Page 1

HP StorageWorks
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for
nl
HP BladeSystem c-Class
User Guide
*5697-0960*
Part Number: 5697-0960
First edition: May 2011
Page 2

Legal and notice information
© Copyright 2008, 2011 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
© Copyright 2008, 2011 Brocade Communications Systems, Incorporated
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set
forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as
constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Microsoft, Windows, and Windows XP are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
Page 3

Contents
About this guide ................................................................................... 9
Intended audience ...................................................................................................................... 9
SAN Switch related documentation ............................................................................................... 9
HP BladeSystem c-Class related documentation ............................................................................... 9
Before you contact HP Technical Support ....................................................................................... 9
HP contact information .............................................................................................................. 10
Document conventions and symbols ............................................................................................. 10
Subscription service .................................................................................................................. 11
Other HP websites .................................................................................................................... 11
Documentation feedback ........................................................................................................... 12
1 Overview ........................................................................................ 13
8Gb SAN Switch features .......................................................................................................... 13
Component identification .................................................................................................... 14
Port side of the 8Gb SAN Switch ................................................................................... 14
Internal ports summary ........................................................................................................ 15
8Gb SAN Switch redundancy .............................................................................................. 15
8Gb SAN Switch licensing .................................................................................................. 15
ISL trunking groups ................................................................................................................... 16
Supported optional software ...................................................................................................... 16
Additional software features in HP BladeSystem c-Class Power Pack+ models .................................... 17
Supported SFP transceiver options ............................................................................................... 17
2 Setup ............................................................................................. 19
Shipping carton contents ........................................................................................................... 19
Installation and safety considerations .......................................................................................... 20
Installing multiple switches ................................................................................................... 20
Electrical considerations ...................................................................................................... 20
Environmental considerations .............................................................................................. 20
Install the 8Gb SAN Switch ........................................................................................................ 20
OA power verification ......................................................................................................... 22
Check LEDs ....................................................................................................................... 23
Set the switch Ethernet IP address ................................................................................................ 23
Using Enclosure Bay IP Addressing (EBIPA) ............................................................................ 23
Using external DHCP .......................................................................................................... 24
Setting the IP address manually ............................................................................................ 24
Configure the 8Gb SAN Switch .................................................................................................. 25
Items required for configuration ............................................................................................ 25
Connect to the Command Line Interface ................................................................................ 26
Setting the date and time .................................................................................................... 26
Verifying installed licenses ................................................................................................... 27
Modifying the FC domain ID (optional) ................................................................................. 27
Disabling and enabling a switch .......................................................................................... 28
Disabling and enabling a port ............................................................................................. 28
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 3
Page 4

Using Dynamic Ports On Demand (DPOD) ............................................................................. 29
DPOD commands ............................................................................................................... 29
Verifying the configuration ................................................................................................... 30
Backing up the configuration ............................................................................................... 31
3 Managing the 8Gb SAN Switch ........................................................ 33
Management features ................................................................................................................ 33
Maintaining the 8Gb SAN Switch ............................................................................................... 34
Installing dust covers in empty ports ...................................................................................... 34
Replacing an SFP transceiver ............................................................................................... 34
Diagnostic tests .................................................................................................................. 35
Powering on and off .................................................................................................................. 36
Interpreting LED activity ............................................................................................................. 36
LED indicators .................................................................................................................... 36
LED patterns ............................................................................................................................. 37
Module status LED patterns .................................................................................................. 37
Port link status LED patterns .................................................................................................. 37
POST and boot specifications ..................................................................................................... 38
POST ................................................................................................................................ 38
Boot ................................................................................................................................. 38
Interpreting POST results ...................................................................................................... 39
Firmware update ....................................................................................................................... 39
About the reset button ............................................................................................................... 40
Rebooting the switch ........................................................................................................... 40
Replacing a faulty 8Gb SAN Switch ............................................................................................ 40
A Regulatory compliance and safety ..................................................... 43
Regulatory compliance .............................................................................................................. 43
Federal Communications Commission notice for Class A equipment .......................................... 43
Modifications .............................................................................................................. 43
Cables ....................................................................................................................... 43
Regulatory compliance identification numbers ........................................................................ 43
Laser device compliance ..................................................................................................... 43
Certification and classification information ...................................................................... 44
Laser product label ...................................................................................................... 44
International notices and statements ............................................................................................ 44
Canadian notice (avis Canadien) ......................................................................................... 44
Class A equipment ....................................................................................................... 44
European union regulatory notice ......................................................................................... 45
BSMI notice ....................................................................................................................... 45
Japanese notice ................................................................................................................. 45
Korean notice .................................................................................................................... 46
Safety ..................................................................................................................................... 46
Battery replacement notice .................................................................................................. 46
Taiwan battery recycling notice ............................................................................................ 47
Power cords ....................................................................................................................... 47
Japanese power cord statement ............................................................................................ 47
B Electrostatic discharge ...................................................................... 49
How to prevent electrostatic discharge ......................................................................................... 49
Grounding methods .................................................................................................................. 49
C SAN Switch technical specifications ................................................... 51
4
Page 5

General specifications ............................................................................................................... 51
Weight and physical dimensions ................................................................................................ 52
Environmental requirements ........................................................................................................ 53
Supported SFPs ........................................................................................................................ 53
Supported HBAs ....................................................................................................................... 53
Glossary ............................................................................................ 55
Index ................................................................................................. 63
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 5
Page 6

Figures
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch components ...................................................................... 141
8Gb SAN Switch external ports ................................................................................ 152
Carton contents ...................................................................................................... 193
Releasing the installation handle ............................................................................... 214
Installing the Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch into an interconnect bay .................................. 225
Verifying power-on LEDs .......................................................................................... 236
Installing an SFP ..................................................................................................... 357
Identifying LEDs ...................................................................................................... 368
Locating the Reset button .......................................................................................... 409
Class 1 laser product label ....................................................................................... 4410
6
Page 7

Tables
Document conventions ............................................................................................. 101
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch components ...................................................................... 212
Identifying 8Gb SAN Switch external ports ................................................................. 153
Optional software kits ............................................................................................. 164
Optional Long Wave 4Gb SFPs ................................................................................ 175
HP 8Gb Short Wave B-Series FC SFP+ 1 Pack, order number AJ716A ........................... 176
HP 4Gb Short Wave B-Series FC SFP 1 Pack, order number AJ715A ............................. 177
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch components ...................................................................... 198
Release mechanism components ............................................................................... 219
Power-on LEDs ........................................................................................................ 2310
8Gb SAN Switch management features ..................................................................... 3311
Connecting with a management station ..................................................................... 3412
SFP components ..................................................................................................... 3513
Front panel LED indicators during normal operation ..................................................... 3614
Module Status LED patterns during normal operation ................................................... 3715
Port link status LED patterns ...................................................................................... 3716
Locating the reset button .......................................................................................... 4017
General specifications ............................................................................................. 5118
8Gb SAN Switch physical dimensions ....................................................................... 5219
Environmental requirements ...................................................................................... 5320
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 7
Page 8

8
Page 9
About this guide
This guide provides information about setting up and configuring the Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for
HP BladeSystem c-Class. Throughout this guide the short product name is used, 8Gb SAN Switch.
Intended audience
This guide is intended for system administrators and technicians with knowledge of:
• Configuration aspects of customer Storage Area Network (SAN) fabric
• Customer host environments, such as Microsoft Windows or Linux
• Command Line Interface (CLI) commands
• Advanced Web Tools graphical user interface (GUI) for configuring the switches through a sup-
ported web browser
SAN Switch related documentation
SAN Switch-related documents and other SAN infrastructure documentation, including white papers
and best practices documents, are available at: http://www.hp.com/support/manuals
Scroll to the storage section of the web page and select Storage Networking for HP StorageWorks
products.
IMPORTANT:
For late-breaking, supplemental information, access the latest version of the
OS release notes
for the 8Gb SAN Switch.
HP BladeSystem c-Class related documentation
HP BladeSystem c-Class enclosure user documentation, including white papers and best practices
documents, are available at:
http://www.hp.com/go/bladesystem/documentation
Before you contact HP Technical Support
Be sure to have the following information available before you call HP:
• Technical support registration number (if applicable)
• Product serial number
• Product model name and number
• Applicable error messages
HP StorageWorks Fabric
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 9
Page 10
• Third-party hardware or software
• Operating system type and revision level
For continuous quality improvement, calls may be recorded or monitored.
HP contact information
For the name of the nearest HP authorized reseller:
• In the United States, see the HP US service locator web page:
nl
http://www.hp.com/service_locator
• In other locations, see the Contact HP worldwide (in English) web page:
nl
http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/en/wwcontact.html
• In the United States, for contact options see the Contact HP United States web page:
nl
http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/en/contact_us.html
• Call 1-800-HP-INVENT (1-800-474-6836). This service is available 24 hours a day, 7 days a
week. For continuous quality improvement, calls may be recorded or monitored.
• If you have purchased a Care Pack (service upgrade), call 1-800-633-3600. For more information
about Care Packs, refer to the HP website:
nl
http://www.hp.com
Document conventions and symbols
Table 1 Document conventions
Bold text
Monospace text
Monospace, italic text
ElementConvention
Cross-reference links and e-mail addressesBlue text: Table 1
website addressesBlue, underlined text: http://www.hp.com
• Keys that are pressed
• Text typed into a GUI element, such as a
box
• GUI elements that are clicked or selected,
such as menu and list items, buttons, tabs,
or check boxes
Text emphasisItalic text
• File and directory names
• System output
• Code
• Commands, their arguments, and argument
values
• Code variables
• Command variables
Monospace, bold text
About this guide10
Emphasized monospace text
Page 11

WARNING!
Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in bodily harm or death.
CAUTION:
Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in damage to equipment or data.
IMPORTANT:
Provides clarifying information or specific instructions.
NOTE:
Provides additional information.
TIP:
Provides helpful hints and shortcuts.
Subscription service
HP strongly recommends that customers register online using the Subscriber's choice website: http:/
/www.hp.com/go/e-updates.
Subscribing to this service provides you with e-mail updates on the latest product enhancements,
newest driver versions, and firmware documentation updates as well as instant access to numerous
other product resources.
After subscribing, locate your products by selecting Business support and then Storage under Product
Category.
Other HP websites
For additional information, see the following HP websites:
• http://www.hp.com
• http://www.hp.com/go/storage
• http://www.hp.com/service_locator
• http://www.docs.hp.com
• http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/en/prodserv/servers.html
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 11
Page 12

Documentation feedback
HP welcomes your feedback.
To make comments and suggestions about product documentation, please send a message to
storagedocsFeedback@hp.com. All submissions become the property of HP.
About this guide12
Page 13

