8bit error correction within a single DRAM. In three-channel memory systems, the third channel is
unused and left unpopulated. The Lockstep Memory mode is the most reliable memory protection
method, but it reduces the total system memory capacity by a third in most systems. Performance is
measurably slower than normal Advanced ECC mode, and uncorrectable memory errors can only be
isolated to a pair of DIMMs instead of a single DIMM. Lock-Step mode is not the default operation; it
must be enabled in BSU.
For additional information about DDR-3 memory, see the technology brief titled “Memory technology
evolution: an overview of system memory technologies” at
http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/S
upportManual/c00256987/c00256987.pdf.
10
Page 11

I/O technologies
ProLiant 100-series G6 servers incorporate PCI Express, Serial-Attached SCSI (SAS), and Serial ATA
(SATA) I/O technologies. PCI Express lets administrators add expansion cards with various
capabilities to the system. SAS is a serial communication protocol for direct-attached storage devices
such as SAS and SATA hard drives.
PCI Express technology
All ProLiant G6 servers support the PCIe 2.0 specification. PCIe 2.0 has a per-lane signaling rate of
5 Gb/s which is double the per-lane signaling rate of PCIe 1.0 (Figure 4).
Figure 4. P
CIe data transfer rates
Lane 1 Send
Lane 1 Send
Lane 1 Receive
Lane 1 Receive
Source
Source
Lane n Send
Lane n Send
Lane nReceive
Lane nReceive
Target
Target
Max. bandwidth
Link
size
x1 250 MB/s 500 MB/s 500 MB/s 1 GB/s
x4 1 GB/s 2 GB/s 2 GB/s 4 GB/s
x8 2 GB/s 4 GB/s 4 GB/s 8 GB/s
x16 4 GB/s 8 GB/s 8 GB/s 16 GB/s
(Send or receive)
PCIe 1.0 PCIe 2.0 PCIe 1.0 PCIe 2.0
Total
(Send and receive)
PCIe 2.0 is completely backward compa
tible with PCIe 1.0. A PCIe 2.0 device can be used in a
PCIe 1.0 slot and a PCIe 1.0 device can be used in a PCIe 2.0 slot. Table 3 shows the level of
interoperability between PCIe cards and PCIe slots.
Table 3. PCIe device interoperability
PCIe
device type
x4 card x4 operation x4 operation x4 operation x4 operation x4 operation
x4 Connector
x4 Link
x8 Connector
x4 Link
x8 Connector
x8 Link
x16 Connector
x8 Link
x16 Connector
x16 Link
x8 card Not allowed x4 operation x8 operation x8 operation x8 operation
x16 card Not allowed Not allowed Not allowed x8 operation x16 operation
HP Smart Array and SAS/SATA technology
The newest serial PCIe 2.0-capable Smart Array controllers use SAS technology, a point-to-point
architecture in which each device connects directly to a SAS port rather than sharing a common bus
as with parallel SCSI devices. Point-to-point links increase data throughput and improve the ability to
locate and fix disk failures. More importantly, SAS architecture solves the parallel SCSI problems of
clock skew and signal degradation at higher signaling rates.
3
For more information about SAS technology, refer to the HP technology brief titled “Serial Attached SCSI storage technology”
available at http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c01613420/c01613420.pdf
3
.
11
Page 12

The latest Smart Array controllers are compatible with SATA technology and include the following
features to enhance performance and maintain data availability and reliability:
• SAS and SATA compatibility — The ability to use either SAS or SATA hard drives lets
administrators deploy drive technology that fits each computing environment. HP Smart Array
controllers can manage both SAS arrays and SATA arrays. Smart Array configuration utilities help
administrators configure arrays correctly so that data remains available and reliable.
• SAS wide port operations — Wide ports contain four single lane (1x) SAS connectors and the
cabling has all four lanes bundled together. SAS wide ports allow balanced SAS traffic distribution
across the links for enhanced performance. In addition, wide ports provide redundancy by
tolerating up to three physical link failures while maintaining the ability to communicate with the
disk drives. The most common use of these wide links is to a JBOD or to an internal server expander
connecting to large numbers of drives. No special configuration is required for this functionality.
• SAS expanders — Low-cost, high-speed switches called expanders can combine multiple single
links to create wide ports and increase available bandwidth. SAS expander devices also offer
higher system performance by expanding the number of hard drives that can be attached to an
HP Smart Array controller. SAS expanders are an aggregation point for large numbers of drives or
servers providing a common connection. By cascading expanders, administrators can chain
multiple storage boxes together. For more information on the HP SAS Expander Card, go to
http://h18004.www1.hp.com/products/servers/pr
oliantstorage/arraycontrollers/sas-
expander/index.html.
SAS-2 standard
4
econd-generation SAS (SAS-2) link speed
The s
of 6 Gb/s is double the SAS-1 transfer rate. SAS-2
link speeds require SAS-2 compliant hard drives. SAS-2 eliminates the distinction between fanout and
edge expanders by replacing them with self-configuring expanders. SAS-2 enables zoning for
enhanced resource deployment, flexibility, security, and data traffic management.
SAS-2 connections have the potential to deliver peak raw data bandwidth of up to 600 megabytes
per second (MB/s) per physical link in each direction. SAS-2 devices are capable of sending and
receiving data simultaneously across each physical link, which is known as full duplex. When
effectively implemented, full duplex, 6 Gb/s SAS connections can deliver peak raw data bandwidth
of up to 1200 MB/s between the controller and storage device. It is important to note that the SAS-2
data bandwidths described here are theoretical speeds identified by the SAS-2 standard. Real-world
performance will be affected by the storage devices attached to the SAS-2 connection.
Smart Array controllers, with releases beginning in the first quarter of 2009, incorporate SAS-2
connections. The SAS-2 standard is compatible with both Serial SCSI and Serial ATA protocols for
communicating commands to SAS and SATA devices. SAS-2 compliant controllers are fully
compatible with 1.5 Gb/s and 3 Gb/s SATA technology.
For an up-to-date listing of HP Smart Array controllers that support the SAS-2 specification, see the
Smart Array controller matrix: www.hp.com/products/smartarray
New generation HP Smart Array controllers
he new Smart Array controllers are modular solutions with a common form factor, hardware, and
T
firmware. The controllers are compatible with all ProLiant G6 servers. All ProLiant 100-series G6
servers incorporate embedded SATA storage controllers, and the Smart Array B110i software RAID is
available. The Smart Array 410 incorporates Zero Memory RAID (ZMR) and is available as an entry
level hardware-based RAID, but users have the option to choose the cache size and to include the
battery backed write cache (BBWC). With these options, ZMR can be upgraded to 512 BBWC.
4
Serial Attached SCSI-2 (SAS-2) is an American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard from the INCITS T10 Technical
Committee on SCSI Storage Interfaces. SAS-2 is the successor to SAS-1.1 and SAS-1.
12
Page 13

