Page 1
HOM
E
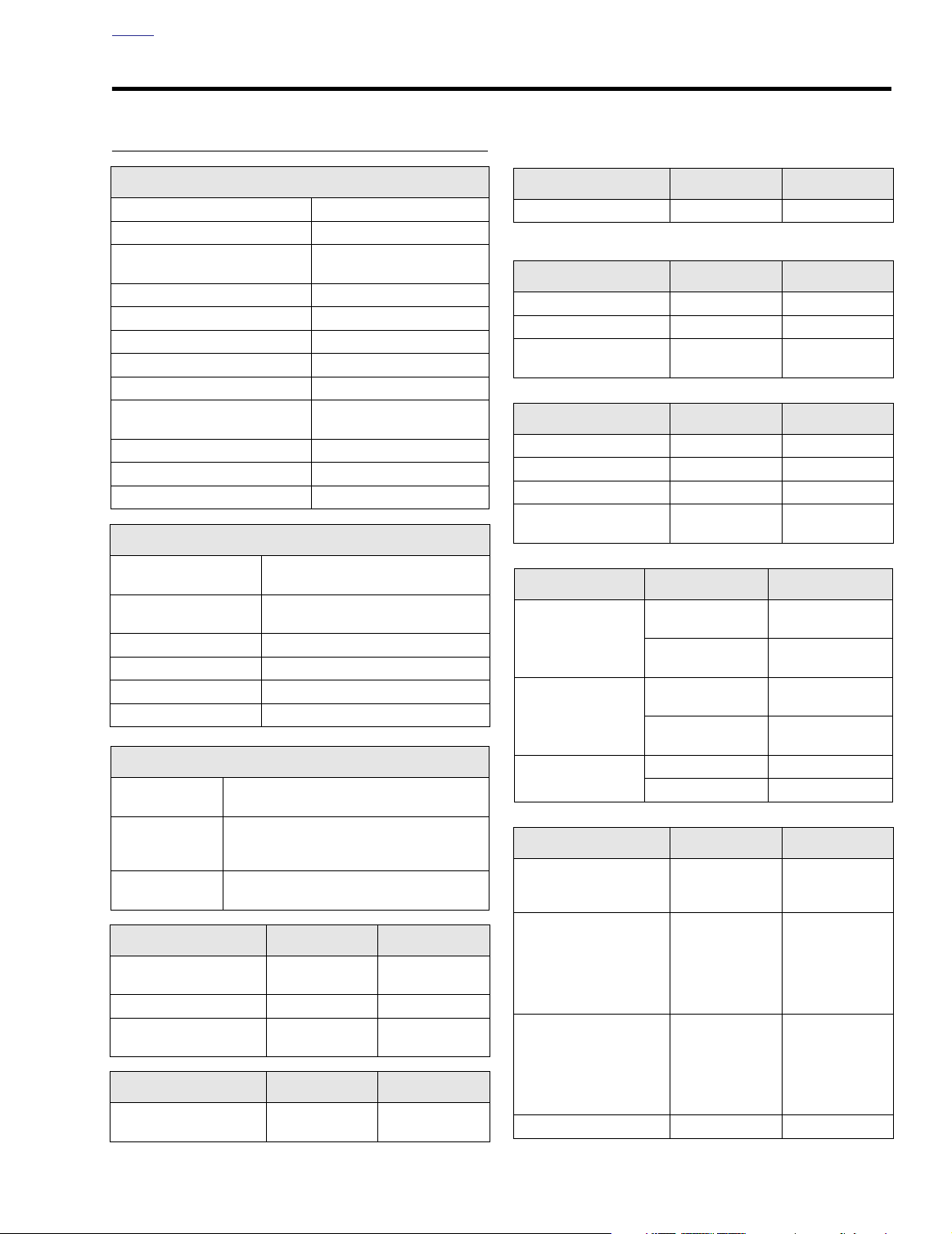
SPECIFICATIONS 3.1
MANUFACTURING TOLERANCES
General
Number of cylinders 2
Ty pe 4-cycle, 45˚V2, air-cooled
To rque
Bore 3.75 in. (95.25 mm)
Stroke 4.00 in. (101.6 mm)
Piston displacement (approx.) 88 cu. in. (1450 cc)
Compression ratio 9.0:1
Combustion chamber 5.187 cu. in. (85 cc) bathtub
Cam system
Max. sustained engine speed 5500 rpm
Idle speed 1000 rpm +/- 50
Weight 165 lbs (74.8 kg)
85 ft-lbs (115.2 Nm) @ 3000
rpm, chrome dual exhaust
Tw in cams, chain driven with
spring loaded tensioners
Ignition System
Ty pe
Ignition timing:
1050 rpm (Hot Idle)
Spark plug size 12 mm
Spark plug type Harley-Davidson 6R12
Spark plug gap 0.038-0.043 in. (0.97-1.09 mm)
Spark plug torque 12-18 ft-lbs (16-24 Nm)
Sequential, non waste spark,
MAP-N control
o
20o-30
Oiling System
Pump
Pressure
Filtration
Rocker Arm
Shaft fit in bushing
(loose)
End clearance 0.003-0.013 0.08-0.33
Bushing fit in rocker arm
(tight)
Rocker Arm Shaft
Shaft fit in rocker arm
support plate (loose)
Tw in gerotor, dual scavenge, crank mounted
and driven, internal oil pump, dry sump
30-38 psi (207-262 kN/m2) at
2000 rpm and normal operating temperature
of 230o F (110o C)
10 micron media,
filtered between pump and engine
IN. MM
0.0005-0.0020 0.013-0.051
0.002-0.004 0.051-0.102
IN. MM
0.0007-0.0022 0.018-0.056
Hydraulic Lifter
Fit in crankcase (loose) 0.0008-0.0020 0.02-0.05
Cylinder Head
Valve guide in head (tight) 0.0020-0.0033 0.051-0.084
Valve seat in head (tight) 0.003-0.0045 0.076-0.114
Head gasket surface
(flatness)
Valve
Fit in guide: exhaust 0.0015-0.0033 0.038-0.084
Fit in guide: intake 0.0008-0.0026 0.020-0.066
Seat width 0.040-0.062 1.02-1.58
Stem protrusion from
cylinder head boss
Valve Spring
Closed
Open
Free length
@ 1.751-1.848 in.
@ 44.45-46.9 mm
@ 1.282-1.378 in.
@ 32.6-35.0 mm
2.105-2.177 in. 1.926-1.996 in.
53.47-55.3 mm 48.9-50.7 mm
Piston
Fit in cylinder:
Early Style Piston
Late Style Piston
Ring end gap:
To p compression ring
2nd compression ring
Oil control ring
Ring side clearance:
To p compression ring
2nd compression ring
Oil control ring
Piston pin fit (loose) 0.0002-0.0005 0.005- 0.013
IN. MM
IN. MM
0-0.006 0-0.0152
IN. MM
1.990-2.024 50.55-51.41
Outer Inner
72-92 lbs
33-42 kg
183-207 lbs
83-94 kg
38-49 lbs
@ 1.577-1.683 in.
17-22 kg
@ 40.1-42.8 mm
98-112 lbs
@ 1.107-1.213 in.
44-51 kg
@ 28.1-30.8 mm
IN. MM
0.0006-0.0017
0.0014-0.0025
0.010-0.020
0.014-0.024
0.010-0.050
0.0012-0.0037
0.0012-0.0037
0.0031-0.0091
0.015-0.043
0.036-0.064
0.25-0.51
0.36-0.61
0.25-1.27
0.030-0.094
0.030-0.094
0.079-0.23
2004 Touring: Engine 3-1
Page 2
HOM
E
MANUFACTURING TOLERANCES (CONT.)
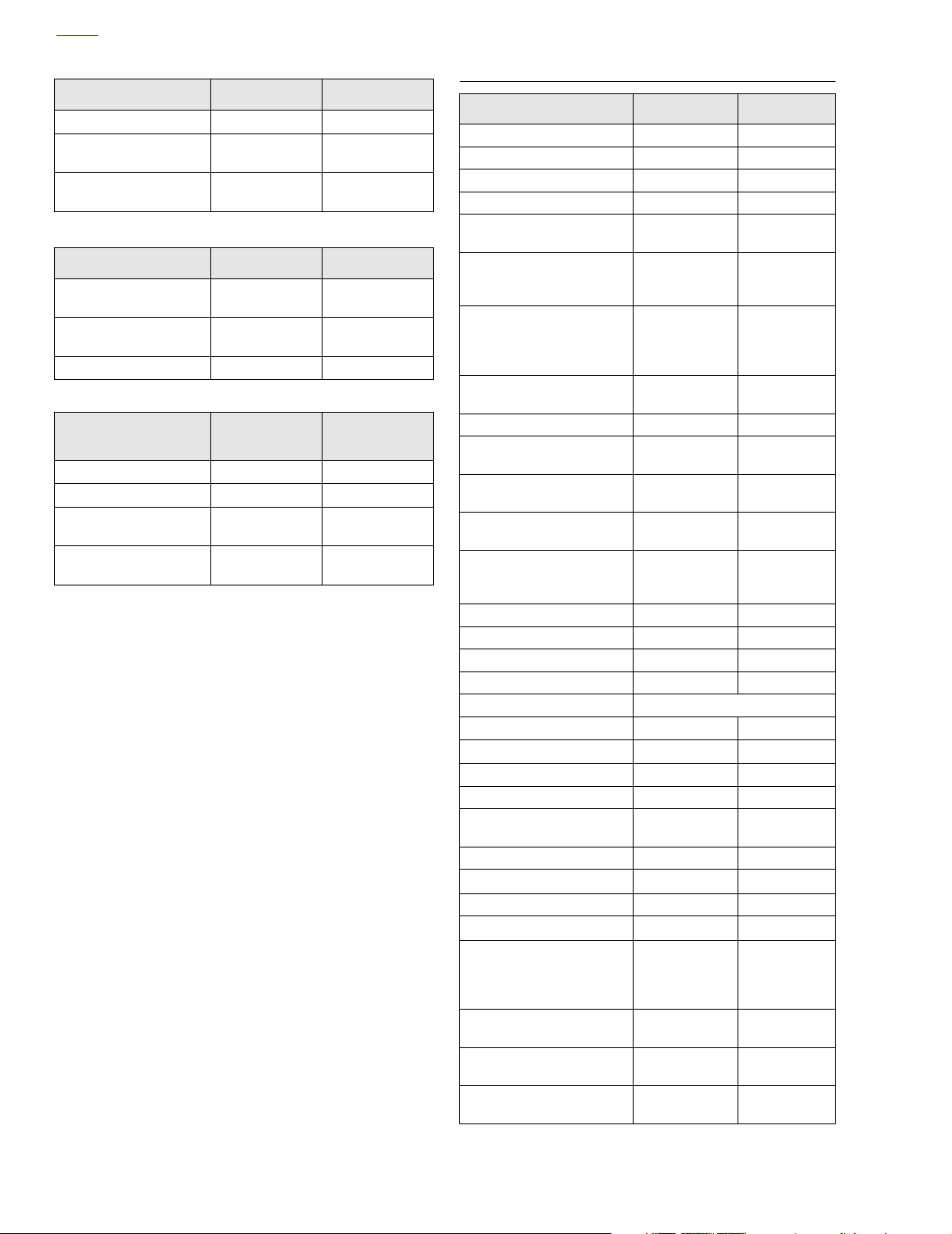
Connecting Rod
Piston pin fit (loose) 0.0007-0.0012 0.018-0.030
Side play between
flywheels
Connecting rod to
crankpin (loose)
Flywheel
Runout
(flywheels at rim)
Runout
(shaft at flywheel)
End play 0.003-0.010 0.076-0.254
Crankshaft/Sprocket
Shaft Bearings
Bearing fit (loose) 0.0002-0.0015 0.005-0.038
Crankshaft runout 0.0-0.003 0.0-0.076
Bearing fit in
crankcase (tight)
Bearing inner race on
crankshaft (tight)
IN. MM
0.005-0.015 0.13-0.38
0.0004-0.0017 0.0102-0.0432
IN. MM
0.000-0.010 0.000-0.254
0.000-0.002 0.000-0.051
IN. MM
0.0038-0.0054 0.097-0.137
0.0004-0.0014 0.010-0.036
TORQUE VALUES
Item
Breather assembly bolts 90-120
Cam cover screws 125-155
Cam cover plate screws 20-30
Cam support plate screws 90-120
Bearing retainer plate
screws
Crank sprocket flange bolt
Primary cam sprocket
flange bolt
Crank position sensor
screw
Piston jet screws 25-35
Tr ansmission housing to
crankcase bolts
Crankcase to front engine
mounting bracket bolts
Crankcase bolts
Cylinder head bolts
Cylinder studs 10-20 ft-lbs 14-27 Nm
Engine oil drain plug 14-21 ft-lbs 19-28 Nm
Lifter cover screws 90-120
Oil pan screws 84-108
Oil filter 1/2-3/4 turn after gasket contact
Oil filter mount 12-16 ft-lbs 16-22 Nm
Crankcase oil fittings/plugs
Oil hose cover screws 84-108
Oil pressure switch/sender 96-120
Rocker arm support
plate bolts
Rocker cover bolts 15-18 ft-lbs 20-24 Nm
Rocker housing bolts
Spark plugs 12-18 ft-lbs 16-24 Nm
Stator screws
Upper engine mounting
bracket:
To cylinder heads
To top stabilizer link
Engine temperature
sensor
Intake flange adapter
screws
Exhaust flange adapter
nuts
ft/in-lbs NM
in-lbs
10-14 Nm
in-lbs
14-18 Nm
in-lbs
2.3-3.4 Nm
in-lbs
10-14 Nm
20-30
in-lbs
2-3 Nm
15 ft-lbs,
loosen one full
turn, 24 ft-lbs
15 ft-lbs,
loosen one full
turn, 34 ft-lbs
90-120
in-lbs
in-lbs
15 ft-lbs,
30-35 ft-lbs
33-38 ft-lbs 45-52 Nm
10 ft-lbs,
15-19 ft-lbs
120-144
in-lbs
15-17 ft-lbs
o
+ 90
turn
in-lbs
in-lbs
120-168
in-lbs
in-lbs
in-lbs
18-22 ft-lbs 24-30 Nm
120-168
in-lbs
55-75
in-lbs
35-40 ft-lbs
18-22 ft-lbs
120-180
in-lbs
96-144
in-lbs
100-120
in-lbs
20.3 Nm,
loosen one full
turn, 32.5 Nm
20.3 Nm,
loosen one
full turn, 46.1
Nm
10.2-13.6 Nm
2.8-4.0 Nm
20 Nm,
41-48 Nm
14 Nm,
20-26 Nm
,
13.6-16.3 Nm,
20.3-23.1 Nm
+ 90o turn
10-14 Nm
9-12 Nm
13.6-18.9 Nm
10-12 Nm
11-14 Nm
13.6-18.9 Nm
6.2-8.5 Nm
48-54 Nm
24-30 Nm
13.6-20.3 Nm
10.9-16.3 Nm
11.3-13.6 Nm
3-2 2004 Touring: Engine
Page 3
HOM
E
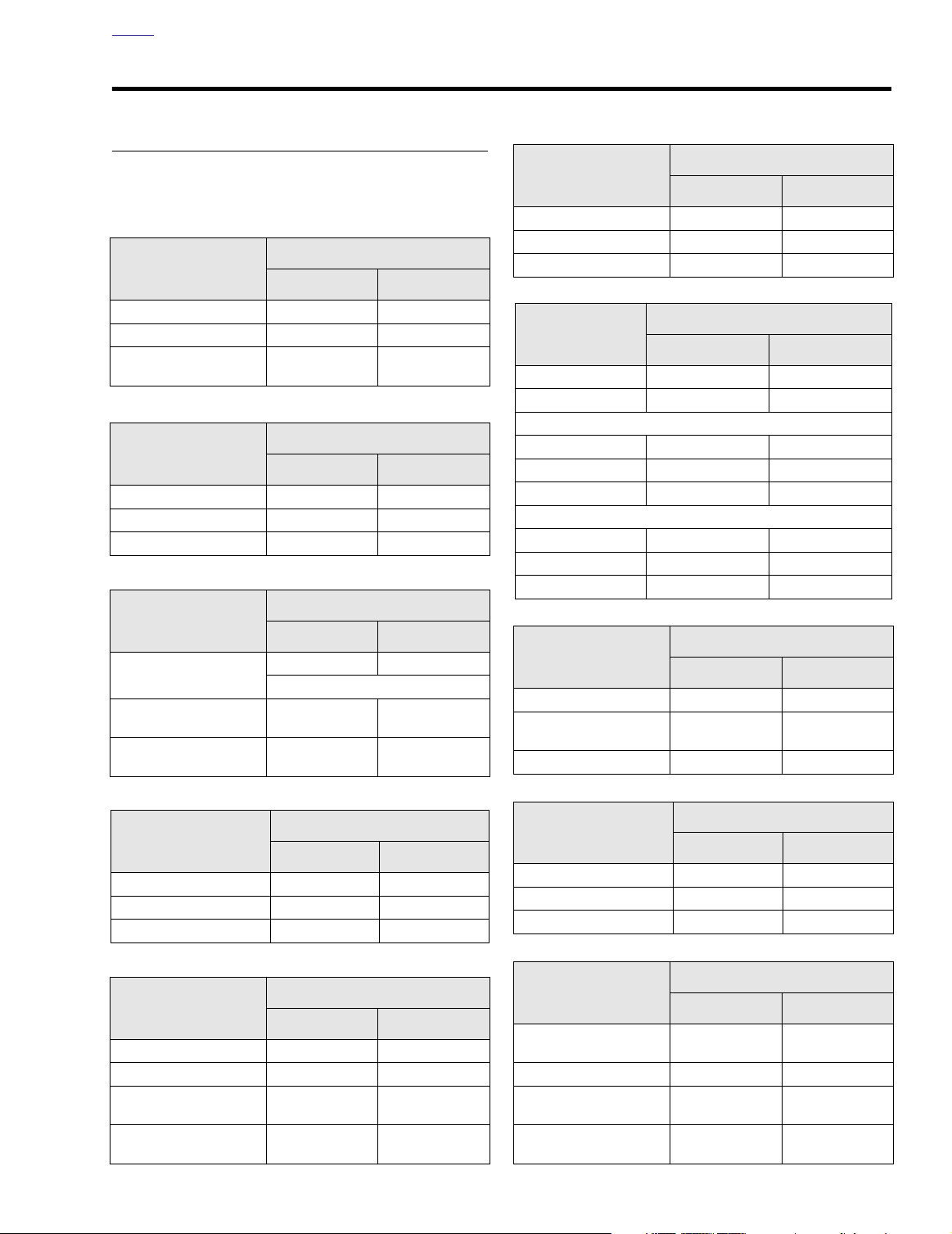
SERVICE WEAR LIMITS 3.2
GENERAL
REPLACE IF
IN. MM
REPLACE IF
IN. MM
REPLACE IF
IN. MM
Wear limits can be used as a guide when deciding whether to
reuse engine parts. Replace used parts whenever the following wear limits are exceeded.
Rocker Arm/
Rocker Arm Shaft
Shaft fit in bushing (loose) More than 0.0035 More than 0.089
End clearance More than 0.025 More than 0.635
Shaft fit in rocker arm
support plate (loose)
More than 0.0035 More than 0.089
REPLACE IF
IN. MM
REPLACE IF
Hydraulic Lifter
IN. MM
Fit in crankcase More than 0.003 More than 0.08
Roller fit More than 0.0015 More than 0.038
Roller end clearance More than 0.015 More than 0.38
REPLACE IF
Cam Support Plate
IN. MM
Cam chain
tensioner shoe wear
Crankshaft bushing fit
in cam support plate
Crankshaft bushing
maximum ID
More than 0.090 More than 2.29
1/2 thickness of shoe
Less than 0.0008 Less than 0.0203
More than 0.8545 More than 21.704
Cylinder Bore
Standard More than 3.752 More than 95.301
0.005 in. oversize More than 3.757 More than 95.428
0.010 in. oversize More than 3.762 More than 95.555
Piston
Fit in cylinder (loose) More than 0.003 More than 0.076
Piston pin fit (loose) More than 0.0008 More than 0.020
Ring end gap
To p compression More than 0.030 More than 0.76
2nd compression More than 0.034 More than 0.86
Oil control ring rails More than 0.050 More than 1.27
Ring side clearance
To p compression More than 0.0045 More than 0.11
2nd compression More than 0.0045 More than 0.11
Oil control ring rails More than 0.010 More than 0.25
Connecting Rod
Piston pin fit (loose) More than 0.002 More than 0.051
Side play between
flywheels
Fit on crankpin (loose) More than 0.002 More than 0.051
More than 0.020 More than 0.508
Cylinder Head
REPLACE IF
IN. MM
Valve guide in head (tight) Less than 0.002 Less than 0.051
Valve seat in head (tight) Less than 0.002 Less than 0.051
Head warpage More than 0.006 More than 0.152
REPLACE IF
Cylinder
IN. MM
Ta per More than 0.002 More than 0.051
Out of round More than 0.002 More than 0.051
Warpage of gasket or
O-ring surfaces: top
Warpage of gasket or
O-ring surfaces: base
More than 0.006 More than 0.152
More than 0.004 More than 0.102
Flywheel
REPLACE IF
IN. MM
Runout (flywheels at rim) More than 0.015 More than 0.381
Runout (shaft at flywheel) More than 0.003 More than 0.076
End play More than 0.010 More than 0.254
Crankshaft/Sprocket
Shaft Bearings
Bearing to shaft
clearance
Shaft runout More than 0.003 More than 0.076
Bearing fit in
crankcase (tight)
Bearing inner race
on shaft (tight)
More than 0.0015 More than 0.038
Less than 0.0038 Less than 0.097
Less than 0.0004 Less than 0.010
REPLACE IF
IN. MM
2004 Touring: Engine 3-3
Page 4
HOM
E
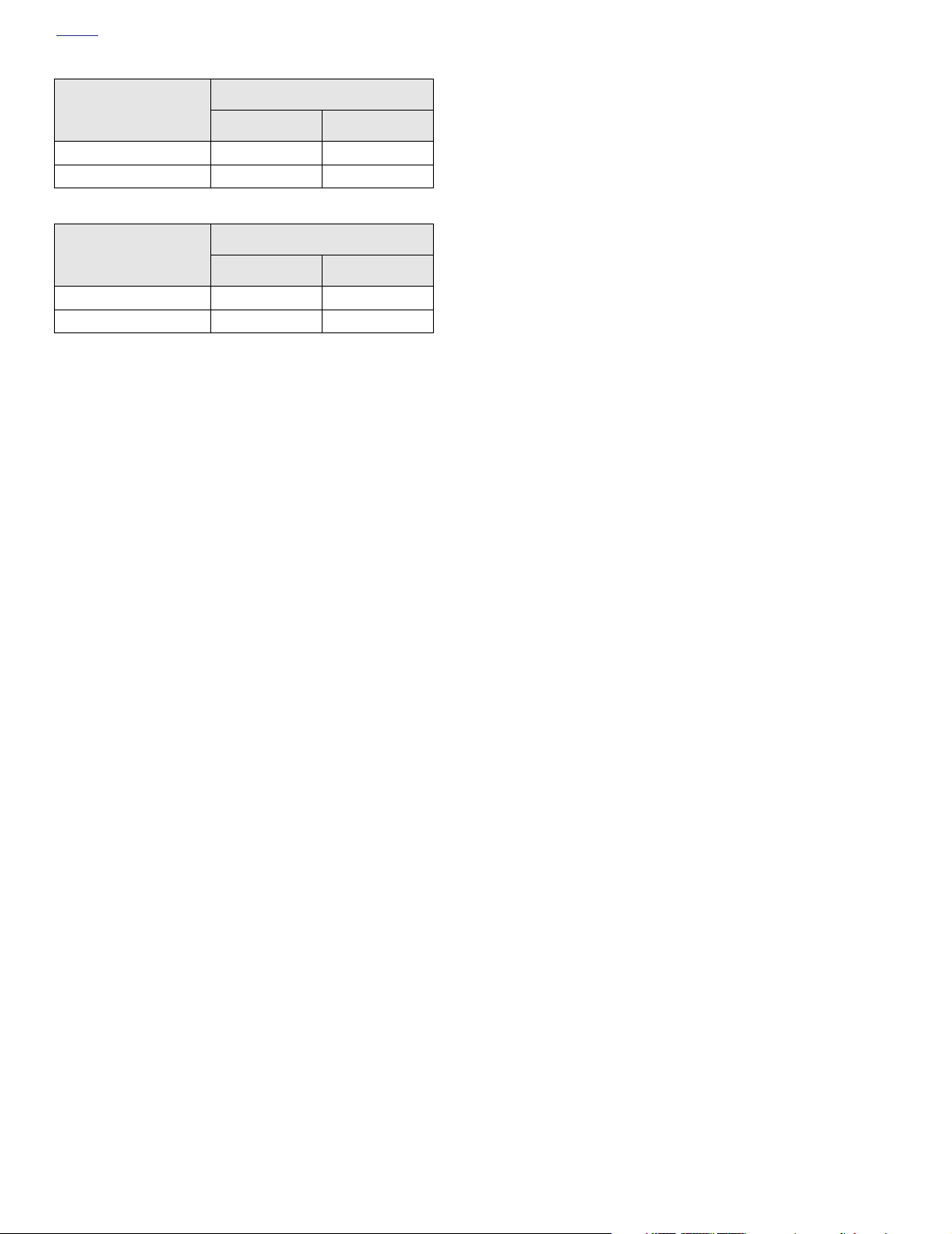
SERVICE WEAR LIMITS (CONT.)
Breather Assembly
REPLACE IF
IN. MM
Breather cover warpage More than 0.005 More than 0.13
Breather baffle warpage More than 0.005 More than 0.13
Valve Stem to
Guide Clearance
Intake More than 0.0035 More than 0.089
Exhaust More than 0.0040 More than 0.102
REPLACE IF
IN. MM
3-4 2004 Touring: Engine
Page 5
HOM
CAUTION
E
GENERAL INFORMATION 3.3
FUEL
Use a good quality leaded or unleaded gasoline (91 pump
octane or higher). Octane rating is usually posted on the
pump.
CAUTION
Using gasolines with alcohol additives (such as methanol) can cause rubber components within the fuel system to fail or result in engine damage.
GASOLINE/ALCOHOL BLENDS
Harley-Davidson motorcycles were designed to give the best
performance using unleaded gasoline. Some fuel suppliers
sell gasoline/alcohol blends as a fuel. The type and amount
of alcohol added to the fuel is important.
●
DO NOT USE GASOLINES CONTAINING METHANOL.
Using gasoline/methanol blends will result in starting
and driveablility deterioration and damage to critical fuel
system components.
●
ETHANOL is a mixture of 10% ethanol (Grain alcohol)
and 90% unleaded gasoline. Gasoline/ethanol blends
can be used in your motorcycle if the ethanol content
does not exceed 10%.
REFORMULATED OR OXYGENATED GASOLINES
●
(RFG): “Reformulated gasoline” is a term used to
describe gasoline blends that are specifically designed
to burn cleaner than other types of gasoline. Your motorcycle will run normally using this type of gas.
Yo u may find that some gasoline blends adversely affect the
starting, driveability or fuel efficiency of your bike. If you
experience one or more of these problems, we recommend
you try a different brand of gasoline or gasoline with a higher
octane rating.
LUBRICATION
CHECKING ENGINE OIL LEVEL
Oil level cannot be accurately measured on a cold
engine. For preride inspection, with motorcycle leaning
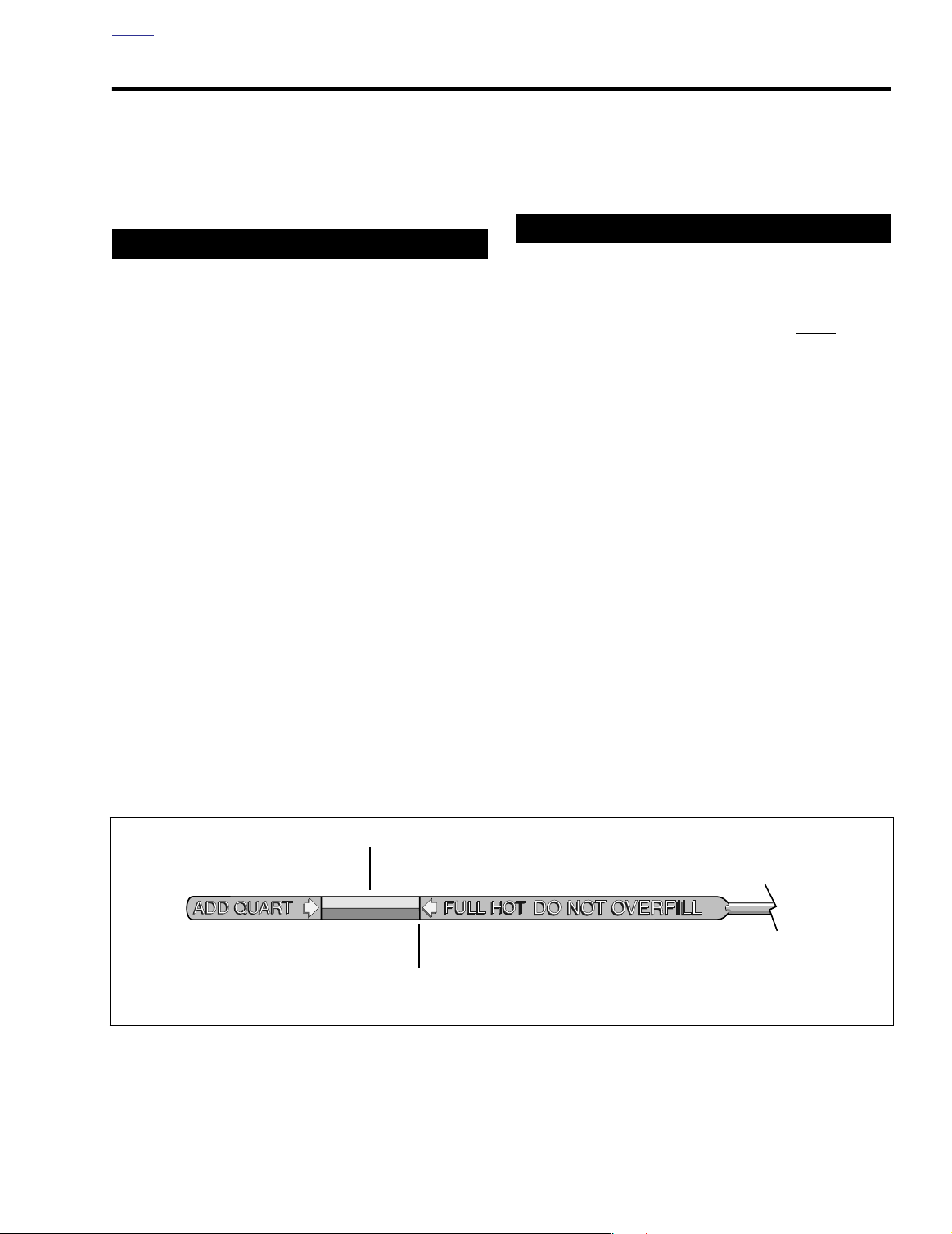
on jiffy stand on level ground, oil should register on dipstick between arrows when engine is cold. Do NOT add
oil to bring the level to the FULL mark on a COLD
1. Perform engine oil level
a. With the vehicle resting on the jiffy stand on level
ground, wipe off the dipstick and insert it back into
the oil pan with the plug pushed completely into the
fill spout.
b. Remove the dipstick and note the level of the oil. Oil
level should register between the two arrows on the
dipstick. See Figure 3-1. If oil level is at or below the
lower arrow, add only enough oil to bring the level
between the two arrows on the dipstick.
2. Perform engine oil level
a. Ride vehicle until engine is at normal operating tem-
perature.
b. With the vehicle resting on the jiffy stand on level
ground, allow engine to idle for 1-2 minutes. Turn
engine off.
c. Wipe off the dipstick and insert it back into the oil
pan with the plug pushed completely into the fill
spout.
d. Remove the dipstick and note the level of the oil.
Add only enough oil to bring the level to the FULL
mark on the dipstick. See Figure 3-1. Do not overfill.
COLD CHECK
HOT CHECK
as follows:
as follows:
engine.
COLD CHECK
HOT CHECK
f1254b3x
Figure 3-1. Engine Oil Dipstick
2004 Touring: Engine 3-5
Page 6
HOM
E
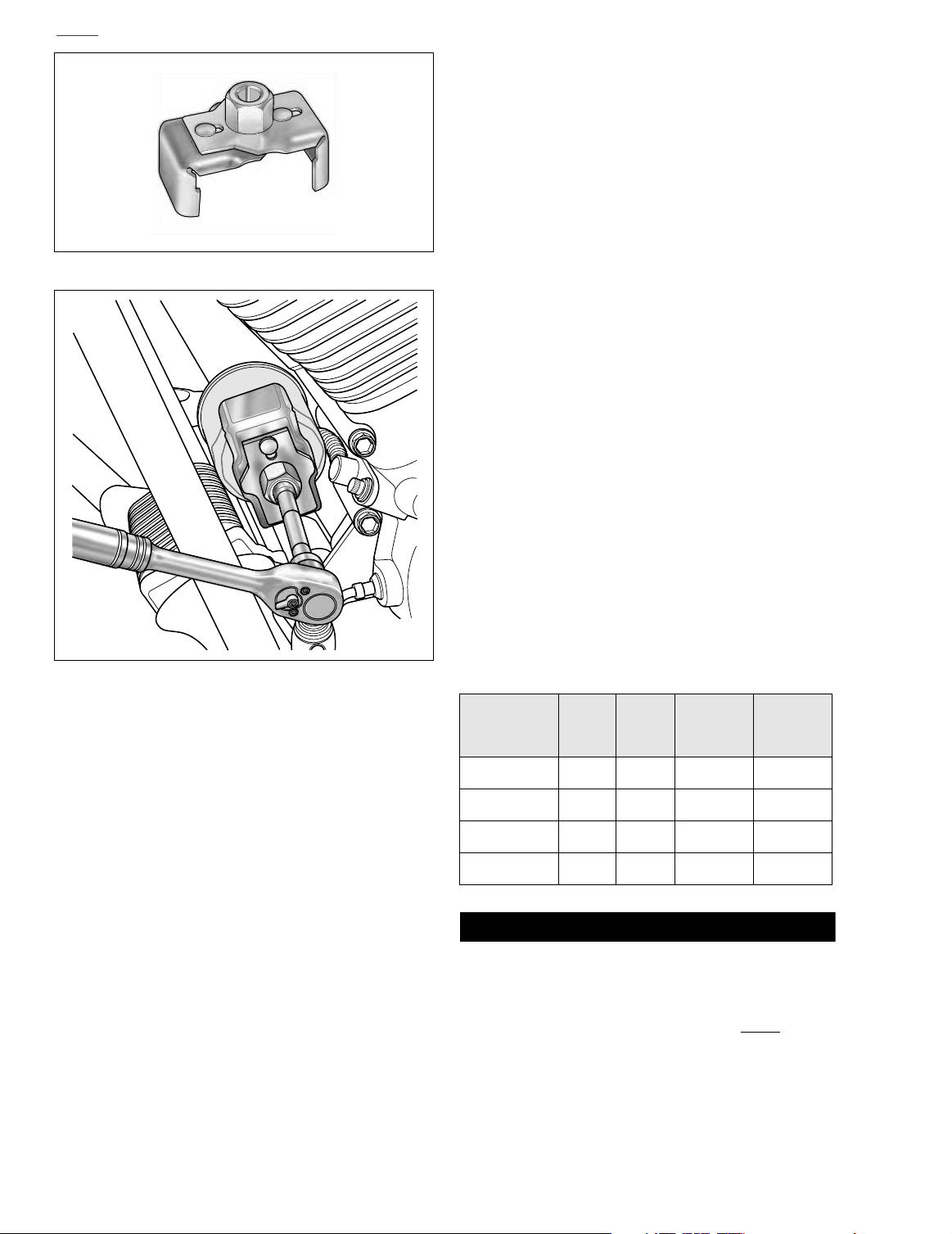
Figure 3-2. Oil Filter Wrench (Part No. HD-42311)
f1641x3x
5. Remove the oil filter as follows:
a. Obtain the OIL FILTER WRENCH (HD-42311). The
tool allows easy removal of the oil filter without risk
of damage to the crankshaft position sensor or
cable.
b. Place the jaws of the wrench over the oil filter with
the tool oriented vertically. See Figure 3-3.
c. Using a 3/8 inch drive with a 4 inch extension, turn
wrench in a counterclockwise direction. Do not use
with air tools.
NOTE
Use OIL FILTER WRENCH (HD-44067) if HD-42311 is not
available.
6. Clean the oil filter mount flange of any old gasket material.
7. Lubricate gasket with clean engine oil and install
new
oil
filter on filter mount. Hand tighten oil filter 1/2-3/4 turn
after gasket first contacts filter mounting surface. Do
NOT
use OIL FILTER WRENCH for oil filter installation.
NOTE
Use of the Premium 10 micron synthetic media oil filter is
highly recommended, Part No. 63798-99 (Chrome) or 6373199 (Black).
Figure 3-3. Remove Engine Oil Filter
CHANGING ENGINE OIL AND FILTER
NOTE
At the 1000 mile (1600 km) service interval, and at every
5000 mile (8000 km) service interval thereafter, change the
engine oil and engine oil filter. If motorcycle is ridden hard,
under dusty conditions or in cold weather, change engine oil
and filter more often.
1. Ride vehicle until engine is at normal operating temperature.
2. Locate oil filler plug/dipstick on right side of vehicle at top
of transmission case. To remove the oil filler plug, pull
steadily while moving plug back and forth.
3. Locate oil drain plug at front left side of the oil pan.
Remove the oil drain plug and allow oil to drain completely.
4. Inspect the oil drain plug O-ring for cuts, tears or signs of
deterioration. Replace as necessary.
8. Install engine oil drain plug with O-ring. Tighten plug to
14-21 ft-lbs (19-28 Nm).
9. With vehicle resting on jiffy stand, add 3-1/2 quarts (3.3
liters) engine oil as specified in Ta bl e 3-1. Use the proper
grade of oil for the lowest temperature expected before
the next oil change.
Table 3-1. Recommended Engine Oils
Harley-Davidson
Type
HD Multi-grade
HD Multi-grade
HD Regular Heavy
HD Extra Heavy
Viscosity
SAE
10W40
SAE
20W50
SAE
SAE
Harley-
Davidson
Rating
HD 360
HD 360
HD 360
50
HD 360
60
CAUTION
Oil level cannot be accurately measured on a cold
engine. For preride inspection, with motorcycle leaning
on jiffy stand on level ground, oil should register on dipstick between arrows when engine is cold. Do NOT add
oil to bring the level to the FULL mark on a COLD
10. Perform engine oil level
COLD CHECK
Lowest
Ambient
Temperature
Below 40˚F
(4˚C)
Above 40˚F
(4˚C)
Above 60˚F
(16˚C)
Above 80˚F
(27˚C)
as follows:
Cold Weather
Starts Below
50˚F (10˚C)
Excellent
Good
Poor
Poor
engine.
3-6 2004 Touring: Engine
Page 7

