Page 1

e
3
5
6
Wireless Dual Discrete
Input Transmitter
User Manual
900 MHz ISM Band
FCC Certification
XYR 5000 Lin
34-XY-25-1
Rev.
08/0
Page 2
Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Switch Input Transmitter
Models WW591, WW592
Versions 1.70 or later
Important Information for the User
• Changes or modifications not expressly approved by Honeywell
may void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
• This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation
is subject to the following two conditions:
1) This device may not cause harmful interference.
2) This device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
• This device is for mobile and fixed use only (not portable or
body-worn). A separation distance of 20 cm must be maintained
at all times between the antenna and the body of the user and
bodies of nearby persons.
• This device has been designed to operate with an antenna
having a maximum gain of 9 dBd. Antenna having a higher gain
is strictly prohibited per regulations of Industry Canada. The
required antenna impedance is 50 Ohms.
• To reduce potential radio interference to other users, the
antenna type and its gain should be so chosen that the EIRP
(Equivalent Isotropically Radiated Power) is not more than that
required for successful communication.
• The installer of this radio equipment must ensure that the
antenna is located or pointed such that it does not emit RF field
in excess of Health Canada limits for the general population;
consult Safety Code 6, obtainable from Health Canada’s
website www.hc-sc.gc.ca/rpb.
FCC Certification
• This product is a frequency hopping RF transceiver module for
the 900 MHz ISM band, designed to meet FCC 15.247, and is
used in industrial control and monitoring applications.
• The antenna is factory installed and MUST NOT be removed or
modified by user.
Honeywell Inc.
Industrial Measurement and Control
2500 West Union Hills Drive
Phoenix, AZ 85027
disclaims the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose and makes
no express warranties except as may be stated in its written agreement with and for its customers.
In no event is Honeywell liable to anyone for any indirect, special or consequential damages. The
Rev 5 User Manual - 2 -
08/06
Copyright 2006 by Honeywell International Inc.
While this information is presented in good faith and believed to be accurate, Honeywell
information and specifications in this document are subject to change without notice.
®
Honeywell
and TotalPlant® are U.S. registered trademarks Of Honeywell International Inc.
Other brand or product names are trademarks of their respective owners.
Rev. 5-08/30/2006
Page 3
Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
About This Document
Revision Notes
The following list provides notes concerning all revisions of this document.
Doc ID Rel ID Date Notes
34-XY-25-13 Rlse. 4 12/05 Initial Release
34-XY-25-13 Rlse. 5 08/06 Initial Release
Contacts
World Wide Web
The following lists Honeywell’s World Wide Web sites that will be of interest to our industrial automation and
control customers
Honeywell Organization WWW Address (URL/e-mail)
.
Corporate http://www.honeywell.com
Industrial Measurement and Control http://content.honeywell.com/imc/
International http://www.honeywell.com/Business/global.asp
Field Instruments http://www.honeywell.com/imc
Technical Assistance Center ACE@Honeywell.com (e-mail)
Telephone
Contact us by telephone at the numbers listed below.
Organization Phone Number
United States and Canada Honeywell Inc.
Industrial Automation and Control
Technical Support Center
Asia Pacific Honeywell Asia Pacific Inc.
Hong Kong
Europe Honeywell PACE
Brussels, Belgium
Latin America Honeywell Inc.
Sunrise, Florida U.S.A.
1-800-343-0228 Sales
1-800-525-7439 Service
1-800-423-9883
(852) 8298298
[32-2] 728-2111
(305) 364-2355
Rev 5 User Manual - 3 -
08/06
Page 4

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Table of Contents
1. INTRODUCTION............................................................................................. 6
1.1. U
1.2. A
1.3. U
SING THIS GUIDE............................................................................ 6
BOUT THE DEVICE .......................................................................... 6
NPACKING ...................................................................................... 7
1.4. SOFTWARE COMPATIBILITY ............................................................... 7
2. QUICK START................................................................................................ 9
3. INSTALLATION............................................................................................ 11
3.1. M
ECHANICAL INSTALLATION ............................................................ 11
3.2. TESTING COMMUNICATIONS ............................................................ 14
3.3. LINK TEST ...................................................................................... 16
3.4. ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION.............................................................. 20
4. GENERAL CONFIGURATION ..................................................................... 24
4.1. N
AVIGATING USER MENUS .............................................................. 24
4.2. TRANSMITTER DISPLAYED MESSAGES ............................................. 25
4.3. OVERALL CONFIGURATION MENU MAP ............................................ 26
4.4. SETTING THE TRANSMITTER TAG NAME ........................................... 26
4.5. SETTING A USER PASSWORD .......................................................... 27
4.6. RESETTING ALL TRANSMITTER SETTINGS......................................... 29
5. CONFIGURING THE RF COMMUNICATIONS ........................................... 30
5.1. RF C
HANNEL SELECTION................................................................ 30
5.2. BAUD RATE SELECTION .................................................................. 31
5.3. RF IDENTIFICATION (RF ID) SELECTION .......................................... 32
6. CONFIGURING THE TRANSMIT AND SAMPLING RATES ...................... 33
6.1. S
ELECTING THE NORMAL TRANSMIT RATE ....................................... 33
6.2. THE SAMPLING RATE ...................................................................... 35
6.3. E
NABLING THE SMART RATE ........................................................... 36
7. MODBUS SUPPLEMENT ............................................................................ 38
8. MAINTAINING THE TRANSMITTER ........................................................... 40
8.1. C
HANGING THE BATTERY ................................................................ 40
9. TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS .................................................................. 42
9.1. WW591, WW592.......................................................................... 42
APPENDIX A: OPENING THE CONFIGURATION BOX IN WMT..................... 50
APPENDIX B: TRANSMITTER DISPLAYED MESSAGE DEFINITIONS.......... 51
APPENDIX C: TRANSMITTER MENU MAP...................................................... 52
Rev 5 User Manual - 4 -
08/06
Page 5

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Table of Figures
FIGURE 2-1: INPUT SWITCH WIRING............................................................................. 9
FIGURE 3-1: EXAMPLES OF INCORRECT TRANSMITTER POSITIONING .............................. 12
FIGURE 3-2: MENU MAP TO RSSI MODE.................................................................... 15
FIGURE 3-3: TRANSMITTER LINK TEST......................................................................... 16
FIGURE 3-4: TRANSMITTER LINK TEST .......................................................................... 18
FIGURE 3-5: WMT TRANSMITTER VIEW ....................................................................... 19
FIGURE 3-6: WIRELESS DATA LOSS TEST ..................................................................... 20
FIGURE 3-7: INPUT SWITCH WIRING DIAGRAM .............................................................. 21
FIGURE 3-8: MENU MAP TO ENABLE THE INPUT SWITCHES ............................................. 22
FIGURE 3-9: INPUT SWITCH CONFIGURATION USING WMT ............................................. 23
FIGURE 4-1: TRANSMITTER POWER-UP AND OPERATIONS LCD SEQUENCES .................. 25
FIGURE 4-2: THE READ-ONLY SEQUENCE .................................................................. 25
FIGURE 4-3: OVERALL CONFIGURATION MENU MAP ..................................................... 26
FIGURE 4-4: MENU MAP TO PASSWORD SETTING ........................................................ 27
FIGURE 4-5: SETTING A USER PASSWORD .................................................................. 28
FIGURE 5-1: MENU MAP TO RF CHANNEL SETTING ..................................................... 31
FIGURE 5-2: MENU MAP TO BAUD RATE SETTING ........................................................ 31
FIGURE 5-3: MENU MAP TO RF ID SETTING ............................................................... 32
FIGURE 6-1: MENU MAP TO THE TRANSMIT RATE SETTING ........................................... 34
FIGURE 6-2: TRANSMIT RATES TAB ........................................................................... 35
FIGURE 6-3: SMART RATE CONFIGURATION USING WMT ............................................. 37
FIGURE 9-1: .......................................................................................................... 44
Rev 5 User Manual - 5 -
08/06
Page 6

