Page 1
Instruction Manual
HI 83226
Multiparameter Bench
Photometer
for Pool & Spa Applications
www.hannainst.com
1
Page 2
Dear Customer,
Thank you for choosing a Hanna product. Please read this instruction manual carefully before using the
instrument. This manual will provide you with the necessary information for the correct use of the
instrument. If you need additional technical information, do not hesitate to e-mail us at tech@hannainst.com.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION .............................................................................................................................................. 3
ABBREVIATIONS ................................................................................................................................................................ 3
GENERAL DESCRIPTION ...................................................................................................................................................... 3
SIGNIFICANCE OF POOL AND SPA TESTING .............................................................................................................................. 4
SPECIFICATIONS ............................................................................................................................................................... 8
PRECISION AND ACCURACY ................................................................................................................................................ 8
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION ................................................................................................................................................. 8
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION .............................................................................................................................................. 10
TIPS FOR AN ACCURATE MEASUREMENT .......................................................................................................................... 11
HEALTH & SAFETY ..........................................................................................................................................................14
METHOD REFERENCE TABLE ............................................................................................................................................. 14
OPERATIONAL GUIDE ....................................................................................................................................................... 15
SETUP ........................................................................................................................................................................... 17
HELP MODE ................................................................................................................................................................... 19
ALKALINITY .................................................................................................................................................................... 20
BROMINE ...................................................................................................................................................................... 22
CALCIUM HARDNESS ....................................................................................................................................................... 24
FREE CHLORINE ............................................................................................................................................................. 27
TOTAL CHLORINE ............................................................................................................................................................ 29
FREE COPPER ................................................................................................................................................................ 31
TOTAL COPPER ............................................................................................................................................................... 33
CYANURIC ACID .............................................................................................................................................................. 35
IRON ............................................................................................................................................................................. 37
OZONE .......................................................................................................................................................................... 39
pH ................................................................................................................................................................................ 42
ERRORS AND WARNINGS ................................................................................................................................................. 44
DATA MANAGEMENT ........................................................................................................................................................ 45
STANDARD METHODS ...................................................................................................................................................... 45
ACCESSORIES ................................................................................................................................................................ 46
WARRANTY .................................................................................................................................................................... 47
HANNA LITERATURE ........................................................................................................................................................ 47
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the written consent of the copyright owner, Hanna
Instruments Inc., Woonsocket, Rhode Island, 02895 , USA.
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION
Please examine this product carefully. Make sure that the instrument is not damaged. If any damage
occurred during shipment, please notify your local Hanna Office.
Each Meter is supplied complete with:
• Four Sample Cuvettes and Caps
• Cloth for wiping cuvettes (1 pcs)
• Scissors
• AC/DC Power Adapter
• Instruction Manual
Note: Save all packing material until you are sure that the instrument works correctly. Any defective item
must be returned in its original packing with the supplied accessories.
ABBREVIATIONS
EPA: US Environmental Protection Agency
°C: degree Celsius
°F: degree Fahrenheit
µg/L: micrograms per liter (ppb)
mg/L: milligrams per liter (ppm)
g/L: grams per liter (ppt)
mL: milliliter
HR: high range
MR: medium range
LR: low range
PAN: 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-naphtol
TPTZ: 2,4,6-tri-(2-pyridyl)-1,3,5-triazine
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
HI 83226 is a multiparameter bench photometer dedicated for Pool & SPA applications. It measures 11
different methods using specific liquid or powder reagents. The amount of reagent is precisely dosed to
ensure maximum reproducibility.
HI 83226 bench photometer can be connected to a PC via an USB cable. The optional HI 92000
Windows® Compatible Software helps users manage all their results.
HI 83226 has a powerful interactive user support that assists the user during the analysis process.
Each step in the measurement process is help supported. A tutorial mode is available in the Setup Menu.
2 3
Page 3

