Page 1

J Adapter Class
Generator User’s Guide
Page 2

Seventh Edition: August 2005
The contents of this manual may be revised without prior notice. No part of this document may
be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any
purpose, without the express written permission of Fujitsu Limited.
© 1996-2005 Fujitsu Limited. All Rights Reserved.
Page 3

Preface
The "NetCOBOL
(adapter class) used to call a Java class. Using the adapter class thus generated
makes the Java class library available from COBOL.
A Java runtime environment must be installed to execute the generator or the
adapter class generated. See "
J Adapter Class Generator
Preparations
" is a tool that generates a COBOL class
" for required products.
Purpose of This Manual
This manual provides information on how to enable COBOL programs to use Java
classes. The information includes the ways of creating adapter classes, writing
programs, and running the programs.
Refer to the
information on how to develop programs using Fujitsu NetCOBOL, refer to the
NetCOBOL User's Guide
Fujitsu NetCOBOL Language Reference
.
for the COBOL syntax. For
Fujitsu
Intended Readers
This manual is intended for persons who develop COBOL programs using Java
classes.
Prerequisites
Readers are required to have the following knowledge to read this manual:
Basic knowledge of COBOL syntax •
• • Basic knowledge of COBOL object-oriented programming
Basic knowledge of Java
Organization of This Manual
This manual consists of the following chapters:
Chapter 1. Outline of J Adapter Class Generator
Chapter 1 explains the function and operating environment of the J adapter class
generator.
Chapter 2. J Adapter Class Generator Framework
Chapter 2 explains the framework of the J adapter class generator.
Chapter 3. Developing Programs
Chapter 3 explains how to develop programs that uses Java classes.
Chapter 4. Using the Generator Command
Chapter 4 explains how to use the generator command (java2cob).
NetCOBOL J Adapter Class Generator User's Guide 3
Page 4
Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference
Chapter 5 provides detailed information on the FJ-JAVA-BASE, FJ-JAVA-CONTROL
and FJ-JAVA-ERROR classes provided by the J adapter class generator, and adapter
classes generated by the J adapter class generator.
Appendix A. Message List
Appendix A explains the messages output by the J adapter class generator, including
the operator responses to the messages.
Appendix B. Exception Type List
The Appendix B describes the types of exception generated by the J adapter class
generator and their remedial measures.
How to Use This Manual
When using the J adapter class generator for the first time, begin to read from
Chapter 1. Chapter 1 provides an outline of the J adapter class generator, Chapter 2
explains the framework, and Chapter 3 explains the procedures from development to
execution.
Chapters 4 and 5 provide detailed information on how to use commands and classes.
Read these chapters for program development.
The Appendix A describes the messages that are output form the J adapter class
generator and the Appendix B describes the exception types that the J adapter class
generator sets. Read them as necessity requires.
Product Names
Product Name Abbreviation
Microsoft® Windows® 98 Operating System Windows® 98
Microsoft® Windows® Me Operating System Windows® Me
Microsoft® Windows NT® Workstation Operating System Version
4.0
Microsoft® Windows NT® Server Network Operating System,
Version 4.0
Microsoft® Windows NT® Server Network Operating System,
Enterprise Edition Version 4.0
Microsoft® Windows® 2000 Professional Operating System Windows® 2000 or
Microsoft® Windows® 2000 Server Operating System Windows® 2000 or
Microsoft® Windows® 2000 Advanced Server Operating System Windows® 2000 or
Microsoft® Windows® 2003 Server Operating System Windows® 2003 or
Windows® 98, Windows® Me, Windows NT®, and Windows® 2000 Windows
Windows NT® or
Windows NT® 4.0
Windows NT® or
Windows NT® 4.0
Windows NT® or
Windows NT® 4.0
Windows® 2000
Professional
Windows® 2000
Server
Windows® 2000
Server
Windows® 2000
Server
®
4 NetCOBOL J Adapter Class Generator User's Guide
Page 5

Registered Trademarks
The registered trademarks appearing in this manual are as follows:
Microsoft, Windows, and Windows NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation in the U.S. and other countries.
Java and other trademarks including Java are trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
in the U.S. and other countries.
J Adapter Class Generator User's Guide
5
Page 6

6 NetCOBOL J Adapter Class Generator User's Guide
Page 7

Contents
Chapter 1. Outline of J Adapter Class Generator.........................................9
What is the J Adapter Class Generator?...............................................................10
What the J Adapter Class Generator Can Do........................................................11
What the J Adapter Class Generator Cannot Do ...................................................11
Preparation.......................................................................................................12
Chapter 2. Adapter Class Generator Framework .......................................13
Adapter Class....................................................................................................14
Adapter Object..................................................................................................15
Chapter 3. Developing Programs ...............................................................17
Creating Adapter Classes ...................................................................................18
Developing an Application That Uses an Adapter Class .........................................22
Running a Program............................................................................................29
Conversion to Java2 ..........................................................................................30
Chapter 4. Using the Generator Command................................................31
Starting the J Adapter Class Generator................................................................32
Optional File .....................................................................................................36
Output .............................................................................................................42
Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference ..........................................................45
Class Configuration............................................................................................46
FJ-JAVA-BASE class ...........................................................................................47
FJ-JAVA-CONTROL class ....................................................................................48
FJ-JAVA-ERROR class.........................................................................................50
Class or Interface Adapter Class .........................................................................51
java-lang-String class.........................................................................................61
Array Adapter Class...........................................................................................65
Numbering Names.............................................................................................69
Chapter 6. Messages ..................................................................................73
Java2cob Command Messages............................................................................74
Messages Output during Generation....................................................................74
NetCOBOL J Adapter Class Generator User's Guide 7
Page 8

Messages Output during Execution .....................................................................77
Chapter 7. Samples ....................................................................................81
Sample 1 – Using Classes...................................................................................81
Sample 2 – Specifying Method............................................................................83
Appendix A. Message List...........................................................................85
Java2cob Command Messages............................................................................86
Messages Output during Generation....................................................................87
Messages Output during Execution .....................................................................90
Appendix B. Exception Type List................................................................93
Index...........................................................................................................97
8 NetCOBOL J Adapter Class Generator User's Guide
Page 9

Chapter 1. Outline of J Adapter Class Generator
This chapter explains the function and operating environment of the J adapter class
generator.
Page 10

10 Chapter 1. Outline of J Adapter Class Generator
What is the J Adapter Class Generator?
Taking advantage of the object-oriented function, Fujitsu NetCOBOL enables
programming using class libraries . The Fujitsu NetCOBOL also provides many useful
foundation classes. Meantime, as Java becomes popular, many Java class libraries
are also provided. However, the class structure varies from language to language
and therefore Java class libraries cannot normally be used from COBOL.
The J adapter class generator provides a framework that enables COBOL to use Java
classes.
The J adapter class generator enables a COBOL program to:
Use a Java class library. •
•
Call a Java application.
•
Use an application program interface (API) provided for Java.
The J adapter class generator enables COBOL to be used for systems that previously
could only have been implemented in Java.
Use of the J adapter class generator is recommended in the following situations:
•
Constructing a COBOL system using Java common parts such as EJB
components.
•
Constructing a COBOL system using whole Java applications.
An outline of the J adapter class generator is given below:
Figure 1.1
Page 11
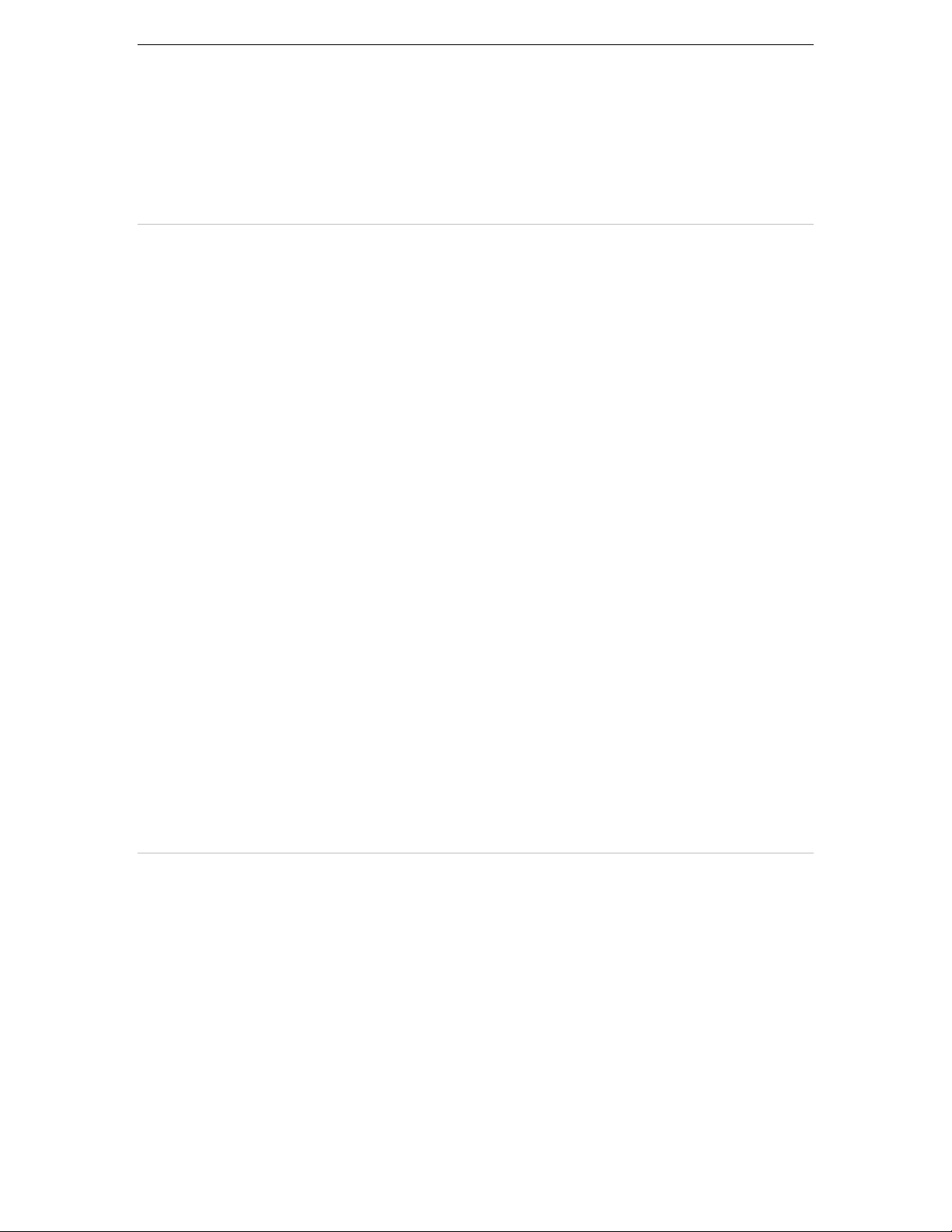
Chapter 1. Outline of J Adapter Class Generator 11
The Java class interface must be converted into the COBOL interface for a COBOL
program to use Java classes. The J adapter class generator generates an adapter
class that converts the Java interface into the COBOL interface.
What the J Adapter Class Generator Can Do
Using adapter classes generated by the J adapter class generator enables the
following types of operation for Java.
To COBOL programs, Java objects seem to be COBOL objects. Therefore, Java
objects can be handled the same way as ordinary COBOL objects.
•
Accessing a class variable
Access to a public class variable (static field) declared in a Java class is enabled.
COBOL handles it as a factory property.
•
Invoking a class method
A public class method (static method) declared in a Java class can be invoked.
COBOL handles it as a factory method.
•
Generating an instance object (invoking a constructor)
Invoking a constructor can create a Java instance object. COBOL handles it as a
factory method that returns an object.
Accessing an instance variable
•
Access to a public instance variable (non-static field) of a Java instance object is
enabled. COBOL handles it as an object property.
Invoking an instance method
•
A public instance method (non-static method) of a Java instance object can be
invoked. COBOL handles it as an object method.
•
Receiving an exception
An exception caused when a class method, constructor, or instance method is
invoked can be trapped to perform error processing. COBOL uses the USE
statement to receive an exception object.
What the J Adapter Class Generator Cannot Do
The J adapter class generator cannot perform the following types of operation:
• • Inheriting a Java class
A COBOL class inheriting a Java class cannot be defined. Even if a COBOL class
inherits an adapter class, the Java class function cannot be overwritten.
Passing a COBOL object as a parameter
No COBOL object can be passed as a parameter for invoking a method, nor can
a COBOL object be set for a Java field. Only an adapter object produced by
wrapping a Java object can be passed to Java.
Page 12

12 Chapter 1. Outline of J Adapter Class Generator
Therefore, the following restrictions apply to COBOL:
- Listener
Java registers a listener object, in which event processing logic is written,
within an object that generates an event. However, since no COBOL object
can be registered in a Java object, COBOL cannot be used to write listeners.
- Collection class
No COBOL object can be registered in a Java collection class. When using
COBOL objects as a collection, use a COBOL collection class.
• • Class having a Japanese name
No class name, field name, and method name can include the Japanese
character set.
Invoking COBOL from Java
No COBOL program can be invoked from Java. A COBOL program invoked from
Java can use no adapter class.
Preparation
The following products are required for the development or execution environment
for using the J adapter class generator.
Fujitsu NetCOBOL or Fujitsu NetCOBOL Runtime System
Fujitsu NetCOBOL is required to develop programs using the J adapter class
generator. Fujitsu NetCOBOL or Fujitsu NetCOBOL Runtime System is required to
execute applications developed by the J adapter class generator.
Java Development Kit or Java Runtime Environment
Java Development Kit (JDK) is provided by Sun Microsystems, Inc. provides the
basic general-purpose class libraries required for program development with Java.
Java 2 SDK (J2SDK) is a software development kit available for creating applications
conforming to Java 2 released by Sun Microsystems, Inc. J2SDK provides basic
general-purpose class libraries required for program development with Java 2.
Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is the JDK runtime environment released by Sun
Microsystems, Inc. It is required to run programs developed with Java.
Java 2 Runtime Environment (J2RE) is the run time environment of applications
conforming Java 2 released by Sun Microsystems, Inc. It is required to run
programs developed with Java 2.
JDK 1.1.8, J2SDK 1.2.2, or a later version is required to develop programs using the
J adapter class generator. JDK 1.1.8, J2SDK 1.2.2, JRE 1.1.8, J2RE 1.2.2, or a later
version is required to run applications developed using the J adapter class generator.
Page 13

Chapter 2. Adapter Class Generator Framework
This chapter explains the framework of the J adapter class generator.
Page 14

14 Chapter 2. Adapter Class Generator Framework
Adapter Class
To make Java classes available to COBOL, a mechanism for converting the Java class
interface into the COBOL interface is required. The J adapter class generator works
as an interface converting mechanism to generate adapter classes corresponding to
Java classes. To use a Java class from a COBOL program, the adapter class created
by the generator can be called. The adapter class is written in COBOL and therefore
can be called in the same manner as a COBOL class.
The relationship between the Java class/interface and adapter class is shown below:
Figure 2.1: Java class/interface and adapter class
Page 15

Adapter Object
At execution time, an adapter class generates the adapter object corresponding to a
Java instance object. The adapter object:
Holds the pointer to the corresponding Java instance object. •
• Calls the corresponding Java method of the corresponding Java instance object
Only the adapter object can be seen from the COBOL program. Every operation on
the adapter object is transmitted to the corresponding Java object. To the COBOL
program, , the adapter object seems as if it were a Java object. The adapter object,
since it works for the Java object, is also called a proxy object. The relationship
between the Java object and adapter object is shown below:
Chapter 2. Adapter Class Generator Framework 15
Figure 2.2. Java object and adapter object
Page 16

