Page 1
QuickSpecs
HPE 6125G/XG Ethernet Blade Switch
Overview
Page 1
HPE 6125G/XG Ethernet Blade Switch
The innovative features of
6125G/XG brings the resiliency of IRF (intelligent Resilient Networking) stacking and the stability o
to the c
link port, the
enclosure, rack or datacenter level into a single virtual switch, and managed through a single IP address. Comware OS provide
common level of features, service and security levels from edge to core. And all network ele
(Intelligent Management Center) providing comprehensive single pane provisioning of the entire network. Truly versatile, the
6125G/XG supports IPv6, full layer 3 routing and distributed trunking. If you're looking for a
protection, flexibility, and scalability for mixed bandwidth applications, the 6125G/XG is the optimal choice for any data center.
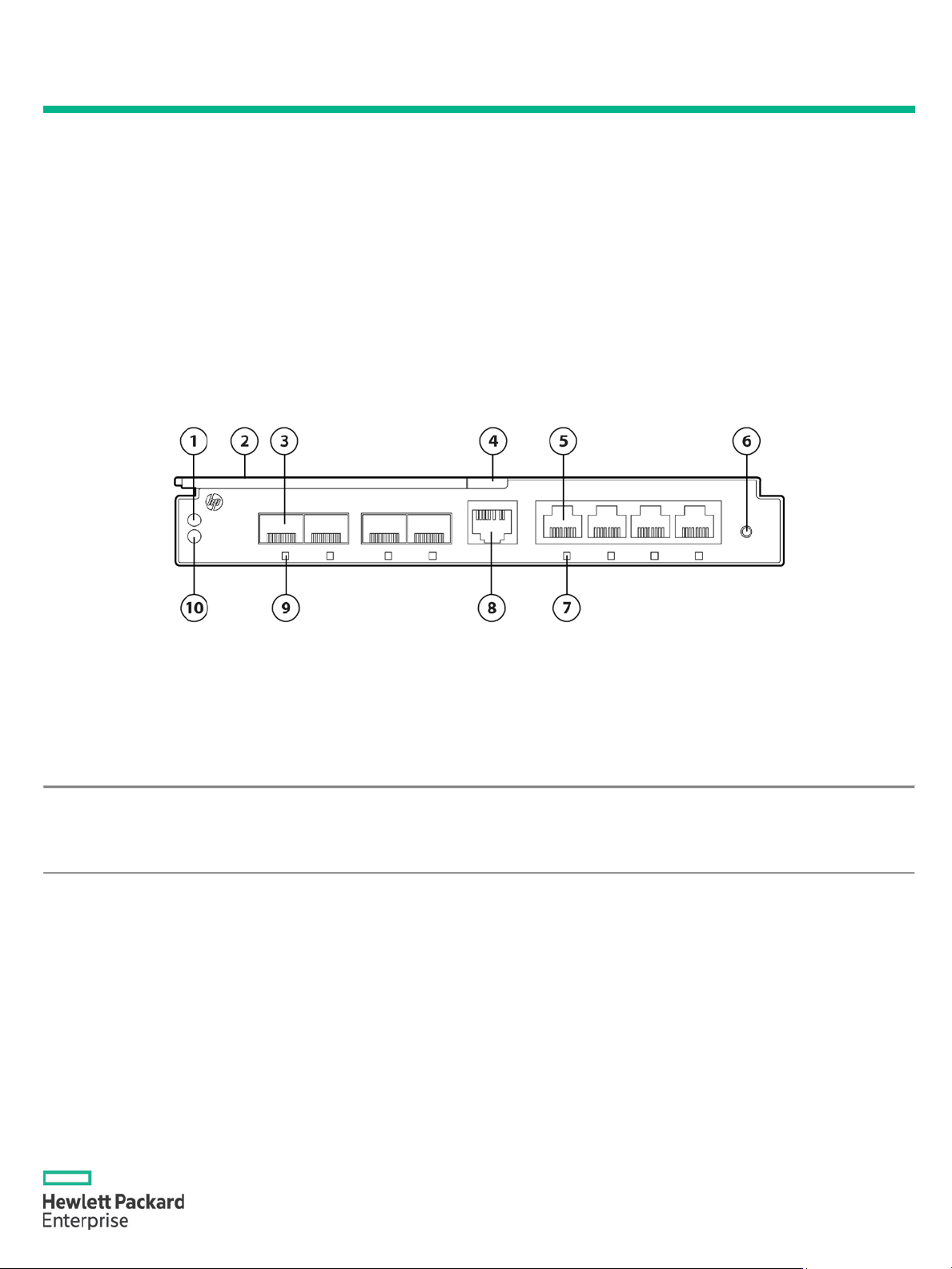
Figure 1 HPE 6125G/XG Blade Switch
1. Unit ID (UID) LED
6. Reset button
2. Ejector lever
7. 10/100/1000Base-T Ethernet port LED
3. SFP+ port
8. Console port
4. Release tab
9. SFP+ port LED
5. 10/100/1000Base
10. Health LED
Models
HPE
B21
HPE
B21
Compatibility
HPE
Servers
HPE
HPE
HPE
HPE
HPE
HPE ProLiant BL460c Gen9
HPE
HPE
HPE
HPE ProLiant BL460c G5
HPE Networking products are now available in a hybrid 1Gb/10Gb blade switch format. The HPE
f the Comware operating system