Battery backed write cache
The BBWC is required for capacity expansion (adding one or more physical disks to an existing
array). The controller recalculates parity and balances the data across all the disks. During the
expansion, the BBWC preserves data and logical structures on the array. The HP 650 mAh P-Series
battery extends battery life up to 48 hours before recharging is necessary.
NOTE:
The Smart Array P212 does not support 512 MB BBWC, and is only upgradeable to
256 MB BBWC
Zero Memory RAID
Using Zero Memory RAID (ZMR), administrators can create a RAID 0-1 configuration without using
any additional memory. Smart Array P410, P411, and P212 controllers include ZMR. The P212
controller does not include ZMR on the external connector. ZMR supports up to eight drives in Zero
Memory Mode, or seven drives and one tape drive. ZMR mode does not support Modular Smart
Array (MSA) products. ZMR does not include any caching. All systems can be upgraded to a BBWC
memory module that can significantly increase performance.
NOTE:
Smart Array Advanced Pack is not available on Zero Memory configurations.
Software RAID
HP has developed a software RAID solution based on the Smart Array firmware. The B110i SATA
Software RAID supports the Array Configuration Utility (ACU), ACU-CLI (command line interface),
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) agents, and Web-Based Enterprise Management
(WBEM) providers.
Supported on the ProLiant DL160, DL170h, DL180, and ML150 G6 servers, the B110i features an
OS-specific driver from HP that uses the embedded ICH10R controller. It can utilize RAID 0, 1, and
1+0 and supports a maximum of two logical drives. The B110i supports up to four 1.5Gb or 3Gb
SATA drives. Administrators can migrate drives to a hardware-based Smart Array controller in a
seamless procedure that maintains the user data and RAID configuration.
For a listing of the complete feature set and support information for the B110i SATA Software RAID,
download the B110i user guide at
http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/S
upportManual/c01706551/c01706551.pdf
Smart Array Advanced Pack
HP Smart Array Advanced Pack (SAAP) firmware provides advanc
ed functionality within Smart Array
controllers. This firmware further enhances performance, reliability, and data availability. SAAP is
hosted on the Smart Array controller hardware firmware stack. It can be enabled beginning with the
present generation of Smart Array controllers.
SAAP requires a license key for activation. After activation, administrators can use several standard
capabilities:
• RAID 6 with Advanced Data Guarding (ADG) protects against failure of any two drives. It requires
a minimum of four drives, but only two will be available for data. ADG can tolerate multiple
simultaneous drive failures without downtime or data loss, and it is ideal for applications requiring
large logical volumes because it can safely protect a single volume of up to 56 disk drives. RAID
ADG also offers lower implementation costs and greater usable capacity per U than RAID 1.
13
Page 14

• RAID 60 allows administrators to split the RAID storage across multiple external boxes. It requires a
minimum of eight drives, but only four will be available for data.
• Advanced Capacity Expansion (ACE) automates higher capacity migration using capacity
transformation to remove logical drives by shrinking and then expanding them online. Standard
drive migration and expansion remain unchanged.
• Mirror Splitting and Recombining in Offline Mode breaks a RAID 1 configuration into two RAID 0
configurations. This is similar to a scaled down rollback functionality that requires two disk drives.
• Drive Erase completely erases physical disks or logical volumes. This capability is useful when
decommissioning, redeploying, or returning hard drives.
• Video On Demand Performance Optimization optimizes performance of video on demand and
improves latency during video streaming.
More information about SAAP is available at www.hp.com/go/SAAP
NOTE:
At a minimum, a 256 MB cache and battery kit is required to enable the SAAP
license key. SAAP is not available on Zero Memory Configurations.
.
Networking technologies
The NC522SFP is a Dual Port 10GbE eight lane (x8) PCI Express (PCIe) 10 Gigabit network adapter.
It is supported on most ProLiant G6 servers. The NC522SFP uses two SFP+ (Small Form-factor
Pluggable) connector cages, providing connectivity in copper or fiber optic environments. For
complete specifications on this and other HP network adapter products, go to
www.hp.com/go/ProLiantNICs
.
Power and thermal technologies
HP engineers have developed a robust set of power and thermal technologies, and components to
manage power in ProLiant 100-series G6 servers. The technologies improve power efficiency
throughout the power delivery chain in several ways:
• Efficient power delivery
• Improved thermal sensors and fan control
• Phase shedding
• Managing processor technologies
• Managing memory technologies
• Managing I/O technologies
• Power efficiency mode
Administrators can disable certain components and capabilities in ProLiant 100-series G6 servers or
reduce capabilities to bring the components to a lower power state.
Efficient power delivery
Power supplies for ProLiant 100-series G6 servers are not hot-pluggable. Common Slot power
supplies are an option in those G6 platforms supporting the Common Slot architecture. Those G6
14
Page 15