16 Chapter 2. Adapter Class Generator Framework
Page 17

Chapter 3. Developing Programs
This chapter explains how to develop programs that use Java classes.
Page 18
18 Chapter 3. Developing Programs
Creating Adapter Classes
This section explains how to generate an adapter class from a Java class.
Investigating the Java Class
First investigate the specifications of the Java class and interface to be used (class
name, package name, usage, and so on) to check whether the J adapter class
generator can handle the class and interface. See "
Generator Can Do
information on which classes and interfaces can be used.
" and "
Generating Adapter Class Source
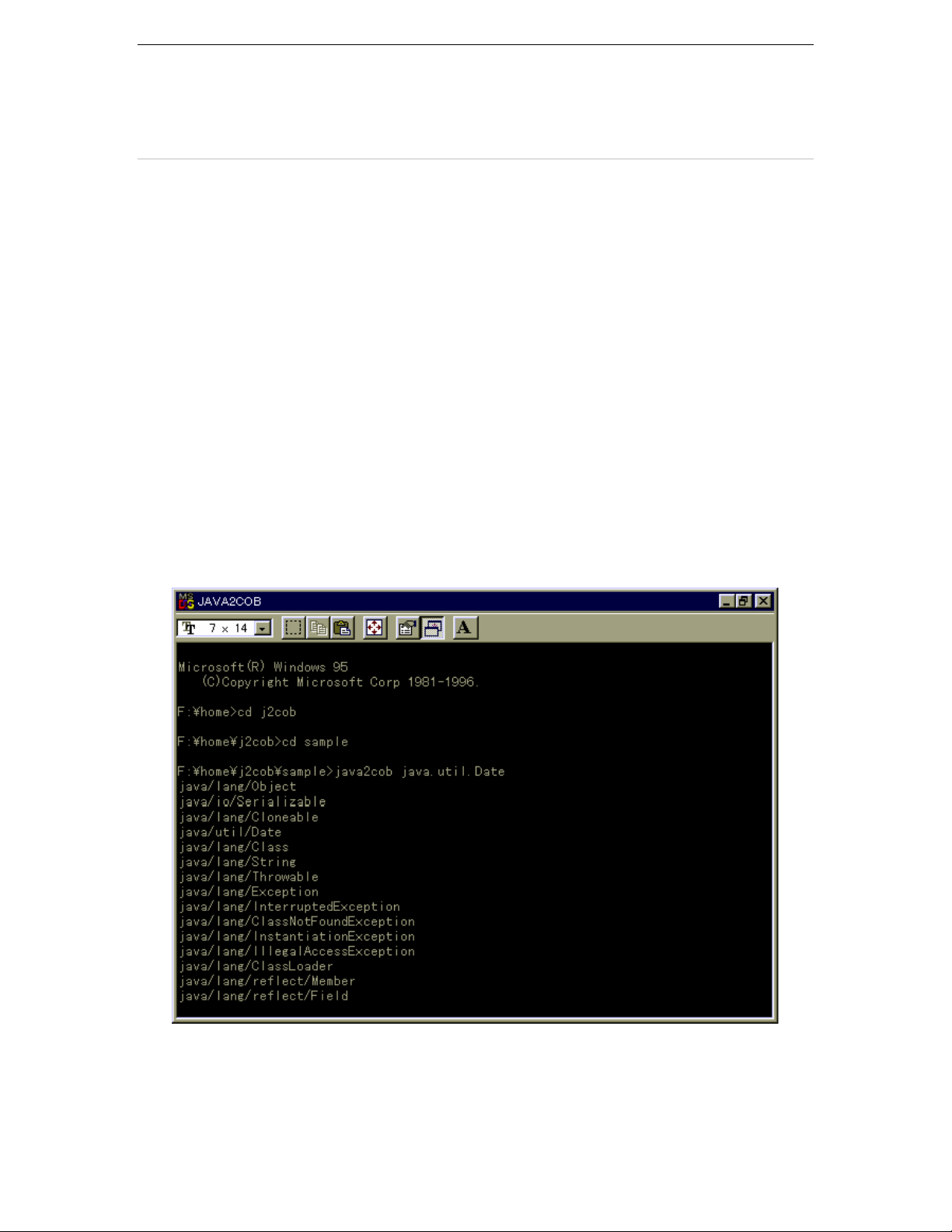
If the target Java class and interface can be used, generate adapter class source.
Use the java2cob command to generate adapter classes. The java2cob command
reads the class file (extension .class) of the Java class/interface and generates the
corresponding adapter class source.
What the J Adapter Class Generator Cannot Do
What the J Adapter Class
" for
The java2cob command generates adapter classes of not only the class specified by
the option but also every other class/interface required to use the class.
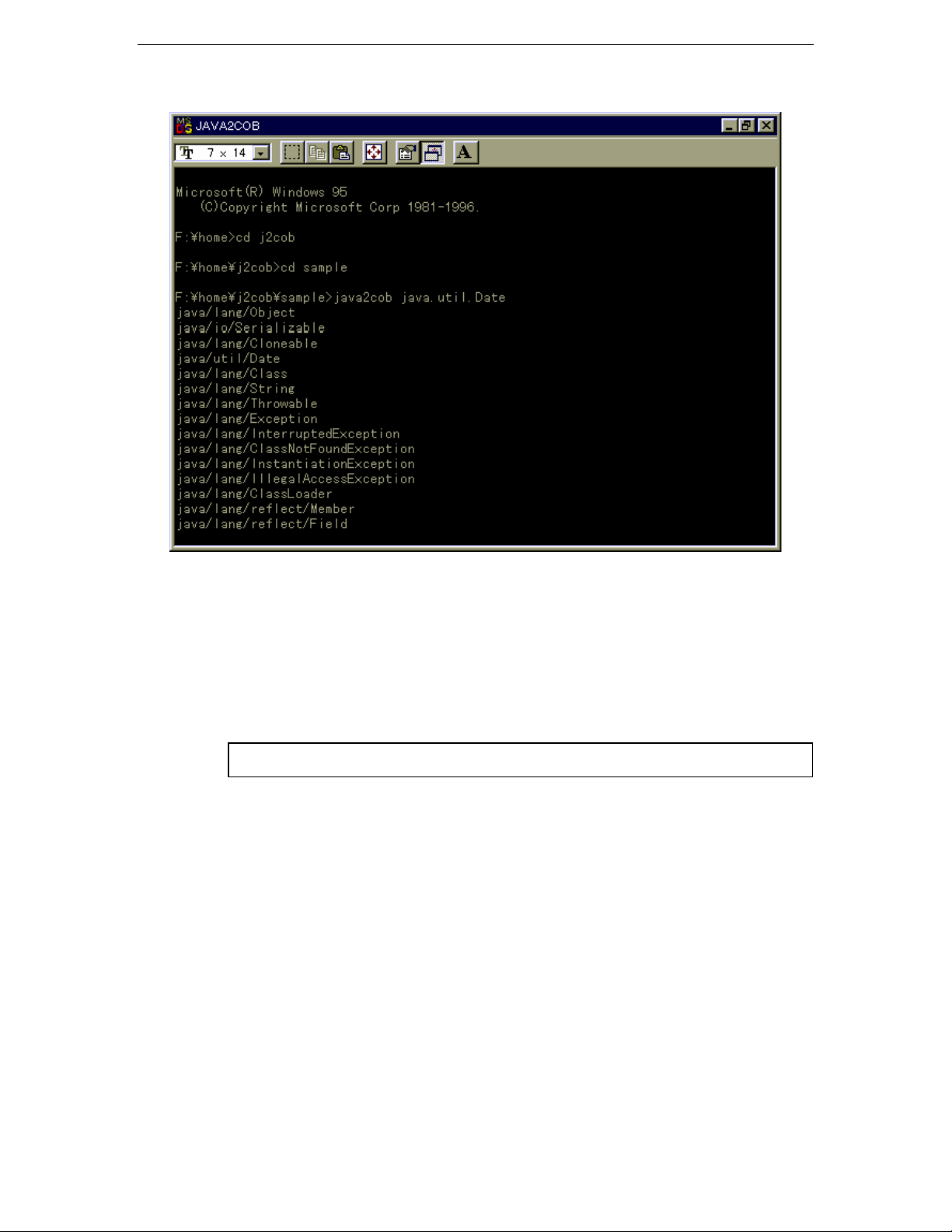
An example of generating adapter class source from the java.util.Date class is shown
below.
Figure 3.1
Note: The class file referenced by the class/interface may not always be available,
depending on the execution environment. For information on how to generate
Page 19

Chapter 3. Developing Programs 19
adapter classes when the class file is not available, see "
when the class file is not available
."
Generating an adapter class
Building an Adapter Class
Finally, compile and link-edit the generated adapter class source to create an adapter
class library (DLL). Use the COBOL project manager to do so.
Refer to the Fujitsu NetCOBOL User's Guide for information on how to use the
COBOL project manager
Follow the procedure below to build an adapter class:
1. Create a new project using the project manager.
2. Register the target DLL.
3. Create a COBOL source file folder and store the generated adapter class in it.
4. Specify compiler options.
- Specify XXX\REP (XXX is the J adapter class generator install folder) for
REPIN.
- Specify ALPHAL (WORD).
- When creating an adapter class running with Unicode, specify RCS (UCS2).
5. To determine the compilation order, select “Repository File Search” from the
“Edit” menu and then select “All”.
.
6. Create a library folder and store the runtime library F3BIJART.LIB of the J
adapter class generator in it. F3BIJART.LIB is available from the LIB folder of
the install folder.
7. Execute "build."
The following files are generated:
• Adapter class DLL file (required for execution)
• Adapter class LIB file (required for link-edition)
• Adapter class repository file (required for compilation)
Generating an Adapter Class When the Class File is Not
Available
The J adapter class generator references the following class information when
generating an adapter class:
• Super class/interface
• Class/interface specified in the public method, constructor parameter, or return
value
• Class/interface specified in the public variable
Page 20

20 Chapter 3. Developing Programs
Therefore, an adapter class cannot be generated normally without these class files.
These class files may not be available depending on the environment. In this case,
to create an adapter class normally, dummy class files having these file names must
be prepared.
Prepare a dummy class file as follows:
1. Create a folder corresponding to the package name. For package name
aaa.bbb.ccc, for instance, create a folder with name aaa\bbb\ccc.
2. Create a Java source program satisfying the following. Assign this file the name
"ClassName.java".
package PackageName;
public class ClassName {}
3. Compile the source program with the Java compiler.
c:\> javac FolderName\ClassName.java
4. Enter the java2cob command.
c:\> java2cob PackageName.ClassName
Note: If a class file is referred to, but does not exist when attempting to generate
an adapter class, processing is terminated with message "
found. Generation was interrupted
."
Class information was not
Reducing the Size of Adapter Class
The adapter class source generated by the J adapter class generator may be simply
compiled and linked before it is used.
Since, however, the adapter source class can include class files, which are not used
by the applications, there might be cases where the size of the DLL file of the
adapter class is significantly larger than necessary. In a case like this, the size of the
adapter class can be reduced by the following methods:
• Specifying the constructor/method/field
• Specifying the -om option or the "Option ReduceClass" parameter
Specifying the Constructor/Method/Field
When the constructors, methods, and fields that are used in the application are
known, the number of the adapter classes generated can be reduced by specifying
them.
The J adapter class generator generates only the adapter classes that are required
by the specified constructors/methods/fields.
Refer to -r option, -gc option, -gm option, -gf option and "Class classname/interface-name" parameters for details of the procedure of specifying the
constructor/method/field.
Page 21

Chapter 3. Developing Programs 21
Example:
When an application uses only the println (Object) method of the java.io.PrintStream
class, specify as follows:
C:\> java2cob -r java.io.PrintStream -gm "println(java.lang.Object)"
Specifying the -om Option or the "Option ReduceClass"
Parameter
Specifying the -om option or the "Option ReduceClass" parameter can reduce the
number of adapter classes generated. To check for parameter validity at method
invocation, the J adapter class generator generates adapter classes corresponding to
individual parameters. Thus many adapter classes are generated for one class.
When the -om option or the "Option ReduceClass" parameter is specified, all objecttype method parameters are mapped to the java-lang-Object class. This function
suppresses the generation of adapter classes corresponding to the method
parameters and thereby reduces the number of adapter classes generated.
Notes:
• When the method of the adapter class generated with the -om option or the
"Option ReduceClass" parameter specified is invoked, BY CONTENT must be
specified as an object reference parameter.
• When the -om option or the "Option ReduceClass" parameter is specified, the
object reference types of method parameters excluding the return value become
java-lang-Object and therefore the original parameter types become uncertain.
Therefore, for a parameter whose object reference type becomes java-langObject, a parameter name is generated according to the following rules so that
the original type information is included in the parameter name.
Pn-ClassName
• P is followed by a parameter serial number (1 to 99).
• The hyphen "-" is followed by an external class name excluding a package name
after conversion into uppercase.
• A parameter name exceeding 30 characters is truncated after the 30th character.
Example:
When the -om option or the "Option ReduceClass" parameter is not specified,
adapter class source java-io-PrintStream.cob of the java.io.PrintStream class
becomes as shown below, and the java-io-OutputStream class is required.
...
REPOSITORY.
CLASS J-OUTPUTSTREAM AS "java-io-OutputStream"
...
LINKAGE SECTION.
01 PARA-1 OBJECT REFERENCE J-OUTPUTSTREAM.
...
When the -om option or the "Option ReduceClass" parameter is specified, the
parameter becomes the java-lang-Object type. Therefore, the java-io-OutputStream
class is not required or generated.
Page 22

22 Chapter 3. Developing Programs
...
REPOSITORY.
CLASS J-OBJECT AS "java-lang-Object"
...
LINKAGE SECTION.
01 P1-OUTPUTSTREAM OBJECT REFERENCE J-OBJECT.
...
Developing an Application That Uses an Adapter Class
This section explains how to develop a program that uses an adapter class.
Outline
The flow of program processing using the adapter class is as follows:
1. Initialization of the Java VM.
2. In the case of a multithreaded application, connection of the current thread to
the Java VM .
3. Generation of the object.
4. Calling the method.
5. In the case of a multithreaded application, disconnection from the Java VM .
6. Termination of the Java VM.
Also, be careful when performing the following operations:
• Manipulating a variable
• Comparing object references
• Assignment to a subclass
• Mapping java.lang.String into PIC X.
• End control of character string
• Exception processing
Initializing the Java VM
To use an adapter class, the Java virtual machine (VM) must first be initialized . Use
the JVM-INIT method or the JVM-ATTACH method of the FJ-JAVA-CONTROL class to
initialize the Java VM.
A coding sample is shown below:
...
REPOSITORY.
CLASS FJ-JAVA-CONTROL
...
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
...
INVOKE FJ-JAVA-CONTROL "JVM-INIT".
...
Page 23

Chapter 3. Developing Programs 23
Terminating the Java VM
When an adapter class is no longer used, the Java VM must be terminated. Use the
JVM-TERMINATE method of the FJ-JAVA-CONTROL class to terminate the Java VM.
A coding sample is shown below:
...
REPOSITORY.
CLASS FJ-JAVA-CONTROL
...
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
...
INVOKE FJ-JAVA-CONTROL "JVM-TERMINATE".
...
Developing a Multithread Application
A multithread application using an adapter class must connect the current thread to
the Java virtual machine (VM). When the multithread application is terminated, the
current thread must first be disconnected from the Java VM.
Use the JVM-INIT method or the JVM-ATTACH method of the FJ-JAVA-CONTROL
class to connect the current thread to the Java VM.
To disconnect the current thread from the Java VM, use the JVM-TERMINATE
method or the JVM-DETACH method of the FJ-JAVA-CONTROL class.
A multithread application sample is shown below:
Figure 3.2
Generating an Object
Generate an object by invoking the adapter class factory method corresponding to
the constructor. Generate the factory method with the following name (see
Constructor
"
Create-JavaClassName-nn (nn is 01 to 99)
").
Page 24

24 Chapter 3. Developing Programs
An example of generating a Date class object is shown below:
...
REPOSITORY.
CLASS J-Date AS "java-util-Date"
...
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION
01 anDate OBJECT REFERENCE J-Date.
...
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
...
INVOKE J-Date "Create-Date-01" RETURNING anDate.
...
Note:
• Since the adapter class name is very long, it is recommended that an alias be
assigned by specifying AS in the REPOSITORY paragraph.
Invoking a Method
Invoke an instance method by invoking the corresponding adapter class object
method. The method name is the same as that of Java. However, if more than one
method is defined with the same name, append a numeric suffix to distinguish them
Class method"
(see "
and
"Instance method
").
An example of invoking the getTime method of the Date class is shown below:
...
REPOSITORY.
CLASS J-Date AS "java-util-Date"
...
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION
01 anDate OBJECT REFERENCE J-Date.
01 currentTime PIC S9(9) COMP-5.
...
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
...
INVOKE anDate "getTime" RETURNING currentTime.
...
Manipulating a Variable
Manipulate a variable through the corresponding adapter class property. The
JF-
property name is a Java field name with the prefix "
field is defined with the same name, append a numeric suffix to distinguish them
Class variable
(see "
" and "
Instance variable
").
". However, if more than one
Page 25

Chapter 3. Developing Programs 25
An example of referencing the class variable AM_PM_FIELD (static field) of the
DateFormat class is shown below:
...
REPOSITORY.
CLASS J-DateFormat AS "java-text-DateFormat"
...
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION
01 FMT-Type PIC S9(9) COMP-5.
...
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
...
MOVE JF-AM_PM_FIELD OF J-DateFormat TO FMT-Type.
...
Comparing Object References
COBOL uses "=" to check whether multiple object references point to the same
object. To check whether the Java objects pointed to by the adapter objects are the
same, COBOL uses the J-EQUALS method of the adapter class instead of "=". The
adapter class always has the J-EQUALS method.
An example of comparing two Date objects is shown below. The condition is met
when Date-1 and Date-2 point to the same Java object.
...
REPOSITORY.
CLASS J-Date AS "java-util-Date"
...
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION
01 Date-1 OBJECT REFERENCE J-Date.
01 Date-2 OBJECT REFERENCE J-Date.
01 rst PIC 1.
...
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
...
INVOKE Date-1 "J-EQUALS" USING CONTENT Date-2 RETURNING rst.
IF rst = B"1" THEN
Condition met
...
Assignment to a Subclass
COBOL uses AS to assign an object to a subclass. However, it uses the J-NARROW
method instead of AS to assign an adapter object. The adapter class always has the
J-NARROW method.
Page 26