1 Overview
The Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class (referred to in the rest of this manual as
the 8Gb SAN Switch) is a Fibre Channel (FC) switch that supports link speeds of up to 8 Gbps. The
8Gb SAN Switch can operate in a fabric containing multiple switches or as the only switch in a fabric.
NOTE:
In this document, the Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch refers to those Brocade FC switch modules compatible
with the HP BladeSystem c-Class enclosure only.
This chapter provides the following information:
• 8Gb SAN Switch features, page 13
• ISL trunking groups, page 16
• Supported optional software, page 16
• Additional software features in HP BladeSystem c-Class Power Pack+ models, page 17
• Supported SFP transceiver options, page 17
8Gb SAN Switch features
The 8Gb SAN Switch provides the following features:
• Fully integrated, embedded FC SAN design that connects directly to the HP BladeSystem c-Class
enclosure midplane
• Dynamic Ports on Demand (DPOD), which automatically detects port connections, assigns port li-
censes, and enables ports
• Easy-to-manage HP Storage Essentials Systems Insight Manager support
• Full compatibility with HP StorageWorks B-Series switches and Brocade fabrics
• Sixteen internal 1/2/4/8 Gbps auto-sensing Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFPs) with the following
characteristics:
• Independent automatic negotiation to the highest common speed for each server FC port connected to the switch
• Universal self-configuring ports, which are capable of becoming F_Ports (fabric enabled)
• Eight external 1/2/4/8 Gbps FC SFP ports, with the following characteristics:
• Automatic negotiation to the highest common speed of all devices connected to the port
• Port-interface-compatible SFP transceivers, both short-wavelength (SWL) and long wavelength
(LWL)
• Universal self-configuring ports, which are capable of becoming F_Ports, FL_Ports (fabric loop
enabled), or E_Ports (expansion ports)
• Heterogeneous support for mixed storage fabrics
• Power supplied and controlled by the BladeSystem enclosure
• Identification to HP chassis management with HP specified SEEPROMs
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 13
Page 14
• Hot-swap capability
• Compatibility with redundant and dual redundant switch configurations in c-Class BladeSystem
• Hot code activation
• Real-time clock
• SFP port monitoring
Component identification
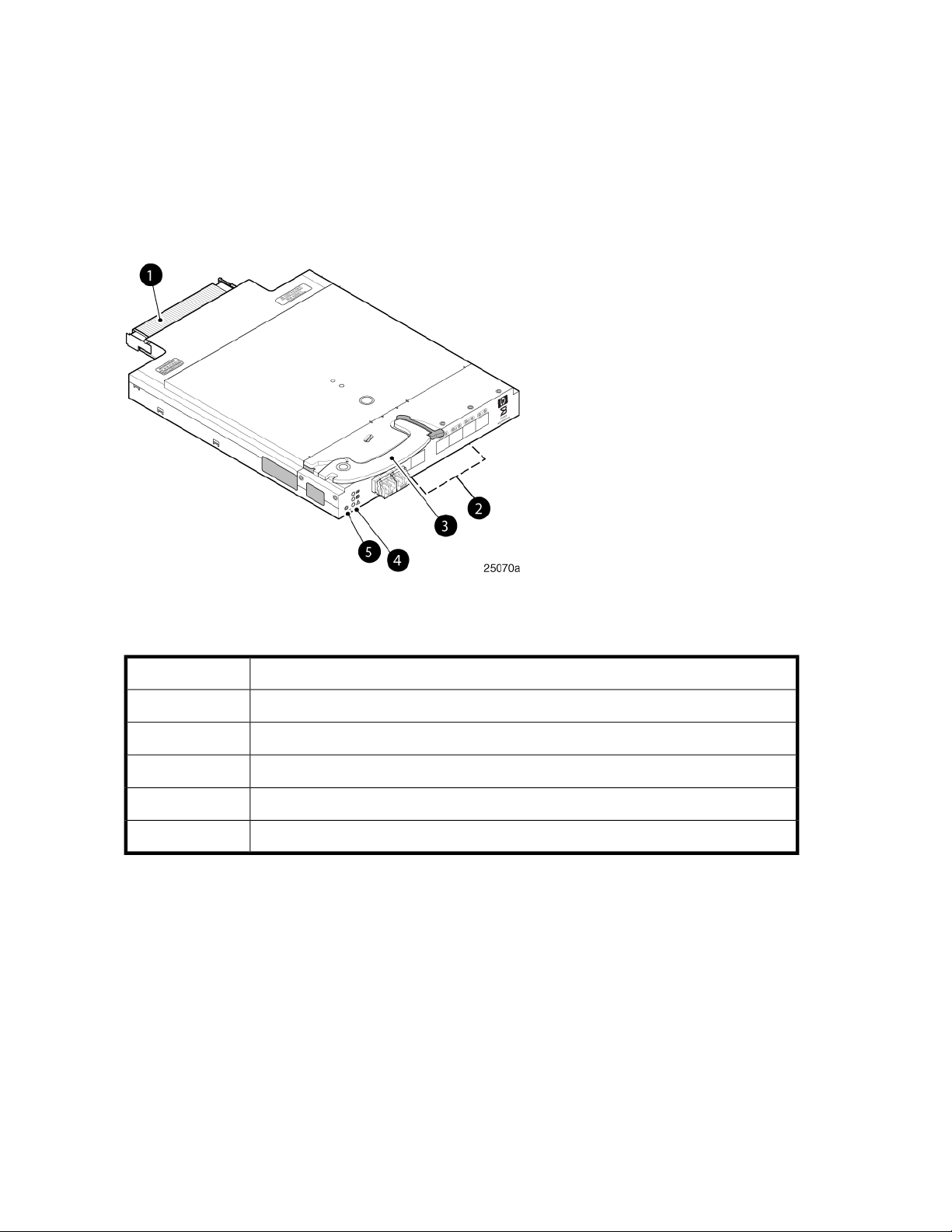
Figure 1 and Table 2 identify the physical components of the 8Gb SAN Switch.
Figure 1 Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch components
.
Table 2 Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch components
DescriptionItem
Midplane connector1
Eight external SFP ports2
Installation handle3
Unit ID (UID), Health, and Status LEDs4
Reset button5
Port side of the 8Gb SAN Switch
Figure 2 and Table 3 identify 8Gb SAN Switch external ports (ports 17 through 20, and ports 21
through 0).
Overview14
Page 15

Figure 2 8Gb SAN Switch external ports
.
Table 3 Identifying 8Gb SAN Switch external ports
NOTE:
Refer to Interpreting LED activity, page 36 for complete information on 8Gb SAN Switch LEDs.
Internal ports summary
Sixteen logical internal ports (numbered 1 through 16) connect sequentially to server bays 1 through
16 with the enclosure midplane. Server bay 1 is connected to Switch Port 1, Server bay 2 is connected
to Switch port 2, and so forth.
8Gb SAN Switch redundancy
DescriptionItem number
Left bank—ports 17, 18, 19, 201
Right bank—ports 21, 22, 23, 02
The HP BladeSystem c-Class was engineered as a no-single-point-of-failure bladed solution. Attributes
that contribute to switch redundancy include:
• Redundant power and cooling
• Redundant HP Onboard Administrator (OA) to ensure management access to the switch
NOTE:
The HP Onboard Administrator is the enclosure management module used to support and manage
the HP BladeSystem c-Class and all managed devices used in the enclosure.
8Gb SAN Switch licensing
The 8Gb SAN Switch integrates one of three license options that complement existing HP product
lines. Some 8Gb SAN Switch models ship with licenses that place limits on the number of domains
that can be used. Models and their specific licenses are as follows:
• Brocade 8/12 SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class, base, integrating 12 active ports (in any
combination of internal/external ports) and two short-wavelength SFPs. Software components include
a Full Fabric license, the Advanced Web Tools GUI and Zoning software
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 15
Page 16
• Brocade 8/24 SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class, base, integrating 24 active ports (16 in-
ternal and 8 external) and four short-wavelength SFPs. Software components include a Full Fabric
license, Advanced Web Tools GUI, and Zoning software
• Brocade 8/24 Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class, Power Pack, integrating 24 active
ports (16 internal and 8 external) and four short-wavelength SFPs. Software components include
a Full Fabric license, Advanced Web Tools GUI, and Zoning software plus these additional software
features:
• Fabric Watch
• ISL Trunking
• Advanced Performance Monitoring (APM)
• Extended Fabric
IMPORTANT:
Upgrade the 8Gb SAN Switch by purchasing optional licenses; access the latest version of the
StorageWorks Fabric OS administrator guide
ISL trunking groups
If your 8Gb SAN Switch is licensed for interswitch link (ISL) trunking, use the trunking groups available
on the switch.
HP
to learn how to add a license.
The FC ports are numbered from left to right, and are part of the same ISL trunking group. The trunking
group consists of the ports shown in Figure 2.
NOTE:
ISL Trunking is optional software that allows you to create trunking groups of ISLs between adjacent
switches. ISL trunking is available on the Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class Power
Pack+ model, or by purchasing the optional license described in ???. For more information about
trunking, refer to the latest version of the
Supported optional software
Table 4 lists the optional software kits and licenses, which can be activated by purchasing the
corresponding license key.
Table 4 Optional software kits
HP StorageWorks Fabric OS administrator guide
Part numberOption
324504-B21Fabric Watch
324505-B21Extended Fabrics
324507-B21Advanced Performance Monitoring (APM)
.
T5527AHP B-series 8-24 Port ISL Trunking LTU
T5524AHP B-series 8-24 Pt Adaptive Network LTU
Overview16
Page 17
Part numberOption
T5521AHP B-series 8-24 Power Pack+ Upgrade
T4269A,
nl
HP StorageWorks Enterprise Edition
v5 Fabric Manager Software
Fabric Manager
nl
T4270A,
nl
Fabric Manager, v5.x Base Edition
(10 domains)
Additional software features in HP BladeSystem c-Class Power Pack+ models
If you purchased the 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class Power Pack+, it includes the
following optional software:
• ISL Trunking
• Fabric Watch
• Advanced Performance Monitoring
• Extended Fabrics
For information on any of these features, refer to the latest version of the HP StorageWorks Fabric
OS administrator guide.
Supported SFP transceiver options
Table 5 through Table 7 lists the only supported SFPs.
Table 5 Optional Long Wave 4Gb SFPs
Table 6 HP 8Gb Short Wave B-Series FC SFP+ 1 Pack, order number AJ716A
Table 7 HP 4Gb Short Wave B-Series FC SFP 1 Pack, order number AJ715A
Part numberOption
AK870AHP 4Gb Long Wave B-Series FC SFP 1 Pack - 10km
AN211AHP 4Gb Long Wave B-Series FC SFP 1 Pack - 30km
OM3 CableOM2 CableDistance
150 meters50 meters8Gb performance
270 meters150 meters4Gb performance
500 meters300 meters2Gb performance
860 meters500 meters1Gb performance
OM3 CableOM2 CableDistance
270 meters150 meters4Gb performance
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 17
Page 18