-Class BladeSystem. With sixteen 1Gb downlink (server) ports, a combination of 1Gb and 10Gb uplink ports, and a 10Gb crossHPE 6125G/XG reduces cost, while increasing datacenter efficiency and capability. Switches can be combined at the
s a
ments can be managed through IMC
HPE
switch that delivers excellent investment
-T auto-sensing Ethernet port
6125G/XG Ethernet Blade Switch 658250-
6125G/XG Ethernet Blade Switch with TAA 737226-
ProLiant
ProLiant BL2x220c G7
ProLiant BL2x220c G5
ProLiant BL260c G5
ProLiant BL280c G6
ProLiant Bl420c Gen8
ProLiant BL460c Gen8
ProLiant BL460c G7
ProLiant BL460c G6
Page 2

QuickSpecs
HPE 6125G/XG Ethernet Blade Switch
Overview
Page 2
HPE
HPE
HPE
HPE
HPE
HPE ProLiant BL465c
HPE
HPE
HPE
HPE
HPE
HPE
HPE
HPE ProLiant BL620c G7
HPE
HPE
HPE
HPE ProLiant BL685 G6
HPE
HPE
HPE
HPE
NOTE:
HPE
Servers
HPE
HPE
HPE Integrity BL860c i4 Server Blade
HPE
HPE
HPE
HPE Integrity BL890c i2 Server Blade
HPE
NOTE: Some servers listed above may be discontinued.
ProLiant BL cClass
Server Blade
Enclosures
HPE
HPE
ProLiant BL460c
ProLiant BL465c Gen8
ProLiant BL465c G7
ProLiant BL465 G6
ProLiant BL465 G5
ProLiant BL480c
ProLiant BL490c G7
ProLiant BL490c G6
ProLiant BL495c G6
ProLiant BL495c G5
ProLiant BL660c Gen8
ProLiant BL660c Gen9
ProLiant BL680c G5
ProLiant BL680c G7
ProLiant BL685c G7
Integrity
ProLiant BL685 G5
ProLiant BL685c
ProLiant WS460c Gen8
ProLiant WS460c Gen9
Some servers listed above may be discontinued.
