Page 1
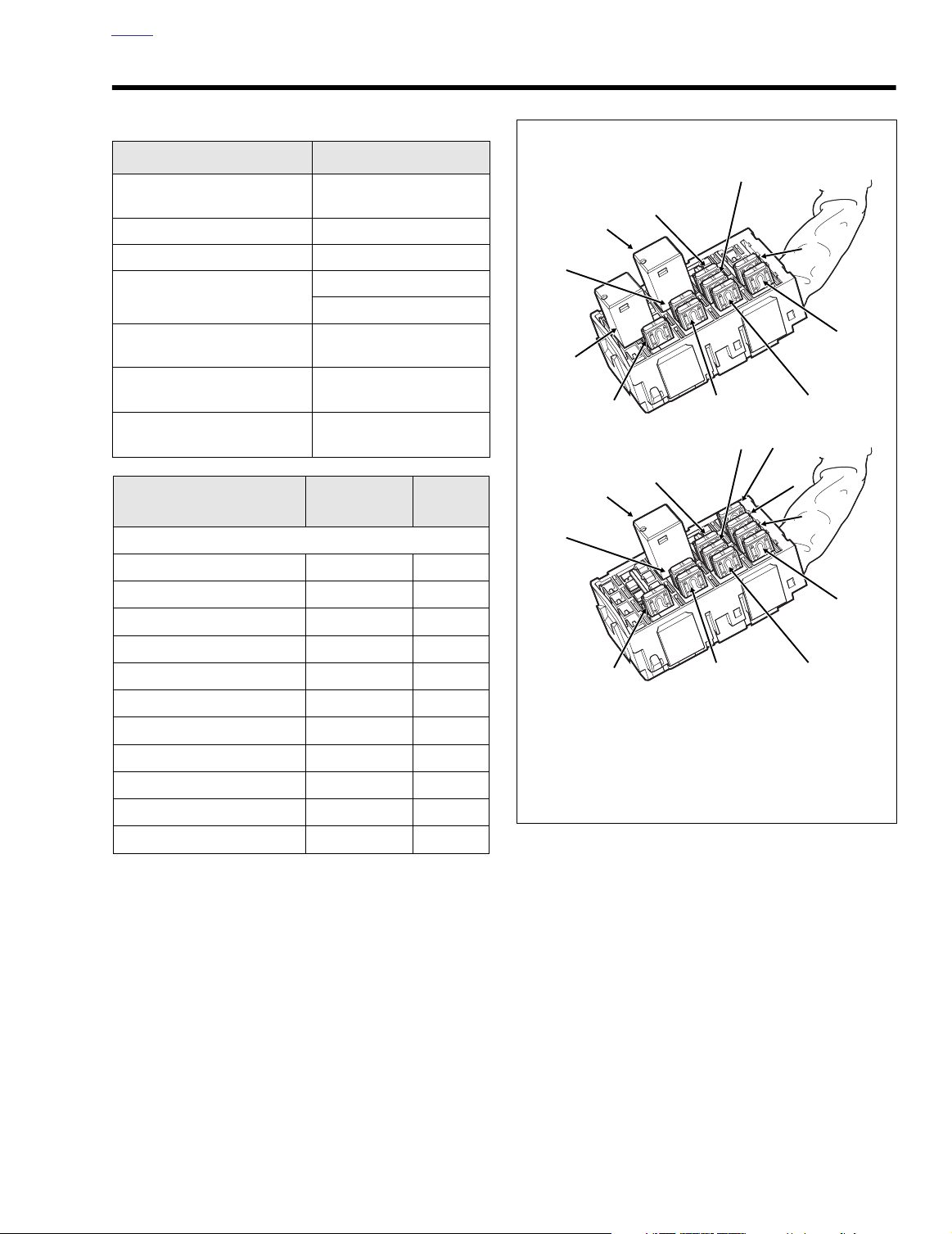
System Fuse Block (Under Left Side Cover)
11
10
9
1
8
5
4
3
2
FLHR/S
11
10
9
1
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
FLHT/C
1. Headlamp
2. Ignition
3. Lighting
4. Instruments
5. Brakes/Cruise
6. Radio Memory
7. Radio Power
8. Accessory
9. Battery
10. Brake Light Relay
11. P&A
12. Starter Relay
12
f2210x8x
f2204x8x
7
HOME
SPECIFICATIONS 4.1
IGNITION
Spark timing advance
Idle speed 1000 ± 50 RPM
Spark plug size 12 mm
Spark plug gap
Spark plug type
Ignition coil primary
resistance
Ignition coil secondary
resistance
CIRCUIT
System Fuses
Maxi-Fuse 40 Orange
Headlamp 15 Blue
Ignition 15 Blue
Lighting 15 Blue
Instruments 15 Blue
Brakes/Cruise 15 Blue
Radio Memory 15 Blue
Radio Power 10 Red
Accessory 15 Blue
Battery 15 Blue
P & A 15 Blue
DATA
0°-50° BTDC (range)
30° BTDC@1000 RPM
0.038-0.043 in
0.97-1.09 mm
Harley-Davidson
No. 6R12 (no substitute)
0.5-0.7 ohms
5500-7500 ohms
RATING
(AMPERES)
COLOR
Figure 4-1. Fuse Locations
2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted) 4-1
Page 2
HOME
0
N
DIAGNOSTIC INTRODUCTION 4.2
SYSTEM PROBLEMS
All system problems fall into at least one of three general categories.
No Start
The engine cranks over freely, but will not start. This does not
include situations where the engine will not crank, such as a
bad starter, dead battery, etc. This condition assumes that all
obvious checks (fuel in tank, etc.) have been made.
Poor Performance
The engine starts but there are performance problems. These
problems may include poor fuel economy, rough idle, engine
misfire, engine hesitation, severe spark knock, etc.
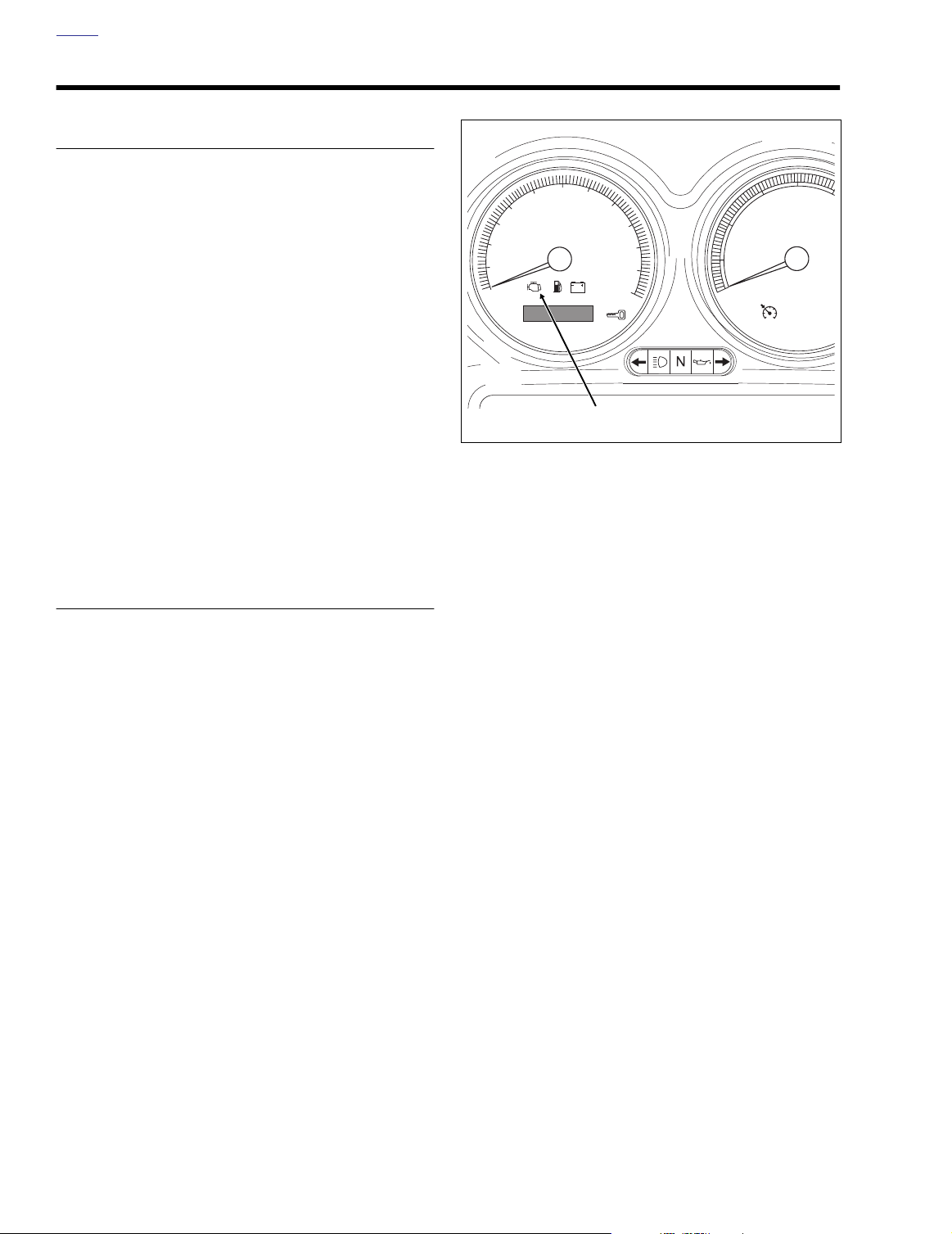
Check Engine Lamp
See Figure 4-2. The check engine lamp indicates the ignition
control module (ICM) has determined a fault condition exists.
There may also be starting or performance problems.
60
50
40
30
20
MPH
10
0
C
E
E
R
I
T
F
I
H
A
R
L
E
V
Y
-
A
D
Check Engine Lamp
Figure 4-2. Speedometer
70
80
90
100
110
120
D
N
O
S
D
I
20
10
0
H
30
A
RPM
R
L
E
40
x100
Y
-
A
D
f2160x8x
5
O
S
D
I
V
RESOLVING PROBLEMS
To resolve system problems, five basic steps are involved. In
order of occurrence, they are:
1. Check for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) by observing
check engine lamp. See 4.3 CHECKING FOR TROUBLE
CODES.
2. Retrieve DTCs using speedometer self diagnostics. See
4.5 SPEEDOMETER SELF DIAGNOSTICS.
3. Diagnose system problems. This involves using special
tools and the diagnostic flow charts in this section.
4. Correct problems through the replacement and/or repair
of the affected components.
5. After repairs are performed, the work must be validated.
This involves clearing the DTCs and confirming proper
vehicle operation as indicated by the behavior of the
check engine lamp.
4-2 2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted)
Page 3
HOME
f1240x2x
CHECKING FOR TROUBLE CODES 4.3
CHECK ENGINE LAMP
To diagnose system problems, start by observing the behavior of the check engine lamp.
NOTE
●
See Figure 4-3. “Key ON” means that the ignition key is
turned to ON and the engine stop switch is set to RUN
(although the engine is
●
When the ignition switch is turned ON, the check engine
lamp will illuminate for approximately four seconds and
then turn off.
●
If the check engine lamp is not illuminated at key ON or if
it fails to turn OFF after the ititial four second period, then
see 4.5 SPEEDOMETER SELF DIAGNOSTICS.
●
If the check engine lamp comes on late (after 20 seconds), the problem is likely a serial data bus failure. Test
for codes using speedometer self diagnostics. See 4.5
SPEEDOMETER SELF DIAGNOSTICS.
●
If the check engine lamp fails to turn OFF after the initial
four second period, then a problem exists in the instrumentation. See 4.5 SPEEDOMETER SELF DIAGNOS-
TICS.
1. When the lamp turns off after being illuminated for the
first four second period, it will:
a. Remain off if there are no fault conditions or trouble
codes currently detected by the ignition control module. See A of Figure 4-4.
b. Come back on for an 8 second period if only historic
codes exist. See B of Figure 4-4.
not
running).
Figure 4-3. Ignition Switch (FLHT/C)
c. Come back on, and remain on, if a current trouble
code exists. See C of Figure 4-4.
2. See CODE TYPES which follows for a complete description of trouble code formats.
NOTE
Tr ouble codes relating to the ignition coil can only be fully
diagnosed during actuation. For example, a problem with the
ignition coil will be considered a current fault even after the
problem is corrected, since the ignition control module will not
know of its resolution until after the coil is exercised by vehicle
start sequence. In this manner, there may sometimes be a
false indication of the current trouble code.
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
A
Key On
B
Key On
C
Key On
4 Sec.
Lamp OFF: No Current or Historic Trouble Codes
Lamp ON 8 Seconds:
Only Historic Trouble Codes Exist
4 Sec.
4 Sec.
8 Sec.
Lamp Remains ON: Current Trouble Code *
4 Sec.
4 Sec.
Figure 4-4. Check Engine Lamp Operation
*
Historic Trouble Codes May Also Exist
2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted) 4-3
Lamp OFF
Page 4