SIGNIFICANCE OF POOL AND SPA TESTING
A major family leisure pursuit is the enjoyment of Swimming Pool and Spa facilities world-wide. A basic necessity
of Pool water treatment, to ensure such enjoyment, is to maintain the water in a safe and pleasant condition
for the bathers.
In order to achieve such an objective, swimming pool water requires testing on daily, and sometimes hourly bases
for disinfection residuals and pH. Equally important, Calcium Hardness and Alkalinity parameters should be
monitored on weekly bases to ensure the pool water is maintained in a balanced condition, thus to avoid system
failure because of corrosion or scale formation.
DISINFECTION RESIDUAL AND pH CONTROL
In terms of swimming pool treatment, disinfection or sanitizing basically means to rid the pool of bather pollution,
destroy bacteria, and control nuisance organisms like algae, which may occur in the pool, filtration equipment,
and piping.
There are a number of techniques used, namely, chlorine, bromine and ozone dosing systems, of which chlorine
is the most common.
Chlorine
Chlorine is a strong oxidizing agent that destroys mostly organic pollutants, bacteria and can combine with
nitrogen containing compounds, forming chloramines. Only a part of the original quantity dosed chlorine,
remains active and continues its disinfecting action.
From the free chlorine you can distinguish combined chlorine, as that part which combines with nitrogen
containing compound and that is less efficient as a disinfectant. The addition of these two parts gives total
chlorine. A pool manager needs to aim perfection where free equals total chlorine, and thus to maintain the
combined chlorine concentration near zero. The presence of chloramines is not desired because of the distinctive
‘swimming pool’ smell caused by combined chlorines like di-chloramines. Beside this unpleasant odour it does
irritate the eyes and the mucous membranes.
Commercially chlorine for disinfection may be available as a gas (Cl2), a liquid like sodium hypochlorite or bleach
(NaOCl) or in a solid state like calcium hypochlorite, chloro-hydantoins or chloro-cyanuric acid compounds. These
compounds, once dissolved in water do establish equilibrium between the hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and the
hypochlorite ions
provides the strongest disinfecting and oxidising characteristic of chlorine solutions.
The amount of hypochlorous acid in chlorinated water dependends upon the pH value of the solution. Changes
in pH value will effect the HOCl equilibrium in relation to the hydrogen and hypochlorite ion.
As depicted by the curve on the next page, HOCl decreases and OCl¯ increases as pH increases. At a low pH,
almost all the free chlorine is in the molecular form HOCl and at a pH of around 7.5, the ratio between HOCl and
OCl¯ is 50:50. Since the ionic form OCl¯ is a slow acting sanitizer while the molecular HOCl is a fast acting, it
is important to measure regularly the pH. As a general rule a pH of about 7.2 is recommended to maintain fast
acting disinfection conditions.
(OCl¯). Although both forms are considered free chlorine, it is the hypochlorous acid that
Bromine
In many countries bromine sanitizing has been introduced as an alternative for chlorine, although it is a less
strong sanitizer. The advantage of bromine is its stability at higher temperatures (advantageous for hot well
pools), and its maintained disinfection power at higher pH. Further it does hardly react with nitrogen
compounds, reducing the unpleasant odour,and eye irritation problems. The main disadvantage of bromine is
the slower acting disinfecting power, making it less suitable for larger pools.
Ozone
Ozone is a very strong oxidizing agent that does destroy most difficult to oxidize organic compounds and
chloramines. It thus allows the pool manager to remove very efficiently combined chlorine without refreshing
frequently large amounts of pool water. In general its application is found just before water passes through the
filter units. Its sanitizing power is not pH related.
Mainly because of its strong oxidizing power the return water may contain only trace concentrations of ozone. It
has to be mentioned that ozone is very unstable and there is anyway the need for low-level chlorination to ensure
sanitizing throughout the whole pool.
THE WATER BALANCE AND LANGELIER INDEX (LI)
The pool water characteristics need to be maintained in a balanced condition to avoid system failure. Measuring
the water balance is extremely important to predict if the water is corrosive, scaling or balanced.
A saturation index developed by Dr. Wilfred Langelier is widely used to predict the balance of swimming pool
waters. It is an estimation of the solutions ability to dissolve or precipitate calcium carbonate deposits. A certain
level of this precipitation (filming) is desired to insulate pipes and boilers from contact with water. When no
protective filming is formed, water is considered to be corrosive. On the other hand scaling does cause failure
because of incrustation problems.
In the treatment and monitoring of pool water, the pool manager must ensure that related parameters as
alkalinity, hardness and pH are duly taken into consideration.
4 5
Page 4
Calcium Hardness
The presence of calcium in the system is desired to ensure filming on those places where the temperature is relatively
high, like in boilers and pipes transporting warm water. Scaling must be avoided because it reduces heat transfer
and pump capacity. Beside the calcium carbonate deposits in the pipes, high scaling values do cause cloudy water.
It is recommended to maintain the calcium hardness value within the range from 200 to 400 ppm as calcium
carbonate (CaCO3).
Alkalinity
Alkalinity is the measure of the total concentration of alkaline substances, mostly bicarbonates, dissolved in the
water. The higher the alkalinity the more resistant the water is to pH change, the alkalinity
At the same time, high alkaline water is a major contributor to scaling problems like incrustation in filtration
equipment, pumps, and piping.
It is recommended to maintain the alkalinity value within the range from 80 to 125 ppm as calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
pH
The pH of the water is an important factor since at lower pH the corrosion rate increases. If the alkalinity values
are sufficiently high it will not be difficult to control the pH. Most pools managers do prefer to keep the pH
between 7.2 and 7.4, that does ensure low corrosion rates and a sufficient activity of chlorine.
Langelier Index (LI)
The Langelier Index is a powerful tool to calculate the water balance, and to predict corrosion or scaling problems.
Theoretically, a LI of zero indicates perfect water condition for swimming pools. If LI>0, scaling and staining of the water
is present, and if LI<0 the water is corrosive and highly irritating. A tolerance of ±0.4 is normally acceptable.
The Langelier formula is expressed as:
LI = pH + TF + HF + AF – 12.5
where:
LI = Langelier Index (also called Saturation Index)
pH = pH of the water
TF = temperature factor
HF = hardness factor, log(Ca Hardness, ppm as CaCO3)
AF = alkalinity factor, log(Alkalinity, ppm as CaCO3)
To calculate the exact Langelier Index of your water please use the WATER INDEX reference tables at the end of
this chapter to find the Temperature, Hardness and Alkalinity factors.
Recommendations
For most pools, water is balanced if:
• The pH value is maintained within the recommended ranges of pH 7.2 - 7.6
• Ideally the Alkalinity should be maintained within a range of 80 - 125 ppm
• The Calcium Hardness should be maintained within a range of 200 - 400 ppm.
To calculate your water balance three tests are required, measure the Calcium Hardness, the Alkalinity and the
pH of the pool water. Find the
The water temperature is in general controlled between 24oC (76oF) and 34oC (94oF) to ensure pleasant bather comfort. The
Temperature Factor in this temperature range has minor importance; therefore an average value of 0.7 may be used
Hardness and Alkalinity Factor in the WATER INDEX reference tables below.
buffers
the water.
A simple calculation classifies your water in corrosive, scaling, acceptable or ideal balanced, with treatment recommendations:
Water Balance = pH + TF + HF + AF
Water Balance
11.0 – 12.0
12.1 – 12.3
12.4 – 12.6
12.7 – 12.9
13.0 – 14.0
Condition of Water
Corrosive
Acceptable Balance
Ideal Balance
Acceptable Balance
Scale forming
Recommendation
Increase pH and/or Alkalinity
Retest water frequently
Retest water frequently
Reduce pH and/or alkalinity
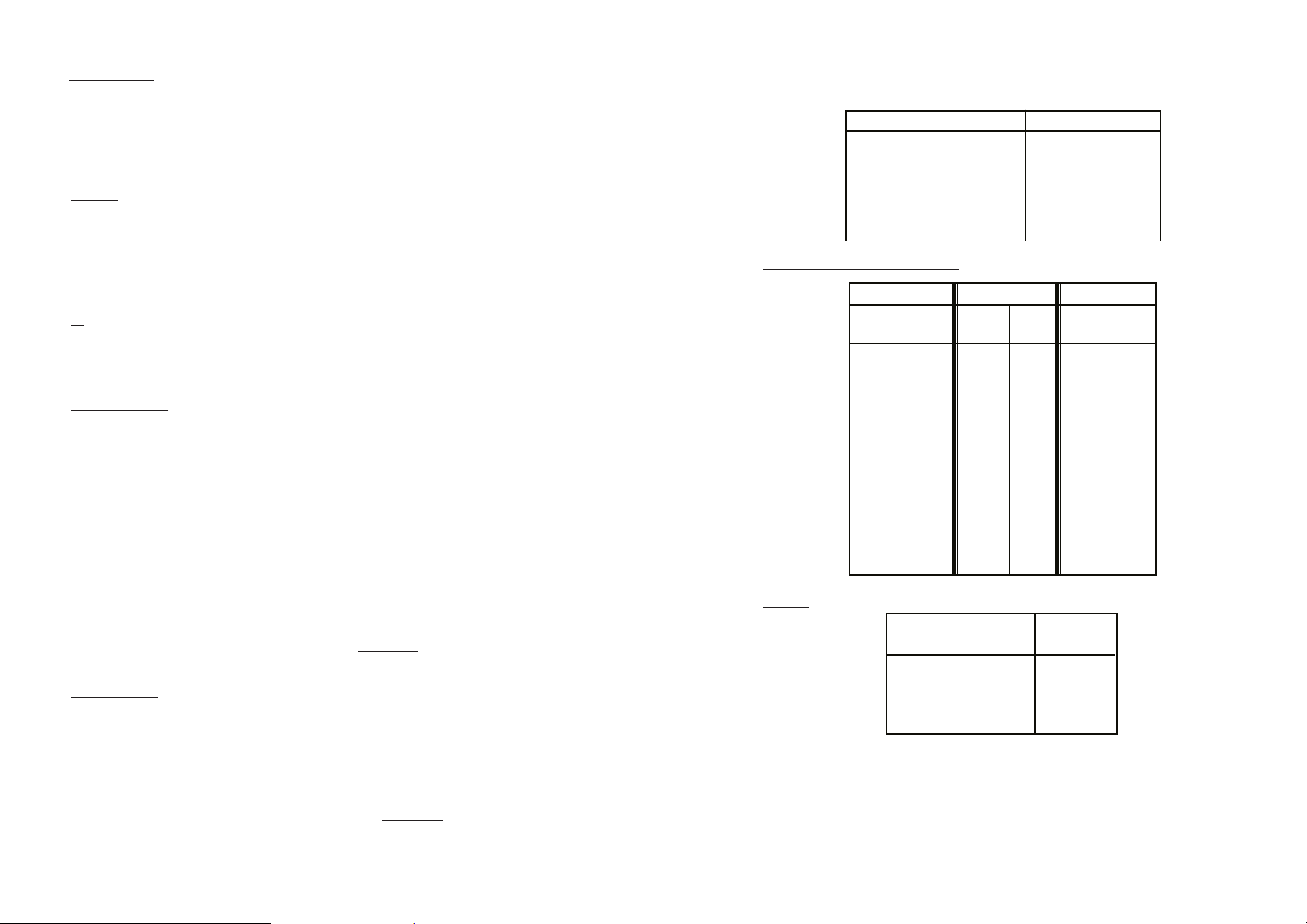
WATER INDEX REFERENCE TABLES
Temperature Calcium Hardness Alkalinity
°C
°F
0
32
4
39
0.1
8
46
0.2
12
54
0.3
16
60
0.4
20
68
0.5
24
75
0.6
28
82
0.7
32
90
0.7
36
97
0.8
40
104
0.9
50
122
1.0
EXAMPLE:
Pool water conditions
Temperature 30°C
pH 7.2
Alkalinity 80 mg/L
Hardness 230 mg/L
Water Balance = pH + TF + HF + AF = 7.2 + 0.7 + 2.4 + 1.9 = 12.2
Conclusion: the water is acceptable balanced but there is some risk that the water becomes corrosive;
frequently testing is recommended.
..
.
..
mg/L
TF
(as CaCO3)
0
25
50
75
100
150
200
250
300
400
500
1000
HF
5
0.7
1.4
1.7
1.9
2.0
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.5
2.6
2.7
3.0
mg/L
(as CaCO3)
5
25
50
75
100
150
200
250
300
400
500
1000
Factor value
(nearest values)
TF = 0.7
pH = 7.2
AF = 1.9
HF = 2.4
AF
0.7
1.4
1.7
1.9
2.0
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.5
2.6
2.7
3.0
6 7
Page 5
SPECIFICATIONS
Light Life Life of the instrument
Light Detector Silicon Photocell
Environment 0 to 50°C (32 to 122°F);
max 90% RH non-condensing
Power Supply external 12 Vdc power adapter
Auto-Shut off built-in rechargeable battery
Dimensions 235 x 200 x 110 mm (9.2 x 7.87 x 4.33")
Weight 0.9 Kg
For specifications related to each single method (e.g. range, resolution, etc.), refer to the related
measurement section.
PRECISION AND ACCURACY
Precision is how closely repeated measurements agree
with each other. Precision is usually expressed as
standard deviation (SD).
Accuracy is defined as the nearness of a test result to
the true value.
Although good precision suggests good accuracy, precise
results can be inaccurate. The figure explains these
definitions.
For each method, the precision is expressed in the
related measurement section.
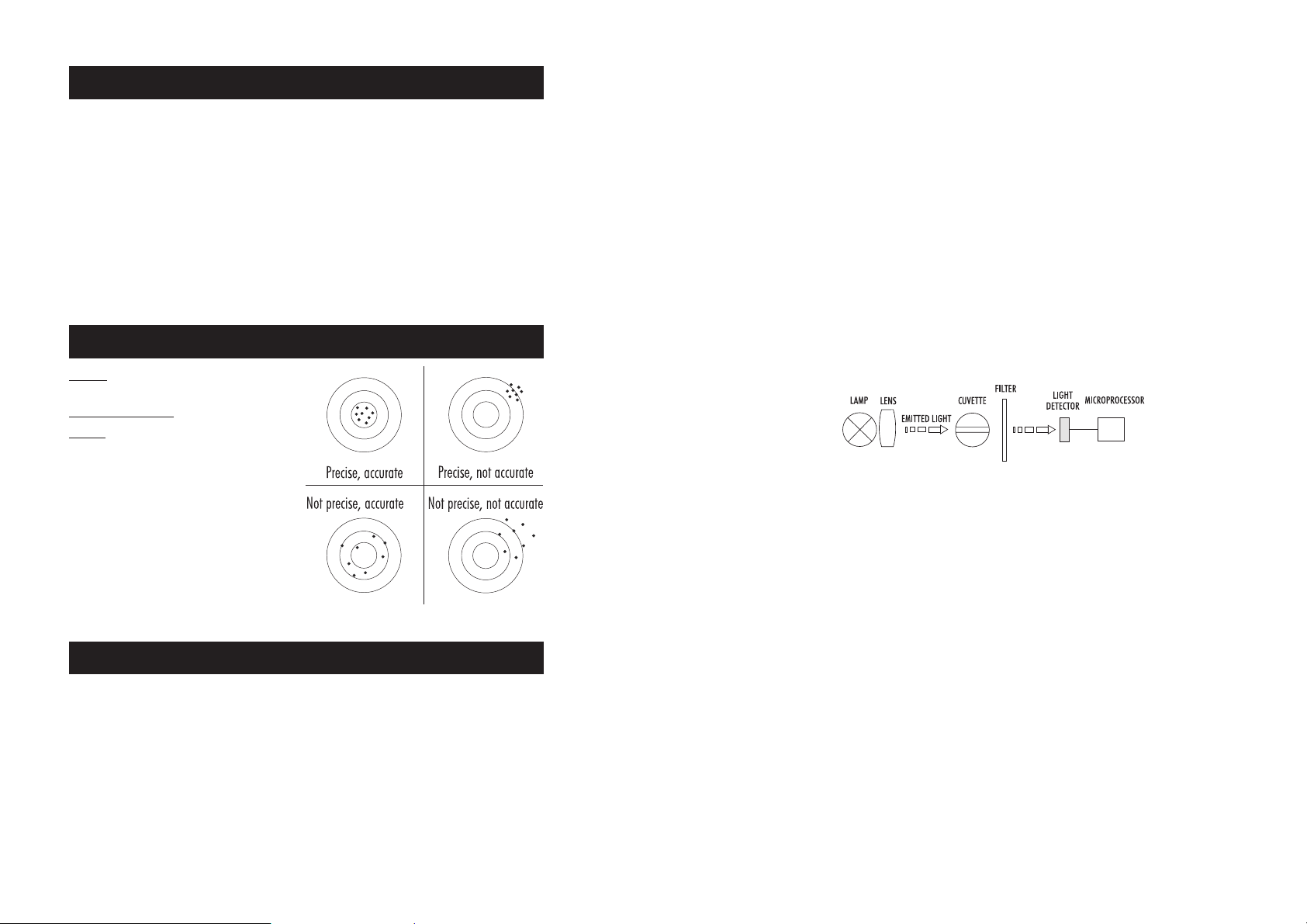
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION
Absorption of light is a typical phenomenon of interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter.
When a light beam crosses a substance, some of the radiation may be absorbed by atoms, molecules or
crystal lattices.
If pure absorption occurs, the fraction of light absorbed depends both on the optical path length through the
matter and on the physical-chemical characteristics of substance according to the Lambert-Beer Law:
-log I/Io = ελ c d
or
A = ελ c d
Where:
-log I/I
Therefore, the concentration "c" can be calculated from the absorbance of the substance as the other factors
are known.
Photometric chemical analysis is based on the possibility to develop an absorbing compound from a specific
chemical reaction between sample and reagents.
Given that the absorption of a compound strictly depends on the wavelength of the incident light beam, a
narrow spectral bandwidth should be selected as well as a proper central wavelength to optimize measurements.
The optical system of HI 83226 is based on special subminiature tungsten lamps and narrow-band
interference filters to guarantee both high performance and reliable results.
Two measuring channels allow a wide range of tests.
A microprocessor controlled special tungsten lamp emits radiation which is first optically conditioned and beamed
through the sample contained in the cuvette. The optical path is fixed by the diameter of the cuvette. Then
the light is spectrally filtered to a narrow spectral bandwidth, to obtain a light beam of intensity Io or I.
The photoelectric cell collects the radiation I that is not absorbed by the sample and converts it into an
electric current, producing a potential in the mV range.
The microprocessor uses this potential to convert the incoming value into the desired measuring unit and to
display it on the LCD.
The measurement process is carried out in two phases: first the meter is zeroed and then the actual
measurement is performed.
The cuvette has a very important role because it is an optical element and thus requires particular
attention. It is important that both the measurement and the calibration (zeroing) cuvette are optically
identical to provide the same measurement conditions. Most methods use the same cuvette for both, so it
is important that measurements are taken at the same optical point. The instrument and the cuvette cap
have special marks that must be aligned in order to obtain better reproducibility.
The surface of the cuvette must be clean and not scratched. This is to avoid measurement interference due
to unwanted reflection and absorption of light. It is recommended not to touch the cuvette walls with hands.
Furthermore, in order to maintain the same conditions during the zeroing and the measurement phases,
it is necessary to cap the cuvette to prevent any contamination.
= Absorbance (A)
o
Io= intensity of incident light beam
I = intensity of light beam after absorption
ελ= molar extinction coefficient at wavelength λ
c = molar concentration of the substance
d = optical path through the substance
Instrument block diagram (optical layout)
8 9
Page 6
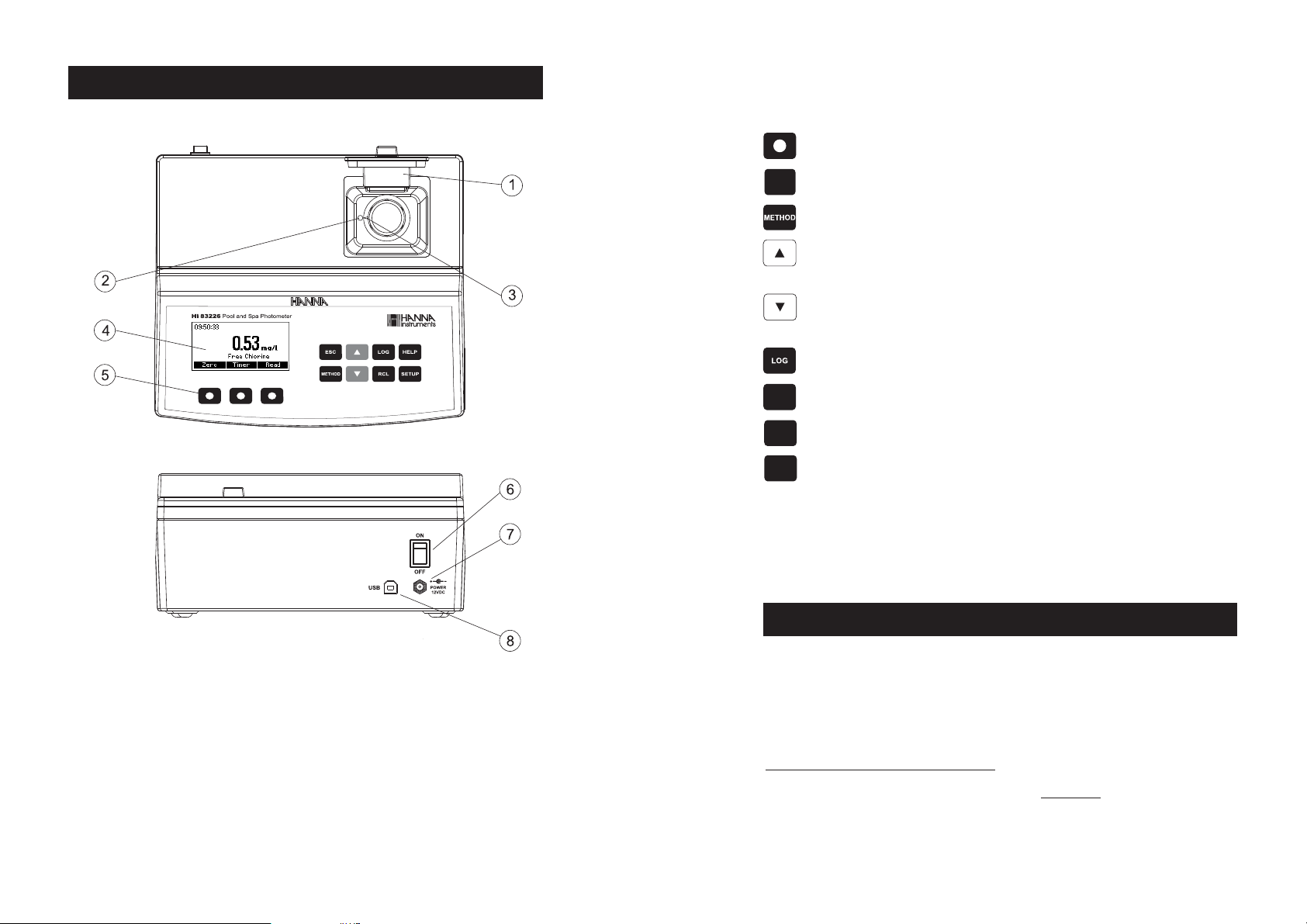
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
ESC
RCL
HELP
SETUP
INSTRUMENT DESCRIPTION
KEYPAD DESCRIPTION
The keypad contains 8 direct keys and 3 functional keys with the following functions:
Press to perform the function displayed above it on the LCD.
Press to exit the current screen.
Press to access the select method menu.
Press to move up in a menu or a help screen, to increment a set value, to access second level
functions.
Press to move down in a menu or a help screen, to decrement a set value, to access second
level functions.
Press to log the current reading.
Press to recall the log.
Press to display the help screen.
Press to access the setup screen.
1) Open Cuvette Lid
2) Indexing mark
3) Cuvette point
4) Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
5) Splash proof keypad
6) ON/OFF power switch
7) Power input connector
8) USB connector
TIPS FOR AN ACCURATE MEASUREMENT
The instructions listed below should be carefully followed during testing to ensure most accurate results.
• Color or suspended matter in large amounts may cause interference, and should be removed by
treatment with active carbon and filtration.
• Ensure the cuvette is filled correctly: the liquid in the cuvette forms a convexity on the top; the bottom
of this convexity must be at the same level as the 10 mL mark.
COLLECTING AND MEASURING SAMPLES
• In order to measure exactly 0.5 mL of reagent with the 1 mL syringe:
(a) push the plunger completely into the syringe and insert the tip into the solution.
(b) pull the plunger up until the lower edge of the seal is exactly on the 0.0 mL mark.
10 11
Page 7
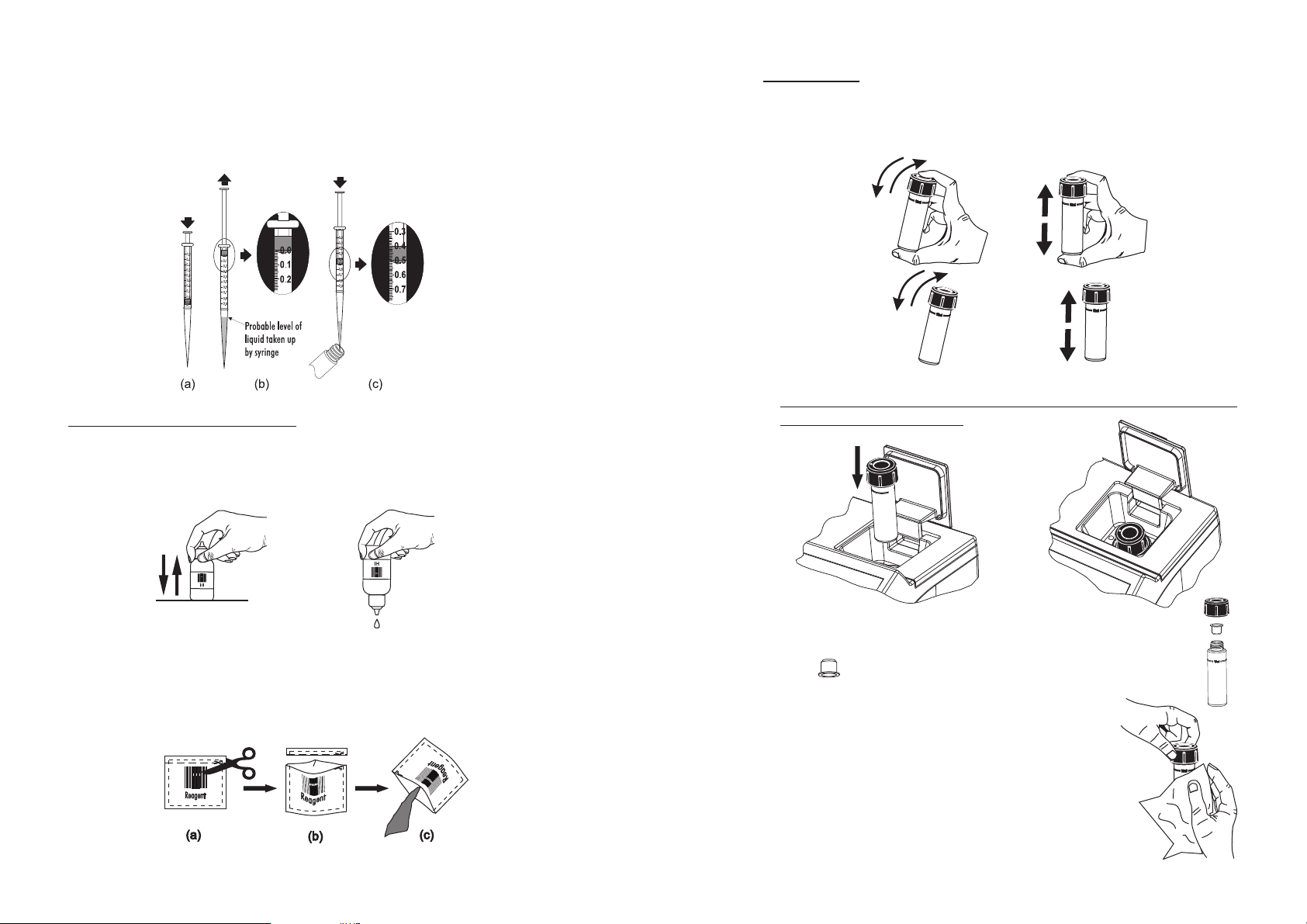
(c) take out the syringe and clean the outside of the syringe tip. Be sure that no drops are hanging
on the tip of the syringe, if so eliminate them. Then, keeping the syringe in vertical position above
the cuvette, push the plunger down into the syringe until the lower edge of the seal is exactly on
the 0.5 mL mark. Now the exact amount of 0.5 mL has been added to the cuvette, even if the
tip still contains some solution.
USING LIQUID AND POWDER REAGENTS
• Proper use of the dropper:
(a) for reproducible results, tap the dropper on the table for several times and wipe the outside of the
dropper tip with a cloth.
(b) always keep the dropper bottle in a vertical position while dosing the reagent.
USING CUVETTES
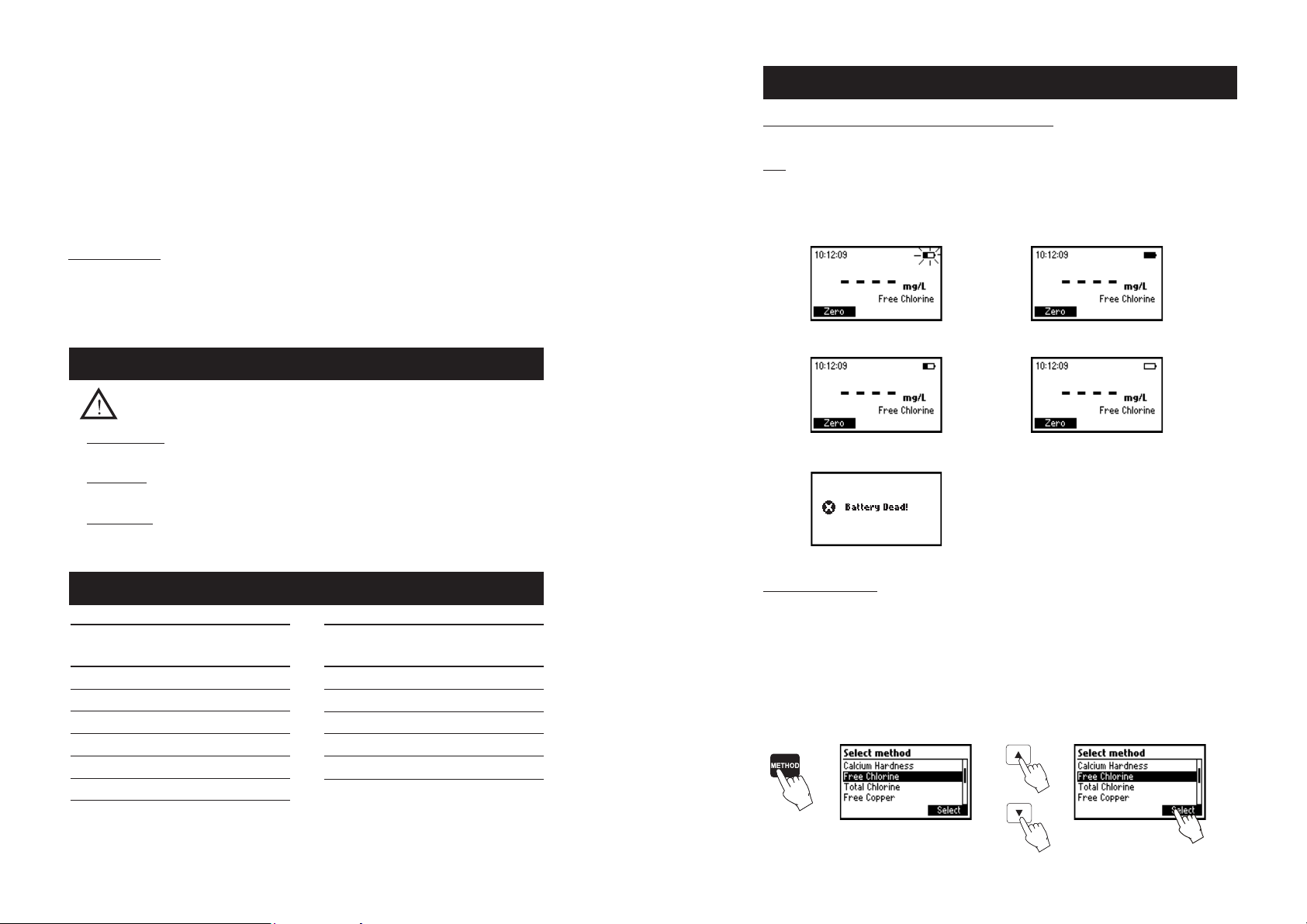
• Proper mixing of the cuvette is done by shaking the cuvette, moving the cuvette up and down. The
movement may be gentle or vigorous. This mixing method is indicated with “shake gently” or “shake
vigorously”, and one of the following icons:
shake gently shake vigorously
• Pay attention to push the cuvette completely down in the holder and to align the white point on the
cap to the indexing mark on the meter.
(a) (b)
• Proper use of the powder reagent packet:
(a) use scissors to open the powder packet;
(b) push the edges of the packet to form a spout;
(c) pour out the content of the packet.
• In order to avoid reagent leaking and to obtain more accurate
measurements, close the cuvette first with the supplied HDPE plastic
stopper and then the black cap.
• Whenever the cuvette is placed into the measurement cell, it must
be dry outside, and free of fingerprints, oil or dirt. Wipe it
thoroughly with HI 731318 or a lint-free cloth prior to insertion.
• Shaking the cuvette can generate bubbles in the sample, causing
higher readings. To obtain accurate measurements, remove such
bubbles by swirling or by gently tapping the cuvette.
• Do not let the reacted sample stand too long after reagent is
added. For best accuracy, respect the timings described in each
12 13
Page 8
specific method.
• It is possible to take multiple readings in a row, but it is recommended to take a new zero reading for
each sample and to use the same cuvette for zeroing and measurement when possible (for most precise
results follow the measurement procedures carefully).
• Discard the sample immediately after the reading is taken, or the glass might become permanently
stained.
• All the reaction times reported in this manual are at 25 °C (77 °F). In general, the reaction time
should be increased for temperatures lower than 20 °C (68 °F), and decreased for temperatures higher
than 25 °C (77 °F).
INTERFERENCES
• In the method measurement section the most common interferences that may be present in an average
sample matrix have been reported. It may be that for a particular treatment process other compounds
do interfere with the method of analysis.
HEALTH & SAFETY
• The chemicals contained in the reagent kits may be hazardous if improperly handled.
• Read the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) before performing tests.
• Safety equipment: Wear suitable eye protection and clothing when required, and follow instructions
carefully.
• Reagent spills: If a reagent spill occurs, wipe up immediately and rinse with plenty of water.
If reagent contacts skin, rinse the affected area thoroughly with water. Avoid breathing released vapors.
• Waste disposal: for proper disposal of reagent kits and reacted samples, refer to the Material Safety
Data Sheet (MSDS).
OPERATIONAL GUIDE
POWER CONNECTION AND BATTERY MANAGEMENT
The meter can be powered from an AC/DC adapter (included) or from the built-in rechargeable battery.
Note: Always turn the meter off before unplugging it to ensure no data is lost.
When the meter switches ON, it verifies if the power supply adapter is connected. The battery icon on the
LCD will indicate the battery status:
- battery is charging from external adapter - battery fully charged (meter connected to AC/DC adapter)
- battery capacity (no external adapter) - battery Low (no external adapter)
- battery Dead (no external adapter)
METHOD REFERENCE TABLE
Method Method Page
description
1 Alkalinity 20
2 Bromine 22
3 Calcium Hardness 24
4 Free Chlorine 27
5 Total Chlorine 29
6 Free Copper 31
METHOD SELECTION
• Turn the instrument ON via the ON/OFF power switch.
Method Method Page
description
7 Total Copper 33
8 Cyanuric Acid 35
9 Iron 37
10 Ozone 39
11 pH 42
14 15
• The meter will perform an autodiagnostic test. During this test, the Hanna Instrument logo will appear
on the LCD. After 5 seconds, if the test was successful, the last method used will appear on the display.
• In order to select the desired method press the METHOD key and a screen with the available methods
will appear.
• Press the s t keys to highlight the desired method. Press Select.
Page 9

