Garmin eTrex H User Manual

cGPSmapper User Manual
First Published Date: 2005-04-01
Version: 2.1
Published Date: 2006-08-13
Total Page Count: 100

cGPSmapper Manual Contents
1 Contents
1 CONTENTS .................................................................................................................. 2
2 INTRODUCTION ........................................................................................................ 5
2.1 PURPOSE OF THIS DOCUMENT .................................................................................. 5
2.2 BASIC CONCEPTS.....................................................................................................5
2.2.1 What is Polish Format (PFM)?...................................................................... 5
2.2.2 What is cGPSmapper?.................................................................................... 5
2.2.3 What is sendmap?........................................................................................... 5
2.3 DOCUMENT CONVENTIONS......................................................................................5
2.3.1 PFM Code ...................................................................................................... 5
2.3.2 cGPSmapper versions .................................................................................... 6
2.4 MANUAL AUTHORS .................................................................................................6
3 OVERVIEW .................................................................................................................7
4 MAP PROJECT ...........................................................................................................8
4.1 MAP CREATION .......................................................................................................8
4.2 PFM SYNTAX DESCRIPTION.....................................................................................8
4.2.1 Header ............................................................................................................ 9
4.2.2 Declarations ................................................................................................. 14
4.2.2.1 Countries........................................................................................................................................ 14
4.2.2.2 Regions .......................................................................................................................................... 14
4.2.2.3 Cities .............................................................................................................................................. 15
4.2.2.4 Chart Info....................................................................................................................................... 15
4.2.3 Advanced Declarations................................................................................. 17
4.2.3.1 Background.................................................................................................................................... 17
4.2.3.2 Dictionary ...................................................................................................................................... 17
4.2.3.3 Highways ....................................................................................................................................... 18
4.2.3.4 ZIP Codes....................................................................................................................................... 18
4.2.3.5 Definitions...................................................................................................................................... 18
4.2.4 Body (Objects) ..............................................................................................18
4.2.4.1 Point of Interest.............................................................................................................................. 18
4.2.4.2 Polygon .......................................................................................................................................... 20
4.2.4.3 Polyline .......................................................................................................................................... 22
4.2.4.4 Point of Interest from OziExplorer................................................................................................. 23
4.2.4.5 Polyline or Polygon from OziExplorer........................................................................................... 23
4.2.4.6 Shapes ............................................................................................................................................ 24
4.2.4.7 MapDekode file.............................................................................................................................. 28
4.2.4.8 File ................................................................................................................................................. 29
4.2.5 Object elevation............................................................................................ 29
4.2.6 Road numbers............................................................................................... 30
4.3 MARINE CHARTS ...................................................................................................31
4.4 LEVELS..................................................................................................................39
4.4.1 Introduction .................................................................................................. 39
4.4.2 Concepts and Terminology........................................................................... 40
4.4.3 Using levels when defining map objects....................................................... 42
4.4.3.1 Tailoring shape according to level. ................................................................................................ 43
4.4.4 Idiosyncrasies of GPS hardware ..................................................................44
4.5 DICTIONARY..........................................................................................................44
4.5.1 Introduction .................................................................................................. 44
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 2 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Contents
4.5.2 Concepts and Terminology........................................................................... 45
4.5.3 Using Dictionary .......................................................................................... 45
5 CREATING CUSTOM TYPE FILE ........................................................................47
5.1 CREATING THE SOURCE FILE.................................................................................. 47
5.2 CUSTOM TYPE DEFINITION.................................................................................... 50
5.3 PUTTING IT ALL TOGETHER .................................................................................... 57
6 MAPSOURCE ............................................................................................................61
6.1 MAPSOURCE DATA STRUCTURE ............................................................................61
6.2 CREATING PREVIEW MAP FILES.............................................................................. 61
6.3 MAKING THE REGISTRY ENTRIES ........................................................................... 61
6.4 LOADING THE MAPS INTO THE GPS .......................................................................63
7 FAQS ...........................................................................................................................65
7.1 NAME VARIABLES AND WHERE THEY SHOW UP...................................................... 65
7.1.1 Introduction .................................................................................................. 65
7.1.2 PFM File ...................................................................................................... 65
11.2.2 PFM Preview File ........................................................................................65
11.2.3 Sendmap ....................................................................................................... 66
7.2 ACTIVATION OF MAPS IN THE GPS......................................................................... 68
7.3 SAVING OBJECTS AS [RGNX0] VS. [POI], [POLYGON], [POLYLINE]............... 69
7.3.1 Equivalences................................................................................................. 69
7.3.2 Impact of saving objects in one format or the other..................................... 69
7.3.3 Preferred method.......................................................................................... 69
7.4 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LEVELS IN THE DETAIL MAPS AND THE PREVIEW MAPS...69
7.5 FILLING (GAS) STATIONS NOT SHOWING IN THE FIND FUNCTION OF THE GPS .......70
7.6 ISLANDS AND CLEARINGS......................................................................................70
8 GLOSSARY ................................................................................................................ 71
9 APPENDICES............................................................................................................. 72
9.1 CGPSMAPPER COMPILATION ERRORS AND WARNINGS.......................................... 72
9.2 EXITS..................................................................................................................... 76
9.2.1 Valid exit facility types .................................................................................76
9.2.2 Directions ..................................................................................................... 76
9.2.3 Facilities .......................................................................................................77
9.3 CGPSMAPPER OBJECT TYPES LIST..........................................................................77
9.3.1 [POI] types ................................................................................................... 77
9.3.2 [POLYLINE] types .......................................................................................88
9.3.3 [POLYGON] types........................................................................................ 90
9.3.4 Custom types name substitution ...................................................................92
9.3.5 How do I create XPM definitions? ............................................................... 93
9.4 CGPSMAPPER VERSIONS........................................................................................94
9.5 CGPSMAPPER FILES...............................................................................................96
10 INDEX AND TABLES........................................................................................... 97
10.1 TABLE OF FIGURES ................................................................................................97
10.2 VERSION CONTROL LOG........................................................................................ 97
10.3 INDEX ....................................................................................................................98
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 3 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Contents
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 4 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Introduction
2 Introduction
The latest version of this document can be found at http://www.cgpsmapper.com/.
Feel free to e-mail your comments / contributions to the present document to
manual@cgpsmapper.com.
2.1 Purpose of this document
This manual explains how to create vector maps and then upload them to your Garmin®
GPS receiver (or see them in the MapSource software), utilizing the cGPSmapper /
sendmap software.
2.2 Basic Concepts
2.2.1 What is Polish Format (PFM)?
Polish Format is a convenient, text based, format used for saving map information on a
computer and transferring map information between computer programs.
Polish format map files cannot be sent directly to a GPS unit. First they must be converted
into a format which is understandable to your GPS receiver. A program which performs
this conversion is called a "map compiler".
2.2.2 What is cGPSmapper?
cGPSmapper is a command line program which "compiles" files in polish format (PFM)
and produces a vector map in file(s) of a format understandable by your GPS receiver and
Garmin® MapSource.
There are different cGPSmapper versions (refer to section 9.3.4 on page 92) with diverse
features.
2.2.3 What is sendmap?
sendmap is a command line program used to transfer vector map files (generated with
cGPSmapper) to your GPS receiver.
2.3 Document Conventions
Text in italics is shown in the Glossary (page 71).
