
Basic
HITACHI SJ Series
Guide
I
nverter
Read this “Basic
P1
Guide
”, and keep it handy for future reference.
If you have any
Refer to
or
C
ontact
for Inverter.
When making a contact, inform
the reference number on below.
Introduction
Contents
Chapter 1
:
Chapter 2
:
Chapter 4
:
Chapter 3
:
I/O Adjustment
Chapter 5
:
Chapter 6
:
Chapter 7
:
Index
inquiry or problem
Chapter 5 Troubleshooting
to
the Technical Inquiry Service
List of contact information
NT
Safety Instructions
Installation and Wiring
Settings
Operation Setting and Examples of
Troubleshooting
Maintenance and Inspection
Specifications
NT2511B
2511
,
X

0-1
Introduction Introduction/Cautions
/Warranty & Contact us
Introduction
Thank you for purchasing Hitachi SJ Series P1 Inverter.
This is a user guide for basic handling and maintenance of
Hitachi SJ Series P1 Inverter.
For the purpose of reduction of paper usage and
provision of the latest information, we enclose the Basic
Guide only while providing the User's Guide for more
detailed description through electronic means instead of
CD or a printed document.
About the Basic Guide (this document)
The Basic Guide provides the minimum information
necessary for handling the product. Please make sure to
read this document as well as the User's Guide with more
detailed information.
About the User's Guide
The User's Guide provides detailed information necessary
for handling the product. Please make sure to read the
User's Guide for proper use.
If future updates make any difference from the Basic
Guide, the description in the User's Guide will have higher
priority. You should use the inverter by observing
specifications described in User's Guide. You should also
prevent risks by performing proper inspection and
maintenance.
Please refer to the following link for download:
Hitachi Industrial Equipment Systems' Website
http://www.hitachi-ies.co.jp/
Please follow as below on the Website.
Product Information -> Inverter -> Download of
technical data
Handling an optional products
If you use the inverter with optional products, also you
should read the instruction enclosed in those products.
Cautions
Proper use of the inverter
Please read the Basic Guide, User's Guide and optional
products instruction before handling. Read carefully the
Basic Guide, User's Guide or optional product instruction
before handling or performing maintenance of the
product.
Before attempting installation, operation, maintenance,
and inspection work, you should understand the
knowledge of equipment, information of safety,
precaution and how to use and service the inverter.
Cautions
No part of this document may be reproduced or reformed
in any form without the publisher's permission.
The contents of the document are subject to change
without prior notice.
If you lose the Basic Guide and need another one in
printed form, you will be charged for resupply, so please
keep it carefully.
You "CANNOT DO" what is not described in Basic Guide or
User's Guide. We are not responsible for any impact from
operations regardless of unexpected failure or accident
due to the operation or handling of the product in a
manner not specified in Basic Guide or User's Guide. We
apologize in advance for any inconvenience this may
cause.
If you find any unclear or incorrect description, missing
description, or misplaced or missing pages, please takes
time to inform Hitachi inverter technical service office.
Note that, the Basic Guide, User's Guide and the
instruction for each optional product enclosed, should be
delivered to the end user of the inverter. And also make
sure to be accessible any other guides or instruction to
the end user.

0-2
Introduction Introduction/Cautions
/Warranty & Contact us
Method of Inquiry and Product Warranty
Method of Inquiry about Product
• For an inquiry about product damage or faults or a question
about the product, notify your supplier or Hitachi inverter
technical service office.
Product Warranty
• The product SJ series P1 inverter will be warranted by Hitachi
Industrial Equipment Systems Co., Ltd., afterward "Hitachi",
during the warranty period from your date of purchase only
under proper usage of product.
• Furthermore, the warranty expressed here is covered only for
the product delivered from Hitachi, and will not be
responsible for others damage or loss of products like a
motor or any equipment or systems damage caused by
improper usage of the product. Minimize the consequence
on equipment or system by applying safety design which is
able to notify a hazard alarm to the user in case of
malfunction or damage of the delivered product. The
selection and application of delivered product must be done
with sufficient margin on performance, as well as other
equipment or system with sufficient redundancy design. Also,
the compatibility of the product with the customer's
intended use is not warranted, hence the validation test
should be done by the customer by their responsibility
before put in operation.
• In case of delivery a defective product, or encountered a
defects on quality during a manufacturing process, Hitachi
will repair or exchange with free of charge, only when the
product is in warranty period (afterward, we call "warranty
service").
• The product will be warranted for one year from your date of
purchase. However, depending on case, sending technical
assistance for repairing will be charged to the customer. Also,
Hitachi will not be responsible of any readjustment or testing
on site.
• After warranty service, the exchanged or repaired part will be
warranted for 6 month from date of warranty service. Hitachi
will be responsible for repair or exchange of defective part
only for the exchanged or repaired part only during this
warranty period.
• In order to receive warranty service, you should present the
recipe issued by product supplier or any other document that
permit to check the purchase date. However, any defects,
damage, malfunction or any other failure caused by one of
the following facts will not be covered by warranty service.
(1) Cannot confirm the purchase date.
(2) The damage or fault resulted from improper usage or
inadequate handling of the product and not conforming
usage described into the user's guide or basic guide.
(3) Incorrect usage of product, inadequate setting of
product and optional product, remodeling or inadequate
repair and repair carried out by unqualified repair
center.
(4) Deterioration and wear resulted from normal operation.
(5) Fault resulted from natural disaster, such as earthquake,
fire disaster, lightning strike, pollution, salt pollution, or
abnormal voltage or any others external factor.
(6) Shock, falling, or Vibration resulted during
transportation or displacement after purchase.
(7) Damage or fault resulted from remodeling firmware by
unqualified personal not belonging to Hitachi.
(8) Damage or fault resulted from customer's made
programing function (EzSQ).
(9) For overseas use.
• By warranty service, might lose the data stored inside the
product, as well as, customers made (EzSQ) program. Make
sure to back up by own responsibility. However, in case of
malfunction resulting from the circuit board of the storage
devices, the backup wil not be possible. It is recommended
to keep a backup during the testing phase by using VOP or PC
software ProDriveNext.
Liability Limitation
• Neither Hitachi-IES, Affiliated company nor related dealer are
liable to the written and unwritten public requirement
including the common sense of the product or requirement
in specific application
• Even more, Hitachi, affiliated company or related dealer are
not responsible of any incidental damage, special damage,
direct loss, or indirect loss (even predictable or not) resulted
on customer because of product defect.
■ Inverter Model: It beginning with P1- in specification label.
■ Manufacturer Number(MFG No.): It shows in specification label.
■ Date of purchase: Customer's purchased period.
■ Inquiry contents:
・ Inform us the defective point and its condition.
・ Inform us the suspicious content and its detail.

0-3
Introduction Introduction/Cautions
/Warranty & Contact us
Warranty Service
• The customer is able to receive a warranty service from
product supplier or service station, if the product does not
meet the function described on basic guide or user's guide.
Moreover, in case of any mismatch occurred between user's
guide and basic guide, user's guide content will take a
priority.
• Contact to your supplier or local Hitachi distributor or service
station for fare-paying services.
Change on Product Specification
• We are sorry because any information described in Brochure,
Basic Guide, User's Guide or Technical Document would be
modified without notice.
Precaution for Product Application
• The product should apply following the condition of use,
handling method and precautions described in User's Guide.
• The installed product should be confirmed previously by own
that the product installation has done as intended in the
customer system.
• When using Hitachi inverter consider on below
(1) Select inverter with sufficient capacity for rate current
and performance.
(2) Safety design, for example, redundant system design.
(3) Equipment design where minimize hazard in case of
inverter failure.
(4) For safety precautions, make a system configuration that
alarms the hazard to user.
(5) Periodic maintenance of Hitachi inverter and customer's
equipment.
• Hitachi inverter is designed and manufactured intentionally
to be applied for general industrial equipment application.
It is not intended to be used for the applications listed
below therefore. In case inverter is used for these
applications, it is out of warranty unless there is a special
written agreement. Otherwise, the product will not be
warranted.
(1) Special application such as aircraft, spacecraft, nuclear,
electric power, passenger transportation, medical,
submarine repeater, etc.
(2) For application such as elevator, amusement equipment,
medical equipment which might have a big effect on
human life and property.
• Even for above application, in case there is an agreement for
the limitation of the purpose and quality, please contact to
our sales office. Further study will be carried out to check
whether inverter is applicable for that specific application or
not.
• For applications that involve human life, or have risk of
important loss, make sure to avoid a critical accident by
installing a fail-safe device, protecting device, detecting
device, alarm device, or spare device, etc.
• This inverter is only for three phase induction motor [IM] or
three phase synchronous motor [SM(SMM)].
• For any other application make inquiries.
Supplement
• Refer to "Chapter 7 Specification" for short lifespan
component.
• For optional product refer attached instruction.
• This warranty term will not restrict a legal right of customer
who has purchased the product.
• Contact to the local supplier for warranty of purchased
product sales in oversea.
Contact Information
Hitachi America, Ltd. (Charlotte Office)
Industrial Components and Equipment Division
6901 Northpark Blvd., Suite A, Charlotte, NC 28216,
U.S.A
TEL : +1(704) 494-3008
FAX : +1(704) 599-4108
Hitachi Europe GmbH
Industrial Components & Equipment Group
Am Seestern 18 (Euro Center),
D-40547 Dusseldorf,
Germany
TEL : +49-211-5283-0
FAX : +49-211-5283-649
Hitachi Asia Ltd.
Industrial Components & Equipment Division
No.30 Pioneer Crescent, #10-15 West Park Bizcentral,
Singapore 628560,
Singapore
TEL : +65-6305-7400
FAX : +65-6305-7401
Hitachi Australia Ltd.
Level 3, 82 Waterloo Road
North Ryde, N.S.W.2113
Australia
TEL : +61-2-9888-4100
FAX : +61-2-9888-4188
Hitachi Industrial Equipment Systems Co., Ltd.
AKS Building, 3, Kanda
Nereibei-cho, Chiyoda-ku,
Tokyo, 101-0022
Japan
TEL : +81-3-4345-6910
FAX : +81-3-4345-6067

●
●
●
●
Contents
Quick start
Introduction/instructions
Types of Warnings
Description of Safety Symbols
Precautions for Installation
Precautions for Wiring
Precautions
Check the Inverter
Install the Inverter
Dimensions Drawing
Inverter Wiring
Wiring of
Recommended
Operation Setting and Examples of IO
Keypad
overview
Monitor
Troubleshooting
Cautions for Maintenance/Inspection
Daily and Periodic Inspections
Method of Checking the Inverter and Converter
Circuits
................................
Specifications Table
Appendix Index
Quick start
Chapter 1 Safety Instructions
Chapter 2 Installation and Wiring
Chapter 3 Operation Setting and Examples of IO Adjustment
Chapter 4 Settings
Chapter 5 Troubleshoot
Chapter 7 Specifications
Chapter 6
................................
................................
to Run
and Test Running
................................
................................
................................
................................
the main circuit
wire gauges, accessories etc.
................................
naming
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
Inspection and
..............................
................................
..............................
................................
................................
................................
..............................
................................
.................
ing
Maintenance
.......
................
.
........
.................
................
................
.............
.....................
.....
.......
Adjustment
..................
..................
4
....................
..................
..
..............
...........
index
Appendix
0-4
0-1
0-2
1-1
1-1
1-2
1-2
1-3
2-1
2-2
2-4
2-6
2-7
2-8
3-1
4-1
-10
5-1
6-1
6-2
6-4
7-1
-1
-1
●
●
Precautions
Precautions for
Other Cautions
Compliance
Compliance
Applicable Circuit Breaker
Ch
opper Breaking Resistor
Wiring
Wiring of the Control Circuit
Control Circuit Wiring Section
Residual Risk
Parameters
DC
-
Output of Life Warning
Methods of Measuring the Input/Output Voltages,
Current, and Power
Method of Inquiry and Product Warranty
Contents
................................
for Maintenance/Inspection
Dispolsal
................................
to European Directive (CE)
to UL standards
................................
................................
naming
Bus Capacitor Life
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
Curve
................................
................................
................................
...............................
.................
............................
......................
.............................
...................
.....................
Contents
.......... 0-3
0-4
1-4
.......... 1-4
1-4
1-5
....... 1-7
......... 2-10
........ 2-12
....... 2-13
..... 2-17
... 2-19
2-24
4-13
........ 6-5
............... 6-5
6-6

0-5
Contents
Contents
(Memo)

Chapter 1
1.1
In the Basic Manual, the severity levels of
precautions and residual risks are classified as:
"
Display
Even more, that "
to a serious risk depend on the circumstances. Be sure to
follow the instruction because whichever contains
important safety description.
Chapter 1
Safety Instructions
Types of Warnings
WARNING"
and
m
eanings
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous
situations, which would most likely result in serious
personal
injury or death,
loss or damage.
Indicates that incorrect
situations, which may result in serious personal injury or
death, and may result in major
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous
situations,
which may result in moderate or slig
personal
injury or damage, and may result
loss or damage.
"
CAUTION
and may result in major physical
WARNING
handling may cause hazardous
CAUTION
CAUTION
".
DANGER
physical loss or damage.
" level description may lead
safety
"
DANGER
ht
only
physical
1-1
",
1.2
It describes annotation of t
to follow and pay attention of content.
Symbols
1.3 Description of Safety Symbols
Read carefully following safety instruction for handling.
Description of Safety Symbols
m
eaning
Indicates a danger, warning or caution notice
for
fire, electric shock and high temperature
while handling the product
Details are indicated in or near
or words.
Indicates “what you must not do”
the described acts
product.
Indicates “what you must do”
the instructions
product.
Safety Instructions
he
s
The
drawing on the left indicates
non-
specific and general
caution”.
The drawing on the left indicates
possible
damage
shock”.
in the operation of the
s
ymbols in context
.
due to electric
in the
operation of the
according to
. Be sure
by pictures
“a
danger or
“a
to prohibit

Chapter 1
1.3.1
Caution
•
•
1.3.2
Precautions for installation
●
•
•
•
•
●
•
1.3.3 P
recautions for Wiring
●
•
•
•
●
•
Caution
Practice
Fire
Injury
Prohibited
Electric
shock Fire
Practice
Failure
Prohibited
Practice
Prohibited
Incorrect handling may result in personal
or severe injury, or may result in damage to
inverter, motor or the whole system.
Be sure to read this Basic Manual and
documents thoroughly
operating, maintaining, inspecting or
inverter.
You run the risk of fire!
Do not place flammable materials near
installed inverter.
Prevent foreign matter (e.g., cut pieces of wire,
sputtering welding materials, iron chips, wire,
and dust) from
Install the inverter on a non
such as, metal
Install the inverter in a well
site
not exposed to direct sunlight.
where the inverter is exposed to high
temperature,
high humidity, condensation, dust,
explosive gases,
gases, g
rinding fluid mist,
You run the risk of injury!
Do not install and operate the inverter
damaged or its parts are missing.
You run the risk of electric shock or
fire!
Be sure to ground
Commit wiring work to
Before wiring, make sure that the power supply
is off.
You
run the risk of failure of the
inverter!
Do not pull the wire after wiring.
before installing, wiring,
penetrating into
-
surface.
corrosive gases, flammable
or salt water.
the inverter.
a qualified electrician.
death
appended
using the
to
the inverter.
flammable surface,
-
ventilated indoor
Avoid places
if it is
WARNING
D
DANGER
1-2
the
the
Failure
Prohibited
AN
GER
Caution
Fall
Injury
Prohibited
Practice
Electric
shock
Injury
Short
circuit
Ground
Prohibited
Practice
Practice
•
Many of the drawings
inverter with covers and/or parts
as removed to
•
Do not operate the inverter in the status shown in
those drawings. If you have removed the
and/or parts, be sure to reinstall them in their
original positions before starting operation,
follow all instructions when operating the inverter.
●
You run the risk of injury due to the
inverter falling
•
Do not hold its cover parts w
inverter.
•
Install the inverter on a structure able to bear
the weight specified in this Basic
•
Install the inverter on a vertical wall that is free
of vibrations.
●
You run the risk of failure of the inverter!
•
The inverter is precision equipment.
allow it to fall or be subject to high impacts.
•
Also do not step on it, or place a heavy load on
it.
●
You run the risk of electric shock and
injury!
•
Perform wiring
●
You run the risk of short circuit and ground
fault!
•
Do not remove rubber bushings from the wiring
section.
may damage the wire.
Safety Instructions
illustrate the details.
only after installing the inverter.
Otherwise, the edges of the wiring cover
in the Basic
blocking your view
hen carrying the
Guide show
the
covers
and
Guide.
Do not

Chapter 1
●
●
1.3.4 P
recautions
●
●
●
Injury
Fire
Practice
Electric
shock
Injury
Prohibited
Electric
shock
Fire
Prohibited
Prohibited
Electric
shock
Prohibited
Injury
Fire
Practice
You run the risk of injury or fire!
•
Do not connect AC power supply to
output terminals (U, V, and W)
•
Make sure that the voltage of AC power supply
matches the rated voltage of your inverter.
You run the risk of electric shock
and injury!
•
Before operating slide switch SW in the
inverter, be sure to turn off the power supply.
•
Since the inverter supports two modes of
cooling-
fan operation, the inverter power is
not always off, even when the cooling fan is
stopped.
Therefore, be su
the power supply is off before wiring.
to
Run and
You run the risk of electric shock or
fire!
•
While power is supplied to the
touch any internal part or terminal of the
inverter. Also do not check signals, or connect
or disconnect any wire or connector.
•
While power is supplied to the inverter, do not
touch any internal part of the in
not insert a
m
You run the risk of electric shock!
•
Be sure to close the terminal block cover
before turning on the inverter power.
open the terminal block cover
being supplied to the inverter or
remains inside.
•
Do not operate switches
You run the risk of injury or fire!
•
While power is supplied to the inverter,
touch the
terminal of the inverter,
has stopped.
Test Running
aterial such as a rod
with wet hands.
any of the
.
re to confirm that
inverter, do not
verter. Also do
and etc.
Do not
while power is
voltage
do not
even if it
WARNING
DANGER
1-3
.
Prohibited
Injury
Damage
Prohibited
Injury
Prohibited
Practice
Practice
●
•
Do not use a single
•
Do not connect a resistor directly to any of the
DC terminals (PD, P, and N).
•
Do not use
the primary and secondary sides of the inverter
to stop its operation.
•
Tighten each screw to the specified torque.
•
No screws must be left loose.
•
Connect an earth
input circuit.
•
Use only the power cables, earth
breaker, and magnetic contactors that have
specified capacity (ratings).
●
• Do
not select the retry mode for controlling an
elevating or traveling device because free
status occurs in retry mode.
●
•
If the retry mode has been selected, the inverter
will restart suddenly after a break in the tripping
status.
the inverter when the inverter is under such
circumstances.
safety can be ensured,
restarts sudden
•
The [STOP] key on the operator keypad is effective
only when its function is enabled by setting.
Prepare an emergency
•
If an operation command has been input to
inverter
inverter may
recovery.
danger,
inverter
•
If an operation command has been input to the
inverter before the inverter enters alarm status,
the inverter will restart suddenly when the alarm
status is reset.
make sure that no operation command
input.
Fire
Safety Instructions
You run the risk of fire!
the magnetic contactor installed on
-
You run the risk of injury and damage to
machine.
You run the risk of injury!
Stay away from the machine controlled by
(Design the machine so that human
ly.)
before a short
restart operation after the power
If such a restart may put persons in
design a control circuit that disables the
rom restarting after power recovery.
Before resetting the alarm status,
-phase input.
-
leakage breaker
even when the inverter
stop switch separately.
-term
power failure, the
to the po
wer
-
leakage
the
-
running
the
has been

Chapter 1
●
1.3.5
Precautions for
●
1.3.6
Precautions for disposal
●
1.3.7 O
ther Cautions
●
•
Injury
Damage
Practice
Electric
shock
Practice
Electric
shock
Fire
Injury
Prohibited
Injury
Explosion
Practice
You run the
machine.
•
The inverter
speed of
operating
capacity and ratings
before operating
•
When you run the motor at a high frequency,
check
and confirm to each manufactures of a
permitting revolution of
and machine
• Check the
rotate
sound,
and vibrations
Maintenance/Inspection
You run the risk of electric shock!
•
Before inspecting the inverter, be sure to turn
off the power supply and
or more.
(Before inspection, confirm
Charge lamp
voltage between terminals P and N is
less.)
You run the risk of injury and
explosion!
•
For disposal of the inverter, outsource to a
qualified
industrial waste disposal contractor.
Disposing of the inverter on your own may
result in an explosion of the capacitor or
produce poisonous gas.
•
Contact us or your distributor
inverter.
You run the risk of electric shock, fire
and injury!
Never modify the inverter.
DANGER
risk of injury and damage to
easily
allows you to
motor.
of the motor or machine
.
the
.
motor
direction
while operating
wait for 10 minutes
on the inverter is off and
c
ontrol the
C
onfirm the
respective
motor
, abnormal
.
that the
the DC
45 V or
for fixing the
WARNING
DANGER
DANGER
1-4
Burn
I
njury
Prohibited
Injury
Practice
Prohibited
Practice
Life cycle
Practice
●
You run the risk of burn injury.
•
Inverter heat sink will heat up during operation.
Do not touch the heat sink
●
You run the risk of injury!
•
Install an external brake system
•
Commit only a designated person to
maintenance,
of parts.
metal accessories, e.g., bracelets,
maintenance and inspection work and to use
insulated tools
•
A qualified waste disposer includes
industr
ind
the
the
c
leansing
●
You run the risk of
the
•
Sterilizing and disinfecting a packaging
materials
fumigation method.
the fumigation treatment,
receive a critical damage
steams
(including fluorine, chlorine, bromine and
iodine)
Safety Instructions
inspection, and the replacement
(Be sure to remove wristwatches and
for the
ial waste collector/transporter
ustrial waste disposal operator
act related to
waste
m
for
disposing of the inverter.
life cycle of
a
use a means other than
.
Especially,
can cause corrosion in
CAUTION
.
if needed.
work.)
procedures stipulated in
anagement and
significantly
product!
If the product is included in
electronic parts
from emitted gases or
halogen disinfectants
the capacitor.
before
and
. Follow
p
ublic
shortening
wood
wood

1.4
(CE)
Compatibility)
The SJ series P1 inverter conforms to requirements of
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive (2014/30/EU).
However, when using the
with the following specifications and requirements to meet the
EMC Directive and other standards in Europe:
1. Power supply requirements
2. Installation requirement
3. Wiring requirements
4. Environmental requirements
Chapter 1
Compliance
1.4.1
Caution for EMC (Electromagnetic
WARNING: This equipment must be installed, adjusted,
and maintained by qualified engineers who have expert
kno
wledge of electric work, inverter operation, and the
hazardous circumstances that can occur. Otherwise,
personal injury may result.
a. Voltage fluctuation must be
b. Voltage imbalance must be ±3% or less.
c. Frequency variation must be ±4% or less.
d. Total harmonic distortion (THD) of voltage must be ±10% or
less.
a. SJ series P1 includes a built
filter must be activated.
b.
According to EN61800
any inverter with only C3 filter inside may NOT be
connected to a low voltage public power supply in
residential areas since for these installations C1 is required.
c.
In case of external filter
required according to EN61800
emit
high frequency interference in residential areas which
may require additional EMC measures”.
d. According to the EN6100
DC choke should
power line.
a. A shielded wire (screened cable) must be used for motor
wiring, and the length of the cable must be according to the
following table (Table 1 on page 1
b. The carrier frequ
following table to meet an EMC requirement (Table1 on
page 1-12).
c. The main circuit wiring must be separated from the control
circuit wiring.
(When an
EMC
a. SJ series P1
must be according to SJ series P1 specifications.
to European Directive
inverter in Europe, you must comply
-
3 it is mandatory to mention that
for
-
3
be installed
ency must be set according to the
filter is used)
inverter that is activated built
-
15% to +10% or less.
-
in EMC filter. The built
C2, an additional note is
-
3 that “this product may
3
-12, an
additional
for reducing harmonics in
-12).
-
in EMC
AC reactor or
-in EMC filter
1-5
Safety Instructions

1-6
Chapter 1
Safety Instructions
Table 1
Model Cat.
Cable
Length
(m)
Carrier
Frequency
(kHz)
Model Cat.
Cable
Length
(m)
Carrier
Frequency
(kHz)
P1-00044-L
(P1-004L)
C3 10 2 - - - -
P1-00080-L
(P1-007L)
C3 10 2
P1-00041-H
(P1-007H)
C3 10 2
P1-00104-L
(P1-015L)
C3 10 2
P1-00054-H
(P1-015H)
C3 10 2
P1-00156-L
(P1-022L)
C3 10 2
P1-00083-H
(P1-022H)
C3 10 2
P1-00228-L
(P1-037L)
C3 10 2
P1-00126-H
(P1-037H)
C3 10 2
P1-00330-L
(P1-055L)
C3 5 2
P1-00175-H
(P1-055H)
C3 5 2
P1-00460-L
(P1-075L)
C3 5 2
P1-00250-H
(P1-075H)
C3 5 2
P1-00600-L
(P1-110L)
C3 5 2
P1-00310-H
(P1-110H)
C3 5 2
P1-00800-L
(P1-150L)
C3 10 1
P1-00400-H
(P1-150H)
C3 10 2
P1-00930-L
(P1-185L)
C3 10 1
P1-00470-H
(P1-185H)
C3 10 2
P1-01240-L
(P1-220L)
C3 10 1
P1-00620-H
(P1-220H)
C3 10 2
P1-01530-L
(P1-300L)
C3 5 2
P1-00770-H
(P1-300H)
C3 5 2
P1-01850-L
(P1-370L)
C3 5 2
P1-00930-H
(P1-370H)
C3 5 2
P1-02290-L
(P1-450L)
C3 5 2
P1-01160-H
(P1-450H)
C3 5 2
P1-02950-L
(P1-550L)
C3 5 2
P1-01470-H
(P1-550H)
C3 5 2
- - - -
P1-01760-H
(P1-750H)
C3 5 2
- - - -
P1-02130-H
(P1-900H)
C3 5 2
- - - -
P1-02520-H
(P1-1100H)
C3 5 2
- - - -
P1-03160-H
(P1-1320H)
C3 5 2

1-7
Chapter 1
Safety Instructions
1.5 Compliance to UL standards
1.5.1 UL CAUTION
GENERAL:
SJ series Type P1 inverter is open type AC Inverter with
three phase input and three phase output. It is intended
to be used in an enclosure. It is used to provide both an
adjustable voltage and adjustable frequency to the AC
motor. SJ-P1 automatically maintains the required
volts-Hz ratio as a function to control motor speed. It is
multi-rated device and the ratings are selectable
according to load types by operator with key pad
operation.
Markings:
Maximum Surrounding Temperature:
- ND (Normal Duty): 50degC
- LD (Low Duty): 45degC
- VLD (Very Low Duty): 40degC
Storage Environment rating:
- 65degC (for transportation)
Instruction for installation:
- Pollution degree 2 environment and Overvoltage
category III
Electrical Connections:
- See “7.5 Main circuit terminal wiring” of user's
guide
Interconnection and wiring diagrams:
- See “7.7 Control circuit terminal wiring” of user's
guide
Short circuit rating and overcurrent protection device
rating:
P1-L series models
- Suitable for use on a circuit capable of delivering not
more than 5,000 rms symmetrical amperes, 240 V
maximum”.
P1-H series models
- Suitable for use on a circuit capable of delivering not
more than 5,000 rms symmetrical amperes, 500 V
maximum”.
Integral:
- Integral solid state short circuit protection does not
provide branch circuit protection. Branch circuit
protection must be provided in accordance with the
National Electrical Code and any additional local
codes

1-8
Chapter 1
Safety Instructions
Terminal size and terminal tightening torque for field
wiring:
- Use 75degC only for temperature rating of field
wiring.
- Use Cupper conductors only.
Model Load Type
Required
Torque
(N.m)
Conductor
size
(AWG)
Model Load Type
Required
Torque
(N.m)
Conductor
size
(AWG)
P1-00044-L
(P1-004L)
VLD
1.4 14
LD
ND
P1-00080-L
(P1-007L)
VLD
1.4 14
P1-00041-H
(P1-007H)
VLD
1.4 14
LD LD
ND ND
P1-00104-L
(P1-015L)
VLD
1.4 14
P1-00054-H
(P1-015H)
VLD
1.4 14
LD LD
ND ND
P1-00156-L
(P1-022L)
VLD
1.4 10
P1-00083-H
(P1-022H)
VLD
1.4 14
LD LD
ND ND
P1-00228-L
(P1-037L)
VLD
1.4 10
P1-00126-H
(P1-037H)
VLD
1.4
12
LD LD
14
ND ND
P1-00330-L
(P1-055L)
VLD
3 8
P1-00175-H
(P1-055H)
VLD
3 10
LD LD
12
ND ND
P1-00460-L
(P1-075L)
VLD
3 6
P1-00250-H
(P1-075H)
VLD
3 8
LD
8 LD
10
ND ND
P1-00600-L
(P1-110L)
VLD
4
4
P1-00310-H
(P1-110H)
VLD
4 8
LD LD
ND 6 ND
P1-00800-L
(P1-150L)
VLD
2.5 – 3.0
3
P1-00400-H
(P1-150H)
VLD
4 8
LD LD
ND 4 ND
P1-00930-L
(P1-185L)
VLD
2.5 – 3.0
1
P1-00470-H
(P1-185H)
VLD
4
6
LD 2 LD
ND 3 ND 8
P1-01240-L
(P1-220L)
VLD
5.5 – 6.6
2/0
P1-00620-H
(P1-220H)
VLD
4
4
LD 1/0 LD
ND 1 ND 6
P1-01530-L
(P1-300L)
VLD
6.0
Parallel of 1/0
P1-00770-H
(P1-300H)
VLD
6.0
1
LD LD 2
ND ND 3
P1-01850-L
(P1-370L)
VLD
15.0
Parallel of 1/0
P1-00930-H
(P1-370H)
VLD
15.0 1
LD
Parallel of 1/0
LD
ND 4/0 ND
P1-02290-L
(P1-450L)
VLD
6.0 – 10.0
Parallel of 2/0
P1-01160-H
(P1-450H)
VLD
6.0 – 10.0
Parallel of 2/0
LD
Parallel of 1/0
LD
Parallel of 1/0
ND
Parallel of 1/0
ND 1
P1-02950-L
(P1-550L)
VLD
19.6
Parallel of 3/0
P1-01470-H
(P1-550H)
VLD
6.0 – 10.0
Parallel of 1/0
LD
Parallel of 3/0
LD
Parallel of 1/0
ND 350kcmil
ND
2/0
1-9
Chapter 1
Safety Instructions
Required protection by Fuse and circuit-breakers:
P1-L series models
Model
Fuse Circuit Breaker
Type
Maximum Rating Maximum Rating
Voltage (V) Current (A) Voltage (V) Current (A)
P1-00044-L
(P1-004L)
Class J or T 600 50 - -
P1-00080-L
(P1-007L)
Class J or T 600 50 - -
P1-00104-L
(P1-015L)
Class J or T 600 50 - -
P1-00156-L
(P1-022L)
Class J or T 600 50 - -
P1-00228-L
(P1-037L)
Class J or T 600 50 - -
P1-00330-L
(P1-055L)
Class J or T 600 100 - -
P1-00460-L
(P1-075L)
Class J or T 600 150 - -
P1-00600-L
(P1-110L)
Class J or T 600 150 - -
P1-00800-L
(P1-150L)
Class J or T 600 150 - -
P1-00930-L
(P1-185L)
Class J or T 600 200 - -
P1-01240-L
(P1-220L)
Class J or T 600 200 - -
P1-01530-L
(P1-300L)
Class J or T 600 300 - -
P1-01850-L
(P1-370L)
Class J or T 600 300
- -
P1-02290-L
(P1-450L)
Class J or T 600 300
- -
P1-02950-L
(P1-550L)
Class J or T 600 350
- -

1-10
Chapter 1
Safety Instructions
P1-H series models
(Memo)
Model
Fuse Circuit Breaker
Type
Maximum Rating Maximum Rating
Voltage (V) Current (A) Voltage (V) Current (A)
P1-00041-H
(P1-007H)
Class J or T 600 30 - -
P1-00054-H
(P1-015H)
Class J or T 600 30 - -
P1-00083-H
(P1-022H)
Class J or T 600 30 - -
P1-00126-H
(P1-037H)
Class J or T 600 30 - -
P1-00175-H
(P1-055H)
Class J or T 600 75 - -
P1-00250-H
(P1-075H)
Class J or T 600 75 - -
P1-00310-H
(P1-110H)
Class J or T 600 75 - -
P1-00400-H
(P1-150H)
Class J or T 600 100 - -
P1-00470-H
(P1-185H)
Class J or T 600 100 - -
P1-00620-H
(P1-220H)
Class J or T 600 100 - -
P1-00770-H
(P1-300H)
Class J or T 600 200 - -
P1-00930-H
(P1-370H)
Class J or T 600 200 - -
P1-01160-H
(P1-450H)
Class J or T 600 200 - -
P1-01470-H
(P1-550H)
Class J or T 600 250 - -

2.1
Check the contents in the package, and
inverter
The model of the product is as follows:
E
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
•
Chapter 2
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
Check the Inverter
model
.g.: 200V
class input voltage for Japan
Applicable motor capacity for ND rating is 3.7kW
ND rated current 17.5A
LD rated current 19.6A
VLD
rated current 22.8A
Series name
Motor maximum rate
00001: 0.1A to 99999: 9999.9A
Input power specification
L: three-
phase 200V class;
H: three-
phase
Panel
B: no operat
F: panel equipped
Region
(None): J
E: Europe/Southeast Asia;
U: North America;
C: China
In case of (None), blank field is omitted.
Integrated noise filter
F: integrated noise filter equipped;
CB: conduit
When both F and CB are equipped, it is indicated as
FCB.
S
pecification label
Description example
(*) means eigenvalues
P1
-
(2)
Inverter model
Input ratings
(Frequency/voltage/No. of
phases/Current)
Output
(Frequency/voltage/No. of
phases/Rate current)
MFG No.; factory serial No.
Inverter
with a
specification label.
P1
d current (at VLD rated current
400V class
or keypad
equipped;
apan;
box equipped
example
for P1-
00228
00228
(3)
ratings
confirm
-LFF
L
F
(4)
(5)
-
Basic
(T
his
the
F
(6) (6)
Guide
document)
Wire separation plate
2-1
Model: P1-
00228
Hitachi Industrial Equipment
Systems Co.,
Input/Entrée:50Hz,60Hz 200
Output/Sortie:0
MFG No. 62AA****** BB001
SJ series type P1
Terminal block
Backing plate
Control circuit
terminal block
Optional slots
Refer to each optional product
instruction
M3×8
screw
S
pacer 4
P1-
01240
Con
figuration and description
depending on the model.
Refer to User
If the
inverter is
products,
optional
P1-00228-
LFF example illustration in below.
-LFF
Ltd.
MADE IN JAPAN
INVERTER
–
240V 3ph 27.1/23.3/20.8A
-590Hz 200–
240V 3ph
cover
Operator keypad
for detail.
USB (Micro-
B)
4pcs
pcs
-L(P1-220L)
Installation and Wiring
'
s Guide for
shipped incorporated with optional
instruction
22.8/19.6/17.5A
Eye bolts for hanging the inverter
P1-
01850L/
(enclosed in the package)
Specification label
contents
more
details.
will be enclosed
Ver.2.00
Date:****
NE18361
-
***
-
00930H or above
Heat sink
Main circuit
terminals
vary
.

