Page 1
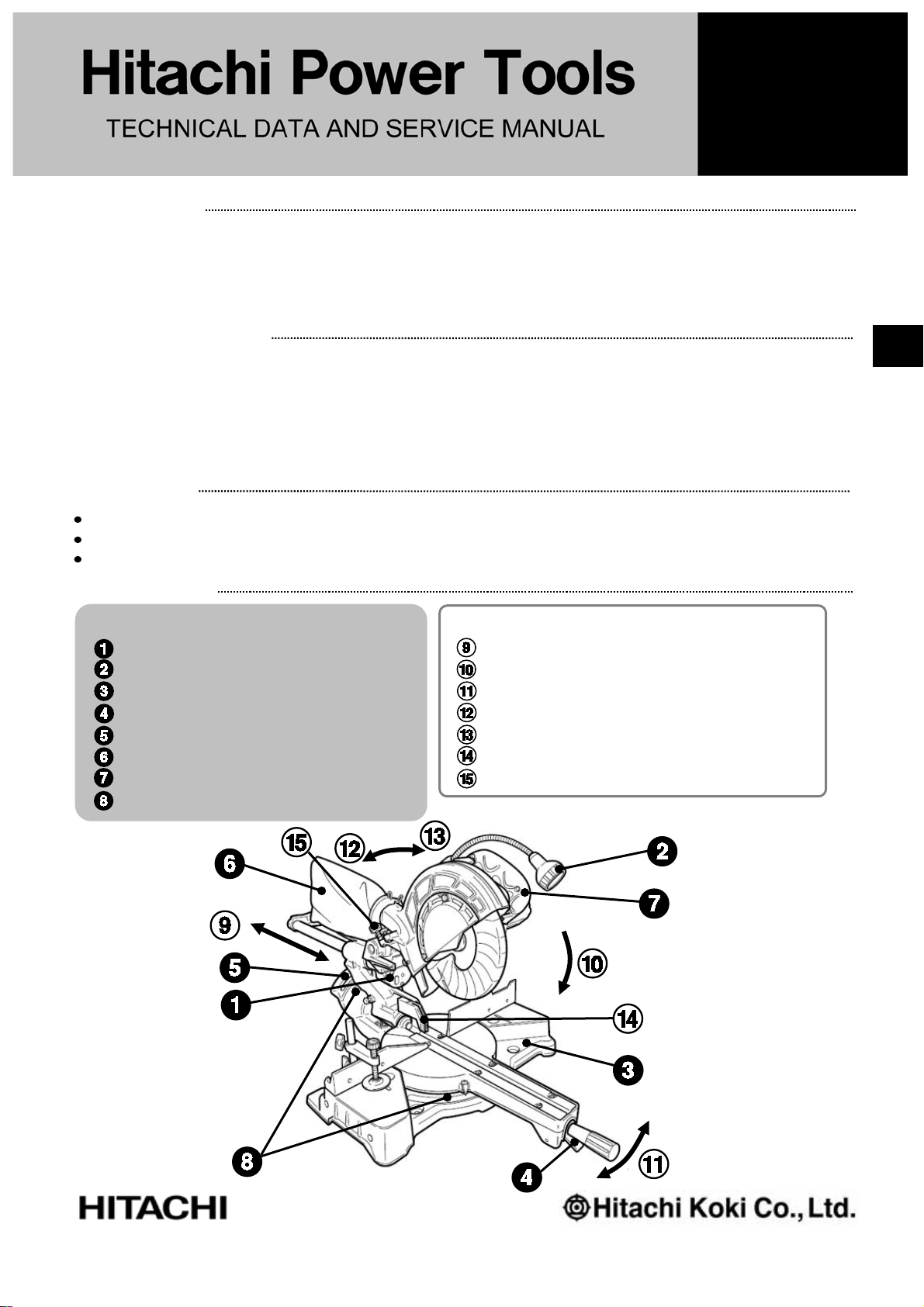
PRODUCT NAME
Hitachi Slide Compound Miter Saw
Models C 8FSE, C 8FSHE
LIST Nos.
C 8FSE: E948
C 8FSHE: E949
Feb. 2008
MARKETING OBJECTIVE
The new slide compound miter saws Models C 8FSE and C 8FSHE are developed to bring to the European
market at the prices as low as the competitors’ products. The Model C 8FSHE is equipped with a laser marker
for easier alignment with the ink line and an LED light to illuminate the working surface brightly. In addition, the
Model C 8FSE that is mostly the same as the Model C 8FSHE except that it is not equipped with the laser
marker and the LED light is introduced in tandem with the Model C 8FSHE. With the new Models C 8FSE and
APPLICA TIONS
Cutting various types of wood workpieces
Cutting workpieces of plywood, decoration panels, soft fiberboards and hard boards
Cutting aluminum sashes
SELLING POINTS
[ NEW FEATURES ]
Laser marker (Only the Model C 8FSHE)
LED light (Only the Model C 8FSHE)
Lightweight
Positive angle stoppers
Bevel cutting range: Left 48° to right 5°
High dust collecting performance
Soft grip handle
Legible scale
<Same features as the conventional models>
Slide cutting
Press cutting
Miter cutting
Right and left bevel cutting
Compound miter and left bevel cutting
Splinter guard, also serving for cut alignment
Groove cutting
SPECIFICATIONS AND PARTS ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE FOR IMPROVEMENT.
C
C 8FSHE
International Sales Division
Page 2

REMARK:
For more information about HANDLING INSTRUCTIONS, visit our website at:
http://www.hitachi-koki.com/manual_view_export/
Throughout this TECHNICAL DATA AND SERVICE MANUAL, a symbol(s) is(are) used in the place of
company name(s) and model name(s) of our competitor(s). The symbol(s) utilized here is(are) as follows:
Symbols Utilized
P1 DEWALT DW707
P2 DEWALT DW777
P3 DEWALT DW712
B BOSCH GCM8S
Competitors
Company Name Model Name
Page 3