HOM
CAUTION
E
a. With the vehicle resting on the jiffy stand on level
ground, wipe off the dipstick and insert it back into
the oil pan with the plug pushed completely into the
fill spout.
b. Remove the dipstick and note the level of the oil. Oil
level should register between the two arrows on the
dipstick. See Figure 3-1. If oil level is at or below the
lower arrow, add only enough oil to bring the level
between the two arrows on the dipstick.
11. Perform engine oil level
a. Ride vehicle until engine is at normal operating tem-
perature.
b. With the vehicle resting on the jiffy stand on level
ground, allow engine to idle for 1-2 minutes. Turn
engine off.
c. Wipe off the dipstick and insert it back into the oil
pan with the plug pushed completely into the fill
spout.
d. Remove the dipstick and note the level of the oil.
Add only enough oil to bring the level to the FULL
mark on the dipstick. See Figure 3-1. Do not overfill.
12. Start engine and carefully check for oil leaks around
drain plug and oil filter.
HOT CHECK
as follows:
WINTER LUBRICATION
Combustion in an engine produces water vapor. During starting and warm-up in cold weather, especially in freezing temperatures, the vapor condenses to water before the
crankcase is hot enough to exhaust it through the breather
system. If the engine is run long enough for the crankcase to
become thoroughly heated, the water returns to vapor and is
then exhausted.
An engine used for only short trips, and seldom allowed to
thoroughly warm up, accumulates increasing amounts of
water in the oil pan. Water mixed with oil forms a sludge that
causes accelerated engine wear. In freezing temperatures,
the water becomes slush or ice, which may clog oil lines and
result in engine failure.
Always change the engine oil more often in winter. If the
engine is used for short runs, change the oil even more frequently. The farther below freezing the temperature drops the
more often the oil should be changed.
OIL PRESSURE INDICATOR LAMP
The
red
OIL PRESSURE indicator lamp illuminates to indicate improper circulation of the engine oil. The lamp illuminates when the ignition is first turned on (before the engine is
started), but should be extinguished once the engine is running.
Check the engine oil level if the oil pressure indicator
lamp remains illuminated. If the oil level is normal, stop
the engine immediately. Do not ride the vehicle until the
probem is located and corrected.
If the indicator lamp is not extinguished, it may be the result
of a low oil level or diluted oil supply. In freezing weather, the
oil feed and return lines can clog with ice or sludge. A defect
in the lamp wiring, faulty oil pressure switch/sender, damaged oil pump, plugged oil filter element, incorrect oil viscosity, broken or weak spring in the oil pressure relief valve and/
or damaged or incorrectly installed O-rings in the engine may
also cause the indicator lamp to remain on.
To troubleshoot the problem, always check the engine oil
level first. If the oil level is OK, determine if oil returns to the
pan from the oil return hose. If oil does not return, shut off the
engine until the problem is located and corrected.
To check the engine oil pressure, proceed as follows:
1. Verify engine oil level. See CHECKING ENGINE OIL
LEVEL in this section.
2. Locate the oil pressure switch/sender at the front right
side of the crankcase.
3. On FLHR/C/S models, pull elbow from post of oil pressure switch. On FLHT/C/U and FLTR models, pull external latch outward and use rocking motion to remove
Packard connector from oil pressure sender.
4. On FLHR/C/S models, use a 15/16 inch Open End Crow
Foot (Snap-On FC30B) to remove oil pressure switch
from crankcase. On FLHT/C/U and FLTR models, use 11/16 inch Open End Crow Foot (Snap-On FC34A) to
remove oil pressure sender.
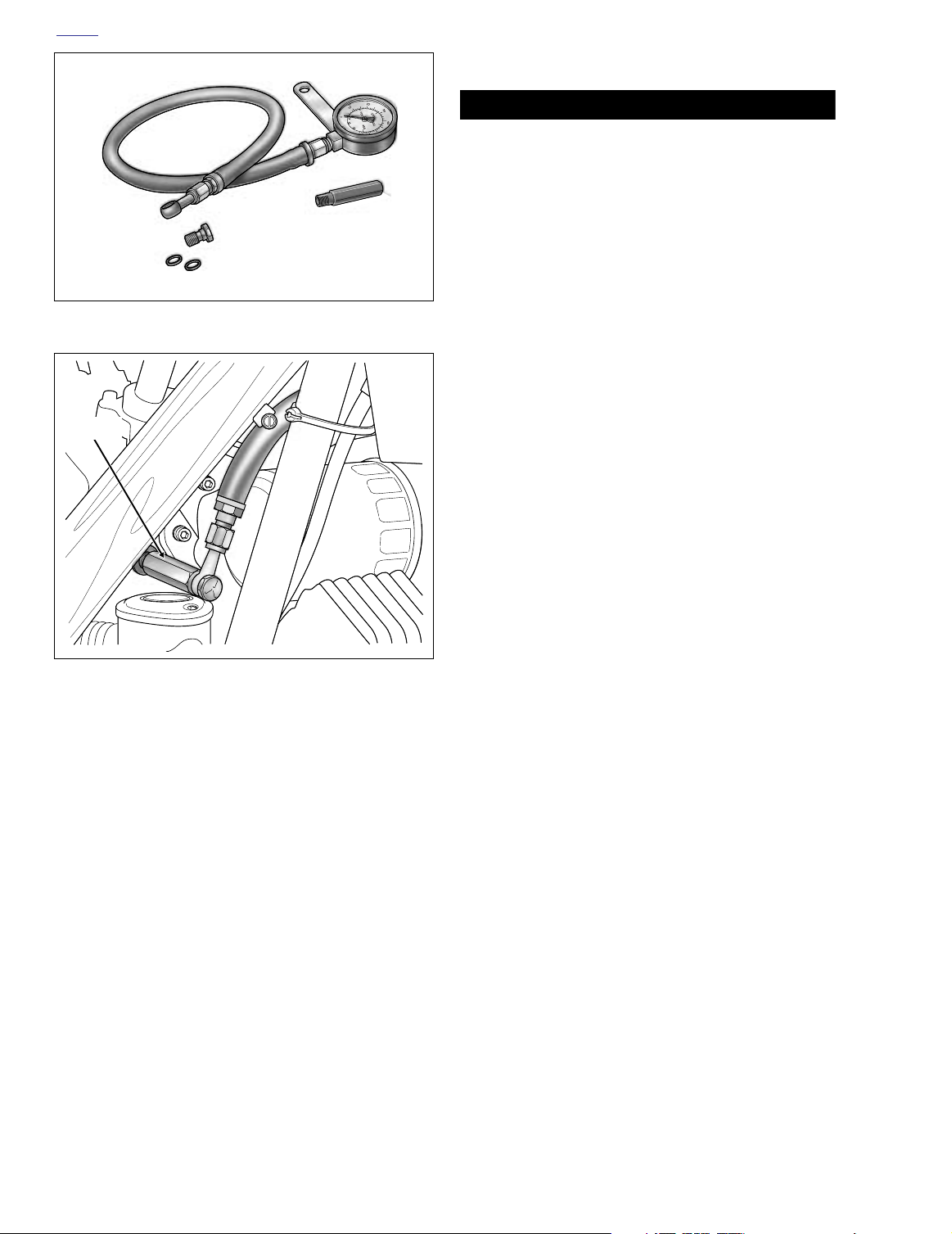
5. Start OIL PRESSURE GAUGE ADAPTER (HD-96921-
110) into crankcase bore. Using a 5/8 inch open end
wrench, turn adapter until snug. See Figure 3-4.
6. Moving to left side of vehicle, route banjo fitting and hose
of OIL PRESSURE GAUGE (HD-96921-52B) over
shifter lever and oil filter to right side of engine. See Fig-
ure 3-5.
7. Slide washer on banjo bolt and insert through banjo fitting on gauge. Install second washer on bolt and thread
into adapter until snug.
8. Run vehicle or simulate road running until engine is at
normal operating temperature, approximately 230
(110o C.). Gauge reading will not be accurate if engine is
not completely warmed.
9. Verify that oil pressure is 30-38 psi (207-262 kN/m2) at
2000 rpm.
10. Remove banjo bolt (and washers) from adapter. Remove
gauge from vehicle and then remove adapter from
crankcase.
o
F.
2004 Touring: Engine 3-7
Page 8
HOM
E
ENGINE OIL FLOW
Gauge
Banjo
Bolt
Washers
Figure 3-4. Oil Pressure Gauge
(Part No. HD-96921-52B)
Adapter
Figure 3-5. Install Adapter and Oil Pressure Gauge
NOTE
If reusing oil pressure switch/sender, apply Loctite Pipe Sealant with Teflon 565 to threads.
11. Start oil pressure switch/sender into crankcase bore.
12. On FLHR/C/S models, use a 15/16 inch Open End Crow
Foot (Snap-On FC30B) to tighten oil pressure switch to
96-120
models, use 1-1/16 inch Open End Crow Foot (Snap-On
FC34A) to tighten oil pressure sender to same torque.
13. On FLHR/C/S models, install elbow on post of oil pressure switch. On FLHT/C/U and FLTR models, install
Packard connector to oil pressure sender.
If wire socket terminal requires replacement, see APPENDIX
B.5 SEALED BUTT SPLICE CONNECTORS.
14. Test oil pressure switch/sender for proper operation.
in-lbs
(11-14 Nm). On FLHT/C/U and FLTR
NOTE
Adapter
Part No. HD-96921-110
f1646x3x
Oil
Filter
CAUTION
The oiling system is carefully designed for optimum efficiency. All oil holes and passageways are specially
sized. Exercise caution to avoid enlarging oil holes during cleaning. Any modification of the oiling system will
adversely affect oil pressure or cooling and lubrication
efficiency.
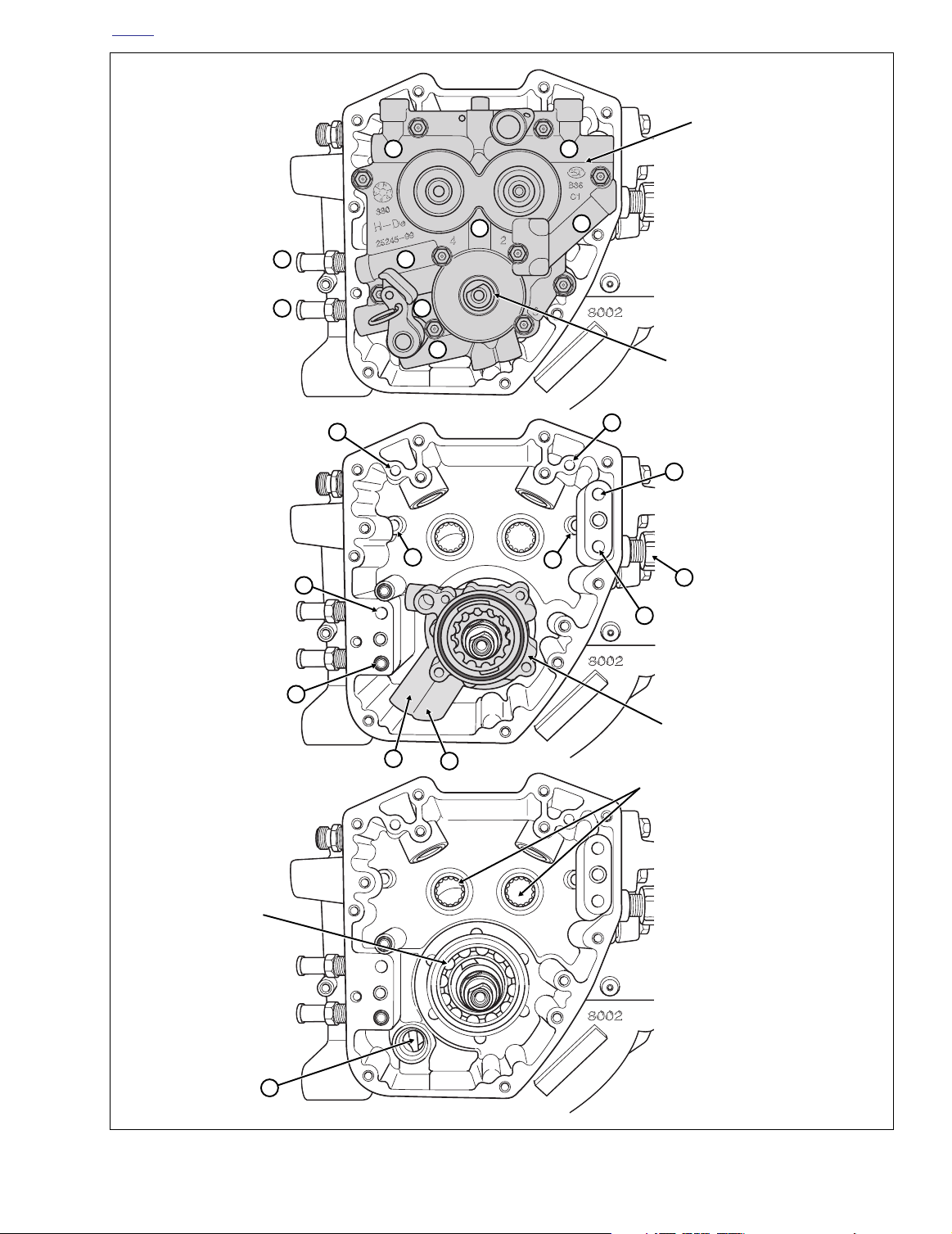
Oil Feed (Figures 3-6, 3-7)
Oil flows from the oil pan through a passageway at the front
of the transmission housing into a flexible hose clamped to
the lower fitting (A1) at the rear right side of the crankcase.
Running through a passageway in the crankcase, the oil exits
a hole in the crankcase flange (B2) and enters a hole on the
inboard side of the cam support plate. Passing through a
channel in the cam support plate (A3), the oil enters the feed
side of the oil pump. See OIL PUMP OPERATION. The feed
gerotors of the pump direct the flow up a second channel in
the cam support plate (A4).
A drilling in this channel connects to a pressure relief valve
mounted in the bypass port of the cam support plate (A5).
When the oil pressure exceeds the setting of the valve spring
(35 psi), the orifice opens to bypass excess oil back to the
feed side of the pump (A3).
Oil not returned to the feed side exits a hole on the inboard
side of the cam support plate and passes through a hole in
the crankcase flange (B6). Flowing through a passageway in
the crankcase, where a reading is taken by the oil pressure
sender (B7), the oil exits the lower hole in the oil filter mount
(D8).
After circulating through the oil filter, the flow of oil is directed
back into the crankcase through the upper hole in the oil filter
mount (D9). Exiting a passageway in the crankcase through
a hole in the crankcase flange (B10), the flow of oil reenters
the cam support plate.
Filtered oil is then routed to the top and bottom ends of the
engine, as described below.
Top End (Figures 3-6, 3-7)
Oil passes through a channel in the cam support plate exiting
the inboard side through two holes near the top (A11, A12).
Entering two holes in the crankcase flange (B13, B14), one
leading to the front cylinder and the other to the rear, the oil
travels through passageways in the crankcase to the hydraulic lifter bores (D15).
Exiting a hole in each lifter bore (E16), the oil flows around
the lifter and enters a hole at the side of the lifter body. As the
chamber inside the lifter body is filled, the push rod socket
rises to achieve the no-lash fit of the valve train components.
The flow of oil then exits a hole centered in the lifter socket
and runs up the hollow push rods.
3-8 2004 Touring: Engine
Page 9
HOM
E
f1581b3x
A
B
Cam Support Plate
12 11
26
38
1
36
3
5
4
Crankshaft
Bushing
14
24
37
23
13
10
7
C
Crankshaft
Bearing
6
2
f1573b3x
Oil Pump
35
25
Cam Needle Bearings
34
f1580b3x
Figure 3-6. Engine Oil Flow - Cam Support Plate/Right Crankcase Half
2004 Touring: Engine 3-9
Page 10

