Page 1

HP V1905 Switch Series
Getting Started Guide
*5998-2235*
Part number: 5998-2235
Document version: 2
i
Page 2

HP V1905 Switch Series Getting Started Guide describes the appearance; installation, configuration, and
troubleshooting of the HP V1905 switch series.
This documentation set is intended for:
Network planners
Field technical support and servicing engineers
Network administrators working with the HP V1910 switches
Legal and notice information
© Copyright 2011 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
No part of this documentation may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
HEWLETT-PACKARD COMPANY MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND WITH REGARD TO THIS
MATERIAL, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Hewlett-Packard shall not be liable for errors contained herein or
for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this
material.
The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements
accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an
additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Warranty
The Hewlett-Packard Limited Warranty Statement for this product and the HP Software License Terms which
apply to any software accompanying this product are available on the HP networking Web site at
http://www.hp.com/networking/warranty. The customer warranty support and services information are
available on the HP networking Web site at http://www.hp.com/networking/support. Additionally, your
HP-authorized network reseller can provide you with assistance, both with services that they offer and with
services offered by HP.
ii
Page 3

Contents
Getting Started ····························································································································································· 1
Introducing the Switch ························································································································································· 1
Overview of the Switch ················································································································································· 1
Summary of Hardware Features ·································································································································· 1
Front View Detail ··························································································································································· 2
LED Status Indicators······················································································································································ 3
System Specifications ···················································································································································· 4
Installing the Switch ····························································································································································· 5
Before You Begin ··························································································································································· 5
Positioning the Switch ···················································································································································· 5
Rack-Mounting or Free-Standing ·································································································································· 6
Supplying Power to the Switch ····································································································································· 7
Checking for Correct Operation ·································································································································· 8
Using SFP Transceivers ·················································································································································· 8
Performing Spot Checks ············································································································································· 10
Configuring IP Address ···················································································································································· 10
Automatic IP Configuration using DHCP ·················································································································· 10
Manual IP Configuration ············································································································································ 10
Connecting To the Web Interface ····························································································································· 12
Requirements for Accessing the Web Interface ············································································································· 12
Choosing a Web Browser ··············································································································································· 12
Default User and Password ·············································································································································· 12
Logging On to the Web Interface ··································································································································· 13
Navigating the Web Interface ········································································································································ 13
Menu ············································································································································································ 13
Buttons ·········································································································································································· 16
Configuring the Switch ·············································································································································· 18
Configuring System Access ·············································································································································· 18
Defining System Access ············································································································································· 18
Modifying System Access ·········································································································································· 19
Removing System Access ··········································································································································· 20
Viewing System Access Settings ······························································································································· 20
Configuring IP and MAC Address Information ············································································································· 21
Defining IP Address ···················································································································································· 21
Configuring ARP Settings ··········································································································································· 21
Configuring MAC Address Table ····························································································································· 24
Configuring Port ································································································································································ 28
Configuring Port Basic Settings ································································································································· 28
Configuring PoE ·························································································································································· 31
Viewing Port Statistics ················································································································································ 34
Configuring VLAN ···························································································································································· 35
Creating VLANs ·························································································································································· 36
Modifying VLAN ························································································································································· 37
Modifying Port VLAN Settings ··································································································································· 38
Renaming VLANs ························································································································································ 38
Removing VLANs ························································································································································ 39
iii
Page 4

Viewing VLAN Details ················································································································································ 39
Viewing VLAN Port Details ········································································································································ 40
Aggregating Port ······························································································································································ 41
Overview ····································································································································································· 41
LACP ············································································································································································· 41
Link Aggregation Types ·············································································································································· 41
Configuring Link Aggregation ··································································································································· 42
Configuring LACP ······················································································································································· 45
Configuring STP ································································································································································ 46
Configuring IGMP Snooping ··········································································································································· 52
Defining IGMP Snooping ··········································································································································· 52
Configuring ACL ······························································································································································· 53
Configuring MAC Based ACL ··································································································································· 53
Configuring IP Based ACL ········································································································································· 57
Configuring ACL Binding ··········································································································································· 62
Configuring QoS ······························································································································································ 64
Configuring CoS ························································································································································· 64
Configuring Queue Algorithm ··································································································································· 65
Configuring CoS to Queue ········································································································································ 66
Configuring DSCP to Queue ····································································································································· 67
Configuring Trust Mode ············································································································································· 69
Configuring Bandwidth Settings ································································································································ 69
Configuring Voice VLAN ··········································································································································· 71
Configuring SNMP ··························································································································································· 76
Defining SNMP Communities ···································································································································· 76
Removing SNMP Communities ·································································································································· 77
Defining SNMP Traps ················································································································································· 77
Removing SNMP Traps ·············································································································································· 78
Configuring LLDP ······························································································································································· 79
LLDP Overview ···························································································································································· 79
Configuring Global LLDP Parameters ······················································································································· 79
Configuring Port-Level LLDP Parameters ···················································································································· 80
Viewing LLDP Information ·········································································································································· 83
Managing Switch Security ··············································································································································· 85
Defining Port-Based Authentication (802.1X) ·········································································································· 85
Defining Radius Client ················································································································································ 89
Configuring LDB ·························································································································································· 89
Configuring Broadcast Storm Control ······················································································································ 93
Managing System Information ········································································································································ 94
Viewing Basic Settings ··············································································································································· 95
Configuring System Name ········································································································································· 96
Configuring System Time ··········································································································································· 97
Save Configuration ····················································································································································· 99
Resetting the Switch ···················································································································································· 99
Managing System Files ···················································································································································· 99
Managing System Logs ·················································································································································· 102
Configuring Logging ················································································································································· 103
Viewing Logs ····························································································································································· 104
Managing Switch Diagnostics ······································································································································· 105
Configuring Port Mirroring ······································································································································ 105
Configuring Cable Diagnostics ······························································································································· 106
iv
Page 5

Troubleshooting ······················································································································································· 108
Resetting to Factory Defaults ·········································································································································· 108
Forgotten Password ························································································································································ 108
Reset the switch ························································································································································· 108
Configure a new user ··············································································································································· 108
Forgotten Static IP Address ············································································································································ 109
Solving LED Issues ··························································································································································· 109
CLI Reference Guide ··············································································································································· 111
Getting Started with the Command Line Interface ······································································································· 111
Prerequisites ······························································································································································· 111
Logging on to the CLI ··············································································································································· 111
CLI Features ····································································································································································· 112
Online Help ······························································································································································· 112
Command History ····················································································································································· 113
Error Messages ························································································································································· 114
Command Edit ·························································································································································· 114
CLI Configuration ···························································································································································· 115
display ip ··································································································································································· 115
display management-vlan ········································································································································ 116
display version ·························································································································································· 116
ip address ·································································································································································· 117
ip address dhcp-alloc ··············································································································································· 117
ip gateway ································································································································································ 118
localuser ····································································································································································· 118
management-vlan ······················································································································································ 118
management-vlan port ·············································································································································· 119
ping ············································································································································································ 120
quit ·············································································································································································· 120
reboot ········································································································································································· 121
restore ········································································································································································ 121
save ············································································································································································ 122
tftp update ································································································································································· 122
Support and other resources ·································································································································· 123
Contacting HP ································································································································································· 123
Related information ························································································································································· 123
Conventions ····································································································································································· 123
Subscription service ························································································································································ 124
Glossary ··································································································································································· 125
Index ········································································································································································ 128
v
Page 6
p
Getting Started
NOTE:
This manual applies to the HP V1905-48 Switch JD994A, HP V1905-24 Switch JD990A, and HP
V1905-24-PoE Switch JD992A, which are referred to as the Switch.
This manual uses the Web interfaces of the HP V1905-24-PoE Switch JD992A in the example text.
This chapter contains introductory information about the installation of the Switch and how the Switch can
be used in your network. It covers the following topics:
Introducing the Switch
Installing the Switch
Configuring IP Address
Introducing the Switch
This chapter covers summary information about the hardware and the following topics:
Overview of the Switch
Summary of Hardware Features
Front View Detail
LED Status Indicators
System Specifications
Overview of the Switch
The HP V1905-24 Switch JD990A is a versatile, easy-to-use configurable switch.
The HP V1905-24-PoE Switch JD992A is a versatile, easy-to-use configurable Power-over-Ethernet
(PoE) Switch.
The HP V1905-48 Switch JD994A is a versatile, easy-to-use configurable switch.
Each Switch is ideal for users who want the high-speed performance of 10/100 switching with the added
functionality of Gigabit copper and fiber links, but do not need sophisticated management capabilities. The
Switch is shipped ready for use. No configuration is necessary.
Summary of Hardware Features
Table 37 summarizes the hardware features supported by the Switch.
Table 37 Hardware Features
Feature Descri
Addresses Up to 8192 supported.
Auto-negotiation Supported on all ports.
tion
1
Page 7

Feature Description
Forwarding Modes
Duplex Modes Half and full duplex on all front panel ports.
Auto MDI/MDIX
Flow Control In full duplex operation all ports are supported.
Traffic Prioritization Four traffic queues per port.
Ethernet Ports
Gigabit Combo Ports
Mounting 19-inch rack or standalone mounting.
Store and Forward.
Supported on all ports. If fiber SFP transceivers are used, Auto
MDIX is not supported.
10/100 Mbps ports.
Each port automatically determines the speed and duplex mode of
the connected equipment and provides a suitable switched
connection. The 10/100 Mbps ports can operate in either
half-duplex or full-duplex mode.
The 2 Gigabit combo ports support fiber Gigabit Ethernet
short-wave (SX) and long-wave (LX) SFP transceivers in any
combination. This offers you the flexibility of using SFP transceivers
to provide connectivity between the Switch and a 1000 Mbps core
network.
When an SFP port is in operation, the corresponding 1000BASE-T
port is disabled. The 1000 Mbps connections can only operate in
full duplex mode.
Fanless design (supported by HP
V1905-24 Switch JD990A and HP
V1905-48 Switch JD994A)
PoE (Only supported by HP
V1905-24-PoE Switch JD992A)
Front View Detail
Figure 46 shows the front panel of the HP V1905-24 Switch JD990A 26-Port unit.
Figure 46 HP V1905-24 Switch JD990A 26-Port—front panel.
Figure 47 shows the front panel of the HP V1905-24-PoE Switch JD992A 26-Port unit.
Silent operation whether used in a rack or desktop situation.
Each RJ-45 port supports the IEEE 802.3af PoE standard. Any
802.3af compliant device attached to a port can directly draw
power from the switch over the Ethernet cable without requiring its
own separate power source. This capability gives network
administrators centralized power control for devices such as IP
phones and wireless access points, which translates into greater
network availability.
2
Page 8

Figure 47 HP V1905-24-PoE Switch JD992A 26-Port—front panel.
Figure 48 shows the front panel of the HP V1905-48 Switch JD994A 50-Port unit.
Figure 48 HP V1905-48 Switch JD994A 50-Port—front panel.
LED Status Indicators
The Switch provides LED indicators on the front panel to monitor the switch. Table 38 describes the
meanings of the LEDs.
Table 38 Description on the LEDs of the Switch
LED Status
Green
Power
10/100BASE-T
port
Link/Activity
10/100/1000
BASE-T port
Yellow The system has failed the POST.
OFF The switch is powered off.
Green
Yellow
OFF
Green
Yellow
OFF
Description
The switch starts normally. The LED flashes when the
system is performing Power-On Self-Test (POST).
The port works at the rate of 100 Mbps; the LED flashes
quickly when the port is sending or receiving data.
The port works at the rate of 10 Mbps; the LED flashes
quickly when the port is sending or receiving data.
The link has not been established, either nothing is
connected to the port, or there is a problem:
Check that the attached device is powered on.
Check that the cable is the correct type and is not
faulty.
If these checks do not identify the cause of the problem, it
may be that the unit or the device connected to the port is
faulty. Contact your supplier for further advice.
The port works at the rate of 1000 Mbps; the LED flashes
quickly when the port is sending or receiving data.
The port works at the rate of 10/100 Mbps; the LED
flashes quickly when the port is sending or receiving
data.
The link has not been established, either nothing is
connected to the port, or there is a problem:
Check that the attached device is powered on.
Check that the cable or fiber is the correct type and is
3
Page 9

p
LED Status
Duplex
Module Active SFP port
PoE Power (Only supported by HP
V1905-24-PoE Switch JD992A)
10/100/1000
BASE-T port
System Specifications
Table 39 contains the system specifications of the Switch.
Table 39 System specifications of the Switch.
Description
not faulty.
For fiber connections, ensure that the receive (RX) and
transmit (TX) cable connectors are not swapped.
If these checks do not identify the cause of the problem, it
may be that the unit or the device connected to the port is
faulty. Contact your supplier for further advice.
Yellow The port is in full duplex mode.
OFF The port is not connected, or is in half duplex mode.
Green The SFP module is inserted.
OFF The SFP module is not inserted or is not recognized.
Green The port is supplying power to the device connected to it.
OFF
The port is not supply power to the device connected to it
or not connected.
ecification V1905-24
S
Physical dimensions
(H×W×D)
Weight 1.6 kg 3.2 kg 2.9 kg
Console port 1 1 1
Ethernet port 24
Gigabit Combo port 2 2 2
AC Input voltage
Power consumption (full
load)
Operating temperature 0°C to 40°C (32°F to 104°F)
Storage temperature –40°C to +70°C (–40°F to 158°F)
Operating humidity
(noncondensing)
Storage humidity
(noncondensing)
44 mm×440 mm×170
mm
Rated voltage range:
100–240V AC, 50/60
Hz
17 W 205 W 26 W
5% to 95%
5% to 95%
V1905-24-PoE
44 mm×440 mm×238
mm
24 (Each port can
provide a power
supply of 25 W)
Rated voltage range:
100–240V AC, 50/60
Hz
V1905-48
44 mm×440 mm×238
mm
48
Rated voltage range:
100–240V AC, 50/60
Hz
4
Page 10

g
g
Installing the Switch
This section contains information that you need to install and set up the switch. It covers the following topics:
Before You Begin
Positioning the Switch
Rack-Mounting or Free-Standing
Supplying Power to the Switch
Checking for Correct Operation
Using SFP Transceivers
Performing Spot Checks
Before You Begin
Before installing or removing any components from the switch or carrying out any maintenance procedures,
read the Safety and Compliance Guide chapter in this guide.
Positioning the Switch
The switch is suitable for use in an office environment where it can be free-standing or mounted in a
standard 19-inch equipment rack.
Alternatively, the switch can be rack-mounted in a wiring closet or equipment room. A mounting kit,
containing two mounting brackets and four screws, is supplied with the switch.
When deciding where to position the switch, ensure that:
It is accessible and cables can be connected easily.
Cabling is away from sources of electrical noise. These include lift shafts, microwave ovens, and air
conditioning units. Electromagnetic fields can interfere with the signals on copper cabling and
introduce errors, thereby slowing down your network.
Water or moisture cannot enter the case of the unit.
Air flow around the unit and through the vents on the side of the case is not restricted (HP recommends
that you provide a minimum of 25 mm (1 in.) clearance).
The air is as free from dust as possible.
Temperature operating limits are not likely to be exceeded. HP recommends that the unit is installed in
a clean, air conditioned environment.
NOTE:
It is always good practice to wear an anti-static wrist strap connected to a ground point when installing
network equipment. If one is not available, try to keep in contact with a
the unit's ports and connectors, if possible. Static discharge can cause reliability problems in your
equipment.
rounded rack and avoid touchin
5
Page 11
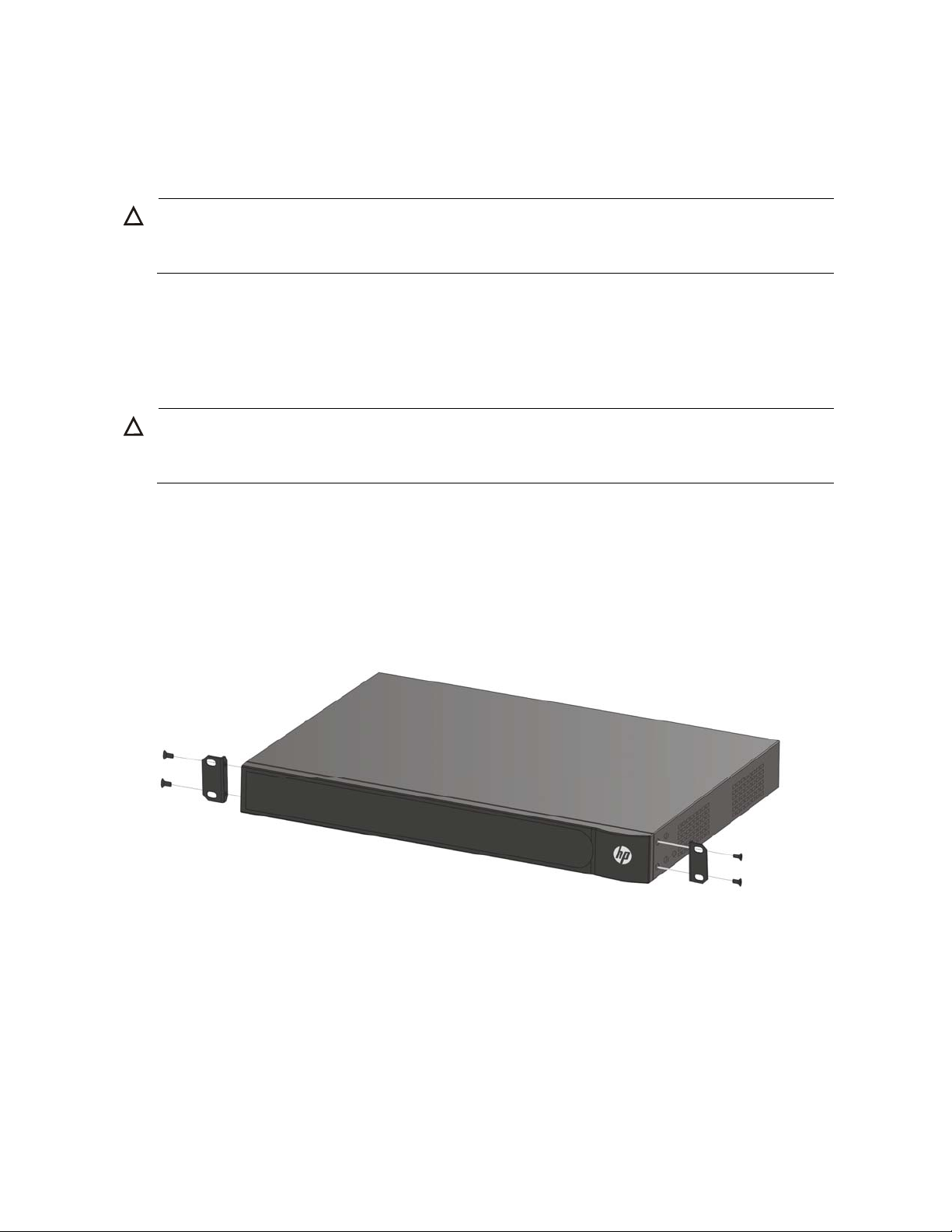
Rack-Mounting or Free-Standing
The unit can be mounted in a 19-inch equipment rack using the mounting kit or it can be free standing. Do
not place objects on top of the unit or stack.
CAUTION:
If installing the switch in a free-standing stack of different size Baseline or Super stack 3 units, the smaller
units must be installed above the larger ones. Do not have a free-standing stack of more than six units.
Using the Mounting Kit
The switch is supplied with two mounting brackets and four screws. These are used for rack mounting the
unit. When mounting the unit, refer to the guidelines given in Positioning the Switch.
The switch is 1U (1.7 inches) high and will fit in a standard 19-inch rack.
CAUTION:
Disconnect all cables from the unit before continuing. Remove the self-adhesive pads from the underside
of unit, if already fitted.
To rack-mount the switch:
1. Place the unit the right way up on a hard, flat surface with the front facing towards you.
2. Locate a mounting bracket over the mounting holes on one side of the unit.
3. Insert the two screws supplied in the mounting kit and fully tighten with a suitable screwdriver, as
shown in Figure 49.
Figure 49 Rack Mounting the Unit
4. Insert the unit into the 19-inch rack and secure with suitable screws (not provided), as shown in Figure
50
6
Page 12