HOME
CODE TYPES
There are two types of
current and historic. If a trouble code is stored, it can be read
using the speedometer self diagnostics. See 4.5 SPEEDOM-
ETER SELF DIAGNOSTICS.
All trouble codes reside in the memory of the ignition control
module (ICM) until cleared using the speedometer self diagnostics. See 4.5 SPEEDOMETER SELF DIAGNOSTICS.
A trouble code is also cleared after a total of 50 trips has
elasped. A trip consists of a start and run cycle, the run cycle
lasting at least 30 seconds. After the 50 trip retention period,
the trouble code is automatically erased from memory providing that no subsequent faults of the same type are detected in
that period.
Current
Current trouble codes are those which presently disrupt
motorcycle operation. See the appropriate flow charts for
solutions.
Historic
If a particular problem happens to resolve itself, the active
status is dropped and it becomes a historic fault rather than a
current fault.
Historic trouble codes can only be retrieved using a computer
based diagnostic package called DIGITAL TECHNICIAN
(Part No. HD-44750).
Historic trouble codes are stored for a length of time to assist
in the diagnosis of intermittent faults.
diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs):
RETRIEVING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
The engine management system provides two levels of diagnostics.
●
The most sophisticated mode employs a computer
based diagnostic package called DIGITAL TECHNICIAN
(Part No. HD-44750).
The second mode requires using the speedometer self
●
diagnostics. Speedometer, tachometer (if equipped),
TSM/TSSM and ECM codes can be accessed and
cleared. See 4.5 SPEEDOMETER SELF DIAGNOS-
TICS.
MULTIPLE DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
While it is possible for more than one fault to occur and set
more than one trouble code, there are several conditions
which may result in
Serial data codes (DTC U1016, U1064, U1097, U1255,
●
U1300 and U1301) may be accompanied by other
codes.
resolving the other codes.
For proper resolution to multiple trouble codes refer to diagnostic code priority chart (Table 4-5.)
one
fault setting
Always
correct the serial data codes before
multiple
trouble codes:
It is important to note that historic trouble codes may also be
present whenever the system indicates the existence of a
current fault. See MULTIPLE DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
CODES if multiple trouble codes are found.
Diagnostic charts are designed for use with current trouble
codes and as a result they frequently suggest part replacement.
4-4 2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted)
Page 5