servers not supporting Common slot architecture use HP industry standard5 power supplies. All
ProLiant 100-series G6 servers use highly efficient power supplies and DC power regulators to deliver
significantly higher power efficiencies.
Common Slot power supplies
The HP G6
Common Slot power strategy provides power supply commonality across supported
ProLiant G6 server lines. HP reduced the number of power supply designs, which reduces the number
of spares the customer must keep in the data center.
By incorporating ”right-sizing,” these power supplies have achieved efficiency ratings of up to 92%.
With the exception of the 1200W power supplies, they meet Climate Savers Gold requirements. The
1200W power supplies (AC and 48VDC) meet Climate Savers Silver requirements.
• 460W AC up to 92% efficiency
• 750W AC up to 92% efficiency
• 1200W AC up to 90% efficiency
• 1200W 48VDC up to 90% efficiency
The power loading efficiency curve for the 750W power supply shown in Figure 5 provides an
example of the high levels of power efficiency present in all new power supplies used in ProLiant G6
servers.
Figure 5. P
Efficiency (%)
ower/Efficiency curve for the 750 W HP power supply
95%
90%
85%
80%
75%
70%
65%
60%
55%
50%
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800
Output Power (Watts)
Represents 92% power efficiencyRepresents 92% power efficiency
5
“Industry standard” power supplies refers to form factors, such as ATX or SSI, that are predefined within the computing
industry
15
Page 16

By introducing these different wattage power supplies, HP gives users the option to choose a power
supply that meets, but does not exceed, their needs. Oversized and lightly loaded power supplies do
not run as efficiently as those that are heavily loaded.
Not all ProLiant 100-series G6 servers have Common Slot power supply compatibility, and not all
servers will support all available power supply wattages. Users can consult the server QuickSpecs or
server documentation for supported power supply options. The HP Power Advisor is available at the
following link to help users define the right power supply for their needs:
www.hp.com/go/hppoweradvisor
Redundant power operation
In support
where power is drawn equally from both power supplies. This mode ensures full redundancy but can
result in higher power consumption when power supplies are operating with reduced loads and lower
power efficiency.
Voltage regulation
Voltage regulators c
voltages used by the different system components. HP has developed higher peak efficiency voltage
regulators that maintain greater than 90% efficiency over a broad range of power requirements. The
net result is about an 8% gain in DC power efficiency, which results in almost a 10% efficiency gain
in AC input power.
ed ProLiant 100-series G6 servers, redundant power supplies operate in “Balanced” mode,
onvert the 12V DC supplied from the server power supply into a variety of lower
.
These efficiency gains come with no loss in performance and require no configuration by the user.
Improved thermal sensors and fan control
HP has added additional thermal sensors throughout the ProLiant 100-series G6 servers. The 100series G6 servers have “zoned” fans that increase cooling and energy efficiencies in the server by
adjusting cooling to those zones when called for by the sensors in that zone. Fan curve mapping
firmware uses temperatures reported by the sensors to control cooling fans in each zone. Fan speed is
based on the highest temperature readings reported by any of the sensors in a given fan zone.
Phase shedding
HP incorporated phase shedding into ProLiant G6 voltage regulators. Modern digital voltage
regulators deliver DC power at the proper voltage to components by using up to five different phases
of high-speed power pulses that charge capacitors. Each phase delivers its power pulses in a rotating
time window with the other phases in the voltage regulator such that the power pulses from one phase
do not overlap with those of another. The width of each pulse determines the total power delivered by
the particular phase.
Phase shedding enables the system BIOS to turn off one or more of the power phases if it determines
that the power requirements are less than the full amount of power from the voltage regulator. This
reduction in phases decreases the maximum power that the voltage regulator can deliver and
increases overall efficiency.
Memory phase shedding
Xeon 550
much the same way as processor-based phase shedding. At power-up, the ROM BIOS determines the
number of phases needed for the memory voltage regulator based on the number of DIMMs installed.
Memory phase shedding can save up to 2.5 W per DIMM socket. This feature is less effective on
servers whose DIMM sockets are fully populated since more phases are required to accommodate
such a configuration. More phases mean more power consumption.
0 Series processors support memory phase shedding. Memory phase shedding operates
16
Page 17