Figure 50 Mount the HP V1905 Switch to a rack
5. Reconnect the cables.
Placing Units On Top of Each Other
If the switch units are free-standing, up to six units can be placed one on top of the other. If you are mixing
a variety of Baseline and Super Stack units, the smaller units must be positioned at the top.
If you are placing switch units one on top of the other, you must use the self-adhesive rubber pads supplied.
Apply the pads to the underside of each switch, sticking one in the marked area at each corner.
Place the switch units on top of each other, ensuring that the pads of the upper unit line up with the recesses
of the lower unit.
Supplying Power to the Switch
Power problems can be the cause of serious failures and downtime in your network. Ensure that the power
input to your system is clean and free from sags and surges to avoid unforeseen network outages. HP
recommends that you install power conditioning, especially in areas prone to blackout, power dips and
electrical storms.
The unit is intended to be grounded. Ensure it is connected to earth ground during normal use. Installing
proper grounding helps to avoid damage from lightning and power surges.
CAUTION:
Before powering on the switch, verify that the network cables and the power cable are securely connected.
To power on the switch:
1. Plug the power cord into the power socket on the rear panel of the switch.
2. Plug the other end of the power cord into a power outlet.
7
Page 13

Checking for Correct Operation
After you power on the switch, it automatically performs a power-on self-test (POST). During POST, the
Power LED on the front panel of the switch flashes green.
When POST is complete, the Power LED turns green. If the Power LED turns yellow after POST, it means that
POST failed and the switch has entered its fail-safe mode.
The following summarizes the possible colors for the Power LED after POST.
Table 40 Summarizes the possible colors for the Power LED after POST
Status Meaning
Green The unit is powered on and ready for use.
Yellow
Off
Power-on self-test or loop back test failed. The switch is in fail-safe mode. This can
happen if a port or ports fail when the switch was powered on.
The unit is not receiving power.
Verify that the power cord is connected correctly, and then try powering on the
switch again
If the switch still does not operate, contact your HP network supplier
If POST fails, try the following:
Power off the switch, and then power it on again. Check the Power LED and see if POST was
successfully completed.
Reset the switch. See “Resetting to Factory Defaults.”
CAUTION:
Resetting the switch to its factory default erases all your settings. You will need to reconfigure the switch
after you reset it.
If these do not resolve the issue, please contact your HP network supplier for assistance.
Using SFP Transceivers
The following sections describe how to insert an SFP transceiver into an SFP slot.
NOTE:
SFP transceivers are hot-insertable and hot-swappable. You can remove them from and insert them into
any SFP port without having to power down the switch.
Inserting an SFP Transceiver
To be recognized as valid, the SFP transceiver must have the following characteristics:
1000BASE-SX or 1000BASE-LX media type:
1000BASE-SX SFP transceiver
Use this transceiver to connect the switch directly to a multimode fiber-optic cable.
1000BASE-LX SFP transceiver
8
Page 14

w
Use this transceiver to connect the switch directly to a single mode fiber-optic cable or to multi-mode fiber
using a conditioned launch cable.
To activate the SFP port:
1. Hold the transceiver so that the fiber connector is toward you and the product label is visible, as shown
in Figure 51.Ensure the wire release lever is closed (in the upright position).
Figure 51 Inserting an SFP Transceiver
2. Gently slide the transceiver into the SFP slot until it clicks into place.
CAUTION:
SFP transceivers are keyed and can be properly inserted only one way. If the transceiver does not click
hen you insert it, remove it, turn it over, and reinsert it.
3. Remove the plastic protective cover, if fitted.
4. Connect the fiber cable.
5. Attach a male duplex LC connector on the network cable into the duplex LC connector on the
transceiver.
6. Connect the other end of the cable to a device fitted with an appropriate Gigabit Ethernet connection.
7. Check the Module Active LEDs on the front of the switch to ensure that the SFP transceiver is operating
correctly.
Removing an SFP Transceiver
To remove an SFP transceiver:
1. Disconnect the cable from the transceiver.
2. Move the wire release lever downwards until it is pointing toward you.
3. Pull the wire release lever toward you to release the catch mechanism.
The SFP transceiver should slide out easily.
9
Page 15

p
Performing Spot Checks
At frequent intervals, you should visually check the switch. Regular checks can give you an early warning
of a possible failure; any problems can then be attended to when there will be least effect on users.
HP recommends periodically checking the items listed in Table 41.
Table 41 Items to Check
Item O
Cooling fan
Cabling
eration
Where possible, check that the cooling fan is operating by listening to the unit. The fan
is fitted near to the front right hand side of the unit (when viewed from the front).
Check that all external cabling connections are secure and that no cables are pulled
taut.
Configuring IP Address
The switch’s IP configuration is determined automatically using DHCP, or manually using values you assign.
By default, the switch will use its default IP information. The default IP address is 169.254.xxx.xxx. If the
MAC address is 08004E000102, the IP address would be 169.254.1.2.
Automatic IP Configuration using DHCP
When you use the automatic IP configuration method, the switch tries to obtain its IP information without
requesting user intervention from a DHCP server on the network.
You should use the automatic IP configuration method if:
Your network uses DHCP to allocate IP information, or
Flexibility is needed. If the switch is deployed onto a different subnet, it will automatically reconfigure
itself with an appropriate IP address, instead of you having to manually reconfigure the switch.
You can use ip address dhcp-alloc command to define automatic IP configuration method and use display
ip command to view the automatically allocated IP Information through the Console Port (see “CLI Reference
Guide”).
Manual IP Configuration
When you configure the IP information manually, the switch remembers the information that you enter until
you change it again.
You should use the manual IP configuration method if:
You do not have a DHCP server on your network, or
You want to remove the risk of the IP address ever changing, or
Your DHCP server does not allow you to allocate static IP addresses.
10
Page 16

NOTE:
For most installations, HP recommends that you configure the switch IP information manually. This makes
management simpler and more reliable as it is not dependent on a DHCP server, and eliminates the risk
of the IP address changing.
You can use ip address command to configure the static IP for your switch through the Console Port (see “CLI
Reference Guide”).
11
Page 17

Connecting To the Web Interface
The switch has a built-in Web interface that you can use to set the user password, change the IP address that
is assigned to the switch, and configure its advanced settings.
This chapter introduces the setting the menu items and buttons that are available on the Web interface. The
following topics are covered:
Requirements for Accessing the Web Interface
Choosing a Web Browser
Default User and Password
Logging On to the Web Interface
Navigating the Web Interface
Requirements for Accessing the Web Interface
To connect to the Web interface, you need the following:
Ensure that the switch is connected to the network using a Category 5 twisted pair Ethernet cable with
RJ-45 connectors.
Ensure that you know your switch’s IP address. See “Configuring IP Address”.
Check that your management workstation is on the same subnet as your switch.
Choose a suitable Web browser.
Choosing a Web Browser
To display the Web interface correctly, use one of the following Web browsers and platform combinations:
Table 42 Supported Web Browsers and Platforms
Browser Windows 2000
Internet Explorer 6 Yes Yes Yes
Internet Explorer 7 Yes Yes Yes
Firefox 3 Yes Yes Yes
Netscape 8 Yes Yes Yes
For the browser to operate the Web interface correctly, JavaScript and Cascading Style Sheets must be
enabled on your browser. These features are enabled on a browser by default. You will only need to enable
them if you have changed your browser settings.
Windows XP
Windows Vista
Default User and Password
If you intend to manage the switch or to change the default password, you must log in with a valid user
name and password. The switch has one default user name. The default user is listed in Table 43.
12
Page 18

Table 43 Default User and Password
User Name Default Password
admin -
Access Level
Management: The user can access and change all
manageable parameters
Logging On to the Web Interface
To log on to the Web interface, do the following:
1. Open your Web browser and enter the IP address of the switch that you wish to manage in the address
bar (For example, in the following format: http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx). The Login Page appears:
Figure 52 Login Page
2. Enter admin as your user name and leave the password field blank.
3. Click Login. The main Web interface page is displayed.
Navigating the Web Interface
The Web interface has been designed to enable you to easily perform advanced configuration tasks and
view information about the switch.
Menu
The menu is located on the left side of the Web interface. When you click an item on the menu, the related
screen appears in the main part of the interface. Some menu items will give you sub-menu tabs to choose
from.
13
Page 19

Figure 53 Switch Screen Layout
Table 44 Available Menu Items
Menu Item Description
Contains tabs that allow you to:
Device Summary
Provide a summary of the switch’s basic settings and versions of
current components.
Display the description for each color coded port.
Save Configuration Saves the switch’s configuration
IP Setup
ARP Setting
Backup & Restore Allows you to backup and restore the switch’s configuration.
Firmware Upgrade Allows you to upgrade the current firmware via TFTP or HTTP
Reset Allows you to reset the switch to factory default settings
Allows you to setup, modify, or view the IP configuration
parameters.
Allows a host to communicate with other hosts when only the IP
address of its neighbors is known.
Contains tabs that allow you to:
Display user summary information.
System Access
Administration
Create a new user.
Modify existing users.
Remove existing users.
System Name Allows you to set the system name.
System Time Allows you to set the system time.
Logging
System Logs record and manage events and report errors and
informational messages
Contains tabs that allow you to:
Add community strings.
SNMP
Remove community strings.
Define SNMP traps
Remove SNMP traps
14
Page 20

Menu Item Description
Contains tabs that allow you to:
Create a VLAN.
Modify a VLAN.
VLAN
Modify VLAN membership for a port.
Rename a VLAN.
Remove a VLAN.
Display VLAN membership for a port.
Display VLAN information.
Allows you to configure a Spanning Tree Protocol.
Contains tabs that allow you to:
Spanning Tree
Display selected spanning tree information for every port.
Display individual port spanning tree information.
Modify the spanning tree settings for a port.
Device
IGMP Snooping
Broadcast Storm Allows you to enable or disable broadcast control.
ACL Configures the ACL.
MAC Based ACL Configures MAC Based ACL on the switch.
IP Based ACL Configures IP Based ACL on the switch.
ACL Binding Configures ACL Binding on the switch.
QoS Configures QoS settings.
CoS
Allows you to enable or disable IGMP snooping and IGMP query
modes.
Contains tabs that allow you to:
Displays CoS default settings assigned to ports.
Defines CoS
Queue Configures Queue Setting.
CoS to Queue Displays and defines CoS to Queue.
DSCP to Queue Contains fields for mapping DSCP settings to traffic queues.
Trust Configures Trust Settings.
Bandwidth Displays and defines Bandwidth Settings.
Contains tabs that allow you to:
Display Voice VLAN summary.
Configure Voice VLAN global settings.
VoIP Traffic Setting
Configure Voice VLAN port settings.
Display port information for Voice VLAN.
Display OUI summary.
Add or remove OUI.
LLDP Allows you to configure LLDP global and port settings.
15
Page 21
Menu Item Description
Contains tabs that allow you to:
Administration
Display selected port information for the entire switch.
Display individual port information.
Modify the port settings.
Contains tabs that allow you to:
Display link aggregation summary.
Link Aggregation
Port
Create an aggregation group.
Modify the port memberships.
Remove an aggregation group.
LACP Configures the LACP.
Security
Monitoring
PoE(Only supported
by V1905-24-PoE
Switch)
Statistics Display statistics for a selected port.
Radius Client
Contains tabs that allow you to:
Display PoE summary.
Configure PoE settings.
Contains tabs that allow you to:
Display Radius Client information.
Configure Radius Client settings and set authentication
parameters.
Contains tabs that allow you to:
802.1X
Display system authentication summary.
Display detailed information per port.
Configure system authentication settings.
Contains tabs that allow you to:
LDB
Configure LDB Parameters
Configure an Authentication Server
Configure a User Account
Address Table Displays MAC address table information for ports and VLANs.
Port Mirroring Monitor traffic going in or out of ports.
Contains tabs that allow you to:
Cable Diagnostics
Display selected cable diagnostics information for all ports.
Display all cable diagnostics information for a single port.
Help
Logout Allows you to securely log off the Web interface.
Displays HP contact information and describes how to use the online
help system.
Buttons
Depending on the screen that is currently displayed, the following buttons may appear:
Apply: Click to apply any changes that you have made.
Cancel: Click to discard any unsaved changes.
16
Page 22