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
1. Introduction
1.1. Using This Guide
This guide is designed to assist in installing, operating, and
maintaining Honeywell Model WW591 and WW592 Transmitters.
The Guide is broken into sections as follows:
Section 2: Quick Start
This section summarizes what must be done in order to get the
device installed, configured, and in operation quickly. However, it
does not provide detailed or how-to information to perform the tasks
outlined.
Section 3: Installation
This section explains how to correctly wire the Input Switches and
ground the Transmitter. Also covered in this section are mechanical
installation considerations such as Transmitter placement.
Section 4: General Configuration
In this section general configuration options such as password
protection and selecting a user password are discussed. Also
covered is the setting of a Transmitter tag name, resetting of all
Transmitter settings, and a discussion of the various messages that
are displayed on the Transmitter LCD.
Section 5: Configuring the RF Communications
This section covers the setup of the Transmitter RF
Communications that allow the Transmitter to achieve
communication with the Base Radio. Parameters discussed are the
Transmitter RF ID, the RF channel setting and the Baud Rate.
Section 6: Configuring the Sampling and Transmission Rates
This section explains the amount of time between each sample of
the process and aids you in selecting the time between each
transmission of this sample to the Base Radio. Use of a smart rate
is also discussed.
Section 7: Maintaining the Transmitter
This section explains how the Transmitter should be cared for once
it has been placed into service and how to change the battery.
Section 8: Technical Specifications
This section lists the technical specifications for this device including
power characteristics, accuracy, and operating characteristics.
1.2. About the Device
The Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter is a reliable Radio
Frequency (RF) transceiver coupled with a dual-channel switch
input that can be used to monitor simple apparatuses in hazardous
and hard-to-reach areas.
Rev 5 User Manual - 6 -
08/06
Page 7
Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
The time and expense of running wires often makes it difficult to
monitor parameters that have an economic impact on your plant
operation, but the Switch Input Transmitters allow you to quickly and
accurately monitor those devices at a fraction of the cost, which
gives you bigger and faster returns on your instrumentation
investments.
The Transmitters communicate in a secure, digital protocol over a
band of frequencies from 902 MHz to 928 MHz. This data
communication technique has been the backbone of the military’s
secure communications protocols for many years. These devices
require no wires, permits or licenses, and they are easily set up and
installed right out of the box.
You can use this device for long term monitoring in remote
locations, for short-term data gathering on process conditions, or to
quickly test the economic viability of a new installation.
The purpose of this Guide is to help you install and maintain your
Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter. Before setting up and
installing the Transmitter, please setup and configure the Base
Radio.
1.3. Unpacking
Remove the Packing List and check off the actual equipment
received. If you have any questions about your shipment, please call
your Honeywell Representative. Upon receiving the shipment,
inspect the container for any signs of damage in transit. Especially
take note of any evidence of rough handling. Report any apparent
damage immediately to the shipping agent.
Please note that sometimes units are assembled with accessories
when shipped. Inspect the shipment carefully if you think that
something is missing. This is rare, as we take considerable care to
pack units for shipment, but it does sometimes happen. Please give
us a call and we may be able to resolve this matter quickly over the
phone.
NOTE
Note The carrier will not honor any claims for damage unless all
shipping materials are saved for their examination. If you find any
damage while you are examining and removing the contents, save
the packing material and the carton.
1.4. Software Compatibility
Software for Honeywell is revised periodically. Internal device
software may contain portions that are not compatible with previous
versions of Wireless Management Toolkit (WMT) software.
To ensure software compatibility, WMT version 1.70.138 or later
must be used.
compatibility issues please call your local representative or email
ACE@Honeywell.com.
. If you believe you are experiencing software
Rev 5 User Manual - 7 -
08/06
Page 8

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
If you use the Analog/Digital Output Module (Models A Option, B
Option or C Option) with this Transmitter, firmware version 1.70
needs to be downloaded to the Analog/Digital Output Module.
Rev 5 User Manual - 8 -
08/06
Page 9
Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
2. Quick Start
This section summarizes what must be done in order to get the
device installed, configured, and in operation quickly. However, it
does not provide detailed or how-to information to perform the tasks
outlined.
[1] Install the Transmitter in the desired location of operation.
[2] Wire input switches as shown in the figure below.
Figure 2-1: Input Switch Wiring
[3] Ground Transmitter via grounding screw provided in
enclosure.
[4] Close enclosure and secure enclosure via set screw.
[5] Turn on Transmitter by pressing ENTER and NEXT buttons
simultaneously and holding until unit powers up.
[6] Set RF CHAN setting equal to the Base Radio’s RF Channel.
[7] Set BAUD RT setting equal to the Base Radio’s Baud Rate.
[8] Set RF ID number to be a unique value between 1 and 100.
[9] Select normal transmission rate.
Rev 5 User Manual - 9 -
08/06
Page 10
Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
If the “RF OFF” message is being displayed on the Transmitter LCD,
perform the following:
• Set the RF CHAN setting equal to the Base Radio’s RF
Channel.
If “NO RF” is being displayed on the Transmitter LCD, check the
following:
• Is the Transmitter set to the above listed configurations?
• Is the Base Radio on?
• Are the Transmitter and Base Radio set to the matching
configurations? (See Section 5 of the Transmitter and Base
Radio User Guides)
• Are the Base Radio and Transmitters unable to communicate
due to obstructions or distance? (See Section 3.1.1 Transmitter
Positioning).
Warning! If the Transmitters have been running for an extended
period of time with no signal from the Base Radio (the Base
Radio is off or not present), the Transmitters will only search for
the Base Radio every one hour or so. Turning the Transmitters
off and back on will cause them to begin searching
immediately.
Rev 5 User Manual - 10 -
08/06
Page 11

