Page 1

SWIFT™
Put Bar Code Here
SMART WIRELESS INTEGRATED FIRE TECHNOLOGY
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C • ECN 15-xxx • 5/8/2015
95-8544-2
Page 2

Fire Alarm & Emergency Communication System Limitations
While a life safety system may lower insurance rates, it is not a substitute for life and property insurance!
An automatic fire alarm system—typically made up of smoke
detectors, heat detectors, manual pull stations, audible warning
devices, and a fire alarm control panel (FACP) with remote notification capability—can provide early warning of a developing fire.
Such a system, however, does not assure protection against
property damage or loss of life resulting from a fire.
An emergency communication system—typically made up of
an automatic fire alarm system (as described above) and a life
safety communication system that may include an autonomous
control unit (ACU), local operating console (LOC), voice communication, and other various interoperable communication methods—can broadcast a mass notification message. Such a
system, however, does not assure protection against property
damage or loss of life resulting from a fire or life safety event.
The Manufacturer recommends that smoke and/or heat
detectors be located throughout a protected premises following
the recommendations of the National Fire Protection Association
Standard 72-2002 (NFPA 72-2002), manufacturer's
recommendations, State and local codes, and the
recommendations contained in the Guide for Proper Use of
System Smoke Detectors, which is made available at no charge
to all installing dealers. This document can be found at http://
www.systemsensor.com/appguides/. A study by the Federal
Emergency Management Agency (an agency of the United
States government) indicated that smoke detectors may not go
off in as many as 35% of all fires. While fire alarm systems are
designed to provide early warning against fire, they do not
guarantee warning or protection against fire. A fire alarm system
may not provide timely or adequate warning, or simply may not
function, for a variety of reasons:
Smoke detectors may not sense fire where smoke cannot
reach the detectors such as in chimneys, in or behind walls, on
roofs, or on the other side of closed doors. Smoke detectors
also may not sense a fire on another level or floor of a building.
A second-floor detector, for example, may not sense a first-floor
or basement fire.
Particles of combustion or “smoke” from a developing fire
may not reach the sensing chambers of smoke detectors
because:
• Barriers such as closed or partially closed doors, walls, chimneys, even wet or humid areas may inhibit particle or smoke
flow.
• Smoke particles may become “cold,” stratify, and not reach
the ceiling or upper walls where detectors are located.
• Smoke particles may be blown away from detectors by air
outlets, such as air conditioning vents.
• Smoke particles may be drawn into air returns before reaching the detector.
The amount of “smoke” present may be insufficient to alarm
smoke detectors. Smoke detectors are designed to alarm at various levels of smoke density. If such density levels are not created by a developing fire at the location of detectors, the
detectors will not go into alarm.
Smoke detectors, even when working properly, have sensing
limitations. Detectors that have photoelectronic sensing chambers tend to detect smoldering fires better than flaming fires,
which have little visible smoke. Detectors that have ionizing-type
sensing chambers tend to detect fast-flaming fires better than
smoldering fires. Because fires develop in different ways and
are often unpredictable in their growth, neither type of detector is
necessarily best and a given type of detector may not provide
adequate warning of a fire.
Smoke detectors cannot be expected to provide adequate warning of fires caused by arson, children playing with matches
(especially in bedrooms), smoking in bed, and violent explosions
(caused by escaping gas, improper storage of flammable materials, etc.).
Heat detectors do not sense particles of combustion and alarm
only when heat on their sensors increases at a predetermined
rate or reaches a predetermined level. Rate-of-rise heat detectors may be subject to reduced sensitivity over time. For this
reason, the rate-of-rise feature of each detector should be tested
at least once per year by a qualified fire protection specialist.
Heat detectors are designed to protect property, not life.
IMPORTANT! Smoke detectors must be installed in the same
room as the control panel and in rooms used by the system for
the connection of alarm transmission wiring, communications,
signaling, and/or power. If detectors are not so located, a developing fire may damage the alarm system, compromising its ability to report a fire.
Audible warning devices such as bells, horns, strobes,
speakers and displays may not alert people if these devices
are located on the other side of closed or partly open doors or
are located on another floor of a building. Any warning device
may fail to alert people with a disability or those who have
recently consumed drugs, alcohol, or medication. Please note
that:
• An emergency communication system may take priority over
a fire alarm system in the event of a life safety emergency.
• Voice messaging systems must be designed to meet intelligibility requirements as defined by NFPA, local codes, and
Authorities Having Jurisdiction (AHJ).
• Language and instructional requirements must be clearly disseminated on any local displays.
• Strobes can, under certain circumstances, cause seizures in
people with conditions such as epilepsy.
• Studies have shown that certain people, even when they hear
a fire alarm signal, do not respond to or comprehend the
meaning of the signal. Audible devices, such as horns and
bells, can have different tonal patterns and frequencies. It is
the property owner's responsibility to conduct fire drills and
other training exercises to make people aware of fire alarm
signals and instruct them on the proper reaction to alarm signals.
• In rare instances, the sounding of a warning device can cause
temporary or permanent hearing loss.
A life safety system will not operate without any electrical
power. If AC power fails, the system will operate from standby
batteries only for a specified time and only if the batteries have
been properly maintained and replaced regularly.
Equipment used in the system may not be technically compatible with the control panel. It is essential to use only equipment
listed for service with your control panel.
Telephone lines needed to transmit alarm signals from a premises to a central monitoring station may be out of service or temporarily disabled. For added protection against telephone line
failure, backup radio transmission systems are recommended.
The most common cause of life safety system malfunction is
inadequate maintenance. To keep the entire life safety system in
excellent working order, ongoing maintenance is required per the
manufacturer's recommendations, and UL and NFPA standards. At a minimum, the requirements of NFPA 72-2002 shall
be followed. Environments with large amounts of dust, dirt, or
high air velocity require more frequent maintenance. A maintenance agreement should be arranged through the local manufacturer's representative. Maintenance should be scheduled
monthly or as required by National and/or local fire codes and
should be performed by authorized professional life safety system installers only. Adequate written records of all inspections
should be kept.
Limit-D-1-2013
2 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 3
Installation Precautions
Adherence to the following will aid in problem-free installation with long-term reliability:
WARNING - Several different sources of power can be
connected to the fire alarm control panel. Disconnect all
sources of power before servicing. Control unit and associated equipment may be damaged by removing and/or inserting cards, modules, or interconnecting cables while the unit is
energized. Do not attempt to install, service, or operate this
unit until manuals are read and understood.
CAUTION - System Re-acceptance Test after Software
Changes: To ensure proper system operation, this product
must be tested in accordance with NFPA 72 after any programming operation or change in site-specific software. Reacceptance testing is required after any change, addition or
deletion of system components, or after any modification,
repair or adjustment to system hardware or wiring. All components, circuits, system operations, or software functions known
to be affected by a change must be 100% tested. In addition,
to ensure that other operations are not inadvertently affected,
at least 10% of initiating devices that are not directly affected
by the change, up to a maximum of 50 devices, must also be
tested and proper system operation verified.
This system meets NFPA requirements for operation at 0-49º
C/32-120º F and at a relative humidity 93% ± 2% RH (noncondensing) at 32°C ± 2°C (90°F ± 3°F). However, the useful
life of the system's standby batteries and the electronic components may be adversely affected by extreme temperature
ranges and humidity. Therefore, it is recommended that this
system and its peripherals be installed in an environment with
a normal room temperature of 15-27º C/60-80º F.
Verify that wire sizes are adequate for all initiating and indicating device loops. Most devices cannot tolerate more than a
10% I.R. drop from the specified device voltage.
Like all solid state electronic devices, this system may
operate erratically or can be damaged when subjected to lightning induced transients. Although no system is completely
immune from lightning transients and interference, proper
grounding will reduce susceptibility. Overhead or outside aerial
wiring is not recommended, due to an increased susceptibility
to nearby lightning strikes. Consult with the Technical Services Department if any problems are anticipated or encountered.
Disconnect AC power and batteries prior to removing or
inserting circuit boards. Failure to do so can damage circuits.
Remove all electronic assemblies prior to any drilling, filing,
reaming, or punching of the enclosure. When possible, make
all cable entries from the sides or rear. Before making modifications, verify that they will not interfere with battery, transformer, or printed circuit board location.
Do not tighten screw terminals more than 9 in-lbs. Overtightening may damage threads, resulting in reduced terminal
contact pressure and difficulty with screw terminal removal.
This system contains static-sensitive components.
Always ground yourself with a proper wrist strap before handling any circuits so that static charges are removed from the
body. Use static suppressive packaging to protect electronic
assemblies removed from the unit.
Follow the instructions in the installation, operating, and programming manuals. These instructions must be followed to
avoid damage to the control panel and associated equipment.
FACP operation and reliability depend upon proper installation.
Precau-D1-9-2005
FCC Warning
WARNING: This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and if not installed and
used in accordance with the instruction manual may
cause interference to radio communications. It has been
tested and found to comply with the limits for class A
computing devices pursuant to Subpart B of Part 15 of
FCC Rules, which is designed to provide reasonable
protection against such interference when devices are
operated in a commercial environment. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interference, in which case the user will be required to correct
the interference at his or her own expense.
Canadian Requirements
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class A limits
for radiation noise emissions from digital apparatus set
out in the Radio Interference Regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications.
Le present appareil numerique n'emet pas de bruits radioelectriques depassant les limites applicables aux appareils numeriques de la classe A prescrites dans le
Reglement sur le brouillage radioelectrique edicte par le
ministere des Communications du Canada.
eVance™ and SWIFT™ are trademarks; and Acclimate®, ECLIPSE®, Filtrex®, FlashScan®, FAAST Fire Alarm Aspiration Sensing Technology®,
Intelligent FAAST®, and Pinnacle® are registered trademarks of Honeywell International Inc. Microsoft® and Windows® are registered trademarks of the
Microsoft Corporation. The Chrome™ browser is a trademark of Google Inc.
©2015 by Honeywell International Inc. All rights reserved. Unauthorized use of this document is strictly prohibited.
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 3
Page 4

Software Downloads
In order to supply the latest features and functionality in fire alarm and life safety technology to our customers, we make
frequent upgrades to the embedded software in our products. To ensure that you are installing and programming the latest
features, we strongly recommend that you download the most current version of software for each product prior to
commissioning any system. Contact Technical Support with any questions about software and the appropriate version for a
specific application.
Documentation Feedback
Your feedback helps us keep our documentation up-to-date and accurate. If you have any comments or suggestions about our
online Help or printed manuals, you can email us.
Please include the following information:
•Product name and version number (if applicable)
•Printed manual or online Help
•Topic Title (for online Help)
•Page number (for printed manual)
•Brief description of content you think should be improved or corrected
•Your suggestion for how to correct/improve documentation
Send email messages to:
FireSystems.TechPubs@honeywell.com
Please note this email address is for documentation feedback only. If you have any technical issues, please contact Technical
Services.
4 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 5

Table of Contents
Section 1: Overview..................................................................................................................8
1.1: Purpose ..........................................................................................................................................................8
1.2: Assumed Knowledge .....................................................................................................................................8
1.3: Additional References ...................................................................................................................................8
1.4: About the Mesh Network...............................................................................................................................8
1.5: Abbreviations.................................................................................................................................................9
Section 2: XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway..................................................................10
2.1: Description...................................................................................................................................................10
2.2: Agency Approvals .......................................................................................................................................10
2.2.1: FCC....................................................................................................................................................10
2.2.2: Industry Canada..............................................................................................................................10
2.2.3: Federal Institute of Telecommunications ..........................................................................................11
2.3: Specifications...............................................................................................................................................11
2.3.1: Environmental Specifications............................................................................................................11
2.4: Magnet Sensors............................................................................................................................................12
2.4.1: Profile Magnetic Sensor ....................................................................................................................12
2.4.2: Mesh Formation Magnetic Sensor.....................................................................................................12
2.5: LED Indicators.............................................................................................................................................12
2.6: Installing the Gateway .................................................................................................................................12
2.6.1: Before Installing ................................................................................................................................12
2.7: Mounting and Wiring...................................................................................................................................13
2.7.1: Mounting ...........................................................................................................................................13
2.7.2: Wiring................................................................................................................................................14
2.7.3: Gateway Powered by the SLC...........................................................................................................15
2.7.4: Gateway Powered by an External, Regulated +24VDC Source........................................................16
2.8: Configuration and Programming .................................................................................................................17
2.8.1: Configuration and Programming Without Using SWIFT Tools .......................................................17
Create a New Profile ............................................................................................................................17
Assign a Previously Created Profile Using a Distributor.....................................................................18
Remove a Profile ..................................................................................................................................18
Create a Mesh Network........................................................................................................................18
2.8.2: Configuration and Programming Using SWIFT Tools .....................................................................19
Assign a Profile ....................................................................................................................................19
Remove a Profile ..................................................................................................................................20
Create a Mesh Network........................................................................................................................21
2.8.3: Profile Distribution............................................................................................................................21
After Creating a Profile ........................................................................................................................21
Activating the Profile Magnetic Sensor ...............................................................................................22
2.8.4: SLC Configuration ............................................................................................................................22
2.9: Operations....................................................................................................................................................22
2.9.1: Modes of Operation...........................................................................................................................22
Start-up Mode.......................................................................................................................................23
Factory Default Mode...........................................................................................................................23
Profile Configured ................................................................................................................................23
Mesh Formation....................................................................................................................................23
Initial Mesh Restructuring Mode..........................................................................................................24
Normal Mode........................................................................................................................................24
Rescue Mode ........................................................................................................................................24
Mesh Restructuring Mode ....................................................................................................................24
Bootloader Mode ..................................................................................................................................24
2.9.2: LED Patterns......................................................................................................................................24
2.9.3: Lock/Unlock the Gateway.................................................................................................................24
Lock/Unlock the Gateway at the FACP ...............................................................................................25
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 5
Page 6

Table of Contents
Lock/Unlock the Gateway Using SWIFT Tools ..................................................................................25
Password Reset .....................................................................................................................................25
2.9.4: Weak Link Trouble Reporting...........................................................................................................25
Disable Trouble Reporting at the Gateway Using SWIFT Tools.........................................................26
Disabling Trouble Reporting at the Panel ............................................................................................26
2.9.5: Collapse Network Command.............................................................................................................27
Collapse Mesh Network Using SWIFT Tools......................................................................................27
Collapse Mesh Network at the Panel....................................................................................................28
2.9.6: Silence Network Command...............................................................................................................28
Silence Mesh Network Using SWIFT Tools........................................................................................28
Silence Mesh Network at the Panel......................................................................................................29
2.9.7: Multiple Wireless Sensor Network Installation Restrictions.............................................................29
2.9.8: Avoiding RF Interference ..................................................................................................................29
2.9.9: Trouble Messages ..............................................................................................................................30
Events History Messages......................................................................................................................31
Section 3: Wireless Devices .................................................................................................. 33
3.1: Description...................................................................................................................................................33
3.2: Agency Approvals .......................................................................................................................................33
3.2.1: FCC....................................................................................................................................................33
3.2.2: Industry Canada ..............................................................................................................................34
3.2.3: Federal Institute of Telecommunications ..........................................................................................34
3.3: Specifications...............................................................................................................................................34
3.4: Installing, Mounting, and Wiring Devices...................................................................................................34
3.5: Configuration and Programming .................................................................................................................34
3.5.1: Assigning Profiles..............................................................................................................................34
Assigning a Profile to a Device (Detector or Module) Using a Gateway or Distributor......................35
Assigning a Profile Using SWIFT Tools..............................................................................................36
3.5.2: Distributor Mode ...............................................................................................................................37
Converting a Device into a Distributor.................................................................................................37
Converting a Distributor Back into a Device .......................................................................................37
3.5.3: Mesh Formation.................................................................................................................................37
Repeater ................................................................................................................................................38
3.5.4: Restoring a Device to Factory Default ..............................................................................................38
Removing Profiles Without Using SWIFT Tools ................................................................................38
Removing a Profile Using SWIFT Tools .............................................................................................38
3.6: Device Operations........................................................................................................................................39
3.6.1: Modes of Operation ...........................................................................................................................39
Factory Default Mode...........................................................................................................................39
Site Survey Mode .................................................................................................................................39
Profile Assigned Mode .........................................................................................................................39
Bootloader Mode ..................................................................................................................................40
Distributor Mode ..................................................................................................................................40
Mesh Participant Modes .......................................................................................................................40
3.6.2: LED Indicators...................................................................................................................................40
3.6.3: Trouble Conditions ............................................................................................................................40
Trouble Conditions with Fire Protection ..............................................................................................40
Trouble States without Fire Protection .................................................................................................41
3.6.4: Background Events............................................................................................................................42
Pre-Class A Fault..................................................................................................................................42
Device Drop..........................................................................................................................................42
Weak Link ............................................................................................................................................42
Section 4: USB Adapter ......................................................................................................... 43
4.1: Introduction..................................................................................................................................................43
4.2: Agency Approvals ......................................................................................................................................43
4.2.1: FCC....................................................................................................................................................43
4.2.2: Industry Canada ..............................................................................................................................44
6 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 7

Table of Contents
4.2.3: Federal Institute of Telecommunications ..........................................................................................44
4.3: Specifications...............................................................................................................................................44
4.3.1: Electrical Specifications ....................................................................................................................44
4.3.2: Serial Communication Specification .................................................................................................44
4.3.3: Mechanical Specifications.................................................................................................................44
4.3.4: Environmental Specifications............................................................................................................44
4.4: Driver Installation........................................................................................................................................45
Appendix A: SWIFT Tools...................................................................................................... 48
A.1: Description..................................................................................................................................................48
A.2: Launching SWIFT Tools.............................................................................................................................48
A.2.1: Creating a New Jobsite .....................................................................................................................49
A.2.2: Opening an Existing Jobsite .............................................................................................................50
Appendix B: Site Survey ........................................................................................................51
B.1: Conduct a Site Survey.................................................................................................................................51
B.1.1: Link Quality Test ..............................................................................................................................51
Basic Requirements of a Link Quality Test .........................................................................................51
Conduct a Link Quality Test ................................................................................................................51
Results of a Link Quality Test..............................................................................................................52
After a Link Quality Test .....................................................................................................................52
B.1.2: RF Scan Test.....................................................................................................................................53
Conduct an RF Scan Test .....................................................................................................................53
Status of an RF Scan Test.....................................................................................................................53
B.1.3: Retrieving Site Survey Results .........................................................................................................53
Appendix C: Troubleshooting and Testing ..........................................................................55
C.1: Troubleshooting ..........................................................................................................................................55
C.2: Testing the Gateway and Devices ...............................................................................................................57
C.2.1: Testing LED Indicators.....................................................................................................................57
C.3: Testing the Wireless Network .....................................................................................................................57
C.3.1: Network Topology............................................................................................................................57
Parent-Child Devices............................................................................................................................57
Orphan Devices ....................................................................................................................................58
Class A Compliance .............................................................................................................................58
C.3.2: History Events...................................................................................................................................58
C.3.3: Network Snapshots ...........................................................................................................................58
C.3.4: Network Statistics .............................................................................................................................58
C.3.5: Device Attributes ..............................................................................................................................58
Appendix D: LED Indicators ..................................................................................................59
Index.........................................................................................................................................63
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 7
Page 8