Select All: Allows the user to select all ports.
Select None: Removes the ports selected.
Help: Click to display the context-sensitive help information for the screen that is currently displayed.
The help pages provide information on the tasks that you can perform on each screen.
17
Page 23
Configuring the Switch
Configuring System Access
Network administrators can define user name, password, and access level for users using the System
Access Interface. The Multi-Session Web feature is enabled on switch and allows 10 users to be created
and access the switch concurrently. Access levels provide read or read/write permissions to users for
configuring the switch. Login information is managed in the local database. A unique password is required
for each user. Two access levels exist on the Web Interface:
Management access level: Provides the user with read/write access rights. There is always one
management level user configured for the switch.
Monitor access level: Provides the user with read-only system access rights.
This section contains the following topics:
Defining System Access
Modifying System Access
Removing System Access
Viewing System Access Settings
CAUTION:
To ensure that unauthorized users do not access the Web interface, HP recommends that you set an admin
password when you first configure the switch.
Defining System Access
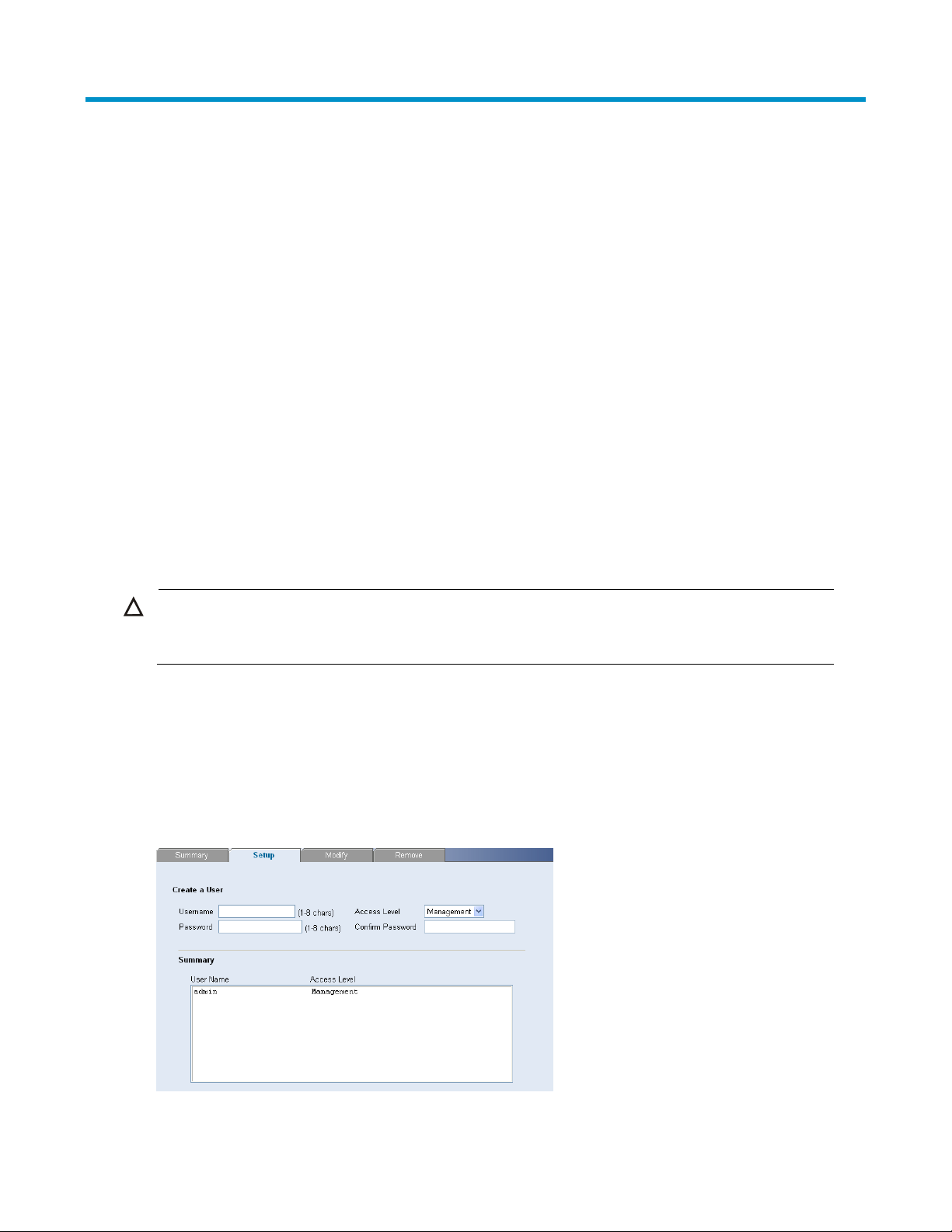
The System Access Setup Page allows network administrators to define users, passwords, and access levels
for users using the System Access Interface.
Click Administration System Access Setup. The System Access Setup Page opens.
Figure 54 System Access Setup Page
18
Page 24
p
p
The System Access Setup Page contains the following fields:
Table 45 System Access Setup Page item description
Item Descri
User Name Defines the user name. The default value is admin.
Defines the user access level. The lowest user access level is Monitor and the
highest is Management.
Access Level
Management: Provides the user with read and write access rights. This is the
tion
default.
Monitor: Provides the user with read access rights.
Password Defines the local user password. The default is blank.
Confirm Password Verifies the password.
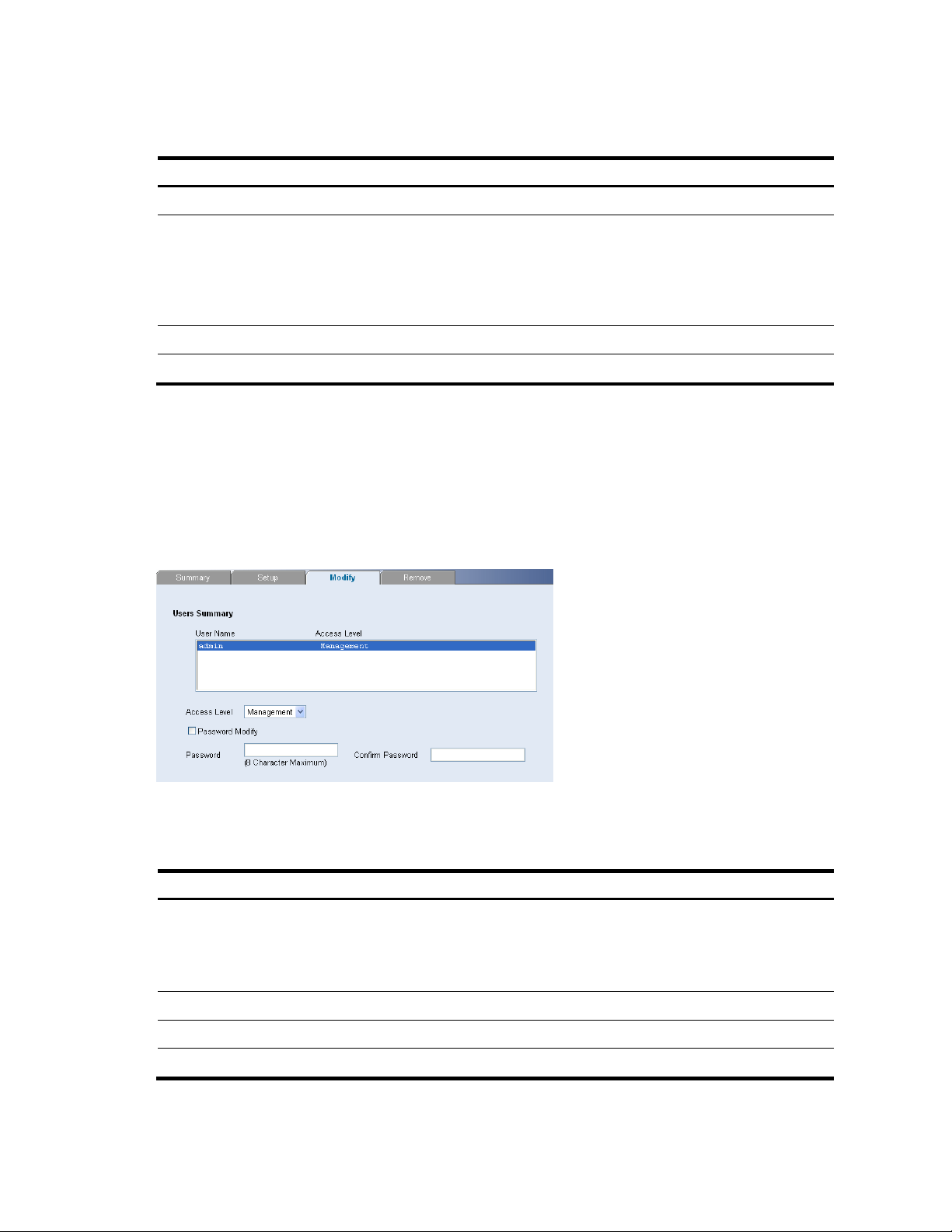
Modifying System Access
The System Access Modify Page allows network administrators to modify users, passwords, and access
levels for users using the System Access Interface.
Click Administration System Access Modify. The System Access Modify Page opens.
Figure 55 System Access Modify Page
The System Access Modify Page contains the following fields:
Table 46 System Access Modify Page item description
Item Descri
Defines the user access level. The lowest user access level is Monitor and the
Access Level
highest is Management.
Management: Provides the user with read and write access rights.
tion
Monitor: Provides the user with read access rights.
Password Modify Enables modifying a password for an existing user.
Password Modifies the local user password.
Confirm Password Verifies the password.
19
Page 25
p
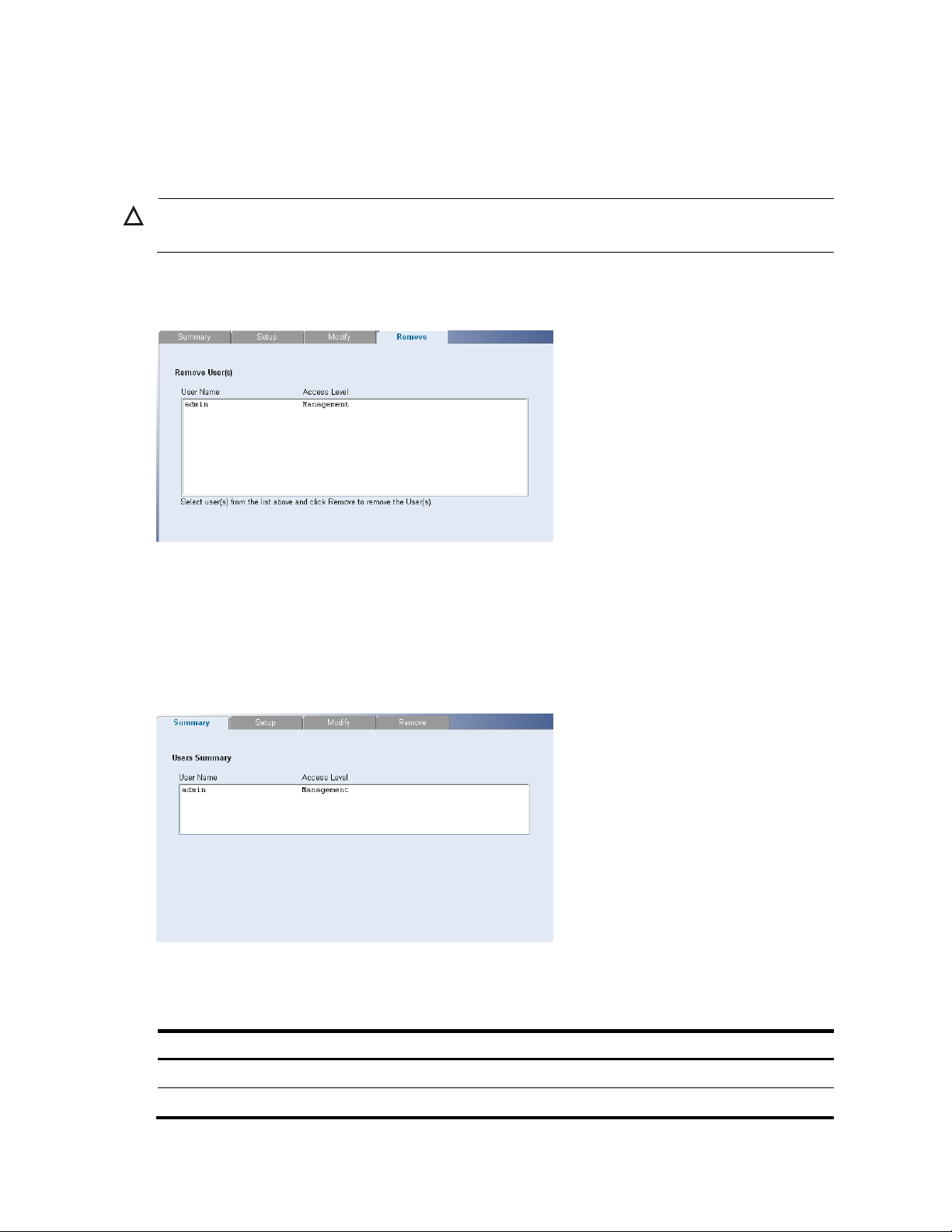
Removing System Access
The System Access Remove Page allows network administrators to remove users from the System Access
Interface.
CAUTION:
The last user with management access may not be deleted.
Click Administration System Access Remove. The System Access Remove Page opens.
Figure 56 System Access Remove Page
Viewing System Access Settings
The System Access Summary Page displays the current users and access levels defined on the switch.
Click Administration System Access Summary. The System Access Summary Page opens.
Figure 57 System Access Summary Page
The System Access Summary Page contains the following fields:
Table 47 System Access Summary Page item description
Item Descri
User Name Displays the user name.
Access Level Displays the user access level.
tion
20
Page 26

p
Configuring IP and MAC Address Information
This section contains information for defining IP interfaces, and includes the following sections:
Defining IP Address
Configuring ARP Settings
Configuring MAC Address Table
Defining IP Address
To enable the other devices on the network to communicate with the switch, you need to assign an IP
address to it: either by DHCP or by assigning a static IP address.
Click Administration IP Setup. The IP Setup Page opens.
Figure 58 IP Setup Page
The IP Setup Page contains the following fields:
Table 48 IP Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Defines whether the IP address is configured statically or dynamically. The
Configuration Method
IP Address
Subnet Mask Defines the subnet mask. The default value is 255.255.0.0.
Gateway Defines the gateway address. The default value is blank.
possible field values are:
Static: Specifies that the IP address is configured by the user.
DHCP: Specifies that the IP address is dynamically obtained by DHCP Server.
Defines the IP address. The default value is 169.254.xxx.xxx. If the MAC address
is 08004E000102, the IP address would be 169.254.1.2.
tion
Configuring ARP Settings
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) converts IP addresses into physical addresses, and maps the IP
address to a MAC address. ARP allows a host to communicate with other hosts when only the IP addresses
of its neighbors are known.
This section includes the following topics:
Defining ARP Settings
21
Page 27

p
Removing ARP Entries
Viewing ARP Settings
Defining ARP Settings
The ARP Settings Setup Page allows network managers to define ARP parameters for specific interfaces.
Click Administration ARP Settings Setup. The ARP Settings Setup Page opens.
Figure 59 ARP Settings Setup Page
The ARP Settings Setup Page contains the following fields:
Table 49 ARP Settings Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Interface Indicates the management VLAN (VLAN 1) for which ARP parameters are defined.
IP Address Defines the static IP address, which is associated with the static MAC address.
MAC Address Defines the static MAC address, which is associated with the static IP address.
ARP Entry Age Out
Removing ARP Entries
The ARP Entries Remove Page provides parameters for removing ARP entries from the ARP Table.
Click Administration ARP Settings Remove. The ARP Entries Remove Page opens.
tion
Specifies the aging time for dynamic ARP entries. After the ARP Entry Age,
dynamic ARP entries are deleted from the table. The range is 1-40000000. The
default value is 1200 seconds.
22
Page 28

p
Figure 60 ARP Entries Remove Page
The ARP Entries Remove Page contains the following fields:
Table 50 ARP Entries Remove Page item description
Item Descri
Clear ARP Table Entries
Interface Indicates the VLAN for which ARP parameters are defined.
IP Address Indicates the IP address which is associated with the MAC address.
MAC Address
Status
Viewing ARP Settings
The ARP Settings Summary Page displays the current ARP settings.
Click Administration ARP Settings Summary. The ARP Settings Summary Page opens.
tion
Specifies the types of ARP entries that are cleared. The possible values are:
None: Maintains the ARP entries.
All: Clears all ARP entries.
Dynamic: Clears only dynamic ARP entries.
Static: Clears only static ARP entries.
Displays the MAC address, which is associated in the ARP table with the IP
address.
Displays the ARP table entry type. Possible field values are:
Dynamic: Indicates the ARP entry is learned dynamically.
Static: Indicates the ARP entry is a static entry.
23
Page 29

p
Figure 61 ARP Settings Summary Page
The ARP Settings Summary Page contains the following fields:
Table 51 ARP Settings Summary Page item description
Item Descri
Interface Indicates the VLAN for which ARP parameters are defined.
IP Address Indicates the IP address, which is associated with the MAC Address.
MAC Address
Status
Displays the station MAC address, which is associated in the ARP table with the IP
address.
Displays the ARP table entry type. Possible field values are:
Dynamic: Indicates the ARP entry is learned dynamically.
tion
Static: Indicates the ARP entry is a static entry.
Configuring MAC Address Table
MAC addresses are stored in either the static address or the dynamic address databases. A packet
addressed to a destination stored in one of the databases is forwarded immediately to the port.
The Dynamic Address Table can be sorted by interface, VLAN, and MAC address. MAC addresses are
dynamically learned as packets from sources arrive at the switch. MAC addresses are associated with ports
by learning the ports from the frames source address. Frames addressed to a destination MAC address that
is not associated with any port are flooded to all ports of the relevant VLAN.
Static addresses are manually configured. In order to prevent the bridging table from overflowing, dynamic
MAC addresses, from which no traffic is seen for a certain period, are erased.
This section includes the following sections:
Adding MAC Addresses to the Address Table
Defining Aging Time
Removing MAC Addresses for the specific port
Removing MAC Addresses from the Address Table
Viewing Address Table Settings
Viewing Port Summary Settings
24
Page 30

p
Adding MAC Addresses to the Address Table
The Address Table Add Page allows the network manager to assign MAC addresses to ports with VLANs.
Click Monitoring Address Table Add. The Address Table Add Page opens.
Figure 62 Address Table Add Page
The Address Table Add Page contains the following fields:
Table 52 Address Table Add Page item description
Item Descri
VLAN ID Selects a VLAN ID.
MAC Address Defines a MAC address to be assigned to the specific port and VLAN ID.
No Aging
Defining Aging Time
The Address Table Aging Time Setup Page allows the network manager to define the Address Table Aging
Time. The Aging Time is the amount of time the MAC addresses remain in the Dynamic Address table before
they are timed out if no traffic from the source is detected. The default value is 300 seconds.
Click Monitoring Address Table Setup. The Address Table Aging Time Setup Page opens.
Figure 63 Address Table Aging Time Setup Page
tion
Marks the aging status of the MAC address assigned by the user. The possible values
are:
Checked: Indicates that the Address Table entry assigned by the user is not aged
out.
Unchecked: Indicates that the Address Table entry assigned by the user is aged
out.
25
Page 31