OM3 CableOM2 CableDistance
500 meters300 meters2Gb performance
860 meters500 meters1Gb performance
Overview18
Page 19
2 Setup
This chapter provides the following information:
• Shipping carton contents, page 19
• Installation and safety considerations, page 20
• Install the 8Gb SAN Switch, page 20
• Set the IP address, page 23
• Configure the 4Gb SAN Switch, page 25
Shipping carton contents
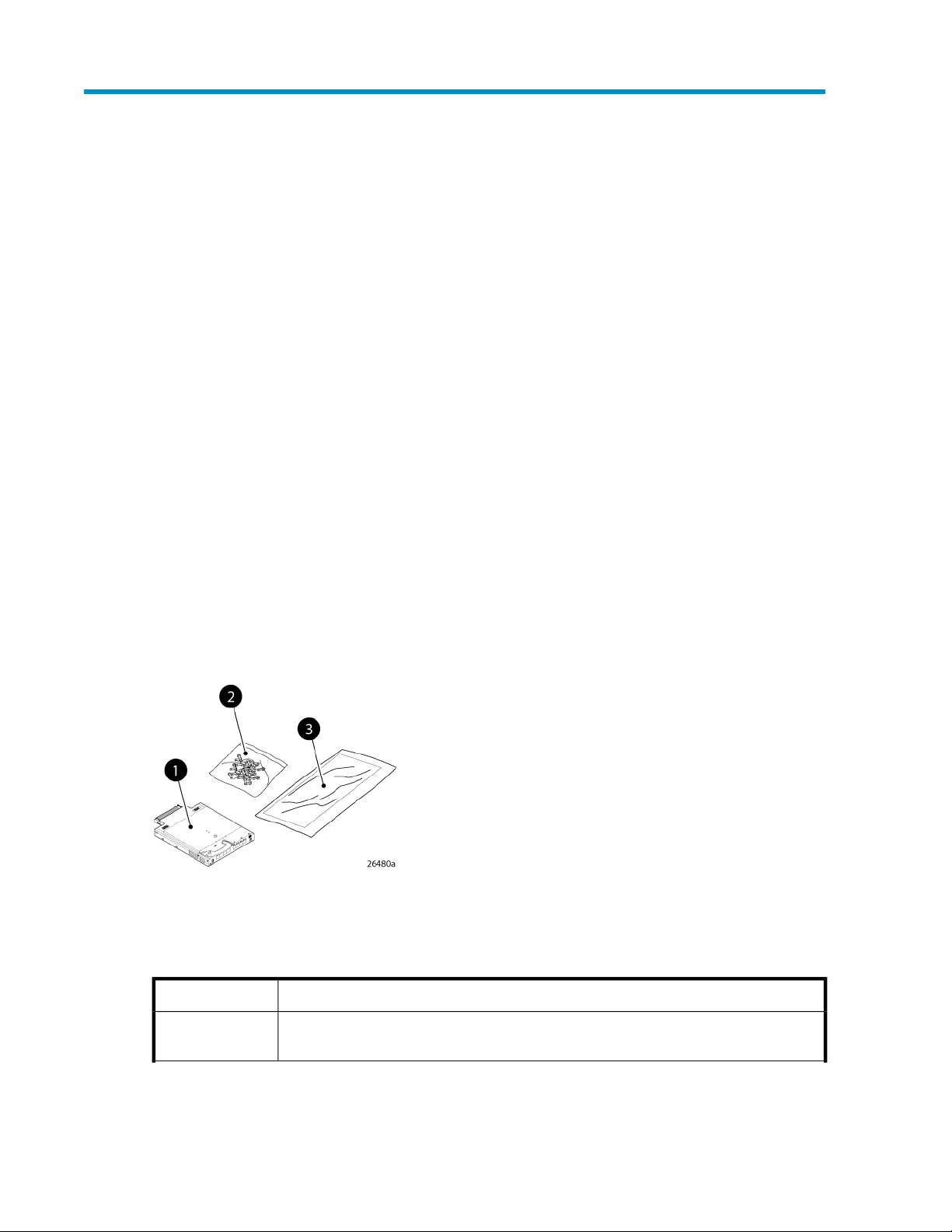
Figure 3 and Table 8 identify the 8Gb SAN Switch shipping carton contents:
• Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class installation instructions
• SFP dust covers (must be inserted in ports where Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) optical trans-
ceivers are not installed)
• Four Short Wavelengh (SWL) 8Gb SFPs, (in styrofoam packing)
• One Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch; models include:
• Brocade 8/12 SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class with twelve active ports
• Brocade 8/24 SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class with sixteen internal and eight external
active ports
• Brocade 8/24 SAN Switch Power Pack+ for HP BladeSystem c-Class with sixteen internal and
eight external active ports
Figure 3 Carton contents
.
Table 5 identifies 8Gb SAN Switch components.
Table 8 Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch components
DescriptionItem
1
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch, ships with four Short Wavelengh (SWL) 8Gb SFPs, (in styrofoam packing)
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 19
Page 20

Dust covers for empty SFP ports2
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class installation instructions3
Installation and safety considerations
The 8Gb SAN Switch installs in the I/O bays in the rear of the HP BladeSystem c-Class enclosure.
Refer to the appropriate BladeSystem Enclosure Setup and Installation Guide for specific enclosure
requirements.
Installing multiple switches
If you do not have a DHCP server connected to the OA, install and configure one 8Gb SAN Switch
at a time. This is required so that Ethernet IP address conflicts do not occur with duplicate default
Ethernet IP addresses.
IMPORTANT:
DHCP is enabled by default on this switch. In cases where DHCP is available, IP address conflicts will
not occur, simplifying multiple switch installations. See Using external DHCP, page 24.
Each switch must be assigned a unique Ethernet IP address during configuration. Once the default
Ethernet IP address on the 8Gb SAN Switch has been changed, you may install additional 8Gb SAN
Switches in the enclosure.
See the appropriate HP BladeSystem Enclosure Setup and Installation Guide for help identifying your
specific enclosure setup, available connections, and power requirements.
Electrical considerations
The 8Gb SAN Switch requires 35 watts, provided by the enclosure. No other power requirement or
provision exists.
Environmental considerations
Ensure proper cooling and ventilation by verifying the following:
• The air vents on the enclosure are not blocked or restricted.
• The ambient air temperature at the front of the enclosure does not exceed 35°C (95°F) while the
switch is operating.
IMPORTANT:
The dust covers that ship with your 8Gb SAN Switch
not installed, to help contain air flow in the BladeSystem chassis.
must
be inserted into any ports where SFPs are
Install the 8Gb SAN Switch
Install the Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch into the enclosure:
Setup20
Page 21

1. Locate the appropriate interconnect bay in the rear of the enclosure as specified in the appropriate
HP BladeSystem Enclosure Setup and Installation Guide provided with your enclosure.
IMPORTANT:
Populate all enclosure I/O bays with the appropriate component (for example a switch,
Pass-Thru, or one of the blank panels provided with the enclosure).
2. Remove the slot cover (if installed).
CAUTION:
Properly ground yourself before handling the switch.
3. Press the handle latch to release the installation handle. See Figure 4.
Figure 4 Releasing the installation handle
.
Table 9 Release mechanism components
DescriptionItem
Installation handle in latched position1
Handle latch2
Installation handle (released)3
NOTE:
The Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch is a hot-pluggable device. The enclosure power may be on
or off during installation.
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 21
Page 22

4. Align the Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch with the appropriate interconnect bay according to your
enclosure’s specific configuration. Push the switch firmly into the interconnect bay. See Figure 5.
Figure 5 Installing the Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch into an interconnect bay
.
5. Press the installation handle into the latch to lock the Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch in place.
CAUTION:
All panels and doors should be in place and securely fastened while the unit is in operation, for proper
cooling and for EMI emissions control.
OA power verification
As defined earlier, the HP BladeSystem Onboard Administrator (OA) is the enclosure management
processor that manages the devices contained within the enclosure. The OA provides a single point
from which to perform basic management tasks on switches or server blades installed in the enclosure.
IMPORTANT:
HP recommends reading the appropriate
BladeSystem Onboard Administrator User Guide
overall understanding of your specific enclosure model.
Once the switch is installed in the interconnect bay, the OA verifies that the switch type matches the
mezzanine cards present on the servers. If there is no mismatch, the OA powers up the switch.
If the switch does not power up, check the enclosure and switch status with the OA web interface.
Refer to the HP BladeSystem Onboard Administrator User Guide.
HP BladeSystem Enclosure User Guide
. Reading these guides in sequence will promote an
and the
HP
Setup22
Page 23

Check LEDs
See Figure 6 to locate power-on LEDs. Verify that the LEDs match the indicators described in Table
10.
Figure 6 Verifying power-on LEDs
.
Table 10 Power-on LEDs
IndicatorsDescriptionItem
OffUID LED1
Steady green lightHealth ID LED2
Set the switch Ethernet IP address
To set the Ethernet IP address:
1. Verify that the enclosure is powered on.
2. Verify that the switch is installed.
3. Choose one of the following methods to set the Ethernet IP address:
• Using Enclosure Bay IP Addressing (EBIPA)
• Using external DHCP
• Setting the IP address manually
Using Enclosure Bay IP Addressing (EBIPA)
To set the Ethernet IP address using EBIPA:
1. Open a web browser and connect to the active OA.
2. Enable EBIPA for the corresponding interconnect bay.
Steady green lightModule status LED3
Steady green lightPort status LED4
3. Click Apply to restart the switch.
4. Verify the IP address using a Telnet or SSH login to the switch, or by selecting the switch in the
OA GUI Rack Overview window.
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 23
Page 24