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
3. Installation
This section discusses both the mechanical and electrical areas of
installation.
3.1. Mechanical Installation
In this section, mechanical installation instructions are discussed for
the various setup capabilities of the Switch Input Transmitter.
The Honeywell Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter is a rugged
device, but it provides much better performance if installed with
careful consideration, as noted in this guide. It may be utilized in any
dry contact switch input service so long as care is exercised to
prevent exposing the switching elements to excess stress or
temperature. Installation practices have a lot to do with these
service parameters and the life that you can expect from your
Honeywell Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter.
Give careful consideration to the environment where you will be
installing your instrument. Avoid installations that expose the device
to excess temperature, high vibration, considerable shock, or
exposure to dripping condensate or corrosive materials. Also avoid
installing the device in an unserviceable location.
Most often these problems can be avoided with some thought at the
time of installation. The practices noted below are generally
recommended, but they can only act as a guideline and cannot
cover all possible variations. The final installation must be made at
the discretion and approval of the user. You must be the judge of
the actual installation.
Dimensioned mechanical drawings for aid in mechanical installation
are located in Section 8: Technical Specifications.
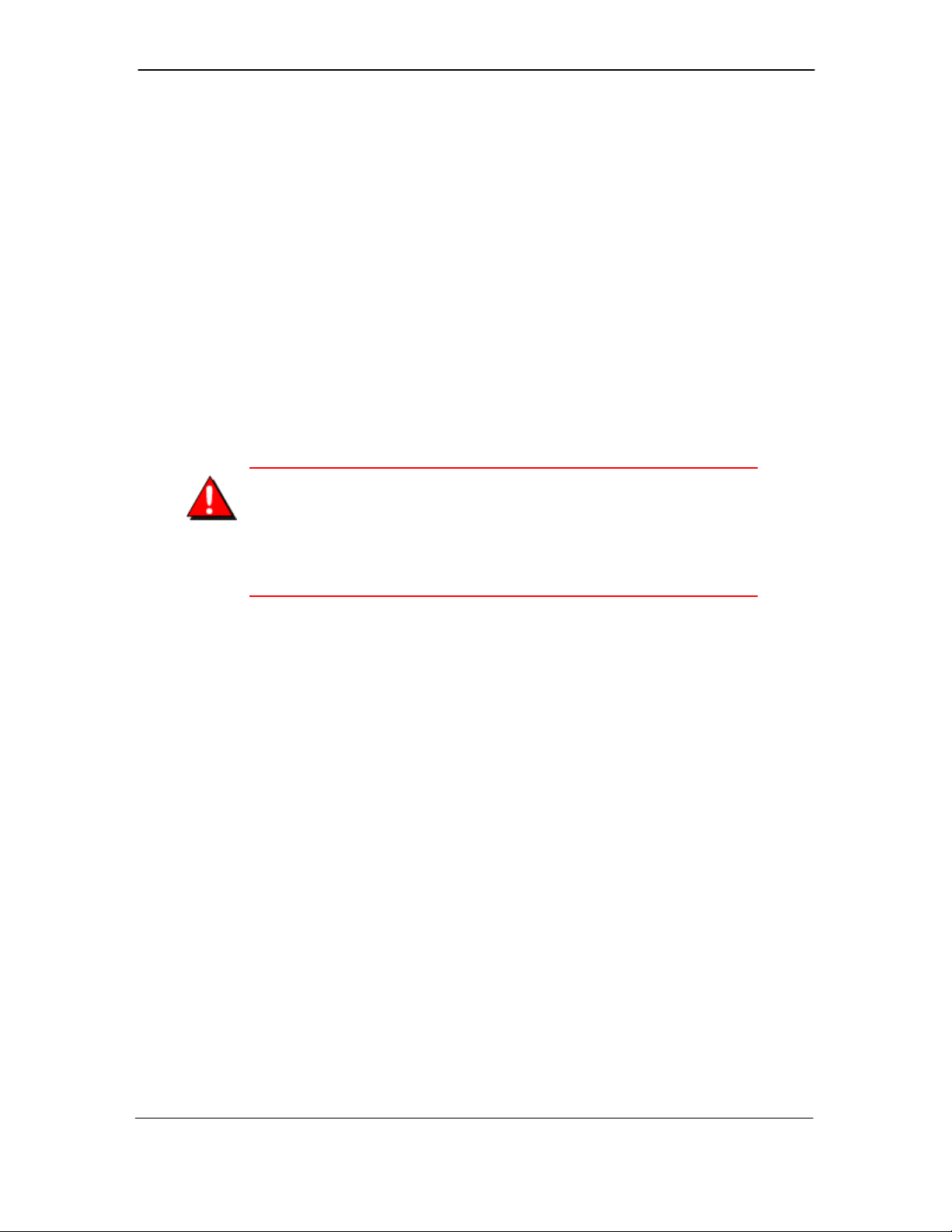
3.1.1. Transmitter Positioning
Correct positioning of the Transmitter will ensure the best
performance of the device. When planning the positioning of the
Transmitters there are a few parameters that must be paid attention
to:
• The top of the Transmitter should point in an upward fashion.
The bottom of the Transmitter should NOT point directly at the
Base Radio and the Transmitter LCD should point away from
the Base Radio.
• All Transmitters should maintain an approximate spacing of at
least six feet apart from one another. Should you need to put
Transmitters closer than six feet, please see Section 3.1.1.1
entitled “Technique for Close Positioning of Transmitters”.
• The line of sight range between a Transmitter and Base Radio
is 2000 feet at the 19.2K baud rate setting. Note that this range
is reduced by the amount of RF Noise present, obstructions,
and the material properties of the obstruction.
Rev 5 User Manual - 11 -
08/06
Page 12
Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
• Only place the Transmitter in ambient operating temperatures of
-40°F to 185°F (-40°C to 85°C).
Figure 3-1, shown below, gives examples of incorrect setups
according to the previously mentioned parameters.
Figure 3-1: Examples of Incorrect Transmitter Positioning
Because there are so many setup possibilities we cannot cover
them all. A correct setup would make sure that the above warnings
are heeded, and that the Transmitter and Base Radio are capable of
communication. The RF Placement Test section will help you to
determine if you have selected the correct installation points and
orientations for your application.
Warning! During installation do not apply force to the
instrument housing or antenna. Use a proper wrench for all
installations. Failure to use correct installation procedures can
cause damage to the Transmitter.
3.1.1.1 Technique for Close Positioning of Transmitters
Transmitters may be placed closely together by carefully following
this procedure. If this procedure is not followed, the communication
range of the Transmitters will be significantly reduced and the
Transmitters may eventually lose communication with the Base
Radio entirely. This procedure is easy to implement, but please read
carefully for a full understanding.
The Base Radio synchronizes with the Transmitters in synch groups
of 7,organized by their RF ID numbers. If you want to place two
Transmitters closer than 6 feet, make sure that you have set them in
Rev 5 User Manual - 12 -
08/06
Page 13
Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
different groups. Note that this only applies to Transmitters that are
communicating with the same Base Radio. The groups are defined
in the following table:
Group RF ID Range
1 1-7
2 8-14
3 15-21
4 22-28
5 29-35
6 36-42
7 43-49
8 50-56
9 57-63
10 64-70
11 71-77
12 78-84
13 85-91
14 92-98
15 99-100
For example, if two Transmitters are placed one foot apart and
the first Transmitter has an RF ID number of 027 that means it is
in the 4th group (22-28). The second Transmitter must have an
RFID number that is in another group (less than 22 or greater
than 28). Setting the RF IDs of two closely spaced Transmitters
so that the RF ID numbers are greater than 7 apart ensures that
the Transmitters are in different Base Radio sync groups. This
allows the closely spaced Transmitters to properly receive their
synchronization signal from the Base Radio and maintain their
proper communication and range.
ou can also ensure that closely spaced Transmitters maintain
Y
their synchronization with their Base Radio by simply assigning
each of the two closely spaced Transmitters to talk to a different
Base Radio.
ither way, following this process will keep the Base Radio and
E
Transmitters properly synchronized for long-term
communication.
Rev 5 User Manual - 13 -
08/06
Page 14

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
3.2. Testing Communications
Remember, proper placement of the Transmitter will optimize
your RF communication range and capabilities. Perhaps the best
test to perform before mechanically mounting the unit is a quick
hand-held test. There are two types of tests you can conduct: the
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) Diagnostic and the
Link Test. The RSSI Diagnostic measures the strength of the
signal at the Transmitter. The Link Test measures the throughput
of data sent to and from the Transmitter. The Link Test may be
conducted from the Transmitter, Base Radio, or through WMT.
The RSSI Diagnostic should be conducted first to determine if
the Base Radio is communicating with the Transmitter. Then the
Link Test may be performed to test the validity of the installation.
To perform these tests you should have a good idea of where
the Base Radio will be placed (for more information see Section
3 of the Base Radio User Manual). Place the Base Radio in the
desired area and power on. Make sure that the Base Radio and
Transmitter are on the same RF Channel and Baud Rate (See
Section 5). You may also have to increment the number of
Transmitters with which the Base Radio is communicating (See
the Base Radio User Manual Section 4.3).
Once both the Base Radio and Transmitter are set up to be on
the same network, make sure communication is established by
looking at the Transmitter LCD for the ‘RF OK’ message in the
Read-Only Sequence (see Section 4.2.1).
After communications have been established, go to Section 3.2.1
for the RSSI Diagnostic or Section 3.2.2 for the Link Test.
3.2.1.
The Transmitter should be placed in RSSI Diagnostic mode to
determine the signal strength at the location of the equipment to be
monitored.
The RSSI Diagnostic, located in the Transmitter’s diagnostic menu,
displays the RF signal strength in one of seven ranges. The signal
strength is displayed on the LCD using a combination of ‘>’ and ‘_’
characters. Full signal strength is displayed as “> > > > > > >” while
minimum signal strength is displayed as “> _ _ _ _ _ _”. If the
Transmitter is not communicating with the Base Radio (i.e. NO RF),
all underscore characters will be displayed (“_ _ _ _ _ _ _”).
The RSSI is measured every time the Transmitter receives a
message from the Base Radio. The signal strength of the received
message from the Base Radio is calculated during this time. The
actual signal strength in dBm for each range is shown below:
Rev 5 User Manual - 14 -
08/06
Transmitter RSSI Diagnostic
Page 15