HOME
INITIAL DIAGNOSTIC CHECK: ICM 4.4
GENERAL
To locate faulty circuits or other system problems, follow the
diagnostic flow charts in this section. For a systematic
approach, always begin with INITIAL DIAGNOSTICS which
follows. Read the general information and then work your way
through the flow chart box by box.
Diagnostic Notes
If a numbered circle appears adjacent to a flow chart box,
then more information is offered in the diagnostic notes. Many
diagnostic notes contain supplemental information, descriptions of various diagnostic tools or references to other parts
of the manual.
Circuit Diagram/Wire Harness Connector Table
When working through a flow chart, refer to the illustrations,
the associated circuit diagram and the wire harness connector table as necessary. The wire harness connector table for
each circuit diagram identifies the connector number, description, type and general location.
In order to perform most diagnostic routines, a Breakout Box
and a DVOM are required. See 4.6 BREAKOUT BOX: ICM.
To perform the circuit checks with any degree of efficiency, a
familiarity with the various wire connectors is necessary.
Reprogramming ICM
Diagnostic charts frequently suggest ICM replacement. In the
event an ignition control module (ICM) needs to be replaced,
it must be reprogrammed using a computer based diagnostic
package called DIGITAL TECHNICIAN (Part No. HD-44750).
See your dealer. Password learn procedure must also be performed. See 3.24 PASSWORD LEARN.
INITIAL DIAGNOSTICS
General Information
The diagnostic check is an organized approach to identifying
a problem caused by an electronic control system malfunction. If no problems are found after completion of the diagnostic check, a comparison of running parameters may be used
to help locate intermittents and out-of-specification sensors.
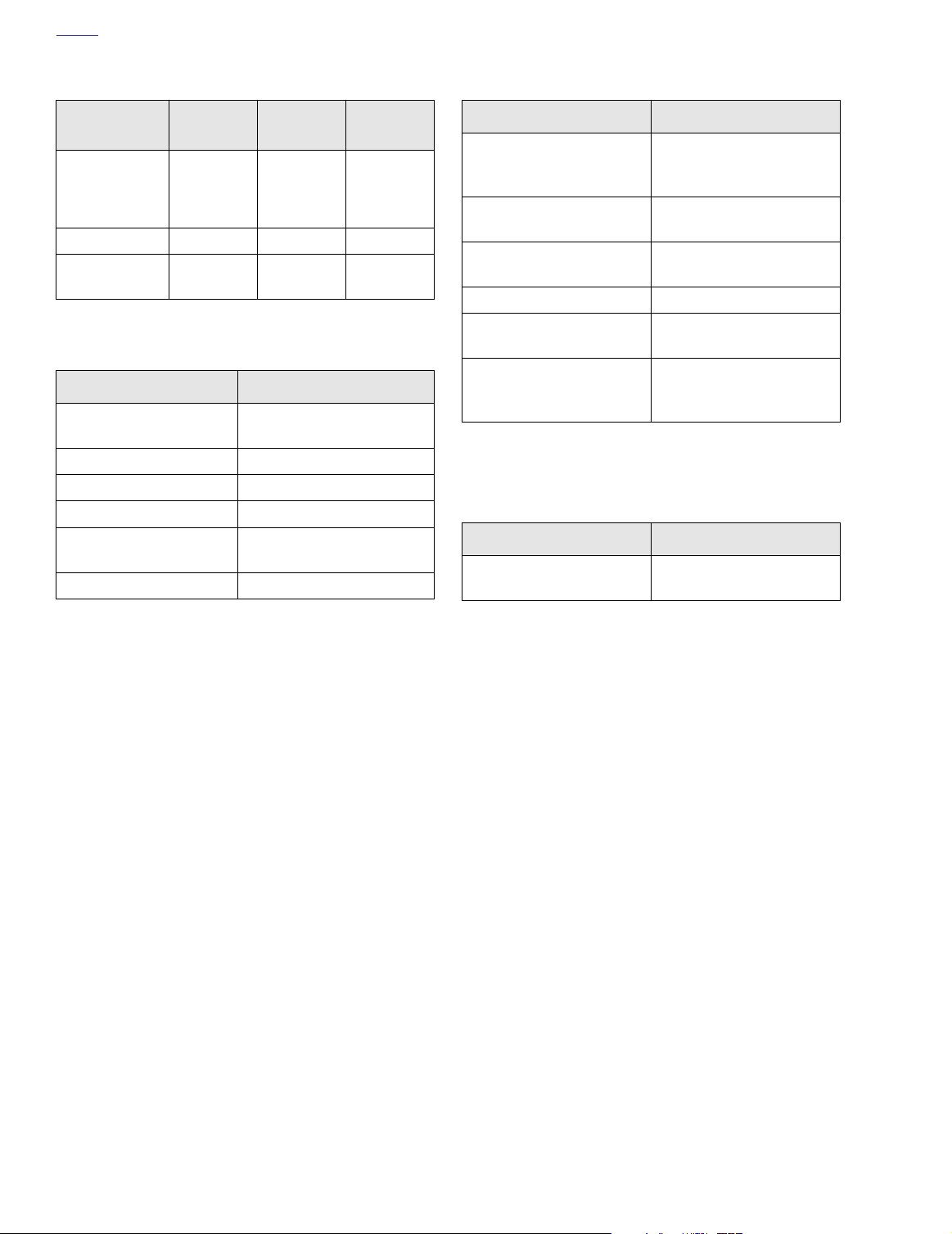
See Ta ble 4-1.
Diagnostic Tips
If Speedometer reads “BUS Er” with the ignition key
●
turned ON (engine stop switch at RUN with the engine
off), check data bus for an open or short to ground
between data connector [91A] terminal 3 and ICM connector [10B] terminal 12, TSSM connector [30B] terminal
3, Speedometer connector [39B] terminal 2 or tachometer (if equipped) connector [108B] terminal 2.
Check for an open diagnostic test terminal between data
●
link connector [91A] terminal 3 and TSM/TSSM connector [30B] terminal 3. With ignition key turned ON, serial
data bus voltage should be typically 0.6-0.8 volts. The
range of acceptable voltage is 0-7.0 volts.
Diagnostic Notes
The reference numbers below correlate with the circled numbers on the diagnostic check flow charts. See page 4-10.
1. Compare engine behavior to symptoms tables in this
section.
a. Starts hard. See Ta ble 4-2.
b. Hesitates, stumbles, surges, misfires and/or slug-
gish performance. See Ta bl e 4-3.
c. Engine exhaust emits black smoke or fouls plugs.
See Ta bl e 4-4.
2. Use HARNESS CONNECTOR TEST KIT (Part No. HD-
41404), black socket probes and patch cord.
3. Connect BREAKOUT BOX (Part No. HD-42682) to igni-
tion control module. See 4.6 BREAKOUT BOX: ICM.
All diagnostic codes are listed in Ta bl e 4-5.
See 3.9 INITIAL DIAGNOSTIC CHECK: TSM/TSSM for any
codes related to the turn signal module (TSM) or turn signal
security module (TSSM).
See 2.5 BREAKOUT BOX: SPEEDOMETER for any codes
related to the speedometer.
2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted) 4-5
Page 6
HOME
Table 4-1. Typical Running Values
ITEM
MAP sensor
RPM 0 5600 1000
Bank angle
sensor
MIN.
VALUE
0.1 V
(high
vacuum)
Run mode
0.45-1.1 V
MAX.
VALUE
4.96 V
(atmo-
spheric
pressure)
Disable
1.8-3.2 V
HOT
IDLE
1.5-3.0 V
Run mode
0.45-1.1 V
Table 4-2. Engine Starts Hard
SYMPTOM
Battery discharged
Spark plugs 4.12 MISFIRE.
Spark plug wires 4.12 MISFIRE
Ignition coil 4.12 MISFIRE.
Valve sticking
Water or dirt in fuel system Drain and refill with fresh fuel.
See charging system troubleshooting in this section.
See Section 3 in Touring Service Manual.
SOLUTION
Table 4-3. Engine Performance Problems
SYMPTOM
Perform intake leak test.
Manifold leak
MAP sensor plugged or not
operating properly
Water or dirt in fuel system
Spark plugs 4.12 MISFIRE.
EVAP hose disconnected
from induction module (CA)
Throttle plates not opening
fully
See 4.8 INTAKE LEAK
TEST.
4.13 DTC P0106, P0107,
P0108
Drain and refill with fresh
fuel.
Connect.
See throttle cable adjustment in Touring Service
Manual.
SOLUTION
Table 4-4. Engine Exhaust Emits
Black Smoke or Fouls Plugs
SYMPTOM
Clogged air filter
See Section 1 in Touring
Service Manual.
SOLUTION
4-6 2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted)
Page 7
HOME
Table 4-5. Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) and Fault Conditions
PRIORITY
RANKING
1 P0605 flash memory error 4.19 DTC P0602, P0603, P0604, P0605, P0607
2 P0603 EEProm memory error 4.19 DTC P0602, P0603, P0604, P0605, P0607
3 P0602 Flash memory error 4.19 DTC P0602, P0603, P0604, P0605, P0607
4 P0604 RAM memory error 4.19 DTC P0602, P0603, P0604, P0605, P0607
5 P0607 A to D error 4.19 DTC P0602, P0603, P0604, P0605, P0607
6“BUS Er” Serial data bus shorted low/open/high 4.10 STARTS, THEN STALLS
7U1300 serial data shorted low 4.10 STARTS, THEN STALLS
8U1301 serial data shorted high 4.10 STARTS, THEN STALLS
9U1064 lost TSM/TSSM communication 4.20 DTC U1064
10 U1097 lost speedometer communication 4.21 DTC U1097
11 U1255 Missing response at TSSM 4.20 DTC U1064
12 U1255 Missing response at speedometer 4.21 DTC U1097
13 P1009
14 P1010
15 P0373 crankshaft position sensor intermittent 4.17 DTC P0373, P0374
16 P0374
17 P0106 MAP sensor rate-of-change error 4.13 DTC P0106, P0107, P0108
18 P0107 MAP sensor failed open/low 4.13 DTC P0106, P0107, P0108
19 P0108 MAP sensor failed high 4.13 DTC P0106, P0107, P0108
21 P1351 Ignition coil driver front low/open 4.16 DTC P1351, P1352, P1354, P1355
20 P1354 Ignition coil driver rear low/open 4.16 DTC P1351, P1352, P1354, P1355
22 P1352 Ignition coil driver front high 4.16 DTC P1351, P1352, P1354, P1355
23 P1355 Ignition coil driver rear high 4.16 DTC P1351, P1352, P1354, P1355
24 P0562 system voltage low 4.14 DTC P0562, P0563
25 P0563 system voltage high 4.14 DTC P0562, P0563
26 P0501 VSS failed low 4.18 DTC P0501, P0502
27 P0502 VSS failed high/open 4.18 DTC P0501, P0502
DTC NO. FAULT CONDITION SOLUTION
TSM/TSSM disabled fuel due to bad
password
TSM/TSSM disabled fuel due to no password (starts then stalls)
crankshaft position sensor not detected/
cannot synchronize
4.15 DTC P1009, P1010
4.15 DTC P1009, P1010
4.17 DTC P0373, P0374
2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted) 4-7
Page 8
HOME
[2A]
[2B]
f2208z8x
321654987121110
321654987121110
Speedometer
15A
Accessory
Fuse
321654987121110
321654987121110
Main to Interconnect
Harness
BK
LtGN/V
O
BN/GY
[39B]
[39A]
[108B]
[108A]
321654987121110
321654987121110
Tachometer
[1B] [1A]
123
123
Main to Interconnect
Harness
6
6
101112 78945
101112 78945
[156B] [156A]
6
6
5
5
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
BN/GY
Main to Interconnect
Harness
LtGN/V
GY
65
4
32
1
1
15A
Ignition
Fuse
6
5
4
32
GY
987
987
321654987121110
321654987121110
TSM/TSSM
BK
[8B]
121110
121110
[8A]
Ignition
Harness
1
2
3
4
Data Link
[91A]
BK
[30B]
[30A]
LtGN/V
15A
Battery
Fuse
[10B]
[10A]
Ignition Control Module
12
12
Serial data
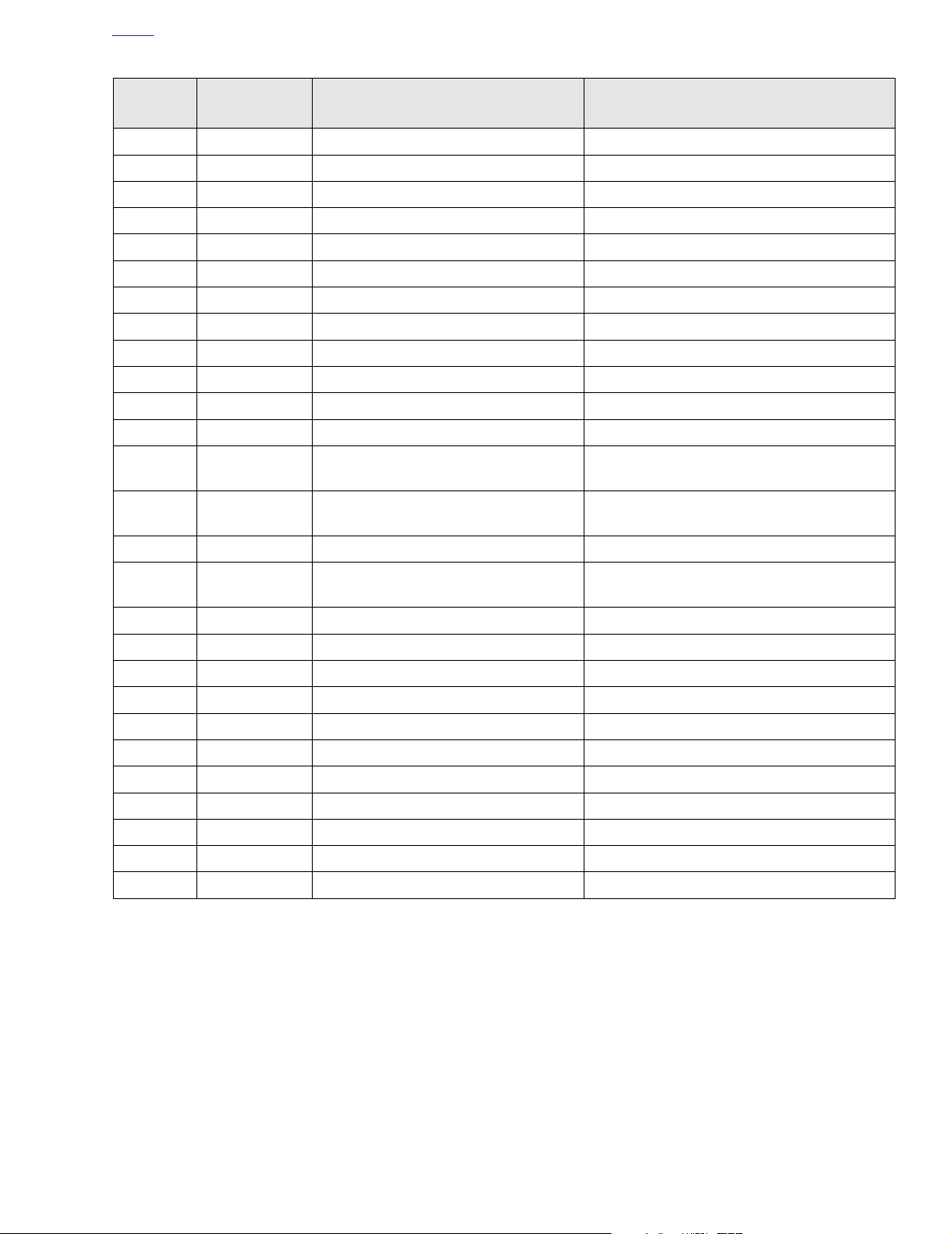
Figure 4-5. Diagnostic Check (FLHT/C)
Table 4-6. Wire Harness Connectors in Figure 4-5.
NO. DESCRIPTION TYPE LOCATION
[1] Main to Interconnect Harness 12-Place Deutsch (Black) Inner Fairing - Right Radio Support Bracket
[2] Main to Interconnect Harness 12-Place Deutsch (Gray) Inner Fairing - Right Fairing Support Brace
[8] Ignition Harness 12-Place Deutsch Under Right Side Cover
[10] Ignition Control Module 12-Place Deutsch Under Right Side Cover
[30] Turn Signal/Security Module 12-Place Deutsch
[39] Speedometer 12-Place Packard Inner Fairing (Back of Speedometer)
[91] Data Link 4-Place Deutsch Under Right Side Cover
[108] Tachometer 12-Place Packard Inner Fairing (Back of Tachometer)
[156] Main to Interconnect Harness 6-Place Deutsch Inner Fairing - Right Fairing Support Brace
Cavity in Crossmember at Rear of
Battery Box (Under Seat)
4-8 2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted)
Page 9
HOME
f2208y8x
BN/GY
BK
321654987121110
321654987121110
15A
Battery
Fuse
Speedometer
LtGN/V
BN/GY
O
15A
Accessory
Fuse
[39B]
[39A]
15A
Ignition
Fuse
LtGN/V
GY
21
21
GY
BK
321654987121110
321654987121110
[30B]
[30A]
TSM/TSSM
BK
[8B]
[8A]
[91A]
Ignition
Harness
1
2
3
4
Data Link
987
6
54
3
98
7
654
3
121110
121110
LtGN/V
[10B]
[10A]
Ignition Control Module
12
12
Serial data
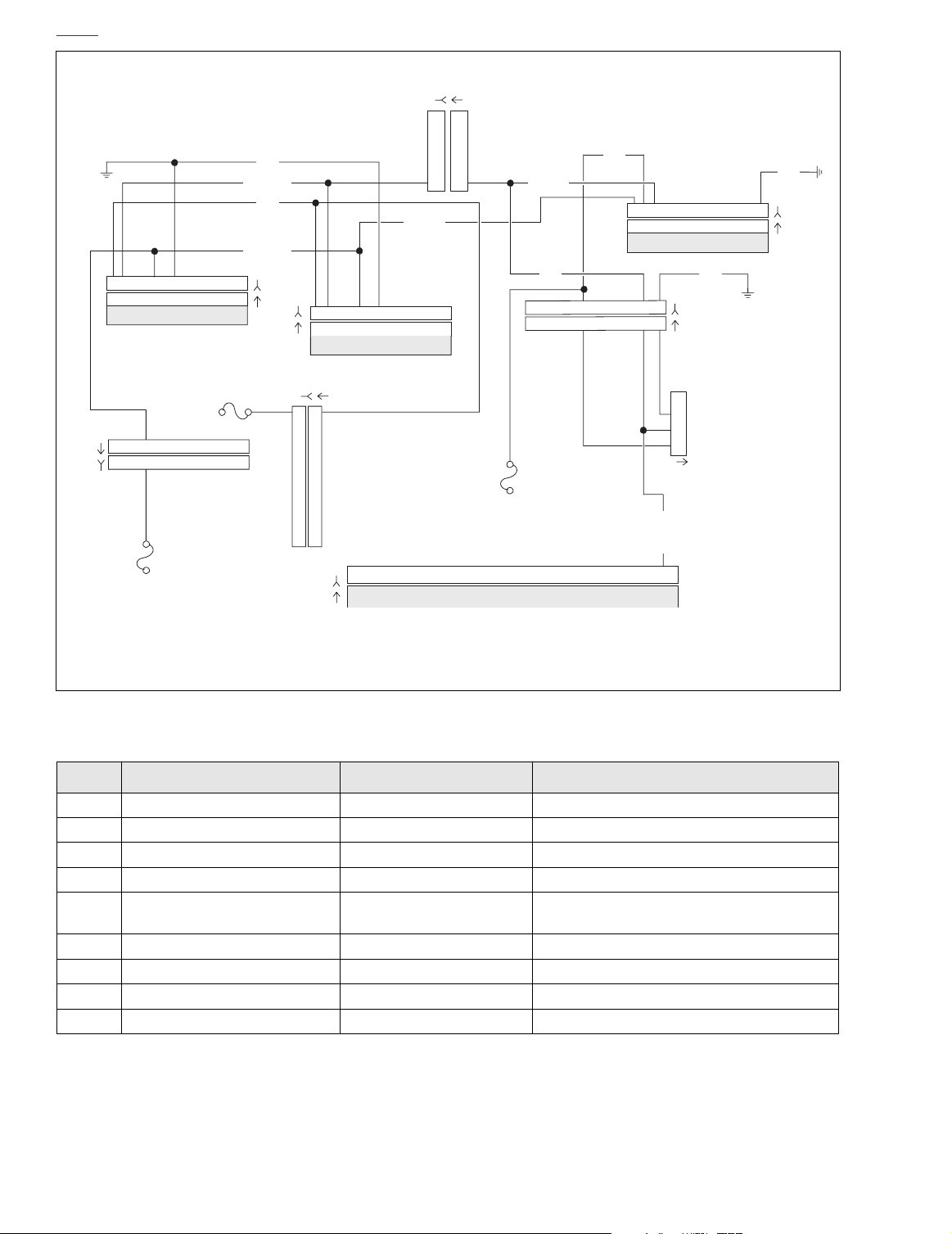
Figure 4-6. Diagnostic Check (FLHR/S)
Table 4-7. Wire Harness Connectors in Figure 4-6.
NO.
[8] Ignition Harness 12-Place Deutsch Under Right Side Cover
[10] Ignition Control Module 12-Place Deutsch Under Right Side Cover
[30] Turn Signal/Security Module 12-Place Deutsch
[39] Speedometer 12-Place Packard Under Console (Back of Speedometer)
[91] Data Link 4-Place Deutsch Under Right Side Cover
DESCRIPTION TYPE LOCATION
Cavity in Crossmember at Rear of
Battery Box (Under Seat)
2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted) 4-9
Page 10
HOME
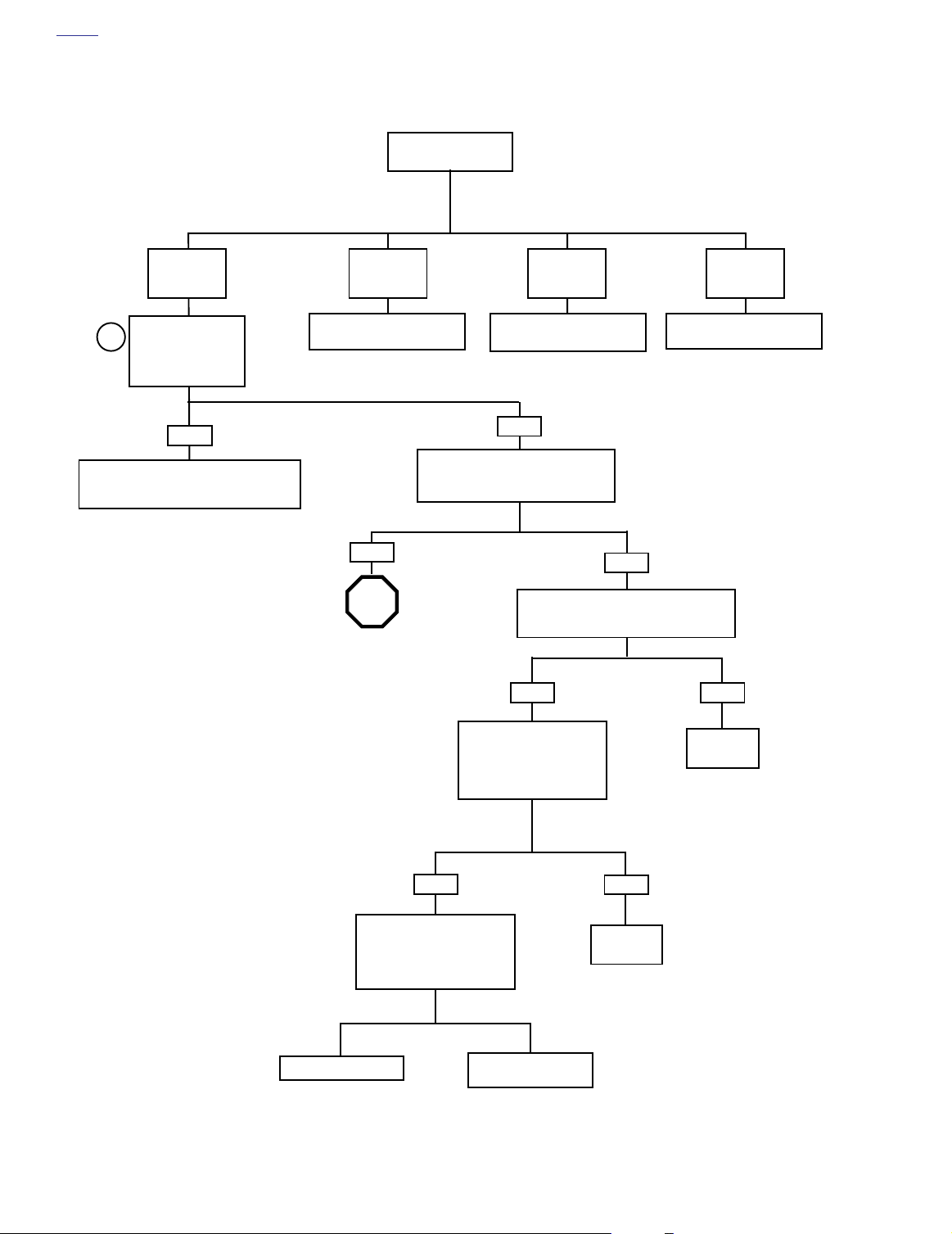
Initial Diagnostic Check (Part 1 of 2)
Does engine
start?
YES.
Starts and
runs.
Check for trouble
codes. See 4.5
1
SPEEDOMETER
SELF DIAGNOSTICS
Codes found?
YES
Refer to applicable trouble code priority chart.
All diagnostic codes are listed on page 4-7 in
Table 4-5. Codes are listed by priority.
YES.
Starts, then
stalls.
See 4.10 STARTS, THEN
STALLS.
YES
STOP
Go to Initial Diagnostic
Check (Part 2 of 2).
NO.
Cranks, but
will not start.
See 4.9 ENGINE CRANKS,
BUT WILL NOT START.
NO
With ignition switch OFF, press and
release odometer reset switch. Does
odometer display appear?
Check for continuity to ground on terminal 7
of speedometer. Wiggle harness during con-
tinuity check. Continuity present?
YES NO
Check for battery voltage at
terminal 5 of speedometer
while wiggling harness. Bat-
tery voltage continuously
present?
NO
NO.
Engine will not
crank.
See 1.2 STARTING SYSTEM
DIAGNOSIS.
Locate and
repair open.
Check continuity (with ignition
switch OFF) between terminals
8 and 11 on breakout box. Con-
tinuity present when speedome-
ter reset switch is depressed?
Replace speedometer.
4-10 2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted)
YES
Replace speedometer
reset switch.
NO
Locate and
repair open.
Page 11