• After the desired method is selected, follow the measurement described in the related section.
• Before performing a test you should read all the instructions carefully.
DATA MANAGEMENT
The instrument features a data log function to help you keep track of all your analysis. The data log can
hold 200 individual measurements. Storing, viewing and deleting the data is possible using the LOG
and
RCL keys
Storing data
stored with date and time stamps.
Viewing and deleting
the last saved measurement. Additionally, you can delete the data records all at once.
..
.
..
: You can store only a valid measurement. Press LOG
: You can view and delete the data log by pressing the RCL key. You can only delete
and the last valid measurement will be
CHEMICAL FORM
Chemical form conversion factors are pre-programmed into the instrument and are method specific. In order
to view the displayed result in the desired chemical form press s or t to access the second level functions
and then press the Chem Frm key to toggle between the available chemical forms for the selected method.
SETUPSETUP
SETUP
SETUPSETUP
In the Setup mode the instrument’s parameters can be changed. Some parameters affect the measuring
sequence and others are general parameters that change the behavior or appearance of the instrument.
Press SETUP to enter the setup mode.
Press ESC or SETUP to return to the main screen.
A list of setup parameters will be displayed with currently
configured settings. Press HELP for additional information.
Press the s t keys to select a parameter and change the
value as follows:
Backlight
Values: 0 to 8.
Press the Modify key to access the backlight value.
Use the ⊳ u functional keys or the s t keys to increase
or decrease the value.
Press the Accept key to confirm or ESC to return to the setup
menu without saving the new value.
Contrast
Values: 0 to 20.
This option is used to set the display’s contrast.
Press the Modify key to change the display’s contrast.
Use the ⊳ u functional keys or the s t keys to increase
or decrease the value.
Press the Accept key to confirm the value or ESC to return to
the setup menu without saving the new value.
SPECIAL CONVERSIONS
For Calcium Hardness, special conversion factors can be used to convert the readings from mg/L to French
degrees (°f), German degrees (°dH) and English degrees (°E) of hardness. This can be achieved by pressing
s or t to access the second level functions and then press the Unit functional key to toggle between
°f, °dH, °E and mg/L.
16 17
Page 10