26 Chapter 3. Developing Programs
An example of assigning an object, which has been referenced with Object class
data, into Data class data is shown below:
...
REPOSITORY.
CLASS J-Object AS "java-lang-Object"
CLASS J-Date AS "java-util-Date"
...
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION
01 anDate OBJECT REFERENCE J-Date.
01 anObject OBJECT REFERENCE J-Object.
...
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
...
INVOKE J-Date "J-NARROW" USING CONTENT anObject RETURNING anDate.
...
Mapping java.lang.String into PIC X
The java.lang.String is mapped into the java-lang-String class in the generation of
the normal adapter class. In this case, creation of the user's application becomes
somewhat complicated because conversion between the String object and the
COBOL data items must be performed using the java-lang-String class method (such
as NEW-STRING-X, GET-STRING-X).
When the adapter class is generated by specifying the -s option or by specifying the
"Option String" parameter, the following items can be handled as alphanumeric items
in the user's applications, since the java.lang.String type is mapped into PIC X ANY
LENGTH:
• Return values of the java.lang.String type in the method
• Argument of the java.lang.String type in the constructor and method
• Fields (class variables and instance variables) of the java.lang.String type
Example: When the -s option and "Option String" parameter are not specified, the
conversion between the String object and the COBOL data items must be performed
in the user's application using the java-lang-String class method (such as NEWSTRING-X and GET-STRING-X).
…
REPOSITORY.
CLASS J-Date AS "java-util-Date"
CLASS J-String AS "java-lang-String"
CLASS J-DateFormat AS "java-text-DateFormat"
…
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION
01 aDateFormat OBJECT REFERENCE J-DateFormat.
01 aDate OBJECT REFERENCE J-Date.
01 dateString OBJECT REFERENCE J-String.
01 dateValue PIC X(30).
…
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
…
MOVE "2000/01/01" & X"00" TO dateValue.
INVOKE J-String "NEW-STRING-X" USING dateValue RETURNING dateString.
INVOKE aDateFormat "parse" USING dateString RETURNING aDate.
…
INVOKE aDate "toString" RETURNING dateString.
INVOKE dateString "GET-STRING-X" RETURNING dateValue.
Page 27

Chapter 3. Developing Programs 27
…
When the -s option or the "Option String" parameter is specified, the conversion
between the String object and the COBOL data items is not necessary since an
alphanumeric item can be specified as the String type argument and returns a value
directly.
…
REPOSITORY.
CLASS J-Date AS "java-util-Date"
CLASS J-DateFormat AS "java-text-DateFormat"
…WORKING-STORAGE SECTION
01 aDateFormat OBJECT REFERENCE J-DateFormat.
01 aDate OBJECT REFERENCE J-Date.
01 dateValue PIC X(30).
…
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
…
MOVE "2000/01/01" & X"00" TO dateValue.
INVOKE aDateFormat "parse" USING dateValue RETURNING aDate.
…
INVOKE aDate "toString" RETURNING dateValue.
…
Notes:
• The return value of the java.lang.String class constructor is the java.lang.String
class
• When the String object method is used, the creation of the object (calling the
String constructor or calling the NEW-STRING-X method) is necessary.
• To refer/set the java.lang.String type field (class variable or instance variable),
specify its size using -s option or "Option String" parameter.
• When you want to handle the String type NULL object, do not use the -s option
and "Option String" parameter.
End Control of Character String
When passing a character string that is shorter than the data item length to an
ordinary adapter class, the end of string (X”00”) must be set. The following example
shows that "ABC" is copied to alphanumeric item initialValue having length of 50
characters and is passed to the NEW-STRING-X method:
…
REPOSITORY.
CLASS J-String AS "java-lang-String"
…
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 initialValue PIC X(50).
01 aString OBJECT REFERENCE J-String.
…
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
…
MOVE "ABC" & X"00" TO initialValue.
INVOKE J-String "NEW-STRING-X" USING initialValue RETURNING aString.
Page 28
28 Chapter 3. Developing Programs
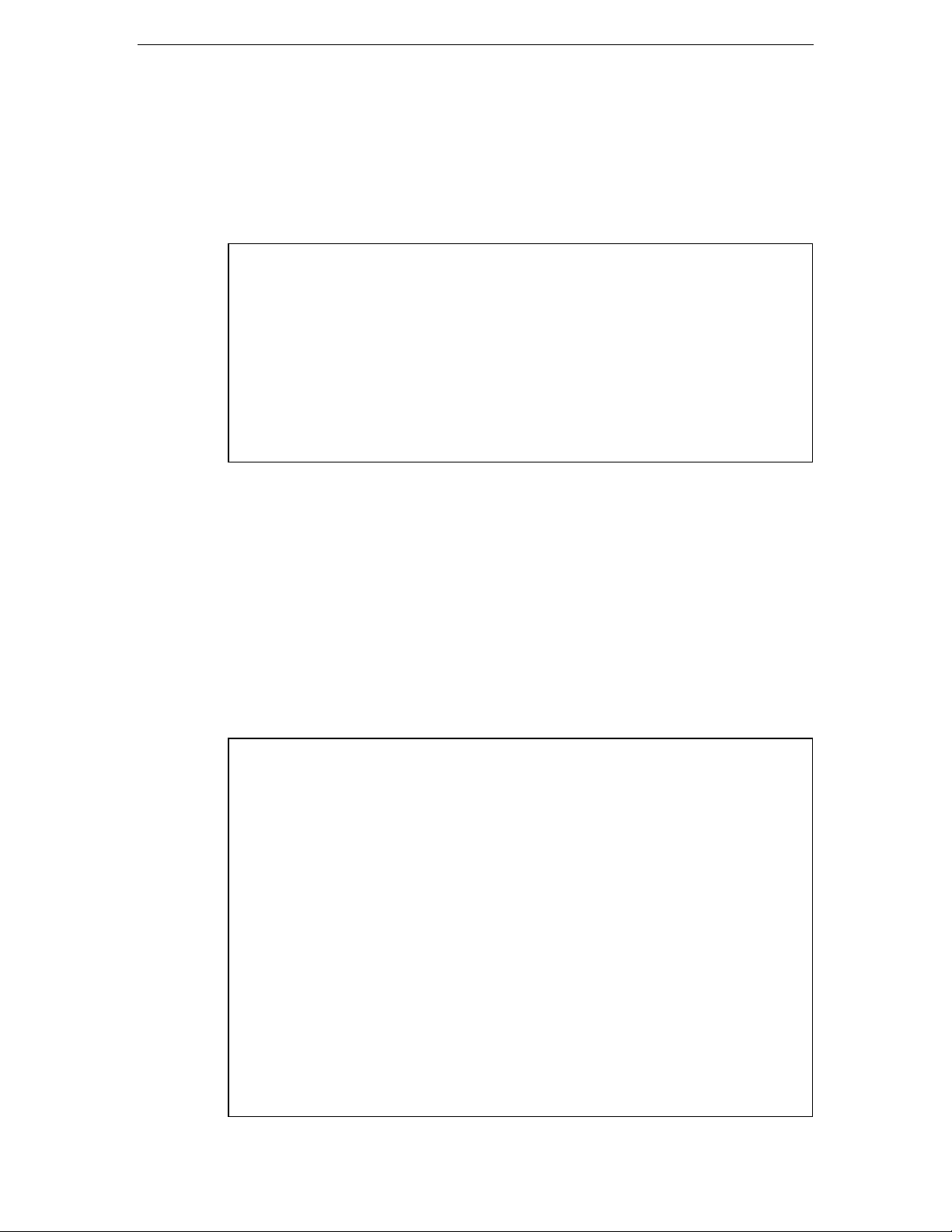
If an adapter class is generated by specifying the -t option or the "Option Terminal"
parameter, the character string that is shorter than the data item length can be
passed to a method without setting the end of string, since the end (X "00") of the
character string is set in the adapter class.
The following example shows that "ABC" is copied to alphanumeric item initialValue
having the length of 50 characters and is passed to the NEW-STRING-X method:
…
REPOSITORY.
CLASS J-String AS "java-lang-String"
…
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 initialValue PIC X(50).
01 aString OBJECT REFERENCE J-String.
…
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
…
MOVE "ABC" TO initialValue.
INVOKE J-String "NEW-STRING-X" USING initialValue RETURNING aString.
Exception Processing
When an adapter class detects an error during processing, the exception object is
generated. FJ-JAVA-ERROR class is the class of the exception object.
In order to detect an exception generated in the adapter class, using the "exception
object", the "exception handling" needs be described in the declaratives of the
procedure division of the program, using the USE statement. When the method of
the FJ-JAVA-ERROR class is used in the exception handling, the exception message,
exception type and Java exception information can be extracted. For the details of
the exception handling using the USE statement, refer to "Defining Exception
Processes" of the "Fujitsu NetCOBOL User's Guide".
Example of coding of the exception handling is shown as follows:
…
REPOSITORY.
CLASS FJ-JAVA-ERROR
…
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION
01 errMessage PIC X(256).
01 expMessage PIC X(1024).
01 expClass PIC X(256).
01 errCode PIC S9(9) COMP-5.
01 errMessageLen PIC S9(9) COMP-5.
01 expMessageLen PIC S9(9) COMP-5.
01 expClassLen PIC S9(9) COMP-5.
01 rc PIC S9(9) COMP-5.
…
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
DECLARATIVES.
ERR SECTION.
USE AFTER EXCEPTION FJ-JAVA-ERROR.
INVOKE EXCEPTION-OBJECT "GET-CODE" RETURNING errCode.
INVOKE EXCEPTION-OBJECT "GET-MESSAGE"
USING errMessage RETURNING errMessageLen.
INVOKE EXCEPTION-OBJECT "GET-EXCEPTION"
USING expMessage expMessageLen expClass expClassLen
RETURNING rc.
Page 29

Chapter 3. Developing Programs 29
DISPLAY "Error Code: " errCode.
DISPLAY "Error Message: " errMessage(1:errMessageLen).
IF rc NOT = -1 THEN
DISPLAY "Java Class Name: " expClass(1:expClassLen)
DISPLAY "Java Exception Message: " expMessage(1:expMessageLen)
END-IF.
END DECLARATIVES.
…
Note: When the exception handling is not described in a program, the program
runtime error (JMP0104I-U) occurs due to the occurrence of the exception object.
Constructing a Program
This section explains how to construct a program that uses an adapter class, by
using the COBOL project manager.
The following files generated from the adapter class are required to construct a
program:
• Adapter class LIB file (for linkage)
• Adapter class repository file (for compilation)
Construct a program as follows:
1. Create a new project using the project manager.
2. Register the target executable program (EXE).
3. Create a COBOL source file folder and store the program source in it.
4. Create a library file folder, and store the adapter class LIB file and J adapter
class generator runtime library F3BIJART.LIB in it. F3BIJART.LIB exists in the
LIB folder of the install folder.
5. Specify compiler and link options:
- For REPIN, specify XXX\REP (XXX is the J adapter class generator install
folder) and the folder containing the adapter class repository.
- Specify ALPHAL (WORD) or NOALPHAL.
- Refer to the
6. Execute "
build
Running a Program
The following file generated from the adapter class is required to run a program:
Fujitsu NetCOBOL User's Guide
."
for other options.
• Adapter class DLL file
Before running the program, add the folder containing the adapter class DLL file to
environment variable PATH.
The program can be run in the same manner as any other COBOL application. Refer
Fujitsu NetCOBOL User's Guide
to the
for details.
Note: The Java VM operating environment can be customized by specifying
environment variables (see ”JVM-INIT method (factory method)”).
Page 30
30 Chapter 3. Developing Programs
Conversion to Java2
When using the resources (execute-form programs (EXE), DLLs, adapter class
source, and program source using adapter classes) created by JDK1.1.x, note the
following:
• Adapter class source and DLLs created by JDK 1.1.x can be used as they are in
the Java2 environment.
• If an adapter class is recreated by Java2, a method name different from one
created by JDK 1.1.x may be generated (see "
the COBOL program using the Java class must be modified. To prevent this
problem, recreate an adapter class with Java2 by using the generation name
management file generated by JDK 1.1.x.
Numbering names
"). In this case,
Page 31

Chapter 4. Using the Generator Command
This chapter explains how to use the generator command (java2cob), optional file
and output result.
Page 32

32 Chapter 4. Using the Generator Command
Starting the J Adapter Class Generator
Command Syntax
When the constructor/method/field is not specified:
java2cob [-classpath
n
]] [-t]
s[
When the constructor/method/field is specified:
java2cob [-classpath
t] –r
[,...]"]] [-gm ["
...
When the optional file is specified:
java2cob -i
Notes on Describing the Command
• The clause that is enclosed by square brackets can be omitted.
• Symbol of the curly brackets indicates selection of clause that is delimited by "|".
• Dot (...) indicates repeated specification.
• Italic type indicates variable character string.
class-name/interface-name
class-name/interface-name
optional-file
class-path
class-path
method-name
] [-d
output-folder
...
] [-d
output-folder
[-gc ["
[(
parameter-type
constructor-name
] [-ov] [-om] [-oi] [-c{s|u}] [-
] [-ov] [-oi] [-c{s|u}] [-s[n]] [-
[(
parameter-type
)] [,...]"]] [-gf [
field-name
[,...]]]
)]
Options
-classpath
Specifies the Java class/interface search path. When specifying two or more folders,
separate them with a semicolon ";".
class-path
When this option is specified, environment variable CLASSPATH is ignored.
This option must be specified right after the java2cob command.
-c{s|u}
Specifies the code used for execution. Specify the same code as the COBOL
program that uses Java classes. The default is native code.
-cs: native code is used for the execution-time code.
-cu: Unicode is used for the execution-time code.
output-folder
-d
Specifies the folder to which an adapter class source is output. The default is the
current folder.
constructor-name
-gc ["
Specify the constructor name generated as an adapter class, for the last classname/interface-name specified before this option. If the constructor name is
omitted, all of the constructors within the corresponding class/interface are
[(
parameter-type
)] [,...]"]
Page 33

Chapter 4. Using the Generator Command 33
generated. When specifying two or more constructors, they must be delimited by
comma (,) or a blank.
When two or more constructors of the same name exist, only the constructor that
matches the parameter type is generated by specifying the parameter-type. If a
parameter type is omitted, all of the constructors of the same name are generated.
When specifying a parameter type, enclose the parameter type with parenthesis
((and)), and enclose the entire option with double quotation (") to specify a
parameter. A parameter type can be specified with the data type name or with the
class name that is modified by the package name. When specifying an internal class
name as the parameter type, specify dollar ($) instead of using period (.) for the
internal class.
This option is valid when the -r option is specified.
This option is exclusive with the -om option.
field-name
-gf [
[,...]]
Specify the field name generated as an adapter class, for the last classname/interface-name specified before this option. If the field name is omitted, all of
the fields within the corresponding class/interface are generated. When specifying
more than one field, they must be delimited by comma (,) or a blank.
This option is valid when the -r option is specified.
This option has exclusive relation with the -om option.
-gm ["
method-name
Specify the method name generated as an adapter class, for the last
[(
parameter-type
)] [,...]"]
class-
name/interface-name specified before this option. If the method name is omitted,
all of the methods within the corresponding class/interface are generated. When
specifying more than one method, they must be delimited by comma (,) or a blank.
When more than one method of the same name exist, only the method that matches
the parameter type is generated by specifying the parameter-type. If a parameter
type is omitted, all of the methods of the same name are generated. When
specifying a parameter type, enclose the parameter type with parenthesis (( )), and
enclose the entire option with double quotation (") to specify a parameter. A
parameter type can be specified by data type name or by the class name that is
qualified by the package name. When specifying an internal class name as the
parameter type, specify dollar ($) instead of period (.) for the internal class name.
This option is valid when the -r option is specified.
This option has exclusive relation with the -om option.
optional-file
-i
Specify an optional file.
When this option is specified, other options in the command line are ignored.
-oi
Specifies that a method name cross-reference list file (listing adapter class methods
corresponding to Java class methods) be output. The method name cross-reference
list file is output with name "adapter-class-source-file-name.txt" for each Java class.
Page 34

34 Chapter 4. Using the Generator Command
-om
Specified to reduce the number of adapter classes generated. When this parameter
is specified, the object reference types of all parameters excluding RETURNING
become java-lang-Object. Instead, the parameter names are generated so that they
include original type information (see "Specifying the -om option or the "Option
ReduceClass" parameter"). The class browser can identify almost every method. If
the class browser cannot identify methods such as because parameter names are too
long, the method name cross-reference list file can be used for identification.
This option is exclusive with the -r option, -gc option, -gm option and –gf option.
-ov
Specifies that any existing adapter class with the same name be overwritten. If this
parameter is omitted, no adapter class is overwritten.
-r
Specify this option when specifying a constructor/method/field generated as an
adapter class, for the
class-name/interface-name
doing so, the size of an adapter class can be reduced. (Refer to "Specifying
constructor/method/field.")
specified right after this option. By
Refer to the -gc option for the procedure of specifying the constructor, to the -gm
option for the procedure of specifying the method and to the -gf option for the
procedure of specifying the field, respectively.
Specify the
class-name/interface-name
When specifying constructor/method/field for more than one
, specify the -r option for each
name
right after this option.
class-names/interface-
class-name/interface-name
.
If there is no single -gc option or -gm option or -gf option that corresponds to this
option, the adapter class without constructor/method/field is generated.
This option has exclusive relation with the -om option.
When this option is used, be sure to create all of the adapters using the java2cob
command only once. If the adapter classes are generated by using the java2cob
command two or more times, a correct adapter class may not be generated.
Creation of an adapter class by specifying the constructor/method/field without
specifying a constructor/method/field is not permitted.
-s[n]
Specify this option when creating the adapter class in which the java.lang.String type
is mapped into alphanumeric item (PIC X). (Refer to the paragraph "Specifying
java.lang.String into PIC X.")
n
specifies the parameter size (PIC X(n)) of the property method that corresponds to
the String type field. When omitted, it is assumed that 256 is specified.
-t
Specify this option when creating an adapter class in which the end of the character
string needs to be set. (Refer to "End control of character string.")
class-name/interface-name
Specifies the Java class name or interface name, for which an adapter class is to be
generated, by qualifying it with a package name. When specifying an internal class
Page 35

