Page 1

C150-E187-01EN
Scanner Utility for
Microsoft Windows
<32bit>
Version 8.0
Page 2

Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the "Scanner Utility for Microsoft Windows V8.0".
This software contains a TWAIN-compliant image scanner driver (simply called "driver" in this
guide) and utilities.
This guide provides a description summary of the driver, as well as a description of the
installation method and procedures for appropriate use. Please read this guide before starting to
use the software.
In addition, read the README.TXT file on the CD-ROM for the latest information not included
in this manual.
In this guide, product names are abbreviated as follows:
•
"Microsoft Windows 95 operating system": "Windows 95"
•
"Microsoft Windows NT Workstation operating system Version 4.0" and "Microsoft
Windows NT Server operating system Version 4.0": "Windows NT 4.0"
•
"Microsoft Windows98 operating system": "Windows98"
•
"Microsoft Windows 2000 operating system": "Windows 2000"
•
"Microsoft Windows Millennium Edition": "Windows Me"
When "Windows 95," "Windows 98," "Windows NT 4.0," "Windows 2000"and
"Windows Me" are referred to collectively, they are simply referred to as "Windows". Unless
otherwise indicated, explanations refer to "Windows 95," "Windows 98," "Windows NT
4.0," "Windows 2000,"and"Windows Me" collectively.
i
Page 3

Trademarks
MS-DOS, Microsoft, Windows, and Windows NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation.
IBM PC/AT and DOS/V are registered trademark of International Business Machine
Corporation.
Adaptec is a registered trademark of Adaptec Inc.
EZ-SCSI is a trademark of Adaptec Inc.
Other product names are the trademarks or registered trademarks of the respective companies.
ii
Page 4

Organization
This manual explains how to install and use this driver, and how to use the TWAIN scanning
utility.
•
TWAIN
This section gives an overview of the TWAIN specification.
•
Installation
This section explains the procedure for installing the environments in which this driver may
operate.
•
Using the Driver
This section explains how to use the driver.
•
Using the Utilities
Use of the following utilities is explained:
−
Using the Gamma Pattern Editor
•
Troubleshooting
This section explains the possible causes of error messages and operation errors and the
corresponding recommended actions.
•
Appendix
The appendix contains the specifications of image scanners.
iii
Page 5

Contents
1. Outline............................................................................................. 1
1.1 Characteristics of this Driver...........................................................................1
1.2 Operating Environment...................................................................................1
1.3 Explanatory Notes..........................................................................................2
1.4 Explanation of terms.......................................................................................3
2. TWAIN ............................................................................................. 4
2.1 TWAIN............................................................................................................4
2.2 TWAIN Application.........................................................................................4
3. Installation ......................................................................................6
3.1 Preparation.....................................................................................................6
3.2 Starting Installation.........................................................................................6
3.3 Uninstall..........................................................................................................7
4. Using the Driver.............................................................................. 8
4.1 Selecting the Driver........................................................................................8
4.2 Screen Configuration......................................................................................9
4.3 Displaying Driver Information .......................................................................10
4.4 Setting Information on Image Scanning .......................................................11
4.5 Specifying Driver Operation..........................................................................18
4.6 Setting "Scanning Area"...............................................................................20
4.7 Setting Options.............................................................................................21
4.8 Setting Advance Options..............................................................................31
4.9 Setting the Configuration Options.................................................................43
4.10 Basic Scan Dialog......................................................................................46
4.11 Download Pattern File................................................................................48
5. Using the Gamma Pattern Editor ................................................ 52
iv
Page 6

5.1 Start-up.........................................................................................................52
5.2 [File] menu....................................................................................................53
5.3 [Help] menu..................................................................................................54
5.4 Gamma Pattern Editing................................................................................55
6. How to Use the FUJITSU Scanner Control Center..................... 56
6.1 Outline..........................................................................................................56
6.2 How to Start the FUJITSU Scanner Control Center .....................................56
6.3 Pop-up Menu................................................................................................57
7. Troubleshooting........................................................................... 62
7.1 Error Messages............................................................................................62
7.1.1 Messages from the TWAIN Driver......................................................................62
7.1.2 Error messages relating to gamma correction pattern editing.............................69
7.1.3 Messages concerning to FUJITSU Scanner Control Center...............................70
8. Appendix....................................................................................... 72
8.1 Relevant Image Scanner Specification.........................................................72
8.2 Maintenance Service....................................................................................87
v
Page 7

