Page 1

Revision 1.3
July 2001
Page 2

Page 3

Contents
1. INTRODUCTION ...............................................................................................................................................1
1.1 C
1.2 A
1.3 P
1.4 T
1.5 S
1.6 C
ONVENTIONS ...................................................................................................................................................1
RGUMENT TYPES.............................................................................................................................................1
RIVILEGE AND CONTEXT LEVELS.....................................................................................................................2
HE COMMAND LINE INTERFACE ......................................................................................................................3
YSTEM HELP ....................................................................................................................................................3
OMMAND LINE EDITING ..................................................................................................................................4
2. COMMAND SUMMARY................................................................................................................................... 5
2.1 USER EXEC COMMANDS ..................................................................................................................................5
2.2 D
2.3 S
IAGNOSTIC COMMANDS ..................................................................................................................................6
YSTEM CONFIGURATION................................................................................................................................11
2.3.1 System commands - EXEC level............................................................................................................11
2.3.2 System Configuration commands..........................................................................................................14
2.4 AUTHENTICATION .....................................................................................................................................16
2.4.1 AUTHENTICATION commands - Configuration level.........................................................................16
2.5 TACACS......................................................................................................................................................... 17
2.5.1 TACACS commands - EXEC level ........................................................................................................17
2.5.2 TACACS commands - Configuration level ...........................................................................................17
2.6 CDP.................................................................................................................................................................17
2.6.1 CDP commands - EXEC level...............................................................................................................17
2.6.2 CDP commands - Configuration level.................................................................................................. 17
2.7 IP S
TACKING ...................................................................................................................................................18
2.7.1 IP Stacking commands - EXEC level ....................................................................................................18
2.7.2 IP Stacking commands - Configuration level .......................................................................................18
ORT SETTINGS ...............................................................................................................................................20
2.8 P
2.8.1 Port commands - EXEC level................................................................................................................20
2.8.2 Ethernet Interface Configuration Commands.......................................................................................22
RUNK CONFIGURATION .................................................................................................................................23
2.9 T
2.9.1 Trunk commands - EXEC level .............................................................................................................23
2.9.2 Trunk commands - Configuration level ................................................................................................24
2.10 S
PANNING TREE..........................................................................................................................................25
2.10.1 Spanning Tree commands - EXEC level ...............................................................................................25
2.10.2 Spanning Tree commands - Configuration level ..................................................................................26
2.11 IP ................................................................................................................................................................28
2.11.1 IP commands - EXEC level...................................................................................................................28
2.11.2 IP commands - Configuration level ......................................................................................................31
2.11.3 IP commands - VLAN Interface level....................................................................................................33
2.12 SNMP.........................................................................................................................................................34
2.12.1 SNMP commands - EXEC level ............................................................................................................34
2.12.2 SNMP commands – Configuration Level..............................................................................................35
2.13 VLAN C
ONFIGURATION.............................................................................................................................36
2.13.1 VLAN commands - EXEC level.............................................................................................................36
2.13.2 VLAN commands – Configuration Level ..............................................................................................36
2.13.3 VLAN Interface commands ...................................................................................................................37
2.14 GVRP .........................................................................................................................................................38
2.14.1 GVRP commands - EXEC level.............................................................................................................38
2.14.2 GVRP commands – Configuration level ...............................................................................................38
2.14.3 Ethernet Interface Configuration commands........................................................................................38
2.15 IGMP..........................................................................................................................................................39
2.15.1 IGMP Commands – EXEC Level .........................................................................................................39
2.15.2 IGMP Configuration commands – Vlan Interface level .......................................................................40
Page 4

2.16 PORT MONITORING.....................................................................................................................................41
2.16.1 Port Monitoring commands - EXEC level ............................................................................................41
2.16.2 Port Monitoring commands - Configuration level................................................................................41
2.16.3 Port Monitoring commands - VLAN Interface level ............................................................................42
2.16.4 Port Monitoring commands - Ethernet Interface level........................................................................42
2.17 P
ORT SECURITY ..........................................................................................................................................42
2.17.1 Port Security commands - EXEC level .................................................................................................42
2.17.2 Port Security commands - Configuration level.....................................................................................43
3. CONSOLE MENU.............................................................................................................................................45
TATUS AND COUNTERS..................................................................................................................................45
3.1 S
3.1.1 General System Information .................................................................................................................46
3.1.2 Management Address Information........................................................................................................46
3.1.3 Module Information ..............................................................................................................................47
3.1.4 Port Status............................................................................................................................................. 47
3.1.5 Port Counters ........................................................................................................................................48
3.1.5.1 Port Counters Details.........................................................................................................................................48
3.1.6 Address Table........................................................................................................................................49
3.1.7 Port Address Table................................................................................................................................49
3.1.8 Spanning Tree Information ...................................................................................................................50
3.1.8.1 Spanning Tree Port Information........................................................................................................................ 50
3.2 CONFIGURATION MENU...................................................................................................................................51
3.2.1 System Information................................................................................................................................52
3.2.2 Port/Trunk Settings ............................................................................................................................... 52
3.2.3 Network Monitoring Port......................................................................................................................53
3.2.4 Spanning Tree Operation......................................................................................................................53
3.2.5 IP Configuration ................................................................................................................................... 54
3.2.6 SNMP Communities ..............................................................................................................................55
3.2.7 Authorized Managers............................................................................................................................ 55
3.2.8 VLAN Menu...........................................................................................................................................56
3.2.8.1 VLAN Support .................................................................................................................................................. 56
3.2.8.2 VLAN Names.................................................................................................................................................... 57
3.2.8.3 VLAN Port Assignment ....................................................................................................................................57
3.3 PASSWORD MENU............................................................................................................................................58
VENT LOG......................................................................................................................................................58
3.4 E
3.5 D
3.6 R
OWNLOAD SCREEN .......................................................................................................................................59
UN SETUP ......................................................................................................................................................59
Page 5

1. Introduction
This document provides a summary of the commands supported on the HP ProCurve 2524,
2512, and 4108gl switches. It is divided into sections that correspond to different modules or
features of the HP switches. Not all sections will apply to all HP switches since each switch
may only support a subset of the total feature set that is described in this document.
1.1 Conventions
Command descriptions use the following conventions:
Vertical bars “|” separate alternative, mutually exclusive elements.
Square brackets “[ ]” indicate optional elements.
Braces “<>” indicate a required choice.
Braces within square brackets “[<>]” indicate a required choice within an optional
element.
Boldface indicates commands and keywords that are entered literally as shown.
Italics indicates arguments for which you must supply a value.
If the no form of a command has exactly the same keywords and arguments as the
command, then no appears in square brackets at the beginning of the command.
Otherwise, the no form of the command is described separately.
If the no form of a command is not explicitly described, then it simply negates the
command. For example, if the command enables a feature, then the no form of the
command would disable it. Also, if the a command was used to add a configuration item,
then the no form of the command would remove it.
1.2 Argument Types
The following argument types are recognized by the CLI and are used in the command
syntax throughout this document:
mac-addr
ip-addr
ip-mask
port-number
– For example, 0060b0-885a80 or 0060b0:885a80.
- IP address in dotted decimal notation. For example, 10.0.16.80
- This is syntactically expressed the same way as ip-addr.
- Devices with fixed port configurations accept port numbers
specified as integers. Modular devices accept port numbers specified with slot
and port number identifiers. For instance, port "A1" indicates Port 1 in Slot A.
1
Page 6
There are three "special" port designations in the switch. You may specify the
i
v
monitoring port by using "mp"; you may specify a trunk port by using "trkX",
where X identifies the numerical trunk group.
port-list
- A port list specifies a group of ports for which the operation being
performed should be applied. A port list consists of individual port identifiers or
ranges of ports separated by commas (e.g., A1-B8, C4, D1). This list includes the
"special" port designations described under port-number.
vlan-id
- The 802.1Q VLAN identifier.
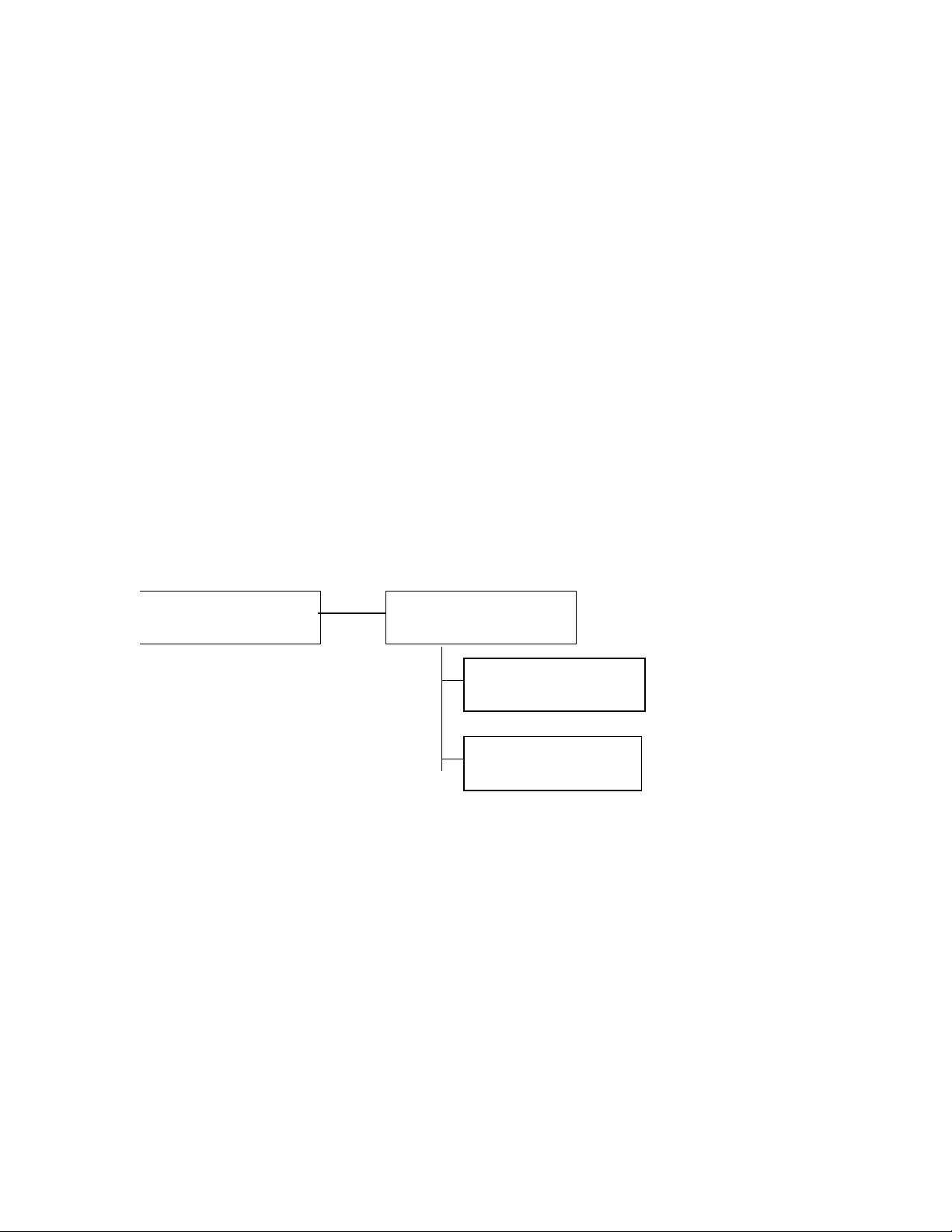
1.3 Privilege and Context levels
The new CLI will support two privilege levels (operator and manager) and several context
levels. As each context level is entered, the context information is displayed as part of the
command prompt. When a context specific command is executed, the context information
is applied to the particular command. For instance, when you attempt to enter the interface
context level, you must specify a port number (see interface ethernet). Subsequent
commands that affect port behavior (e.g., flow-control) will be applied to the port number
specified when entering the level, so the specified port need not be re-specified on the
command line.
EXEC level
HP 4108GL>
Global configuration level
HP 4108GL(config)
nterface config level
HP 4108GL(if-A1)
lan config level
HP 4108GL(vlan-1)
Figure 1: Command and context levels
When you log onto the switch, you will be placed at the operator EXEC level and the
system will display the following prompt:
HP 4108GL>
2
Page 7