HOM
E
NOTE
Note that there is one additional hole drilled into the inside
lifter bores- while the oblong hole circulates oil around the
lifter body as described, the round hole (E17) feeds oil to the
piston jets in the flywheel compartment.
Exiting holes at the top of the hollow push rods, oil enters a
hole at the bottom of the intake and exhaust rocker arms.
Lubricating the rocker arm bushings, oil flows down the
rocker arm shafts and exits a pin hole in the outboard side of
each rocker arm housing (F18) where it sprays the valve
springs and the top of the valve stem.
Oil runs down to the low side of the rocker housing and
enters the exhaust valve spring pocket where a drain hole
(G19) leads to a passageway in the cylinder head casting.
Oil exits the bottom of the cylinder head and passes through
a ring dowel (H20) on the “down side” of the cylinder flange.
The oil runs through a vertical passageway in the cylinder,
passes through a second ring dowel on the “down side” of
the cylinder deck (I21) and enters the left crankcase half.
Flowing through a horizontal passageway in the left crankcase half (J22), oil runs through a third ring dowel (K23) to
the right crankcase half where it travels through another passageway before emptying into the cam compartment (B23,
B24).
Oil collecting in the cam compartment is picked up by one of
two scavenge lobes on the oil pump (B25).
Bottom End (Figures 3-6, 3-7, 3-8)
Oil travels down the center passage of the cam support plate
(A26) and sprays out through pin holes on each side of the
casting to lubricate both the primary and secondary cam
chains. Oil also passes through a hole in the crankshaft
bushing where the flow enters a drilling in the crankshaft
(L27).
Oil runs down the center of the crankshaft and then up a
cross drilling into the right side of the flywheel. The flow exits
a drilling in the crank pin bore, enters the crank pin and then
sprays out through three holes to lubricate the lower rod
bearing set.
The oil splash and mist created by the action of the flywheel
lubricates the crankshaft bearing and the camshaft needle
bearings in the right crankcase half. This same action serves
to lubricate the sprocket shaft bearing in the left crankcase
half (M28).
Since the oil mist also lubricates the cylinder walls, three
holes on each side of the piston (in the area of the third ring
land) evacuate excess oil scraped from the walls on the piston downstroke.
The piston jets (N29), which receive a supply of oil from the
intake lifter bores, spray the underside of the piston for cooling of the piston crown and skirt area. A check valve in each
jet opens only when the oil pressure reaches 12-15 psi, at
which point the engine is operating above idle speed. At idle
speeds (9-12 psi), the valve remains closed to prevent over
oiling and to ensure proper system operating pressure.
Oil spray from each piston jet also enters a hole at the bottom
of each pin boss (O30) for lubrication of the piston pin.
Another hole at the top of the connecting rod (D31) allows a
portion of the oil to reach the upper rod bushing.
Surplus oil falls back to the bottom of the flywheel compartment where it collects in the sump area (P32). Oil in the
sump is drawn to the cam compartment through an internal
channel (P33, C34) that connects with the second scavenge
lobe of the oil pump (B35).
Oil Return (Figures 3-6, 3-8)
The “dual kidney” designation given to the oil pump refers to
its two scavenging functions, whereby it simultaneously
draws oil from both the cam and flywheel compartments.
Oil sucked up by the scavenge lobes passes through the
scavenge gerotors of the oil pump and is directed through a
return channel in the cam support plate (A36). See OIL
PUMP OPERATION.
Exiting a hole on the inboard side of the cam support plate,
the oil enters a hole in the crankcase flange (B37).
The oil flows through a passageway in the crankcase and
exits the upper fitting at the rear right side of the crankcase
(A38). Passing through a flexible hose connection, the flow of
oil runs through a passageway at the front of the transmission housing (Q39) before emptying into the oil pan at the
front of the baffle (R40).
The oil flows to the rear of the oil pan along each side of the
baffle. Spring tension holds the unit tight against the bottom
of the pan to prevent oil from entering or escaping around the
perimeter of the baffle. At the back of the oil pan, the oil
enters the open side of the baffle where it is redirected forward. The baffle plates slow the circulation of the oil through
the pan to enhance cooling.
Oil pickup occurs in the front compartment of the baffle
where a passageway in the casting (S41) directs the flow
upward. Passing through a second passageway in the transmission housing (Q42), the flow of oil enters the flexible hose
connection (A1) to repeat the circuit.
Also note that a third flexible hose clamped to a fitting behind
the rear lifter cover connects the cam compartment with the
oil filler spout. This crankcase breather connection provides
the pressure balance necessary for oil circulation.
Oil Pump Operation
The oil pump consists of a housing containing two gerotor
gear sets, one feed and the other scavenge. Driven by the
crankshaft, the feed gerotor set distributes oil to the engine,
while the scavenge gerotor set draws oil from the cam and
flywheel compartments and returns it to the oil pan.
3-10 2004 Touring: Engine
Page 11