NOTE:
Refer to the
HP BladeSystem Onboard Administrator user guide
Using external DHCP
To set the Ethernet IP address using external DHCP:
1. Connect to the active OA with a web browser.
2. Document the DHCP-assigned address by selecting the switch from the OA GUI Rack Overview
window.
3. Verify the IP address using a Telnet or SSH login to the switch, or select the switch in the OA GUI
Rack Overview window.
Setting the IP address manually
To set the IP address manually:
NOTE:
As an alternate method to using a null modem cable, use Telnet or SSH to access the IP address of
the Onboard Administrator, resuming at step 9 below.
for additional information on EBIPA.
1. Obtain the following items to set the IP address with a serial connection:
• Computer with a terminal application (such as HyperTerminal in a Windows environment or
TERM in a UNIX environment)
• Null modem serial cable
nl
2. Replace the default IP address (if present) and related information with the information provided
by your network administrator. By default, the IP address is set to 10.77.77.77 for switches with
revision levels earlier than 0C.
3. Verify that the enclosure is powered on.
4. Identify the active OA in the BladeSystem.
5. Connect a null modem serial cable from your computer to the serial port of the active OA.
6. Configure the terminal application as follows:
In a Windows environment, enter:
• Bits per second—9600
• Databits—8
• Parity—None
• Stop bits—1
• Flow control—None
In a UNIX environment, enter: tip /dev/ttyb –9600
7. Log in to the OA.
8. Press Enter to display the switch console.
Setup24
Page 25

9. Identify the interconnect bay number where the switch is installed. At the OA command line,
enter:
connect interconnect x
Where x is the interconnect bay slot where the switch is installed.
a. User: admin
b. Password: password
NOTE:
Enter entries as shown, because commands are case sensitive.
10. Or, follow the onscreen prompts to change your password now.
11. The OA will then connect its serial line to the Switch in the specified interconnect bay. A prompt
displays indicating that the escape character for returning to the OA is Ctrl __ (underscore).
12. At the command line, enter: ipaddrset.
13. Enter the remaining IP addressing information, as prompted.
14. Optionally, enter ipaddrshow at the command prompt to verify that the IP address is set correctly.
15. Record the IP addressing information, and store it in a safe place.
16. Enter Exit, and press Enter to log out of the serial console.
17. Disconnect the serial cable. For additional assistance with operating the Onboard Administrator
CLI, refer to the Onboard Administrator Command Line Interface user guide for your specific
enclosure, available at http://www.hp.com.
Configure the 8Gb SAN Switch
The 8Gb SAN Switch must be configured to ensure correct operation within a network and fabric.
For instructions about configuring the switch to operate in a fabric containing switches from other
vendors, refer to the HP StorageWorks SAN Design reference guide:
http://h18000.www1.hp.com/products/storageworks/san/documentation.html.
For more information about the CLI, refer to the latest version of the Fabric OS command reference
guide.
Items required for configuration
The following items are required for configuring and connecting the 8Gb SAN Switch for use in a
network and fabric:
• 8Gb SAN Switch installed in the enclosure
• IP address and corresponding subnet mask and gateway address recorded during the Set the IP
address, page 23 procedure
• Ethernet cable
• SFP transceivers and compatible optical cables, as required
• Access to an FTP server for backing up the switch configuration (optional)
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 25
Page 26

Connect to the Command Line Interface
Make an Ethernet connection and log in to the 8Gb SAN Switch:
1. Connect the workstation to the Ethernet network containing the OA. If the OA is not on a network,
connect directly to the OA/iLO Ethernet port on the active OA.
IMPORTANT:
Verify that the switch is not being reconfigured from any other connections during the remaining
steps.
2. Open a Telnet connection using the IP address set earlier. The login prompt displays when the
Telnet connection locates the switch in the network.
3. Enter the user name, using the administrative account admin.
4. Enter the password. The default password is password.
NOTE:
You can run up to two simultaneous admin sessions and four user sessions.
If you have not changed the system passwords from the default, you are prompted to change
them. Enter the new system passwords, or press Ctrl-c to skip the password prompts.
5. Verify that the login was successful. If successful, the prompt displays the switch name and user
ID to which you are connected.
Setting the date and time
The date and time are used for logging events. 8Gb SAN Switch operation does not depend on the
date and time; a switch with an incorrect date and time value will function properly.
To set the date and time using the CLI:
1. If you have not already done so, connect to the switch and log in as admin as described in
Connect to the Command Line Interface, page 26.
Setup26
Page 27

2. Issue the date command using the following syntax:
date mmddHHMMyy”
where:
• mm is the month; valid values are 01 through 12.
• dd is the date; valid values are 01 through 31.
• HH is the hour; valid values are 00 through 23.
• MM is minutes; valid values are 00 through 59.
• yy is the year; valid values are 00 through 99 (values greater than 69 are interpreted as
1970–1999, and values less than 70 are interpreted as 2000–2069).
For example:
switch:admin> date
nl
Fri Jan 29 17:01:48 UTC 2000
nl
switch:admin> date 0227123003
nl
Thu Feb 27 12:30:00 UTC 2003
nl
switch:admin>
For details about changing time zones, see the tsTimeZone command in the latest version of
the Fabric OS command reference guide.
Verifying installed licenses
To determine the type of licensing included with your 8Gb SAN Switch, enter licenseshow at the
command prompt, as in the following example:
nl
switch:admin> licenseshow
nl
nl
XXXnnXXnXnnXXX:
nl
nl
Fabric Watch license
nl
nl
Release v5.0 license
nl
nl
XXXnnXXnXnnXXX:
nl
nl
Zoning license
nl
nl
XXXnnXXnXnnXXX:
nl
nl
Web license
nl
nl
XXXnnXXnXnnXXX:
nl
nl
Full Fabric
NOTE:
For more information about the CLI, refer to the latest version of the
guide
.
Modifying the FC domain ID (optional)
Fabric OS command reference
If desired, you can modify the FC domain ID. The default FC domain ID is domain 1. If the 8Gb SAN
Switch is not powered on until after it is connected to the fabric, and the default FC domain ID is
already in use, the domain ID for the new switch is automatically reset to a unique value. If the switch
is connected to the fabric after is has been powered on and the default domain ID is already in use,
the fabric segments.
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 27
Page 28

Enter fabricshow to determine the domain IDs that are currently in use. The maximum number of
domains with which the 8Gb SAN Switch communicates is determined by this switch's fabric license.
To modify the domain ID:
1. Enter switchdisable to disable the switch.
2. Enter configure, and then enter a new value.
Or press Enter to accept each default value.
3. At the Fabric parameters prompt, enter Y and press Enter:
Fabric parameters (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
4. Enter a unique domain ID. For example:
Domain: (1..239) [1] 3
5. Complete the remaining prompts, or press Ctrl+D to accept the remaining default settings.
6. Enter switchenable to re-enable the switch.
7. Enter fabricshow to confirm any changes made to the domain ID.
8. Optionally, verify switch policy settings, and specify any custom status policies that need to
change:
a. Enter switchstatuspolicyshow to verify the current policy settings. If desired, enter
switchstatuspolicyset at the prompt to change switch policy settings. This command
sets the policy parameters that determine the overall switch status.
b. Customize the status policies as desired.
9. To deactivate the alarm for a particular condition, enter 0 at the prompt for that condition.
Disabling and enabling a switch
By default, the switch is enabled after power on and after the diagnostics and switch initialization
routines complete. You can disable and re-enable the switch as necessary.
To disable:
1. If you have not already done so, connect to the switch, and log in as admin, as described in
Connect to the Command Line Interface.
2. Issue the switchDisable command.
All Fibre Channel ports on the switch are taken offline. If the switch was part of a fabric, the
fabric reconfigures.
To enable:
1. If you have not already done so, connect to the switch and log in as admin as described in
Connect to the Command Line Interface, page 26.
2. Issue the switchEnable command.
All Fibre Channel ports that pass the Power-on Self Test (POST) are enabled. If the switch has
interswitch links (ISLs) to a fabric, it joins the fabric.
Disabling and enabling a port
To enable a port:
Setup28
Page 29

1. Connect to the switch and log in as admin as described in Connect to the Command Line
Interface, page 26.
2. Issue portenable portnumber where portnumber is the port number of the port you want
to enable.
To disable:
1. If you have not already done so, connect to the switch and log in as admin as described in
Connect to the Command Line Interface, page 26.
2. Issue portdisable portnumber where portnumber is the port number of the port you
want to disable.
Using Dynamic Ports On Demand (DPOD)
DPOD functionality does not require a predefined assignment of ports. Port assignment is determined
by the total number of ports in use as well as the number of purchased ports.
In summary, the DPOD feature simplifies port management by:
• Automatically detecting HBA connected server ports or cabled ports
• Automatically enabling ports
• Automatically assigning port licenses
To initiate DPOD, use the licensePort command, as described in DPOD commands, page 29.
IMPORTANT:
For the Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch, DPOD works only if the server blade is installed with an HBA
present. A server blade that does not have a functioning HBA will not be treated as an active link for
the purpose of initial POD port assignment.
DPOD commands
Use the licensePort command to manage dynamic POD assignments with the following options:
• licensePort –reserve portnum reserves a future license assignment for a specific port,
even if the port is currently offline.
• licensePort –release portnum removes a license from a port.
• portCfgPersistentDisable blocks a specific port from future assignments.
• licensePort -show displays an overview of the POD license status and port assignments.
nl
The following shows examples of the licensePort -show command for a Brocade 8/12 SAN
Switch and a Brocade 8/24 SAN Switch:
Example for Brocade 8/12 SAN Switch
swd77:admin> licenseport -show
24 ports are available in this switch
No POD licenses are installed
Dynamic POD method is in use
12 port assignments are provisioned for use in this switch:
12 port assignments are provisioned by the base switch license
*6 port assignments added if the 1st POD license is installed
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 29
Page 30

*6 more assignments added if the 2nd POD license is installed
4 ports are assigned to installed licenses:
4 ports are assigned to the base switch license
Ports assigned to the base switch license:
15, 16, 17, 18*
Ports assigned to the first POD license:
None
Ports assigned to the second POD license:
None
Ports not assigned to a license:
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 19
20, 21, 22, 23
Example for Brocade 8/24 SAN Switch
cp081044:admin> licenseport --show
24 ports are available in this switch
Full POD license is installed
Dynamic POD method is in use
24 port assignments are provisioned for use in this switch:
12 port assignments are provisioned by the base
12 port assignments are provisioned by a full POD license
11 ports are assigned to installed licenses:
11 ports are assigned to the base switch license
0 ports are assigned to the full POD license
Ports assigned to the base switch license:
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 17*, 18*, 19*
Ports assigned to the full POD license:
None
Ports not assigned to a license:
0, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 20, 21, 22, 23
13 license reservations are still available for use by unassigned
ports
3 license assignments are held by offline ports (indicated by *)
NOTE:
The DPOD feature does not consider disabled ports as candidates for license assignments. You can
persistently disable an otherwise withble port to cause it not to come online and preserve a license
assignment for future use.
Verifying the configuration
After setting initial parameters, verify the configuration as follows:
1. Check the LEDs to verify that all components are functional.
For information about LED patterns, refer to Interpreting LED activity, page 36 .
2. Enter switchshow to get information about the switch and port status.
3. Enter fabricshow to get general information about the fabric.
Setup30
Page 31