If an operator password has been set (see password in the global configuration section),
then the system would have displayed the following prompt before entering the operator
EXEC level:
Password:
You can enter the manager EXEC level from the operator EXEC level by using the enable
command. If a manager level password has been configured, then you will be prompted for
the manager password after executing the enable command.
1.4 The Command Line Interface
The new CLI will not be case sensitive. As a short cut, you can abbreviate commands and
keywords as long they contain enough letters to be distinguished from any other currently
available commands or keywords.
When the command text exceeds the length of the command line, the current command line
will scroll upwards, yet the cursor will shift to the first character on the last line on the
screen. This is opposed to shifting the command line horizontally each time the command
exceeds the number of characters that can be displayed at one time on the screen.
1.5 System Help
You can enter help or ? at a particular command level to see the commands available at that
level. You can enter a command followed by help or ? in order to get the system to display
the command description for that particular command. The command description would be
similar to what is presented for each command in the Command Reference section of this
document.
In order to see the list of possible word completions or to complete the current word, you
may use the Tab key immediately after the last letter of the last keyword on the command
line. For example, if the system was currently in the global configuration level and you typed
tab immediately after the t in step (1), the system would display the options seen in section
(2) and the system would return to the configuration level prompt with the partially
completed command line seen in (3):
(1) HP 4108GL(config) t
(2) trunk
trap
trap-send-authentication
telnet-server
(3) HP 4108GL(config)t
3
Page 8
If you had already typed in trap- on line (1) and then pressed the tab character, the system
would complete the keyword trap-send-authentication, for it is the only possible
completion for trap-, and display the completed command line as shown below:
1. HP 4108GL(config) trap-
2. HP 4108GL(config) trap-send-authentication
1.6 Command Line Editing
Before you press return, the current command line can be edited using special keys
including arrows and control characters. The following table describes the supported
command editing keys and their function:
Keystroke Function
Ctrl-A Jumps to the first character of the command line.
Ctrl-B; left arrow Moves the cursor back one character.
Ctrl-C Escapes and terminates prompts and lengthy tasks.
Ctrl-D Deletes the character at the cursor.
Ctrl-E Jumps to the end of the current command line.
Ctrl-F; right arrow Moves the cursor forward one character.
Ctrl-K Deletes from the cursor to the end of the command line.
Ctrl-L; Ctrl-R Repeats current command line on a new line.
Ctrl-N; down arrow Enters next command line in the history buffer.
Ctrl-P; up arrow Enters previous command line in the history buffer.
Ctrl-U; Ctrl-X Deletes from the cursor to the beginning of the command line.
Ctrl-W Deletes last word typed.
Esc B Moves the cursor backward one word.
Esc D Deletes from the cursor to the end of the word.
Esc F Moves the cursor forward one word.
Delete; Backspace
Erases mistake when entering a command; reenter command after using this
key.
4
Page 9

2. Command Summary
2.1 User EXEC Commands
enable
Enters the manager EXEC level. If a manager password is set, the system will first
prompt for the password. Echoing is disabled while you enter the password. Initially
there are no passwords for the two levels of users in the system: manager and
operator. When you first connect to the console or telnet into the system, you will be
placed into the Operator EXEC level. At that time, you can enter the above enable
command without a password in order to be granted manager access to the switch
and to be placed into the manager EXEC level. Passwords are set and changed
through the password command at the global configuration level.
configure [terminal]
Used to enter the global configuration level.
end
This command sets the current command or context level to the manager EXEC
level.
exit
This command sets the current command level to the previous command level. At
the operator EXEC level, this command acts the same as logout.
interface [ethernet] <port-list>
Enters the Ethernet interface configuration context for the port-list.
logout
Terminates this console/telnet session.
menu
Used to enter the menu system. For more information, see the Console Menu
section of this document.
setup
Used to setup initial switch configuration.
5
Page 10

[no] page
Toggles the paging mode for display commands so that the “—more –“ will appear
or not appear.
repeat
Repeatedly executes the previous command until a key is pressed.
vlan <vlan-name | vlan-id>
Enters the VLAN interface configuration context for the VLAN.
2.2 Diagnostic Commands
boot [system [flash <primary|secondary>]]
Performs cold reboot of switch.
write terminal
This command displays the running configuration.
write memory
This command saves the running configuration to Flash.
erase startup-config
Deletes the configuration stored in flash so that the switch will reverted to it’s
default configuration upon reboot.
erase flash <primary|secondary>
Deletes the configuration stored in flash so that the switch will reverted to it’s
default configuration upon reboot.
copy tftp <startup-config|flash> <ip-addr> <remote-file>
Retrieves a configuration or OS file on the remote host, and overwrites the switch's
corresponding file with the remote file.
[primary|secondary]
6
Page 11

copy <startup-config|running-config|crash-log|event-log|crash-rec|Command>
tftp <ip-addr> <remote-file>
This command writes the switch's configuration file, crashrec, eventlog or the output
from a command specified by Command to the remote file on the remote host.
show startup-config
Displays the configuration stored in flash.
show running-config
Displays the configuration stored in flash.
show boot-history
Displays the switch shutdown history.
kill
This command kills all other active sessions.
show logging [-a] [<search-text>]
Displays the switch's event log. If -a is specified then entire internal switch log is
displayed. If search-text is specified then only events that contain that text are
displayed.
print <command>
Used to execute a command and captures its output using a terminal emulator. This
command will display “Press RETURN when ready…” to allow the terminal
emulator to be set up to for the capture and “Press RETURN when done…” once
the output is complete.
show history
Displays the current command history.
reload
Performs a warm reboot.
clear arp
To clear the arp cache of all non-permanent entries.
7
Page 12

clear intrusion-log
To clear the intrusion log.
clear statistics [ethernet] <port-list>
To reset counters displayed by the console. If a new console session is initiated, the
counters will revert back to the values maintained by the switch hardware.
telnet <ip-addr>
To initiate a telnet session with another network device.
telnet <0..15>
To initiate a telnet session to a member switch in the stack.
Parameters:
<0..15> specifies the number of the switch to be contacted.
getmib <object-name> [<object-name> …]
Retrieves and displays the MIB object defined by object-name.
walkmib <object-name>
This command shows a group of managed object values.
8
Page 13