Date / Time
This option is used to set the instrument’s date and time.
Press the Modify key to change the date/time.
Press the ⊳ u functional keys to highlight the value to be
modified (year, month, day, hour, minute or second). Use the
s t keys to change the value.
Press the Accept key to confirm or ESC to return to the setup
without saving the new date or time.
Time format
Option: AM/PM or 24 hour.
Press the functional key to select the desired time format.
Date format
Press the Modify key to change the Date Format.
Use the s t keys to select the desired format.
Press Accept key to confirm or ESC to return to the setup menu
without saving the new format.
Instrument ID
Option: 0 to 9999.
This option is used to set the instrument’s ID (identification
number). The instrument ID is used while exchanging data with
a PC.
Press the Modify key to access the instrument ID screen. Press
the s t keys in order to set the desired value.
Press the Accept key to confirm the value or ESC to return to the
setup menu without saving the new value.
Meter information
Press the Select key to view the instrument model, firmware
version, language version and instrument serial number.
Press ESC to return to the Setup mode.
Language
Press the corresponding key to change the language.
If the new language cannot be loaded, the previously selected
language will be reloaded.
Tutorial
Option: Enable or Disable.
If enabled this option will provide the user short guide related to
the current screen.
Press the functional key to enable/disable the tutorial mode.
Beeper
Option: Enable or Disable.
When enabled, a short beep is heard every time a key is pressed.
A long beep alert sounds when the pressed key is not active or an
error is detected.
Press the functional key to enable/disable the beeper.
18 19
HELP MODEHELP MODE
HELP MODE
HELP MODEHELP MODE
HELP MODE
HI 83226 offers an interactive contextual help mode that assists the user at any time.
To access the help screens press HELP.
The instrument will display additional information related to the
current screen. To read all the available information, scroll the
text using the s t keys.
Press the Support key to access a screen with Hanna service
centers and their contact details.
Press the Accessories key to access a list of instrument reagents
and accessories.
To exit support or accessories screens press ESC and the
instrument will return to the previous help screen.
To exit help mode press the HELP or ESC key again and the
meter will return to the previously selected screen.
Page 11