2.2 Install the Inverter
Chapter 2
T
ransportation
•
The inverter
carrying the inverter, handle it carefully to prevent
damage to the parts.
•
Do not carry the inverter by holding the front or
terminal block cover. Doing so may
inverter to fall.
•
Do not install and operate the inverter if it is
damaged or its parts are missing.
A
mbient temperature
•
Avoid installing the inverter in a place where the
ambient temperature goes above or below the
allowable range defined by
specification.
Ambient temperature:
ND rated
LD rated
VLD rated
•
Keep
Measure the temperature in a position about 5 cm
distant from the bottom
inverter, and check that the measured
temperature
Operating the inverter at a temperature outside
this range will shorten the inverter life (especially
the capacitor life), resulting in damage to the
inverter.
Do not install
h
umidity
•
Avoid installing the inverter in a place where the
relative humidity goes above or below the range
(20% to 90% RH), as defined by the standard
inverter specification. Avoid a p
inverter is subject to condensation.
•
Condensation inside the inverter will result in
short circuits, which may c
inverter.
exposed to direct sunlight.
is made of plastics
: -
10 to 50°C
: -
10 to 45°C
: -
10 to 40°C
suffici
ent space around the inverter.
is within the allowable range.
on
or easily condensa
Also avoid places where the inverter is
component
the standard inverter
-
center poi
a high temperature, high
ause
. When
cause the
nt of the
tion
area
lace where the
damage
to the
2-2
Air flow
For
P1-
00044
(P1
-
or
P1-
00041
(P1
-
or more
I
nstall inverter on
(e.g.
metal) surface.
•
The inverter will reach a high temperature (up to
about 150°C) during operation. Install the inverter
on a vertical wall surface made of nonflammable
material (e.g., metal) to avoid the risk of fire.
•
In particular, keep
inverter and other heat sources (e.g., braking
resistors and reactors) if they are installed in the
vicinity.
Inverter
Wall
-L to P1-
02950
004L to P1-
550L)
-H to P1-
01800
007H to P1-
550H)
In
order to replace life cycle parts on following models require
a clearance of 22cm or more:
• P1-00800-
L (P1
• P1-00380-
H (P1
In order to replace life cycle parts on following models is
required to
remove the installed units:
• P1-00044-
L (P1
• P1-00041-H (P1
5 cm
10 cm
or more
10 cm
or more
Installation and Wiring
nonflammable
sufficient distance between the
•
Keep enough clearance
between the inverter and the
above and below
to prevent
ventilation from
For dimension drawing of
inverter
-L
-H
-150L) to P1
-
-
150H) to P1
-004L) to P1
-
-
007H) to P1
5 cm
or more
For
P1
(P1
see
chapter
01240-L (P1-
220L)
-00620-H (P1-
220H)
00600-L (P1-
110L)
-
00310-H (P1-110H)
30 cm
or more
30 cm
or more
5 cm
or more
-02160-
H to P1
-750H to P1-
1320H)
wiring ducts
cooling air
obstructing.
2-5.
5 cm
or more
-03610-H

Chapter 2
Installation environment
•
Avoid installing the inverter in a place where the
inverter is subject to dust, corrosive gases,
explosive
mist, or salt water.
•
Foreign
failure
.
dusty environment, install the inverter inside a
totally enclosed panel.
Installation method and position
•
Install the inverter vertically and securely with
screws or bolts on a surface that is free from
vibrations and that can bear the inverter weight.
•
If the inverter is not installed properly, its cooling
performance may be degraded and tripping or
inverter damage may result.
Mounting in an enclosure
•
When mounting multiple inverters in an enclosure
with a ventilation fan, carefully design the layout
of the ventilation fan, air intake port, and inverters.
An inappropriate layout will reduce t
inverter
temperature.
inverter ambient temperature will remain within
the range specified in the specification table.
When
the
the incoming dust may
a position to avoid this falling dust
(Acceptable)
Inverter
Screw
S
crew
gases, flammable gases, grinding fluid
particles entering the i
If you use the inverter in a considerably
-
cooling effect and
Plan the layout
inverter is installed
adhere to
Ventilation
Position of ventilation fan
nverter will cause
raise the ambient
properly
below ventilatio
the inverter.
.
(Unacceptable)
Inverter
Screw
Screw
so that the
n fan,
P
lace in
Ventilation
2-3
of
he
Reduction of enclosure size
•
External heat sink installation may reduce internal
heat emission
•
External heat sink mounting for the inverter
P1-00044
-
and
P1-00041
-
requires an optional
•
Other models than above can be installed with the
originally attached metal
inverter
enclosure panel according to the specified cutting
dimensions.
•
The cooling s
positioned outside the enclosure has a cooling fan.
Therefore, do not place the enclosure in any
environment where it is exposed to water
oil mist, or dust.
•
T
he heat sink part reaches a high temperature.
Install a pr
Installation and Wiring
and reduce the enclosure si
L to P1-
00228
H to P1-
00126
metal
for external heat sink, cut out the
ection (including the heat sink)
otection cover as needed.
-L (P1-
004L to P1
-H (P1-
007H to P1
fitting.
fitting
. To mount the
ze.
-
037L)
-
037H)
drops,

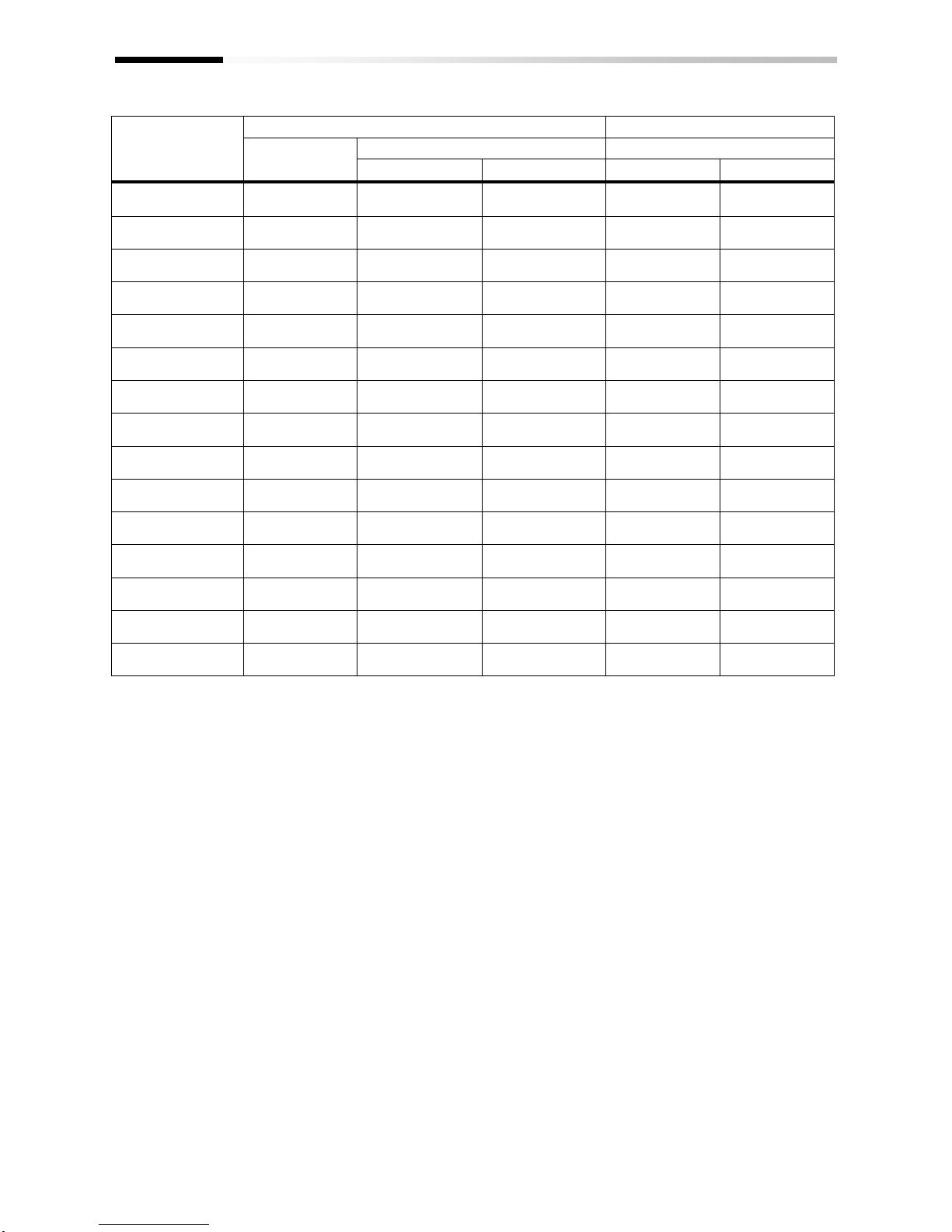
2.3 Dimension Drawing
Chapter 2
If you add optional parts to the inverter, some extra
space is required in the direction of the depth of the
inverter d
clearance of 50 mm or more.
instruction manual for each optional product.
Model P1-
*****
200V class:
00044
0104
400V class:
00041
00126
Dimension
Model P1-
*****
200V class:
00330
400V class:
00175
Dimension
epending on the wiring layout.
-* (P1-
*****
-
L(004L)
, 00080
-L(015L),
00156
-H(007H),
00054
-H(037H)
W(mm)
150
-* (P1-
*****
-
L(055L), 00460
-
H(055H), 00250
W(mm)
210
For details, refer
-*)
-
L(007L),
-
L(022L), 00228
-H(015H),
00083
H(mm)
255
-*)
-
L(075L), 00600
-H(075H),
00310
H(mm)
260
Keep
to the
-L(037L)
-H(022H),
D(mm)
140
-
L(110L)
-H(110H)
D(mm)
170
2-4
a
(E
g.
VLD rated current
(ND rat
class
Model (P1
200V class:
400V class
Dimension
Model P1
200V class:
400V class:
Dimension
) See "C
hapter 7
ed
motor capacity is
,
while H indicates 400V class.
-
*****
00800
:
00400
-*****
-
01530
00770
Installation and Wiring
Specifications
for 00046-
L(004L) is 4.6A
0.4kW), and L indicates 200V
-*)
-
L(150L), 00930
-
H(150H), 00470
W(mm)
245
* (P1-*****-
*)
-
L(300L)
-H(300H)
W(mm)
540
"
for details.
-
L(185L), 01240
-H(185H),
00620
H(mm)
390
H(mm)
300
,
-
L(220L)
-H(220H)
D(mm)
190
D(mm)
195
2-5
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
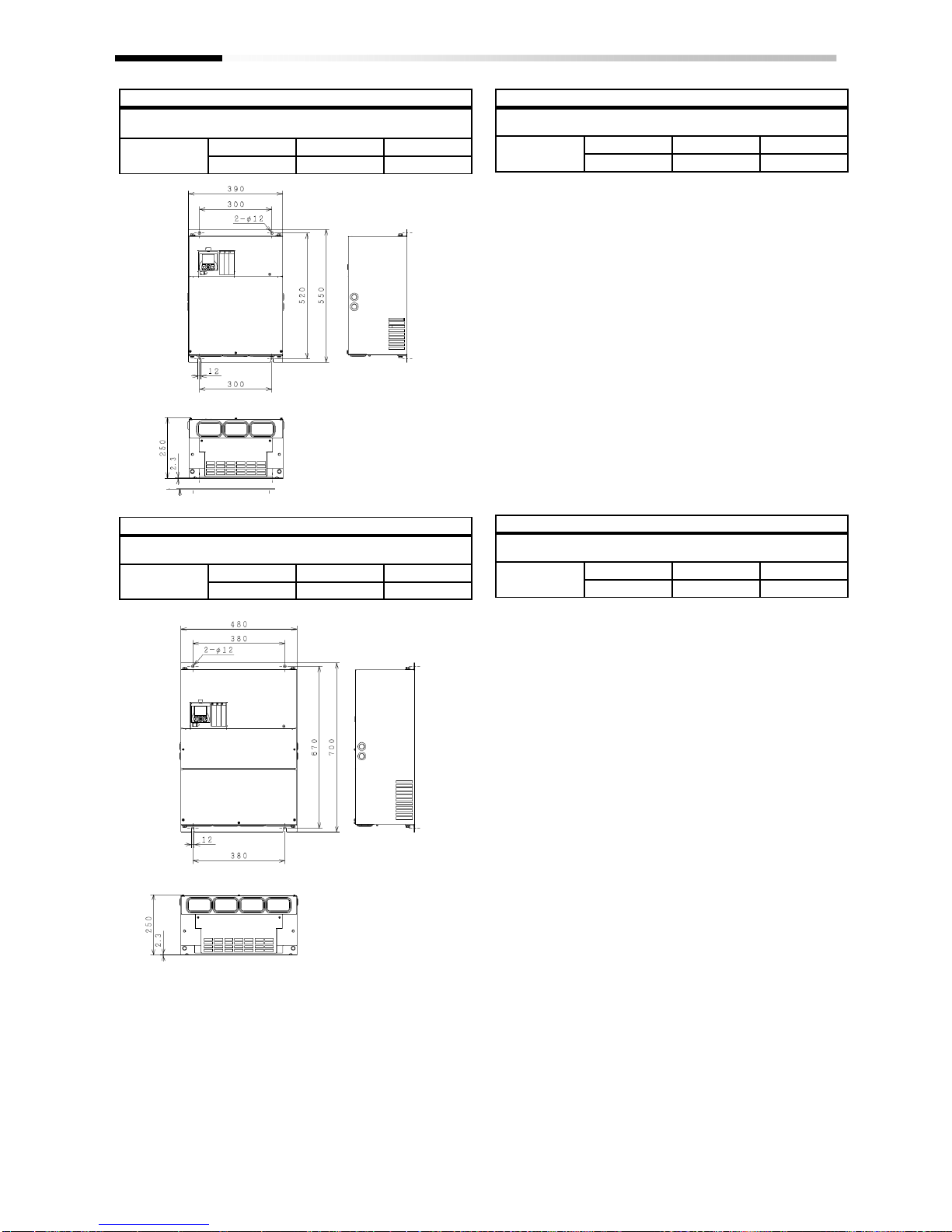
Model P1-*****-* (P1-*****-*)
200V class: 01850
-
L(370L), 02290
-
L(450L),
400V class: 00930-H(370H),01160-H(450H),01470-H(550H)
Dimension
W(mm) H(mm) D(mm)
550 390 250
Model P1-*****-* (P1-*****-*)
200V class: 02950-L(550L)
Dimension
W(mm) H(mm) D(mm)
700 480 250
Model P1-*****-* (P1-*****-*)
400V class: 01760-H(750H), 02130-H(900H)
Dimension
W(mm) H(mm) D(mm)
700 390 270
(in preparation)
Model P1-*****-* (P1-*****-*)
400V class: 02520-H(1100H), 03160-H(1320H)
Dimension
W(mm) H(mm) D(mm)
740 480 270
(in preparation)

2.
Chapter 2
4
Inverter Wiring
Applicable peripheral equipment
R S T
R0
T0
Power
supply
U
V
W
PD
P
N
Motor
M
RB
INV
<12>
<13>
<1>
<2>
<3>
<4>
<5>
<6>
<7>
<8>
<9>
<10>
<11>
<12>
<13>
<14>
No.
<1> Electric wire
<2> Earth-leakage circuit breaker EL
MCCB
<3> Magnetic contacto
<4> Input
AC
(For harmonic control, power supply
coordination, and power factor
correction)
<5> Noise
filter for inverter
<6> Radio noise filter
(Zero-
phase reactor)
<7> Radio noise filter on the input side
(Capacitor filter)
<8> DC
Choke
<9> Braking resistor
<10> Regenerative braking unit
<11> Noise filter on the output side
<12> Radio noise filter
(Zero-
phase reactor)
<13> Output
For reducing vibrations and
preventing thermal relay
malfunction
<14> LCR filter
Notes:
•
The description of peripheral equipment is for Hitachi 3
•
Select breakers with proper interrupting capacity. (Use inverter
•
Use
•
Use copper electric wire (HIV cable) with allowable temperature rating 75°C or more.
•
If the power line exceeds 20 m, use cable with ma
•
Tighten each termina
Loose terminal screws may cause short circuits and fire.
Excessive tightening torque may cause damage to the terminal block or inverter body.
•
When selecting a rated sensitivity current for earth
separated breaker considering a total cable length of between Inverter
Inverter
Use a delayed
•
When using a CV cable for wiring through a metal conduit, the average current leakage
would be 30mA/km.
•
When using a high relative dielectric constant cable such as IV cable, the leakage current is
about eight times as high as the standard cable. Therefore, when using an IV cable, use
ELCB with rated sensitivity current by eight times
cable length exceeds 100 m, use a CV cable.
•Do not pull the power line cable after wiring. Doing so may cause screw loosening.
Name
r MC
reactor
AC reactor
earth-
leakage circuit breakers
–
Motor distance. Do not use a high
-
type circuit breaker, because the high
2-6
See "Recommended cable
terminals” on Page 2
C
B or
Use
voltage imbalance exceeds 3% or more, or
capacity is
change rapidly. This reactor also improves the power factor.
This noise filter reduces the conductive noise that is generated by
the inverter and transmitted in cables. Connect this noise filter to
the primary side (input side) of the inverter.
The inverter may generate radio noise through power supply wiring
during operation.
Use this noise filter to reduce the radio noise (radiant noise).
Use this noise filter to reduce the radiant
cables.
Use
Use these devices to increase the braking torque of the inverter for
operation in which the inverter turns the connected
very frequently or decelerates the load running with a high moment
of inertia.
Connect this noise filter between the inverter and motor to reduce
the radiant noise
the electromagnetic interference with radio and television reception
and preventing malfunctions of measuring equipment and sensors.
Use this noise filter to
side of the inverter. (This noise filter can be used on both the input
and output sides.)
I
nverter drive
commercial power supply direct
Connect
the pulsation of motor. Also, connect
cable length between
to prevent thermal relay malfunction due to the harmonic waves
generated by switching operation o
relay can be replaced with a current sensor to avoid the
malfunction.
Connect
the inverter output into a sinusoidal waveform and to reduce the
motor vibration, motor noise and the radiant noise radiated from
cables. Surge voltage can be also controlled.
l screw with the specified tightening torque.
input reactor
over
500 kVA or more, or when the power voltage may
DC
chokes
to
nverter drive
n motor may cause large vibrations compared
Output
AC reactor between inverter and motor to lessen
this noise filter between the inverter and motor to convert
(ELB or MCB)
-
speed type of earth
Installation and Wiring
Total cable length
100 m or less
300 m or less
Function
gauges, wiring accessories, and crimp
-9.
for
harmonic wave
reduce
the harmonic generated by the inverter.
radiated from cables for the purpose of reducing
reduce the noise generated on the output
start
inverter and mo
-
phase, 4
to ensure safety.
j
or wire size for the power line.
-
leakage circu
-
speed typ
higher
in the table bel
Sensitivity current (mA)
control, or when power supply
when the power supply
noise radiated from input
motor.
output
AC reactor, when the
tor is long
er
f
inverter. Note that the thermal
-
pole squirrel
-
ready breakers)
it breaker, use a
-
Power supply and
-
leakage circuit breaker.
e may malfunction.
ow. If the total
50
100
load on and off
to
(10 m or more),
-cage motor.

2-7
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
2.5 Wiring of the main circuit
Wire the main circuit of the inverter.
The following illustration shows the power supply and
wiring connections to a motor only.
Open a terminal block cover to wire the terminal block in
the main circuit.
Explanation of main circuit terminal block
See “Chapter 1 Safety Instructions” for response to CE and UL
standards.
The screw size may vary depending on terminal. Refer to Page
2-8/2-9 for the size of the terminal screw for the power line cable
while for other terminals, refer to the drawings of the wiring on
Page 2-13 or later.
The tables on Page 2-8/2-9 list the specifications of cables, crimp
terminals, and terminal screw tightening torques for reference.
Recommended wire gauges vary depending on the rated load
settings (ND/LD/VLD).
Symbol
Terminal name
Description
R,S,T
(L1,L2,L3)
Main power input
Connect to the AC power supply. Leave these terminals unconnected
when using a regenerative converter.
U,V,W
(T1,T2,T3)
Inverter output Connect a Three-phase motor.
PD,P
(+1,+)
DC
choke
connection terminal
Remove the
PD-P
jumper from terminals, and connect the opt
ional
DC
choke for power factor improvement.
P,RB
(+,RB)
External
chopper
braking resistor
connection terminal
Connect the optional external braking resistor. See “Chapter 7
Specifications” for built-in braking circuit inverter models.
P,N
(+,-)
Regenerative
braking
unit connection
terminal
Connect the optional regenerative braking unit.
Inverter ground
terminal
This serves as a ground terminal for the inverter
chassis
to ground.
Connect 200V class and 400V class models to Type-D grounding and
Type-C grounding, respectively.
ELB
Earth-leakage
circuit breaker
Magnetic
contactor
MC
Three-
phase
AC power
supply
P+
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
R0
T0
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3
Control circuit
power supply
Type-D grounding
(200 V class model)
Type-C grounding
(400 V class model)
J51 connector
Three
-
phase
M
Main circuit
terminal section
3φ
P
/+ PD
/+1
RB
N/-
Jumper
Internal EMC filter
Jumper or terminal
Disable
Enable
200V class:
200 to 240Vac
400V class:
380 to 500Vac

2-8
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
2.6 Recommended wire gauges, wiring
accessories, and crimp terminals
200V class
The wire gauges in the above table shows the designed values
based on HIV cables (with thermal resistance of 75°C).
Please use the round type crimp terminals (for the UL standard)
suitable for the use electric wire when you connect the electric
wire with the main circuit terminal block. Please put on pressure
to the crimp terminals with a crimp tool that the crimp terminal
maker recommends.
Applicable P1
inverter model
P1-*******
Rating
setting
Power line cable
AWG(mm2)
R,S,T,U,V,W,
P,PD,N
Grounding
cable
AWG(mm2)
External braking
resistor
between P and
RBAWG(mm2)
Power line cable
Terminal screw
size
Crimp
terminal
Tightening
torque
N•m
P1-00044-L
(P1-004L)
ND
14(2.1) 14(2.1) 14(2.1) M4 2-4/2-4 1.4 LD
VLD
P1-00080-L
(P1-007L)
ND
14(2.1)
14(2.1)
14(2.1) M4 2-4/2-4 1.4 LD
VLD
P1-00104-L
(P1-015L)
ND
14(2.1)
14(2.1)
14(2.1) M4 2-4/2-4 1.4 LD
VLD
P1-00156-L
(P1-022L)
ND
14(2.1) 14(2.1) 14(2.1)
M4
2-4/2-4
1.4 LD
VLD 10(5.3) 10(5.3) 10(5.3) 5.5-4/5.5-4
P1-00228-L
(P1-037L)
ND
10(5.3) 10(5.3) 10(5.3) M4 5.5-4/5.5-4
1.4 LD
VLD
P1-00330-L
(P1-055L)
ND
8(8.4) 8(8.4) 8(8.4) M5 8-5/8-5 3.0 LD
VLD
P1-00460-L
(P1-075L)
ND
8(8.4)
6(13.3)
8(8.4)
M5
8-5/8-5
3.0 LD
VLD 4(21.2) 6(13.3) 14-5/8-5
P1-00600-L
(P1-110L)
ND 6(13.3)
6(13.3)
6(13.3)
M6
14-6/14-6
4.0 LD
4(21.2) 4(21.2) 22-6/14-6
VLD
P1-00800-L
(P1-150L)
ND 4(21.2)
6(13.3)
4(21.2)
M6
22-6/14-6
2.5 to 3.0 LD
3(26.7) 3(26.7) 38-6/14-6
VLD
P1-00930-L
(P1-185L)
ND 3(26.7)
6(13.3)
3(26.7)
M6
38-6/14-6
5.5 to 6.6 LD 2(33.6) 2(33.6)
60-6/14-6
VLD 1(42.4) 1(42.4)
P1-01240-L
(P1-220L)
ND 1(42.4)
6(13.3)
1(42.4)
M8
60-8/14-6
5.5 to 6.6 LD 1/0(53.5) 1/0(53.5)
VLD 2/0(67.4) 2/0(67.4) 70-8/14-6
P1-01530-L
(P1-300L)
ND 2/0(67.4)
4(21.2) ― M8
70-8/22-8
6.0 LD
1/0×2(53.5×2) 60-8/22-8
VLD
P1-01850-L
(P1-370L)
ND 4/0(107.2)
4(21.2) ― M8
100-8/22-6
15.0 LD
1/0×2(53.5×2) 60-8/22-6
VLD
P1-02290-L
(P1-450L)
ND
1/0×2(53.5×2)
4(21.2) ― M8
60-8/22-6
6.0 to 10.0 LD
VLD 2/0×2(67.4×2) 70-8/22-6
P1-02950-L
(P1-550L)
ND 350kc(177)
3(26.7) ― M10
180-8/38-6
19.6 LD
3/0×2(85.0×2) 80-8/38.6
VLD

2-9
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
400V class
The wire gauges in the above table shows the designed values
based on HIV cable (with thermal resistance of 75°C).
Please use the round type crimp terminals (for the UL standard)
suitable for the use electric wire when you connect the electric
wire with the main circuit terminal block. Please put on pressure
to the crimp terminals with a crimp tool that the crimp terminal
maker recommends.
Applicable P1
inverter model
P1-*******
Rating
setting
Power line cable
AWG(mm2)
R,S,T,U,V,W,
P,PD,N
Grounding
cable
AWG(mm2)
External braking
resistor
between P and
RBAWG(mm2)
Power line cable
Terminal screw
size
Crimp
terminal
Tightening
torque
N•m
P1-00041-H
(P1-007H)
ND
14(2.1) 14(2.1) 14(2.1) M4 2-4/2-4 1.4 LD
VLD
P1-00054-H
(P1-015H)
ND
14(2.1) 14(2.1) 14(2.1) M4 2-4/2-4 1.4 LD
VLD
P1-00083-H
(P1-022H)
ND
14(2.1) 14(2.1) 14(2.1) M4 2-4/2-4 1.4 LD
VLD
P1-00126-H
(P1-037H)
ND 14(2.1) 14(2.1) 14(2.1)
M4
2-4/2-4
1.4 LD
12(3.3) 12(3.3) 12(3.3) 5.5-4/5.5-4
VLD
P1-00175-H
(P1-055H)
ND 12(3.3) 12(3.3) 12(3.3)
M5 5.5-5/5.5-5
3.0 LD
10(5.3) 10(5.3) 10(5.3)
VLD
P1-00250-H
(P1-075H)
ND 10(5.3) 10(5.3) 10(5.3)
M5
5.5-5/5.5-5
3.0 LD
8(8.4) 8(8.4) 8(8.4) 8-5/8-5
VLD
P1-00310-H
(P1-110H)
ND
8(8.4) 8(8.4) 8(8.4) M6 8-6/8-6 4.0 LD
VLD
P1-00400-H
(P1-150H)
ND
8(8.4) 8(8.4) 8(8.4) M6 8-6/8-6 4.0 LD
VLD
P1-00470-H
(P1-185H)
ND 8(8.4)
8(8.4)
8(8.4)
M6
8-6/8-6
4.0 LD
6(13.3) 6(13.3) 14-6/8-6
VLD
P1-00620-H
(P1-220H)
ND 6(13.3)
8(8.4)
6(13.3)
M6
14-6/8-6
4.0 LD
4(21.2) 4(21.2) 22-6/8-6
VLD
P1-00770-H
(P1-300H)
ND 3(26.7)
6(13.3) - M8
38-8/14-8
6.0 LD 2(33.6)
VLD 1(42.4) 60-8/14-8
P1-00930-H
(P1-370H)
ND
1(42.4) 6(13.3) - M8 60-8/14-8 15.0 LD
VLD
P1-01160-H
(P1-450H)
ND 1(42.4)
6(13.3) - M8
60-8/14-8
6.0~10.0
LD 1/0(53.5)
VLD 2/0(67.4) 70-8/14-8
P1-01800-H
(P1-550H)
ND 2/0(67.4)
4(21.2) - M8
70-8/22-8
6.0~10.0
LD
1/0×2(53.5×2) 60-8/22-8
VLD
P1-02160-H
(P1-750H)
ND
― ― ― ― ― ― LD
VLD
P1-02600-H
(P1-900H)
ND
― ― ― ― ― ― LD
VLD
P1-03250-H
(P1-1100H)
ND
― ― ― ― ― ― LD
VLD
P1-03610-H
(P1-1320H)
ND
― ― ― ― ― ― LD
VLD

2-10
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
2.7 Applicable circuit breaker
200V class
• For ND rating
• For LD/VLD rating
Device model name on above table shows example selection. The
device selection should be made in base on rated current, short
circuit current capability and accordance to the local electrical
legislation.
Applicable motor capacity is based on Hitachi 200Vac, 60Hz, 4 pole
IE3 motor.
Refer to the wire gauge table on chapter 2-8 for power line cable.
Electrical endurance for AC-1 magnetic contactor is 500000 times,
however, for emergency stop in motor operation will be only 25
times.
Select AC-3 class magnetic contactor for inverter output for
application which has an emergency stop or commercial power line
operation.
When selecting oversize inverter capacity compare to motor rating,
select magnetic contactor according to the inverter capacity
Model
P1-*******
(P1-****)
Applicable
Motor
(kW)
Applicable devices (Input Voltage 200~220V)
Without reactor
(DCL or
ACL)
With reactor
(DCL or
ACL)
Earth-leakage breaker
(ELB)
Magnetic Contactor
(MC)
Earth-leakage breaker
(ELB)
Magnetic Contactor
(MC)
Example
model
Current
Rate
AC-1 AC-3
Example
model
Current
Rate
AC-1 AC-3
P1-00044-L(P1-004L) 0.4 EB-30E 5 HS8 HS8 EB-30E 5 HS8 HS8
P1-00080-L(P1-007L) 0.75 EB-30E 10 HS8 HS8 EB-30E 5 HS8 HS8
P1-00104-L(P1-015L) 1.5 EB-30E 15 HS8 HS8 EB-30E 10 HS8 HS8
P1-00156-L(P1-022L) 2.2 EB-30E 20 HS8 HS8 EB-30E 15 HS8 HS8
P1-00228-L(P1-037L) 3.7 EB-30E 30 HS8 HS20 EB-30E 20 HS8 HS20
P1-00330-L(P1-055L) 5.5 EB-50E 40 HS20 HS25 EB-30E 30 HS8 HS20
P1-00460-L(P1-075L) 7.5 EB-50E 50 HS35 HS35 EB-50E 40 HS20 HS25
P1-00600-L(P1-110L) 11 EB-100E 75 HS50 H65C EB-100E 60 HS35 HS50
P1-00800-L(P1-150L) 15 RXK125
-S
125 H65C H80C EB-100E 100 HS50 H65C
P1-00930-L(P1-185L) 18.5 RXK125
-S
125 H80C H100C
EB-
100E 100 HS50 H65C
P1-01240-L(P1-220L) 22 EXK225
150 H80C H125C
RXK125
-S
125 H65C H80C
P1-01530-L(P1-300L) 30 EXK225
200 H125C
H150C
EXK225
150 H80C H125C
P1-01850-L(P1-370L) 37 RXK250
-S
250 H150C
H200C
EXK225
200 H100C
H125C
P1-02290-L(P1-450L) 45 EX400 300 H200C
H250C
EXK225
225 H125C
H150C
P1-02950-L(P1-550L) 55 EX400 400 H200C
H300C
EX400 300 H150C
H250C
Model
P1-*******
(P1-****)
Applicable
Motor
(kW)
Applicable devices(Input Voltage 200~220V)
Without reactor
(DCL or ACL)
With reactor
(DCL or ACL)
Earth-leakage breaker
(ELB)
Magnetic Contactor
(MC)
Earth-leakage breaker
(ELB)
Magnetic Contactor
(MC)
Example
model
Current
Rate
AC-1 AC-3
Example
model
Current
Rate
AC-1 AC-3
P1-00044-L(P1-004L) 0.75 EB-30E 10 HS8 HS8 EB-30E 5 HS8 HS8
P1-00080-L(P1-007L) 1.5 EB-30E 15 HS8 HS8 EB-30E 10 HS8 HS8
P1-00104-L(P1-015L) 2.2 EB-30E 20 HS8 HS8 EB-30E 15 HS8 HS8
P1-00156-L(P1-022L) 3.7 EB-30E 30 HS8 HS20 EB-30E 20 HS8 HS20
P1-00228-L(P1-037L) 5.5 EB-50E 40 HS20 HS25 EB-30E 30 HS8 HS20
P1-00330-L(P1-055L) 7.5 EB-50E 50 HS35 HS35 EB-50E 40 HS20 HS25
P1-00460-L(P1-075L) 11 EB-100E 75 HS50 H65C EB-100E 60 HS35 HS50
P1-00600-L(P1-110L) 15 RXK125
-S
125 H65C H80C EB-100E 100 HS50 H65C
P1-00800-L(P1-150L) 18.5 RXK125
-S
125 H80C H100C
EB-
100E 100 HS50 H65C
P1-00930-L(P1-185L) 22 EXK225
150 H80C H125C
RXK125
-S
125 H65C H80C
P1-01240-L(P1-220L) 30 EXK225
200 H125C
H150C
EXK225
150 H80C H125C
P1-01530-L(P1-300L) 37 RXK250
-S
250 H150C
H200C
EXK225
200 H100C
H125C
P1-01850-L(P1-370L) 45 EX400 300 H200C
H250C
EXK225
225 H125C
H150C
P1-02290-L(P1-450L) 55 EX400 400 H200C
H300C
EX400 300 H150C
H250C
P1-02950-L(P1-550L) 75 EX600B
500 H300C
H400C
EX400 400 H200C
H300C

2-11
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
400V class
• For ND rating
• For LD/VLD rating
Device model name on above table shows example selection. The
device selection should be made in base on rated current, short
circuit current capability and accordance to the local electrical
legislation.
Applicable motor capacity is based on Hitachi 400Vac, 60Hz, 4 pole
IE3 motor.
Refer to the wire gauge table on chapter 2-8.
Electrical endurance for AC-1 magnetic contactor is 500000 times,
however, for emergency stop in motor operation will be only 25
times.
Select AC-3 class magnetic contactor for inverter output for
application which has an emergency stop or commercial power line
operation.
When selecting oversize inverter capacity compare to motor rating,
select according to the inverter capacity
Model
P1-*******
(P1-****)
Applicable
Motor
(kW)
Applicable devices (Input Voltage 400~440V)
Without reactor
(DCL or ACL)
With reactor
(DCL or ACL)
Earth-leakage breaker
(ELB)
Magnetic Contactor
(MC)
Earth-leakage breaker
(ELB)
Magnetic Contactor
(MC)
Example
model
Current
Rate
AC-1 AC-3
Example
model
Current
Rate
AC-1 AC-3
P1-00041-H(P1-007H) 0.75 EX50C 5 HS8 HS8 EX50C 5 HS8 HS8
P1-00054-H(P1-015H) 1.5 EX50C 10 HS8 HS8 EX50C 5 HS8 HS8
P1-00083-H(P1-022H) 2.2 EX50C 10 HS8 HS8 EX50C 10 HS8 HS8
P1-00126-H(P1-037H) 3.7 EXK50-C 15 HS8 HS10 EX50C 10 HS8 HS10
P1-00175-H(P1-055H) 5.5 EXK50-C 20 HS8 HS20 EXK50-C 15 HS8 HS20
P1-00250-H(P1-075H) 7.5 EXK50-C 30 HS8 HS25 EXK50-C 20 HS20 HS25
P1-00310-H(P1-110H) 11 EXK50-C 40 HS20 HS35 EXK50-C 30 HS25 HS35
P1-00400-H(P1-150H) 15 EXK50-C 50 HS25 HS50 EXK50-C 40 HS35 HS50
P1-00470-H(P1-185H) 18.5 EXK100
-C 75
HS35 HS50 EXK50-C 50 HS50 HS50
P1-00620-H(P1-220H) 22 EXK100
-C 75
HS50 H65C EXK60-C 60 HS50 H65C
P1-00770-H(P1-300H) 30 EXK100
-C
100 HS50 H80C EXK100
-C 75
H80C H80C
P1-00930-H(P1-370H) 37 RXK125
-S
125 H80C H100C
EXK100
-C
100 H80C H100C
P1-01160-H(P1-450H) 45 EXK225
150 H80C H125C
RXK125
-S
125 H100C
H125C
P1-01470-H(P1-550H) 55 EXK225
200 H100C
H125C
EXK225
150 H150C
H125C
P1-01760-H(P1-750H) 75 RXK250
-S
250 H150C
H200C
EXK225
200 H200C
H200C
P1-02130-H(P1-900H) 90 EX400 300 H200C
H250C
EXK225
225 H200C
H250C
P1-02520-H(P1-1100H)
110 EX400 400 H200C
H300C
EX400 300 H250C
H300C
P1-03160-H(P1-1320H)
132 EX600B
500 H250C
H300C
EX400 350 H400C
H400C
Model
P1-*******
(P1-****)
Applicable
Motor
(kW)
Applicable devices (Input Voltage 400~440V)
Without reactor
(DCL or ACL)
With reactor
(DCL or ACL)
Earth-leakage breaker
(ELB)
Magnetic Contactor
(MC)
Earth-leakage breaker
(ELB)
Magnetic Contactor
(MC)
Example
model
Current
Rate
AC-1 AC-3
Example
model
Current
Rate
AC-1 AC-3
P1-00041-H(P1-007H) 1.5 EX50C 10 HS8 HS8 EX50C 5 HS8 HS8
P1-00054-H(P1-015H) 2.2 EX50C 10 HS8 HS8 EX50C 10 HS8 HS8
P1-00083-H(P1-022H) 3.7 EXK50-C 15 HS8 HS10 EX50C 10 HS8 HS8
P1-00126-H(P1-037H) 5.5 EXK50-C 20 HS8 HS20 EXK50-C 15 HS8 HS20
P1-00175-H(P1-055H) 7.5 EXK50-C 30 HS8 HS25 EXK50-C 20 HS8 HS20
P1-00250-H(P1-075H) 11 EXK50-C 40 HS20 HS35 EXK50-C 30 HS8 HS25
P1-00310-H(P1-110H) 15 EXK50-C 50 HS25 HS50 EXK50-C 40 HS20 HS35
P1-00400-H(P1-150H) 18.5 EXK100
-C 75
HS35 HS50 EXK50-C 50 HS20 HS35
P1-00470-H(P1-185H) 22 EXK100
-C 75
HS50 H65C EXK60-C 60 HS35 HS50
P1-00620-H(P1-220H) 30 EXK100
-C
100 HS50 H80C EXK100
-C 75
HS50 H65C
P1-00770-H(P1-300H) 37 RXK125
-S
125 H80C H100C
EXK100
-C
100 HS50 H65C
P1-00930-H(P1-370H) 45 EXK225
150 H80C H125C
RXK125
-S
125 H65C H80C
P1-01160-H(P1-450H) 55 EXK225
200 H100C
H125C
EXK225
150 H80C H100C
P1-01470-H(P1-550H) 75 EX400 250 H150C
H200C
EXK225
200 H100C
H125C
P1-01760-H(P1-750H) 90 EX400 300 H200C
H250C
EXK225
225 H125C
H150C
P1-02130-H(P1-900H) 110 EX400 400 H200C
H300C
EX400 300 H150C
H250C
P1-02520-H(P1-1100H)
132 EX600B
500 H250C
H300C
EX400 350 H200C
H250C
P1-03160-H(P1-1320H)
160 EX600B
600 H400C
H400C
EX400 400 H250C
H300C