2.3.1 PFM Code
Text in monospace font represents literals (to be inserted literally in the PFM file).
Text in underlined monospace font represents metavariables - which appear to the
right of the equals sign (=) in many statements. Metavariables should be replaced with
appropriate values, as described in the explanation (or self-evident).
Text in normal font is explanatory and should not be inserted into the source file.
The number sign special metavariable (#) takes a numeric value. E.g. Data# stands for
Data0, Data1, etc.
The special iteration operator ... in a statement line has its intuitive meaning. This operator
in a separate line denotes that the preceding statement may be repeated zero or more times
with various (typically consecutive) values of the metavariable #. If the iteration operator is
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 5 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Introduction
preceded by a pair of statements with # metavariables, the whole pair should be repeated
(see specific statements for examples).
Text in orange colour (e.g. Name=) are mandatory statements in the given section. Text in
olive colour (e.g. Label=) are optional statements.
2.3.2 cGPSmapper versions
The table below contains the meaning of the different symbols used in this document to
represent the cGPSmapper Version to which a certain concept applies.
Symbol cGPSmapper Version
φ
σ
τ
π
Routable
The different cGPSmapper versions are explained in section 9.3.4, on page 92.
Freeware
Shareware
Standard
Pro
2.4 Manual Authors
This manual was written by Stanislaw Kozicki (the author of cGPSmapper), Gary Turner,
Graham Bowring, Hans Scheffler, Keith Sheppard, Greg Rikker and Mauricio Zalba.
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 6 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Overview
3 Overview
Creating a map to be uploaded to a GPS receiver may be compared to programming: you
write a program (i.e. a map) in the programming language (i.e. in PFM) and then compile
it. Alternatively - just as with programming - tools exist to generate the source code
visually or semi-automatically or to assist in other ways in the code preparation.
The source code format used by the cGPSmapper compiler is referred to as PFM (Polski
Format Mapy - Polish Map Format) or the "Polish format". The standard file extension for
maps in the PFM format is .mp (in previous versions, the .txt extension was used, which is
still acceptable, but not recommended).
A map consists of map objects which fall into four categories: POIs (points of interest, e.g.
hotel, restaurant), points (non-indexed point objects, e.g. summit, building), polylines
(linear objects, e.g. street, stream), and polygons (area objects, e.g. lake, forest). For nondimensional objects (POIs and points), it is necessary to define the object attributes, such as
label and type, as well as the object coordinate pair (latitude, longitude). For dimensional
objects (polylines and polygons), it is necessary to define the object attributes, as well as
coordinate pairs of all object vertices. Providing the coordinates is the most laborious part
of map authoring.
You may prepare the map source file (.mp) using various methods: by writing the complete
source code with any text editor, by generating it visually (by drawing on the screen) with
any visual editor, by importing objects (waypoints and tracks) created by the OziExplorer
mapping software, or by various combinations of those methods.
When you have finished your map, you can compile it with cGPSmapper (a number of
methods are available) and preview it after compilation. The standard file extension for
compiled maps is .img. Finally, you can upload the resulting compiled map file (.img) to
your GPS with sendmap or MapSource. All those operations and variants are described in
relevant sections below.
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 7 of 100
cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
4 Map Project
4.1 Map Creation
You write the source file in the PFM format (the .mp file) using any text editor. All maprelated information is provided in relevant statements. Then the map is compiled with the
cGPSmapper compiler and the resulting .img file is uploaded using sendmap or
MapSource.
The PFM format is described section 4.2 (PFM syntax Description), on page 8.
When you have finished your map (or at any time during the map creation process), you
may preview it on the computer screen. Some software packages allow you to preview
PFM format files directly. Alternatively you can compile it and preview the resultant .img
file using MapSource. Finally the .img file may be uploaded to your GPS.
4.2 PFM syntax Description
A PFM format file contains comment lines and statements. Blank lines are also permitted
A comment line starts with the ";" character. Comment lines and blank lines may appear at
anywhere in the file and are ignored1 by the compiler.
Statements are grouped into sections. Sections are identified with a section name, enclosed
between "[]" and finish with an [END] identifier.
[END-section_identifier] can also be used to finish a section. E.g. [IMG ID]
... [END-IMG ID], instead of [IMG ID] ... [END].
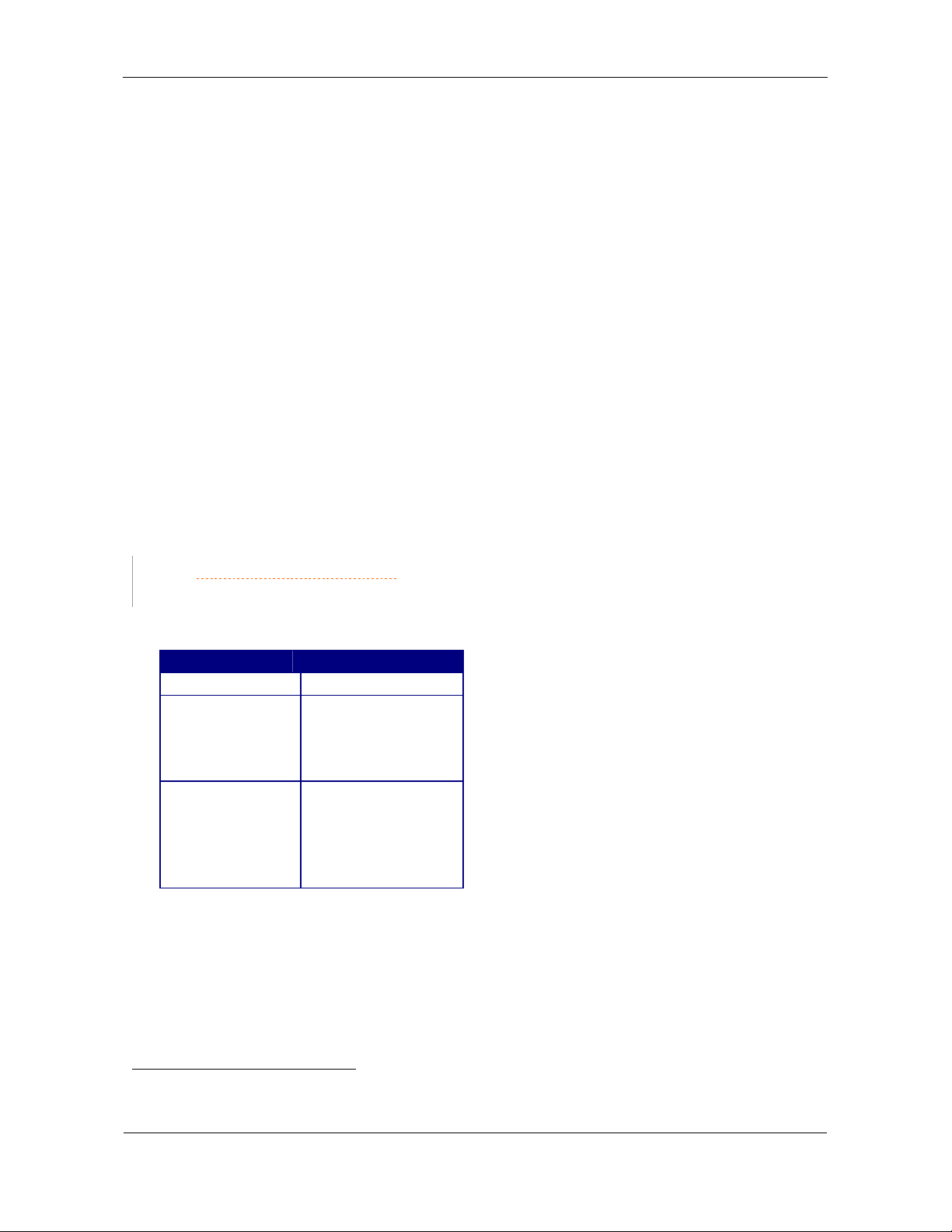
The following types of sections exist:
Section Type Identifier(s)
Header
Declarations
Advanced
Declarations
1
However, GPSMapEdit uses special syntax of comments to specify attachments and such
comments are interpreted by GPSMapEdit.