CONTENTS
Page
SELLING POINT DESCRIPTIONS-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1
SPECIFICATIONS --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------6
1. Specifications
COMPARISONS WITH SIMILAR PRODUCTS--------------------------------------------------------------------------8
1. Specification comparisons
PRECAUTIONS IN SALES PROMOTION------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 12
1. Safety instructions
2. Precautions requiring particular attention during sales promotion
ADJUSTMENT AND OPERATIONAL PRECAUTIONS------------------------------------------------------------- 16
1. Confirmation of saw blade lower limit position
2. Confirmation for use of sub fence (Optional accessory)
3. Position adjustment of laser line (Only the Model the C 8FSHE)
4. How to use the vise assembly
5. Adjustment of table insert position
6. Cutting operation
ADJUSTMENT OF COMPONENTS ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 24
1. Bevel angle adjustment
2. Ball bushing (Linear bearing)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 6
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 8
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 12
------------------------------------------ 15
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- 16
---------------------------------------------------------- 16
-------------------------------------------- 17
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 18
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 18
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 19
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 24
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 24
PACKING ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 25
REPAIR GUIDE---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 26
1. Precautions in disassembly and reassembly
2. Troubleshooting guide
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 43
---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 26
STANDARD REPAIR TIME (UNIT) SCHEDULES-------------------------------------------------------------------- 48
Assembly diagram for C 8FSHE
Assembly diagram for C 8FSE
Page 4
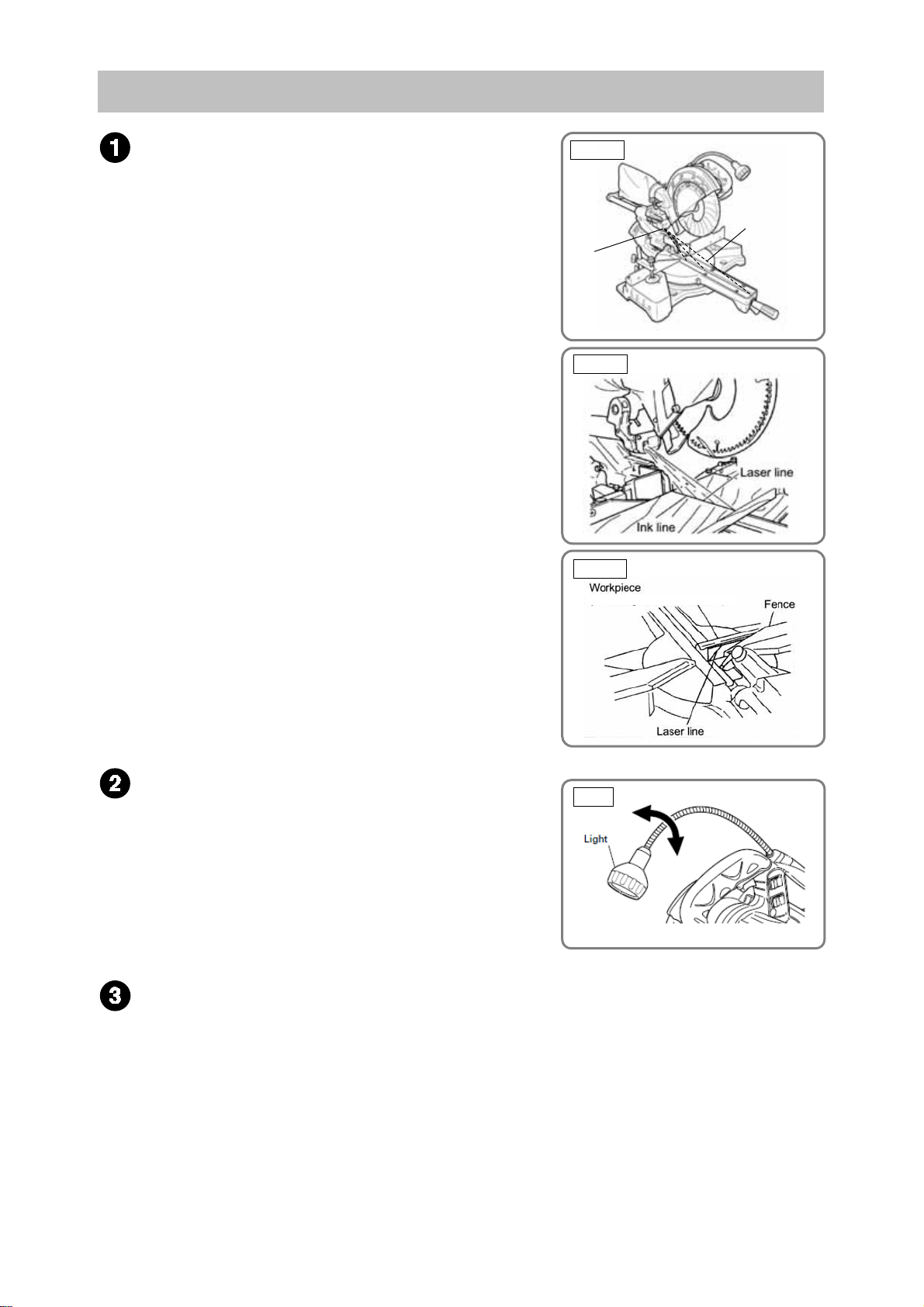
SELLING POINT DESCRIPTIONS
r
r
Laser marker (Only the Model C 8FSHE)
Use the laser marker for aligning with the ink line on the
workpiece.
(1) Cutting position can be properly adjusted by aligning the
positioning ink line with the laser line. There is no need to
make a long ink line on the workpiece.
(2) There is no need to lower the motor head to align with the
ink line because the laser marker makes a laser line on the
workpiece. In addition, cutting position can be easily
adjusted because the operator can hold the workpiece with
both hands to move.
(3) Cutting position can be easily adjusted because the laser
line can be aligned with an optionally angled ink line.
(4) Even the workpieces such as crown moldings and base
boards that have decorative surfaces and are difficult to be
made an ink line can be cut just by aligning the laser line
with the ink line on the fence side. The laser line is
adjusted to the width of the saw blade at the time of factory
shipment. Depending upon the user's cutting choice, the
laser line can be aligned with the left side of the cutting
width (saw blade) or the ink line on the right side. Adjust
the position of the laser line according to "Position
adjustment of laser line" on page 17.
Fig. 1-a
Lase
marke
Fig. 1-b
Fig. 1-c
(molding, base board, etc.)
Laser beam
LED light (Only the Model C 8FSHE)
The Model C 8FSHE is equipped with an LED light to light up
over a table brightly. The two LEDs incorporated in it light up the
materials and the point of the saw blade brightly. The LED light
can freely move at the time of right and left bevel cutting
because the support is flexible. Therefore, it lights up the
materials and the point of the saw blade brightly at any time.
Fig. 2
Lightweight
The Model C 8FSE is most lightweight (14 kg) in the class of 8” (216 mm) slide compound miter saws
because the reinforcement rib of the table is placed in the most suitable position.
-1-
Page 5
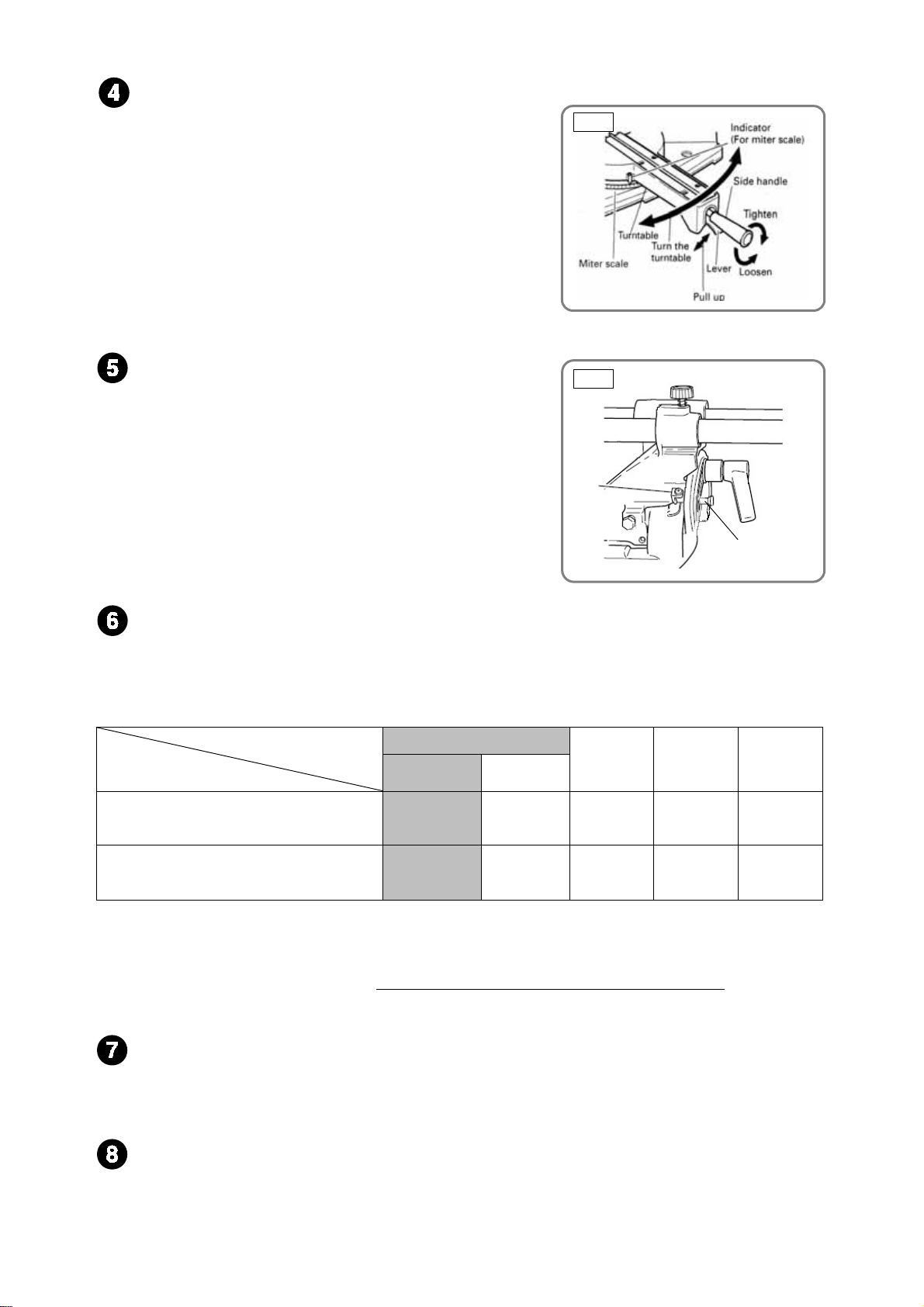
Positive angle stoppers
The Models C 8FSE and C 8FSHE have positive angle
stoppers in the turn table at the right and the left of the 0°
center setting, at 15°, 22.5°, 31.6° and 45° settings.
Thanks to the positive angle stoppers, positioning can be
done more securely than the ball index method utilized in
the current Model C 8FB2. In addition, a lever is provided
at the lower tip of the turn table to secure or release the
positive angle stoppers.
Adjustment of the turn table and positioning can be easily
done while holding the side handle.
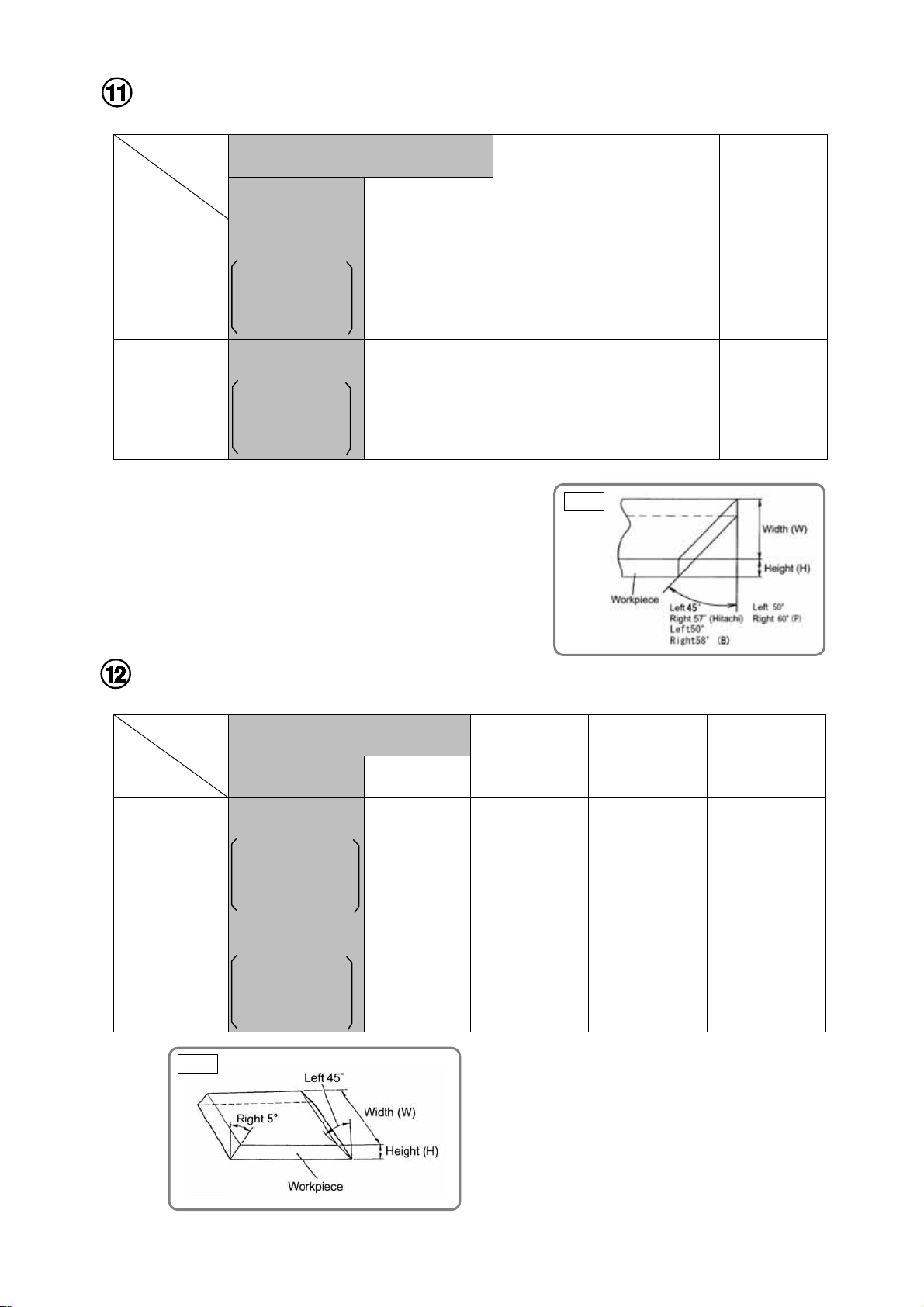
Bevel cutting range: Left 48° to right 5°
Possible range of bevel cutting is from left 48 degrees to right 5
degrees. By the simple operation of the set pin, you can set the
position of the right angle and left 45 degrees.
In addition, setting to approximately 30 degrees and 33.9
degrees for crown molding cutting can be done by this set pin.
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Set pin
High dust collecting performance
The dust collecting performance of the Models C 8FSE and C 8FSHE are remarkably higher than the other
models thanks to the adoption of new dust guide and gear case.
Table 1
Cutting
method
Press cutting *
(Size of the workpiece:
60 mm x 60 mm (2-3/8” x 2-3/8”))
Slide cutting *
(Size of the workpiece:
30 mm x 150 mm (1-3/16” x 5-29/32”))
*1: This is a method to cut a workpiece by shaking the motor head.
*2: This is a method to cut a workpiece by sliding the motor head from the front.
The dust collecting performance is obtained from the following formula:
Dust collecting performance (%) = x 100
1
2
Maker
Model
C 8FSHE
Weight of sawdust accumulated in the dust bag (g)
HITACHI
C 8FSE
75.0 25.0 5.9 31.3 62.2
80.0 45.0 11.0 72.3 74.5
Weight of all sawdust during cutting (g)
C 8FB2
P1 and P2 P3 B
(%)
Soft grip handle
The handles are widely covered with soft-touch elastomer (rubber-like soft resin).
It is slip-resistant and securely fits in the palm of a hand even if the gripping hand sweats.
Legible scale
The Models C 8FSE and C 8FSHE have legibly labeled angle scale and bevel scale while the current
Model C 8FB2 has the scale printed on the die casting.
-2-
Page 6
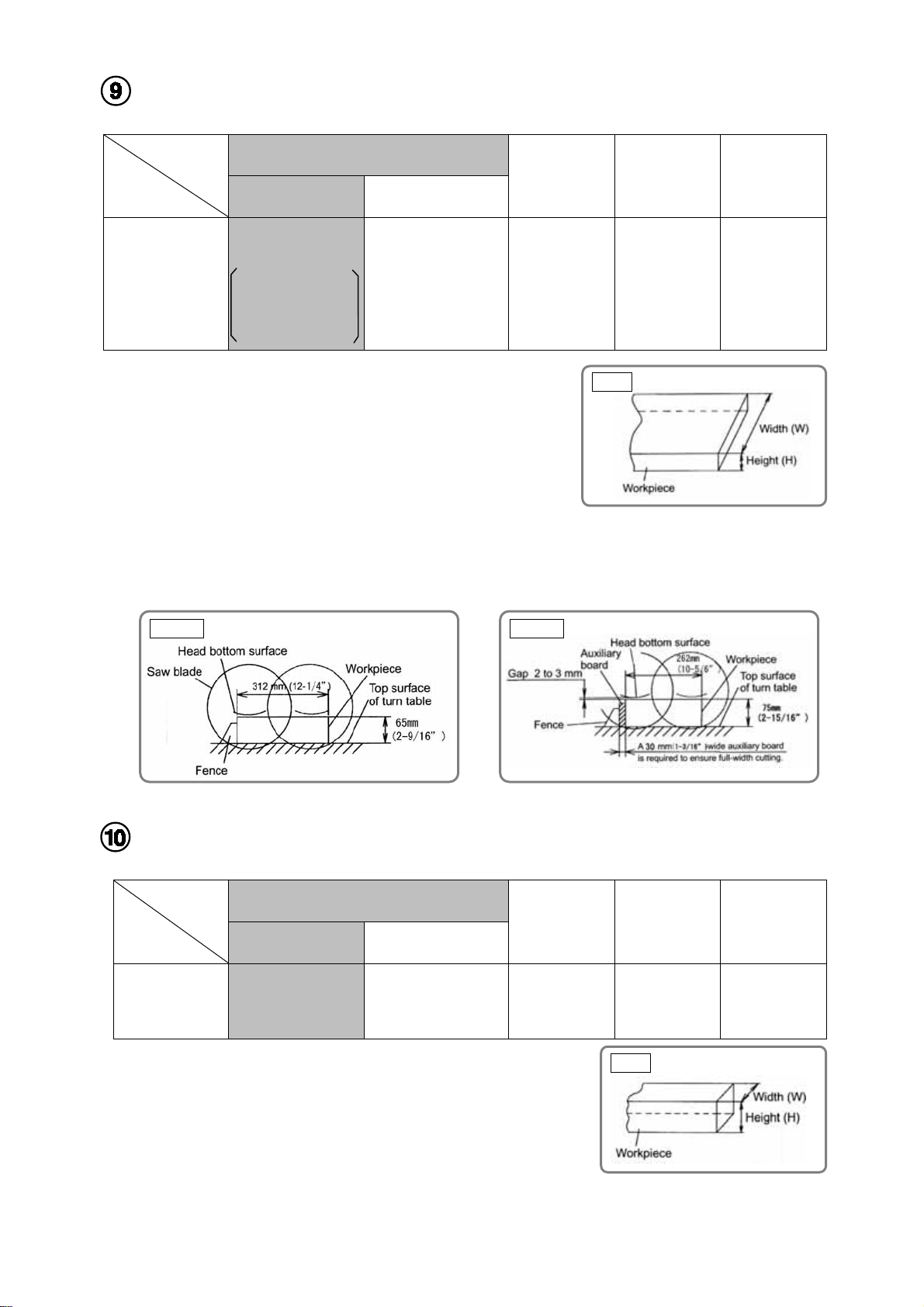
Slide cutting
dimensio
dimensio
Table 2
Maker
Max.
Model
cutting
n
Height x Width
(H x W)
C 8FSE
C 8FSHE
65 x 312
(2-9/16” x 12-1/4”)
75 x 262
(2-15/16” x 10-5/6”)
with aux. board
width 30 (1-3/16”)
HITACHI
C 8FB2
65 x 305
(2-9/16” x 12”)
75 x 265
(2-15/16” x 10-7/16”)
P1 and P2 P3 B
60 x 270
(2-3/8” x 10-3/8”)
Workpieces as wide as shown in Table 2 can be cut with the motor
70 x 300
(2-3/4” x 11-13/16”)
Fig. 5
Unit: mm (inch)
60 x 270
(2-3/8” x 10-3/8”)
head sliding. The lower limit position of the saw blade is factoryadjusted so that workpieces up to 65 mm (2-9/16") high and 312 mm
(12-1/4") wide can be cut as shown in Fig. 6-a. When cutting a
workpiece of 75 mm (2-15/16") in height as indicated in [ ] in Table 2,
adjust the saw so that there is a clearance of 2 to 3 mm (3/32" to 1/8")
between the bottom surface of the head and the top surface of the
workpiece at the lower limit position of the saw blade as shown in Fig. 6-b. (See the Instruction Manual
"Lower limit position of saw blade when cutting a large workpiece.")
Please note that, when cutting in this position, it is necessary to use an auxiliary board of 30 mm (1-3/16")
wide so that the workpiece on the fence side can be cut fully in width.
Fig. 6-bFig. 6-a
Press cutting
Table 3
Maker
Max.
cutting
Height x Width
Model
n
(H x W)
C 8FSE
C 8FSHE
65 x 65
(2-9/16” x 2-9/16”)
Press cutting with the head swiveling enables cutting square
workpieces as large as shown in Table 3 in a single sawing
operation. It is convenient for cutting narrow workpieces (Fig. 7).
HITACHI
65 x 65
(2-9/16” x 2-9/16”)
C 8FB2
60 x 60
(2-3/8” x 2-3/8”)
Unit: mm (inch)
P1 and P2 P3 B
70 x 40
(2-3/4” x 1-9/16”)
Fig. 7
60 x 68
(2-3/8” x 2-11/16”)
-3-
Page 7
Miter cutting
dimensio
dimensio
Table 4
Unit: mm (inch)
Maker
Max.
Model
cutting
n
Right and
left 45°
Height x Width
(H x W)
Right 57°
Height x Width
(H x W)
C 8FSE
C 8FSHE
65 x 220
(2-9/16” x 8-21/32”)
75 x 185
(2-15/16” x 7-1/4”)
with aux. board
width 20 (13/16”)
65 x 170
(2-9/16” x 6-11/16”)
75 x 140
(2-15/16” x 5-1/2”)
with aux. board
width 20 (13/16”)
HITACHI
C 8FB2
65 x 220
(2-9/16” x 8-21/32”)
65 x 175
(2-9/16” x 6-7/8”)
Wide workpieces as wide as shown in Table 4 can be cut
by swiveling the turn table (right and left).
The maximum cutting dimensions in [ ] in Table 4 are those
obtained by adjusting the lower limit position of the saw
blade indicated in Fig. 6-b, also with an auxiliary board.
P1 and P2 P3 B
60 x 190
(2-3/8” x 7-15/32”)
-
70 x 212
(2-3/4” x 6-11/32”)
70 x 160
(2-3/4” x 6-5/16”)
60 x 190
(2-3/8” x 7-15/32”)
60 x 155
(2-3/8” x 6-3/32”)
Fig. 8
Right and left bevel cutting
Maker
Max.
Model
cutting
n
Left 45°
Height x Width
(H x W)
Right 5°
Height x Width
(H x W)
Fig. 9
C 8FSE
C 8FSHE
45 x 312
(1-25/32” x 12-1/4”)
50 x 252
(1-15/16” x 9-15/16”)
with aux. board
width 30 (1-3/16”)
60 x 312
(2-9/16” x 12-1/4”)
70 x 252
(2-3/4” x 9-15/16”)
with aux. board
width 30 (1-3/16”)
HITACHI
C 8FB2
45 x 305
(1-25/32” x 12”)
Table 5
P1 and P2 P3 B
48 x 270
(1-7/8” x 10-3/8”)
--
50 x 300
(1-15/16” x 11-13/16”)
-
Unit: mm (inch)
42 x 270
(1-21/32” x 10-3/8”)
-
-4-
Page 8
Compound miter and bevel cutting
dimensio
Table 6
Max.
cutting
Maker
Model
n
C 8FSE
C 8FSHE
HITACHI
C 8FB2
Unit: mm (inch)
P1 and P2 P3 B
Miter left/right
45°
Bevel left 45°
Height x Width
(H x W)
Miter left/right
45°
Bevel right
45°
Height x Width
(H x W)
45 x 220
(1-25/32” x 8-21/32”)
50 x 170
(1-15/16” x 6-11/16”)
with aux. board
width 30(1-3/16”)
60 x 220
(2-9/16” x 8-21/32”)
70 x 170
(2-3/4” x 6-11/16”)
with aux. board
width 30(1-3/16”)
45 x 220
(1-25/32” x 8-21/32”)
----
48 x 190
(1-7/8” x 7-15/32”)
50 x 212
(1-15/16” x 6-11/32”)
42 x 190
(1-21/32” x 7-15/32”)
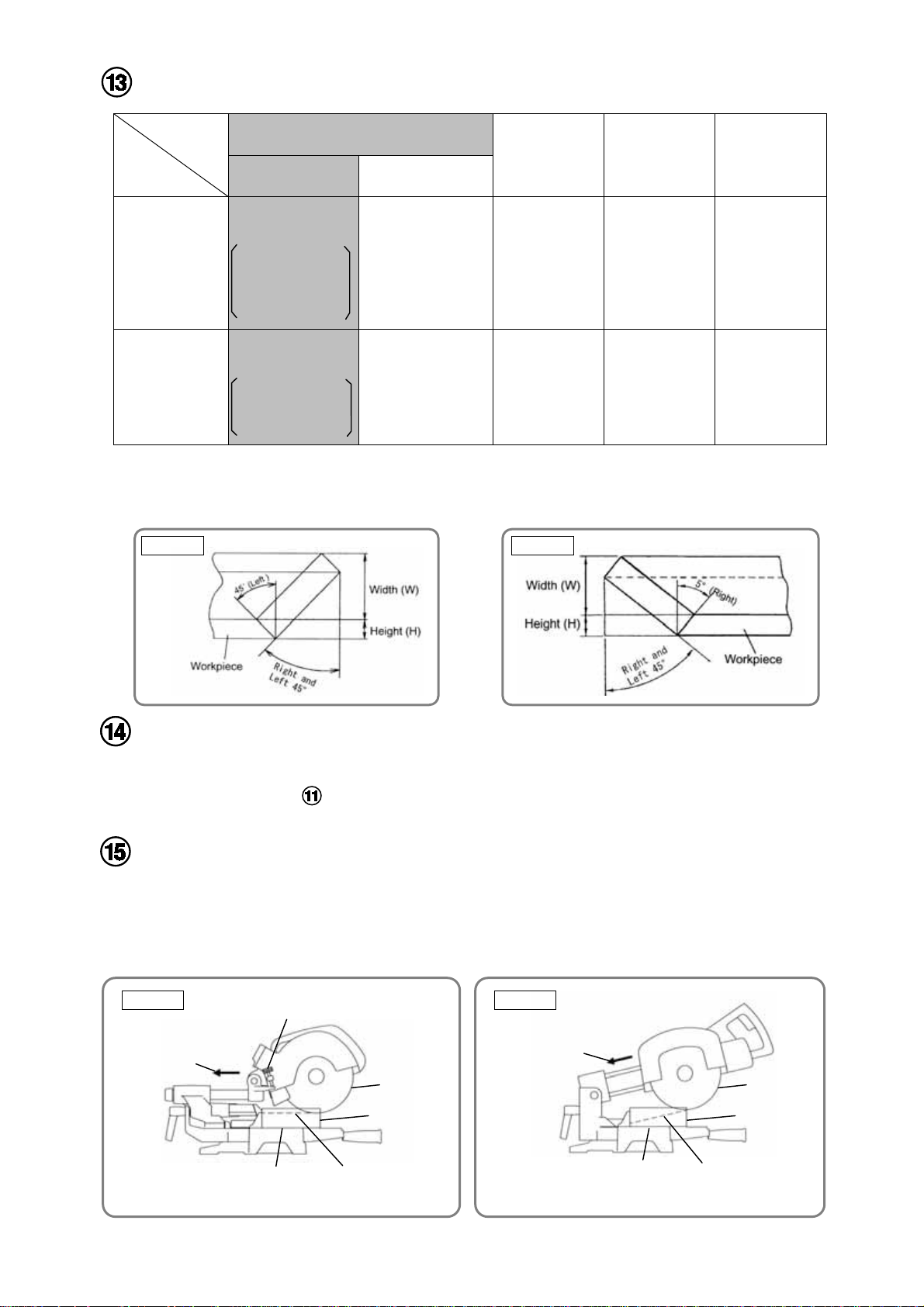
By turning the turn table to the left or right and inclining the saw blade section (head) to the left or right, the
Models C 8FSE and C 8FSHE are capable of compound cutting (bevel and miter, see Figs. 10-a and 10-b)
of workpieces with the maximum dimensions shown in Table 6.
Fig. 10-bFig. 10-a
Splinter guard, also serving for cut alignment
When cutting the ends of a workpiece, splinters may drop on the saw blade and be cut into pieces. The
Models C 8FSE and C 8FSHE are equipped with a splinter guard to prevent such splinter cutting.
(Refer to "SELLING POINTS .") Safe cutting is also ensured in bevel cutting because the splinter guard
is tilted with the saw blade.
Groove cutting
The Models C 8FSE and C 8FSHE can cut grooves at desired depth by adjusting the 6-mm depth adjustment bolt
manually. (Refer to "Groove cutting procedures" described in the Instruction Manual for details.)
NOTE: The Models C 8FSE and C 8FSHE cannot cut grooves at const ant depth unless the sa w blade
slides in parallel with the base surface.
Fig. 11-a
Slide direction
6 mm depth adjustment bolt
Base surface
[Model C 8FSE/C 8FSHE]
Saw blade
Workpiece
Groove
Fig. 11-b
Slide direction
Base surface
[Model P1 and P2]
Saw blade
Workpiece
Groove
-5-
Page 9
1. Specifications
SPECIFICATIONS
Model
0°(Right angle)
Left/right 45°
Miter
Maximum
Right 57°
cutting
dimensions
Height x
Width
mm (inch)
Bevel
Left 45°
Right 5°
Miter left/right 45°+
bevel left 45°
Miter left/right 45°+
bevel right 5°
Miter cutting ranges
Bevel cutting ranges
Compound (miter + bevel)
cutting ranges
Angle stopper positions
Applicable saw blade
Saw blade bore
External diameter of applicable
saw blades
Lower guard lock
Laser marker
(Only the
Model
C 8FSHE)
Maximum output < 1 mW (CLASS II)
Wave length 400 nm to 700 nm
Laser medium Laser diode
Power source type and voltage
Type of motor
Full-load current
No-load rotation speed
Max. output
Main unit dimensions
(Width x depth x height)
Weight
Coating
Packaging
Cord
C 8FSE/C 8FSHE
65 mm x 312 mm (2-9/16” x 12-1/4”),
75 mm x 262 mm (2-15/16” x 10-5/6”) (with aux. board 30 mm (1-3/16”))
65 mm x 220 mm (2-9/16” x 8-21/32”),
75 mm x 185 mm (2-15/16” x 7-1/4”) (with aux. board 20 mm (13/16”))
65 mm x 170 mm (2-9/16” x 6-11/16”),
75 mm x 140 mm (2-15/16” x 5-1/2”) (with aux. board 20 mm (13/16”))
45 mm x 312 mm (1-25/32” x 12-1/4”),
50 mm x 252 mm (1-15/16” x 9-15/16”) (with aux. board 30 mm (1-3/16”))
60 mm x 312 mm (2-3/8” x 12-1/4”),
70 mm x 252 mm (2-3/4” x 9-15/16”) (with aux. board 30 mm (1-3/16”))
45 mm x 220 mm (1-25/32” x 8-21/32”),
50 mm x 170 mm (1-15/16” x 6-11/16”) (with aux. board 30 mm (1-3/16”))
60 mm x 220 mm (2-3/8” x 8-21/32”),
70 mm x 170 mm (2-3/4” x 6-11/16”) (with aux. board 30 mm (1-3/16”))
Left 0° - 45°, Right 0° - 57°
Left 0° - 48°, Right 0° - 5°
Miter left 45° to right 45° + left bevel 0° to 45°
Miter left 45° to right 45° + right bevel 0° to 5°
0°, Right/left 15°, 22.5°, 31.6° and 45°
216 mm (8-1/2") external dia.
U.S.A./Canada Europe/Australia Others
15.9 mm (5/8”) 30 mm (1-11/64”) 25.4 mm (1”)
200 mm to 220 mm (7-7/8" to 8-21/32")
U.S.A./Canada Europe/Australia Others
Not provided Provided Not provided
AC single phase 50/60 Hz, 110 V, 120 V, 220 V to 240 V
AC single phase commutator series motor
110 V: 10 A, 120 V: 9.2 A, 220 V: 5 A, 230 V: 4.8 A, 240 V: 4.6 A
5,500 min
Approx. 2,100 W
555 mm x 790 mm x 485 mm (21-27/32" x 31-3/32" x 19-3/32")
C 8FSE 14 kg (31 lbs.) C 8FSHE 14.5 kg (32 lbs.)
-1
Gunmetallic silver
Corrugated cardboard box
Type: 2-conductor cabtire cable Length: 1.8 m (6 ft)
-6-
Page 10
Standard accessories
Optional accessories
·
216 mm (8-1/2") TCT saw blade (15.9 mm (5/8”) bore, NT24,
Code No. 998840 for USA/CAN) --------------------- for wood cutting
·
216 mm (8-1/2") TCT saw blade (30 mm (1-11/64”) bore, NT24,
Code No. 998859 for Europe/AUS) ----------------- for wood cutting
·
216 mm (8-1/2") TCT saw blade (25.4 mm (1”) bore, NT24,
Code No. 998858 for others) ------------------------- for wood cutting
·
Dust bag
·
Vise ass’y
·
10 mm box wrench
·
Holder
·
Side handle
·
Sub fence (for USA/CAN)
·
216 mm (8-1/2") TCT saw blade (15.9 mm (5/8”) bore, NT36,
Code No. 998860 for USA/CAN) ------------------- for wood cutting
·
216 mm (8-1/2") TCT saw blade (30 mm (1-11/64”) bore, NT36,
Code No. 998861 for Europe/AUS) --------------- for wood cutting
·
216 mm (8-1/2") TCT saw blade (25.4 mm (1”) bore, NT36,
Code No. 996210 for others) ----------------------- for wood cutting
·
216 mm (8-1/2") TCT saw blade (15.9 mm (5/8”) bore, NT60,
Code No. 998862 for USA/CAN) ---------- for aluminum sash cutting
·
216 mm (8-1/2") TCT saw blade (30 mm (1-11/64”) bore, NT60,
Code No. 998863 for Europe/AUS) ------ for aluminum sash cutting
·
216 mm (8-1/2") TCT saw blade (25.4 mm (1”) bore, NT60,
Code No. 996288 for other) ---------------- for aluminum sash cutting
·
Extension holder and stopper (Code No. 321553)
·
Crown molding vise ass’y (Code No. 329782)
(Including crown molding stopper (L))
·
Crown molding stopper (L) (Code No. 321374)
·
Crown molding stopper (R) (Code No. 321373)
·
Sub fence ass’y (Code No. 329464)
-7-
Page 11
COMPARISONS WITH SIMILAR PRODUCTS
1. Specification comparisons
[For Europe and others (Except for the U.S.A and Canada)]
Maker
Model name
0゚(Right angle)
Miter
Bevel
Left/right 45°
Right 57°
Left 45°
Right 5°
65 x 312 (2-9/16” x 12-1/4”)
75 x 262 (2-15/16” x 10-5/6”)
(with aux. board 30 (1-3/16”))
65 x 220 (2-9/16” x 8-21/32”)
75 x 185 (2-15/16” x 7-1/4”)
(with aux. board 20 (13/16”))
65 x 170 (2-9/16” x 6-11/16”)
75 x 140 (2-15/16” x 5-1/2”)
(with aux. board 20 (13/16”))
45 x 312 (1-25/32” x 12-1/4”)
50 x 252 (1-15/16” x 9-15/16”)
(with aux. board 30 (1-3/16”))
60 x 312 (2-3/8” x 12-1/4”)
70 x 252 (2-3/4” x 9-15/16”)
(with aux. board 30 (1-3/16”))
HITACHI
C 8FSE/C 8FSHE
P1 P2 B
60 x 270
(2-3/8” x 10-3/8”)
60 x 190
(2-3/8” x 7-15/32”)
--
48 x 270
(1-7/8” x 10-3/8”)
---
60 x 270
(2-3/8” x 10-3/8”)
60 x 190
(2-3/8” x 7-15/32”)
48 x 270
(1-7/8” x 10-3/8”)
(Superior specifications:
60 x 270
(2-3/8” x 10-3/8”)
60 x 190
(2-3/8” x 7-15/32”)
60 x 155
(2-3/8” x 6-3/32”)
42 x 270
(1-21/32” x 10-3/8”)
)
Miter left/right 45°+
bevel left 45°
Maximum cutting dimensions: Height x Width mm (inch)
Miter left/right 45°+
bevel right 5°
Groove cutting width
Miter cutting ranges
Bevel cutting ranges
Compound
(miter + bevel)
cutting ranges
45 x 220 (1-25/32” x 8-21/32”)
50 x 170 (1-15/16” x 6-11/16”)
(with aux. board 30 (1-3/16”))
60 x 220 (2-3/8” x 8-21/32”)
70 x 170 (2-3/4” x 6-11/16”)
(with aux. board 30 (1-3/16”))
Possible
(with bolt height
adjustment)
Left 0° - 45°
Right 0°
Left 0° - 48°
Right 0° - 5°
Miter left and right
0°
Bevel left 0°
Miter left and right
0° - 45°
Bevel right 0° - 5°
-
45°
-
57°
-
45°
48 x 190
(1-7/8” x 7-15/32”)
--
Impossible Impossible
-
-
45°
50°
-
50°
-
Left 0°
Right 0°
Left 0° - 48° Left 0° - 48° Left 0° - 45°
Miter left and right
0°
Bevel left 0°
48 x 190
(1-7/8” x 7-15/32”)
Left 0°
Right 0°
Miter left and right
0°
Bevel left 0°
45°
-
45°
-
50°
-
50°
-
42 x 190
(1-21/32” x 7-15/32”)
-
Possible
(with screw height
adjustment)
Left 0°
Right 0°
Miter left and right
0°
-
45°
Bevel left 0°
45°
-
50°
-
58°
-
45°
Angle stopper positions
Saw blade external
diameter mm (inch)
(No. of teeth)
0°, Right/left 15°, 22.5°,
31.6° , 45°
216 (8-1/2") (24P) 216 (8-1/2") (24P) 216 (8-1/2") 216 (8-1/2") (24P)
0°, Right/left 15°,
22.5°, 30°, 45°, 50°
0°, Right/left 15°,
22.5°, 30°, 45°, 50°
0°, Right/left 15°,
22.5°, 30°, 45°
-8-
Page 12
Maker
Model name
Laser marker
Laser output
Light
Full-load current (A)
No-load revolution
Motor
-1
(min
)
Insulation structure
Splinter guard
Type of angle stopper
HITACHI
P1 P2 B
C8FSE/C8FSHE
Provided Not provided Not provided Provided
< 1 mW
--
< 1 mW
Provided (2 LEDs) Not provided Not provided Provided
230 V - 4.8 A 230 V - 5.6 A 230 V 230 V - 6.1 A
5,500 6,700 6,300 5,000
Double insulation Double insulation Double insulation Double insulation
Provided Provided Not provided Not provided
Positive stopper Positive stopper Positive stopper Positive stopper
Sub fence
Capacity of dust bag (l)
Main unit dimensions
[Width x Depth x Height]
mm (inch)
Product weight kg (lbs.)
Standard accessories
Optional accessories
Not provided (Option) Not provided
2
555 x 790 x 485
(21-27/32" x 31-3/32"
x 19-3/32")
C 8FSE: 14 (31)
C 8FSHE: 14.5 (32)
·
216 mm (8-1/2") TCT
saw blade (NT24)
for wood cutting
·
Dust bag --------------1
·
Vise ass’y ------------ 1
·
10 mm box wrench ---1
·
Holder ---------------- 1
·
Sub fence------------- 1
(for USA/CAN)
· Extension holder and
stopper
·
Crown molding vise
ass’y (Including crown
molding stopper (L))
·
Crown molding
stopper (L)
·
Crown molding
stopper (R)
-------1
460 x 560 x 590
(18-1/8” x 22-1/16”
x 23-7/32”)
·
216 mm (8-1/2") TCT
saw blade (NT24)
for wood cutting
·
Hex. bar wrench -- 2
·
Fence insert------- 1
·
Legstand
·
Vise ass’y
· Roller table
Length stop for short
·
workpieces
-
14.5 (32) 14 (31) 15 (33.1)
460 x 560 x 590
(18-1/8” x 22-1/16”
x 23-7/32”)
·
216 mm (8-1/2") TCT
saw blade
--- 1
for wood cutting
·
Hex. bar wrench -- 2
·
Dust bag ----------1
·
Dust extraction
nozzles
·
Legstand
·
Vise ass’y
· Roller table
Length stop for short
·
workpieces
·
Dust extraction tubes
·
Three-way connector
Provided Not provided
2
450 x 610 x 510
(17-23/32” x 24”
x 20-3/32”)
·
216 mm (8-1/2")
TCT saw blade
--- 1
(NT24)
·
·
Vise ass’y ------1
Hex. bar wrench
---------1
-----------------1
----------- 2
·
Extension bars
·
216 mm (8-1/2")
TCT saw blade
(NT48)
-9-
Page 13