2-12
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
2.8 Chopper Braking Resistor
•
SJ Series P1 has a built-in chopper braking circuit in model below.
P1-00044-L (004L) to P1-01240-L (022L)
P1-00041-H (007H) to P1-00930-H (370H)
•
By using an optional braking resistor, permit to use for high
regeneration load application such as lift or high speed load.
200V class
Model
P1-******
(P1-****)
Appli
cable
motor
(kW)
Min.
Resis
tor
(Ω)
Resistor
selection
Ex. (Ω)
Braking
Resistor
Model
Usage
ratio
(%)
Short
period
capacity
(kW)
Rated
capacity
(kW)
00044-L
(004L)
0.4 50 180 SRB200-1 10 0.7 0.2
00080-L
(007L)
0.75 50 100 SRB200-1 10 0.7 0.2
00104-L
(015L)
1.5 35 100 SRB200-2 7.5 1.25 0.2
00156-L
(022L)
2.2 35 50 SRB300-1 7.5 2.5 0.3
00228-L
(037L)
3.7 35 35 SRB400-1 7.5 3.6 0.4
00330-L
(055L)
5.5 16 17 RB3 10 7.7 1.2
00460-L
(075L)
7.5 10 17 RB3 10 7.7 1.2
00600-L
(110L)
11 10 11.7
RB2 ×3
parallel
10 11.4 1.8
00800-L
(150L)
15 7.5 8.5
RB3 ×2
parallel
10 15.4 2.4
00930-L
(185L)
18.5 7.5 8.5
RB3 ×2
parallel
10 15.4 2.4
01240-L
(220L)
22 5 5.7
RB3 ×3
parallel
10 23.1 3.6
When using RB2×2series×2parallel, will require in total 4 RB2 units.
•
SJ Series P1 can offer when desired a built-in chopper braking circuit
in models below.
P1-01160-H (450H) to P1-01470-H (550H)
•
Using optional braking unit or regenerative unit, permit to use on
high regenerative load application even for models without built-in
chopp er braking circuit.
•
The table below shows an example selection of braking resistor to
output 100% of braking torque for each motor rating on list.
■400V
Model
P1-******
(P1-****)
Appli
cable
motor
(kW)
Min.
Resis
tor
(Ω)
Resistor
selection
Ex. (Ω)
Braking Resistor
Model
Usage
ratio
(%)
Short
period
capacity
(kW)
Rated
capacity
(kW)
00041-H
(007H)
0.75 100 360
SRB200-1
×2series
10 1.4 0.4
00054-H
(015H)
1.5 100 100
SRB200
-1
×2series
10 1.4 0.4
00083-H
(022H)
2.2 100 100
SRB200
-2
×2series
7.5 2.5 0.4
00126-H
(037H)
3.7 70 100
SRB300
-1
×2 series
7.5 5 0.6
00175-H
(055H)
5.5 70 100
SRB300
-1
×2 series
7.5 5 0.6
00250-H
(075H)
7.5 35 70
SRB400
-1
×2 series
7.5 7.2 0.8
00310-H
(110H)
11 35 50
RB1
×2 series
×2 parallel
10 10.4 1.6
00400-H
(150H)
15 24 35
RB2
×2 series
×2parallel
10 15.2 2.4
00470-H
(185H)
18.5 24 35
RB2
×2 series
×2parallel
10 15.2 2.4
00620-H
(220H)
22 20 25
RB1
×2 series
×4parallel
10 20.8 3.2
00770-H
(300H)
30 15 17
RB3
×2 series
×2parallel
10 30.8 4.8
00930-H
(370H)
37 15 17
RB3
×2 series
×2parallel
10 30.8 4.8
01160-H
(450H)
45 10 10
CA-KB
(10Ω5unit)
20 45 17
01800-H
(550H)
55 10 10
CA-KB
(10Ω5unit)
20 45 17

2.9
00044
00104
00228
00054
00126
Screw size
00330
00175
Screw size
00600
Screw size
Model
200V class:
400V class:
Control circuit termina
Chapter 2
Wiring
When J51 connector is removed, charge lamp doesn't
indicate R0
and care for
off before handling the inverter.
-
L/00080
-L/
-L/00156-L/
-L/00041-H/
-H/00083-H/
-H
R0,T0: M4
Ground terminal:
M4
Other terminals
: M4
Control circuit termina
Switch
EMC jumper
Model
P1- *****
200V class: 00330
400V
class: 00175
-L/00460-L/
-H/00250-H
R0,T0: M4
Ground terminal: M5
Other terminals: M5
-L/00310-H
R0,T0: M4
Ground terminal: M6
Other terminals: M6
Switch
EMC jumper
P1-
*****
00044
00156
00041
00126
-
T0 status. Please make sure that power is off
safety
. For
R0
R
(L1)
EMC
filter
disabled
OFF
G ON
Power input line
l
to
enable
-*(P1-****)
-
L(055L), 00460
-
H(055H), 00250
T0
EMC
filter
disabled
OFF
G ON
R0
Power input line
to enable
-*(P1-****)
-
L(004L), 00080
-
L(022L),00228
-
H(007H), 00054
-H(037H)
l
own
safety, make sure to power
S
(L2)
T
(L3)
T0 G
EMC filter
enabled
RB
(RB)
PD
(+1)
Motor output line
M
ain circuit terminal
or
disable the EMC filter.
-
L(075L), 00600
-
H(075H), 00310
R
(L1)
S
(L2)
T
(L3)
G
P
(+)
EMC filter
enabled
PD
(+1)
or
disable the EMC filter.
-
L(007L), 00104
-
-L(037L)
-H(015H), 00
083
M
U
(T1)
V
(T2)
W
(T3)
P
(+)
N
(-)
G
PD-P Jumper
Charge lamp
(Turn-
on while
energized)
-
L(110L)
-H(110H)
U
(T1)
V
(T2)
W
(T3)
RB
(RB)
G
PD-P Jumper
Charge lamp
(Turn-
on while
energized)
N
(-)
Motor output line
L(015L),
-H(022H),
ain circuit terminal
2-13
Model
200V class: 00800
Model
400V
Charge lamp
(Turn
energized)
Control circuit termina
P1- *****-*
(P1
-
L(150L)/00930
To enable or disable
EMC jumper of the ground terminal.
P1- *****-*
(P1
class: 00400
-
H(150H), 00470
T0
EMC filter
disabled
-on while
OFF G ON
R0
Power input line
Switching the short
EMC filter.
Control circuit
terminal
Installation and Wiring
-
****)
-
L(185L)/01240
the EMC filter, insert or remove the
-
****)
-
H(185H), 00620
R
(L1)
S
(L2)
T
(L3)
G
P
(+)
EMC filter
enabled
PD
(+1)
-
circuit connector can enable/disable the
l
-
L(220L)
-
H(220H)
U
(T1)
V
(T2)
W(T3)
RB
(RB)
G
PD-P Jumper
N
(-)
Motor output line
Screw size
R0,T0: M4
Ground terminal: M
Other terminals:
M
ain circuit terminal
M
ain circuit terminal
6
M6
Ground
terminal
(With jumper)
Fix the jumper by
using 2 screws.

2-14
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
Model P1
- *****-*(P1-****)
200V class: 01
530-
L(300L)
Jumper bar for
EMC filter
Enable
Disable
R0 T0
Screw size
R0,T0 : M4
Ground Terminal: M6
Other Terminal
: M8
Charge Lamp
R
(L1)
S
(L2)
T
(L3)
U
(T1)
V
(T2)
W
(T3)
PD
(+1)
P
(+)
N
(-)
Power Line Input Line
Motor Output Line
G
G
Switch the jumper bar to enable or disable the EMC filter.
Model P1
- *****-*(P1-****)
400V class: 00
770-H(300H)
Jumper bar for
EMC Filter
enabled
Disabled
R0 T0
Screw size
R0,T0: M4
Ground terminal: M8
Other terminals: M8
Charge Lamp
R
(L1)
S
(L2)
T
(L3)
U
(T1)
V
(T2)
W
(T3)
PD
(+1)
P
(+) N (-)
RB
(RB)
PD-P Jumper
Power input line
Motor output line
G
G
Switch the jumper bar to enable or disable the EMC filter.
Model P1
- *****-*(P1-****)
200V class: 01850
-
L(370L)
R0
EMC
filter short bar
T0
Screw Size
R0,T0 : M4
Ground terminal : M8
Other Terminal
: M8
Charge Lamp
enables
disabled
R
(L1)
S
(L2)
T
(L3)
U
(T1)
V
(T2)
W
(T3)
PD
(+1)
P
(+)
N
(-)
Power Line Input Line
Motor Output Line
G
G
Switch the jumper bar to enable or disable the EMC filter.
Model P1
- *****-*(P1-****)
400V class: 00930
-
H(370H)
EMC
Filter Short bar
enables
disabled
R
(L1)
S
(L2)
T
(L3)
U
(T1)
V
(T2)
W
(T3)
PD
(+1)
P
(+) N (-)
RB
(RB)
PD-P Jumper
Power input line
Motor output line
G
G
R0 T0
Screw size
R0,T0 : M4
Ground Terminal : M8
Other : M8
Charge lamp
Switch the jumper bar to enable or disable the EMC filter.

2-15
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
Model P1
- *****-*(P1-****)
200V class: 02290
-
L(450L)
R
(L1)
S
(L2)
T
(L3)
U
(T1)
V
(T2)
W
(T3)
PD
(+1)
P
(+) N (-)
PD-P Jumper
Input power line
Motor output line
G
G
R0
Jumper bar
for EMC filter
T0
Enable
Disable
Screw size
R0,T0: M4
Ground terminal: M8
Other terminals: M8
Switch the jumper bar to enable or disable the EMC filter.
Model P1
- *****-*(P1-****)
400V class: 01160
-
H(450H)
R0
Jumper bar
for EMC filter
T0
Enable
Disable
Screw size
R0,T0: M4
Ground terminal: M8
Other terminals: M8
R
(L1)
S
(L2)
T
(L3)
U
(T1)
V
(T2)
W
(T3)
PD
(+1)
P
(+) N (-)
RB
(RB)
PD-P Jumper
Input power line
Motor output line
G
G
Switch the jumper bar to enable or disable the EMC filter.
Disable Switching(screw) Enable
Model P1
- *****-*(P1-****)
200V class: 02
590-L(5
50L)
R
(L1)
S
(L2)
T
(L3)
U
(T1)
V
(T2)
W
(T3)
PD
(+1)
P
(+) N (-)
PD-P Jumper
Input power line
Motor output line
G
G
R0
Jumper bar
for EMC filter
T0
Enable
Disable
Screw size
R0,T0: M4
Ground terminal: M8
Other terminals: M8
Switch the jumper bar to enable or disable the EMC filter.
Model P1
- *****-*(P1-****)
400V class: 01
470-H(5
50H)
R
(L1)
S
(L2)
T
(L3)
U
(T1)
V
(T2)
W
(T3)
PD
(+1)
P
(+) N (-)
PD-P Jumper
Input power line
Motor output line
G
G
R0
Jumper bar
for EMC filter
T0
Enable
Disable
Screw size
R0,T0: M4
Ground terminal: M8
Other terminals: M8
Switch the jumper bar to enable or disable the EMC filter.

2-16
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
Model P1
- *****-*(P1-****)
200V class: 0
1760-H(750H)
(In preparation)
Model P1
- *****-*(P1-****)
400V class: 0
2130-H(900H)
(In preparation)
Model P1
- *****-*(P1-****)
200V class: 0
2520-H(
1100H)
(In preparation)
Model P1
- *****-*(P1-****)
400V class: 0
3160-H(
1320H)
(In preparation)

2-17
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
2.10 Wiring of the control circuit
An example for sink logic.
Switch configuration
Label Switch Name
Description
Ai1
(SW1)
Analog input 1
switch
It c
hanges
the input specification
of Analog input 1
(Ai1 terminal).
10V: Voltage input is available.
20mA: Current input is available.
Ai2
(SW2)
Analog input 2
switch
It c
hanges
the input
specification of Analog input 2
(Ai2 terminal).
10V: Voltage input is available.
20mA: Current input is available.
Ao1
(SW3)
Analog output 1
switch
It c
hanges
the output specification of Analog output 1
(Ao1 terminal).
10V: Voltage output is applied.
20mA: Current output is applied.
Ao2
(SW4)
Analog output 2
switch
It c
hanges
the output specification of Analog output 2
(Ao2 terminal).
10V: Voltage output is applied.
20mA: Current output is applied.
P.SEL
(SW5)
Power supply
input switch
It c
hanges
the power
source for
input terminals.
IN: Internal power source.
EX: External power source.
(While setting EX, it requires an external power supply
between input terminals and COM terminal)
SRC/SINK
(SW6)
Input terminal
Sink/Source
logic switching
It changes the s
ink or source logic
for
input terminal
.
Is enabled when SW5 is in IN position.
SINK: Switch to Sink logic.
SRC: Switch to Source logic.
SW4
SW3
SW2
SW1
SW5
SW6
10V
20mA
10V
20mA
10V
20mA
10V
20mA
IN
EX
SINK
SRC
Ao2
Ao1
Ai2
Ai1 P.SEL
(SW4) (SW3) (SW2) (SW1) (SW5) (SW6)
Control circuit terminal
Make sure to power-off previous to change any
switches. Otherwise, may damage the inverter.
Control circuit terminal
section
24V power
supply terminal
P-
1/RS
2/SCHG
3/JG
4/FRS
5/2CH
6/CF1
7/CF2
8/RV
9/FW
A/EXT
B/USP
COM
Interface
24V power source terminal
P24
H
Ai1
Ai2
Ai3
L
Analog
input 1
(+)
(-)
(±)
(0)
TH+
AL2
AL1
AL0
16a
16c
11/FA1
12/RUN
13/OL
14/OTQ
15/WAF
CM2
FM
CM1
Ao1
Ao2
L
SP
SN
SP
SN
RP
P24S
STC
CMS
ST1
ST2
ED+
ED-
TH-
Alarm relay
1C contact points
Relay
1A contact points
Output terminals
*Sink/source supported
L
L
10V
20mA
10V
20mA
10V
10V
20mA
20mA
Voltage input
Current input
Input terminals
Thermistor
RS485
Functional safety input
STO input
Functional safety
confirmation output
STO output
Sink or source logic
for input terminal is
switched by SW6.
P24
CM1
DC24V
P24
CM1
P24
IN
EX
Source
Sink
(SW5)
(SW6)
(SW1)
(SW2)
(SW3)
(SW4)
Analog
input 2
Analog
input 3
Voltage input
Current input

2-18
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
■ Recommended terminals for wiring
• The following ferrule terminals are recommended for
signal cable for easy wiring and improved reliability of
connectivity.
Ferrule terminal with sleeves
*) Manufacturer: Phoenix Contact
■ Wiring procedure
1. Push the gray part on the control circuit terminal block
into the socket with a slotted screwdriver (with a wide
of 2.5mm or less). (Insertion hole will open)
2. Insert the wire or ferrule terminal into the wire
insertion hole (round) while pressing the gray part with
a slotted screwdriver.
3. The wire is connected when release the screw driver.
Crimping tool: CRIMPFOX UD 6-4 or CRIMPFOX ZA 3
• Even for pulling out the wire from the socket, press the
gray part with a slotted screwdriver (the insertion hole
will be opened while pressing).
Power cable size
mm2 (AWG)
Ferrule
terminal
model*
L1 [mm] L2 [mm]
φ
d [mm]
φ
D [mm]
0.25 (24) AI 0,25-8YE 8 12.5 0.8 2.0
0.34 (22) AI 0,34-8TQ 8 12.5 0.8 2.0
0.5 (20) AI 0,5-8WH 8 14 1.1 2.5
0.75 (18) AI 0,75-8GY 8 14 1.3 2.8
Push the
gray part into
the socket with a slotted
screwdriver
Insert the wire
The wire is connected
when release the screw
driver
2.5mm

2-19
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
2.11 Control circuit wiring section
■ Input terminals
• All COMs have the same electric potential.
• Change SW5 to external power source (EX) to connect
the power source between Input terminals 1 to 9, A or
B, and COM.
• Sink or source logic of the input terminal is switched by
SW6.
(Wiring example)
• [] it means factory default settings.
■
Terminal’s default function ([symbol: setting No.])
[RS:028]Reset
• Reset at every trip.
[SCHG:015]Command source change
• Change to the main speed command [AA101](OFF) or
sub-speed command[AA102](ON).
[JG:029]Jogging
• Run at a frequency of [AG-20] upon receipt of the operation
command by [JG]ON.
[FRS:032]Free-run stop
• [FRS]ON sets the motor in a free-run state.
[2CH:031]Two-step acceleration/deceleration
• [2CH]ON enables acceleration/deceleration
time-2[AC124][AC126].
[EXT:033]External trip
• [EXT]ON issues Trip[Er012].
[FW:001]Forward rotation and [RV:002]Reverse rotation
Forward
Reverse
Description
OFF OFF No
command
ON OFF Forward rotation command operation
OFF ON Reverse rotation command operation
ON ON No command (inconsistent logic)
[CF1:003]Multispeed-1 and [CF2:004]Multispeed-2 commands
Multispeed
-
1
CF1
Multispee
d-2 CF2
Description
OFF
OFF The set frequency source is enabled.
ON
OFF The frequency source of [Ab-11] is enabled.
OFF
ON The frequency source of [Ab-12] is enabled.
ON
ON The frequency source of [Ab-13] is enabled.
*) Setting CF3 and 4 allows you to set up to 16-speed.
[USP:034]Unattended start protection
• In a [USP]ON state, if an operation command has been input
before the power supply is ON, Trip[Er013] is issued.
Terminal
label
Terminal
name
Description Electric characteristics
Intelligent input terminal
Digital input
Contact
9, 8,
7, 6,
5, 4,
3, 2,
1
Input
terminal
Terminal functions are selectable according to the
parameter settings for each terminal.
Switching SW6 to SRC or SINK allows you to select SINK or
Source logic.
V
oltage between each input and
COM terminals
• ON voltage Min.DC18V
• OFF voltage Max.DC3V
• Max. allowable voltage DC27V
• Load current 5.6mA(at DC27V)
Pulse
A Pulse input-A
This is a terminal for pulse input. A and B terminals can be
used also as an input terminal.
Terminal functions are selectable according to the
parameter settings for each terminal.
The maximum input pulse rate is 32kpps.
V
oltage between an input and
COM terminals
• ON voltage Min.DC18V
• OFF voltage Max.DC3V
• Max. allowable voltage DC27V
• Load current 5.6mA(at DC27V)
• Max input pulse rate 32kpps
B Pulse input-B
Common
COM
Input
(common)
This is a common terminal for digital input terminals
(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A and B). Three COM terminals are
available.
Control circuit terminal
SW6
SW5
Input terminal
1
[RS]
2
[SCHG]
3
[JG]
4
[FRS]
5
[2CH]
6
[CF1]
7
[CF2]
8
[RV]
9
[FW]
A
[EXT]
B
[USP]
COM
COM
COM

2-20
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
■Output terminals
(Wiring example)
[AL]
[ZS]
: Equipment including lamps, relays and PLC
: Relays
• [] it means factory default settings.
■
Terminal’s default function
[RUN:001]Running signal
• Turns ON during operation (PWM output).
[FA1:002]Frequency-arrival signal
• Turns ON when the output frequency reaches the control
frequency.
[FA1:003]Frequency-arrival signal 2
• Turns ON when the output frequency reaches the control
frequency [CE-10] to [CE-13].
[IRDY:007]
• Turns ON when is ready for operation.
[OL:035]Overload notice advance signal
• Turns ON when the current exceeds the overload warning
level.
[ZS:040]0Hz speed detection signal
• Turns ON when the inverter output frequency falls below the
threshold frequency [CE-33].
[AL:017]Operation
• In case of [CC-17]=00 (factory setting)
Power
supply
Status AL0-AL1 AL0-AL2
ON
Normal
operation
Open Closed
ON Tripping Closed Open
OFF – Open Closed
• In case of [CC-17]=01
Power
supply
Status AL0-AL1 AL0-AL2
ON
Normal
operation
Closed Open
ON Tripping Open Closed
OFF – Open Closed
Terminal label
Terminal name
Description
Electric characteristics
Intelligent output terminals
Digital output
Open collector
15
14
13
12
11
Output terminal
Terminal functions are selectable according
to the parameter settings for each terminal.
This is available for both SINK and Source
logics.
Open collector output
Between each terminal and CM2
• Voltage drop when turned on: 4 V
or less
• Max. allowable voltage 27V
• Max. allowable current 50mA
CM2 Output (common)
This is a common terminal for output
terminals 11 to 15.
Relay
16A
16C
1a relay terminal Relays for A contact output
Maximum contact capacity
• AC250V, 2A(resistance)
• AC250V, 1A(inductive load)
(Minimum contact capacity)
• DC1V, 1mA
AL0
AL1
AL2
1c relay terminal Relays for C contact output
Maximum contact capacity
AL1/AL0:
• AC250V, 2A(resistance)
• AC250V, 0.2A(inductive load)
AL2/AL0:
• AC250V, 1A(resistance)
• AC250V, 0.2A(inductive load)
Minimum contact capacity (common)
• AC100V, 10mA
• DC5V, 100mA
11
[FA1]
12
[RUN]
13
[OL]
14
[OTQ]
15
[WAF]
CM2
Output
RY RY RY
RY RY
AL2 AL1 AL0
Alarm relay
Output terminal
X
X
16A 16C
Relay
Output terminal
X
RY
Control circuit terminal

2-21
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
■Analog input/output
(Wiring example)
■External thermistor
(Wiring example)
•
When variable resistor is connected on H-Ai1-L terminal, voltage
input is given to inverter, Sw1 for analog input 1 (Ai1) is to be set
on "voltage" side therefore.
•
If a frequency meter connected in left example is current type (4
to 20mA), set SW3 for analog output 1 (Ao1) as current output.
•
Twist the cables connected from a thermistor to the TH terminal
only between TH+ and TH-, and separate the twisted cables from
other cables.
•
Since very low current flows through the cables connected to the
thermistor, separate the cables from those (power line cables)
connected to the main circuit.
•
The length of the cables connected to the thermistor must be 20 m
or less.
Terminal
label
Terminal name
Description Electric characteristics
Voltage/current switchable analog input/output terminal
Power supply
L
COM for analog
power supply
COM terminals for analog input terminals
(Ai1,Ai2,Ai3) and
analog output terminals (Ao1,Ao2). Two L terminals are
available.
H
Speed setting
power supply
DC10V power supply. Used for voltage input with analog
input terminals (Ai1,Ai2,Ai3) using a variable resister.
Max. allowable input current 20mA
Analog input
Ai1
Analog input
terminal 1
(Voltage/current
selector SW1)
Either Ai1 or Ai2 can be used by switching the selector
switch to DC0 to 10V voltage input or 0- to 20mA current
input. Used as speed input and feedback input.
For voltage input:
• Input impedance Approx.10kΩ
•
Allowable input voltage DC-0.3V to
12V
For current input:
• Input impedance Approx.100Ω
•
Max. allowable input current 24mA
Ai2
Analog input
terminal 2
(Voltage/current
selector SW2)
Ai3
Analog input
terminal 3
DC-10 to 10V voltage input is available.
Used as speed input and feedback input.
Voltage input only:
• Input impedance Approx.10kΩ
•
Allowable voltage input DC-12V to
12V
Analog output
Ao1
Analog output
terminal 1
(Voltage/current
selector SW3)
Either Ao1 or Ao2 can be used as an output for inverter
monitoring data by switching the selector switch to DC0 to
10V voltage output or 0 to 20mA current output.
For voltage output:
• Max. allowable output current 2mA
•
Output voltage accuracy ±10%
(Ambient temperature: 25±10
degrees C)
For current input:
•
Allowable load impedance
250Ω or less
•
Output current accuracy ±20%
(Ambient temperature: 25±10
degrees C)
Ao2
Analog output
terminal 2
(Voltage/current
selector SW4)
Terminal
label
Terminal
name
Description Electric characteristics
Thermistor terminal
Analog input
TH+
External
thermistor
input
Connect to an external thermistor to make the inverter trip if an
abnormal temperature is detected.
Connect the thermistor to TH+ and TH-. The impedance to detect
temperature errors can be adjusted within the range 0Ω to
9,999Ω.
[Recommended thermistor properties]
Allowable rated power: 100 mW or more
Impedance at temperature error: 3kΩ
DC0 to 5V
[Input circuit]
TH-
Common
terminal for
external
thermistor
input
TH-
TH+
External thermistor
terminals
Thermistor
DC5V
1kΩ
2kΩ
TH-
TH
Thermistor
Control circuit terminal
Ao2 Ao1
Analog input/output
H Ai1
Ai2
Ai3
L L
Potentiometer for frequency source
(0.5kΩ to 2kΩ)
* 1kΩ, 1W or more recommended
Frequency
meter
SW4 SW3 SW2 SW1
Control circuit terminal

2-22
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
■Functional safety STO terminals
Refer to the “Functional Safety Guide”
for using a safety functions.
■FM output terminals
(Wiring example)
•
FM output is selectable from PWM output with a fixed cycle of
6.4ms or pulse output with a variable cycle.
•
FM output is adjustable by parameter settings.
Terminal
label
Terminal name
Description
P24S
24V output power source
terminal
Refer to the appended
“Functional Safety
Guide” for details.
CMS
COM terminal for
functional safety
STC Logic switching terminal
ST1 STO input1
ST2 STO input2
ED+
Output terminal for
monitoring
ED-
Output COM terminal for
monitoring
Terminal
label
Terminal name Description Electric characteristics
FM output
terminal
FM output
Monitor
output
FM
Digital monitor
(voltage)
Digital monitor output is selectable from PWM
output with 6.4ms cycle or pulse output with a
variable duty cycle of approx. 50%.
Pulse train output DC0 to 10V
•
Max. allowable output current
1.2mA
•
Maximum frequency 3.60kHz
CM1
COM for
digital
monitor
This is a common terminal for digital monitor.
This is also used as 0V reference potential for P24.
Frequency meter
(PWM)
ED+
ED-
Safety confirmation
terminal
STO Safety terminal
P24S STC CMS
ST1
ST2 STC
Control circuit terminal
FM CM1
Digital output
Control circuit terminal

2-23
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
■Serial communication
(Wiring example)
■24V power supply input/output
(Wiring example)
•
SP and SN with the same name are internally connected, which are
available for a plurality of wiring.
•
For the use of Modbus communication, refer to the “User’s guide”
to obtain a more detailed description.
•
Connecting DC24V external power supply into the terminal P+ and
P-, permit to change parameters and perform optional
communication without the main power source. Is also allowable
when connecting into the main power supply.
Terminal
label
Terminal name
Description Electric characteristics
RS485 communication
Serial communication
SP
SN
RP
(CM1)
MODBUS
terminal
(RS-485)
SP terminal:
RS-
485 differential(+) signal
SN terminal: RS-485 differential(-) signal
RP terminal: Connect to SP through a termination
resistor
CM1 terminal: Connect to the signal ground of
external communication devices.
There are two SP and two SN terminals, which are
connected internally.
The maximum baud rate is 115.2kbps.
Termination resistor (120Ω) integrated
Enabled: RP-SN shorted
Disabled: RP-SN opened
Terminal
label
Terminal name
Description Electric characteristics
24V power supply
Power input
P24
24V output
power source
terminal
This terminal supplies DC24V power for contact signals. Max. output 100mA
CM1
Reference
terminal for
24V output
This serves as a 0V reference terminal for contact signal.
This is used also as a common terminal for FM output.
P+
Terminal
for
external 24V
input (24V)
Input external DC24V power supply to the inverter.
24V power supply input permit to change parameter
settings and perform optional communication
operations without control power supply.
Allowable input voltage
DC24V±10%
Max. allowable current 1A
P-
Terminal for
external 24V
input (0V)
Connect CM1
Into the SG (signal ground) of
external devices,
For enabling the termination
resistor, short-circuit between
RP and SN.
Control circuit terminal
RP
SN SP SN SP
CM1
Modbus communication
(+) (-)
Power supply
24V terminal
External 24V
terminal
P+
P24
P-
External DC24V power supply
Control circuit terminal

2.12
Please check for any residual risk upon completion of the
installation before
■
Chapter 2
Residual risk
Parts subject to residual risk
Residual risk checklist No.
Residual risk checklist
The installation, wiring and setting work must be
conducted by qualified engineers.
No.
Name of part
(A)
Main circuit
terminal
(B)
Heat sink
(C)
Input/output
terminal block
-
Unspecified
parts
No.
Operational
phase
1
Installation
2
Installation
3
Installation
4
Installation
5
Installation
6
Installation
7
Installation
8
Installation
Maintenance
9
Installation
Maintenance
10
Use
Maintenance
11
Use
Maintenance
power on
block
Work
Installation
Installation
Installation
Installation
Installation
Installation
Installation
Wiring
Wiring
Wiring
Inspection
Wiring
Inspection
.
DANGER
8,10
4
11,12
9
Part
Residual
(B)
CAUTION
- CAUTION
- CAUTION
(B)
DANGER
- CAUTION
- CAUTION
- CAUTION
(A)
DANGER
-
DANGER
(A)
DANGER
(C)
DANGER
WARNING
risk
Details of harm or damage
Damage due to rough transportation.
Shortened lifetime of parts due to the use
in places where the product is exposed to
direct sunlight or the temperature is not
within the specified range.
Short-
circuit failure due to the use in
places where the temperature is not
within the specified range or
condensation occurs.
A cooling fan reaching a high temperature
exceeding 150 °C causes a fire on a
flammable wall.
Damage to parts due to entry of dust and
corrosive gases.
Shortened lifetime of parts due to
reduced cooling capability by placing the
product horizontally.
A cooling fan failed due to waterdrops
oil mist when the heat sink is positioned
outside.
A fire is caused inside by an arc due to
screws
loosened by vibrations.
A fire from flammable materials caused
by an arc due to screws loosened by
vibrations.
Electric shock by touching a high voltage
part with the cover removed.
Electric shock by touching a high voltage
part with a tool with the cover removed.
2-24
CAUTION
1
2,3,5,6,7
loosened by vibrations.
or
(C)
Installation and Wiring
Preventive measures
Do not let the product fall. Do not apply
force when handing the cover and
operator
keypad.
Verify that the ambient temperature is
within the
specified range throughout the
year by means of cooling or ventilation.
Verify that the
within the specified range throughout the
year by means of cooling or ventilation.
Install the product in places where no
condensation occurs.
Install the product on a non
metal wall.
Install the product inside a totally
enclosed panel.
Install the product vertically.
With the heat sink positioned outside,
install the product in places free from
waterdrops and oil mist.
Regularly check the tightening of screws.
Regularly check the tightening of screws.
Do not place
flammable materials near
the product.
Do not open the cover when the power is
on.
Wait for 10 minutes or more after the
power is off,
and then confirm that the
voltage between P and N is significantly
less than 45Vdc to start the work.
Do not open the
on.
Wait for 10 minutes or more after the
power is off, and then confirm that the
voltage between P and N is significantly
less than 45Vdc to start the work.
ambient temperature is
-
flammable
cover when the power is
(A)
✓
□
□
□
□
□
□
□
□
□
□
□
(B)

2-25
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
The installation, wiring and setting work must be
conducted by qualified engineers.
For using [SET] function of input terminal, similarly, set the
related 2nd parameters settings.
No.
Operational
phase
Work Part
Residual
risk
Details of harm or damage Preventive measures
✓
12
(a)
Installation Wiring - DANGER
Motor insulation damage due to surge
caused by long distance motor wiring.
When the motor wiring distance exceeds
20m or more, try to shorten the wiring.
Use LCR filter or output AC reactor.
□
12
(b)
Installation Wiring - DANGER
Motor damage due to insulation failure
caused by motor voltage unmatched.
Use motor according to the inverter
voltage class.
□
12
(c)
Installation Wiring - DANGER
Motor damage due to unstable power
supply, caused by power supply
unbalance, low voltage or excessive
voltage drop.
Confirm the inverter power supply
voltage, feeding method and capacity.
□
12
(d)
Use
Maintenance
Wiring
Inspection
- DANGER
Motor damage due to continue ran in
open phase on motor output line.
V
erify the motor output line that not
being in open phase.
□
12
(e)
Use
Maintenance
Setting - DANGER
Motor damage due high current on motor
caused by inadequate parameter setting.
Set adequate value for related function
parameter of motor electronic thermal
level [bC-01] to [bC125].
□
Set adequate value for base frequency,
motor rated current, control mode,
motor constant, load rating, direct
current output related parameters.
(representative parameter)
Motor related parameter:
IM: [Hb102] to [Hb118]
SM(PMM): [Hd102] to [Hd118]
Control mode: [AA121]
Load rating: [Ub-03]
DC braking: [AF101] to [AF109]
13 Use Operation (C) DANGER
The motor once stopped runs
automatically.
I
f automatic restart after motor stop is set
by a function, make sure to clearly
describe that in the system.
□
14 General General - DANGER
Damage or injury
occurrence
from a
hidden risk.
Confirm that
system
is structured
for fail
safe considering a risk assessment.
□
15 General General
Damage or injury occurrence by missing
acquisition of information related to risk
Obtain the latest
version of user
’
s guide
to make those information available.
Inform users appropriately.
□

2-26
Chapter 2
Installation and Wiring
(Memo)

3-1
Chapter 3
Operation Setting and Examples of I/O Adjustment
Chapter 3
Operation Setting and
Examples of I/O Adjustment
This chapter describes basic settings, frequency source
required for operation, examples of run command
source settings and examples of adjusted I/O terminals.
Basic settings 1
3.1 Set the load rating
•
Select [Ub-03] load specification selection on the
parameter setting screen.
Menu Option
60.00
Ub-03
Load type selection
oFW
STOP
M1 H03
00 V-Low Duty
01 Low Duty
02 Normal Duty
•
When [Ub-03] is changed, the parameters set for the
current are automatically adjusted in proportion to the
changed rated current, and the set values are changed.
•
If the current value is set as overload restriction,
electronic thermal and warning functions, those are to
be reconfirmed after changing this setting. Load
specification selection is to be set at first therefore.
Parameter
Parameter
Details
Setting data
[Ub-03]
Select the load
specification.
00: V-Low Duty (VLD)
01: Low Duty (LD)
02: Normal Duty (ND)
*) The underlined value is set by default.
See “Chapter 4 Settings” for detailed operating
instructions
Basic settings 2
3.2 Set the motor data
•
Set the parameters listed in the table below on the
parameter setting screen according to the motor you
use (e.g. induction motor and permanent-magnet
motor).
Menu Option
60.00
AA121
Control mode_M1
oFW
STOP
M1 H03
0 VFC-VC
1 VFC-VP
2 VFC-FREE
3 VFC-A.bst
Parameter
Induction motor (IM)
Parameter
Details
Setting data
[AA121]
Control pulse setting
00: V/f control constant
torque characteristic , etc.
[Hb102]
Capacity selection
0.01 to 630.00 (kW)
[Hb103]
Motor poles setting
2 to 48 (poles)
[Hb104]
Base frequency
10.00 to 590.00 (Hz)
[Hb105]
Maximum frequency
10.00 to 590.00 (Hz)
[Hb106]
Rated voltage
1 to 1000 (V)
[Hb108]
Rated current
0.01 to 9999.99 (A)
Synchronous motor (permanent-magnet motor)
(SM(PMM))
Parameter
Details
Setting data
[AA121]
Control pulse setting
09: PM motor
[Hd102]
Capacity selection
0.01 to 630.00 (kW)
[Hd103]
Motor poles setting
2 to 48 (poles)
[Hd104]
Base frequency
10.00 to 590.00 (Hz)
[Hd105]
Maximum frequency
10.00 to 590.00 (Hz)
[Hd106]
Rated voltage
1 to 1000 (V)
[Hd108]
Rated current 0.01 to 9999.99 (A)
Note: Motor constant setting is required for driving SM.

