Page 1
Instruction Manual
HI 38023
Total
Chlorine
Extended Range
SPECIFICATIONS
Range 10 to 200 mg/L (ppm) as Chlorine
Smallest Increment 10 mg/L as Chlorine
Analysis Method Drop count titration
Sample Size 1 mL
Number of Tests 100
Case Dimensions 235x175x115 mm (9.2x6.9x4.5")
Shipping Weight 547 g (19.3 oz.)
INSTRUCTIONS
READ THE ENTIRE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE USING THE KIT
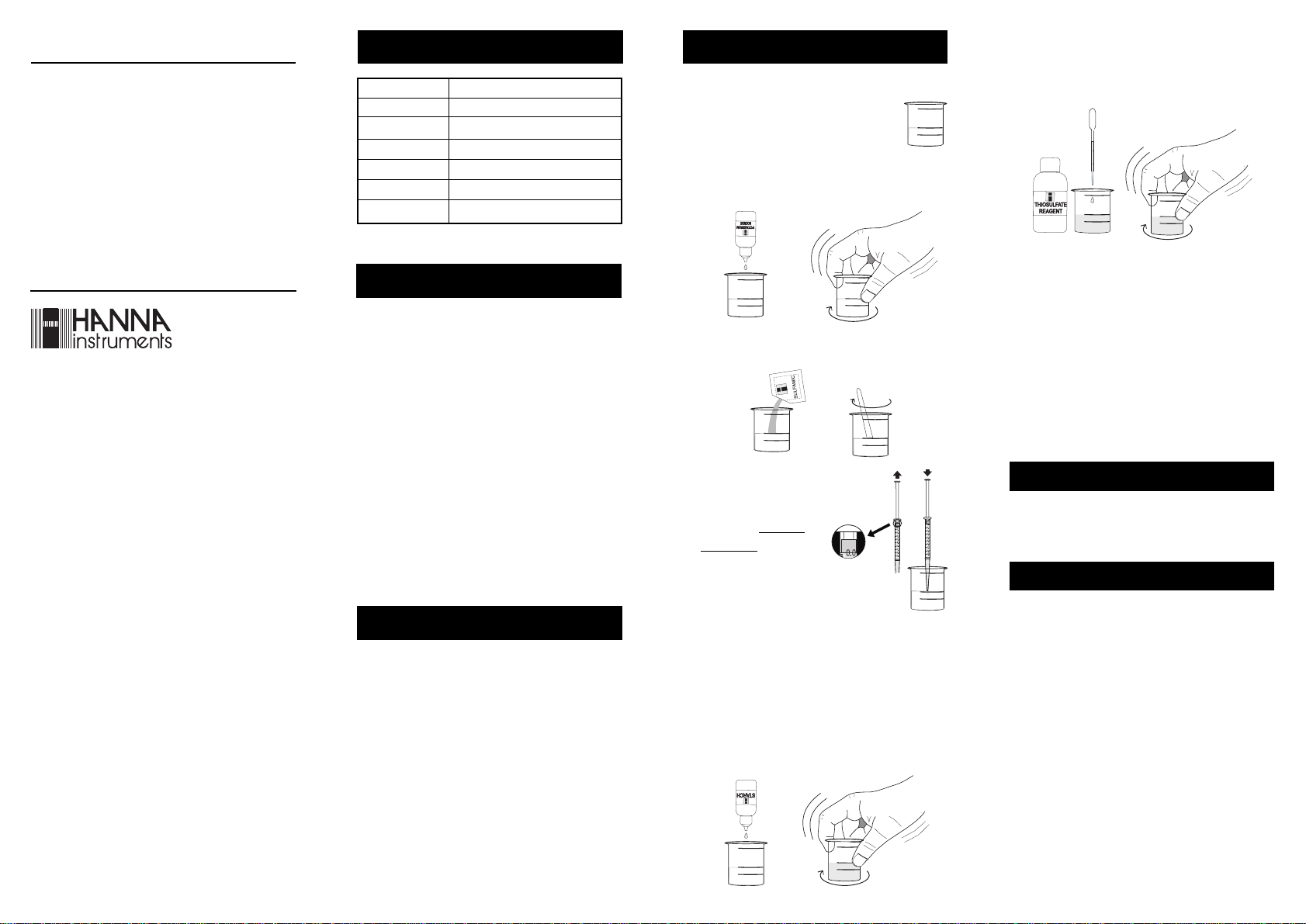
1- Fill the calibrated vessel with tap
water up to the 50 mL mark (the
residual chlorine in tap water will
not affect the test).