[For the U.S.A and Canada]
Maker
Model name
C 8FSE/C 8FSHE C 8FB2
HITACHI
(Superior specifications:
P3
)
0° (Right angle)
Left/right 45°
Miter
Right 57°
Left 45°
Bevel
Right 5°
Miter left/right 45°+
bevel left 45°
Maximum cutting dimensions: Height x Width mm (inch)
Miter left/right 45°+
bevel right 5°
65 x 312 (2-9/16” x 12-1/4”)
75 x 262 (2-15/16” x 10-5/6”)
(with aux. board 30 (1-3/16”))
65 x 220 (2-9/16” x 8-21/32”)
75 x 185 (2-15/16” x 7-1/4”)
(with aux. board 20 (13/16”))
65 x 170 (2-9/16” x 6-11/16”)
75 x 140 (2-15/16” x 5-1/2”)
(with aux. board 20 (13/16”))
45 x 312 (1-25/32” x 12-1/4”)
50 x 252 (1-15/16” x 9-15/16”)
(with aux. board 30 (1-3/16”))
60 x 312 (2-3/8” x 12-1/4”)
70 x 252 (2-3/4” x 9-15/16”)
(with aux. board 30 (1-3/16”))
45 x 220 (1-25/32” x 8-21/32”)
50 x 170 (1-15/16” x 6-11/16”)
(with aux. board 30 (1-3/16”))
60 x 220 (2-3/8” x 8-21/32”)
70 x 170 (2-3/4” x 6-11/16”)
(with aux. board 30 (1-3/16”))
65 x 305 (2-9/16” x 12”)
75 x 265 (2-15/16” x 10-7/16”)
65 x 220
(2-9/16” x 8-21/32”)
65 x 175
(2-9/16” x 6-7/8”)
45 x 305
(1-25/32” x 12”)
--
45 x 220
(1-25/32” x 8-21/32”)
--
70 x 300
(2-3/4” x 11-13/16”)
70 x 212
(2-3/4” x 6-11/32”)
70 x 160
(2-3/4” x 6-5/16”)
50 x 300
(1-15/16” x 11-13/16”)
50 x 212
(1-15/16” x 6-11/32”)
Groove cutting width
Miter cutting ranges
Bevel cutting ranges
Compound
(miter + bevel)
cutting ranges
Angle stopper positions
Saw blade external
diameter mm (inch)
(No. of teeth)
Possible
(with bolt height adjustment)
Left 0° - 45°
Right 0° - 57°
Left 0° - 48°
Right 0° - 5°
Miter left and right
0° - 45°
Bevel left 0° - 45°
Miter left and right
0° - 45°
Bevel right 0° - 5°
0°, Right/left 15°, 22.5°,
31.6° , 45°
216 (8-1/2") (24P) 216 (8-1/2") (24P) 216 (8-1/2") (30P)
Possible
(with screw height
adjustment)
Left 0° - 45°
Right 0° - 57°
Left 0° - 45°
Miter left and right
0° - 45°
Bevel left 0° - 45°
0°, Right/left 15°, 22.5°,
31.6°, 35.3°, 45°
Possible
(with screw height
adjustment)
Left 0° - 50°
Right 0° - 60°
Left 0° - 48°
Right 0° - 2°
Miter left and right
0° - 45°
Bevel left 0° - 45°
0°, Right/left 10°,15°, 22.5°,
31.6°, 45°,
Left 50°, Right 60°
-10-
Page 14
Maker
Model name
Laser marker
Laser output
Light
Full-load current (A)
No-load revolution
Motor
-1
(min
)
Insulation structure
Splinter guard
Type of angle stopper
HITACHI
P3
C 8FSE/C 8FSHE C 8FB2
Provided Not provided Not provided
< 1 mW
--
Provided (2 LEDs) Not provided Not provided
120 V – 9.2 A 115 V – 9.5 A 120 V - 15 A
5,500 4,900 5,400
Double insulation Double insulation Double insulation
Provided Provided
Not provided
(Option)
Positive stopper Ball index Positive stopper
Sub fence
Provided Not provided Provided
Capacity of dust bag (l) 2 2
Main unit dimensions
[Width x Depth x Height]
mm (inch)
Product weight kg (lbs.)
Standard accessories
Optional accessories
555 x 790 x 485
(21-27/32" x 31-3/32"
x 19-3/32")
C 8FSE: 14 (31)
C 8FSHE: 14.5 (32)
·
216 mm (8-1/2") TCT
saw blade (NT24)
for wood cutting
·
Dust bag ------------------ 1
·
Vise ass’y ---------------- 1
·
10 mm box wrench ------- 1
·
Holder -------------------- 1
·
Sub fence----------------- 1
(for USA/CAN)
· Extension holder and
stopper
·
Crown molding vise
ass’y (Including crown
molding stopper (L))
·
Crown molding
stopper (L)
·
Crown molding
stopper (R)
----------- 1
520 x 755 x 500
(20-15/32” x 29-23/32”
x 19-11/16”)
17.5 (38.6) 19.5 (43)
·
216 mm (8-1/2") TCT
saw blade (NT24)
for wood cutting
·
Dust bag ----------------- 1
·
10 mm box wrench. ----- 1
·
Vise ass’y ---------------- 1
·
Slide fence ass’y --------- 1
·
Stopper
·
216 mm (8-1/2") TCT
saw blade (NT36)
for wood cutting
·
216 mm (8-1/2") TCT
saw blade (NT60)
for wood cutting
·
216 mm (8-1/2") TCT
saw blade (NT60)
for aluminum cutting
---------- 1
-
580 x 720 x 555
(22-27/32” x 28-11/32”
x 21-27/32”)
·
216 mm (8-1/2")
TCT saw blade
(NT30)
·
·
·
·
·
------------------- 1
Blade spanner------------ 1
Legstand
Fence insert
Dust extraction kit
Carrying strap
-11-
Page 15
PRECAUTIONS IN SALES PROMOTION
1. Safety instructions
In the interest of promoting the safest and most efficient use of the Models C 8FSE and C 8FSHE Slide
Compound Miter Saws by all of our customers, it is very important that at the time of sale the salesperson
carefully ensures that the buyer seriously recognizes the importance of the contents of the Instruction
Manual, and fully understands the meaning of the precautions listed on the Warning Labels, Warning Signs
and Caution Labels attached to each machine.
A. Instruction manual
Although every effort is made in each step of design, manufacture and inspection to provide protection
against safety hazards, the dangers inherent in the use of any slide compound miter saw cannot be
completely eliminated. Accordingly, general precautions and suggestions for the use of electric power tools,
and specific precautions and suggestions for the use of the slide compound miter saw are listed in the
Instruction Manual to enhance the safe, efficient use of the tool by the customer. Salespersons must be
thoroughly familiar with the contents of the Instruction Manual to be able to offer appropriate guidance to
the customer during sales promotion.
B. Warning labels and caution labels
(1) Precautions on the name plate
Each of the Models C 8FSE and C 8FSHE is furnished with a Name Plate that lists the following precautions.
For the U.S.A. and Canada
Fig. 12-a
For Europe
Fig. 12-b
For Australia and Asia
Fig. 12-c
For China
Fig. 12-d
-12-
Page 16