The frequency source and run command source are
necessary to drive the motor.
3.3
•
•
Eg.) For [FA
•
*
Chapter 3
Frequency source 1
F
requency
Select [AA101]
setting screen.
Changing
frequency
(1) [FA-01]
for frequency setting from keypad
(2)
[Ab110]
-
01]
Menu
Output frequency
STOP
FA-
01
Set
speed
Frequency source
Change the frequency source setting [Ab110] to
"Multispeed
arrow keys.
Parameter
Parameter
[AA101]
[FA-01]*)
[Ab110]*)
) While
[AA101]
or [Ab110] will be automat
other.
When no change can be made or is reflected
in [FA-
01], the
command source by the
[AA101].
You need to set the frequency value to a value other
than 0.00.
setting from
= 07
Frequency source
setting from each
for
frequency setting
(Keypa
oFW
-M
(Keypad)
-
0 speed No.1" by using the up and down
Details
Frequency
from
Main speed command
Multispeed
= 07
, a change made in either [FA
operator keypad is not specified as a
keypad
at
multispeed
60.00
0.00 Hz
M1
60.0
source
setting
keypad
-
0 speed No. 1
ically reflected in
terminal function or
from
parameter
source
or
profile
Option
H03
0
Hz
Setting
data
07
0.00Hz
0.00Hz
the
3-2
Operation Setting and Examples of I/O Adjustment
.
-01]
Run command source 1
3.4
•
Select [AA111]
RUN
Run/stop command
Press the RUN key and STOP key on the operator
keypad to start and stop the inverter, respectively.
Parameter
Parameter
Run using the operator keypad
from
keypad.
[AA111]
RUN key (start)
= 02
on the parameter setting screen to
Details
Run by pressing the
RUN key
of keypad
.
STOP key (stop)
Setting data
02

3-3
Chapter 3
Operation Setting and Examples of I/O Adjustment
Frequency source 2
3.5 Multispeed terminals command
•
While multispeed command is off, the speed command
will follow the parameter setting [AA101].
•
To use multispeed 0, select [AA101] = 07 frequency
source selection.
Frequency source
•
Change the frequency command by turning ON/OFF
from multispeed input terminals [CF1] and [CF2].
Parameter
Parameter
Details
Setting
data
[AA101]
Frequency setting
from
keypad
07
[FA-01]
*1)
Main speed source 0.00Hz
[Ab110]
*1)
Multispeed
0 setting
1st
motor
([CF1]OFF/[CF2]OFF)
0.00Hz
[Ab-11]
*2)
Multispeed 1 setting
([CF1]ON/[CF2]OFF)
0.00Hz
[Ab-12]
*2)
Multispeed 2 setting
([CF1]OFF/[CF2]ON)
0.00Hz
[Ab-13]
*2)
Multispeed 3 setting
([CF1]ON/[CF2]ON)
0.00Hz
[CA-06] The terminal 6
for [CF1] 001
[CA-07] The terminal 7
for [CF2] 002
*1) While [AA101] = 07, a change made in either
[FA-01] or [Ab110] will be automatically reflected
in the other. When no change can be made or is
reflected in [FA-01], the operator keypad is not
specified as a command source by the terminal
function or [AA101].
*2) Set the frequency value for multispeed selection.
Run command source 2
3.6 Operate using FW/RV terminal
•
Select [AA111] = 00 [FW][RV] terminal from parameter
setting screen.
Run/stop command
•
Run or stop by turning either [FW] terminal or [RV]
terminal ON/OFF.
Parameter
Parameter
Details
Setting
data
[AA111]
Run using FW/RV terminal
00
[CA-09] The terminal 9
for [FW] 001
[CA-08] The terminal 8
for [RV] 002
Input terminals
5
6
[CF1]
7
[CF2]
8
COM
COM
Input terminals
7
8
[RV]
9
[FW]
A
COM

3-4
Chapter 3
Operation Setting and Examples of I/O Adjustment
Frequency source 3
3.7 Potentiometer frequency command
•
Select [AA101] = 01 Ai1 terminal input from parameter
setting screen.
* Select voltage input (0 to 10V) for Ai1 switch of control
circuit board.
Frequency command
•
Adjust the position of the knobs on the potentiometer
to change the frequency command.
Parameter
Parameter
Details
Setting
data
[AA101]
Set
as
frequency
command
for Ai1 input terminal.
01
Run command source 3
3.8 Operate using 3WIRE terminal
•
Select [AA111] = 01 to 3WIRE function from parameter
setting screen. In this section, 3WIRE functions are
assigned into the input terminals.
* Terminal 7[CA-07] = 016; terminal 8[CA-08] = 017;
terminal 9[CA-09] = 018
Run/stop command
•
To run turn ON [STA] terminal, and turn ON [STP]
terminal to stop. Select the rotation direction with [FR]
terminal.
Parameter
Parameter Details
Setting
data
[AA111]
Set the operation command
for 3WIRE function.
01
[CA-09] The terminal 9 is [FR]. 018
[CA-08] The terminal 8 is [STP]. 017
[CA-07] The terminal 7 is [STA]. 016
Analog input/output
H Ai1
Ai2
Ai3
L
Potentiometer for frequency
command (1kΩ to 2kΩ)
R
ecommendation: 1k
Ω 1W
Input terminals
7*
[STA]
8*
[STP]
9*
[FR]
A
COM
Control circuit terminal
SW1
10V
20mA
Ai1

3-5
Chapter 3
Operation Setting and Examples of I/O Adjustment
Example for adjusting I/O terminals 1
3.9 Adjust the analog input (Ai1/Ai2)
E.g.) Adjust operation (E.g. for Ai1)
•
Set the ratio to input to limit the operating range of
the frequency command.
(When selecting the frequency through terminal input)
Parameter
Parameter
Details
Ai1 Ai2
[Cb-03] [Cb-13]
Set the frequency source ratio to the
start ratio of the analog input.
[Cb-04] [Cb-14]
Set the frequency source ratio to the
end ratio of the analog input.
[Cb-05] [Cb-15]
Set the start ratio of the analog input 0
to 10V/0 to 20mA.
[Cb-06] [Cb-16]
Set the end ratio of the analog input 0
to 10V/0 to 20mA.
•
Ai2 adjustment can be done in similar way to Ai1 by
using Ai2 parameters in order to Ai1.
E.g.) Make a fine adjustment (E.g. for Ai1)
Parameter
Parameter
Details
Ai1 Ai2
[Cb-30] [Cb-32]
Adjust the zero-point reference line for
voltage input 10V/current input 20mA
and the maximum frequency.
[Cb-31] [Cb-33]
Adjust the slope of the reference line
for voltage input 10V/current input
20mA.
*) Use the switch on control circuit terminal board to
change for voltage/current input.
Example for adjusting I/O terminals 2
3.10 Adjust the analog output
(Ao1/Ao2/FM)
E.g.) Adjust operation (E.g. for Ao1)
•
Set a value equivalent to 0% output first.
•
Then, adjust a value equivalent to 100% output.
Parameter
Parameter
Details
Ao1 Ao2 FM
[Cd-23] [Cd-33]
-
Adjust the zero-point
reference line for voltage
output 10V/current output
20mA and data at 100%.
[Cd-24] [Cd-34]
-
Adjust the slope for voltage
output 10V/current output
20mA and data at 100%.
- - [Cd-13]
Adjust the zero-point
reference line for 100%
duty cycle output and data
at 100%.
- - [Cd-14]
Adjust the slope for 100%
duty cycle output and data
at 100%.
Maximum
frequency
100%
[Cb-04]
[Cb-03]
0
[Cb-05] [Cb-06] 100
(0V/0mA)
(10V/20mA)
Analog input
(V/mA)
While setting
[Cb-07] = 00,
the frequency command
from 0% to [Cb-05] will be
set by [Cb-03].
100(%)
0
Parallel
slide
[Cb-30]=-50.0(%)
[Cb-30]=0.0(%)
Max. 0
50
-50
Change the
Slope angle
[Cb-30]=50.0(%)
[Cb-31]=200.0(%)
[Cb-31]=50.0(%)
[Cb-31]=100.0(%)
Output scale
t/T(%)
100
0
Parallel
slide
Output
range
[Cd-23]=50.0(%)
[Cd-23]=-50.0(%)
[Cd-23]=0.0(%)
Max.
0
50
-50
Full scale (FS)
t/T(%)
100
0
Output
range
[Cd-24]=200.0(%)
[Cd-24]=50.0(%)
[Cd-24]=100.0(%)
Max.
0
50
-50
[Cd-24]=-50.0(%)
Change the
slope
angle

3-6
Chapter 3
Operation Setting and Examples of I/O Adjustment
Example for adjusting I/O terminals 3
3.11 Adjust the analog input (Ai3)
E.g.) Adjust operation (E.g. for Ai3)
Parameter
Parameter
Details
Ai3
[Cb-23]
Set the frequency source ratio to the start
ratio of the analog input.
[Cb-24]
Set the frequency source ratio to the end
ratio of the analog input.
[Cb-25]
Set the start ratio of the analog input -10V
to 10V.
[Cb-26]
Set the end ratio of the analog input -10V
to 10V.
E.g.) Make a fine adjustment
■Parameter
Parameter
Details
Ai3
[Cb-34]
Adjust -10V on the reference line for
-10V/10V and the frequency.
[Cb-35] Adjust the slope of the reference line.
Example for adjusting I/O terminals 4
3.12 Prevent input terminal malfunction
•
Set a response time for input terminal to prevent a
malfunction due to noise input.
Parameter
Input
terminal
Response
time
Input
terminal
Response
time
1 [CA-41] 7 [CA-47]
2 [CA-42] 8 [CA-48]
3 [CA-43] 9 [CA-49]
4 [CA-44] A [CA-50]
5 [CA-45] B [CA-51]
6 [CA-46]
Example of adjusted I/O terminals 5
3.13 Stabilize an output terminal
•
Set the delay time to stabilize an output terminal from
a sensitive reaction of internal functions.
■Parameter
Output
terminal
On-delay time Off-delay time
11 [CC-20] [CC-21]
12 [CC-22] [CC-23]
13 [CC-24] [CC-25]
14 [CC-26] [CC-27]
15 [CC-28] [CC-29]
16A-16C [CC-30] [CC-31]
AL1-AL0/
AL2-AL0
[CC-32] [CC-33]
Forward operation
Maximum frequency
Reverse operation
Maximum frequency
[Cb-23]
[Cb-26]
[Cb-25]
[Cb-24]
(-10V)
-100%
100%
(+10V)
Analog input
(Ai3)
100(%)
-100
Parallel
[Cb-34]=50.0(%)
[Cb-34]=-50.0(%)
[Cb-34]=0.0(%)
Max.
0
0
Slope
[Cb-35]=200.0(%)
[Cb-35]=100.0(%)
[Cb-35]=50.0(%)
Operation of
the input
Operation of
the internal
[CA-41]
[CA-41]
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
Selected output
Operation of
the output
[CC-20] [CC-21]
ON
OFF
OFF
ON

Chapter 4
Chapter
4.1
4
Keypad
4.1.1 H
ow to use
Image
colour
4.1.2 D
isplay mode
(D)
(A)
①
⑧
③
4 Settings
overview
the
keypad
may differ from the real product.
⑥
(E)
(B)
(F)
(C)
<b>
<a>
<g>
<h>
⑥
⑤
(G)
<d>
<c>
<f> <e>
4-1
Number
①
②
③
④
⑤
⑥
⑦
⑧
Number
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(E)
(F)
(G)
Number
<a>
<b>
<c>
<d>
<e>
<f>
<g>
<h>
②
⑦
④
For parameter configuration
Name
F1 key
F2 key
RUN
key
STOP/RESET
UP/DOWN/
LEFT/RIGHT key
& SEL key
(
centre
Monitor screen
RUN LED
POWER LED
Description
Operation status
Warning status
Data/parameters
Function assigned to F1 key
Function of RUN key
Frequency r
Inverter Name, Clock
Selected by F2 Option
Function
Name
Pow
SET
Prm
No.
STO
Cntrl
EzSQ
Spcl
For more detail
status” or
users’ guide
Transition to home, cancel,
etc. Function
indicated at the bottom
of the screen.
Save data
the key
bottom right of the screen.
Motor motion s
this key is
keys
Decelerate to stop or reset
the tripping.
s
)
To
screen
LEFT/RIGHT. To select the
data
Display parameters and
data
Turns
command is in execution
Turns ON while the
i
s power
.
.
.
eference, Torque
assigned to F2 key
Type of power supply (Input)
SET terminal for 1st/2nd motor setting
Parameter display mode
Screen number
Functional Safety
Control mode
EzSQ
program
Special functions
, refer to
“C
.
Description
of the key
, etc. Function
is indicated at the
pressed
move between
/data
use UP/DOWN/
, press
the SEL key.
.
ON while RUN
ed-
on
.
.
reference
, etc.
.
Description
.
.
. STO
.
.
.
hapter 5.2
Confirming the
is
left
of
tarts when
.
the
.
keypad
.
,
.
.

4-2
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
4.1.3 Monitor mode
For screens not described below, refer to User’s Guide.
Pressing F1 key will return to any monitor screen.
1. 3 lines screen
[multi monitor]
2. Reference screen
[
While screen
]
4.Trip history screen
[whole display]
Menu
Option
46.49Hz
Output frequency
29.51
Hz
Output current
11.9 A
Input terminal monitor
LLLLLLLLLLL
oFW
RUN
FW
M1 H01
M
enu
Option
46.49Hz
Output Frequency
29.51 Hz
oFW
RUN
FW
M1 H03
FA-01
Main Speed Reference (panel)
29.51
Hz
[0.00-
60.00]
M
enu
Option
46.49Hz
oFW
RUN
FW
M1 H04
dA-01
Output frequency
29.51
Hz
----
D
etail
46.49Hz
Trip History
TRotal Count
18回
oFW
RUN
FW
M1 H06
1. E001 16/12/25 22:15
2. E007 16/12/25 20:33
3. E009 16/12/02 17:24
4. E012 16/10/10 08:50
5. E001 16/09/21 14:43
3. Large monitor screen
[
Huge monitor
]
(Menu)
(
Home
)
1 1
5.Retry history screen
[why retry history]
----
Detail
46.49Hz
Retry History
oFW
RUN
FW
M1 H06
1. r001 16/12/25 22:15
2. r007 16/12/25 20:33
3. r009 16/12/02 17:24
4. r012 16/10/10 08:50
5. r001 16/09/21 14:43
Home ----
46.49Hz
oFW
RUN
FW
M1
M01
Menu
01 Scroll Mode
02 Read/Write
03 System Setting

Chapter 4
4.1.3.1
Ch
Using
code to be monitored can be changed, pressing again the
SEL (O) key give access to the function parameter.
key
.
Parameter setting screen
ange the
parameter.
Menu
Output frequency
RUN
FW
FA-
01
Set Speed
Press the SEL (O) key.
An area in the screen will be
Menu
Output frequency
RUN
FW
FA-
01
W
ith UP/DOWN (
monitor area then will be
If SEL (O) key is pressed, the parameter code can be
changed.
Back
Output frequency
RUN
FW
FA-
01
UP/DOWN/LEFT/RIGHT (
to return back
oFW
-M (
Keypad
oFW
Set S
peed
)
keys
oFW
Set S
peed
.
29.51
29.51 Hz
M1
)
29.51 Hz
highlighted.
29.51
M1
-M (
Keypad
select either parameter or
highlight
ed
29.51
29.51 Hz
M1
-M (
Keypad
) keys the function
Option
H03
Option
29.51 Hz
H03
)
29.5
1 Hz
.
Option
H03
)
29.5
1 Hz
Press
4-3
1
・
In the case of a numerical value:
・
In the case of
For parameter configuration
Back
Output frequency
RUN
FW
FA-01
Set S
peed
With
UP/DOWN/LEFT/RIGHT (
change the
parameter
And then press the SEL (O) key to save the changes.
a selection menu
The upper area of the display shows the
function
description
Back
AA111
RUN command selection_M1
RUN
FW
00
:[FW]/[RV] terminal
01:3-
wire
02:
Keypad
03
:RS485
With
UP/DOWN (
the available choices.
And then press the SEL (O) key to save the changes.
oFW
-M (
keypad
s value,
.
oFW
’s RUN key
) keys
29.51
29.51 Hz
M1
)
3
9.51 Hz
) keys
:
29.51
M1
you can move between
----
H03
selected
----
H03

Chapter 4
4.1.3.2
To change the monitor details.
3 lines monitor
Menu
Output frequency
Output frequency
Input terminal monitor
RUN
FW
Press the
SEL (
highlighting the first line
Menu
Output frequency
Output current
Input terminal monitor
RUN
FW
T
hen with UP/DOWN (
one
desired
Pressing the SEL (O) key, the
Back
RUN
FW
d
A
Output frequency
Making use of
the code
of the parameter to be monitored can be
changed,
and then with the
change.
Press 1 key to return back.
oFW
O)
key while on the 3 lines screen
oFW
of the three monitors.
oFW
-01
UP/DOWN/LEFT/RIGHT
46.49
46.49 Hz
LLLLLLLLLLL
M1
as result.
46.49
46.49Hz
LLLLLLLLLLL
M1
) is possible to highlight
code
can be accessed.
46.49
M1
29.51 Hz
SEL (O)
key confirm the
Option
11.9 A
H01
,
Option
11.9 A
H01
the
Option
H01
( )
keys
4-4
the
,
4.1.3.3
On tripping event
With UP/DOWN (
confirmed.
Trip history
In the Trip history screen press the SEL
UP/DOWN
(O)
*) For more details
to
*)
Put a battery f
For parameter configuration
Trip history screen
Menu
Trip event
Overcurrent error
TRIP
E001 16/12/25 22:15
Output frequency
Output current
DC voltage
Status
1
Also, the background will become red.
.
Menu
Trip history
Total count
TRIP
1. E001 16/12/25 22:15
2. E007 16/12/25 20:33
3. E009 16/12/02 17:24
4. E012
5. E001 16/09/21 14:43
(
)
key to access
“
Chapter 5 Troubleshooting
.
46.49
oFW
: +29.51 Hz
: 47.71 A
: 290.2 Vdc
: Run
NRDY
) keys, the
18 times
oFW
16/10/10 08:50
NRDY
keys
highlight
the details
regarding that trip status
about the
detailed history, please refer
clock function.
46.49
M1
trip
status can be
46.49
M1
(O)
key, and with
a history,
the
”.
----
Detail
H06
n
press SEL
.

Chapter 4
・
4.1.4.1
・
※
4.1.4.2
・
※
4.1.4.3
※
4.1.4 D
oing a test
This explains the method to how to do a test run using
the keypad
.
Menu
Output frequency
Output current
Input terminal monitor
RUN
FW
Confirm the operation command.
I
n the position
displayed FW
enabled.
⇒
Go to
In the
cases that is not displayed, and want
from the
keypad
reference
to FW
RUN command selection.
⇒Go to
[
4.
F
requency reference
In the upper illustration, in the position (F), when values
other than 0.00
is already set.
In the case that
change the
case that
you want to change to an
such, the f
requency command selection must be
changed.
⇒
Go to
Start the
key
and the motor will accelerate.
When the motor does not rotate, please refer to the
troubleshooting.
run…
Home screen
oFW
(E)↑ (F)↑
(E)
of the upper illustration
or RV,
the RUN key of the
[4.1.4.2]
, or want to change the RUN command
terminal
1.4.4 Run Command reference change
are displayed
⇒Go to
[
4.1.4.
0.00
is displayed, is necessary to
value of the
frequency reference. In the
[4.1.4.5]
output
46.49
46.49 Hz
LLLLLLLLLLL
M1
, is necessary to change the
status checking
, the frequency reference
3]
analog
by pressing the RUN
Option
11.9 A
H01
, when is
keypad is
to operate
input and
4-5
]
.
4.
1.4.4
①
parameter setting screen and by pressing the SEL(O)
key, the parameter section of the parameter setting
screen will blink.
②
(
③
keys select the RUN operation to be executed
all the choices
one
④
in the position (E) FW or RV
the
⇒
Go to
For parameter configuration
RUN command
Press the
RIGHT
Back
Output frequency
STOP
FA-01
Set Speed
Change
the code
)
keys to
Back
Output frequency
STOP
AA111
RUN command selection_M1
01:[FW]/[RV] terminal
Press the
SEL
. In this case
selected.
Back
AA111
RUN command selection_M1
STOP
00:[FW]/[RV] terminal
01:3-
wire
02:
Keypad
03
:RS485
To save the
F1 key
, and will
[4.1.4.
2
( )
key, after moving to the
oFW
-
M (Keypad
with UP/DOWN/LEFT/RIGHT
[AA111].
oFW
(O) key
and then
[
oFW
’s RUN key
changes press
go
to Home screen.
]
reference
change
Option
29.51
0.00 Hz
M1
)
29.51 Hz
Option
29.51
0.00 Hz
M1
with UP/DOWN
03:Keypad
’s RUN key]
Option
29.51
M1
the SEL (O)
should be
displayed. Press
H03
H03
[1-
8]
(
between
is
the
H03
key
and then
)
Chapter 4
4.1.4.5
①
②
frequency reference
③
(
④
Changing frequency reference
Press
the
parameter
setting screen, press the SEL (O) key, the
parameter section of the parameter setting screen will
blink.
Back
Output frequency
STOP
FA-
01
Set
S
With UP/DOWN/LEFT/RIGHT
the code
to [
(keypad)
] shall be
be chosen.
⇒Go to
③
If the displayed screen is different, change the
Press
the
)
keys change
Back
Output frequency
STOP
FA-
01
Set
S
To save the changes press
that
in the position (F) should be displayed the
frequency. Press the
⇒Go to
[
4.1.4.3
RIGHT ( )
key
oFW
peed-M (
Keypad
FA-01],
then
displayed, the frequency setting can
source
SEL(O)
key, with UP/DOWN/LEFT/RIGHT
the
oFW
peed-M (
Keypad
F1 key, and will go to Home screen
]
and
after moving to the
0.00
M1
)
(
[Main speed reference
. ⇒Go to
⑤
frequency
value
0.00
M1
)
46.4
(F)↑
the
SEL (O)
Option
0.00 Hz
H03
0.00 Hz
) keys
change
.
-
0.00 Hz
H03
9
Hz
key, and
after
set
4-6
.
⑤
the function code
⑥
select the frequency reference
[0
⑦
the position (E)
the
⇒
For parameter configuration
W
ith UP/DOWN/LEFT/RIGHT
Back
Output frequency
STOP
AA101
Main speed
01:Analogue input[Ai1]
Press the
SEL
7:Keypad
] is selected in this case
Back
Output frequency
STOP
07:
Keypad
08
:RS485
09
:Option
10
:Option
To save
changes
F1 key, and will go to Home screen.
Go to
[
4.1.4.2
to [AA10
1
oFW
source
_M1
(O)
key and with UP/DOWN
oFW
-1
-2
press
the
,
FW or RV should be displayed. Press
]
(
].
Option
0.00
0.00 Hz
M1
source
to be used.
.
Option
0.00
0.00 Hz
M1
SEL (O)
key, and then in
) keys
change
( )
keys,
H03

4-7
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
4.1.5 Copying data
Data can be stored in the keypad and then copied to
other inverter unit. It is strongly recommended to backup
the data just in case.
Refer to user’s guide for a more detailed explanation.
① Select R/W from menu
Home Option
46.49
oFW
STOP
M1
M01
Menu
01 Scroll mode
02 Read / Write
03 System setting
②.”Read” function is used for storing the data from the
inverter to the keypad.
②’ 2-2. “Write” function is used for copying the data
stored in the keypad to the inverter
(Sequential writing function is used for copying the
data one after another)
Back ----
46.49
oFW
STOP
M1
R01
Read / Write
01 READ
02 WRITE
For more information, refer to the user’s guide.
4.1.6 Automatic functions of the keypad
With the system configuration, you can set and adjust
keypad related parameters.
Home ----
46.49
oFW
STOP
M1
M01
Menu
01 Scroll mode
02 Read/Write
03 System
setting
・Available actions in the system configuration
Name Memo
Language selection Change the language.
Date function *1) Time setting, display format, and
the settings for the battery
warning.
Read lock Limits the reading property of the
data.
R/W write mode Change the R/W data
parameters.
Home automatic
transition timer
Sets the time for the automatic
home screen return function.
Initial home screen
selection
Sets which screen is displayed at
the home screen when turns-on.
Brightness Adjust the brightness of the
keypad.
Auto backlight-off
function *2)
Set the turn-off time and
brightness.
Blinking at trip Sets the screen blinking when
trips.
Background color Set the background color.
Basic information monitor Check the software information.
Keypad mode Use this setting when connecting
to older models.
Keypad version Display the keypad version.
Keypad initialization Initialize the keypad
Self-diagnostic mode Will be executed Self-diagnostic
mode.
*1) Battery is required to use date function.
Recommend: Hitachi Maxwell CR2032, 3V
The battery is to be replacing every two years while the
inverter is power off.
*2) The auto backlight-off function will deactivate during
in trip status until trip reset. For more information, refer
to the user’s guide.

Chapter 4
In scroll mode, p
monitoring
please refer to “
4.1.7.1
①
②
display scroll menu,
scroll menu screen.
③Press SEL
4.1.7
To check parameters in scroll
.
To set parameters by monitoring monitor,
try scroll mode
Press the F1 key on F [][home] screen
Menu
Output Frequency
Output Current
Input terminal monitor
STOP
Home
STOP
Menu
01
02
03
With UP/DOWN
Return
STOP
Scroll Menu
All Parameters
d:Monitor
F:
Ref
A:
Standard
b:
Fine Tuning Func
(0) key
the monitor
For example,
SEL (0) key.
mode
arameter can
4.1.3.1 Parameter setting screen
oFW
oFW
Scroll mode
Read/Write
System
setting
( )
key select scroll mode to
then,
press SEL
oFW
-
Mon./Setting
Func.
follow to
group,
then return to parameter
selecting
“A:
be change while
0.00Hz
LLLLLLLLLLL
M1
0.00Hz
M1
key select scroll mode to
(0) key to display
0.00Hz
M1
UP/DOWN
Standard Func.
Option
0.00 Hz
0.00 A
H01
----
M01
----
L01
( )
key select
list.
”
then press
4-8
④
Press the SEL
select parameters to change
⑤
-
Press UP/DOWN
(
S
⑤
-
Press UP/DOWN/LEFT/RIGHT
data and press F2
parameter list.
(Tips)
・
Press F1 (
storing the parameter change.
・
Parameter selected for reference screen is show in
upper line on ⑤
・
When scroll screen is set as initial mode, dA
dA
For parameter configuration
S-Menu
STOP
A:
Standard Func.
AA101Main Speed
AA102 Sub
AA104
1
When the parameter is to be set as alternative,
ave
) key to store
Return
AA101
Main S
peed
STOP
7
Keypad
8 RS485 Setting
9 Option 1
10 Option 2
2
When the parameter is to be set
Return
Output Frequency
STOP
AA104
Sub Speed Reference
R
eturn) key to return to parameter list without
-
03 are displayed as initial setting.
0.00Hz
oFW
sou..
Speed
sour..
(O) key,
then,
( )
key to select data and press F2
then
return to parameter list
0.00Hz
source
M1
oFW
(Save
) key to store to return to
0.0
oFW
-2.
Next
0.00Hz
M1
07:
Keypad
00:
Disable
t..
0.00Hz
w
ith UP/DOWN
.
0.00Hz
M1
is a numerical
( )
key to change
0.00Hz
0.
00
M1
000.
0
Gr.
L02
( )
keys
.
Save
value,
Save
Hz
0
Hz
-01, dA-
02,

Chapter 4
4.1.7.2
①Press LEFT/RIGHT
of each group.
(
Group Jump Function
…
⇔
All parameters
Monitor/Setting
Parameters
②
F2(Next)Key
(
)
⇔
d:Monitor
⇔…⇔
U:Initial Setting
⇔…)
Menu
oFW
STOP
A: Operation Function
AA101 Main Speed Reference_M1
AA102 Sub
AA104 Sub Speed Reference
Jump by
key to jump to 1
⇔
F:Command
0.00Hz
07:
Parameter Setting
Speed Reference
Menu
STOP
A: Operation Function
Ab -
01 Frequency Scaling Conversion
Ab -
03 Multispeed Operation
Ab110 Multispeed
st
parameter
、
PDN⇔All
Next
M1 L02
00:I
0.00Hz
0.00Hz
oFW
00:Binary (16Speed)
-
0 M1
Menu
STOP
A:Opertion Function
AC
00:Parameter Setting
AC
AC
2
4-9
②When to jump to the detailed subgroup (AA, Ab etc) in
parameter group, press F2 key.
A group for example : …
Next
M1
1.00
0.00Hz
oFW
-
01 Accel/Decel time
-
02 Multispeed Accel/Decel
-
03 Accel Curve Selection
(Next Group)
2
For parameter configuration
Menu
oFW
STOP
b: Protection Function
bA102 Frequency Upper Limit_M1
bA103 Frequency Upper Limit
bA110
Torque Limit Slection_M1
L02
0.00Hz
M1
00:Common
(Next Group)
①LEFT/RIGHT
⇒
AA
⇒
0.00Hz
07: Parameter Setting
next
L02
2
( )
key to jump
Ab⇒AC
⇒
…
Next
M1
L02
0.00Hz
0.00Hz
(Next Group)
⇒AJ⇒AA⇒
…

4-10
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[dA-01]~[dA-41]
Monitor naming (Nomenclature)
Description of monitor functions
※
For more detail, please refer to P1 user’s guide.
Monitors for all data
■Monitor mode (d code)
Code/Name
Range (unit)
dA-01
Output frequency
monitor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
<Actual frequency output>
dA-02
Output current monitor
0.0~655.35(A)
dA-03
Rotation direction
monitor
F(forward)/r(reverse)/
d(0Hz output)/o(shut down)
dA-04
Frequency reference
monitor (After calculation)
0.00~590.00(Hz)
<as target value>
dA-06
Output frequency scale
conversion monitor
0.00~59000.00(Hz)
dA-08
Detect speed monitor
-590.00~590.00(Hz)
<Encoder feedback required>
dA-12
Output frequency
monitor (signed)
-590.00~590.00(Hz)
dA-15
Torque reference
monitor (After calculation)
-500.0~500.0(%)
<Torque control mode required>
dA-16
Torque limit monitor
-500.0~500.0(%)
dA-17
Output Torque monitor
-500.0~500.0(%)
dA-18
Output Voltage monitor
0.0~800.0(V)
dA-20
Current position
monitor
When
[AA123]=02
-268435455~+268435455(pulse)
When [AA123]=03
-1073741823~+1073741823(pulse)
dA-26
Pulse train position
deviation monitor
-2147483647~+2147483647(pulse)
dA-28
Pulse count monitor
0~2147483647(pulse)
dA-30
Input power monitor
0.00~600.00(kW)
dA-32
Accumulation input
power monitor
0.00~100000.00(kWh)
dA-34
Output power monitor
0.00~600.00(kW)
dA-36
Accumulated output
power monitor
0.00~100000.00 (kWh)
dA-40
DC-bus voltage monitor
0.0~1000.0(V)
dA-41
BRD load rating
monitor
0.00~100.00(%)
[dA-42]~[dA-83][db-01]~[db-20]
Code/Name
Range (unit)
dA-42
Electronic thermal load
rating monitor (MTR)
0.00~100.00(%)
dA-43
Electronic thermal load
rating monitor (CTL)
dA-45
Safety STO monitor
00(no input)/01(P-1A)/
02(P-2A)/03(P-1b)/04(P-2b)/
05(P-1C)/06(P-2C)/07(STO)
dA-46
Safety Option Hardware
Monitor
(Refer to FS option guide for
detail)
dA-47
Safety Option Function
Monitor
dA-50
Control terminal status
00(P1-TMA)/01(P1-TMB)/
02(Others)
dA-51
Input terminal monitor
LLLLLLLLLLL~HHHHHHHHHHH
[L:OFF/H:ON]
[Left](B)(A)(9)(8)(7)(6)
(5)(4)(3)(2)(1)[Right]
dA-54
Output terminal monitor
LLLLLLL~HHHHHHH
[L:OFF/H:ON]
[Left](AL)(16c)(15)(14)(13)
(12)(11)[Right]
dA-60
Analog input/output status monitor
*(1)
AAAAAAAA~VVVVVVVV
[A:Current/V:Voltage]
[Left](EAo2)(EAo1)(Ai6)(Ai5)
(Ao2)(Ao1)(Ai2)(Ai1)[Right]
dA-61
Analog input [Ai1] monitor
0.00~100.00(%)
dA-62
Analog input [Ai2] monitor
dA-63
Analog input [Ai3] monitor
-100.00~100.00(%)
dA-64
Analog input [Ai4] monitor
-100.00~100.00(%)
dA-65
Analog input [Ai5] monitor
0.00~100.00(%)
dA-66
Analog input [Ai6] monitor
dA-70
Pulse train input monitor
(internal)
0.00~100.00(%)
dA-81
Option slot-1 status
00:(none)/01:(P1-EN)/
02:(P1-DN)/03:(P1-PB)/
04:(P1-FB)/05:(P1-RLV)/
06:(P1-DG)/07:(P1-AIO)/
08:(P1-RY)/09:(P1-TMP)/
10:(P1-FS)
dA-82
Option slot-2 status
dA-83
Option slot-3 status
*(1)dA-60 is available also for the terminals of the option terminal board
dA - 01
Parameter
Group
Value in the
group

4-11
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[db-01]~[db-64]
Code/Name
Range (unit)
db-01
Program download monitor
00(
Program
is not
installed)/
01(Program is
installed)
db-02
Program No. monitor
0000~9999
db-03
Program counter (Task-1)
0~1024
db-04
Program counter (Task-2)
db-05
Program counter (Task-3)
db-06
Program counter (Task-4)
db-07
Program counter (Task-5)
db-08
User monitor -0
-2147483647
~+2147483647
db-10
User monitor -1
db-12
User monitor -2
db-14
User monitor -3
db-16
User monitor -4
db-18
Analog output monitor YA0
0~10000
db-19
Analog output monitor YA1
db-20
Analog output monitor YA2
db-21
Analog output monitor YA3
db-22
Analog output monitor YA4
db-23
Analog output monitor YA5
Code/Name
Range (unit)
db-30
PID1 feedback value 1 monitor
0.00~100.00(%)
db-32
PID1 feedback value 2 monitor
db-34
PID1 feedback value 3 monitor
db-36
PID2 feedback value monitor
db-38
PID3 feedback value monitor
db-40
PID4 feedback value monitor
db-42
PID1 target value monitor
0.00~100.00(%)
db-44
PID1 feedback value monitor
0.00~100.00(%)
db-50
PID1 output monitor
-100.00~+100.00(%)
db-51
PID1 deviation monitor
-100.00~+100.00(%)
db-52
PID1 deviation 1 monitor
db-53
PID1 deviation 2 monitor
db-54
PID1 deviation 3 monitor
db-55
PID2 Output monitor
-100.00~+100.00(%)
db-56
PID2 deviation monitor
-100.00~+100.00(%)
db-57
PID3 Output monitor
-100.00~+100.00(%)
db-58
PID3 deviation monitor
-100.00~+100.00(%)
db-59
PID4 Output monitor
-100.00~+100.00(%)
db-60
PID4 deviation monitor
-100.00~+100.00(%)
db-61
Current PID P-Gain monitor
0.0~100.0
db-62
Current PID I-Gain monitor
0.0~3600.0(s)
db-63
Current PID D-Gain monitor
0.0~100.0(s)
db-64
PID feedforward monitor
0.00~100.00(%)
[dC-01]~[dC-50]
Code/Name Range (unit)
dC-01
Inverter load type status
00(Very Low duty)/
01(Low duty)/
02(Normal duty)
dC-02
Rated current monitor
1)
dC-07
Main speed input source monitor
1)
dC-08
Sub speed input source monitor
1)
dC-10
RUN command input source monitor
1)
dC-15
Cooling fin temperature monitor
-20.0~200.0(°C)
dC-16
Life assessment monitor
LL~HH
[L:Normal/H:Fatigued]
[Left](FAN lifespan)
(board capacitor life
span)[Right]
dC-20
Accumulation Start number monitor
1~65535(cycles)
dC-21
Accumulation Power-on timer monitor
dC-22
Accumulated time monitor in RUN status
monitor
1~1000000(hour)
dC-24
Accumulation Power-on time monitor
dC-26
Accumulation cooling-fan running time
monitor
dC-37
icon 2 LIM monitor
dC-38
icon 2 ALT monitor
dC-39
icon 2 RETRY detail monitor
dC-40
icon 2 NRDY detail monitor
dC-45
IM/SM monitor
00 (IM selected)/
01 (SM selected)
dC-50
Firmware ver. Monitor
00.000~99.99
1) Refer to users guide for detail
Code/Name
Range (unit)
dE-50
warning monitor
Refer to users guide