HOME
Initial Diagnostic Check (Part 2 of 2)
Continued from Initial Diagnostic
Check (Part 1 of 2).Turn ignition
switch ON, is odometer backlight
present?
YES
Turn key to ACC. Is
backlight present?
YES
No trouble found.
Is problem intermittent?
YES
Perform “wow” test. See 4.5 SPEEDOMETER SELF DIAGNOSTICS.
1) backlight should illuminate
2) needle should sweep its full range of motion
3) LED’s should illuminate:
• check engine
• battery
• security (all models)
• low fuel (EFI models)
• cruise (even though not cruise equipped)
The following features should be functional
Are all features functional?
1
Check for battery voltage
at terminal 6. Battery volt-
age present?
YES
NO
NO
YES
Replace speedometer.
NO
Check for battery voltage at
terminal 1 of breakout box.
Battery voltage present?
YES
NO
Replace Speedometer.
NO
Is instrument
fuse blown?
NO
Replace speedometer.
YES
Repeat Diagnostic
Check while wiggling
harnesses.
Locate and repair open on
O/W wire between terminal 6
and accessory fuse.
Speedometer Inoperative
Remove and inspect vehi-
cle speed sensor. Debris
Remove debris. Reinstall
NO.
(no vehicle speed).
present?
YES
Vehicle speed sensor.
Locate and repair
source of fault.
Tachometer Inoperative
See Test 2.4 (Part 1 of 2)
under 2.4 SPEEDOMETER/
NO
Check for damaged wiring/
loose connection between
vehicle speed sensor and ICM.
Is wiring damage/loose
connection present?
YES
Locate and repair
source of fault.
Replace fuse.
NO.
(no engine speed).
TACHOMETER.
NO
Replace Speedometer.
Locate and repair open
between terminal 1 and
instrument fuse.
2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted) 4-11
Page 12