Integrity BL860c Server Blade
Integrity BL860c i2 Server Blade
Integrity BL870c Server Blade
Integrity BL870c i2 Server Blade
Integrity BL870c i4 Server Blade
Integrity BL890c i4 Server Blade
BladeSystem c3000 Enclosure
BladeSystem c7000 Enclosure
Page 3

QuickSpecs
HPE 6125G/XG Ethernet Blade Switch
Standard Features
Page 3
Standard Features
Performance
Management
Management
Layer 2 Switching
• Non blocking architecture
• Wire speed switching and IPv4/IPv6 routing on all ports
• Separate 10Gb Internal cross connect between switches
• Combine up to 10 switches into a single virtual switch
• RJ45 ports support 1Gb
• SFP+ ports support either 1Gb or10Gb depending on module inserted
• Any SFP+ port can be used for IRF connections
• Mix any combination of HPE 6125G and HP6125G/XG in a single IRF domain
• Store and Forward Switching
• Hardware-based wire-speed access control lists (ACLs)
• Remote configuration and management through Web browser or CLI
• Secure Web-based management through HTTPS
• Standards based SNMP management via SNMPv1, v2c and v3
• OOBM via Onboard Administrator
• GUI Management via Intelligent Management Center
• RJ45 console port
• sFlow and RMON network monitoring
• Manager and operator privilege levels
• Command authorization via RADIUS
• Complete session logging for problem resolution
• LLDP Discovery protocol
• IPv6 management
• Dual flash images
• Multiple configuration files
• Syslog
• Network Time Protocol (NTP)
• IEEE 802.1X user authentication
• MAC-based authentication with RADIUS server
• Access Control Lists (ACLs)
• Secure FTP
• STP Root Guard
• DHCP Protection from unauthorized DHCP servers
• IP Source Guard
• Dynamic ARP protection to prevent eavesdropping
• Guest VLAN
• Endpoint Admission Defense (EAD)
• RADIUS/TACACS+
• Secure management via SSHv2 and SNMPv3
• Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding (URPF)
• 32K MAC addresses
•
4094 VLANs
Page 4

QuickSpecs
HPE 6125G/XG Ethernet Blade Switch
Standard Features
Page 4
Layer 3 Routing
•
Quality of Service
(QoS)
•
Resiliency and
Hig
Creates virtual resilient switching fabrics, where two or more switches
Monitoring and
Diagnostics
Security
• FIPS 140-2
h Availability
• IEEE 802.1ad QinQ VLANs
• Jumbo packet support
• GVRP VLAN Registration Protocol
• Port Aggregation
• Spanning Tree Protocol, PVST, MSTP, RSTP, STP Root Guard
• Smart Link fast uplink failure recovery
• IP Multicast Snooping and data-driven IGMP
• Policy Based Routing
IPv4 routing protocols - static routes, RIP, OSPF and BGP
• IPv6 routing protocols - static routes, RIPng, OSPFv3 and BGP+
• IPv6 tunneling
• IP Multicast - PIM-SSM, PIM-DM, PIM-SM, IGMP for IPv4 and IPv6
• Equal-Cost Multipath (ECMP)
• Policy-based routing
• DHCP and DHCPv6 client
• VRRP
Advanced classifier-based QoS - classifies traffic using multiple match criteria based on Layer 2, 3 and
4 information; applies QoS policies such as priority level and rate limit to selected traffic on a per-port
or per-VLAN basis
• Traffic policing - supports Committed Access Rate (CAR) and line rate
• Powerful QoS feature - creates traffic classes based on access control lists (ACL), IEEE 802.1p
precedence, IP, DSCP or Type of Service (ToS) precedence; supports filter, redirect, mirror or remark;
supports the following congestion actions: strict priority (SP) queuing, weighted round robin (WRR),
weighted fair queuing (WFQ), and weighted random early discard (WRED)
• Storm restraint - allows limitation of broadcast, multicast, and unknown unicast traffic rate to cut down
on unwanted broadcast traffic on the network
• Intelligent Resilient Fabric (IRF) -
perform as a single Layer 2 switch and Layer 3 router; Switches do not have to be co-located and can
be part of a disaster recovery system; Servers or switches can be attached using standard LACP for
automatic load balancing and high availability; Simplifies network operation by eliminating Spanning
Tree, ECMP and VRRP
• Device Link Detection Protocol (DLDP) - Monitors Link connectivity and shuts down ports at both
ends if unidirectional traffic is detected
• Rapid Ring Protection Protocol (RRPP) - Connects multiple switches in a high-performance ring using
standard Ethernet technology; traffic can be rerouted around the ring in less than 50 ms upon failure
• Smart Link - Allows 50 ms failover between links
• Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)
• OAM (802.3ah) - Detects data link layer problems in the "last mile"; monitors link status between two
devices
• CFD (802.1ag) - Connectivity Fault Detection (CFD) provides L2 link OAM mechanism used for link
connectivity detection and fault location
• Mirroring - Port mirroring enables traffic on a port to be simultaneously sent to a network analyzer for
monitoring; Flow-based mirroring
Page 5

QuickSpecs
HPE 6125G/XG Ethernet Blade Switch
Standard Features
Page 5
• IPsec
• IKE (Internet Key Exchange)
• Self-signed certificate for HTTPS
•
Disable password recovery
Page 6

QuickSpecs
HPE 6125G/XG Ethernet Blade Switch
Service and Support
Page 6
Service and Support
HPE
When you buy
services.
complex infrastructure problems, giving you one call to make, fast answers, and global reach. We help keep
your business running,
Protect your business beyond warranty with
HPE
to meet your IT and business needs.