Removing MAC Addresses for the specific port
The Port Remove Page allows the network manager to remove MAC Addresses for the specific port from the
Address Table.
Click Monitoring Address Table Port Remove. The Port Remove Page opens.
Figure 64 Port Remove Page
1. Select a port to remove MAC Addresses.
2. Select entries from the address table to be removed.
3. Click Remove.
Removing MAC Addresses from the Address Table
The Address Table Remove Page allows the network manager to remove current MAC addresses from the
Address Table.
Click Monitoring Address Table Remove. The Address Table Remove Page opens.
Figure 65 Address Table Remove Page
1. Select entries from the address table to be removed.
2. Click Remove.
Viewing Address Table Settings
The Address Table Summary Page displays the current MAC address table configuration.
Click Monitoring Address Table Summary. The Address Table Summary Page opens.
26
Page 32

p
Figure 66 Address Table Summary Page
The Address Table Summary Page contains the following fields:
Table 53 Address Table Summary Page item description
Item Descri
State
MAC Address
VLAN ID Displays the VLAN ID associated with the port and MAC address.
State
Port Index Displays the port through which the address was learned.
Aging Time
Viewing Port Summary Settings
tion
Filters the list of MAC addresses displayed according to the type of MAC address
configuration. Possible values are:
All: Displays all MAC addresses.
Static: Displays the statically configured MAC addresses.
Dynamic: Displays the dynamically learned MAC addresses.
Displays the current MAC addresses listed in the MAC address table, filtered by
the selected value of the State field.
Displays the MAC address configuration method. Possible values are:
Config Static: Displays the statically configured MAC address.
Config Dynamic: Displays the dynamically learned MAC address.
Displays that the MAC address is aged out or not. Possible values are:
NOAGED: Indicates that the MAC address is not aged out.
AGING: Indicates that the MAC address is aged out.
The Port Summary Page allows the network administrator to view the MAC addresses assigned to specific
ports.
Click Monitoring Address Table Port Summary. The Port Summary Page opens.
27
Page 33

p
Figure 67 Port Summary Page
The Port Summary Page contains the following fields:
Table 54 Port Summary Page item description
Item Descri
State
MAC Address
VLAN ID Displays the VLAN ID associated with the port and MAC address.
State
Port Index Displays the port through which the address was learned.
Aging Time
Configuring Port
tion
Filters the list of MAC addresses displayed according to the type of MAC address
configuration. Possible values are:
All: Displays all MAC addresses.
Static: Displays the statically configured MAC addresses.
Dynamic: Displays the dynamically learned MAC addresses.
Displays the current MAC addresses listed in the MAC address table, filtered by
the selected value of the State field.
Displays the MAC address configuration method. Possible values are:
Config Static: Displays the statically configured MAC address.
Config Dynamic: Displays the dynamically learned MAC address.
Displays that the MAC address is aged out or not. Possible values are:
NOAGED: Indicates that the MAC address is not aged out.
AGING: Indicates that the MAC address is aged out.
This section includes the following topics:
Configuring Port Basic Settings
Configuring PoE
Viewing Port Statistics
Configuring Port Basic Settings
This section contains information for configuring Port Basic Settings, and includes the following topics:
28
Page 34

p
Defining Port Settings
Viewing Port Settings
Viewing Port Details
Defining Port Settings
The Port Setup Page allows network managers to configure port parameters for specific ports.
Click Port Administration Setup. The Port Setup Page opens.
Figure 68 Port Setup Page
The Port Setup Page contains the following fields:
Table 55 Port Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Enables and disables the port. The possible field values are:
Port State
No Change: Retains the current port status.
Enabled: Enables the port.
tion
Disabled: Disables the port.
Enables and disables flow control on the port. When flow control is enabled for the
port, the switch regulates the packet flow so that a sending device does not transmit
more packets than a receiving device can process. If flow control is disabled, packets
Flow Control
may be dropped under certain periods of high traffic. The possible values are:
No Change: Retains the current flow control status on the port.
Enabled: Enables flow control on the port.
Disabled: Disables flow control on the port.
Specifies the configured rate for the port. The port speed determines what speed
setting options are available. Port speeds can only be configured when
auto-negotiation is disabled. The possible field values are:
No Change: Retains the current port speed.
Speed
Auto: Use to automatically configure the port.
10: Indicates the port is currently operating at 10 Mbps.
100: Indicates the port is currently operating at 100 Mbps.
1000: Indicates the port is currently operating at 1000 Mbps.
Duplex
Specifies the port duplex mode. The possible field values are:
No Change: Retains the current port duplex mode.
29
Page 35

g
g
p
Item Description
CAUTION:
Before manually setting a port to full-duplex mode, verify that the device connected to the port is also
manually set to the same speed and duplex setting. If connecting link partners are left to autonegotiate for a link manually set on this switch to full-duplex, they will always negotiate to half-duplex,
resultin
in a duplex mismatch. This can result in a significant reduction in network performance. If you
are unsure of how to configure the speed/duplex setting, simply enable auto- ne
1000 Mbps connections are always full-duplex. Half-duplex connections are only available for 10
Mbps and 100 Mbps settings.
Viewing Port Settings
The Port Summary Page permits the network manager to view the current configuration for all the ports.
Click Port Administration Summary. The Port Summary Page opens.
Auto: Use to automatically configure the port.
Full: The interface supports transmission between the switch and its link partner in
both directions simultaneously.
Half: The interface supports transmission between the switch and its link partner
in only one direction at a time.
otiation for the port.
Figure 69 Port Summary Page
The Port Summary Page contains the following fields:
Table 56 Port Summary Page item description
Item Descri
tion
Indicates whether the port is currently operational or non-operational. The possible
State
field values are:
Enabled: Indicates the port is currently operating.
Disabled: Indicates the port is currently not operating.
30
Page 36

Item Description
Displays the flow control status on the port. The possible field values are:
Flow Control
Enabled: Enables flow control on the port.
Disabled: Disables flow control on the port.
Displays the configured rate for the port. The port type determines what speed setting
options are available. Port speeds can only be configured when auto negotiation is
disabled. The possible field values are:
Speed
Auto: Use to automatically configure the port.
10M: Indicates the port is currently operating at 10 Mbps.
100M: Indicates the port is currently operating at 100 Mbps.
1000M: Indicates the port is currently operating at 1000 Mbps.
Dis p lays the port duple x mode. The port spee d i s set to 10M or 100M or 1 0 00M per
second. The possible field values are:
Auto: Use to automatically configure the port.
Duplex
Full: The interface supports transmission between the switch and its link partner in
both directions simultaneously.
Half: The interface supports transmission between the switch and the client in only
one direction at a time.
PVID Indicates VLAN ID of this port for untagged packets.
Viewing Port Details
The Port Detail Page displays the current port configuration for specific ports.
Click Port Administration Detail. The Port Detail Page opens.
Figure 70 Port Detail Page
Configuring PoE
Power over Ethernet (PoE) provides power to devices over existing LAN cabling, without updating or
modifying the network infrastructure. Power over Ethernet removes the necessity of placing network devices
next to power sources.
CAUTION:
PoE is only supported by V1905-24-PoE Switch.
This section contains the following topics:
31
Page 37

p
Defining Port PoE
Viewing PoE
Defining Port PoE
The Port PoE Setup Page allows the network manager to configure port PoE settings.
Click Port PoE Setup. The Port PoE Setup Page opens.
Figure 71 Port PoE Setup Page
The Port PoE Setup Page contains the following fields:
Table 57 Port PoE Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Defines the port PoE state. The possible values are:
PoE State
Enable: Enables the port for PoE. This is the default.
tion
Disable: Disables the port for PoE.
Defines the power mode for the selected port. The possible values are:
Power Mode
Normal: The port can provide 25W power for access device max. This is the
default.
High Power: The port can provide 30W power for access device max
PoE Mode for selected &
enabled ports
Defines the PoE mode for the selected port.
Displays guaranteed and total PoE power:
Total PoE Available: The total amount of PoE power that can be provided by
the switch.
Guarantee PoE: The maximum amount of PoE power that has been guaranteed
Guarantee Power
Summary
for selected ports. This value is defined by the number of ports you have set to
Guarantee.
Remaining (Available - Guarantee): The minimum amount of non-guaranteed
PoE power left over after allocating the Guarantee PoE power. This value is a
guideline for assigning guarantee ports. The actual amount of power used and
available is displayed on the Port PoE Summary page.
32
Page 38

p
Item Description
Selected Ports Displays the PoE configuration for the selected ports.
Viewing PoE
The Port PoE Summary Page displays the switch and port PoE settings.
Click Port PoE. The PoE Summary Page opens.
Figure 72 Port PoE Summary Page
The Port PoE Summary Page contains the following fields:
Table 58 Port PoE Summary Page item description
Item Descri
Indicates the power source status. The possible field values are:
tion
On: Indicates that the power supply unit is functioning.
State
Off: Indicates that the power supply unit is not functioning.
Faulty: Indicates that the power supply unit is functioning, but an error has
Device
Power
Display
Ports
Power
Display
Power
Max(watts)
Power
Used(watts)
Power
Free(watts)
State
Mode
occurred. For example, a power overload or a short circuit.
Indicates the maximum amount of power the switch can supply. The field value is
displayed in Watts.
Indicates the actual amount of power currently used by the switch. The field value is
displayed in Watts.
Indicates the amount of additional power currently available to the switch. The field
value is displayed in Watts.
Indicates if the port is enabled to deliver power to powered devices. The possible
field values are:
Enable: Indicates the switch is delivering power. This is the default.
Disabled: Indicates the switch is not delivering power.
Indicates the port power mode. The possible field values are:
Auto: Power is automatically allocated to the port, according to port number.
Lower numbered ports are assigned a higher priority for power delivery. This is
the default.
33
Page 39

p
Item Description
Guarantee: Power is guaranteed to the selected port, provided that the power
is available. This setting overrides the priority assigned to lower port numbers
by the auto mode.
Power
Max(watts)
Power
Used(watts)
Indicates the maximum amount of power available to the interface. The field value
is displayed in Watts.
Indicates the actual amount of power currently used by the interface. The field value
is displayed in Watts.
Viewing Port Statistics
The Port Statistics Summary Page contains fields for viewing information about switch utilization and errors
that occurred on the switch.
Click Port Statistics Summary. The Port Statistics Summary Page opens.
Figure 73 Port Statistics Summary Page
The Port Statistics Summary Page contains the following fields:
Table 59 Port Statistics Summary Page item description
Item Descri
Defines the amount of time that passes before the interface statistics are refreshed.
The possible field values are:
tion
No Refresh: Indicates that the port statistics are not refreshed.
Refresh Rate
15 Sec: Indicates that the port statistics are refreshed every 15 seconds.
30 Sec: Indicates that the port statistics are refreshed every 30 seconds.
60 Sec: Indicates that the port statistics are refreshed every 60 seconds.
Clear All Counters Clears the port statistics counters and the new statistics are displayed.
Displays the number of octets received on the interface since the switch was last
Received Bytes (Octets)
Received Packets
refreshed. This number includes bad packets and FCS octets, but excludes framing
bits.
Displays the number of packets received on the interface, including bad packets,
Multicast and broadcast packets, since the switch was last refreshed.
34
Page 40

Item Description
Broadcast Packets
Received
Multicast Packets
Received
CRC & Align Errors
Undersize Packets
Oversize Packets
Fragments
Jabbers
Collisions
Frames of 64 Bytes
Displays the number of good broadcast packets received on the interface since the
switch was last refreshed. This number does not include Multicast packets.
Displays the number of good Multicast packets received on the interface since the
switch was last refreshed.
Displays the number of CRC and Align errors that have occurred on the interface
since the switch was last refreshed.
Displays the number of undersized packets (less than 64 octets) received on the
interface since the switch was last refreshed.
Displays the number of oversized packets (over 9216 octets) received on the
interface since the switch was last refreshed.
Displays the number of fragments (packets with less than 64 octets, excluding
framing bits, but including FCS octets) received on the interface since the switch was
last refreshed
Displays the total number of received packets that were longer than 9216 octets. This
number excludes frame bits, but includes FCS octets that had either a bad Frame
Check Sequence (FCS) with an integral number of octets (FCS Error) or a bad FCS
with a non-integral octet (Alignment Error) number. The field range to detect jabbers
is between 20 ms and 150 ms.
Displays the number of collisions received on the interface since the switch was last
refreshed.
Displays the number of 64-byte frames received on the interface since the switch was
last refreshed.
Frames of 65 to 127
Bytes
Frames of 128 to 255
Bytes
Frames of 256 to 511
Bytes
Frames of 512 to 1023
Bytes
Frames of 1024 to
1522 Bytes
Displays the number of 65 to 127 byte frames received on the interface since the
switch was last refreshed
Displays the number of 128 to 255 byte frames received on the interface since the
switch was last refreshed.
Displays the number of 256 to 511 byte frames received on the interface since the
switch was last refreshed.
Displays the number of 512 to 1023 byte frames received on the interface since the
switch was last refreshed.
Displays the number of 1024 to 1522 byte frames received on the interface since the
switch was last refreshed.
Configuring VLAN
VLANs are logical subgroups with a Local Area Network (LAN) which combine user stations and network
devices into a single unit, regardless of the physical LAN segment to which they are attached. VLANs allow
network traffic to flow more efficiently within subgroups. VLANs use software to reduce the amount of time
it takes for network changes, additions, and moves to be implemented. VLANs restrict traffic within the
VLAN.
VLANs have no minimum number of ports, and can be created per unit, per device, or through any other
logical connection combination, since they are software-based and not defined by physical attributes.
35
Page 41

p
VLANs function at Layer 2. Since VLANs isolate traffic within the VLAN, a Layer 3 router working at a
protocol level is required to allow traffic flow between VLANs. Layer 3 routers identify segments and
coordinate with VLANs. Broadcast and Multicast traffic is transmitted only in the VLAN in which the traffic
is generated.
VLAN tagging provides a method of transferring VLAN information between VLAN groups. VLAN1 is the
default VLAN and always contains untagged ports. All ports are members of VLAN1 by default. If the
untagged port is moved to a new VLAN, the port is removed from VLAN1. For example: If an untagged port
24 is moved to VLAN 5, the port will no longer be a member of VLAN1. However, if the port is added to
VLAN5 as a tagged port it then remains untagged in VLAN1.
This section contains the following topics:
Creating VLANs
Modifying VLAN
Modifying Port VLAN Settings
Renaming VLANs
Removing VLANs
Viewing VLAN Details
Viewing VLAN Port Details
Creating VLANs
The VLAN Setup Page allows the network administrator to create or rename VLANs.
Click Device VLAN Setup. The VLAN Setup Page opens.
Figure 74 VLAN Setup Page
The VLAN Setup Page contains the following fields:
Table 60 VLAN Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Create VLANs Enter ID of configured VLANs.
tion
Create Creates the VLAN IDs.
ID Displays the VLAN ID.
Name Displays the user-defined VLAN name.
36
Page 42

A
g
p
V
Modifying VLAN
The Modify VLAN Page allows the network manager to change VLAN membership.
CAUTION:
t least one port must always be an untagged member of VLAN 1 (the management VLAN). If you choose
to connect all ports to VLANs other than VLAN 1, you will no lon
If this happens, you will need to reset the switch to factory settings.
Click Device VLAN Modify VLAN. The Modify VLAN Page opens.
Figure 75 Modify VLAN Page
er be able to access the Web interface.
The Modify VLAN Page contains the following fields:
Table 61 Modify VLAN Page item description
Item Descri
Select a VLAN to
modify
Selects a VLAN to modify its settings.
Selects the membership type for each port on the VLAN. The possible field values
are:
tion
Untagged: Indicates the interface is an untagged member of the VLAN.
Select membership type
Tagged: Indicates the interface is a tagged member of a VLAN. VLAN tagged
frames are forwarded by the interface. The frames contain VLAN information.
Not A Member: Indicates the interface is not a member of the VLAN.
Not available for selection: Indicates the interface is not available for selection.
Untagged membership Indicates the port is an untagged member of the VLAN.
Tagged membership
Indicates the port is a tagged member of a VLAN. VLAN tagged frames are
forwarded by the interface. The frames contain VLAN information.
NOTE:
By default, all ports belong to VLAN 1 as an untagged member. However, they can belong to multiple
LANs as a tagged member. Also, newly created VLANs will initially have no ports associated with them.
37
Page 43

p
Modifying Port VLAN Settings
The Modify Port VLAN Page allows the network manager to modify port VLAN settings.
Click Device VLAN Modify Port. The Modify Port VLAN Page opens.
Figure 76 Modify Port VLAN Page
The Modify Port VLAN Page contains the following fields:
Table 62 Modify Port VLAN Page item description
Item Descri
Select membership type
VLAN ID Defines the VLAN ID to which the port is to be assigned.
Renaming VLANs
The VLAN Rename Page allows the network manager to select a VLAN from the list to be renamed.
Click Device VLAN Rename. The VLAN Rename Page opens.
Figure 77 VLAN Rename Page
tion
Selects the membership type for each port on the VLAN. The possible field values
are:
Untagged: Indicates the interface is an untagged member of the VLAN.
Tagged: Indicates the interface is a tagged member of a VLAN. VLAN tagged
frames are forwarded by the interface. The frames contain VLAN information.
Not A Member: Indicates the interface is not a member of the VLAN.
Not available for selection: Indicates the interface is not available for selection.
38
Page 44

Removing VLANs
The VLAN Remove Page allows the network administrator to remove VLANs.
Click Device VLAN Remove. The VLAN Remove Page opens.
Figure 78 VLAN Remove Page
Viewing VLAN Details
The VLAN Detail Page provides information and global parameters on the VLANs configured on the system.
Click Device VLAN VLAN Detail. The VLAN Detail Page opens.
Figure 79 VLAN Detail Page
The VLAN Detail Page contains the following information:
39
Page 45

p
p
Table 63 VLAN Detail Page item description
Item Descri
Select a VLAN to
Display
Selects a VLAN to be display its settings
Displays the membership type for each VLAN. The possible field values are:
Untagged: Indicates the interface is an untagged member of the VLAN.
Tagged: Indicates the interface is a tagged member of a VLAN. VLAN tagged
Not A Member: Indicates the interface is not a member of the VLAN
Each port on the switch is capable of passing tagged or untagged frames.
The following describes how the switch will handle tagged and untagged frames.
Membership type
When a port receives a tagged frame with a VLAN ID and the port is a member
When a port receives an untagged frame and the port is an untagged member of
The switch will only forward a frame to ports that are members (tagged or untagged)
of the VLAN to which the frame is assigned. If the port is an untagged member, the
egress frame will be stripped of the VLAN tag and forwarded as untagged.
However, if the port is a tagged member, the egress frame is forwarded as tagged.
tion
frames are forwarded by the interface. The frames contain VLAN information.
(untagged or tagged) of that VLAN, the frame is accepted. Otherwise if the port
is not a member of that VLAN, the frame is discarded.
a VLAN, the frame is accepted and assigned to that VLAN ID. Otherwise if the
port is not an untagged member of any VLAN, the frame is discarded.
Viewing VLAN Port Details
The VLAN Port Detail Page provides information on VLAN configured ports.
Click Device VLAN Port Detail. The VLAN Port Detail Page opens.
Figure 80 VLAN Port Detail Page
The VLAN Port Detail Page contains the following information:
Table 64 VLAN Port Detail Page item description
Item Descri
Untagged Membership Indicates the port is an untagged member of the VLAN.
tion
Tagged membership
Indicates the port is a tagged member of a VLAN. VLAN tagged frames are
forwarded by the interface. The frames contain VLAN information.
40
Page 46

g
Aggregating Port
Overview
Link aggregation aggregates multiple physical Ethernet ports into one logical link, called a Link
Aggregation Group (LAG).
It allows you to increase bandwidth by distributing traffic across the member ports in the aggregation group.
In addition, it provides reliable connectivity because these member ports can dynamically back up each
other.
LACP
Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) based on the IEEE802.3ad standard can be used for dynamic
link aggregation. An LACP-enabled port sends link aggregation control protocol data units (LACPDUs) to tell
the peer about its system priority, system MAC address, port priority, port number and operation key. After
receiving the information from the sender, the receiver compares it with the locally saved information about
other ports, chooses member ports for the aggregation group and reaches agreement about whether a port
can join or leave a dynamic aggregation group.
NOTE:
link aggregation, LACP generates a configuration mix according to the port configuration (rate,
Durin
duplex, basic configuration, management key), which is called an operation key.
Link Aggregation Types
The switch supports two link aggregation types:
Manual Aggregation
Static LACP Aggregation
1. Manual Aggregation
Manual aggregation is configured manually, and cannot be added or removed automatically. A manual or
static LACP aggregation group must contain at least one member port. Member ports in a manual
aggregation are LACP-disabled.
A port in a manual aggregation group can be in one of the two states: selected or unselected. In a manual
aggregation group, only the selected ports can forward user service packets.
In a manual aggregation group, the system sets the ports to selected or unselected state according to the
following rules.
Among the ports in an aggregation group that are in an up state, the system determines the port with
one of the following settings being the highest as the master port (in descending order): full
duplex/high speed, full duplex/low speed, half duplex/high speed, half duplex/low speed. The ports
with their rate, duplex mode and link type being the same as that of the master port are selected ports,
and the rest are unselected ports.
There is a limit on the number of selected ports in an aggregation group. If the number of the selected
ports in an aggregation group exceeds the maximum number supported by the switch, those with
lower port numbers operate as the selected ports, and others as unselected ports.
41
Page 47