HOM
E
D
15
31
9
8
H
20
E
F
17
16
18
I
J
21
22
G
19
K
23
Figure 3-7. Engine Oil Flow - Top End
2004 Touring: Engine 3-11
Page 12

HOM
E
L
M
P
27
32
33
Q
28
42
39
N
O
R
40
29
30
S
41
3-12 2004 Touring: Engine
Figure 3-8. Engine Oil Flow - Bottom End
Page 13

f1562x3x
B
A
C
Inner
Gerotor
Outer
Gerotor
Seal
Oil In
Seal
Oil Out
HOM
E
Each gerotor gear set has two parts, an inner and outer gerotor. The inner and outer gerotors have fixed centers that are
slightly offset to one another. Also, the inner gerotor has one
less tooth.
As the crankshaft rotates, the cavity between the inner and
outer gerotors on the inlet side of the pump increases in volume. This creates a vacuum causing oil to be drawn in. The
cavity continues to increase until the volume is equivalent to
that of the missing tooth on the inner gerotor. Also note that
the inlet and outlet sides of the pump are sealed by the tips
and lobes of the inner and outer gerotors. See A of Figure 3-
9.
Continued rotation moves the pocket of oil to the outlet side
of the pump. In this area, the cavity decreases in volume as
the gerotor teeth mesh causing the oil to be squeezed out the
discharge port. As the cavity on the outlet side is emptied, a
second seal formed by the tips and lobes of the inner and
outer gerotors prevents oil on the outlet side (high pressure)
from being transferred to the inlet side (low pressure). See B
of Figure 3-9.
In operation, the gerotors provide a continuous flow of oil.
See C of Figure 3-9.
Breather Operation
NOTE
The crankcase breather system relieves crankcase pressure
produced by the downstroke of the pistons and allows crankcase vapors vacated from each cylinder to be directed into
the air filter element. Through effective recirculation of crankcase vapors, the system serves to eliminate the pollutants
normally discharged from the crankcase.
As each piston pushes downward on its power and intake
stroke, displaced air in the flywheel compartment is vented
through the crankshaft bearing into the cam compartment
and then up the push rod covers into the rocker housing.
Air rushes under the rocker arm support plate, which is elevated slightly, and passes through an opening at the bottom
of the plate to enter the breather baffle compartment.
In the baffle compartment, the flow of air passes upward
through the oil filter gauze, where the oil is removed from the
air. Two pin holes in the rocker arm support plate act as drain
holes to rid the baffle compartment of the oil separated from
the air.
Passing through the oil filter gauze, the flow of air passes
through the umbrella valve into the breather compartment.
The flaps of the umbrella valve only allow air to be vented
one way, rising to allow the passage of air, but then falling
back into place to seal the vent holes as the flow of air stops.
In the breather compartment, the flow of air reverses direction passing downward through holes aligned in the breather
baffle, rocker arm support plate and rocker housing. Exiting
the rocker housing, the air enters a passageway cast into the
top of the cylinder head. Proper orientation of the rocker
housing gasket is critical for effective sealing of this passageway.
Figure 3-9. Gerotor Operation
Flowing through the cylinder head passageway, the air
passes through a drilling in the air cleaner backplate bolt and
then through a breather tube into the air filter element.
NOTE
Air cleaner mounting without installation of the breather
tubes allows crankcase vapors to be vented into the atmosphere in violation of legal emissions standards.
2004 Touring: Engine 3-13
Page 14