setmib <object-name> <type> <value> [<object-name> <type> <value> …]
This command sets the MIB object defined by object-name. The options for the type
parameter are case sensitive as shown below:
-i Integer
-o Octet string
-d Object identifier
-a IP address (nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn)
-c Counter
-g Gauge
-t Time tick
-u Unsigned integer
-D Display string (“value”)
-N Null
show version
Displays software version information.
show flash
Displays software version information for images in flash.
show tech
Displays switch information needed by HP support for diagnostics.
copy xmodem < startup-config |flash [primary|secondary]>
Retrieves a configuration file using the Xmodem protocol and then writes the
retrieved file to the switch's flash.
copy <startup-config|running-config|crash-log|event-log|crash-rec|Command>
xmodem [ pc | unix ]
Writes either the configuration file, crashrec, eventlog, or the output from a
command specified by command using the Xmodem protocol.
9
Page 14

link-test <mac-addr> [vlan <vlan-id>] [repetitions <1..999>] [timeout <1..256>]
Tests the connection to a MAC station on the LAN by sending a 802.2 test packet to
a specific target node on a network directly attached to a port in that LAN. The
target node must be able to respond to this test packet with an 802.2 Test Response
packet in order for the test to work. The switch produces the following output if the
link test succeeds:
link-test passed
otherwise, the following is displayed:
link-test failed
Parameters:
<mac-addr> - MAC address of the station to send link test to.
vlan <vlan-id> - Expected VLAN on which the station is expected to be present.
If this argument is not present then the VLAN used is 1.
repetitions <1..9999> - Number of test packets to send; the default value is 1.
timeout <1..256> - Seconds within which a response is required before the test
is considered as failed; the default value is 5.
ping <ip-addr> [repetitions <1..999>] [timeout <1..256>]
Issues an IP Ping requests to an IP device on the network and the system displays
the following output at the CLI if a response is received from the specified IP
address:
192.32.36.75 is alive, time = 10 ms
If no response is received the system displays the following:
Target did not respond
Parameters:
<ip-addr> - Network IP address of station to send IP Ping to.
repetitions <1..999>- Number of times to send IP Ping; the default value is 1.
timeout <1..256> - Seconds within which a response is required before the test
is considered as failed; the default value is 5.
10
Page 15
2.3 System Configuration
2.3.1 System commands - EXEC level
show console
Displays the console parameters.
Output Format:
Switch Configuration - Console/Serial Link
Inbound Telnet Enabled [Yes] : Yes
Web Agent Enabled [Yes] : Yes
Terminal Type [VT100] : VT100
Screen Refresh Interval (sec) [3] : 3
Displayed Events [All] : All
Baud Rate [Speed Sense] : Speed Sense
Flow Control [XON/XOFF] : XON/XOFF
Connection Inactivity Time (min) [0] : 0
show mac-address [vlan <vlan-id>]
Displays the MAC addresses that the switch has learned from the network devices
attached to the switch, and the port on which each address was learned. If no vlan is
specified, then all MAC addresses that are know to the switch are shown.
Output Format:
Status and Counters - Address Table
MAC Address Located on Port
------------00105a-8abed4 1
00105a-cac0e8 1
0060b0-881c00 1
009004-8e3178 1
00c0f0-1c65ee 1
00c0f0-30d74a 1
080009-3515f9 1
080009-782368 1
080009-7b8cc4 1
080009-919b30 1
080009-959e2c 1
---------------
11
Page 16
show mac-address <port-list>
Displays the MAC addresses that the switch has learned from the network devices
attached to the specified switch port.
Output Format:
Status and Counters - Port Address Table - Port 1
MAC Address
------------00105a-8abed4
00105a-cac0e8
009004-8e3178
00c0f0-1c65ee
00c0f0-1c66ea
00c0f0-30d74a
080009-3515f9
080009-782368
080009-7b8cc4
080009-919b30
080009-959e2c
show management
Displays configured addresses that are used to manage the switch.
Output Format:
Time Server Address :
MAC Address : 0060b0-885a80
IP Address : 192.32.36.96
IPX Network Number :
Status and Counters - Management Address Information
12
Page 17
show modules
Displays the modules that are present on the switch.
Output Format:
Slot Module Type Module Description
---A Slot Available
show system-information
Displays the status of and current configuration of all the switch internal resources.
Output Format:
Status and Counters - Module Information
-----------------------------------------------------------
System Information
..System Name :
System Contact :
System Location :
Address Age Interval (min) [5] : 5
Time Zone [0] : 0
Daylight Time Rule [None] : User defined
Beginning month [April] : April
Ending month [October] : October
Firmware revision : C.08.XX
ROM Version : C.05.X1
Up Time : 17 hours
CPU Util (%) : 2
IP Mgmt - Pkts Rx : 14,496
Pkts Tx : 9463
Beginning day [1] : 1
Ending day [1] : 1
Base MAC Addr : 0060b0-885a80
Serial Number : +
Memory - Total : 7,669,088
Free : 4,871,840
Packet - Total : 462
Buffers Free : 296
Lowest : 237
Missed : 0
13
Page 18

2.3.2
System Configuration commands
mac-age-time <1..100000>
Sets the number of seconds a MAC address stays in the switch address table before
being aged out. Aging out occurs if traffic isn't received from that MAC station
within the age interval. The default value is 300.
console [terminal <vt100 | ansi> [screen-refresh <value>] [events <none | all | non-
info | critical | debug>] [baud-rate <value>] [flow-control <xon/xoff | none>]
[inactivity <value>]
Sets the console parameters.
Parameters:
terminal <vt100 | ansi> - Type of terminal being used (default is vt100).
screen-refresh <1|3|5|10|20|30|45|60> - Sets the number of seconds before a
refresh is done on the “Status and Counters” screens (default is 3).
events <none | all | non-info | critical | debug>] – The level of Switch events
displayed in Events Log. all - display all; none - display no events; not-info - display
all events except informational-only; critical - display only critical-level events;
debug (reserved for Internal use only).
baud-rate <speed-sense | 1200 | 2400 | 4800 | 9600 | 19200 | 38400 | 57600
| 115200>] - Sets the data transmission speed for switch connect sessions initiated
through the Console port. Default is speed-sense.
flow-control <xon/xoff | none> - Flow Control Method; default is xon-xoff.
inactivity-timer <0 | 1 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 60 | 120> - Sets the number of
minutes of inactivity allowed by the switch before the switch will terminate the
communication session. 0 means never terminate the session; default is 0 .
[no] auto-tftp <ip-addr filename>
Enables/disables automatic OS image download via TFTP.
14
Page 19

time [mm/dd/yy] [hh:mm:ss] [timezone <value>] [daylight-time-rule <value>] [begin-date
<mm/dd> end-date <mm/dd>]
This command display switch's date & time or optionally sets it.
Parameters:
timezone <-1440..1440> - Sets the number of minutes your location is to the
West(+) or East(-) of GMT (default is 0).
daylight-time-rule <alaska | none | continental-us-canada | middle-europe-
and-portugal | southern-hemisphere | western-europe | user-defined> -
Sets the daylight savings time rule for your location. None (default) means that no
time adjustment will be made.
begin-date <mm/dd> end-date <mm/dd > - begin-date and end-date are only
valid if the daylight time rule is set to user-defined.
snmp-server [contact <sys-contact>] [location sys-location>]
Sets the switch contact and location for administrative purposes.
Parameters:
contact <sys-contact> - Up to 48 characters. Name of the switch administrator.
location <sys-location> - Up to 48 characters. Description of the switch location.
hostname <name-string>
Sets the switch name for administrative purposes.
15
Page 20

[no] telnet-server
Enables remote telnet access to the switch.
[no] web-management
Enables the web browser to interact with the web agent on the switch.
[no] password <operator | manager>
Sets passwords for different classes of users. This command causes the switch to
prompt for a password twice, once for the new password and once to verify it was
typed correctly, and disables echoing while you type the password.
Parameters:
<operator | manager> - Class of user.
2.4 AUTHENTICATION
2.4.1 AUTHENTICATION commands - Configuration level
aaa authentication console <enable|login>
<primary-method> [<backup-method>]
Configures authentication mechanism used to control access to the switch.
aaa authentication telnet <enable|login>
<primary-method> [<backup-method>]
Configures authentication mechanism used to control access to the switch.
16
Page 21

2.5 TACACS
2.5.1 TACACS commands - EXEC level
show tacacs
Displays TACACS configuration.
2.5.2 TACACS commands - Configuration level
[no] tacacs-server host <ip-addr> [key <key-string>]
Configures a TACACS server.
tacacs-server timeout <1-255>
Sets up the TACACS timeout interval in seconds.
2.6 CDP
2.6.1 CDP commands - EXEC level
show cdp [neighbor [port-num] [detail]]
Displays CDP configuration and neigbors discovered.
2.6.2 CDP commands - Configuration level
[no] cdp
Enables/disables CDP on the switch.
cdp timer <5-254>
Sets the CDP transimit interval in seconds.
cdp holdtime <10-255>
Sets the CDP holdtime in seconds.
cdp enable [ethernet] <port-list>
Enables/disables CDP on a particular port.
17
Page 22

2.7 IP Stacking
2.7.1 IP Stacking commands - EXEC level
show stack [candidates | all]
Displays status information for the stacking feature. ‘show stack’ with no arguments
displays the status of this switch’s stack. If the keyword candidates is supplied then
this command displays a list of candidates on the local network segment. If the
keyword all is supplied then this command displays all the member switches of all
stacks on the local network segment and all candidate switches.
2.7.2 IP Stacking commands - Configuration level
[no] stack
Enables/disables the stacking feature. If the stacking features is disabled, then the
switch will reject a join request originating from a command switch.
[no] stack commander <commander-name>
Creates a command switch, and the no form of the command disperses the member
switches from this command switch’s stack, making them available to join another
stack.
[no] stack member <switch-num> mac-address <mac-addr> [password <password-str>]
Configures the candidate switch identified by the MAC address to be a member for
this switch’s stack. The no form of the command removes the switch identified by
switch-num from the stack
Parameters:
<switch-num> - A number between 1 and 15 to uniquely identify each switch; a
switch-num of zero always belongs to the command switch.
password <password-str> - is the manager password configured on the candidate
switch. If the candidate switch does not have a manager password then none
should be supplied.
[no] stack join <mac-addr>
Causes a candidate switch to join the stack whose command switch is identified by
mac-addr. The no form of the command causes the member switch to leave its
current stack.
18
Page 23