HOME
SPEEDOMETER SELF DIAGNOSTICS 4.5
GENERAL
The speedometer is capable of displaying and clearing
speedometer, tachometer, TSM/TSSM, and ICM/ECM trouble
codes (diagnostic mode).
DIAGNOSTICS
Diagnostic Tips
For a quick check of speedometer function, a “wow” test
●
can be performed. Press and hold odometer reset switch
then turn ignition switch ON. Release reset switch. Background lighting should illuminate, speedometer needle
should sweep its full range of motion, and indicator
lamps [battery, security, low fuel (EFI models) check
engine and cruise] should illuminate. Some lamps may
illuminate even though they do not apply to the vehicle.
For example, the cruise lamp may illuminate even though
the motorcycle may not be cruise equipped.
●
If instrument module fails “wow” test, check for battery,
ground, ignition, speedometer reset switch and accessory to speedometer. If any feature in the speedometer is
non-functional, see 2.2 INITIAL DIAGNOSTIC CHECK:
SPEEDOMETER.
d0715x8x
1
1. Cruise On/Engaged
2. Check Engine
3. Low Fuel
2
Figure 4-7. Speedometer (FLHR/S)
3
4. Battery
5. Security
4
5
Diagnostic Notes
Use of speedometer self diagnostics assumes that DIGITAL
TECHNICIAN (Part No. HD-44750) is
The reference numbers below correlate with the circled numbers in the Speedometer Self Diagnostics (chart)
1. To exit diagnostic mode, turn ignition switch OFF.
2. To clear DTCs for selected module, press speedometer
reset switch for more than 5 seconds when code is displayed. This procedure will clear all codes for selected
module.
not
available.
4-12 2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted)
Page 13

HOME
Speedometer Self Diagnostics (chart)
1
While holding odometer reset switch in,
turn ignition switch to IGN. Make sure
Run/Stop switch is in RUN position.
Release reset switch.
Does “diag” appear?
YES
”P” flashing.
To choose TSM/
TSSM, press and
release reset switch.
”S” flashing.
To choose Speedometer,
press and release reset
switch.
”SP” flashing.
To choose Tachometer,
press and release reset
switch.
”T” flashing.
To choose ICM, press and
release reset switch.
To display DTCs for the
ICM, press and hold
reset switch for more
than 5 seconds.
To display DTCs for
TSM/TSSM, press and
hold reset switch for
more than 5 seconds.
To display DTCs for
speedometer, press and
hold reset switch for more
than 5 seconds.
To display DTCs for
tachometer, press and
hold reset switch for more
than 5 seconds.
NO
See 2.2 INITIAL DIAGNOSTIC
CHECK: SPEEDOMETER.
Device
response?
YES
“none” displayed.
Press and release
reset switch. Part num-
ber of module will be
displayed.
DTC
2
displayed.
Press and release
reset switch.
Are more DTCs
displayed?
YES
NO
“no rsp” displayed.*
Tachometer malfunction.
2.4 SPEEDOMETER/
See
TACHOMETER.
* Models not equipped
with a tachometer will
display “no rsp” normally.
NO
“end” displayed.
To clear all DTCs for
selected module hold reset
switch for more than 5 seconds. If DTCs are not to be
cleared, Press and release
reset switch. Part number of
module will be displayed.
Press and release reset
switch again to continue to
next module.
Figure 4-8. Speedometer Self Diagnostics
2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted) 4-13
Page 14