4-12
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[FA-01]~[FA-36]
■
Variable mode monitor (F code)
・If a [FA] parameter that can be modified is selected, it can be modified
in the display monitor.
Code/Name
Range (unit)
FA-01
Main speed reference monitor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
FA-02
Sub-speed reference monitor
FA-10
Acceleration time monitor
0.00~3600.00(s)
FA-12
Deceleration time monitor
FA-15
Torque reference monitor
-500.0~500.0(%)
FA-16
Torque bias monitor
-500.0~500.0(%)
FA-20
Position reference monitor
When [AA123]=02
-268435455~+268435455(pulse)
When [AA123]=03
-1073741823
~
+1073741823(pulse)
FA-30
PID1 set value 1 monitor
-100.00~100.00(%)
FA-32
PID1 set value 2 monitor
FA-34
PID1 set value 3 monitor
FA-36
PID2 set value monitor
FA-38
PID3 set value monitor
FA-40
PID4 set value monitor

4-13
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
Parameter naming (Nomenclature)
※
By default the motor 1 is enabled in the case that
08:[SET] is not assigned in the Intelligent Input
terminals [CA-01]~[CA-11].
[SET] function enable code example.
[SET]
OFF [SET]ON
[**-**] type
[**-**] type
[**1**] type
[**2**] type
(Example)
[SET]
OFF [SET]ON
[AH-01] [AH-01]
[Ub-01] [Ub-01]
・・・ ・・・
[Hb102] [Hb202]
[Ab110] [Ab210]
[bA122] [bA222]
・・・ ・・・
※When using 2nd motor parameter setting by [SET]
function of terminal, description as 1st motor setting
in the following part is to be replaced with that of 2nd
motor setting.
4.5Parameter arrangement
Next is the parameter explanation, such as the parameter
group and the internal group number line-up.
The [SET] classification numbers “-“ and “1” are lined
without distinction, except “2” which is lined-up after
“-“ and “1”.
Example) Regarding the order
[AA101]⇒[AA102]⇒[AA104]⇒[AA105]⇒…
⇒
[AA123]⇒[AA201]⇒…⇒[AA223]⇒
[Ab-01]⇒[Ab-03]⇒[Ab110]⇒[Ab-11]⇒…
(Last two digits are order by numerical order)
⇒
[Ab-25]⇒[Ab210]⇒
[AC-01]⇒…
(After the middle values of “-” and “1”, using “2”
changes the group)
※
Related parameters might be described together in
relevant parts.
[AA101]~[AA106]
Parameter explanation
・To set parameters, please read an understand
the P1 user’s guide first.
・For the motor protection, the following
parameters are necessary to be set.
-[Hb102]~[Hb108](If [IM])
-[Hd102]~[Hd108](If [SM/PMM])
-[bC110](Motor overload protection current)
※
The initial value format may be different.
Format: P1-(numeral)-(voltage)(keypad)(area)(filter)
(Example) Japan 200V Class P1-00044-LFF
Europe 400V Class P1-00054-HFEF
Voltage rating: The voltage class is L(200V)/H(400V)
Other formats:
Area; None(JPN)/E(EU,ASIA)/U(USA)/C(CHN)
※
When option is connected, parameters to display or
setting range may be added. Refer to user’s gude for
detail.
■
Parameter mode (A code)
Frequency reference selection
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
AA101
Main speed
input source selection,
1st-motor
01~16 *1)
09(JPN)/
01(EU)(USA)
(ASIA)(CHN)
AA102
Sub speed
input source selection,
1st-motor
00~16 *1)
00
AA104
Sub speed setting,
1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
AA105
Calculation symbol
selection for Speed
reference, 1st motor
00(Disable)/
01(Addition)/
02(Subtraction)/
03(Multiplication)
00
*1)00(Disable)/01(Ai1 terminal)/02(Ai2 terminal)/03(Ai3
terminal)/09(Parameter)/10(By RS485)/11(Option-1)/12(Option-2)/
13(Option-3)/14(Pulse train input:main)/16(EzSQ)/17(PID function)
・To change the frequency input reference, use [AA111].
Example: to set by [FA-01] -> [AA101]=07
To set by Analog(voltage) to set -> [AA101]=01(Ai1)
・To change between main and sub speed is possible with the math
operator.
・If [AA105]=00, the Intelligent input terminal 032[SCHG] can change
between the main(OFF) and sub(ON) speed.
・Through the [AA105] selection, the operator for the main and sub
speed frequency calculation is set.
Temporary frequency addition
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
AA106
Add frequency
setting, 1st-motor
-590.00~+590.00(Hz)
0.00
・When the [ADD] terminal is active the frequency set in [AA106] will be
temporally added to the frequency reference.
AA 1 01
Parameter
group
ー:Common for 1st and 2nd motor
1:1st motor enabled if function [SET] is OFF
2:2nd motor enabled if function [SET] is ON
Internal number
in the group
Working
parameters

4-14
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[AA111]~[AA115][bb-40]
RUN command selection
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
AA111
RUN command
input source
selection,
1st-motor
00~03
02(JPN)/
00(EU)
(USA)
(ASIA)
(CHN)
*1) 00([FW]/[RV] terminal)/01(3-wire)/02(Keypad’s RUN key)/03(RS485)
・Select in which way will be operated.
In case it does not work, please review it.
Keypad keys settings
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
AA-12
RUN key of
keypad rotation direction,
1st-motor
00(Forward)/
01(Reverse)
00
AA-13
STOP key enable
at RUN command from
terminal , 1st-motor
00(Disable)/01(Enable)/
02(Enable only at trip)
01
・[AA-12] specifies in which direction (forward/reverse)
will be the rotation after pressing the RUN key in the
operation keypad.
・[AA-13] changes the operation of the STOP key.
Independently of the actual setting of the STOP key it
performs a stop. The STOP circumstances can be
changed only by the setting selected in [AA-13],.
RUN command direction restriction
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
AA114
RUN direction
restriction,1st-motor
00(
No restriction
)/
01(Only forward)/
02(Only reverse)
00
・It will avoid that the output goes over the imposed
limitation in case of a mistaken operation.
Restart operation after decel/free-run STOP
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
AA115
STOP mode
selection, 1st-motor
00(Deceleration stop)/
01(Free-run stop)
00
bb-40
Restart mode after FRS
release
00(
Start with
0Hz)/
01(Start with frequency
matching)/
02(Start with Active
frequency matching)/
03(Detect speed)
00
・For when a stop command is executed, deceleration
stop or free-run stop can be selected.
・If input terminal 032[FRS] is active (ON), free-run stop is
possible.
・With [bb-40], a restart with the release of the [FRS], or a
restart operation that will be executed after the full
stop of the free-run can be selected.
・In free-run stop it can be configured to stop by inertia if
the [E007] overvoltage error occurs during deceleration
(The torque will be lost).
[AA121]~[AA223]
Control mode selection
Code/Name
Range (unit)
AA121
Control mode
selection,
1st-motor
00~03, 08, 09, 11 *2)
00
*2) IM control: 00([V/f] constant torque)/01([V/f] reduced torque)/
02([V/f] Free V/f)/03([V/f] constant torque with Automatic-trq boost)/
08(Sensorless vector control)/
09(0Hz-area sensorless vector control)/
SM/PMM control: 11(Sensorless vector control (SM/PMM))
・Generally for a light duty control (such as fans or pumps),
the [V/f] control with constant torque or the [V/f]
control with reduced torque are more closer to the
operation characteristics of fans and pumps.
・For heavy duty (Cranes, etc…), sensorless vector
control is the typically used. In the case there is an
encoder, use the vector control with encoder.
・For a magnet motor select the sensorless vector control
(SM/PMM).
※
With a standard duty (ND) all the options are available,
but for Light and Very Light duty (LD/VLD) the option
09 is not available.
Vector control with encoder mode
Code/Name
Range (unit)
AA123
Vector control
mode selection,
1st-motor
00(Speed/Torque control mode)/
01(Pulse train position control)/
02(Position control)/
03(High-resolution position control)
00
・For Vector control with encoder ([A121]=10) select
Speed/Torque control (00) or Position control (02).
・For more information, refer to the user’s guide.
2nd motor When Intelligent Input terminal 024[SET] is enabled.
Code/Name
Range
(unit)
Initial
value
AA201
Main speed
input source
selection,
2nd-motor
Same as AA101
AA202
Sub speed
input source
selection,
2nd-motor
Same as AA102
AA204
Sub speed setting, 2nd
-
motor Same as
AA104
AA205
Calcuration symbol selection
for speed reference,
2nd-motor
Same as AA105
AA206
Add f
requency
setting,
2nd-motor Same as
AA106
AA211
RUN-
command
input source
selection, 2nd-motor
Same as AA111
AA214
RUN-direction restriction selection
,
1st-motor
Same as AA114
AA215
STOP mode selection,
1st-motor Same as
AA115
AA221
Control mode
selection
2nd-motor Same as
AA121
AA223
Vector control mode selection,
2nd-motor
Same as AA123

4-15
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[Ab-01]~[Ab-25]
Scaled Output Frequency gain monitor [dA-06]
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
Ab-01
Frequency
conversion gain
0.00~100.00
1.00
・The visualized “Scaled Output frequency [dA-06]” is
equal to the “Output frequency [dA-01]” multiplied by the
“Frequency scaling conversion factor[Ab-01]”.
Multispeed command
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial
value
Ab-03
Multispeed operation
selection
00(16 speeds)/
01(8 speeds)
00
Ab110
Multispeed-0, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
Ab-11
Multispeed-1, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
Ab-12
Multispeed-2, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
Ab-13
Multispeed-3, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
Ab-14
Multispeed-4, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
Ab-15
Multispeed-5, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
Ab-16
Multispeed-6, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
Ab-17
Multispeed-7, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
Ab-18
Multispeed-8, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
Ab-19
Multispeed-9, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
Ab-20
Multispeed-10, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
Ab-21
Multispeed-11, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
Ab-22
Multispeed-12, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
Ab-23
Multispeed-13, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
Ab-24
Multispeed-14, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
Ab-25
Multispeed-15, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
・For the 16 speeds selection, set [Ab-03]=03 for
assigning the intelligent terminals 003[CF1] to
006[CF4] makes available the use of the speeds 0 to
15.
Multispeed
CF4 CF3 CF2 CF1
Speed 0 OFF OFF OFF OFF
Speed 1 OFF OFF OFF ON
Speed 2 OFF OFF ON OFF
Speed 3 OFF OFF ON ON
Speed 4 OFF ON OFF OFF
Speed 5 OFF ON OFF ON
Speed 6 OFF ON ON OFF
Speed 7 OFF ON ON ON
Speed 8 ON OFF OFF OFF
Speed 9 ON OFF OFF ON
Speed 10 ON OFF ON OFF
Speed 11 ON OFF ON ON
Speed 12 ON ON OFF OFF
Speed 13 ON ON OFF ON
Speed 14 ON ON ON OFF
Speed 15 ON ON ON ON
[Ab210][AC-01]~[AC-02]
・For the 8 speeds selection, set [Ab-03]=01 assigning the
intelligent terminals 007[SF1] to 013[SF7] makes
available the use of the speeds 0 to 7.
SF7 SF6 SF5 SF4 SF3 SF2 SF1
Speed 0 OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
Speed 1 - - - - - - ON
Speed 2 - - - - - ON OFF
Speed 3 - - - - ON OFF OFF
Speed 4 - - - ON OFF OFF OFF
Speed 5 - - ON OFF OFF OFF OFF
Speed 6 - ON OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
Speed 7 ON OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
2nd motor When Intelligent Input terminal 024[SET] is enabled.
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
Ab210
Multispeed
-
0, 2nd-motor Same as
Ab110
Input method for Acc/Decel time
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AC-01
Acceleration/Deceleration
Time input selection
00(Parameter
)/
01(Option 1)/
02(Option 2)/
03(Option 3)/
04(Function EzSQ)
00
・[AC-01] changes the reference target for the Acc/Decel
command.
Individual Acc/Decel for Multispeed
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
AC-02
Acceleration/
Deceleration selection
00(Common)/01(Multi) 00
・When [AC-02]=00, the acceleration/deceleration time
settings [AC120][AC122] or [AC124][AC126] will be in
effect.
・2-stage acceleration/deceleration functions from
[AC115] to [AC117] can be set.
・When [AC-02]=01, the acceleration/deceleration time
[AC-30]~[AC-88] for each multispeed control (from
speed 1 to 15) are enabled.
・When [AC-02]=01, while in Multspeed-0 command,
Acc/Decel setting [AC120] [AC122] or Acc/Decel setting
[AC124] [AC126] are enabled.
・During remote control up/down [FUP]/[FDN]
(parameters [CA-64] and [CA-66]) and PID soft start
(parameter [AH-78]), those parameters can be
overwritten.

4-16
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[AC-03]~[AC117]
Acceleration/deceleration curve selection
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AC-03
Acceleration curve
selection
00(Linear)/
01(S-curve)/
02(U-curve)/
03(Inverted-U-curve)/
04(EL-S-curve)
00
AC-04
Deceleration curve
selection
00
AC-05
Acceleration curve
constant setting
1~10
2
AC-06
Deceleration curve
constant setting
2
AC-08
EL-S-curve ratio at start
of acceleration 1
0~100
25
AC-09
EL-S-curve ratio at end
of acceleration 2
25
AC-10
EL-S-curve ratio at start
of deceleration 1
25
AC-11
EL-S-curve ration at end
of deceleration 2
25
・When [AC-03]/[AC-04]=00(Linear), decelerates at
regular intervals towards the target value.
・When [AC-03]/[AC-04]=01(S-curve), for a shockless
operation proceeds gradually at the beginning and at
the end of the acceleration and deceleration.
・When [AC-03]/[AC-04]=02(U-curve), proceeds gradually
at the start of the acceleration and deceleration.
・When [AC-03]/[AC-04]=03(Inverted-U-curve), proceeds
gradually at the end of the acceleration and
deceleration.
・For S-curve, U-curve and Inverted-U-curve, the degree
in which the operation accelerates and decelerates can
be set with [AC-05]/[AC-06].
・When AC-03]/[AC-04]=04 (EL-S-curve), proceeds
gradually at the beginning and the end of the
acceleration and deceleration.
・For EL-S-curve shockless operation, the beginning and
the end of the acceleration and deceleration [AC-08]~
[AC-11] should be adjusted.
Two-stage Acc/Decel change
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AC115
Select method to switch to
Acc2/Decel2 profile, 1st-motor
00([2CH]
terminal
)/
01(Set by parameter)/
02(Switch only when
rotation is inverted)
00
AC116
Acc1 to Acc2 frequency
transition point, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
AC117
Decel1 to Decel2 frequency
transition point, 1st-motor
0.00
・In the Acc2/Decel2 time, forward/reverse change can be
done when intelligent input terminal 031[2CH] is ON
and the set frequency in [AC116]/ [AC117] is reached.
・Sets Acc/Decel time 1[AC120][AC122] and Acc/Decel
time 2 [AC124] [AC126].
[AC120]~[AC126]
Acceleration/deceleration time setting
Code/Name Range (unit)
Unit
value
AC120
Acceleration time
setting 1, 1st-motor
0.00~3600.00(s)
30.00
AC122
Deceleration time
setting 1, 1st-motor
30.00
AC124
Acceleration time
setting 2, 1st-motor
15.00
AC126
Deceleration time
setting 2, 1st-motor
15.00
・Assign the Acc/Decel time that takes from 0Hz to reach
the maximum frequency.
・In case that the two-stage Acc/Decel function is not
meant to be used, the Acceleration time 1 [AC120] and
Deceleration time 1 [AC122] are used.
・Example of using the two-stage Acc/Decel function.
With[AC115]=00
*) Acc/Decel time is what takes from 0Hz to reach the
maximum frequency.
Output
frequency
Set
output frequency
Maximum
frequency
[Hb105]
or
[Hd105]
Actual
acceleration
time
[AC120]
Actual
deceleration
time
[AC122]
Time
Output
frequency
2CH
FW
Acc.
time 1
Decel.
time 1
Decel.
Time 2
Acc.
time 2

4-17
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[AC-30]~[AC-88]
Setting for two-stage Acc/Decel time
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Unit value
AC-30
Acc. time for Multispeed-1
0.00~
3600.00(s)
30.00
AC-32
Decel. time for Multispeed-1
30.00
AC-34
Acc. time for Multispeed-2
30.00
AC-36
Decel. time for Multispeed-2
30.00
AC-38
Acc. time for Multispeed-3
30.00
AC-40
Decel. time for Multispeed-3
30.00
AC-42
Acc. time for Multispeed-4
30.00
AC-44
Decel. time for Multispeed-4
30.00
AC-46
Acc. time for Multispeed-5
30.00
AC-48
Decel. time for Multispeed-5
30.00
AC-50
Acc. time for Multispeed-6
30.00
AC-52
Decel. time for Multispeed-6
30.00
AC-54
Acc. time for Multispeed-7
30.00
AC-56
Decel. time for Multispeed-7
30.00
AC-58
Acc. time for Multispeed-8
30.00
AC-60
Decel. time for Multispeed-8
30.00
AC-62
Acc. time for Multispeed-9
30.00
AC-64
Decel. time for Multispeed-9
30.00
AC-66
Acc. time for Multispeed-10
30.00
AC-68
Decel. time for Multispeed-10
30.00
AC-70
Acc. time for Multispeed-11
30.00
AC-72
Decel. time for Multispeed-11
30.00
AC-74
Acc. time for Multispeed-12
30.00
AC-76
Decel. time for Multispeed-12
30.00
AC-78
Acc. time for Multispeed-13
30.00
AC-80
Decel. time for Multispeed-13
30.00
AC-82
Acc. time for Multispeed-14
30.00
AC-84
Decel. time for Multispeed-14
30.00
AC-86
Acc. time for Multispeed-15
30.00
AC-88
Decel. time for Multispeed-15
30.00
・Individual Acc/Decel times can be set for multispeed
functions[Ab-11]~[Ab-25].
[AC215]~ [Ad-15]
2nd motor When Intelligent Input terminal 024[SET] is enabled.
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
AC215 Select method to switch to
Acc2/Decel2 Profile, 2nd-motor
Same as AC115
AC216 Acc1 to Acc2
f
requency
transition point, 2nd-motor
Same as AC116
AC217 Decel1 to Decel2
f
requency
transition point, 2nd-motor
Same as AC117
AC220 Acceleration time
1, 2nd-motor Same as
AC120
AC2
22 Deceleration time 1, 2nd
-
motor Same as
AC122
AC2
24 Acceleration time
2
, 2nd-motor Same as
AC
124
AC2
26 Deceleration time
2, 2nd-motor Same as
AC
126
Torque control function setting
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
Ad-01
Torque reference input
source selection
01~06/09~18 *1)
07
Ad-02
Torque reference value
setting
-500.0~500.0(%)
0.0
Ad-03
Polarity selection for
torque reference
00(
According to
sign)/
01(Depend
on the
operation direction)
00
Ad-04
Switching time of speed
control to torque control
0~1000(ms)
0
・Operations settings of torque control.
For more information, refer to the User’s guide.
Torque bias setting
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
Ad-11
Torque bias input
source selection
01~06/09~18 *1)
07
Ad-12
Torque bias value setting
-500.0~500.0(%)
0.0
Ad-13
Polarity selection for torque bias
00(
According to
sign)/
01(Depend on the
operation direction)
00
Ad-14
Terminal [TBS] active
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
00
・For setting the torque bias.
For more information, refer to the User’s guide.
Speed limitation for torque control
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
Ad-40
Input selection for
speed limit at torque control
01~13 *1)
07
Ad-41
Speed limit at torque
control (at Forward rotation)
0.00~
590.00(Hz)
0.00
Ad-42
Speed limit at torque
control (at Reverse rotation)
0.00
・In middle of the torque control the speed limit can be
set.
For more information, refer to the User’s guide.
*1)00(Disable)/01(Ai1 terminal)/02(Ai2 terminal)/03(Ai3 terminal)/
07(Parameter)/08(RS485)/13(Pulse train input:main)/ 14(Program
function)/15(PID calc.)
Speed 2 [Ab-12]
Speed 3 [Ab-13],
Speed 4
[Ab-14]
Speed 1 [Ab-11]
Multispeed
FW
Speed 1
Speed
Speed
Speed
Speed
Speed
Speed
Speed 4
Acc/decel time
Acc. 1
[AC-30]
Acc. 2
[AC-34]
Acc. 3
[AC-38]
Decel. 3
[AC-40]
Acc. 4
[AC-42]
Same
as
before
Decel. 3
[AC-40]
Acc. 4
[AC-42]
Decel. 4
[AC-44]
This will be effective only for Acc./Dec.
time if the set frequency is the same.

4-18
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[AE-01]~[AE-13]
Position control
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AE-01
Electronic gear
setting point selection
00(Feedback)/
01(Reference)
00
AE-02
Electronic gear ration
numerator
1~10000
1
AE-03
Electronic gear ration
denominator
1~10000
1
AE-04
Positioning complete
range setting
0~10000(Pulse)
5
AE-05
Positioning complete
delay time setting
0.00~10.00(s)
0.00
AE-06
Position feedforward
gain setting
0~655.35
0.00
AE-07
Position loop gain
setting
0.00~100.00
0.50
AE-08
Position bias value
setting
-2048~2048(Pulse)
0
・Feedback signal is needed to perform the position
control.
For more information, refer to the User’s guide.
Home search function setting
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AE-10
Stop position
reference selection for
Home search function
00(Parameter
)/
01(Option 1)/
02(Option 2)/
03(Option 3)/
09
AE-11
Stop position of
Home search function
0~4096
0
AE-12
Speed reference
of Home search function
0.00~120.00(Hz)
0.00
AE-13
Direction of
Home search function
00(Forward)/01(Reverse) 00
・Adjust the Home search function of the position
control.
For more information, refer to the User’s guide.
[AE-20]~[AE-62]
Absolute position control
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
AE-20
Position reference 0
When [AA123]≠03
-268435455~
+268435455(pulse)
When [AA123]=03
-1073741823~
+107374182(pulse)
0
AE-22
Position reference 1
0
AE-24
Position reference 2
0
AE-26
Position reference 3
0
AE-28
Position reference 4
0
AE-30
Position reference 5
0
AE-32
Position reference 6
0
AE-34
Position reference 7
0
AE-36
Position reference 8
0
AE-38
Position reference 9
0
AE-40
Position reference 10
0
AE-42
Position reference 11
0
AE-44
Position reference 12
0
AE-46
Position reference 13
0
AE-48
Position reference 14
0
AE-50
Position reference 15
0
AE-52
Position control
range setting (forward)
When
[AA123]
≠03
0~+268435455(pulse)/
When [AA123]=03
0~+107374182(pulse)
0
AE-54
Position control
range setting (reverse)
When
[AA123]
≠03
-268435455~0(pulse)/
When [AA123]=03
-1073741823~0(pulse)
0
AE-56
Position control
mode selection
00(Limited)/
01(Not limited)
00
・Sets the absolute position function.
For more information, refer to the User’s guide.
Teach-in function
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
AE-60
Teach-in function
target selection
00~15(X00~X15)
00
・Set auto-learning position for the absolute position
mode.
For more information, refer to the User’s guide.
Enable position saving when power is cut off
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
AE-61
Current Position
saving at power off
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
00
・Saves the absolute position when the power supply is
cut-off.
For more information, refer to the User’s guide.
Pre-set position
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
AE-62
Preset position data
When
[AA123]
≠03
-268435455~+268435455(pulse)
When [AA123]=03
-1073741823~+107374182(pulse)
0
・In the absolute position mode sets the pre-set position.
For more information, refer to the User’s guide.

4-19
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[AE-64]~[AE-76]
Positioning function adjustment
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
AE-64
Deceleration stop
distance calculation gain
50.00~200.00(%)
100.00
AE-65
Deceleration stop
distance calculation bias
0.00~655.35(%)
0.00
AE-66
Speed Limit in APR
control
0.00~100.00(%)
1.00
AE-67
APR start speed
0.00~100.00(%)
0.20
・Adjustment of control operation for positioning control.
For more information, refer to the user’s guide.
Homing (Return to reference position)
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AE-70
Homing function selection
00(
Low-speed)/
01(High-Speed 1)/
02(High-Speed 2)
00
AE-71
Direction of homing function
00(Forward)/
01(Reverse)
00
AE-72
Low-speed of homing
function
0.00~10.00(Hz)
0.00
AE-73
High-Speed of homing
function
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
・Sets the Zero-return function for absolute position mode.
For more information, refer to the user’s guide.
[AF101]~[AF109]
DC braking (DB) function
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AF101
DC braking
selection, 1st-motor
00(Disable)/01(Enable)/
02(Frequency reference)
00
AF102
Braking type
selection, 1st-motor
00(DC braking)/
01(Speed servo-lock)/
02(Position servo-lock)
00
AF103
DC braking
frequency, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
AF104
DC braking delay
time, 1st-motor
0.00~5.00(s)
0.00
AF105
DC braking force
setting, 1st-motor
0~100(%)
30
AF106
DC braking active
time at stop, 1st-motor
0.00~60.00(s)
0.00
AF107
DC braking
operation method selection ,
1st-motor
00(Edge)/
01(Level)
01
AF108
DC braking force at
start, 1st-motor
0~100(%)
30
AF109
DC braking active
time at start, 1st-motor
0.00~60.00(s)
0.00
・DB at stop/start [AF101]=01 or DB at frequency
reference [AF101]=02 can be selected.
・DC braking can be used if Intelligent input terminal
030[DB] is ON.
・In vector control with encoder, use the [AF102]
Servo-lock function.
・Stop DB example (Braking force adjusted by AF105)
・Start DB example (Braking force adjusted by AF108)
・Frequency reference DB example (Braking force adjusted
by AF105)
・When the DC braking time is set as 0.00(s), DC braking is
not operational.
[AF103]
[AF106]
DC braking
Operation
command
Output
frequency
[AH109]
DC braking
Operation
command
Output
frequency
ON
Operation
command
Frequency
reference
Output
frequency
[AF103]
ON
AF106

4-20
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[AF120]~[AF144]
Brake control function
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AF120
Contactor control
enable, 1st-motor
00(
Disable
)
01(Enable: primary side)
02(Enable: secondary side)
00
AF121
Run delay time,
1st-motor
0.00~2.00(s)
0.20
AF122
Contactor off
delay time, 1st-motor
0.00~2.00(s)
0.10
AF123
Contactor answer
back check time, 1st-motor
0.00~5.00(s)
0.10
AF130
Brake control enable,
1st-motor
00(
Disable
)/
01(Brake control 1:
Common)/
02(Brake control 1:
Separate)/
03(Brake control 2)
00
AF131
Brake wait time for
release, 1st-motor (Forward)
0.00~5.00(s)
0.00
AF132
Brake wait time for
Acc., 1st-motor (Forward)
0.00~5.00(s)
0.00
AF133
Brake wait time for
Stop, 1st-motor (Forward)
0.00~5.00(s)
0.00
AF134
Brake wait time for
confirmation, 1st-motor
(Forward)
0.00~5.00(s)
0.00
AF135
Brake release frequency,
1st-motor (Forward)
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
AF136
Brake release
current, 1st-motor (Forward)
Inverter rated current
×(0.20~2.00)
*1)
AF137
Brake frequency,
1st-motor (Forward)
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
AF138
Brake wait time for
release, 1st-motor (Reverse)
0.00~5.00(s)
0.00
AF139
Brake wait time for Acc. ,
1st-motor (Reverse)
0.00~5.00(s)
0.00
AF140
Brake wait time for
Stop, 1st-motor (Reverse)
0.00~5.00(s)
0.00
AF141
Brake wait time for
confirmation, 1st-motor
(Reverse)
0.00~5.00(s)
0.00
AF142
Brake release frequency,
1st-motor (Reverse)
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
AF143
Brake release
current, 1st-motor (Reverse)
Inverter rated current
×(0.20~2.00)
*1)
AF144
Brake frequency,
1st-motor (Reverse)
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
*1) Inverter rated current × 1.00.
[AF150]~[AF254]
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AF150
Brake open delay time,
1st-motor
0.00~2.00(s) 0.20
AF151
Brake close delay time,
1st-motor
0.00~2.00(s) 0.20
AF152
Brake check time, 1st-motor
0.00~5.00(s) 0.10
AF153
Servo lock/ DC injection time
at start, 1st-motor
0.00~10.00(s) 0.60
AF154
Servo lock/ DC injection time
at stop, 1st-motor
0.00~10.00(s) 0.60
・Operations settings of brake control.
For more information, refer to the User’s guide.
2nd motor When Intelligent Input terminal 024[SET] is enabled.
Code/Name
Range
(unit)
Initial
value
AF201 DC braking
enable
, 2nd-motor Same as
AF101
AF202 Braking type selection, 2nd
-
motor Same as
AF102
AF203 DC braking frequency, 1st
-
motor Same as
AF103
AF204 DC braking delay time, 2nd
-
motor Same as
AF104
AF205 DC braking force
while stopping
, 2nd-motor Same as
AF105
AF206 DC braking active time at stop, 2nd
-
motor Same as
AF106
AF207 DC braking
trigger selection
, 2nd-motor Same as
AF107
AF208 DC braking force while starting
, 2nd-motor Same as
AF108
AF209 DC braking active time at start, 2nd
-
motor Same as
AF109
AF220 Contactor
control
e
nable, 2nd
-
motor Same as
AF120
AF221 Activation
delay time, 2nd
-
motor Same as
AF121
AF222 Deactivation delay time, 2nd
-
motor Same as
AF122
AF223 Contactor
check time, 2nd
-
motor Same as
AF123
AF230 Brake control
e
nable, 2nd
-
motor Same as
AF130
AF231 Brake wait time for
r
elease, 2nd
-
motor
(Forward)
Same as AF131
AF232 Brake w
ait time for Acc
., 2nd-motor
(Forward)
Same as AF132
AF233 Brake w
ait time for Stop, 2nd
-
motor
(Forward)
Same as AF133
AF234 Brake wait time for
c
onfirmation, 2nd
-
motor
(Forward)
Same as AF134
AF235 Brake release
f
requency,
2nd-motor
(Forward)
Same as AF135
AF236 Brake release
c
urrent, 2nd
-
motor (Forward)
Same as
AF136
AF237 Brake f
requency, 2nd
-
motor (Forward)
Same as
AF137
AF238 Brake wait ti
me for r
elease, 2nd
-
motor
(Reverse)
Same as AF138
AF239 Brake w
ait t
ime for
Acc., 2nd
-
motor (Reverse)
Same as
AF139
AF240 Brake w
ait time for Stop, 2nd
-
motor
(Reverse)
Same as AF140
AF241 Brake wait time for
c
onfirmation, 2nd
-
motor
(Reverse)
Same as AF141
AF242 Brake release
f
requency, 2nd
-
motor (Reverse)
Same as
AF142
AF243 Brake release
c
urrent, 2nd
-
motor (Reverse)
Same as
AF143
AF244 Braking
f
requency, 2nd
-
motor (Reverse side)
Same as
AF144
AF250 Brake open delay time, 2nd
-
motor Same as
AF150
AF251 Brake close delay time, 2nd
-
motor Same as
AF151
AF252 Brake check time, 2nd
-
motor Same as
AF152
AF253 Servo lock/
DC injection time at start,
2nd-motor
Same as AF153
AF254 Servo lock/
DC injection time at stop,
2nd-motor
Same as AF154

4-21
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[AG101]~[AG113]
Resonant frequency avoidance (Jump)
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AG101
Jump frequency 1, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz) 0.00
AG102
Jump frequency width 1,
1st-motor
0.00~10.00(Hz) 0.00
AG103
Jump frequency 2, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz) 0.00
AG104
Jump frequency width 2,
1st-motor
0.00~10.00(Hz) 0.00
AG105
Jump frequency 3, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz) 0.00
AG106
Jump frequency width 3,
1st-motor
0.00~10.00(Hz) 0.00
・Prevents the passing of the output frequency in a
resonant point. Output frequency changes continuously.
Motor Acc/Decel dwell (Hold)
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AG110
Acceleration stop frequency
setting, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz) 0.00
AG111
Acceleration stop time setting,
1st-motor
0.00~60.00(s) 0.00
AG112
Deceleration stop frequency
setting, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz) 0.00
AG113
Deceleration stop time setting,
1st-motor
0.00~60.00(s) 0.00
・By using the dwell function when the inertial load is
considerable, if the set frequency is reached in the set
time the Acc/Decel of the frequency will be stopped.
・If the Intelligent input terminal function 100[HLD] is in
ON state, the acceleration and deceleration will be
stopped (Hold activation).
[AG-20]~[AG213]
Jogging function
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AG-20
Jogging
frequency
0.00~10.00(Hz)
0.00
AG-21
Jogging stop
selection
00(free
-
running, disabled during operation)
01(decel/stop, disabled during operation)
02(DC braking, disabled during operation)
03(free-running, enabled during operation)
04(decel/stop, enabled during operation)
05(DC braking, enabled during operation)
00
・When Input terminal [JG] is active (ON), if the operation
command is given the jogging frequency is outputted.
The frequency and stop method can be set when
performing jogging motion.
2nd motor When Intelligent Input terminal 024[SET] is enabled.
Code/Name
Range
(unit)
Initial
value
AG201
Jump frequency 1, 2nd
-
motor Same as
AG101
AG202
Jump frequency
width 1, 2nd-motor Same as
AG102
AG203
Jump
frequency 2, 2nd
-
motor Same as
AG103
AG204
Jump frequency
width 2, 2nd-motor Same as
AG104
AG205
Jump frequency 3, 2nd
-
motor Same as
AG105
AG206
Jump frequency
width 3, 2nd-motor Same as
AG106
AG210
Acceleration stop
frequency setting,
2nd-motor
Same as AG110
AG211
Acceleration stop time setting
2nd-motor Same as
AG111
AG212
Deceleration stop frequency setting,
2nd-motor
Same as AG112
AG213
Deceleration stop time setting,
,
2nd-motor
Same as AG113
Output
frequency
Frequency
reference
[AG101]
[AG103]
[AG105]
[AG102]
[AG102]
[AG104]
[AG104]
[AG106]
[AG106]
[AG111]
[AG110]
Output
Frequency
Time
[AG112]
[AG113]
JG
FW
RV
Output
Frequency
[AG-20]