For Taiwan
Fig. 12-e
(2) Warning label (A) (for the U.S.A. and Canada)
Fig. 13
Warning label (A) specified by the UL is affixed on the left side of the gear case.
Please instruct users to strictly observe the 11 items of precautions in warning label (A) shown above.
(3) Caution labels (A) and (B) (at the front of the base)
·
Caution label (A) (at the front of the base)
For the U.S.A., Canada, Europe, Australia and Asia
Fig. 14-a
·
Caution label (B) (at the front of the base)
For China
Fig. 14-b
-13-
Page 17
(4) Caution label (J) (at the front of the hinge) and caution labels (C) and (E) (at the front left of the turn
table) (only the Model C 8FSHE)
Do not stare into laser beam. If your eye is exposed directly to the laser beam, it can be hurt. Caution
label (J) and caution labels (C) and (E) are adhered to each machine to comply with the
standards for the safe use of laser equipment.
·
Caution label (J) (at the front of the hinge) (only the Model C 8FSHE)
Fig. 15-a
·
Caution labels (C) and (E) (at the front left of the turn table) (only the Model C 8FSHE)
For the U.S.A. and Canada
Fig. 15-b
For Europe, Australia, China and Asia
Fig. 15-c
C. Relative standards
Standards, regulations and guidelines for the safe use of laser equipment
[The U.S.A.] FDA CDRH 21 CFR
[AUS/NZL] AS/NZS 2211.1: 2001
[Europe] EN 60825-1: 2001-11
D. Laser marker (only the Model C 8FSHE)
The Model C 8FSHE is equipped with the laser marker that complies with the Class II requirements of the
standard specified in "Relative standards." The Class II laser is defined as follows:
·
The laser power is low and it is safe by the protective measures such as blinking.
However, it is dangerous if the operator’s eyes are exposed directly to the laser for a protracted period.
·
The operator can use the laser equipment without particular training and instruction.
·
The amount of light exposure (output) is 1 mW or less at the position where the operator can be exposed
to the laser radiation during operation. (This is in the case of the U.S.A. The measuring methods and the
output values are different depending on the standards.)
The saw blade unit prevents access of the operator’s eye to the laser-emitting aperture less than 65 mm.
In addition, the amount of light exposure (output) is 1 mW or less (about 0.4 mW) at this position. Thus
the Model C 8FSHE satisfies the Class II requirements adequately. There is no ill effect on the operator’s
body if looking at the laser line on the workpiece during operation.
-14-
Page 18
CAUTION: (1) Be sure to disconnect the power cord plug from the receptacle before removing the
laser marker for repair. If it is unavoidable to check the operation of the removed
laser marker with the power turned on, face the laser emitting aperture to the ground
to show the laser line on the ground.
(2) Laser radiation when open. DO NOT STARE INTO BEAM OR VIEW DIRECTL Y WITH
OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS.
The life span of the laser marker in the Model C 8FSHE is about 3,600 hours. (About 3 years: 5 hours of
use/day x 240 days/year)
2. Precautions requiring particular attention during sales promotion
A. Ambient illuminance and visibility of laser line (only the Model C 8FSHE)
The visibility of the laser line on the workpiece changes depending on the brightness of the working
environment. Instruct the customer to consider the brightness of the working environment when using the
laser marker referring to the following table.
Table 7 Ambient illuminance and visibility of laser line
Illuminance (lux) 3000 or more 3000 or more 3000 - 2500 800 - 600 300 - 200 150 - 80 30 or less
Outdoor
Ambient
conditions
(reference)
Indoor
Laser line Invisible Visible Visible Visible Visible Glaring Glaring
Under direct
sunlight of fine
weather
-
Shaded area
in fine weather
Near the
window under
fine weather
Cloudy
weather
Indoor under
fine weather
Shaded area
in cloudy
weather
Near the
window
under
cloudy
weather
Just before
the sunset in
cloudy
weather
Indoor under
cloudy
weather
-
Near the
window
under cloudy
weather, just
before the
sunset
Ink line is
invisible.
(The working environment where the illuminance is 200 luxes or less is dark and difficult to operate the
Model C 8FSHE.)
The laser line is invisible under direct sunlight of fine weather. Prepare a shaded area or relocate to a
shaded area to operate the Model C 8FSHE.
When a laser line is dazzling, please light up the laser line with a LED light. You can watch a laser line if you
do so.
B. Precautions concerning brake
The Models C 8FSE and C 8FSHE are equipped with a "brake" that stops running when the switch is
turned off. Normally the operation is stopped in 5 - 6 seconds when the switch is turned off. If it takes 10
seconds or more to stop, absolutely avoid further use of this machine. In this event, ensure that your
customers bring this machine in their local Hitachi power tools dealer or Hitachi power tools center for
servicing.
(1) Be sure to use the carbon brushes dedicated to the Models C 8FSE and C 8FSHE (110 V to 120 V:
Code No. 999021, 220 V to 240 V: Code No. 999001). Use of other carbon brushes will adversely affect
the brake performance.
(2) If the brake should fail to work, check the carbon brushes. Replace the carbon brushes with new ones if
their length is shorter than 6 mm. If the brake still does not work, replace the armature ass’y.
-15-
Page 19
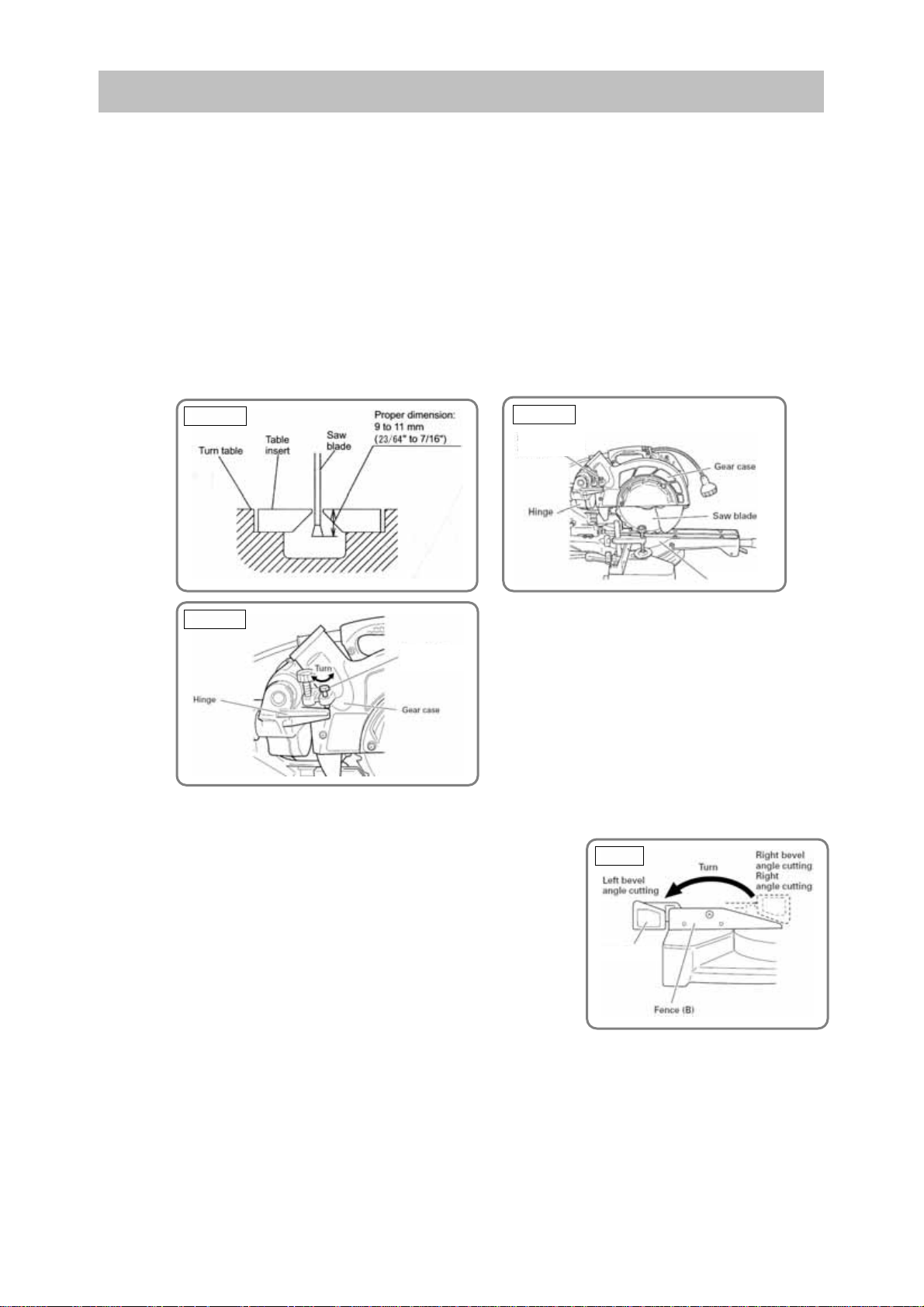
ADJUSTMENT AND OPERATIONAL PRECAUTIONS
1. Confirmation of saw blade lower limit position
The lower limit of the saw blade cutting depth is factory-adjusted so that when the saw blade is fully
lowered, its cutting edge is 10 to 11 mm (13/32" to 7/16") below the upper surface of the turn table in order
to cut workpieces completely without cutting the bottom of the turn table groove. Lower the saw blade and
check that it stops at the correct position (Fig. 16-a).
When changing the position of the 8 mm depth adjustment bolt that serves as the lower limit position
stopper of the saw blade, perform the following steps.
(1) Make the tip of the 8 mm depth adjustment bolt contact with the hinge.
(2) Turn the 8 mm depth adjustment bolt with a 13-mm wrench to adjust the lower limit position of the saw
blade (Fig. 16-c).
CAUTION: Perform the adjustment carefully to ensure that the saw blade does not cut into the turn
table.
Fig. 16-a
Fig. 16-b
8 mm depth
adjustment bolt
Turn table
Fig. 16-c
8 mm depth
adjustment bolt
2. Confirmation for use of sub fence (Optional accessory)
The sub fence is optionally available (located at the front right of the
base). Use the sub fence for miter cutting and right bevel cutting. The
sub fence supports the workpiece widely for stable cutting. In the
case of left bevel cutting, raise the sub fence as illustrated in Fig. 17
and turn it counterclockwise.
*For the U.S.A. and Canada, the Models C 8FSHE and C8FSE are
equipped with the sub fence as a standard accessory.
Fig. 17
Sub fence
NOTE: Mount the sub fence as follows.
Insert the flat-head sc re w M6 into f ence (B) and mo unt t he sub fe nce a nd the plate. Then t ig hten
the nylon nut M6 with the attach ed 10-mm box wrench so th at the sub fence c an turn smoothly.
WARNING: In the case of left bevel cutting, turn the sub fence counterclockwise. Otherwise the
main body or the saw blade may contact the sub fence resulting in an injury. Be sure to
instruct the customers to tu rn the s ub fence c ountercl ock wise in the case of l ef t bev el
cutting.
-16-
Page 20

3. Position adjustment of laser line (Only the Model C 8FSHE)
The laser line is adjusted to the width of the saw blade at the
time of factory shipment. Depending upon the cutting choice,
align the laser line with the left side of the cutting width (saw
blade) or the right side according to the following procedure.
First, make a right-angle ink line on the workpiece that is about
20 mm (25/32") in height and 150 mm (5-29/32") in width.
To cut the right side of the ink line with the saw blade as shown
in Fig. 18, align the left side of the saw blade with the ink line
on the workpiece and make a groove of about 5 mm deep on
the workpiece to the middle. Hold the grooved workpiece by
the vise as it is and do not move it. (For grooving work, refer to
the Instruction Manual "Groove cutting procedures.")
Light up the laser marker. Turn the adjuster to align the laser
line with the ink line. (Turning the adjuster clockwise will shift
the laser line position to the right and turning counterclockwise
will shift to the left.) (Fig. 19)
Thus the cutting position matches the laser line position. Align
the ink line on the workpiece with the laser line. When aligning
the ink line, slide the workpiece little by little and secure it by
vise at a position where the laser line overlaps with the ink line
(Fig. 20). Work on the grooving again and check the position
of the laser line. When the ink line and the laser line are
overlapped, the strength and weakness of light will change,
resulting in a stable cutting operation because you can easily
discern the conformity of lines. This ensures the minimum
cutting errors.
Fig. 18
Fig. 19
Vise
assembly
Fig. 20
WARNING:
• Make sure before plugging the power plug into the receptacle tha t the main body and the laser
marker are turned off.
• Exercise utmost caution in handling a switch trigger for the position adjustment of the laser line,
as the power plug is plugged into the receptacle during operation. If the switch trigger is pulled
inadvertently, the saw blade can rotate and result in unexpected accidents.
• Do not remove the laser marker to be used for other purposes.
CAUTION:
• Laser radiation - Do not stare into beam.
• Laser radiation on work table - Do not stare into beam.
If your eye is exposed directly to the laser beam, it can be hurt.
• Do not dismantle it.
• Do not give strong impact to the laser marker (main body of tool); otherwise, the position of a
laser line c a n go out of o r d e r, res u l t i n g i n t h e d a m a g e o f t h e l a s e r m a r k e r a s we l l as a short e n e d
service life.
• Keep the laser marker lit only during a cutting operation. Prolonged lighting of the laser marker
can result in a shortened service life.
NOTE:
• Perform cutting by overlapping the ink line with the laser line. When the ink line and the laser line
are overlapped, the strength and weakness of light will change, resulting in a stable cutting operati on
because you can easily discern the conformity of lines. This ensures the minimum cutting errors.
• In outdoor or near-the-window operations, it may become difficult to obs erve the laser line due to
the sunlight. Under such circumstances, move to a place that is not directly under the sunlight
and engage in the operation.
• Do not tug on the cord behind the motor head or hook your finger, wood and the like around it;
otherwise, the cord may come off and the laser marker may not be lit up.
Instruct the above precautions on the laser marker to the customers.
-17-
Page 21
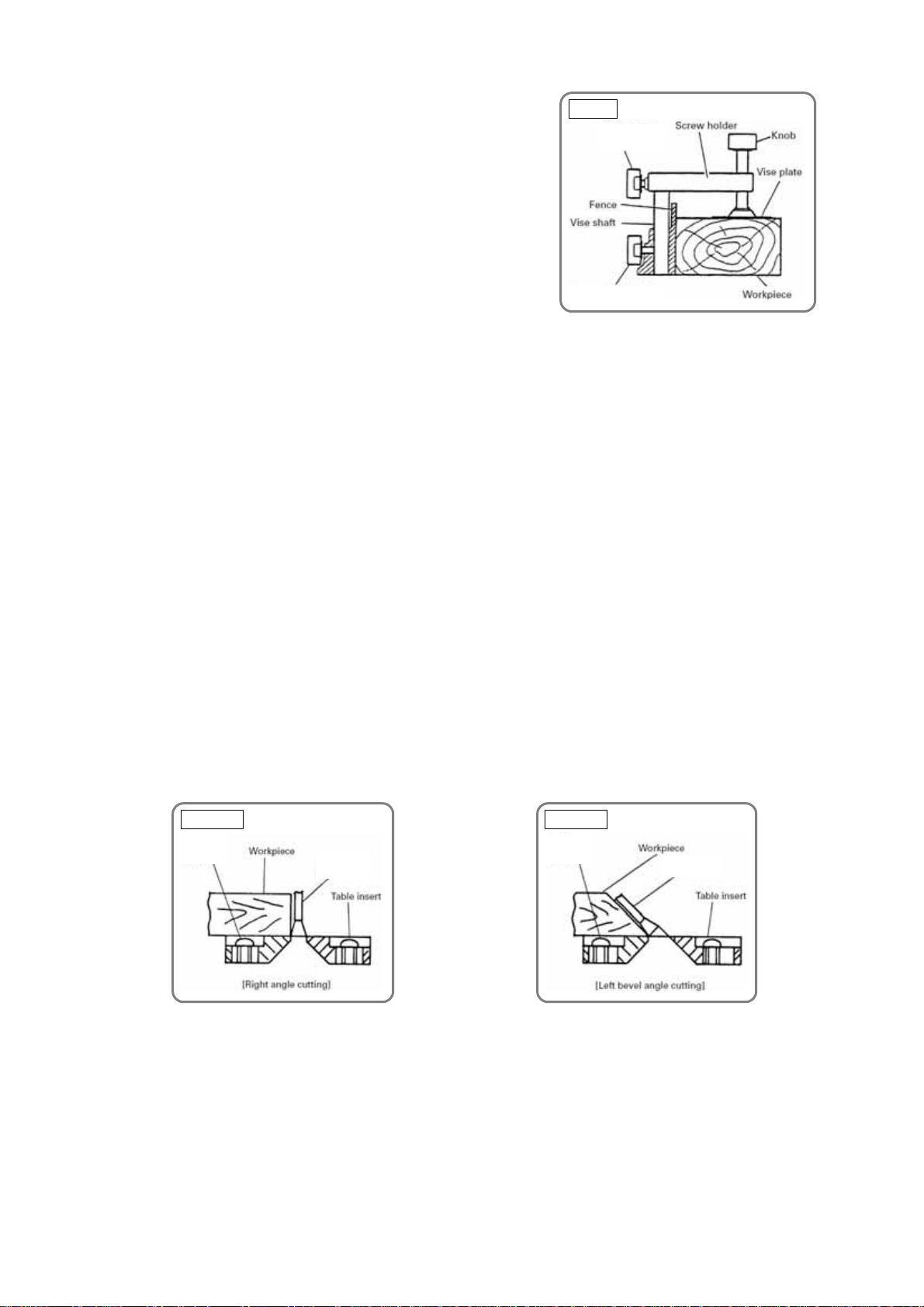
4. How to use the vise assembly
(1) The vise assembly can be mounted on either the left fence
(fence (B)) or the right fence (fence (A)) by loosening 6 mm
wing bolt (A).
(2) The screw holder can be raised or lowered according to the
height of the workpiece by loosening 6 mm wing bolt (B).
After the adjustment, firmly tighten 6 mm wing bolt (B) and fix
the screw holder.
(3) Turn the upper knob and securely fix the workpiece in position
(Fig. 21).
WARNING: Always firmly clamp or vise to secure the workpiece to the fence; otherwise the
workpiece might be thrust from the table and cause bodily harm.
CAUTION: Always confirm that the motor head does no t contact the vise assembly when it is
lowered for cutting. If there is any danger that it may do so, loosen 6 mm wing bolt (B)
and move the vise assembly to a position where it will not contact the saw blade.
Fig. 21
6 mm wing
bolt (B)
6 mm wing bolt (A)
5. Adjustment of table insert position
The table inserts are installed on the turn table. When the machine is shipped from the factory, the table
inserts are positioned so that there is no chance that the saw blade will come in contact with either side of
the saw blade slot even if the machine is used for 45° bevel cutting. Before operating the machine, adjust
the position of the table inserts so that the sides of the saw blade align with the edges of the table inserts
according to the following procedure.
First, loosen the three 6-mm machine screws that fasten the table inserts, and temporarily tighten the two
outside screws (front and back). Next, clamp a workpiece (about 200 mm (7-7/8") wide) with the vise
assembly and cut the workpiece. Align the cutting surfaces with the table inserts as shown in Figs. 22-a and
b, and securely tighten the front and back 6-mm machine screws. Finally, remove the workpiece and
securely tighten the middle 6-mm machine screw.
If adjustment is done as described, workpieces can be cut precisely by aligning the appropriate side edge
of the table inserts with the ink line on the workpiece. Adjust the table inserts as necessary for the type of
cutting desired (right-angle or left bevel cutting).
6 mm
machine
screw
Saw blade
-18-
Fig. 22-bFig. 22-a
6 mm
machine
screw
Saw blade
Page 22

6. Cutting operation
(1) Cutting efficiency will be reduced if a dull saw blade is used,
if an excessively long extension cord is used, or if the wire
gauge of the extension cord is too small. (For details, refer
to the Instruction Manual "USE PROPER EXTENSION
CORD.") This is particularly important when cutting materials
with dimensions which are at or near the maximum capacity
for the machine.
(2) The customer should be advised to thoroughly inspect the
workpiece to ensure that there are no metallic objects (nails
in particular), sand, or other foreign matter in or on the
workpiece. Contacting such foreign matter will not only
shorten the service life of the saw blade, but could cause
serious accident. Should the saw blade tips be broken off,
the tips may fly toward the operator.
Fig. 23
(3) Press cutting ( 3
in Fig. 23)
The Models C 8FSE/C 8FSHE can be used for press
cutting of workpieces up to 65 mm square in a single
operation by simply pushing the saw blade section
3
downward in the same manner as the Model C 8FB2.
Slide the hinge to the end of holder (A) and tighten the slide
securing knob securely.
CAUTION: (For Europe and Australia)
This slide compound miter saw is equipped with a saw head lock as a safety device.
T o lo wer the saw head to cut, the lock must be released by pressing the lock lever with your thumb.
(4) Slide cutting ( 1
to 5 in Fig. 23)
Slide cutting procedures and precautions are described below.
1 Loosen the slide securing knob.
2 Grip the handle and pull the saw blade section in the arrow direction (toward the operator).
3 Push the handle downward and cut the workpiece (press cutting).
(For Europe and Australia)
Push the handle downward while holding down the lock lever with your thumb and cut the workpiece.
CAUTION: If the handle is pushed down forcibly and excessively fast, it could cause the saw blade
vibration and partial sliding which would leave unwanted cutting marks on the
workpiece. Instruct the customer to slowly and carefully press down the handle.
4 While pressing down on the handle, slide the saw blade section in the arrow direction and cut the
workpiece.
CAUTION: Interrupting the cutting operation partway through the material or sliding the saw blade
section in a jerky manner will produce unwanted cutting marks similar to those
described in
3 above. As a guide, instruct the customer to cut a workpiece of 30 mm
(1-3/16") high and 300 mm (11-7/8") wide in 10 to 15 seconds.
Carefully instruct the customer never, ever to perform slide cutting in the direction toward the operator
(reverse direction of the above). Such operation is extremely hazardous, as the saw blade could ride up
over the workpiece and cause the saw blade section to kick upward unexpectedly, causing possible serious
injury. Instruct the customer to always slide the saw blade section toward the fence while cutting, as shown
by the arrow 4 in Fig. 23.
5 On completion of the cutting operation, turn the switch off and wait for the saw blade to come to a
complete stop before raising the handle to its original position. Raising the handle while the saw blade
is still rotating may cause unwanted cutting marks on the workpiece.
-19-
Page 23