[IMG ID]
[COUNTRIES]
[REGIONS]
[CITIES]
[CHART INFO]
[DICTIONARY]
[BACKGROUND]
[HIGHWAYS]
[ZIPCODES]
[DEFINITIONS]
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 8 of 100
cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
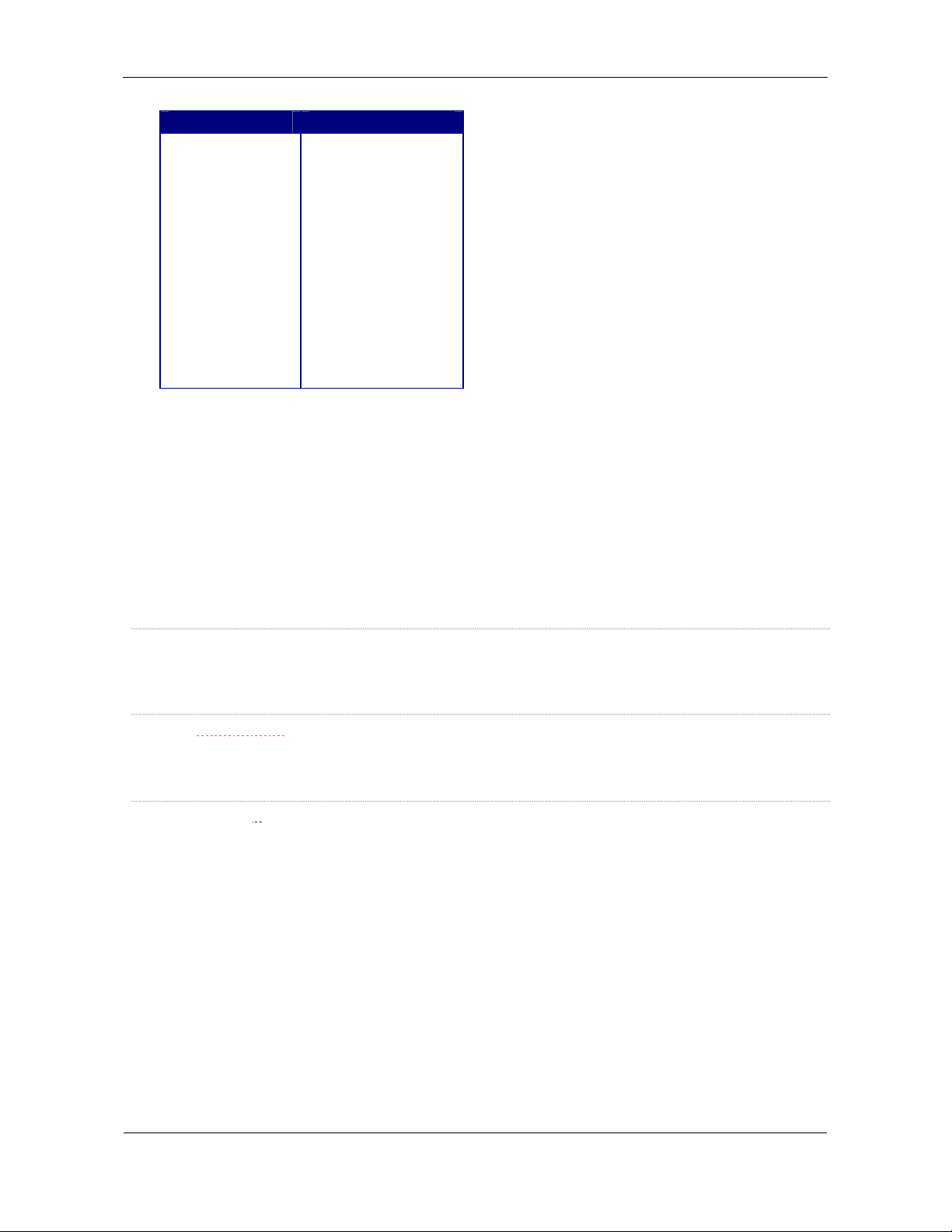
Section Type Identifier(s)
Body (Objects)
The header section is mandatory and must appear as the first section in the source file. All
other sections are optional. Declaration and advanced sections (if any) must appear after the
header section, in the order specified here. These sections cannot be repeated.
Objects must appear after declaration and advanced sections (if any), may be in any order,
and may be repeated as many times as necessary.
The order of statements in the section body (i.e. between the section keyword statement and
the [END] statement) is insignificant.
[POI]
[POLYLINE]
[POLYGON]
[PLT]
[WPT]
[DBX]
[SHP]
[FILE]
[RGN10]
[RGN20]
[RGN40]
[RGN80]
4.2.1 Header
[IMG ID]
ID=########
Name=map_name
LBLcoding=x
Section identifier
Unique identifier (up to 8 decimal digits) for the map.
May be only written in a decimal format
11000204
Map name to be displayed in the GPS receiver's Map Info
menu.
Refer to section 7.1 (on page 65) for details.
80 characters maximum.
6 compressed label coding (smallest maps)
9 full-byte (8-bit) coding (supports national
characters, depending on the GPS firmware)
10 Unicode / MBCS (depending on the GPS
firmware)
Default = 6
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 9 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
Codepage=xx
Datum=xxx
Transparent=x
MG=x
Numbering=x
π
Routing=x
0 full-byte (8-bit) character coding with the
specified codepage is used (depending on the GPS
firmware)
0 single-byte coding
Note: All labels must be written in CAPITALS if a codepage
is used
Note: The delimiters for road numbers ( refer to section
4.2.6, on page 30, for details) are different if full-byte coding
is used.
Note: Special codes are different for 8-bit coding!
Default = 0
W84 WGS-84
Custom Custom
dx, dy, dz, semiMajorAxis, invFlattening
E.g. for (for WGS84): Custom: 0,0,0,6378137.000,
298.257223563
W84 & Custom refer to the
Datum_List.txt file (in the cGPSmapper directory)
for the full list of supported datums
Default = W84
Y a transparent map will be created
N a transparent map will not be created
Default = N
When a transparent map is displayed on a GPS unit, features
in the unit's basemap will also be visible. If your map is not
transparent, it will obscure the basemap when visible.
Lock on road, search for intersection and show next street
name active:
Y Yes
N no
Default = N
Lock on road, show next street name and house numbers
along street active:
Y Yes
N no
Default = N
Lock on road, show next street name active, house numbers
along street and routable maps active:
Y Yes
N no
Note: for routable maps a special data format required!