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
> > > > > > >
Less than Between Between Between Between Between
-105 dBm
To place the Transmitter in RSSI Diagnostic mode follow the menu
map shown in Figure 3-2. Note that the RSSI menu is under the
DIAGNSE menu and not the CONFIG menu.
-105 dBm &
-100 dBm
-100 dBm &
-95 dBm
Figure 3-2: Menu Map to RSSI Mode
-95 dBm &
-90 dBm
90 dBm &
-85 dBm
-85 dBm & 80 dBm
Greater
than
-80 dBm
Now that the Transmitter is in the RSSI mode, bring the Transmitter
close to the equipment you wish to monitor. Look at the LCD; notice
the ‘>’ will constantly fluctuate. One should estimate an average
value based on these fluctuations. The ideal signal integrity is seven
arrows.
Once you have verified that you are receiving a signal, you should
check to make sure the Transmitter is communicating properly with
the Base Radio. To do so, exit the RSSI by pressing ENTER, and
then navigate to EXIT? of the diagnostic menu and return to the
Operations Sequence shown in Figure 4-1 in Section 4.2.
If you see a NO RF message, then you do not have satisfactory RF
communication with the Base Radio. If your application allows,
move the Transmitter to a different position and check again for
communications. If your application only allows you to mount at this
particular point, you may want to try a slower baud rate setting for
an increased range.
Note While using a slower baud rate increases communication
distance, it also increases the minimum transmit time. See Section
5.2 for a list of the fastest transmit rates for each baud rate. This
may not be suitable for your application.
One final solution is to reposition the Base Radio. However, this
may affect communications with previously installed Transmitters,
and if so, may require the use of a second Base Radio for your
application. To select a better spot for the Base Radio, see Section
3.1.1 of the Base Radio User Manual.
Rev 5 User Manual - 15 -
08/06
Page 16
Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
3.3. Link Test
The Link Test measures the wireless link performance of a
Transmitter running in its normal operating mode. Messages are
sent from the Transmitter to the Base Radio at a predefined
interval called the Transmit Rate (see Section 6.1). Each
message contains data for the previous time period (since the
last transmit). The Link Test looks at the wireless performance
going in both directions, from the Transmitter to the Base Radio
and vice versa, and comes up with a rating. The result that
appears on the display shows the determined link strength.
In order to perform this test, the Transmitter must be
communicating on the same channel and baud rate as the Base
Radio. See Section 5 to configure communications.
The Link Test may be conducted from the Transmitter, Base
Radio, or through WMT. Running the Link Test from WMT is
ideal for testing communications for an installation with remote or
hard-to-get-to Transmitters. To conduct the Link Test from a
Base Radio, see Section 3.2.2.2. To conduct the Link Test from
WMT, see Section 3.2.2.3.
3.3.1.
Conducting a Link Test from the Transmitter
The Link Test is located in the Transmitter’s diagnostic menu
(see Figure 3-3).
Figure 3-3: Transmitter Link Test
Using the NEXT and ENTER buttons, navigate to Link Test, and
press the ENTER button to begin the test. The Transmitter will
begin to test the link in both directions (to and from the Base
Radio). During this time, the word TEST will appear on the LCD
display. When the test is complete, the Transmitter will display
the quality of the link. Be aware that the Transmitter uses the
configured Baud Rate and transmission rate to perform this test.
The length of time it will take to perform this test is dependent
upon how fast the device is normally transmitting.
Rev 5 User Manual - 16 -
08/06
Page 17

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
When enough messages have been observed, a link strength
will be shown on the display. >>>>> indicates the strongest link,
while > indicates the weakest link. The Link Test will continue to
be evaluated and the rating on the screen may adjust itself.
Keep in mind that the longer the Link Test runs the more data
the Transmitter will have to evaluate.
The Transmitter installation site should strive to place the
Transmitter in a location where it receives the highest number
possible. A stronger link means less data re-transmits and better
battery life.
3.3.2.
Conducting a Link Test from the Base Radio
When the Link Test is conducted from a Base Radio, it measures
the link strength between a selected Transmitter and the Base
Radio. The Link Test data must be configured to match the
communication parameters of the Transmitter from which you
want to test. The Link Test is located in the Base Radio's
diagnostic menu (see Figure 3-4).
To conduct a Link Test from the Base Radio, Navigate to Link
Test, and press the Enter button. Next enter the RF ID for the
Transmitter that you want to test. Then select the Normal
Transmit rate that matches that of the Transmitter. If the
Transmitter is transmitting at a different rate than the one you
select in this menu, your results will be invalid.
Once the Normal Transmit Rate is selected, the Link Test will
immediately start. The Base Radio will begin to test the link from
the Transmitter. During this time, the word TEST will appear on
the LCD display. When the test is complete, the Base Radio will
display the quality of the link. Be aware that the length of time it
takes to perform this test is dependent upon how fast the
Transmitter is normally transmitting.
Rev 5 User Manual - 17 -
08/06
Page 18

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Figure 3-4: Transmitter Link Test
When enough messages have been observed, a link strength
will be shown on the display. >>>>> indicates the strongest link,
while > indicates the weakest link. The Link Test will continue to
be evaluated and the rating on the screen may adjust itself.
Keep in mind that the longer the Link Test runs the more data
the Transmitter will have to evaluate.
The Transmitter installation site should strive to place the
Transmitter in a location where it receives the highest number
possible. A stronger link means less data re-transmits and better
battery life.
3.3.3.
Conducting a Link Test from WMT
To conduct a Link Test from WMT, make sure that WMT is
running on the PC attached to the Base Radio. Then go to the
Transmitter view, and right-click on the Transmitter you want to
test Received data transmission from (Figure 3-5).
Rev 5 User Manual - 18 -
08/06
Page 19

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Figure 3-5: WMT Transmitter View
Select Wireless Data Loss Test… from the popup menu.
The Wireless Data Loss Test window appears (Figure 3-6). The
name of the Transmitter being tested appears in the title bar in
parenthesis.
Rev 5 User Manual - 19 -
08/06
Page 20

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Figure 3-6: Wireless Data Loss Test
In the top of the window, you can configure the test to run for a
specified amount of time. The longer the test, the more data the
test will have to do an evaluation. Type the length of time that
you want to run the test and click Begin to start. Once the test
starts, WMT will reconfigure the Transmitter’s Transmit Rate to
the fastest possible for the selected Baud Rate. These rates are
listed in Section 5.2. After the test has completed, it will restore
the previously configured Transmit Rate.
During the test, the communications reliability is evaluated while
the Transmitter is running under normal operating conditions. As
the test runs, a link strength will be shown in the lower right hand
corner of the window. >>>>> indicates the strongest link, while >
indicates the weakest link. The Link Test will continue to be
evaluated and the rating on the screen may adjust itself for the
specified amount of time.
3.4. Electrical Installation
In this section wiring instructions are discussed for the various setup
capabilities of the Switch Input Transmitter. The subsections are as
follows:
3.4.1: Electrical Specifications
3.4.2: Wiring the Input Switches
Caution! Remember to turn off all power BEFORE hooking up
any wires!
3.4.1. Electrical Specifications
Input Switch Characteristics
• For simple device monitoring only (i.e., contact closures)
Warning! Explosions may result in death or serious injury. Do
not remove the instrument cover or open wiring housing in
explosive atmospheres when power and communications are
on.
3.4.2. Wiring and Configuring the Input Switches
To properly wire a switch input device to the Switch Input
Transmitter, simply follow the wiring diagram in Figure 3-7. Please
note that circuit power does NOT need to be supplied as the
Transmitter supplies the monitoring power. The Switch Input
Transmitter has the capability of monitoring two input switches.
Rev 5 User Manual - 20 -
08/06
Page 21