HPE
industry
your IT and business needs. If you are running bus
offers Proactive Care. This service helps you deliver high levels of system availability through proactive service
management and advanced technical response.
Recommended HPE Care Pack Services for your HPE product
Recommended
Services
3
This service gives you combined reactive and proactive support including rapid access to our Advanced
Solution Center to manage and prevent problems and a Tec
technical knowledge that will engage with additional technical expertise as needed from
Enterprise
http://h20195.www2.hp.com/v2/GetPDF.aspx/4AA3
HPE
This easy
hardware
Related HPE Care Pack Services to enhance your HPE product experience
Related Services
3-Year HPE 6 hour Call to Repair Response, Proactive Care*
Combined reactive and proact
delivering high levels of availability through proactive service management and advanced technical response.
Hardware problem resolution to return the hardware in operating condition within 6 hours of the initial service
request. A Technical Account Manager, as your single point of contact, will own your call or issue end to end
until resolved.
http://h20195.www2.hp.com/v2/GetPDF.aspx/4AA3-8855EEE.pdf
Additional Services
HPE
Provides a flexible way to purchase
services. You can buy Proactive Select Service Credits when
credits over the next 12 months.
NOTE: Additional HPE Care Pack services can be found at: http://h20558.www2.hp.com/portal/site/cpc
Insight
Online/Insight
Remote Support
HPE
resolution. This comes at no additional cost with your
Insight Remote Support
http://h18013.www1.hp.com/products/servers/management/insight
Technology Services
HPE BladeSystem Options for your HPE BladeSystem, it is also good time to think about
HPE Technology Services offers you technical consultants and support expertise to solve your most
boost availability, and avoid downtime.
HPE Care Pack Services
Care Pack services provide total care and support expertise with committed response choices designed
Foundation Care services offer scalable reactive support-packages for Hewlett Packard Enterprise
-standard servers and software. You can choose the type and level of service that is most suitable for
iness critical environments, Hewlett Packard Enterprise
-Year HPE 24x7 4 hour response, Proactive Care Service*
hnical Support Specialist with a broad level of
vast global resources.
-8855EEE.pdf
Installation of ProLiant Add On Options Service
-to-buy, easy-to-use HPE Care Pack service helps ensure that your new Hewlett Packard Enterprise
is installed smoothly, efficiently, and with minimal disruption of your IT and business operations
ive support for hardware and software helping optimize your systems and
Proactive Select Service
Hewlett Packard Enterprise best-in-class consultancy and technical
you purchase your hardware and then use the
http://h20195.www2.hp.com/V2/GetPDF.aspx/4AA2-3842ENN.pdf
Insight Remote Support provides 24 X 7 remote monitoring, proactive notifications, and problem
Hewlett Packard Enterprise solution. Learn more about
http://www.hp.com/go/insightremotesupport and Insight Online
-online/index.html
the Hewlett Packard
Page 7

QuickSpecs
HPE 6125G/XG Ethernet Blade Switch
Service and Support
Page 7
NOTE:
Services above.
HPE Support Center
Personalized
Enterprise business products
access support resources or collaborate with peers. Lea
The HPE Support
live support. Now, you can get access to personalized IT support anywher
HPE
Packard Enterprise
NOTE: HPE Support Center Mobile App above is subject to local availability.
Parts and materials
Hewlett Packard Enterprise will
maintain the covered hardware product in operating condition, including parts and materials for
recommended engineering improvements. Supplies and consumable parts will not be provided as part of this
service; standard warranty terms and conditions apply. Parts and components that have exceeded their
maximum supported lifetime and/or t
operating manual or the technical product data sheet will not be provided, repaired or replaced as part of this
service.