Default = N
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 10 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
Lock=x
Final IMG file will require unlock code specific for each
GPS device.
Y Yes
N no
Default = N
ProductCode=x
Subfamily identifier used for locked IMG files only – value
between 1 and 255. Each subfamily can be unlocked with
universal unlock code or separately with individual unlock
code.
Default = 1
CopyRight=xxxxxxx
τ
π
Elevation=x
Text visible in welcome page of GPS.
Refer to section 7.1 (on page 65) for details.
80 characters maximum.
m metres
f feet
Default = f
POIOnly=x
Generate map with only POI and cities2:
Y Yes
N no
Default = N
POIIndex=x
σ
τ
π
N objects will be indexed only if POI index info is
explicitly provided
Y all POI objects will automatically be indexed (may
be searched by the Find function in the GPS)
Default = N
POINumberFirst=x
τ
π
POIZipFirst=x
τ
π
N the house number will be after the street name
Y the house number will be before the street name
Default = Y
N the ZIP code will be after the street name
Y the ZIP code will be before the street name
Default = Y
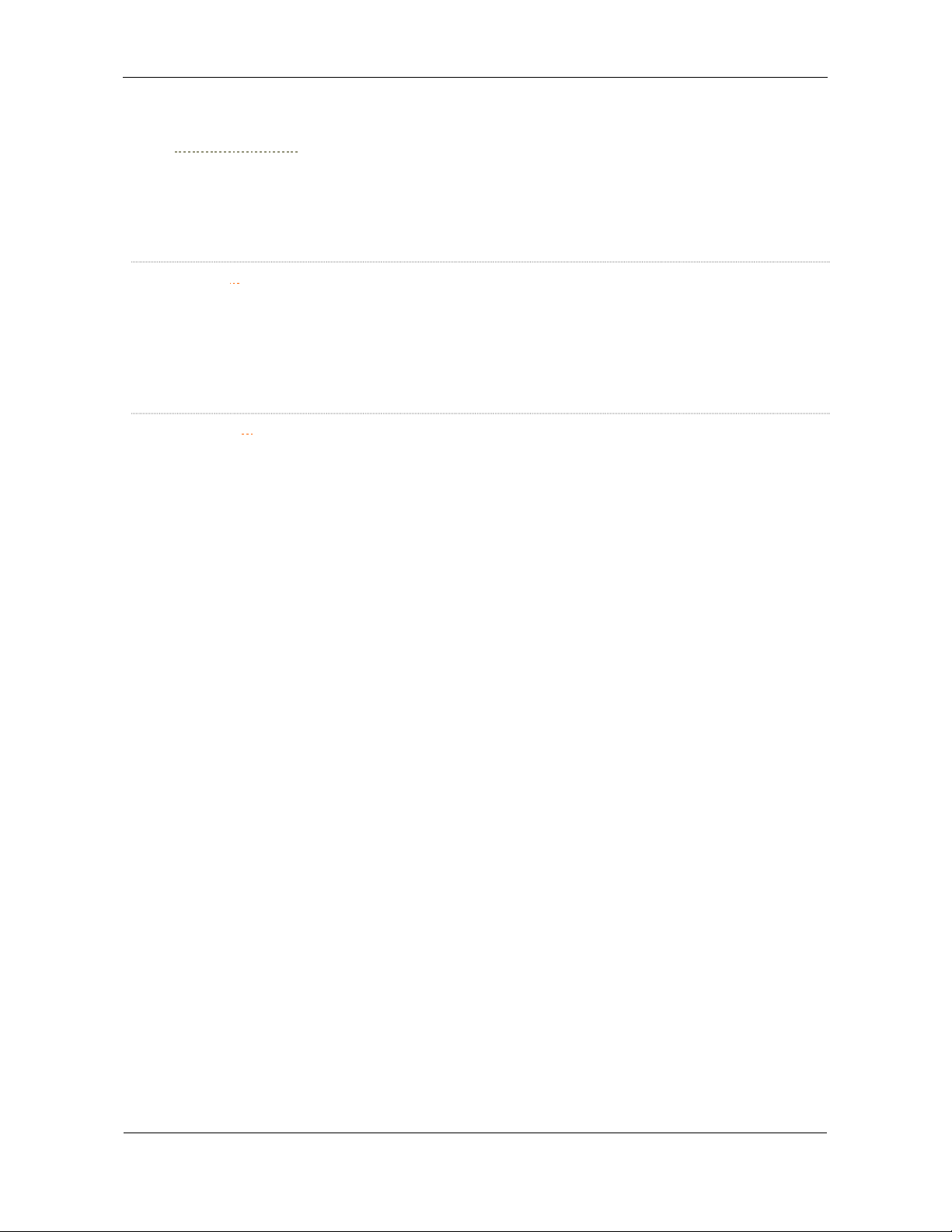
DefaultCityCountry
σ
=country_name
τ
π
Should be used in conjunction with
DefaultRegionCountry.
Defines the default region name for automatic city indexing.
If not defined, cities will be indexed only if city index info is
explicitly provided.
80 characters maximum.
2
Same effect if switch -i is used.
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 11 of 100
cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
DefaultRegionCount
σ
ry=region_name
τ
π
TreSize=n
RgnLimit=n
Should be used in conjunction with
DefaultCityCountry.
Defines the default country name for automatic city
indexing.
If not defined, cities will be indexed only if city index info is
explicitly provided.
80 characters maximum.
Maximum allowed region size. A higher value increases the
allowable region size, but may decrease the map
performance; a lower value may increase the map size.
Suggested values:
topo maps: 1000-2000
city (dense streets): 2000-5000
countryside: 6000-10000
Maximal number of elements in one region.
Can be any value between ~50 and 1024 (values less than 50
don't make sense).
Recent experiments show that this parameter does not impact
map performance and can be set to maximum allowed value:
1024.