4-22
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[AH-01]~[AH-06]
PID1 function
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
AH-01
PID1 enable
00(
Disable
)/
01(Enable)/
02(Enable:inverted output)
00
・Validates the PID1 operation.
・If [AH-01]=01 when the PID output reaches negative
value, the PID output is limited to 0.
・If [AH-01]=02 when the PID output reaches negative
value, the PID output lets out an inverted output.
・When the PID output is negative, the motor will rotate
in the contrary direction.
・If [PID] terminal is ON, the PID control is disabled and
the [PID] target value becomes the frequency
reference.
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
AH-02
PID1 deviation inverse
00(
Disable
)/
01(Enable)
00
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AH-03
unit selection for PID1
<unit
table
> at the end
of the document can
be consulted
03
AH-04
PID1 adjustment (0%)
-10000~10000
0
AH-05
PID1 adjustment
(100%)
-10000~10000
10000
AH-06
PID1 Adjustiment
(decimal point)
0~4
2
・The unit and display data related to the output of the
PID control can be changed.
[AH-07]~[AH-50]
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AH-07
Target value 1 reference
selection for PID1
00~06/09~15
*1)
09
AH-10
PID1 target value-1
0.00~100.00(%)
*1)
0.00
AH-12
PID1 Multistage set point 1
0.00
AH-14
PID1 Multistage set point 2
0.00
AH-16
PID1 Multistage set point 3
0.00
AH-18
PID1 Multistage set point 4
0.00
AH-20
PID1 Multistage set point 5
0.00
AH-22
PID1 Multistage set point 6
0.00
AH-24
PID1 Multistage set point 7
0.00
AH-26
PID1 Multistage set point 8
0.00
AH-28
PID1 Multistage set point 9
0.00
AH-30
PID1 Multistage set point 10
0.00
AH-32
PID1 Multistage set point 11
0.00
AH-34
PID1 Multistage set point 12
0.00
AH-36
PID1 Multistage set point 13
0.00
AH-38
PID1 Multistage set point 14
0.00
AH-40
PID1 Multistage set point 15
0.00
AH-42
Input source selection of Set
point 3 for PID1
00~13*2)
00
AH-44
PID1 target value-2
0.00~100.00(%)
0.00
AH-46
Target value 3 reference
selection for PID1
00~13*2)
0.00
AH-48
PID1 target value-3
0.00~100.00(%)
0.00
AH-50
Math operator selection of
PID1 target value 1
01(Addition)
02(Subtraction)
03(Multiplication)
04(Division)
01
*1) Display range can be set by [AH-04], [AH-05] and [AH-06].
*2) 00(Disabled)/01(Ai1 terminal)/02(Ai2 terminal)/
03(Ai3 terminal)/07(Parameter)/08(RS485)/14(Pulse train
input:main)/
・For PID1 target value, two targets are selected, target value 1 and
target value 2, the result of the operation carried out between these
two targets constitutes the PID1 target value.
・If Input terminal function 051[SVC1]~054[SVC4] are used, the PID
target value can be changed for the Multistage.
Multistage
value
SVC4 SVC3 SVC2 SVC1
Target value
0
OFF OFF OFF OFF
Target value
1
OFF OFF OFF ON
Target value
2
OFF OFF ON OFF
Target value
3
OFF OFF ON ON
Target value
4
OFF ON OFF OFF
Target value
5
OFF ON OFF ON
Target value
6
OFF ON ON OFF
Target value
7
OFF ON ON ON
Target value
8 ON
OFF OFF OFF
Target value
9 ON
OFF OFF ON
Target value
10 ON
OFF ON OFF
Target value
11 ON
OFF ON ON
Target value
12 ON ON
OFF OFF
Target value
13 ON ON
OFF ON
Target value
14 ON ON ON
OFF
Target value
15 ON ON ON ON
PID
operation
PID target value
Feedback
+
00
01
+
-
Reverse
PID1
[AH-02]
-
PID1
target value
PID1 target [AH-10]
RS485
communication
Option 1
Option 2
Option 3
[AH-07]
Multistage target 1~15
Analog input 1
Analog input 2
Analog input 3
Not used
[SVC1-4]
[AH-50]
+, -, x, ÷
[AH-42]
01
02
03
09
10
11
12
13
00
PID1 target [AH-44]
09
01
00

4-23
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[AH-51]~[AH-54]
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial
value
AH-51
Input source selection
of process data 1 for PID1
00~06/08~13 *1)
01
AH-52
Input source selection
of process data 2 for PID1
00
AH-53
Input source selection
of process data 3 for PID1
00
AH-54
Calculation symbol
selection of Process data for PID1
01(Addition)/
02(Subtraction)/
03(Multiplication)/
04(Division)
05(Square Root FB1)
06(Square Root FB2)
07(Square Root
FB1-FB2)
08(Average of
three inputs)
09(Minimum of
three inputs)
10(Maximum of
three inputs)
01
*1)00(Not used)/01(Ai1 terminal)/02(Ai2 terminal)/03(Ai3 terminal)/
04(Ai4 input)/05(Ai5 input)/06(Ai6 input)
08(RS485)/ 09(Option 1)/10(Option 2)
11(Option 3)/12(Pulse train input:main)/13(Pulse train input:option)
・For PID1 feedback, two targets are selected, feedback
data 1 and feedback data 2, the result of the operation
carried out between these two constitutes the PID1
feedback value.
[AH-60]~[AH-70]
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
PID1
AH-60
PID1 gain
change method selection
00(Constant gain [1])/
01([PRO] terminal)
00
AH-61
PID1
proportional gain 1
0.0~100.0
1.0
AH-62
PID1 integral
time constant 1
0.0~3600.0(s)
1.0
AH-63
PID1 derivative
gain 1
0.0~100.0(s)
0.0
AH-64
PID1
proportional gain 2
0.0~100.0
0.0
AH-65
PID1 integral
time constant 2
0.0~3600.0(s)
0.0
AH-66
PID1 derivative
gain 2
0.0~100.0(s)
0.0
AH-67
PID1 gain
change time
0~10000(ms)
100
・If [PIDC] terminal is active (ON), the value of the integral
constant is purged. If done while operating, the
operation can become instable/insecure.
・With [PRO] terminal, the gain can be changed. If the
state is OFF, Gain 1 is used, if the state is ON, Gain 2 is
used.
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AH-70
PID1 feedforward selection
00~03 *2)
00
*2) 00(Not used)/01(Ai1 terminal)/02(Ai2 terminal)/03(Ai3 terminal)
・To perform the PID feedforward control, an input is
selected.
PID feedback
value
RS485
communication
Option 1
Option 2
Option 3
[AH-51]
Analog input 1
Analog input 2
Analog input 3
Not used
[AH-54]
+, -, x, ÷
[AH-52]
01
02
03
08
09
10
11
00
Pulse train
input (internal)
12
01
00
Pulse train
input (option)
13
PID operation
result
Terminal [PRO]
PID
deviation
+
P
I
D
+
+
P 1 [AH-61]
P 2 [AH
-
64]
I 1 [AH-62]
I 2 [AH
-
65]
D 1 [AH
-
63]
D 2 [AH
-
66]
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
PID feedforward value
[AH-70]
01
02
03
Analog input 1
Analog input 2
Analog input 3
Not used
01
02
03
00
00

Chapter 4
[AH
・
・
・
PID
Target
value
Terminal
045
Operation
command
-71]
~
Code/Name
AH-71
PID1 output
Limits
the output range of the PID.
limit is disabled.
Code/Name
AH-72
PID1
d
level
When the
PID
output terminal function 045[OD] is activated.
Code/Name
AH-73
PID feedback compare
signal turn-
off level
AH-74
PID feedback compare
signal turn-on
level
If the PID
feedback
output terminal function 046[FBV] is deactivated (OFF).
If it crosses
PID Output (%)
PID
deviation
0%
[OD]
PID
feedback
0%
Output
terminal
046[
FBV
]
[AH-7
4
variable
eviation over
deviation
pass over the
cross over the [AH
under the [AH
(%)
ON
(%)
ON
]
Range (unit)
0.00~
100.00(%)
If
[AH
Range (unit)
0.00~
100.00(%)
±[AH
Range (unit)
0.00~
100.00(%)
0.00~
100.00(%)
-
74] level, is activated (ON).
PID Output variable range
ON
ON
ON
Initial value
0.00
-71]=0.00
the
Initial value
3.00
-72],
the
Initial
value
100.00
0.00
-
73] level, the
Time(s)
[AH-71]
[AH-71]
Time(s)
[AH-72]
[AH-72]
Time
(s)
[AH-73]
[AH-74]
4-24
AH
enable
AH
level
AH
setting
AH
AH
detection
AH
level
・
For a shockless
made the target value,
・
In the case of a soft start, the acceleration time can be
set with [AH
AH
PID sleep trigger selection
AH
PID sleep start level
AH
PID sleep active time
AH
Setpoint boost before PID sleep
enable
AH
Setpoint boost time
AH
Setpoint boost value
AH
Minimum RUN time befor
sleep
AH
Minimum active time of PID
sleep
・
The PID sleep function temporally reduces the PID
output, achieving an energy saving state.
PID
operation
[AH
For parameter configuration
Code/Name
-75
PID soft start function
-76
PID soft start target
-78
Acceleration time
for PID soft start
-80
PID soft start time
-81
PID soft
start
enable
-76
PID soft start
-
78].
Code/Name
-85
-86
-87
-88
-89
-90
-91
-92
[AH
-76]
Output frequency
[AH
error
target
operation, base frequency×[AH
with the [AH
e PID
-80]
Abides by [AH-
78] acceleration
PID feedback
PID Target value
-75]
~
Range (unit)
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
0.00~
100.00(%)
0.00~
3600.00(s)
0.00~
100.00(s)
00(Disable)/
01(Enable
: Error
02(Enable: Warning)
0.00~
100.00(%)
-
80] output time.
Range (unit)
00(
Disable
)/
01(Low output
)/
02([SLEP]
terminal
0.00~
590.00(Hz)
0.0~100.0(s)
00(Disable)/01(Enab
le)
0.00~
100.00(s)
0.00~
100.00(%)
0.00~
100.00(s)
0.00~
100.00(s)
78] acceleration
ON
[AH-
92
Initial
value
00
100.00
30.00
0.00
)
00
100.00
-76] is
Initial
value
)
00
0.00
0.0
00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
Time
]

4-25
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[AH-93]~[AH-96]
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AH-93
PID sleep trigger
selection
01(Deviation)/
02(Falling feedback)/
03( [WAKE] terminal)
01
AH-94
PID wake-up start level
0.00~100.00(%)
0.00
AH-95
PID wake-up start time
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
AH-96
PID wake-up
start deviation value
0.00~100.00(%)
0.00
・Operation example of the sleep function.
Example 1) [AH-85]=01(Low output)
[AH-93]=01(Deviation)
Example 2) [AH-85]=01(Low output)
[AH-93]=02(Low feedback)
Example 3) [AH-85]=02([SLEP] terminal)
[AH-93]=03([WAKE] terminal)
[AJ-01]~[AJ-10]
PID2 function
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AJ-01
PID2
enable
00(Disable)/01(Enable)/
02(Enable:inverted output)
00
・Validates the PID2 operation.
・If [AJ-01]=01 when the PID output reaches a negative
value, the PID output is limited to 0.
・If [AJ-01]=02 when the PID output reaches a negative
value, the PID output lets out an inverted output.
・By activating the [PID2] terminal, the PID2 output
becomes 0.
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
AJ-02
PID2 deviation inverse
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
00
・PID2 deviation can be reversed.
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AJ-03
PID2 unit selection
<unit table> at the end
of the document can
be consulted
03
AJ-04
PID2 scale adjustment
(0%)
-10000~10000
0
AJ-05
PID2 scale adjustment
(100%)
-10000~10000
10000
AJ-06
PID2 scale adjustment
(decimal point)
0~4
2
・You can switch the display data and the display unit
involved in the output of the PID control by the
calculation.
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial
value
AJ-07
Input source selection
of set-point for PID2
00~08, 12, 13, 15 *1)
07
AJ-10
Set point setting for
PID2
-100.00~100.00(%)
0.00
・When PID2 target value input is selected, if the selected
is the parameter setting, [AJ-10] gets enabled.
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
AJ-12
Feedback data
reference selection for PID2
00~08, 12, 13, 15 *1)
02
・Selects the PID2 feedback reference.
*1)00(Not used)/01(Ai1 terminal)/02(Ai2 terminal)/03(Ai3 terminal)/
04(Ai4 terminal)/05(Ai5 terminal)/06(Ai6 terminal)/07(Parameter)/
08(RS485)/ 12(Pulse train input: main)/ 13(Pulse train input:
option)/15(PID1 output)
PID Target value
[AH-94]
[AH-86]
Output frequency
[AH-95]
Feedback value
[AH-87]
PID Target value
[AH-94]
[AH-86]
Output frequency
[AH-95]
Feedback value
[AH-87]
Feedback value
PID Target value
Output frequency
Terminal [SLEP]
Terminal [WAKE]
ON
ON
[AH-87] [AH-95]
PID
operation
PID target
value
Feedback
value
+
00
01
+
-
R
everse
PID
2
[AJ-02]
-

Chapter 4
・
・
・
・
・
PID
Target
value
PID feedback (%)
048[FBV2]
Operation
command
[AJ-13]
~
Code/Name
AJ-13
PID2 proportional gain
AJ-14
PID2 integral time constant
AJ-15
PID2 derivative gain
S
ets the PID
If [PIDC]
terminal
integral constant is purged.
operation can become
Code/Name
AJ-16
PID2 output
Limits the output range of the PID.
limit is disabled.
Code/Name
AJ-17
PID2 deviation
over
When the PID deviation pass over
terminal function 04
Code/Name
AJ-18
PID2 feedback compare
signal turn-
off level
AJ-19
PID2
signal turn-
on level
When the PID
output terminal function 048[FBV2] is deactivated
(OFF). If it
crosses
(ON).
PID output (%)
PID deviation (%)
0%
Output
terminal
047[OD2]
0%
[AJ-19
]
2 gain.
is active (ON), the value of the
instable
variable
level
7
[OD
feedback
compare
feedback
cross over the [AJ
under the [AJ
ON
ON
]
Range (unit)
0.0~
100.0
0.0~
3600.0(s)
0.0~
100.0(s)
If done while operating, the
/insecure.
Range (unit)
0.00~
100.00(%)
If
[AJ
Range (unit)
0.00~
100.00(%)
±[A
J
2
] is activated
Range (unit)
0.00~
100.00(%)
0.00~
100.00(%)
-
19] level, is activated
PID output range
ON
ON
ON
Initial
value
1
.0
1
.0
0.0
Initial value
0.00
-16]=0.00
the
Initial value
3.00
-17],
the output
.
Initial
value
10
0.00
0.00
-
18] level, the
Time(s)
[AJ-16]
[AJ-16
Time(s)
[AJ-17]
[AJ-17]
Time(s)
[AJ-18]
[AJ-19]
4-26
PID3 function
AJ
enable
・
Validates the PID3 operation.
・
If [AJ
value, the PID output is limited to 0.
・
If [AJ
value, the PID output l
・
By activating the [PID3] terminal, the PID3 output
becomes 0.
AJ
・
PID3 deviation can be reversed.
AJ
AJ
PID3 sc
AJ
PID3 scal
AJ
(decimal point)
・
You can switch the display data and the display unit
involved in the output of the
calculation.
AJ
of set
AJ
PID3
・
When PID3 target value input is selected, if the selected
is the parameter setting, [AJ
AJ
of process data
・
Selects the PID
*1)
00(Not used)/01(Ai1 terminal)/02(Ai2 terminal)/03(Ai3 terminal)/
04(Ai4 terminal)/05(Ai5
08(RS485)/ 12(Pulse train input: main)/ 13(Pulse train input:
option)/15(PID1 output)
PID
value
Feedback
value
For parameter configuration
Code/Name
-21
PID3
-
21]=01 when the PID output reaches a negative
-
21]=02 when the PID output reaches a negative
Code/Name
-22
PID3 deviation
Code/Name
-23
PID3 unit selection
-24
ale adjustment
-25
e adjustment
-26
PID3 scal
e adjustment
Code/Name
-27
Input source selection
-
point for PID3
-30
set point setting for
Code/Name
-32
input source
for PID3
target
Range (unit)
00(Disable)/01(Enable)/
02(Enable:inverted output)
ets out an inverted output.
inverse
(0%)
(100%)
00
-
100.00
selection
00
3
feedback reference.
terminal)/06(Ai6 terminal)/07(Parameter)/
+
+
-
-
[AJ-21]
~
Range (unit)
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
Range (unit)
<unit table> at the end
of the document can
be consulted
-10000~
10000
-10000~
10000
0~4
PID control by the
Range
(unit)
~08, 12, 13,
15 *1)
100.00
~
100.00(%)
-30] gets
enabled.
Range (unit)
~
08, 12, 13, 15 *1)
00
01
R
everse
PID
3
[AJ-22]
[AJ-
30
Initial
value
00
Initial value
00
Initial
value
03
0
10000
2
Initial
value
07
0.00
Initial
value
02
PID
operation
]

Chapter 4
・
・
・
・
・
PID
Target
value
PID feedback (%)
048[FBV3]
Operation
command
[AJ-33]
~
Code/Name
AJ-33
PID3 proportional gain
AJ-34
PID3 integral time
AJ-35
PID3 derivative gain
Sets the PID3 gain.
If [PIDC] terminal is active (ON), the value of the
integral constant is purged. If done while operating, the
operation can become instable/insecure.
Code/Name
AJ-36
PID3 output
Limits the output range of the PID. If [AJ
limit is
disabled.
Code/Name
AJ-37
PID3 deviation
level
When the PID deviation pass over ±[AJ
terminal function 0
Code/Name
AJ-38
PID3
feedback
signal turn-
off level
AJ-39
PID3
feedback
signal turn-
on level
When the PID feedback cross over the [AJ
output terminal function 0
(OFF). If it crosses under the [AJ
(ON).
PID output (%)
PID deviation (%)
0%
Output
terminal
047[OD3]
0%
[AJ-39
]
constant
variable
over
89
[OD3] is activated.
compare
compare
ON
ON
]
Range (unit)
0.0~
100.0
0.0~
3600.0(s)
0.0~
100.0(s)
Range (unit)
0.00~
100.00(%)
Range (unit)
0.00~
100.00(%)
Range (unit)
0.00~
100.00(%)
0.00~
100.00(%)
90[FBV3
] is deactivated
-3
9] level, is activated
PID output range
ON
ON
ON
Initial
value
1.0
1.0
0.0
Initial value
0.00
-3
6]=0.00 the
Initial value
3.00
-
37], the output
Initial
value
100.00
0.00
-
18] level, the
Time(s)
[AJ-36]
[AJ-36
Time(s)
[AJ-37]
[AJ-37]
Time(s)
[AJ-38]
[AJ-39]
4-27
PID3 function
AJ
enable
・
Validates the PID
・
If [AJ
value, the PID output is limited to 0.
・
If [AJ
value, the PID output lets out an inverted output.
・
By activating the [PID
becomes 0.
AJ
・
PID
AJ
AJ
PID
AJ
PID
AJ
(decimal point)
・
You can switch the display data and the display
involved in the output of the PID control by the
calculation.
AJ
of process data for PID4
AJ
PID4
・
When PID
is the parameter setting, [AJ
AJ
reference selection for PID
・
Selects the PID
*1)
00(Not used)/01(Ai1 terminal)/02(Ai2 terminal)/03(Ai3 terminal)/
04(Ai4 terminal)/05(Ai5 terminal)/06(Ai6 terminal)/07(Parameter)/
08(RS485)/ 12(Pulse train input: main)/ 13(Pulse train input:
option)/15(PID1 output)
PID target
value
Feedback
value
For parameter configuration
Code/Name
-41
PID4
-4
1]=01 when the PID output reaches a negative
-4
1]=02 when the PID output reaches a negative
Code/Name
-42
PID4
deviation
4
deviation can be reversed.
Code/Name
-43
PID4
unit selection
-44
4 scale
adjustment
-45
4 scal
e adjustment
-46
PID4 scal
e adjsutment
Code/Name
-47
Input source selection
-50
Set point setting for
4
target value input is selected, if the selected
Code/Name
-52
Feedback data
Range (unit)
00(Disable)/01(Enable)/
02(Enable:inverted output)
4
operation.
4
] terminal, the PID
inverse
(0%)
(100%)
00
-
100.00
4
00
4 feedba
ck reference.
+
+
-
-
[AJ-41]
~
Range (unit)
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
Range (unit)
<unit table>
at the end
of the document can
be consulted
-10000~
10000
-10000~
10000
0~4
Range (unit)
~08, 12, 13,
15 *1)
100.00
~
100.00(%)
-5
0] gets enabled.
Range (unit)
~
08, 12, 13, 15 *1)
00
01
Reverse PID4
[AJ-42]
[AJ-5
0
Initial
value
00
4 output
Initial value
00
Initial
value
03
0
10000
2
unit
Initial
value
07
0.00
Initial
value
02
PID
operation
]

Chapter 4
[AJ
・
・
・
・
・
PID
Target
value
PID feedback (%)
092[FBV4]
Operation
command
-53]
~
Code/Name
AJ-53
PID4 proportional gain
AJ-54
PID4 integral time constant
AJ-55
PID4 derivative gain
Sets the PID4 gain.
If [PIDC] terminal is active (ON), the value of the
integral constant is
operation
can become instable/insecure.
Code/Name
AJ-56
PID4 output
Limits the output range of the PID. If [AJ
limit is disable
Code/Name
AJ-57
PID4 deviation
level
When the PID deviation pass over ±[AJ
terminal function 091[OD4] is activated.
Code/Name
AJ-58
PID4 feedback
signal turn-
off level
AJ-59
PID4 feedback
signal turn-
on level
When the PID feedback cross over the [AJ
output terminal function 092[FBV4] is
(OFF). If it crosses under the [AJ
(ON).
PID output (%)
PID deviation (%)
0%
Output
terminal
091[OD4]
0%
[AJ-59]
purged. If done while operating, the
variable
d.
over
compare
compare
ON
ON
Range (unit)
0.0~
100.0
0.0~
3600.0(s)
0.0~
100.0(s)
Range (unit)
0.00~
100.00(%)
Range (unit)
0.00~
100.00(%)
Range (unit)
0.00~
100.00(%)
0.00~
100.00(%)
-
59] level, is activated
PID output range
ON
ON
ON
Initial
value
1.0
1.0
0.0
Initial value
0.00
-
56]=0.00 the
Initial value
3.00
-
57], the output
Initial
value
100.00
0.00
-
58] level, the
deactivated
Time(s)
[AJ-36]
[AJ-36
Time(s)
[AJ-37]
[AJ-37]
Time(s)
[AJ-58]
[AJ-59]
4-28
■
Parameter mode
Frequency limit
bA102
Frequency
bA103
Frequency
・
Sets u
Torque limit
bA110
Torque limit selection, 1st
bA1
parameter
1st
bA112
(Forward driving), 1st
bA113
regenerative), 1st
bA114
driving), 1st
bA115
(forward
4-
quadrant mode)
bA116
selection, 1st
*1)
01(
08
・
In the case of vector control
0Hz
output torque
For parameter configuration
(b
Code/Name
upper
limit, 1st
lower l
imit, 1st
pper and lower limit
Code/Name
11
Torque limiting
mode
selection,
-motor
Torque limit 1
Torque limit 2 (Reverse
-
motor
Torque limit 3 (Reverse
-motor
Torque limit (4)
-
regenerating in
, 1st
Torque limit LADSTOP
-
motor
Ai1 terminal
)/02(
(RS485)
) the tor
que limit
.
[
b
code)
-motor
-motor
s
-motor
-motor
-motor
Ai2 terminal
)/03(
function
b
A102]
~
Range (unit)
0.00~
590.00(Hz)
0.00~
590.00(Hz)
of the frequency
Range (unit)
01~03/
07, 08 *1)
00(4 quadrants)/
01([TRQ]
terminal
0.0~500.0(%)
0.0~500.0(%)
0.0~500.0(%)
0.0~500.0(%)
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
Ai3 terminal
)/
(With sensor
can limit the motor
[bA11
5
Initial
value
0.00
0.00
.
Initial value
27
)
00
120.0(%)
120.0(%)
120.0(%)
120.0(%)
00
07(Parameter
)/
– Sensorless
]
–

4-29
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[bA120]~[bA128]
Overcurrent suppression function setting
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
bA120
Overcurrent
suppression enable, 1st-motor
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
00
bA121
Overcurrent
suppression level, 1st-motor
Inverter ND rated
current×(0.20~2.00)
*1)
*1) Inverter ND rated current×1.80
・Overcurrent can be suppressed, but in that case torque
drop can occur. Disable it in cases such as cranes.
Overload restriction function settings
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
bA122
Overload restriction 1
enable, 1st-motor
00(
Disable
)/
01(Enable during Acc. and
constant speed)/
02(Constant speed only)/
03(Enable during Acc. and
constant speed-Acc. during
regeneration)
01
bA123
Overload restriction 1
level, 1st-motor
Inverter rated current
×(0.20~2.00)
*2)
bA124
Overload
restriction 1 deceleration
time, 1st-motor
0.10~3600.00(s)
1.00
bA126
Overload restriction 2
enable, 1st-motor
00(Disable)/
01(Enable during Acc. and
constant speed)/
02(Constant speed only)/
03(Enable during Acc. and
constant speed - Increase
frequency during
regeneration)
00
bA127
Overload restriction 2
level, 1st-motor
Inverter rated current
×(0.20~2.00)
*2)
bA128
Overload
restriction 2 deceleration
time, 1st-motor
0.10~3600.00(s)
1.00
*2) Inverter rated current×1.50
・When the current is increased, the overload restriction
function reduces the current automatically by lowering
the frequency.
・Using [OLR] function state, the overload restriction 1
(OFF) and overload restriction 2 (ON) can be used.
[bA-30]~[bA145]
Deceleration / stop at power loss (Non-stop)
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
bA-30
Selection of
deceleration/stop in the
event of a power loss
00(
Disable
)/
01(Decel. stop)/
02(Decel. stop: with
resume)/
03(Decel. stop:
return to origin)
00
bA-31
DC voltage trigger
level during power loss
(200V class)
0.0~400.0(Vdc)
(400V class)
0.0~800.0(Vdc)
(200V class)
220.0
(400V class)
440.0
bA-32
Overvoltage
threshold during power loss
(200V class)
0.0~400.0(Vdc)
(400V class)
0.0~800.0(Vdc)
(200V class)
360.0
(400V class)
720.0
bA-34
Deceleration time
during power loss
0.01~3600.00(s)
1.00
bA-36
Initial output
frequency decrease during
power loss
0.00~10.00(Hz))
0.00
bA-37
Proportional gain
for operation at power loss
0.00~2.55
0.20
bA-38
Integral time for
operation at power loss
0.000~65.535(s)
0.100
・If the DC voltage of the main circuit is lower than the
level of [bA-31], the inverter decelerates to create a
regenerative state.
・When [bA-30]=01, if the DC voltage drops, deceleration
starts from the value of the actual frequency command
to the [bA-36], according to the deceleration time
[bA-34]. Once the DC voltage exceeds the [bA-32], the
deceleration is temporally stopped.
・When [bA-30]=02/03, if the DC voltage drops below DC
target level setting [bA-32], the output frequency is
decreased by PI control to put in regenerative mode
and the DC voltage is maintained at [bA-32] target
level.
Overvoltage suppression - deceleration
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
bA140
Overvoltage suppression
enable, 1st-motor
00(
Disable
)/
01(DC, constant decel.)
02(Enable acceleration)/
03(Enable Acc. at
constant speed & decel.)
00
bA141
Overvoltage suppression
level, 1st-motor
(200V class)
330.0~390.0(Vdc)
(400V class)
660.0~780.0(Vdc)
(200V class)
380
(400V class)
760
bA142
Overvoltage
suppression action time,
1st-motor
0.00~3600.00(s)
1.00
bA144
Overvoltage
suppression proportional
gain, 1st-motor
0.00~2.55
0.50
bA145
Overvoltage suppression
integral time, 1st-motor
0.000~65.535(s)
0.060
・When [bA140]=01, the deceleration time is increased
until stop so the DC voltage do not cross over the
[bA141] level.
・When [bA140]=02/03, accelerates temporally so the DC
voltage do not cross over [bA141] level.
Inverter output
frequency
Overload restriction level
[bA123]/[bA127]
Output current
Reference
frequency
Deceleration according to
the deceleration time at
overload restriction
[bA124]/[bA128]
Maximum frequency
[Hb105]
[Hd105]

4-30
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[bA146]~[bA149] [bA-60]~[bA-63]
Overvoltage suppression - Over-excitation
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
bA146
Over
magnetization
function selection
(V/f) , 1st-motor
00(Disable)/01(Always ON)/
02(Only at deceleration)/
03(Operation at set level)/
04(Only at Decel. and level)
02
bA147
Time constant of
over-magnetisation
output filter (V/f) ,
1st-motor
0.00~1.00(s)
0.30
bA148
Over-magnetisation
voltage gain (V/f) ,
1st-motor
50~400(%)
100
bA149
Over-magnetization
control level setting
(V/f) , 1st-motor
(200V Class)
330.0~390.0(Vdc)
(400V Class)
660.0~780.0(Vdc)
(200V Class)
380
(400V Class)
760
・This function disables the AVR function output voltage,
works while in over-excitation.
・When [AA121]=00~02, 04~06, (V/f) is enabled.
・When [bA146]=03/04, it will be operative if DC voltage
exceeds [bA-149] level.
Dynamic braking (BRD) function
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
bA-60
Dynamic braking usage ratio
0.0~100.0(%)
10.0
bA-61
Dynamic braking control
00(
Disable
)/
01(Only while running)
02(Enable during stop)
00
bA-62
Dynamic braking
activation level
(200V class)
330.0~390.0(V)
(400V class)
660.0~780.0(V)
(200V class)
360.0
(400V class)
720.0
bA-63
Dynamic braking
resistor value
Inverter minimum
resistor value 600(Ω)
Minimum
resistance
・This function operates the braking resistor of the built-in
braking circuits models. To use the BRD, setting [bA-60]
and [bA-61] is required.
[bA-70]~[bA249]
Cooling-fan operation
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
bA-70
Cooling fan
control selection
00(
Always
ON)/
01(While inverter operates)/
02(Depends on temperature)
00
bA-71
Cooling fan
control selection
00(Disable)/01(Clear) 00
・The Inverter cooling fan can be stopped.
・If you change the cooling-fan, assigning [bA-71]=01 you
will be able to clear the accumulated operation time.
2nd motor When Intelligent Input terminal 024[SET] is enabled.
Code/Name
Range
(unit)
Initial
value
bA202
Frequency upper
limit, 2nd motor
Same as
bA102
bA203
Frequency lower limit, 2nd motor
Same as
bA103
bA210
Torque limit selection
, 2nd motor
Same as
bA110
bA211
Torque limit LADSTOP enable, 2nd motor
Same as
bA111
bA212
Torque limit (1) (forward
-
driving in
4-quadrant mode), 2nd motor
Same as bA112
bA213
Torque limit (2) (reverse
- regenerating in
4-quadrant mode), 2nd motor
Same as bA113
bA214
Torque limit (3) (reverse
-
driving in
4-quadrant mode), 2nd motor
Same as bA114
bA215
Torque limit (4) (forward
- regenerating in
4-quadrant mode), 2nd motor
Same as bA115
bA220
Overcurrent suppression
enable, 2nd
motor
Same as bA120
bA221
Overcurrent suppression level, 2nd
-
motor Same as
bA121
bA222
Overload
restriction 1 selection, 2nd
-
motor
Same as
bA122
bA223
Overload restriction 1 level, 2nd
-
motor Same as
bA123
bA224
Overload restriction 1
active time
,
2nd-motor
Same as bA124
bA22
6 Overload restriction 2 selection, 2nd
-
motor
Same as
bA126
bA2
27 Overload restriction 2 level, 2nd
-
motor Same as
bA127
bA2
28 Overload restriction 2
active time
,
2nd-motor
Same as bA128
bA240
Overvoltage suppression enable,
2nd-motor
Same as bA140
bA241
Overvoltage suppression level
, 2nd-motor Same as
bA141
bA242
Overvoltage suppression
action time
,
2nd-motor
Same as bA142
bA244
Over
voltage
suppression
proportional gain
,
2nd-motor
Same as bA144
bA245
Over
voltage
suppression
integral
time,
2nd-motor
Same as bA145
bA246
Over-excitation function selection
,
2nd-motor
Same as bA146
bA247
Time constant of
o
ver-excitation
output
filter (V/f) , 2nd-motor
Same as bA147
bA248
Over-excitation
voltage gain
, 2nd-motor Same as
bA148
bA249
Over-excitation
control level setting
,
2nd-motor
Same as bA149

4-31
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[bb101]~[bb-42]
Reduction of electromagnetic sound
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
bb101
Carrier
frequency, 1st-motor
0.5~16.0(kHz)
2.0
bb102
Sprinkle carrier
pattern selection,
1st-motor
00(
Disable
)/
01(Enable: Patern-1)/
02(Enable: Patern-2)/
03(Enable: Patern-3)
00
bb103
Automatic carrier
frequency reduction
selection, 1st-motor
00(Disable)/
01(Enable: Current)/
02(Enable: Temperature)
00
・To decrease noise, [bb101] should be set small. To lower
electromagnetic sound, [bb101] has to be set bigger.
・By setting the duty specification selection [Ub-03], the
carrier frequency is internally limited.
・For the sake of the inverter protection, the Automatic
carrier reduction [bb103] decreases the carrier in
certain cases.
Reset operation after error event
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
bb-10
Automatic
error reset selection
00(
Disable
)/
01(If RUN command is OFF)
02(After set time)/
04(Emergency force drive)
00
bb-11
Automatic
error reset wait time
00(Enable)/
01(Disable)
00
bb-12
Automatic
reset waiting time
0.0~600.0(s)
2.0
bb-13
Automatic
error reset number
0~10(count)
3
・Adjustment of the automatic reset that follows an error
event. In the case that RUN command was on
execution, after the reset, is followed by the setting of
[bb-41].
Retry/trip setting in error event
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
bb-20
Retry count after power loss
event
0~16/255
0
bb-21
Retry count after
undervoltage event
0~16/255
0
bb-22
Retry count after
overcurrent event
0~5
0
bb-23
Retry count after
overvoltage event
0~5
0
・Sets number of retries before tripping.
・If 0 is set, as soon as an error occurs, it will trip.
・If you want to reset the retry count, assign any value
other than 0.
[bb-45]~[bb-59]
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
bb-24
Selection of restart mode at
Instantaneous power failure/
under-voltage trip
*3) 00
bb-25
Allowable under-voltage
power failure time
0.3~25.0(s)
1.0
bb-26
Retry wait time before motor
restart
0.3~100.0(s)
1.0
bb-27
Instantaneous power
failure/under-voltage trip alarm enable
00(
Disable
)/
01(Enable)/
02(Disable at
Stop/Decel. stop)
00
bb-28
Selection of restart mode at
over-current
*3) 00
bb-29
Wait time of restart at
over-current
0.3~100.0(s)
1.0
bb-30
Selection of restart mode at
over-voltage
*3) 00
bb-31
Wait time of restart at
over-voltage
0.3~100.0(s)
1.0
*3) 00(Restart motor with 0Hz)/01(Restart with a matching
frequency)/02(Restart with active frequency matching)/03(Detect
speed)/04(Decelerate and stop with a matching frequency and then
trip)
・Regarding the restart, after the waiting time is
completed the selected restart method is carried out.
Restart mode after FRS/RS
Code/Name
Range
(unit)
Initial
value
bb-40
Restart mode after FRS release
*4)
00
bb-41
Restart mode after RS release
00
*4) 00(Start with 0Hz)/01(Start with matching frequency)/02(Start with
active frequency matching)/03(Detect speed)/
・When using Intelligent input terminals [FRS] and [RS],
restart mode can be selected.
・[bb-40] allows you to select the restart operation after a
free-run stop.
・[bb-41] allows you to select the restart operation after a
trip or reset event.
Minimum level of frequency matching
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
bb-42
Restart frequency
threshold
0.00~590.00(Hz)
0.00
・The matching frequency function adopts the motor
frequency for a shockless start-up.
・If at the restart the frequency is under the [bb-42]
frequency, a 0Hz restart will be used instead.
Retry wait time
Free-run (FRS)
Primary
cut off
Inverter
output
Motor speed
Lower limit
[bb-42]
Restart with matching
frequency