HOM
E
HOW TO USE THIS SECTION 3.4
GENERAL
Three basic levels of service are presented in this section:
top end overhaul, bottom end overhaul and subassembly service and repair. The manner in which these instructions are
used depends upon the level of disassembly required.
Top End Overhaul
If servicing only cylinder head components, pistons, cylinders
and/or upper rod bushings, see Section 3.5 STRIPPING
MOTORCYCLE FOR SERVICE, and then proceed to Section
3.9 TOP END OVERHAUL, DISASSEMBLY. During top end
disassembly, the engine may be left in the chassis for service.
NOTE
If the engine is to be removed from the chassis, see Section
3.7 REMOVING ENGINE FROM CHASSIS in lieu of Section
3.5 STRIPPING MOTORCYCLE FOR SERVICE.
In the top end disassembly instructions, references are made
to Section 3.11 SUBASSEMBLY SERVICE AND REPAIR for
service of all top end subassemblies.
To rebuild the engine after a top end overhaul is complete,
perform the steps under Section 3.9 TOP END OVERHAUL,
ASSEMBLY, immediately following the disassembly instruc-
tions. Then, refer to Section 3.6 ASSEMBLING MOTORCY-
CLE AFTER STRIPPING to complete the project.
NOTE
For clarity, all artwork in this section shows the engine
removed from the chassis for service.
Bottom End Overhaul
Bottom end service may require either partial or complete
disassembly of the engine. Servicing components in the cam
compartment requires only partial disassembly, while servicing those in the flywheel compartment requires complete disassembly. An easy rule to remember is that any time the
crankcase halves must be split, complete disassembly needs
to occur. The cam compartment can be accessed through
removal of the cam cover making complete engine disassembly unnecessary.
During bottom end service that requires complete disassembly, the engine must be removed from the chassis and placed
in an engine stand. To begin, see Section 3.7 REMOVING
ENGINE FROM CHASSIS.
After the motorcycle has been stripped and the engine
removed, follow all of the steps under Section 3.9 TOP END
OVERHAUL, DISASSEMBLY. When finished, continue with
disassembly of the bottom half by performing those steps
listed under Section 3.10 BOTTOM END OVERHAUL, DIS-
ASSEMBLY.
Engine in Chassis Engine Removed
Top End Overhaul,
Service and Repair-
Top End Overhaul,
Motorcycle After
Engine in Chassis Engine Removed
Compartment.
Motorcycle for
Top End Overhaul,
Service and Repair-
Top End Overhaul,
Motorcycle After
TOP END SERVICE
Stripping
Motorcycle for
Service.
Disassembly.
Subassembly
To p End.
Assembly.
Assembling
Stripping.
BOTTOM END SERVICE
Cam
Stripping
Service.
Disassembly,
Steps 1-11.
Bottom End
Overhaul,
Disassembly,
Steps 1-14.
Subassembly
Bottom End.
Bottom End
Overhaul,
Assembly,
Steps 6-25.
Assembly,
Steps 29-39.
Assembling
Stripping.
Flywheel Compartment
Removing Engine
From Chassis.
Top End Overhaul,
Disassembly.
Subassembly
Service and Repair-
To p End.
Top End Overhaul,
Assembly.
Installing Engine
In Chassis.
or Complete Engine
Overhaul.
Removing Engine
From Chassis.
To p End Overhaul,
Disassembly.
Bottom End
Overhaul,
Disassembly.
Subassembly
Service and Repair-
To p End.
Subassembly
Service and Repair-
Bottom End.
Bottom End
Overhaul,
Assembly.
To p End Overhaul,
Assembly.
Installing Engine
In Chassis.
3-14 2004 Touring: Engine
Figure 3-10. Top/Bottom End Service
Page 15

HOM
E
As with the top end disassembly instructions, references are
made to Section 3.11 SUBASSEMBLY SERVICE AND
REPAIR for service of bottom end subassemblies.
Since it is standard practice to inspect and clean all oil passages when the engine is completely disassembled, a
detailed explanation of the engine oil circuit is presented
under Section 3.3 GENERAL INFORMATION, ENGINE OIL
FLOW.
To rebuild the engine after a bottom end overhaul is complete, perform the steps under Section 3.10 BOTTOM END
OVERHAUL, ASSEMBLY, and then proceed to Section 3.9
TOP END OVERHAUL, ASSEMBLY, to rebuild the upper
end.
Once the engine is assembled, refer to Section 3.8 INSTALL-
ING ENGINE IN CHASSIS to complete the project.
The flow charts on the preceding page show how the same
subsections are used for various levels of service.
Subassembly Service and Repair
Finally, if the task entails servicing of only one particular subassembly, then move directly to Section 3.11 SUBASSEM-
BLY SERVICE AND REPAIR for all service instructions.
For example, if just installing new cams, then refer to Section
3.11 SUBASSEMBLY SERVICE AND REPAIR, CAM SUPPORT PLATE.
The steps under Section 3.9 TOP END OVERHAUL and Sec-
tion 3.10 BOTTOM END OVERHAUL that need to be fol-
lowed for the removal and installation of the cam support
plate are given.
Furthermore, detailed instructions for disassembling, cleaning, inspecting, replacing and assembling cam support plate
components are provided.
2004 Touring: Engine 3-15
Page 16

HOM
E
STRIPPING MOTORCYCLE FOR SERVICE 3.5
PROCEDURE
NOTE
If performing top end service (or both cam compartment and
top end), follow steps 1-21. If servicing cam compartment
components only, perform steps 1-12.
1. Drain and remove fuel tank. Proceed as follows:
Carbureted:
RETED), COMPLETE REMOVAL, FLHT/C, or FLHR/S.
Fuel Injected:
INJECTED), COMPLETE REMOVAL, FLHT/C/U/I,
FLTRI, or FLHR/C/S/I.
2. Remove left side saddlebag. See Section 2.25 SAD-
DLEBAG, REMOVAL.
3. Gently pull left side cover from frame downtubes (no
tools required).
4. On Ultra models, hold locknut at bottom of left fairing
lower, and using a T40 TORX drive head, turn inside
screw to free assembly from engine guard clamp. Discard rubber washer.
5. Repeat steps 2-4 to remove saddlebag, side cover and
fairing lower on right side of vehicle.
6. Remove the air cleaner and backplate. See Section 4.5
AIR CLEANER, REMOVAL.
7. Remove two allen head socket screws (with lockwashers
and flat washers) to release right side front footboard
brackets from frame weldment. For best results,
approach from left side of vehicle using a 3/8 inch ball
allen with extension.
8. Remove exhaust system in two sections as follows:
a. Open two worm drive clamps to release heat shield
over rear header pipe to crossover pipe connection
(above starter).
b. Loosen TORCA clamp between rear header pipe
and crossover pipe. Remove Keps nut and pull
bracket tab and stud from slots in TORCA clamp
and exhaust support bracket.
c. Spray PB Blaster or other suitable penetrating oil in
and around joint between rear header pipe and
crossover pipe.
d. Moving to left side of vehicle, remove two bolts (with
lockwashers) to detach left side muffler from the
lower saddlebag support rail.
See Section 4.7 FUEL TANK (CARBU-
See Section 9.4 FUEL TANK (FUEL
e. Pull and twist on crossover pipe to remove left side
exhaust from vehicle. For best results, be sure to
allow sufficient time for the penetrating oil to work.
f. Remove TORCA clamp assembly from crossover
pipe and discard.
NOTE
To ensure sealing integrity of TORCA clamps and prevent the
possibility of leakage, Harley-Davidson recommends that
TORCA assemblies be discarded and replaced each time
they are removed.
g. Moving to right side of vehicle, open two worm drive
clamps and release heat shield from front header
pipe. Using an impact wrench with long 1/2 inch
swivel socket, remove two exhaust flange nuts to
release front header pipe from studs of front cylinder head. Slide exhaust flange down header pipe to
improve clearance around exhaust port.
h. Open two worm drive clamps and release heat
shield from rear header pipe. Remove two exhaust
flange nuts to release rear header pipe from studs
of rear cylinder head.
i. Open two worm drive clamps to release heat shield
over front header pipe to rear header pipe connection (outboard of transmission side door).
j. Remove bolt (with flat washer and locknut) from
transmission exhaust bracket clamp on front header
pipe. Use a channel lock to open clamp and then
remove from header pipe and transmission exhaust
bracket.
k. Remove two bolts (with lockwashers) to detach right
side muffler from the lower saddlebag support rail.
l. Depressing rear brake pedal, remove right side
exhaust from vehicle.
m. Remove and discard gaskets from front and rear
exhaust ports.
9. Moving to left side of vehicle, pull boots on spark plug
cables to release from spark plug and ignition coil towers. Release cables from three cable clips at bottom of
frame backbone.
10. Remove spark plugs.
11. Pull external latch outward and use rocking motion to
remove electrical connector from left side of ignition coil.
12. Pull sides of ignition coil bracket outward to remove from
bosses of front fuel tank mount.
13. Remove connections to carburetor or induction module.
Proceed as follows:
3-16 2004 Touring: Engine
Page 17

HOM
E
Carbureted:
a. Standing on left side of vehicle, remove electrical
connector from manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
sensor at top of intake manifold.
b. Locate the fuel enrichener knob under the left side
of the fuel tank, and loosen hex nut at backside of
mounting bracket. Slide cable assembly free of slot
in mounting bracket.
Fuel Injected:
a. Standing on right side of vehicle, remove idle air
control and manifold absolute pressure sensor connectors. Pull external latch(es) outward and use
rocking motion to separate pin and socket halves.
b. Depress wire form to remove electrical connectors
from front and rear fuel injectors.
c. Remove throttle position sensor and intake air tem-
perature sensor connectors.
d. Moving to left side of vehicle, pull back boot to
reveal engine temperature sensor at back of front
cylinder. Pull external latch outward and remove
connector. Cut cable strap to release conduit from
horn bracket.
e. Tuck free ends of EFI wire harness under main wire
harness on frame backbone to keep conduit and
connectors out of the way.
a. Remove right side allen head socket screws from
front and rear cylinder head flange adapters. For
best results, use a long 1/4 inch ball allen head
socket with end driver 4 inches long.
b. Moving to opposite side of vehicle, just loosen left
side allen head socket screws from flange adapters.
Slots in flanges make removal of left side screws
unnecessary.
c. Remove intake manifold/carburetor or induction
module from right side of vehicle.
18. Standing on left side of vehicle, remove two hex head
bolts (with flat washers) to release top engine mounting
bracket from cylinder heads.
19. Leaving ground wire ring terminal in place, detach
socket terminal of yellow lead from spade contact at
back of horn. Release wire conduit from J-clamp.
20. Moving to right side of vehicle, turn hex head bolt to
release stabilizer link from frame weldment.
21. Remove horn, top engine mounting bracket and stabilizer link as an assembly.
14. Remove idle and throttle control cables as follows:
Carbureted:
idle cable barrel from upper inboard hole in throttle
wheel. Pull throttle cable barrel from remaining hole.
Release idle and throttle cables from guides in throttle
cable bracket.
Fuel Injected:
idle cable barrel from upper hole in throttle wheel. Pull
throttle cable barrel from lower hole. Using slots, release
idle and throttle cables from guides in throttle cable
bracket.
15. Free idle and throttle control cables from J-clamp fastened to right side of frame backbone. Move cables up
and out of the way.
16. If equipped with cruise control, remove E-clip from
sleeve at end of cruise cable housing. Using slot,
remove cable housing from cable guide in throttle cable
bracket. Push the plastic end fitting on the cruise cable
to the outboard side to release from wheel pin. Move
cable up and out of the way.
17. Remove intake manifold/carburetor or induction module.
Proceed as follows:
Using a needle nose pliers, carefully pull
Using a needle nose pliers, carefully pull
2004 Touring: Engine 3-17
Page 18

HOM
E
ASSEMBLING MOTORCYCLE AFTER STRIPPING 3.6
PROCEDURE
NOTE
If top end service was performed (or both cam compartment
and top end), follow steps 1-19. If only cam compartment
components were serviced, perform steps 8-18.
1. Install intake manifold/carburetor or induction module.
Proceed as follows:
a. With the counterbore facing outward, slide cylinder
head flange adapters onto outlet ports of intake
manifold/induction module. The flange adapters are
not interchangeable. Look next to the slotted bolt
hole for a stamp that indicates F(ront) and R(ear)
cylinder.
b. Place a
beveled side in against the counterbore.
c. Standing on right side of engine, slide intake mani-
fold/induction module toward installed position so
that open-ended slots on flange adapters begin to
engage allen head socket screws loosely installed
on left side.
d. Align fixed holes in flange adapters with those in
cylinder heads and start allen head socket screws.
For best results, use a long 1/4 inch ball allen head
socket with end driver 4 inches long.
e. Use the air cleaner backplate or INDUCTION SYS-
TEM ALIGNMENT BRACKET (P&A Part No.
40054-01) to properly locate carburetor/induction
module. Proceed as follows:
Backplate
plate to front and rear cylinder heads. Install three
T27 TORX screws to secure backplate to face of
carburetor/induction module.
Alignment bracket
into holes in face of carburetor/induction module,
install two breather bolts to fasten bracket to front
and rear cylinder heads.
f. Tighten allen head socket screw in fixed holes of
flange adapters until snug. Moving to left side of
engine, tighten screws in slotted holes to 96-144
lbs
g. Remove breather bolts and T27 TORX screws to
remove backplate, if installed.
h. Tighten allen head socket screws in fixed holes of
flange adapters to 96-144
i. Remove breather bolts to remove alignment
bracket, if installed.
new
seal in each flange adapter with the
: Install two breather bolts to fasten back-
: Fitting pins on inboard side
(10.9-16.3 Nm).
in-lbs
(10.9-16.3 Nm).
in-
2. Install horn, top engine mounting bracket and stabilizer
link as an assembly. Proceed as follows:
a. Moving to right side of vehicle, turn hex head bolt to
secure stabilizer link to frame weldment. Tighten
bolt to 18-22 ft-lbs (24-30 Nm).
b. Attach socket terminal of yellow lead to spade con-
tact at back of horn. Capture wire conduit in Jclamp.
c. Standing on left side of vehicle, install two hex head
bolts (with flat washers) to secure top engine
mounting bracket to front and rear cylinder heads.
Alternately tighten bolts to 35-40 ft-lbs (48-54 Nm).
3. If equipped with cruise control, slide groove in cruise
cable end fitting over cap of wheel pin. Push on end fitting until it snaps in place. Using slot, slip cruise cable
housing into cable guide in throttle cable bracket. Install
new
E-clip on sleeve at end of cruise cable housing.
4. Route idle and throttle control cables through J-clamp
fastened to right side of frame backbone.
5. Install idle and throttle control cables as follows:
Carbureted:
shorter cable guide in throttle cable bracket. Drawing
throttle cable downward, fit barrel end into lower outboard hole in throttle wheel. Install sleeve and spring on
idle cable housing into longer cable guide inserting barrel end into upper inboard hole in throttle wheel.
Induction Module:
ing into shorter cable guide at top of throttle cable
bracket. Drawing throttle cable downward, fit barrel end
into lower hole in throttle wheel. Install sleeve and spring
on idle cable housing into longer cable guide at bottom
of throttle cable bracket inserting barrel end into upper
hole in throttle wheel.
6. Adjust cables as necessary to keep barrel ends from dislodging. Verify that cables are seated in channel of throttle wheel. Verify operation by turning throttle grip and
observing cable action.
7. Install connections to carburetor or induction module.
Standing on left side of vehicle, proceed as follows:
Install sleeve on throttle cable housing into
Install sleeve on throttle cable hous-
Carbureted:
a. Moving to left side of vehicle, install electrical con-
nector to manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
at top of intake manifold.
b. Slide threaded portion of enrichener cable into slot
of mounting bracket. Flat on threads must face rear
of vehicle for script on enrichener knob to be right
side up. With the external tooth lockwasher and hex
nut positioned on the inboard side of the mounting
bracket, tighten hex nut to 20-35
Nm).
in-lbs
(2.3-4.0
3-18 2004 Touring: Engine
Page 19