Among the selected ports in an aggregation group, the one with smallest port number operates as the
master port. Other selected ports are the member ports.
2. Static LACP Aggregation
A static LACP aggregation group is also manually created. All its member ports are manually added and
can be manually removed (this prevents the system from automatically adding or removing ports from the
group). LACP is enabled on each of the member ports in the static aggregation group. When you remove
a static aggregation group, all the member ports in the up state form one or multiple dynamic aggregations
with LACP enabled.
A port in a static aggregation group can be in one of the two states: selected or unselected.
Both the selected and the unselected ports in the up state can receive and send LACP protocol packets.
Only the selected ports can receive and send service packets; the unselected ports cannot.
In a static aggregation group, the system sets the ports to selected or unselected state according to the
following rules.
Among the ports in an aggregation group that are in an up state, the system determines the port with
the following settings being the highest as the master port (in descending order): full duplex/high
speed, full duplex/low speed, half duplex/high speed, half duplex/low speed. The ports with their
rate, duplex mode and link type being the same as that of the master port are selected ports, and the
rest are unselected ports.
The ports connected to a peer device different from the one the master port is connected to, or those
connected to the same peer device as the master port but to a peer port that is not in the same
aggregation group as the peer port of the master port, are unselected ports.
The system sets the ports with basic port configuration different from that of the master port to
unselected state.
There is a limit on the number of selected ports in an aggregation group. Therefore, if the number of
the selected ports in an aggregation group exceeds the maximum number supported by the switch,
those with lower port numbers operate as the selected ports, and others as unselected ports.
Configuring Link Aggregation
This section includes the following topics:
Defining Link Aggregation
Modifying Link Aggregation
Removing Link Aggregation
Viewing Link Aggregation
Defining Link Aggregation
The Link Aggregation Create Page allows network managers to create LAGs and add ports to a LAG.
Click Port Link Aggregation Create. The Link Aggregation Create Page opens.
42
Page 48

p
Figure 81 Link Aggregation Create Page
The Link Aggregation Create Page includes the following fields:
Table 65 Link Aggregation Create Page item description
Item Descri
Enter Aggregation
Group ID
Manual Defines Manual Aggregation
Static Defines Static LACP Aggregation
To create a new link aggregation group:
1. Enter a LAG ID in the box field.
2. Select Link Aggregation Type (Manual or Static)
3. Select the ports to add to the group.
4. Click Apply.
Modifying Link Aggregation
The Link Aggregation Modify Page allows network managers to select or deselect port for the specific LAG.
Click Port Link Aggregation Modify. The Link Aggregation Modify Page opens.
tion
Defines the group ID
43
Page 49

Figure 82 Link Aggregation Modify Page
Removing Link Aggregation
The Link Aggregation Remove Page allows the network manager to remove group IDs containing member
ports.
Click Port Link Aggregation Remove. The Link Aggregation Remove Page opens.
Figure 83 Link Aggregation Remove Page
Viewing Link Aggregation
The Link Aggregation Summary Page displays the state of the current link aggregation.
Click Port Link Aggregation Summary. The Link Aggregation Summary Page opens.
Figure 84 Link Aggregation Summary Page
44
Page 50

p
p
The Link Aggregation Summary Page includes the following fields:
Table 66 Link Aggregation Summary Page item description
Item Descri
Group ID Displays the Link Aggregated Group ID. The field range is 1-6.
Type
Ports Displays the member ports included in the specified LAG.
Configuring LACP
This section includes the following topics:
Modify LACP
Viewing LACP
Modify LACP
The Link Aggregation Modify Page allows the network manager to modify fields for LACP.
Click Port Link Aggregation Modify. The Link Aggregation Modify Page opens.
Figure 85 Link Aggregation Modify Page
tion
Displays the type of link aggregation for the Group ID. The possible field value is
Static or LACP.
The Link Aggregation Modify Page contains the following fields:
Table 67 Link Aggregation Modify Page item description
Item Descri
LACP System Priority
LACP Port Priority
LACP Timeout
Viewing LACP
The LACP Summary Page displays fields for LACP.
tion
Specifies system priority value. The default value is 32768. The field range is
0-65535.
Specifies the LACP priority value for the port. The default is 32768. The field range
is 0-65535.
Selects the administrative LACP timeout. The possible field values are:
Long: Specifies the long timeout value. This is the default.
Short: Specifies the short timeout value.
45
Page 51

p
Click Port Link Aggregation LACP. The LACP Summary Page opens.
Figure 86 LACP Summary Page
The LACP Summary Page contains the following fields:
Table 68 LACP Summary Page item description
Item Descri
Port-Priority Displays the LACP priority value for the port.
Displays the administrative LACP timeout. The possible field values are:
LACP Timeout
Long: Specifies the long timeout value. This is the default.
Short: Specifies the short timeout value.
Group ID Display LAG ID which the port belongs to. N/A: unassigned.
Configuring STP
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) is a bridge-based system for providing fault tolerance on networks and can be
used to detect and disable network loops. The spanning tree ensures that the optimal path is maintained
between spanning tree-compliant networked devices by:
Disabling redundant paths when the main paths are operational.
Enabling redundant paths if the main paths fail.
Spanning tree uses a distributed algorithm to select a bridging device that serves as the root of the spanning
tree network.
The bridging device, known as the Root Bridge, generates bridge protocol data units (BPDUs) on all ports
at a regular interval known as the Hello Time. All other spanning tree-compliant devices on the network have
a designated Root Port. This is the Port nearest the Root Bridge and it is used for receiving the BPDUs
initiated by the Root Bridge. If a bridge does not get a Hello BPDU after a predetermined interval, the bridge
assumes that the link to the Root Bridge is down. This bridge will then initiate negotiations with other bridges
to reconfigure the network to reestablish a valid network topology.
tion
46
Page 52

After all the bridges on the network have determined the configuration of their ports, each bridge only
forwards traffic between the Root Port and the ports that are the Designated Bridge Ports for each network
segment. All other ports are blocked, which means that they are prevented from forwarding traffic.
The device supports the following STP versions:
Classic STP: Provides a single path between end stations, avoiding and eliminating loops.
Rapid STP: Detects and uses network topologies that provide faster convergence of the spanning tree,
without creating forwarding loops. While Classic STP prevents Layer 2 forwarding loops in a general
network topology, convergence can take between 30-60 seconds.
This section contains the following topics:
Defining STP Global Parameters
Modifying STP Interface Parameters
Viewing STP
Defining STP Global Parameters
The STP Global Setup Page allows network managers to assign STP global settings.
Click Device Spanning Tree Setup. The STP Global Setup Page opens.
Figure 87 STP Global Setup Page
The STP Global Setup Page contains the following fields:
47
Page 53

p
Table 69 STP Global Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Defines whether STP is enabled on the switch. The possible field values
Spanning Tree
State
are:
Disable: Disables STP and RSTP on the switch.
Classic: Enables STP on the switch.
RSTP: Enables RSTP on the switch.
Determines how BPDU packets are managed when STP is disabled on the
port or switch. BPDUs are used to transmit spanning tree information. The
possible field values are:
Global
Settings
BPDU Handling
Filtering: Filters BPDU packets when spanning tree is disabled on an
interface.
Flooding: Floods BPDU packets when spanning tree is disabled on an
interface. This is the default value.
Specifies the method used to assign default path cost to STP ports. The
possible field values are:
Path Cost Default
Values
Short: Specifies 1 through 65535 ranges for port path cost. This is the
default value.
Long: Specifies 1 through 200000000 ranges for port path cost. The
default path cost assigned to an interface varies according to the
selected method (Hello Time, Max Age, or Forward Delay).
Specifies the bridge priority value. When switches or bridges are running
STP, each is assigned a priority. After exchanging BPDUs, the switch with
Priority
the lowest priority value becomes the Root Bridge. The field range is
0-61440. The default value is 32768. The port priority value is provided
in increments of 4096.
tion
Bridge Settings
Designated
Root
Specifies the switch Hello Time. The Hello Time indicates the amount of
Hello Time
Max Age
Forward Delay
Bridge ID Identifies the Bridge priority and MAC address.
Root Bridge ID Identifies the Root Bridge priority and MAC address.
Root Port
Root Path Cost Indicates the cost of the path from this bridge to the Root Bridge.
Topology
Changes Counts
Last Topology
Change
time in seconds a Root Bridge waits between configuration messages.
The default is 2 seconds.
Specifies the switch Maximum Age Time. The Maximum Age Time is the
amount of time in seconds a bridge waits before sending configuration
messages. The default Maximum Age Time is 20 seconds.
Specifies the switch Forward Delay Time. The Forward Delay Time is the
amount of time in seconds a bridge remains in a listening and learning
state before forwarding packets. The default is 15 seconds.
Indicates the port number that offers the lowest cost path from this bridge
to the Root Bridge. This field is significant when the bridge is not the Root
Bridge. The default is zero.
Indicates the total amount of STP state changes that have occurred.
Indicates the amount of time that has elapsed since the bridge was
initialized or reset, and the last topographic change that occurred. The
time is displayed in a day-hour-minute-second format, such as 2 days 5
48
Page 54

p
Item Description
Modifying STP Interface Parameters
The STP Interface Parameters Modify Page allows network managers to modify STP parameters to specific
interfaces.
Click Device Spanning Tree Modify. The STP Interface Parameters Modify Page opens.
Figure 88 STP Interface Parameters Modify Page
hours 10 minutes and 4 seconds.
The STP Interface Parameters Modify Page contains the following fields:
Table 70 STP Interface Parameters Modify Page item description
Item Descri
Specifies if STP is enabled on the port. The possible field values are:
STP
No Change: Retains the current port status.
Enabled: Indicates that STP is enabled on the port.
tion
Disabled: Indicates that STP is disabled on the port. This is the default value.
Specifies if Fast Link is enabled on the port. If Fast Link mode is enabled for a port, the
port is automatically placed in the Forwarding state when the port link is up. Fast Link
optimizes the STP protocol convergence. STP convergence takes 30 seconds and is
Port Fast
not dependent on the number of switches in the network. The possible field values
are:
No Change: Retains the current port status.
Enabled: Indicates fast link is enabled on the port.
Disabled: Indicates fast link is disabled on the port. This is the default value.
Restricts the interface from acting as the root port of the switch. The possible field
values are:
Root Guard
No Change: Retains the current port status.
Enabled: Indicates Root Guard is enabled on the port.
Disabled: Indicates Root Guard is disabled on the port. This is the default value.
Default Path Cost
Specifies if Default Path Cost is enabled. The possible field values are:
No Change: Retains the current port status.
49
Page 55

p
Item Description
Enabled: Enables the default path cost on the port. This is the default value.
Disabled: Disables the default path cost on the port.
Defines the port contribution to the root path cost. When Default Path Cost is
disabled, you can configure it; when Default Path Cost is enabled, you cannot
Path Cost
configure it. The possible field values are:
65535: Indicates Path Cost Default Values is short. This is the default value.
200000000: Indicates Path Cost Default Value is long.
Defines the priority value of the port. The priority value influences the port choice
Port Priority
when a bridge has two ports connected in a loop. The priority value is between
0-240. The default is 128.
Specifies whether a Point-to-Point link is established, or if the switch is permitted to
establish a Point-to-Point link. The possible field values are:
No Change: Retains the current port status.
RSTP Link Type
Auto: Enables the switch to establish automatically Point-to-Point link. This is the
default value.
Point to Point: Indicates if a Point-to-Point link is currently established on the port.
Ports set to Full Duplex modes are considered Point-to-Point port links.
Shared: Enables the switch to establish a shared link.
Viewing STP
The STP Summary Page displays the current STP parameters for all ports.
Click Device Spanning Tree Summary. The STP Summary Page opens.
Figure 89 STP Summary Page
The STP Summary Page contains the following fields:
Table 71 STP Summary Page item description
Item Descri
Indicates if STP is enabled on the port. The possible field values are:
STP
Enabled: Indicates that STP is enabled on the port.
tion
Disabled: Indicates that STP is disabled on the port.
50
Page 56

Item Description
Indicates if Fast Link is enabled on the p o r t . I f F ast Link mode is enabled for a port, the
Port Fast
Root Guard
port is automatically placed in the Forwarding state when the port link is up. Fast Link
optimizes the STP protocol convergence. STP convergence takes 30 seconds and is
not dependent on the number of switches in the network.
Indicates if the interface is acting as the root port of the switch. The possible field
values are:
Enabled: Indicates Root Guard is enabled on the port.
Disabled: Indicates Root Guard is disabled on the port.
Displays the current STP state of a port. If enabled, the port state determines what
action is taken on traffic. Possible port states are:
Disable: Indicates that STP is currently disabled on the port. The port forwards
traffic while learning MAC addresses.
Blocking: Indicates that the port is currently blocked and cannot forward traffic or
learn MAC addresses. Blocking is displayed when Classic STP is enabled.
Port State
Listening: Indicates that the port is in listening mode. The port cannot forward
traffic nor can it learn MAC addresses.
Learning: Indicates that the port is in learning mode. The port cannot forward
traffic, however it can learn new MAC addresses.
Forwarding: Indicates that the port is in forwarding mode. The port can forward
traffic and learn new MAC addresses.
Discarding: Indicates that the port is in discarding mode. The port is listening to
BPDUs, and discards any other frames it receives.
Displays the port role assigned by the STP algorithm to provide to STP paths. The
possible field values are:
Disable: Indicates that the port or LAG is currently disabled on the port
Designated: The port or LAG through which the designated switch is attached to
Port Role
the LAN.
Alternate: Provides an alternate path to the root switch from the root interface.
Backup: With the designated port being blocked, the backup port becomes the
new designated port fast and begins to forward data seamlessly.
Root: Provides the lowest cost path to forward packets to the root switch.
Speed Indicates the speed at which the port is operating.
Path Cost
Priority
Link Type
Indicates the port contribution to the root path cost. The path cost is adjusted to a
higher or lower value, and is used to forward traffic when a path is re-routed.
Indicates the priority value of the port. The priority value influences the port choice
when a bridge has two ports connected in a loop. The priority range is between
0-240.
Indicates whether a Point-to-Point link is established, or if the switch is permitted to
establish a Point-to-Point link. The possible field values are:
Auto: Enables the switch to establish automatically point-to-point link.
Point to Point: Indicates if a point-to-point link is currently established on the port.
Ports set to Full Duplex modes are considered Point-to-Point port links.
Shared: Enables the switch to establish a shared link.
Designated Bridge ID Indicates the bridge priority and the MAC Address of the designated bridge.
Designated Port ID Indicates the selected port priority and interface.
51
Page 57