Service Coverage
HPE Care Pack services for the c7000 and c3000 enclosures cover the HPE 6125G/XG Ethernet Blade Switch.
For more
information
To learn more on
representative or
http://www.hpe.com/services/bladesystem
For more
information
To learn more on services for
representative or
http://www.hpe.com/services/proliant
http://www.hpe.com/services/bladesystem
Insight Remote Support is a prerequisite for HPE Proactive Care referenced in Additional
online support portal with access to information, tools and experts to support Hewlett Packard
. Submit support cases online, chat with Hewlett Packard Enterprise experts,
rn more http://www.hp.com/go/hpsc
Center Mobile App allows you to resolve issues yourself or quickly connect to an agent for
e, anytime.
Insight Remote Support and HPE Support Center are available at no additional cost with a Hewlett
warranty, HPE Care Pack or Hewlett Packard Enterprise contractual support agreement.
provide HPE-supported replacement parts and materials necessary to
available and
he maximum usage limitations as set forth in the manufacturer's
HPE BladeSystem services, please contact your Hewlett Packard Enterprise sales
Hewlett Packard Enterprise Authorized ServiceONE Channel Partner. Or visit:
HPE ESSN Options, please contact your Hewlett Packard Enterprise sales
Hewlett Packard Enterprise Authorized Channel Partner. Or visit:
or
Page 8

QuickSpecs
HPE 6125G/XG Ethernet Blade Switch
Related Options
Page 8
SFP Options
HPE X125 1G SFP LC LH40 1310nm Transceiver
JD061A
HPE X120 1G SFP LC LH40 1550nm Transceiver
JD062A
HPE X125 1G SFP LC LH70 Transceiver
JD063B
HPE X120 1G SFP RJ45 T Transceiver
JD089B
HPE X120 1G SFP LC SX Transceiver
JD118B
HPE X12
JD119B
HP BladeSystem c-Class Virtual Connect 1G SFP RJ-45 Transceiver
453154-B21
HP BladeSystem c
B21
SFP+ Options
HPE X130 10G SFP+ LC SR Transceiver
JD092B
HPE X130 10
JD093B
HPE X130 10G SFP+ LC LR Transceiver
JD094B
Direct Attach Cables
HPE FlexNetwork X240 10G SFP+ to SFP+ 0.65m Direct Attach Copper Cable
JD095C
HPE FlexNetwork X240 10G SFP+ to SFP+ 1.2m Direct Attach Copper Cable
JD096C
HPE FlexNetwork X240 10G SFP+ to SFP+ 3m Direct Attach Copper Cable
JD097C
HPE FlexNetwork X240 10G SFP+ to SFP+ 5m Direct Attach Copper Cable
JG081C
HPE FlexNetwork X240 10G SFP+ SFP+ 7m Direct Attach Copper Cable
JC784C
NOTE:
work with this product. Transceiver and DAC cables from any manufacturer will be
accepted, but they will not be supported by Hewlett Packard Enterprise.