Backing up the configuration
To back up the switch configuration to an FTP server, enter configupload and follow the prompts.
The configupload command copies the switch configuration to the server, making it available for
downloading to a replacement switch, if necessary.
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 31
Page 32

Setup32
Page 33

3 Managing the 8Gb SAN Switch
This chapter provides the following information:
• Management features, page 33
• Maintaining the 8Gb SAN Switch, page 34
• Powering on and off, page 36
• Interpreting LED activity, page 36
• LED patterns, page 37
• POST and boot specifications, page 38
• Firmware update, page 39
• About the reset button, page 40
• Replacing a faulty 8Gb SAN Switch
Management features
The management tools built into the 8Gb SAN Switch (listed in Table 11) can be used to monitor
fabric topology, port status, physical status, and other information used for performance analysis and
system debugging.
When running IP over FC, these management tools must be run on both the Fibre Channel host and
the switch and must be supported by the Fibre Channel host driver. For a list of Fibre Channel hosts
supported by the 8Gb SAN Switch, contact your HP representative.
Table 11 8Gb SAN Switch management features
In-band supportOut-of-band supportManagement tool
CLI—Run up to two admin sessions and four user sessions
simultaneously. For more information, refer to the latest version of the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS administrator guide
and the Fabric OS command reference guide.
Advanced Web Tools—For information, refer to the latest
version of the Fabric OS Web Tools administrator's guide.
Standard SNMP applications—For information, refer to the
latest version of the Fabric OS MIB reference guide.
Management Server—For more information, refer to the latest
version of the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS administrator
guide and the Fabric OS command reference guide.
You can connect a management station to one switch with Ethernet while managing other switches
connected to the first switch with FC. To do so, set the FC gateway address of each of the other
switches to be managed to the FC IP address of the first switch.
Ethernet or serial connection
Ethernet connection
IP over FC
IP over FCEthernet connection
IP over FCEthernet connection
SMI-S compliant
management program
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 33
Page 34

The gateway address of the first switch should be set to whatever the gateway address is for the
subnet on which the first switch resides. See Table 12.
Table 12 Connecting with a management station
Maintaining the 8Gb SAN Switch
The 8Gb SAN Switch does not require any regular physical maintenance.
However, it is critical that environmental conditions, described in Environmental requirements, page 53,
are met to help prevent switch failure due to heat stress or improper air flow.
Installing dust covers in empty ports
The dust covers included in the 8Gb SAN Switch shipping carton (see Figure 1) must be inserted in
ports where SFPs are not installed. Installing dust covers ensures proper air flow and helps reduce
dust contamination of the switch.
Third switchSecond switchFirst switchManagement station
204.1.1.12204.1.1.11192.168.1.10192.168.1.09Ethernet
192.168.65.12192.168.65.11192.168.65.10192.168.65.09FCIP
192.168.1.10192.168.1.10any, not self192.168.1.10Gateway
Replacing an SFP transceiver
In some cases, you might need to reinstall an SFP transceiver.
To remove an SFP transceiver:
1. Press and hold the cable release.
2. Remove the cable from the transceiver.
3. Pull the bail (wire handle) to release the transceiver.
4. Grasp the bail, and gently but firmly pull the transceiver out of the port.
5. Repeat this procedure for the remaining ports as required.
To install a replacement SFP:
1. Make sure that the bail is in the unlocked position.
Managing the 8Gb SAN Switch34
Page 35

2. Orient the SFP with the appropriate port. See Figure 7 and Table 13.
Figure 7 Installing an SFP
.
Table 13 SFP components
DescriptionItem
bail1
3. Insert the SFP into the port until you hear a click.
4. Close the bail.
Diagnostic tests
In addition to POST, Fabric OS includes diagnostic tests to help troubleshoot the hardware and the
firmware including tests of internal connections and circuitry, fixed media, and the transceivers and
cables in use.
Initiate diagnostic tests with the command line, using a Telnet session or a terminal setup with a serial
connection to the switch. Some tests require the ports to be connected by external cables to allow
diagnostics to verify the serializer/deserializer interface, transceiver, and cable. For information on
available diagnostic tests, enter diagHelp.
All diagnostic tests are run at link speeds of 1 Gbps, 2 Gbps, 4 Gbps, and 8 Gbps.
CAUTION:
Diagnostic tests can temporarily lock the transmit and receive speed of the links during diagnostic
testing.
SFP2
For information about specific diagnostic tests, refer to the latest version of the HP StorageWorks
Fabric OS administrator guide, or enter help followed by the name of the diagnostic test.
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 35
Page 36

Powering on and off
8Gb SAN Switch power is provided by the enclosure. The 8Gb SAN Switch runs POST by default
each time power to the enclosure is turned on. The POST process can last as long as three minutes.
To remove power from the switch, remove the 8Gb SAN Switch from the enclosure interconnect bay.
NOTE:
Each time the 8Gb SAN Switch is powered on, its settings are restored to the last saved configuration.
Interpreting LED activity
You can monitor switch activity and status by checking 8Gb SAN Switch LEDs.
There are three possible LED states: no light, a steady light, or a flashing light. The steady lights and
flashing lights can be green or amber.
The LEDs flash any of these colors during boot, POST, or other diagnostic tests. This is normal and
does not indicate a problem unless the LEDs do not indicate a healthy state after all boot processes
and diagnostic tests are complete. A healthy state is indicated by a steady green light. See Table
15, page 37 for details about LED activity.
LED indicators
All 8Gb SAN Switch LEDs are located on the port side. See Figure 8 and Table 14.
Figure 8 Identifying LEDs
.
Table 14 Front panel LED indicators during normal operation
LED indicatorsDescriptionItem Number
Steady blue lightUnit ID (UID) LED1
Steady green lightHealth ID LED2
Steady green lightModule status LED3
Steady green lightPort status LED4
Managing the 8Gb SAN Switch36
Page 37

LED patterns
Table 15 and Table 16 summarize LED color, and meaning, as well as any recommended user
response.
Module status LED patterns
The system and power LED patterns are shown in Table 15.
Table 15 Module Status LED patterns during normal operation
name
Recommended actionStatus of hardwareLED colorLED
No light
Module
Status
Flashing green (on
1 second, off 1
second)
Amber
Port link status LED patterns
Table 16 shows the LED color, meaning, and recommended action.
Table 16 Port link status LED patterns
No light
Switch is off, boot is not complete, or
boot failed.
One or both of the following are true:
• One or more environmental ranges
are exceeded.
• Error log contains one or more port
diagnostic error messages.
Boot-up state, switch is disabled or offline.
No light or signal carrier (transceiver or cable)
detected.
Verify that switch is on and completed
booting.
No action required.Switch is on and functioning.Steady green
Check environmental conditions, error
log, Port Status LEDs, transceivers,
cables, and loopback plugs. Correct
error condition. Clear error log. Rerun
diagnostics to verify fix.
Needs attention.
Recommended actionStatus of hardwareLED colorLED name
Check transceiver and cable.
Port Status
Steady green
Slow-flashing green
(on 1 second, off 1
second)
Fast-flashing green (on
1/2 second, off 1/2
second)
Steady amber
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 37
Port is online (connected to external device)
but has no traffic.
Port is online but segmented, indicating a
loopback cable or incompatible switch.
Port is receiving light or signal carrier, but is
not yet online.
No action required.
Verify that the correct device is connected to
port and that the switch and port settings are
correct.
No action required.Port is in internal loopback (diagnostic).
No action required.Port is online with traffic flowing through port.Flickering green
No action required.
Page 38

Recommended actionStatus of hardwareLED colorLED name
Slow-flashing amber
(on 1 second, off 1
second)
Fast-flashing amber (on
1/2 second, off 1/2
second)
Alternating green and
amber
POST and boot specifications
POST is a system check that is performed each time the switch is powered on, rebooted, or reset.
During POST, the LEDs flash different colors. Any errors that occur during POST are listed in the error
log.
The 8Gb SAN Switch performs POST when it is turned on or rebooted. Total boot time with POST is
approximately three minutes.
POST can be omitted for subsequent reboots by using the fastboot command. For more information
about this command, refer to the latest version of the Fabric OS command reference guide. If you
suspect a problem with the switch, enable POST to obtain more information on any failure.
Port is disabled as a result of diagnostics or
portDisable command. If the LEDs for all
ports are slow-flashing amber, the switch could
be disabled.
Port is faulty.
Enable the port using the portEnable com-
mand; If the LEDs for all ports are slow-flashing
amber, enable the switch by entering the
switchEnable command.
Check the Port Status LEDs, error log, transceiv-
er, and cable or loopback plug. Clear the error
log. Rerun the diagnostics to verify that the er-
ror condition is fixed.
Check configuration of FC loop.Port is bypassed.
POST
Boot
The success/failure results of the diagnostic tests that run during POST can be monitored through the
error log or the command line interface.
POST includes the following steps:
• Preliminary POST diagnostics are run.
• Operating system is initialized.
• Hardware is initialized.
• Diagnostic tests are run on several functions, including circuitry, port functionality, memory, statistics
counters, and serialization.
Boot completes in approximately three minutes if POST is run. Boot includes the following tasks after
POST completes:
• Universal port configuration
• Links initialized
• Fabric is analyzed; if any ports are connected to other switches, the 8Gb SAN Switch participates
in a fabric configuration
• The 8Gb SAN Switch obtains a domain ID and assigns port addresses
• Unicast routing tables constructed
• Normal port operation enabled
Managing the 8Gb SAN Switch38
Page 39

Interpreting POST results
To determine whether POST completed successfully and whether any errors were detected:
1. Verify that the 8Gb SAN Switch LEDs indicate all components are healthy. See Table 16, page
37 for description and interpretation of LED patterns. If one or more LEDs do not display a Healthy
state, use the switchshow command to verify that the LEDs on the switch are not set to “beacon”.
2. Verify that the 8Gb SAN Switch prompt appears on the terminal of a computer workstation
connected to the switch. If there is no switch prompt when POST completes, press Enter. If the
switch prompt still does not appear, try opening another Telnet session or another management
tool. If this is not successful, the 8Gb SAN Switch did not successfully complete POST; contact
HP.
3. Review the switch system log for errors. Any errors detected during POST are written to the system
log, accessible through the errshow command.
For information about all referenced commands and accessing the error log, refer to the latest
version of the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS administrator guide. For information about error
messages, refer to the Fabric OS system error messages reference manual.
Firmware update
To achieve best performance, HP recommends running the latest firmware release. Obtain the most
current Fabric OS firmware, configuration files, and MIB files that support this switch from the following
HP website:
http://www.hp.com/go/8gbswitchforbladesystemc-class
To download firmware from the web to another computer (like an FTP server):
NOTE:
Web retrieval procedures may be subject to change.
1. Go to the Support section, located on the far right side of the web page. Click Software and
Drivers.
2. Locate the Tasks for Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class section.
3. Click Download drivers and software.
a. Select the applicable switch model.
b. Go to the Select Operating System section. Click Cross operating system (BIOS, Firmware,
Diagnostics, etc.)
c. Scroll down to the firmware section of the web page and locate the Firmware table.
d. Locate the latest firmware.
e. Click Download button>> in the last column and follow the prompts in the File Download
dialog box.
4. To download the code from an FTP server to the switch, connect an Ethernet cable from the FTP
server to the iLO RJ45 on the active OA.
5. Telnet to the switch, and issue firmwaredownload at the command line.
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 39
Page 40