Chapter 4. Using the Generator Command 35
name, replace the period "." of the internal class name with a dollar sign "$". More
than one class name or interface name can be specified.
Environment Variable
CLASSPATH
Specifies the Java class/interface search path. When -classpath is specified, the
CLASSPATH environment variable is ignored.
Notes:
• When specifying constructor/method/field, be sure to specify the -r option,
name/interface-name
, -gc option, -gm option and -gf option successively. If
class-
another option is specified among these options, specification error is generated.
• The Japanese cannot be included in class names or interface names.
• When Unicode is specified for the execution-time code, specify RCS(UCS2) in a
compiler option (see "
Building an adapter class
").
Example
Using the options is described in the following examples of the java2cob command.
• All of the adapter classes that are related to the java.io.PrintStream class and the
java.util.Date class are generated.
c:\> java2cob java.io.PrintStream java.util.Date
• The adapter class that is related to all println methods of the java.io.PrintStream
class and that is related to all constructors of the java.util.Date class are
generated.
c:\> java2cob -r java.io.PrintStream -gm println -r java.util.Date -gc
• Only the adapter classes that are related to the println(Object) of the
java.io.PrintStream class and to the Date() constructor of the java.util.Date class
are generated.
c:\> java2cob -r java.io.PrintStream -gm "println(java.lang.Object)" -r
java.util.Date -gc "Date()"
Page 36

36 Chapter 4. Using the Generator Command
Optional File
The optional file is a text format file used to define generator options in a file instead
of on the command line. The optional file is specified in a command line of the
java2cob command.
For example, specifying the many method names, etc. in the command line every
time is troublesome during the specification of the constructor/method/field. It can
be more readily and accurately accomplished by creating the optional file. (Refer to
the paragraph "
When the optional file is specified
Format
The parameters that can be placed in an optional file, are as follows:
Parameter name Explanation Note
Class c
lass-
name/interface-name
Option ClassPath Specify a search path of the Java class/interface. Omission is allowed.
Option Code Specify a code system during execution time. Omission is allowed.
Option
CommandOptions
Option GenOnlyUsed Specify whether or not to specify a
Option MethodTable Specify whether or not to output the method
Option OutPutPath Specify a folder to output the source of the
Option OverWrite Specify to overwrite an existing adapter class or
Option ReduceClass Specify whether or not to reduce the number of
Option String Specify whether or not to generate an adapter
Option Terminal Specify whether or not to generates an adapter
Specify a class name or interface name of Java
that generates the adapter class. If necessary,
specify the constructor/method/field generated as
an adapter class.
Specify directly options of the java2cob
command.
constructor/method/field generated as an adapter
class.
name cross-reference list file.
adapter class.
not to overwrite it when an adapter class of the
same name already exists.
adapter classes.
class in which the java.lang.String type is mapped
into alphanumeric item.
class in which the end character string setting is
made, for the method that has the parameter of
String type field and the String type.
" of command syntax.)
Omission is not allowed.
Multiple settings are
allowed.
Multiple setting is not
allowed.
Multiple setting is not
allowed.
Omission is allowed.
Multiple setting is not
allowed.
Omission is allowed.
Multiple setting is not
allowed.
Omission is allowed.
Multiple setting is not
allowed.
Omission is allowed.
Multiple setting is not
allowed.
Omission is allowed.
Multiple setting is not
allowed.
Omission is allowed.
Multiple setting is not
allowed.
Omission is allowed.
Multiple setting is not
allowed.
Omission is allowed.
Multiple setting is not
allowed.
Page 37

Chapter 4. Using the Generator Command 37
Notes on describing the optional file:
• Clauses enclosed by square brackets can be omitted.
• Curly brackets indicate selection of clause that is delimited by ”| ”.
• Italic type indicates a variable character string.
Class class-name/interface-name
Specification format
class-name/interface-name
Class
]
option
Specification contents
Specify the Java class name or interface name that generates an adapter class.
Also specify constructor/method/field specifying options when
constructor/method/fields are generated as an adapter class, for that
name/interface-name
Meaning of the parameter
class-name/interface-name
•
Specifies a class name or interface name that is qualified by the package name.
When specifying an internal class name as the parameter type, specify dollar ($)
instead of period (.) of the internal class.
constructor/method/field-specifying-option
•
Specify a constructor/method/field using the format of -gc option, -gm option
and -gf option of the java2cob command.
constructor/method/field-specifying-option
The
GenOnlyUsed" parameter specifies YES.
constructor/method/field-specifying-option
If
"Option GenOnlyUsed" parameter specifies YES, an adapter class without
constructor/method/field is generated.
.
[ =
constructor/method/field-specifying-
is valid when the "Option
is not specified even though the
class-
Option ClassPath
Specification format
Option ClassPath =
Specification contents
Specify a search path of the Java class/interface. When specifying two or more
folders, delimit the folders using semi-colon (;).
When a blank is included in the class path, enclose the entire class path with double
quotation (").
When this option is specified, the environment variable CLASSPATH is ignored.
class-path
Page 38

38 Chapter 4. Using the Generator Command
Option Code
Specification format
Option Code = { SJIS | UNICODE }
Specification contents
Specify a code system during execution time. Specify the same code system as that
of the COBOL program that uses the Java class.
When omitted, it is assumed that SJIS is specified.
Meaning of the parameter
• SJIS
Specify it when the code system during execution time is native code.
• UNICODE
Specify it when the code system during execution time is Unicode.
Option CommandOptions
Specification format
Option CommandOptions =
Specification contents
Specify options of the java2cob command directly. But the -i option cannot be
specified.
When a parameter of the same type as the
optional file, the specified value of the
command-options
command-options
command-options
overrides the option file.
is specified as an
Option GenOnlyUsed
Specification format
Option GenOnlyUsed = { YES | NO }
Specification contents
Specify whether or not specify a constructor/method/field generated as an adapter
class. When a constructor/method/field is specified, size of the adapter class can be
reduced. (Refer to "Specify the constructor/method/field")
When omitted, it is assumed that NO is specified.
The specification value of the "Option GenOnlyUsed" parameter affects all of the
class-name/interface-name
"Class
The "Option GenOnlyUsed" parameter is exclusive with the "Option ReduceClass"
parameter.
" inside the optional file.
Meaning of the parameter
• YES
Specifies the constructor/method/field.
• NO
Does not specify constructor/method/field.
Page 39

Chapter 4. Using the Generator Command 39
Option MethodTable
Specification format
Option MethodTable { YES | NO }
Specification contents
Specify whether or not to output the method name cross-reference list file (list of
adapter class methods that correspond to the Java class methods). If omitted, it is
assumed that NO is specified.
The method name cross-reference list file is output using the format of "
.txt" of the adapter class for each Java class.
name
Meaning of the parameter
• YES
The method name cross-reference list file is output.
• NO
The method name cross-reference list file is not output.
source-file-
Option OutPutPath
Specification format
Option OutPutPath=
Specification contents
Specify the folder to which source of the adapter class is output.
When a folder include a blank, enclose the entire output target folder with double
quotation (").
If omitted, it is generated in the current directory.
output-folder
Option OverWrite
Specification format
Option OverWrite = { YES | NO }
Specification contents
Specify whether to overwrite an existing adapter class or to overwrite it when an
adapter class of the same name already exists.
If omitted, it is assumed that NO is specified.
Meaning of the parameter
• YES
Overwrite is executed.
• NO
Overwrite is not executed.
Page 40

40 Chapter 4. Using the Generator Command
Option ReduceClass
Specification format
Option ReduceClass = { YES | NO }
Specification contents
Specify whether or not to reduce the number of adapter classes. When YES is
specified, the type of object reference except RETURNING becomes java-lang-Object,
and the parameter name is generated so as to include the original type information
instead. (Refer to "Specifying the -om option or "Option ReduceClass" parameter.")
Thus, method can be distinguished with the class browser in most cases. If method
cannot be distinguished with the class browser because the parameter name is too
long and because of other reasons, it can be distinguished using the method name
cross-reference list file.
If omitted, it is assumed that NO is specified.
Meaning of the parameter
• YES
Reduces the number of adapter classes.
• NO
The number of adapter classes is not reduced.
Option String
Specification format
n
Option String = { YES [
Specification contents
Specify whether or not to generate an adapter class in which the java. lang. String
type is mapped into the alphanumeric item (PIC X). (Refer to "Mapping the java.
lang. String into PIC X.")
If omitted, it is assumed that NO is specified.
Meaning of the parameter
n
• YES [
]
The java.lang.String type is mapped into the alphanumeric item.
n
specifies the parameter size (PIC X(n)) of the property method that corresponds to
the String type field. If omitted, it is assumed that 256 is specified.
• NO
The java.lang.String type is not mapped into the alphanumeric item.
] | NO }
Page 41

Chapter 4. Using the Generator Command 41
Option Terminal
Specification format
Option Terminal = { YES | NO }
Specification contents
Specify whether or not to generate an adapter class allowed to set end character
strings, for the method that has string-type fields and string-type parameters.
(Refer to "End control of character string.")
If omitted, it is assumed that NO is specified.
Meaning of the parameter
• YES
Generate an adapter class in which the end character string setting is made.
• NO
Does not generate an adapter class in which the end character string setting is
made.
Example
When creating only an adapter class that is related to the println (Object) method of
the java.io.PrintStream class or related to the Date ( ) constructor of the
java.util.Date class, specify as follows.
Option GenOnlyUsed = YES
Class java.io.PrintStream = -gm "println(java.lang.Object)"
Class java.util.Date = -gc "Date()"
Notes
• When two or more parameter of the same type are specified, the parameter that
is specified last becomes valid. But the parameters of "Class
name/interface-name
" become valid respectively.
class-
• The line in which "#" is described in the first column is ignored as the comment
line.
• The line in which "\" is described as the end of the line is continued on to the
next line.
Page 42

42 Chapter 4. Using the Generator Command
Output
The generator outputs the following files:
• Adapter class source file
• Generation name management file
• Method name cross-reference list file
Adapter Class Source File
The adapter class source file corresponding to the specified Java class or interface is
generated. If the specified class or interface refers to other classes or interfaces, the
adapter classes corresponding those classes or interfaces are also generated. This
processing is recursive until the following conditions are met:
• No other classes or interfaces are referenced.
• Adapter classes corresponding to the referenced classes or interfaces have all
been generated.
• A source file with the same name already exists in the output destination while
overwriting is not specified.
The name of a generated source file is created from the class name or interface
name qualified by the package name according to the following rules:
• Period and dollar are converted into hyphen.
.cob
• The extension is fixed to "
When the java2cob command is executed, the names of the adapter classes being
generated are displayed.
".
Page 43
Chapter 4. Using the Generator Command 43
Figure 4.1
Generation Name Management File
The J adapter class generator uses a generation name management file to manage
the correspondence between the names used in Java classes and adapter classes.
The generation name management file is generated with the following name in the
adapter class output folder:
java2cob.mgt
See "
Numbering names
" for information on how to use the generation name
management file.
Method Name Cross-Reference List File
A method name cross-reference list file is output so that the operator can check the
correspondence between Java class methods and adapter class methods. The
method name cross-reference list file is generated, when the -oi option or the
"Option MethodTable" parameter is specified, in the adapter class output folder
according to the following rules:
• Period or dollar used in the class name or interface name qualified by a package
name is changed to hyphen.
.txt
• The extension is fixed to "
".
Page 44

44 Chapter 4. Using the Generator Command
A method name cross-reference list file is output in the following format:
[Java] java-class-name
[COBOL] cobol-external-class-name
(1) [Java] type java-method-name (argument-type)
[COBOL] cobol-external-method-name
(2) [Java] type java-method-name (argument-type) OVERRIDE
[COBOL] -None ...
(n) [Java] type java-method-name ()
[COBOL] cobol-external-method-name
java-class-name Class name or interface name qualified by a package name
cobol-external-class-name External class name of the adapter class corresponding to the Java
class
java-method-name Java class method
type Return type of Java method
argument-type Argument type of Java method
OVERRIDE Added when a super class method is overridden
cobol-method-name External method name of the adapter class corresponding to the
Java method
-None- Indicated when no adapter class method corresponds to the Java
method
No method name cross-reference list file is output for the following adapter class:
• Array adapter class
The following methods of the java-lang-String class are not output to the method
name cross-reference list file:
• NEW-STRING-X
• NEW-STRING-N
• GET-STRING-X
• GET-STRING-N
• GET-STRING-LENGTH-X
• GET-STRING-LENGTH-N
Page 45

Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference
This chapter provides detailed information on the FJ-JAVA-BASE, FJ-JAVA-CONTROL
and FJ-JAVA-ERROR classes provided by the J adapter class generator, and adapter
classes generated by the J adapter class generator.
Page 46

46 Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference
Class Configuration
The figure below shows the hierarchical relationships among the FJ-JAVA-BASE, FJJAVA-CONTROL and FJ-JAVA-ERROR classes provided by the J adapter class
generator, and adapter classes generated by the J adapter class generator.
Figure 5.0.1
Class Hierarchy
• FJ-JAVA-BASE: Super class of every adapter class
• FJ-JAVA-CONTROL: Initializes or terminates the Java VM, or connects or
disconnects a thread to the Java VM.
• FJ-JAVA-ERROR: Class of exception object generated in the adapter class.
• Class adapter class: An adapter class (java-lang-Object) of the java.lang.Object
class is generated as a subclass of FJ-JAVA-BASE. Other adapter classes having
the same inheritance relationships as Java classes are generated. An adapter
class of the class in which a Java interface is installed inherits an interface
adapter class as well.
• Interface adapter class: The adapter class of an interface that inherits no other
interface is generated as a subclass of java-lang-Object. The adapter class of an
interface that inherits another interface is generated so that it has the same
inheritance relationship as the Java interface.
• Array adapter class: Every array adapter class is generated as a subclass of
java-lang-Object.
Page 47

FJ-JAVA-BASE class
The FJ-JAVA-BASE class is the super class of every adapter class.
The FJ-JAVA-BASE class has the methods shown below.
Method name Type Function
J-NARROW Factory Assigns an object to a subclass.
J-DUPLICATE Object Duplicates an adapter object.
J-EQUALS Object Checks whether the Java objects indicated by two adapter
J-NARROW Method (factory method)
Explanation
This method assigns an adapter object to a subclass.
Syntax
Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference 47
objects are equal.
INVOKE
Parameter and return value
class-name:
Specifies the class name of assignment target data.
• object-1 (attribute: OBJECT REFERENCE FJ-JAVA-BASE)
• object-2 (attribute: OBJECT REFERENCE SELF)
class-name "J-NARROW
Specifies the object to be assigned.
Returns the object that was converted into the assignment target class.
" USING
object-1
RETURNING
object-2
J-DUPLICATE Method (object method)
Explanation
This method duplicates an adapter object. It duplicates no Java object. A duplicated
adapter object points to the same Java object as the original adapter object.
Syntax
INVOKE
Parameter and return value
• anObject (attribute: OBJECT REFERENCE adapter class)
anObject
"J-DUPLICATE" RETURNING
duplicatedObject
Specifies the adapter object to be duplicated.
• duplicatedObject (attribute: OBJECT REFERENCE CLASS OF SELF)
Returns the duplicated object.
Page 48

48 Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference
J-EQUALS Method (object method)
Explanation
This method checks whether the Java objects indicated by two adapter objects are
equal.
Syntax
INVOKE
Parameter and return value
• object-1, object-2 (attribute: OBJECT REFERENCE FJ-JAVA-BASE)
• result (attribute: PIC 1)
object-1
Specifies the adapter objects to be compared.
Returns B'1' if a match occurs; otherwise, returns B'0'.
"J-EQUALS" USING
FJ-JAVA-CONTROL class
The FJ-JAVA-CONTROL class controls the Java VM.
The FJ-JAVA-CONTROL class has the methods shown below:
Methods used to control Java VM
Method name Type Function
JVM-INIT Factory Initializes the Java VM (Only at the first calling). Connects
JVM-ATTACH Factory Same as JVM-INIT
JVM-TERMINATE Factory Terminates the Java VM (Only at the last calling).
JVM-DETACH Factory Disconnects the current thread from the Java VM
object-2
the current thread to the Java VM
Disconnects the current thread from the Java VM
RETURNING
result
JVM-INIT Method (factory method)
Explanation
When it is called initially in a process, Java VM is initialized. This must be executed
before using the adapter class.
Also, the current thread is connected to Java VM. In the multithread applications,
the current thread must be connected to Java VM for each thread.
This is equivalent to the JVM-ATTACH method.
Syntax
INVOKE FJ-JAVA-CONTROL "JVM-INIT"
Environment variable
The Java VM execution environment can be customized by specifying the following
environment variables. Refer to the
on how to specify the environment variables.
Fujitsu NetCOBOL User's Guide
for information
Page 49

Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference 49
Environment variable name Function
COBJNI_MAX_NSTACK Specifies the maximum size (bytes) of the stack used for
the native code. The default is 128 kilobytes.
COBJNI_JAVA_STACK Specifies the maximum size (bytes) of the stack used for
the Java code. The default is 400 kilobytes.
COBJNI_MIN_HEAP Specifies the startup size of the memory allocation pool
in bytes. The default is 1 megabyte.
COBJNI_MAX_HEAP Specifies the maximum size of the memory allocation
pool in bytes. The default is 16 megabytes.
COBJNI_CLASSPATH Specifies the execution-time class path.
Environment variable CLASSPATH specifies the
generation-time class path and has no effect at
execution time.
Caution
An error occurs when this method is invoked two or more times in one process.
JVM-TERMINATE Method (factory method)
Explanation
The current thread is isolated from the Java VM. In the multithread applications, the
current thread must be isolated from Java VM before the thread is terminated.
Also, when it is called by the last thread in a process, Java VM is terminated. It is
used when the adapter class is used no more.
Syntax
INVOKE FJ-JAVA-CONTROL "JVM-TERMINATE"
Caution
An error occurs when this method is invoked two or more times in one process.
JVM-ATTACH Method (factory method)
Explanation
The current thread is isolated from the Java VM. In the multithread applications, the
current thread must be isolated from Java VM before the thread is terminated.
Syntax
INVOKE FJ-JAVA-CONTROL "JVM-ATTACH"
JVM-DETACH method (factory method)
Explanation
This is equivalent to the JVM-TERMINATE method.
Syntax
INVOKE FJ-JAVA-CONTROL "JVM-DETACH"
Page 50

50 Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference
FJ-JAVA-ERROR class
The adapter class generates the exception object when some error is detected
during execution period. The FJ-JAVA-ERROR class is the class of that exception
object. The exception message, exception type and exception information of Java
can be acquired by using the FJ-JAVA-ERROR class method.
Refer to "Fujitsu NetCOBOL User's Guide" for details of the exception processing.
The FJ-JAVA-ERROR class has the following methods.
Methods that Acquire Exception Information
Method name Type Function
GET-MESSAGE Object Returns the exception message.
GET-CODE Object Returns the type of exception
GET-EXCEPTION Object Returns the Java exception information.
GET-MESSAGE method (object method)
Explanation
Returns the exception message. It is used to indicate the error content.
Syntax
INVOKE EXCEPTION-OBJECT "GET-MESSAGE" USING
messageLength
Parameter and return value
• message (attribute: PIC X ANY LENGTH)
Specifies the data item that stores the exception message.
• messageLength (attribute: PIC S9(9) COMP-5)
Length (number of bytes) of the exception message is returned.
message
RETURNING
GET-CODE method (object method)
Explanation
Returns the type of exception.
Syntax
code
INVOKE EXCEPTION-OBJECT "GET-CODE" RETURNING
Parameter and return value
• code (attribute: PIC S9(9) COMP-5)
Type of exception is returned.
Page 51

Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference 51
GET-EXCEPTION method (object method)
Explanation
The Java exception information is returned.
Syntax
INVOKE EXCEPTION-OBJECT "GET-EXCEPTION" USING
class classLength
RETURNING
result
Parameter and return value
• message (attribute: PIC X ANY LENGTH)
Specifies the data item that stores the Java exception message.
• messageLength (attribute: PIC S9(9) COMP-5)
Length (number of bytes) of Java exception message is returned.
• class (attribute: PIC X ANY LENGTH)
Specifies the data item that stores the Java exception class.
• classLength (attribute: PIC S9(9) COMP-5)
Length (number of bytes) of Java exception message is returned.
• result (attribute: PIC S9(9) COMP-5)
"0" is returned when Java exception information exists. "-1" is returned when
Java exception information does not exist.
Notes: The Java exception information can be acquired only when the exception
type is "1".
Class or Interface Adapter Class
message messageLength
A COBOL class (adapter class) is generated for a Java class or interface. This section
explains how Java class and interface elements are mapped to COBOL class
elements.
The Java language elements are mapped to the COBOL language elements as shown
below:
Java COBOL
Class Class
Interface Class
Constructor Factory method
Class variable (static field) Factory property
Class method (static method) Factory method
Instance variable (nonstatic field) Object property
Instance method (nonstatic field) Object method
Java basic data type COBOL basic data type
Only public elements are mapped to COBOL. Any class, interface, constructor, field,
and method that are not public are not mapped to COBOL.
Page 52

52 Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference
Data types
The Java data types are mapped to the COBOL data types as shown below:
Java data
type
boolean PIC 1
byte PIC X
char
short PIC S9(4) COMP-5
int PIC S9(9) COMP-5
long PIC S9(18) COMP-5
float COMP-1
double COMP-2
Array Object reference array adapter class
Object Object reference adapter class
COBOL data type
PIC X(2)
• When an ANK character is stored, the first byte is used and the second
byte is X'00'.
• When a Japanese character is stored, two bytes are used.
• Data is mapped when code option -cs (native code) or no code option is
specified.
PIC N
• When an ANK character is stored, the first byte is used and the second
byte is X'00'.
• When a Japanese character is stored, two bytes are used.
• Data is mapped when code option -cu (Unicode) is specified.
Class and interface
Explanation
Public classes and interface are mapped to COBOL classes. The inheritance
relationships of adapter classes are the same as those of the corresponding Java
classes. Note that the following Java class inherits no other classes or interfaces but
the adapter classes generated inherit JF-JAVA-BASE.
• java.lang.Object class
Similarly, the following interface inherits no other classes or interfaces but the
adapter classes generated inherit java.lang.Object.
• Interface that inherits no other interface
Page 53

Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference 53
Expansion format
CLASS-ID. internal-class-name-1 AS "external-class-name" INHERITS internalclass-name-2.
...
FACTORY.
...
<<Factory method corresponding to a constructor>>
<<Property method corresponding to a class variable>>
<<Factory method corresponding to a class method>>
END FACTORY.
OBJECT.
...
<<Property method corresponding to an instance variable>>
<<Object method corresponding to an instance method>>
END OBJECT.
END CLASS internal-class-name-1.
Generation rules
1. Internal class names 1 and 2 are internally used by the J adapter class generator
and are not viewed from the class user.
2. The external class name is used to identify the class. The class user can identify
the class with the external class name.
3. An external class name is generated according to the following rules:
[PackageName-[PackageName-...]] ClassName/InterfaceName
- Period "." used in the class name or interface name fully qualified with a
package name is replaced with hyphen "-".
- A name exceeding 160 characters is truncated after the 160th character.
4. The following three methods are generated in the FACTORY definition:
- Factory method corresponding to a constructor
- Property method corresponding to a class variable
- Factory method corresponding to a class method
5. The following two methods are generated in the OBJECT definition:
- Property method corresponding to an instance variable
- Object method corresponding to an instance method
Generation example
The adapter class of the java.util.Date class is generated as shown below:
CLASS-ID. J-DATE AS "java-util-Date" INHERITS J-OBJECT. [1]
...
REPOSITORY.
CLASS J-OBJECT AS "java-lang-Object". [2]
...
END CLASS J-DATE.
1. The name of the adapter class of the java.util.Date class is java-util-Date.
2. The external name of J-OBJECT in the INHERIT clause is java-lang-Object. That
is, java-util-Date inherits java-lang-Object.
Page 54

54 Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference
Note: Fujitsu NetCOBOL does not distinguish between uppercase and lowercase
letters of a class name. Therefore, class names whose external class names are
different only in uppercase and lowercase letters cannot be used concurrently.
Supplement
When the adapter class of java.lang.String is generated, the public method defined
in the java.lang.String class is generated. In addition, a method for referencing or
setting character string data is generated (see "
Constructor
Explanation
A public constructor is mapped to a COBOL factory method.
Expansion format
METHOD-ID internal-method-name AS "external-method-name".
...
DATA DIVISION.
LINKAGE SECTION.
01 generated-object OBJECT REFERENCE SELF.
[parameter ...]
PROCEDURE DIVISION [USING parameter ...] RETURNING generated-object
[RAISING exception-class-name].
END METHOD internal-method-name.
java-lang-String class
").
Generation rules
1. The internal method name is internally used by the J class method generator and
are not viewed from the class user.
2. The external method name is used to identify the method. The class user can
identify the method with the external method name.
3. An external method name is generated according to the following rules:
Create-JavaClassName-nn
- "Create-" is followed by a Java class name with a hyphen "-" followed by a
two-digit number (nn).
- The Java class name does not include the package name.
- nn is a serial number assigned in order from 01 to 99 to methods having the
same Java class name.
- If a super class has classes having the same Java class names, serial
numbers are assigned to such classes in order from the super class. (See
Numbering names
"
- A name exceeding 160 characters is truncated after the 160th character.
.")
4. When a parameter is declared for the constructor, the corresponding parameter
is generated. See "
Data types
" for the correspondence between parameter data
types.
5. The generated object is the unique object reference name used to store the
object reference to the generated adapter object.
Page 55

Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference 55
6. When an exception is declared for the constructor, the RAISING specification is
generated.
Generation example
The factory method corresponding to constructor Date() of the java.util.Date class is
generated as shown below:
METHOD-ID. CREATE-01 AS "Create-Date-01". [1]
...
LINKAGE SECTION.
01 CREATED-OBJECT OBJECT REFERENCE SELF.
PROCEDURE DIVISION RETURNING CREATED-OBJECT.
...
END METHOD CREATE-01.
1. The factory method of java-util-Date is generated with name "Create-Date"
followed by a number.
The factory method corresponding to the constructor Date (long) of the
java.sql.Date class (java.util.Date subclass) is generated as shown below:
METHOD-ID. CREATE-08 AS "Create-Date-08". [1]
...
LINKAGE SECTION.
01 CREATED-OBJECT OBJECT REFERENCE SELF.
01 PARA-1 PIC S9(18) COMP-5.
PROCEDURE DIVISION USING PARA-1 RETURNING CREATED-OBJECT.
...
END METHOD CREATE-08.
2. The factory method of java-sql-Date is also generated with name "Create-Date"
followed by a number. To prevent name duplication, serial numbers including
java-util-Date factory methods are assigned.
Supplement
A factory method name is generated from a constructor, a number is assigned to the
name to secure the uniqueness of the name. The class browser or method name
cross-reference list file can be used to check the correspondence between
constructors and factory methods. In the case of class browser, it can be identified
from the parameter that appears during method selection. In the case of method
name cross-reference list file, it can be identified from the type of argument of the
constructor.
Page 56

56 Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference
Class variable
Explanation
A public class variable (static field) is mapped to a COBOL property method (factory).
Expansion format
METHOD-ID. GET PROPERTY property-name.
...
LINKAGE SECTION.
01 property-value data-description-entry.
PROCEDURE DIVISION RETURNING property-value.
...
END METHOD property-name.
METHOD-ID. SET PROPERTY property-name.
...
LINKAGE SECTION.
01 property-value data-description-entry
PROCEDURE DIVISION USING property-value.
...
END METHOD property-name.
Generation rules
1. The property name is used to identify the property. The class user can identify
the property with the property name.
2. A property name is generated according to the following rules:
JF-JavaFieldName[-nn]
- "JF-" is followed by a Java field name in uppercase.
- If the property name has already been assigned, the second and subsequent
property names are each suffixed with a hyphen "-" followed by a two-digit
number (01 to 99) to prevent name duplication. (See "
- A name exceeding 30 characters is truncated after the 30th character.
Numbering names
.")
3. When FINAL is specified, no property method with the SET specification is
generated.
4. The property value is a parameter used to transfer a property value. The data
description entry expands the COBOL description entry corresponding to the Java
field attribute. See "
Data types
" for the correspondence of data types.
Generation rules
The property method corresponding to the class variable out (static final field) of the
java.lang.System class is generated as shown below:
METHOD-ID. GET PROPERTY JF-OUT. [1]
...
LINKAGE SECTION.
01 GET-VALUE OBJECT REFERENCE J-PRINTSTREAM. [2]
PROCEDURE DIVISION RETURNING GET-VALUE.
...
END METHOD JF-OUT.
1. The property name is generated by adding "OUT", which is the uppercase of the
Java field name, to "JF-".
Page 57

Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference 57
2. "out" is mapped to J-PRINTSTREAM (internal class name of java-io-PrintStream)
because its attribute is java.io.PrintStream.
Supplement
When a property name is generated from a field name, a number is assigned to
secure the uniqueness of the name. The class browser can be used to check the
correspondence between fields and properties.
Class method
Explanation
A public class method (static method) is mapped to a COBOL factory method.
Expansion format
METHOD-ID. internal-method-name AS "external-method-name" [OVERRIDE].
...
DATA DIVISION.
LINKAGE SECTION.
[parameter ...]
[return-value ...]
PROCEDURE DIVISION [USING parameter ...] [RETURNING return-value]
[RAISING exception-class-name].
END METHOD internal-method-name.
Generation rules
1. The internal method name is internally used by the J adapter class generator
and cannot be viewed from the class user.
2. The external method name is used to identify the method. The class user
identifies the method with the external method name.
3. An external method name is generated according to the following rules:
JavaMethodName[-nn]
- A Java method name is used as is as a COBOL method name.
- If a same method name has already been assigned, the second and
subsequent method names are each suffixed with a hyphen "-" followed by a
two-digit number (01 to 99) to prevent name duplication. (See "
names
.")
- A name exceeding 160 characters is truncated after the 160th character.
Numbering
4. When a parameter is declared for the method, the corresponding parameter is
generated. See "
Data types
" for the correspondence between parameter data
types.
5. When a return value is declared for the method, the corresponding return value
is generated. See "
Data types
" for the correspondence between return value
data types.
6. When an exception is declared for the constructor, the RAISING specification is
generated.
Page 58

58 Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference
Generation example
The factory method corresponding to class method abs (long) of the java.lang.Math
class is generated as shown below:
METHOD-ID. JM-ABS-01 AS "abs-01". [1]
...
LINKAGE SECTION.
01 RTN-VALUE PIC S9(18) COMP-5.
01 PARA-1 PIC S9(18) COMP-5.
PROCEDURE DIVISION USING PARA-1 RETURNING RTN-VALUE.
...
END METHOD JM-ABS-01.
1. Since more than one "abs" method is declared, a method with name "abs-01" is
generated for abs (long) that is declared second.
Supplement
When a COBOL method name is generated from a Java method name, a number is
assigned to secure the uniqueness of the name. The class browser or method name
cross-reference list file can be used to check the correspondence between Java
methods and COBOL methods. In the case of class browser, it can be identified
from the parameter that appears during method selection. In the case of method
name cross-reference list file, it can be identified from the type of argument of the
constructor.
Instance variable
Explanation
A public instance variable (non-static field) is mapped to a COBOL property method
(object).
Expansion format
METHOD-ID. GET PROPERTY property-name.
...
LINKAGE SECTION.
01 property-value data-description-entry.
PROCEDURE DIVISION RETURNING property-value.
...
END METHOD property-name.
METHOD-ID. SET PROPERTY property-name.
...
LINKAGE SECTION.
01 property-value data-description-entry
PROCEDURE DIVISION USING property-value.
...
END METHOD property-name.
Generation rules
1. The property name is used to identify the property. The class user can identify
the property with the property name.
2. A property name is generated according to the following rules:
JF-JavaFieldName[-nn]
- "JF-" is followed by a Java field name in uppercase.
Page 59

Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference 59
- If a same property name has already been assigned, the second and
subsequent property names are each suffixed with a hyphen "-" followed by
a two-digit number (01 to 99) to prevent name duplication. (See
Numbering names.
"
- A name exceeding 30 characters is truncated after the 30th character.
")
3. When FINAL is specified, no property method with the SET specification is
generated.
4. The property value is a parameter used to transfer a property value. The data
description entry expands the COBOL description entry corresponding to the Java
field attribute. See "
Data types
" for the correspondence of data types.
Generation rules
The property method corresponding to the instance variable nval of the
java.io.StreamTokenizer class is generated as shown below:
METHOD-ID. GET PROPERTY JF-NVAL. [1]
...
LINKAGE SECTION.
01 GET-VALUE COMP-2. [2]
PROCEDURE DIVISION RETURNING GET-VALUE.
...
END METHOD JF-NVAL.
METHOD-ID. SET PROPERTY JF-NVAL. [3]
...
LINKAGE SECTION.
01 SET-VALUE COMP-2.
PROCEDURE DIVISION USING SET-VALUE.
...
END METHOD JF-NVAL.
1. The property name is generated by adding "NVAL", which is the uppercase of
the Java field name, to "JF-".
2. "nval" is mapped to COMP-2 because its attribute is double.
3. Since FINAL is not specified, a property method with the SET specification is also
generated.
Supplement
When a property name is generated from a field name, a number is assigned to
secure the uniqueness of the name. The class browser can be used to check the
correspondence between fields and properties.
Page 60