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
The most common application for the switch inputs is to monitor a
contact closure. However, the input switches must only be attached
to simple devices. A simple device is one that meets the conditions
set forth in the Intrinsic Safety Control Drawing, which can be found
in the Technical Specifications section of this guide.
Warning! Wiring the Switch Input Transmitter to a non-simple device
(such as an explosion proof device) voids the intrinsic safety of the
Transmitter. A simple device is one that meets the conditions set forth
in the intrinsic safety Control Drawing found in the Technical
Specifications section of this guide.
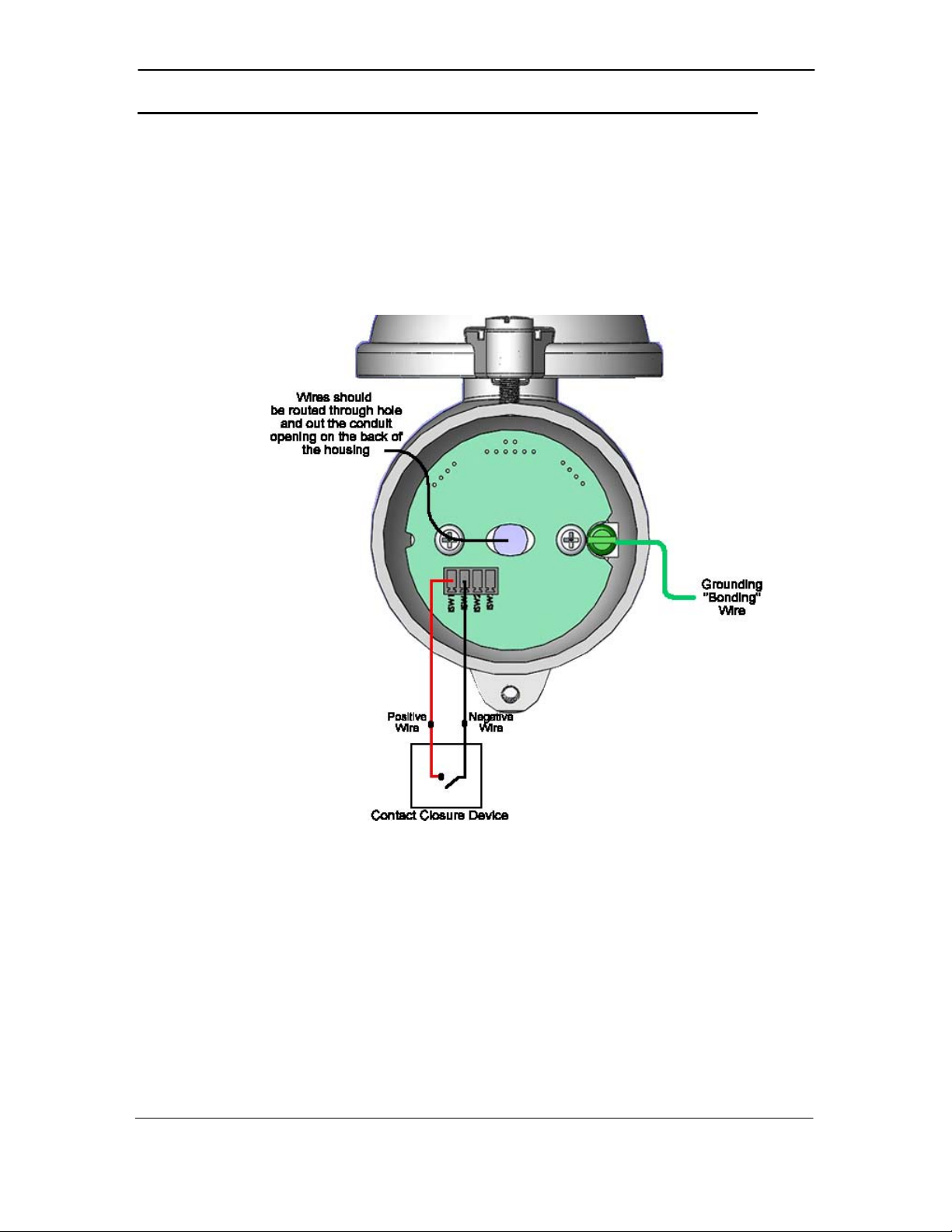
The diagram shown in Figure 3-7 refers to the circuit board found at
the base of the Transmitter, within the junction box. Before
connecting wires to the terminal blocks, the input wires should be
routed into the back of the enclosure and threaded through center of
the circuit board.
Figure 3-7: Input Switch Wiring Diagram
Messages indicating the status of both monitored contact closure
switches are displayed on the Transmitter LCD. This is displayed as:
S1 OPEN/CLSD and: S2 OPEN/CLSD. If no input is available then:
S1 N-A is shown. This is illustrated in figure 4-1. The status of the
input switches can also be found in WMT under the Transmitter
View. An open contact closure is indicated as an ‘O’ and a closed
Rev 5 User Manual - 21 -
08/06
Page 22

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
contact closure is indicated as a ‘C’ on the Transmitter View for
each input switch (see WMT User Guide section 8.1).
After the Input Switch has been wired, it needs to be enabled.
Switches can be enabled from the Transmitter front panel or the
Transmitter Configuration Menu in WMT. To enable a switch from
the Transmitter, follow the menu map in figure 3-8:
Figure 3-8: Menu Map to Enable the Input Switches
In WMT, go to the Input Switches configuration tab. For more details
on how to access this menu see Section 9.2 of the WMT User
Guide. Check the Enable Input check box to enable a switch.
Rev 5 User Manual - 22 -
08/06
Page 23

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Figure 3-9: Input Switch Configuration using WMT
Rev 5 User Manual - 23 -
08/06
Page 24

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
4. General Configuration
This section discusses general configuration of the Transmitter via
the NEXT and ENTER buttons. The subsections are as follows:
4.1: Navigating User Menus
4.2: Transmitter Displayed Messages
4.3: Overall Configuration Menu Map
4.4: Setting the Transmitter Tag Name
4.5: Setting a User Password
4.6: Resetting All Transmitter Settings
4.1. Navigating User Menus
Pressing either the NEXT or ENTER buttons located on the front of
the Transmitter or Base Radio just below the LCD screen is all that
is needed to navigate the respective menus. Pressing both of these
buttons for one second will turn the unit on.
Pressing the NEXT button at any time while the Transmitter is
cycling through the normal messages causes the Transmitter to
enter the setup mode. The NEXT button is then used to step
through menu options, and the ENTER button is used to enter a sub
menu of what is displayed on the LCD at that time. If no button is
pressed within a 30 second period the unit goes back to the normal
display mode.
If you enter a sub menu that requires a numerical input, such as
001, the left most 0 will be blinking. This indicates that pressing the
NEXT button will increment this value with each press from 0 to 9
and back to 0 again. Pressing the ENTER button will move to the
next available value. If the last value is blinking, pressing ENTER
will save the entered values and return from the sub menu.
If both the NEXT and ENTER buttons are depressed at the same
time, a message on the LCD displaying OFF? will appear. If both
buttons are released upon appearance of this message the user will
be returned to the scrolling main screen. If both buttons are not
released for the duration of the OFF? message, you will be
prompted for the password. Upon entering the correct password, the
unit will power down and turn off.
Note If the unit is turned off while entering values in a sub menu,
those values will NOT be saved.
Note There are several menu options that will automatically turn off
if you are using WMT. All changes to these Transmitter menu
options should then be made through WMT instead. This is to
prevent simultaneous changes from taking place. If you wish to
discontinue use of the software and want these menus re-instated,
you must contact your Honeywell Sales Representative.
Rev 5 User Manual - 24 -
08/06
Page 25