[no] stack auto-join
Causes the switch to advertise, via the discovery protocol, that it wants to
automatically join any stack operating on the local LAN segment. Switches with
passwords will not auto-join.
[no] stack auto-grab
Enables/disables auto-grab mode for stacking on the command switch. If enabled,
the command switch will attempt to grab new candidate switches and make them
members of the stack.
stack transmission-interval <n>
Sets the transmission interval for stacking.
19
Page 24

2.8 Port Settings
2.8.1 Port commands - EXEC level
show interfaces config
Displays the basic configuration of the switch ports.
Output Format:
Switch Configuration - Port Settings
Port
---1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
show statistics
Displays a summary of the network traffic handled by the switch.
Output Format:
Type Enabled Mode Flow Ctrl Bcast Limit
-------- + ------- ------------ --------- ----------10/100TX | Yes Auto Disable 0
10/100TX | Yes Auto Disable 0
10/100TX | Yes Auto Disable 0
10/100TX | Yes Auto Disable 0
10/100TX | Yes Auto Disable 0
10/100TX | Yes Auto Disable 0
10/100TX | Yes Auto Disable 0
10/100TX | Yes Auto Disable 0
10/100TX | Yes Auto Disable 0
10/100TX | Yes Auto Disable 0
10/100TX | Yes Auto Disable 0
Status and Counters - Port Counters
Port Total Bytes Total Frames Errors Rx Drops Tx
---- ------------- ------------- ------------- ------------1 83,612,741 446,524 3 0
2 0 0 0 0
3 0 0 0 0
4 0 0 0 0
5 0 0 0 0
6 0 0 0 0
7 0 0 0 0
8 15,080 10 0 0
9 0 0 0 0
10 0 0 0 0
11 0 0 0 0
20
Page 25

show statistics <port-number>
Displays the network traffic statistics for the specified port.
Output Format:
Status and Counters - Port Counters - Port 1
Link Status : Up
Bytes Rx : 83,290,873 Bytes Tx : 1,234,430
Unicast Rx : 395,490 Unicast Tx : 14,995
Bcast/Mcast Rx : 40,161 Bcast/Mcast Tx : 180
FCS Rx : 3 Drops Tx : 0
Alignment Rx : 1 Collisions Tx : 25
Runts Rx : 0 Late Colln Tx : 0
Giants Rx : 0 Excessive Colln : 0
Total Rx Errors : 4 Deferred Tx : 17
21
Page 26

show interfaces
Displays the status and current configuration of all the switch ports.
Output Format:
Port Type Alert Enabled Status Mode Ctrl Limit
---1 10/100TX No Yes Up 0
2 10/100TX No Yes Down 0
3 10/100TX No Yes Down 0
4 10/100TX No Yes Down 0
5 10/100TX No Yes Down 0
6 10/100TX No Yes Down 0
7 10/100TX No Yes Down 0
8 10/100TX No Yes Down 0
9 10/100TX No Yes Down 0
10 10/100TX No Yes Down 0
Status and Counters - Port Status
Intrusion Flow Bcast
--------------- ---------- ------ ------- --------- --------
2.8.2 Ethernet Interface Configuration Commands
To enter the Ethernet Interface Configuration level, use the Interface command described
above. Note that a port-list may be used to configure these options on more than one port
and that any of the following commands can be appended to the Interface command to
simply change the configuration. For example:
HP 4108GL(config)# interface ethernet A1,A3 disable
broadcast-limit <0..99>
Sets the theoretical maximum of network bandwidth in percentage that can be used
for broadcast traffic. Any broadcast traffic exceeding that limit will dropped. 0 means
the feature is disabled.
disable
Disables the port.
enable
Enables the port.
22
Page 27

[no] flow-control
Enables or disables flow control on the port.
Note: Full-duplex ports only.
speed-duplex <10-full | 10-half | 100-full | 100-half | 1000-full | 10-auto | auto>
Sets the mode of operation for the port.
[no] lacp [active|passive]
enables or disables LACP on the port.
2.9 Trunk Configuration
2.9.1 Trunk commands - EXEC level
show trunks [<port-list>]
Displays trunks that are configured on the system. This does not include dynamic
trunks that have been formed by LACP.
Output Format:
Port
----
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
-------- + ----- -------- | ---- -------- + ----10/100TX | | 9 10/100TX |
10/100TX | Trk1 FEC | 10 10/100TX |
10/100TX | Trk1 FEC | 11 10/100TX |
10/100TX | | 12 10/100TX |
10/100TX | Trk2 Trunk | 13 10/100TX |
10/100TX | Trk2 Trunk | 14 10/100TX |
10/100TX | | 15 10/100TX |
10/100TX | | 16 10/100TX |
Switch Configuration - Trunks
Type Group Type | Port Type Group
Type
--------
23
Page 28

show lacp
Displays LACP status information.
Output Format:
P0RT LACP TRUNK PORT LACP LACP
NUMB ENABLED GROUP STATUS PARTNER STATUS
----
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Active Dyn1 Up Yes Success
Passive Trk1 Down No Failure
Active Blocked No Failure
Active Disabled
Active Dyn1 Up Yes Success
Active Standby
Active Up
Active Up
2.9.2 Trunk commands - Configuration level
LACP
------------------ -------- ----- --------
[no] trunk <trk1..trk24 > [trunk | fec | lacp] <port list>
This command configures each port in the switch to either be a Trunked, SA Only
Trunked, FEC Trunked port, or a regular singular port.
For Trunks: All ports in a Trunked group, 1 to 4 ports maximum, must have the same
port type.
General Considerations: (1) To avoid broadcast storms, or loops in your network
while configuring trunks, first disable or disconnect all the ports you wish to add or
remove from both sides of the trunk. Once done configuring the trunk, enable or reconnect the ports. (2) If you have multiple groups of the same or different types and/or
singular connections between two switches, you have created a loop in the network. You
must enable Spanning Tree on both switches to avoid a broadcast storm or other
network problems. See the Switch Management and Configuration Guide for more
information.
Parameters:
<trk1..trk24 |none> - Determines the group that a port is configured to be a
member of: trkX indicates a general group of trunked ports; none indicates that the
associated port is a singular independent port (i.e., not part of a trunk).
24
Page 29

[type <trunk | fec | lacp>] - Determines the method by which the switch
distributes the traffic load across the multiple links in the trunk group: trunk - uses
source and destination MAC addresses for load distribution (select this to connect to
devices such as the HP Switch 2000 or the Sun Trunk Server); fec - uses an
automatic protocol for load distribution (select this to connect to devices that
support Cisco's Fast EtherChannel trunking).
2.10 Spanning Tree
2.10.1 Spanning Tree commands - EXEC level
show spanning-tree config
Displays spanning tree configuration information.
Output Format:
Switch Configuration - Spanning Tree Operation
Spanning Tree Enabled [No] : No
STP Priority [32768] : 32768 Hello Time [2] : 2
Max Age [20] : 20 Forward Delay [15] : 15
Port
----
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Type Cost Pri Mode | Port Type Cost Pri Mode
-------- + ----- --- ---- | ---- -------- + ----- --- ---10/100TX | 10 128 Norm | 9 10/100TX | 10 128 Norm
10/100TX | 10 128 Norm | 10 10/100TX | 10 128 Norm
10/100TX | 10 128 Norm | 11 10/100TX | 10 128 Norm
10/100TX | 10 128 Norm | 12 10/100TX | 10 128 Norm
10/100TX | 10 128 Norm | 13 10/100TX | 10 128 Norm
10/100TX | 10 128 Norm | 14 10/100TX | 10 128 Norm
10/100TX | 10 128 Norm | 15 10/100TX | 10 128 Norm
25
Page 30

show spanning-tree
Displays bridge-level spanning tree information.
Output Format:
STP Enabled : Yes
Switch Priority : 32,768
Hello Time : 2
Max Age : 20
Forward Delay : 15
Topology Change Count : 1
Time Since Last Change : 4 mins
Root MAC Address : 0060b0-885a80
Root Path Cost : 0
Root Port : This switch is root
Root Priority : 32768
Port Type Cost Priority State Designated Bridge
----
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
10/100TX 10 128 Forwarding 0060b0-885a80
10/100TX 10 128 Disabled
10/100TX 10 128 Disabled
10/100TX 10 128 Disabled
10/100TX 10 128 Disabled
10/100TX 10 128 Disabled
10/100TX 10 128 Disabled
10/100TX 10 128 Disabled
10/100TX 10 128 Disabled
10/100TX 10 128 Disabled
10/100TX 10 128 Disabled
Status and Counters - Spanning Tree Information
--------------------------- -------- ----- --------
2.10.2 Spanning Tree commands - Configuration level
[no] spanning-tree
Enables or disables spanning tree on the device.
26
Page 31