ALKALINITY
SPECIFICATIONS
Range 0 to 500 mg/L (as CaCO3)
Resolution 5 mg/L
Accuracy ±5 mg/L ±10% of reading at 25 °C
Typical EMC ±5 mg/L
Deviation
Light Source Tungsten lamp with narrow band interference filter @ 575 nm
Method Colorimetric Method. At different alkalinity levels a distinctive range of colors from yellow
to green and greenish blue will develop.
REQUIRED REAGENTS
Code Description Quantity/test
HI 93755-0 Alkalinity Indicator Reagent 1 mL
REAGENT SETS
HI 93755-01 Reagents for 100 tests
HI 93755-03 Reagents for 300 tests
For other accessories see page 46.
MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
• Select the
Method Selection
• Fill the cuvette with 10 mL of unreacted sample, up to the mark,
and replace the cap.
Alkalinity
method using the procedure described in the
section (see page 15).
10 mL
• Remove the cuvette.
Note: Any chlorine present in the sample will interfere with the
reading. To remove the chlorine interference add one drop
of HI 93755-53 Chlorine Remover to the unreacted sample.
• Carefully add exactly 1 mL of HI 93755-0 Liquid Alkalinity
Reagent using the supplied syringe.
• Replace the cap and invert 5 times.
• Reinsert the cuvette into the instrument and close the lid.
• Press Read to start the reading.
• Place the cuvette into the holder and close the lid.
• Press the Zero key. The display will show “-0.0-” when the meter is zeroed and ready for
measurement.
Alkalinity
20 21
• The instrument displays the results in mg/L of alkalinity (CaCO3).
Note: If using a meter with software version 1.14 or earlier, readings can be improved for samples
with less than 75 ppm alkalinity by adding 0.7 mL of reagent instead of 1.0 mL.
Page 12