HOM
CAUTION
E
Fuel Injected:
a. Install electrical connectors on fuel injectors.
b. Install manifold absolute pressure sensor and idle
air control connectors.
c. Install intake air temperature sensor and throttle
position sensor connectors.
d. Moving to left side of vehicle, install connector to
engine temperature sensor at back of front cylinder.
Pull boot over sensor to keep out dirt and debris.
Install
new
cable strap to secure connector conduit
to horn bracket.
8. Install exhaust system as follows:
a. Install
b. Place right side exhaust into position on vehicle and
c. Start two bolts (with lockwashers) to secure right
d. Start two exhaust flange nuts to secure rear header
e. Engaging transmission exhaust bracket, capture
To ensure sealing integrity of TORCA clamps and prevent the
possibility of leakage, Harley-Davidson recommends that
TORCA assemblies be discarded and replaced each time
they are removed.
f. Moving to left side of vehicle, slide
g. Twist and push left side exhaust onto crossover
h. Start two bolts (with lockwashers) to secure left side
i. Returning to left side of vehicle, position TORCA
Verify that the exhaust pipes do not contact the vehicle
frame or any mounted components. Contact will cancel
the effect of the rubber isolation mounts and transmit
vibration to the rider via the vehicle frame.
j. Tighten the exhaust system as follows:
new
gaskets in both the front and rear cylin-
der head exhaust ports (with the tapered side out).
start two exhaust flange nuts to secure front header
pipe to studs of front cylinder head.
side muffler to the lower saddlebag support rail.
pipe to studs of rear cylinder head.
front header pipe in transmission exhaust bracket
clamp. Use a channel lock to close clamp, if necessary. Finger tighten clamp bolt (with flat washer and
locknut).
NOTE
new
TORCA
clamp assembly onto crossover pipe.
pipe.
muffler to the lower saddlebag support rail.
clamp between rear header pipe and crossover
pipe. Fit bracket tab into slot of TORCA clamp
engaging stud in slot of exhaust support bracket.
Start Keps nut on stud.
CAUTION
Using a long 1/2 inch swivel socket, tighten the top
●
nut of the front cylinder head exhaust flange to 9-18
in-lbs
(1-2 Nm). Tighten the bottom nut to 100-120
in-lbs
(11.3-13.6 Nm). Final tighten the top nut to
100-120
●
Tighten the bottom nut of the rear cylinder head
exhaust flange to 9-18
top nut to 100-120
tighten the bottom nut to 100-120
in-lbs
(11.3-13.6 Nm).
in-lbs
(1-2 Nm). Tighten the
in-lbs
(11.3-13.6 Nm). Final
in-lbs
(11.3-13.6
Nm).
●
Tighten the transmission exhaust bracket clamp bolt
to 60-96
●
Tighten the two bolts (with lockwashers) to fasten
in-lbs
(6.8-10.8 Nm).
the right side muffler to the lower saddlebag support
rail.
Tighten the two bolts (with lockwashers) to fasten
●
the left side muffler to the lower saddlebag support
rail.
Verify that all exhaust pipes are in alignment and do
●
not contact the vehicle frame or mounted components.
Tighten the TORCA clamp between the rear header
●
pipe and crossover pipe to 45-60 ft-lbs (61-81 Nm).
●
Tighten Keps nut securing bracket tab to exhaust
support bracket.
Verify that the heat shields do not contact the vehicle
frame or any mounted components. Contact will cancel
the effect of the rubber isolation mounts and transmit
vibration to the rider via the vehicle frame.
NOTE
Position worm drive clamps so that screws are on the outboard side in the most accessible position.
k. Open worm drive clamps and install heat shields as
follows:
Over front header pipe (below exhaust port).
●
●
Over rear header pipe (below exhaust port).
Over front header pipe to rear header pipe connec-
●
tion (outboard of transmission side door).
Over rear header pipe to crossover pipe connection
●
(above starter).
l. Position each worm drive clamp so that screw is on
the outboard side in the most accessible position
and then tighten to 20-40
in-lbs
(2.3-4.5 Nm).
9. Insert two allen head socket screws (with lockwashers
and flat washers) through frame weldment into right side
front footboard brackets. For best results, approach from
left side of vehicle using a 3/8 inch ball allen with extension.
10. Install the backplate and air cleaner. See Section 4.5
AIR CLEANER, INSTALLATION.
2004 Touring: Engine 3-19
Page 20

HOM
E
11. On Ultra models, place fairing lower into position on right
side of vehicle. Holding T40 TORX screw inside fairing
lower, install
attach fairing bottom to engine guard. Do not tighten
locknut.
12. Align barbed studs in right side cover with grommets in
frame downtubes and push firmly into place (no tools
required).
13. Install right side saddlebag. See Section 2.25 SADDLE-
BAG, INSTALLATION.
14. Repeat steps 11-13 to install side cover, saddlebag and
fairing lower on left side of vehicle.
15. Install spark plugs in front and rear cylinder heads.
Install the plugs finger tight and then tighten to 12-18 ftlbs (16-24 Nm).
16. Install ignition coil and spark plug cables as follows:
a. With the coil towers facing rear of vehicle, hold igni-
tion coil and bracket at bottom of frame backbone.
Pull sides of bracket outward and install on bosses
of front fuel tank mount. See Figure 3-11.
b. Install electrical connector on left side of ignition
coil.
c. Install spark plug cable to front cylinder onto left
side coil tower. Verify that spark plug cable is captured in double-sided cable clip at bottom left side of
frame backbone. Install
damaged or missing.
d. Install spark plug cable to rear cylinder onto right
side coil tower. Verify that spark plug cable is captured in two single-sided cable clips at bottom left
side of frame backbone. Install
studs if damaged or missing.
new
rubber washer, clamp and locknut to
new
cable clip on T-stud if
new
cable clips on T-
17. Install the fuel tank. Proceed as follows:
Carbureted:
RETED), INSTALLATION (AFTER COMPLETE
REMOVAL), FLHT/C, or FLHR/S.
Fuel Injected:
INJECTED), INSTALLATION (AFTER COMPLETE
REMOVAL), FLHT/C/U/I, FLTRI, or FLHR/C/S/I.
18. On Ultra models, hold locknut at bottom of fairing lower,
and using a T40 TORX drive head, turn inside screw to
fasten assembly to engine guard clamp. Tighten screw
to 90-100
site side of vehicle.
19. Adjust idle and throttle control cables as follows:
Non-Cruise:
(NON-CRUISE), ADJUSTMENT.
Cruise Equipped:
TROL (FLHRC, FLTR, FLHTCU), CABLE ADJUSTMENT.
See Section 4.7 FUEL TANK (CARBU-
See Section 9.4 FUEL TANK (FUEL
in-lbs
(10.2-11.3 Nm). Repeat step on oppo-
See Section 2.21 THROTTLE CABLES
See Section 8.30 CRUISE CON-
3-20 2004 Touring: Engine
Page 21

HOM
E
REMOVING ENGINE FROM CHASSIS 3.7
PROCEDURE
1. Drain and remove fuel tank. Proceed as follows:
Carbureted:
RETED), COMPLETE REMOVAL, FLHT/C, or FLHR/S.
Fuel Injected:
INJECTED), COMPLETE REMOVAL, FLHT/C/U/I,
FLTRI, or FLHR/C/S/I.
2. Remove the primary chaincase. See Section 6.5 PRI-
MARY CHAINCASE, REMOVAL, steps 2-18.
3. Remove left side saddlebag. See Section 2.25 SAD-
DLEBAG, REMOVAL.
4. Gently pull left side cover from frame downtubes (no
tools required).
5. On Ultra models, hold locknut at bottom of left fairing
lower, and using a T40 TORX drive head, turn inside
screw to free assembly from engine guard clamp. Discard rubber washer.
6. Repeat steps 3-5 to remove saddlebag, side cover and
fairing lower on right side of vehicle.
7. Remove the air cleaner and backplate. See Section 4.5
AIR CLEANER, REMOVAL.
8. Remove two allen head socket screws (with lockwashers
and flat washers) to release right side front footboard
brackets from frame weldment. For best results,
approach from left side of vehicle using a 3/8 inch ball
allen with extension.
9. Remove exhaust system in two sections as follows:
a. Open two worm drive clamps to release heat shield
over rear header pipe to crossover pipe connection
(above starter).
b. Loosen TORCA clamp between rear header pipe
and crossover pipe. Remove Keps nut and pull
bracket tab and stud from slots in TORCA clamp
and exhaust support bracket.
c. Spray PB Blaster or other suitable penetrating oil in
and around joint between rear header pipe and
crossover pipe.
d. Moving to left side of vehicle, remove two bolts (with
lockwashers) to detach left side muffler from the
lower saddlebag support rail.
e. Pull and twist on crossover pipe to remove left side
exhaust from vehicle. For best results, be sure to
allow sufficient time for the penetrating oil to work.
f. Remove TORCA clamp assembly from crossover
pipe and discard.
See Section 4.7 FUEL TANK (CARBU-
See Section 9.4 FUEL TANK (FUEL
NOTE
To ensure sealing integrity of TORCA clamps and prevent the
possibility of leakage, Harley-Davidson recommends that
TORCA assemblies be discarded and replaced each time
they are removed.
g. Moving to right side of vehicle, open two worm drive
clamps and release heat shield from front header
pipe. Using an impact wrench with long 1/2 inch
swivel socket, remove two exhaust flange nuts to
release front header pipe from studs of front cylinder head. Slide exhaust flange down header pipe to
improve clearance around exhaust port.
h. Open two worm drive clamps and release heat
shield from rear header pipe. Remove two exhaust
flange nuts to release rear header pipe from studs
of rear cylinder head.
i. Open two worm drive clamps to release heat shield
over front header pipe to rear header pipe connection (outboard of transmission side door).
j. Remove bolt (with flat washer and locknut) from
transmission exhaust bracket clamp on front header
pipe. Use a channel lock to open clamp and then
remove from header pipe and transmission exhaust
bracket.
k. Remove two bolts (with lockwashers) to detach right
side muffler from the lower saddlebag support rail.
l. Depressing rear brake pedal, remove right side
exhaust from vehicle.
m. Remove and discard gaskets from front and rear
exhaust ports.
10. Remove connections to carburetor or induction module.
Proceed as follows:
Carbureted:
a. Moving to left side of vehicle, pull external latch out-
ward and use rocking motion to remove electrical
connector from manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
sensor at top of intake manifold.
b. Locate the fuel enrichener knob under the left side
of the fuel tank, and loosen hex nut at backside of
mounting bracket. Slide cable assembly free of slot
in mounting bracket.
Fuel Injected:
a. Standing on right side of vehicle, remove idle air
control and manifold absolute pressure sensor connectors. Pull external latch(es) outward and use
rocking motion to separate pin and socket halves.
b. Depress wire form to remove electrical connectors
from front and rear fuel injectors.
2004 Touring: Engine 3-21
Page 22

HOM
E
8316
Figure 3-11. Remove Ignition Coil Bracket From Vehicle
c. Remove throttle position sensor and intake air tem-
perature sensor connectors.
d. Moving to left side of vehicle, pull back boot to
reveal engine temperature sensor at back of front
cylinder. Pull external latch outward and remove
connector. Cut cable strap to release conduit from
horn bracket.
e. Tu ck free ends of EFI wire harness under main wire
harness on frame backbone to keep conduit and
connectors out of the way.
11. Remove idle and throttle control cables as follows:
Carbureted:
Using a needle nose pliers, carefully pull
idle cable barrel from upper inboard hole in throttle
wheel. Pull throttle cable barrel from remaining hole.
Release idle and throttle cables from guides in throttle
cable bracket.
Fuel Injected:
Using a needle nose pliers, carefully pull
idle cable barrel from upper hole in throttle wheel. Pull
throttle cable barrel from lower hole. Using slots, release
idle and throttle cables from guides in throttle cable
bracket.
12. Free idle and throttle control cables from J-clamp fastened to right side of frame backbone. Move cables up
and out of the way.
13. If equipped with cruise control, remove E-clip from
sleeve at end of cruise cable housing. Using slot,
remove cable housing from cable guide in throttle cable
bracket. Push the plastic end fitting on the cruise cable
to the outboard side to release from wheel pin. Move
cable up and out of the way.
14. Moving to left side of vehicle, pull boots on spark plug
cables to release from spark plug and ignition coil towers. Release cables from three cable clips at bottom of
frame backbone.
15. Remove spark plugs.
16. Pull external latch outward and use rocking motion to
remove electrical connector from left side of ignition coil.
17. Pull sides of ignition coil bracket outward to remove from
bosses of front fuel tank mount. See Figure 3-11.
18. Moving to right side of vehicle, remove two allen head
socket screws to release oil hose cover.
19. Using a side cutters, cut and remove clamps on engine
side of oil hoses. Pull hoses from crankcase fittings.
20. Cut and remove clamp on breather hose behind rear
lifter cover. Pull hose from crankcase fitting and tuck
behind transmisson to engine flange to keep out of the
way.
21. Remove the voltage regulator. See Section 8.9 VOLT-
AGE REGULATOR, REMOVAL.
22. To release stator cable conduit, remove P-clip from left
side stud on lower frame crossmember. Remove P-clip
from cable conduit. Draw stator connector and cable
conduit to rear of engine stabilizer link and then up to
area in front of primary chaincase.
23. Depress tangs inside socket housing and back out sockets through wire end of connector. Proceed as follows:
a. Looking into the socket housing, take note of the
cavity on each side of the terminal.
b. Gently insert pick (Snap-On TT600-3) into the cavity
about 1/4 inch (6.4 mm) or until it stops, and pivot
the side of the pick toward the terminal body.
Repeat step on other cavity. See Figure 3-12.
c. Gently tug on cable to pull terminal from chamber. If
terminal is still locked, one or both tangs are not
fully depressed. Repeat steps 24(b) and 24(c) as
necessary.
d. Repeat procedure to release second terminal.
f1911x8x
Pick
Figure 3-12. Remove Socket Terminals
From Stator/Voltage Regulator Connector
3-22 2004 Touring: Engine
Page 23