Dynamic CPU phase shedding
On entry into a low power state (less than 20 W), the Intel Xeon 5500 Series processors will activate
the Power Status Indicator (PSI). When PSI is engaged, ProLiant G6 servers turn off voltage regulator
phases, thereby saving power and increasing power efficiency.
Managing processor technologies
QuickPath Interconnect power
The Xeon 5500 Series processor lets the QuickPath Interconnect (QPI) buffers enter a sleep state to
reduce power requirements when the QPI links are not active. HP enables this Intel feature for G6
servers through BSU. Once this feature is enabled, the Intel processor determines when to put the QPI
buffers into a sleep state. It appears that QPI power management has no measureable impact on
performance.
Disabling processor cores
Thro
ugh BSU, administrators can disable one or more cores in the Xeon 3400 and 5500 Series
processors (per physical processor). When enabled, the command will apply to all physical
processors in the server. Engaging this capability saves power and has the potential to improve
performance in servers running single workloads or applications with low threading requirements.
C-state package limit setting
The Xeon 34
states define the power state of system processors and are an open specification of the ACPI group.
The micro-architecture of the Xeon 5500 Series processors supports processor C-states C0, C1, C3,
and C6. C-state C0 represents a fully active core that is executing instructions. The other C-states
represent further power reduction levels for idle cores. The micro-architecture of the Xeon 3400 Series
processor supports processor C-states C1e, C3, and C6. Any core within the processor can change
C-states independently from the other cores.
00 and 5500 Series processor supports C-states for each core within the processor. C-
Parameters for the maximum C-state allowable for an idle processor are set through the BSU and
initiated by the OS. The higher the C-state allowed at idle, the more power savings, but only at idle.
Also, the higher the C-state, the higher the latency involved when the core returns to activity.
Managing memory technologies
Memory channel interleaving
As described in the memory section, the alternate routing used for channel interleaving decreases
memory access latency and increases performance.
Memory interleaving is configured in the BSU. Disabling memory channel interleaving makes access
to contiguous memory addresses revert to one channel. Single-channel access degrades performance,
but makes it possible for the memory controller to place less frequently accessed DIMMs into a low
power state which saves power. Memory interleaving can have a negative performance effect based
on the application load of the server. Administrators should perform testing in their application
environment to determine the trade-off between power savings and performance.
Maximum memory data rates
The maxim
um memory data rate is effectively 1333 MHz for ProLiant G6 Intel platforms.
on the memory configuration and the processor that is installed, the system may automatically reduce
the Quick Path Interconnect speed. While the “Auto“ setting (which equates to 1333 MHz) is the
default setting, users have the option to manually lower the effective data rates to 1066 MHz or 800
6
Depending
6
The memory operates in a double-pumped manner so that the effective bandwidth is double the physical clock rate of the
memory. Mega-transfers/second describes the data rate.
17
Page 18

MHz. This will save power, but may incur some performance penalty. Administrators can configure
the maximum memory data rate through the BSU.
Managing I/O technologies
Disable PCIe 2.0
All ProLiant G6 servers include an option that allows all expansion slots to run at PCIe 1.0 speed
rather than PCIe 2.0 speed. Enabling this option saves power and provides backward compatibility
with cards that may not correctly operate in PCIe 2.0 slots. Administrators can control expansion slot
speed through the BSU.
Power Efficiency Mode
In ProLiant 100-series G6 servers, the BSU can enable three different settings for the Power Efficiency
Mode: Efficiency, Performance, and Custom. As implied, the Efficiency setting provides the greatest
efficiency, while the Performance setting provides the highest performance. The Custom setting is
simply any combination of user settings that do not match the pre-sets for Efficiency and Performance.
The Power Efficiency Mode directly effects the operation of select power features identified earlier in
this section.
Power Performance Benchmarks
The Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation (SPEC) is a non-profit corporation formed to
establish, maintain and endorse a standardized set of relevant benchmarks that can be applied to the
newest generation of high-performance computers.
SPECpower_ssj2008 is the first industry-standard SPEC benchmark that evaluates the power and
performance characteristics of volume server class computers. As of this writing, SPECpower
benchmark results are available for the ProLiant DL170h and the ProLiant DL380 G6 servers
(www.spec.org/power_ssj2008/results/power_ssj2008.html
gains achieved over the last generation of ProLiant servers.
NOTE:
These power performance benchmarks do not include servers using the Xeon 3400
series processor.
). The test results show performance
Security
The Trusted Platform Module™ (TPM) and Microsoft® BitLocker® technology are supported in all
ProLiant 100-series G6 servers by means of the Trusted Platform Module option kit.
Trusted Platform Module
The Trusted Platform Module v1.2 supported on ProLiant G6 servers is a microcontroller chip that can
create, securely store, and manage artifacts such as passwords, certificates, and encryption keys that
are used to authenticate the server platform. The TPM 1.2 chip provides a unique Endorsement Key
(EK) and a unique Storage Root Key (SRK). It provides data encryption and uses RSA, SHA-1, RNG
cryptographic functions to provide access protection, OS level protection, and stolen disk protection.
The TPM 1.2 chip can also store platform measurements (hashes) to help ensure that the platform
remains trustworthy. TPM enables Microsoft BitLocker, part of Windows® Server 2008.
18
Page 19

TPM is an option on all ProLiant 100-series G6 servers. For more information about TPM, go to
www.hp.com/go/TPM
BitLocker Drive Encryption
Microsoft BitLocker Drive Encryption (BitLocker) is a data protection feature available in Windows
Server 2008. BitLocker uses the enhanced security capabilities of TPM version 1.2 to protect data and
to ensure that a server running Windows Server 2008 has not been compromised while the system
was offline.
Implementing BitLocker requires the following:
• The Master Boot Record (MBR), a small, encrypted system partition of approximately 50 MB to
contain boot utilities
• TPM version 1.2
• Trusted Computing Group (TCG) compliant firmware including support of “Static Root of Trust”
• Two NTFS partitions on the boot drive
During the boot process, the TPM will not release the encryption key until completing a comparison of
operating system configuration information (or hash) with an earlier snapshot of the same data. If any
part of the hash is compromised (for example by introduction of malicious code), the TPM ensures that
the volume encryption key is never released.
Server management and deployment
ProLiant ML and DL 100-series G6 server users each have different computing requirements.
Consequently, the way in which customers manage, deploy, and control servers can differ. With
these requirements in mind, this section examines the following management topics:
• Systems management and monitoring
• Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) 2.0 and Data Center Management Interface
(DCMI) 1.0 Standards
• HP ProLiant Onboard Administrator Powered by Lights-Out 100i remote management and control
• Server deployment
Some of these technologies are new tools for the ProLiant 100-series G6 servers, while others have
been available with previous generations of ProLiant 100-series servers. Users may already be
familiar with Agents, SmartStart Scripting Toolkit (SSSTK), and software Smart Components. These
tools are now available for ProLiant 100-series G6 servers. The tools let users deploy many servers at
once and manage them with HP SIM and Insight Management Agents.
Systems management and monitoring
Unplanned downtime can be significantly reduced through alerting provided by Insight Management
Agents, which are based on Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). SNMP is the protocol
developed to manage nodes (such as servers, workstations, routers, switches, and hubs) on an IP
network. Network management systems learn of problems by receiving traps or change notices from
network devices implementing SNMP.
Insight Management Agents
ProLiant 1
supported by other ProLiant servers. This means that administrators can use SIM 5.3 and greater to
manage ProLiant 100-series G6 servers. Administrators can also use any other SNMP- based
management tool. Support Automation Services are provided on 100-series G6 servers through these
00-series G6 servers can use the same SNMP-based Insight Management Agents that are
19
Page 20