About the reset button
The Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch integrates a Reset button, (Figure 9). The Reset button is a small,
recessed micro-switch that is accessed by inserting a pin (or object of similar size) in the small hole.
Use the Reset button to reboot the switch.
Figure 9 Locating the Reset button
.
Table 17 Locating the reset button
DescriptionItem
Port side of switch1
Reset button2
Rebooting the switch
Depress the Reset button for up to 5 seconds to reboot the switch.
Replacing a faulty 8Gb SAN Switch
To replace a faulty switch in the c-Class enclosure:
IMPORTANT:
For supplemental information on any of these steps, refer to the latest
administrator guide
website:
nl
http://www.hp.com/support/manuals
To access the guides, scroll to the storage section of the web page, and select Storage Networking
for HP StorageWorks products.
In addition to these guides, refer to the Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP c Class BladeSystem—Setup,
Configuration and Installation Procedures available on http://www.hp.com for initial installation
instructions of the new switch.
and
Fabric OS Advanced Web Tools administrator guide
HP StorageWorks Fabric OS
, available at the HP
Managing the 8Gb SAN Switch40
Page 41

1. Create a backup of the existing configuration file.
NOTE:
It is critical to back up the switch configuration to a remote server on a regular basis. Repeat
for each switch in your SAN whenever configuration changes occur. Configuration backups
can be done with the CLI, integrated Web Tools GUI, or the optional Fabric Manager GUI.
2. Locate the faulty switch.
3. Disconnect all external Fibre Channel cables.
4. Remove the faulty 8Gb SAN Switch from the enclosure.
5. Insert the replacement switch into the enclosure.
6. Log in to the Onboard Administrator CLI.
7. Connect to the switch console, enter:
connect interconnect <bay number>
8. Change the password when prompted by the switch.
9. To restore the configuration, you must disable the switch with the CLI, the integrated Web Tools
GUI, or the optional Fabric Manager GUI.
NOTE:
If using the CLI, enter switchDisable at the prompt. Refer to the
guide
for additional command information.
10. Continue with the switch configuration. Enter the appropriate information when prompted. Make
sure that the data entered matches the settings on the faulty switch.
11. Install the same Fabric OS version as the faulty switch using the CLI command
firmwareDownload, the integrated Web Tools GUI, or the optional Fabric Manager GUI.
12. Verify that the appropriate licenses are installed on the replacement switch.
13. Save the switch configuration file after making your edits; enter:
configupload
14. Restore the switch configuration from the remote server using the backup configuration file from
step 1.
15. Enable the switch. Use the CLI command switchenable, the integrated Web Tools GUI or the
optional Fabric Manager GUI.
16. Connect all external FC cables in the same port locations as before. To connect to the external
switch ports without connectivity to external devices, the external switch port must be disabled
prior to inserting the cable and then re enabled after inserting the cable to establish connectivity.
17. Verify that the switch is joined to the fabric and all connected devices log in to the switch; enter:
Fabric OS command reference
switchshow
18. Save the configuration file.
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 41
Page 42

IMPORTANT:
HP recommends upgrading all switches in the enclosure to the latest available firmware. Check
http://www.hp.com for updates.
Managing the 8Gb SAN Switch42
Page 43

A Regulatory compliance and safety
Regulatory compliance
Federal Communications Commission notice for Class A equipment
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case
the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense. The end user of this product
should be aware that any changes or modifications made to this equipment without the approval of
Hewlett-Packard could result in the product not meeting the Class A limits, in which case the FCC
could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
Modifications
The FCC requires the user to be notified that any changes or modifications made to this device that
are not expressly approved by Hewlett-Packard Company my void the user's authority to operate the
equipment.
Cables
Connections to this device must be made with shielded cables with metallic RFI/EMI connector hoods
in order to maintain compliance with FCC Rules and Regulations.
Regulatory compliance identification numbers
For the purpose of regulatory compliance certifications and identification, your product has been
assigned a unique Regulatory Model Number. The RMN can be found on the product nameplate
label, along with all required approval markings and information. When requesting compliance
information for this product, always refer to this RMN. The Regulatory Model Number should not be
confused with the marketing name or model number of the product.
Laser device compliance
The fiber optic transceiver contains a laser that is classified as a “Class 1 Laser Product” in accordance
with US FDA regulations and the IEC 60825-1. The product does not emit hazardous laser radiation.
This laser product complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 except for editions pursuant to Laser
Notice No. 50, dated May 27, 2001; and with IEC 60825-1:1993/A2:2001.
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 43
Page 44

WARNING!
Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified herein or in
the laser product’s installation guide may result in hazardous radiation exposure. To reduce the risk
of exposure to hazardous radiation:
• Do not try to open the laser device enclosure. There are no user-serviceable components inside.
• Do not operate controls, make adjustments, or perform procedures to the laser device other than
those specified herein.
• Allow only HP authorized service technicians to repair the laser device.
Certification and classification information
This product contains a laser internal to the fiber optic (FO) transceiver for connection to the Fibre
Channel communications port.
In the USA, the FO transceiver is certified as a Class 1 laser product conforming to the requirements
contained in the Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) regulation 21 CFR, Subchapter
J. A label on the plastic FO transceiver housing indicates the certification.
Outside the USA, the FO transceiver is certified as a Class 1 laser product conforming to the
requirements contained in IEC 825–1:1993 and EN 60825–1:1994, including Amendment 11:1996
and Amendment 2:2001.
Laser product label
The optional label in Figure 10 or equivalent may be located on the surface of the HP supplied laser
device.
Figure 10 Class 1 laser product label
.
This optional label indicates that the product is classified as a CLASS 1 LASER PRODUCT. This label
may appear on the laser device installed in your product.
International notices and statements
Canadian notice (avis Canadien)
Class A equipment
This Class A Digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment
Regulations.
Regulatory compliance and safety44
Page 45

Cet appareil numérique de la classe A respecte toutes les exigences du Règlement sur le matériel
brouilleur du Canada.
European union regulatory notice
BSMI notice
Japanese notice
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 45
Page 46

Korean notice
Safety
Battery replacement notice
Your switch is equipped with a lithium manganese dioxide, a vanadium pentoxide, or an alkaline
internal battery or battery pack. There is a danger of explosion and risk of personal injury if the battery
is incorrectly replaced or mistreated. Replacement is to be done by an HP authorized service provider
using the HP spare part designated for this product. For more information about battery replacement
or proper disposal, contact an HP authorized service provider.
WARNING!
Your switch contains an internal lithium manganese dioxide, a vanadium pentoxide, or an alkaline
battery pack. There is risk of fire and burns if the battery pack is not properly handled. To reduce the
risk of personal injury:
• Do not attempt to recharge the battery.
• Do not expose to temperatures higher than 60 ºC.
• Do not disassemble, crush, puncture, short external contacts, or dispose of in fire or water.
• Replace only with the HP spare part designated for this product.
Batteries, battery packs, and accumulators should not be disposed of together with the general
household waste. To forward them to recycling or proper disposal, please use the public collection
system or return them to HP, an authorized HP Partner, or their agents.
For more information about battery replacement or proper disposal, contact an HP authorized reseller
or service provider.
Regulatory compliance and safety46
Page 47

Taiwan battery recycling notice
The Taiwan EPA requires dry battery manufacturing or importing firms in accordance with Article 15
of the Waste Disposal Act to indicate the recovery marks on the batteries used in sales, giveaway,
or promotion. Contact a qualified Taiwanese recycler for proper battery disposal.
Power cords
The power cord set must meet the requirements for use in the country where the product was purchased.
If the product is to be used in another country, purchase a power cord that is approved for use in that
country.
The power cord must be rated for the product and for the voltage and current marked on the product
electrical ratings label. The voltage and current rating of the cord should be greater than the voltage
and current rating marked on the product. In addition, the diameter of the wire must be a minimum
of 1.00 mm2or 18 AWG, and the length of the cord must be between 1.8 m (6 ft) and 3.6 m (12
ft). If you have questions about the type of power cord to use, contact an HP authorized service
provider.
NOTE:
Route power cords so that they will not be walked on and cannot be pinched by items placed upon
or against them. Pay particular attention to the plug, electrical outlet, and the point where the cords
exit from the product.
Japanese power cord statement
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 47
Page 48

Regulatory compliance and safety48
Page 49

B Electrostatic discharge
This appendix provides the following information:
• How to prevent electrostatic discharge, page 49
• Grounding methods, page 49
How to prevent electrostatic discharge
To prevent damage to the system, you must follow certain precautions when setting up the system or
handling parts. A discharge of static electricity from a finger or other conductor may damage system
boards or other static-sensitive devices. This type of damage may reduce the life expectancy of the
device.
To prevent electrostatic damage, observe the following precautions:
• Avoid hand contact by transporting and storing products in static-safe containers.
• Keep electrostatic-sensitive parts in their containers until they arrive at static-free workstations.
• Place parts on a grounded surface before removing them from their containers.
• Avoid touching pins, leads, or circuitry.
• Always make sure you are properly grounded when touching a static-sensitive component or as-
sembly.
Grounding methods
There are several methods for grounding. Use one or more of the following methods when handling
or installing electrostatic-sensitive parts:
• Use a wrist strap connected by a ground cord to a grounded workstation or chassis. Wrist straps
are flexible straps with a minimum of 1 megohm ± 10 percent resistance in the ground cords. To
provide proper ground, wear the strap snug against the skin.
• Use heel straps, toe straps, or boot straps at standing workstations. Wear the straps on both feet
when standing on conductive floors or static-dissipating floor mats.
• Use conductive field service tools.
• Use a portable field service kit with a folding static-dissipating work mat.
If you do not have any of the suggested equipment for proper grounding, have an HP authorized
reseller install the part.
NOTE:
For more information on static electricity, or for assistance with product installation, contact your HP
authorized reseller.
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 49
Page 50