spanning-tree [forward-delay <seconds>]
[hello-time <seconds>]
[maximum-age <seconds>]
[priority <0..65535>]
spanning-tree <[ethernet] port-list>[path-cost <1..65535>]
[priority <0..255>]
[mode <norm|fast>]
This command configures the parameters for operation of the switch in a spanning
tree topology. Note - the default spanning tree configuration complies with the
IEEE 802.1D standard recommended values and should not be changed without
thorough knowledge of spanning tree operation. Note: As per IEEE 802.1Q
Standard, this switch implements a single instance of Spanning Tree operating over
all VLANs.
Parameters:
path-cost <port-list><1..65535> - Individual port cost used to determine which
ports are forwarding ports. The defaults is 100 for 10 Mbps ports, 10 for
10/100TX and 100FX ports, and 5 for 100/1000TX and 1Gbps ports.
priority <port-list><0..255> - Another value used by spanning tree to the
forwarding ports. The port with the lowest number has the highest priority. The
default is 128.
mode <port-list> [norm | fast] (default: norm) - norm (for normal) mode causes
the port to operate according to the standard Spanning Tree Protocol - when
connected, the port progresses through the Listening, Learning, and either
Blocking or Forwarding states. fast mode causes the port to immediately
operate in the Forwarding State when a device is connected to it. Use this setting
only on ports that are connected to end nodes (for example: PCs, Workstation,
or printers). Caution: Changing the Mode to fast on ports connected to a hub or
switch may cause loops in your network that STP may not be able to detect, in
all cases.
forward-delay <seconds> - Time the switch waits between transition from
listening to learning and from learning to forwarding states. The range is 4 to 30.
The default is 15.
hello-time <seconds> - Time (in seconds) between messages transmitted when
the switch is root. The range is 1 to 10. The default is 2.
maximum-age <seconds> - Maximum message age (in seconds) of received
STP information before it is discarded. The range is 6 to 40. The default is 20.
priority <0..65535> - Switch (or bridge) priority used along with the switch
MAC address to determine which device is the root. The default is 32768.
27
Page 32

2.11 IP
2.11.1 IP commands - EXEC level
show ip
Displays the IP configuration on the switch.
Output Format
There are two different IP configuration screens. The first is displayed when no
vlans are configured on the switch; the second is displayed when vlans are
configured.
Switch Configuration - Internet (IP) Service
Default Gateway: 192.32.36.1
TimeP Config [DHCP]: DHCP TimeP Poll Interval (min) [720]: 720
IP Config [DHCP/Bootp] : DHCP/Bootp
IP Address : 192.32.36.96 Subnet Mask : 255.255.255.192
Switch Configuration - Internet (IP) Service
Default Gateway: 192.32.36.1
TimeP Config [DHCP]: DHCP TimeP Poll Interval (min) [720]: 720
VLAN IP Config IP Address Subnet Mask
------------ + ----------
DEFAULT_VLAN | Manual 192.32.36.91 255.255.255.192
vlan2 | DHCP/Bootp
------------------------------
28
Page 33

show ip authorized-managers
Displays the current configuration's IP managers access records.
Output Format:
Authorized Manager IP IP Mask Access Level
----------------------
192.32.36.78 255.255.255.255 Manager
show arp
Displays the ARP cache of the switch.
Output Format
Switch Configuration - IP Managers
-----------------------------------------
IP Address MAC Address VLAN
--------------
192.32.36.78 080009-012345 orange-lan
show ip route
Displays active IP route entries used by the switch.
Output Format
Network Addr Network Mask Gateway Port Cost Type
--------------
192.32.36.0 255.255.255.0 192.32.36.1 A1 1 R
ARP Cache
------------------------
IP Route Entries
-------- ---- ----------- -------------
29
Page 34

show timp
Displays active Timep configuration.
Output Format
show sntp
Displays active SNTP configuration.
Output Format
Timep Configuration
Time Sync Mode: Timep
TimeP Mode [Disabled] : Manual Server Address : 15.29.16.105
Poll Interval (min) [720] : 600
SNTP Configuration
Time Sync Mode: Timep
SNTP Mode [Disabled] : Disabled
Poll Interval (min) [720] : 600
30
Page 35

2.11.2 IP commands - Configuration level
[no] ip authorized-managers <ip-addr>
[mask <ip-mask>]
[operator | manager]
Sets the IP addresses you will allow to access the switch’s Web browser interface, to
telnet to the switch console, and to perform TFTP operations. A maximum of 10
addresses is supported.
Parameters:
<ip-addr> - The IP address of an authorized manager.
mask <ip-mask> - The default mask is 255.255.255.255. A mask that allows you
to define which portions of the listed IP address need to be matched by an
incoming request. For example, with an authorized address of 10.8.11.1 and a
mask of 255.255.255.255, only access from 10.8.11.1 is allowed. With a mask of
255.255.255.0, access from any IP address with 10.8.11.x is allowed.
<operator | manager> - The default access level is manager. A designation of
the management capabilities that are accessible to the authorized manager.
manager allows full access to all web browser and the CLI for viewing and
setting the switch configuration, and for performing all other interface
operations, including all TFTP operations. operator allows view-only access
from the web browser and the CLI, but does not allow changing the switch
configuration or any TFTP operations.
[no] timesync <timep | sntp >
Configures the network time protocol to be used by the switch.
[no] timep <dhcp | manual <ip-addr>> [interval <1..9999>]
Configures Timep on the switch.
Parameters:
<dhcp | manual> - The method the switch uses to acquire the Timep server
address: dhcp - from a DHCP server; manual - you manually enter the Timep
server address; disable - the switch will not attempt to get its time from a Timep
server.
interval <1..9999> (default is 720) How often (in minutes) the switch tries to
get the current time.
<ip-addr> - The IP address of the Timep server that the switch gets the current
time from.
31
Page 36

[no] sntp < server <ip-addr> [version]> [poll-interval <30-720>]
Configures SNTP on the switch.
ip default-gateway <ip-addr>
Assigns an IP address to be used as the default gateway when the switch is not in
routing mode.
ip route <<ip-addr>/<1..32> | <ip-addr> <ip-mask>> <ip-addr>
Used to configure a static IP route for the switch.
ip ttl <value>
Sets the maximum time that a packet will live on the network.
[no] arp <ip-addr> [mac-addr]
Used to modify the arp cache.
32
Page 37

2.11.3 IP commands - VLAN Interface level
[no] ip address <dhcp-bootp | <<ip-addr>/<1..32> |
<ip-addr> <ip-mask>] [secondary]>
This command configures the IP address for the switch. Note, by default this
command uses a VLAN identifier of one. Although this command is duplicated at
the VLAN context level, it is defined here for those customers who do not want to
be exposed to VLAN distinctions.
Parameters:
dhcp-bootp - The method the switch uses to acquire its IP Service configuration:
dhcp-bootp - the switch attempts to get its IP configuration, or its complete
configuration, from a DHCP/Bootp server, depending on how the server is
configured. If the 'address' is specified at the command line then the interface uses
a 'manual' method in which the IP address and subnet mask are explicitly specified.
If the modal operation 'no' is specified for the interface then the interface becomes
disabled and all IP communication with the switch ceases. This includes SNMP,
management, Web browser access, and telnet access.
<ip-addr>/<1..32> - IP address for the switch (or VLAN) IP interface. <1..32> is
the number of bits present in the subnet mask used by all devices in the IP subnet
being configured.
<ip-addr> <ip-mask> - This is an alternative syntax for specifying the IP address
and subnet mask described above.
33
Page 38

2.12 SNMP
2.12.1 SNMP commands - EXEC level
show snmp-server
Displays the SNMP communities which may be used to access the switch along with
the network management stations configured to receive SNMP traps.
Output Format:
Community Name MIB View Write Access
--------------
public Manager Unrestricted
Send Authentication Traps [No] : No
Address Community Events Sent in Trap
----------------------
192.32.36.78 public None
SNMP Server
---------------------
-----------------------------------
34
Page 39

2.12.2 SNMP commands – Configuration Level
[no] snmp-server community <community-name>
[manager | operator]
[restricted | unrestricted]
Used to configure a new SNMP community or to edit the configuration for an
existing one
Parameters:
<community-name> - Enter (up to 16 characters) the SNMP community name.
[manager | operator] - Manager - the community can access all MIB objects;
Operator - the community can access all except the CONFIG MIB.
[restricted | unrestricted] - Unrestricted - any MIB variable that has read/write
access can be set; Restricted - MIB variables cannot be set, only read.
[no] snmp-server host <ip-addr> <community-name> [none | all | non-info | critical |
debug]
Configures which network management stations will receive SNMP event log
messages from the switch and the types of events for which the switch will send
these messages.
Parameters:
<ip-addr> - Address of the network management station.
<community-name> - The name of the SNMP community to which the network
management station belongs.
[none | all | non-info | critical | debug] - The level of Switch events that will
generate a Trap to be sent: None - send no log message; All - send all log
messages; Not INFO - send each log message that is not informational-only;
Critical - send critical-level log messages; Debug (reserved for Internal use).
[no] snmp-server enable traps authentication
Enables authentication traps to be sent when a management station attempts an
unauthorized access.
35
Page 40