60 Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference
Instance Method
Explanation
A non-public instance method (non-static method) is mapped to a COBOL object
method.
Expansion format
METHOD-ID. internal-method-name AS "external-method-name" [OVERRIDE].
...
DATA DIVISION.
LINKAGE SECTION.
[parameter ...]
[return-value ...]
PROCEDURE DIVISION [USING parameter ...] [RETURNING return-value]
[RAISING exception-class-name].
END METHOD internal-method-name.
Generation rules
1. The internal method name is internally used by the J adapter class generator
and cannot be viewed from the class user.
2. The external method name is used to identify the method. The class user
identifies the method with the external method name.
3. An external method name is generated according to the following rules:
JavaMethodName[-nn]
- A Java method name is used as is as a COBOL method name.
- If a same method name has already been assigned, the second and
subsequent method names are each suffixed with a hyphen "-" followed by a
two-digit number (01 to 99) to prevent name duplication. (See "
.")
names
- A name exceeding 160 characters is truncated after the 160th character.
Numbering
4. When a parameter is declared for the method, the corresponding parameter is
generated. See "
Data types
" for the correspondence between parameter data
types.
5. When a return value is declared for the method, the corresponding return value
is generated. See "
Data types
" for the correspondence between return value
data types.
6. When an exception is declared for the constructor, the RAISING specification is
generated.
Page 61

Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference 61
Generation example
The object method corresponding to instance method getTime() of the java.util.Date
class is generated as shown below:
METHOD-ID. JM-GETTIME AS "getTime". [1]
...
LINKAGE SECTION.
01 RTN-VALUE PIC S9(18) COMP-5.
PROCEDURE DIVISION RETURNING RTN-VALUE.
...
END METHOD JM-GETTIME.
1. Since there is only one method with name "getTime," a method with name
"getTime" is generated with no number assigned.
Supplement
When a COBOL method name is generated from a Java method name, a number is
assigned to secure the uniqueness of the name. The class browser or method name
cross-reference list file can be used to check the correspondence between Java
methods and COBOL methods. In the case of class browser, it can be identified
from the parameter that appears during method selection. In the case of method
name cross-reference list file, it can be identified from the type of argument of the
constructor.
java-lang-String class
Like other classes, the java.lang.String class is mapped to the java-lang-String class.
However, the java-lang-String class has the following methods for referencing or
setting character string data, in addition to the methods defined in the
java.lang.String class:
Method name Type Function
NEW-STRING-X Factory Generates a String object having the specified
NEW-STRING-N Factory Generates a String object having the specified
GET-STRING-X Object Fetches the character string as an alphanumeric data
GET-STRING-N Object Fetches the character string as a national data item.
GET-STRING-LENGTH-X Object Determines alphanumeric data item length.
GET-STRING-LENGTH-N Object Determines national data item length.
NEW-STRING-X method (factory method)
Explanation
This method generates a String object having the character string specified for the
alphanumeric data item as an initial value.
alphanumeric data item as the initial value.
national data item as the initial value.
item.
Syntax
INVOKE
class-name
"NEW-STRING-X" USING
initialValue
RETURNING
createdObject
Page 62
62 Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference
Parameter and return value
• class-name
Specifies the internal class name of the java-lang-String class declared in the
REPOSITORY paragraph.
• initialValue (attribute: PIC X ANY LENGTH)
Specifies an alphanumeric data item as the initial value of the String object.
• createdObject (attribute: OBJECT REFERENCE SELF)
Returns the generated object.
Supplement
When a data name is specified for initialValue, a String object as long as data item
length is generated. However, inserting X”00” in the statement can generate a
String object shorter than data item length.
...
REPOSITORY.
CLASS J-String AS "java-lang-String"
...
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 initialValue PIC X(50).
01 aString OBJECT REFERENCE J-String.
...
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
...
MOVE "ABC" TO initialValue.
INVOKE J-String "NEW-STRING-X" USING initialValue RETURNING aString.
[1]
...
MOVE "ABC" & X"00" TO initialValue.
INVOKE J-String "NEW-STRING-X" USING initialValue RETURNING aString.
[2]
1. A String object consisting of 50 characters with the last 47-character area
padded with blanks is generated.
2. A String object consisting of three characters is generated.
NEW-STRING-N method (factory method)
Explanation
This method generates a String object having the character string specified for the
national data item as an initial value.
Syntax
INVOKE
class-name
Parameter and return value
• class-name
Specifies the internal class name of the java-lang-String class declared in the
REPOSITORY paragraph.
• initialValue (attribute: PIC N ANY LENGTH)
Specifies a national data item as the initial value of the String object.
"NEW-STRING-N" USING
initialValue
RETURNING
createdObject
Page 63

Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference 63
• createdObject (attribute: OBJECT REFERENCE SELF)
Returns the generated object.
Supplement
When a data name is specified for initialValue, a String object as long as data item
length is generated. However, inserting X”0000” in the statement can generate a
String object shorter than data item length.
...
REPOSITORY.
CLASS J-String AS "java-lang-String"
...
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 initialValue PIC N(50).
01 aString OBJECT REFERENCE J-String.
...
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
...
MOVE NC"Two-byte-code" TO initialValue.
INVOKE J-String "NEW-STRING-N" USING initialValue RETURNING aString. [1]
...
MOVE NC"Two-byte-code" & X"0000" TO initialValue.
INVOKE J-String "NEW-STRING-N" USING initialValue RETURNING aString. [2]
1. A String object consisting of 50 characters with the last 47-character area
padded with blanks is generated.
2. A String object consisting of three characters is generated.
GET-STRING-X method (object method)
Explanation
This method fetches the character string from the String object as an alphanumeric
data item.
Syntax
INVOKE
anObject
Parameter and return value
• anObject
Specifies the String object from which a character string is to be fetched.
• stringValue (attribute: PIC X ANY LENGTH)
Returns the character string fetched from the String object. If the specified data
item is shorter than the fetched character string, it is truncated. If the specified
data item is longer than the fetched character string, the trailing area is padded
with blanks.
"GET-STRING-X" RETURNING
stringValue
Page 64

64 Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference
GET-STRING-N method (object method)
Explanation
This method fetches the character string from the String object as a national data
item.
Syntax
INVOKE
Parameter and return value
• anObject
• stringValue (attribute: PIC N ANY LENGTH)
anObject
Specifies the String object from which a character string is to be fetched.
Returns the character string fetched from the String object. If the specified data
item is shorter than the fetched character string, it is truncated. If the specified
data item is longer than the fetched character string, the trailing area is padded
with blanks.
"GET-STRING-N" RETURNING
stringValue
GET-STRING-LENGTH-X method (object method)
Explanation
This method returns the length of the character string of the String object as the
length (number of characters) of the alphanumeric data item.
Syntax
INVOKE
Parameter and return value
• anObject
anObject
"GET-STRING-LENGTH-X" RETURNING
stringLength
Specifies the String object whose character length is to be checked.
• stringLength (attribute: PIC S9(9) COMP-5)
Returns character string length.
Page 65

Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference 65
GET-STRING-LENGTH-N method (object method)
Explanation
This method returns the length of the character string of the String object as the
length (number of characters) of the national data item.
Syntax
INVOKE
Parameter and return value
• anObject
• stringLength (attribute: PIC S9(9) COMP-5)
anObject
Specifies the String object whose character length is to be checked.
Returns character string length.
"GET-STRING-LENGTH-N" RETURNING
Array Adapter Class
A Java array is handled as an object in COBOL. Therefore, an adapter class is
generated for each array attribute (element type and number of dimensions). This
section explains how Java arrays are mapped to COBOL classes.
Array class
Explanation
An adapter class corresponding to the array is generated when:
• An array is used as a parameter of a public constructor.
• The type of a public field (static or non-static) is an array.
stringLength
• An array is used as a parameter or return value of a public method (static or
non-static).
Arrays whose attributes shown below match are associated with the same adapter
class:
• Array element type
• Number of dimensions
Page 66

66 Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference
Expansion format
CLASS-ID. internal-class-1 AS "external-class-name" INHERITS internalclass-name-2.
...
FACTORY.
...
<<NEW-ARRAY method>>
END FACTORY.
OBJECT.
...
<<GET-ARRAY-LENGTH method>>
<<GET-ARRAY-ELEMENT method>>
<<SET-ARRAY-ELEMENT method>>
END OBJECT.
END CLASS internal-class-name-1.
Generation rules
1. Internal class names 1 and 2 are internally used by the J adapter class generator
and are not viewed from the class user.
2. The external class name is used to identify the class. The class user can identify
the class with the external class name.
3. An external class name is generated according to the following rules:
JA-NumberOfDimensions-ElementTypeName
- "JA-" is followed by the number of dimensions (1 to 9) and element type
name with a hyphen "-" inserted in between them.
- An element type name is generated depending on the type in the following
format:
- Object: External class name of the adapter class corresponding to the Java
class (See "
- Basic type: Java keyword representing a type (boolean, byte, char, short,
Class and interface
.")
int, long, float, or double)
- An external class name exceeding 160 characters is truncated after the
160th character.
4. The following methods are generated in the factory or method definition:
Method name Type Function
NEW-ARRAY Factory Generates an array object.
GET-ARRAY-LENGTH Object Obtains the number of elements of an array.
GET-ARRAY-ELEMENT Object Fetches a value from an array element.
SET-ARRAY-ELEMENT Object Sets a value in an array element.
5. An n-dimensional array is handled as a one-dimensional array having an n-1dimensional array as an element. Therefore, for n-dimensional array, n adapter
classes (JA-n-XYZ, JA-(n-1)-XYZ, ..., JA-1-XYZ) are generated. JA-n-XYZ is a
one-dimensional array having JA-(n-1)-XYZ as an element.
Generation example
The adapter class for java.lang.String[] is generated as shown below:
Page 67

Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference 67
CLASS-ID. JA-1-STRING AS "JA-1-java-lang-String" INHERITS J-OBJECT.
...
END CLASS JA-1-STRING.
Adapter classes of int [] [] [] are generated as shown below:
CLASS-ID. JA-3-INT AS "JA-3-int" INHERITS J-OBJECT. [1]
...
END CLASS JA-3-INT.
CLASS-ID. JA-2-INT AS "JA-2-int" INHERITS J-OBJECT. [2]
...
END CLASS JA-2-INT.
CLASS-ID. JA-1-INT AS "JA-1-int" INHERITS J-OBJECT. [3]
...
END CLASS JA-1-INT.
1. One-dimensional array having a JA-2-int class object as an element
2. One-dimensional array having a JA-1-int class object as an element
3. One-dimensional array having int as an element
Note: No array exceeding 9 dimensions can be handled.
NEW-ARRAY method (factory method)
Explanation
This method generates an array object.
Syntax
INVOKE
class-name
Parameter and return value
• class-name
Specifies the internal class name of the array class declared in the REPOSITORY
paragraph.
• elmNum (attribute: PIC S9(9) COMP-5)
Specifies the number of elements of the array to be generated.
• createdObject (attribute: OBJECT REFERENCE SELF)
Returns the array object generated.
Supplement
When a multidimensional array is generated, a (n-1)-dimensional array is generated
and stored in each element of the n-dimensional array. For instance, a (n x m) twodimensional array is generated as follows:
"NEW-ARRAY" USING
elmNum
RETURNING
createdObject
Page 68

68 Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference
...
REPOSITORY.
CLASS JA-2-INT AS "JA-2-int"
CLASS JA-1-INT AS "JA-1-int"
...
01 anArray OBJECT REFERENCE JA-2-INT.
01 wArray OBJECT REFERENCE JA-1-INT.
...
INVOKE JA-2-INT "NEW-ARRAY" USING n RETURNING anArray. [1]
PERFORM VARYING I FROM 0 BY 1 UNTIL I >= n
INVOKE JA-1-INT "NEW-ARRAY" USING m RETURNING wArray [2]
INVOKE anArray "SET-ARRAY-ELEMENT" USING I wArray [3]
END-PERFORM.
SET wArray TO NULL.
1. A two-dimensional array object of int is generated (number of elements = n).
2. A one-dimensional array object of int is generated (number of elements = m).
3. The one-dimensional array generated in [2] is set in each element of the first
dimension of anArray.
GET-ARRAY-LENGTH method (object method)
Explanation
This method returns the number of elements of an array object.
Syntax
INVOKE
anObject
"GET-ARRAY-LENGTH" RETURNING
elmNum
Parameter and return value
• anObject
Specifies the array object from which the number of elements is obtained.
• elmNum (attribute: PIC S9(9) COMP-5)
Returns the number of elements of an array.
GET-ARRAY-ELEMENT method (object method)
Explanation
This method fetches an element from an array object.
Syntax
INVOKE
anObject
Parameter and return value
• anObject
"GET-ARRAY-ELEMENT" USING inx RETURNING
elemValue
Specifies the array object from which an element is to be fetched.
• inx (attribute: PIC S9(9) COMP-5)
Specifies the subscript of the element to be fetched. The subscript begins
from 0.
• elemValue (attribute: Array element type)
Returns the value of the array element fetched.
Page 69

Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference 69
SET-ARRAY-ELEMENT method (object method)
Explanation
This method sets an element of an array object.
Syntax
INVOKE
anObject
Parameter and return value
• anObject
Specifies the array object in which an element is to be set.
• inx (attribute: PIC S9(9) COMP-5)
Specifies the subscript of the element to be set. The subscript begins from 0.
• elemValue (attribute: Array element type)
Specifies the value to be set in the array element.
Numbering Names
The J adapter class generator generates adapter class names from the names used
for Java classes or interfaces. However, some names cannot be used in both Java
and COBOL because different syntax rules are used. For instance, Java permits
multiple methods with the same name to be defined within the same class if they
have different parameters, while COBOL does not permit such definition. In this
case, methods with the same name in Java must be generated so that they
correspond to different names in COBOL. The J adapter class generator generates a
unique name from each corresponding Java name by adding a hyphen "-" followed
by a number.
"SET-ARRAY-ELEMENT" USING
inx elemValue
This section explains the rules of assigning numbers to names used for adapter
classes.
Effective range of name
The names handled by the J adapter class generator are classified into the following
three types depending on the effective range of a name:
• Name that is always unique according to generation rules
- Class name
- Array class name
• Name that needs to be unique between super classes/subclasses
- Factory method name corresponding to constructor
• Name that needs to be unique within an entire run unit
- Method name (class/instance)
- Field (variable) name (class/instance)
Page 70

70 Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference
Name that is always unique according to generation rules
A class name is generated from a class name or interface name qualified by a Java
package name. Since the qualified name is unique, the COBOL name generated
from it is always unique. The same applies to an array class name.
Thus, no class names and array class names are numbered.
Name that needs to be unique between super
classes/subclasses
A factory method name corresponding a constructor is generated from a class name
that is not qualified by a package name. Factory method names including methods
inherited from the super classes must all be unique to one another. However,
names conflict when:
• Super classes have a same name qualified by different packages.
• Two or more constructors are defined for one class.
In this case, the J adapter class generator assigns numbers to the methods with a
same name according to the following rules:
1. Number 01 is assigned to the name that appears first and then serial numbers
are assigned in ascending order to the subsequent names.
2. The above rule is applied to names in order from the constructor defined in the
super class. When two or more constructors are defined for one class, the rule
is applied to them in order they are defined.
Example
The factory methods corresponding to the constructor of the java.util.Date class and
java.sql.Date class (subclass of the java.util.Date class) are assigned names as
shown below:
Java constructor COBOL factory method
java.util.Date class
Date() Create-Date-01
Date(int, int, int) Create-Date-02
Date(int, int, int, int, int) Create-Date-03
Date(int, int, int, int, int,
int)
Date(long) Create-Date-05
Date(String)
Date(int, int, int) Create-Date-07 java.sql.Date class
Date(long)
ava-util-Date class
Create-Date-04
Create-Date-06
java-sql-Date class
Create-Date-08
Name that needs to be unique within an entire run unit
Java method names are normally used as they are in COBOL. However, Java
permits multiple methods with a same name to be defined if they have different
parameters. In this case, numbers are assigned to COBOL method names for
identification. However, to take advantage of polymorphism (diversification) that is
the characteristics of object-oriented programming, methods having the same name
and parameter are always assigned the same name. This correspondence
relationship must be consistent within the run unit of the COBOL program that uses
Page 71

Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference 71
the J adapter class generator. For instance, the java.io.ObjectInputStream class
inherits the java.io.ObjectInput interface and java.io.InputStream class (see the
figure below).
Figure 5.2
Relationships among java.io.ObjectInput interface, java.io.InputStream
class, and java.io.ObjectInputStream class
For the adapter class corresponding to these interface and classes, methods of the
same name must be generated for the read methods having the same parameters.
The J adapter class generator uses the generation name management file to manage
the correspondence of method names across classes or interfaces. It then assigns
numbers to methods with the same name according to the following rules:
1. The J adapter class generator searches the generation name management file
for a method having the same name and parameter.
2. If a matching method is found, it uses the corresponding COBOL method name.
3. If no matching method is found, it generates a new COBOL method and adds it
to the generation name management file.
4. A COBOL method name is generated according to the following rule:
- The COBOL method name that is first added is the same as the Java method
name.
- The second and subsequent COBOL method names are assigned number in
ascending order from 01.
Example
The object methods corresponding to the read methods of the java.io.ObjectInput
interface, java.io.InputStream class, and java.io.ObjectInputStream class are
assigned names as shown below:
Java method COBOL method
Page 72