SNMP agents. The agents are included on the ProLiant 100-series model-specific “Easy Set-up” CDs.
They are also available at www.hp.com/servers/easysetup
The SNMP agents enable the following capabilities on 100-series G6 servers:
• Health monitoring capabilities, including monitoring for drives, fans, network, power supplies, and
temperature
• Alerting capabilities, including basic alert notification for Smart Array drive pre-failure only
• Performance monitoring capabilities providing information on processor, memory, disk free space,
network utilization, and I/O
.
Remote management and control
All ProLiant 100-series G6 servers include ProLiant Onboard Administrator Powered by LO100i.
ProLiant Onboard Administrator represents the core embedded management functions in ProLiant DL
and ML 100-series G6 servers. LO100i works in concert with HP SIM, BSU, and Option ROM
Configuration for Arrays (ORCA) to provide remote management, deployment, and control functions
without additional software. This functionality is available locally though the BSU, or remotely with a
web browser through HP SIM. Additional software functionality can be added with the HP Lights-Out
100i Advanced Licenses which include Virtual KVM (remote graphical console) and virtual media
capabilities.
HP Lights-Out 100i
HP LO10
control capabilities through an Ethernet interface. The HP LO100i management interface is active
even when the OS is not operating. The LO100i management processor obtains its power from the
auxiliary power plane of the server, so it is available as long as the server is plugged into an active
power source. HP LO100i Remote Management is compatible with industry standards including IPMI
2.0 for hardware health, DCMI 1.0, as well as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Secure Shell (SSH)
technology for secure communications over public and private local area networks. HP LO100i is fully
accessible using popular web browsers. HP LO100i is also accessible using System Management
Architecture for Server Hardware Command line Protocol (SMASH CLP) for Telnet and SSH sessions.
NOTE:
ProLiant 100-series G6 servers do not support LO100i Select and LO100c.
LO100i Advanced Pack capabilities are available through an optional license key. Table 4 shows the
differences in functionality between LO100i Standard, which comes with all 100-series G6 servers,
and LO100i Advanced Pack.
0i Remote Management is hardware and firmware that provides remote server access and
20
Page 21

Table 4. LO100i functionality
Features
Technical Support and Upgrade Licensing Yes -- G6 only
Flatpack and electronic key delivery Yes
Host access to IPMI environment HW status Yes Yes
Unencrypted browser for power, SEL, health,
and key activation
Shared and dedicated network port * Yes Yes
DCMI 1.0 Yes -- G6 only Yes -- G6 only
SSL & SSH security (setup in factory) Yes -- Included with G6 Yes
DNS registered names ** Yes Yes
License manager support Yes -- G6 only Yes -- G6 only
IPv6 support (coexistence at launch) Yes -- G6 only Yes -- G6 only
Virtual KVM License Upgrade
Virtual media (CD/DVD, floppy, ISO Image
files)
Power Capping Yes – DL1000 only
LO100i Standard
with every ProLiant 100series server
Yes
License Upgrade
LO100i Advanced
(license upgrade options)
Yes
* Shared and dedicated network port is currently an optional feature on some ProLiant 100-series G6 servers
and may be purchased as an option.
** The DNS registered names require high speed network ports to accommodate the large packet sizes
associated with this feature. High speed network ports are included on most ProLiant DL series servers. The
shared low speed network ports on the ProLiant ML series and DL120 G6 servers do not support DNS
registered names.
LO100i includes the following features:
• Improvements to HP SIM support through the addition of Insight Management (SNMP) Agents
– A new Health driver supports gathering and delivering LO100i management information from
SNMP Agents
– SNMP agents store the information and deliver it to HP SIM through SNMP as requested
– HP SIM discovers and makes associations with the LO100i instances in the network
– HP SIM displays URL links to launch the LO100i web interface for a given server
• Host access to in-band IPMI 2.0 features supported by IPMI-aware operating systems
• DNS Registration — LO100i on 100-series G6 servers comes with default host names and will
automatically register with the DNS if DHCP is enabled
LO100i shared and dedicated networks
In ProLiant DL
100-series G6 servers (with the exception of the DL120 G6), LO100i supports a fullspeed shared Ethernet port and a dedicated Ethernet port. LO100i and the server share the full-speed
Ethernet port, utilizing the system network for both. Since the connection is full speed, it supports
Graphic Remote Console and virtual media.
The dedicated Ethernet port is provided for DL 100-series G6 servers by means of an optional
mezzanine card and enables a separate management network. LO100i implementation varies
depending on whether the 100-series G6 server is a DL, SL, or an ML platform.
21
Page 22