2.13 VLAN Configuration
2.13.1 VLAN commands - EXEC level
show vlans
Displays the current VLANs.
Output Format:
Switch Configuration - VLAN Information
VLAN Support [No] : Yes
Maximum VLANs to support [8] : 8
Primary VLAN: DEFAULT_VALN
802.1Q VLAN ID Name
--------------
1 DEFAULT_VLAN
show vlans <vlan-id>
Displays which ports are assigned to particular VLANs.
Output Format:
Port DEFAULT_VLAN vlan2 | Port DEFAULT_VLAN vlan2
---- + ------------ | ---- + ------------
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| Untagged No | 9 | Untagged No
| Untagged No | 10 | Untagged No
| Untagged No | 11 | Untagged No
| Untagged No | 12 | Untagged No
| Untagged No | 13 | Untagged No
| Untagged No | 14 | Untagged No
| Untagged No | 15 | Untagged No
| Untagged No | 16 | Untagged No
Type Status
------------ ------------
Static Up
Switch Configuration - VLAN - VLAN Port Assignment
------------------------
2.13.2 VLAN commands – Configuration Level
max-vlans <1..256>
Sets the maximum number of VLANs on the system. The default value is 8.
36
Page 41

primary-vlan <vlan-id>
Sets the primary VLAN used for network management.
[no] vlan <vlan-id>
Creates a new VLAN or changes the system context to the VLAN configuration
level. Note that vlan-name can be substituted for the vlan-id when using this command.
static-vlan <vlan-id>
Creates a new static VLAN from one which has been dynamically created by GVRP.
[no] vlan-support
Enables VLAN support on the switch.
2.13.3 VLAN Interface commands
To enter the VLAN Interface Configuration level, use the vlan command described above.
Note that any of the following commands can be appended to the vlan command to simply
change the configuration. For example:
HP 4108GL(config)# add vlan 2 name orange-lan
name <vlan-name>
Changes the current VLAN identifier’s name.
[no] tagged <port-list>
Assigns ports to current VLAN identifier as tagged.
[no] untagged <port-list>
Assigns ports to current VLAN identifier as untagged.
[no] forbid <port-list>
Forbids the ports from ever becoming a member of the current VLAN.
37
Page 42

auto <port-list>
Causes each port identified in the port-list to learn their VLAN membership using
the Group VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP). This command is only valid when
GVRP is enabled.
2.14 GVRP
2.14.1 GVRP commands - EXEC level
show gvrp
Displays the current VLANs.
Output Format:
Switch Configuration - GVRP Information
GVRP Enabled [No] : Yes
Port Type | Unknown VLAN
----
-------- + -----------A1 10/100TX | Learn
A2 10/100TX | Learn
A3 10/100TX | Learn
A4 10/100TX | Learn
2.14.2 GVRP commands – Configuration level
[no] gvrp
Enables the Group VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) on the switch.
2.14.3 Ethernet Interface Configuration commands
unknown-vlans <learn | block |disable>
Defines what the port will do when it encounters GVRP packet requested it to join a
VLAN. If learn is specified then the port will join the advertised VLAN and
propagate a VLAN join requests through all other forwarding ports that are
participating in GVRP. If block is specified then the port will not join the advertised
VLAN and will not propagate any VLAN joins for the advertised VLAN.
38
Page 43

2.15 IGMP
2.15.1 IGMP Commands – EXEC Level
show ip igmp [vlan-id] config
Displays IGMP configuration information.
Output Format:
Switch Configuration - IGMP Service
IGMP Enabled [No] : No
Forward with High Priority [No] : No
Port Type IP Mcast | Port Type IP Mcast
---- -------- + -------- | ---- -------- + -------3 10/100TX | Auto | 11 10/100TX | Auto
4 10/100TX | Auto | 12 10/100TX | Auto
5 10/100TX | Auto | 13 10/100TX | Auto
6 10/100TX | Auto | 14 10/100TX | Auto
7 10/100TX | Auto | 15 10/100TX | Auto
8 10/100TX | Auto | 16 10/100TX | Auto
9 10/100TX | Auto | Mesh Mesh | Auto
10 10/100TX | Auto |
show ip igmp [<vlan-id> | group <group-address>]
When IGMP is enabled, this command shows a summary of the IGMP status for all
the IP Multicast groups used by the selected VLAN. If the feature is not enabled,
then this command displays “IGMP not enabled”.
Output Format:
Status and Counters - IP Multicast (IGMP) Status
Active Group Addresses Reports Queries Querier Access Port
----------------------
Active Group Address :
Port Type Access
----
Active Group Address :
Port Type Access
----
Age timer Leave timer
Age timer Leave timer
----------------------------- -------
-------------------- ----------- --------
-------------------- ----------- --------
39
Page 44

2.15.2 IGMP Configuration commands – Vlan Interface level
[no] ip igmp
Enables the IP Multicast (IGMP) feature for IGMP communication between
Multicast Routers, Multicast Servers, and Multicast Clients connected to the switch
or selected VLAN.
[no] ip igmp high-priority-forward
Determines whether the switch forwards all IP Multicast traffic at high priority.
[no] ip igmp querier
Determines whether the switch is querier or not.
ip igmp <auto|block|forward> <port-list>
Instructs the switch's IGMP feature to control the action taken with an IGMP
frame.
40
Page 45

2.16 Port Monitoring
2.16.1 Port Monitoring commands - EXEC level
show mirror-port
Displays the configuration of the monitoring port.
Output Format:
Switch Configuration - Network Monitoring Port
Monitoring Enabled [No] : Yes
Monitoring Port : 3
Monitor : Ports
Port Type Action | Port Type Action
---- -------- + ------- | ---- -------- + ------3 10/100TX | | 11 10/100TX |
4 10/100TX | | 12 10/100TX |
5 10/100TX | | 13 10/100TX |
6 10/100TX | | 14 10/100TX |
7 10/100TX | | 15 10/100TX |
8 10/100TX | | 16 10/100TX |
9 10/100TX | | Mesh Mesh |
2.16.2 Port Monitoring commands - Configuration level
[no] mirror-port [<port-num>]
This command defines the switch port that will be used as the Monitoring Port for
diagnostic purposes. The switch ports that will be monitored are defined through the
monitor command at the Ethernet Interface Configuration Level. All the network
traffic seen by the monitored ports is copied to the Monitoring Port to which a
network analyzer can be attached.
Note: When monitoring multiple ports in a busy network, some frames may not be
copied to the monitoring port.
Parameters:
port-num - Port that will be acting as the monitoring port. A configured trunk port
cannot be used.
41
Page 46

2.16.3 Port Monitoring commands - VLAN Interface level
[no] monitor
Used to enable/disable monitoring of the VLAN.
2.16.4 Port Monitoring commands - Ethernet Interface level
[no] monitor
Used to enable/disable monitoring of the port.
2.17 Port Security
2.17.1 Port Security commands - EXEC level
show port-security
Displays the per-port security configuration for the switch.
Output Format:
Switch Configuration - Port Security
Port Learn Mode Action
------ ---------- -------------------3 Continuous None
4 Continuous None
5 Continuous None
6 Continuous None
7 Continuous None
8 Continuous None
9 Continuous None
10 Continuous None
11 Continuous None
12 Continuous None
13 Continuous None
42
Page 47

show port-security [ethernet] <port-list>
Displays the port security configuration for an individual port.
Output Format:
Switch Configuration - Port Security
Port : 3
Learn Mode [Continuous] : Continuous
Action [None] : None
show port-security intrusion-log
Displays information on any port security intrusions that have occurred on the
switch.
Output Format:
Status and Counters – Intrusion Log
Port MAC Address Date / Time
----
---------------------------------------
2.17.2 Port Security commands - Configuration level
port-security <port-list>
[learn-mode < continuous | static >]
[address-limit <1..8>]
[action <none | send-alarm | send-disable>]
[no] port-security <port-list>
[mac-address <mac-addr>]
This command configures port security on the switch.
Parameters:
learn-mode - If continuous is selected, the switch learns any new address from
packets received on the port. If static is selected, up to the number of addresses
43
Page 48

defined by the "address-limit" parameter are learned or entered for the port.
These addresses are static; they are not aged out.
addr-limit <1..8> - This parameter is valid only if static is selected for the
learn-mode. This parameter defines the number of network devices that are
authorized to communicate through the switch port. Up to 8 devices can be
authorized for any port.
addr-list <mac-addr> - This parameter is valid only if static is selected for the
learn-mode. If you enter no authorized addresses, the switch will learn and
configure authorized addresses as it detects them on the port, up to the addresslimit number of addresses, and make these the static authorized addresses for the
port. If you enter fewer addresses than the Address Limit, the switch will learn
the additional addresses up to the address-limit. If you enter more addresses than
the address-limit, an error message is displayed when you attempt to Save the
configuration.
action - Indicates the action the switch will take if an intruder is detected on the
port.
44
Page 49

3. Console Menu
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
1. Status and Counters...
2. Switch Configuration...
3. Console Passwords…
4. Event Log
5. Command Line (CLI)
6. Reboot Switch
7. Download OS
8. Run Setup
0. Logout
Provides the menu to display configuration, status, and counters.
To select menu item, press item number, or highlight item and press <Enter>.
Main Menu
3.1 Status and Counters
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
1. General System Information
2. Switch Management Address Information
3. Module Information
4. Port Status
5. Port Counters
6. Address Table
7. Port Address Table
8. Spanning Tree Information
0. Return to Main Menu...
Displays switch management information including software versions.
To select menu item, press item number, or highlight item and press <Enter>.
Status and Counters Menu
45
Page 50