2- Add 5 drops of Potassium Iodide Solution and swirl
gently to mix.
50 mL
6- Using the 1 mL plastic pipette, add Thiosulfate Reagent
drop by drop, swirling after each drop, while keeping
an accurate count of the drops being added to the
solution.
Test Kit
www.hannainst.com
Dear Customer,
Thank you for choosing a Hanna Product.
Please read the instruction sheet carefully before using the
test kit. It will provide you with the necessary information
for correct use of the kit. If you need additional information,
do not hesitate to e-mail us at tech@hannainst.com.
Remove the chemical test kit from the packing material and
examine it carefully to make sure that no damage has
occurred during shipping. If there is any noticeable damage, notify your Dealer or the nearest Hanna office
immediately.
Each kit is supplied with:
Potassium Iodide Solution, 1 bottle with dropper (30 mL);
•
Sulfamic Reagent, packets (100 pcs);
•
• Starch Indicator, 1 bottle with dropper (25 mL);
Thiosulfate Reagent, 1 bottle (100 mL);
•
• 1 calibrated plastic vessel (50 mL)
• 1 syringe (1 mL) with tip;
• 1 plastic pipette (1 mL);
• 1 spoon.
;
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The chlorination of water supplies and polluted waters is
used mainly to destroy or deactivate disease-producing
microorganisms. It also serves to improve the quality of
drinking waters, as chlorine reacts with ammonia, iron,
manganese, sulfide and some organic substances.
Nevertheless high amounts of chlorine will produce adverse
effects, like formation of compounds which are potentially
carcinogenic (e.g. chloroform) or harmful to aquatic life
(e.g. chloramines). Thus it is essential to control that the
proper amount of chlorine has been added in order to
fulfill the primary purpose of disinfecting and to minimize
any adverse effect.
Note: mg/L is equivalent to ppm (parts per million).
CHEMICAL REACTION
An iodometric titration method is used. The water sample is
treated with potassium iodide and strongly acidified with
acid. The amount of iodine generated is equivalent to the
chlorine in the sample; the concentration of iodine is
calculated by titration with thiosulfate ions that reduce
iodine back to iodide ions.
3- Add 1 packet of Sulfamic Reagent and use the spoon to
mix and dissolve.
4- Use the syringe to add
1 mL of your sample to
the vessel, dispensing
the sample below the
solution level in the vessel.
Note: To measure exactly
1.0 mL of sample
with the syringe, push the plunger completely into
the syringe and insert the tip into sample. Pull the
plunger out until the lower edge of the seal is on the
0.0 mL mark of the syringe. Insert the syringe into
the vessel and push the sample out until the lower
edge of the seal is on the 1.0 mL mark.
5- Add 4 drops of Starch Indicator and swirl gently to mix.
If chlorine is present, the solution will turn a blue color.
7- Continue adding Thiosulfate Reagent until the solution
changes from blue to colorless.
8- To obtain the concentration in mg/L (or ppm) of total
chlorine in your sample, multiply by 10 the number of
drops of Thiosulfate Reagent used to turn the solution
from blue to colorless.
drops x 10 = mg/L Total Chlorine
REFERENCES
Standard methods for the Examination of Water and
Wastewater, 20th Ed., 1998, APHA-AWWA-WEF
HEALTH AND SAFETY
The chemicals contained in this kit may be hazardous if
improperly handled. Read the relevant Health and Safety
Data Sheet before performing this test.
Note: Any damaged or defective item must be returned in
its original packing materials.
ISTR38023 12/00 PRINTED IN ITALY
Page 2

 Loading...
Loading...