BROMINE
SPECIFICATIONS
Range 0.00 to 10.00 mg/L
Resolution 0.01 mg/L
Accuracy ±0.08 mg/L ±3% of reading at 25 °C
Typical EMC ±0.01 mg/L
Deviation
Light Source Tungsten lamp with narrow band interference filter @ 525 nm
Method Adaptation of the
20th edition
pink tint in the sample.
Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater,
, DPD method. The reaction between bromine and the reagent causes a
REQUIRED REAGENTS
Code Description Quantity
HI 93716-0 DPD Reagent 1 packet
REAGENT SETS
HI 93716-01 Reagents for 100 tests
HI 93716-03 Reagents for 300 tests
For other accessories see page 46.
MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
• Select the
Method Selection
Bromine
method using the procedure described in the
section (see page 15).
• Remove the cuvette and add the content of one packet of
HI 93716-0 DPD reagent. Replace the cap and shake
gently for about 20 seconds to dissolve most of the
reagent.
• Reinsert the cuvette into the instrument.
• Press Timer and the display will show the countdown prior to the measurement or, alternatively, wait
for 2 minutes and 30 seconds and press Read. When the timer ends the meter will perform the
reading.
• The instrument displays the results in mg/L of bromine.
10 mL
• Fill the cuvette with 10 mL of unreacted sample (up to the mark)
and replace the cap.
• Place the cuvette into the holder and close the lid.
• Press the Zero key. The display will show “-0.0-” when the meter is zeroed and ready for
measurement.
Bromine
22 23
INTERFERENCES
Interference may be caused by: Chlorine, Iodine, Ozone, Oxidized forms of Chromium and Manganese.
In case of water with hardness greater than 500 mg/L CaCO3, shake the sample for approximately
2 minutes after adding the reagent.
In case of water with alkalinity greater than 250 mg/L CaCO3 or acidity greater than 150 mg/L CaCO3,
the color of the sample may develop only partially, or may rapidly fade. To resolve this, neutralize the
sample with diluted HCl or NaOH.
Bromine
Page 13

CALCIUM HARDNESS
SPECIFICATIONS
Range 0 to 500 mg/L (as CaCO3)
Resolution 5 mg/L
Accuracy ±10 mg/L ±5% of reading at 25 °C
Typical EMC ±5 mg/L
Deviation
Light Source Tungsten lamp with narrow band interference filter @ 525 nm
Method Adaptation of the
18th edition,
reddish-violet tint in the sample.
REQUIRED REAGENTS
Code Description Quantity
HI 93720A-0 Ca & Mg indicator 0.5 mL
HI 93720B-0 Alkali solution 0.5 mL
HI 93720C-0 EGTA solution 1 drop
REAGENT SETS
HI 93720-01 Reagents for 100 tests
HI 93720-03 Reagents for 300 tests
For other accessories see page 46.
MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
• Select the
• Rinse a graduated beaker several times with deionized
Calcium Hardness
described in the
Method Selection
water, fill a 1 mL syringe with the sample, and inject
0.5 mL into the beaker. Fill the beaker up to the 50 mL
mark with hardness-free water.
Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater,
Calmagite method. The reaction between calcium and reagents causes a
method using the procedure
section (see page 15).
• Add 1 drop of HI 93720C-0 EGTA solution to one cuvette (# 1), replace
the cap and invert the cuvette several times to mix. This is the blank.
# 1
# 1
• Place the blank (# 1) into the holder and close the lid.
• Press the Zero key. The meter will show “-0.0-” when the meter is zeroed and ready for
measurement.
# 2
• Remove the blank and insert the second cuvette (# 2) into
the instrument.
• Press Read to start the reading. The instrument displays concentration in mg/L of calcium hardness,
as CaCO3.
• Add 0.5 mL of HI 93720A-0 Calcium indicator solution
and swirl to mix.
• Add 0.5 mL of HI 93720B-0 Alkali solution and swirl to
mix. Use this solution to rinse 2 cuvettes before filling
them up to the 10 mL mark.
Calcium Hardness
24 25
• Press s or t to access the second level functions.
• Press the Chem Frm key to convert the result in mg/L of Calcium (Ca).
# 1 # 2
Calcium Hardness
Page 14

• Press the Unit key to change the current measurement unit. The results can be converted to French
degrees (°f), German degrees (°dH) and English degrees (°E).
• Press s or t to return to the measurement screen.
Note: This test will detect any calcium contamination in the beaker, measuring syringes or sample cells. To
test cleanliness, repeat the test multiple times until you obtain consistent results.
Note: For better accuracy wash glassware with HCl 6N.
INTERFERENCES
Interference may be caused by excessive amounts of heavy metals.
FREE CHLORINE
FREE CHLORINEFREE CHLORINE
FREE CHLORINE
FREE CHLORINEFREE CHLORINE
SPECIFICATIONS
Range 0.00 to 5.00 mg/L
Resolution 0.01 mg/L from 0.00 to 2.50 mg/L;
0.10 mg/L above 2.50 mg/L
Accuracy ±0.03 mg/L ±3% of reading at 25 °C
Typical EMC ±0.01 mg/L
Deviation
Light Source Tungsten lamp with narrow band interference filter @ 525 nm
Method Adaptation of the USEPA method 330.5 and
Water and Wastewater, 20th edition
the DPD reagent causes a pink tint in the sample.
, 4500-Cl G. The reaction between free chlorine and
Standard Methods for the Examination of
REQUIRED REAGENTS
Code Description Quantity
HI 93701-0 DPD powder Reagent 1 packet
REAGENT SETS
HI 93701-01 Reagents for 100 tests
HI 93701-03 Reagents for 300 tests
For other accessories see page 46.
MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
• Select the
Free Chlorine
Method Selection
method using the procedure described in the
section (see page 15).
10 mL
Calcium Hradness
• Fill the cuvette with 10 mL of unreacted sample (up to the mark)
and replace the cap.
• Place the cuvette into the holder and close the lid.
26 27
Free Chlorine
Page 15

• Press the Zero key. The meter will show “-0.0-” when the meter is zeroed and ready for measurement.
• Remove the cuvette.
• Add the content of one packet of HI 93701-0 DPD reagent. Replace
the cap and shake gently for 20 seconds.
• Reinsert the cuvette into the instrument.
• Press Timer and the display will show the countdown prior to the measurement or, alternatively, wait
for 1 minute and press Read. When the timer ends the meter will perform the reading.
TOTAL CHLORINE
SPECIFICATIONS
Range 0.00 to 5.00 mg/L
Resolution 0.01 mg/L from 0.00 to 2.50 mg/L;
0.10 mg/L above 2.50 mg/L
Accuracy ±0.03 mg/L ±3% of reading at 25 °C
Typical EMC ±0.01 mg/L
Deviation
Light Source Tungsten lamp with narrow band interference filter @ 525 nm
Method Adaptation of the EPA method 330.5 and
Water and Wastewater, 20th edition
DPD reagent causes a pink tint in the sample.
REQUIRED REAGENTS
POWDER:
Code Description Quantity
HI 93711-0 DPD Powder Reagent 1 packet
REAGENT SETS
HI 93711-01 Reagents for 100 tests
HI 93711-03 Reagents for 300 tests
For other accessories see page 46.
Standard Methods for the Examination of
, 4500-Cl G. The reaction between chlorine and the
• The instrument displays the results in mg/L of free chlorine.
INTERFERENCES
Interference may be caused by: Bromine, Chlorine Dioxide, Iodine, Ozone (all these interferences give positive errors).
Alkalinity above 250 mg/L CaCO3 will not reliably develop the full amount of color or it may rapidly fade.
To resolve this, neutralize the sample with diluted HCl.
In case of water with hardness greater than 500 mg/L CaCO3, shake the sample for approximately
2 minutes after adding the powder reagent.
Free Chlorine
28 29
MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
• Select the
• Fill the cuvette with 10 mL of unreacted sample (up to the mark)
• Place the cuvette into the holder and close the lid.
Total Chlorine
Method Selection
and replace the cap.
section (see page 15).
method using the procedure described in the
10 mL
Total Chlorine
Page 16