Item Description
Designated Cost
Forward Transitions
Indicates the cost of the port participating in the STP topology. Ports with a lower cost
are less likely to be blocked if STP detects loops.
Indicates the number of times the port has changed from Forwarding state to Blocking
state.
Configuring IGMP Snooping
This section contains information for configuring IGMP Snooping.
When IGMP Snooping is enabled, all IGMP packets are forwarded to the CPU. The CPU analyzes the
incoming packets and determines:
Which ports want to join which Multicast groups.
Which ports have Multicast routers generating IGMP queries.
Which routing protocols are forwarding packets and Multicast traffic.
Ports requesting to join a specific Multicast group issue an IGMP report, specifying that Multicast group is
accepting members. This results in the creation of the Multicast filtering database.
This section contains the following topic:
Defining IGMP Snooping
Defining IGMP Snooping
The IGMP Snooping Setup Page allows network managers to define IGMP Snooping parameters for
VLANs.
Click Device IGMP Snooping Setup. The IGMP Snooping Setup Page opens.
Figure 90 IGMP Snooping Setup Page
The IGMP Snooping Setup Page contains the following fields:
52
Page 58

p
Table 72 IGMP Snooping Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Defines whether IGMP Snooping is enabled on the switch. The possible field values
are:
IGMP Snooping Status
IGMP Query Status
Select VLAN ID Specifies the VLAN ID
IGMP Snooping Status
IGMP Query Status
Enabled: Indicates that IGMP Snooping is enabled on the switch.
Disabled: Indicates that IGMP Snooping is disabled on the switch. This is the
Defines whether IGMP Query is enabled on the switch. The possible field values are:
Enabled: Indicates that IGMP Query is enabled on the switch.
Disabled: Indicates that IGMP Query is disabled on the switch. This is the default
Defines whether IGMP snooping is enabled on the VLAN. The possible field values
are:
Enabled: Enables IGMP Snooping on the VLAN.
Disabled: Disables IGMP Snooping on the VLAN. This is the default value.
Defines whether IGMP query is enabled on the VLAN. The possible field values are:
Enabled: Enables IGMP Query on the VLAN.
Disabled: Disables IGMP Query on the VLAN. This is the default value.
tion
default value.
value.
Configuring ACL
Access Control List (ACL) allows network managers to define classification actions and rules for specific
ingress ports. A network manager can configure an ACL on an ingress port so that packets are either
admitted entry or denied entry. The user can also specify that when packets are denied entry, the ingress
port is also disabled.
This section includes the following topics:
Configuring MAC Based ACL
Configuring IP Based ACL
Configuring ACL Binding
Configuring MAC Based ACL
This section includes the following topics:
Defining MAC Based ACL
Modifying MAC Based ACL
Removing MAC Based ACL
Viewing MAC Based ACL
Defining MAC Based ACL
The MAC Based ACL Setup Page allows network managers to define MAC Based ACL.
Click Device ACL MAC Based ACL Setup. The MAC Based ACL Setup Page opens.
53
Page 59

p
Figure 91 MAC Based ACL Setup Page
The MAC Based ACL Setup Page contains the following fields:
Table 73 MAC Based ACL Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Selection ACL Selects an existing MAC-based ACL to which rules are to be added.
Defines a new user-defined MAC-based Access Control List. The options are as
follows:
Create ACL
ACL Priority: Sets the ACL priority. The possible field values are 1-100.
tion
Rule Priority Type: Sets the rule priority type. CONFIG: You will have to configure
the ACL rule priority by yourself, AUTO: the ACL rule priority will be configured
automatically.
Priority
Source MAC Address Matches the source MAC address to which packets are addressed to the rule.
Source Mask
Sets the rule priority, which determines which rule is matched to a packet on a
first-match basis. The possible field values are 1-65535.
Defines the source MAC Address wildcard mask.
Wildcards are used to mask all or part of a source MAC address. Wildcard masks
specify which bits are used and which are ignored. A wildcard mask of
FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF indicates that no bit is important. A wildcard of
00.00.00.00.00.00 indicates that all bits are important.
For example, if the source MAC address is 00:AB:22:11:33:00 and the wildcard
mask is 00:00:00:00:00:FF, the first five bytes of the MAC are used, while the last
byte is ignored. For the source MAC address 00:AB:22:11:33:00, this wildcard
mask matches all MAC addresses in the range 00:AB:22:11:33:00 to
00:AB:22:11:33:FF.
Destination MAC
Address
Destination Mask
Matches the destination MAC address to which packets are addressed to the rule.
Defines the destination MAC Address wildcard mask.
Wildcards are used to mask all or part of a destination MAC address. Wildcard
masks specify which bits are used and which are ignored. A wildcard mask of
FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF indicates that no bit is important. A wildcard mask of
00.00.00.00.00.00 indicates that all bits are important.
For example, if the destination MAC address is 00:AB:22:11:33:00 and the
wildcard mask is 00:00:00:00:00:FF, the first five bytes of the MAC are used, while
the last byte is ignored. For the destination MAC address 00:AB:22:11:33:00, this
wildcard mask matches all MAC addresses in the range 00:AB:22:11:33:00 to
00:AB:22:11:33:FF.
54
Page 60

Item Description
VLAN ID Matches the packet's VLAN ID to the rule. The possible field values are 1 to 4094.
CoS Classifies traffic based on the CoS tag value.
CoS Mask Defines the CoS mask used to classify network traffic.
Ethertype Provides an identifier that differentiates between various types of protocols.
Specifies the ACL forwarding action. In addition, the port can be shut down, a trap
can be sent to the network administrator, or packet is assigned rate limiting
Action
restrictions for forwarding. The options are as follows:
Permit: Forwards packets which meet the ACL criteria.
Deny: Drops packets which meet the ACL criteria.
To create a new MAC-based ACL:
1. Select Create ACL.
2. Enter the name of the new ACL.
3. Click Create. The new ACL is created, and the switch is updated.
To define a new MAC-based ACL rule:
1. Select Selection ACL.
2. Select the ACL from the list.
3. Define the fields for the new ACL rule.
4. Click Apply.
Modifying MAC Based ACL
The MAC Based ACL Modify Page allows the network administrator to modify an existing MAC-based ACL
rule.
Click Device ACL MAC Based ACL Modify. The MAC Based ACL Modify Page opens.
Figure 92 MAC Based ACL Modify Page
NOTE:
The description of parameters in the page refers to Defining MAC Based ACL.
1. Selects the ACL to be modified.
2. Selects the Rule to be modified.
3. Modifies the fields of the Rule.
55
Page 61

p
4. Click Apply.
Removing MAC Based ACL
The MAC Based ACL Remove Page allows the network administrator to remove MAC-based ACL or
MAC-based ACL rules.
Click Device ACL MAC Based ACL Remove. The MAC Based ACL Remove Page opens.
Figure 93 MAC Based ACL Remove Page
The MAC Based ACL Remove Page contains the following fields:
Table 74 MAC Based ACL Remove Page item description
Item Descri
ACL Name Selects a MAC-based ACL for removal.
Remove ACL Enables the ACL to be removed.
To remove MAC-based ACL:
1. Select the ACL Name to be removed
2. Check Remove ACL.
3. Click Remove.
To remove MAC-based ACL rules:
1. Select the ACL Name containing the rules to be deleted.
2. For each rule to be removed, check the box to the left of the row in the rules table. To remove all rules,
the topmost box may be checked.
3. Click Remove.
Viewing MAC Based ACL
The MAC Based ACL Summary Page displays information regarding MAC Based ACL configured on the
switch.
tion
Click Device ACL MAC Based ACL. The MAC Based ACL Summary Page opens.
56
Page 62

p
Figure 94 MAC Based ACL Summary Page
The MAC Based ACL Summary Page contains the following fields:
Table 75 MAC Based ACL Summary Page item description
Item Descri
ACL Name Contains a list of the MAC-based ACL.
ACL Priority Indicates the ACL Priority.
Priority
Source Address Indicates the source MAC address.
Source Mask Indicates the source MAC address Mask.
Destination Address Indicates the destination MAC address.
Destination Mask Indicates the destination MAC address Mask.
VLAN ID
CoS Classifies traffic based on the CoS tag value.
CoS Mask Displays the CoS mask used to filter CoS tags.
Ethertype Provides an identifier that differentiates between various types of protocols.
Action
Indicates the rule priority, which determines which rule is matched to a packet on a
first match basis.
Matches the packet's VLAN ID to the ACL rule. The possible field values are 1 to
4094.
Indicates the ACL forwarding action. In addition, the port can be shut down, a trap
can be sent to the network administrator, or a packet can be assigned rate limiting
restrictions for forwarding. The possible field values are:
tion
Permit: Forwards packets which meet the ACL criteria.
Deny: Drops packets which meet the ACL criteria.
Configuring IP Based ACL
This section includes the following topics:
Defining IP Based ACL
Modifying IP Based ACL
Removing IP Based ACL
Viewing IP Based ACL
Defining IP Based ACL
The IP Based ACL Setup Page allows network managers to define IP Based ACL.
57
Page 63

p
Click Device ACL IP Based ACL Setup. The IP Based ACL Setup Page opens.
Figure 95 IP Based ACL Setup Page
The IP Based ACL Setup Page contains the following fields:
Table 76 IP Based ACL Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Selection ACL Selects an existing IP-based ACL to which rules are to be added.
Defines a new user-defined IP-based Access Control List. The options are as follows:
tion
ACL Priority: Sets the ACL priority. The possible field values are 1-100.
Create ACL
Priority
Protocol
Rule Priority Type: Sets the rule priority type. CONFIG: You will have to configure the
ACL rule priority by yourself, AUTO: the ACL rule priority will be configured
automatically.
Sets the rule priority, which determines which rule is matched to a packet on a first-match
basis. The possible field values are 1-65535.
Defines the protocol in the rule to which the packet is matched. The possible fields are:
Select from List: Selects a protocol from a list by which packets are matched to the
rule.
Protocol ID: Selects a protocol ID from a list by which packets are matched to the rule.
Defines the source port that is used for matched packets. Enabled only when TCP or UDP
Source Port
Destination Port
are selected in the Protocol list. The field value is either user defined or Any. If Any is
selected, the IP based ACL is applied to any source port.
Defines the destination port that is used for matched packets. Enabled only when TCP or
UDP are selected in the Protocol list. The field value is either user defined or Any. If Any
is selected, the IP based ACL is applied to any destination port.
If checked, enables configuration of TCP flags matched to the packet. The possible fields
are:
Urg: Urgent pointer field significant. The urgent pointer points to the sequence
number of the octet following the urgent data.
Ack: Acknowledgement field significant. The acknowledgement field is the byte
TCP Flags
number of the next byte that the sender expects to receive from the receiver.
Psh: Push (send) the data as soon as possible, without buffering. This is used for
interactive traffic.
Rst: Reset the connection. This invalidates the sequence numbers and aborts the
session between the sender and receiver.
Syn: Synchronize Initial Sequence Numbers (ISNs). This is used to initialize a new
58
Page 64

Item Description
connection.
Fin: Finish. This indicates there is no more data from the sender. This marks a normal
closing of the session between the sender and receiver.
If selected, enables matching the source port IP address to which packets are addressed
Source IP Address
Dest IP Address
Match DSCP If selected, matches the packet DSCP value to the ACL.
to the rule, according to a wildcard mask. The field value is either user defined or Any. If
Any is selected, accepts any source IP address and disables wildcard mask filtering.
If selected, enables matching the destination port IP address to which packets are
addressed to the rule, according to a wildcard mask. The field value is either user defined
or Any. If Any is selected, accepts any destination IP address and disables wildcard mask
filtering.
Match IP
Precedence
Action
If selected, Matches the packet IP Precedence value to the ACL.
Defines the ACL forwarding action. In addition, a trap can be sent to the network
administrator, or packet is assigned rate limiting restrictions for forwarding. The options
are as follows:
Permit: Forwards packets which meet the ACL criteria.
Deny: Drops packets which meet the ACL criteria.
To create a new IP-based ACL:
1. Select Create ACL.
2. Enter the name of the new ACL.
3. Click Create.
To define a new IP-based ACL rule:
1. Select Selection ACL.
2. Select the ACL from the list.
3. Define the fields for the new ACL rule.
4. Click Apply.
Modifying IP Based ACL
The IP Based ACL Modify Page allows the network administrator to modify IP Based ACL rules.
Click Device ACL IP Based ACL Modify. The IP Based ACL Modify Page opens.
59
Page 65

p
Figure 96 IP Based ACL Modify Page
NOTE:
The description of parameters in the page refers to Defining IP Based ACL.
1. Selects the ACL to be modified.
2. Selects the Rule to be modified.
3. Modifies the fields of the Rule.
4. Click Apply.
Removing IP Based ACL
The IP Based ACL Remove Page allows the network administrator to remove IP-based ACL or IP-based ACL
rules.
Click Device ACL IP Based ACL Remove. The IP Based ACL Remove Page opens.
Figure 97 IP Based ACL Remove Page
The IP Based ACL Remove Page contains the following fields:
Table 77 IP Based ACL Remove Page item description
Item Descri
ACL Name Selects an IP-based ACL for removal.
Remove ACL Enables the ACL to be removed.
tion
To remove an IP-based ACL:
1. Select an ACL Name to be removed.
2. Check Remove ACL.
3. Click Remove.
60
Page 66

p
To remove IP-based ACL rules:
1. Select an ACL Name.
2. For each rule to be removed, check the box to the left of the row in the rules table. To remove all rules,
the topmost box may be checked.
3. Click Remove.
Viewing IP Based ACL
The IP Based ACL Summary Page displays information regarding IP-based ACL configured on the switch.
Click Device ACL IP Based ACL. The IP Based ACL Summary Page opens.
Figure 98 IP Based ACL Summary Page
The IP Based ACL Summary Page contains the following fields:
Table 78 IP Based ACL Summary Page item description
Item Descri
ACL Name Contains a list of the IP Based ACL
ACL Priority Indicates the ACL Priority.
Indicates the rule priority, which determines which rule is matched to a packet on a
Priority
Protocol Indicates the protocol in the rule to which the packet is matched.
Source Port
Destination Port
Flag Set Indicates the TCP flag to which the packet is mapped.
Source IP Address Matches the source IP address to which packets are addressed to the ACL.
Source Mask Indicates the source IP address mask.
Destination IP Address Matches the destination IP address to which packets are addressed to the ACL.
first-match basis. The possible field values are 1-65535, with 1 being the highest
priority.
Indicates the source port that is matched packets. Enabled only when TCP or UDP are
selected in the Protocol list.
Indicates the destination port that is matched packets. Enabled only when TCP or
UDP are selected in the Protocol list.
tion
Destination Mask Indicates the destination IP address mask.
DSCP
IP Precedence Indicates matching IP precedence with the packet IP precedence value.
Matches the packet DSCP value to the ACL. Either the DSCP value or the IP
Precedence value is used to match packets to ACLs.
61
Page 67

p
Item Description
Indicates the ACL forwarding action. In addition, the port can be shut down, a trap
Action
can be sent to the network administrator, or packet is assigned rate limiting
restrictions for forwarding.
Configuring ACL Binding
This section includes the following topics:
Defining ACL Binding
Removing ACL Binding
Viewing ACL Binding
Defining ACL Binding
The ACL Binding Setup Page allows the network administrator to bind specific ports to MAC or IP based
ACLs.
Click Device ACL ACL Binding Setup. The ACL Binding Setup Page opens.
Figure 99 ACL Binding Setup Page
The ACL Binding Setup Page contains the following fields:
Table 79 ACL Binding Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Bind ACL Assigns ACL type
Select ACL Selects the ACL from a list of previously defined ACLs to which the port can be bound.
Removing ACL Binding
The ACL Binding Remove Page allows the network administrator to remove user-defined ACLs from a
selected interface.
Click Device ACL ACL Binding Remove. The ACL Binding Remove Page opens.
tion
62
Page 68

p
Figure 100 ACL Binding Remove Page
The ACL Binding Remove Page contains the following fields:
Table 80 ACL Binding Remove Page item description
Item Descri
Remove All Port
Binding By ACL
ACL Name Displays the name of ACL to be removed from the selected port.
To remove ACL Binding:
1. Select an ACL Name from “Remove All Port Binding By ACL” or “ACL Name”.
2. Click Remove.
Viewing ACL Binding
The ACL Binding Summary Page displays the user-defined ACLs mapped to the interfaces.
Click Device ACL ACL Binding. The ACL Binding Summary Page opens.
Figure 101 ACL Binding Summary Page
tion
Remove all the port binding according to the current ACL.
The ACL Binding Summary Page contains the following fields:
63
Page 69

p
Table 81 ACL Binding Summary Page item description
Item Descri
MAC-based ACL Displays the MAC based ACL to which the interface is assigned.
IP-based ACL Displays the IP based ACL to which the interface is assigned
Configuring QoS
Quality of Service (QoS) provides the ability to implement QoS and priority queuing within a network. For
example, certain types of traffic that require minimal delay, such as Voice, Video, and real-time traffic can
be assigned a high priority queue, while other traffic can be assigned a lower priority queue. The result is
an improved traffic flow for traffic with high demand.
This section contains information for configuring QoS, and includes the following topics:
Configuring CoS
Configuring Queue Algorithm
Defining CoS to Queue
Configuring DSCP to Queue
Configuring Trust Mode
Configuring Bandwidth Settings
Configuring Voice VLAN
tion
Configuring CoS
Defining CoS
The CoS Setup Page contains information for enabling QoS globally and setting default CoS value to the
interfaces.
Click Device QoS CoS Setup. The CoS Setup Page opens.
Figure 102 CoS Setup Page
The CoS Setup Page contains the following fields:
64
Page 70

p
p
Table 82 CoS Setup Page item description
Item Descri
QoS Mode
Set Default
Restore Default Restores the switch factory defaults for CoS values.
Viewing CoS Settings
The CoS Summary Page displays CoS default settings assigned to ports.
Click Device QoS CoS. The CoS Summary Page opens.
Figure 103 CoS Summary Page
tion
Specifies if QoS is enabled on the switch. The possible values are:
Disabled: Restores the switch factory defaults for QoS values and disables
configure QoS values on the switch.
Enabled: Enables configure QoS values on the switch.
Sets the default user priority. The possible field values are 0-7, where 0 is the lowest
and 7 is the highest priority.
The CoS Summary Page contains the following fields:
Table 83 CoS Summary Page item description
Item Descri
Port Displays the interface for which the CoS default value is defined.
Default CoS
Displays the default CoS value for incoming packets for which a VLAN priority tag is
not defined.
tion
Configuring Queue Algorithm
The Queue Setup Page contains the queue algorithm information.
Click Device QoS Queue. The Queue Setup Page opens.
65
Page 71