Suggested value:
1024
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 12 of 100
cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
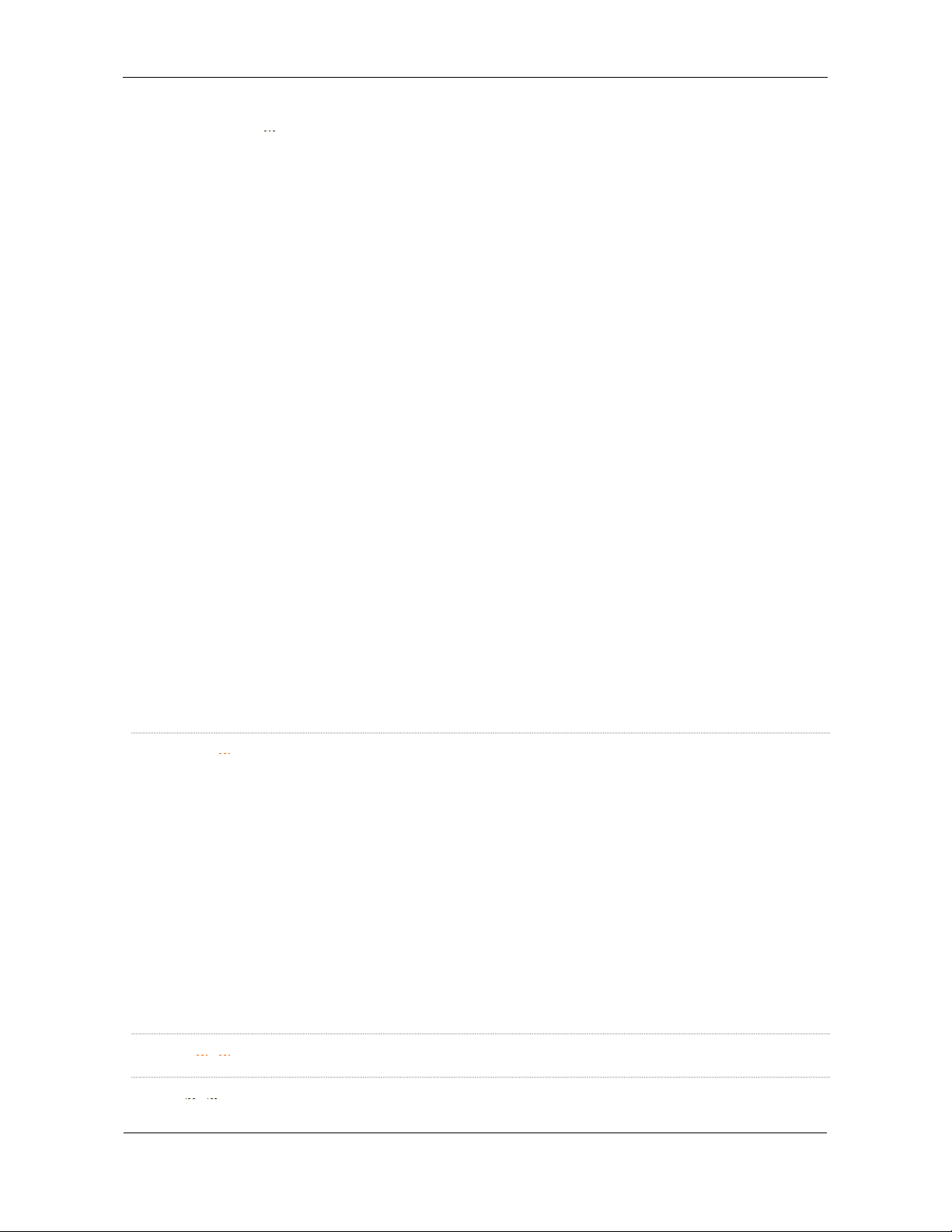
PreProcess=x
Levels=n
Level#=g
Zoom#=#
Kind of pre-processing:
G generalization only (faster method, but 'crossroad'
nodes might be removed).
Also the nodes from intersections may be removed.
Data will be simplified using Douglas-Peucker polyline
simplification algorithm which will ensure that the output
is not jagged.
F (or Y) full generalization + intersection detection.
Unnecessary nodes are not removed if there are
intersections (this is important for more advanced maps -
at intersections, all the intersecting roads have to have
nodes or 'find intersection' won't work).
This is very similar to 'G' with one important exception -
all intersection points of the roads are preserved too
(even if according to the simplification algorithm these
points should be reduced) - this is especially important
when we are interested in using 'find intersection'
functionality.
N no generalization and no intersection detection.
Unnecessary nodes (from the resolution point of view)
will be removed automatically.
There will be no reduction of the 'oversampled' points in
the objects - the only reduction of the points will be done
because of alignment to the same coordinates.
This option should be used if input data is prepared
separately for each layer - the data for each layer having
already been adjusted to the map author's requirements.
Used only if you explicitly provide data for all layers.
Default = F
Refer to section 4.4 (on page 39) for details.
Number of levels (layers) in the map (at least 2, not more
than 10).
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Note: the last layer must always be empty, e.g. Levels=3
means that two layers only are available for map objects.
Grid size for layer # (layer 0 is the most detailed one).
Refer to section 4.4 (on page 39) for details.
Refer to section 4.4 (on page 39) for details.
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 13 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
Preview=x
AlignMethod
BlockSize
LevelFill
LevelLimit
WorldMap
DrawPriority=#
Marine=x
[END]
Refer to section 6.2 (Creating preview map files), on
page 61, for details.
N map designated for use with GPS will be created
Y map designated for use as preview map for
MapSource will be created
Default = N
No longer used / supported.
No longer used / supported.
No longer used / supported.
No longer used / supported.
No longer used / supported.
Value between 1 and 255 indicating the priority used by the
GPSr to draw the map. The GPSr will show first the maps
with lower numbers.
Default = 25.
Indicates if the map is of marine type.
N or 0 non-marine map
Y or 1 marine map
Default = N.
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
Section terminator.
4.2.2 Declarations
The DECLARATION elements must be in the order shown herewith.
4.2.2.1 Countries
Although this section is obsolete, it is still supported.
[COUNTRIES]
Country#=country_n
ame~[0x1d]abbrevia
tion
...
[END]
Declares all countries used for city indexing
Name and abbreviation used to identify country #.
The first # must always be one.
E.g.: Country1=United States~[0x1d]US
80 characters maximum.
The statement above can be repeated as needed.
# must be in ascending order.
Section terminator
4.2.2.2 Regions
Although this section is obsolete, it is still supported.
[REGIONS]
Region#=region_nam
e~[0x1d]abbreviati
on
Declares all regions used for city indexing
Name and abbreviation used to identify region #.
The first # must always be one. Subsequent # must be
ordered ascending.
E.g.: Region1=New York~[0x1d]NY
80 characters maximum.
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 14 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
CountryIdx#=countr
y_index
The country_index represents the number in the
corresponding Country# statement.
The first # (CountryIdx) must always be one.
Subsequent3 # must be in ascending order.
If included, there must be at least 1 region per country. In
theory, the limit is 13,107.
E.g.: CountryIdx1=1, means that the current region is located
in country 1 (right side of the equals sign).
...
[END]
The statements above can be repeated as needed.
Section terminator.
4.2.2.3 Cities
Although this section is obsolete, it is still supported.
[CITIES]
City#=ciy_name
RegionIdx#=region_
index
...
[END]
Declares all cities used for indexing
Name used to identify the city #.
The first # must always be one. Subsequent # must be in
ascending order.
E.g.: City1=New York
80 characters maximum.
The region_index represents the number in the
corresponding Region# statement.
The first # (RegionIdx) must always be one. Subsequent4
# must be in ascending order.
If included, there must be at least 1 city per Region. In
theory, the limit is 13,107.
E.g.: RegionIdx1=1, means that the current city is located in
Region 1 (right side of the equal sign).
The statements above can be repeated as needed.
Section terminator.
4.2.2.4 Chart Info
[CHART INFO]
Name=xxx
Number=xxx
Projection=xxx
Published=xxx
Scale=###
3
Unlikely, since each region normally is located in a single country.
4
Unlikely, since each city normally is located in a single region.
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 15 of 100
Declarations for marine charts, attached to the 'marine chart'
object - which is created automatically as well (similar to the
background object) - and also attached to the 'marine border'
line.
This section should only be present if in the [IMG ID]
section, there is a definition Marine=Y
Chart Name (e.g. La Plata to Nueva Palmira).
Chart Code (e.g. Gb3561(a)).
Chart Projection (e.g. Mercator).
Place where the chart was published (e.g. United Kingdom).
Map scale (e.g. 1:100000).

cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
DeltaSN=###
DeltaWE=###
IALA=x
Print=mmyyyy
Edition=mmyyyy
Correction=ddmmyyy
y
Text=xxx
σ
τ
π
TextFile=file_name
σ
τ
π
Longitude Delta.