Section 1: Overview
1.1 Purpose
The SWIFT™ Network Manual provides an overview of the following:
• Wireless fire alarm system
• Instructions for installing and configuring the wireless devices
• Information on monitoring the status of the wireless devices
• Removal and replacement procedures of the Wireless Gateway
• Testing, maintenance, and firmware upgrade information of the Wireless Gateway
1.2 Assumed Knowledge
This document is created with the assumption that all users are familiar with working on a PC and
laptop for configuration purposes. Installers should be familiar with the fire alarm and related service standards. The terminology and level of details of this document reflect this assumption.
1.3 Additional References
The table below provides a list of documents referenced in this manual, as well as documents for
selected other compatible devices.
Honeywell SLC Wiring Manual 51932
XLS3000 Fire Alarm Control Panel LS10006-052XL-E
XLS-NCA2 Network Control Annunciator 52561
XLS140-2 Fire Alarm Control Panel LS10010-052XL-E
XLS120 Fire Alarm Control Panel LS10011-052XL-E
TC806W1000 Wireless FlashScan Photo Detector I56-4077
TC840W1000 Wireless FlashScan Photoelectric Detector I56-4077
TC808W1000 Wireless FlashScan Rate of Rise Heat Sensor I56-4078
TC808W2010 Wireless FlashScan Fixed Heat Sensor I56-4078
TC809W1000 Wireless FlashScan Monitor Module I56-4079
TC810WR1000 Wireless FlashScan Relay Module I56-
B210W Wireless Detector Base I56-4064
Table 1.1 Related Documentation
1.4 About the Mesh Network
Use of these products in combination with non-Honeywell products in a wireless mesh network, or
to access, monitor, or control devices in a wireless mesh network via the internet or another external wide area network, may require a separate license from Sipco, LLC. For more information, contact Sipco, LLC or IntusIQ (Ipco), LLC at 8215 Roswell Rd, Building 900, Suite 950. Atlanta, GA
30350, or at www.sipcollc.com or www.intusiq.com.
8 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 9
Abbreviations Overview
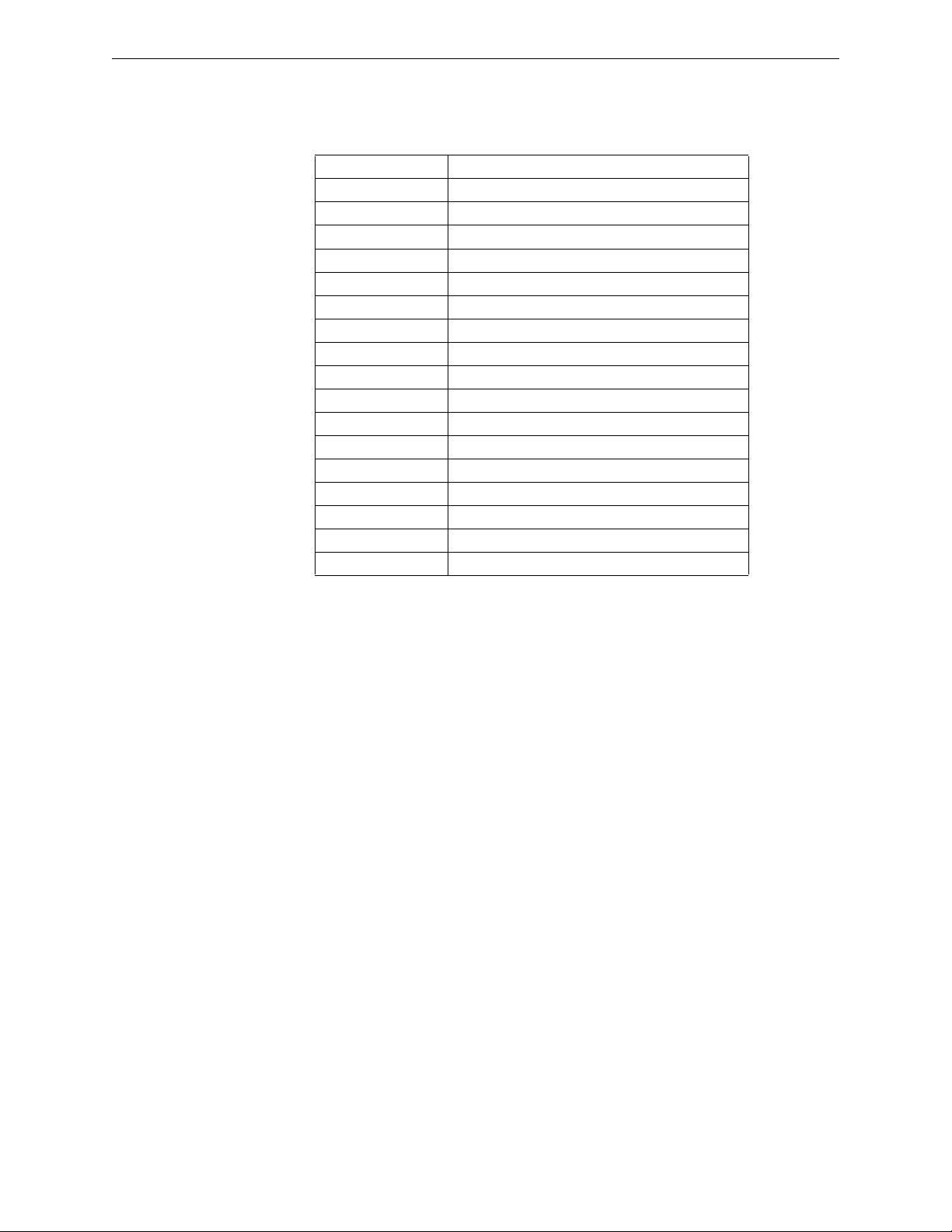
1.5 Abbreviations
The following table lists the abbreviations and their definitions used in this manual.
Abbreviation Definition
AHJ Authority Having Jurisdiction
ANSI American National Standards Institute
dBm Units of RF power (0dBm = 1mW)
FACP Fire Alarm Control Panel
FCC Federal Communications Commission
ISM Band Industrial, Scientific and Medical Radio Bands
LCD Liquid Crystal Display
LED Light Emitting Diode
mA Milliampere
MHz Megahertz
NFPA National Fire Protection Association
PC Personal Computer
RF Radio Frequency
SLC Signaling Line Circuit
UI User Interface
UL Underwriters Laboratories
XLS-WSG Wireless Sensor Gateway
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 9
Page 10
Section 2: XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway
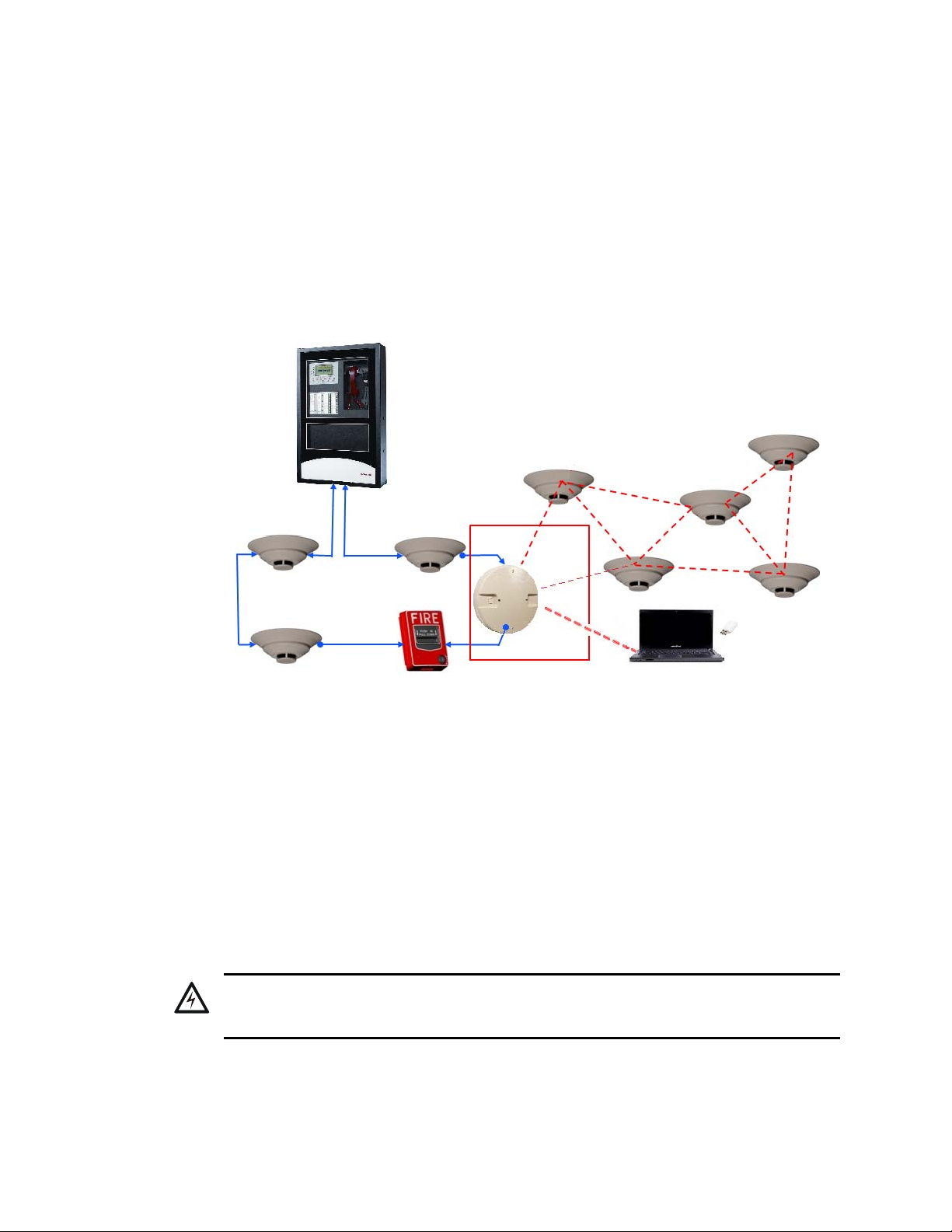
Figure 2.1 SWIFT Network
FACP
SLC
wired SLC devices
XLS-WSG
Gateway
wireless mesh
network
SWIFT
Tools
xlswirelessfirealarmsystem_gateway.png
USB adapter
!
2.1 Description
The XLS-WSG is a device in a wireless fire system that acts as a bridge between fire alarm control
panels (FACPs) and wireless fire devices. All wireless fire devices communicate with the gateway
over the wireless network formed by the devices and the gateway.
The gateway is powered by either the SLC loop or by any external +24VDC UL listed power supply. The gateway uses the FlashScan protocol on the SLC to communicate with the panel and a proprietary wireless protocol to communicate with wireless fire devices. The following graphic is an
illustration of the components of the SWIFT Network.
2.2 Agency Approvals
2.2.1 FCC
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
2.2.2 Industry Canada
10 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
1. This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
FCC ID: PV3WFSGW
WARNING: DO NOT MAKE CHANGES TO THE EQUIPMENT
CHANGES OR MODIFICATIONS NOT EXPRESSLY APPROVED BY THE MANUFACTURER
COULD VOID THE USER’S AUTHORITY TO OPERATE THE EQUIPMENT.
This device complies with Industry Canada license-exempt RSS standard(s). Operation is subject to
the following two conditions:
Page 11
Specifications XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway
1. This device may not cause interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause undesired
operation of the device.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d'Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio
exempts de licence. L'exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes :
1. L'appareil ne doit pas produire de brouillage, et
2. L'utilisateur de l'appareil doit accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique subi, même si le
brouillage est susceptible d'en compromettre le fonctionnement.
IC: 12252A-WFSGW
2.2.3 Federal Institute of Telecommunications
This device utilizes the Honeywell915 rev A radio module and complies with IFETEL standard(s).
IFT: RCPHOSW14-1983
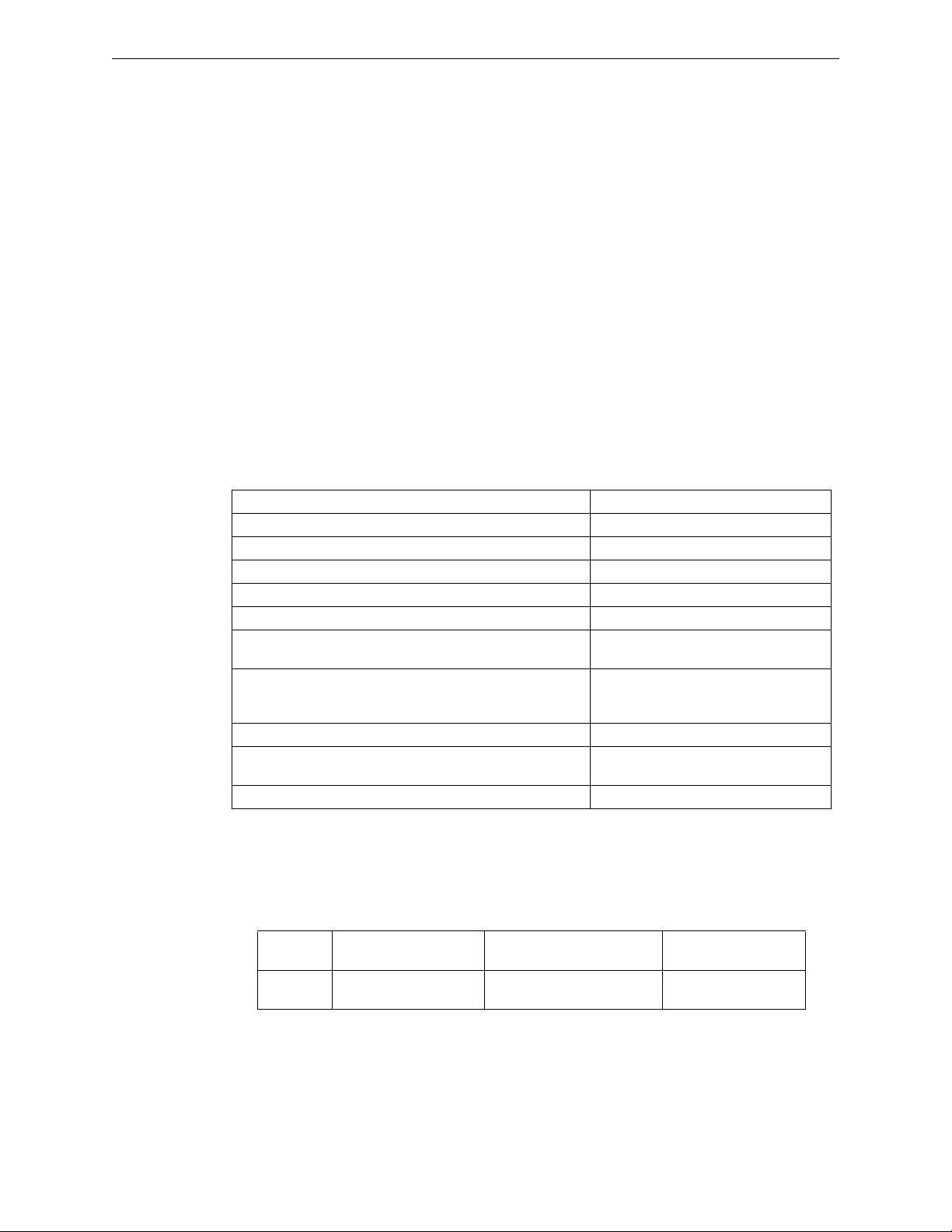
2.3 Specifications
Following are the specifications of the wireless gateway.
Specifications Data
External Supply Electrical Ratings 18V-30V
SLC Electrical Ratings 15V-30V
Maximum current when using the external supply 40mA
Maximum current when using the SLC power supply 24mA
Maximum SLC Resistance 50Ω
Minimum signal strength level needed at the receiver for a
primary path with weak link trouble reporting enabled.
Minimum signal strength level needed at the receiver for a
secondary path or primary path with weak link trouble
reporting disabled.
Maximum ambient noise level -85dBm
Maximum RF Power Output +17dBm (Tx power level without
Radio Frequency Lower ISM Band (902 - 928MHz).
1 Ensure that the primary path signal strength level is within recommended guidelines
to assure proper communication in the mesh network.
2.3.1 Environmental Specifications
System
Gateway 0°C-49°C / 32°F-120°F -10°C- 60°C / 14°F-140°F 10 to 93% RH
Operating
Temperature
Storage
Temperature
-55dBm
Must be 18 dBm higher than the noise
floor down to a minimum of -80dBm
1
antenna)
Humidity
Non-condensing
1
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 11
Page 12
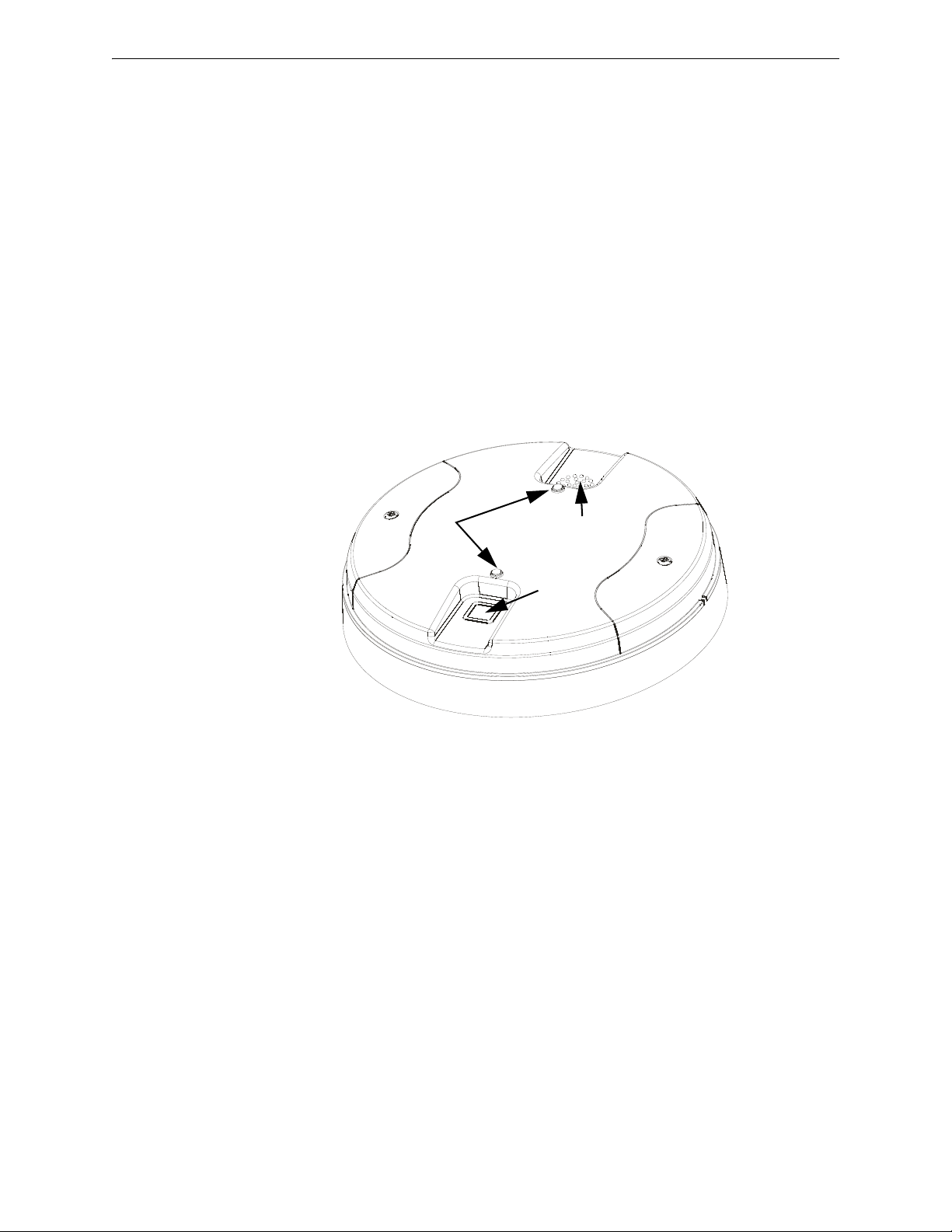
XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway Magnet Sensors
Figure 2.2 LEDs and Magnetic Sensors on the XLS-WSG
LEDs
Mesh
Formation
Magnetic
Sensor
Profile
Magnetic
Sensor
cover.wmf
2.4 Magnet Sensors
2.4.1 Profile Magnetic Sensor
The profile magnetic sensor (refer to Figure 2.2) is used to create a unique profile upon start-up. It
can also be used to start profile distribution for a gateway that contains a profile. The LED next to
the profile magnet sensor turns on green for ½ a second when the sensor is activated.
2.4.2 Mesh Formation Magnetic Sensor
The mesh formation magnetic sensor (refer to Figure 2.2) toggles the gateway in and out of mesh
formation mode. The initial activation of the sensor puts the gateway in mesh formation mode (as
long as it contains a profile). A subsequent activation of the magnetic sensor toggles the gateway
out of mesh formation and into the initial mesh restructuring and normal mode. The gateway can be
placed back into mesh formation mode by activating the magnet sensor once again. The LED next
to the profile magnet sensor turns on green for ½ a second when the sensor is activated.
The Mesh formation magnetic sensor can also be used to create a profile on start-up for a gateway
that does not already contain a profile.
2.5 LED Indicators
The two LEDs on the gateway blink in the same pattern to allow the LED to be viewed from any
angle. LED patterns are explained in Appendix D.
2.6 Installing the Gateway
2.6.1 Before Installing
Choose a location for the gateway that is clean, dry, and vibration-free. The area should be readily
12 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
accessible with sufficient room to easily install and maintain the gateway. Metal obstructions
impede the radio frequency communication and should be avoided. Carefully unpack the system
and inspect for shipping damage if any. All wiring must comply with the national and local codes
for fire alarm systems.
Page 13
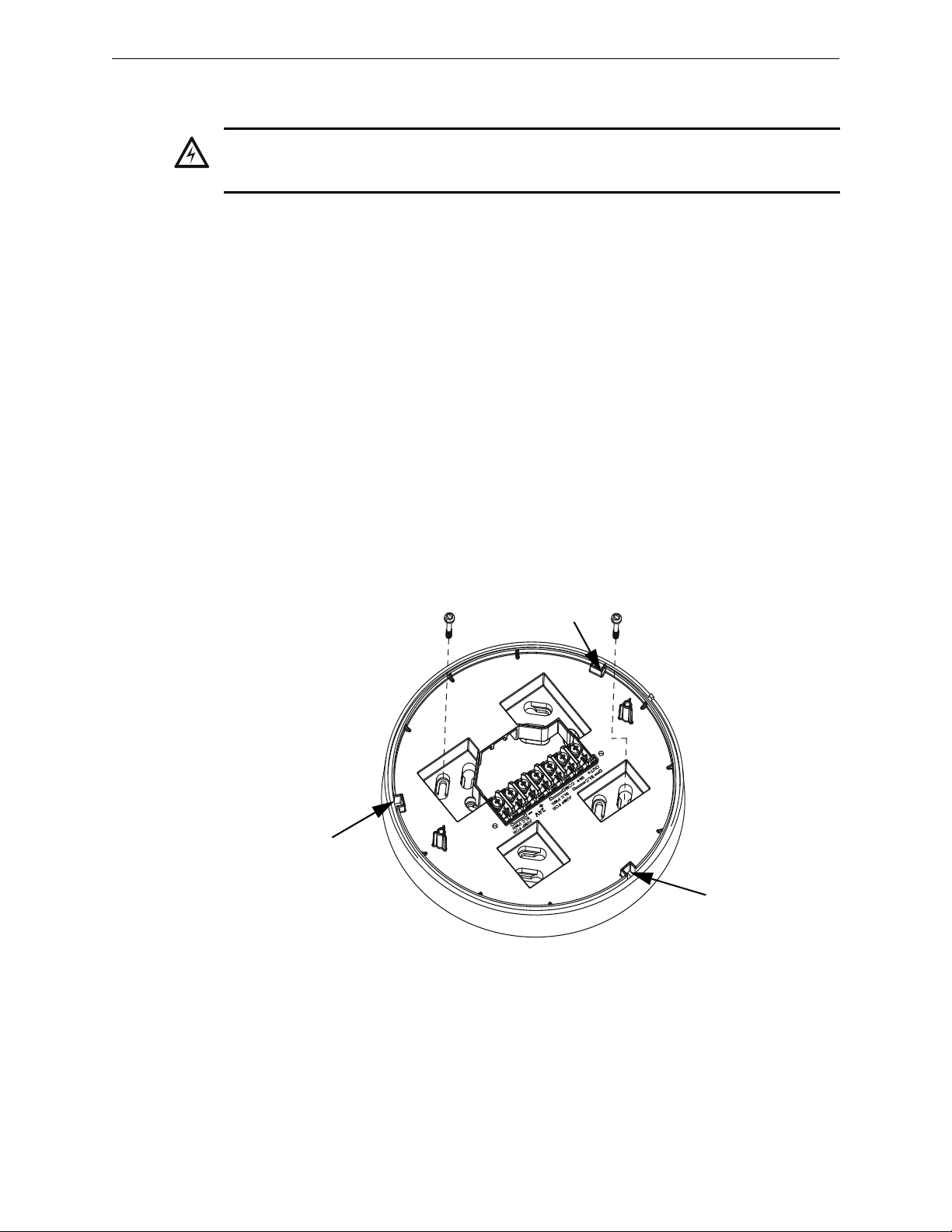
Mounting and Wiring XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway
!
Figure 2.3 Mounting Plate for Wireless Gateway
2.2.wmf
locating pin
locating pin
locating pin
2.7 Mounting and Wiring
WARNING: FORMEX SHEET
ENSURE THAT THE FORMEX SHEET INSIDE THE GATEWAY IS NOT REMOVED OR
TAMPERED WHILE INSTALLING OR CLEANING.
2.7.1 Mounting
The gateway has two major pieces, the cover and the mounting plate. The mounting plate is
mounted to the wall or ceiling, and field wiring is connected to it. The cover contains the printed
circuit board and is fastened to the mounting plate once the wiring is completed.
Mount the mounting plate directly to an electrical box on the ceiling or wall. The plate mounts
directly to a 4˝ square (with and without plaster ring), 4˝ octagon, 3 1/2˝octagon, single gang or
double gang junction boxes. If an electrical box is not available, the mounting plate can be mounted
to any flat surface and the wiring can be connected via the knockout points in the mounting plate.
To mount the gateway:
1. Pull the wiring through the opening in the mounting plate.
2. Mount the mounting plate to the junction box or ceiling. See Figure 2.3 below.
3. Connect field wiring to the terminals, as described in Section 2.7.2.
4. Connect necessary jumpers where applicable, as described in Section 2.7.3.
5. To mount the cover, align the locating pins on the cover to the corresponding slots in the
mounting plate. See Figure 2.4.
6. Secure the cover by tightening the mounting screws.
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 13
Page 14
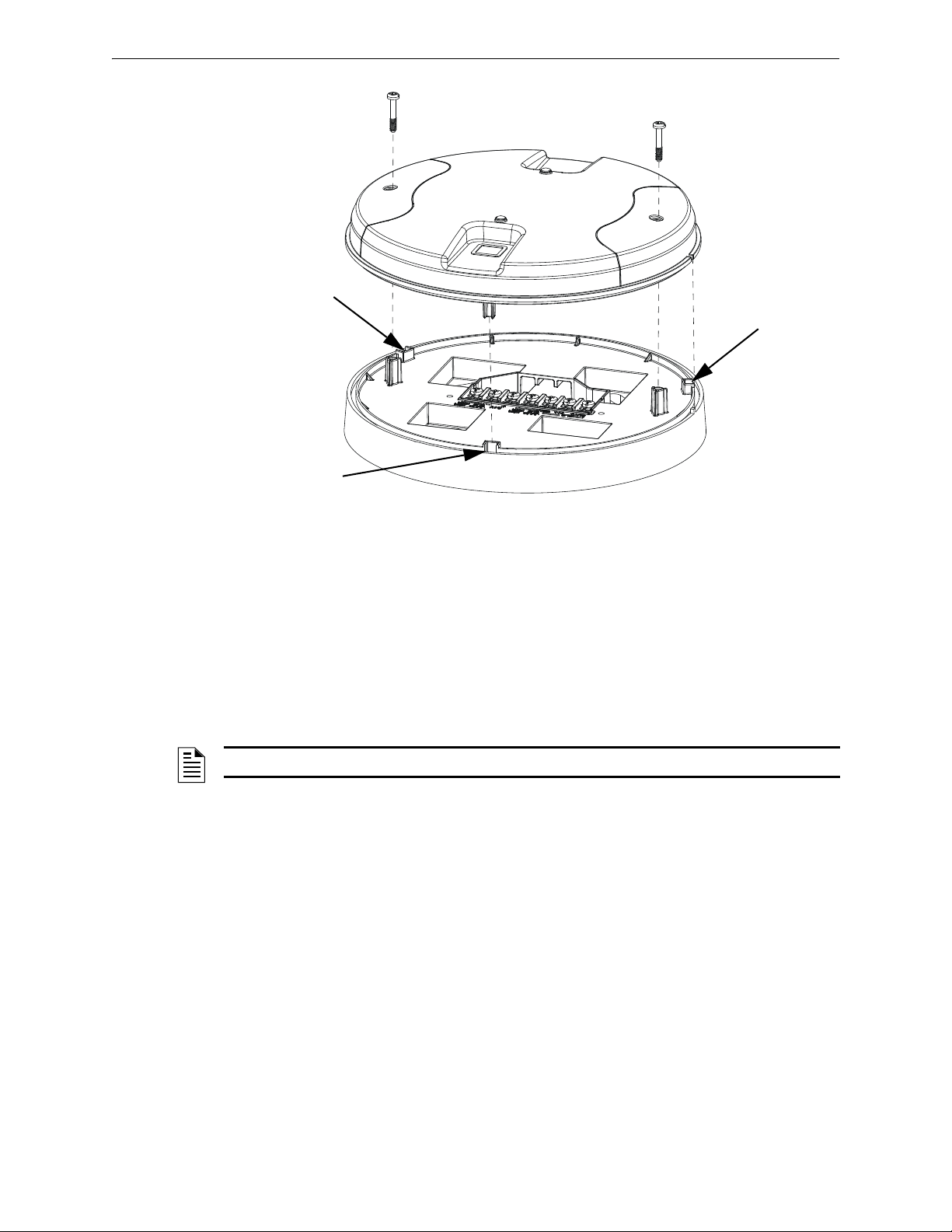
XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway Mounting and Wiring
Figure 2.4 Attaching Cover to Mounting Plate
2.3.wmf
locating pin
locating pin
locating pin
2.7.2 Wiring
• All wiring must be installed in compliance with the National Electrical Code and the local
codes having jurisdiction.
• 12-18 AWG is recommended.
For wiring connections:
1. Strip about 3/8” of insulation from the end of the wire.
2. Slide the stripped end of the wire under the appropriate terminal and tighten the screw.
NOTE: Do not loop the wire under the screw terminals.
14 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 15
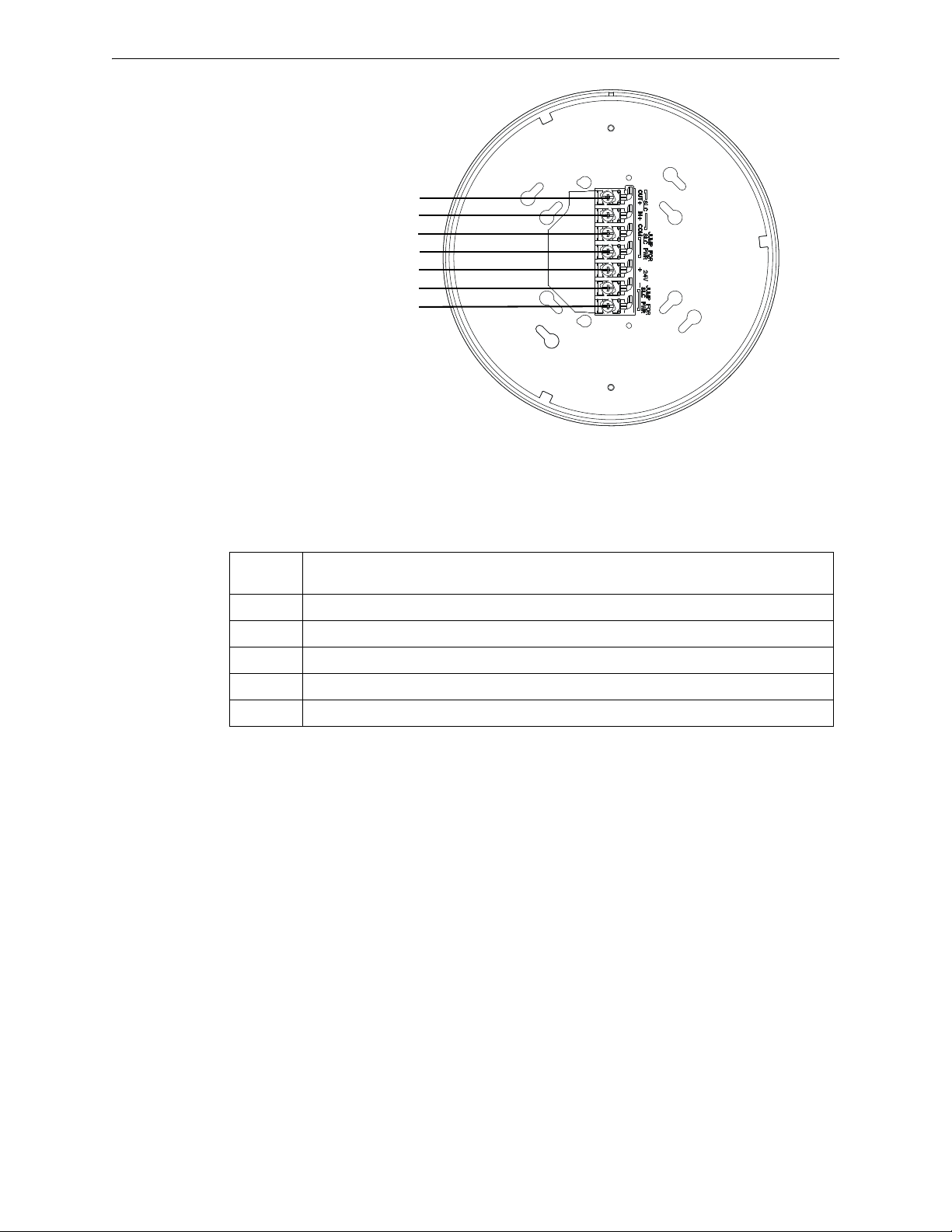
Mounting and Wiring XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway
Figure 2.5 XLS-WSG Mounting Plate - Terminal Layout
A7 - SLC Out+/In+
A6 - SLC In+/Out +
A5 - SLC- (Common)
A4 - SLC Power Select 2
A3 - Power +24VDC
A2 - Power Ground
A1 - SLC Power Select 1
2.4.wmf
2.7.3 Gateway Powered by the SLC
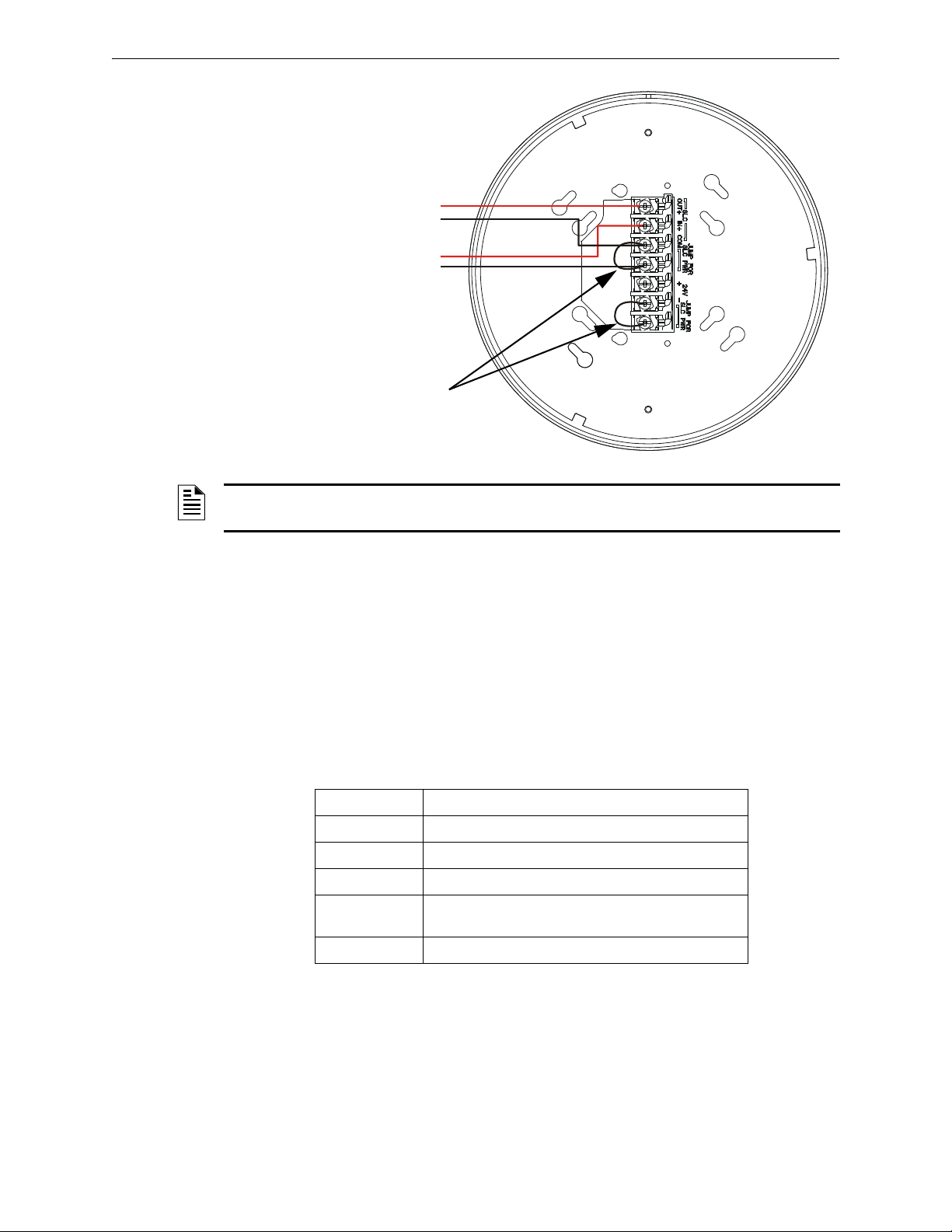
To power the gateway using the signaling line circuit, connect the gateway as described in the table
and graphic below:
Ter min al
Pins
A5 and A7 SLC - (Common) & SLC Output +
A5 and A6 SLC - (Common) & SLC Input +
A4 and A5 Jumper selection to enable power from the SLC supply. (Insert Jumper when using SLC power.)
A3 Unused
A1 and A2 Jumper selection to enable power from the SLC supply. (Insert Jumper when using SLC power.)
Description
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 15
Page 16
XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway Mounting and Wiring
+
+
-
-
Figure 2.6 Wiring Connections: XLS-WSG Powered by the SLC
SLC out to next device (Class B)
or SLC return to FACP (Class A)
SLC in from FACP/device
jumpers
2.5.wmf
NOTE: Use of the same wire gauge is recommended if there are multiple connections to the
same terminal.
The gateway provides isolation of short circuits on the SLC in Class A (Style 6) installations. SLC
connections are power-limited by the panel. An interruption in the SLC that causes a loss of power
at the gateway for more than 100ms may result in a trouble condition and loss of fire protection
provided by the wireless devices for approximately 15 minutes. Use of an external +24V power
source (not SLC power) is recommended for installations that require fire protection in the presence of short circuits, including Class A applications and applications that use isolator modules.
Refer to the SLC Wiring Manual for more information on wiring using isolators.
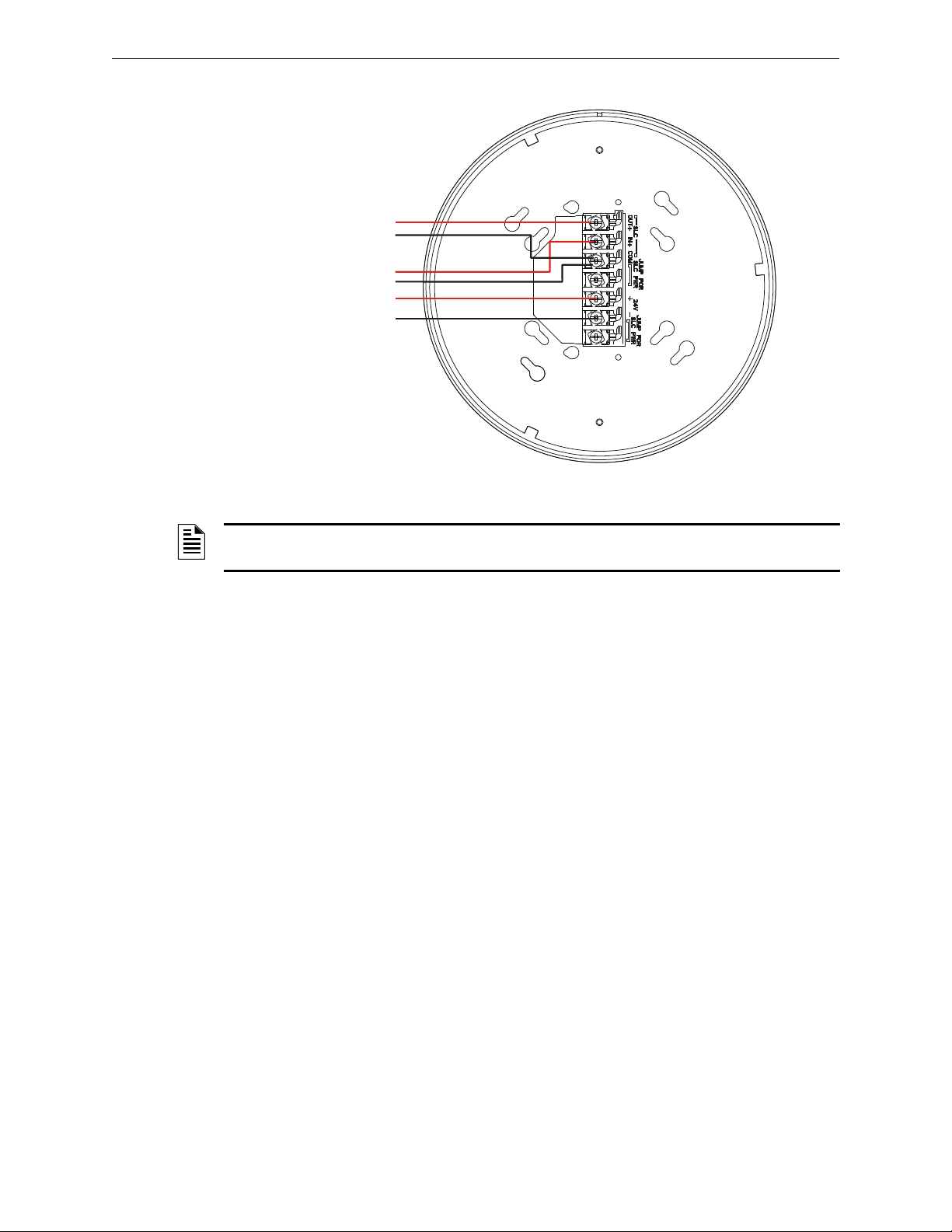
2.7.4 Gateway Powered by an External, Regulated +24VDC Source
To power the gateway using an external, regulated +24VDC source, connect the gateway as
described in the table and drawing below.
Terminal Pins Devices Powered
A5 & A7 SLC Output
A5 & A6 SLC Input
A4 Unused
A2 & A3 +24VDC input. Voltage range from +18VDC to +30VDC.
Use only power-limited device circuits.
A1 Unused
16 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 17
Configuration and Programming XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway
+
+
-
-
+
-
Figure 2.7 Wiring Connections: XLS-WSG Powered by an External, Regulated +24VDC Source
SLC in from FACP/device
External +24VDC Power
SLC out to next device (Class B)
or SLC return to FACP (Class A)
2.6.wmf
NOTE: It is recommended to use the same wire gauge if there are multiple connections to the
same terminal.
The gateway provides isolation of short circuits of the SLC in Class A (Style 6) installations. SLC
connections are power-limited by the panel. +24VDC must be power-limited by the source.
2.8 Configuration and Programming
To successfully configure and/or program the gateway:
1. Create a profile. A profile binds a gateway and the devices in a mesh network together. The
profile will contain a mesh ID that is used when forming the associations. All devices,
including the gateway, require a common profile.
2. Distribute the profile. Distribute the profile to every device that will be a part of the mesh. This
will enable all the devices that have that profile to form associative links when the mesh is
formed.
3. Form the mesh. The mesh cannot be formed until the profile is assigned to the gateway and
distributed to its devices.
These steps may be performed with or without using SWIFT Tools.
2.8.1 Configuration and Programming Without Using SWIFT Tools
This section explains the configuration of the gateway using only a magnet and a screw driver. For
configuration instructions using SWIFT Tools, refer to Section 2.8.2.
There are two ways to provide a gateway with a profile without using SWIFT Tools.
Create a new profile using the gateway.
Assign a previously created profile to the gateway using a distributor.
Create a New Profile
To create a unique profile in the gateway without using SWIFT Tools:
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 17
Page 18

XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway Configuration and Programming
1. Start with the gateway powered off. The profile creation process is performed during start-up.
2. Power on the gateway using SLC power or external +24V. Refer to Sections 2.7.3 and 2.7.4 for
more information.
3. Ensure that the gateway is in the factory default state. If the gateway is in the factory default
state, both the LEDs on the gateway will double blink red every second for ten seconds. If the
LEDs are yellow, refer to “Remove a Profile” on page 18.
4. Activate either magnetic sensor with a magnet within ten seconds of starting up the gateway
while the double red blink is active on the gateway. Refer to Section 2.4, “Magnet Sensors” for
further information on activating magnetic sensors. The LED next to the magnetic sensor emits
a red light for one second when it is activated. If the ten second window is missed, power
down the gateway and repeat the process starting at step 1.
A profile has been created successfully; the LEDs on the gateway will light green and stay on
steady for ten seconds. The profile has been created containing a mesh ID and a default password.
The default password is ‘12345’ and is needed if the gateway is locked by the FACP and later
accessed by SWIFT Tools.
Immediately after successful profile creation, the gateway starts the profile distribution mode.
Refer to Section 2.8.3 for further information on profile distribution mode.
Assign a Previously Created Profile Using a Distributor
Instead of creating a new profile, an existing profile can be distributed by a device with an existing
profile. To distribute the existing profile:
1. Ensure that the gateway or other mesh device with the profile is set for distribution. Refer to
Section 2.8.3, “Profile Distribution” or Section 3.5.2, “Distributor Mode”.
2. Bring the profile distributor within 20 feet of the gateway.
3. 10 seconds after the initial start-up, the LEDs on the gateway switch from a double red blink to
a single red blink. The single red blink indicated the gateway is ready.
4. Use a magnet to activate either of the magnetic sensors. The LED will blink a single red every
half-second indicating that it is searching for a profile.
When the profile is successfully received from the distributor, the LEDs on the gateway will turn
on green steady for five seconds.
Remove a Profile
To remove a profile from a gateway:
1. Start with the gateway powered off. The process is performed during start-up.
2. Power on the gateway using SLC power or external +24V. Refer to Sections 2.7.3 and 2.7.4
for more information.
3. Verify the gateway is in the profile modification state. The gateway is in the profile
modification state when both the LEDs on the gateway double blink yellow every second for
ten seconds.
4. Activate both magnetic sensors on the gateway within ten seconds of start-up while the double
yellow blink is active. If the ten second window is missed, power down the gateway and repeat
the process starting at step 1.
The LEDs on the gateway will blink green every second for five seconds indicating that the profile
is removed.
Create a Mesh Network
The gateway communicates with all devices in range that have a common profile and establishes
communication links with all the devices. This creates a mesh network. Once a device joins the
mesh, that device acts as a repeater for devices out of the range of the gateway. All devices must be
18 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 19
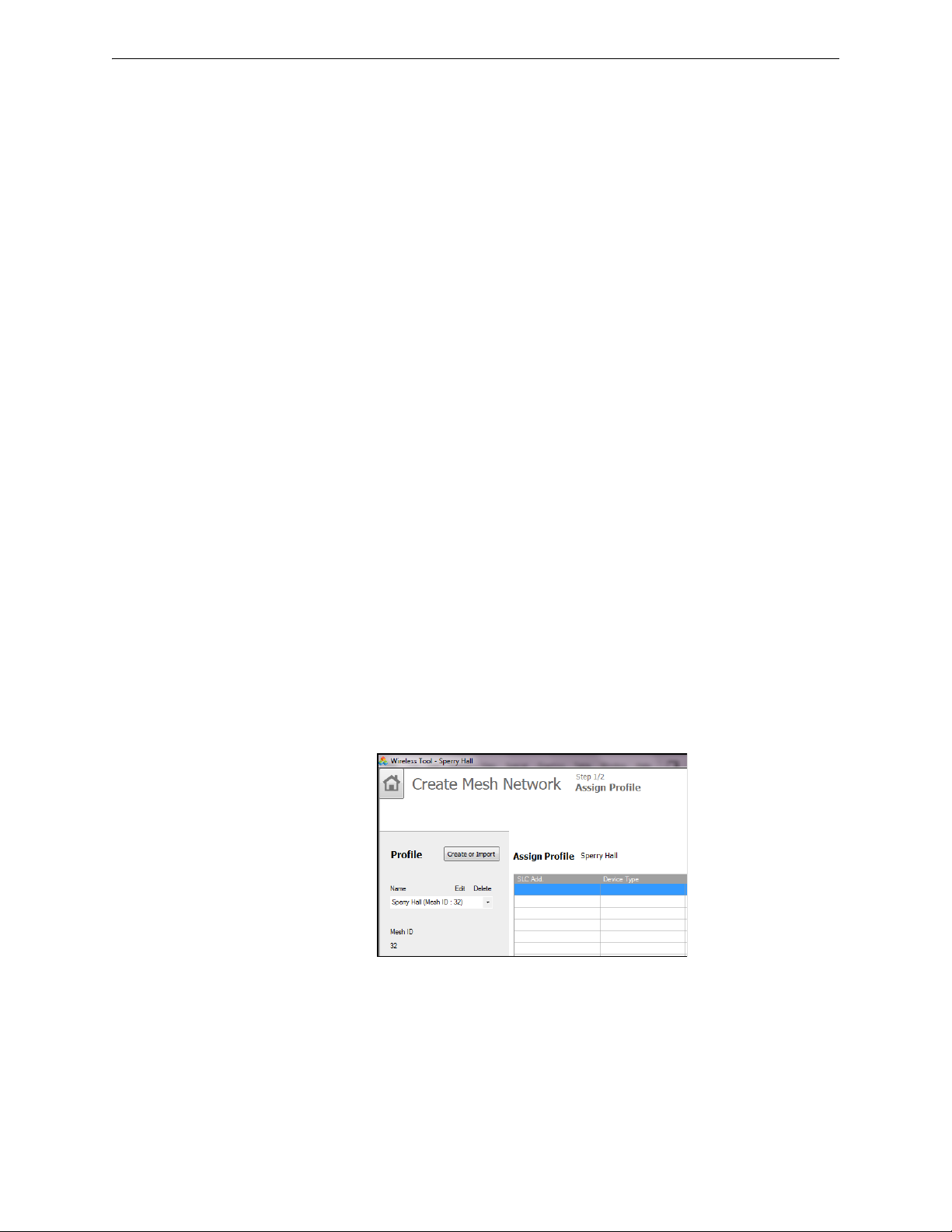
Configuration and Programming XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway
Figure 2.8 Creating or Importing a Profile
createprofile.wmf
in their final mounting locations prior to initiating the mesh formation. The mesh formation is
initiated by the gateway upon user activation and terminated by the gateway when all possible
devices join the network or when terminated by the user.
To form a mesh network, ensure that the gateway is powered on and contains a profile. (Refer to
Section 2.5 on page 12 for information on how the gateway indicates its status). Activate the “Mesh
Formation” magnet sensor on the gateway. Refer to Figure 2.2 for sensor location.
The gateway will then transition to the mesh formation mode and establish communication with all
the devices containing a common profile. The blink pattern on the gateway indicates that it is in
mesh formation mode. At this stage, both the LEDs on the gateway will blink twice every 7 seconds.
• The first blink is green and the second blink is red when the gateway is acting as a profile
distributor and forming the mesh.
• The first blink is green and the second blink is yellow when the gateway is only forming the
mesh.
Mesh formation typically takes one minute for each device in the mesh. Mesh formation automatically terminates 10 minutes after the last device joins the mesh. Mesh formation can be terminated
manually by the user by again activating the mesh formation magnetic sensor.
Once the mesh formation is complete, the network automatically transitions to restructure the
mesh. For operating instructions, refer to Section 2.9, “Operations”.
2.8.2 Configuration and Programming Using SWIFT Tools
Assign a Profile
To assign a profile to the gateway using SWIFT Tools:
1. Connect the W-USB dongle device to your laptop. For more information on the USB dongle,
refer to Section 4, “USB Adapter”, on page 43.
2. Launch SWIFT Tools. Refer to Appendix A for more information.
3. From the Home Screen, select the Create Mesh Network function.
4. Create a new profile or Import an existing profile as required.
5. Select and open the profile to be assigned to the gateway from the Name drop-down box in the
Profile section.
6. Power on the gateway within approximately 20 feet of the laptop running SWIFT Tools.
7. Ensure that the Scan On selection box in the Communicator Window is checked.
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 19
Page 20
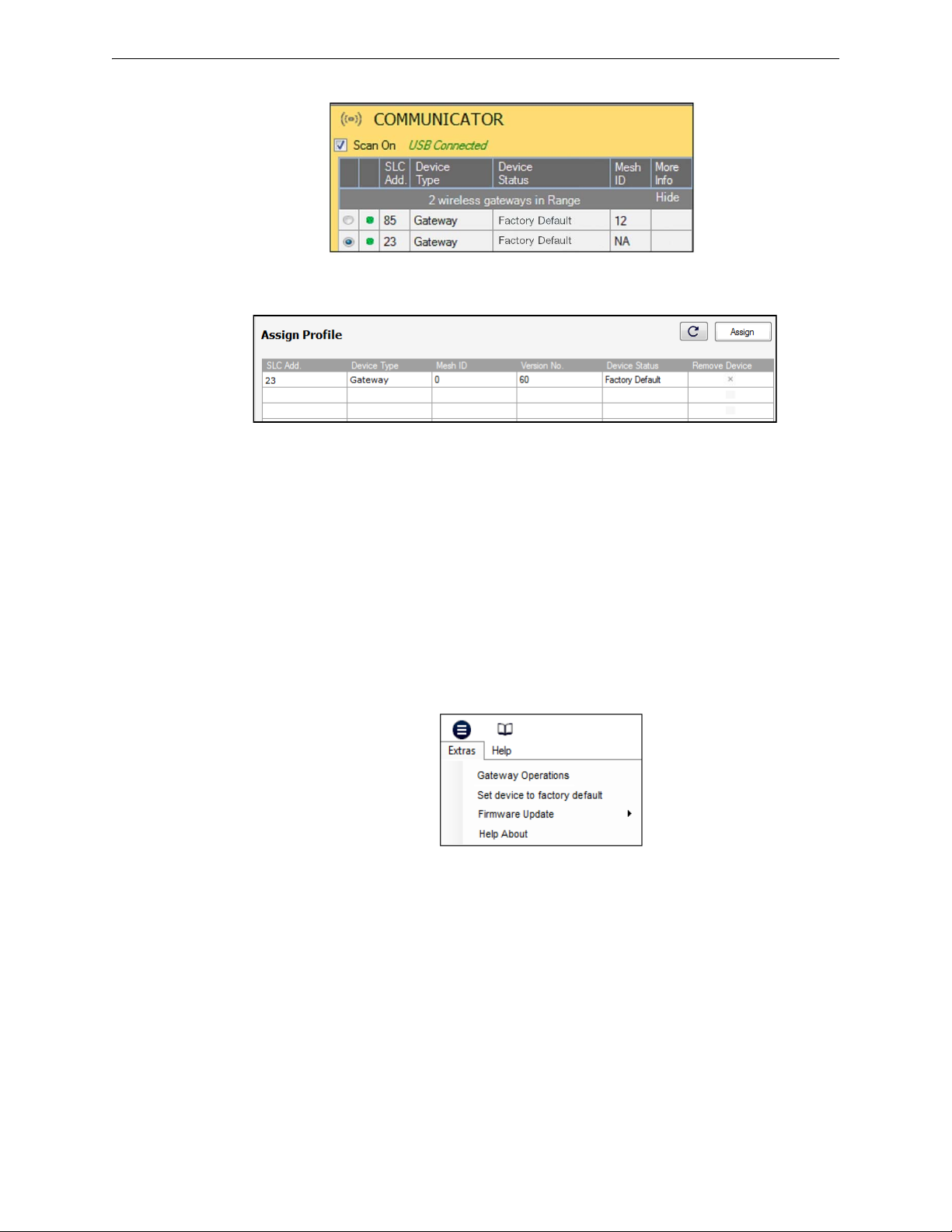
XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway Configuration and Programming
Figure 2.9 Gateway Selection
selcomm.png
assignprofile_III.png
Figure 2.10 Assign a Profile
extras.png
Figure 2.11 Extras Menu
8. Select the gateway from the Communicator Window on the right side of the Tools screen.
9. Click Assign.
The gateway is now included in the list of devices with a profile assigned. The LEDs on the gateway will turn on green for 10 seconds after the profile has been received.
Remove a Profile
To remove a profile from a gateway using the SWIFT Tools application:
1. Connect the W-USB dongle device to your laptop. For more information on the USB dongle,
refer to Section 4, “USB Adapter”, on page 43.
2. Launch SWIFT Tools. Refer to Appendix A, “SWIFT Tools” for more information on
launching the SWIFT Tools application.
3. From the Home Screen, select the Site Survey, Create Mesh Network, or Diagnostics
function.
4. Click Extras and select Set device to factory default.
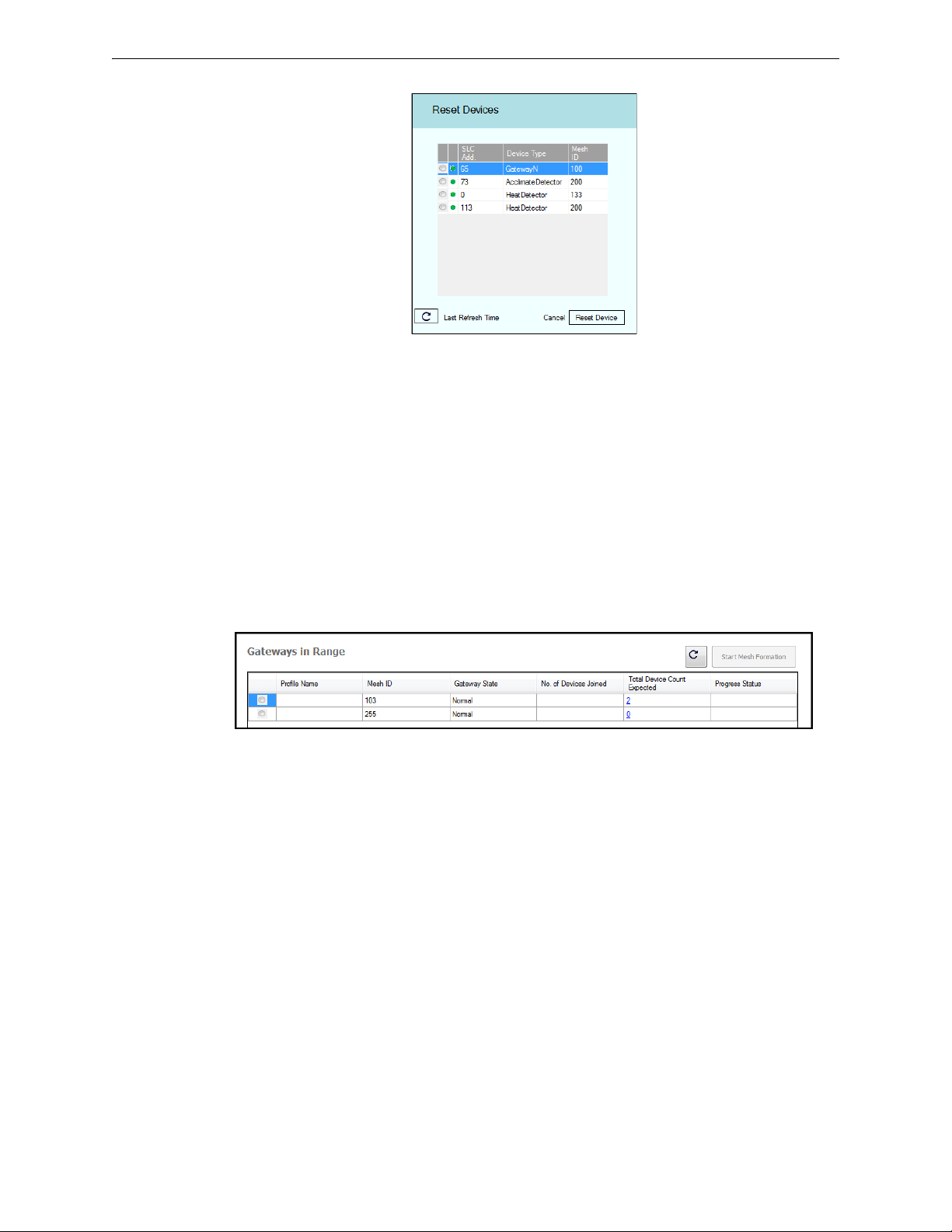
5. The Reset Devices screen appears, displaying the gateway and other devices that have a
profile assigned. Click to select the gateway and click Reset Device to remove the profile.
20 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 21
Configuration and Programming XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway
resetdevices.png
Figure 2.12 Reset Devices Screen
meshoptools.png
Figure 2.13 Gateways in Range Table
The profile is removed and the gateway is reset to factory default state.
Create a Mesh Network
To create a mesh network using the SWIFT Tools, perform the following steps.
1. Connect the W-USB dongle device to your laptop. For more information on the USB dongle,
refer to Section 4, “USB Adapter”, on page 43.
2. Launch SWIFT Tools. Refer to Appendix A for more information.
3. From the Home Screen, select the Create Mesh Network function.
4. Proceed to the second step of the Create Mesh Network function by clicking the arrow
marked Next at the top of the screen.
5. Click to select the desired gateway displayed in the Gateways in Range table and then click
Start Mesh Formation.
While the mesh is formed, SWIFT Tools helps track the number of devices that have joined the
mesh and view the progress. Mesh formation terminates 10 minutes after the last device joins the
mesh. In addition, mesh formation can be manually terminated by clicking the Start Mesh
Restructuring button.
Once mesh formation is complete, the network automatically transitions to restructure the mesh.
For further operating instructions, refer to Section 2.9, “Operations”.
2.8.3 Profile Distribution
There are two ways to initiate profile distribution from the gateway.
• Automatically after creating a profile if the profile was not created by SWIFT Tools
• Activating the profile-creating magnetic sensor when the gateway has a profile.
After Creating a Profile
Profile distribution is automatically enabled from the gateway after creating a profile using either
magnetic sensor upon the gateway’s start-up. The profile distribution automatically terminates after
10 minutes.
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 21
Page 22

XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway Operations
TENS
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
ONES
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Figure 2.14 Address Rotary Switches
SLC-setaddtph.wmf
Figure 2.15 Gateway Modes Of Operation
opmodes.wmf
Start-up
Factory
Default
Profile
Configured
Mesh
Formation
Initial Mesh
Restructuring
Normal
Mode
Mesh
Restructuring
Rescue
Mode
Fire Protection Provided
Activating the Profile Magnetic Sensor
Activating the profile magnetic sensor (refer to Figure 2.2) when the gateway has a profile will put
the gateway in a mode of distributing the profile to any device that requests a profile. The gateway’s LED pattern will be altered when it is distributing a profile for easy identification. Profile
distribution will automatically terminate after 10 minutes. For more information on gateway LED
patterns, refer to Section 2.5 on page 12.
2.8.4 SLC Configuration
The gateway:
communicates with the control panel via the SLC.
is a FlashScan-only device.
does not support CLIP mode.
is only compatible with FACPs version 24 or higher.
occupies one module SLC address. Set the address using the rotary dials on the gateway
prior to installation.
The SLC point uses the following configuration parameters:
• Module Type: Monitor
• Type Code Label: RF GATEWAY
• FlashScan Type: RF GATEWAY
A gateway does not initiate alarms but the point is used for event reporting.
2.9 Operations
2.9.1 Modes of Operation
22 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 23