HOME
BREAKOUT BOX: ICM 4.6
GENERAL
The BREAKOUT BOX (Part No. HD-42682) splices into the
main harness. Used in conjunction with a DVOM, it allows circuit diagnosis of wiring harness and connections without having to probe with sharp objects.
INSTALLATION
1. Remove right saddlebag and side cover.
2. Depress latches on connector [10] to separate pin and
socket halves.
3. Attach Breakout Box as follows:
a. Mate black socket housing on Breakout Box with
ICM connector [10A].
b. Mate black pin housing on Breakout Box with har-
ness connector [10B].
REMOVAL
f2191x8x
Ignition Control Module
Connector [10]
Figure 4-9. Electrical Bracket (Under Right Side Cover)
1. Remove Breakout Box as follows:
a. Remove black socket housing on Breakout Box from
ICM connector [10A].
b. Remove black pin housing on Breakout Box from
harness connector [10B].
2. Mate pin and socket halves of ICM connector [10].
3. Install side cover and saddlebag.
f2001x8x
Connect Black Side
Only for Tests
f1998x9x
Figure 4-10. Breakout Box (Part No. HD-42682)
4-14 2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted)
Page 15

HOME
hd39978
WIGGLE TEST 4.7
GENERAL
The wiggle test indicates the presence of intermittents in a
wiring harness.
PROCEDURE
1. See Figure 4-11. Connect DVOM (Part No. HD-39978) to
wiring harness between the suspect connections. When
diagnosing ignition module connections, a BREAKOUT
BOX (Part No. HD-42682) may be used to simplify the
procedure. See 4.6 BREAKOUT BOX: ICM.
2. Set DVOM to read voltage changes.
3. Start motorcycle engine and run at idle.
4. Shake or wiggle harness to detect intermittents. If intermittents are present, radical voltage changes will register
on the DVOM.
Figure 4-11. Fluke 78 Multimeter (DVOM)
(Part No. HD-39978)
2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted) 4-15
Page 16

HOME
INTAKE LEAK TEST 4.8
GENERAL
1WARNING1WARNING
Propane is an extremely flammable liquid and vapor.
Vapor may cause flash fire. Keep away from heat, sparks
and flame. Keep container closed. Use only with adequate ventilation.
1WARNING1WARNING
Read all directions and warnings on propane bottle. Failure to follow all directions and warnings on bottle could
result in death or serious injury.
●
To prevent false readings, keep airbox cover installed
when performing test.
Do not direct propane into air cleaner, false readings will
●
result.
LEAK TESTER
Parts List
●
Standard 14 oz. propane cylinder.
9648
9649
Figure 4-12. Nozzle
1
3
2
4
5
6
Snap-on YA7148 Propane Enrichment Kit.
●
12 inches (304 mm) long-1/4 inch (6 mm) diameter cop-
●
per tubing.
Tester Assembly
1. Cut rubber hose from kit to 18 inches (457 mm) in length.
2. See Figure 4-12. Flatten one end of copper tube to form
a nozzle.
3. Insert round side of copper tube into end of tubing.
1. Nozzle
2. Copper tube
3. Hose
4. Valve
5. Knob
6. Propane bottle
Figure 4-13. Leak Tester
4-16 2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted)
Page 17

HOME
10054
INTAKE LEAK TESTING
1. Start engine.
2. Warm engine to operating temperature.
3. See Figure 4-13. Tu rn knob counterclockwise to open
propane bottle.
1WARNING1WARNING
Propane is an extremely flammable liquid and vapor.
Vapor may cause flash fire. Keep away from heat, sparks
and flame. Keep container closed. Use only with adequate ventilation.
NOTE
Do not direct propane stream toward front of engine. If propane enters air cleaner, a false reading will be obtained.
4. See Figure 4-14. Aim nozzle toward possible sources of
leak such as fuel injectors and intake tract.
5. See Figure 4-13. Push valve opane enters source of
leak.
Figure 4-14. Checking for Leaks
2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted) 4-17
Page 18

HOME
ENGINE CRANKS, BUT WILL NOT START 4.9
GENERAL
If starter will not crank engine, the problem is not ignition
related. Refer to SECTION 1-STARTING & CHARGING.
DIAGNOSTICS
Diagnostic Notes
The reference numbers below correlate with the circled numbers on the Test 4.9 flow charts.
1. Check for trouble codes. See RETRIEVING DIAGNOS-
TIC TROUBLE CODES under 4.3 CHECKING FOR
TROUBLE CODES.
2. Check the condition of the battery. Perform a voltage test
and recharge if below 12.60V. Check battery connections
and perform load test. Replace the battery if necessary.
3. Remove spark plug cable from spark plug.
a. Visually check condition of plug.
d0273x8x
Figure 4-15. Spark Tester
7863
b. See Figure 4-15. Attach cable to SPARK TESTER
(Part No. HD-26792). Clip tester to cylinder head
bolt.
c. While cranking engine, look for spark. Repeat pro-
cedure on other spark plug cables.
NOTE
Engine will not spark with both spark plugs removed. When
checking for spark, use SPARK TESTER (Part No. HD-
26792) with both plugs installed.
4. Use HARNESS CONNECTOR TEST KIT (Part No. HD-
41404) gray pin probes and patch cords.
5. See Figure 4-16. Plug IGNITION COIL CIRCUIT TEST
ADAPTER (Part No. HD-44687) and FUEL INJECTOR
TEST LAMP (Part No. HD-34730-2C) into Breakout Box.
Note that cranking the engine with test lamp in place of
the ignition coil can sometimes cause a DTC P1351,
P1352, P1354 or P1355. This condition is normal and
does not by itself indicate a malfunction. Clear codes
afterward.
6. Connect BREAKOUT BOX (Part No. HD-42682). See 4.6
BREAKOUT BOX: ICM.
Figure 4-16. Ignition Coil Circuit Test
7. Use HARNESS CONNECTOR TEST KIT (Part No. HD-
41404), gray pin probe and patch cord.
8. Use HARNESS CONNECTOR TEST KIT (Part No. HD-
41404), brown socket probe and patch cord.
4-18 2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted)
Page 19

HOME
Crankshaft
Position
Sensor
21
[79A]
[79B]
Ignition Control Module
R/BK To Ignition Switch
15 Amp
Ignition Fuse
To TSM/TSSM
[22B]
[22A]
Ignition
GY
[1B]
[1A]
GY
Engine Stop Switch
Coil
[83B]
A
B
C
W
\
B
K
56784321 9101112
56784321 9101112
FLHT/C Only
W \ BK
6-Place on FLHR/S
56784321 9101112
BK
R
Y \ BE
BE \ O
[8A]
[8B]
Ground Stud
BK
To
Data Link
W \ BK
[10B]
9
8
7
6
5
1
[10A]
Crank Sensor (-)
Crank Sensor (+)
Rear Coil
Front Coil
Ground
Key ON Power
Figure 4-17. Ignition Circuit
Table 4-8. Wire Harness Connectors in Figure 4-17.
NO.
[1]
[8] Ignition Harness All 12-Place Deutsch Under Right Side Cover
[10] Ignition Control Module All 12-Place Deutsch (Black) Under Right Side Cover
[22]
[83] Ignition Coil All 3-Place Packard Below Fuel Tank (Left Side)
DESCRIPTION MODEL TYPE LOCATION
Main to Interconnect
Harness
Interconnect to Right
Handlebar Switch Controls
FLHT/C 12-Place Deutsch (Black) Inner Fairing - Right Radio Support Bracket
FLHT/C 12-Place Deutsch Inner Fairing- Right Fairing Support Brace
FLHR/S 6-Place Deutsch Inside Headlamp Nacelle
2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted) 4-19
Page 20

HOME
Test 4.9 (Part 1 of 3)
ENGINE CRANKS, BUT WILL NOT START
Fresh fuel in tank?
Spark plug wires firmly
connected to proper coil
terminals?
Add fuel and
NO
YES
connect spark
plugs.
Check for trouble
1
Codes found?
See priority listing
in Table 4-5.
codes.
YES
NO
Check battery connections
and voltage. Is voltage
above 12.60?
2
YES
Does battery pass
load test?
YES
Check spark plug condition,
3
replace if fouled. Check
spark at both plugs while
cranking. Spark present?
YES
Check compression. If compression is
good, check fuel system.
NO
Recharge battery.
NO
Replace battery.
NO
Turn ignition ON and engine
stop switch to RUN.
Does check engine lamp
illuminate for 4 seconds?
immediately after Key ON?
Check battery voltage at
4
Terminal B of coil connector
[83B] using DVOM. Battery
voltage present?
4-20 2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted)
YES
YES
STOP
Go to Test 4.9
(Part 2 of 3).
NO
4.11 NO SPARK/NO ICM
Locate and repair open on W/
See
POWER.
NO
BK wire to coil.
Page 21