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
4.2. Transmitter Displayed Messages
To turn the Transmitter on, press and hold both the NEXT and
ENTER buttons for a few seconds. Upon power up, the Transmitter
will display the Power-Up Sequence, and then go into the
Operations Sequence. These Sequences are shown in Figure 4-1
below:
Figure 4-1: Transmitter Power-Up and Operations LCD Sequences
Note During configuration and testing, keep Transmitters at least six
feet from the Base Radio and other Transmitters to ensure good
communications.
4.2.1. The Read-Only Sequence
Once the Transmitter is in the Operations Sequence, a user may
access the Read-Only Sequence without a password by simply
pressing the ENTER button at any time. The Read-Only Sequence,
as shown in Figure 4-2, displays extra information about the current
settings of the Transmitter that are not seen during the Operations
Sequence, but does not allow any changes to be made to these
settings.
Figure 4-2: The Read-Only Sequence
Rev 5 User Manual - 25 -
08/06
Page 26

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
4.3. Overall Configuration Menu Map
A complete Transmitter Menu Map is shown in Appendix C. Below is
an overall view of the configuration menu to aid the user in setting
up the Transmitter for proper operation.
Figure 4-3: Overall Configuration Menu Map
Note The user must enter a four-digit password to enter the
CONFIG and DIAGNSE menus. The default user password is 0000.
The FACTORY menu is for factory use only. For more information
on the password see Section 4.5.
4.4. Setting the Transmitter Tag Name
Note Once WMT has been used to configure the Transmitter, this menu
option will be disabled on the Transmitter LCD menu. See Section 4.1
for more details.
Each Transmitter has a user-settable Transmitter Tag Name. This
Tag Name is displayed upon Transmitter power up, and when the
Read-Only Sequence is selected. The Tag Name is a 21-character
string that is displayed in three separate 7-character flashes on the
Transmitter LCD.
Rev 5 User Manual - 26 -
08/06
Page 27

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
The user may choose from A-Z, 0-9, a dash (“-“), and an underscore
(“_”). The underscore has a special meaning to the software inside
the Transmitter. For example, if you have a Tag Name that is only 5
characters long, then you do not want to wait for the rest of the 16
characters to be displayed on the LCD. So if your Tag Name was
“TANK1”, you would want to enter the Tag Name like this: “TANK1_
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _”.
The Tag Name can also be entered via WMT. To do so, when the
software is in the Transmitter view (See Appendix A), right-click the
Transmitter icon, select Rename, and then enter the Tag Name you
wish the Transmitter to have.
This Tag Name will then be uploaded to the Transmitter and can be
displayed by pressing the ENTER button when the unit is in the
Operations Sequence (See Section 4.2.1 of this manual).
4.5. Setting a User Password
Note Once WMT has been used to configure the Transmitter, this
menu option will be disabled on the Transmitter LCD Menu. See
Section 4.1 for more details.
Each Transmitter has a password that will lock out undesired users
from making changes to the Transmitter. Any user may still view
some of the Transmitter settings by pressing the ENTER key during
the Operations Sequence and viewing the Read-Only Sequence.
The password is a four-digit password. The factory default is 0000. If
you wish to select a different password, follow the Transmitter Menu
Map shown in Figure 4-4 to change it.
Figure 4-4: Menu Map to Password Setting
The password can also be configured via WMT. To do so, enter the
configuration dialog box (See Appendix A). From the configuration
dialog box click on the General tab to bring up the general
information as shown in Figure 4-5.
Rev 5 User Manual - 27 -
08/06
Page 28

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Figure 4-5: Setting a User Password
You can set the Transmitter password for this device by entering a
four-digit number in the Transmitter Password field. Once a
password has been entered, click OK to save and download the
password to the Transmitter.
Please note that the password only protects the Transmitter from
unauthorized configuration via the NEXT and ENTER buttons. WMT
requires a user login password to gain access to all configuration
parameters. However, user accounts are available and can be set
with different access levels and restrictions (For more information on
user accounts see the WMT User Manual Section 8.4).
Rev 5 User Manual - 28 -
08/06
Page 29

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
4.6. Resetting All Transmitter Settings
To reset all Transmitter settings to their default state, you must
navigate to the DEFAULT menu option in the CONFIG menu via the
keypad.
Note Once at the default menu option, pressing the ENTER button
will display ‘RESET?’ on the LCD; which asks if you are sure you
want to reset the device to its default configuration. You will then be
prompted with ‘NO’ on the LCD. Pressing the ENTER button while
‘NO’ is being displayed will NOT reset the device. Pressing the
NEXT button will display ‘YES’ on the LCD. If you press the ENTER
button while ‘YES’ is being displayed the device will be reset.
Note Resetting the Transmitter by using the DEFAULT menu option
will not reset the TRIM or OFFSET values.
Rev 5 User Manual - 29 -
08/06
Page 30

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
5. Configuring the RF Communications
In order for the Transmitter and the Base Radio to communicate,
they must be on the same RF Channel and must be transmitting at
the same Baud Rate. While all Transmitters and Base Radios are
set to default configurations at the factory, if any configuration
differences are present, the Base Radio will not be able to
communicate with the Transmitters. The subsections are as follows:
5.1: RF Channel Selection
5.2: Baud Rate Selection
5.3: RF Identification Selection
Warning! If the Transmitters have been running for an extended
period of time with no signal from the Base Radio (the Base
Radio is off or not present), the Transmitters will only search for
the Base Radio every one hour or so. Turning the Transmitters
off and back on will cause them to begin searching
immediately.
5.1. RF Channel Selection
The RF Channel defines a set of frequencies on which
communication takes place between the Base Radio and the
Transmitter. Each RF Channel has a different set of frequencies,
thus allowing the user to have multiple different wireless networks
co-existing throughout the same facility.
All Base Radios and Transmitters can be set to one of 16 different
RF channels. The only Transmitters recognized by a particular Base
Radio are the units that are on the same RF Channel as that Base
Radio. This allows the user to decide which Transmitters
communicate with each Base Radio.
The RF Channel can be thought of as a set of walkie-talkies. If both
walkie-talkies are on channel one they can communicate. If a
walkie-talkie is on channel one and the other is on channel two, they
cannot communicate. Likewise, if two walkie-talkies are on channel
one and two other walkie-talkies are on channel two, the walkietalkies on channel one cannot hear what is being transmitted by the
walkie-talkies on channel two.
Each Transmitter comes from the factory with the RF Channel set to
OFF. This means the Transmitter will not communicate to any Base
Radio. To set the Transmitter for communication, first determine the
channel that you want to use. Then follow the Transmitter menu
map shown in Figure 5-1 to configure the RF Channel.
Rev 5 User Manual - 30 -
08/06
Page 31

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Figure 5-1: Menu Map to RF Channel Setting
Once in the RF Channel menu, increment it by pressing the NEXT
button. When selecting this value, do not choose an RF Channel
that is currently being used by other Honeywell Wireless Systems as
this can cause communication problems.
5.2. Baud Rate Selection
The RF Baud Rate refers to the speed at which the Base Radio and
Transmitters communicate. The RF baud rate for the Base Radio
and the Transmitter must be the same in order for successful
communication to occur. There are three selectable settings with the
fastest update times and ranges listed below:
• 4.8K - Rate of 4.8 Kbaud (Update every 20 seconds)
- Range of 3000ft (Line of Sight)
• 19.2K - Rate of 19.2 Kbaud (Update every 5 seconds)
- Range of 2000ft to 2500ft (Line of Sight)
• 76.8K - Rate of 76.8 Kbaud (Update every 1 second)
- Range of 500ft to 750ft (Line of Sight)
A faster RF Baud Rate allows the user to transmit more information
in a given period of time, but it will also limit the Transmitter’s range.
If you need more distance out of your Transmitters or are
encountering difficulties by frequently losing communications, then
select a slower baud rate.
Follow the Base Radio menu map shown in Figure 5-2 to configure
the RF Baud Rate. The factory default is the 19.2K Baud Rate.
Figure 5-2: Menu Map to Baud Rate Setting
Note If you change the baud rate of a Transmitter, you must also
change the baud rate of the Base Radio and all other Transmitters
that are communicating with that Base Radio.
Rev 5 User Manual - 31 -
08/06
Page 32