HOM
1CAUTION
E
24. Remove conduit from stator cables. For best results, pull
one cable and socket terminal through conduit at a time.
Ta pe cables to crankcase so that they are out of the way
and will not be pinched or cut during engine removal.
25. Remove crankshaft position sensor and oil pressure
switch/sender as follows:
a. Locate crankshaft position sensor connector [79], 2-
place Mini-Deutsch, next to oil filter mount. Depress
button on socket terminal side and pull apart pin
and socket halves.
b. Remove allen head socket screw to free crank posi-
tion sensor mount from crankcase. Pull sensor from
bore. Remove O-ring from groove on sensor body.
Discard O-ring.
Figure 3-13. Engine/Transmission Bench Stand
(Part No. HD-42310)
c. Locate the oil pressure switch/sender at the front
right side of the crankcase. On FLHR/C/S models,
pull elbow from post of oil pressure switch. On
FLHT/C/U and FLTR models, pull external latch outward and use rocking motion to remove Packard
connector from oil pressure sender.
d. On FLHR/C/S models, use a 15/16 inch Open End
Crow Foot (Snap-On FC30B) to remove oil pressure
switch from crankcase. On FLHT/C/U and FLTR
models, use 1-1/16 inch Open End Crow Foot
(Snap-On FC34A) to remove oil pressure sender.
26. Coil main harness conduit and allow to hang below
lower frame tube at front of vehicle. If harness is not
moved out of the way, it may be damaged during engine
removal.
27. Place jack under oil pan at rear of vehicle. Using a block
of wood to distribute pressure across the length of the
casting, raise the jack until firm contact is made with the
bottom of the oil pan.
28. Standing on left side of vehicle, remove two hex head
bolts (with flat washers) to release top engine mounting
bracket from cylinder heads.
29. Remove elbow terminals from spade contacts at back of
horn. Release wire harness conduit from J-clamp.
30. Moving to right side of vehicle, turn hex head bolt to
release stabilizer link from frame weldment.
35. Cover lower frame tubes (both left and right side) with
foam padding or bubble pack. Split loom conduit or a half
shell of PVC tubing will also produce good results. Protection is necessary to prevent nicks or paint damage to
left frame tube and chafing, cutting or kinking of the
brake line, wire cables and conduit at the top of the right
frame tube.
36. Cover rocker covers of front and rear cylinders with foam
padding or bubble pack.
The engine weighs approximately 165 pounds (74.8 kg).
Use a suitable lifting device, if necessary. Exercise caution to avoid personal injury.
37. Move engine forward far enough to clear two ring dowels
in lower flange of transmission housing. Raise engine
and remove from right side of vehicle. Exercise caution
to avoid contact with rear brake master cylinder reservoir
and brake line, wire cables and conduit at top of lower
frame tube.
38. Using the TWIN CAM 88 CRADLE (HD-42310-2), install
engine in BENCH STAND (HD-42310) or ROLLING
STAND (HD-43646A). See Figure 3-13.
39. Remove intake manifold/carburetor or induction module.
Proceed as follows:
31. Remove horn, top engine mounting bracket and stabilizer link as an assembly.
32. Remove four bolts (with flat washers) to free rear of
crankcase from transmission housing. Loosen and
remove bolts in a crosswise pattern.
33. Remove two bolts (with flat washers) to free front of
crankcase from front engine mounting bracket.
34. Wrap rear master cylinder reservoir with foam padding
or bubble pack.
a. Remove right side allen head socket screws from
front and rear cylinder head flange adapters. For
best results, use a long 1/4 inch ball allen head
socket with end driver 4 inches long.
b. Moving to opposite side of vehicle, just loosen left
side allen head socket screws from flange adapters.
Slots in flanges make removal of left side screws
unnecessary.
c. Remove intake manifold/carburetor or induction
module from right side of vehicle.
2004 Touring: Engine 3-23
Page 24

HOM
E
40. Remove the rotor as follows:
1CAUTION
The high-output rotor is used on fuel injected vehicles,
FLHR/C/S/I excepted. Since the high-output rotor contains magnets that are considerably more powerful than
those used on low-output rotors, the ROTOR REMOVER/
INSTALLER and SHAFT PROTECTOR SLEEVE (HD-
41771) must be used to prevent parts damage and possible hand injury during removal and installation.
High Output Rotor - 45 Amp
a. Verify that threads of engine sprocket shaft are
clean, especially of old Loctite material. Thread the
Shaft Protector Sleeve onto the shaft.
b. Tu rn thumbscrews of Rotor Remover/Installer into
threaded holes in rotor face.
c. Rotate handle of forcing screw in a clockwise direc-
tion to remove rotor from shaft.
Low Output Rotor - 38 Amp
CAUTION
Do not strike or drop rotor. Damage to magnet adhesive
may result in rotor failure.
a. Fabricate wire hooks or use the ends of two allen
wrenches to carefully pull rotor at holes in rotor
face.
b. Pull rotor from stator. Magnets in rotor cause some
resistance during removal.
41. Remove stator as follows:
a. Using a T27 TORX drive head, remove four screws
to free stator from crankcase. Discard screws.
b. Using point of awl, carefully lift capped rib on grom-
met away from crankcase and then insert into bore
between grommet and casting. See Figure 3-14. Tilt
awl slightly squirting isopropyl alcohol or glass
cleaner into opening. Repeat this step at one or two
other locations around grommet.
c. While pushing on capped rib from outside of crank-
case, draw grommet through bore by pulling on
cable stop with needle nose pliers. Rock grommet
back and forth to facilitate removal, if necessary.
Exercise caution to avoid damaging ribs on grommet if stator is to be reused.
42. Remove the oil filter as follows:
a. Obtain the OIL FILTER WRENCH (HD-42311). The
tool allows easy removal of the oil filter without risk
of damage to the crankshaft position sensor or
cable.
b. Place the jaws of the wrench over the oil filter with
the tool oriented vertically.
Capped
Rib
Awl
Stator
Opening
f1634x8x
Figure 3-14. Remove Grommet From Crankcase
c. Using a 3/8 inch drive with a 4 inch extension, turn
wrench in a counterclockwise direction until loose.
Do not use with air tools.
NOTE
Use OIL FILTER WRENCH (HD-44067) if HD-42311 is not
available.
43. Remove oil filter mount as follows:
a. Carefully bend corners on lockplate away from
heads of top and bottom bolts in oil filter mount.
Remove top and bottom bolts, lockplate and flat
washers. Discard lockplate.
b. Remove middle bolt with flat washer to free filter
mount from crankcase.
c. Remove two O-rings from inboard side of filter
mount. Discard O-rings.
NOTES
Remove and clean the oil pan under any of the following conditions:
● Metal debris is found in the engine or crankcase.
● Oil contamination is suspected.
● A complete engine overhaul is being performed as a
result of a major engine failure.
● The engine is being replaced with a new one.
44. To remove the oil pan, proceed as follows:
3-24 2004 Touring: Engine
Page 25

HOM
E
RIGHT SIDE LEFT SIDE
f2025x3x
Strap
Strap
Frame
Backbone
Mainshaft
Hook
Rubber Coated
Transmission
Bracket
f1791x2x
Hook
Rubber Coated
Figure 3-15. Secure Transmission Using Transmission Exhaust Bracket and Mainshaft
a. Use a tie down strap to hold the transmission. Lay
strap over frame backbone placing one rubber
coated hook through the transmission exhaust
bracket on the right side of the vehicle and the other
around the mainshaft on the left. Using buckle,
tighten strap until taut. See Figure 3-15.
b. Lower and remove jack under oil pan.
c. Locate oil drain plug at front of the oil pan. See Fig-
ure 3-16. Remove the plug and allow oil to drain
completely.
d. Locate transmission drain plug on right side of the
oil pan. See Figure 3-16. Remove the plug and
drain the transmission lubricant into a suitable container.
e. Alternately loosen and then remove the twelve allen
head socket screws to release the oil pan from the
transmission housing. Follow the pattern shown in
Figure 3-16.
f. Remove gasket from oil pan and discard.
2004 Touring: Engine 3-25
Page 26

HOM
E
INSTALLING ENGINE IN CHASSIS 3.8
PROCEDURE
NOTE
If oil pan was drained and removed, start at step 1. If oil pan
was neither drained nor removed, move to step 13.
1. Coat gasket surface of oil pan with a thin coat of HYLOMAR® gasket sealer.
2. Place gasket on oil pan and allow sealer to dry until
tacky.
3. Position oil pan under transmission housing and start the
twelve allen head socket screws. Tighten each screw
about two turns after initial thread engagement.
4. Inspect the oil pan gasket to verify that it is properly positioned.
5. Alternately tighten the oil pan screws to 84-108 in-lbs
(9-12 Nm) following the pattern shown in Figure 3-16.
6. Remove any foreign material from magnet of oil drain
plug. Also check the O-ring for tears, cuts or general
deterioration. Replace as necessary.
7. Install the engine oil drain plug in front of the oil pan.
Tighten plug to 14-21 ft-lbs (19-28 Nm).
8. Remove the transmission filler plug from the clutch
release cover on the right side of the transmission case.
Check the O-ring for tears, cuts or general deterioration.
Replace as necessary.
9. Remove any foreign material from magnet of transmission drain plug. Also check the O-ring for tears, cuts or
general deterioration. Replace as necessary.
10. Install the transmission lubricant drain plug in right side
of the oil pan and tighten to 14-21 ft-lbs (19-28 Nm).
1WARNING1WARNING
When draining or adding lubricant, do not allow dirt,
debris or other contaminants to enter the transmission
case. Exercise caution so that lubricant does not contact
rear wheel, tire and brake components. Such contact
can adversely affect traction and may lead to loss of
vehicle control, which could result in death or serious
injury.
11. Fill the transmission with 20-24 oz. (590-710 ml) of
transmission lubricant or until the lubricant level on the
dipstick of the filler plug is at the F(ULL) mark with the
motorcycle in a level, upright position and the filler plug
resting on the threads.
Use only Harley-Davidson TRANSMISSION LUBRICANT: Part No.’s 99892-84 (quart), 98853-96 (case of
quarts), 99891-84 (gallon), or 98852-96 (case of gallons).
7
5
RIGHT
SIDE
11
1
Transmission
Drain Plug
9
3
2
4
10
LEFT
SIDE
6
12
Engine Oil
Drain Plug
f1677x3x
8
Figure 3-16. Oil Pan Torque Sequence
12. Install the transmission filler plug/dipstick in the clutch
release cover. Tighten the plug to 25-75 in-lbs (2.8-8.5
Nm).
13. Place jack under oil pan at rear of vehicle. Using a block
of wood to distribute pressure across the length of the
casting, raise the jack until firm contact is made with the
bottom of the oil pan.
14. Remove strap from frame backbone disengaging hooks
from mainshaft and transmission exhaust bracket.
15. Install spark plugs in front and rear cylinder heads.
Install the plugs finger tight and then tighten to 12-18 ftlbs (16-24 Nm).
16. Install oil filter mount as follows:
a. Install two new O-rings on inboard side of filter
mount.
b. Place flat washers in recessed bolt holes at top and
bottom of filter mount flange.
c. Align holes in lockplate with holes in flat washers.
d. Slide two hex head bolts through lockplate, flat
washers and filter mount flange. Apply Loctite
Medium Strength Threadlocker 243 (blue) to
threads of installed bolts.
CAUTION
To avoid cross threading tapped holes, exercise care
when starting hex head bolts in crankcase.
e. Align holes in filter mount flange with holes in crank-
case and tighten bolts until snug.
3-26 2004 Touring: Engine
Page 27

HOM
1CAUTION
1CAUTION
E
f. Install flat washer on remaining bolt, apply Loctite
Medium Strength Threadlocker 243 (blue) to
threads, and install in middle hole of filter mount
flange.
g. Starting at the top, alternately tighten three hex
head bolts to 12-16 ft-lbs (16-22 Nm). Re-tighten
middle bolt when done.
h. To prevent rotation, carefully bend outside corners
of lockplate against heads of top and bottom bolts.
17. Clean oil filter mount flange of any old gasket material.
Lubricate gasket of new oil filter with clean engine oil
and install on filter mount. Hand tighten oil filter 1/2-3/4
turn after gasket first contacts filter mounting surface. Do
NOT use OIL FILTER WRENCH for oil filter installation.
NOTE
Use of the Premium 10 micron synthetic media oil filter is
highly recommended, Part No. 63798-99 (Chrome) or 6373199 (Black).
18. Install stator as follows:
a. From inside crankcase, feed socket terminals and
stator cable through hole in crankcase.
b. Thoroughly lubricate grommet with isopropyl alco-
hol or glass cleaner. To avoid leakage, ribs of grommet must be free of dirt and oily residue.
c. Carefully grasp cable stop behind grommet with a
needle nose pliers. Push grommet into crankcase
bore while carefully pulling on outside cable. Installation is complete when cable stop contacts casting
and capped rib of grommet exits crankcase bore.
The high-output rotor is used on fuel injected vehicles,
FLHR/C/S/I excepted. Since the high-output rotor con-
tains magnets that are considerably more powerful than
those used on low-output rotors, the ROTOR REMOVER/
INSTALLER and SHAFT PROTECTOR SLEEVE (HD-
41771) must be used to prevent parts damage and possi-
ble hand injury during removal and installation.
High Output Rotor - 45 Amp
a. Install the Shaft Protector Sleeve and Rotor
Remover/Installer, if removed.
NOTE
The Shaft Protector Sleeve not only protects the threads from
the splines of the rotor, but acts as a guide to ensure that the
rotor is properly centered.
b. Center ball on forcing screw in recess at end of
engine sprocket shaft. Rotate the handle of the tool
in a counterclockwise direction to ease rotor into
position over stator.
c. Loosen thumbscrews and remove Rotor Remover/
Installer. Remove Shaft Protector Sleeve.
d. Install the shaft extension on the engine sprocket
shaft. (No alternator rotor spacer is provided.)
Low Output Rotor - 38 Amp
a. Slide rotor over stator with the concave side
inboard.
d. If necessary, carefully run awl around edge of
capped rib so that it rests flat against seating surface on crankcase.
CAUTION
Do not reuse T27 TORX screws. The threads of the
screws contain a locking compound in pellet form. When
the screw is started, the pellet breaks releasing the compound.
e. Using a T27 TORX drive head, install four new
screws to fasten stator to crankcase. Alternately
tighten screws to 55-75 in-lbs (6.2-8.5 Nm).
f. Coil stator connector cable lengths so that they are
out of the way and will not be pinched or cut during
engine installation.
19. Install the rotor as follows:
When installing rotor, keep fingers away from edge that
mates with crankcase. Since rotor is magnetized, as it
nears the crankcase it may be pulled in with consider-
able force, resulting in pinched fingers or other hand
injury.
b. Install the 0.020 inch (0.508 mm) thick alternator
rotor spacer and the shaft extension on the engine
sprocket shaft.
20. Install intake manifold/carburetor or induction module.
Proceed as follows:
a. With the counterbore facing outward, slide cylinder
head flange adapters onto outlet ports of intake
manifold/induction module. The flange adapters are
not interchangeable. Look next to the slotted bolt
hole for a stamp that indicates F(ront) and R(ear)
cylinder.
b. Place a new seal in each flange adapter with the
beveled side in against the counterbore.
2004 Touring: Engine 3-27
Page 28