HOME
Test 4.9 (Part 2 of 3)
ENGINE CRANKS, BUT WILL NOT START
Continued from Test 4.9 (Part 1 of 3).
Install Breakout Box and test light for the next
5
6
Front coil code: Check between
Terminals 1 and 6 on Breakout Box.
Terminals 1 and 7 on Breakout Box.
Does test lamp flash when engine is cranked?
inspection.
Rear coil code: Check between
YES
Check coil connections.
Connections OK?
YES
Test spark plug cable resis-
tance. See 4.12 MISFIRE.
Resistance OK?
YES
Plug wires in correct
coil towers?
YES NO
Replace
coil.
NO
Repair.
NO
Replace spark
plug cables.
Route
correctly.
NO
Connect Breakout Box. Check continuity
between socket A of connector [83B]
and terminal 7 (BK) on Breakout Box.
Measure resistance between socket C of
7
connector [83B] and terminal 6 (BK) on
Connect DVOM to terminals 8 and 9
(BK) of connector [10] on Breakout Box
and set it for AC volts. Crank engine.
Does DVOM read 1 VAC minimum?
Breakout Box.
Is resistance less than 1.0 ohm?
YES
YES
STOP
Go to Test 4.9
(Part 3 of 3).
NO
Poor connection at con-
nector [10B] or open in
harness between coil
and ICM. Repair open.
NO
Disconnect connector [79].
8
Check connector for moisture
and corrosion. Check wires for
chafing. Connect DVOM to ter-
minals 1 and 2 of connector
[79A]. Crank engine. Does
DVOM read 1 VAC minimum?
YES NO
Check for continuity between
socket 1 of connector [79B]
and terminal 8 of connector
[10] on Breakout Box.
Continuity present?
YES
Locate and repair open on
BK wire between socket 2 of
connector [79B] and socket 9
of connector [10B].
NO
Locate and repair open on
R wire between socket 1 of con-
nector [79B] and socket 8 of
connector [10B].
With meter still connected,
check for resistance.
Is resistance 600-1200 ohms?
YES
Remove and inspect CKP
sensor. Remove any debris on
sensor. Reinstall sensor.
NO
Replace CKP
sensor.
2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted) 4-21
Page 22

HOME
Test 4.9 (Part 3 of 3)
ENGINE CRANKS, BUT WILL NOT START
Replace ignition control module (ICM). Reprogram and
perform password learn. Does vehicle start?
Continued from Test 4.9 (Part 2 of 3).
YES
System OK.
NO
Mechanical failure. Inspect for
sprocket gear, timing chain or
other mechanical failure.
4-22 2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted)
Page 23

HOME
f2191x8x
Data Link
Connector [91]
STARTS, THEN STALLS 4.10
GENERAL
Diagnostic Trouble Codes U1300, U1301, P1009, P1010 or “BUS Er”
See Figure 4-18. The typical serial data voltage range is 0
volts (inactive) to 7 volts (active). Due to the short pulse, voltages will be much lower on a DVOM. In analog mode, a
DVOM reading serial data will show continuous voltage when
active, typically 0.6-0.8 volts. The range for acceptable operations is 0-7.0 volts.
NOTE
Problems in the fuel system or idle air control system may
also create this symptom.
Table 4-9. Code Description
DTC
U1300 Serial data low
U1301 Serial data open/high
DESCRIPTION
DIAGNOSTICS
Diagnostic Tips
If serial data is shorted, these codes will automatically
●
trip the check engine light. The odometer will read “Bus
Er” in this condition.
DTCs P1009 and P1010 may accompany DTCs U1300
●
and U1301.
Diagnostic Notes
The reference numbers below correlate with the circled numbers on the Test 4.10 flow charts.
1. Check for trouble codes. See RETRIEVING DIAGNOS-
TIC TROUBLE CODES under 4.3 CHECKING FOR
TROUBLE CODES.
2. Connect BREAKOUT BOX (Part No. HD-42682) as fol-
lows:
a. Mate black socket housing on Breakout Box with
ICM connector [10A].
b. Mate black pin housing on Breakout Box with har-
ness connector [10B].
c. Mate gray socket housing on Breakout Box with
TSM/TSSM connector [30A].
d. Mate gray pin housing on Breakout Box with har-
ness connector [30B].
Figure 4-18. Electrical Bracket (Under Right Side Cover)
3. Use HARNESS CONNECTOR TEST KIT (Part No. HD-
41404), black socket probes and patch cord.
4. Historic code U1300 would have been set. Clear historic
codes.
2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted) 4-23
Page 24

HOME
[2A]
[2B]
f2208z8x
321654987121110
321654987121110
Speedometer
15A
Accessory
Fuse
321654987121110
321654987121110
Main to Interconnect
Harness
BK
LtGN/V
O
BN/GY
[39B]
[39A]
[108B]
[108A]
321654987121110
321654987121110
Tachometer
[1B] [1A]
123
123
Main to Interconnect
Harness
6
6
101112 78945
101112 78945
[156B] [156A]
6
6
5
5
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
BN/GY
Main to Interconnect
Harness
LtGN/V
GY
65
4
32
1
1
15A
Ignition
Fuse
6
5
4
32
GY
987
987
321654987121110
321654987121110
TSM/TSSM
BK
[8B]
121110
121110
[8A]
Ignition
Harness
1
2
3
4
Data Link
[91A]
BK
[30B]
[30A]
LtGN/V
15A
Battery
Fuse
[10B]
[10A]
Ignition Control Module
12
12
Serial data
Figure 4-19. Serial Data Circuit (FLHT/C)
Table 4-10. Wire Harness Connectors in Figure 4-19.
NO. DESCRIPTION TYPE LOCATION
[1] Main to Interconnect Harness 12-Place Deutsch (Black) Inner Fairing - Right Radio Support Bracket
[2] Main to Interconnect Harness 12-Place Deutsch (Gray) Inner Fairing - Right Fairing Support Brace
[8] Ignition Harness 12-Place Deutsch Under Right Side Cover
[10] Ignition Control Module 12-Place Deutsch Under Right Side Cover
[30] Turn Signal/Security Module 12-Place Deutsch
[39] Speedometer 12-Place Packard Inner Fairing (Back of Speedometer)
[91] Data Link 4-Place Deutsch Under Right Side Cover
[108] Tachometer 12-Place Packard Inner Fairing (Back of Tachometer)
[156] Main to Interconnect Harness 6-Place Deutsch Inner Fairing - Right Fairing Support Brace
Cavity in Crossmember at Rear of
Battery Box (Under Seat)
4-24 2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted)
Page 25

HOME
f2208y8x
BN/GY
BK
321654987121110
321654987121110
15A
Battery
Fuse
Speedometer
LtGN/V
BN/GY
O
15A
Accessory
Fuse
[39B]
[39A]
15A
Ignition
Fuse
LtGN/V
GY
21
21
GY
BK
321654987121110
321654987121110
[30B]
[30A]
TSM/TSSM
BK
[8B]
[8A]
[91A]
Ignition
Harness
1
2
3
4
Data Link
987
6
54
3
98
7
654
3
121110
121110
LtGN/V
[10B]
[10A]
Ignition Control Module
12
12
Serial data
Figure 4-20. Serial Data Circuit (FLHR/S)
Table 4-11. Wire Harness Connectors in Figure 4-20.
NO.
[8] Ignition Harness 12-Place Deutsch Under Right Side Cover
[10] Ignition Control Module 12-Place Deutsch Under Right Side Cover
[30] Turn Signal/Security Module 12-Place Deutsch
[39] Speedometer 12-Place Packard Under Console (Back of Speedometer)
[91] Data Link 4-Place Deutsch Under Right Side Cover
DESCRIPTION TYPE LOCATION
Cavity in Crossmember at Rear of
Battery Box (Under Seat)
2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted) 4-25
Page 26

HOME
Test 4.10 (Part 1 of 2)
ASTARTS, THEN STALLS: DTC U1300, U1301,
P1009, P1010 or “BUS Er”
1
Check for DTCs using 4.5 SPEEDOMETER
Is there fresh
fuel in tank?
SELF DIAGNOSTICS.
Any DTCs found?
NOYES
Add fuel.
YES.
DTC P1009,
P1010 found. See
4.15 DTC P1009,
P1010.
YES.
DTC U1300 or
U1301 are found.
YES.
BUS Er present.
Speedometer will not
communicate with other
modules.
STOP
Go to Test 4.10
(Part 2 of 2).
Replace intake
manifold seals.
Clear codes using speedometer self diagnostics.
See 4.5 SPEEDOMETER SELF DIAGNOSTICS.
Confirm proper operation with no check engine
lamp.
NO.
No DTCs found.
Inspect intake manifold for
leaks using intake leak test.
See 4.8 INTAKE LEAK TEST.
Are leaks present (runs longer
when propane is present)?
YES
Reprogram and learn
NO
Replace ICM.
password.
4-26 2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted)
Page 27

HOME
Test 4.10 (Part 2 of 2)
STARTS, THEN STALLS: DTC U1300, U1301, P1009,
P1010 or “BUS Er”
2
Continued from Test 4.10 (Part 1 of 2)
Test the four data connector terminals for continuity.
Leave ICM disconnected
at connector [10]. Does
speedometer display TSM/
YES
Replace ICM. Reprogram
and learn password.
YES
TSSM data?
4
3
NO
Disconnect connector [30]. Check for
continuity to ground at terminal 3 of con-
nector [91A]. Continuity to ground?
DIAGNOSTIC LINK
CONNECTOR [91A]
Terminal Wire Color Terminal
1 N/A N/A
2BK 5
3 Lt. GN/V 12
4GYGY terminal on left
Continuity present in all three circumstances?
NO
Inspect terminals
for damage or repair
opens as necessary.
BREAKOUT BOX
(BLACK)
side of ignition fuse
Locate and repair short
to ground.
Locate and repair short
to voltage.
NOYES
Check for voltage at
terminal 3 of connector
[91A]. Voltage present?
Replace TSM/TSSM. Repro-
gram and learn password.
YES
System
OK.
NOYES
System OK?
NO
Disconnect connector
[39]. System OK?
YES NO
Replace
speedometer.
Replace
tachometer if
equipped.
2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted) 4-27
Page 28