NOTE:
Techniques to avoid unwanted cutting marks
Uneven and unwanted cutting marks can be avoided by shifting from 3 press cutting to 4 slide
cutting in a single, uninterrupted motion.
Techniques to avoid burnt marks
Burnt marks can be avoided by shifting from 3 press cutting to 4 slide cutting in a single,
uninterrupted motion in the same manner as the above, applying a slight lateral force toward the
cut-off side. Advise the customer that he or she will quickly develop a "feel" and skill for smooth
cutting after performing two or three practice cutting operations.
(5) Miter cutting
Miter cutting is accomplished by turning the turn table. (For details, please refer to the Instruction
Manual "Miter cutting procedures.")
(6) Bevel cutting
Bevel cutting of 0 - 45° to the left or 0 - 5° to the right is accomplished by inclining the motor head
section. (For details, refer to the Instruction Manual "Bevel cutting procedures.")
WARNING: When the workpiece is secured on the left or right side of the blade, the short cut-off
portion will come to rest on the right or left side of the saw blade. Always turn the power
off and let the saw blade stop completely before raising the handle from the workpiece.
If the handle is raised while the saw blade is still rotating, the cut-off piece may become
jammed against the saw blade causing fragments to scatter a bout dangerously. When
stopping the bevel cutting operation halfway, start cutting after pulling back the motor
head to the initial position. Starting from half way, without pulling back, causes the
safety cover to be caught in the cutting groove of the workpiece and to contact the saw
blade.
CAUTION: When cutting a workpiece of 50 mm (1-15/16”) height in the le f t 45° bev el cutting position
or a workpiece of 70 mm (2-3/4”) height in the right 5° bevel cutting position, adjust the
lower limit position of the motor head so that the gap between the lower edge of the
motor head and the workpiece will be 2 to 3 mm (5/64" to 1/8") at the lower limit position
(refer to the Instruction Manual "Checking the saw blade lower limit position").
(7) Compound (miter + bevel) cutting
Compound (miter + bevel) cutting can be accomplished by combining the miter cutting and bevel cutting
operations described in paragraphs (5) and (6) above. (For details, refer to the Instruction Manual
"Compound cutting procedures.") When the saw blade is inclined 45° to the left, the turn table can be
turned up to 45° to the left and right.
(8) Cut surface quality during miter/bevel cutting
The quality of the cut surface depends on the type
Fig. 24
of cutting operation (miter or bevel), the type and
sharpness of the saw blade, whether the workpiece
is cut to the left or right, and various other factors.
In miter and bevel cutting in particular, cutting is
performed across the wood grain, so the condition
of the cut surface depends on whether the wood is
cut with or against the grain. This is the same as
when using electric portable planers. Customers
should be advised of these phenomena so that they
understand that in cases when the cut surface may
not be as smooth as expected or hoped for, it is not
caused by the performance of the saw blade or the
Models C 8FSE/C 8FSHE.
In the cutting examples illustrated in Fig. 24, the cut surfaces on the sides marked ( A ) (cut with the
-20-
Page 24

grain) are better than those on the sides marked ( B ).
(9) Crown molding cutting
This machine can cut two types of crown molding workpieces by combining the miter and bevel cutting
operations. Figure 25 shows two common crown molding types having angles of (θ) 38° and 45°. For
the typical crown molding fittings, see Fig. 26.
Fig. 26Fig. 25
The table below shows the miter angle and the bevel angle settings that are ideal for the two crown molding
types.
NOTE : For convenience, positive stops are provided for the miter setting (left and right 31.6°)
positions.
For miter cut setting
If the turn table has been set to either of the angles described, move the turn table adjusting side handle
a little to the right and left to stabilize the position and to properly align the miter scale and the tip of the
indicator before the operation starts.
For bevel cut setting
Move handle on miter section to the right and left and check that the position is stable and the angle
scale and the tip of the indicator are properly aligned. Then tighten the clamp lever.
Table 8
Type of
crown
molding
45° type Right 35.3°
38° type Right 31.6°
To process crown molding at positions
1 and 4 in Fig. 26.
Miter angle
setting
Bevel angle
setting
Left 30°
( mark)
( mark)
Left 33.9°
( mark)
( mark)
30° and 33.9° left slant setting method
1 Loosen the clamp lever and slant to the left a little at a time
while pushing the set pin into the main unit. At this time, the
set pin will enter one step and fit into the 30° left slant and
33.9° left slant setting slots.
2 With the set pin in the slot as described above, setting to the
30° left slant position is possible by pushing to the right side.
3 Also, with the set pin in the slot as described above, setting
to the 33.9° left slant position is possible by pushing to the
left side.
4 Look at the bevel scale and indicator to recheck whether or
not the settings match and then tighten the clamp lever.
To process crown molding at positions
2 and 3 in Fig. 26.
Miter angle
setting
Left 35.3°
( mark)
Left 31.6°
( mark)
Bevel angle
setting
Left 30°
( mark)
Left 33.9°
( mark)
Fig. 27
Clamp
lever
Tight en
Bevel scale
(1) Setting to cut crown moldings at positions
1 and 4 in Fig. 26 (see Fig. 28; tilt the head to the left):
1 Turn the turn table to the right and set the miter angle as follows:
* For 45° type crown moldings: 35.3° ( mark)
* For 38° type crown moldings: 31.6° ( mark)
-21-
Page 25

2 Tilt the motor head to the left and set the bevel angle as follows:
* For 45° type crown moldings: 30° ( mark)
* For 38° type crown moldings: 33.9° ( mark)
3 Position the crown molding so that the upper surface (
in Fig. 25) contacts the fence as indicated in
Fig. 30.
(2) Setting to cut crown moldings at positions
2 and 3 in Fig. 26 (see Fig. 29; tilt the head to the left):
1 Turn the turn table to the left and set the miter angle as follows:
* For 45° type crown moldings: 35.3° ( mark)
* For 38° type crown moldings: 31.6° ( mark)
2 Tilt the head to the left and set the bevel angle as follows:
* For 45° type crown moldings: 30° ( mark)
* For 38° type crown moldings: 33.9° ( mark)
3 Position the crown molding so that the lower surface (
in Fig. 25) contacts the fence as shown in Fig. 31.
Fig. 29Fig. 28
Turn table
Fig. 31Fig. 30
Turn table
Cutting method of crown molding without tilting the saw blade
(1) Crown molding stoppers (L) and (R) (optional accessories)
allow easier cuts of crown molding without tilting the saw
blade. Mount them to both sides the base as shown
in Fig. 32-a. After mounting, tighten the 6 mm knob bolts to
secure the crown molding stoppers.
[Optional accessories used]
• Crown molding vise ass’y (including crown molding stopper (L))
• Crown molding stopper (L)
• Crown molding stopper (R)
(2) The crown molding vise (B) (optional accessory) can be
mounted on either the left fence (fence (B)) or the right
fence (fence (A)). It can unite with the slope of the crown
molding and the vice can be pressed down.
Then turn the upper knob, as necessary, to securely attach
the crown molding in position. To raise or lower the vise
assembly, first loosen the 6 mm knob bolt.
After adjusting the height, firmly tighten the 6 mm wing bolt;
then turn the upper knob, as necessary, to securely attach
the crown molding in position. (see Fig. 32-b)
Fig. 32-a
Crown molding vise ass’y
(optional accessory)
6 mm knob bolt
6 mm wing bolt
Fig. 32-b
Crown molding vise ass’y
(optional accessory)
6 mm knob bolt
6 mm wing bolt
Crown molding stopper (R)
(optional accessory)
6 mm knob
bolt
Crown molding stopper (L)
(optional accessory)
-22-
Page 26

WARNING: Always firmly clamp or vise to secure the crown molding to the fence; otherwise the
crown molding might be thrust from the table and cause bodily harm.
Do not perform bevel cutting. The main body or the saw blade may contact the sub
fence, resulting in an injury.
CAUTION: Always confirm that the motor head does not cont act the cro wn molding vise ass’y when
it is lowered for cutting. If there is any danger that it may do so, loosen the 6 mm knob
bolt and move the crown molding vise ass’y to a position where it will not contact the
saw blade.
Position crown molding with its WALL CONTACT EDGE against the guide fence and its CEILING
CONTACT EDGE against the crown molding stoppers as shown in Fig. 32-b. Adjust the crown molding
stoppers according to the size of the crown molding. Tighten the 6 mm wing bolt to secure the crown
molding stoppers. Refer to the following table for the miter angle.
Table 9
For inside corner
For outside corner
Position in Fig. 26
1
2
3
4
Miter angle Finished piece
Right 45° Save the right side of blade
Left 45°
Save the left side of blade
Save the right side of blade
Right 45° Save the left side of blade
-23-
Page 27

ADJUSTMENT OF COMPONENTS
1. Bevel angle adjustment
Before shipping from the factory, the height of 8-mm bolts (A) and (B) is adjusted so that the saw blade
section (head) will stop at 0° (right angle), and 45° to the left. To change the head stop positions, instruct
the customer to adjust the height of 8-mm bolts (A) and (B) by turning them.
CAUTION:
If there is any clearance between the tip of 8-mm bolt (A) (stopper for 0°) and the fixing pin, the
angle of the saw blade relative to the upper surface of the turn table may not be an exact right angle.
(8-mm bolts (A) and (B) are located at the holder (A).) Press do wn on holder (A) and lock it in
position with the clamp lever so that there is no clearance between the fixing pin and 8-mm bolt (A).
Fig. 33-bFig. 33-a
8 mm bolt (A)
(Stopper for 0°)
8 mm bolt (B)
(Stopper for left 45° bevel angle)
2. Ball bushing (Linear bearing)
(1) Structure of the ball bushing
The ball bushing is commonly called a linear
ball bearing. Inside the bearing is elongated
guide grooves in which steel balls circulate
and roll when a load is applied. (as indicated
by the arrow marks in Fig. 34). This type of
device is widely used in automated machine
tools. The advantage of the ball bushing is
that its friction coefficient remains largely
unchanged even when the load is increased,
ensuring smooth sliding movement.
In addition, slide pipe (B), made of bearing steel and heat treated to a high degree of hardness (HRC 62
to 65), is highly resistant to wear.
Sales persons should have a good understanding of the structure and rugged characteristics of this
exceptional mechanism to enhance sales promotion.
(2) Lubrication
If it is necessary to replace the ball bushing, apply approximately 2 grams (0.1 oz) of grease (Nippeco
SEP 3A) on the steel balls and within the guide grooves of the new ball bushing. If grease is not applied,
it will shorten the service life of the ball bushing, and subsequent abrasive contact between the steel
balls and slide pipe (B) will cause abnormal noise during slide cutting operations. Customers should be
instructed to thoroughly remove sawdust and other foreign matter from slide pipe (A) and slide pipe (B)
and liberally coat them with machine oil at least once a month.
Fig. 34
-24-
Page 28

PACKING
(1) How to install packings (A) and (B)
Remove the dust bag from the main body. Slide
the head section toward the operator and insert
packing (A) between the slide pipe, hinge and
holder (A). Push the head back and secure the
slide in position with packing (A) inserted by
means of the slide securing knob.
Turn the turn table to the right 57° and remove
the side handle. Place packing (B) under the
head and push the head down. Insert the locking
pin while pressing packing (B) to secure the
head section in position (Fig. 35).
Fig. 35
Turn table
Packing (A)
Packing (B)
Slide securing knob
(2) How to install packings (C) and (D)
Put the main body mounted with packings (A)
and (B) in the carton box aligning with the base
packing and the inner frame (Fig. 36).
Put packing (C) in the left side of the carton box
on the top of holder (A).
Put packing (D) in the right side of the carton box
on the top of the switch handle.
Place the accessories in the space at the rear
of the base (Fig. 37).
(3) How to install top packing (E)
Insert packing (E) in packings (C) and (D).
Close the lids of the carton box and bind them
together (Fig. 38).
Fig. 36
Inner frame
Fig. 37
Packing (C) Packing (D)
Fig. 38
Lid
Base packing
Packing (E)
-25-
Packing (C)
Packing (D)
Page 29

REPAIR GUIDE
y
Before attempting disassembly or reassembly, ensure without fail that the switch is turned off and the plug
is disconnected from the power source outlet.
1. Precautions in disassembly and reassembly
Special attention in disassembly should be given to the following items. The circled numbers in the figures
and the [Bold] numbers in the descriptions below correspond to the item numbers in the parts list and
exploded assembly diagram of the Model C 8FSHE. For the Model C 8FSE, refer to the parts list
separately.
* Be sure to first disconnect the power plug when performing disassembly or replacement of the saw blade.
[Only the Model C 8FSHE]
Do not stare into the laser emitting aperture during disassembly and reassembly of the laser marker. Do not
observe beam directly with an optical instrument. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of
procedures other than those specified in this TECHNICAL DATA AND SERVICE MANUAL and the
Instruction Manual may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
Disassembl
1. Turn table and base ass'y
(1) Remove the Tapping Screw (W/Flange) D5 x 25 (Black) [122] and then remove the Guard Ass’y [125].
(2) Hold the Nylon Nut M6 [48] with a 10-mm wrench and remove the Flat Hd. Screw M6 x 25 [51] then
remove the Sub Fence [50] and the Plate [49].
(3) Remove the four Bolts M8 x 35 [43], Spring Washer M8 [44] and Bolt Washer M8 [45]. And then
remove Fence (A) [55] and Fence (B) [47].
(4) Loosen the Clamp Lever [2] and remove the Machine Screw (W/Washers) M4 x 12 (Black) [1]. Turn the
Bolt (Left Hand) D10 [3] to remove from Holder (A) [124].
(5) Remove the Hex. Socket Set Screw M6 x 8 [121] and tap the end of Hinge Shaft (A) [9] with a flat-blade
screwdriver and a hammer to remove it from the Turn Table [13]. This enables to remove the head and
the slide mounted on Holder (A) [124] together from the Turn Table [13].
(6) Remove Shaft (B) [14] and remove the Turn Table [13] from the Base Ass'y [56].
(7) Remove the Side Handle [23] and Retaining Ring (E-Type) for D5 Shaft [22]. Then pull out Shaft (A)
[21].
(8) Remove the Machine Screw M4 x 8 [7]. Then Spring (E) [30], Stopper (A) [31] and Pin Cover [34] can
be removed from the Turn Table [13].
(9) Remove the Seal Lock Hex. Socket Set Screw M6 x 6 [29] and pull out the Lever Shaft [24]. Then the
Lever [25] and Spring (D) [26] can be removed. Shaft (C) [28], Cover (B) [32] and Thrust Washer [33]
can be removed from the Turn Table [13] by removing the Machine Screw M4 x 8 [7].
(10) Remove each mounting screw of Spacer (A) [20] and the Table Insert [19] to remove Spacer (A)
and the Table Insert [19] from the Turn Table [13].
(11) Pull out four Base Rubbers [57] from the Base Ass'y [56].
[20]
-26-
Page 30

Fig. 39-a
Fig. 39-b
-27-
Page 31

2. Lower guard, link, spindle ass'y and dust guide
(1) Remove the Bolt (W/Washers) M6 x 16 (Black) [207] and the Machine Screws (W/Washers) M5 x 8
[191] with the Box Wrench 10 mm [501]. Remove the Spindle Cover [192] from the Gear Case [198].
(2) Remove the Bolt (Left Hand) W/Washer M7 x 17.5 [210] with the Box Wrench 10 mm [501]. Remove
Washer (D) [221], TCT Saw Blade [211] and Washer (D) [221] in this order from the Spindle Ass’y
[217].
(3) Remove the two Flat Hd. Screws M4 x 10 [213]. Remove the Cover [214] and the Lower Guard [215]
from the Bearing Holder [219].
NOTE: Be sure to release the hook of the Return Spring [216] from the groov e of the Lower Guard
[215] then remove the Lower Guard [215] from the Bearing Holder [219].
(4) Remove the Machine Screw M5 x 12 [89] then remove the Spacer [90] and the Link [91] from Hinge (A)
Ass’y [87].
(5) Remove the two Machine Screws M5 x 20 [222] and then remove the Spindle Ass'y [217] by gently
hammering the Gear Case [198] with a plastic hammer.
(6) Remove the Machine Screws (W/Washers) M4 x 12 (Black) [194] and then remove the Dust Guide
[208] and the Guide Holder [209].
Fig. 40
3. Spring, support, hinge ass'y, ball bushing, bushing, holder (A) and gear case
(1) Remove the Machine Screw (W/Washers) M4 x 12 (Black) [111] to remove the Nylon Clip [112].
Remove the Machine Screw (W/Washers) M4 x 12 (Black) [195] and remove the Nylon Clip [196] from
the Gear Case [198] (head).
(2) Push out the Cord Bush [154] from the inside of the Housing Ass’y [155]. Disconnect the connector of
the Switching Power Supply Ass’y [165] and the Laser Marker [107]. Open the Cord Bush [154] to
remove it from the cord of the Laser Marker [107].
(3) Remove the Seal Lock Hex. Socket Hd. Bolt M5 x 10 [197].
NOTE: The Seal Lock Hex. Socket Hd. Bolt M5 x 10 [197] acts as the up per limit stopper of the Gear
Case [198] (head). Be careful that the Gear Case [198] (he ad) is raised by the force of the
Spring [85] when the Seal Lock Hex. Socket Hd. Bolt M5 x 10 [197] is removed.
(4) Remove the Hex. Socket Set Screw M6 x 8 [121]. Make a flat-blade screwdriver contact with the end
surface of Hinge Shaft (A) [92] and lightly tap the screwdriver with a plastic hammer to remove Hinge
Shaft (A) [92].
NOTE: Be sure to hold the Gear Case [198] (head) with hand during disassembly to prevent the
Gear Case [198] (head) from being dropped when removing Hinge Shaft (A) [92] from the
hole of the Gear Case [198] (head). Then the Spring [85] and the Sleev e [84] can be remov ed
from the Gear Case [198] (head).
(5) Remove the two Hex. Socket Set Screws M8 x 10 [86]. Then gently hammer the Support [113] outward
and remove it from slide pipes (A) and (B).
-28-
Page 32

(6) Remove the Knob Bolt M6 x 25 [116] and the Lock Spring [117]. Remove Hinge (A) Ass'y [87] from
Holder (A) [124] by sliding Hinge (A) Ass'y [87].
(7) Remove the Machine Screw M4 x 8 [81]. Lightly tap the end surface of Holder (A) [124] with a plastic
hammer to remove the Ball Bushing [114].
(8) Remove the Seal Lock Hex. Socket Set Screw M6 x 10 [118] from Holder (A) [124]. Remove the
Bushing [115] from Holder (A) [124].
NOTE: Prepare a shaft of 25 mm in diameter and 50 mm in length. Make the shaft contact with the
end surface of the Bushing [115] and lightly tap the shaft with a plastic hammer to remove
the Bushing [115] from Holder (A) [124].
Fig. 41
-29-
Page 33

4. Armature ass'y and lock lever
(1) Remove the Brush Cap [161] and the Carbon Brush [160].
(2) Removing the three Machine Screws (W/Washers) M5 x 40 (Black) [157] allows you to remove the
Housing Ass’y [155] together with the Handle Cover [164] from the Gear Case [198].
(3) Remove the Lock Lever [177] and the Spring [176].
(4) Remove the two Special Screws M6 [205] and remove the Lock Lever [204] and the Lock Lever Spring
[203].
(5) Disassembly of the Armature Ass'y [187]
(a) Remove the Housing Ass'y [155] from the Gear Case [198] according to the above step 4-(1)(2). If
the Rubber Bushing [186] stays in the Housing Ass’y [155], remove it with long nose pliers.
(b) Remove the Armature Ass'y [187] by gently hammering the Gear Case [198] with a plastic hammer.
Fig. 42
-30-
Page 34