Electrostatic discharge50
Page 51

C SAN Switch technical specifications
This appendix provides the following information:
• General specifications, page 51
• Weight and physical dimensions, page 52
• Environmental requirements, page 53
• Supported SFPs, page 53
• Supported HBAs, page 53
General specifications
Table 18 lists general specifications for the 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class.
Table 18 General specifications
DescriptionSpecification
Configurable port types
Media types
EMC emissions
F_Port, FL_Port, and E_Port
Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) laser. 1/2/4/8Gb short
wave up to 500 m (1,640 ft.) and 1/2/4/8Gb long wave
up to 10 km
Note: 4Gb SFPs support 1/2/4 Gbps, and the 8Gb SFPs
support 2/4/8 Gbps.
An operating SAN Switch conforms to the emissions
requirements specified by the following regulations:
• FCC Rules and Regulations, Part 15 subpart B, Class A
• CSA C108.8 Class A
• VCCI Class A ITE
• CISPR 22 Class A
• EN55022 Class A
• AS/NZF 3548: 1995 Class A
• CNS13438 Class A
• ICES-003 Class A
• Korean EMC Requirements
• BSMI Standard CNS 13438
• EMC Directive 89/336/EEC
• EN5022 Level A
• EN50082-2/EN55024: 1998
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 51
Page 52

EMC immunity
DescriptionSpecification
• IEC 61000-4-2 Severity Level 3 for Electrostatic Discharge
• IEC 61000-4-3 Severity Level 3 for Radiated Fields
• IEC 61000-4-4 Severity Level 3 for Fast Transients
• IEC 61000-4-5 Severity Level 3 for Surge Voltage
• IEC 61000-4-6 Conducted Emissions
• IEC 61000-4-11 Voltage Variations
• EN 61000-4-12 Oscillatory Waves Immunity
• EN 61000-3-2 Limits for Harmonic Current Emissions
• EN 61000-3-3 JEIDA
System architecture
ANSI protocol
Modes of operation
Maximum frame size
Port-to-port latency
Nonblocking shared-memory switch
FC-PH (FC Physical and Signalling Interface standard)
FC Class 2, Class 3, and Class F
2112-byte
Less than 2 microseconds with no contention (destination port
is free)
Weight and physical dimensions
nl
Table 19 lists physical properties.
Table 19 8Gb SAN Switch physical dimensions
MeasurementDimension
Height
Width
Depth
29.3 mm (1.15 in)
208 mm (8.19 in)
280 mm (11.02 in)
Weight
1.27 kg (2.8 lb)
SAN Switch technical specifications52
Page 53

Environmental requirements
To ensure proper operation, the switch must not be subjected to environmental conditions beyond
those for which it was tested. The ranges specified in Table 20 list the acceptable environment for
both operating and nonoperating conditions.
Table 20 Environmental requirements
Ambient temperature
Humidity
Supported SFPs
Do not use unsupported SFPs. They may not fit correctly and may void your warranty. Any port with
an unsupported SFP will automatically be disabled by switch firmware, leaving the port non-operational.
See Supported SFP transceiver options, page 17 for a list of supported SFPs.
For a complete list of supported devices, refer to the latest version of the HP StorageWorks SAN
design reference guide at the HP website:
nl
http://h18000.www1.hp.com/products/storageworks/san/documentation.html.
Acceptable range during operationCondition
104°F/40 °C at sea level, derated 1 C
per 1000 ft above sea level
5% to 90% relative humidity, non-condensing
Acceptable range during non-operation
-40°C to 70°C with maximum rate of
change of 20 C /hr
50% to 80% relative humidity, noncondensing
0 to 40,000 ft (12 km) above sea level0 to 10,000 ft (3 km) above sea levelAltitude
140 G, 2mS,40 G, 2mS durationShock
2.0 G, 5–500 Hz0.5 G, 10–500 HzVibration
None required47 cubic ft/minuteAirflow
Supported HBAs
For a list of HBAs that have been tested and are known to work with the SAN switches, refer to the
latest version of the HP StorageWorks SAN design reference guide at the HP website:
nl
http://h18000.www1.hp.com/products/storageworks/san/documentation.html.
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 53
Page 54

SAN Switch technical specifications54
Page 55

Glossary
This glossary defines terms used in this guide or related to this product. It is not a comprehensive
glossary of computer terms.
AL_PA Arbitrated loop physical address. A unique 8-bit value assigned during loop
alias server A fabric software facility that supports multicast group management.
API Application programming interface. A defined protocol that allows applications
arbitrated loop A shared 100 Mb/s Fibre Channel transport structured as a loop. Supports up
AW_TOV Arbitration wait time-out value. The minimum time an arbitrating L_Port waits for
backup FCS switch Backup fabric configuration server switch. The switch or switches assigned as
bandwidth The total transmission capacity of a cable, link, or system. Usually measured in
initialization to a port in an arbitrated loop. See also non-participating mode.
to interface with a set of services.
to 126 devices and one fabric attachment. See also public device, public loop.
a response before beginning loop initialization.
backup in case the primary FCS switch fails.
bits per second (b/s). May also refer to the range of transmission frequencies
available to a link or system.
broadcast The transmission of data from a single source to all devices in the fabric,
regardless of zoning.
buffer-to-buffer
flow control
CLI Command line interface. Interface that depends entirely on the use of commands,
compact flash Flash (temporary) memory that is used in a manner similar to hard disk storage.
configuration The way a system is set up. May refer to hardware or software:
CRC Cyclic redundancy check. A check for transmission errors that is included in
Management of the frame transmission rate in either a point-to-point topology
or an arbitrated loop. See also arbitrated loop, point-to-point, topology.
such as through Telnet or SNMP, and does not involve a GUI.
It is connected to a bridging component that connects to the PCI bus of the
processor. Not visible within the processor's memory space.
• Hardware: The number, type, and arrangement of components that make up
a system or network.
• Software: The set of parameters that guide switch operation. May include
general system parameters, IP address information, domain ID, and other
information. Modifiable by any login with administrative privileges. May also
refer to a set of zones.
every data frame.
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 55
Page 56

data word A type of transmission word that occurs within frames. The frame header, data
field, and CRC all consist of data words.
defined zone
configuration
The set of all zone objects defined in the fabric. May include multiple zone
configurations. See also zone, zone configuration.
directory service See SNS.
DLS Dynamic load sharing. Dynamic distribution of traffic over available paths. Allows
for recomputing of routes when an Fx_Port or E_Port changes status.
domain ID Unique identifier used in routing frames for all switches in a fabric. Usually
assigned by the principal switch, but can be assigned manually. The domain ID
for an HP switch can be any integer between 1 and 239. The default domain
ID is usually 1.
E_D_TOV Error-detect time-out value. The minimum time a target waits for a sequence to
complete before initiating recovery. Can also be defined as the maximum time
allowed for a round-trip transmission before an error condition is declared.
E_Port Expansion port. A type of switch port that can be connected to an E_Port on
another switch to create an ISL. See also ISL trunking, U_Port.
EE_Credit End-to-end credit. The number of receive buffers allocated by a recipient port to
an originating port. Used by Class 1 and Class 2 services to manage the
exchange of frames across the fabric between source and destination.
EIA rack A storage rack that meets the standards set by the Electronics Industry Association
(EIA).
enabled zone
configuration
end-to-end flow
The currently enabled configuration of zones. Only one configuration can be
enabled at a time. See also zone, zone configuration.
A facility that governs flow of class 1 and class 2 frames between N_Ports.
control
error With respect to FC, a missing or corrupted frame, time-out, loss of
synchronization, or loss of signal (link error).
exchange The highest-level FC mechanism used for communication between N_Ports.
Composed of one or more related sequences; can work in one or both directions.
F_Port Fabric port. A port that is able to transmit under fabric protocol and interface
over links. Can be used to connect an N_Port to a switch. See also U_Port.
fabric An FC network containing two or more switches in addition to hosts and devices.
May also be called a switched fabric.
fabric name The unique identifier assigned to a fabric and communicated during login and
port discovery.
FCIA Fibre Channel Industry Association. An international organization of FC industry
professionals. Among other things, provides oversight of ANSI and industry
standards.
FCP Fibre Channel Protocol. Mapping of protocols onto the FC standard protocols.
For example, SCSI FCP maps SCSI-3 onto FC.
Glossary56
Page 57

FCS switch Fabric Configuration Server switch. One or more designated HP switches that
store and manage the configuration and security parameters for all switches in
the fabric.
Fibre Channel The primary protocol for building SANs to transmit data between servers,
switches, and storage devices. Unlike IP and Ethernet, Fibre Channel is designed
to support the needs of storage devices of all types. It is a high-speed, serial,
bidirectional, topology-independent protocol, and is a highly scalable
interconnection between computers, peripherals, and networks.
fill word An IDLE or ARB ordered set that is transmitted during breaks between data frames
to keep the link active.
FLOGI The process by which an N_Port determines whether a fabric is present and, if
so, exchanges service parameters with it. See also PLOGI.
FL_Port Fabric loop port. A port that is able to transmit under fabric protocol and has
arbitrated loop capabilities. Can also be used to connect an NL_Port to a switch.
See also U_Port.
frame The Fibre Channel structure used to transmit data between ports. Consists of a
start-of-frame delimiter, header, optional headers, data payload, cyclic
redundancy check, and end-of-frame delimiter. There are two types of frames:
link control frames and data frames. See also packet.
FRU Field-replaceable unit. A component that can be replaced on site.
FS Fibre Channel Service. A service that is defined by FC standards and exists at
a well-known address. The Simple Name Server, for example, is an FC service.
FSP Fibre Channel Service Protocol. The common protocol for all fabric services; it
is transparent to the fabric type or topology.
FSPF Fabric shortest path first. HP routing protocol for FC switches.
Fx_Port A fabric port that can operate as an F_Port or FL_Port.
G_Port Generic port. A port that can operate as an E_Port or F_Port. A port is defined
as a G_Port when it is not yet connected or has not yet assumed a specific
function in the fabric. See also E_port, F_port, U_Port.
hard address The AL_PA that an NL_Port attempts to acquire during loop initialization. See
also defined zone configuration.
idle Continuous transmission of an ordered set over an FC link when no data is being
transmitted, to keep the link active and maintain bit, byte, and word
synchronization.
integrated fabric The fabric created by connecting multiple HP switches with multiple ISL cables,
and configuring the switches to handle traffic as a seamless group.
ISL trunking The distribution of traffic over the combined bandwidth of multiple ISLs. A set of
trunked ISLs is called a trunking group; the ports in a trunking group are called
trunking ports.
isolated E_Port An E_Port that is online but not operational due to overlapping domain IDs or
nonidentical parameters (such as E_D_TOVs). See also E_D_TOV.
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 57
Page 58