p
Figure 104 Queue Setup Page
The Queue Setup Page contains the following fields:
Table 84 Queue Setup Page item description
Item Descri
HQ-WRR
WRR(ratio 1:2:10:15)
This highest queue is transmitted first if any packets are in the highest queue. When
the highest queue is exhausted, the remaining queues are served by WRR.
This queue algorithm specifies which port queue that each packet should be sent to.
The actual bandwidth of each port queue is determined by the weight, whose values
are 1,2,10 and 15.
tion
Configuring CoS to Queue
Defining CoS to Queue
The CoS to Queue Setup Page contains fields for mapping CoS values to traffic queues. Four traffic priority
queues are supported on the switch, with 1 representing the lowest queue and 4 as the highest. The highest
priority queue functions with strict priority while queues 1-3 function with WRR priority with the following
weights (1, 2, 10 and 15) respectively.
Click Device QoS CoS to Queue Setup. The CoS to Queue Setup Page opens.
Figure 105 CoS to Queue Setup Page
The CoS to Queue Setup Page contains the following fields:
66
Page 72

p
p
Table 85 CoS to Queue Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Restore Defaults Restores the switch factory defaults for mapping CoS values to forwarding queues.
Class of Service Specifies the CoS priority tag values, where 0 is the lowest and 7 is the highest.
Queue Defines the traffic forwarding queue to which the CoS priority is mapped.
Viewing CoS to Queue
The CoS to Queue Summary Page contains a table that displays the CoS values mapped to traffic queues.
Click Device QoS CoS to Queue. The CoS to Queue Summary Page opens.
Figure 106 CoS to Queue Summary Page
tion
The CoS to Queue Summary Page contains the following fields:
Table 86 CoS to Queue Summary Page item description
Item Descri
Class of Service Displays the CoS priority tag values, where 0 is the lowest and 7 is the highest.
Queue
Indicates the traffic forwarding queue to which the CoS priority is mapped. Four
traffic priority queues are supported.
tion
Configuring DSCP to Queue
Defining DSCP to Queue
The DSCP to CoS Setup Page contains fields for mapping DSCP settings to CoS priority tag values. For
example, In default, a packet with a DSCP tag value of 3 can be assigned to queue 1.
Click Device QoS DSCP to Queue Setup. The DSCP to Queue Setup Page opens.
67
Page 73

p
Figure 107 DSCP to Queue Setup Page
The DSCP to Queue Setup Page contains the following fields:
Table 87 DSCP to Queue Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Restore Defaults
DSCP Displays the incoming packet’s DSCP value.
CoS Specifies the CoS value forwarding queue to which the DSCP priority is mapped.
Viewing DSCP to Queue
The DSCP to CoS Summary Page contains a table that displays the DSCP values mapped to CoS values.
Click Device QoS DSCP to Queue. The DSCP to Queue Summary Page opens.
Figure 108 DSCP to Queue Summary Page
tion
Restores the switch factory defaults for mapping DSCP values to a traffic forwarding
queue.
The DSCP to Queue Summary Page contains the following fields:
68
Page 74

p
p
Table 88 DSCP to Queue Summary Page item description
Item Descri
DSCP Displays the incoming packet’s DSCP value.
CoS
Indicates the CoS value forwarding queue to which the DSCP priority is mapped. The
possible field values are 0-7.
Configuring Trust Mode
The Trust Setup Page contains information for configuring trust mode on the switch.
Click Device QoS Trust Setup. The Trust Setup Page opens.
Figure 109 Trust Setup Page
tion
The Trust Setup Page contains the following fields:
Table 89 Trust Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Specifies which packet fields to use for classifying packets entering the switch. When
no rules are defined, the traffic containing the predefined packet CoS field is
mapped according to the relevant trust modes table. Traffic not containing a
Trust Mode
predefined packet field is mapped to “best effort”. The possible Trust Mode field
values are:
tion
CoS: Classifies traffic based on the CoS tag value.
DSCP: Classifies traffic based on the DSCP tag value.
Configuring Bandwidth Settings
Defining Bandwidth Settings
The Bandwidth Setup Page allows network managers to define the bandwidth settings for a specified
interface.
Click Device QoS Bandwidth Setup. The Bandwidth Setup Page opens.
69
Page 75

p
Figure 110 Bandwidth Setup Page
The Bandwidth Setup Page contains the following fields:
Table 90 Bandwidth Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Enable
Ingress Rate
Ingress
Rate Limit
Egress
Shaping
Rates
Limit
Ingress Rate
Limit
Enable
Egress
Shaping
Rate
Committed
Information
Rate (CIR)
Committed
Burst Size
(CbS)
Viewing Bandwidth Settings
The Bandwidth Summary Page displays bandwidth settings for a specified interface.
Click Device QoS Bandwidth Summary. The Bandwidth Summary Page opens.
tion
Enables setting an Ingress Rate Limit.
Defines the ingress traffic limit for the port. The field range of normal port is 3500
- 100,000 kbits per second, and the field range of combo port is 3500 1,000,000 kbits per second.
Enables setting Egress Shaping Rates.
Defines the CIR for the interface. The field range of normal port is 64 - 100,000
kbits per second, and the field range of combo port is 64 - 1,000,000 kbits per
second.
Defines the CbS for the interface. The field range is 4,096 bytes - 133,120 bytes
per second.
70
Page 76

p
Figure 111 Bandwidth Summary Page
The Bandwidth Summary Page contains the following fields:
Table 91 Bandwidth Summary Page item description
Item Descri
Indicates the ingress rate limiting status on the interface. The possible field values
are:
Enabled: Ingress rate limiting is enabled on the interface.
Disabled: Ingress rate limiting is disabled on the interface. This is the default.
Indicates the egress traffic shaping status for the interface. The possible field values
are:
Enabled: Egress traffic shaping is enabled for the interface.
Disabled: Egress traffic shaping is disabled for the interface. This is the default.
Ingress
Rate Limit
Egress
Shaping
Rates
Status
Rate Limit Indicates the ingress traffic limit for the port.
Status
CIR Indicates the Committed Information Rate (CIR) for the interface.
CbS Indicates the Committed Burst Size (CbS) for the interface.
tion
Configuring Voice VLAN
Voice VLAN allows network administrators to enhance VoIP service by configuring ports to carry IP voice
traffic from IP phones on a specific VLAN. VoIP traffic has a preconfigured Organizationally Unique
Identifier (OUI) prefix in the source MAC address. Network Administrators can configure VLANs on which
voice IP traffic is forwarded. Non-VoIP traffic is dropped from the Voice VLAN in auto Voice VLAN secure
mode. Voice VLAN also provides QoS to VoIP, ensuring that the quality of voice does not deteriorate if the
IP traffic is received unevenly. The system supports one Voice VLAN.
NOTE:
The HP V1905-48 Switch JD994A does not support improving the priority of voice streams.
There are two operational modes for IP Phones:
IP phones are configured with VLAN-mode as enabled, ensuring that tagged packets are used for all
communications.
71
Page 77

p
If the IP phone’s VLAN-mode is disabled, the phone uses untagged packets. The phone uses untagged
packets while retrieving the initial IP address through DHCP. The phone eventually uses the Voice
VLAN and starts sending tagged packets.
This section contains the following topics:
Modifying OUI Definitions
Defining Voice VLAN Global Settings
Defining Voice VLAN Port Settings
Viewing Voice VLAN Port Settings
Viewing OUI Summaries
Viewing Voice VLAN
Modifying OUI Definitions
The Voice VLAN OUI Modify Page allows network administrators to add new OUIs or to remove previously
defined OUIs from the Voice VLAN. The packet priority is derived from the source/destination MAC prefix.
The packet gets a higher priority when there is a match with the OUI list. Using the OUI, network managers
can add a specific manufacturer’s MAC addresses to the OUI table. Once the OUIs are added, all traffic
received on the Voice VLAN ports from the specific IP phone with a listed OUI is forwarded on the voice
VLAN.
Click Device QoS VoIP Traffic Setting OUI Modify. The Voice VLAN OUI Modify Page opens.
Figure 112 Voice VLAN OUI Modify Page
The Voice VLAN OUI Modify Page contains the following fields:
Table 92 Voice VLAN OUI Modify Page item description
Item Descri
Telephony OUI
Defines a new or existing OUI on the Voice VLAN. The field contains the 3 most
significant bytes of the MAC address.
tion
Description Enters a user-defined OUI description. The field may contain up to 32 characters.
Add Allows the user to add a new OUI.
Remove Allows the user to delete an existing OUI.
Defining Voice VLAN Global Settings
72
Page 78

p
The Voice VLAN Setup Page provides information for enabling and defining Voice VLAN globally on the
switch.
Click Device QoS VoIP Traffic Setting Setup. The Voice VLAN Setup Page opens.
Figure 113 Voice VLAN Setup Page
The Voice VLAN Setup Page contains the following fields:
Table 93 Voice VLAN Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Voice VLAN State Enables or disables Voice VLAN is enabled on the switch.
Voice VLAN ID Defines the Voice VLAN ID number.
Input the aging time. Defines the amount of time after the last IP phone's OUI is aged
out for a specific port. The Voice VLAN aging time starts after the MAC Address is
aged out from the Dynamic MAC Address table. The port will age out after the bridge
Voice VLAN Aging
Time
and voice aging times. The default bridge aging time is 300 seconds. The default
voice aging time is 1 day. The possible fields are:
Day: The field range is 0-30.
Hour: The field range is 0-23.
Minute: The field range is 0-59.
Defining Voice VLAN Port Settings
The Voice VLAN Port Setup Page contains information for defining Voice VLAN port mode and Security.
Click Device QoS VoIP Traffic Setting Port Setup. The Voice VLAN Port Setup Page opens.
Figure 114 Voice VLAN Port Setup Page
tion
The Voice VLAN Port Setup Page contains the following fields:
73
Page 79

p
Table 94 Voice VLAN Port Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Specifies the Voice VLAN mode. The possible field values are:
No Changes: Maintains the current Voice VLAN port settings.
None: Indicates that the selected port will not be added to a Voice VLAN. This is
Manual: Adding a selected port to a Voice VLAN.
Voice VLAN Port Mode
Voice VLAN Port
Security
Auto: Indicates that if traffic with an IP Phone MAC Address is transmitted on the
Specifies if port security is enabled on the Voice VLAN. Port security ensures that
packets arriving with an unrecognized MAC address are dropped. Port Security is
only applicable when Voice VLAN Port Mode is set to Auto.
No Changes: Maintains the current Voice VLAN port security settings.
Enable: Enables port security on the Voice VLAN.
Disable: Disables port security on the Voice VLAN. This is the default value.
Viewing Voice VLAN Port Settings
The Voice VLAN Port Details Page displays the Voice VLAN port settings for specific ports.
tion
the default value.
port, the port joins the Voice VLAN. The port is aged out of the voice VLAN if the
IP phone’s MAC address (with an OUI prefix) is aged out and exceeds the
defined voice VLAN aging time. If the MAC Address of the IP phones OUI was
added manually to a port/LAG in the Voice VLAN, the user cannot add it to the
Voice VLAN in Auto mode, only in Manual mode.
Click Device QoS VoIP Traffic Setting Port Detail. The Voice VLAN Port Details Page opens.
Figure 115 Voice VLAN Port Details Page
Select a port and the Voice VLAN port settings are displayed in the text box.
Viewing OUI Summaries
The Voice VLAN OUI Summary Page lists the Organizationally Unique Identifiers (OUIs) associated with the
Voice VLAN. The first three bytes of the MAC Address contain a manufacturer identifier while the last three
bytes contain a unique station ID.
Click Device QoS VoIP Traffic Setting OUI Summary. The Voice VLAN OUI Summary Page opens.
74
Page 80

p
Figure 116 Voice VLAN OUI Summary Page
Viewing Voice VLAN
The Voice VLAN Summary Page contains information about the Voice VLAN currently enabled on the switch,
including the ports enabled and included in the Voice VLAN.
Click Device QoS VoIP Traffic Setting. The Voice VLAN Summary Page opens.
Figure 117 QoS VoIP Summary Page
The Voice VLAN Summary Page contains the following fields:
Table 95 Voice VLAN Summary Page item description
Item Descri
Indicates if Voice VLAN is enabled on the switch. The possible field values are:
Voice VLAN State
Enabled: Voice VLAN is enabled on the switch.
tion
Disabled: Voice VLAN is disabled on the switch. This is the default value.
Voice VLAN ID Indicates the Voice VLAN ID number.
Voice VLAN Aging
Time
Ports Enabled for Voice
VLAN
Ports in the Voice VLAN Displays the ports which are included in the Voice VLAN.
Indicates the amount of time after the last IP phone's OUI is aged out for a specific
port.
Displays the ports for which Voice VLAN is enabled.
75
Page 81

Configuring SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) provides a method for managing network devices. The
switch supports the following SNMP versions:
SNMP version 1
SNMP version 2c
The SNMP agents maintain a list of variables, which are used to manage the switch. The variables are
defined in the Management Information Base (MIB). The SNMP agent defines the MIB specification format,
as well as the format used to access the information over the network. Access rights to the SNMP agents are
controlled by access strings.
This section contains the following topics:
Defining SNMP Communities
Removing SNMP Communities
Defining SNMP Traps
Removing SNMP Traps
Defining SNMP Communities
Access rights are managed by defining communities in the SNMP Communities Setup Page. When the
community names are changed, access rights are also changed. SNMP communities are defined only for
SNMP v1 and SNMP v2c.
Click Administration SNMP Communities Setup. The SNMP Communities Setup Page opens.
Figure 118 SNMP Communities Setup Page
The SNMP Communities Setup Page contains the following fields:
76
Page 82

p
Table 96 SNMP Communities Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Specifies if SNMP is enabled on the switch. The possible field values are:
SNMP Status
Enabled: Enables SNMP on the switch.
tion
Disabled: Disables SNMP on the switch.
Insert New Community Enables adding an SNMP community.
Selects pre-defined community strings. The possible field values are:
Standard
Public: Displays the pre-defined public community string name.
Private: Displays the pre-defined private community string name.
User Defined Defines a user-defined community string name.
Defines the access rights of the community. The possible field values are:
Read Only: Management access is restricted to read-only, and changes cannot
Access Mode
be made to the community.
Read Write: Management access is read-write and changes can be made to the
switch configuration, but not to the community.
Removing SNMP Communities
The SNMP Communities Remove Page allows the system manager to remove SNMP Communities.
Click Administration SNMP Communities Remove. The SNMP Communities Remove Page opens.
Figure 119 SNMP Communities Remove Page
To Remove SNMP Communities:
1. Select the SNMP Communities.
2. Click Remove.
Defining SNMP Traps
The SNMP Traps Setup Page allows the system manager to defining filters that determine whether traps are
sent to specific users, and the trap type sent.
Click Administration SNMP Traps Setup. The SNMP Traps Setup Page opens.
77
Page 83

Figure 120 SNMP Traps Setup Page
The SNMP Traps Setup Page contains the following fields:
Table 97 SNMP Traps Setup Page item description
Item Description
Recipients IP Address Defines the IP address to which the traps are sent.
Community String Defines the community string of the trap manager.
Defines the trap type. The possible field values are:
Trap Version
SNMP V1: Indicates that SNMP Version 1 traps are sent.
SNMP V2c: Indicates that SNMP Version 2 traps are sent.
Removing SNMP Traps
The SNMP Traps Remove Page allows the system manager to remove SNMP Traps.
Click Administration SNMP Traps Remove. The SNMP Traps Remove Page opens.
Figure 121 SNMP Traps Remove Page
To Remove SNMP Traps:
1. Select the SNMP Traps.
2. Click Remove.
78
Page 84

Configuring LLDP
LLDP Overview
The Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) operates on the data link layer. With LLDP, a device can store and
maintain information about itself and the directly-connected neighbor devices for network administrators to
check link status.
LLDP Operating Mode
LLDP can operate in one of the following modes:
TxRx: A port in this mode sends and receives LLDPDUs.
Tx: A port in this mode only sends LLDPDUs.
Rx: A port in this mode only receives LLDPDUs.
Disable: A port in this mode does not send or receive LLDPDUs.
TLV Types
TLVs encapsulated in LLDPDUs fall into these categories: basic TLVs, organizationally specific TLVs, and
media endpoint discovery (MED) related TLVs.
Basic TLVs are the base of network device management. Organizationally specific TLVs are defined by the
standard organization, while MED related TLVs are vendor specific for enhanced device management and
are optional to LLDPDUs.
Configuring Global LLDP Parameters
Click Device LLDP Global Setup. The Global LLDP Parameters Page opens.
Figure 122 Global LLDP Parameters Page
The Global LLDP Parameters Page contains the following fields:
79
Page 85

p
Table 98 Global LLDP Parameter Page item description
Item Descri
Enable/disable LACP globally. Two options are available:
LLDP
Transmit Interval
TLL Hold Multiplier
Fast Count
Enabled: Enables LLDP globally.
Disabled: Disables LLDP globally.
By default, LLDP is disabled globally.
Set the interval for sending LLDPDUs.
A port operating in TxRx mode or Tx mode sends LLDPDUs to its directly connected
device periodically.
By default, the interval is 30 seconds.
Set the TTL multiplier.
You can configure the TTL of locally sent LLDPDUs to determine how long they can
be saved on a neighbor device by setting the TTL hold multiplier. The TTL is
expressed as:
TTL multiplier × LLDPDU sending interval
By default, the TTL multiplier is 4.
Set the number of successive fast-sent LLDPDUs.
This fast sending mechanism allows your LLDPDU switch to be discovered by its
neighbors quickly. After the specified numbers of LLDPDUs are sent, the normal
sending interval restores.
The default fast count is 3.
tion
Set the delay time of an LLDP-enabled port to prevent frequent port LLDP
Initialization Delay
Send packet Delay
Trap Interval
initializations.
The default delay of a port is 2 seconds.
Set the delay before sending next LLDPDUs.
This parameter is introduced to avoid sending excessive number of LLDPDUs caused
by frequent local configuration changes.
By default, the delay is 2 seconds.
Set the interval for sending LLDP remote change trap.
By default, the interval for sending trap is 5 seconds.
Configuring Port-Level LLDP Parameters
Click Device LLDP Port Setup. The Port-Level LLDP Parameters Page opens.
80
Page 86