• Press the Zero key. The meter will show “-0.0-” when the meter is zeroed and ready for measurement.
• Remove the cuvette.
• Add 1 packet of HI 93711-0 DPD reagent. Replace the
cap and shake gently for 20 seconds.
FREE COPPER
SPECIFICATIONS
Range 0.00 to 5.00 mg/L
Resolution 0.01 mg/L
Accuracy ±0.02 mg/L ±4% of reading at 25 °C
Typical EMC ±0.01 mg/L
Deviation
Light Source Tungsten lamp with narrow band interference filter @ 575 nm
Method Adaptation of the
reagent causes a purple tint in the sample.
EPA method.
The reaction between copper and the bicinchoninate
• Reinsert the cuvette into the instrument.
• Press Timer and the display will show the countdown prior to the measurement or, alternatively, wait
for 2 minutes and 30 seconds and press Read. When the timer ends the meter will perform the
reading.
• The instrument displays the results in mg/L of total chlorine.
INTERFERENCES
Interference may be caused by: Bromine, Chlorine Dioxide, Iodine, Ozone (all these interferences give positive errors).
Alkalinity above 250 mg/L CaCO3 will not reliably develop the full amount of color or it may rapidly fade.
To resolve this, neutralize the sample with diluted HCl.
In case of water with hardness greater than 500 mg/L CaCO3, shake the sample for approximately
2 minutes after adding the powder reagent.
REQUIRED REAGENTS
Code Description Quantity/test
HI 93702-0 Bicinchoninate 1 packet
REAGENT SETS
HI 93702-01 Reagents for 100 tests
HI 93702-03 Reagents for 300 tests
For other accessories see page 46.
MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
• Select the
the
• Fill the cuvette with 10 mL of unreacted sample (up to the mark)
and replace the cap.
• Place the cuvette into the holder and close the lid.
• Press the Zero key. The meter will show “-0.0-” when the meter is zeroed and ready for measurement.
Free Copper
Method Selection
method using the procedure described in
section (see page 15).
10 mL
Total Chlorine
30 31
Free Copper
Page 17

• Remove the cuvette.
TOTAL COPPER
• Add the content of one packet of HI 93702-0
Copper Reagent. Replace the cap and shake gently
for 15 seconds.
• Reinsert the cuvette into the instrument.
• Press Timer and the display will show the countdown prior to the measurement or, alternatively, wait
for 45 seconds and press Read. When the timer ends the meter will perform the reading.
• The instrument displays the results in mg/L of copper.
SPECIFICATIONS
Range 0.00 to 5.00 mg/L
Resolution 0.01 mg/L
Accuracy ±0.02 mg/L ±4% of reading at 25 °C
Typical EMC ±0.01 mg/L
Deviation
Light Source Tungsten lamp with narrow band interference filter @ 575 nm
Method Adaptation of the USEPA approved method. The reaction between free copper and the
bicinchoninate reagent causes a purple tint in the sample.
REQUIRED REAGENTS
Code Description Quantity/test
HI 93702-0 Bicinchoninate 1 packet
HI 93702T-0 Decomplexing Agent 1 packet
REAGENT SETS
HI 93702T-01, HI 93702-01 Reagents for 100 tests
HI 93702T-03, HI 93702-03 Reagents for 300 tests
For other accessories see page 46.
MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
• Select the
the
Total Copper
Method Selection
method using the procedure described in
section (see page 15).
10 mL
INTERFERENCES
Interference may be caused by:
Silver
Cyanide
For samples overcoming buffering capacity of reagent (around pH 6.8), pH should be adjusted between
6 and 8.
Free Copper
32 33
• Fill the cuvette with 10 mL of unreacted sample (up to the mark)
and replace the cap.
• Place the cuvette into the holder and close the lid.
• Press the Zero key. The meter will show “-0.0-” when the meter is zeroed and ready for measurement.
Total Copper
Page 18

• Remove the cuvette.
• Add the content of one packet of HI 93702-0
Copper Reagent. Replace the cap and shake gently
for 15 seconds.
• Add the content of one packet of HI 93702T-0
Copper Total Reagent. Replace the cap and shake
vigorously for 15 seconds.
• Replace the cuvette into the holder and ensure that
the notch on the cap is positioned securely into the
groove.
• Press Timer and the display will show the countdown prior to measurement or, alternatively, wait for
45 seconds and press Read. When the timer ends the meter will perform the reading.
• The instrument displays concentration in mg/L of total copper.
CYANURIC ACID
SPECIFICATIONS
Range 0 to 200 mg/L
Resolution 1 mg/L from 0 to 100 mg/L;
10 mg/L above 100 mg/L
Accuracy ±1 mg/L ±15% of reading at 25 °C
Typical EMC ±1 mg/L
Deviation
Light Source Tungsten lamp with narrow band interference filter @ 525 nm
Method Adaptation of the turbidimetric method. The reaction between cyanuric acid and the
reagent causes a white suspension in the sample.
REQUIRED REAGENTS
Code Description Quantity
HI 93722-0 Powder reagent 1 packet
REAGENT SETS
HI 93722-01 Reagents for 100 tests
HI 93722-03 Reagents for 300 tests
For other accessories see page 46.
MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
• Select the
described in the
• Fill the cuvette with 10 mL of unreacted sample (up to the
mark) and replace the cap.
Cyanuric Acid
Method Selection
method using the procedure
section (see page 15).
10 mL
Total Copper
• Place the cuvette into the holder and close the lid.
• Press the Zero key. The meter will show “-0.0-” when the meter is zeroed and ready for
measurement.
• Add the content of one packet of HI 93722-0 Cyanuric
Acid Reagent. Replace the cap and shake gently for
about 10 seconds (dissolution is not complete).
Cyanuric Acid
34 35
Page 19

IRON
• Reinsert the cuvette into the instrument.
• Press Timer and the display will show the countdown prior to the measurement or, alternatively, wait
for 45 seconds and press Read. When the timer ends the meter will perform the reading.
• The instrument displays concentration in mg/L of cyanuric acid.
INTERFERENCES
Turbidity preexisting in the sample causes interference during measurement.
SPECIFICATIONS
Range 0.00 to 5.00 mg/L
Resolution 0.01 mg/L
Accuracy ±0.04 mg/L ±2% of reading at 25 °C
Typical EMC ±0.01 mg/L
Deviation
Light Source Tungsten lamp with narrow band interference filter @ 525 nm
Method Adaptation of the
The reaction between iron and reagents causes an orange tint in the sample.
EPA Phenantroline method 315B,
for natural and treated waters.
REQUIRED REAGENTS
Code Description Quantity/test
HI 93721-0 Iron High Range Reagent 1 packet
REAGENT SETS
HI 93721-01 Reagents for 100 tests
HI 93721-03 Reagents for 300 tests
For other accessories see page 46.
MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
• Select the
Selection
• Fill the cuvette with 10 mL of unreacted sample (up to the mark)
and replace the cap.
Iron
method using the procedure described in the
section (see page 15).
Method
10 mL
Cyanuric Acid
• Place the cuvette into the holder and close the lid.
• Press the Zero key. The meter will show “-0.0-” when the meter is zeroed and ready for
measurement.
• Remove the cuvette and add the content of one packet of
HI 93721-0 reagent. Replace the cap and shake until dissolution is
complete.
Iron
36 37
Page 20

• Reinsert the cuvette into the instrument.
• Press Timer and the display will show the countdown prior to the measurement or, alternatively, wait
for 3 minutes and press Read. When the timer ends the meter will perform the reading.
• The instrument displays concentration in mg/L of iron.
INTERFERENCES
Interference may be caused by:
Molybdate Molybdenum above 50 ppm
Calcium above 10000 ppm (as CaCO3)
Magnesium above 100000 ppm (as CaCO3)
Chloride above 185000 ppm.
OZONE
SPECIFICATIONS
Range 0.00 to 2.00 mg/L
Resolution 0.01 mg/L
Accuracy ±0.02 mg/L ±3% of reading at 25 °C
Typical EMC ±0.01 mg/L
Deviation
Light Source Tungsten lamp with narrow band interference filter @ 525 nm
Method Colorimetric DPD Method. The reaction between ozone and the DPD reagent causes a
pink tint in the sample.
REQUIRED REAGENTS
Code Description Quantity/test
HI 93757-0 DPD Powder Reagent 1 packet
HI 93703-52-0 Glycine Powder (Optional Reagent) 1 packet
REAGENT SETS
HI 93757-01 Reagents for 100 tests
HI 93757-03 Reagents for 300 tests
HI 93703-52 Glycine Powder, Optional Reagent for 100 tests
For other accessories see page 46.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Chlorine is a strong interferent for ozone determination. If the sample is suspected to
contain chlorine residues (free or total chlorine), please follow the alternative measurement procedure
described below:
• Perform the Standard Measurement Procedure and take note of the reading:
• On a fresh sample perform the Additional Measurement Procedure and take note of the reading:
• Subtract reading B from reading A to obtain the ozone concentration in mg/L:
mg/L (O3) =
value A
–
value B
.
value A
.
value B
.
Iron
STANDARD MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
• Select the
in the
• Fill the cuvette with 10 mL of unreacted sample, up to
the mark, and replace the cap.
• Place the cuvette into the holder and close the lid.
38 39
Ozone
method using the procedure described
Method Selection
section (see page 15).
10 mL
Ozone
Page 21