4-32
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[bb-43]~[bb-62]
Active frequency matching
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
bb-43
Restart level of Active
frequency matching
Inverter rated
current
×(0.20~2.00)
Inverter
rated
current×1.00
bb-44
Restart
constant(speed) of Active
Frequency matching
0.10~30.00(s)
0.5
bb-45
Restart constant(Voltage) of
Active Frequency matching
0.10~30.00(s)
0.5
bb-46
OC-supress level of Active
frequency matching
Inverter rated
current
×(0.20~2.00)
Inverter
rated
current×1.00
bb-47
Restart speed selection of
Active frequency matching
00(
Frequency set
when inverter
output shut off)/
01(Maximum
frequency)/
02(Set frequency)
00
・The reset interval is set with [bb-46].
・Starts scanning from the frequency set in [bb-47].
Overcurrent level
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
bb160
Over current
detection level, 1st-motor
Inverter rated
current × (0.20~2.20)
Inverter rated
current×2.20
・The motor protection level for overcurrent can be set.
・In the case of a permanent magnet motor is set lower
than the motor demagnetizing level.
Overvoltage warning
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
bb-61
Power supply over
voltage selection
00(Warning)/
01(Error)
00
bb-62
Power supply over
voltage level setting
(200V Class)
300.0~400.0(V)
(400V Class)
600.0~800.0(V)
(200V Class)
390.0
(400V Class)
780.0
・When the input suffers an overvoltage and if the DC
voltage is higher than the value in [bb-62], a warning is
issued in accordance with [bb-61].
[bb-65]~[bb260]
Phase loss detection
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
bb-65
Input phase loss enable
00(Disable)/01(Enable) 00
bb-66
Output phase loss enable
00(Disable)/01(Enable) 00
bb-67
Output phase loss
detection sensitivity
1~100(%)
10
・Detects the disconnection of the supply RST input line
and UVW output line.
Thermistor error detection
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
bb-70
Thermistor error level
0~10000(Ω)
3000
Cb-40
Thermistor type selection
00(
Disable
)/
01(PTC)/02(NTC)
00
・In [TH] terminal must be attached the kind of thermistor
specified in [CA-60].
・If [CA-60]=01 or 02, error level must be set in [bb-70].
Overspeed control
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
bb-80
Overspeed detection level
0.0~150.0(%)
135.0
bb-81
Overspeed detection time
0.0~5.0(s) 0.5
・In vector control, when speed arrives to “maximum
speed”×[bb-75], and pass over [bb-76], results in error.
Abnormal deviation in speed control
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
bb-82
Speed deviation error
mode selection
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
00
bb-83
Speed deviation error
detection level
0.0~100.0(%)
15.0
bb-84
Speed deviation error
detection time
0.0~5.0(s)
0.5
・In vector control, when speed arrives to “maximum
speed”×[bb-83] and pass over [bb-84], results in error.
Abnormal deviation in position control
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
bb-85
Position deviation error
mode selection
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
00
bb-86
Position deviation error
detection level
0~65535
(×100pulse)
4096
bb-87
Position deviation error
detection level
0.0~5.0(s)
0.5
・During position control, if the position deviation exceeds
the [bb-86], if exceeds the [bb-87] time, will result in an
error.
2nd motor When Intelligent Input terminal 024[SET] is enabled.
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
bb201 Carrier frequency, 2nd
-
motor Same as
bb101
bb203 Automatic carrier frequency
reduction enable, 2nd-motor
Same as bb103
bb260 Overcurrent detection level,
2nd-motor
Same as bb160
Retry waiting time
Free-run
Primary
cut off
Inverter output
frequency
Motor speed
Lower limit
setting
[bb-59]
Start with matching frequency
Output
current
Active
frequency
current level
[bb-43]
Frequency selected in [bb-47]
Deceleration according to[bb
-
44]

4-33
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[bC110]~[bC125]
Electronic thermal protection
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
bC110
Electronic thermal
level setting, 1st-motor
Motor rated
current ×
(0.20~3.00)
Motor rated
current
×1.00
bC111
Electronic thermal characteristic
selection, 1st-motor
00(
Reduced
torque (VT))/
01(Constant
torque (CT))/
02(Free setting)
00(JPN)/
01(EU)(USA)
(ASIA)(CHN)
bC112
Electronic thermal Subtraction
function enable, 1st-motor
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
01
bC113
Electronic thermal
Subtraction time, 1st-motor
1~1000(s)
600
bC-14
Electronic thermal counter
memory selection at Power-off
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
01
bC120
Free electronic thermal
frequency-3, 1st-motor
0.00
~bC122(Hz)
0.00
bC121
Free electronic thermal
current-1, 1st-motor
Inverter rated
current ×
(0.00~1.00)
0.00
bC122
Free electronic thermal
frequency-2, 1st-motor
bC120
~bC124(Hz)
0.00
bC123
Free electronic thermal
current-2, 1st-motor
Inverter rated
current ×
×(0.00~1.00)
0.00
bC124
Free electronic thermal
frequency-3, 1st-motor
bC122
~590.00(Hz)
0.00
bC125
Free electronic thermal
current-3, 1st-motor
Inverter rated
current ×
×(0.00~1.00)
0.00
・With [bC112], it is possible to subtract the thermal
integral value of the motor.
(Example) When [bC111]=00, Inverter rated current:64A, [bC110]=64(A),
Base frequency [Hb104]=60Hz, Output frequency=20Hz
・In case of output frequency = 16Hz (base=50Hz) or 20Hz
(base = 60hz), the reduction scale is ×0.8, then the
inverter will trip when the output current of
120%(150%×0.8) flows continuously within 60s
according to the curve.
[bC210]~[bC225]
(Example) When [bC111]=01, Inverter rated current:64A,[bC110]=64(A),
Base frequency[Hb103]=60Hz, Output frequency=2.5Hz
・In case of output frequency = 2.5Hz, the reduction scale
is x0.9, then, the inverter will trip when the output
current of 135%(=150%×0.9) flows continuously within
60s according to the curve.
(Example) When [bC111]=02, and there is Output frequency [bC122]
2nd motor When Intelligent Input terminal 024[SET] is enabled.
Code/Name
Range
(unit)
Initial
value
bC210 Electronic thermal level
, 2nd-motor Same as
bC110
bC211 Electronic thermal characteristic
selection, 2nd-motor
Same as bC111
bC21
2 Electronic
thermal subtraction function
selection, 2nd-motor
Same as bC112
bC21
3 Electronic thermal subtraction time
,
2nd-motor
Same as bC113
bC2
20
Free setting, electronic thermal
frequency (1), 2nd-motor
Same as bC120
bC221 Free setting, electronic thermal
current
(1), 2nd-motor
Same as bC121
bC222 Free setting, electronic thermal
frequency (2), 2nd-motor
Same as bC122
bC223 Free setting, electronic thermal current
(2), 2nd-motor
Same as bC123
bC224 Free setting, electronic thermal
frequency (3), 2nd-motor
Same as bC124
bC225 Free setting, electronic thermal current
(3), 2nd-motor
Same as bC125
Reduction
scale
Inverter output
frequency (Hz)
X1.0
5 16
50
X0.8
X0.6
0
6
20
60
0
Base frequency
55.8
(87.2%)
76.8
(120%)
102.4
(160%)
0
Motor current (A)
(Ratio to the inverter
rated current)
60
3.0
Trip time (s)
Reduction
scale
Inverter output
frequency (Hz)
X1.0
0
60
X0.9
X0.8
5
2.5
62.8
(98.1%)
86.4
(135%)
115.2
(180%)
Motor current
(A)
(Ratio to the inverter
rated current)
60
3.0
0
Trip time(s)
Maximu
m frequency (Hz)
[Hb105][Hd105]
[bC125]
[
bC123]
[bC125]
[bC120]
[bC122]
[bC124]
0
Current
output (A)
Trip time (s)
60
3.0
(x) (y) (z) 0
Output current (A)
(x):[bC123]×109%
(y):[bC123]×150%
(z):[bC123]×200%

4-34
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[bd-01]~[bd-04][bE-02]~[bE-18]
Safety terminal
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
bd-01
STO input display
selection
00(
Display
)/
01(No display)/
02(Trip)
00
bd-02
STO input change time
0.00~60.00(s)
1.00
bd-03
Display selection at STO
input change time
00(Display)/
01(No display)
00
bd-04
Action selection after STO
input change time
00(
Trip)/
01(Maintain current
status)/
02(Disable)
00
・For more information, refer to the user’s guide.

4-35
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[CA-01]~[CA-31]
■Parameter mode (C code)
Input terminal settings
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
CA-01
Input terminal [1] function
Reference
<Input
terminal
function list>
103 [PLA] Pulse
train input A is
restricted to
[CA-10],
104 [PLB] Pulse
train input B is
restricted to
[CA-11],
028
CA-02
Input terminal [2] function
015
CA-03
Input terminal [3] function
029
CA-04
Input terminal [4] function
032
CA-05
Input terminal [5] function
031
CA-06
Input terminal [6] function
003
CA-07
Input terminal [7] function
004
CA-08
Input terminal [8] function
002
CA-09
Input terminal [9] function
001
CA-10
Input terminal [A] function
033
CA-11
Input terminal [B] function
034
・The functions for the input terminals 1~9,A,B are
assigned in [CA-01]~[CA-09],[CA-10],[CA-11].
Input terminal NO/NC settings
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
CA-21
Input terminal [1] active state
00(Normally
Open: NO)/
01(Normally
Closed: NC)
00
CA-22
Input terminal [2] active state
00
CA-23
Input terminal [3] active state
00
CA-24
Input terminal [4] active state
00
CA-25
Input terminal [5] active state
00
CA-26
Input terminal [6] active state
00
CA-27
Input terminal [7] active state
00
CA-28
Input terminal [8] active state
00
CA-29
Input terminal [9] active state
00
CA-30
Input terminal [A] active state
00
CA-31
Input terminal [B] active state
00
・The functions for the Intelligent input terminals 1~
9,A,B are assigned in [CA-21]~[CA-29],[CA-30],[CA-31].
・However, in the case of [RS] assignment the NO/NC will
not apply, only NO will apply.
[CA-41]~[CA-55]
Output terminal chatter prevention
Code/Name
Range
(unit)
Initial
value
CA-41
Input terminal [1] response time
0~400(ms)
2
CA-42
Input terminal [2] response time
2
CA-43
Input terminal [3] response time
2
CA-44
Input terminal [4] response time
2
CA-45
Input terminal [5] response time
2
CA-46
Input terminal [6] response time
2
CA-47
Input terminal [7] response time
2
CA-48
Input terminal [8] response time
2
CA-49
Input terminal [9] response time
2
CA-50
Input terminal [A] response time
2
CA-51
Input terminal [B] response time
2
・Sets the time to wait after the input change has ended,
and for the input to become stable and responsive.
Time allowed in simultaneous terminal change
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
CA-55
Multistage input
determination time
0~2000(ms)
0
・Sets the dead time for multistage speed and position
terminals change.

4-36
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[Input terminal function list]
Functio
n code
Symb
ol
Function
name
Description
000 no
Not use
-
001 FW
Forward rotation
Activating (ON) only one of them
will grant forward or reverse
rotation command. ⇒ [AA111]
002 RV
Reverse rotation
003 CF1
Multi speed
selection 1
Changing the states of these
terminals, allows to set different
motor speeds and change among
them.
⇒[Ab110]~[Ab-25],
[Ab210]
004 CF2
Multi speed
selection 2
005 CF3
Multi speed
selection 3
006 CF4
Multi speed
selection 4
007 SF1
Multi speed Bit-7
008 SF2
Multi speed Bit-2
009 SF3
Multi speed Bit-3
010 SF4
Multi speed Bit-4
011 SF5
Multi speed Bit-5
012 SF6
Multi speed Bit-6
013 SF7
Multi speed Bit-6
014 ADD
Trigger for
frequency
addition[Ab105]
When is turned ON, adds the
specified frequency value.
⇒[AA106]
015
SCH
G
Speed reference
change
Main speed(OFF)/Sub-speed (ON),
to change between them use ⇒
[AA105].
016 STA
3-wire Start
If [STA] is ON, start the motor. If
[STP] is ON stop the motor.
Forward operation direction if [FR]
is (OFF), reverse operation direction
if is (ON).
⇒[AA111]
017 STP
3-wire Stop
018 FR
Forward Over
Travel
019 AHD
analog command
holding
When the Analog inputs Ai1,2,3 are
in use, if AHD terminal is in ON
state, holds the Analog terminal
value.
⇒[AA101]
020 FUP
Remote control
Speed-UP
function
If the frequency can be set ([AHD]
ON included), [FUP] ON accelerates,
and [FDN] ON decelerates. [UDC]
returns to the saved value. ⇒
[CA-62]~[CA-66]
021 FDN
Remote control
Speed-DOWN
function
022 UDC
Remote control
data clearing
023 F-OP
Force operation
If ON, switch set parameters.
⇒[CA-68],[CA-69]
024 SET
2nd-motor
control
Change between 1st-motor (OFF)
and 2nd-motor (ON).
⇒By parameter
028 RS
Reset
Reset trip⇒[CA-61],[bb-41]
029 JG
Jogging
Activates Jogging operation.
⇒[AG-20],[AG-21]
030 DB
External Dynamic
brake
Enables the DC braking operation⇒
[AF101]~[AF109]
031 2CH
2-step
Acceleration/Dec
eleration
If ON, changes the Acc/Decel time.
⇒[AC115]
032 FRS
Free run stop
If ON allows the motor to free run.
⇒[AA115],[bb-40]
033 EXT
External fault
If ON error E012 occurs.
⇒Trip E012
034 USP
unattended
start protection
ON if at the start-up, the RUN
command was issued right at the
start up, E013 error.
⇒Tripping E013
035 CS
Commercial
Supply change
When changing to the public
electric grid, if it is ON, will cut the
output.
036 SFT
Soft-Lock
If ON, disables parameter changes.
⇒[UA-21]
037 BOK
Answer back
from Brake
Here is inputted the brake
confirmation signal for the brake
control.
[Input terminal function list]
Function
code
Symbol Function name Description
038 OLR
Accumulation
input power
clearance
Switches between Overload limit
1(OFF) and 2(ON).
⇒[bA122]~[bA128]
039 KHC
Accumulation
output power
clearance
If ON, clears the Accumulated input
power monitor.
⇒[UA-14]
040
OKHC
Disable PID1 If ON, clears the Accumulated
output power monitor.
⇒[UA-12]
041 PID
PID1
integration
reset
If ON, disables PID1 and changes
the PID target value for the
frequency reference.
⇒[AH-01]
042 PIDC
Disable PID2 If ON, clears the integral value of
the control.
⇒[AH-62],[AH-65]
043 PID2
PID2
integration
reset
If ON, disables PID2 and changes
the PID target value for the
frequency reference.
⇒[AJ-01]
044
PIDC2
Disable PID3 If ON, clears the integral value of
the control. ⇒[AJ-14]
046
PID3
PID3
integration
reset
If ON, disables PID3 and changes
the PID target value for the
frequency reference.
⇒[AJ-21]
046
PIDC3
Disable PID4 If ON, clears the integral value of
the control. ⇒[AJ-34]
047
PID4
PID4
integration
reset
If ON, disables PID4 and changes
the PID target value for the
frequency reference.
⇒[AJ-41]
048
PIDC4
Multi set-point
selection 1
If ON, clears the integral value of
the control. ⇒[AJ-54]
051 SVC1
Multi set-point
selection 2
The target value can be selected by
changing the pattern of ON/OFF
states.
⇒[AH-06]
052 SVC2
Multi set-point
selection 3
053 SVC3
Multi set-point
selection 4
054 SVC4
PID gain change
055 PRO
PID output
switching 1
Switches between Gain 1(OFF) and
Gain 2(ON).
056 PIO
PID output
switching 2
Switches PID Output 1 to 4 by
(PIO1:PIO2).
PID1 Enable(OFF:OFF)
PID2 Enable(OFF:ON)
PID3 Enable(ON:OFF)
PID4 Enable(ON:ON)
057 PIO2
SLEEP condition
ativation
058 SLEP
WAKE condition
ativation
In case it is used in Sleep terminal
functions, when ON, it activates. ⇒
[AH-85]
059
WAKE
Torque limit
enable
In case it is used in Wake terminal
functions, when ON, it activates. ⇒
[AH-93]
060 TL
Torque limit
selection bit 1
If ON, enables torque limit.
061
TRQ1
Torque limit
selection bit 2
The target value can be selected by
changing the pattern of ON/OFF
states.
062
TRQ2
Accumulation
input power
clearance

4-37
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[Input terminal function list]
Function
code
Symbol Function name Description
063 PPI
P/PI control mode
selection
For drooping control, switches
between PI control (OFF) and P
control (ON).
064 CAS
Control gain
change
Changes between the PI gain 1
(OFF) and 2(ON) of the speed
control system.
065 SON
Servo-on
If ON, executes the Servo
-
Lock
operation.
066 FOC
Forcing
If ON, performs a forcible
operation, will accelerate the rise
of the torque.
067 ATR
Permission of
torque control
If ON, enables the torque limit.
068 TBS
Torque Bias
enable
If ON, enables the torque bias.
069 ALP
Home search
function
If ON, when in position control
mode, stops by home search.
071 LAC
Acceleration/Dece
leration
cancellation
If ON, forces Acc/Decel time to
0.00s.
072 PCLR
Clearance of
position deviation
Clears the position deviation of
position control mode.
073 STAT
pulse train
position
command input
enable
In the pulse train position control,
if is ON, the input is enabled.
074 PUP
Position bias
(ADD)
If in position control mode, if
[PUP] is ON, adds, if
[PDN] is ON, subtracts.
075 PDN
Position bias
(SUB)
076 CP1
Multistage
position settings
selection 1
The position reference can be
selected by changing the pattern
of ON/OFF states.
077 CP2
Multistage
position settings
selection 2
078 CP3
Multistage
position settings
selection 3
079 CP4
Multistage
position settings
selection 4
080 ORL
Limit signal of
Homing function
Used by the Zero-Return position
operations of the position
control.
081 ORG
Start signal of
Homing function
082 FOT
Forward Over
Travel
Limits forward motion by forward
limit torque.
083 ROT
Reserve Over
Travel
Limits reverse motion by reverse
limit torque.
084 SPD
speed / position
switching
Switches position control(OFF)
and speed control(ON).
085 PSET
Position data
presetting
If ON, sets the actual position as
the origin point.
086 MI1
General
-
purpose
input 8
To be set if you want to make use
of an input signal for EzSQ
function.
087 MI2
General
-
purpose
input 11
088 MI3
General
-
purpose
input 11
089 MI4
General
-
purpose
input 11
090 MI5
General
-
purpose
input 11
091 MI6
General
-
purpose
input 11
092 MI7
General
-
purpose
input 11
093 MI8
General
-
purpose
input 11
094 MI9
General
-
purpose
input 9
095 MI10
General
-
purpose
input 10
096 MI11
General
-
purpose
input 11
097 PCC
Pulse counter
clearing
Clear the count for the pulse
counter function.
[Input terminal function list]
Function
code
Symbol Function name Description
098 ECOM
EzCOM
activation
If ON, activates EzCOM.
099 PRG
Program RUN
If ON, EzSQ is executed.
100 HLD
Acceleration/D
eceleration
disable
If ON, temporally stagnates
Acc/Decel.
101 REN
RUN enable
If ON, operation is
enable. If it is
not assigned, it disables
operation.
102 DISP
Display lock
If made ON, the keypad screen is
lock and the RUN key is disabled.
103 PLA
Pulse count A
For pulse train input use.
104 PLB
Pulse count B
For pulse train input use.
105 EMF
Emergency-Forc
e Drive
activation
Forces the set operation in
emergency state.
107 COK
Contactor check
signal
Regarding the braking control,
check signal for the contactor.
108 DTR
Data trace start
If ON, starts data trace function.
109 PLZ
Pulse train
input Z
110 TCT
Teach-in signal
If ON, starts function.

4-38
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[CA-60]~[CA-84]
[FUP]/[FDN] operations
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
CA-60
FUP/FDN overwrite
target selection
00(Speed reference)
01(PID)
00
CA-61
FUP/FDN data save
enable
00(No save)/
01(Save)
00
CA-62
UDC terminal mode
selection
00(0Hz)/
01(Save data)
00
CA-64
Acceleration time for
FUP/FDN function
0.00~3600.00(s)
30.00
CA-66
Deceleration time for
FUP/FDN function
30.00
・[CA-60] sets as operation target the frequency reference
or the PID target value for 020[FUP]/021[FDN].
・[CA-61] sets if the modified values of [FUP] / [FDN]
should be saved or not in the storage memory.
・[CA-62] selects the frequency in which will change the
frequency reference for when [UDC] terminal is ON.
・If [FUP]/[FDN] is turn ON, in the case the frequency
reference is changed you can set the acceleration and
deceleration time [CA-64][CA-66].
[F-OP] Speed/Operation change
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
CA-70
Speed command
selection when [F-OP] active
01~03、07、08、12、14、
15 *1)
01
CA-71
Operation command
reference selection when
[F-OP] active
00~03 *2)
01
・If Intelligent input terminal 023[F-OP] is ON the change
is carried out.
*1)01(Ai1 terminal)/02(Ai2 terminal)/03(Ai3 terminal)/ 07(Parameter)/ 08(RS485)/
12(Pulse train input:main)/14(EzSQ function)/15(PID result)
*2) 00([FW]/[RV] terminal)/01(3-wire)/02(Keypad’s RUN key)/03(RS485)
Reset terminal [RS]
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
CA-72
Reset mode
selection
00(Trip release at turn-ON)/
01(Trip release at turn-OFF)/
02(Effective only in trip ON condition)/
03(Effective only in trip OFF condition)
00
・Output is shut off when reset terminal is ON.
This terminal is valid only while in trip status.
Main encoder input
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
CA-81
Encoder constant setting
0~65535(Pls)
1024
CA-82
Encoder phase selection
00(Phase A precedent)/
01(Phase B precedent)
00
CA-83
Numerator of the
motor gear ratio
1~10000
1
CA-84
Denominator of the
motor gear ratio
1~10000
1
・Sets the main encoder input and the motor gear ratio
involved in the encoder feedback.
[CA-90]~[CA-99]
Pulse train input terminal
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
Pulse train input
(main)
CA-90
Pulse train detection
object selection
00(
Frequency reference
)/
01(Pulse count)/
02(Speed feedback :
sensor-V/f)
00
CA-91
Mode selection of
pulse train input
00(90º-
phase-shift)/
01(Forward/reverse
operation and direction of
rotation)/
02(Forward/reverse
operation with pulse train)
00
Pulse train frequency
(main)
CA-92
pulse train
frequency Scale
0.05~32.0(kHz)
25.0
CA-93
pulse train
frequency filter time
constant
0.01~2.00(s)
0.10
CA-94
pulse train
frequency Bias value
-100.0~100.0(%)
0.0
CA-95
Pulse train
frequency high limit
0.0~100.0(%)
100.0
CA-96
Pulse train
frequency detection
Low level
0.0~100.0(%)
0.0
・A pulse train is introduced in functions [PLA][PLB]
assigned to terminals A,B. If [CA-90]=01, pulses in
terminals A & B are counted. Only terminal A in case
that is a single phase input.
Pulse train counter
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
CA-97
Comparing match output
ON-level for pulse count
0~65535
0
CA-98
Comparing match output
OFF-level for pulse count
0~65535
0
CA-99
Comparing match output Maximum value
for pulse count
0~65535
65535
・Set 091[PCMP] to output the compare results of the
pulse train counters of functions 103[PLA]/104[PLB].
・Turning 097[PCC] terminal in ON state resets the
counter.
・In the following example, when [CA-81]=01, inputting a
pulse train in terminal A.
Internal counter
0
Max. count value
[CA-79]
OFF level [CA-78]
ON level [CA-77]
[PLA] input
[PCC] input
[PCMP] output

4-39
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[Cb-01]~ [Cb-35]
Analog input acquisition
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
[Ai1] terminal
Cb-01
Time constant of filter
1~500(ms)
16
Cb-03
Start value
0.00~100.00(%)
0.00
Cb-04
End value
0.00~100.00(%)
100.00
Cb-05
Start ratio
0.0~[Cb-06](%)
0.0
Cb-06
End ratio
[Cb-05]~100.0(%)
100.0
Cb-07
Start selection
00(Initial value)/
01(0%)
01
[Ai2] terminal
Cb-11
Time constant of filter
1~500(ms)
16
Cb-13
Start value
0.00~100.00(%)
0.00
Cb-14
End value
0.00~100.00(%)
100.00
Cb-15
Start ratio
0.0~[Cb-16](%)
0.0
Cb-16
End ratio
[Cb-15]~100.0(%)
100.0
Cb-17
Start selection
00(Initial value)/
01(0%)
01
[Ai3] terminal
Cb-21
Time constant of filter
1~500(ms)
16
Cb-22
Operation selection
00(Individual)/
01(Ai1/Ai2 add:
with inversion/
02(Ai1/Ai2 add:
without inversion)
00
Cb-23
Start value
-100.00~100.00(%)
-100.00
Cb-24
End value
-100.00~100.00(%)
100.00
Cb-25
Start ratio
-100.0~[Cb-26]
-100.0
Cb-26
End rattio
[Cb-25]~100.0
100.0
・Regarding the adjustment method of the Analog input,
please refer to the chapter 3 example of I/O terminals
adjustment.
Analog input fine tuning
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
Cb-30
[Ai1] Voltage/Current zero-bias
adjustment
-200.00 ~
200.00(%)
0.00
Cb-31
[Ai1] Voltage/Current gain
adjustment
-200.00 ~
200.00(%)
100.00
Cb-32
[Ai2] Voltage/Current
zero-bias adjustment
-200.00 ~
200.00(%)
0.00
Cb-33
[Ai2] Voltage/Current gain
adjustment
-200.00 ~
200.00(%)
100.00
Cb-34
[Ai3] Voltage -10 bias
adjustment
-200.00 ~
200.00(%)
0.00
Cb-35
[Ai3] Voltage gain adjustment
-200.00 ~
200.00(%)
100.00
・Regarding the adjustment method of the Analog input,
please refer to the chapter 3 example of I/O terminals
adjustment.
・The thermistor adjustment, when recognizes an increase
in the adjustment value, reduces the resistor value.
[CA-40][Cb-41][CC-01]~[CC-17]
Thermistor error detection
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
CA-40
Thermistor type
selection
00(Disable)/
01(PTC)/02(NTC)
00
Cb-41
Thermistor gain adjustment
0.0~1000.0
100.0
・Set [CA-40] according to the connected thermistor in TH input
terminal.
・When [CA-40]=01 or 02, with [bb-70] the error level is set. Refer to
[bb-70].
・[Cb-41] thermistor gain adjustment, when the adjustment value is
raised the resistance value is lowered.
Output terminal settings
Code/Name
Range
(unit)
Initial
value
CC-01
Output terminal [11] function
Reference
<Intelligent
output
terminal
function
list>
002
CC-02
Output terminal [12] function
001
CC-03
Output terminal [13] function
035
CC-04
Output terminal [14] function
019
CC-05
Output terminal [15] function
030
CC-06
Output terminal [16] function
018
CC-07
Output terminal [AL] function
017
・The functions for the output terminals 11~15,16A,AL are
assigned in [CC-01]~[CC-05],[CC-06],[CC-07].
Output terminal NO/NC settings
Code/Name
Range
(unit)
Initial
value
CC-11
Output terminal [11] active state
00(Normally
open: NO)/
01(Normally
closed: NC)
00
CC-12
Output terminal [12] active state
00
CC-13
Output terminal [13] active state
00
CC-14
Output terminal [14] active state
00
CC-15
Output terminal [15] active state
00
CC-16
Output terminal [16] active state
00
CC-17
Output terminal [AL] active state
01
・The functions for the Intelligent output terminals 11~
15,16,AL are assigned in [CC-11]~[CC-15], [CC-16],
[CC-17].

4-40
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[CC-20]~[CC-33]
Output terminal response
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
CC-20
Output terminal [11] on-delay time
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
CC-21
Output terminal [11] off-delay time
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
CC-22
Output terminal [12] on-delay time
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
CC-23
Output terminal [12] off-delay time
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
CC-24
Output terminal [13] on-delay time
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
CC-25
Output terminal [13] off-delay time
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
CC-26
Output terminal [14] on-delay time
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
CC-27
Output terminal [14] off-delay time
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
CC-28
Output terminal [15] on-delay time
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
CC-29
Output terminal [15] off-delay time
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
CC-30
Output terminal [16] on-delay time
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
CC-31
Output terminal [16] off-delay time
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
CC-32
Output terminal [AL] on-delay time
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
CC-33
Output terminal [AL] off-delay time
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
・Sets the delay time since the output terminal changes,
until it actually become responsive.
[Intelligent output terminal function list]
Function
code
Symbol Function name Description
000 no Not use
001 RUN Running
While output is active
002 FA1
Constant
-
speed
reached
When constant speed
reached, ON
003 FA2
Set speed
overreached
ON at reaching the specified
frequency or more
004 FA3
Set frequency
reached
ON only at reaching the
specified frequency
005 FA4
Set speed
overreached 2
ON at reaching the specified
frequency 2 or more
006 FA5 Set speed reached
ON only at reaching the
specified frequency 2
007 IRDY inverter ready
ON when inverter is ready
008 FWR Forward rotation
ON while in forward drive
009 RVR Reverse rotation
ON while in reverse drive
010 FREF
Speed referenc =
Keypad is selected
ON if the frequency
reference is from keypad
011 REF
Run command =
Keypad is selected
ON if the motion
operation is from
operation keypad
012 SETM
2nd control is
selcted
ON if 2nd-motor selected
016 OPO Option output
Controlled by the Option
017 AL Alarm ON when trip happens
018 MJA Major failure
ON if major failure trips
019 OTQ Over-torque
ON if torque is exceeded
020 IP
Instantaneous
power failure
ON if control power drops
021 UV Undervoltage
ON if main voltage drops
022 TRQ Torque limited
ON if torque limit operates
023 IPS
IP-Non stop function
is active
ON if set in power loss
024 RNT
Accumulated
operation time over
ON if set time is exceeded
025 ONT
Accumulated
power-on time over
ON if set time is exceeded
026 THM
Electronic thermal
alarm signal(MTR)
ON if motor thermal
integral value exceeds set
value
027 THC
Electronic thermal
alarm signal(CTL)
ON if inverter thermal
integral value exceeds set
value
029 WAC
Capacitor life
warning
ON by life warning
030 WAF
Cooling
-
fan speed
drop
ON by life warning
031 FR
Starting contact
signal
On while in operation
032 OHF
Heat sink overheat
warning
ON when the
heatsink
is
overheated.
033 LOC
Low-current
indication signal
ON if output current is less
that the specified value
034 LOC2
Low-current
indication signal 2
ON if output current is less
that the specified value
035 OL
Overload notice
advance signal (1)
ON if output current
exceeds specified value
036 OL2
Overload notice
advance signal (2)
ON if output current
exceeds specified value
037 BRK Brake release
ON when brake releases
038 BER Brake error
ON if abnormality in
sequence happens
039 CON Contactor control
ON if contactor releases

4-41
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[Output terminal function list]
Function
code
Symbol Function name Description
040 ZS
Zero speed
detection
ON if output frequency is
less than set value
041 DSE
Speed deviation
over
ON if speed deviation
exceeds the set value
042 PDD
Position deviation
over
ON
if position deviation
exceeds the set value
043 POK
Positioning
completed
ON if positioning is
completed
044 PCMP
Pulse count
compare match
output
ON when set value and
pulse train comparator
matches.
045 OD
Deviation over for
PID control
ON if PID
control deviation
exceeds the set value
046 FBV
PID1 feedback
comparison
ON if PID feedback is
within range
047 OD2
OD:Deviation over
for PID2 control
ON if PID control deviation
exceeds the set value
048 FBV2
PID2 feedback
comparison
ON if PID feedback
is
within range
049 NDc
Communication line
disconnection
ON if communication is
lost with operation keypad
050 Ai1Dc
Analog [Ai1]
disconnection
detection
ON if Analog input 1 is less
than the set value
051 Ai2Dc
Analog [Ai2]
disconnection
detection
ON if Analog input 2 is less
than the set value
052 Ai3Dc
Analog [Ai3]
disconnection
detection
ON if Analog input 3 is less
than the set value
053 Ai4Dc
Analog [Ai4]
disconnection
detection
ON if Analog input 4 is less
than the set value
054 Ai5Dc
Analog [Ai5]
disconnection
detection
ON if Analog input 5 is less
than the set value
055 Ai6Dc
Analog [Ai6]
disconnection
detection
ON if Analog input 6 is less
than the set value
056 WCAi1
Window
comparator Ai2
ON if
Analog
input 1 is
within range
057 WCAi2
Window
comparator Ai2
ON if
Analog
input 2 is
within range
058 WCAi3
Window
comparator Ai3
ON if
Analog
input 3 is
within range
059 WCAi4
Window
comparator Ai4
ON if
Analog
input 4
is
within range
060 WCAi5
Window
comparator Ai5
ON if
Analog
input 5
is
within range
061 WCAi6
Window
comparator Ai6
ON if
Analog
input 6
is
within range
062 LOG1
Logical operation
result 1
Determined by the
calculation results of two
output terminals
063 LOG2
Logical operation
result 2
064 LOG3
Logical
operation
result 3
065 LOG4
Logical operation
result 4
066 LOG5
Logical operation
result 5
067 LOG6
Logical operation
result 6
068 LOG7
Logical operation
result 7
[Output terminal function list]
Function
code
Symbol Function name Description
069 MO1
General
-
purpose
output 1
Set if case of use of EzSQ
070 MO2
General
-
purpose
output 2
071 MO3
General
-
purpose
output 3
072 MO4
General
-
purpose
output 4
073 MO5
General
-
purpose
output 5
074 MO6
General
-
purpose
output 6
075 MO7
General
-
purpose
output 7
076 EMFC
Bypass mode
indicator
ON while in force
operation
077 EMBP
Speed deviation
over
ON while in bypass
operation
078 WFT
Trace function
waiting for trriger
ON while in waiting status
079 TRA
Trace function data
logging
ON while in stand-by
080 LBK
Low-battery of
keypad
ON while in low battery or
when no contain battery
on keypad
081 OVS
Over-Voltage power
Supply
ON when become
overvoltage in stop status
084 AC0 Alarm code bit
-0
ON if detects low battery
Alarm information is
delivered as bit.
Use the user’s guide for
more information.
085 AC1 Alarm code bit
-1
086 AC2 Alarm code bit
-2
087 AC3 Alarm code bit-3
089 OD3
Deviation over for
PID control
ON when PID deviation
exceeds the value [AJ-37]
090 FBV3
PID3 feedback
comparison
ON when
PID feedback is
between [AJ-38]/[AJ-39]
091 OD4
Deviation over for
PID4 control
ON when PID deviation
exceeds the value [AJ-57]
092 FBV4
PID4 feedback
comparison
ON when
PID feedback is
between [AJ-58]/[AJ-59]
093 SSE PID soft start error
ON when
PID soft start
became in warning status

4-42
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[CC-40]~[CC-60]
Combinational output terminal
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
Logical output signal
CC-40
Logical calculation
target 1 selection of LOG1
<
Intelligent o
utput
terminal function list>
reference
00
CC-41
Logical calculation
target 2 selection of LOG1
<Intelligent output
terminal function list>
reference
00
CC-42
Logical calculation
Symbol selection of LOG1
00(AND)/01(OR)/
02(XOR)
00
CC-43
Logical calculation
target 1 selection of LOG2
<
Intelligent o
utput
terminal function list>
reference
00
CC-44
Logical calculation
target 2 selection of LOG2
<
Intelligent o
utput
terminal function list>
reference
00
CC-45
Logical calculation
Symbol selection of LOG2
00(AND)/01(OR)/
02(XOR)
00
CC-46
Logical calculation
target 1 selection of LOG3
<
Intelligent o
utput
terminal function list>
reference
00
CC-47
Logical calculation
target 2 selection of LOG3
<
Intelligent o
utput
terminal function list>
reference
00
CC-48
Logical calculation
Symbol selection of LOG3
00(AND)/01(OR)/
02(XOR)
00
CC-49
Logical calculation
target 1 selection of LOG4
<
Intelligent o
utput
terminal function list>
reference
00
CC-50
Logical calculation
target 2 selection of LOG4
<
Intelligent o
utput
terminal function list>
reference
00
CC-51
Logical calculation
Symbol selection of LOG4
00(AND)/01(OR)/
02(XOR)
00
CC-52
Logical calculation
target 1 selection of LOG5
<
Intelligent o
utput
terminal function list>
reference
00
CC-53
Logical calculation
target 2 selection of LOG5
<
Intelligent o
utput
terminal function list>
reference
00
CC-54
Logical calculation
Symbol selection of LOG5
00(AND)/01(OR)/
02(XOR)
00
CC-55
Logical calculation
target 1 selection of LOG6
<
Intelligent o
utput
terminal function list>
reference
00
CC-56
Logical calculation
target 2 selection of LOG6
<
Intelligent o
utput
terminal function list>
reference
00
CC-57
Logical calculation
Symbol selection of LOG6
00(AND)/01(OR)/
02(XOR)
00
CC-58
Logical calculation
target 1 selection of LOG7
<
Intelligent o
utput
terminal function list>
reference
00
CC-59
Logical calculation
target 2 selection of LOG7
<
Intelligent o
utput
terminal function list>
reference
00
CC-60
Logical calculation
Symbol selection of LOG7
00(AND)/01(OR)/
02(XOR)
00
・The logical operation function is used to output the
combinational result of two selected output terminals.
[Cd-01]~[Cd-35]
Analog output terminal adjustment
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
Cd-01
[FM] monitor output
wave form selection
00(PWM)/
01(Frequency)
00
Cd-02
[FM] monitor base
frequency (at PWM output)
0~3600(Hz)
2880
Cd-03
[FM] Monitor output
selection
Set monitor code
dA-01
Cd-04
[Ao1] Monitor output
selection
dA-01
Cd-05
[Ao2] Monitor output
selection
dA-01
Cd-10
Analog monitor adjust
mode enable
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
00
Cd-11
Filter time constant of
[FM] monitor
1~500(ms)
10
Cd-12
[FM] monitor output
data type selection
00(Absolute value)/
01(Signed value)
00
Cd-13
[FM] monitor bias
adjustment
-100.0~100.0(%)
0.0
Cd-14
[FM] gain adjustment
-1000.0~1000.0(%)
100.0
Cd-15
Output level setting at
[FM] adjustment mode
0.0~300.0(%)
100.0
Cd-21
Filter time constant of
[Ao1] monitor
1~500(ms)
10
Cd-22
[Ao1] data type
selection
00(Absolute value)/
01(Signed value)
00
Cd-23
[Ao1] bias adjustment
-100.0~100.0(%)
100.0
Cd-24
[Ao1] gain adjustment
-1000.0~1000.0(%)
100.0
Cd-25
Output level setting at
[Ao1] adjustment mode
0.0~300.0(%)
100.0
Cd-31
Filter time constant of
[Ao2] monitor
1~500(ms)
10
Cd-32
[Ao2] data type se
lection
00(Absolute value)/
01(Signed value)
00
Cd-33
[Ao2] bias adjustment
-100.0~100.0(%)
0.0
Cd-34
[Ao2] gain adjustment
-1000.0~1000.0(%)
100.0
Cd-35
Output level setting at
[Ao2] adjustment mode
0.0~300.0(%)
100.0
・Regarding the adjustment method of the Analogue
output, please refer to the chapter 3 example of I/O
terminals adjustment.