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
5.3. RF Identification (RF ID) Selection
Each Transmitter is identified by the Base Radio and WMT,
according to the RF ID given to that particular unit. Two Transmitters
on the same RF Channel CANNOT have the same RF ID (if you do
not know the RF Channel, see section 5.1). When the Transmitter is
in the Operations Sequence, pressing the ENTER button displays
the Read-Only Sequence on the LCD. The RF of that unit will be
displayed in the format: ID 3.
All Transmitters in your system are set to a default RF ID number
upon shipment. For example, if you have ordered a Base Radio and
three Transmitters, the Transmitters will be configured to ID’s 0, 0
and 0. You must set these units to three different RF IDs between 1
and 100. The Transmitters in this example could be set to RF IDs 1,
2, and 3.
First determine the RF ID’s you’d like to give each unit. Then follow
the menu map shown in Figure 5-3 to configure the RF ID. The
factory default is RF ID 0, which disables the RF communication of
the unit.
Figure 5-3: Menu Map to RF ID Setting
Once you have selected the RF ID you wish to use for this particular
Transmitter, exit the menus and return to the Operations Sequence.
The Transmitter should now be successfully configured to the Base
Radio. To check this, press ENTER while the Transmitter is in the
Operations Sequence for the Read-Only Sequence to be displayed.
You may see an RF SYNC message displayed on the Transmitter
LCD. This means that the Transmitter and Base Radio are
attempting to synchronize communications. If this is successful, the
RF Status will display an RF OK message. If this is unsuccessful,
the RF Status will display a NO RF message.
Also notice the two small arrows on either side of the LCD; if they
are fluctuating up and down, that indicates the Transmitter and Base
Radio are successfully communicating. If only one or none of the
arrows are moving then they are not communicating successfully.
Rev 5 User Manual - 32 -
08/06
Page 33

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
6. Configuring the Transmit and Sampling Rates
The Transmitter reads the inputs at a rate called the Sampling Rate.
For the Switch Input Transmitter this rate is not configurable. The
Transmit Rate is the rate at which the Transmitter communicates
with the Base Radio. This rate is configurable. This section will walk
you through the initial configuration of the Transmit settings. The
subsections are as follows:
6.1: Selecting the Normal Transmission Rate
6.2: The Sampling Rate
6.3: Enabling the Smart Rate
6.1. Selecting the Normal Transmit Rate
The Switch Input Transmitter will read its inputs at an interval called
the Sampling Rate. It then transmits these readings to the Base
Radio at an interval determined by the Normal Transmit Rate.
Notice that the fastest update rate of the Normal Transmit Rate is
dependent on the baud rate setting you selected earlier (see Section
5.2). The transmit rates cannot update data faster than their
communication speed allows. Thus, if you selected the 19.2K Baud
Rate setting, your fastest transmit rate will be 5 seconds. The
Transmitter automatically determines these settings and adjusts the
menu options accordingly. A complete table of these parameters is
shown below:
Baud Rate
(communication range)
(fastest speed of updates)
Normal Transmit Rates 1 Second or Greater 5 Seconds or Greater 20 Seconds or Greater
In order to properly set the Normal Transmission Rate, you must
first determine how often you need updates from the Transmitter.
You have a selectable range of 1-5, 10, 15, 20, 40 seconds and 1
minute. The factory default is 10 seconds.
If all of the data does not get through, the data is resent the
following second. This prevents data from being lost. However, if the
Transmission Rate is set to the maximum (1 second; 76.8K baud),
then the data cannot be resent the following second because the
next set of data must be sent in order to meet the Transmission
Rate.
76.8K 19.2K 4.8K
500-750 feet 2000-2500 feet 3000 feet
1 Second 5 Seconds 20 Seconds
Rev 5 User Manual - 33 -
08/06
Page 34

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
6.1.1. Configure the Normal Transmit Rate from the
Transmitter
Follow the menu map below.
Note Once WMT has been used to configure the Transmitter, this
menu option will be disabled on the Transmitter LCD Menu.
Figure 6-1: Menu Map to the Transmit Rate Setting
Rev 5 User Manual - 34 -
08/06
Page 35

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
6.1.2. Configure the Normal Transmit Rate with WMT
[1] Open the configuration dialog box (See Appendix A).
[2] In the configuration dialog box click the Transmit Rates tab
to display the Normal Transmit Rate information as shown
below.
Figure 6-2: Transmit Rates Tab
[3] Select one of the time periods from the Normal Transmit Rate
drop-down list box.
[4] Click OK to save and download the configuration changes to
the Transmitter.
6.2. The Sampling Rate
The Sampling rate for the Switch Input Transmitter is not
configurable. The Transmitter reads the inputs 11 times per second.
It then takes the majority of the 11 readings for that second and
sends that value to the Base Radio based on the Transmit Rate. For
example, if 7 of the readings were Open and 4 were Closed, it would
send a value of Open.
Rev 5 User Manual - 35 -
08/06
Page 36

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
However, anytime there is a change in any of the 11 readings, along
with the state of the input, a status byte is set to indicate a transition
occurred and the Device Status field in WMT will display the value:
Transaction.
6.3. Enabling the Smart Rate
The Smart Rate is a feature used to trigger radio transmission of the
data immediately any time the value of the monitored input changes.
The Smart Rate cannot be configured from the Transmitter. The
Smart Rate can only be enabled using WMT.
Rev 5 User Manual - 36 -
08/06
Page 37

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
6.3.1. Configure the Smart Rate with WMT
[1] Open the configuration dialog box (See Appendix A).
[2] Click on the Transmit Rates tab to display the SmartRate
information as shown below.
Figure 6-3: Smart Rate Configuration Using WMT
[3] Select the Enable SmartRate check box for Input 1 or Input 2
or for both.
[4] Click OK to save and download the configuration changes to
the Transmitter.
Rev 5 User Manual - 37 -
08/06
Page 38

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
7. Modbus Supplement
This section applies only if you are using the Modbus
communications option for the Base Radio. If you are not using
this option please skip this section.
Modbus configuration is discussed in detail in Section 6 of the
Base Radio User Guide. This section discusses elements that
are specific to the Switch Input Transmitter and Switch Input with
Output Option Transmitter.
The following tables contain holding register values that differ for
the Switch Input Transmitter. These registers are bit field
registers composed of two 16-bit registers and interpreted as an
IEEE 32-bit floating point value for Transmitters.
Device Type Holding Registers
The following values are for the Device Type holding registers.
Value Device Type
26 Switch Input Transmitter
27 Switch Input Transmitter with Output Option
Device Status Holding Registers
The following values are for the Device Status holding registers.
Value Device Status
1 Device (Transmitter) Online
2 Low Battery
4 Alarm Condition
8 Transition on Input Switch 1
16 Transition on Input Switch 2
32 System Error Condition
64 Input Switch 1 Position = Closed
128 Input Switch 2 Position = Closed
The above values are still converted from Modbus as 32-bit
floating point values. For ease of use, we’ve arranged each
status to correspond to a bit in an imaginary 8-bit binary field,
logic high.
The status can be resolved by subtracting the largest number
listed above from the value received from the holding register,
and then subtracting the next highest and so on until the result is
0. Each of the values used indicates the respective condition
listed above.
Example #1: If the holding register reads 65, subtract 64 and get
1. Then subtract 1 from 1 and get 0. Thus from the list below,
Input Switch 1 is closed (64) and the Transmitter is online (1).
Example #2: If Input Switch 1 is Open and Input Switch 2 is
Open, and no additional conditions exist, the value is 1. Now if
Rev 5 User Manual - 38 -
08/06
Page 39

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Input Switch 2 changes to closed, the value first displays 17 and
then 129. 17 shows us that Input Switch 2 is in Transition (17-16)
and 129 shows us that Input Switch 2 is now Closed (129-128).
Note The Output Option status is not shown under the Device
Status field. For this status, use the Primary and Secondary Sensor
Status registers
.
Primary and Secondary Sensor Status Holding Registers
The following values are for the Primary and Secondary Sensor
Status holding registers. If the Transmitter does not contain the
Output option, then the second two values do not pertain.
Primary (& Secondary) Sensor Status
Value Input Switch 1 (or 2) Output Switch 1 (or 2)
0.0 Open Open
1.0 Closed Open
2.0 Open Closed
3.0 Closed Closed
Rev 5 User Manual - 39 -
08/06
Page 40