Figure 123 Port-Level LLDP Parameters Page
The Port-Level LLDP Parameters Page contains the following fields:
81
Page 87

p
Table 99 Port-Level LLDP Parameters Page item description
Item Descri
Enable/disable LLDP on a port. Two options are available:
LLDP
Enabled: Enables LLDP on the port.
Disabled: Disables LLDP on the port.
By default, LLDP is enabled on a port.
Set the LLDP operating mode.
Send Only: Sets the port LLDP to operate in Tx mode to
send LLDPDUs only.
Receive Only: Sets the port LLDP to operate in Rx mode to
receive LLDPDUs only.
Administrator Status
Send&Receive: Sets the port LLDP to operate in TxRx mode
to both send and receive LLDPDUs.
Disable: Sets the port LLDP to operate in disable mode to
neither send nor receive LLDPDUs.
By default, the port LLDP operating mode is Send&Receive,
namely TxRx.
Enable/disable remote port up/down event reporting.
By default, remote port up/down event reporting is enabled.
LLDPDUs can be encapsulated in Ethernet II or SNAP frames.
Port Basic Settings
Notification Remote
Change
Direct: an LLDP port sends LLDPDUs in Ethernet II frames
and processes only Ethernet II encapsulated incoming
LLDPDUs.
Snap: an LLDP port sends LLDPDUs in SNAP frames and
Frame Format
processes only SNAP encapsulated incoming LLDPDUs.
By default, LLDPDUs are encapsulated in Ethernet II frames. If
the neighbor devices encapsulate LLDPDUs in SNAP frames,
you can configure the encapsulation format for LLDPDUs as
SNAP, thus guaranteeing communication with the other
devices in the network.
tion
After checking the Polling Interval option, you can set the
polling interval value.
Device checks for the local configuration changes periodically
within the polling interval. Upon detecting a configuration
change, the device sends LLDPDUs to inform the neighboring
devices of the change
Polling is disabled by default.
Check the Port management address option to encapsulate the
management IP address of the device in the LLDPDUs to be
sent.
The basic LLDP TLVs include the following:
Port Description: Description string of the Ethernet port.
System Name: Device name.
System Description: Description of the system.
TLV Settings
Polling Interval
Port management
address
Basic Information
System Capabilities: Primary function(s) of the system.
If you check the option of All Basic Information, all the above
82
Page 88

Item Description
basic TLVs will be sent within LLDPDUs.
The IEEE 802.1 defined LLDP TLVs supported by the device
include the following:
Port Vlan ID: Checked to include the VLAN ID(s) on the
port.
IEEE 802.1
Protocol Vlan ID: Checked to include the IDs of the protocol
VLAN(s) on the port.
Vlan Name: Checked to include the VLAN names on the
port.
Check the option of All IEEE802.1, all the above IEEE802.1
organizationally specific TLVs will be sent within LLDPDUs
The IEEE 802.3 defined LLDP TLVs supported by the device
include the following:
MAC/PHY: The rate, duplex mode, and speed
auto-negotiation state of the port.
POE Power: Power supply capability of the port.
Link Aggregation: Indicates the support of the port for link
aggregation, and the aggregation status (whether the link
IEEE 802.3
is in an aggregation).
Maximum Frame Size: Supported maximum frame size.
Currently, it takes the MTU of the port.
Stateful Control: Provides the supported maximum power
of the port to a device connected with it, then the device
decides whether to supply power.
If you check the option of All IEEE802.3, all the above
IEEE802.3 organizationally specific TLVs will be sent within
LLDPDUs
The MED related LLDP TLVs include the following
Capability: MED device type of the device, and types of
LLDP MED TLVs that can be encapsulated in LLDPDUs.
Network Policy: VLAN ID of the port, supported
applications (voice and video, for example), and priority
and policy of each application.
LLDP-MED
Power Over Ethernet: Power supply capability of the port.
Inventory: Inventory information of the local device,
including Hardware Revision TLV, Firmware Revision TLV,
Software Revision TLV, Serial Number TLV, Manufacturer
Name TLV, Model Name TLV, Asset ID TLV used for
inventory management and asserting tracking.
If you check the option of All LLDP-MED to encapsulate all
LLDP-MED TLVs supported by the device
Viewing LLDP Information
Viewing Global LLDP Information and Received LLDP Information
Click Device LLDP Global Summary. The Global LLDP Information and Received LLDP Information Page
opens.
83
Page 89

p
Figure 124 Global LLDP Information and Received LLDP Information Page
The Global LLDP Information and Received LLDP Information Page contains the following fields:
Table 100 Global LLDP Information and Received LLDP Information Page item description
Item Descri
Added Neighbor Total number of discovered neighbors
Deleted Neighbor Total number of deleted neighbors
Discarded LLDP's Packet Total number of dropped LLDPDUs
Aginged Neighbor Total number of aged LLDP neighbor entries
Neighbor index Index of each discovered neighbor
Local Port Local port name of each neighbor
Chassis ID type, including:
tion
Chassis component
Interface alias
Chassis type
Port component
MAC address
Network address
Interface name
Locally assigned, namely, local configuration
Chassis ID Chassis ID
Port ID type, including:
Interface alias
Port component
Port ID type
MAC address
Network address
Interface name
Agent circuit ID
Locally assigned, namely, the local configuration
Port ID Port ID
System capabilities enabled
Functions enabled on the system, which can be:
Bridge, indicating the switching function is enabled.
Router, indicating the routing function is enabled.
Repeater, indicating the forwarding function is enabled.
84
Page 90

Viewing Port-Level LLDP Information
Click Device LLDP Port Summary. The Port-Level LLDP Information Page opens.
Figure 125 Port-Level LLDP Information Page
Select a port, and then the LLDP information of the port will be displayed in the Summary box. The displayed
information includes LLDP status and statistics of the port and the status of the TLVs sent by the port.
Managing Switch Security
The Management Security section provides information for defining RADIUS authentication and port-based
authentication.
This section includes the following topics:
Defining Port-Based Authentication (802.1X)
Defining Radius Client
Configuring LDB
Configuring Broadcast Storm Control
Defining Port-Based Authentication (802.1X)
Port-based authentication authenticates users on a per-port basis via an external server. Only authenticated
and approved system users can transmit and receive data. Ports are authenticated via the RADIUS server
using the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP). Port-based authentication includes:
Authenticators: Specifies the switch port which is authenticated before permitting system access.
Supplicants: Specifies the host connected to the authenticated port requesting to access the system
services.
Authentication Server: Specifies the server that performs the authentication on behalf of the
authenticator, and indicates whether the supplicant is authorized to access system services.
Port-based authentication creates two access states:
Controlled Access: Permits communication between the supplicant and the system, if the supplicant is
authorized.
85
Page 91

p
Uncontrolled Access: Permits uncontrolled communication regardless of the port state.
This section includes the following topics:
Defining 802.1X Authentication
Viewing 802.1X Authentication
Defining 802.1X Authentication
The 802.1X Setup Page contains information for configuring 802.1X global settings on the switch and
defining specific 802.1X setting for each port individually.
Click Security 802.1X Setup. The 802.1X Setup Page opens.
Figure 126 802.1X Setup Page
The 802.1X Setup Page contains the following fields:
Table 101 802.1X Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Specifies if Port Authentication is enabled on the switch. The possible field values
Port Based Authentication
State
are:
Enabled: Enables port-based authentication on the switch.
tion
Disabled: Disables port-based authentication on the switch. This is the default
value.
Reauthentication Period
Enable Guest VLAN
Guest VLAN ID Specifies the guest VLAN ID.
Defines the time span (in seconds) in which the selected port is reauthenticated.
The field default is 3600 seconds.
Provides limited network access to authorized ports. If a port is denied network
access via port-based authorization, but the Guest VLAN is enabled, the port
receives limited network access. For example, a network administrator can use
Guest VLANs to deny network access via port-based authentication, but grant
Internet access to unauthorized users.
86
Page 92

Item Description
Specifies the admin port authorization state. The possible field values are:
Auto: Enables port based authentication on the switch. The interface moves
between an authorized or unauthorized state based on the authentication
exchange between the switch and the client.
Admin Port Control
Force Authorized: Places the interface into an authorized state without being
authenticated. The interface re-sends and receives normal traffic without client
port based authentication. This is the default value.
Force Unauthorized: Denies the selected interface system access by moving
the interface into unauthorized state. The switch cannot provide authentication
services to the client through the interface.
Specifies whether the Guest VLAN is enabled on the port. The possible field values
are:
Guest VLAN
Enabled: Enables using a Guest VLAN for unauthorized ports. If a Guest VLAN
is enabled, the unauthorized port automatically joins the VLAN selected from
the Guest VLAN ID dropdown list.
Disabled: Disables Guest VLAN on the port. This is the default.
Enables periodic reauthentication on the port.
Periodic Reauthentication
Enabled: Enables the periodic reauthentication on the port.
Disabled: Disables the periodic reauthentication on the port. This is the default
value.
Periodic Handshake
Multicast Trigger
Viewing 802.1X Authentication
The 802.1X Summary Page allows the network administrator to view port-based authentication settings.
Click Security 802.1X Summary. The 802.1X Summary Page opens.
Indicates if periodic handshake is enabled on the port. The possible field values
are:
Enable: periodic handshake is enabled on the port. This is the default value.
Disable: periodic handshake is disabled on the port.
Indicates if multicast trigger is enabled on the port. The possible field values are:
Enable: multicast trigger is enabled on the port. This is the default value.
Disable: multicast trigger is disabled on the port.
87
Page 93

p
Figure 127 802.1X Summary Page
The 802.1X Summary Page contains the following fields:
Table 102 802.1X Summary Page item description
Item Descri
Current Port Control Displays the current port authorization state.
Indicates whether an unauthorized port is allowed to join the Guest VLAN. The
Guest VLAN
possible field values are:
Enable: Enables an unauthorized port to join the Guest VLAN.
tion
Disable: Disables an unauthorized port to join the Guest VLAN.
Indicates if periodic reauthentication is enabled on the port. The possible field
Periodic Reauthentication
values are:
Enable: Periodic reauthentication is enabled on the port.
Disable: Periodic reauthentication is disabled on the port. This is the default.
Indicates if periodic handshake is enabled on the port. The possible field values
Periodic Handshake
are:
Enable: periodic handshake is enabled on the port. This is the default value.
Disable: periodic handshake is disabled on the port.
Indicates if multicast trigger is enabled on the port. The possible field values are:
Multicast Trigger
Enable: multicast trigger is enabled on the port. This is the default value.
Disable: multicast trigger is disabled on the port.
88
Page 94

p
Defining Radius Client
Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service (Radius) is a logon authentication protocol that uses software
running on a central server to control access to Radius-aware devices on the network. An authentication
server contains a database of multiple user name/password pairs with associated privilege levels for each
user or group that require management access to a switch.
The Radius Client Setup Page allows the administrator to configure the parameters for the switch acting as
the RADIUS client.
Click Security RADIUS Client Setup. The Radius Client Setup Page opens.
Figure 128 Radius Client Setup Page
The Radius Client Setup Page contains the following fields:
Table 103 Radius Client Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Host IP Address Defines the RADIUS Server IP address.
Authentication Port
Number of Retries
Timeout for Reply
Key String
Defines the authentication port. The authentication port is used to verify the
RADIUS server authentication. The authentication port default is 1812.
Defines the number of transmitted requests sent to the RADIUS server before a
failure occurs. Possible field values are 1-20. The default value is 5.
Defines the amount of time (in seconds) the switch waits for an answer from the
RADIUS server before retrying the query, or switching to the next server. Possible
field values are 1-20. The default value is 5.
Defines the default key string used for authenticating and encrypting all
Radius-communication between the switch and the Radius server. This key must
match the Radius encryption.
tion
Configuring LDB
If your switch is not enabled with an advanced authentication method, like RADIUS, for authentication, you
can use the local database (LDB) feature to perform local authentication (port-based authentication). After
the switch is enabled with the LDB feature and related access rights are configured, a user trying to access
an address through the switch will be authenticated. After successful authentication, the switch allows the
user to use the corresponding port. Otherwise, the port is blocked.
89
Page 95

p
Configuring LDB Parameters
On this page, you can enable or disable the LDB feature and configure the global LDB parameters.
Click Security LDB Setup. The LDB Setup Page opens.
Figure 129 Configure LDB parameters
Table 104 LDB parameter description
Item Descri
Enable/disable port-based authentication globally.
Disabled by default.
Port Based Authentication State
NOTE:
The enabled LDB feature is effective on a port only after this item is
After successful authentication, the port is in Normal state.
Set the maximum number of authentication attempts.
3 by default
Reauthentication Times
Sleep Period
Aging time
NOTE:
If the number of authentication attempts reaches the preset value but the
authentication still fails, the port connected to the user enters the Sleep state
for a period of time (sleep period).
Set the authentication sleep period.
5 minutes by default
NOTE:
Within the authentication sleep period, no users on this port are allowed to
try to pass authentication.
Set the aging time.
1 hour by default
tion
enabled.
90
Page 96

Item Description
Ldb
Configuring an Authentication Server
On this page, you can configure different authentication servers for different VLANs.
Select Security LDB Authentication IP. The Authentication Server Configuration Page opens.
Figure 130 Authentication server configuration page
NOTE:
If there is no traffic of authenticated users through a port within the aging
time, the port will be aged out and enters the Block state.
Enable/disable the LDB feature on a port.
Disabled by default
Click Add, select the VLAN interface, and specify the authentication server IP address and subnet mask to
establish an association between a VLAN and an authentication server, as shown in Figure 131.
Figure 131 Configure an authentication server
Configuring a User Account
On this page, you can configure user accounts for local authentication.
Select Security LDB User Configuration. The User Account Configuration Page opens.
91
Page 97

p
Figure 132 Configure a user account
To add a user account, click Add.
To modify the password of a user, select the user, enter a new password in the Password text box, and
Displaying LDB
On this page, you can view the LDB mode, state and user passing authentication on each port.
Select Security LDB Summary. The LDB Related Information Page Opens.
Figure 133 Display LDB
Table 105 LDB state parameter description
click Modify.
Item Descri
Ldb Mode Displays whether the LDB feature is enabled on the port.
Current Port State Displays the current state of the port.
tion
92
Page 98

Item Description
NORMAL: The user on the port passed the authentication.
BLOCK: The port is in the initial state after the LDB feature is enabled or
the port is aged out.
SLEEP: The number of the user’s authentication attempts exceeded the
preset maximum value.
User Displays the user passing the authentication.
MAC Displays the MAC address of the user passing the authentication.
Configuring Broadcast Storm Control
Broadcast Storm Control limits the amount of Multicast and Broadcast frames accepted and forwarded by
the switch. When Layer 2 frames are forwarded, Broadcast and Multicast frames are flooded to all ports on
the relevant VLAN. This occupies bandwidth, and loads all nodes on all ports.
A Broadcast Storm is a result of an excessive amount of broadcast messages simultaneously transmitted
across a network by a single port. Forwarded message responses are heaped onto the network, straining
network resources or causing the network to time out.
Broadcast Storm is enabled for all Gigabit ports by defining the packet type and the rate the packets are
transmitted. The system measures the incoming Broadcast and Multicast frame rates separately on each port,
and discards the frames when the rate exceeds a user-defined rate.
Packet threshold is ignored if Broadcast Storm Control is disabled.
This section contains the following topic:
Defining Broadcast Storm Control
Viewing Broadcast Storm Control
Defining Broadcast Storm Control
The Broadcast Storm Setup Page allows network managers to define Broadcast Storm Traffic.
Click Device Broadcast Storm Setup. The Broadcast Storm Setup Page opens.
Figure 134 Broadcast Storm Setup Page
The Broadcast Storm Setup Page contains the following fields:
93
Page 99

p
p
Table 106 Broadcast Storm Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Broadcast Mode
Broadcast Rate Threshold
Viewing Broadcast Storm Control
The Broadcast Storm Summary Page displays the current broadcast storm control parameters for all ports.
Click Device Broadcast Storm Summary. The Broadcast Storm Summary Page opens.
Figure 135 Broadcast Storm Summary Page
tion
Defines whether forwarding broadcast packet type is enabled on the interface. The
possible field values are:
Disabled: Disables broadcast control on the selected port. This is the default.
Broadcast: Enables broadcast control on the selected port.
Broadcast&Multicast: Enables broadcast and multicast control on the selected
port.
Defines the maximum rate (kilobits per second) at which broadcast-only or
broadcast and multicast packets are forwarded. The default value is 3500
The Broadcast Storm Summary Page contains the following fields:
Table 107 Radius Client Setup Page item description
Item Descri
Broadcast Mode Displays the broadcast storm control mode.
Broadcast Rate Threshold Displays the broadcast storm threshold.
tion
Managing System Information
This section contains information for configuring general system information, and includes the following:
Viewing Basic Settings
Configuring System Name
94
Page 100

p
Configuring System Time
Save Configuration
Resetting the Switch
Viewing Basic Settings
The Device Summary Page, which automatically loads after you log on to the Web interface, provides a
snapshot of the switch’s basic settings and versions of current components.
The Device Summary Section contains the following topics:
Viewing Device Settings
Viewing Color Keys
Viewing Device Settings
The Device View Page displays parameters for viewing general switch information, including the system
name, location, and contact, the system MAC Address, System Object ID, and more.
Click Device Summary Device View. The Device View Page opens.
Figure 136 Device View Page
The Device View Page contains the following fields:
Table 108 Device View Page item description
Item Descri
Product Description Displays the switch model number and name.
System Name Defines the user-defined switch name.
System Location Defines the location where the system is currently running.
System Contact Defines the name of the contact person.
Product 3C Number Displays the HP switch 3C number
MAC Address Displays the switch MAC address.
System Up Time
Software Version Displays the installed software version number.
Bootrom Version Displays the current bootrom version running on the switch.
Displays the amount of time since the most recent switch reset. The system time is
displayed in the following format: Weeks, Days, Hours, Minutes, and Seconds.
tion
95
 Loading...
Loading...