Figure 6 shows the two implementations available for the DL 100-series G6 servers.
Figure 6. LO100i sideband architecture for DL00-series G6 servers
System Network
System Network
System Network
Port
Port
Port
Embedded 2 Port
Embedded 2 Port
Embedded 2 Port
System Network
System Network
Port
Port
Embedded 2 Port
Embedded 2 Port
Intel NIC
Intel NIC
Intel NIC
Intel NIC
Intel NIC
Port
Port
Port
Port
Port
Full speed sideband
Full speed sideband
G6 DL100 series
G6 DL100 series
Management Network
Management Network
Dedicated NIC
Dedicated NIC
Dedicated NIC
Dedicated NIC
G6 DL100 series
G6 DL100 series
LO100i
LO100i
Optional
LO100i
LO100i
Shared NIC DL100 G6 Configuration
The system NIC ports are shared with
LO100i for management.
Dedicated NIC DL100 G6 Configuration
A management network can be
employed by adding an optional
dedicated NIC via a mezzanine card.
The management network is physically
separated from the system network.
Figure 7 indicates that the ML100-series G6 and DL120 G6 serv
ers have a dedicated Ethernet
management port. This port cannot be used by the system network.
Figure 7. LO100i sideband architecture for ML100-series G6 servers and the DL120 G6
System Network
Port
Limited speed sideband
Embedded NIC
ML100 G6 series/DL120 G6
System Network
Port
Embedded NIC
Management Network
ML100 G6 series/DL120 G6
LO100i
Dedicated NIC
Dedicated NIC
LO100i
Shared ML100 G6 & DL120 G6
Configuration
A limited speed shared network
configurati
for LO100 Standard features.
LO100 Advanced features, including
Graphic Remote Console and
Virtual Media, are not supported in
Dedicated NIC ML100 G6 & DL120
G6 Configuration
The ML100 series G6/DL120 G6
ships with a dedicated NIC port for
management. This NIC port can be
connected to the system network, or
to a separate management network.
Virtual KVM and Virtual Media, are
supported in dedicated NIC
configurations.
on can be used
22
Page 23

IPMI 2.0 and DCMI 1.0
ProLiant 100-series G6 servers and LO100i conform to IPMI 2.0 and DCMI 1.0 standards so that
customers in heterogeneous environments can manage these servers with either industry standard.
The following are basic compliance mandates:
• The implementation of all mandatory IPMI 2.0 and DCMI 1.0 in-band and out-of-band commands
• Reliable local and remote power on/off/reset through IPMI chassis commands
• Per IPMI 2.0, console redirection over telnet or SSH
• Identification of the server by device ID, globally unique identifier (GUID), asset tag, and chassis ID
• Accurate System Event Logging using IPMI
• Reliable in-band keyboard controller style (KCS) interface and out-of-band LAN interface
For more information on HP Lights-Out 100i Remote Management, go to www.hp.com/go/LO100
.
Server deployment
Prior to G6, ProLiant 100-series server administrators could not deploy servers using methods similar
to 300 series servers. The Easy Set-up CD now provides a user experience similar to SmartStart with
deployment tools that reduce the time required for server setup and updates.
Easy Set-up CDs and their ISO images are provided with each ProLiant G6 100-series server and are
used to perform assisted installations for one or two servers. Users performing multi-server installations
involving large numbers of servers require the following deployment tools:
• Software Smart Components — Self-executable software consisting of driver and software
• SmartStart Scripting Toolkit (DL100s) — Automated scalable deployment utility
HP ProLiant Easy Set-up CDs
Easy Set-u
web download. HP ProLiant Easy Set-up CDs provide easy, step-by-step, single and multi-server server
utilities to streamline server setup for 100-series G6 servers. Each Easy Set-up CD includes the
following:
• Boot environment and GUI
• Assisted Installation: Windows 2003 Server and Windows 2008 Server drivers
• Manual installation: Windows 2003 Server, Windows 2008 Server, and Linux drivers (specific OS
support varies by server. Refer to each server's QuickSpecs for supported versions)
• HP Insight Diagnostics
• Combined Array Configuration Utility (ACU) and Array Diagnostics Utility (ADU) to offer both array
controller and storage device configuration and array controller hardware testing
• SmartStart Scripting Toolkit (SSSTK) and Smart Components for software and drivers
p CDs are available on all 100-series G6 servers and are also available as an ISO image
OS support
HP performs extensive testing, qualification, and certification on the latest server operating systems to
ensure maximum performance and reliability. HP resells and provides full service and support for
Microsoft® Windows® operating systems, Red Hat Linux subscriptions, Novell SUSE Linux
subscriptions, Sun Solaris subscriptions, Citrix XenServer, and VMware hypervisors. The latest
information regarding support and deployment can be found at www.hp.com/go/ossupport
.
23
Page 24