Latitude Delta.
IALA system. The areas that use the 'B' system are the
Americas, Japan and the Philippines. The remainder of the
world uses the 'A' system.
A
B
Default = A
Paper chart print date.
Note that MapSource will show the day as "01" (the day
field is not available in the GPS).
Paper chart edition date.
Note that MapSource will show the day as "01" (the day
field is not available in the GPS).
Paper chart correction date.
Very long description / information.
There could be several Text entries in a single object.
16kb maximum (each entry).
File containing a very long description / information.
There could be several TextFile entries in a single object.
The path could be either
absolute or
relative to the current directory.
For platform portability, it is recommended to use slashes "/"
instead of backslashes "\" to separate directories in the path.
In Unix, file_name is case sensitive.
16kb maximum (each entry).
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 16 of 100
cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
ReferenceEllipsoid
=###
[END]
Reference Ellipsoid.
0 Krassovsky
1 Airy
2 Modified Airy
3 Australian National
4 Bessel 1841
5 Bessel 1841 (Namibia)
6 Clarke 1866
7 Clarke 1880
8 Everest (Brunei)
9 Everest (India 1830)
10 Everest (India 1956)
11 Everest (W Malaysia 1948)
12 Everest (W Malaysia 1969)
13 Modified Everest
14 Fischer 1960/Mercury
15 Modified Fischer 1960
16 Fischer 1968
17 GRS 1967
18 GRS 1980
19 Helmert 1906
20 Hough
21 International
22 South American 1969
23 WGS-60
24 WGS-66
25 WGS-72
26 WGS-84
27 Unknown
Section terminator.
4.2.3 Advanced Declarations
The ADVANCED DECLARATIONS elements must be in the order shown herewith.
4.2.3.1 Background
[BACKGROUND]
Name=file_name
[END]
τ π Declares a custom shape for the map – another way to
define a custom shape for the map is to use a [POLYGON]
section (or [RGN80]) as described in section 4.2.4.2 .
Name of the ESRI file without extension
This should be the full or relative path for the ESRI file,
without the extension (which should be .shp for files
containing ESRI data)
Section terminator.
4.2.3.2 Dictionary
[DICTIONARY]
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 17 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
Level#RGNnn=bitmas
k
[END]
Refer to section 4.5 (on page 44) for details.
bitmask mask used to show / hide the objects.
# level on which the bitmask is applied.
nn type of object to which the bitmask is applied.
Section terminator.
4.2.3.3 Highways
This section will be further documented in a future version of this manual.
[HIGHWAYS]
[END]
Section terminator.
4.2.3.4 ZIP Codes
Although this section is obsolete, it is still supported.
This section will be further documented in a future version of this manual.
[ZIPCODES]
[END]
Section terminator.
4.2.3.5 Definitions
This section will be further documented in a future version of this manual.
[DEFINITIONS]
[END]
Section terminator.
4.2.4 Body (Objects)
BODY objects may be specified in any order.
4.2.4.1 Point of Interest
[POI]
Type=object_type
SubType=object_typ
e
Point of interest section identifier. [RGN10] (meaning point
of interest) and [RGN20] (meaning point) may be used
instead.
Type of element, may be written in hex or decimal or as a
name (valid names are defined in file RGNtyps.txt which
you can customised to your requirements).
SubType defines the second byte of the Type value.
The type of element can be defined either by using the Type
key only or by using the Type and SubType keys.
Example:
Type=0x0211
can be also written as:
Type=0x02
SubType=0x11
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 18 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
City=x
Indicates if the POI is a city.
Only used if the [POI] alias is used.
N or 0 not a city (instead of [RGN10])
Y or 1 city (instead of [RGN20])
Default = N
Label=object_name
Name of the object to be shown on the map.
80 characters maximum.
EndLevel=#
Refer to section 4.4 (on page 39) for details.
The coordinates in the lowest numbered Data# line apply
up to the specified EndLevel=#.
Data#=(lat,lon)
Origin#=(lat,lon) may be used instead.
Object data for layer #.
Refer to section 4.4 (on page 39) for details.
Coordinates are in degrees, using the datum defined in the
header5 (or default).
StreetDesc=xxx
Applies to [RGN10] only.
Address for the [RGN10] object.
80 characters maximum.
OvernightParking=x
Applies to [RGN10] only.
Indicates if 24 hr parking is allowed.
N or 0 No
Y or 1 POI at the exit of a highway will have an
'overnight parking' flag.
Default = N
Highway=xxx
Applies to [RGN10] only.
Name of the Highway.
This name will be added to the list of available highways, so
it can be searched in some GPS devices.
Garmin does not support this feature.
80 characters maximum.
CityName=xxx
σ
τ
π
For [RGN20] CityName has the same meaning as Label.
If both Label and CityName are provided, the one which
appears later in the file is used.
For [RGN10] CityName is the name of the city to which
the object belongs.
Can be used only together with keys RegionName and
CountryName.
80 characters maximum.
RegionName=xxx
σ
τ
π
Name of region to which the object belongs.
Can be used only together with keys CityName and
CountryName.
80 characters maximum.
5
Refer to section 4.2.1, on page 9, for further details.
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 19 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
CountryName=xxx
σ
τ
π
Zip=xxx
σ
τ
π
Exit#=(type_of_exi
t_facility),(direc
tion_to_facility),
(facilities),(labe
l)
[END]
4.2.4.2 Polygon
[POLYGON]
Type=object_type
SubType=object_typ
e
Label=object_name
EndLevel=#
Name of country to which the object belongs.
Can be used only together with keys RegionName and
CityName.
80 characters maximum.
Object Zip Code.
80 characters maximum.
Applies to [RGN10] only.
Additional facilities available at the exit.
+ type_of_exit_facility
+ direction_to_facility
+ facilities
+ label
Integer hex or decimal values as indicated on section 9.2
(Exits), on page 76.
80 characters maximum.
Section terminator.
Polygon section identifier. [RGN80] may also be used
instead. It is used to define lakes, parks, forests, etc.
Refer to section 4.2.4.1 (on page 18) for details.
SubType defines the second byte of the Type value.
The type of element can be defined either by using the Type
key only or by using the Type and SubType keys.
Example:
Type=0x0211
can be also written as:
Type=0x02
SubType=0x11
Refer to section 4.2.4.1 (on page 18) for details.
Refer to section 4.2.4.1 (on page 18) for details.
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 20 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
Background=x
Declare the custom shape of the map.
The background object defines the area of the basemap
which is covered by this map.
It is recommended that background be only used with maps
which have irregular boundaries.
If there is only one object set as the background, then the
EndLevel is automatically set to 9.
If there is no background object, or more than one, then the
EndLevel is not changed.
''It is a common mistake to use a background object when
defining an island. An island is implemented simply as a
hole in the containing polygon. Refer to section 7.6 for
details. To create a background object in the shape of the
island is quite wrong.
A background object is not a 'land'. It should only be
used to describe the total area covered by your map.
Most maps do not require the use of this object at all!
The only exception is when you want to create map
with an irregular boundary. In which case you should
create ONLY ONE BACKGROUND OBJECT
which covers the whole map.
If you create a lot of background objects - don't be
surprised that map is 'strange', slow etc...
N No
Y Yes
Default = N
Data#=(lat1,lon1),
(lat2,lon2)...