HOM
E
f1684x3x
2
4
RIGHT
SIDE
3
1
Figure 3-17. Transmission Housing to Crankcase
Torque Sequence
c. Standing on right side of engine, slide intake mani-
fold/induction module toward installed position so
that open-ended slots on flange adapters begin to
engage allen head socket screws loosely installed
on left side.
d. Align fixed holes in flange adapters with those in
cylinder heads and start allen head socket screws.
For best results, use a long 1/4 inch ball allen head
socket with end driver 4 inches long.
e. Use the air cleaner backplate or INDUCTION SYS-
TEM ALIGNMENT BRACKET (P&A Part No.
40054-01) to properly locate carburetor/induction
module. Proceed as follows:
Backplate: Install two breather bolts to fasten backplate to front and rear cylinder heads. Install three
T27 TORX screws to secure backplate to face of
carburetor/induction module.
Alignment bracket: Fitting pins on inboard side
into holes in face of carburetor/induction module,
install two breather bolts to fasten bracket to front
and rear cylinder heads.
f. Tighten allen head socket screw in fixed holes of
flange adapters until snug. Moving to left side of
engine, tighten screws in slotted holes to 96-144 in-
lbs (10.9-16.3 Nm).
g. Remove breather bolts and T27 TORX screws to
remove backplate, if installed.
h. Tighten allen head socket screws in fixed holes of
flange adapters to 96-144 in-lbs (10.9-16.3 Nm).
i. Remove breather bolts to remove alignment
bracket, if installed.
21. Cover rocker covers of front and rear cylinders with foam
padding or bubble pack.
22. Cover lower frame tubes (both left and right side) with
foam padding or bubble pack. Split loom conduit or a half
shell of PVC tubing will also produce good results. Protection is necessary to prevent nicks or paint damage to
left frame tube and chafing, cutting or kinking of the
brake line, wire cables and conduit at the top of the right
frame tube.
23. Wrap rear master cylinder reservoir with foam padding
or bubble pack.
24. Remove engine from BENCH STAND (HD-42310) or
ROLLING STAND (HD-43646A) and set on floor on right
side of chassis.
1CAUTION
The engine weighs approximately 165 pounds (74.8 kg).
Use a suitable lifting device, if necessary. Exercise caution to avoid personal injury.
25. Raise engine and install in chassis from right side of
vehicle setting front of crankcase onto front engine
mounting bracket. Engine must be set forward far
enough to clear two ring dowels in lower flange of transmission housing. Exercise caution to avoid contact with
rear brake master cylinder reservoir and brake line, wire
cables and conduit at top of lower right frame tube.
26. Move engine rearward to fully engage two ring dowels in
lower flange of transmission housing.
27. Secure the engine as follows:
a. Hand tighten four bolts (with flat washers) to secure
transmission housing to rear of crankcase.
b. Hand tighten two bolts (with flat washers) to secure
front of crankcase to front engine mounting bracket.
c. Tighten the four transmission housing to crankcase
bolts to 15 ft-lbs (20.3 Nm) in the sequence shown
in Figure 3-17.
NOTE
For best results, use Open End Crowfoot (Snap-On FC018)
on upper left and upper right transmission housing to
crankcase bolts.
d. Following the same sequence, final tighten the four
transmission housing to crankcase bolts to 30-35 ftlbs (40.7-47.5 Nm).
e. Tighten the two crankcase to front engine mounting
bracket bolts to 33-38 ft-lbs (44.8-51.5 Nm).
28. Install horn, top engine mounting bracket and stabilizer
link as an assembly. Proceed as follows:
a. Moving to right side of vehicle, turn hex head bolt to
secure stabilizer link to frame weldment. Tighten
bolt to 18-22 ft-lbs (24-30 Nm).
3-28 2004 Touring: Engine
Page 29

HOM
E
X-Acto Knife
Tang
f1913x8x
Figure 3-18. Bend Tangs Outward on Socket Terminals
of Stator/Voltage Regulator Connector
b. Install elbow terminals onto spade contacts at back
of horn. Capture wire harness conduit in J-clamp.
c. Standing on left side of vehicle, install two hex head
bolts (with flat washers) to secure top engine
mounting bracket to front and rear cylinder heads.
Alternately tighten bolts to 35-40 ft-lbs (48-54 Nm).
29. Lower and remove jack under oil pan.
30. Install conduit onto stator cables. For best results, feed
one socket terminal and cable through conduit at a time.
31. Install sockets into stator connector as follows:
a. Using a fingernail or a thin flat blade, like that on an
X-Acto knife, carefully bend the tangs outward away
from each terminal body. See Figure 3-18.
b. Feed each socket into wire end of stator connector
until it “clicks” in place.
c. Verify that sockets will not back out of chambers. A
slight tug on each cable will confirm that it is locked.
32. Install P-clip on stator cable conduit approximately five
inches (127 mm) from socket housing. Slide P-clip over
left side stud on lower frame crossmember. Properly oriented, P-clip is positioned at front of stud with the open
side up and angled so that it is inline with the lower rail of
the engine guard.
33. Uncoil main harness conduit and allow to hang below
lower frame tube at front of vehicle.
34. Install oil pressure switch/sender and crankshaft position
sensor as follows:
a. Start oil pressure switch/sender into crankcase bore
at the front right side of the crankcase. On FLHR/C/
S models, use a 15/16 inch Open End Crow Foot
(Snap-On FC30B) to tighten oil pressure switch to
96-120 in-lbs (11-14 Nm). On FLHT/C/U and FLTR
models, use 1-1/16 inch Open End Crow Foot
(Snap-On FC34A) to tighten oil pressure sender to
same torque.
b. On FLHR/C/S models, install elbow on post of oil
pressure switch. On FLHT/C/U and FLTR models,
install Packard connector to oil pressure sender .
c. Install new O-ring in groove on crank position sen-
sor body. Apply a very thin film of clean H-D 20W50
engine oil to O-ring before installation.
d. Push sensor into bore aligning hole in sensor mount
with hole in spot face. Install allen head socket
screw (1/4 x 1 inch) and tighten to 90-120 in-lbs
(10.2-13.6 Nm).
e. Locate crankshaft position sensor connector [79], 2-
place Mini-Deutsch, next to oil filter mount. Mate pin
and socket halves of connector.
35. Install the voltage regulator. See Section 8.9 VOLTAGE
REGULATOR, INSTALLATION.
36. Slide new clamp onto free end of breather hose behind
rear lifter cover. Install hose onto crankcase fitting.
Crimp clamp using HOSE CLAMP PLIERS (HD-9708765B).
37. Slide new clamps onto free ends of oil hoses. Install
hoses onto crankcase fittings. Crimp clamps.
38. Install two allen head socket screws to secure oil hose
cover to transmission and engine housings. Longer
screw goes to engine housing. Alternately tighten
screws to 84-108 in-lbs (10-12 Nm).
39. Install ignition coil and spark plug cables as follows:
a. With the coil towers facing rear of vehicle, hold igni-
tion coil and bracket at bottom of frame backbone.
Pull sides of bracket outward and install on bosses
of front fuel tank mount. See Figure 3-11.
b. Install electrical connector on left side of ignition
coil.
c. Install spark plug cable to front cylinder onto left
side coil tower. Verify that spark plug cable is captured in double-sided cable clip at bottom left side of
frame backbone. Install new cable clip on T-stud if
damaged or missing.
d. Install spark plug cable to rear cylinder onto right
side coil tower. Verify that spark plug cable is captured in two single-sided cable clips at bottom left
side of frame backbone. Install new cable clips on Tstuds if damaged or missing.
40. If equipped with cruise control, slide groove in cruise
cable end fitting over cap of wheel pin. Push on end fitting until it snaps in place. Using slot, slip cruise cable
housing into cable guide in throttle cable bracket. Install
new E-clip on sleeve at end of cruise cable housing.
41. Route idle and throttle control cables through J-clamp
fastened to right side of frame backbone.
42. Install idle and throttle control cables as follows:
2004 Touring: Engine 3-29
Page 30

HOM
E
Carbureted: Install sleeve on throttle cable housing into
shorter cable guide in throttle cable bracket. Drawing
throttle cable downward, fit barrel end into lower outboard hole in throttle wheel. Install sleeve and spring on
idle cable housing into longer cable guide inserting barrel end into upper inboard hole in throttle wheel.
Induction Module: Install sleeve on throttle cable housing into shorter cable guide at top of throttle cable
bracket. Drawing throttle cable downward, fit barrel end
into lower hole in throttle wheel. Install sleeve and spring
on idle cable housing into longer cable guide at bottom
of throttle cable bracket inserting barrel end into upper
hole in throttle wheel.
43. Tighten cables as necessary to keep barrel ends from
dislodging. Verify that cables are seated in channel of
throttle wheel. Verify operation by turning throttle grip
and observing cable action.
44. Install connections to carburetor or induction module.
Standing on left side of vehicle, proceed as follows:
Carbureted:
a. Moving to left side of vehicle, install electrical con-
nector to manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
at top of intake manifold.
b. Slide threaded portion of enrichener cable into slot
of mounting bracket. Flat on threads must face rear
of vehicle for script on enrichener knob to be right
side up. With the external tooth lockwasher and hex
nut positioned on the inboard side of the mounting
bracket, tighten hex nut to 20-35 in-lbs (2.3-4.0
Nm).
Fuel Injected:
a. Install electrical connectors on fuel injectors.
b. Install manifold absolute pressure sensor and idle
air control connectors.
c. Install intake air temperature sensor and throttle
position sensor connectors.
d. Moving to left side of vehicle, install connector to
engine temperature sensor at back of front cylinder.
Pull boot over sensor to keep out dirt and debris.
Install new cable strap to secure connector conduit
to horn bracket.
45. Install the primary chaincase. See Section 6.5 PRI-
MARY CHAINCASE, INSTALLATION, steps 1-29.
46. Install exhaust system as follows:
a. Install new gaskets in both the front and rear cylin-
der head exhaust ports (with the tapered side out).
b. Place right side exhaust into position on vehicle and
start two exhaust flange nuts to secure front header
pipe to studs of front cylinder head.
c. Start two bolts (with lockwashers) to secure right
side muffler to the lower saddlebag support rail.
d. Start two exhaust flange nuts to secure rear header
pipe to studs of rear cylinder head.
e. Engaging transmission exhaust bracket, capture
front header pipe in transmission exhaust bracket
clamp. Use a channel lock to close clamp, if necessary. Finger tighten clamp bolt (with flat washer and
locknut).
NOTE
To ensure sealing integrity of TORCA clamps and prevent the
possibility of leakage, Harley-Davidson recommends that
TORCA assemblies be discarded and replaced each time
they are removed.
f. Moving to left side of vehicle, slide new TORCA
clamp assembly onto crossover pipe.
g. Twist and push left side exhaust onto crossover
pipe.
h. Start two bolts (with lockwashers) to secure left side
muffler to the lower saddlebag support rail.
i. Returning to left side of vehicle, position TORCA
clamp between rear header pipe and crossover
pipe. Fit bracket tab into slot of TORCA clamp
engaging stud in slot of exhaust support bracket.
Start Keps nut on stud.
CAUTION
Verify that the exhaust pipes do not contact the vehicle
frame or any mounted components. Contact will cancel
the effect of the rubber isolation mounts and transmit
vibration to the rider via the vehicle frame.
j. Tighten the exhaust system as follows:
● Using a long 1/2 inch swivel socket, tighten the top
nut of the front cylinder head exhaust flange to 9-18
in-lbs (1-2 Nm). Tighten the bottom nut to 100-120
in-lbs (11.3-13.6 Nm). Final tighten the top nut to
100-120 in-lbs (11.3-13.6 Nm).
● Tighten the bottom nut of the rear cylinder head
exhaust flange to 9-18 in-lbs (1-2 Nm). Tighten the
top nut to 100-120 in-lbs (11.3-13.6 Nm). Final
tighten the bottom nut to 100-120 in-lbs (11.3-13.6
Nm).
● Tighten the transmission exhaust bracket clamp bolt
to 60-96 in-lbs (6.8-10.8 Nm).
● Tighten the two bolts (with lockwashers) to fasten
right side muffler to lower saddlebag support rail.
● Tighten the two bolts (with lockwashers) to fasten
left side muffler to lower saddlebag support rail.
● Ver ify that all exhaust pipes are in alignment and do
not contact the vehicle frame or mounted components.
● Tighten the TORCA clamp between the rear header
pipe and crossover pipe to 45-60 ft-lbs (61-81 Nm).
● Tighten Keps nut securing bracket tab to exhaust
support bracket.
3-30 2004 Touring: Engine
Page 31

HOM
E
COLD CHECK
HOT CHECK
Figure 3-19. Engine Oil Dipstick
CAUTION
Verify that the heat shields do not contact the vehicle
frame or any mounted components. Contact will cancel
the effect of the rubber isolation mounts and transmit
vibration to the rider via the vehicle frame.
NOTE
Position worm drive clamps so that screws are on the outboard side in the most accessible position.
k. Open worm drive clamps and install heat shields as
follows:
● Over front header pipe (below exhaust port).
● Over rear header pipe (below exhaust port).
● Over front header pipe to rear header pipe connec-
tion (outboard of transmission side door).
● Over rear header pipe to crossover pipe connection
(above starter).
l. Position each worm drive clamp so that screw is on
the outboard side in the most accessible position
and then tighten to 20-40 in-lbs (2.3-4.5 Nm).
47. Insert two allen head socket screws (with lockwashers
and flat washers) through frame weldment into right side
front footboard brackets. For best results, approach from
left side of vehicle using a 3/8 inch ball allen with extension. Alternately tighten screws to 30-35 ft-lbs (41-48
Nm).
48. Install the backplate and air cleaner. See Section 4.5
AIR CLEANER, INSTALLATION.
49. On Ultra models, place fairing lower into position on right
side of vehicle. Holding T40 TORX screw inside fairing
lower, install new rubber washer, clamp and locknut to
attach fairing bottom to engine guard. Do not tighten
locknut.
50. Align barbed studs in right side cover with grommets in
frame downtubes and push firmly into place (no tools
required).
51. Install right side saddlebag. See Section 2.25 SADDLE-
BAG, INSTALLATION.
f1254b3x
52. Repeat steps 49-51 to install side cover, saddlebag and
fairing lower on left side of vehicle.
53. Install the fuel tank. Proceed as follows:
Carbureted: See Section 4.7 FUEL TANK (CARBU-
RETED), INSTALLATION (AFTER COMPLETE
REMOVAL), FLHT/C, or FLHR/S.
Fuel Injected: See Section 9.4 FUEL TANK (FUEL
INJECTED), INSTALLATION (AFTER COMPLETE
REMOVAL), FLHT/C/U/I, FLTRI, or FLHR/C/S/I.
54. On Ultra models, hold locknut at bottom of fairing lower,
and using a T40 TORX drive head, turn inside screw to
fasten assembly to engine guard clamp. Tighten screw
to 90-100 in-lbs (10.2-11.3 Nm). Repeat step on opposite side of vehicle.
55. Adjust idle and throttle control cables as follows:
Non-Cruise: See Section 2.21 THROTTLE CABLES
(NON-CRUISE), ADJUSTMENT.
Cruise Equipped: See Section 8.30 CRUISE CON-
TROL (FLHRC, FLTR, FLHTCU), CABLE ADJUSTMENT.
NOTE
If oil pan was not
drained, move to step 60.
56. With vehicle resting on jiffy stand, add 3-1/2 quarts (3.3
liters) engine oil as specified in Ta bl e 3-2. Use the proper
grade of oil for the lowest temperature expected before
the next oil change.
Table 3-2. Recommended Engine Oils
Harley-Davidson
Type
HD Multi-grade
HD Multi-grade
HD Regular Heavy
HD Extra Heavy
Viscosity
SAE
10W40
SAE
20W50
SAE
50
SAE
60
Harley-
Davidson
Rating
HD 360
HD 360
HD 360
HD 360
Lowest
Ambient
Temperature
Below 40˚F
(4˚C)
Above 40˚F
(4˚C)
Above 60˚F
(16˚C)
Above 80˚F
(27˚C)
Cold Weather
Starts Below
50˚F (10˚C)
Excellent
Good
Poor
Poor
2004 Touring: Engine 3-31
Page 32

HOM
E
CAUTION
Oil level cannot be accurately measured on a cold
engine. For preride inspection, with motorcycle leaning
on jiffy stand on level ground, oil should register on dipstick between arrows when engine is cold. Do NOT add
oil to bring the level to the FULL mark on a COLD
engine.
57. Perform engine oil level COLD CHECK as follows:
a. With the vehicle resting on the jiffy stand on level
ground, wipe off the dipstick and insert it back into
the oil pan with the plug pushed completely into the
fill spout.
b. Remove the dipstick and note the level of the oil. Oil
level should register between the two arrows on the
dipstick. See Figure 3-19. If oil level is at or below
the lower arrow, add only enough oil to bring the
level between the two arrows on the dipstick.
58. Perform engine oil level HOT CHECK as follows:
a. Ride vehicle until engine is at normal operating tem-
perature.
b. With the vehicle resting on the jiffy stand on level
ground, allow engine to idle for 1-2 minutes. Turn
engine off.
c. Wipe off the dipstick and insert it back into the oil
pan with the plug pushed completely into the fill
spout.
d. Remove the dipstick and note the level of the oil.
Add only enough oil to bring the level to the FULL
mark on the dipstick. See Figure 3-19. Do not overfill.
59. Start engine and carefully check for oil leaks around
drain plug and oil filter.
3-32 2004 Touring: Engine
 Loading...
Loading...