DL1000 Multi Node server design for scale out computing
The HP ProLiant DL1000 G6 Multi Node system is designed for scale out computing in environments
where failover is handled at the application level and where hardware redundancy plays a smaller
role. These are environments that typically require greater compute density and additional cost
efficiencies.
The HP ProLiant DL170h G6 server is the first server to launch in the HP ProLiant DL1000 system Multi
Node series. The server can be used in a single node (DL170h), two-node (DL2x170h), or four-node
configuration (DL4x170h) in the HP ProLiant h1000 G6 chassis. The DL1000 is mechanically unique
in its chassis design, server node configuration, thermal management, and power supply utilization
when compared to other ProLiant Intel-based G6 100-series DL traditional rack-mount servers.
However, while the mechanical architecture of the DL1000 is unique, it uses the same HP certified
components and management tools as the rest of the ProLiant 100-series G6 family.
Chassis design
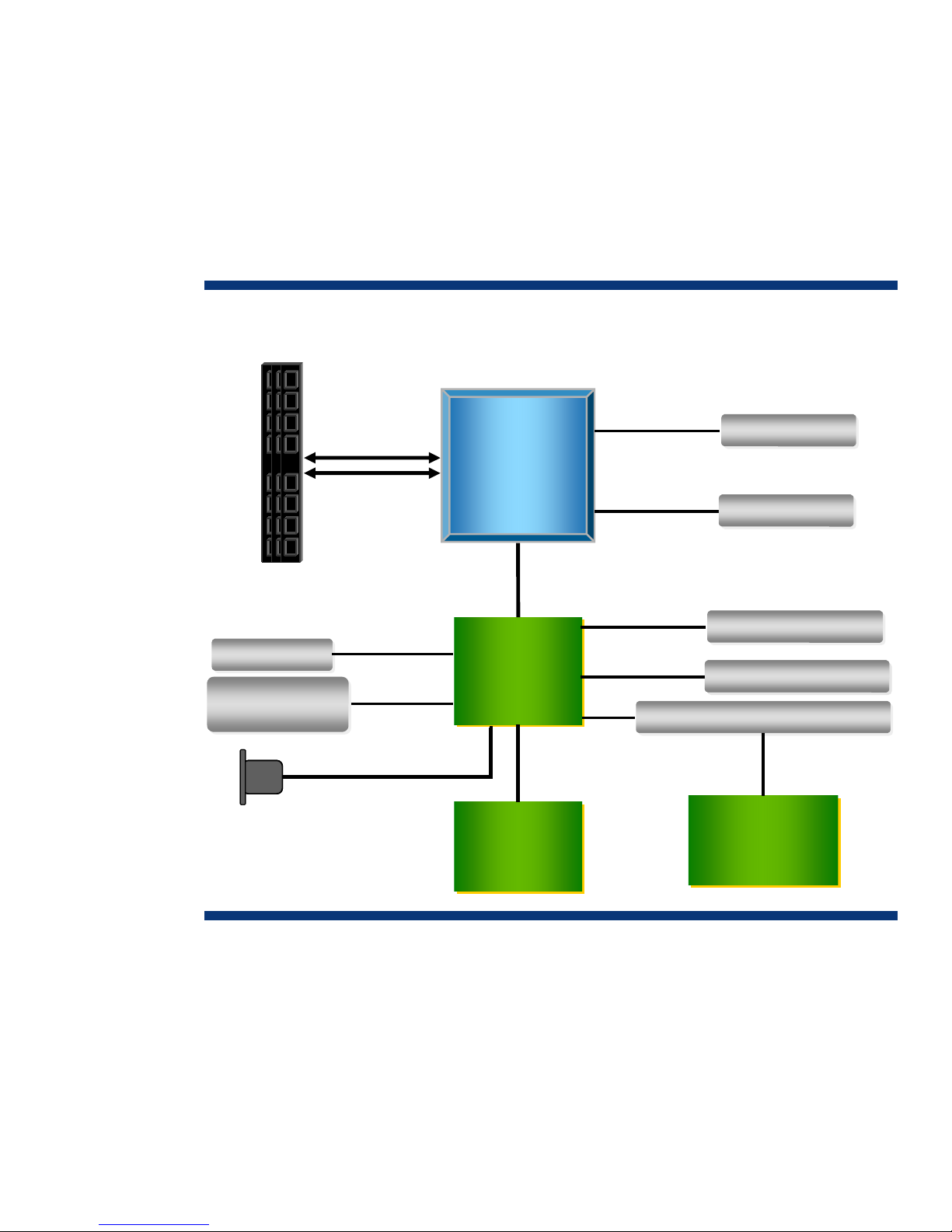
The HP ProLiant h1000 G6 chassis can hold up to four half-width HP ProLiant DL170h G6 server
nodes in a 2U space (Figure 8). The HP h1000 chassis provides shared power supplies and fans
across all server nodes, as well as the flexibility to configure for various application demands.
Figure 8. DL1
000 platform in four node configuration
The h1000 G6 chassis design includes the following:
• Up to four ind
processors and 16 DDR3 DIMM slots
• Choice of up to 16 small form factor (SFF) or 8 large form factor (LFF) hard disk drives
• Expanded PCIe Riser Options for 2-node configurations (half-width boards) requiring additional I/O
ependent ProLiant DL170h half-width server nodes, each using two Xeon 5500 Series
24
Page 25

• HP Common Slot and industry-standard power supply options (all nodes share redundant power
across the chassis)
Shared power
The DL1000
displays the four server node configuration and available ports for each server node.
system shares power supplies and thermal management across all nodes. Figure 9
Figure 9. DL1000 fou
r node configuration – rear chassis view
Four node 2U
configuration
Redundant
power
Riser options
Three PCI
limits the riser options to two-node configurations only. The riser boards support both full and half
length PCIe 2.0 cards (Figure 10).
Figure 10. 2U riser options
e riser options are available for half-width servers. Available space in the h1000 chassis
Half length riser
Full length riser
Fans and fan control
Standard fan configuration for the h1000 chassis includes four, 80mm non-redundant fans. Figure 11
illustrates how the server nodes share thermal management.
25
Page 26