Origin#=(lat1,lon1),(lat2,lon2) may be used
instead.
Object data for layer #.
Refer to section 4.4 (on page 39) for details.
Coordinates are in degrees, using the datum defined in the
header6 (or default).
Normally there will be no more than one data# line for each
level. The exception is when creating a polygon with holes in
it. Holes in polygons are used to represent islands in lakes or
seas, clearings in woods etc.
Refer to section 7.6 for information on creating polygons
with holes.
[END]
Section terminator.
6
Refer to section 4.2.1, on page 9, for further details.
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 21 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
4.2.4.3 Polyline
[POLYLINE]
Type=object_type
SubType=object_typ
e
Label=object_name
Label2=object_name
EndLevel=#
Data#=(lat1,lon1),
(lat2,lon2)...
StreetDesc=xxx
DirIndicator=x
CityName=xxx
σ
τ
π
RegionName=xxx
σ
τ
π
CountryName=xxx
σ
τ
π
Zip=xxx
σ
τ
π
RoadID=xxx
Numbers#=xxx
π
Polyline section identifier. [RGN40]may also be used
instead. It is used to define linear objects such as streets,
streams, etc.
Refer to section 4.2.4.1 (on page 18) for details.
SubType defines the second byte of the Type value.
The type of element can be defined either by using the Type
key only or by using the Type and SubType keys.
Example:
Type=0x0211
can be also written as:
Type=0x02
SubType=0x11
Refer to section 4.2.4.1 (on page 18) for details.
Secondary name of the object –only applies to roads.
Refer to section 4.2.4.1 (on page 18) for details.
Refer to section 4.2.4.2 (on page 20) for details.
Street alias or secondary street name.
80 characters maximum.
Show direction of the road when selecting intersection in
GPS
0 No
1 Yes
Default = 0
Name of city to which this object belongs.
Can be used only together with keys RegionName and
CountryName.
80 characters maximum.
Name of region to which this object belongs.
Can be used only together with keys CityName and
CountryName.
80 characters maximum.
Name of country to which this object belongs.
Can be used only together with keys RegionName and
CityName.
80 characters maximum.
Object Zip Code.
80 characters maximum.
Refer to section 4.2.6 (on page 30) for details.
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 22 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
Routeparam=xxx
NodID#=xxx
[END]
Section terminator.
4.2.4.4 Point of Interest from OziExplorer
[WPT]
RgnType=object_cat
egory
Type=object_type
EndLevel=#
File#=file_name
[END]
Point of interest section identifier, with data imported from
an OziExplorer .wpt file.
The object labels are derived from the waypoint description
field, not from the waypoint name field
0x10 POI
0x20 point
Refer to section 4.2.4.1 (on page 18) for details.
Refer to section 4.2.4.1 (on page 18) for details.
.wpt file from which data will be imported to layer #.
The path could be either
absolute or
relative to the current directory.
For platform portability, it is recommended to use slashes "/"
instead of backslashes "\" to separate directories in the path.
In Unix, file_name is case sensitive.
Section terminator.
4.2.4.5 Polyline or Polygon from OziExplorer
[PLT]
RgnType=object_cat
egory
Type=object_type
Label=object_name
DirIndicator=#
EndLevel=#
Polygon / Polyline section identifier, with data imported
from an OziExplorer .plt file.
0x40 polyline
0x80 polygon
Refer to section 4.2.4.1 (on page 18) for details.
Refer to section 4.2.4.1 (on page 18) for details.
If the track imported in the [PLT] section contains multiple
segments (i.e. objects), all segments will take the same label
(name), as defined by the Label statement. However, it is
possible to give a different name to each segment. To
achieve this, omit the Label statement and specify the names
in an additional file, which should have the same name as the
.plt file (including the extension) and the additional
extension .txt, e.g. Highways.plt.txt). The file must be in the
same directory as the .plt file. Each line in this file specifies
the name for the corresponding track segment.
Direction indicator, only for streets, highways, etc.
0 no direction
1 the GPS will show direction of the road (calculated
internally by GPS)
Default = 0
Refer to section 4.2.4.1 (on page 18) for details.
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 23 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
File#=file_name
[END]
.plt file from which data will be imported to layer #.
The path could be either
absolute or
relative to the current directory.
For platform portability, it is recommended to use slashes "/"
instead of backslashes "\" to separate directories in the path.
In Unix, file_name is case sensitive.
Section terminator.
4.2.4.6 Shapes
[SHP]
σ
τ
π
name=file_name
Type=xxx
LabelField=field_n
ame
Label2Field=field_
name
TypeField=field_na
me
SubTypeField=field
_name
ESRI shape file section identifier.
Name of the ESRI files without extension.
This should be the full or relative path for the ESRI files,
without the extension (which should be .shp for files
containing ESRI data).
Type of objects to be imported from the ESRI files
16 or RGN10 POI
32 or RGN20 cities
64 or RGN40 lines
128 or RGN80 polygons
2 or RGN02 marine polygons
3 or RGN03 marine lines
4 or RGN04 marine points
Name of the field - in the associated .dbf file - from which
cGPSmapper will get the Label for each object.
Secondary name for roads. Used in cases where you want a
road to have a numeric ID and a name.
The secondary name of the road (road number if highway for
example) - is not visible in the GPS but is used when
searching street by name.
Name of the field - in the associated .dbf file - from which
cGPSmapper will get the object_type for each object.
The field_name field must contain a decimal or
hexadecimal value representing the object type.
If both DefaultType and TypeField are specified, an
error occurs, but at least one of them must be specified.
Refer to section 4.4 (on page 39) for details on the valid
object types.
Name of the field – in associated .dbf file – from which
cGPSmapper will get the second byte of the object_type
this is an optional field because the object_type can be
defined using only TypeField
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 24 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
DirField=field_nam
e
N or 0 Hide street direction on crossroads
Y or 1 Show street direction on crossroads
Default = N
Level=#
EndLevel=#
Level into which objects will be imported.
Refer to section 4.4 (on page 39) for details.
The coordinates from Level=# line apply up to the
specified EndLevel=#.
DefaultType=object
_type
Decimal or hexadecimal value representing the object type to
be applied when the TypeField is not specified.
If both DefaultType and TypeField are specified, an
error occurs, but at least one of them must be specified.
Refer to section 4.4 (on page 39) for details on the valid
object types.
CityName=field_nam
σ
e
τ
π
Name of the field - in the associated .dbf file - from which
cGPSmapper will get the CityName for each object.
Only used for polylines (i.e. when Type=RGN40 or
Type=64) and POIs (i.e. when Type=RGN20 or Type=32
or Type=RGN10 or Type=16).
RegionName=field_n
σ
ame
τ
π
Name of the field - in the associated .dbf file - from which
cGPSmapper will get the RegionName for each object.
Should not be present if the DefaultRegionCountry
element is present in the [IMG ID] section.
Only used for polylines (i.e. when Type=RGN40 or
Type=64) and POIs (i.e. when Type=RGN20 or Type=32
or Type=RGN10 or Type=16).
CountryName=field_
σ
name
τ
π
Name of the field - in the associated .dbf file - from which
cGPSmapper will get the CountryName for each object.
Should not be present if the DefaultCityCountry
element is present in the [IMG ID] section.