Operations XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway
Start-up Mode
Start-up mode is a temporary mode of operation. During start-up mode a profile can be created or
removed. The start-up period lasts for 10 seconds. If a particular unit contains a profile, the LEDs
double blink yellow every second. If the unit does not contain a profile, the LEDs double blink red
every second.
During start-up, the gateway does not provide fire protection nor does it respond to the FACP.
After start-up, the gateway proceeds to the factory default mode if no profile exists. In the presence of a profile, the gateway will proceed to mesh formation mode if it was previously part of a
mesh network or normal mode if it was not previously part of a mesh network.
Factory Default Mode
Factory default mode is the initial mode of the gateway. In this mode, the gateway and peripheral
devices do not provide any fire protection. The gateway does not communicate with wireless detectors or modules in factory default mode. The only wireless communication in factory default mode
is between the gateway and SWIFT Tools. SWIFT Tools must be within 20 feet of the gateway for
proper communication. The gateway must be assigned a profile before continuing configuration.
The gateway reports a ‘PROFILE MISSING' or ‘PR MIS’ trouble to the FACP. The gateway
reports “Factory Default” to the communicator display of SWIFT Tools.
Profile Configured
The gateway enters the profile configured mode once a profile is assigned by SWIFT Tools or a
distributor; or after creating a profile using the magnetic sensor. Profile configured mode is a temporary mode before the gateway transitions to mesh formation or normal mode.
The gateway does not provide fire protection in the profile configured mode. While in the profile
configured mode, the gateway reports a "MESH NOT FORMED" or "NO MSH" trouble to the
FACP. The gateway reports “Profile Assigned” to the communicator display of the SWIFT Tools
application.
Mesh Formation
The gateway must have a profile before entering mesh formation mode. The gateway and the
peripheral devices do not provide any fire protection in this mode. The gateway enters mesh formation mode:
after creating a profile using the mesh formation sensor.
after activating the mesh formation sensor with a magnet when the gateway contains a
profile.
automatically after start-up when the gateway was previously part of a mesh.
by a command from the SWIFT Tools application.
by a command from the FACP.
A gateway in mesh formation mode instructs all devices in the mesh to also transition to mesh formation mode. The gateway and all communicating devices search for new or lost devices with the
same profile to join the network.
If the gateway automatically entered mesh formation after start-up, mesh formation will terminate
10 minutes after the last device has joined or after all existing devices are recovered. If new
devices are found or if mesh formation was initiated by the user, then mesh formation terminates
after a period of 10 minutes without any new devices joining the mesh. At any point Mesh formation can be terminated by user interaction by activating the magnet sensor again, by using the
SWIFT Tools application, or by using the FACP.
The gateway reports a “NO WIRELESS DEVS” or “NO DEV” trouble when it is in Mesh Formation mode without any attached devices. The gateway reports a “MESH IS FORMING” or “MS
FRM” trouble when it is mesh formation mode with additional devices in the mesh. The gateway
reports “Mesh Formation” to the communicator display of the SWIFT Tools application.
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 23
Page 24

XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway Operations
Initial Mesh Restructuring Mode
Initial mesh restructuring mode automatically runs after each mesh formation. The gateway and
peripheral devices do not provide fire protection during the initial mesh restructuring mode. Mesh
restructuring analyzes signal strengths between devices. The gateway designates the primary and
secondary communication paths between devices that provide a redundant path for all transmissions. Mesh restructuring automatically terminates once all devices have a redundant communication path and signal strengths that meet the requirements of primary and secondary transmission
paths. Any device that does not have a redundant path or meet the requirements for signal strength
will report a fault.
The gateway reports a ‘RESTRUCTURING’ or ‘RSTRCT’ trouble to the FACP. The gateway
reports “Restructuring” to the communicator display of the SWIFT Tools application.
Normal Mode
Normal mode is the network’s standard operating state. The mesh network has been formed and is
providing fire protection. The mesh network will continuously search for additional devices with a
matching profile to join the mesh. To avoid interference, the mesh network periodically checks for
adjacent mesh networks created by Honeywell. The gateway reports “Normal” to the communicator display of the SWIFT Tools application.
Rescue Mode
During normal mode, if an out-of-network device with a matching profile is discovered by the network, the gateway will trigger rescue mode in all communicating devices. All devices in communication continue to provide fire protection during rescue mode but also search for a lost or added
device. Rescue mode automatically terminates 3 minutes after the last device is rescued and returns
to normal mode. The gateway does not report troubles during rescue mode but reports “Rescue” to
the communicator display of the SWIFT Tools application.
Mesh Restructuring Mode
In addition to the initial mesh restructuring mode, mesh restructuring is automatically performed
after any restoration of communication to a device or to recover from a link failure (Class A fault).
Mesh restructuring that occurs during normal mode does not generate a trouble message. During
mesh restructuring, fire protection is provided by all devices that are participating in the mesh communication. The gateway reports “Restructuring” to the communicator display of the SWIFT Tools
application.
Bootloader Mode
The gateway enters the bootloader mode when its firmware is being updated using SWIFT Tools.
The gateway does not communicate with the FACP during bootloader mode. The gateway reports
“Bootloader” to the communicator display of the SWIFT Tools application.
2.9.2 LED Patterns
The LED indicator patterns are provided in Appendix D on page 59.
2.9.3 Lock/Unlock the Gateway
The gateway can be locked to prevent access to the magnetic sensors and to password-protect all
wireless interactions. The lock function can be performed by SWIFT Tools or by the FACP. When
SWIFT Tools is used to lock the gateway, a password must be provided for all future interactions,
including unlocking the gateway. When the gateway is locked by the FACP for the first time, a
default password of “12345” is applied. If the gateway was previously locked with a password from
SWIFT Tools, the previous password will be applied. Use this password for all future interactions
with the SWIFT Tools application.
24 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 25

Operations XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway
extras.png
Figure 2.16 Extras Menu
lock_unlcok_gateway.png
Figure 2.17 Lock/Unlock Screen
Lock/Unlock the Gateway at the FACP
The lock/unlock function for the gateway is accessible using the point programming menu. For
more information refer to the XLS3000 Manual. The lock/unlock function for the XLS140-2 with
XLS-NCA2 as primary display is accessible using the VeriFire® Tools programming utility. For
more information refer to the XLS-NCA2 Manual.
Lock/Unlock the Gateway Using SWIFT Tools
To lock/unlock the gateway:
1. Connect the W-USB dongle device to your computer. For more information on USB dongle,
refer to Section 4.
2. Launch the SWIFT Tools application. Refer to Appendix A, “SWIFT Tools” for more
information.
3. From the Home Screen, select the Site Survey, Create Mesh Network, or Diagnostics
function.
4. Click Extras. The following screen is displayed.
5. Select Gateway Operations to lock/unlock the gateway. The Lock/Unlock gateway screen
appears, displaying the gateway that is locked.
6. Select desired gateway and click Lock or Unlock as required.
• Lock - The Lock Gateway screen is displayed. Create a password and click Lock. The
gateway is locked.
• Unlock - The Enter password for Gateway screen is displayed. Enter the password and
click Unlock. The gateway is unlocked.
Password Reset
To reset the password, contact technical support.
2.9.4 Weak Link Trouble Reporting
The SWIFT Network uses two paths of communication for each device. To establish the link
between devices as a viable communication path, the signal strengths must meet the limits provided
in Section 2.3. The SWIFT Network implements a higher threshold for primary connections to pro-
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 25
Page 26

XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway Operations
Figure 2.18 Communicator Panel
selcomm.png
advfuncdrop.wmf
Figure 2.19 Advanced Functions Options
advfuncdrop.wmf
Figure 2.20 Report Weak Links Troubles Option
vide an extra layer of robustness and immunity from interference. A weak link trouble condition is
initiated for any device that does not have at least one connection at the primary threshold. This is
an optional setting that can be disabled to ignore the weak link trouble condition. The trouble can
be disabled at the gateway or at the FACP (XLS3000 or XLS140-2 with XLS-NCA2 only). Disabling the trouble reporting at the panel will prevent the event from registering as a trouble but still
enters into history as a background event. Disabling the trouble reporting at the gateway prevents
the event from being reported to the FACP as a trouble or a non-trouble event. To enable trouble
reporting, turn on the settings at both locations.
Disable Trouble Reporting at the Gateway Using SWIFT Tools
To disable trouble reporting at the gateway through SWIFT Tools:
1. Connect the W-USB dongle device to your computer. For more information on the USB
dongle, refer to Section 4.
2. Launch the SWIFT Tools application. Refer to Appendix A, “SWIFT Tools” for more
information.
3. From the Home Screen, select the Diagnostics function.
4. Select the desired gateway from the communicator panel.
5. Click View Mesh.
6. Click Advanced Functions. A drop-down list is displayed.
7. Click Weak links troubles (On). The Report weak links troubles screen is displayed.
8. Click Turn off reporting. The trouble reporting is now disabled.
Disabling Trouble Reporting at the Panel
To disable trouble reporting at the panel, refer to the XLS3000 or XLS-NCA2 Manual.
26 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 27

Operations XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway
!
advfuncdrop.wmf
Figure 2.21 Advanced Functions Options
collapsemesh.png
Figure 2.22 Collapse Mesh Network Option
collapsemeshnetworkconfirm.jpg
Figure 2.23 Collapse Mesh Network Confirmation
2.9.5 Collapse Network Command
The collapse command is a diagnostic function to break the mesh network. All devices will retain
the profile information but will be removed from the mesh. The mesh can be reformed by activating
mesh formation.
CAUTION: FIRE PROTECTION DISABLED
FIRE PROTECTION FROM WIRELESS DEVICES IS DISABLED WHEN A COLLAPSE
NETWORK COMMAND IS ISSUED.
The mesh network can be collapsed using SWIFT Tools. The mesh network can also be collapsed
at the XLS3000 panel or XLS-NCA2 when used as a primary display with the XLS140-2.
Collapse Mesh Network Using SWIFT Tools
To collapse the mesh network using the SWIFT Tools:
1. Connect the W-USB dongle device to your computer. For more information on the USB
dongle, refer to Section 4.
2. Launch the SWIFT Tools application. Refer to Appendix A, “SWIFT Tools” for more
information on launching the SWIFT Tools application.
3. From the Home Screen, select the Diagnostics function.
4. Select a Gateway from the communicator panel.
5. Click View Mesh. The mesh is displayed.
6. Click Advanced Functions on top of the mesh display. A drop-down list is displayed.
7. Click Collapse Mesh. The Collapse mesh network screen is displayed.
8. Click Ye s . The network is now collapsed and a confirmation message is displayed as shown
below.
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 27
Page 28

XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway Operations
!
advfuncdrop.wmf
Figure 2.24 Advanced Functions Options
silencemeshnetwork.jpg
Figure 2.25 Silence Mesh Network Screen
Collapse Mesh Network at the Panel
To collapse the mesh network using the XLS3000 or XLS-NCA2 with XLS140-2 FACP, refer to
the “shutdown wireless” section of the XLS3000 or XLS-NCA2 Manual.
2.9.6 Silence Network Command
The silence network command is a diagnostic function to turn off all radio communication from the
wireless devices for a set amount of time. All devices will retain the profile information but will be
removed from the mesh. The devices will not send or receive any wireless communication until the
set time expires or the device is rebooted. The mesh network can be reformed at the end of the
silence period or after the device is restarted.
CAUTION: FIRE PROTECTION DISABLED
FIRE PROTECTION FROM WIRELESS DEVICES WILL BE DISABLED WHEN A SILENCE
COMMAND IS ISSUED.
The mesh network can be silenced using SWIFT Tools.
Silence Mesh Network Using SWIFT Tools
To silence the mesh network:
1. Connect the W-USB dongle device to your computer. For more information on the USB
dongle, refer to Section 4.
2. Launch the SWIFT Tools application. Refer to Appendix A, “SWIFT Tools” for more
information.
3. From the Home Screen, select the Diagnostics function.
4. Select a Gateway from the communicator panel.
5. Click View Mesh. The mesh is displayed.
6. Click Advanced Functions on top of the mesh display. A drop-down list is displayed.
7. Click Silence Devices. The Silence mesh network screen is displayed.
8. Select the time interval to silence the wireless devices from the dropdown list and click Yes.
28 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 29

Operations XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway
silencemeshconfirm.jpg
Figure 2.26 Silence Mesh Network Confirmation Message
9. Enter the Verification Password in the Gateway Password screen. The network is silenced and
confirmation is displayed as shown below.
Silence Mesh Network at the Panel
To silence the mesh network using the XLS3000 or XLS-NCA2 with XLS140-2 FACP, refer to the
“shutdown wireless” section of the XLS3000 or XLS-NCA2 Manual.
2.9.7 Multiple Wireless Sensor Network Installation Restrictions
The SWIFT Network technology shares the RF spectrum with other Honeywell Wireless Sensor
Network systems. Honeywell has established a limit of 4 overlapping networks to avoid congestion
in the RF spectrum. If the 4 network limit is exceeded, a system trouble will be generated by the
system that detects 4 or more adjacent networks. To resolve this trouble, the instances of overlap
need to be removed. Refer to Appendix C:, "Troubleshooting and Testing" for suggestions on
removing overlap between wireless networks. The trouble will be self-restoring up to 36 hours after
the condition is resolved. To expedite the trouble resolution, toggle the network that is reporting the
trouble in and out of mesh formation mode.
2.9.8 Avoiding RF Interference
The SWIFT wireless mesh network uses radio frequency hopping spread spectrum technology to
communicate in the 900 MHz ISM band (902MHz to 928MHz). Other commercial and industrial
products also operate in this band. If two-way radios or other wireless communication devices are
used during the installation process, it is recommended that they be kept at least 4 feet away from
the Honeywell wireless devices or that they operate on a different frequency band to ensure rapid
mesh formation.
A properly installed SWIFT wireless mesh network with primary link reporting enabled will be
highly immune to RF interference from other wireless products even when they are nearby. The use
of the weak link reporting feature is highly recommended. If the system is installed in a controlled
environment where other 900 MHz ISM band devices will not be present, the primary link reporting feature may be disabled to permit greater distances between installed devices if required.
The SWIFT wireless mesh network will be able to automatically detect and avoid certain types of
in-band channel interference (often caused by two-way radios) by using an alternate channel set.
The system will log detection and avoidance of this kind of interference in the gateway history as
“Walkie Talkie Mode” Entry or Exit and in the XLS3000 history as Alternate Channel Set or Normal Channel Set.
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 29
Page 30

XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway Operations
2.9.9 Trouble Messages
XLS3000
XLS-NCA2
XLS-WKS
RADIO JAMMING JAM Non-latching The gateway is being
INCOMPAT SOFT IN SFT Non-latching Software mismatch
MESH IS
FORMING
MESH NOT
FORMED
RESTRUCTURING RSTRCT Non-latching The gateway is performing
XLS140-2
XLS120
MS FRM Non-latching The gateway and attached
NOMESH Non-latching The gateway contains a
Type Description Course of Action
overloaded with RF energy
and is unable to receive
messages from other
devices.
between the application
code for the RF processor
and the SLC processor.
devices are searching for
additional devices to join
the mesh. The wireless
system is not able to
provide fire protection
during this time.
profile but has not formed a
mesh.
the initial identification and
assignment of optimal
communication paths for
the mesh network. The
wireless system is not able
to provide fire protection
during this time.
Identify any RF emitters in close proximity
of the gateway and remove them or
relocate the gateway.
Use SWIFT Tools to identify the mismatch,
and update the processors as necessary
for compatibility.
Wait until all desired wireless devices are
communicating and are members of the
mesh network. Once all desired devices
are in the mesh network, the mesh forming
mode can be terminated by the user by
activating the Mesh formation magnetic
sensor or by using the SWIFT Tools. If no
action is taken, this mode will
automatically exit 10 minutes after the last
device joins.
To form a mesh, refer to, "Create a Mesh
Network".
No action needed. The duration of this
event correlates to the number of devices
in the mesh. A fully loaded mesh may take
up to 5 minutes to restructure.
PROFILE MISSING PR MIS Non-latching The gateway is in the
NO WIRELESS
DEVS
ADDRESS FAULT ADRFLT Non-latching There is either a device in
MAX GATEWAYS MAX GW Non-latching Wireless communication
NO DEV Non-latching The gateway is functional
factory default state and is
not providing fire
protection.
but is not in communication
with any wireless devices.
the mesh set to address 0
or there is a duplicate
address used for another
wireless module at the
address of the gateway.
reliability is compromised
due to the installation limits
of Honeywell wireless
systems being exceeded.
Table 2.1 Trouble Messages
A profile needs to be created or assigned
to the gateway before a mesh can be
formed.
Verify the desired wireless devices are in
range, have matching profiles assigned,
have fresh batteries, and are not in the
tampered condition. Initiate “Mesh
Formation mode” to actively search for
devices.
The offending device (detector or module
set at address 0 or module at the same
address as the gateway) will be indicating
the LED pattern for address fault. Find and
resolve that device.
Investigate for overlapping or adjacent
wireless systems produced by Honeywell.
Reduce the instances of overlap by
removing systems, or devices in the
overlapping region. Refer to Section 2.9.7
on the installation limits for the Honeywell
wireless system.
30 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 31

Operations XLS-WSG Wireless System Gateway
XLS3000
XLS-NCA2
XLS-WKS
RF DEV NO
ANSWER
XLS140-2
XLS120
RF DEV Latching trouble;
Type Description Course of Action
remains active for
the first 180
seconds before it
can be cleared
with a system
reset.
A wireless device that was
part of the mesh has
dropped from the mesh.
The trouble is reported at
the FACP 180 seconds
after the device drops from
the mesh.
Initiate a system reset at the FACP at least
3 minutes after the trouble was initiated to
clear.
If the device was intentionally removed, no
further action is needed.
If the device was not intentionally
removed, refer to panel history or active
panel troubles to investigate the cause of
the disturbance.
Table 2.1 Trouble Messages
Events History Messages
XLS3000 Description
PR A profile has been received, assigned by either SWIFT Tools or a distributor device.
PC A profile has been created.
B The system is currently operating in the alternate channel set due to the presences of an interference
source such as a walkie-talkie.
SLOT REALIGNMENT
(TEMP CHAN SET)
Slot assignments are being re-assigned to avoid empty slots. The system is currently operating in the
alternate channel set due to the presences of an interference source such as a walkie-talkie.
SLOT REALIGNMENT Slot assignments are being re-assigned to avoid empty slots.
RESTRUCTURING
(TEMP CHAN SET)
RESTRUCTURING The gateway is performing a routine identification and assignment of optimal communication paths for
RESCUE MODE (TEMP
CHAN SET)
RESCUE MODE A device has been removed or dropped from the mesh. The mesh network is currently scanning for
TEMP CHANNEL SET The system is currently operating in the alternate channel set due to the presence of an interference
NORMAL CHANNEL SET The system is normal.
PROFILE DISTRIBUTION
DISABLED
PROFILE DISTRIBUTION
ENABLED
SWITCH ACCESS
ENABLED
SWITCH ACCESS
DISABLED
The gateway is performing a routine identification and assignment of optimal communication paths for
the mesh network. The system is currently operating in the alternate channel set due to the presences
of an interference source such as a walkie-talkie.
the mesh network.
A device has been removed or dropped from the mesh. The mesh network is currently scanning for
the return of the device or others with a matching profile. The system is currently operating in the
alternate channel set due to the presences of an interference source such as a walkie-talkie.
the return of the device or others with a matching profile.
source such as a walkie-talkie.
The gateway has terminated the distribution of its profile.
The gateway has started the distribution of its profile.
The gateway is unlocked and the magnetic sensors on the front of the gateway are enabled.
The gateway is locked and the magnetic sensors on the front of the gateway are disabled. Attempts to
active the sensors will not be recognized.
MAXIMUM DEVICE
COUNT EXCEEDED
More than 50 devices are attempting to join the mesh network. This is beyond the capacity of the
mesh network.
Table 2.2 Events History Messages
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 31
Page 32

Notes
32 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 33

3.1 Description
!
The SWIFT Network consists of the following devices:
TC806W1000 - Wireless Photoelectric Smoke Detector -FCC ID: AUBWFSSD
The wireless photoelectric smoke detector is powered by four CR123A batteries. It has a sensor
head to detect smoke and LEDs to indicate the activation and trouble status.
TC840W1000 - Wireless Acclimate Detector FCC ID: AUBWFSSD
The wireless Acclimate detector is powered by four CR123A batteries. It has a sensor head to
detect smoke and LEDs to indicate activation and trouble status.
TC808W1000 - Wireless Rate of Rise Heat Detector FCC ID: AUBWFSSD
The rate of rise heat detectors are powered by four CR123A batteries. The detectors have LEDs to
indicate the activation and trouble status.
TC808W2010 - Wireless 135° Fixed Heat Detector FCC ID: AUBWFSSD
The fixed heat detectors are powered by four CR123A batteries. The detectors have LEDs to indicate the activation and trouble status.
TC809W1000 - Wireless Addressable Monitor Module FCC ID: AUBWFSMM
The wireless monitor module is powered by four CR123A batteries. It can be connected to a switch
within three feet of its location or wired directly to the pull station. The module has LEDs to indicate the activation and trouble status.
Section 3: Wireless Devices
TC810RW1000 - Wireless Addressable Relay Module FCC ID:
The wireless relay module is powered by four CR123A batteries
contact output for activating a variety of auxiliary devices, such as fans, dampers, control equipment, etc. Addressability allows the dry contact to be activated, either manually or through panel
programming, on a select basis. The module has an LED to indicate the activation and trouble status.
For more information on the LED indicators, refer to Section 3.6.2.
3.2 Agency Approvals
3.2.1 FCC
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
WARNING: DO NOT MAKE CHANGES TO THE EQUIPMENT.
CHANGES OR MODIFICATIONS NOT EXPRESSLY APPROVED BY THE MANUFACTURER
COULD VOID THE USER’S AUTHORITY TO OPERATE THE EQUIPMENT.
. It provides the system with a dry-
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 33
Page 34

Wireless Devices Specifications
3.2.2 Industry Canada
This device complies with Industry Canada license-exempt RSS standard(s). Operation is subject to
the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause undesired
operation of the device.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d'Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio
exempts de licence. L'exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes :
1. L'appareil ne doit pas produire de brouillage, et
2. L'utilisateur de l'appareil doit accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique subi, même si le
brouillage est susceptible d'en compromettre le fonctionnement.
IC: 573X-WFSSD for detectors and IC: 573X-WFSMM for the monitor module
3.2.3 Federal Institute of Telecommunications
This device utilizes the Honeywell915 rev A radio module and complies with IFETEL standard(s).
IFT: RCPHOSW14-1983
3.3 Specifications
The following are the specifications for the wireless devices.
Specification Data
Radio Frequency Lower ISM Band (902-928 MHz)
Maximum power output +17dBm
Minimum signal strength level needed at the receiver for a primary path
with weak link trouble reporting enabled.
Minimum signal strength level needed at the receiver for a secondary
path or primary path with weak link trouble reporting disabled.
Maximum ambient noise level -85dBm
Minimum battery life 2 years
Table 3.1 Wireless Device Specifications
3.4 Installing, Mounting, and Wiring Devices
For information on installing the wireless devices, refer to the documents referenced in Table 1.1.
3.5 Configuration and Programming
-55dBm
Must be 18 dBm higher than the
noise floor down to -80dBm
Device configuration starts with assigning a profile.
3.5.1 Assigning Profiles
To assign a profile, the device must be in a factory default state. A single red light flashes on the
LED confirming that the device is in the default state. To restore the device to factory default state,
refer to Section 3.5.4, “Restoring a Device to Factory Default”.
There are two methods to assigning a profile.
34 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 35

Configuration and Programming Wireless Devices
Figure 3.1 Magnetic Sensor on a Detector
magnetdet.wmf
LED
LED
Magnet test
switch
Tamper
magnet
Assigning a Profile to a Device (Detector or Module) Using a Gateway or Distributor
A gateway that has a profile can be used to distribute that profile to other devices. The gateway
must be in distributor mode before it can distribute a profile. For more information on converting a
gateway to a distributor, refer to Section 2.8.3. A device with a profile can be used to distribute the
profile. To put a device into distributor mode, refer to topic, “Converting a Device into a Distributor” on page 37.
Distribute a Profile from a Gateway/Distributor to a Detector
To transfer a profile from a gateway/distributor to a detector:
1. Bring the detector within 20 feet of the gateway/distributor.
2. Power on the detector. Ensure the detector is in factory default state. The LED on the detector
will single-blink or double-blink red confirming that it is in the factory default state.
3. Activate the magnet test switch shown in the figure below. Once the magnet sensor has been
activated, the LED blinks red every half second indicating that it is requesting a profile. If the
profile is successfully received, the green LED turns on steady for 10 seconds. If the profile is
not received within 1 minute, the LED blinks red every ten seconds indicating that it has
stopped requesting a profile.
Distribute a Profile from a Gateway/Distributor to a Module
To transfer a profile from a gateway/distributor to a module:
1. Bring the detector within 20 feet of the gateway/distributor.
2. Power on the module. Ensure the module is in factory default state. If the module is in factory
default state, the LED blinks red once.
3. Toggle the state of the tamper condition to instruct the module to request a profile. To toggle
the tamper condition state, start with the faceplate removed.
4. Quickly replace then remove the faceplate from the module. Do not attach the mounting
screws for the faceplate during this step. The LED blinks red every half second indicating that
it is requesting a profile. The green LEDs turn on steady for ten seconds indicating that the
profile has been assigned. If the profile is not received within 1 minute, the LED blinks red
every ten seconds indicating that it has stopped requesting a profile.
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 35
Page 36

Wireless Devices Configuration and Programming
Figure 3.2 Magnetic Sensor on a Module
m
a
g
n
e
t
m
o
n
.
w
m
f
Magnetic
sensor
Figure 3.3 Creating or Importing a Profile
createprofile.wmf
Assigning a Profile Using SWIFT Tools
To assign a profile to the device using the SWIFT Tools application, do the following:
1. Connect the W-USB dongle device to your computer. For more information on the USB
dongle, refer to Section 4.
2. Launch the SWIFT Tools application. Refer to Appendix A, “SWIFT Tools” for more
information.
3. From the Home Screen, select the Create Mesh Network function.
4. Create a new profile or import an existing profile as required.
5. Select and open the profile to be assigned to the gateway from the Name drop-down box in the
Profile section.
6. Power on the device within approximately 20 feet of the laptop running SWIFT Tools.
7. Ensure that the Scan On selection box is checked.
36 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 37

Configuration and Programming Wireless Devices
Figure 3.4 Selecting a Device
assignprofile.png
Figure 3.5 Assigning a Profile
assignprofile2.png
8. Select the device from the Communicator panel.
9. Click Assign.
The device is now included in the list of devices with a profile assigned. When the profile is
assigned, the green LEDs turn on steady for 10 seconds.
3.5.2 Distributor Mode
Converting a Device into a Distributor
NOTE: Only a device with a profile can be used as a distributor.
To turn a device into a distributor:
1. Power up the device with one battery installed.
2. Ensure that the device is in the profile modification mode. If the device is in profile
modification mode, the yellow LED will blink once every 5 seconds. The profile modification
mode times out if the device has not received a command in one minute.
3. Toggle the SLC address wheel between 0-1-0-1. To toggle the SLC address wheel, use a
common screwdriver to adjust the rotary switches on the device to:
1. Set the address to 0.
2. Change the address to 1.
3. Change the address back to 0.
4. Change the address back to 1.
NOTE: The green LED blinks every half second when the device is functioning as a distributor.
Converting a Distributor Back into a Device
To return a distributor device back to a network device, replace the batteries and provide a proper
SLC address. A normal device requires four batteries for proper operation. It is recommended to
use fresh batteries after the distributor mode.
3.5.3 Mesh Formation
To add a device to a mesh, refer to the topic, "Create a Mesh Network". To form a mesh network,
ensure that the gateway is powered on and contains a profile. Activate the mesh formation (refer to
Figure 2.2) magnetic sensor on the gateway.
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 37
Page 38

Wireless Devices Configuration and Programming
TENS
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
ONES
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Figure 3.6 Address Rotary Switches
SLC-setaddtph.wmf
extras.png
Figure 3.7 Extras Menu
Repeater
The SWIFT Network does not require the use of a dedicated repeater as all wireless devices act as
repeaters. When the repeater function is needed in a location where no specific fire function is
required, a wireless monitor module or another device can be installed to act as a repeater.
3.5.4 Restoring a Device to Factory Default
Removing Profiles Without Using SWIFT Tools
A device can be restored to factory default state:
1. Start with the device powered off. The process is performed during start-up.
2. Power on the device by inserting a single battery into any slot in the device. The LEDs will
blink yellow twice every five seconds for one minute after inserting the battery.
3. Toggle the SLC address wheel between 0-159-0. To toggle the SLC address wheel, use a
common screwdriver to adjust the rotary switches on the device to:
1. Set the address to 0.
2. Change the address to 159 (tens set to 15, ones set to 9).
3. Change the address back to 0.
NOTE: The above illustration depicts the rotary switches being set at address 35 (rotary switch
on 'TENS' set at 3 and rotary switch on 'ONES’ set at 5. Ensure that the code wheel address
pattern is toggled within 1 minute of inserting the battery.
After the address wheel pattern is set, the LEDs in the device blink green five times followed by a
single or double red blink confirming that the device has been reverted back to factory default condition.
Removing a Profile Using SWIFT Tools
To remove a profile in a device using SWIFT Tools:
1. Connect the W-USB dongle device to your computer. For more information on the USB
dongle, refer to Section 4.
2. Launch the SWIFT Tools application. Refer to Appendix A, “SWIFT Tools” for more
information on launching the SWIFT Tools application.
3. From the Home Screen, select the Site Survey, Create Mesh Network, or Diagnostics
function.
4. Click Extras and select Set device to factory default.
38 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 39

Device Operations Wireless Devices
resetdevice_detector.png
Figure 3.8 Reset Devices Screen
5. The Reset Devices screen appears, displaying the gateway and other devices that have a
profile assigned. Click to select the desired device and click Reset Device to remove the
profile.
The profile is removed and the device is reset to the factory default state.
3.6 Device Operations
3.6.1 Modes of Operation
Factory Default Mode
In this mode, the devices are not associated with the gateway. A profile must be assigned to associate the device with the gateway. For further information on assigning a profile, refer to “Assigning
a Profile to a Device (Detector or Module) Using a Gateway or Distributor” on page 35. A device
cannot perform any fire protection in the factory default state. In default mode, the devices will be
viewable in the communicator window of SWIFT Tools with the state displayed as “Factory
Default”. A device in factory default can be used for site survey.
Site Survey Mode
A site survey assesses and qualifies a site for installing a SWIFT network. The site survey view in
SWIFT Tools gives the Radio Frequency (RF) assessment of the site. The tool reports the suggested
device spacing based on the data collected during the site survey. This helps to improve the reliability and performance of a SWIFT network in the wireless fire alarm system. A device cannot perform any fire protection in the site survey mode. A device that is ready to enter site survey will
indicate “pending site survey” in the communicator section of SWIFT Tools. A device in site survey will not communicate with SWIFT Tools and will be listed as “offline” in the communicator
section. For more information on performing a site survey, refer to Appendix B.
Profile Assigned Mode
In this mode, devices are associated with the gateway but are not active participants in the mesh
network. A device that is not in the tampered state can join a mesh network in formation or during
rescue mode. For further information on mesh formation, refer to “Mesh Formation Mode” on
page 40. For more information on rescue mode, refer to “Rescue Mode” on page 40. A device with
an assigned profile can also be used to distribute profiles. Refer to Section 3.5.2.
Devices are not enabled for fire protection until they become part of a mesh network. A device will
show an invalid reply or no answer at the FACP.
In this mode, devices are viewable in the communicator window of SWIFT Tools. If the device has
a profile and is in the tampered state, it will indicate a status as “Profile Assigned-Tamper”. A nontampered device will indicate “active scan” as it searches for a mesh network.
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 39
Page 40

Wireless Devices Device Operations
Bootloader Mode
In this mode, a device is ready for an update. It cannot participate in a mesh network and cannot
provide fire protection. The device is viewable in the communicator window of SWIFT Tools with
the status “Bootloader”. To remove a device from bootloader mode, refer to Appendix C.
Distributor Mode
In this mode, a device is functioning as a profile distributor. The device cannot participate in a mesh
network and cannot provide fire protection while it is in distributor mode. A device in distributor
mode will be used as a mobile unit to share the profile with other devices. The distributing device
will be available in the communicator window of the SWIFT Tools with the status “Distributor”.
For more information, refer to Section 3.5.2.
Mesh Participant Modes
Devices that are in the mesh network no longer communicate directly with SWIFT Tools. SWIFT
Tools must communicate with the gateway for status information on a device. The gateway will
respond to the FACP for the device at the address set with the SLC rotary address wheels.
Mesh Formation Mode
In this mode, a device is an active participant in a mesh that is forming. The LED will blink green
then yellow every 7 seconds. The device cannot perform any fire protection in this state. The device
responds to its SLC address with a “INIT MODE” or “INIT” trouble. For further information on
mesh formation mode, refer to “Section 3.5.3”.
Initial Mesh Restructuring Mode
In this mode, the mesh network is formed and is in the process of establishing stronger communication paths. The LED will blink yellow every 6.8 seconds. The device cannot perform any fire protection in this state. The device responds to its SLC address with a “DEVICE INIT” or “INIT”
trouble.
Normal Mode
In normal mode, the mesh network is formed and provides fire protection. The LED will blink
green every 14 seconds. The LED flash can be disabled by panel configuration. If a device is in
trouble, it is indicated by the trouble messages. For information on trouble messages, refer to
Section 3.6.3.
Rescue Mode
In rescue mode, a devices is an active participant of a mesh network. It will search and retrieve any
device that has lost communication with the network. Rescue mode is indicated by a green LED
blink every 7 seconds.
3.6.2 LED Indicators
The two LEDs on the devices blink in the same pattern to allow the LEDs to be viewed from any
angle. The LED indicators are provided in Appendix D on page 59.
3.6.3 Trouble Conditions
The following trouble conditions are unique to the battery powered RF devices. Multiple troubles
states may be active for a single device, but only the highest priority trouble event will be displayed.
Trouble Conditions with Fire Protection
The devices (on an XLS3000 only) indicate the following trouble conditions with a single yellow
LED blink every 14 seconds. The wireless device will still perform fire protection during the following trouble states.
40 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 41