Figure 11. Thermal management across server
Fan Control
fan1 fan2 fan3 fan4
Board
Node 3 Node 1
Node 4 Node 2
Power supply support
nodes as seen in the front view of the DL1000 G6 system
The DL1000 Multi Node server supports both HP Common Slot and HP industry-standard power
supplies. Three Common Slot power supply options allow users to choose the best power supply for
each configuration to maximize efficiency and performance: 460 W, 750 W, or 1200W.
The DL1000 system can also use a low cost, industry-standard 750W power supply option that does
not support hot-plug or power capping functionality (it is not a “Common Slot” power supply).
For more information on HP Common Slot and Industry Standard power supplies, see the section titled
“Efficient power delivery.”
Advanced Power Management
In addition to the efficiencies gained by the shared power infrastructure, the DL1000 system contains
advanced power metering and capping technologies. The Power Interface Controller (PIC) lets users
configure the system for full AC redundancy or AC redundancy with power throttling depending on
the system configuration. With the optional power capping mode, the DL1000 system can boost data
center capacity by reclaiming trapped power and cooling capacity.
Power Interface Controller
In order to maintain a pre-set power budget, the embedded Power Interfa
power consumption and throttles processors and memory speed in each node within the chassis. HP
provides a simple command-line utility for reading and configuring the power control logic of the
server nodes. Versions are available for MS Windows Server OS (2003 and 2008) and Linux OS
with the requirement that the OS IPMI Driver be installed. Administrators can configure the controller
for the following Power Management modes:
ce Controller monitors
• Power Control Disabled - No power throttling will occur.
• Maximum Performance with Redundancy (AC Redundancy with power throttling) - This mode is the
default setting and allows all nodes to share both power supplies and run at maximum performance
with no power caps. Power control logic will only throttle performance of each node if the chassis
26
Page 27

has only one operational power-supply. In this mode, the chassis is expected to survive an
unexpected AC power loss to one of power supplies.
• Maximum Redundancy (Full AC/DC Redundancy) - Power control logic will maintain a power cap
value for the chassis at the DC rating of a single power supply (460W, 750W, or 1200W). If one
power supply experiences a DC or AC failure, the chassis should remain on-line and operational.
• User Selectable Power Cap Mode (Optional) - The user specifies the power envelope for the 2U
chassis within the capabilities of the installed hardware. Users run a utility to calibrate the minimum
and maximum power consumption envelope for the chassis. To avoid any performance impact from
throttling, the Power Cap value should not be set below the minimum power value provided by the
utility. This functionality is available with Lights Out 100 Advanced Pack.
Summary
The HP ProLiant 100-series G6 servers help administrators increase business performance, lower
power costs, and manage their server hardware more easily. To improve performance, the 100-series
G6 servers use Intel Xeon 3400 or 5500 Series processor technologies with integrated memory
controllers and DDR-3 memory with increased bit rates. The latest Smart Array controllers use serial
SAS 2 technology as well as improved firmware capabilities to double the RAID performance
compared to the previous generation of controllers. HP spent significant engineering time improving
the thermal controls —incorporating multiple thermal sensors and allowing customers to constrain
server power according to their needs. Using HP Common Slot power supplies is another means for
customers to refine and constrain server power based on their data center requirements. ProLiant
OnBoard Administrator Powered by Lights-Out 100i and the Insight Management Agents facilitate
management by incorporating HP Systems Insight Manager. Servers can be easily deployed with the
Easy Set-up CD and its ISO image or with the multi-server deployment capabilities for the DL 100series G6 servers. Finally, the multi node server DL1000 architecture brings a new level of density
and power sharing to rack-based servers. With up to four nodes in a single chassis, the DL1000
architecture lets customers maximize data center floor space and provide flexible configurations that
fit into existing industry standard racks. The embedded Power Interface Controller monitors and
throttles power consumption across the multiple nodes in the chassis for optimum power efficiency.
27
Page 28

For more information
For additional information, refer to the resources listed below.
Resource description Web address
DDR-3 Memory Configuration Tool http://h18004.www1.hp.com/products/servers/options/tool/hp_m
emtool.html
SAS and SATA technology www.hp.com/go/serial
Smart Array Advance Pack
Smart Array controllers www.hp.com/products/smartarray
HP Network Adapters for ProLiant DL
and ML Servers
HP ProLiant 100-series Easy Set-up
CDs
HP ProLiant DL120 G6 Server
HP ProLiant DL160 G6 Server
HP ProLiant DL180 G6 Server
HP ProLiant ML110 G6 Server
HP ProLiant ML150 G6 Server
HP ProLiant DL170h G6 Server
overview
HP ProLiant DL1000 G6 Multi Node
Server
http://h18004.www1.hp.com/products/servers/proliantstorage/arr
aycontrollers/smartarray-advanced/index.html
http://media.hpvitc.veplatform.com/content/HP_Network_Adapters_fo
r_ProLiant_DL_Family_data_sheet_1237839147.pdf
www.hp.com/servers/easysetup
http://h18004.www1.hp.com/products/quickspecs/13504_na/135
04_na.html
http://h18004.www1.hp.com/products/quickspecs/13247_na/132
47_na.html
http://h18004.www1.hp.com/products/quickspecs/13248_na/132
48_na.html
http://h18004.www1.hp.com/products/quickspecs/13477_na/134
77_na.html
http://h18004.www1.hp.com/products/quickspecs/13249_na/132
49_na.html
www.hp.com/servers/proliantdl170h
www.hp.com/servers/proliantdl1000
HP ProLiant Onboard Administrator
Powered by LO100 (remote
management)
ISS Technology Communications
briefs:
Memory technology evolution: an
overview of system memory
technologies
ISS Technology Communications
briefs:
Serial Attached SCSI storage
technology brief
ProLiant 100 Series Core
Management Software
www.hp.com/go/lo100
http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs
256987/c00256987.pdf
http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c01
613420/c01613420.pdf
/support/SupportManual/c00
www.hp.com/go/coremanagement
Page 29

Call to action
Send comments about this paper to TechCom@HP.com.
© 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information
contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for
HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements
accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed
as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or
editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Microsoft, Windows, and BitLocker are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation.
Linux is a U.S. registered trademark of Linux Torvalds
Intel and Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or
its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries and is used under
license.
TC091203TB, December 2009
 Loading...
Loading...