Only used for polylines (i.e. when Type=RGN40 or
Type=64) and POIs (i.e. when Type=RGN20 or Type=32
or Type=RGN10 or Type=16).
HouseNumber=field_
τ
name
π
StreetDesc=field_n
τ
ame
π
House number written as a string.
Used for address search and routing.
Only used for POIs (Type=RGN10 or Type=16).
Street name or additional description.
Only used for POIs (Type=RGN10 or Type=16).
PhoneNumber=field_
τ
name
π
Phone number written as a string.
Only used for POIs (Type=RGN10 or Type=16).
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 25 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
Zip=field_name
τ
π
RoadID=field_name
SpeedType=field_na
me
RoadClass=field_na
me
OneWay=field_name
Toll=field_name
VehicleE=field_nam
e
VehicleD=field_nam
e
VehicleC=field_nam
e
VehicleB=field_nam
e
VehicleT=field_nam
e
VehicleP=field_nam
e
Name of the field - in the associated .dbf file - from which
cGPSmapper will get the Zip for each object.
Only used for polylines (i.e. when Type=RGN40 or
Type=64) and POIs (Type=RGN10 or Type=16).
Unique ID number for the road. This is internally used by
cGPSmapper to maintain routing data creation.
Used for routing.
This attribute defines the maximum allowed speed - it is
used mainly for calculating fastest possible route.
There are 8 of them:
7 128 km/h
6 108 km/h - Can be adjusted in MapSource
5 93 km/h - Can be adjusted in MapSource
4 72 km/h - Can be adjusted in MapSource
3 56 km/h - Can be adjusted in MapSource
2 40 km/h - Can be adjusted in MapSource
1 20 km/h
0 8 km/h (ferry)
Used for routing.
This attribute defines the importance of the road for routing.
It is one of the most important attributes for routing.
The lowest importance is 0, the highest is 4.
Road class 4 should be used for Major highways and other
main roads.
Used for routing.
1 one way road, where the permitted direction is
always from the beginning of the road to the end,
considering the digitalisation direction.
-1 one-way road, opposite to the digitalisation
direction.
0 two-way road.
Used for routing.
Defines that it is a toll road.
1 no emergency vehicles allowed on the road.
1 no delivery vehicles allowed on the road.
1 no cars allowed on the road.
1 no buses allowed on the road.
1 no taxis allowed on the road.
1 no pedestrians allowed on the road.
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 26 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
VehicleI=field_nam
1 no bicycles allowed on the road.
e
VehicleR=field_nam
1 no trucks allowed on the road.
e
TextFileLines=fiel
d_name
TextStart=line_num
Name of the file with long text for very long description of
the object
Starting line number from TextFileLines file to be imported
ber
TextEnd=line_numbe
Ending line number from TextFileLines file to be imported
r
TextFile=file_name
Color=field_name
Style=field_name
Height=field_name
Depth=field_name
DepthUnit=field_na
Text file name to be imported
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
me
HeightUnit=field_n
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
ame
Position=field_nam
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
e
DepthFlag=field_na
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
me
FoundationColor=fi
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
eld_name
Light=field_name
LightType=field_na
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
me
Note=field_name
σ
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
τ
π
LocalDesignator=fi
σ
eld_name
τ
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
π
InternationalDesig
σ
nator=field_name
τ
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
π
Period=field_name
σ
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
τ
π
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 27 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
HeightAboveFoundat
σ
ion=field_name
τ
π
HeightAboveDatum=f
σ
ield_name
τ
π
HeightAboveFoundat
σ
ionUnit=field_name
τ
π
HeightAboveDatumUn
σ
it=field_name
τ
π
LeadingAngle=field
σ
_name
τ
π
Racon=field_name
σ
τ
π
DoubleLights=field
σ
_name
τ
π
DoubleLightsHorizo
σ
ntal=field_name
τ
π
FacilityPoint=fiel
d_name
[END]
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
Refer to section 0 (on page 30) for details.
Section terminator.
4.2.4.7 MapDekode file
This section will be further documented in a future version of this manual.
[DBX]
name=file_name
[END]
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 28 of 100
Name of a MapDekode file (including extension) to be
processed in the current compilation.
Section terminator.
cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
4.2.4.8 File
[FILE]
name=file_name
[END]
4.2.5 Object elevation
By default, the elevation is defined in feet in PFM. To define the elevation in metres, the
Elevation=m statement should be defined in the header section ( refer to section
4.2.1 on page 9). Since this is a global definition, all elevations on a map must be in the
same units (either all in feet or all in metres).
Elevation can be specified for POI objects like summit (Type 0x6616) and depth / height
points (Types 0x6200 & 0x6300) as well as for polyline objects like land / depth contours
(Types=0x20 to 0x25).
The elevation is entered in the label field of the objects. The following code extract defines
a height point with elevation of 668 m (assuming Elevation=m is defined in the header
section):
[RGN10]
Type=0x6300
Label=668
Origin0=(-33.93497,18.38925)
[END-RGN10]
A minor land contour with elevation of 1080 m can be defined like this:
[RGN40]
Type=0x20
Label=1080
Data0=(-33.96727,18.42540),(-33.96725,18.42557),
(-33.96709,18.42600),(-33.96693,18.42624),(-
33.96682,18.42630),
(-33.96662,18.42627),(-33.96646,18.42581),(-
33.96641,18.42557)
[END-RGN40]
Text can be combined with the elevation in the label by using the ~[0x1f] delimiter to
indicate the elevation. Example of a summit with 1084 m elevation:
Lists other PFM files to be included in the current
compilation.
Name of a PFM file (including extension) to be processed in
the current compilation.
The compiler processes all the objects (and sections) in the
specified file as if they were part of the current file.
The file included may contain any section but the [IMG
ID] section.
You may specify either the full path or the path relative to
the current directory.
Section terminator.
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 29 of 100

cGPSmapper Manual Map Project
[RGN10]
Type=0x6616
Label=Table Mountain~[0x1f]1084
Origin0=(-33.96664,18.42569)
[END-RGN10]
4.2.6 Road numbers
Road numbers can be defined using NUMBERS# key within [RGN40] declaration. There
could be up to 60 definitions of numbers for a single road.
Each definition consist from the NumbersX definition where X is increasing value from 1
up to 60
[RGN40]
Type=6
Numbers1=0,E,1,9,O,4,20,2999,2999,Warszawa,Mazowieckie,Polska
,Warszawa,Mazowieckie,Polska
Numbers2=3,B,21,40,N,0,0,2999,2999,Warszawa,Mazowieckie,Polsk
a,Warszawa,Mazowieckie,Polska
[END-RGN10]
Where –
NumbersX=
[index of point in the polyline – 0 based],
[left side numbering style],
[first number on left side],
[last number on left side],
[right side numbering style],
[first number on right side],
[last number on right side],
[left side zip code],
[right side zip code],
[left side city],
[left side region],
[left side country],
[right side city],
[right side region],
[right side country]
Some of the information are optional – if no zip code – it can be replaced by ‘-1’, if no city,
region and country info – also it can be replaced by ‘-1’
Numbers1=0,E,1,9,O,4,20,-1,-1,-1,-1
First ‘-1’ replaces zip code on left side, second – zip code on the right side, then ‘-1’
replaces city/region/country info on left side and the last – on the right side.
http://cgpsmapper.com/ 30 of 100
 Loading...
Loading...