• Press the Zero key. The display will show “-0.0-” the meter is zeroed and ready for measurement.
• Remove the cuvette.
• Add the content of one packet of HI 93757-0 Ozone
Reagent. Replace the cap and shake gently for 20
seconds.
• Replace the cuvette into the holder and close the lid.
• Press the Zero key. The display will show “-0.0-” when the meter is zeroed and ready for
measurement.
• Remove the cuvette.
• Add the content of one packet of the optional reagent HI93703-52-0
Glycine Powder. Replace the cap and shake gently until
completely dissolved.
• Press Timer and the display will show the countdown
prior to the measurement or, alternatively, wait for
2 minutes and press Read. When the timer ends the
meter will perform the reading.
• The instrument displays concentration in mg/L of ozone (chlorine free samples only).
ADDITIONAL MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
For samples containing chlorine
• Select the
Selection
• Fill the cuvette with 10 mL of unreacted sample, up to the mark, and
replace the cap.
• Place the cuvette into the holder and close the lid.
Ozone
method using the procedure described in the
section (see page 15).
Method
10 mL
• Add the content of one packet of HI 93757-0 Ozone Reagent.
Replace the cap and shake gently for 20 seconds.
• Replace the cuvette into the holder and close the lid.
• Press Timer and the display will show the countdown prior to
the measurement or, alternatively, wait for 2 minutes and press
Read. When the timer ends the meter will perform the reading.
• The instrument displays a concentration value refering to chlorine interference. Subtract this value from
the reading from the Standard Measurement Procedure: this will be the concentration in mg/L of
ozone in the sample.
INTERFERENCES
Interference may be caused by: Bromine, Chlorine Dioxide, Iodine.
Alkalinity above 250 mg/L CaCO3 will not reliably develop the full amount of color or it may rapidly fade.
To resolve this, neutralize the sample with diluted HCl.
In case of water with hardness greater than 500 mg/L CaCO3, shake the sample for approximately
2 minutes after adding the powder reagent.
Ozone
40 41
Ozone
Page 22

pH
SPECIFICATIONS
Range 6.5 to 8.5 pH
Resolution 0.1 pH
Accuracy ±0.1 pH at 25 °C
Typical EMC ±0.1 pH
Deviation
Light Source Tungsten lamp with narrow band interference filter @ 525 nm
Method Adaptation of the Phenol Red method. The reaction with the reagent causes a yellow
to red tint in the sample.
REQUIRED REAGENTS
Code Description Quantity
HI 93710-0 Phenol Red Indicator 5 drops
REAGENT SETS
HI 93710-01 Reagents for 100 pH tests
HI 93710-03 Reagents for 300 pH tests
For other accessories see page 46.
MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
• Select the pH method using the procedure described in the
Method
section (see page 15).
Selection
10 mL
• Remove the cuvette and add 5 drops of HI 93710-0 Phenol
Red Indicator. Replace the cap and mix the solution.
• Reinsert the cuvette into the instrument.
• Press the Read key to start the reading. The instrument displays the pH value.
• Fill the cuvette with 10 mL of unreacted sample (up to the
mark)
and replace the cap.
• Place the cuvette into the holder and close the lid.
• Press the Zero key. The display will show “-0.0-” when the meter is zeroed and ready for
measurement.
pH
42 43
pH
Page 23

ERRORS AND WARNINGS
DATA MANAGEMENT
The instrument shows clear warning messages when erroneous conditions appear and when measured values are
outside the expected range. These messages are described bellow.
No Light: The light source is not functioning properly.
Light Leak: There is an excess amount of ambient light reaching the
detector.
Inverted cuvettes: The sample and the zero cuvettes are inverted.
Battery Low: The battery capacity is lower than 10%.
The analyzed data can be managed using Hanna’s product HI92000, Windows® Compatible Software.
STANDARD METHODS
Light Low: The instrument cannot adjust the light level. Please check
that the sample does not contain any debris.
Light High: There is too much light to perform a measurement. Please
check the preparation of the zero cuvette.
44 45
Description Range Method
Alkalinity 0 to 500 mg/L Colorimetric
Bromine 0.00 to 10.00 mg/L DPD
Calcium Hardness 0 to 500 mg/L Colorimetric
Chlorine, Free 0.00 to 5.00 mg/L DPD
Chlorine, Total 0.00 to 5.00 mg/L DPD
Copper, Free 0.00 to 5.00 mg/L Bicinchoninate
Copper, Total 0.00 to 5.00 mg/L Bicinchoninate
Cyanuric Acid 0 to 200 mg/L Turbidimetric
Iron 0.00 to 5.00 mg/L Phenantroline
Ozone 0.00 to 2.00 mg/L DPD
pH 6.5 to 8.5 pH Phenol Red
Windows® is registered Trademark of "Microsoft Co."
Page 24

ACCESSORIES
REAGENT SETS
HI 93701-01 100 free chlorine tests (powder)
HI 93701-03 300 free chlorine tests (powder)
HI 93701-F 300 free chlorine tests (liquid)
HI 93703-52 Glycine Powder, Optional Reagent for 100 tests
HI 93711-01 100 total chlorine tests (powder)
HI 93711-03 300 total chlorine tests (powder)
HI 93701-T 300 total chlorine tests (liquid)
HI 93711-03 300 total chlorine tests
HI 93702-01 100 free copper tests
HI 93702-03 300 free copper tests
HI 93702T-01 100 total copper tests
HI 93702T-03 300 total copper tests
HI 93710-01 100 pH tests
HI 93710-03 300 pH tests
HI 93716-01 100 bromine tests
HI 93716-03 300 bromine tests
HI 93720-01 100 Ca hardness tests
HI 93720-03 300 Ca hardness tests
HI 93721-01 100 iron tests
HI 93721-03 300 iron tests
HI 93722-01 100 cyanuric acid tests
HI 93722-03 300 cyanuric acid tests
HI 93755-01 100 alkalinity tests
HI 93755-03 300 alkalinity tests
HI 93755-53 Chlorine Remover
HI 93757-01 100 ozone tests
HI 93757-03 300 ozone tests
WARRANTY
All Hanna Instruments meters are warranted for two years against defects in workmanship and materials
when used for its intended purpose and maintained according to the instructions.
This warranty is limited to repair or replacement free of charge.
Damages due to accident, misuse, tampering or lack of prescribed maintenance are not covered.
If service is required, contact your dealer. If under warranty, report the model number, date of purchase,
serial number and the nature of the failure. If the repair is not covered by the warranty, you will be notified
of the charges incurred.
If the instrument is to be returned to Hanna Instruments, first obtain a Returned Goods Authorization Number
from the Customer Service Department and then send it with shipment costs prepaid. When shipping any
instrument, make sure it is properly packaged for complete protection.
To validate your warranty, fill out and return the enclosed warranty card within 14 days from the date of
purchase.
Recommendations for Users
Before using these products, make sure that they are entirely suitable for your specific application and for the environment in which they are used.
Operation of these instruments may cause unacceptable interferences to other electronic equipments, this requiring the operator to take all necessary steps to
correct interferences.
Any variation introduced by the user to the supplied equipment may degrade the instruments' EMC performance.
To avoid damages or burns, do not put the instrument in microwave ovens. For yours and the instrument safety do not use or store the instrument in hazardous
environments.
Hanna Instruments reserves the right to modify the design, construction and appearance of its products
without advance notice.
OTHER ACCESSORIES
HI 740226 5 mL graduated syringe
HI 731318 cloth for wiping cuvettes (4 pcs)
HI 731321 glass cuvettes (4 pcs)
HI 731325W new cap for cuvette (4 pcs)
HI 740034 cap for 100 mL beaker (6 pcs)
HI 740036 100 mL plastic beaker (6 pcs)
HI 740038 60 mL glass bottle and stopper
HI 740142 1 mL graduated syringe
HI 740143 1 mL graduated syringe (6 pcs)
HI 740144 pipette tip (6 pcs)
HI 740157 plastic refilling pipette (20 pcs)
HI 740220 25 mL glass cylinders with caps (2 pcs)
HI 92000 Windows compatible software
HI 920013 PC connection cable
HI 93703-50 Cuvette cleaning solution (230mL)
46 47
HANNA LITERATURE
Hanna publishes a wide range of catalogs and handbooks for an equally wide range of applications. The
reference literature currently covers areas such as:
• Water Treatment
• Process
• Swimming Pools
• Agriculture
• Food
• Laboratory
and many others. New reference material is constantly being added to the library.
For these and other catalogs, handbooks and leaflets contact your dealer or the Hanna Customer Service
Center nearest to you. To find the Hanna Office in your vicinity, check our home page at www.hannainst.com.
Page 25

Hanna Instruments Inc.
Highland Industrial Park
584 Park East Drive
Woonsocket, RI 02895 USA
Technical Support for Customers
Tel. (800) 426 6287
Fax (401) 765 7575
E-mail tech@hannainst.com
www.hannainst.com
Local Sales and Customer Service Office
Printed in EUROPE
(ROMANIA)
MAN83226 04/12
48
 Loading...
Loading...