3.1.1 General System Information
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
System Contact :
System Location :
Firmware revision : E.08.XX Base MAC Addr : 0060b0-882200
ROM Version : E.05.X1 Serial Number :
Up Time : 40 mins Memory - Total : 5,803,088
CPU Util (%) : 1 Free : 2,230,032
Status and Counters - General System Information
IP Mgmt - Pkts Rx : 11 Packet - Total : 438
Actions-> Back Help
Return to previous screen.
Use arrow keys to change action selection and <Enter> to execute action.
Pkts Tx : 0 Buffers Free : 272
Lowest : 199
Missed : 0
3.1.2 Management Address Information
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
Time Server Address :
MAC Address : 0060b0-882200
IP Address : 10.0.8.105
IPX Network Number :
Status and Counters - Management Address Information
Actions-> Back Help
Return to previous screen.
Use arrow keys to change action selection and <Enter> to execute action.
46
Page 51

3.1.3 Module Information
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
Slot Module Type Module Description
---A Slot Available
B Slot Available
C Slot Available
D Slot Available
E Slot Available
F Slot Available
G Slot Available
H Slot Available
Actions-> Back Help
Return to previous screen.
Use up/down arrow keys to scroll to other entries, left/right arrow keys to
change action selection, and <Enter> to execute action.
Status and Counters - Module Information
------------------------------------------------------------
3.1.4 Port Status
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
Port Type
---1 10/100TX
2 10/100TX
3 10/100TX
4 10/100TX
5 10/100TX
6 10/100TX
7 10/100TX
8 10/100TX
9 10/100TX
10 10/100TX
Actions-> Back Intrusion log Help
Return to previous screen.
Use up/down arrow keys to scroll to other entries, left/right arrow keys to
change action selection, and <Enter> to execute action.
Status and Counters - Port Status
Intrusion Flow Bcast
Alert Enabled Status Mode Ctrl Limit
--------------- ---------- ------ ------- --------- --------
No Yes Up 100HDx off 0
No Yes Down 10HDx off 0
No Yes Down 10HDx off 0
No Yes Down 10HDx off 0
No Yes Down 10HDx off 0
No Yes Down 10HDx off 0
No Yes Down 10HDx off 0
No Yes Down 10HDx off 0
No Yes Down 10HDx off 0
No Yes Down 10HDx off 0
47
Page 52

3.1.5 Port Counters
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
Port Total Bytes Total Frames Errors Rx Drops Tx
---1 16,448 217 0 0
2 0 0 0 0
3 0 0 0 0
4 0 0 0 0
5 0 0 0 0
6 0 0 0 0
7 0 0 0 0
8 0 0 0 0
9 0 0 0 0
10 0 0 0 0
11 0 0 0 0
Actions-> Back Show details Reset Help
Return to previous screen.
Use up/down arrow keys to scroll to other entries, left/right arrow keys to
change action selection, and <Enter> to execute action.
Status and Counters - Port Counters
-------------------------- ------------- -------------
3.1.5.1 Port Counters Details
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
Link Status : Up
Bytes Rx : 16,088 Bytes Tx : 360
Unicast Rx : 88 Unicast Tx : 4
Bcast/Mcast Rx : 124 Bcast/Mcast Tx : 1
FCS Rx : 0 Drops Tx : 0
Alignment Rx : 0 Collisions Tx : 0
Runts Rx : 0 Late Colln Tx : 0
Giants Rx : 0 Excessive Colln : 0
Total Rx Errors : 0 Deferred Tx : 0
Actions-> Back Reset Help
Return to previous screen.
Use arrow keys to change action selection and <Enter> to execute action.
Status and Counters - Port Counters - Port 1
48
Page 53

3.1.6 Address Table
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
MAC Address Located on Port
------------0060b0-e26440 1
080009-092851 1
080009-76ac55 1
080009-97aad2 1
Actions-> Back Search Next page Prev page Help
Return to previous screen.
Use up/down arrow keys to scroll to other entries, left/right arrow keys to
change action selection, and <Enter> to execute action.
Status and Counters - Address Table – VLAN ID 23
---------------
3.1.7 Port Address Table
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
MAC Address
------------0060b0-e26440
080009-092851
080009-76ac55
080009-97aad2
Actions-> Back Search Next page Prev page Help
Return to previous screen.
Use up/down arrow keys to scroll to other entries, left/right arrow keys to
change action selection, and <Enter> to execute action.
Status and Counters - Port Address Table - Port A1
49
Page 54

3.1.8 Spanning Tree Information
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
STP Enabled : Yes
Switch Priority : 32,768
Hello Time : 2
Max Age : 20
Forward Delay : 15
Topology Change Count : 1
Time Since Last Change : 4 mins
Root MAC Address : 0060b0-885a80
Root Path Cost : 0
Root Port : This switch is root
Root Priority : 32768
Actions-> Back Show ports Help
Return to previous screen.
Use arrow keys to change action selection and <Enter> to execute action.
Status and Counters - Spanning Tree Information
3.1.8.1 Spanning Tree Port Information
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
Port Type Cost Priority State Designated Bridge
----
1 10/100TX 10 128 Forwarding 0060b0-885a80
2 10/100TX 10 128 Disabled
3 10/100TX 10 128 Disabled
4 10/100TX 10 128 Disabled
5 10/100TX 10 128 Disabled
6 10/100TX 10 128 Disabled
7 10/100TX 10 128 Disabled
8 10/100TX 10 128 Disabled
9 10/100TX 10 128 Disabled
Actions-> Back Help
Return to previous screen.
Use up/down arrow keys to scroll to other entries, left/right arrow keys to
change action selection, and <Enter> to execute action.
Status and Counters - Spanning Tree - Port Information
--------------------------- -------- ----- ------------
50
Page 55

3.2 Configuration Menu
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
1. System Information
2. Port/Trunk Settings
3. Network Monitoring Port
4. Spanning Tree Operation
5. IP Configuration
6. SNMP Community Names
7. Authorized Managers
8. VLAN Menu...
0. Return to Main Menu...
Configures system-level information including system identification.
To select menu item, press item number, or highlight item and press <Enter>.
Switch Configuration Menu
51
Page 56

3.2.1 System Information
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
System Name : DEFAULT_CONFIG
System Contact :
System Location :
Switch Configuration - System Information
Inactivity Timeout (min) [0] : 0
Inbound Telnet Enabled [Yes] : Yes
Time Zone [0] : 0
Daylight Time Rule [None] : None
Actions-> Cancel Edit Save
Cancel changes and return to previous screen.
Use arrow keys to change action selection and <Enter> to execute action.
Address Age Interval (min) [5] : 5
Web Agent Enabled [Yes] : Yes
Help
3.2.2 Port/Trunk Settings
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
Port Type Enabled Mode Flow Ctrl Group Type
---- -------- + ------A1 10/100TX | Yes
A2 10/100TX | Yes
A3 10/100TX | Yes
A4 10/100TX | Yes
A5 10/100TX | Yes
A6 10/100TX | Yes
A7 10/100TX | Yes
A8 10/100TX | Yes
A9 10/100TX | Yes
A10 10/100TX | Yes
A11 10/100TX | Yes
Switch Configuration – Port/Trunk Settings
--------------------- --------- ----------
Auto Disable Dyn LACP
Auto Disable Dyn LACP
Auto Disable Trk1 Trunk
Auto Disable Trk1 Trunk
Auto Disable
Auto Disable Trk2 FEC
Auto Disable Trk2 FEC
Auto Disable Dyn LACP
Auto Disable Trk2 FEC
Auto Disable MESH
Auto Disable MESH
Actions-> Cancel Edit Save Help
Cancel changes and return to previous screen.
Use arrow keys to change action selection and <Enter> to execute action.
52
Page 57

3.2.3 Network Monitoring Port
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
Monitoring Enabled [No] : Yes
Monitoring Port : A1
Monitor : Ports
Switch Configuration – Network Monitoring Port
Port Type Action
---- -------- + ------A1 10/100TX |
A2 10/100TX |
A3 10/100TX |
A4 10/100TX |
A5 10/100TX |
A6 10/100TX |
Actions-> Cancel Edit Save
Cancel changes and return to previous screen.
Use arrow keys to change action selection and <Enter> to execute action.
Port
----
A7
A8
B1
B2
B3
B4
Type Action
-------- + ------10/100TX |
10/100TX |
10/100TX |
10/100TX |
10/100TX |
10/100TX |
Help
3.2.4 Spanning Tree Operation
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
Spanning Tree Enabled [No] : No
STP Priority [32768] : 32768
Max Age [20] : 20
Switch Configuration – Spanning Tree Operation
Hello Time [2] : 2
Forward Delay [15] : 15
Port Type Cost
---- -------- + ----A1 10/100TX | 10
A2 10/100TX | 10
A3 10/100TX | 10
A4 10/100TX | 10
A5 10/100TX | 10
A6 10/100TX | 10
A7 10/100TX | 10
A8 10/100TX | 10
Actions-> Cancel Edit Save Help
Cancel changes and return to previous screen.
Use arrow keys to change action selection and <Enter> to execute action.
Pri Mode
-------
128 Norm
128 Norm
128 Norm
128 Norm
128 Norm
128 Norm
128 Norm
128 Norm
53
Page 58