5. Handle cover, switch, light, cord, stator ass'y and housing ass'y
(1) Remove the motor section according to the above step 4-(1)(2).
(2) Remove the seven Tapping Screws (W/Flange) D4 x 20 (Black) [163] and remove the Handle Cover
[164].
(3) Disconnect the connectors of the Switching Power Supply Ass’y [165] and Light (H) Ass’y [175] and
remove Light (H) Ass’y [175].
(4) Turn Cap (A) [174] and remove it, then you can remove the Clear Cover [173].
(5) (For the U.S.A. and Canada)
Cut off the two Connectors [168] that are crimped onto the internal wires coming from the Stator Ass'y
[181] and the Switch (3P Faston Type) W/O Lock [170].
(Except for the U.S.A. and Canada)
Loosen the screw of Pillar Terminal(A) [171] with a flatblade screwdriver and disconnect the internal
wires.
(6) Removal of the Switch (3P Faston Type) W/O Lock [170]:
(a) Remove the Handle Cover [164] from the Housing Ass'y [155] according to the above step 5-(1)(2).
Then the Switch (3P Faston Type) W/O Lock [170] can be removed.
(b) The Stator Ass’y [181] and Internal Wire (G) [169] are provided with a claw to prevent coming off of
the connector. When removing the Stator Ass’y [181] and Internal Wire (G) [169] from the Switch
(3P Faston Type) W/O Lock [170], pull out the Stator Ass’y [181] and Internal Wire (G) [169] while
pressing the claw.
(7) Disconnect the faston of the Switching Power Supply Ass’y [165] from the two Switches (W/Cover)
[167] for the Laser Marker [107] and Light (H) Ass’y [175]. Push the Switch (W/Cover) [167] from the
inside of the Housing Ass’y [155] and remove the Switch (W/Cover) [167].
(8) Remove the Tapping Screw (W/Flange) D4 x 16 [151] and remove the Switching Power Supply Ass’y
[165] from the Housing Ass’y [155].
(9) Removal of the Stator Ass’y [181]:
(a) Remove the Fan Guide [178] from the Housing Ass’y [155].
(b) Remove the two Hex. Hd. Tapping Screws D4 x 60 [179] that secure the Stator Ass’y [181] to the
Housing Ass’y
(c) Pull out the Stator Ass’y [181] by lightly tapping the Housing Ass’y [155] at the surface where the
Gear Case [198] is mounted with a plastic hammer.
(10) Remove the two Tapping Screw (W/Flange) D4 x 16 [151] and remove the Cord [110] and the Cord
Armor D10.1 [152].
[155]. Remove the two Brush Terminals [180] from the Brush Holder [159].
Fig. 43
-31-
Page 35

6. Laser marker
(1) Remove the Machine Screw M4 x 8 [81] and
remove the Cover [83] from the rear of Hinge (A)
Ass’y [87].
(2) Remove the three Machine Screws M4 x 8 [108]
and remove Plate (A) [105] and Cover (A) [104]
from Hinge (A) Ass’y [87].
(3) Remove the Adjuster [88] and push the Clutch
Screw [96] from behind Hinge (A) Ass’y [87].
Then Holder (B) [106] can be removed together
with the Laser Marker [107].
NOTE: At this time, the Spring [100] and the
Clutch Spring [101] pop out. Be careful
not to lose them.
(4) Remove the Clutch Screw [96]. Then the Laser
Marker [107] can be removed from Holder (B)
[106].
NOTE: At this time, the two Springs [102] pop out.
Be careful not to lose them.
Fig. 44
7. Vise ass’y
(1) Remove the Wing Bolt M6 x 15 [36] to remove the
Vise Shaft [39].
(2) Remove the Machine Screw M4 x 10 [41] to
remove the Vise Plate [40].
(3) Remove the Knob Bolt M10 x 66 [35] from the
Screw Holder [37].
Fig. 45
-32-
Page 36

Reassembl
y
1. Special attention
Reassembly can be accomplished by following the disassembly procedures in reverse. However, special
attention should be given to the following items.
(1) Prior to reassembly, measure the insulation
resistance of the armature, stator, switch and
other electrical components and confirm that
the insulation resistance of each part is more
than 5 MΩ.
(2) When replacing the Spring [85], apply 3 grams
of Hitachi Motor Grease to the inner
circumference of the new spring prior to
assembly.
(3) When replacing or reassembling the Liner [54],
ensure that it is positioned and assembled as
illustrated in Fig. 46. In addition, coat 10 grams
of Hitachi Motor Grease on the liner sliding
portion of the Turn Table [13].
(4) When replacing the Laser Marker [107], screw the two Seal Lock Hex. Socket Set Screws M5 x 6 [103]
into the Laser Marker [107]. To adjust the accuracy of the Laser Marker [107] easily, protrude the tips of
the two Seal Lock Hex. Socket Set Screws M5 x 6 [103] about 1.5 mm from the Laser Marker [107]
using the 2.5-mm hex. bar wrench so that Holder (B) [106] and the Laser Marker [107] become almost
parallel as shown in Fig. 47-a and Fig. 47-b. Refer to "Adjustment of Laser Marker Accuracy" for
adjustment of the laser marker accuracy.
Fig. 46
Fig. 47-a Fig. 47-b
Cross section viewed from the front
-33-
Page 37

2. Wiring diagram
Carefully ensure that wiring is accomplished as illustrated below. As incorrect wiring will result in lack of
rotation, reverse rotation or other malfunctions, close attention is absolutely necessary.
WARNING: Be sure to turn off the two Switches (W/Cover) [167] on the side of the Housing Ass'y
[155] (Model C 8FSHE) and unplug the power cord plug from the receptacle before
replacing the Laser Marker [107] and the Switching Power Supply Ass’y [165]. Do not
disconnect the connector that connects the Laser Marker [107] with the Switching
Power Supply Ass’y [165] while the Laser Marker [107] is lighting. Otherwise, the Laser
Marker [107] may be damaged due to surge (electricity stored in the Switching Power
Supply Ass’y [165]). Do not stare into beam while the Laser Marker [107] is lighting.
(1) Wiring diagram
Model C 8FSHE for the U.S.A. and Canada
Fig. 48-a
-34-
Page 38

Model C 8FSHE for Europe, Australia and Asia
Fig. 48-b
Model C 8FSE for the U.S.A. and Canada
Fig. 49-a
Model C 8FSE for Europe, Australia and Asia
Fig. 49-b
-35-
Page 39

(2) Actual wiring diagram
Model C 8FSHE for the U.S.A. and Canada
Fig. 50-a
Model C 8FSHE for Europe, Australia and Asia
Fig. 50-b
-36-
Page 40

Model C 8FSE for the U.S.A. and Canada
Fig. 51-a
Model C 8FSE for Europe, Australia and Asia
Fig. 51-b
-37-
Page 41

3. Checking of insulation distance
Do not remove too much of the insulation coating at the internal wire connection. Take care not to let the
core of the internal wire stick out the Connector 50092 [168] or let the internal wires get caught in a joint
between the Housing Ass’y [155] and the Handle Cover [164].
4. No-load current
After no-load operation for 30 minutes, the no-load current values should be as follows.
Voltage 110 V, 120 V 220 V, 230 V, 240 V
No-load current 4.7 A max. 2.5 A max.
5. Reassembly requiring adjustment
(1) Adjustment of squareness between the saw blade (dummy disc) and the fences
It is necessary to check and adjust the right-angle
orientation between the saw blade (dummy disc)
and the fence after disassembly and replacement of
the Base Ass’y [56], Turn Table [13], Fence (A) [55],
Fence (B) [47], Holder (A) [124] and Hinge (A)
Ass’y [87] and after disassembly, reassembly and
adjustment of the Ball Bushing [114]. Adjust the
squareness (rated value 0.15/100 mm) by moving
the fences along the saw blade (dummy disc).
First, adjust the squareness between the saw blade
and either fence. Then adjust flatness of the two
fences by applying a straight edge to the right and
left fence surfaces. Finally, apply a square to the
fence surface that has not been checked yet and
make sure it forms squareness (rated value
0.15/100 mm) with the saw blade.
Fig. 52
(2) Adjustment of the lower limit position of the saw blade
Adjust the unit so that the saw blade (216 mm (8-1/2")) is 10 to 11 mm (13/32" to 7/16") below the base
surface (or top surface of the table insert). Lower the Gear Case [198] (head) and make Hinge (A) Ass’y
[87] contact with the Nylock Bolt M8 x 25 [190] for lower limit position adjustment. Turn the Nylock Bolt
M8 x 25 [190] with a 13-mm wrench and change the height to adjust the lower limit position of the saw
blade.
Fig. 53
8-mm depth
adjustment bolt
Fig. 54
8-mm depth
adjustment bolt
-38-
Page 42

(3) Reassembly of the ball bushing
The Ball Bushing [114] and Holder (A) [124] are
maintained at a smooth fit. When placing the Ball
Bushing [114] into Holder (A) [124], gently hammer it
with a plastic hammer so that the Ball Bushing [114]
is seated into Holder (A) [124] in parallel. After
reassembly, lubricate around the steel balls inside the
Ball Bushing [114] with 2 grams of Nippeco SEP 3A
grease. Apply machine oil to slide pipe (A) and slide
pipe (B) of Hinge (A) Ass’y [87]. When reassembling,
put the Ball Bushing [114] inside Holder (A) [124] as
indicated in (A) of Fig. 55. Visual observation will do
for this insertion. Layout in (A) offers about 30%
higher rated load in (B).
Fig.55
6. Lubrication
Advise the customer to lubricate the machine as indicated below at least once a month. Also, prior to
applying lubricant, any sawdust, dirt or other foreign matter should be thoroughly wiped away with a soft
cloth.
(1) Swiveling section of the gear case
Coat machine oil on the swiveling and sliding portions of the Gear Case [198] and Hinge (A) Ass’y [87].
(2) Vise section
Coat machine oil on the screw thread portion of the Knob Bolt M10 x 66 [35] of the Vise Ass’y [42].
(3) Holder (A)
Coat machine oil on the swiveling and sliding portions of Holder (A) [124] and the Hinge Shaft (A) [9].
7. Product precision
On completion of reassembly, confirm precision tolerances.
Item To le r anc e
Deflection of dummy disc 0.15/φ200
Squareness between base and fence (A) and fence (B)
Flatness of fence (A) and fence (B) 0.15
Squareness between dummy disc and fence (A) and fence (B) 0.15/100
Squareness between fence (A) and fence (B) and slide pipes
(Place a square against fences (see Fig. 56), slide the head and
check for any clearance between the dummy disc and the square.)
Squareness between dummy disc and turn table 0.15/100
Surface alignment of base and turn table
(Use the upper surface of the base as a reference.)
Fig. 56
0.1/65 (Height of fence (A))
0.1/49 (Height of fence (B))
0.15/180
(+) 0.1
(-) 0.2
-39-
Page 43

8. Adjustment of laser marker accuracy
(1) Construction of laser marker and functions of each component
The Adjuster [88] located at the side of Hinge (A) Ass’y [87] is a screw used for moving the
Laser Marker [107] horizontally. The laser line can be aligned with the left side of the cutting width
(saw blade) or the ink line on the right side by means of the Adjuster [88]. The accuracy of the
Laser Marker [107] is adjusted by the two Seal Lock Hex. Socket Set Screws M5 x 6 [103].
The Seal Lock Hex. Socket Set Screw M5 x 6 [103] located at the front is mainly used for
adjusting the squareness with the fence surface.
The Seal Lock Hex. Socket Set Screw M5 x 6 [103] located under the Laser Marker [107] is mainly
used for adjusting the squareness with the base surface (Fig. 57-a).
The laser line will shift to the right in parallel when the Adjuster [88] is turned clockwise, and shift to
the left when turned counterclockwise.
CAUTION: Exercise utmost caution in handling the switch trigger for the position adjustment of
the laser line, as the power plug is plugged into the receptacle during operation.
If the switch trigger is pulled inadvertently, the saw blade can rotate and result in
unexpected accidents.
Do not stare into beam while the laser marker is lighting.
Do not observe beam directly with an optical instrument.
If your eye is exposed directly to the laser beam, it can be hurt.
Instruct the customer not to stare into beam. In addition, instruct the cu stomer not to
give strong impact to the laser marker (m ain body of tool) and not to dismantle the laser
marker. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those
specified in this TECHNICAL DATA AND SERVICE MA NUAL and the Instruction Manual
may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
Fig. 57-a
Fig.55-a
Hinge (A) Ass’y [87]
Laser Marker [107]
-40-
Page 44

Adjustment of squareness with the fence surface Adjustment of squareness with the base surface
Fig. 57-b
The laser line inclines to the left by turning the Seal
Lock Hex. Socket Set Screw M5 x 6 [103]
clockwise and inclines to the right by turning
counterclockwise. The squareness of the laser line
with the fence surface can be adjusted in this
manner.
Fig. 57-c
The laser line inclines to the right by turning the
Seal Lock Hex. Socket Set Screw M5 x 6 [103]
clockwise and inclines to the left by turning
counterclockwise. The squareness of the laser line
with the base surface can be adjusted in this
manner.
(2) Adjustment of the laser marker
Adjust the laser marker according to the following steps from 1) to 5).
Adjust the product accuracy first because the accuracy of the laser marker is adjusted aligning the cut
surface of the workpiece.
1) First, hold a workpiece of 60 mm (2-3/8") in height and 150 mm
Fig. 58-a
(5-15/16") in width with the vise and perform right-angle cutting.
At this time, check that Plate (A) [105], Cover (A) [104] and
the inlet of a hex. bar wrench at Hinge (A) Ass’y [87] (Fig. 57-a)
are closed to prevent saw dust from entering the laser marker.
If they are not closed, block them with tapes.
2)
Light up the Laser Marker [107] with the workpiece held in the
vise. Turn the Adjuster [88] to shift the laser line onto the cutting
surface, top edge or rear edge of the cutting surface.
3) Next, insert a 2.5-mm hex. bar wrench into the inlet and adjust
the two Seal Lock Hex. Socket Set Screws M5 x 6 [103] so that
laser beam is applied to the entire cutting surface. (Before
adjustment of the Laser Marker [107] using a 2.5-mm hex. bar
wrench, remove Caution Label (J) [109], Base Rubber [93] and
the tape adhered to the inlet.) If the laser line gets out of the
cutting surface during the laser line adjustment using the two
Seal Lock Hex. Socket Set Screws M5 x 6 [103], turn the
Adjuster [88] to shift the laser line onto the cutting surface, top
edge or rear edge of the cutting surface then adjust the accuracy
-41-
Fig. 58-b
Page 45

of the laser line. (Repeat this operation 3 or 4 times depending on
the adjusting conditions of the laser marker.) Refer to the above
"(1) Construction of laser marker and functions of each
component" for the relation between the two Seal Lock Hex.
Socket Set Screws M5 x 6 [103] and the laser line.
4) To check the accuracy of the Laser Marker [107], move the Laser
Marker [107] horizontally using the Adjuster [88] again and
check that the laser beam is applied to the entire cutting surface.
If the laser beam is applied to the cutting surface in parallel, the
fine fuzz reflects the laser beam and the entire cutting surface
becomes bright.
5) Make a right-angle ink line on the workpieces of 20 mm (13/16")
in height and 150 mm (5-15/16") in width and 60 mm (2-3/8") in
height and 150 mm (5-15/16") in width respectively. Adjust the
laser marker and perform cutting. If the ink line matches the
cutting position, the accuracy adjustment is completed. (Visually
check that the laser marker accuracy is 0.35/100 or less for both
the squareness with the base surface and the squareness with
the fence surface.)
Fig. 58-c
-42-
Page 46

2. Troubleshooting guide
Item Phenomenon Cause
1 Inaccurate cutting
--- Inaccurate
squareness of the
cut surface
--- Cut surfaces do not
fit together properly.
(a) Inaccurate
squareness between
the turn table and the
saw blade causes the
saw blade to cut into
the workpiece at an
angle.
(b) Excessive deflection
of the saw blade
(Excessive vibration)
Fig. 59
(c) Inaccurate
squareness between
fence (A) and fence
(B) and the saw blade
(d) Surfaces of fence (A)
and fence (B) are not
accurately aligned,
causing workpiece to
deviate from proper
Fig. 60
squareness.
(e) Inaccurate surface
flatness of the turn
table.
Factory
standard
0.15/100
(Dummy disc)
(Fig. 59)
When sliding (tip)
0.25/100
(Dummy disc)
/φ205
0.15
(Dummy disc)
0.15/100
(Fig. 60)
0.10 or less
(Fig. 61)
0.15 or less
Inspection, repair or adjustment
• Readjust squareness with the
Nylock Bolt M8 x 25 [123].
• Replace Hinge (A) Ass’y [87]
or Gear Case [198] or Turn
Table [13] or Base Ass’y [56]
(if deformed).
• Replace the TCT Saw Blade
[211].
• Check for surface defects on
Washer (D) [221] and repair
with a file as necessary.
• Replace Washers (D) [221].
• Loosen the Bolt M8 x 35 [43]
and adjust as necessary.
• Replace Fence (A) [55] and
Fence (B) [47].
• Loosen the Bolt M8 x 35 [43]
and adjust surface alignment
of Fence (A) [55] and Fence
(B) [47] as necessary.
• Replace Fence (A) [55] or
Fence (B) [47].
• Replace the Turn Table [13].
Fig. 61
(f) Squareness between
the saw blade and the
turn table is changed
when sliding.
Same as (a)
(Fig. 62)
• Check precision after press-
fitting slide pipes (A) and (B)
of Hinge (A) Ass'y [87].
If precision is poor, replace
them as necessary. (Fig. 62)
-43-
Page 47

Item Phenomenon Cause
1 • Adjust the clearance between
Slide pipe (A)
Hinge (A) ass’y
Factory
standard
Inspection, repair or adjustment
the Bushing [115] and slide
pipe (A) with the Seal Lock
Hex. Socket Set Screw M6 x
10 [118]. Ensure that slide pipe
section slides smoothly with a
slide load of within 3 kgf.
Slide pipe (B)
Fig. 62
(g) Inaccurate
squareness between
fences (A) and (B),
turn table and base
causes the workpiece
to tilt at an angle and
prevent accurate
0.1/65
(height of Fence (A)
[55])
0.1/49
(height of Fence (B)
[47])
(Fig. 63)
• Replace Fence (A) [55] or
Fence (B) [47] as necessary.
cutting.
Fig. 63
(h) Loose fitting of
swiveling portion of
hinge (A) ass’y and
gear case, or sluggish
movement. As a result,
components may be
deformed because of
unstable gear case or
because the operator
must apply excessive
pressure during
operation.
(i) Excessively fast cutting
speed causes
deflection of saw blade
and inaccurate cutting.
(j) Excessive cutting force
(pressure) is required
because of dull saw
blade.
(k) The workpiece moves
during cutting because
it is bent or deformed.
- • Check the fitting surfaces of
Hinge (A) Ass’y [87], Gear
Case [198] and Hinge Shaft
(A) [92] for any foreign
substance (such as cutting
dust) and remove it as
necessary.
- • Reduce the cutting speed
(appropriately 6 seconds for a
square wood workpiece of 60
mm (2-3/8")).
- • Sharpen the saw blade again.
- • Correct bend, flex or other
deformation by planing and try
cutting.
-44-
Page 48

Item Phenomenon Cause
2 Rough cut surface
Parallelism (A)= 0.02/43
(a) Large deflection of
saw blade.
(Causes rough cut
surface.)
Factory
standard
0.15
/φ205
(Dummy disc)
Inspection, repair or adjustment
• Same as Item 1- (b).
Fig. 64
(b) Poor movement of
slide pipe section
prevents smooth
cutting.
(c) Excessive clearance
at the slide pipe
section.
(d) Surface parallelism of
washers (D) is
inaccurate due to
surface defects such
as impact marks and
scratches.
(e) Improper slide cutting
technique.
(f) Inaccurate squareness
between turn table and
saw blade, causing
saw blade to cut at an
improper angle and
make cutting marks.
Slide load should be
within 3 kgf.
-
0.02/43
(Fig. 64)
- • See paragraph "Slide
0.15/100
(Fig. 59)
• Apply machine oil to the slide
pipe section.
• Check the slide pipe section
for any scratches or the like.
• Repair as necessary.
• Readjust the Bushing [115].
• Readjust the Bushing [115].
• Replace Hinge (A) Ass’y [87],
or the Ball Bushing [114] as
necessary.
• Repair impact marks or
scratches at Washer (D) [221].
• Replace them if necessary.
Cutting." Do not apply
unnecessary force for
successful slide cutting.
• Same as Item 1- (a).
(g) Excessively fast
cutting speed.
(h) Improper clamping of
workpiece.
(i) Turn table is not fixed
with side handle.
(j) Loose fitting of
swiveling portion of
hinge and gear case,
or sluggish movement.
(k) Cutting operation
becomes sluggish
because workpiece is
warped or bent.
(l) Excessive vibration - • Recheck items (a), (c), (d) and
- • Reduce cutting speed.
- • Properly clamp workpiece with
Vise Ass’y [42].
- • During cutting, fix the Turn
Table [13] in position with the
Side Handle [23] without fail.
- • Same as Item 1- (h).
- • Correct warp or bend with
planer.
(i).
-45-
Page 49