Device Operations Wireless Devices
Low Battery
The low battery event denotes:
• The device has a minimum of one week power left to perform the required operations.
Or
• One (or more) of the batteries is missing or dead.
The low battery event is a latching condition. To clear the low battery event, tamper the device and
replace all the four batteries. When a device is tampered, it drops out of the mesh network and
attempts to rejoin as soon as the batteries are replaced and the tamper event is cleared. If the device
has dropped from the mesh prior to the tamper event, a system reset has to be issued to clear the
low battery trouble. The panel displays “BATTERY LOW” or “BAT LOW” during a low battery
condition.
Weak Link
The weak link trouble denotes a connection of insufficient primary parent link signal strength. To
resolve a weak link, reduce the distance between devices, place them away from obstructions, or
add a repeater. Tamper the device when moving it to a new location. Restart mesh formation after
a repeater is installed or after a device has been relocated and the tamper condition is cleared. Terminate mesh formation once the devices have joined the mesh or allow mesh formation to timeout.
Restructuring will automatically start and the gateway will reevaluate the link connectivity between
all devices and select suitable signal paths.
Weak link trouble reporting can be disabled at the FACP or at the gateway for installations not
requiring primary link connectivity. Refer to Section 2.9.4 for more information on disabling weak
link trouble reporting. Refer to the troubleshooting section for more information on resolving a
weak link condition.
The panel displays “WEAK LINK FAULT” or “WEAK” for a device that is in the weak link condition.
Class A Fault
The Class A fault denotes a single connection path from the device. The wireless system is a
Class A system requiring two communication paths for normal operations. To remedy the Class A
fault, ensure adequate device spacing. The use of a repeater may be required. The wireless mesh is
a self-healing network. If the trouble is not cleared within 5 minutes, additional actions may be
required. Refer to the troubleshooting section for tips on resolving Class A fault conditions.
The panel will display “CLASS A FAULT” or “CL A” during a Class A fault condition.
Trouble States without Fire Protection
Jamming
Jamming occurs when a device is overloaded with an interfering RF signal but is able to send outgoing messages. A jamming event is detected after 20 seconds of exposure to the jamming signal.
In the event of jamming, the device will drop from the mesh network. The panel displays “RADIO
JAMMING” or “JAM” during a jamming condition.
Duplicate Address
Two wireless devices on the same mesh network that are set to the same address will report a duplicate address trouble at the FACP. The gateway will respond to the panel with the device type of the
first device to join.
The panel displays “DUAL ADDR” or “DUALAD” during a duplicate address condition.
Tamper
A tamper trouble indicates that a detector is not firmly attached to its base or the cover plate is not
properly attached to a module. The tamper condition is annunciated in the following ways:
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 41
Page 42

Wireless Devices Device Operations
Device Indication The yellow LED on the device turns on steady for 4 seconds followed by a
blink pattern of yellow, yellow, red every 15 seconds immediately after the tamper condition.
Panel Indication Devices that are in the tampered condition report a latching trouble event. The
event is active for 180 seconds before it can be removed with a system reset. Once the event is
removed, the device reports a “NO ANSWER” or “INVREP” until the device is restored or the
point is removed from the database.
Clearing the Tamper To clear the tamper,
• For a detector, ensure that the detector is locked together with its base.
• For a module, ensure that there is a magnet in the cover plate and it is securely fastened to the
device in the correct orientation.
Once the tamper event is cleared, the LEDs in the device turn on steady for 2.5 seconds, in the following color patterns that denote the battery status.
• Green - All the four batteries are installed and fresh. The device has a minimum one year of
normal operation.
• Yellow - All the four batteries are installed, and one or more is no longer fresh. This device has
between a minimum of 1 month and 1 year of operation.
• Red - One or more of the batteries are low in power and/or the device has a minimum of one
week of operation.
After the device displays the current battery condition, it attempts to join the mesh network in the
rescue mode or normal mode. This is indicated by a double yellow blink every 3.4 seconds. If a
device does not find its mesh in the rescue mode, it searches for its mesh under formation. This is
indicated by a double yellow blink every 20 seconds.
No Answer
A device that is not in the mesh, displays a “NO ANSWER”, “NO ANS”, or “INVREP” message at
the FACP. Follow the steps in “Mesh Formation Mode” on page 40 to have a device join the mesh.
Device Initialization
A device reports a device initialization trouble when it is part of a mesh network but is not capable
of performing fire protection. This is the case for mesh networks that are still forming or going
through initial restructuring. The panel displays “INIT MODE” or “INIT” during a device initialization condition.
3.6.4 Background Events
The following conditions are not considered a trouble, supervisory, or alarm condition. These
events are stored in the history of the XLS3000 FACP only.
Pre-Class A Fault
A device will report a pre-Class A event when it first identifies a single connection path condition.
If the connection path is not restored or replaced with another viable connection path within 180
seconds, a Class A fault condition will be reported. The history event reports this condition as
“PRE-CLASS A FAULT”.
Device Drop
A device will report a device drop if it has lost complete communication with the mesh network. If
the device does not recover in 180 seconds or less, a “NO ANSWER” or “INVREP” trouble is
reported for the address. The history event will report as a “DEVICE DROPPED”.
Weak Link
When weak link reporting is enabled by the gateway and disabled in the FACP, then all weak link
conditions will be entered as background events in history. The history event is reported as a
“WEAK LINK FAULT” or “WEAK” for a device that is in the weak link condition.
42 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 43

4.1 Introduction
Figure 4.1 USB Adapter
usb.wmf
!
The W-USB is a software interface that can be connected to a PC (running SWIFT Tools) through a
USB port. It communicates with the RF devices using the same frequencies as the mesh protocol.
This device is powered directly by the USB port.
The LED gives an indication of power and initialization status.
The W-USB has an adjustable USB connector to facilitate connection by reducing the size when
connected to a laptop/tablet.
Section 4: USB Adapter
Color Description
Red Device has power but is not initialized or the driver is missing.
Yellow Device is initialized and ready.
Blue Device is updating or failed to load properly. Complete the update or re-
power the device. If problems persist, contact technical support.
4.2 Agency Approvals
4.2.1 FCC
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
FCC ID: PV3WFSADPT
WARNING: DO NOT MAKE CHANGES TO THE EQUIPMENT.
CHANGES OR MODIFICATIONS NOT EXPRESSLY APPROVED BY THE MANUFACTURER
COULD VOID THE USER’S AUTHORITY TO OPERATE THE EQUIPMENT.
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 43
Page 44

USB Adapter Specifications
4.2.2 Industry Canada
This device complies with Industry Canada license-exempt RSS standard(s). Operation is subject to
the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause undesired
operation of the device.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d'Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio
exempts de licence. L'exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes :
1. L'appareil ne doit pas produire de brouillage, et
2. L'utilisateur de l'appareil doit accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique subi, même si le
brouillage est susceptible d'en compromettre le fonctionnement.
IC: 12252A-WFSADPT
4.2.3 Federal Institute of Telecommunications
This device utilizes the Honeywell915 rev A radio module and complies with IFETEL standard(s).
IFT: RCPSYWU14-1829
4.3 Specifications
4.3.1 Electrical Specifications
• Operating voltage: 4.3 VDC - 5.5 VDC (5VDC typical)
• Supply current: 25 mA - 85 mA (33 mA typical)
4.3.2 Serial Communication Specification
• USB standard 2.0
4.3.3 Mechanical Specifications
• USB Connector type A
• Length with connector closed: 3 in. (76.2 mm)
• Length with connector open: 3.8 in. (96.2 mm)
• Thickness on connector side: 0.5 in (13 mm)
• Thickness on antenna side: 0.3 in. (8.4 mm)
• Width: 1.2 in. (31.2 mm)
• Weight: 0.7 oz. (19.5 g)
4.3.4 Environmental Specifications
• Humidity: 10%RH - 93%RH, non-condensing
• Maximum operating temperature: 32°F - 122°F (0°C - 50°C)
• Storage temperature: 14°F - 140°F (-10°C - 60°C)
44 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 45

Driver Installation USB Adapter
Figure 4.2 Computer Management Screen
devcemanager1.png
Figure 4.3 Update Driver Software
devcemanager2.png
4.4 Driver Installation
NOTE: Install SWIFT Tools before attempting to install the driver.
To install a driver:
1. Insert the adapter into the PC. The adapter is detected and is displayed in the Computer
Management screen as a Wireless Fire System Dongle.
2. Right click on Wireless Fire System Dongle and select Update Driver Software.
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 45
Page 46

USB Adapter Driver Installation
Figure 4.4 Browse Computer for Driver Software
devcemanager3.png
Figure 4.5 Browse Folder for Driver Software
devcemanager4.png
3. Select the Browse my computer for driver software option.
4. The Browse dialog box appears. Click Browse. Navigate to the folder: C:\Program
Files\Honeywell\Device Driver. Click Next.
46 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 47

Driver Installation USB Adapter
Figure 4.6 Driver Software Update Confirmation
devcemanager5.png
Figure 4.7 New Communications Port
devcemanager6.png
5. The confirmation message displays when the driver software is updated successfully.
The newly installed device will now display on the computer management screen under Ports.
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 47
Page 48

A.1 Description
startxls.wmf
Figure A.1 SWIFT Tools Start Screen
SWIFT Tools is a standalone desktop Windows® application. It is a configuration and maintenance
tool for the gateway and devices of the SWIFT Network. Site surveys, device configurations, and
diagnostic functions are all part of SWIFT Tools. SWIFT Tools can be installed on a PC or a laptop
and communicates with the gateway and wireless devices through USB-based user interface. Connect the W-USB adapter to the computer to invoke the SWIFT Tools application. At any point, only
one instance of SWIFT Tools can run on a laptop or PC.
SWIFT Tools has the following utilities:
Site Survey view
Creating Mesh Network
Diagnostic view
SWIFT Tools works in a wireless environment with the gateway and devices within a range of
approximately 20 feet.
SWIFT Tools is designed for systems running Microsoft Windows. Minimum system requirements
are listed below.
Component Minimum Requirement
Operating System Windows XP Professional (SP3), Vista, Windows 7, and Windows 8 (32 bit and 64 bit)
Appendix A: SWIFT Tools
Hard Drive 20 GB hard drive space with minimum 1GB free space on hard disk.
RAM Minimum 512MB RAM
Processor speed 1GHz minimum (2.4 GHz recommended) Processor, 512K Cache
Table A.1 System Requirements
A.2 Launching SWIFT Tools
To la u n c h S W I F T To o l s ,
1.Click Start, point to All Programs, click SWIFT Tool, and then SWIFT Tool.
The following screen is displayed. Alternatively, SWIFT Tools can be opened
through a shortcut located on the desktop. When installing the tools for Honeywell,
an option is given to also allow for the installation of Fire•Lite equipment with the
same Tools package.
48 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 49

Launching SWIFT Tools SWIFT Tools
swifttools.wmf
Figure A.2 SWIFT Tools Screen
homepage_xls.wmf
Figure A.3 Home Screen
2. Click Start Using. The SWIFT Tools screen is displayed. You can create a new jobsite or
open an existing one.
A.2.1 Creating a New Jobsite
To create a new jobsite:
1. Click Create from the PC Tools screen.
2. Enter the name of the new jobsite in the Jobsite Name field.
3. Enter the Location/Description if any, and click Create.
4. The Create Project dialog box opens. Navigate to the desired folder location where the project
will be saved.
5. Click Save.
The jobsite is created and the following screen is displayed. From this screen a site survey may be
conducted, a mesh network may be created, and troubleshooting may be performed. Click the Start
button for the desired function.
For more information on performing a site survey, refer to Appendix B. To create a mesh network,
see page 21. For help with diagnostics, refer to Appendix C.
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 49
Page 50

SWIFT Tools Launching SWIFT Tools
homepage_xls.wmf
Figure A.4 Home Screen
A.2.2 Opening an Existing Jobsite
To open an existing jobsite:
1. Click Open from the PC Tools screen.
2. Navigate to the folder containing the jobsite file. Select to highlight the file and click Open.
The existing jobsite is opened and the following screen is displayed. From this screen a site survey
may be conducted, a mesh network may be created, and troubleshooting may be performed. Click
the Start button for the desired function.
For more information on performing a site survey, refer to Appendix B. To create a mesh network,
see page 21. For help with diagnostics, refer to Appendix C.
50 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 51

Appendix B: Site Survey
A site survey is recommended to assess and qualify the site prior to installing a SWIFT network.
The site survey consists of a link quality test and RF scan test. After both tests are completed, the
results of the site survey can be obtained using SWIFT Tools. The information provided by SWIFT
Tools is used for site qualification, maximum device spacing identification, and configuring the
network. This helps to improve the reliability and performance of the wireless network in the wireless fire alarm system.
B.1 Conduct a Site Survey
B.1.1 Link Quality Test
A link quality test is a quick and repeatable test that provides immediate feedback on device connectivity. The link quality test sends data from one device to another to test for data loss and measure the signal strength. In a link test, the device addresses are set in the range of 001 to 150. A
minimum of two devices are needed to conduct a link quality test.
A link test is conducted between two or more devices. The link test starts when a device that is in
the “pending site survey” state has its tamper condition cleared. The device will send a burst of data
to the next address lower than its own address. The lower addressed device will automatically
return the link quality test results for display using the device LEDs. For example, clearing the tamper condition on a detector set to address 2 (D002) will make the detector enter the link quality test.
D002 will send a burst of data to a device at address 001 (either detector or module). The device at
address 001 will measure the signal strength and count the data received in the burst and return the
information to D002. The results of the test will be displayed at D002. The test can be repeated by
tampering D002 to return it to the “pending site survey” mode and then clearing the tamper.
Basic Requirements of a Link Quality Test
To conduct a link test:
two or more devices (detectors) are required.
devices must be in factory default state. The LEDs on the device will blink single or double
red to confirm it is in the factory default state. Refer to Section 3.5.4 on page 38 for more
information on setting the device to factory default state.
device addresses can bet set in the range of 1 to 150.
Conduct a Link Quality Test
To conduct a link quality test:
1. Remove the batteries from the devices that will be used for the site survey and set the SLC
address. To set an SLC address, use a common screwdriver to adjust the rotary switches on the
device.
a. For the first device used in a site survey, set the SLC address to 001.
b. For each subsequent device, use the next highest SLC address (up to address 150). For
example, the first device was set to 001, set the second device to 002, and the third device
to 003, etc.
2. Bring the first device (001) to the first location to conduct the test.
3. Insert one battery into the device. Inserting more than one battery deters the device from
entering the site survey mode. The device is ready for site survey mode if the LED blinks red
twice
every 5 seconds.
4. Clear the tamper condition to proceed with the test. To clear the tamper condition on a detector,
insert the detector into the base and twist to lock the detector completely into the base. To clear
the tamper condition on a module, attach the faceplate to the module. When the tamper is
cleared, the LEDs on the device starts blinking yellow every ½ second for approximately 20
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 51
Page 52

Site Survey Conduct a Site Survey
seconds. The results appear in approximately 20 seconds and the LEDs on the first device
change to solid red. This is due to the absence of a lower-addressed device with which to form
a pair. This result is expected from the 1st device when a link quality test is performed.
5. Bring the second device (002) to the second location and repeat steps 3 and 4.
6. The device will conduct a link test to the next lowest address; in this case device 001. The
result of the link test from 002 to 001 is displayed by the LEDs on device 002. Refer to
Table B.1 below.
7. Once the link test is complete between 002 and 001, continue for address 003, 004, etc. for all
devices that will be used in the site survey. This test may be repeated any number of times. For
devices addressed to 101 or higher, the test must be repeated, if desired, within five minutes of
the last concluded test or the devices will start an RF scan test.
Results of a Link Quality Test
The following table explains the LED patterns before and during a link quality test.
State Pattern LED Results & Description
Site survey pending Double blink every 5 seconds Red Device is tampered, ready and waiting
to start a site survey link quality test
Link quality test in progress Single blink every ½ seconds Yellow Transmission of data to another device.
Link quality test complete On steady Red Failure - no data received
Link quality test complete Single blink every 5 seconds Red Poor - partial data received or signal
strength measured lower than the
acceptable limit for a primary or
secondary link (-81dBm or lower)
Link quality test complete 2 blinks every 5 seconds Green Marginal - all data received at a signal
strength acceptable for a secondary link
but not for a primary link (-66dBm to
-80dBm)
Link quality test complete 3 blinks every 5 seconds Green Good - all data received at a signal
Link quality test complete 4 blinks every 5 seconds Green Excellent - all data received at a signal
strength acceptable for a secondary link
and marginally acceptable for a primary
link (-51dBm to -65dBm)
strength acceptable for a primary link
(-50dBm or better)
Table B.1 LED Patterns of Link Quality Test Results
The LED pattern for a link quality test will continue to be displayed until the device is tampered or
the batteries die for a device that is addressed 100 or lower. For devices addressed 101 to 150, the
result will be displayed until the device starts the RF Scan.
To repeat the link quality test, toggle the tamper state. To toggle the tamper state on a detector, twist
the detector in the base counter-clockwise as if removing the detector from the base, then twist it
back in clockwise to lock it in. To toggle the tamper state on a module, remove the faceplate and
then reconnect it. Once the device is tampered, it will return to the pending site survey state. Once
the tamper is cleared, the link quality test will be restarted. Only the results for the last link quality
test are retained.
After a Link Quality Test
Retrieve the link quality test results for devices 001-100. To retrieve the site survey results, refer to
the topicB.1.3, "Retrieving Site Survey Results"at the end of this section. For devices 101-150, wait
to retrieve the link quality results until the device starts an RF Scan test.
52 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 53

Conduct a Site Survey Site Survey
!
B.1.2 RF Scan Test
A Radio Frequency scan test is conducted to assess and measure the background noise and interference from other wireless systems if any, in the site. The RF Scan test can be conducted individually
or following the link quality test. An RF Scan test will be conducted for any device with an SLC
address set between 101 and 150 at the end of a Link Quality Test.
Conduct an RF Scan Test
To conduct an RF scan test, follow the same procedure for a link quality test. However, the device
addresses for an RF scan test must start at 101 and have the subsequent devices address set as 102,
103, etc. Each device will conduct the link quality test as described above, then transition to the RF
scan test 5 minutes after the last link quality test is performed to or from that device.
If several devices are being tested, it is possible that some devices will start and complete the link
test and progress to the RF scan test while other devices are finishing the link quality test. The RF
Scan test may take up to 70 minutes. The time remaining and the test status are displayed at the
device using the LEDs. The LED patterns are shown below.
Status of an RF Scan Test
State Pattern LED Status
In Progress- 70 minutes remaining 7 short blinks every 30 seconds
In Progress- 60 minutes remaining 6 short blinks every 30 seconds
In Progress- 50 minutes remaining 5 short blinks every 30 seconds
In Progress- 10 minutes remaining 1 short blink every 30 seconds
RF Scan Test Complete On Steady
Table B.2 RF Scan Test Status - LED Pattern
B.1.3 Retrieving Site Survey Results
To retrieve the site survey results:
1. Return the device to “Pending Site Survey” or “Factory Default” mode. This is done by
tampering devices that have completed a link quality test or by rebooting devices that have
completed an RF scan test.
Red Bad
Green Good
Red Bad
Green Good
Red Bad
Green Good
Red Bad
Green Good
Red Bad
Green Good
CAUTION: SITE SURVEY RESULTS WILL BE REPLACED
DO NOT CLEAR THE TAMPER ON A DEVICE THAT IS IN THE “PENDING SITE SURVEY” STATE
OR THE EXISTING RESULTS WILL BE REPLACED.
2. Plug the USB adapter into the laptop/PC where SWIFT Tools has been installed.
3. Bring the devices within a range of approximately 20 feet from the USB adapter connected to
the laptop/PC.
4. Logon to SWIFT Tools and retrieve the data.
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 53
Page 54