72 Chapter 5. Adapter Class Reference
java.io.ObjectInput
interface
java.io.InputStream
class
m class
read() read
read(byte[]) read-01
read(byte[], int, int)
read() read
read(byte[]) read-01
read(byte[], int, int)
read() read java.io.ObjectInputStrea
read(byte[], int, int)
java-io-ObjectInput
class
java-io-InputStream
class
java-ioObjectInputStream
class
read-02
read-02
read-02
Note: The way of assigning numbers may be different depending on the order
adapter classes are generated. Use the same generation name management file to
generate adapter classes to be used under the same environment.
Supplement
• These naming rules also apply to class methods.
• Java fields (variables) (class/instance) are associated with COBOL property
methods. The same rules as those for methods also apply to property methods.
• The way of assigning numbers may be different depending on the version of JDK
or J2SDK used for adapter class generation.
Page 73

Chapter 6. Messages
This chapter explains the messages output by the J adapter class generator,
including the operator responses to the messages.
Page 74

74 Chapter 6. Messages
Java2cob Command Messages
This section explains the messages output by the java2cob command, including the
operator responses to the messages.
Adapter class generation failed because of a memory space shortage.
Terminate unnecessary applications and retry.
A memory space shortage occurred. Terminate unnecessary applications, then
reenter the java2cob command.
Java VM could not be started. Check the JDK environment definition
(PATH, CLASSPATH) and JDK installation.
The JDK or J2SDK environment contains an error. Check whether environment
variables PATH and CLASSPATH are set normally and whether JDK or J2SDK is
installed normally.
Java2cob class loading failed. Reinstall the J adapter class generator and
retry.
The J adapter class generator is not installed normally. Reinstall the J adapter
class generator.
Messages Output during Generation
This section explains the messages output during adapter class generation, including
the operator responses to the messages.
The message format is shown below:
Message type: Message text
The message types are shown below:
Message type Level Meaning
Error Severe No adapter class is generated.
Warning Cautionary An adapter class is generated. However, the user must
check whether it has been generated as expected.
Error: An invalid option "xxx" was specified. The option was ignored to
continue processing.<<Since processing continues, should this not be a
Warning?>>
Specify a valid option and retry.
Error: A required class name or interface name was missing. Generation
was interrupted.
Specify a valid class name or interface name and retry.
Page 75

Chapter 6. Messages 75
Error: An invalid class name "xxx" was specified. Specify a Java class
name or interface name qualified by a package name.
Specify a valid class name or interface name and retry.
Error: A valid directory name was missing. The option was ignored to
continue processing.<<Same as above>>
Specify a valid directory name and retry.
Error: An invalid directory name "xxx" was specified. Generation was
interrupted.
Specify a valid directory name and retry.
Warning: The generation name management file could not be generated.
Check whether the correct folder name was specified in the -d option or whether
the generation name management file (java2cob.mgt) is write-protected, then
retry.
Error: The serial number exceeded 99.<<Should be SUFFIX, not
SERIAL>> Generation was interrupted.
Decrease the number of classes, fields (variables), or methods having the same
name, then retry. Alternatively, retry while specifying the -om option.
Error: The status of file "xxx" is invalid for generation. Check the file
status.
Check the file status (whether the folder name specified in the -d option is valid
or whether the file is write-protected), then retry.
Error: An error occurred during writing to file "xxx".
Check whether the output destination has enough free space, then retry.
Warning: The name of class "xxx" exceeded 160 characters. The
characters after the first 160 characters were deleted.
Check whether deleting the characters after the first 160 characters results in an
unusable name.
Warning: The property name of field "xxx" exceeded 30 characters. The
characters after the first 30 characters were deleted.
Check whether deleting the characters after the first 30 characters results in an
unusable name.
Warning: The name of method "xxx" exceeded 160 characters. The
characters after the first 160 characters were deleted.
Check whether deleting the characters after the first 160 characters results in an
unusable name.
Page 76

76 Chapter 6. Messages
Warning: The method name of constructor "xxx" exceeded 160
characters. The characters after the first 160 characters were deleted.
Check whether deleting the characters after the first 160 characters results in an
unusable name.
Error: Class information was not found. Generation was interrupted.
Check whether there is a class/interface class file referenced from the
class/interface (see "
available
Error: A memory space shortage occurred. Generation was interrupted.
Terminate unnecessary applications and retry.
Error: A system error occurred. Generation was interrupted.
The J adapter class generator failed. Collect failure information and call your
Fujitsu systems engineer.
Generating an adapter class when the class file is not
").
Page 77
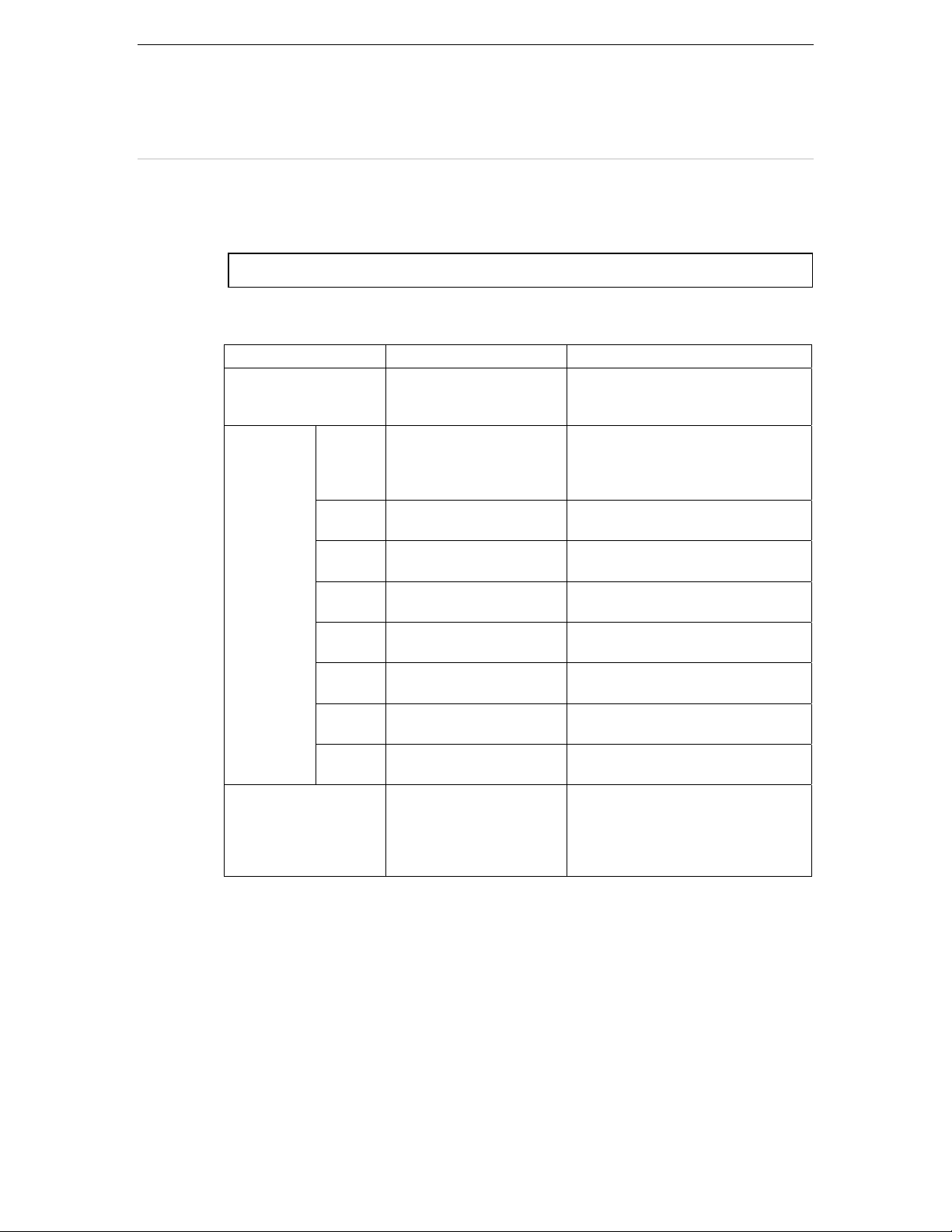
Messages Output during Execution
This section explains the messages output during execution of programs using
adapter classes, including the operator responses to the messages.
The message format is shown below:
Class name information: Message text
Class name information indicates the adapter class in which an error occurred. The
format of class name information varies depending on the class type.
Adapter class type Format Explanation
Class/interface package-name/ ... /class-
name
Array of
basic data
type
Class/interface array [L package-name/ ...
boolean [Z The number of "[" indicates the
byte [B The number of "[" indicates the
char [C The number of "[" indicates the
short [S The number of "[" indicates the
int [I The number of "[" indicates the
long [J The number of "[" indicates the
float [F The number of "[" indicates the
double [D The number of "[" indicates the
/class-name;
Chapter 6. Messages 77
Class name fully qualified by a
package name. Package and class
names are separated by "/".
number of dimensions. For
instance, "[[Z" is used for a 2dimensional array.
number of dimensions.
number of dimensions.
number of dimensions.
number of dimensions.
number of dimensions.
number of dimensions.
number of dimensions.
The number of "[" indicates the
number of dimensions. A class
name fully qualified by a package
name is enclosed between "L" and
";".
Execution-time messages are output to the same destination as the COBOL DISPLAY
statement. Refer to the COBOL97 User's Guide for the output destination of the
DISPLAY statement.
Java VM initialization failed. Check the environment variables (PATH,
COBJNI_CLASSPATH) and JDK or JRE install environment.
The JDK, J2SDK, JRE, or J2RE environment contains an error. Check whether
the environment variables PATH and COBJNI_CLASSPATH are correct or whether
JDK, J2SDK, JRE, or J2RE is installed properly.
Page 78

78 Chapter 6. Messages
The current thread could not be connected to Java VM.
Check whether the program properly invokes the JVM-ATTACH method.
The current thread could not be disconnected from Java VM.
Check whether the program properly invokes the JVM-DETACH method.
The adapter class generated by the J adapter class generator contains a
Java class name in invalid format. Contact the J adapter class generator
supplier.
The J adapter class generator failed. Collect failure information and call your
Fujitsu systems engineer.
A same name is used for a parent and its child in the Java class/interface
definition. Use different names for the parent and child.
The Java class/interface definition contains an error. Check the Java
class/interface.
A required Java class/interface definition is not found. Check the
environment variable (COBJNI_CLASSPATH).
No Java class/interface is found on the search path. Check whether the value of
the environment variable (COBJNI_CLASSPATH) is valid.
A memory space shortage occurred. Increase the values of environment
variables (COBJNI_MAX_NSTACK, COBJNI_JAVA_STACK,
COBJNI_MIN_HEAP, and COBJNI_MAX_HEAP), then retry.
A memory space shortage occurred in the Java VM. Increase the values of
environment variables (COBJNI_MAX_NSTACK, COBJNI_JAVA_STACK,
COBJNI_MIN_HEAP, and COBJNI_MAX_HEAP) to increase memory space
available for the Java VM.
No Java interface/abstract class instance can be generated. Check
whether the Java class/interface was changed after the J adapter class
generator was executed.
A constructor was executed in an abstract class. The Java class/interface was
probably changed after generation of an adapter class. Check the Java
class/interface.
Type conversion failed. Check the parameter passed to the J-NARROW
method.
The object specified in the parameter is not a subclass or object of the class.
Check the parameter passed to the J-NARROW method.
Page 79

Chapter 6. Messages 79
No Java field is found. Check whether the Java class/interface was
changed after execution of the J adapter class generator.
The Java class/interface was probably changed after generation of an adapter
class. Check the Java class/interface.
Java class initialization failed. Call the J adapter class generator supplier.
The J adapter class generator failed. Collect failure information and call your
Fujitsu systems engineer.
No Java method is found. Check whether the Java class/interface was
changed after execution of the J adapter class generator.
The Java class/interface was probably changed after generation of an adapter
class. Check the Java class/interface.
The character string could not be fetched from the String object. Call the J
adapter class generator supplier.
The J adapter class generator failed. Collect failure information and call your
Fujitsu systems engineer.
The subscript of the array object is invalid. Specify a subscript within the
array range.
The subscript value is outside the range from "0 to (element count - 1)." Specify
a valid subscript.
The class of the set object is invalid. Specify a subclass of the array
element class.
An attempt was made to set an invalid class object in an array element. Set an
object of a valid class. An object of the array element class or its subclass must
be set.
An internal logical error (inconsistency between the return value and
object reference) occurred. Call the J adapter class generator supplier.
The J adapter class generator failed. Collect failure information and call your
Fujitsu systems engineer.
Java VM detected an error. Remove the error cause. (exception name:
supplementary information)
The Java VM detected an execution-time error. Determine the error cause from
the exception name and supplementary information and remove it.
An internal logical error (failure of the error detecting feature) occurred.
Call the J adapter class generator supplier.
The J adapter class generator failed. Collect failure information and call your
Fujitsu systems engineer.
Page 80

80 Chapter 6. Messages
Page 81

Chapter 7. Samples
Sample 1 – Using Classes
Example 1: Example of using java.lang.System,
java.io.PrintStream, and java.util.Date classes
This section explains the “Sample Program - Example 1 ” provided with this product.
Example 1 shows how the java.lang.System, java.io.PrintStream, and java.util.Date
classes of Java are used from COBOL.
Outline
Generate an instance of the java.util.Date class and place the content on the
standard output (class variable out of the java.lang.System class).
Distribution files
JADP01.TXT (program description)
JAVA2COB.MGT (generation name management file)
DATEMAIN.PRJ (project file)
DATEMAIN.CBI (compiler option file)
DATEMAIN.COB (COBOL source program)
DATE01JAVA.PRJ (project file)
DATE01JAVA.CBI (compiler option file)
DATE01JAVA2.PRJ (project file)
DATE01JAVA2.CBI (compiler option file)
COBOL functions used
Object-oriented programming functions:
Object generation
Method invocation
Java classes used
java. lang. System
java. io. PrintStream
java. util. Date
Page 82

82 Chapter 7. Samples
Generating adapter classes
Generate adapter classes using the java2cob command.
java2cob java. lang. Object [1]
java2cob java.lang. System [2]
java2cob java. until. Data [3]
1. Generate an adapter class of the java.lang.Object class (required for calling
Java).
2. Generate an adapter class of the java.lang.System class used for standard
output. An adapter class of the java.util.PrintStream class referenced from the
java.lang.System class is also generated.
3. Generate an adapter class of the java.util.Date class.
Project build or rebuild function
This section explains how to create an executable program using the build function
of the project manager. Refer to the “Fujitsu COBOL User’s Guide” for detailed
information on how to use the project manager.
1. When using Java(JDK 1.1.x), open project file “DATE01JAVA.PRJ”. When using
Java2(J2SDK 1.2.2 or later), open project file “DATE01JAVA2.PRJ”.
2. Select “Build” from the “Project“ menu. An adapter class DLL (DATE.DLL) is
generated.
3. Open project file “DATEMAIN.PRJ.”
4. Select “Build” from the “Project“ menu.
Running the program
Run the executable program from the MS-DOS prompt. The date and time are
displayed.
Page 83

Sample 2 – Specifying Method
Example 2: Example of generating an adapter class by
specifying constructor/method/field
This program description explains “Sample Program - Example 2” provided with this
product.
Example 2 shows how to generate the adapter class specifying
constructor/method/field.
Outline
The program contents are the same as example 1. However, example 2 generates
the adapter class specifying the Java constructor/method/field name used by the
program.
Distribution files
JADP02.TXT (program description)
Chapter 7. Samples 83
JAVA2COB.MGT (generation name management file)
DATEMAIN.PRJ (project file)
DATEMAIN.CBI (compiler option file)
DATEMAIN.COB (COBOL source program)
DATE02JAVA.PRJ (project file)
DATE02JAVA.CBI (compiler option file)
DATE02JAVA2.PRJ (project file)
DATE02JAVA2.CBI (compiler option file)
COBOL functions used
Object-oriented programming functions
Object generation
Method invocation
Java classes and constructor/method/field used
java.lang.System class -- out field
java.io.PrintStream class -- println(java.lang.Object) method
java.util.Date class -- Date() constructor
Page 84

84 Chapter 7. Samples
Generating adapter classes
Generate adapter classes using the java2cob command.
java2cob -r java.lang.System -gf out \ [1]
-r java.io.PrintStream -gm "println(java.lang.Object)" \ [2]
-r java.util.Date -gc "Date()" [3]
Note: “\” shows the continuance line.
1. Generate an adapter class of the java.lang.System class that contains the out
field used for standard output.
2. Generate an adapter class of the java.io.PrintStream class that contains the
println(java.lang.Object) method used for standard output.
3. Generate an adapter class of the java.util.Date class that contains the Date()
constructor.
Project build or rebuild function
This section explains how to create an executable program using the build function
of the project manager. Refer to the “Fujitsu COBOL User’s Guide” for detailed
information on how to use the project manager.
1. When using Java(JDK 1.1.x), open project file “DATE02JAVA.PRJ”. When using
Java2(J2SDK 1.2.2 or later), open project file “DATE02JAVA2.PRJ”.
2. Select “Build” from the “Project” menu. An adapter class DLL (DATE.DLL) is
generated.
3. Open project file “DATEMAIN.PRJ.”
4. Select “Build” from the “Project” menu.
Running a program
Run the executable program from the MS-DOS prompt. The date and time are
displayed.
Page 85