Item Phenomenon Cause
3 Saw blade is locked. (a) Excessively fast
cutting speed
Factory
standard
Inspection, repair or adjustment
- • Reduce cutting speed.
4 Saw blade does not
rotate when switch is
triggered.
(b) Core diameter of
extension cord is too
small.
(c) Excessive cutting
force is applied due to
dull saw blade.
(d) Incorrect saw blade is
used.
(e) The saw blade binds
in workpiece during
cutting because
workpiece is warped
or bent.
(a) Power cord is not
connected to power
supply.
(b) Carbon brush wear
exceeds allowable
limit (5 mm).
- • Use a thicker and shorter
extension cord.
- • Resharpen saw blade.
- • Use a suitable Hitachi
supplied saw blade.
• An increased number of teeth
on the saw blade increases
the cutting resistance. When
using a saw blade with a large
number of teeth, reduce the
cutting speed.
- • Correct workpiece
deformation with planer.
- • Check power supply voltage.
• Connect the power cord to
power supply.
- • Check the Carbon Brushes
[160] for wear.
• Replace the Carbon Brushes
[160].
5 Saw blade runs too
slow
(4,950 min
-1
or less).
6 Light (H) Ass’y does
not light.
(Only Model C 8FSHE)
(c) Contact failure of the
switch
- • Check the Switch (3P Faston
Type) W/O Lock [170] for
conductivity.
• Replace the Switch (3P
Faston Type) W/O Lock [170].
(a) Power supply voltage
is lower than rated
voltage.
- • Check for power supply
voltage.
• Check if extension cord is
appropriate. See Instruction
Manual for appropriate
extension cords.
(a) Improper wiring - • Check the wiring.
(b) Switch failure - • Check the Switch (W/Cover)
[167] for conductivity.
• Replace the Switch (W/Cover)
[167].
(c) Switching power
supply failure
- • Check the Switching Power
Supply Ass’y [165] for
conductivity, input and output
referring to "Wiring diagram."
• Replace the Switching Power
Supply Ass’y [165].
(d) Light (H) Ass’y failure - • Replace the Light (H) Ass’y
[175].
-46-
Page 50

Item Phenomenon Cause
7 Laser marker does not
light.
(Only Model C 8FSHE)
(a) Improper wiring - • Check the wiring.
(b) Switch failure - • Check the Switch (W/Cover)
Factory
standard
Inspection, repair or adjustment
[167] for conductivity.
• Replace the Switch (W/Cover)
[167].
8 Laser light is poor or
strong.
(Only Model C 8FSHE)
9 Laser line does not
match the ink line.
(Only Model C 8FSHE)
Fig. 65
(c) Switching power
supply failure
(d) Laser marker failure - • Replace the Laser Marker
(a) Switching power
supply failure
(b) Laser marker failure. - • Same as item 6-(d).
(a) Ink line is not right
angle.
(b) Laser marker
accuracy is not
adjusted properly.
(c) Product accuracy is
not good.
- • Check the Switching Power
Supply Ass’y [165] for
conductivity, input and output
referring to "Wiring diagram."
• Replace the Switching Power
Supply Ass’y [165].
[107].
- • Same as item 6-(c).
- • Make a correct ink line again.
0.35/100
(Fig. 65 and Fig. 66)
- • Readjust the accuracy of the
• Readjust the accuracy of the
laser marker.
(Refer to "Adjustment of laser
marker accuracy.")
product and the laser marker.
• If the forward position of the
laser line is different from the
backward position when
sliding, slide pipe (A) is not
parallel with slide pipe (B).
Replace Hinge (A) Ass'y [87].
Fig. 66
10 Laser line does not
match the cutting
position.
(Only Model C 8FSHE)
(a) Laser marker is
horizontally deviated
from the saw blade.
(b) Laser marker
accuracy is not
adjusted properly.
- • Adjust the position of the laser
line. (Refer to "Position
adjustment of laser line.")
0.35/100
(Fig. 65 and Fig. 66)
• Same as item 9-(b).
-47-
Page 51

STANDARD REPAIR TIME (UNIT) SCHEDULES
MODEL
C 8FSHE
Variable
Fixed
General assembly
10 20 30 40 50 60
Work Flow
Spacer
Link
Ball Bearing
(606ZZ)
Lower Guard
Dust Guide
Guide Holder
Sleeve
Spring
Lock Lever
Stopper Pin
Clamp Lever
Bolt (Left Hand)
Spindle Ass’y
Ball Bearing
(6003VV)
Ball Bearing
(608VV)
Handle Cover
Cord
Cord Armor
Switching
Power Supply
Switch
Light (H) Ass’y
Switch
(W/Cover)
Set Pin
Hinge
Shaft (A)
Bearing
Holder
Ball Bearing
(6000VV)
Ball Bearing
(608VV)
Support
Housing
Ass’y
Stator Ass’y
Armature
Ass’y
Holder (B)
Laser Marker
Hinge (A) Ass’y
Ball Bushing
Holder (A)
Gear Case
Table In se r t
x 2
Sub Fence
Guard
Vise Plate
Vise Shaft
Fence (A)
Fence (B)
Shaft (B)
Spring
Liner
Spacer (A)
Turn Table
Base Ass’y
-48-
Page 52

y
STANDARD REPAIR TIME (UNIT) SCHEDULES
MODEL
C 8FSE
Variable
Fixed
General assembl
10 20 30 40 50 60
Work Flow
Spacer
Link
Ball Bearing
(606ZZ)
Lower Guard
Dust Guide
Guide Holder
Sleeve
Spring
Lock Lever
Stopper Pin
Clamp Lever
Bolt (Left Hand)
Spindle Ass’y
Ball Bearing
(6003VV)
Ball Bearing
(608VV)
Handle Cover
Cord
Cord Armor
Switch
Set Pin
Hinge
Shaft (A)
Bearing
Holder
Ball Bearing
(6000VV)
Ball Bearing
(608VV)
Support
Housing
Ass’y
Stator Ass’y
Armature
Ass’y
Hinge (A) Ass’y
Ball Bushing
Holder (A)
Gear Case
Table In se r t
x 2
Sub Fence
Guard
Vise Plate
Vise Shaft
Fence (A)
Fence (B)
Shaft (B)
Spring
Liner
Spacer (A)
Turn Table
Base Ass’y
-49-
Page 53

SLIDE COMPOUND SAW
LIST NO. E949
43
44
45
601
Model C 8FSHE
1
2
3
4
5
6
9
605
604
7
8
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
48
601
46
47
607
602
(E1)
14
15
12
10
13
11
16
8
17
18
611
19
20
8
7
A
30
31
34
8
7
42
49
50
603
604
51
52
53
27
28
32
8
7
29
33
8
7
A
43
44
45
54
55
620
56
57
612
613
614
615
616
617
618
619
606 611
21
22
23
26
25
24
633
607 620
621
626
626
627
628
629
630
624
623
622
625
621
58
631
630
632
606
608
59
609
610
Page 54

C 8FSHE
81
82
89
90
91
83
92
96
93
97
85
84
86
87
88
94
95
99
98
100
110
111
112
86
113
81
82
114
115
106
116
117
118
107
120
101
102
103
104
105
103
102
82
108
109
119
82
121
122
123
124
125
2 - 08- 2 -
Page 55

501
151
152
153
154
155
C 8FSHE
156
157
162
163
502
164
151
165
166
168 169
176
177
167
170
175
173
171
172
174
178
179
158
159
160
161
181
180
186
185
184
183
191
206
207
192
193
188
189
190
194
121
199
208
200
201
209
195
202
196
210
197
182
221
198
211
203
212
187
204
221
213
205
214
215
216
217
220
219
218
223
222
2 - 08
- 3 -
Page 56

PART
S
ITEM
NO.
CODE NO.
DESCRIPTION REMARKS
NO.
USED
C 8FSHE
1 935-196 MACHINE SCREW (W/WASHERS) M4X12 (BLACK) 1
2 312-488 CLAMP LEVER 1
3 329-409 BOLT (LEFT HAND) D10 1
4 965-077 SPECIAL WASHER 1
5 325-028 SET PIN 1
6 996-407 O-RING (1AP-12) 1
7 949-215 MACHINE SCREW M4X8 (10 PCS.) 5
8 949-429 BOLT WASHER M4 (10 PCS.) 6
9 320-141 HINGE SHAFT (A) 1
10 329-417 SCALE (B) 1
11 329-408 LINER (A) 1
12 312-481 SPRING 1
13 329-422 TURN TABLE 1 INCLUD. 10
14 329-418 SHAFT (B) 1
15 949-437 BOLT WASHER M12 (10 PCS.) 2
16 949-217 MACHINE SCREW M4X12 (10 PCS.) 1
17 321-329 INDICATOR 1
18 949-256 MACHINE SCREW M6X16 (10 PCS.) 6
19 329-421 TABLE INSERT 2
20 321-342 SPACER (A) 1
21 329-416 SHAFT (A) 1
22 673-489 RETAINING RING (E-TYPE) FOR D5 SHAFT 1
23 322-283 SIDE HANDLE 1
24 321-339 LEVER SHAFT 1
25 321-338 LEVER 1
26 321-340 SPRING (D) 1
* 27 CAUTION LABEL (D) 1
* 27 CAUTION LABEL (C) 1
28 329-415 SHAFT (C) 1
29 987-860
SEAL LOCK HEX. SOCKET SET SCREW M6X6 1
30 321-417 SPRING (E) 1
31 322-280 STOPPER (A) 1
32 324-395 COVER (B) 1
33 875-249 THRUST WASHER 1
34 321-336 PIN COVER 1
35 302-522 KNOB BOLT M10X66 1
36 301-806 WING BOLT M6X15 1
37 SCREW HOLDER 1
38 949-432 BOLT WASHER M6 (10 PCS.) 1
39 329-859 VISE SHAFT 1
40 302-532 VISE PLATE 1
41 949-216 MACHINE SCREW M4X10 (10 PCS.) 1
42 329-860 VISE ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 35-41
43 949-678 BOLT M8X35 (10 PCS.) 4
44 949-457 SPRING WASHER M8 (10 PCS.) 4
45 949-433 BOLT WASHER M8 (10 PCS.) 4
46 307-937 WING BOLT (A) 1
47 329-420 FENCE (B) 1
48 963-837 NYLON NUT M6 1
49 329-465 PLATE 1
- 4 - 2 - 08
*ALTERNATIVE PARTS
Page 57

PART
S
ITEM
NO.
CODE NO.
DESCRIPTION REMARKS
NO.
USED
C 8FSHE
* 50 SUB FENCE 1 FOR USA, CAN
51 949-342 FLAT HD. SCREW M6X25 (10 PCS.) 1
52 998-844 HOLDER 1
53 949-610 BOLT M6X10 (10 PCS.) 1
54 324-400 LINER 3
55 329-419 FENCE (A) 1
56 329-414 BASE ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 53, 57, 58
57 323-606 BASE RUBBER 4
58 315-210 SCALE (A) 1
* 59 CAUTION LABEL (A) 1
* 59 CAUTION LABEL (B) 1 FOR CHN
81 949-215 MACHINE SCREW M4X8 (10 PCS.) 2
82 949-429 BOLT WASHER M4 (10 PCS.) 6
83 329-491 COVER 1
84 322-889 SLEEVE 1
85 329-410 SPRING 1
86 961-554 HEX. SOCKET SET SCREW M8X10 4
87 329-427 HINGE (A) ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 86, 113
88 319-270 ADJUSTER 1
89 949-237 MACHINE SCREW M5X12 (10 PCS.) 1
90 998-980 SPACER 1
91 329-411 LINK 1
92 320-141 HINGE SHAFT (A) 1
93 323-606 BASE RUBBER 1
94 984-528 O-RING (P-6) 1
95 302-518 STOPPER PIN ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 94
96 305-180 CLUTCH SCREW 1
97 305-179 CLUTCH SPRING 1
98 962-614 ADJUSTING WASHER (B) T0.5 1
99 319-268 PLATE (B) 1
100 319-267 SPRING 1
101 305-179 CLUTCH SPRING 1
102 319-267 SPRING 2
103 319-541
SEAL LOCK HEX. SOCKET SET SCREW M5X6 2
104 319-271 COVER (A) 1
105 322-291 PLATE (A) 1
106 319-269 HOLDER (B) 1
107 329-863 LASER MARKER 1
108 949-215 MACHINE SCREW M4X8 (10 PCS.) 3
109 CAUTION LABEL (J) 1
* 110 500-234Z CORD 1 (CORD ARMOR D10.1)
* 110 500-247Z CORD 1
(CORD ARMOR D10.1) FOR FIN, DEN, SWE, NOR
* 110 500-434Z CORD 1 (CORD ARMOR D10.1) FOR USA, CAN
* 110 500-439Z CORD 1 (CORD ARMOR D10.1) FOR AUS
* 110 500-423Z CORD 1 (CORD ARMOR D10.1) FOR KUW, SIN
* 110 500-456Z CORD 1 (CORD ARMOR D10.1) FOR CHN
* 110 500-435Z CORD 1 (CORD ARMOR D10.1) FOR HKG
* 110 500-455Z CORD 1 (CORD ARMOR D10.1) FOR THA
111 935-196
MACHINE SCREW (W/WASHERS) M4X12 (BLACK) 1
112 948-614 NYLON CLIP 1
2 - 08 - 5 -
*ALTERNATIVE PARTS
Page 58

PART
S
ITEM
NO.
CODE NO.
DESCRIPTION REMARKS
NO.
USED
C 8FSHE
112 948-193 NYLON CLIP 1
113 329-492 SUPPORT 1
114 329-424 BALL BUSHING 1
115 326-141 BUSHING 1
116 324-418 KNOB BOLT M6X25 1
117 947-859 LOCK SPRING 1
118 307-956
SEAL LOCK HEX. SOCKET SET SCREW M6X10 1
119 949-217 MACHINE SCREW M4X12 (10 PCS.) 1
120 321-329 INDICATOR 1
121 301-575 HEX. SOCKET SET SCREW M6X8 2
122 305-558
TAPPING SCREW (W/FLANGE) D5X25 (BLACK) 1
123 303-409 NYLOCK BOLT M8X25 2
124 329-428 HOLDER (A) 1
125 324-372 GUARD ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 122
151 984-750 TAPPING SCREW (W/FLANGE) D4X16 3
152 938-051 CORD ARMOR D10.1 1
153 937-631 CORD CLIP 1
154 319-349 CORD BUSH 1
155 329-490 HOUSING ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 158, 159
156 NAME PLATE 1
157 322-123
MACHINE SCREW (W/WASHERS) M5X40 (BLACK) 3
158 938-477 HEX. SOCKET SET SCREW M5X8 2
159 957-571 BRUSH HOLDER 2
* 160 999-001 CARBON BRUSH (1 PAIR) 2
* 160 999-021 CARBON BRUSH (1 PAIR) 2 FOR USA, CAN
161 931-266 BRUSH CAP 2
162 303-970 TAPPING SCREW (CLASS 2) D4X14 1
163 301-653
TAPPING SCREW (W/FLANGE) D4X20 (BLACK) 7
164 329-438 HANDLE COVER 1
* 165 329-488 SWITCHING POWER SUPPLY ASS'Y 1
* 165 329-487 SWITCHING POWER SUPPLY ASS'Y 1 FOR USA, CAN
166 324-518 FERRITE CORE 1
167 319-503 SWITCH (W/COVER) 2
* 168 959-141 CONNECTOR 50092 (10 PCS.) 2 FOR USA, CAN
* 169 329-461 INTERNAL WIRE (G) 1
* 169 329-430 INTERNAL WIRE (G) 1 FOR USA, CAN
170 324-424 SWITCH (3P FASTON TYPE) W/O LOCK 1
* 171 958-308Z PILLAR TERMINAL (A) 1 EXCEPT FOR USA, CAN
* 172 930-039 NOISE SUPPRESSOR 1 EXCEPT FOR USA, CAN
173 329-821 CLEAR COVER 1
174 322-375 CAP (A) 1
175 329-489 LIGHT (H) ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 173, 174
176 323-433 SPRING 1
177 323-432 LOCK LEVER 1
178 329-436 FAN GUIDE 1
179 960-108 HEX. HD. TAPPING SCREW D4X60 2
180 931-867 BRUSH TERMINAL 2
* 181 340-729D STATOR ASS'Y 120V 1 INCLUD. 180
* 181 340-729E STATOR ASS'Y 220V-230V 1 INCLUD. 180
* 181 340-729F STATOR ASS'Y 240V 1 INCLUD. 180
- 6 - 2 - 08
*ALTERNATIVE PARTS
Page 59

PART
S
ITEM
NO.
CODE NO.
DESCRIPTION REMARKS
NO.
USED
C 8FSHE
182 608-VVM BALL BEARING 608VVC2PS2L 1
183 315-877 DUST SEAL 1
184 600-0VV BALL BEARING 6000VVCMPS2L 1
185 322-089 BEARING BUSHING 1
186 322-090 RUBBER BUSHING 1
* 187 360-839U ARMATURE ASS'Y 110V-120V 1 INCLUD. 182-184
* 187 360-839E ARMATURE ASS'Y 220V-230V 1 INCLUD. 182-184
* 187 360-839F ARMATURE ASS'Y 240V 1 INCLUD. 182-184
188 961-468 KNOB BOLT M6X37 1
189 988-821 LOCK SPRING 1
190 303-409 NYLOCK BOLT M8X25 1
191 996-274 MACHINE SCREW (W/WASHERS) M5X8 1
192 329-425 SPINDLE COVER 1
* 193 WARNING LABEL (A) 1 FOR USA, CAN
194 935-196
195 935-196
MACHINE SCREW (W/WASHERS) M4X12 (BLACK) 1
MACHINE SCREW (W/WASHERS) M4X12 (BLACK) 1
196 980-523 NYLON CLIP 1
197 877-839 SEAL LOCK HEX. SOCKET HD. BOLT M5X10 1
198 329-431 GEAR CASE 1
199 949-260 MACHINE SCREW M6X25 (10 PCS.) 1
200 606-ZZM BALL BEARING 606ZZC2PS2L 1
201 949-455 SPRING WASHER M6 (10 PCS.) 1
202 949-425 WASHER M6 (10 PCS.) 1
* 203 329-463 LOCK LEVER SPRING 1 EXCEPT FOR USA, CAN, KUW, CHN,
HKG, THA, INA, SIN
* 204 329-462 LOCK LEVER 1 EXCEPT FOR USA, CAN, KUW, CHN,
HKG, THA, INA, SIN
* 205 322-950 SPECIAL SCREW M6 2 EXCEPT FOR USA, CAN, KUW, CHN,
HKG, THA, INA, SIN
206 328-922 HITACHI PLATE 1
207 308-259 BOLT (W/WASHERS) M6X16 (BLACK) 1
208 321-364 DUST GUIDE 1
209 312-492 GUIDE HOLDER 1
210 998-335 BOLT (LEFT HAND) W/WASHER M7X17.5 1
* 211 TCT SAW BLADE 216MM-D15.88 HOLE-NT24 1
* 211 TCT SAW BLADE 216MM-D25.4 HOLE-NT24 1
* 211 TCT SAW BLADE 216MM-D30 HOLE-NT24 1
* 212 974-663Z COLLAR (A) FOR D30 HOLE 1 FOR EUROPE, AUS
* 212 976-819 COLLAR (B) FOR D25.4 HOLE 1
FOR KUW, CHN, HKG, IND, THA, INA, SIN
213 949-322 FLAT HD. SCREW M4X10 (10 PCS.) 2
214 307-731 COVER 1
215 329-412 LOWER GUARD 1
216 317-203 RETURN SPRING 1
217 329-432 SPINDLE ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 218-220
218 327-694
BALL BEARING 6003VVCM (NYLON RETAINER) 1
219 329-435 BEARING HOLDER 1
220 608-VVM BALL BEARING 608VVC2PS2L 1
221 308-789 WASHER (D) 2
222 949-241 MACHINE SCREW M5X20 (10 PCS.) 2
223 949-454 SPRING WASHER M5 (10 PCS.) 2
2 - 08 - 7 -
*ALTERNATIVE PARTS
Page 60