3.2.5 IP Configuration
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
Default Gateway : 10.0.8.1
Time Protocol Config [DHCP] : DHCP
TimeP Poll Interval (min) [720] : 720
IP Config [DHCP/Bootp] : Manual
IP Address : 10.0.8.105
Subnet Mask : 255.255.248.0
Actions-> Cancel Edit Save Help
Cancel changes and return to previous screen.
Use arrow keys to change action selection and <Enter> to execute action.
Switch Configuration - Internet (IP) Service
With multiple Vlans configured:
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
Default Gateway : 10.0.8.1
Time Protocol Config [DHCP] : DHCP
TimeP Poll Interval (min) [720] : 720
VLAN IP Config Ip Address Subnet Mask
----------- + --------Orange Lan | Manual 10.0.8.105 255.255.248.0
Yellow Lan | Disabled
Actions-> Cancel Edit Save Help
Cancel changes and return to previous screen.
Use arrow keys to change action selection and <Enter> to execute action.
Switch Configuration - Internet (IP) Service
---------------------------
54
Page 59

3.2.6 SNMP Communities
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
Community Name MIB View Write Access
---------------public Manager Unrestricted
Actions-> Back Add Edit Delete Help
Return to previous screen.
Use up/down arrow keys to change record selection, left/right arrow keys to
change action selection, and <Enter> to execute action.
Switch Configuration - SNMP Communities
--------------------
3.2.7 Authorized Managers
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
Authorized Manager IP Mask Access Level
--------------------
15.29.16.80 255.255.255.255 Manager
Actions-> Back Add Edit Delete Help
Return to previous screen.
Use up/down arrow keys to change record selection, left/right arrow keys to
change action selection, and <Enter> to execute action.
Switch Configuration – Authorized Managers
---------------------------
55
Page 60

3.2.8 VLAN Menu
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
1. VLAN Support
2. VLAN Names
3. VLAN Port Assignment
4. Return to Previous Menu...
0. Return to Main Menu...
Return to previous screen.
Use up/down arrow keys to change record selection, left/right arrow keys to
change action selection, and <Enter> to execute action.
Switch Configuration - VLAN Menu
3.2.8.1 VLAN Support
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
Activate VLANs [No] : Yes
Maximum Vlnas to support [8] : 8
Primary VLAN : DEFAULT_VLAN
GVRP Enabled [No] : No
Actions-> Back Add Edit Delete Help
Return to previous screen.
Use up/down arrow keys to change record selection, left/right arrow keys to
change action selection, and <Enter> to execute action.
Switch Configuration - VLAN Support
56
Page 61

3.2.8.2 VLAN Names
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
Name 802.1Q VLAN ID
-----------DEFAULT_VLAN 1
Actions-> Back Add Edit Delete Help
Return to previous screen.
Use up/down arrow keys to change record selection, left/right arrow keys to
change action selection, and <Enter> to execute action.
--------------
Switch Configuration - VLAN Names
3.2.8.3 VLAN Port Assignment
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
Port DEFAULT_VLAN | Port DEFAULT_VLAN
---- + ------------ | ---- + -----------A1 | Tagged
A2 | Tagged
A3 | Tagged
A4 | Tagged
A5 | Tagged
A6 | Tagged
A7 | Tagged
A8 | Tagged
A9 | Tagged
A10 | Tagged
A11 | Tagged
A12 | Tagged
Actions-> Cancel Edit Save Help
Use arrow keys to change field selection, <Space> to toggle field choices,
and <Enter> to go to Actions.
Switch Configuration - VLAN Port Assignment
| E1 | Untagged
| E2 | Untagged
| E3 | Untagged
| E4 | Untagged
| E5 | Untagged
| E6 | Untagged
| E7 | Untagged
| E8 | Untagged
| E9 | Untagged
| E10 | Untagged
| E11 | Untagged
| E12 | Untagged
57
Page 62

3.3 Password Menu
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
1. Set Operator Password
2. Set Manager Password
3. Delete Password Protection
4. Return to Previous Menu...
0. Return to Main Menu...
Prompts you to enter an Operator-level password.
To select menu item, press item number, or highlight item and press <Enter>.
Set Password Menu
3.4 Event Log
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
M 01/01/90 00:00:07 sys: 'System reboot due to Power Failure'
I 01/01/90 00:00:07 system: -------------------------------------------------I 01/01/90 00:00:07 system: System went down without saving crash information
I 01/01/90 00:00:29 timep: timep client enabled
I 01/01/90 00:00:29 garp: GARP Protocol enabled
I 01/01/90 00:00:31 tftp: Enable succeeded
I 01/01/90 00:00:31 system: System Booted.
I 01/01/90 00:00:37 ports: port 1 is now on-line
I 01/01/90 00:00:37 ip: network enabled on 10.0.8.105
I 01/01/90 00:39:55 mgr: SME CONSOLE Session - MANAGER Mode established
----
Log events stored in memory 1-13. Log events on screen 1-13.
Actions-> Back Next page Prev page End Help
Return to previous screen.
Use up/down arrow scroll log one line, left/right arrow keys to
change action selection, and <Enter> to execute action.
58
Page 63

3.5 Download Screen
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
Current Firmware revision : E.08.XX
Method [TFTP] : TFTP
TFTP Server :
Remote File Name :
Actions-> Cancel Edit eXecute Help
Select the file transfer method (TFTP and XMODEM are currently supported).
Use arrow keys to change field selection, <Space> to toggle field choices,
and <Enter> to go to Actions.
Download OS
3.6 Run Setup
HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx 01-Apr-2000
==========================- CONSOLE - MANAGER MODE -============================
System Name : HP ProCurve Switch xxxxx
System Contact :
Manager Password : Confirm Password:
Logon Default : Menu Time Zone [0] : 0
Community Name : public Spanning Tree Enabled [No] : No
Default Gateway : 10.0.8.1
TimeP Config [DHCP] : DHCP
IP Config [DHCP/Bootp] : Manual
IP Address : 10.0.8.80 Subnet Mask : 255.255.248.0
Actions-> Cancel Edit eXecute Help
Select the file transfer method (TFTP and XMODEM are currently supported).
Use arrow keys to change field selection, <Space> to toggle field choices,
and <Enter> to go to Actions.
Switch Setup
59
Page 64

Index
A
aaa authentication console ................................16
aaa authentication telnet....................................16
arp......................................................................32
auto....................................................................38
auto-tftp.............................................................14
B
boot......................................................................6
broadcast-limit ..................................................22
C
cdp.....................................................................17
cdp enable .........................................................17
cdp holdtime......................................................17
cdp timer ...........................................................17
clear arp...............................................................7
clear intrusion-log ...............................................8
clear statistics ......................................................8
configure .............................................................5
console ..............................................................14
copy.................................................................6, 9
D
daylight-time-rule .............................................15
disable ...............................................................22
E
enable ............................................................5, 22
end.......................................................................5
erase flash............................................................6
erase startup-config.............................................6
exit.......................................................................5
F
flow-control.......................................................23
G
getmib..................................................................8
gvrp ...................................................................38
H
hostname ...........................................................15
I
interface...............................................................5
ip 33
ip authorized-managers.....................................31
ip default-gateway.............................................32
ip igmp ..............................................................40
ip igmp high-priority-forward...........................40
ip igmp querier ..................................................40
ip route ..............................................................32
ip ttl ...................................................................32
K
kill .......................................................................7
L
lacp ....................................................................23
link-test................................................................9
logout ..................................................................5
M
mac-age-time.....................................................14
max-vlans ..........................................................36
menu....................................................................5
mirror-port.........................................................41
monitor ..............................................................42
N
name ..................................................................37
P
page .....................................................................6
password............................................................16
ping....................................................................10
port-security ......................................................43
primary-vlans ....................................................37
print .....................................................................7
R
reload...................................................................7
repeat ...................................................................6
S
setmib ..................................................................9
setup ....................................................................5
show arp ............................................................29
show boot-history................................................7
show cdp ...........................................................17
show console .....................................................11
show flash ...........................................................9
show gvrp..........................................................38
show history ........................................................7
show interfaces..................................................22
show interfaces config ......................................20
show ip ..............................................................28
show ip authorized-managers ...........................29
show ip igmp.....................................................39
show ip igmp config..........................................39
show ip route.....................................................29
show lacp...........................................................24
show logging .......................................................7
show mac-address ...................................... 11, 12
60
Page 65

show management.............................................12
show mirror-port ...............................................41
show modules....................................................13
show port-security.......................................42, 43
show port-security intrusion log .......................43
show running-config ...........................................7
show snmp-server community ..........................34
show sntp...........................................................30
show spanning-tree ...........................................26
show spanning-tree config ................................25
show stack .........................................................18
show startup-config.............................................7
show statistics ...................................................20
show system-information..................................13
show tacacs .......................................................17
show tech.............................................................9
show timep ........................................................30
show trunks .......................................................23
show version .......................................................9
show vlans.........................................................36
snmp-server.......................................................15
snmp-server community....................................35
snmp-server enable traps...................................35
snmp-server host ...............................................35
sntp ....................................................................32
spanning-tree.....................................................26
speed-duplex .....................................................23
stack ..................................................................18
stack auto-grab ..................................................19
stack auto-join ...................................................19
stack commander...............................................18
stack join ...........................................................18
stack member ....................................................18
stack transmission-interval................................19
static-vlan ..........................................................37
W
walkmib...............................................................8
web-management ..............................................16
write memory ......................................................6
write terminal ......................................................6
T
tacacs-server host ..............................................17
tacacs-server timeout ........................................17
tagged ................................................................37
telnet....................................................................8
telnet-server.......................................................16
time....................................................................15
timep..................................................................31
timesync ............................................................31
time-zone...........................................................15
trunk ..................................................................24
U
unknown-vlans ..................................................38
untagged ............................................................37
V
vlan................................................................6, 37
vlan-support ......................................................37
61
Page 66

 Loading...
Loading...