Notes
54 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 55

Appendix C: Troubleshooting and Testing
C.1 Troubleshooting
Problem Description Action
Class A fault condition Device has a single parent connection, and is
missing the redundant class A connection.
Jamming Jamming occurs when a device is overloaded
with an interfering RF signal and is unable to
process incoming messages, but is able to
report the condition to its parents.
Low battery One or more of the four batteries are
missing/dead and/or the device has a
minimum of one week of operation remaining.
Duplicate address/
Illegal address
Mesh formation does
not find all devices
Mesh restructuring does
not end
Devices drop during
operation
Two or more wireless devices on the same
mesh network that are set to the same
address report a duplicate address trouble. An
address set to zero will report an illegal
address.
A device does not connect to the
gateway/mesh network
The gateway/mesh network appears to be
stuck in mesh restructuring
A device drop event is indicated in history. Device drop is the predecessor to a No Answer/Invalid
If a suitable parent is available, the background mesh
restructuring routine should self-heal the network. If the
network does not self-heal after ten minutes, reduce
spacing between devices or utilize SWIFT Tools for
suggested repeater placement to add stronger parents.
Toggle mesh formation to trigger a mesh restructuring
routine to re-evaluate the trouble condition after taking
action.
A jammed device will automatically remove itself from
the mesh network after reporting the jamming. The
device will attempt to self-heal and recover into the
network. Identify any possible sources of the jamming
signal and see if the spacing from the device to the
jamming source can be increased to an acceptable
range. A site survey RF scan test can be used to
categorize the jamming signal.
To clear the low battery event, tamper the device and
replace all four batteries. When a device is tampered, it
drops out of the mesh network and attempts to rejoin as
soon as the batteries are replaced and the tamper event
is cleared. Once a low battery trouble is indicated there
is a minimum of one week of operation before the device
is non-functional.
Change the address of the device(s) to avoid duplication
and error.
Verify the device has a profile. Verify that the profile
matches the profile in the gateway. Two different profiles
may use the same mesh ID. Remove and re-profile the
device to guarantee the correct profile. Verify the device
is powered and the tamper condition is cleared. Check
the device spacing and the range from the device to the
mesh. A site survey link test can be used to verify
connectivity from one location to another.
Use SWIFT Tools or panel history to investigate for the
presence of walkie talkie interference or unstable
devices (dropping and joining). Walkie talkie
interference will prohibit restructuring from fully
executing. Devices joining a mesh will delay the
restructuring event.
reply trouble. Inspect the area for any changes to the
environment that could block radio communication. Use
a site survey RF Scan to check for any interference and
use a site survey link test to check the connectivity from
the device to its closest neighbor.
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 55
Page 56

Troubleshooting and Testing Troubleshooting
Problem Description Action
Max gateway trouble
reported
Device does not rejoin
the mesh after battery
replacement
Low battery trouble
reported after battery
replacement
Site survey does not
find a link
SWIFT Tools does not
import site survey data
SWIFT Tools says
device/gateway is out of
range
Scan does not find any
devices
Site survey devices are
not displayed in the
communicator of
SWIFT Tools.
FACP reports invalid
reply/No Answer for the
gateway
FACP reports invalid
reply/No answer for the
wireless detectors
FACP reports invalid
reply/No answer for the
wireless modules
The number of Honeywell SWIFT systems
that can co-exist in range of each other has
been exceeded.
Device is an invalid reply/no answer after
replacing the batteries.
Low battery trouble is still indicated after
replacement.
Solid red results for the link test Verify the addresses of the devices used during the test.
Selecting the device in the communicator in
SWIFT Tools does not have an effect
Device or gateway is not communicating to
SWIFT Tools
All devices are out of range Verify at least one device is in range of SWIFT Tools, the
Verify the device is in the pending site survey mode or
Gateway is not communicating with the panel Verify the loop is running in FlashScan for detectors and
FACP does not recognize the detectors Verify the loop is running in FlashScan for the detectors.
FACP does not recognize the modules Verify the loop is running in FlashScan for the modules.
Use the network statistics provided by SWIFT Tools to
identify the interfering networks and the nature of the
fault. The networks will be listed by a unique number;
this is not the serial number of the gateway. One or more
of the systems will need to be powered down to clear
the fault. Where possible, maximize the number of
devices on a mesh network to reduce the number of
total mesh networks; i.e. use one mesh network with 50
devices instead of two mesh networks with 25 each.
Restructure the layout of the mesh networks to group
devices and the gateway to avoid overlap. It may take
36 hours for the fault to clear. This can be expedited by
toggling the state of mesh formation.
Verify the tamper condition is cleared. Use mesh
formation to have the device rejoin the mesh network.
Low battery and tamper are both latching conditions.
Ensure a reset has been initiated to clear those events.
Use the network statistics provided in SWIFT Tools to
see the battery voltage measured for each individual
battery. Verify that each battery is present and at a
suitable voltage level. The low battery trouble is a
latching trouble, ensure a reset has been initiated since
the replacement.
The lower addressed device must complete its link test
before the device at the next higher address starts the
link test. Verify the devices are in range of each other.
The device does not have any site survey results to be
imported. It has not found a link during the link test
and/or it has not collected any data for an RF Scan.
Verify the device or gateway is powered on and in a
state that supports SWIFT Tools communication. For
instance, a device in the mesh network does not
communicate to SWIFT Tools. It communicates to the
gateway. A device that has completed a site survey
does not communicate to SWIFT Tools until it returns to
the pending site survey state or factory default state.
Move the Adapter in range of gateway/devices.
USB adapter is connected, and the scan is on. SWIFT
Tools processes the messages faster with multiple
devices in range. If only one device is in range it can
take up to 1 minute for the scan to detect the device.
factory default mode. The device will not communicate
with SWIFT Tools while it is in site survey mode.
modules. Verify the gateway is set to a valid address.
Verify using SWIFT Tools that the detectors are part of
the mesh network.
Verify using SWIFT Tools that the modules are part of
the mesh network.
56 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 57

Testing the Gateway and Devices Troubleshooting and Testing
Problem Description Action
Device does not receive
a profile
Application download
fails
Device is in bootloader Device/Gateway is indicating the LED pattern
A profile request has been initiated but timed
out before receiving a profile
SWIFT Tools failed to finish a download Verify the number of devices in range of the USB
for bootloader and it is indicated as being in
bootloader in the communicator of SWIFT
Tools.
Ensure the gateway or distributor is still in distributor
mode. Ensure the device is in range of the gateway or
distributor. If there are multiple devices in range, the
might be interfering with the profile transfer. Move the
distributor and device to a different area or shut down
the peripheral devices.
adapter during the download does not exceed the
recommended limit of 10 devices. Verify the device is in
range and powered on during the download process.
The device failed to load or initialize the application.
Reboot the device. If it is still in bootloader, the
application will need to be updated using SWIFT Tools.
If problem persists, contact technical support.
C.2 Testing the Gateway and Devices
The gateway must be tested after installation and be part of a periodic maintenance program. The
testing methods must satisfy the Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ). The gateway provides optimum performance when tested and maintained in compliance with NFPA 72 ordinances.
C.2.1 Testing LED Indicators
For more information on LED indicators, refer to Appendix D, “LED Indicators”, on page 59.
C.3 Testing the Wireless Network
Using the SWIFT Tools application, users can:
• Diagnose and troubleshoot the wireless network and connectivity of the devices.
• Monitor the wireless network topology, quality of the communication links between the
devices, live and historical event reports for troubleshooting purposes.
• View the parent-child relationship and the signal strength between the two devices, and
identify the device that has lost the communication link with the wireless network.
In addition, SWIFT Tools:
• Communicates with the gateway to retrieve live information about the connectivity and status
of the devices.
• Stores the wireless network data such as network map, parent-child information, device
information, history events, and network statistics.
The SWIFT Tools application allows retrieval of the following information for diagnosing and
troubleshooting purposes.
• Network Topology
• History of Events
• Network Snapshots
• Network Statistics
• Device Attributes
C.3.1 Network Topology
Parent-Child Devices
The parent-child relationship between the devices in the wireless network is displayed using the
directional arrows.
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 57
Page 58

Troubleshooting and Testing Testing the Wireless Network
Orphan Devices
A device that is not linked with any other device in the wireless topology is an orphan device. The
device is represented as an orphan device due to one of the following reasons:
• The device was originally a part of the wireless network and was dropped.
• When the network topology was retrieved, the device detail was not retrieved.
• The network connections are saturated and parent-child connection with the device is not
established.
Class A Compliance
Each device must comply with Class A guidelines. Every device must have two parent devices to
be compliant with the Class A guidelines.
NOTE: The device image in SWIFT Tools is altered to depict that it does not meet the required
guidelines.
NOTE: Class A guidelines are not applicable to the gateway.
Selecting a device from the graphical representation and clicking either left or right allows you to
view the following details. The Network Topology window allows you to click either left or right
on any connected or orphan device.
C.3.2 History Events
History events of the wireless network can be retrieved and viewed using SWIFT Tools for troubleshooting purposes. This report provides information on when the device gets connected with the
wireless network, mode change, and slot change details.
C.3.3 Network Snapshots
Network snapshots can be retrieved and viewed using SWIFT Tools for troubleshooting purposes.
The network snapshot helps to analyze how the wireless network is functioning over a period of
time.
C.3.4 Network Statistics
Network statistics of the wireless network can be retrieved and viewed using SWIFT Tools for
troubleshooting purposes. The network statistics provide information on the attributes and RSSI of
a device. The attributes provide information on the retransmission count and device re-join events.
The retransmission count is the number of times a device retransmits the wireless signal. The
device re-join events is the number of times the devices get disconnected from the wireless network
and get connected with the wireless network. The RSSI of a device displays the parent-child relationship between the devices.
C.3.5 Device Attributes
Device attributes can be retrieved and viewed using SWIFT Tools for troubleshooting purposes.
The attributes of a device such as low indication, removal indication, level, tamper fault, and others
are retrieved.
58 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 59

Appendix D: LED Indicators
LED Pattern Condition Action Required
Bootloader
normal
Bootloader
Firmware update
Mesh formation
Mesh formation
with profile
distribution
Profile removed
Profile accepted
Normal mode/
background mesh
restructuring
Normal mode/
background mesh
restructuring with
profile distribution
Rescue mode
Device is ready to update.
New application code is being
downloaded.
Gateway is forming the mesh and
looking for devices that are not in the
mesh.
Wait until all devices join the
mesh and then terminate
mesh formation.
Gateway is forming the mesh and looking
for devices that are not in the mesh. The
gateway is also distributing a profile to
any device that requests a profile.
Wait until all devices join the
mesh and then terminate
mesh formation or wait until
the gateway automatically
terminates mesh formation.
Gateway has returned to the
factory default state.
Gateway is now profile assigned.
Normal operation of the gateway
Normal operation of the gateway. The
gateway is also distributing a profile to
any device that requests a profile.
Gateway and the mesh network are
searching for any device that is not in the
mesh network with the same profile.
Legend
Number of blinks
LED color
Interval between blink patterns
Duration of LED state
Indicates value is approximate
Two blinks in this pattern
First blink is green. Second is yellow
7 seconds between blink patterns
Will transition to next state after
approximately 20 minutes
Example:
All units are in seconds. Minute is indicated by “M”.
ledgate1.wmf
7
20
M
7
20
M
1
5
10
14
14
7
3
M
7
3
M
Rescue mode with
profile distribution
Gateway and the mesh network are
searching for any device that is not in the
mesh network with the same profile. The
gateway is also distributing a profile to
any device that requests a profile.
Solid
7
20
M
Gateway LED Patterns
The LED indicator patterns for the wireless gateway and wireless devices are shown in the tables
below.
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 59
Page 60

LED Indicators
LED Pattern Condition Action Required
Profile assigned;
pending magnetic
sensor activations
1st mesh
restructuring
1st mesh
restructuring with
profile distribution
Trouble
Trouble with
profile distribution
Address zero
trouble
Factory default;
pending magnetic
sensor activation
Waiting for a profile
Searching for a
profile
Gateway is starting up with a
profile.
Activate both magnetic sensors
simultaneously within 10 seconds
to remove a profile.
Mesh is formed and initializing.
Mesh is formed and initializing.
The gateway is also distributing a
profile to any device that requests
a profile.
The gateway has a trouble
condition.
Refer to the FACP to identify
the trouble and possible
solution.
The gateway has a trouble
condition. The gateway is also
distributing a profile to any device
that requests a profile.
The gateway address is set to zero.
Gateway is starting up without a
profile.
Gateway is in factory default mode.
Gateway is in factory default mode
and requesting a profile from a
distributor or another gateway.
Legend
Number of blinks
LED color
Interval between blink patterns
Duration of LED state
Indicates value is approximate
Two blinks in this pattern
First blink is green. Second is yellow
7 seconds between blink patterns
Will transition to next state after
approximately 20 minutes
Example:
All units are in seconds. Minute is indicated by “M”.
ledgate2.wmf
Create profile Gateway is creating a profile.
10
1
5
M
7
5
M
7
14
14
4
10
1
10
60
0.5
1
Ensure all devices in the mesh
have a valid address.
Refer to the FACP to identify
the trouble and possible
solution.
Ensure all devices in the mesh
have a valid address.
Activate either magnetic sensor
within 10 seconds to create a
profile.
Use SWIFT Tools to assign a
profile or activate magnetic sensor
to search for a profile.
7
20
M
Gateway LED Patterns (Continued)
60 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 61

LED Pattern Condition Action Required
Bootloader
normal
Slot request
rejected
Mesh forming
Sustained tamper
Bootloader
firmware update
Profile received
Battery check: all
batteries are fresh
Profile removed
Device is ready to update.
Device is not permitted
into the mesh.
Device is part of the mesh
and looking for devices that
are not in the mesh.
New application code is
being downloaded.
Device is now profile
assigned.
Maximum life of installed
batteries remaining in
device
Device has returned to the
factory default mode.
Legend
Number of blinks
LED color
Interval between blink patterns
Duration of LED state
Indicates value is approximate
Two blinks in this pattern
First blink is green. Second is yellow
7 seconds between blink patterns
Will transition to next state after
approximately 20 minutes
Example:
All units are in seconds. Minute is indicated by “M”.
Confirm device count and
software version.
Device is tampered.
Solid
Solid
Distributor mode Device is distributing its
profile to other devices
which requested a profile.
leddev1.wmf
8
7
20
M
15
5
1
10
2.5
0.5
Ensure detector is seated in the
base and the module has the
faceplate on.
14
7
3
M
Rescue mode Device is functioning as
normal and searching for
lost devices.
Normal mode Device is distributing as
normal
720
M
Device LED Patterns
Use SWIFT Tools to initiate
download.
Self test fail
Low battery cut-off
Device has failed internal
self diagnostics.
Device is functioning. Replace batteries.
Restart the device. If problem
persists, contact technical support.
1
Solid
LED Indicators
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 61
Page 62

LED Indicators
LED Pattern Condition Action Required
Legend
Number of blinks
LED color
Interval between blink patterns
Duration of LED state
Indicates value is approximate
Two blinks in this pattern
First blink is green. Second is yellow
7 seconds between blink patterns
Will transition to next state after
approximately 20 minutes
Example:
All units are in seconds. Minute is indicated by “M”.
leddev2.wmf
7
20
M
Device LED Patterns (Continued)
Battery Check: all
batteries present
Searching for mesh
(in rescue mode)
Profile
modification
1st mesh
restructuring
Generic device trouble
(dual address, low
battery, etc.)
Searching for mesh
(in formation mode)
Minimum of 6 months battery
life remaining.
Device has a profile and
can be set as a distributor
or have profile removed.
Mesh is formed and
initializing.
Device is in the mesh and in
a trouble condition.
Profile is assigned and device
is searching for the mesh.
Profile is assigned and device
is searching for the mesh.
Tamper entry Device has just been
tampered.
Ensure the mesh is in rescue
mode or wait for timeout to search
mesh in formation mode.
Discovered mesh Device discovered the
mesh.
60
Solid
2.5
Toggle SLC address dials to
respective pattern to enter
desired mode.
90
3
Ensure the mesh is in formation
mode.
25
7
5
M
Refer to the FACP to identify the
trouble and possible resolution.
The XLS140-2/XLS-120 does not
support trouble indication.
14
4
Ensure detector is seated in the base
and the module has a faceplate.
Solid
6
5
Solid
Waiting for a profile
Searching for a profile
Pending site survey
Alarm state
Battery Check:
weak
Device is in factory default
mode.
Device is in factory default
mode and requesting a profile
from a distributor or gateway.
Device is in factory default
mode and is ready to enter
site survey mode.
Less than 6 months
battery life left or not all 4
batteries are present.
Device is functioning as
normal and has been
activated.
Use SWIFT Tools to assign a
profile or activate magnetic sensor
to search for a profile.
Ensure all 4 batteries are present
or replace the batteries.
Clear the tamper condition within 1
minute to enter site survey mode.
10
5
Solid
2.5
3
0.5
1
M
62 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 63

Index
A
abbreviations 9
additional references
assign profile
assumed knowledge
attributes
58
8
34, 35, 39
8
B
background events 42
bootloader
24, 40
C
Class A compliance 58
class A fault
clear tamper
collapse network command
configuration
configure profile
CR123A batteries
create profile
creating jobsite
41
42
17
23
33
17
49
D
detector
assign profile
transfer profile
device
attributes
bootloader
distributor
factory default
initial mesh restructuring mode
LED indicators
mesh formation
mesh participant
network snapshots
network statistics
normal mode
profile assigned
rescue mode
site survey
device drop
device indication
device initialization
device operations
device spacing
devices
33
Class A compliance
configuration and programming
installing
orphan
35
35
58
40
40
39
40
40
40
58
58
40
39
40
39
42
42
42
39
51
58
34
58
27
40
34
parent-child
disable trouble reporting
distributor
distributor mode
dongle
43
duplicate address
57
40
37
41
E
event reporting 22
events
background
existing profile
42
18
F
factory default 23, 38, 39
G
gateway 10
bootloader
collapse network
configuration
create mesh network
description
disable trouble reporting
existing profile
factory default
initial mesh restructuring
LED indicators
lock/unlock
mesh formation
mesh restructuring
mounting
new profile
normal mode
password reset
power
profile configure
profile distribution
programming
remove profile
rescue mode
restrictions
RF interference
silence network
SLC configuration
SLC connections
specifications
start-up
weak link trouble
wiring
24
27
17
10
18
23
12
24
21, 23
24
13
17
24
25
16
23
17
18
24
29
29
28
22
15
11
23
25
14
26
18
26
24
21
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 63
Page 64

H–T Index
H
heat detector 33
I
initial mesh restructuring 24
initial mesh restructuring mode
initialization
installing devices
interference
isolator modules
42
34
29
16
40
J
jamming 42
jobsite
new
49
open
50
jumper
13
L
LED indicators 12, 18, 19, 40
link quality test
procedure
requirements
lock
24
low battery
51
51
51
41
M
magnetic sensor 12, 18, 19, 21, 22, 37
mesh formation
mesh network
mesh participant
mesh restructuring
modes of operation
module
assigning profiles
batteries
module configuration
module installation
monitor module
mounting
19, 21, 23, 37, 40
18, 23
40
24
22, 39
34
33
34
34
33
13
N
network installation restrictions 29
network limit
network snapshots
network statistics
network topology
no answer
normal mode
29
58
58
57
42
24, 40
O
opening jobsite 50
operations
22
orphan devices
overlapping networks
58
29
P
panel indication 42
parent-child devices
password reset
pre-class A fault
profile
assigned
configure
create new
remove
removing
profile distribution
programming
pull station
33
57
25
42
39
23
17
20, 38
18
21
17
R
related documents 8
remove profile
repeater
rescue mode
restrictions
installation
RF interference
RF scan test
status
RF spectrum
rotary switches
18, 20, 38
41
24, 40
29
29
29
53
53
29
38
S
sensor
magnetic
silence network command
site survey
SLC configuration
SLC connections
smoke detector
specifications
spectrum
RF
spread
spread spectrum
start-up
SWIFT Tools
19
39, 51
22
15
33
11, 44
29
29
29
29
23
48, 57
T
tamper 41
clear
42
testing
57
transfer profile
transmission
trouble condition
35
24
24, 26, 40
28
64 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 65

Index U–X
trouble messages 30
trouble reporting
disable
26
troubleshooting
55
U
unlock 24
USB adapter
specifications
43
44
W
walkie talkie mode 29, 31
weak link
wireless devices
wireless gateway
wiring
41, 42
trouble reporting
33
10
14
25
X
XLS-WSG 10
specifications
11
SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 65
Page 66

Notes
66 SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015
Page 67

SWIFT™ Wireless Manual — Form Number 95-8544-2 P/N LS10036-000XL-E:C 5/8/2015 67
Page 68

Automation and Control Solutions
Honeywell International Inc. Honeywell Limited-Honeywell Limitée
1985 Douglas Drive North 35 Dynamic Drive
Golden Valley, MN 55422 Scarborough, Ontario M1V 4Z9
customer.honeywell.com
® U.S. Registered Trademark
© 2015 Honeywell International Inc.
95-8544-2 C. Rev. 05-15
 Loading...
Loading...