Service and Support
Offerings
Hardware
HPE 3 year Proactive Care 24x7 c7000 Enclosure Service
U3C33E
HPE 3 year Proactive Care Call to Repair c7000 Enclosure Service
U3C36E
Installation Services
HPE Installation of ProLiant Add On/In Options Service
UH745E
Additional
http://h20558.www2.hp.com/portal/site/cpc
NOTE:
http://www.hp.com/services/bladesystemservices
0 1G SFP LC LX Transceiver
-Class Virtual Connect 1G SFP SX Transceiver 453151-
G SFP+ LC LRM Transceiver
The transceivers and cables listed above have been qualified and certified to
Services On-site Service
HPE Care Pack services can be found at:
For more HPE BladeSystem information, customer/resellers can contact:
Page 9

QuickSpecs
HPE 6125G/XG Ethernet Blade Switch
Technical Specifications
Page 9
Shipping
Dimensions
Length
11.54 in (293 mm)
Width
14.57 in (370 mm)
Height
3.54 in (95 mm)
Shipping Weight
1.9 kg (4.19 lbs)
Product
Specifications
Hardw
Performance
44 Gbps uplink port bandwidth; 16 Gbps downlink (server) port bandwidth; 10Gbps
cross
Forwarding rate 1.5 million pps per Gigabit port, (64
pps per 10 Gig port
Non
and auto
Forwarding Mode
Store and forward
MAC Addresses
Supports 32K MAC addresses per switch in a
BladeSystem Enclosure
Forwarding Table Age
Time
(Maximum
10 to 1,000,000 seconds
(default: 300 seconds)
VLAN IDs
4094
Jumbo Frame
9220 Byte
IGMP Groups
1024
Memory
1 GB Main, 256MB flash and 3MB packet buffer
Connectors and
Cabling
Connector
4 RJ
4 SFP+/SFP (1Gb/10Gb/IRF)
1 RJ45 Management
Cable Support
FCC Class A
ICES
AS/NZS 3548 Class A
VCCI Class A
Indicators
Module health, amber/green
Module locator (UID), blue
10/100/100Base
SFP port link/activity, green
SFP+ port link/activity, green
Dimensions
Length
10.5 in (267.7 mm)
Width
7.5 in (192.79 mm)
Height
1.1 in (27.94 mm)
Weight
1.32 kg (2.9 lbs)
Environmental
Ranges
Temperature Range
Operating
50° to 95° F (10° to 35° C)
Non-operating
-40° to 158° F (-40° to 70° C)
Relative Humidity
(non-condensing)
Operating 5% to 95%
-link bandwidth
are
-blocking, full-wire speed for all connections Auto-MDI/MDIX, auto-negotiation
-sensing with full-duplex support.
age)
-T port speed/link/activity, amber/green
-byte packets) and 14.8 million
-45
-003 Class A
Page 10

QuickSpecs
HPE 6125G/XG Ethernet Blade Switch
Technical Speci
fications
Page 10
Power Specification
Power Requirements
41W
Standards Support
General protocols
IEEE 802.1ag Service Layer OAM
IEEE 802.1D MAC Bridges
IEEE 802.1p Priority
IEEE
IEEE 802.1s (MSTP)
IEEE 802.1v VLAN classification by Protocol and Port
IEEE 802.1w Rapid Reconfiguration of Spanning Tree
IEEE 802.1X PAE
IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
IEEE 802.3ae 10
IEEE 802.3x Flow
RFC 768 UDP
RFC 792 ICMP
RFC 793 TCP
RFC 826 ARP
RFC 854 TELNET
RFC 925 Multi
RFC 951 BOOTP
RFC 1058 RIPv1
RFC 1350 TFTP Protocol (revision 2)
RFC 1519 CIDR
RFC 1542 BOOTP Extensions
RFC 2131 DHCP
RFC 2453 RIPv2
RFC 3768 VRRP
RFC 4675 RADIUS VLAN & Priority
802.1r
Protocol (GPRP)
IP Multicast
RFC 2934 Protocol Independent Multicast MIB for IPv4
RFC 3376 IGMPv3 (host joins only)
RFC 3618 Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP)
RFC 3
RFC 4601 PIM Sparse Mode
IPv6
RFC 4443 ICMPv6
RFC 4541 IGMP & MLD Snooping Switch
RFC 4861 IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
RFC 4862 IPv6 Stateless Address Auto
MIBs
IEEE 8021
IEEE 8021
IEEE 8023
802.1Q VLANs
-Gigabit Ethernet
Control
-LAN Address Resolution
- GARP Proprietary Attribute Registration
973 Draft 2 PIM Dense Mode
-PAE-MIB
-CFM-MIB
-LAG-MIB
-configuration
Page 11

QuickSpecs
HPE 6125G/XG Ethernet Blade Switch
Technical Speci
fications
Page 11
RF
RFC 1493 Bridge MIB
RFC 1657 BGP
RFC 1724 RIPv2 MIB
RFC 1850 OSPFv2 MIB
RFC 2011 SNMPv2 MIB for IP
RFC 2013 SNMPv2 MIB for UDP
RFC 2096 IP Forwarding Table MIB
RFC 2233 Interface MIB
RFC 2273 SNMP
RFC 2452 IPV6
RFC 2454 IPV6
RFC 2465 IPv6 MIB