4-43
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[CE101]~[CE107]
Low-current detection signal
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
CE101
Low-current
indication signal mode
selection, 1st-motor
00(During Acc/Decel and
constant-speed operation)
01(only during
constant-speed operation)
01
CE102
Low-current detection
level 1, 1st-motor
Inverter rated
current×(0.00~2.00)
Inverter
rated current
×1.00
CE103
Low-current detection
level 2, 1st-motor
Inverter rated
current×(0.00~2.00)
Inverter
rated current
×1.00
・In the case of low-current, outputs a signal.
Overload detection signal
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
CE105
Overload warning signal
mode selection, 1st-motor
00(During
Acc/Decel
and constant speed)/
01(During constant
speed only)
01
CE106
Overload
warning level 1, 1st-motor
Inverter rated
current×(0.00~2.00)
Inverter
rated current
×1.00
CE107
Overload
warning level 2, 1st-motor
Inverter rated
current×(0.00~2.00)
Inverter
rated current
×1.00
・In the case of overload, outputs a signal.
[CE-10]~[CE-31]
Frequency arrival signal
Code/Name
Range
(unit)
Initial
value
CE-10
Arrival frequency for acceleration 1
0.00~
590.00(Hz)
0.00
CE-11
Frequency arrival for deceleration 1
0.00
CE-12
Arrival frequency for acceleration 2
0.00
CE-13
Frequency arrival for deceleration 2
0.00
・Sets the operation of the arrival signal.
(Example) In FA2/FA4 case:
(Example) In FA3/FA5 case:
Over-torque signal
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
CE120
Over-torque level (Forward
during), 1st-motor
0.0~300.0(%)
100.0
CE121
Over-torque level (Reverse
driving), 1st-motor
100.0
CE122
Over-torque level (Forward
regenerative), 1st-motor
100.0
CE123
Over-torque level (Forward
driving), 1st-motor
100.0
・Sets the level to output the 019[OTQ] signal, when using
vector control and the torque goes over the limit.
Electronic thermal warning
Code/Name
Range
(unit)
Initial
value
CE-30
Electronic thermal level (motor)
0.00~
100.00(%)
80.00
CE-31
Electronic thermal level (inverter)
80.00
・Sets the level to output the motor electronic thermal
warning 026[THM].
・Sets the level to output the inverter electronic thermal
warning 027[THC].
Output current(A)
Low-current
indication signal
detection level
[CE102]/[CE103]
[LOC]/[LOC2]
indication signal
ON ON
Overload warning
level [CE106]/[CE107]
Output current
OL/OL2
output
fon:
Maximum frequency 1%
foff:
Maximum frequency 2%
[CE-10]/[CE
-
12] [CE-11]/[CE
-
13]
f
on
f
off
Output
frequency
FA2/FA4
fon:Maximum frequency 1%
foff:Maximum frequency 2%
fon
fon
foff
foff
[CE-11]/[CE
-
13]
[CE-10]/[CE-12]
Output frequency
FA3/FA5

Chapter 4
[CE
・
・
・
Window comparator
Disconnection detection
・
・
-33]
~
0Hz
speed detection signal
Code/Name
CE-33
Zero speed detection level
Sets the level in which the Inverter
detection signal 040[ZS]
Cooling fan
Code/Name
CE-34
Cooling fan overheat
warning level
Sets the level in which outputs the Heat sink overheat
warning 032[OHF].
Signals for
Code/Name
CE-36
Accum. RUN(RNT) /
Accum.Power-
ON(ONT) time setting
Sets the level in which the Inverter outputs the
beyond
time
025[ONT].
Window comparator
disconnection)
Code/Name
Window comparator
CE-40
[Ai1]
CE-41
[Ai1]
CE-42
[Ai1]
CE-43
[Ai2]
CE-44
[Ai2]
CE-45
[Ai2]
CE-46
[Ai3]
CE-47
[Ai3]
CE-48
[Ai3]
Disconnection detection
CE-50
[Ai1]
CE-51
[Ai1]
CE-52
[Ai2]
CE-53
[Ai2]
CE-54
[Ai3]
CE-55
[Ai3]
Outputs a signal whenever the
within or out of range.
As for disconnection detection, if is within
range, a
value can be set for the operation
[CE-55
]
overheat warning signal
RUN/ON
beyond
024[RNT]
and the Power
Upper limit
Lower limit
Hysteresis width
Upper limit
Lower limit
Hysteresis width
Upper limit
Lower limit
Hysteresis width
Operation level
Level enable
Operation level
Level enable
Operation level
Level enable
Range (unit)
0.00~
100.00(
outputs the 0Hz
Range (unit)
0~
200(°C)
time
Range (unit)
0
~
1000
-
(detection of terminal
Range (unit)
0~
100(%)
0~
100(%)
0~
10(%)
0~
100(%)
0~
100(%)
0~
10(%)
-100~
100(%)
-100~
100(%)
0~
10(%)
0~
100(%)
00(
Disable
01(
Inside range
02(
Out of range
0~
100(%)
00(
Disable
01(
Inside range
02(
Out of range
-100~
100(%)
00(
Disable
01(
Inside range
02(
Out of range
Analog
Initial
value
Hz)
0.00
Initial value
120
Initial
value
00(hour)
RUN
on beyond
time
Initial
value
100
0
0
100
0
0
100
-
100
0
0
)/
)/
)
00
0
)/
)/
)
00
0
)/
)/
)
00
input value is
or out of
.
4-44
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
If [CE
2nd motor
CE201
output mode selection
CE202
2nd
CE203
2nd
CE205
mode selection
CE206
2nd
CE207
2nd
CE220
regenerative)
CE221
driving)
CE222
regenerative)
CE223
driving)
[WC1]/[WC2]/
[WC3]
Max(100%)
Min
(Ai1/Ai2:0%)
(Ai3:
Ai1/Ai2/Ai3 Input
For parameter configuration
-51][CE-53][CE-
55]=02
When Intelligent Input
Code/Name
Low-current indication signal
Low-current detection level 1,
-motor
Low-current detection level 2
-motor
Overload warning signal output
, 2nd
Overload warning level 1
-motor
Overload warning level 2
-motor
Over-torque level (Reverse
, 2nd-
motor
Over-torque level (Reverse
, 2nd-
motor
Over-torque level (Forward
, 2nd-
motor
Over-torque level (Forward
, 2nd-
motor
-100%)
Analog
Hysteresis width
[CE-
42]/[CE
[CF2
terminal 024[SET] is enabled.
, 2nd-motor
-motor
,
,
Analog
adopted value
input value
-45]/[CE-48]
01]
~
Range (unit)
Same as
Same as
,
Same as
Same as
Same as
Same as
Same as
Same as
Same as
Same as
[CF2
23
Initial
value
CE101
CE102
CE103
CE105
CE106
CE107
CE120
CE121
CE122
CE123
Analog
operation level
at disconnection
CF-80/CF-82/CF-
84
Maximum-
limit level
of window comparator
CF-70/CF-73/CF-
76
Minimum-
limit level of
window comparator
CF-71/CF-74/CF-
77
]

4-45
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[CF-01]~[CF-10]
Modbus communication
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
CF-01
RS485 communication baud
rate selection
03(2400bps)/
04(4800bps)/
05(9600bps)/
06(19.2kbps)/
07(38.4kbps)/
08(57.6kbps)/
09(76.8kbps)/
10(115.2kbps)
05
CF-02
RS485 communication
Node allocation
1~247
1
CF-03
RS485 communication
parity selection
00(
Absent
)/
01(Even parity)/
02(Odd parity)
00
CF-04
RS485
communication stop-bit
selection
01(1bit)/02(2bit) 01
CF-05
RS485 communication
erroort selection
00(
Error
)/
01(Tripping after
deceleration and
stopping the
motor)/
02(Ignore errors)/
03(Stopping the
motor after
free-run)/
04(Deceleration and
stopping the motor)
02
CF-06
RS485 communication trip limit
time setting (timeout)
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
CF-07
RS485 communication
wait time
0~1000(ms)
0
CF-08
RS485 communication
mode selection
01(Modbus
-
RTU)/
02(EzCOM)/
03(EzCOM control)
01
・Sets the Modbus communication function for its use.
・When using communication function between inverter
EzCOM, set a value except 01 for [CF-08].
[CF-20]~[CF-50]
EzCOM peer to peer communication
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
CF-20
EzCOM Start node No.
01~08
01
CF-21
EzCOM End node No.
01~08
01
CF-22
EzCOM Start selection
00(
Terminal
ECOM)/
01(Always)
00
CF-23
EzCOM data size
01~05
05
CF-24
EzCOM destination address 1
1~247
1
CF-25
EzCOM destination register 1
0000~FFFF
0000
CF-26
EzCOM source register 1
0000~FFFF
0000
CF-27
EzCOM destination address 2
1~247
2
CF-28
EzCOM destination register 2
0000~FFFF
0000
CF-29
EzCOM source register 2
0000~FFFF
0000
CF-30
EzCOM destination address 3
1~247
3
CF-31
EzCOM destination register 3
0000~FFFF
0000
CF-32
EzCOM source register 3
0000~FFFF
0000
CF-33
EzCOM destination address 4
1~247
4
CF-34
EzCOM destination register 4
0000~FFFF
0000
CF-35
EzCOM source register 4
0000~FFFF
0000
CF-36
EzCOM destination address 5
1~247
5
CF-37
EzCOM destination register 5
0000~FFFF
0000
CF-38
EzCOM source register 5
0000~FFFF
0000
・Set for the use of EzCOM function.
・For more information, refer to the User’s guide.
USB node code
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
CF-50
USB communication
node selection
1~247
1
・Sets the USB code in the case of multiple inverter
connections with ProDriveNext(PC software), as is also
required in the ProDriveNext side.

4-46
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[HA-01]~[HA135]
■Parameter mode (H code)
Auto-tuning
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
HA-01
Auto-tuning selection
00(
Disable
)/
01(No-rotation)/
02(Rotation)/
00
HA-02
RUN command selection
at Auto-tuning
00(
RUN-key)/
01(By [AA111]/
and [AA211])
00
HA-03
Online auto-tuning selection
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
00
・After setting the motor basic parameters, by the
auto-tuning operation you can get the constant of the
motor.
・For no-rotation auto-tuning, the following variables are
acquired, IM:[Hb110]~[Hb114], SM(PMM):[Hd110]~
[Hd114].
・For rotation auto-tuning, the following variables are
acquired, IM:[Hb110]~[Hb118]. Keep the operation
conditions, as the motor can rotate.
・Auto-tuning start is done by the RUN-key ([HA-02] Initial
value)
・If [HA-04] is changed, the display unit will change also.
Motor stabilization (Hunting)
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
HA110
Stabilization
constant, 1st-motor
0~1000(%)
100
・For hunting in driving pumps or fans, lower the value of
the stabilization constant for adjustment.
・In the case that the duty is relatively light, and occurs
hunting, increase the stabilization constant.
Control mode response adjustment
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
HA115
Speed response, 1st motor
0~1000(%)
100
・You can adjust the speed response in the operation
control of the inverter.
⇒
[AA121] control mode
[HA140]~[HA154]
Control response gain
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
HA120
ASR gain switching
mode selection, 1st-motor
00([CAS] terminal)/
01(Change set)
00
HA121
Gain switching time,
1st-motor
0~10000(ms) 100
HA122
ASR gain mapping
intermediate speed 1, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz) 0.00
HA123
ASR gain mapping
intermediate speed 2, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz) 0.00
HA124
ASR gain mapping
Maximum speed, 1st-motor
0.00~590.00(Hz) 0.00
HA125
ASR gain mapping
P-gain 1, 1st-motor
0.0~1000.0(%) 0.0
HA126
ASR gain mapping I-
gain
1, 1st-motor
0.0~1000.0(%) 0.0
HA127
ASR gain mapping
P-gain 1 at P-control, 1st-motor
0.00~10.00 1.00
HA128
ASR gain mapping
P-gain 2, 1st-motor
0.0~1000.0(%) 100.0
HA129
ASR gain mapping I-
gain
2, 1st-motor
0.0~1000.0(%) 100.0
HA130
ASR gain mapping
P-gain 2 at P-control, 1st-motor
0.00~10.00 1.00
HA131
ASR gain mapping
P-gain 3, 1st-motor
0.0~1000.0(%) 100.0
HA132
ASR gain mapping I-
gain
3, 1st-motor
0.0~1000.0(%) 100.0
HA133
ASR gain mapping
P-gain 4, 1st-motor
0.0~1000.0(%) 100.0
HA134
ASR gain mapping I-
gain
4, 1st-motor
0.0~1000.0(%) 100.0
・Current response of the motor control ca be changed.
・In case of [CAS] terminal switching, [HA140]=00
・In case of Control Gain Mapping, [HA140]=01
Terminal [CAS]
ON
[HA141] set time
[HA150]/
[HA151]/
[HA152]
[HA153]/
[HA154]/
[HA155]
0Hz
Intermediate
frequency 1
Intermediate
frequency 2
Maximum
frequency
Gain 1
Gain 2
Gain 3
Gain 4
Highest
frequency

4-47
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[HA230]~[HA254]
2nd motor When Intelligent Input terminal 024[SET] is enabled.
Code/Name
Range
(unit)
Initial
value
HA210
Stabilization constant, 2nd-motor
0~1000(%)
100
HA215
Speed response, 2nd motor
Same as HA115
HA220
ASR gain switching mode selection,
2nd-motor
Same as HA120
HA221
Gain switching time, 2nd-motor
Same as HA121
HA222
ASR gain mapping intermediate
speed 1, 2nd-motor
Same as HA122
HA223
ASR gain mapping intermediate
speed 2, 2nd-motor
Same as HA123
HA224
ASR gain mapping Maximum speed,
2nd-motor
Same as HA124
HA225
ASR gain mapping P-gain 1,
2nd-motor
Same as HA125
HA226
ASR gain mapping I-gain 1,
2nd-motor
Same as HA126
HA227
ASR gain mapping P-gain 1 at
P-control, 2nd-motor
Same as HA127
HA228
ASR gain mapping P-gain 2,
2nd-motor
Same as HA128
HA229
ASR gain mapping I-gain 2,
2nd-motor
Same as HA129
HA230
ASR gain mapping P-gain 2 at
P-control, 2nd-motor
Same as HA130
HA231
ASR gain mapping P-gain 3,
2nd-motor
Same as HA131
HA232
ASR gain mapping I-gain 3,
2nd-motor
Same as HA132
HA233
ASR gain mapping P-gain 4,
2nd-motor
Same as HA133
HA234
ASR gain mapping I-gain 4,
2nd-motor
Same as HA134
[Hb102]~[Hb108]
Basic parameters for Induction motor
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
Induction motor (IM)
Hb102
Async.
Motor capacity
setting, 1st-motor
0.01 ~ 630.00
(kW)
Motor capacity setting
Hb103
Async.
Motor poles
setting, 1st-motor
2~48 (Pole)
4
Hb104
Async.
Motor Base
frequency setting,
1st-motor
10.00 ~ 590.00
(Hz)
60.00(JPN)(USA)/
50.00(EU)(ASIA)(CHN)
Hb105
Async.
Motor Maximum
frequency setting,
1st-motor
10.00 ~ 590.00
(Hz)
60.00(JPN)(USA)/
50.00(EU)(ASIA)(CHN)
Hb106
Async.
Motor rated
voltage, 1st-motor
1~1000 (V)
(200V Class)
200(JPN)
230(EU)(USA)(ASIA)(CHN)
(400V Class)
400(JPN)(EU)(ASIA)(CHN)
460(USA)
Hb108
Async.
Motor rated
current,
1st-motor
0.01~10000.00
(A)
Motor capacity setting
・If the motor capacity [Hb102] and number of poles
[Hb103] are changed, the motor characteristics are set
according to the internal Hitachi table values.
・The output is decided by setting the frequency and
voltage. Below there is an example of V / f control.
・By setting the motor rated current, a reference current
for the motor protection is set.
※
Initial value depends on the inverter.
Motor t
ypical data
Code Range of values
(Unit)
Capacity
[Hb102]
0.01~630.00 (kW)
Number of poles
[Hb103]
2~48 (poles)
Frequency
[Hb104]
10.00~590.00 (Hz)
[Hb105]
10.00~590.00 (Hz)
Voltage
[Hb106]
1~1000 (V)
Current
[Hb108]
0.01~9999.99 (A)
Output
voltage
Motor rated
voltage
(Ex.)200V
Command
frequency (Hz)
Base frequency
(Eg.)60Hz
Maximum
frequency

4-48
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[Hb110]~[Hb131]
Induction motor constants
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
Induction Motor (IM)
Hb110
Async.
Motor constant R1,
1st-motor
0.000001~1000.000000 (Ω)
Motor
capacity
setting
Hb112
Async.
Motor constant R2,
1st-motor
0.000001~1000.000000 (Ω)
Motor
capacity
setting
Hb11
Async.
Motor constant L,
1st-motor
0.000001~1000.000000 (mH)
Motor
capacity
setting
Hb116
Async.
Motor constant Io,
1st-motor
0.01~1000.00 (A)
Motor
capacity
setting
Hb118
Async.
Motor constant J,
1st-motor
0.00001~10000.00000 (kgm2)
Motor
capacity
setting
・If the motor capacity[Hb102] and number of poles
[Hb103] are changed, the motor characteristics are set
according to the internal Hitachi table values.
・For no-rotation auto-tuning, the following variables
are acquired:[Hb110]~[Hb114].
・For rotation auto-tuning, the following variables are
acquired:[Hb110]~[Hb118]
・It is possible to input the data obtained from the motor
manufacturer. However, it must also include the data of
the wiring and the like.
Minimum frequency setting
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
Hb130
Minimum frequency,
1st-motor
0.00~10.00(Hz)
0.50
Hb131
Reduced voltage start
time, 1st-motor
0~2000(ms)
36
・If the torque at the time of start-up is not enough, you
can change the settings to raise the lowest frequency.
・Raise the minimum frequency, if the trip occurs, set a
longer time of reduced voltage start selection.
[Hb140]~[Hb146]
Manual torque boost adjustment
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
Hb140
Manual torque
boost operational mode
selection, 1st-motor
00(
Disabled
)/
01(Enabled)/
02(Only forward)/
03(Only reverse)
01
Hb141
Manual torque
boost value, 1st-motor
0.0~20.0(%)
1.0
Hb142
Manual torque
boost Peak speed, 1st-motor
0.0~50.0(%)
5.0
・In the manual boost operation mode only forward or
reverse boost can be selected.
・Example [Hb140]=02
Eco Drive function
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
Hb145
Eco drive enable,
1st-motor
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
00
Hb146
Eco drive response
adjustment, 1st-motor
0~100(%)
50
・In V/f control, if the energy saving operations is enabled,
enters an energy saving control.
FW
Output
frequency
Output
voltage
Minimum frequency
[Hb130]
00 10ms 60ms
・・・
Reduced voltage
start [Hb131]
Output
frequency
Base frequency (100%)
[Hb141]
[Hb142]
100
Output voltage (%)
Forward
Reverse
Base frequency (100%)

4-49
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[Hb150]~[Hb180]
Free V/f setting
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
Hb150
Free-V/f frequency 1,
0.00
~
[Hb152](Hz)
0.00
Hb151
Free V/f voltage 1
0.0~1000.0(V) 0.0
Hb152
Free V/f frequency 2
[Hb150]
~
[Hb154](Hz)
0.00
Hb153
Free V/f voltage 2
0.0~1000.0(V) 0.0
Hb154
Free V/f frequency 3
[Hb152]
~
[Hb156](Hz)
0.00
Hb155
Free V/f voltage 3
0.0~1000.0(V) 0.0
Hb156
Free V/f frequency 4
[Hb154]
~
[Hb158](Hz)
0.00
Hb157
Free V/f voltage 4
0.0~1000.0(V) 0.0
Hb158
Free V/f frequency 5
[Hb156]
~
[Hb160](Hz)
0.00
Hb159
Free V/f voltage 5
0.0~1000.0(V) 0.0
Hb160
Free V/f frequency 6
[Hb158]
~
[Hb162](Hz)
0.00
Hb161
Free V/f voltage 6
0.0~1000.0(V) 0.0
Hb162
Free V/f frequency 7
[Hb160]
~
[Hb105](Hz)
0.00
Hb163
Free V/f voltage 7
0.0~1000.0(V) 0.0
・Frequency 1(f1)~frequency (f7) and the corresponding
voltage 1(V1)~voltage 7(V7) are set below the base
frequency and rated voltage. In the case of a
high-frequency motor, set the base/highest frequency
the first.
V/f feedback control adjustment
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
Hb170
Slip Compensation
P-gain with encoder
0~1000(%)
100
Hb171
Slip Compensation
I-gain with encoder
0~1000(%)
100
・When [AA121] is set as feedback control, slip
compensation is possible.
Output adjustment gain
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
Hb180
Output voltage gain
0~255(%)
100
・When the motor is hunting, you might want to improve
the adjustment of the voltage gain.
[Hb202]~[Hb280]
2nd motor When Intelligent Input terminal 024[SET] is enabled.
Code/Name
Range
(unit)
Initial
value
Induction Motor (IM)
Hb202
Capacity selection
,
2nd-motor Same as
Hb102
Hb203
Number of poles
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb103
Hb204
Base frequency
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb104
Hb205
Maximum frequency
,
2nd-motor
Same as Hb105
Hb206
Rated voltage
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb106
Hb208
Rated current
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb108
Hb210
Constant
R1
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb110
Hb212
Constant
R2
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb112
Hb214
Constant
L
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb114
Hb216
Constant
Io
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb116
Hb218
Constant
J
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb118
2nd motor When Intelligent Input terminal 024[SET] is enabled.
Code/Name
Range
(unit)
Initial
value
Hb230
Minimum frequency
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb130
Hb231
Reduced voltage start
time
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb131
Hb240
Manual torque boost operation mode
selection, 2nd-motor
Same as Hb140
Hb241
Manual torque boost value
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb141
Hb242
Manual torque boost peak
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb142
Hb245
Energy saving operation selection
,
2nd-motor
Same as Hb145
Hb246
Energy saving mode adjustment
,
2nd-motor
Same as Hb146
Hb250
Free V/f
frequency (1)
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb150
Hb251
Free V/f
voltage (1)
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb151
Hb252
Free V/f
frequency (2)
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb152
Hb253
Free V/f voltage (2)
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb153
Hb254
Free V/f frequency (3)
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb154
Hb255
Free V/f voltage (3)
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb155
Hb256
Free V/f frequency (4)
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb156
Hb257
Free V/f voltage (4)
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb157
Hb258
Free V/f frequency (5)
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb158
Hb259
Free V/f voltage (5)
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb159
Hb260
Free
V/f frequency (6)
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb160
Hb261
Free V/f voltage (6)
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb161
Hb262
Free V/f frequency (7)
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb162
Hb263
Free-setting V/f voltage (7)
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb163
Hb270
Slip Compensation P
-
gain with encoder
,
2nd-motor
Same as Hb170
Hb271
Slip Compensation I
-
gain with encoder
,
2nd-motor
Same as Hb171
Hb280
Output voltage gain
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hb180
Output
frequency(Hz)
f1 f2 f3 f4 f5 f6 f7
0
V2,V3
V1
V5
V6
V7
V4
Output voltage(V)
Base
frequency
Maximum
frequency
Voltage
rated value

4-50
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[HC101]~[HC121]
Automatic torque boost adjustment
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
HC101
Automatic torque boost
voltage compensation gain, 1st-motor
0~255(%)
100
HC102
Automatic torque boost slip
compensation gain, 1st-motor
0~255(%)
100
・If is chosen the automatic torque boost control
function in [AA121], adjustments can be made.
For more information, refer to the user’s guide.
Sensorless vector control start
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
HC110
Zero speed area limit,
1st-motor
0~100(%)
80
HC111
Boost value at start,
1st-motor (IM-SLV,IM-CLV)
0~50(%)
10
HC112
Boost value at start,
1st-motor (IM-0Hz-SLV)
0~50(%)
10
・When [AA121] is Sensorless vector control or 0Hz-Area
sensor less vector control, start boost is possible.
Secondary resistor compensation function
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
HC113
Secondary resistance
correction, 1st-motor
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
00
・This control method, in vector control (with encoder/
sensorless/0Hz), gets the temperature of the motor,
and reduces the speed variation due to temperature
change.
・If you want to use this function, use a thermistor PB-41E
from Shibaura Electronics(Ltd.) with [Cb-40]=02(NTC).
Reverse run protection function
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
HC114
Reverse run
protection enable, 1st-motor
00(Disable)/01(Enable) 00
・This function is to prevent reverse output in a low
frequency range for vector control such as (SLV/0Hz
SLV/CLV)
Motor control adjustment gain
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
HC120
Time constant of torque current
reference filter, 1st-motor
0~100(ms)
2
HC121
Feedforward gain compensation
adjustment for speed, 1st-motor
0~1000(%)
0
・[HC120] can put into effect a filter for torque command
of sensorless vector control, 0Hz sensorless vector
control and vector control with encoder.
・[HC121] adjust the compensation of the feedforward for
torque command of sensorless vector control, 0Hz
sensorless vector control and vector control with
encoder.
[HC201]~[HC220]
2nd motor When Intelligent Input terminal 024[SET] is enabled.
Code/Name
Range
(unit)
Initial
value
HC201
Automatic torque boost voltage
compensation gain, 2nd-motor
Same as HC101
HC202
Automatic torque boost slip
compensation gain, 2nd-motor
Same as HC102
HC210
Zero speed area limit, 2nd-motor
Same as HC110
HC211
Boost value at start, 2nd-motor
(IM-SLV,IM-CLV)
Same as HC111
HC212
Boost value at start, 2nd-motor
(IM-0Hz-SLV)
Same as HC112
HC213
Secondary resistor compensation
enable, 2nd-motor
Same as HC113
HC214
Counter direction run protection
selection, 2nd-motor
Same as HC114
HC220
Torque current reference filter time
constant, 2nd-motor
Same as HC120
HC221
Speed feedforward compensation
gain, 2nd-motor
Same as HC121
4-51
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[Hd102]~[Hd118]
(SM/PMM) basic parameters
Code/Name
Range (unit)
Initial value
Permanent Magnet Sync. Motor(SM/PMM)
Hd102
Sync.
Motor capacity
setting, 1st-motor
0.01~630.00
(kW)
Factory setting
Hd103
Sync.
Motor capacity
setting, 1st-motor
2~48(Pole)
4
Hd104
Sync.
Base frequency
setting, 1st-motor
10.00~590.00
(Hz)
60.00(JPN)(USA)/
50.00(EU)(ASIA)(CHN)
Hd105
Sync.
Maximum
frequency setting,
1st-motor
10.00~590.00
(Hz)
60.00(JPN)(USA)/
50.00(EU)(ASIA)(CHN)
Hd106
Sync.
Motor rated
voltage, 1st-motor
1~1000
(V)
(200V Class)
200(JPN)
230(EU)(USA)(ASIA)(CHN)
(400V Class)
400(JPN)(EU)(ASIA)(CHN)
460(USA)
Hd108
Sync.
Motor rated
current, 1st-motor
0.01~10000.00
(A)
Factory setting
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
Permanent Magnet
Synchronous Motor
(SM/PMM)
Hd110
Sync. Motor
Constant R, 1st-motor
0.000001~
1000.000000 (Ω)
Factory
setting
Hd112
Sync. Motor
Constant Ld, 1st-motor
0.000001~
1000.000000 (mH)
Factory
setting
Hd114
Sync. Motor
Constant Lq, 1st-motor
0.000001~
1000.000000 (mH)
Factory
setting
Hd116
Sync. Motor
Constant Ke, 1st-motor
0.1~100000.0
(mVs/rad)
Factory
setting
Hd118
Sync. Motor
Constant J, 1st-motor
0.00001~
10000.00000 (kgm2)
Factory
setting
・Motor capacity and number of poles will be set by
Hitachi characteristics table
・For SM/PMM, frequency, voltage, and the motor
characteristics are necessary.
・If the maximum current is decided, sets with a margin
the overcurrent detection level [bb160].
Motor typical data
Code Range of values (unit)
Capacity
[Hd102]
0.01~630.00 (kW)
Number of poles
[Hd103]
2~48 (Poles)
Frequency
[Hd104]
10.00~590.00 (Hz)
[H
d105]
10.00~590.00 (Hz)
Voltage
[Hd106]
1~1000 (V)
Current
[Hd108]
0.01~10000.00 (A)
※
Initial value depends on the inverter.
・If motor capacity [Hd102], number of poles [Hd103] are
changed, the motor characteristics are set according to
the internal Hitachi table values.
・By auto-tuning at stop, values of [Hd110]~[Hd114]
can be acquired.
[Hd130]~[Hd218]
Minimum frequency settings
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
Hd130
Minimum Frequency for
Sync.M, 1st-motor
0~50(%)
8
Hd131
No-Load current for
Sync.M, 1st-motor
0~100(%)
10
・By base frequency[Hd104]×[Hd130], change from Sync.
to sensorless is possible.
・By [Hd131], the sensorless vector control no-load
current is set.
Magnetic pole position estimation SM(PMM)
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
Hd132
Starting Method for
Sync.M, 1st-motor
00(
Synchronous
)/
01(Initial position
estimate)
00
Hd133
IMPE 0V wait number for
Sync.M, 1st-motor
0~255
3
Hd134
IMPE detect wait
number for Sync.M, 1st-motor
0~255
3
Hd135
IMPE detect number for
Sync.M, 1st-motor
0~255
10
Hd136
IMPE voltage gain for
Sync.M, 1st-motor
0~200(%)
100
Hd137
IMPE Mg-pole position
offset, 1st-motor
0~359(°)
15
・By setting [Hd132] to initial position estimate, it will
estimate the pole position, for next runs will use the
saved position, unless it gets disconnected
・Offset [Hd137] is added at the first start when doing
reverse motion.
IVMS setting
Code/ Range(unit)
Initial
Value
Hd-41
Carrier frequency at IVMS
0.5~16.0(kHz)
2.0
Hd-42
Filter gain of current
detection at IVMS
0~1000
100
Hd-43
VMS P-Gain for speed
control, SM(PMM)-IVMS
00,01,02,03 00
Hd-44
Open phase switching
threshold compensation
00(disable)/01(enable) 00
Hd-45
P gain for speed control
SM(PMM)-IVMS
0~1000
100
Hd-46
I gain for speed control
SM(PMM)-IVMS
0~10000
100
Hd-47
IVMS Wait time for open
phase switching
0~1000
100
Hd-48
Limitation of decision about
the drive direction, SM(PMM)-IVMS
00(disable)/01(enable) 00
Hd-49
open phase voltage detection
timing adjustment, SM(PMM)-IVMS
0~1000
10
Hd-50
Minimum pulse width
adjustment, SM(PMM)-IVMS
0~1000
100
Hd-51
IVM threshold current limit
0~255
100
Hd-52
IVMS threshold gain
0~255
100
・Above parameters are for adjustment in SM(PMM) driving with
IVMS

4-52
Chapter 4
For parameter configuration
[Hd202]~[Hd241]
2nd motor When Intelligent Input terminal 024[SET] is enabled.
Code/Name
Range
(unit)
Initial
value
Perm. Magnet Sync. Motor (SM/PMM)
Hd202
Sync. Motor capacity setting, 2nd-motor
Same as Hd102
Hd203
Sync. Motor poles setting, 2nd-motor
Same as Hd103
Hd204
Sync. Base frequency setting,
2nd-motor
Same as Hd104
Hd205
Sync. Maximum frequency setting,
2nd-motor
Same as Hd105
Hd206
Sync. Motor rated voltage,
2nd-motor
Same as Hd106
Hd208
Sync.Motor rated current,
2nd-motor
Same as Hd108
Hd210
Sync.Motor constant R, 2nd
-
motor Same as
Hd110
Hd212
Sync.Motor constant
Ld
,
2nd-motor
Same as Hd112
Hd214
Sync.Motor constant
Lq
,
2nd-motor
Same as Hd114
Hd216
Sync.Motor constant
Ke
,
2nd-motor
Same as Hd116
Hd218
Sync.Motor constant
J
, 2nd-motor Same as
Hd118
2nd motor When Intelligent Input terminal 024[SET] is enabled.
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
Hd230
Minimum Frequency for Sync.M,
2nd-motor
Same as Hd130
Hd231
No-
Load current for Sync.M,
2nd-motor
Same as Hd131
Hd232
Starting Method for Sync.M,
2nd-motor
Same as Hd132
Hd233
IMPE 0V wait number for
Sync.M, 2nd-motor
Same as Hd133
Hd234
IMPE detect wait number for
Sync.M, 2nd-motor
Same as Hd134
Hd235
IMPE detect number for Sync.M,
2nd-motor
Same as Hd135
Hd236
IMPE voltage gain for Sync.M,
2nd-motor
Same as Hd136
Hd2
37 IMPE Mg
-
pole position offset,
2nd-motor
Same as Hd137
[oA-10]~[oA-32][ob-01]~[ob-04]
■Parameter mode (o code)
・o parameters are displayed by the [UA-11] = 01. This
configuration is not necessary except when option is
used.
・For more information, refer to the User’s guide of the
corresponding option.
Optional board error operation
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
Slot 1
oA-10
Operation
selection on option card
error (SLOT-1)
00(Error)/
01(Continue operation)
00
oA-11
Communication
Watch Dog Timer (SLOT-1)
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
oA-12
Action selection
at communication error
(SLOT-1)
00(Error)/
01(Tripping after decelerating
and stopping the motor)/
02(Ignore error)/
03(Free-run stop)/
04(Decelerating and stopping)
00
oA-13
RUN command
selection at start up
(SLOT-1)
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
0.00
Slot 2
oA-20
Operation
selection on option card
error (SLOT-2)
00(Error)/
01(Continue operation)
00
oA-21
Communication
Watch Dog Timer (SLOT-2)
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
oA-22
Action selection
at communication error
(SLOT-2)
00(Error)/
01(Tripping after decelerating
and stopping the motor)/
02(Ignore error)/
03(Free-run stop)/
04(Decelerating and stopping)
00
oA-23
RUN command
selection at start up
(SLOT-2)
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
0.00
Slot 3
oA-30
Operation
selection on option card
error (SLOT-3)
00(Error)/
01(Continue operation)
00
oA-31
Communication
Watch Dog Timer (SLOT-3)
0.00~100.00(s)
0.00
oA-32
Action selection
at communication error
(SLOT-3)
00(Error)/
01(Tripping after decelerating
and stopping the motor)/
02(Ignore error)/
03(Free-run stop)/
04(Decelerating and stopping)
00
oA-33
RUN command
selection at start up
(SLOT-3)
00(Disable)/
01(Enable)
0.00
・
For more information, refer to the User’s guide.
P1-FB Optional board encoder input setting
Code/Name Range (unit)
Initial
value
ob-01
Encoder constant setting
0~65535(Pulse)
1024
ob-02
Encoder position selection
00(A Phase, Cos lead)/
01(B Phase, Sin lead)
0
ob-03
Motor gear ratio
Numerator
1~10000
1
ob-04
Motor gear ratio
Denominator
1~10000
1
 Loading...
Loading...