STANDARD ACCESSORIE
S
S
ITEM
NO.
CODE NO.
DESCRIPTION REMARKS
501 940-543 BOX WRENCH 10MM 1
502 322-955 DUST BAG (BLACK) 1
NO.
USED
OPTIONAL ACCESSORIE
ITEM
ITEM
CODE NO.
NO.
NO.
CODE NO.
DESCRIPTION REMARKS
601 963-837 NYLON NUT M6 1
602 329-465 PLATE 1
603 SUB FENCE 1
604 949-342 FLAT HD. SCREW M6X25 (10 PCS.) 1
605 329-464 SUB FENCE ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 601-604
606 321-374 CROWN MOLDING STOPPER (L) ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 607-610
607 960-017 KNOB BOLT M6X32 1
608 321-390 CROWN MOLDING STOPPER HOLDER 1
609 CROWN MOLDING STOPPER (L) 1
610 301-806 WING BOLT M6X15 1
611 322-957 VISE (B) ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 612-618
612 998-836 KNOB BOLT M6X11 1
613 SCREW HOLDER (B) 1
614 306-985 WASHER (H) 1
615 964-851 BASE RUBBER 1
616 304-043
MACHINE SCREW (W/WASHERS) M4X10 (BLACK) 1
617 318-967 VISE SHAFT 1
618 321-551 KNOB BOLT M10X54 1
619 329-426 CROWN MOLDING VISE ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 606, 611
620 974-561 STOPPER 1
621 949-404 WING BOLT M6X20 (10 PCS.) 1
622 321-390 CROWN MOLDING STOPPER HOLDER 1
623 CROWN MOLDING STOPPER (R) 1
624 301-806 WING BOLT M6X15 1
625 321-373 CROWN MOLDING STOPPER (R) ASS'Y 1
626 HOLDER ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 627-632
627 321-549 HOLDER 2
628 949-313 WING NUT M6 (10 PCS.) 2
629 949-556 NUT M6 (10 PCS.) 2
630 967-329 WASHER (H) 4
631 996-261 VISE PLATE 2
632 996-283 HIGH TENSION BOLT M6X65 2
633 321-553 GUIDE ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 607, 620, 621, 626
634 998-840 TCT SAW BLADE 216MM-D15.88 HOLE-NT24 1
635 998-858 TCT SAW BLADE 216MM-D25.4 HOLE-NT24 1
636 998-859 TCT SAW BLADE 216MM-D30 HOLE-NT24 1
NO.
NO.
USED
USED
C 8FSHE
- 8 - Printed in Japan 2 - 08
*ALTERNATIVE PARTS
(080219N)
Page 61

SLIDE COMPOUND SAW
LIST NO. E948
42
43
44
601
Model C 8FSE
1
2
3
4
5
6
9
605
604
7
8
47
601
45
46
607
602
(E1)
14
15
12
10
13
11
16
8
17
18
611
19
20
8
7
A
29
30
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
48
603
8
7
41
49
604
50
51
8
7
53
52
27
31
28
32
8
7
A
42
43
44
54
55
620
56
57
612
613
614
615
616
617
618
619
623
625
22
624
606 611
26
633
607 620
621
23
626
626
627
628
629
630
631
630
632
21
25
24
622
621
606
608
58
609
610
Page 62

85
C 8FSE
82
81
83
84
88
87
86
89
90
94
95
96
83
97
98
92
99
100
101
102
103
92
105
91
92
93
104
106
107
108
109
110
2 - 08- 2 -
Page 63

C 8FSE
161
501
502
162
151
163
164
152
169
165
170
153
171
166
167
168
154
172
173
155
156
157
158
159
160
175
174
180
179
178
177
185
191
192
186
187
182
183
184
188
106
193
200
194
195
201
196
202
189
176
213
190
203
197
204
181
198
213
205
199
206
207
208
209
212
211
210
215
214
2 - 08
- 3 -
Page 64

PART
S
ITEM
NO.
CODE NO.
DESCRIPTION REMARKS
NO.
USED
C 8FSE
1 935-196 MACHINE SCREW (W/WASHERS) M4X12 (BLACK) 1
2 312-488 CLAMP LEVER 1
3 329-409 BOLT (LEFT HAND) D10 1
4 965-077 SPECIAL WASHER 1
5 325-028 SET PIN 1
6 996-407 O-RING (1AP-12) 1
7 949-215 MACHINE SCREW M4X8 (10 PCS.) 5
8 949-429 BOLT WASHER M4 (10 PCS.) 6
9 320-141 HINGE SHAFT (A) 1
10 329-417 SCALE (B) 1
11 329-408 LINER (A) 1
12 312-481 SPRING 1
13 329-422 TURN TABLE 1 INCLUD. 10
14 329-418 SHAFT (B) 1
15 949-437 BOLT WASHER M12 (10 PCS.) 2
16 949-217 MACHINE SCREW M4X12 (10 PCS.) 1
17 321-329 INDICATOR 1
18 949-256 MACHINE SCREW M6X16 (10 PCS.) 6
19 329-421 TABLE INSERT 2
20 321-342 SPACER (A) 1
21 329-416 SHAFT (A) 1
22 673-489 RETAINING RING (E-TYPE) FOR D5 SHAFT 1
23 322-283 SIDE HANDLE 1
24 321-339 LEVER SHAFT 1
25 321-338 LEVER 1
26 321-340 SPRING (D) 1
27 329-415 SHAFT (C) 1
28 987-860
SEAL LOCK HEX. SOCKET SET SCREW M6X6 1
29 321-417 SPRING (E) 1
30 322-280 STOPPER (A) 1
31 324-395 COVER (B) 1
32 875-249 THRUST WASHER 1
33 321-336 PIN COVER 1
34 302-522 KNOB BOLT M10X66 1
35 301-806 WING BOLT M6X15 1
36 SCREW HOLDER 1
37 949-432 BOLT WASHER M6 (10 PCS.) 1
38 329-859 VISE SHAFT 1
39 302-532 VISE PLATE 1
40 949-216 MACHINE SCREW M4X10 (10 PCS.) 1
41 329-860 VISE ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 34-40
42 949-678 BOLT M8X35 (10 PCS.) 4
43 949-457 SPRING WASHER M8 (10 PCS.) 4
44 949-433 BOLT WASHER M8 (10 PCS.) 4
45 307-937 WING BOLT (A) 1
46 329-420 FENCE (B) 1
* 47 963-837 NYLON NUT M6 1 FOR USA, CAN
* 48 329-465 PLATE 1 FOR USA, CAN
* 49 SUB FENCE 1 FOR USA, CAN
* 50 949-342 FLAT HD. SCREW M6X25 (10 PCS.) 1 FOR USA, CAN
- 4 - 2 - 08
*ALTERNATIVE PARTS
Page 65

PART
S
ITEM
NO.
CODE NO.
DESCRIPTION REMARKS
NO.
USED
C 8FSE
51 998-844 HOLDER 1
52 949-610 BOLT M6X10 (10 PCS.) 1
53 324-400 LINER 3
54 329-419 FENCE (A) 1
55 329-414 BASE ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 52, 56, 57
56 323-606 BASE RUBBER 4
57 315-210 SCALE (A) 1
* 58 CAUTION LABEL (A) 1
* 58 CAUTION LABEL (B) 1 FOR USA, CAN
81 322-889 SLEEVE 1
82 329-410 SPRING 1
83 961-554 HEX. SOCKET SET SCREW M8X10 4
84 329-427 HINGE (A) ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 83, 97
85 949-237 MACHINE SCREW M5X12 (10 PCS.) 1
86 998-980 SPACER 1
87 329-411 LINK 1
88 320-141 HINGE SHAFT (A) 1
89 984-528 O-RING (P-6) 1
90 302-518 STOPPER PIN ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 89
91 324-058 HINGE COVER 1
92 949-429 BOLT WASHER M4 (10 PCS.) 5
93 949-215 MACHINE SCREW M4X8 (10 PCS.) 3
* 94 500-234Z CORD 1 (CORD ARMOR D10.1)
* 94 500-247Z CORD 1
(CORD ARMOR D10.1) FOR FIN, DEN, SWE, NOR
* 94 500-461Z CORD 1 (CORD ARMOR D10.1) FOR GBR (110V)
* 94 500-435Z CORD 1 (CORD ARMOR D10.1) FOR GBR (230V)
* 94 500-447Z CORD 1 (CORD ARMOR D10.1) FOR SUI
* 94 500-434Z CORD 1
(CORD ARMOR D10.1) FOR USA, CAN
* 94 930-055 CORD 1 (CORD ARMOR D10.1) FOR VEN
* 94 500-439Z CORD 1 (CORD ARMOR D10.1) FOR AUS
* 94 500-423Z CORD 1 (CORD ARMOR D10.1) FOR KUW, SIN
* 94 500-456Z CORD 1 (CORD ARMOR D10.1) FOR CHN
* 94 500-455Z CORD 1 (CORD ARMOR D10.1) FOR THA
* 94 500-234Z CORD 1 (CORD ARMOR D10.1) FOR INA
95 935-196
MACHINE SCREW (W/WASHERS) M4X12 (BLACK) 1
* 96 948-614 NYLON CLIP 1
* 96 948-193 NYLON CLIP 1
FOR GBR (110V), USA, CAN, VEN, TPE
97 329-492 SUPPORT 1
98 949-215 MACHINE SCREW M4X8 (10 PCS.) 1
99 329-424 BALL BUSHING 1
100 326-141 BUSHING 1
101 324-418 KNOB BOLT M6X25 1
102 947-859 LOCK SPRING 1
103 307-956
SEAL LOCK HEX. SOCKET SET SCREW M6X10 1
104 949-217 MACHINE SCREW M4X12 (10 PCS.) 1
105 321-329 INDICATOR 1
106 301-575 HEX. SOCKET SET SCREW M6X8 2
107 305-558
TAPPING SCREW (W/FLANGE) D5X25 (BLACK) 1
108 303-409 NYLOCK BOLT M8X25 2
109 329-428 HOLDER (A) 1
2 - 08 - 5 -
*ALTERNATIVE PARTS
Page 66

PART
S
ITEM
NO.
CODE NO.
DESCRIPTION REMARKS
NO.
USED
C 8FSE
110 324-372 GUARD ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 107
151 984-750 TAPPING SCREW (W/FLANGE) D4X16 2
152 938-051 CORD ARMOR D10.1 1
153 937-631 CORD CLIP 1
154 329-437 HOUSING ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 157, 158
155 NAME PLATE 1
156 322-123
MACHINE SCREW (W/WASHERS) M5X40 (BLACK) 3
157 938-477 HEX. SOCKET SET SCREW M5X8 2
158 957-571 BRUSH HOLDER 2
* 159 999-001 CARBON BRUSH (1 PAIR) 2
* 159 999-021 CARBON BRUSH (1 PAIR) 2
FOR GBR (110V), USA, CAN, VEN, TPE
160 931-266 BRUSH CAP 2
161 301-653
TAPPING SCREW (W/FLANGE) D4X20 (BLACK) 7
162 329-438 HANDLE COVER 1
163 324-518 FERRITE CORE 1
* 164 959-141 CONNECTOR 50092 (10 PCS.) 2 FOR USA, CAN
* 165 329-461 INTERNAL WIRE (G) 1
* 165 329-430 INTERNAL WIRE (G) 1 FOR USA, CAN
166 324-424 SWITCH (3P FASTON TYPE) W/O LOCK 1
* 167 958-308Z PILLAR TERMINAL (A) 1 EXCEPT FOR USA, CAN
* 168 329-861 NOISE SUPPRESSOR 220V-240V 1
EXCEPT FOR GBR (110V), USA, CAN, VEN
* 168 329-862 NOISE SUPPRESSOR 110V 1 FOR GBR (110V), VEN, TPE
169 329-439 CAP 1
170 323-433 SPRING 1
171 323-432 LOCK LEVER 1
172 329-436 FAN GUIDE 1
173 960-108 HEX. HD. TAPPING SCREW D4X60 2
174 931-867 BRUSH TERMINAL 2
* 175 340-729C STATOR ASS'Y 110V 1 INCLUD. 174
* 175 340-729D STATOR ASS'Y 120V 1 INCLUD. 174
* 175 340-729E STATOR ASS'Y 220V-230V 1 INCLUD. 174
* 175 340-729F STATOR ASS'Y 240V 1 INCLUD. 174
176 608-VVM BALL BEARING 608VVC2PS2L 1
177 315-877 DUST SEAL 1
178 600-0VV BALL BEARING 6000VVCMPS2L 1
179 322-089 BEARING BUSHING 1
180 322-090 RUBBER BUSHING 1
* 181 360-839U ARMATURE ASS'Y 110V-120V 1 INCLUD. 176-178
* 181 360-839E ARMATURE ASS'Y 220V-230V 1 INCLUD. 176-178
* 181 360-839F ARMATURE ASS'Y 240V 1 INCLUD. 176-178
182 961-468 KNOB BOLT M6X37 1
183 988-821 LOCK SPRING 1
184 303-409 NYLOCK BOLT M8X25 1
185 996-274 MACHINE SCREW (W/WASHERS) M5X8 1
186 329-413 SPINDLE COVER 1
187 WARNING LABEL 1
188 935-196
MACHINE SCREW (W/WASHERS) M4X12 (BLACK) 1
189 877-839 SEAL LOCK HEX. SOCKET HD. BOLT M5X10 1
190 329-431 GEAR CASE 1
191 328-922 HITACHI PLATE 1
- 6 - 2 - 08
*ALTERNATIVE PARTS
Page 67

PART
S
ITEM
NO.
CODE NO.
DESCRIPTION REMARKS
192 308-259 BOLT (W/WASHERS) M6X16 (BLACK) 1
193 949-260 MACHINE SCREW M6X25 (10 PCS.) 1
194 606-ZZM BALL BEARING 606ZZC2PS2L 1
195 949-455 SPRING WASHER M6 (10 PCS.) 1
196 949-425 WASHER M6 (10 PCS.) 1
* 197 329-463 LOCK LEVER SPRING 1
* 198 329-462 LOCK LEVER 1 EXCEPT FOR USA, CAN, VEN, KUW, IND,
* 199 322-950 SPECIAL SCREW M6 2 EXCEPT FOR USA, CAN, VEN, KUW, IND,
200 321-364 DUST GUIDE 1
201 312-492 GUIDE HOLDER 1
202 998-335 BOLT (LEFT HAND) W/WASHER M7X17.5 1
* 203 TCT SAW BLADE 216MM-D15.88 HOLE-NT24 1
* 203 TCT SAW BLADE 216MM-D25.4 HOLE-NT24 1
* 203 TCT SAW BLADE 216MM-D30 HOLE-NT24 1
* 204 976-819 COLLAR (B) FOR D25.4 HOLE 1
* 204 974-663Z COLLAR (A) FOR D30 HOLE 1 FOR EUROPE, AUT, GBR, FIN, DEN,
205 949-322 FLAT HD. SCREW M4X10 (10 PCS.) 2
206 307-731 COVER 1
207 329-412 LOWER GUARD 1
208 317-203 RETURN SPRING 1
209 329-432 SPINDLE ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 211-213
210 327-694
BALL BEARING 6003VVCM (NYLON RETAINER) 1
211 329-435 BEARING HOLDER 1
212 608-VVM BALL BEARING 608VVC2PS2L 1
213 308-789 WASHER (D) 2
214 949-241 MACHINE SCREW M5X20 (10 PCS.) 2
215 949-454 SPRING WASHER M5 (10 PCS.) 2
NO.
USED
EXCEPT FOR USA, CAN, VEN, KUW, IND,
INA, CHN, THA, TPE, SIN, KOR
INA, CHN, THA, TPE, SIN, KOR
INA, CHN, THA, TPE, SIN, KOR
FOR VEN, KUW, IND, INA, CHN, THA, TPE, SIN, KOR
SWE, NOR, SUI, AUS
C 8FSE
2 - 08 - 7 -
*ALTERNATIVE PARTS
Page 68

STANDARD ACCESSORIE
S
S
ITEM
NO.
CODE NO.
DESCRIPTION REMARKS
501 940-543 BOX WRENCH 10MM 1
502 322-955 DUST BAG (BLACK) 1
NO.
USED
OPTIONAL ACCESSORIE
ITEM
ITEM
CODE NO.
NO.
NO.
CODE NO.
DESCRIPTION REMARKS
601 963-837 NYLON NUT M6 1
602 329-465 PLATE 1
603 SUB FENCE 1
604 949-342 FLAT HD. SCREW M6X25 (10 PCS.) 1
605 329-464 SUB FENCE ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 601-604
606 321-374 CROWN MOLDING STOPPER (L) ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 607-610
607 960-017 KNOB BOLT M6X32 1
608 321-390 CROWN MOLDING STOPPER HOLDER 1
609 CROWN MOLDING STOPPER (L) 1
610 301-806 WING BOLT M6X15 1
611 322-957 VISE (B) ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 612-618
612 998-836 KNOB BOLT M6X11 1
613 SCREW HOLDER (B) 1
614 306-985 WASHER (H) 1
615 964-851 BASE RUBBER 1
616 304-043
MACHINE SCREW (W/WASHERS) M4X10 (BLACK) 1
617 318-967 VISE SHAFT 1
618 321-551 KNOB BOLT M10X54 1
619 329-426 CROWN MOLDING VISE ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 606, 611
620 974-561 STOPPER 1
621 949-404 WING BOLT M6X20 (10 PCS.) 1
622 321-390 CROWN MOLDING STOPPER HOLDER 1
623 CROWN MOLDING STOPPER (R) 1
624 301-806 WING BOLT M6X15 1
625 321-373 CROWN MOLDING STOPPER (R) ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 607, 622-624
626 HOLDER ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 627-632
627 321-549 HOLDER 2
628 949-313 WING NUT M6 (10 PCS.) 2
629 949-556 NUT M6 (10 PCS.) 2
630 967-329 WASHER (H) 4
631 996-261 VISE PLATE 2
632 996-283 HIGH TENSION BOLT M6X65 2
633 321-553 GUIDE ASS'Y 1 INCLUD. 607, 620, 621, 626
634 998-840 TCT SAW BLADE 216MM-D15.88 HOLE-NT24 1
635 998-858 TCT SAW BLADE 216MM-D25.4 HOLE-NT24 1
636 998-859 TCT SAW BLADE 216MM-D30 HOLE-NT24 1
NO.
NO.
USED
USED
C 8FSE
- 8 - Printed in Japan 2 - 08
*ALTERNATIVE PARTS
(080219N)
 Loading...
Loading...