K28.5 A special 10-bit character that indicates the beginning of a transmission word
that performs FC control and signaling functions. The first seven bits are the
common pattern.
kernel flash Flash (temporary) memory connected to the peripheral bus of the processor and
visible within the processor's memory space. Also called a user flash.
L_Port Loop port. A node port (NL_Port) or fabric port (FL_Port) that has arbitrated loop
capabilities. An L_Port can be in one of two modes:
• Fabric mode: Connected to a port that is not loop capable and is using fabric
protocol.
• Loop mode: In an arbitrated loop and using loop protocol. An L_Port in loop
mode can also be in participating mode or non-participating mode.
See also non-participating mode.
latency The time required to transmit a frame from the time it is sent until it arrives.
Together, latency and bandwidth define the speed and capacity of a link or
system.
link With respect to FC, a physical connection between two ports, consisting of both
transmit and receive fibers.
link services A protocol for link-related actions.
LIP Loop initialization primitive. The signal that begins initialization in a loop. It
indicates either loop failure or the resetting of a node.
LM_TOV Loop master time-out value. The minimum time that the loop master waits for a
loop initialization sequence to return.
loop failure Loss of signal within a loop for any period of time; loss of synchronization for
longer than the time-out value.
Loop_ID A hexadecimal value representing one of the 127 possible AL_PA values in an
arbitrated loop. See also AL_PA.
loop initialization The logical procedure used by an L_Port to discover its environment. Can be
used to assign AL_PA addresses, detect loop failure, or reset a node. See also
AL_PA.
LPSM Loop port state machine. The logical entity that performs arbitrated loop protocols
and defines the behavior of L_Ports when they require access to an arbitrated
loop. See also L_Port.
LWL Long wavelength. A type of fiber optic cabling that is based on 1300 mm lasers
and supports link speeds up to 2 Gb/s. May also refer to the type of transceiver.
See also SWL.
master port The port that determines the routing paths for all traffic flowing through a trunking
group. One of the ports in the first ISL in the trunking group is designated as the
master port for that group. See also ISL trunking.
MIB Management Information Base. An SNMP structure to help with device
management, providing configuration and device information. See also SNMP.
Glossary58
Page 59

multicast The transmission of data from a single source to multiple specified N_Ports (as
opposed to all ports on the network).
N_Port Node port. A port on a node that can connect to an FC port or to another N_Port
in a point-to-point connection.
name server A term frequently used to indicate a Simple Name Server (SNS). See also SNS.
NL_Port Node loop port. A node port that has arbitrated loop capabilities. Used to
connect an equipment port to the fabric in a loop configuration through an
FL_Port. See also node.
node An FC device that contains an N_Port or NL_Port.
non-participating
mode
Nx_Port A node port that can operate as an N_Port or NL_Port.
Onboard
Administrator (OA)
packet A set of information transmitted across a network.
participating mode A mode in which an L_Port in a loop has a valid AL_PA and can arbitrate, send
path selection The selection of a transmission path through the fabric. HP switches use the FSPF
phantom address An AL_PA value assigned to a device that is not physically in the loop. Also
phantom device A device that is not physically in an arbitrated loop but is logically included
A mode in which an L_Port in a loop is inactive and cannot arbitrate or send
frames, but can retransmit any received transmissions. This mode is entered if
there are more than 127 devices in a loop and an AL_PA cannot be acquired.
See also L_Port, AL_PA.
The HP BladeSystem Onboard Administrator (OA) is the enclosure management
processor, subsystem, and firmware base used to support the HP BladeSystem
c7000 or HP BladeSystem c3000 and all the managed devices contained within
the enclosure.
frames, and retransmit received transmissions.
protocol for transmission path selection.
known as phantom AL_PA. See also AL_PA, phantom device.
through the use of a phantom address. See also phantom address.
PLOGI Port login. The port-to-port login process by which initiators establish sessions
with targets. See also FLOGI.
point-to-point An FC topology that employs direct links between each pair of communicating
entities. See also buffer-to-buffer flow control.
port cage The metal casing extending out of the FC port on the switch and into which a
GBIC or SFP transceiver can be inserted.
Port_Name The unique identifier assigned to an FC port. It is communicated during login
and port discovery.
POST Power-on self-test. A series of diagnostic tests run by a switch after it is powered
on.
primary FCS switch Primary Fabric Configuration Server switch. The switch that actively manages
the configuration and security parameters for all switches in the fabric.
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 59
Page 60

private loop An arbitrated loop that does not include a participating FL_Port.
private NL_Port An NL_Port that communicates only with other private NL_Ports in the same loop
and does not log in to the fabric.
public device A device that supports arbitrated loop protocol, can interpret 8-bit addresses,
and can log in to the fabric. See also arbitrated loop.
public loop An arbitrated loop that includes a participating FL_Port and may contain both
public and private NL_Ports. See also arbitrated loop.
public NL_Port An NL_Port that logs in to the fabric, can function within a public or private loop,
and can communicate with private or public NL_Ports. See also private loop.
quad A group of four adjacent ports that share a common pool of frame buffers.
R_A_TOV Resource allocation time-out value. The maximum time a frame can be delayed
in the fabric and still be delivered.
RAID Redundant Array of Independent Disks. A collection of disk drives that appear
as a single volume to the server and are fault tolerant through mirroring or parity
checking.
request rate The rate at which requests arrive at a servicing entity.
route With respect to a fabric, the communication path between two switches. May
also apply to the specific path taken by an individual frame from source to
destination.
routing The assignment of frames to specific switch ports according to frame destination.
RR_TOV Resource recovery time-out value. The minimum time a target device in a loop
waits after a LIP before logging out a SCSI initiator.
RSCN Registered state change notification. A switch function that allows notification of
fabric changes to be sent from the switch to the specified nodes.
SAN Storage area network. A network of systems and storage devices that
communicate using FC protocols.
SDRAM Synchronous dynamic random access memory. The main memory for a switch.
See also switch.
sequence A group of related frames transmitted in the same direction between two N_ports.
service rate The rate at which an entity can service requests.
single mode The fiber optic cabling standard that corresponds to distances up to 10 km
between devices.
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol. An Internet management protocol that
uses either IP for network-level functions and UDP for transport functions, or TCP/IP
for both. SNMP can be made available over other protocols (such as UDP/IP)
because it does not rely on the underlying communication protocols. See also
MIB, trap (SNMP).
Glossary60
Page 61

SNS Simple Name Server. A switch service that stores names, addresses, and attributes
for up to 15 minutes, and provides them as required to other devices in the fabric.
May also be referred to as a directory service.
switch Hardware that routes frames according to FC protocol and is controlled by
software.
switch port A port on a switch. Switch ports can be E_Ports, F_Ports, or FL_Ports.
SWL short-wavelength. A type of fiber optic cabling that is based on 850 mm lasers
and supports link speeds up to 2 Gb/s. May also refer to the type of transceiver.
tenancy The time span that begins when a port wins arbitration in a loop and ends when
the same port returns to the monitoring state. Also called loop tenancy.
throughput The rate of data flow achieved within a cable, link, or system. Usually measured
in bits per second (b/s).
topology With respect to FC, the configuration of the FC network and the resulting
communication paths allowed. There are three possible topologies:
• Point-to-point: A direct link between two communication ports
• Switched fabric: Multiple N_Ports linked to a switch by F_Ports
• Arbitrated loop: Multiple NL_Ports connected in a loop
transmission
character
transmission word A group of transmission characters.
trap (SNMP) The message sent by an SNMP agent to inform the SNMP management station
U_Port Universal port. A switch port that can operate as a G_Port, E_Port, F_Port, or
well-known
address
workstation A computer used to access and manage the fabric. May also be called a
WWN World wide name. An identifier that is unique worldwide. Each entity in a fabric
zone A set of devices and hosts attached to the same fabric and configured as being
A 10-bit character encoded according to the rules of the 8b/10b algorithm.
of a critical error. See also SNMP.
FL_Port. A port is defined as a U_Port when it is not connected or has not yet
assumed a specific function in the fabric. See also E_port, F_port, G_Port.
With respect to FC, a logical address defined by the FC standards as assigned
to a specific function and stored on the switch.
management station or host.
has a distinct WWN.
in the same zone. Devices and hosts within the same zone have access permission
to others in the zone, but are not visible to any outside the zone. See also defined
zone configuration, enabled zone configuration.
zone configuration A specified set of zones. Enabling a configuration enables all zones in that
configuration. See also defined zone configuration, enabled zone configuration.
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 61
Page 62

Glossary62
Page 63

Index
A
advanced web tools, 33
advanced zoning, 17
audience, 9
B
boot, 38
boot specifications, 38
C
command line interface, 33
conventions
document, 10
text symbols, 11
D
diagnostics, 35
document
conventions, 10
related documentation, 9
documentation
providing feedback, 12
grounding methods, 49
H
HBAs, supported, 53
help
obtaining, 9
HP
storage website, 11
Subscriber's choice website, 11
technical support, 9
I
IP address, 20, 25
ISL
trunking groups, 16
L
LED
interpreting activity, 36
location, 36
patterns, 37
LED patterns, 37
licenseshow, 27
long wavelength, see LWL, 13
E
EIA, 20
environmental requirements, 53
Ethernet connection, 26
F
fabric license
full, 16
fabric license
base, 15
Power Pack, 16
fabric licenses, 15
Fibre Channel
FC domain ID, 27
G
general specifications, 51
M
management station, 34
P
port
configurable types, 13
speed, 13
port LED patterns, 37
POST, 38
POST results, 39
POST specifications, 38
Power Pack, 16
R
related documentation, 9
Brocade 8Gb SAN Switch for HP BladeSystem c-Class 63
Page 64

S
SAN Switch
configuration, 25
installing, 20
licensing, 15
maintenance, 34
management features, 33
port diagram, 14
power, 36
SFP transceiver, 25
removing, 34
SFP transceivers
supported, 53
shipping carton contents, 19
SNMP applications, 33
specifications
environmental requirements, 53
general, 51
physical, 52
Subscriber's choice, HP, 11
supported HBAs, 53
supported sfp options, 17
supported SFPs, 53
symbols in text, 11
T
technical support
HP, 9
text symbols, 11
transceiver, 13, 14, 25, 35, 37, 38
W
web tools, 17
websites
HP documentation, 11
HP storage, 11
HP Subscriber's choice, 11
64
 Loading...
Loading...