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
8. Maintaining the Transmitter
Warning! Explosions may result in death or serious injury. Do
not remove the instrument cover or open wiring housing in
explosive atmospheres when power and communications are
on. Instead, remove the Transmitter from the hazardous
location and then proceed to open the instrument cover and
replace the battery
The Switch Input Transmitter is extremely easy to maintain in that it
requires no periodic calibration or system checks. The Transmitter
has a self-diagnostic that is constantly checking the internal system.
If any errors are found, they are reported via the LCD, Base Radio,
or WMT. A simple yearly visual inspection for the following is all that
is needed:
• Is the Transmitter still securely fastened to the equipment being
monitored?
• Are there any visible corrosions, cracks or residue build-ups on
the unit?
• Has anything about the application changed from the original
intended use?
.
8.1. Changing the Battery
The battery will need to be changed within one month of seeing a
‘LOW BAT’ message on the Transmitter. This is a simple process:
[1] Make sure you have the correct replacement battery:
TADIRAN™ Lithium Inorganic Battery (non-rechargeable)
Size “C” – 3.6Volts
#TL2200/S
[2] Power down the Transmitter by pressing and holding both the
NEXT and ENTER buttons for a few seconds and then
entering the password
[3] Remove the 4 set screws on the sides of the Transmitter
housing with a standard screwdriver.
[4] Remove the housing and locate the battery.
Warning! When removing the housing do not twist or bend the
green flex cable! Doing so may cause the tether to improperly
seat next to the antenna and greatly reduce operable RF
distances. Do not allow the housing to flop around while
hanging by the tether.
[5] Remove the old battery and replace it with the new battery,
positive end first.
.
Rev 5 User Manual - 40 -
08/06
Page 41

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Note The positive end of the battery clip is the end with the red wire.
Putting the battery in backwards will blow a fuse.
[6] Replace the housing and screw the housing back on.
Power up the unit by pressing and holding both the NEXT
and ENTER buttons for a few seconds.
[7] Properly dispose of the used battery.
Rev 5 User Manual - 41 -
08/06
Page 42

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
9. Technical Specifications
9.1. WW591, WW592
RF Characteristics
• 902 MHz – 928 MHz Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum,
FCC certified ISM license-free band
• Up to 3000’ range from Base Radio with clear line of sight; 500’
to 1000’ range with obstructions
• The RF module in each Transmitter is individually tested and
calibrated over the full temperature range to ensure reliable
wireless operation
Operating Temperature Range
• -40°F to +185°F (-40°C to +85°C) electronics
• -4°F to +158°F (-20°C to +70°C) display (full visibility)
• -4°F to +158°F (-20°C to +70°C) display (with reduced visibility)
Physical Characteristics
• Aluminum junction box
• GE Lexan® cover. V-0 rating and UV stable
Operating Vibration and Shock Characteristics
• Certified per IEC EN00068 2 -6 (vibration) and 2-27 (shock)
Random Vibration Characteristics
• Certified to withstand 6 g’s, 15 minutes per Axis from 9 – 500 Hz
Electromagnetic Compatibility (CE Compliance)
• Operates within specification in fields from 80 to 1,000 MHz with
Field strengths to 10 V/m. Meets EN 50082-1 general immunity
standard and EN 55011 compatibility emissions standard
Industrial Certification
• Rated for industrial use -40°F to 185°F (-40°C to 85°C)
• FM NEMA 4 weather-proof housing
• FM rated intrinsically safe for Class I/II/III, Division 1, Groups
A,B,C,D,E,F&G; Class I/II/III, Division 2, Groups A,B,C,D,F&G
Rev 5 User Manual - 42 -
08/06
Page 43

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Input Characteristics
• Max switch impedance 1.0 kOhm
• Input Isolation between Input 1 to Input 2 = 20 kOhm
Local Configuration
• Integrated LCD display with membrane switch buttons
• Display cycles through Input 1, Input 2 and error messages, if
applicable
• Configure RF parameters locally using membrane switch
buttons
Power Characteristics
• Self-contained power
• ‘C’ Size 3.6 V lithium battery
• Up to five year battery life (depends on sample rate and RF
update rate), field replaceable
Self-Diagnostics
• Low battery alarm– indicates the need to replace the battery
(approximately one month warning)
• Contains extensive self-checking software and hardware that
continuously monitors the operation. Any device parameter out
of spec is identified and reported.
Intrinsic Safety Entity Parameters
• V
• I
• P
= 30 VDC
Max
100 mA
Max =
900 mW
Max =
• Maximum operating temperature = 85 °C
• Temperature Class T4
Rev 5 User Manual - 43 -
08/06
Page 44

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Figure 9-1: Dimensioned Mechanical Drawing
Rev 5 User Manual - 44 -
08/06
Page 45

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Rev 5 User Manual - 45 -
08/06
Page 46

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Rev 5 User Manual - 46 -
08/06
Page 47

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Rev 5 User Manual - 47 -
08/06
Page 48

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Rev 5 User Manual - 48 -
08/06
Page 49

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Rev 5 User Manual - 49 -
08/06
Page 50

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Appendix A: Opening the Configuration box in WMT
In WMT, go to the Transmitter View. This view shows the
Transmitter information, and allows you to configure and view
individual Transmitter data. This view can be accessed at any time
by clicking on the Transmitters icon in the Views pane. The
Transmitter View is shown below. More information is found in
Sections 8 and 9 of the WMT User Guide.
Transmitter Group Tre
Transmitter Pane
Figure A- 1: WMT with All Transmitters view
The Transmitters are displayed in the Transmitter Pane based on
the selection in the Transmitter Group Tree.
To open the Configuration dialog box, right mouse click a
Transmitter and select Configuration from the Right Mouse Button
menu:
Rev 5 User Manual - 50 -
Rev 5 User Manual - 50 -
08/06
08/06
Page 51

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Appendix B: Transmitter Displayed Message Definitions
his section covers the various messages, displayed on the
T
Transmitter LCD, that occur during operation of the device.
Operations Sequence
• RF Link Status
⇒ RF OK – Transmitter and Base Radio are
communicating properly
⇒ RF SYNC – Transmitter and Base Radio are attempting
to synchronize communications.
⇒ RF F Channel is set to RF OFF
⇒ NO RF – Transmitter and Base Radio have no
• Switch Input
⇒ S1/S2 OPEN – Open
⇒ S1/S2 CLSD – Closed
⇒ S1/S2 N-A – Not Available
Error Messages
If an error is detected with the operation of the Transmitter a
message will be displayed on the Transmitter LCD (a corresponding
message may also appear on the Base Radio LCD).
There are two types of error messages, warning and fatal. Warning
messages are displayed as part of the normal cycling message
sequence. These are:
• LOW BAT - battery should be replaced as soon as possible
• NO RF - can not detect Base Radio
Fat l cycling message
al error messages will replace the norma
sequence and will flash. A fatal message indicates the Transmitter is
no longer operating normally and requires repair. These are:
RF ERR - fatal error within RF communications
•
• SEN ERR - fatal error within the sensor electronics
• SYS
• RF CAL - fatal error within the RF calibration system
OFF – Transmitter’s R
communications
ERR - fatal error within the microprocessor system
Rev 5 User Manual - 51 -
08/06
Page 52

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Appendix C: Transmitter Menu Map
Transmitter Menu Map
Rev 5 User Manual - 52 -
08/06
Page 53

Honeywell Industrial Wireless Wireless Dual Discrete Input Transmitter
Industrial Measurement and Control
2500 W. Union Hills Drive
Phoenix, AZ 85027
Honeywell
 Loading...
Loading...