HOME
NO SPARK/NO ICM POWER 4.11
GENERAL
The ignition control module turns on when power is applied to
Pin 1 of [10], the black connector. The ignition control module
goes through an initialization sequence every time power is
removed and re-applied to Pin 1. The only visible part of this
sequence is the check engine lamp. Upon starting, the check
engine lamp will illuminate for 4 seconds and then (if parameters are normal) go out.
R/BK To Ignition Switch
[83B]
A
B
C
15 Amp
Ignition Fuse
Ignition
GY
Coil
W
\
B
K
DIAGNOSTICS
Diagnostic Notes
The reference numbers below correlate with the circled numbers on the Test 4.11 flow chart.
1. See FUSES in the Touring Service Manual.
2. Connect BREAKOUT BOX (Part No. HD-42682). See 4.6
BREAKOUT BOX: ICM.
3. Use HARNESS CONNECTOR TEST KIT (Part No. HD-
4104), black pin probe and patch cord.
4. Remove headlamp assembly on FLHR/S models or
outer fairing on FLHT/C.
Ignition Control Module
Y \ BE
BE \ O
BK
7
6
5
Rear Coil
Front Coil
Ground
To TSM/TSSM
[22B]
[22A]
[1B]
[1A]
GY
Engine Stop Switch
56784321 9101112
56784321 9101112
FLHT/C Only
W \ BK
6-Place on FLHR/S
56784321 9101112
[8A]
[8B]
Ground Stud
Figure 4-21. Ignition Control Module Power Circuit
To
Data Link
W \ BK
[10B]
1
[10A]
Key ON Power
4-28 2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted)
Page 29

HOME
Test 4.11
NO SPARK/NO ICM POWER
1
Check Ignition
Fuse. Is Fuse
OK?
NO
Replace Fuse
and Find
Source of Fault.
YES
Replace ICM.
YES
2
Connect Breakout Box. With Igni-
tion ON, Place Multimeter Red
3
Wire to Terminal 1 of Connector
[10] on Breakout Box, Multimeter
Black Wire to Terminal 5 of Con-
nector [10] on Breakout Box. Is
Voltage 12V± 1.0V.?
3
Check Continuity Between Terminal
5 of Connector [10] on Breakout Box
and Ground. Continuity Present in
NO
Repair Open in BK
Wire (Pin 5) to
Ground.
NO
Both Places?
3
4
3
YES
Check Continuity Between Pin
4 (W/BK) of Connector [22A]
and Terminal 1 of Connector
[10] on Breakout Box.
Is Continuity Present?
YES
Check Continuity
Between Sockets 4
(W/BK) and 3 (GY) of
Connector [22B]. With
Engine Stop Switch
ON, Is Continuity
Present?
NO
Locate and Repair
Open in W/BK Wire
Between Connectors
[22] and [10].
YES
Locate and Repair
Open in GY Wire
Between Connector
[22A] and Fuse Block.
NO
Replace
Engine Stop
Switch.
Table 4-12. Wire Harness Connectors in Figure 4-21.
NO. DESCRIPTION MODEL TYPE LOCATION
Main to Interconnect
[1]
Harness
[8] Ignition Harness All 12-Place Deutsch Under Right Side Cover
[10] Ignition Control Module All 12-Place Deutsch (Black) Under Right Side Cover
Interconnect to Right
[22]
Handlebar Switch Controls
FLHT/C 12-Place Deutsch (Black) Inner Fairing - Right Radio Support Bracket
FLHT/C 12-Place Deutsch Inner Fairing- Right Fairing Support Brace
FLHR/S 6-Place Deutsch Inside Headlamp Nacelle
2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted) 4-29
Page 30

HOME
MISFIRE 4.12
GENERAL
Misfire at Idle or Under Load
● Battery condition and connections may also cause mis-
fires.
● Fuel system problems may also cause misfires. Refer to
Ta bl e 4-3.
DIAGNOSTICS
Diagnostic Notes
The reference numbers below correlate with the circled numbers on the Test 4.12 flow chart.
1WARNING1WARNING
Any open spark around gasoline or other combustibles
may result in fire or explosion. Thoroughly wipe up any
spilt fuel and dispose of rags in a suitable manner. Inadequate safety precautions could result in death or serious
injury.
d0273x8x
Figure 4-22. Spark Tester
c. Compare resistance values to Ta b le 4-13. Replace
cables not meeting specifications. Reinstall and
repeat procedure on other spark plug cable.
Table 4-13. Spark Plug Cables
LOCATION LENGTH RESISTANCE
Front/Rear 20.2 inch (513 mm) 4975-11960
1. See Figure 4-22. Use the SPARK TESTER (Part No. HD-
26792) to verify adequate secondary voltage (25,000
volts) at the spark plug.
a. Turn Ignition/Light Key Switch to IGNITION.
b. Remove spark plug cable from spark plug. Visually
check plug condition.
c. Attach cable to SPARK TESTER. Clip tester to cylin-
der head bolt.
d. While cranking engine, watch for spark to jump
tester gap on leads.
IMPORTANT NOTE
Spark will not be present when cranking with both spark
plugs removed. When checking for spark, use SPARK
TESTER with both spark plugs installed and one plug
wire connected to SPARK TESTER.
e. Reinstall and repeat procedure on other spark plug
cable.
2. Perform spark plug cable resistance test.
a. Remove spark plug cable from spark plug and igni-
tion coil. For best results, use a needle nose pliers
for removal/installation on coil. Gently grasp cable
as close to terminals as possible.
b. Using an ohmmeter, touch probes to terminals on
each end plug wire.
3. This test can also be performed by substituting a known
good coil for one causing the no spark condition. The coil
does not require full installation to be functional. Verify
faulty coil by performing resistance test.
4. Use HARNESS CONNECTOR TEST KIT (Part No. HD-
41404), gray pin probe and patch cord to the coil connector [83B].
5. Inspect for corrosion at battery terminals, maxi fuse terminals, ignition fuse terminals GY and R/BK, right handlebar switch controls connector [22], and ignition coil
connector [83].
4-30 2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted)
Page 31

HOME
R/BK To Ignition Switch
15 Amp
Ignition Fuse
To TSM/TSSM
[22B]
[22A]
Ignition
GY
[1B]
[1A]
GY
Engine Stop Switch
Coil
[83B]
A
B
C
W
\
B
K
56784321 9101112
56784321 9101112
FLHT/C Only
W \ BK
6-Place on FLHR/S
56784321 9101112
Y \ BE
BE \ O
[8A]
[8B]
Ground Stud
Ignition Control Module
BK
W \ BK
[10B]
To
Data Link
7
6
5
1
[10A]
Rear Coil
Front Coil
Ground
Key ON Power
Figure 4-23. Ignition Coil Circuit
Table 4-14. Wire Harness Connectors in Figure 4-23.
NO. DESCRIPTION MODEL TYPE LOCATION
Main to Interconnect
[1]
Harness
[8] Ignition Harness All 12-Place Deutsch Under Right Side Cover
[10] Ignition Control Module All 12-Place Deutsch (Black) Under Right Side Cover
Interconnect to Right
[22]
Handlebar Switch Controls
[83] Ignition Coil All 3-Place Packard Below Fuel Tank (Left Side)
FLHT/C 12-Place Deutsch (Black) Inner Fairing - Right Radio Support Bracket
FLHT/C 12-Place Deutsch Inner Fairing- Right Fairing Support Brace
FLHR/S 6-Place Deutsch Inside Headlamp Nacelle
2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted) 4-31
Page 32

HOME
Test 4.12
MISFIRE AT IDLE OR UNDER LOAD
Is fuel contaminated?
YES
Replace
intake seals.
YES
Drain and flush
tank. Refill with
fresh fuel.
YES
Inspect intake manifold for leaks.
See 4.8 INTAKE LEAK TEST.
Leaks present?
Turn Ignition Switch OFF.
Disconnect one spark plug lead at a time
1
and install Spark Tester (HD-26792). See
Crank engine to induce spark. Observe
spark tester during test.
Spark should jump tester lead gap during
• Faulty, worn or cracked spark plug(s).
• Plug fouling due to engine
mechanical fault.
• Faulty or poor connection at plug.
NO
Figure 4-22.
test. Did it?
YES
Check for:
NO
Remove air cleaner cover. Start engine.
Open throttle quickly. Does slide move up
and down with throttle opening?
NO
Inspect CV carburetor diaphragm for leaks. Replace
or repair as necessary.
NO
Check resistance of each spark plug
2
cable that did not fire the spark tester.
Also, check for faulty plug wire connections.
Are wires OK?
YES
Original ignition coil
is faulty. Replace.
Clear codes using speedometer self diagnostics.
See 4.5 SPEEDOMETER SELF DIAGNOSTICS.
Confirm proper operation with no check engine
lamp.
4-32 2004 Touring: Engine Management (Carbureted)
YES
Switch coil with unit
known to be good.
3
Perform spark test.
Did spark jump gap
during engine cranking?
4
5
Replace ignition control
module. Reprogram and
Replace
faulty wires.
NO
Remove test coil. Disconnect negative bat-
tery cable. Measure resistance between bat-
tery positive and coil connector [83B]
Terminal B (W/BK). Wiggle harness. Is resis-
tance continuously less than 1.0 ohm?
YES
Find source of
learn password.
intermittent and repair.
NO
NO
 Loading...
Loading...