RFC 2466 ICMPv6 MIB
RFC 2571 SNMP Framework MIB
RFC 2572 SNMP
RFC 2573 SNMP
RFC 2618 RADIUS Client MIB
RFC 2620 RADIUS Accounting MIB
RFC 2665 Ethernet
RFC 2674 802.1p and IEEE 802.1
RFC 2688 MAU
RFC 2787 VRRP MIB
RFC 2819 RMON MIB
RFC 2925 Ping MIB
RFC 2933 IGMP MIB
RFC 3414 SNMP
RFC 3415 SNMP
RFC 3418 MIB for SNMPv3
RFC 3636 IEEE 802.3 MAU MIB
RFC 3826 AES for SNMP's USM MIB
RFC 4
RFC 4878 Ethernet OAM MIB
LLDP
LLDP
LLDP-MIB
Safety and
Compliance
Safety
Certifications
Complies with UL 60950
CE Marking
RoHS 6/6 comp
Electromagnetic
Emissions
Certifications FCC
Part 15 Class A
FCC Part 15 Class A
EN 55022: 1998 (CISPR22)
EN 55024: 1998 (CISPR24)
VCCI Class A
AS/NZS 3548 Class A CE
CNS 13438 Class A MIC
MIC
C 1213 MIB II
-4 MIB
-NOTIFICATION-MIB
-TCP-MIB
-UDP-MIB
-MPD MIB
-Notification MIB
-Like-MIB
Q Bridge MIB
-MIB
-User based-SM MIB
-View based-ACM MIB
133 Entity MIB (Version 3)
-EXT-DOT1-MIB
-EXT-DOT3-MIB
-1, CAN/CSA C22.2 No. 60950-1 and EN 60950-1. UL certified.
liant
Page 12

QuickSpecs
HPE 6125G/XG Ethernet Blade Switch
Technical Speci
fications
Page 12
Environment
friendly Products
and App
. These instructions may be used by recyclers
-
roach
End-of-life
Management and
Recycling
Hewlett Packard Enterprise offers end-of-life Hewlett Packard Enterprise product
return, trade-in, and recycling programs in many geographic areas. For trade-in
information, please go to http://www.hp.com/go/green
. To recycle your product,
please go to: http://www.hp.com/go/green or contact your nearest Hewlett
Packard Enterprise sales office. Products returned to Hewlett Packard Enterprise will
be recycled, recovered or disposed of in a responsible manner.
The EU WEEE directive (2002/95/EC) requires manufacturers to provide treatment
information for each product type for use by treatment facilities. This information
(product disassembly instructions) is posted on the Hewlett Packard Enterprise web
site at: http://www.hp.com/go/green
and other WEEE treatment facilities as well as Hewlett Packard Enterprise OEM
customers who integrate and re-sell Hewlett Packard Enterprise equipment.
Page 13

QuickSpecs
HPE 6125G/XG Ethernet Blade Switch
Summary of Changes
Page 13
Date
Version History
Action
Description of Change
15-Nov-2014
From version 7 to 8
Changed
Compatibility section was updated.
and descriptions
Sign up for updates
Rate this document
© Copyright 201
subject to change without notice. The only warranties for Hewlett Packard Enterprise products and
serv
Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. Hewlett Packard Enterprise
shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or om
Microsoft and Windows are US registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
c04111502
08-Apr-2016 From Version 9 to 10 Changed Minor changes made on Standard Features, SKU descriptions
updated.
17-Dec-2015 From Version 8 to 9 Changed Overview and Related Options sections were updated.
21-Oct-2014 From version 6 to 7 Changed Service and Support, Service Coverage were revised
18-Apr-2014 From Version 5 to 6 Changed Related Services was revised.
30-Sep-2013 From Version 4 to 5 Changed Changes made in the Overview and Related Options sections
28-Jun-2013 From Version 3 to 4 Changed Changes made in the Related Options section only.
15-Mar-2013 From Version 2 to 3 Changed Changes made throughout the Standard Features Section-
25-Sep-2012 From Version 1 to 2 Changed Change made throughout the QuickSpecs.
only.
Added Security information
Changes made in the Related Options Section- Added new
part numbers and descriptions as well as deleted part numbers
ices are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services.
6 Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP. The information contained herein is
issions contained herein.
- 14428 - Worldwide - V10 - 08-April-2016
 Loading...
Loading...