Appendix A. Message List
This chapter explains the messages output by the J adapter class generator,
including the operator responses to the messages.
Page 86

86 Appendix A. Message List
Java2cob Command Messages
This section explains the messages output by the java2cob command, including the
operator responses to the messages.
Adapter class generation failed because of a memory space shortage.
Terminate unnecessary applications and retry.
A memory space shortage occurred. Terminate unnecessary applications, then
reenter the java2cob command.
Java VM could not be started. Check the JDK environment definition
(PATH, CLASSPATH) and JDK installation.
The JDK or J2SDK environment contains an error. Check whether environment
variables PATH and CLASSPATH are set normally and whether JDK or J2SDK is
installed normally.
Java2cob class loading failed. Reinstall the J adapter class generator and
retry.
The J adapter class generator is not installed normally. Reinstall the J adapter
class generator.
Failed to open the optional file. Check the file status. Generation was
interrupted.
Check status of the optional file (if the filename that is specified with the -i
option is correct or not, if the file is set to read protection), and re-execute the
processing.
Optional filename is not specified. Generation was interrupted.
Specify the filename of the -i option and re-execute the processing.
Page 87

Messages Output during Generation
This section explains the messages output during adapter class generation, including
the operator responses to the messages.
The message format is shown below:
Message type: Message text
The message types are shown below:
Message type Level Meaning
Error Severe No adapter class is generated.
Warning Cautionary An adapter class is generated. However, the user must
check whether it has been generated as expected.
Warning: An invalid option "xxx" was specified. The option was ignored
to continue processing.
Appendix A. Message List 87
Specify a valid option and retry.
Error: A required class name or interface name was missing. Generation
was interrupted.
Specify a valid class name or interface name and retry.
Error: An invalid class name "xxx" was specified. Specify a Java class
name or interface name qualified by a package name.
Specify a valid class name or interface name and retry.
Warning: A valid directory name was missing. The option was ignored to
continue processing.
Specify a valid directory name and retry.
Error: An invalid directory name "xxx" was specified. Generation was
interrupted.
Specify a valid directory name and retry.
Warning: "xxx" specified for class "xxx" was not generated. Check the
specified name (and parameter).
Check whether the correct constructor/method/field was specified, then retry
(see "Specifying the constructor/method/field").
Warning: The generation name management file could not be generated.
Check whether the correct folder name was specified in the -d option or “Option
OutPutPath” parameter, or whether the generation name management file
(java2cob.mgt) is write-protected, then retry.
Page 88

88 Appendix A. Message List
Error: The suffix number exceeded 99. Generation was interrupted.
Retry while specifying –r option, -gc option, -gm option, -gf option, -om option,
constructor/method/field-specifying-option
parameter, or “Option ReduceClass” parameter to decrease the number of
classes, fields (variables), or methods.
Error: The status of file "xxx" is invalid for generation. Check the file
status.
Check the file status (whether the folder name specified in the -d option or
“Option OutPutPath” parameter is valid or whether the file is write-protected),
then retry.
Error: An error occurred during writing to file "xxx".
Check whether the output destination has enough free space, then retry.
Error: Both of the -om option (Option ReduceClass) and the -r option
(Option GenOnlyUsed) cannot be specified at the same time. Generation
was interrupted.
in “Class
class-name/interface-name
”
Specify either -om option (or "Option ReduceClass" parameter) or the -r option
(or "Option GenOnlyUsed" parameter) and re-execute the processing. The -r
option (or "Option GenOnlyUsed" parameter) is recommended.
Error: Both of the -om option (Option ReduceClass) and the -s option
(Option String) cannot be specified at the same time. Generation was
interrupted.
Specify either -om option (or "Option ReduceClass" parameter) or the -s option
(or "Option String " parameter) and re-execute the processing.
Error: Failed to open the optional file. Check the file status. Generation
was interrupted.
Check status of the optional file (if the filename that is specified with the -i
option is correct, if the file is set to read protection), and re-execute the
processing.
Error: An invalid definition "xxx" was specified in the optional file. The
definition was ignored to continue processing.
Specify the correct definition and re-execute the processing.
Warning: The name of class "xxx" exceeded 160 characters. The
characters after the first 160 characters were deleted.
Check whether deleting the characters after the first 160 characters results in an
unusable name.
Page 89

Appendix A. Message List 89
Warning: The property name of field "xxx" exceeded 30 characters. The
characters after the first 30 characters were deleted.
Check whether deleting the characters after the first 30 characters results in an
unusable name.
Warning: The name of method "xxx" exceeded 160 characters. The
characters after the first 160 characters were deleted.
Check whether deleting the characters after the first 160 characters results in an
unusable name.
Warning: The method name of constructor "xxx" exceeded 160
characters. The characters after the first 160 characters were deleted.
Check whether deleting the characters after the first 160 characters results in an
unusable name.
Error: Class information was not found. Generation was interrupted.
Check whether there is a class/interface class file referenced from the
class/interface (see "Generating an adapter class when the class file is not
available").
Error: A memory space shortage occurred. Generation was interrupted.
Terminate unnecessary applications and retry.
Error: A system error occurred. Generation was interrupted.
The J adapter class generator failed. Collect failure information and call your
Fujitsu systems engineer.
Page 90

90 Appendix A. Message List
Messages Output during Execution
This section explains the messages output during execution of programs using
adapter classes, including the operator responses to the messages.
Messages given while execution is underway are output to the same target output as
that of the DISPLAY statement that is specified by UPON SYSERR of COBOL. Refer
to "Fujitsu COBOL User's Guide" for the target output of the DISPLAY statement that
is specified by UPON SYSERR of COBOL.
Output of the messages given while execution is underway can be suppressed by
setting "YES" to the environment variable COBJNI_NOMESSAGE.
The message format is shown below:
Class name information: Message text
Class name information indicates the adapter class in which an error occurred. The
format of class name information varies depending on the class type.
Adapter class type Format Explanation
Class/interface package-name/ ...
/class-name
Array of
basic
data
type
Class/interface array [L package-name/ ...
boolean [Z The number of "[" indicates the number of dimensions.
byte [B The number of "[" indicates the number of dimensions.
char [C The number of "[" indicates the number of dimensions.
short [S The number of "[" indicates the number of dimensions.
int [I The number of "[" indicates the number of dimensions.
long [J The number of "[" indicates the number of dimensions.
float [F The number of "[" indicates the number of dimensions.
double [D The number of "[" indicates the number of dimensions.
/class-name;
Class name fully qualified by a package name. Package
and class names are separated by "/".
For instance, "[[Z" is used for a 2-dimensional array.
The number of "[" indicates the number of dimensions. A
class name fully qualified by a package name is enclosed
between "L" and ";".
Java VM initialization failed. Check the environment variables (PATH,
COBJNI_CLASSPATH) and JDK or JRE install environment.
The JDK, J2SDK, JRE, or J2RE environment contains an error. Check whether
the environment variables PATH and COBJNI_CLASSPATH are correct or whether
JDK, J2SDK, JRE, or J2RE is installed properly.
The current thread could not be connected to Java VM.
Check whether the program properly invokes the JVM-INIT method or the JVMATTACH method.
The current thread could not be disconnected from Java VM.
Check whether the program properly invokes the JVM-TERMINATE method or
the JVM-DETACH method.
Page 91

Appendix A. Message List 91
The adapter class generated by the J adapter class generator contains a
Java class name in invalid format. Contact the J adapter class generator
supplier.
The J adapter class generator failed. Collect failure information and call your
Fujitsu systems engineer.
A same name is used for a parent and its child in the Java class/interface
definition. Use different names for the parent and child.
The Java class/interface definition contains an error. Check the Java
class/interface.
A required Java class/interface definition is not found. Check the
environment variable (COBJNI_CLASSPATH).
No Java class/interface is found on the search path. Check whether the value of
the environment variable (COBJNI_CLASSPATH) is valid.
A memory space shortage occurred. Increase the values of environment
variables (COBJNI_MAX_NSTACK, COBJNI_JAVA_STACK,
COBJNI_MIN_HEAP, and COBJNI_MAX_HEAP), then retry.
A memory space shortage occurred in the Java VM. Increase the values of
environment variables (COBJNI_MAX_NSTACK, COBJNI_JAVA_STACK,
COBJNI_MIN_HEAP, and COBJNI_MAX_HEAP) to increase memory space
available for the Java VM.
No Java interface/abstract class instance can be generated. Check
whether the Java class/interface was changed after the J adapter class
generator was executed.
A constructor was executed in an abstract class. The Java class/interface was
probably changed after generation of an adapter class. Check the Java
class/interface.
Type conversion failed. Check the parameter passed to the J-NARROW
method.
The object specified in the parameter is not a subclass or object of the class.
Check the parameter passed to the J-NARROW method.
No Java field is found. Check whether the Java class/interface was
changed after execution of the J adapter class generator.
The Java class/interface was probably changed after generation of an adapter
class. Check the Java class/interface.
Java class initialization failed. Call the J adapter class generator supplier.
The J adapter class generator failed. Collect failure information and call your
Fujitsu systems engineer.
Page 92

92 Appendix A. Message List
No Java method is found. Check whether the Java class/interface was
changed after execution of the J adapter class generator.
The Java class/interface was probably changed after generation of an adapter
class. Check the Java class/interface.
The character string could not be fetched from the String object. Call the J
adapter class generator supplier.
The J adapter class generator failed. Collect failure information and call your
Fujitsu systems engineer.
The subscript of the array object is invalid. Specify a subscript within the
array range.
The subscript value is outside the range from "0 to (element count - 1)." Specify
a valid subscript.
The class of the set object is invalid. Specify a subclass of the array
element class.
An attempt was made to set an invalid class object in an array element. Set an
object of a valid class. An object of the array element class or its subclass must
be set.
An internal logical error (inconsistency between the return value and
object reference) occurred. Call the J adapter class generator supplier.
The J adapter class generator failed. Collect failure information and call your
Fujitsu systems engineer.
Java VM detected an error. Remove the error cause. (exception name:
supplementary information)
The Java VM detected an execution-time error. Determine the error cause from
the exception name and supplementary information and remove it.
An internal logical error (failure of the error detecting feature) occurred.
Call the J adapter class generator supplier.
The J adapter class generator failed. Collect failure information and call your
Fujitsu systems engineer.
Page 93

Appendix B. Exception Type List
The exception types that can be acquired by the GET-CODE method of the FJ-JAVAERROR class are described in this chapter.
1
Meaning
Java VM detected an error. Remove the error cause.
Response
The Java VM detected an execution-time error. Determine the error cause from the
exception information returned by the GET-EXCEPTION method of FJ-JAVA-ERROR
class, and remote it.
2
Meaning
No Java method is found. Check whether the Java class/interface was changed after
execution of the J adapter class generator.
Response
The Java class/interface was probably changed after generation of an adapter class.
Check the Java class/interface.
3
Meaning
Java class initialization failed. Call the J adapter class generator supplier.
Response
The J adapter class generator failed. Collect failure information and call your Fujitsu
systems engineer.
4
Meaning
A memory space shortage occurred. Increase the values of environment variables
(COBJNI_MAX_NSTACK, COBJNI_JAVA_STACK, COBJNI_MIN_HEAP, and
COBJNI_MAX_HEAP), then retry.
Response
A memory space shortage occurred in the Java VM. Increase the values of
environment variables (COBJNI_MAX_NSTACK, COBJNI_JAVA_STACK,
COBJNI_MIN_HEAP, and COBJNI_MAX_HEAP) to increase memory space available
for the Java VM.
Page 94

94 Appendix B. Exception Type List
5
Meaning
No Java field is found. Check whether the Java class/interface was changed after
execution of the J adapter class generator.
Response
The Java class/interface was probably changed after generation of an adapter class.
Check the Java class/interface.
6
Meaning
The subscript of the array object is invalid. Specify a subscript within the array
range.
Response
The subscript value is outside the range from "0 to (element count - 1)." Specify a
valid subscript.
7
Meaning
The adapter class generated by the J adapter class generator contains a Java class
name in invalid format. Contact the J adapter class generator supplier.
Response
The J adapter class generator failed. Collect failure information and call your Fujitsu
systems engineer.
8
Meaning
A same name is used for a parent and its child in the Java class/interface definition.
Use different names for the parent and child.
Response
The Java class/interface definition contains an error. Check the Java class/interface.
9
Meaning
The class of the set object is invalid. Specify a subclass of the array element class.
Response
An attempt was made to set an invalid class object in an array element. Set an
object of a valid class. An object of the array element class or its subclass can be
set.
Page 95

Appendix B. Exception Type List 95
10
Meaning
A required Java class/interface definition is not found. Check the environment
variable (COBJNI_CLASSPATH).
Response
No Java class/interface is found on the search path. Check whether the value of the
environment variable (COBJNI_CLASSPATH) is valid.
11
Meaning
No Java interface/abstract class instance can be generated. Check whether the Java
class/interface was changed after the J adapter class generator was executed.
Response
A constructor was executed in an abstract class. The Java class/interface was
probably changed after generation of an adapter class. Check the Java
class/interface.
12
Meaning
Java VM initialization failed. Check the environment variables (PATH,
COBJNI_CLASSPATH) and JDK or JRE install environment.
Response
The JDK, J2SDK, JRE, or J2RE environment contains an error. Check whether the
environment variables PATH and COBJNI_CLASSPATH are normal or whether JDK,
J2SDK, JRE, or J2RE is installed normally.
13
Meaning
The character string could not be fetched from the String object. Call the J adapter
class generator supplier.
Response
The J adapter class generator failed. Collect failure information and call your Fujitsu
systems engineer.
14
Meaning
Type conversion failed. Check the parameter passed to the J-NARROW method.
Response
The object specified in the parameter is not a subclass or object of the class. Check
the parameter of the J-NARROW method.
Page 96

96 Appendix B. Exception Type List
15
Meaning
An internal logical error (inconsistency between the return value and object
reference) occurred. Call the J adapter class generator supplier.
Response
The J adapter class generator failed. Collect failure information and call your Fujitsu
systems engineer.
16
Meaning
Java VM detected an error. Remove the error cause. (exception name:
supplementary information)
Response
The Java VM detected an execution-time error. Determine the error cause from the
exception name and supplementary information and remote it.
17
Meaning
An internal logical error (failure of the error detecting feature) occurred. Call the J
adapter class generator supplier.
Response
The J adapter class generator failed. Collect failure information and call your Fujitsu
systems engineer.
18
Meaning
The current thread could not be connected to Java VM.
Response
Check whether the program normally invokes the JVM-INIT method or the JVMATTACH method.
19
Meaning
The current thread could not be disconnected from Java VM.
Response
Check whether the program normally invokes the JVM-TERMINATE method or the
JVM-DETACH method.
Page 97

Index
adapter class, 14, 34, 46, 51
adapter object, 15
alphanumeric item, 27, 28, 34, 40
array, 65
assign, 25
-c, 32, 54, 63
class file, 18, 20
class method, 11, 26, 57
class variable, 11, 25, 26, 56
classpath, 35, 37
-classpath, 32
constructor, 32, 34, 37, 51, 54, 55, 57, 70
See
constructors.
cross-reference, 33, 39, 42, 43, 58
-d, 32
Environment variable, 48
exception, 11, 28, 46, 50, 54, 55, 57, 60
constructor
Inheriting a Java class, 11
Initialization, 22
instance method, 11, 24, 60
instance object, 11
instance variable, 11, 26, 58
interface name, 34, 37, 42, 53
internal class, 53
Invoking COBOL from Java, 12
Japanese, 12, 35
Java class, 11, 14, 18, 34, 37, 51
Java object, 11, 25
Java VM, 22, 23, 29, 46, 48
J-DUPLICATE, 47
J-EQUALS, 48
J-NARROW, 47
JVM-ATTACH, 49
JVM-DETACH, 49
external class, 21, 53
external method, 57
factory, 11, 23, 54, 55, 57, 70
-gc, 20, 32, 34
generation name, 30, 43, 71
GET-ARRAY-ELEMENT, 68
GET-ARRAY-LENGTH, 68
GET-CODE, 50
GET-EXCEPTION, 51
GET-MESSAGE, 50
GET-STRING-LENGTH-N, 65
GET-STRING-LENGTH-X, 64
GET-STRING-N, 64
GET-STRING-X, 63
-gf, 33
-gm, 33
JVM-INIT, 48
JVM-TERMINATE, 49
method name, 24, 33, 43, 70, 71
multithread, 23, 48, 49
name duplication, 56
NEW-ARRAY, 67
NEW-STRING-N, 62
NEW-STRING-X, 61
-oi, 33, 43
-om, 20, 21, 33, 34, 40
optional file, 31, 33, 36, 38
OutPutPath, 39
-ov, 34
OverWrite, 39
property method, 56
public elements, 51
Page 98

98 Index
-r, 20, 33, 34, 58
ReduceClass, 40
restrictions, 12
return value, 57
Runtime, 12
-s[n], 34
SET-ARRAY-ELEMENT, 69
source file, 19, 29, 42
String class, 26, 44, 54, 61
-t, 34
Termination, 22
Unicode, 35, 38
unique name, 69
98
 Loading...
Loading...