1. Outline
1.1 Characteristics of this Driver
•
This driver complies with TWAIN regulations V1.8 (the latest version as of May 2000),
which are global standards for image scanners. The driver can be used in all TWAINcompliant applications.
•
This driver also supports an image scanner that has the "double-sided scan" function. If the
application supports continuous scan, a double-sided document can be scanned.
1.2 Operating Environment
This driver can be used in the following systems:
•
An IBM PC/AT compatible machine (recommended: Intel Pentium 100MHz or higher) on
which one of the following operating systems are installed
−
Microsoft Windows 95
−
Microsoft Windows 98
−
Microsoft Windows Me
−
Microsoft Windows NT Server Version 4.0 (Installation of Service Pack 3 or later
recommended)
−
Microsoft Windows NT Workstation Version 4.0 (Installation of Service Pack 3 or
later recommended)
−
Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional Edition
•
Adaptec SCSI adapter or Fujitsu FMV SCSI adapter
−
In some cases, the driver may not operate with the above systems. Please check in
advance with your place of purchase.
−
Notes are provided on the accepted SCSI adapters in README.TXT, which is included
in the installation media. Please read these notes before use.
•
Adaptec EX-SCSITM Pro Version 4.5 or later or the following 32-bit versions of ASPI
Manager (included, for example, in the Adaptec SCSI installer for Windows 95/Windows
NT or on Fujitsu SCSI driver disk V1.2):
Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT 4.0
Windows 2000, Professional Edition
•
RAM of 16 megabytes or more
•
Free hard disk space of 4 megabyte or more
•
CD-ROM drive (required for installation)
•
Mouse (recommended)
V4.01 or later
V4.60 or later
1
Page 8
1.3 Explanatory Notes
The descriptions in this manual are prepared based on the following rules:
◊
Menus and buttons
The menus and buttons used in the program description are enclosed in [].
Example: [File] menu, [OK] button
◊
Keyboard
The keytop indications comply with the standard keyboard of the Fujitsu FMV series.
Major differences between the Fujitsu FMV keyboard and other keyboards are shown below.
FMV keytops Other possible keytops
Alt Previous screen, GRPH
Ctrl CTRL
Esc ESC
Enter Return,
Shift SHIFT
Back space Backspace, BS
F1 PF1, f-1
◊
Terms related to mouse operation
Terms related to major mouse operations are explained below.
Click: To press and release the mouse button
Double click: To quickly press the mouse button twice
Drag: Move the mouse while keeping the mouse button pressed
◊
Notes on operation procedures
If some menus need to be operated in a certain order, the procedural order is described as
follows:
[A] - [B] - [C]
In accordance with this description, operation [A] is executed first, followed by [B] and [C]
in that order.
◊
Figures
Figures and screen operations in this guide refer to Microsoft Windows 2000. They are
also followed when using other operating systems.
Note that the expressions may vary with the type of scanner connected.
2
Page 9

1.4 Explanation of terms
◊
IPC option board
IPC-2/2D in this guide refers to the IPC-2 and IPC-2D image processing circuit.
IPC-3/3D in this guide refers to the IPC-3 and IPC-3D option board.
3
Page 10

2. TWAIN
2.1 TWAIN
TWAIN is the specification that defines the standard software protocol and application
programming interface (API) for data exchange between a software application program and an
image input device such as the image scanner.
[TWAIN development background]
In the past, development of a new scanner inevitably required the development of a compatible
driver and a sample (demonstration) program exclusively designed for the new scanner. As the
scanner is upgraded, the driver may need to be upgraded as well to maintain its compatibility
with the upgraded scanner. Therefore, the use is most likely to be restricted to one specific
scanner model to avoid the complication of learning new operation methods and replacing the
peripheral driver, etc., involved in scanner replacement.
In view of the incompatibility among different scanners and peripheral equipment and the
accompanying inconvenience, there was a demand for standardization of the related hardware
and software, and TWAIN was established as a result.
The user may now choose among all the input devices and software (driver or application
programs) conforming to the TWAIN standard, and configure a most suitable system for himself,
without being restricted to the products of a certain series or a certain manufacturer.
2.2 TWAIN Application
TWAIN mainly applies to the following three software components:
• Application software
‚ Source manager
ƒ Source
The components are related to each other as shown below.
4
Page 11

Application software
Image scanner
, etc.
•
(photo retouching software, etc)
Source manager
‚
(TWAIN.DLL/TWAIN_32.DLL, etc)
Source
ƒ
(Image scanner control of the driver, etc)
Figure TWAIN Application
5
Page 12

3. Installation
3.1 Preparation
1. Check that the operating system is installed correctly.
2. Check that the SCSI adapter is connected to the computer.
3. Check whether the SCSI driver and ASPI manager are installed correctly and operating (For
windows 2000, 4.60 or later)
Note
Version 4.01 or later of the ASPI Manager is required. Use Explorer or a similar program
to check the version number of the WNASPI32.DLL file.
The environment setup tools described later can be used for checking.
4. If the previous version was installed, first confirm that it has been uninstalled (deleted).
5. Confirm that there is sufficient free space on the hard disk to install the software.
3.2 Starting Installation
1. Start Windows.
Note
A user name with administrator authority must be used to log on to Windows(R) 2000 or
Windows NT(R) 4.0.
Ask the system administrator for the details of logging on.
2. Close any other currently open applications.
3. Insert the setup CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive. Here, the CD-ROM drive is temporarily
called "D:". (If the environment you are using is different, replace the appropriate parts
below.)
4. Double-click on "install.exe" in the "D: \Driver1\ASPI" folder of the CD-ROM using
Explorer. Then, installation starts.
When an automatic start is specified, the start screen of the setup disk is displayed.
Installation can be started from this screen too.
5. When the setup screen is displayed, continue the process by following the on-screen
instructions.
6. Confirm that the following group is created when setup has been completed. The displayed
icon depends on the selection of "Components" during installation.
6
Page 13

3.3 Uninstall
The uninstall process removes the software and returns the hard disk to its pre-installation state.
1. Click on [Start], followed by [Settings], and then [Control Panel]. The Control Panel is then
2. Double-click on "Add/Remove Programs" from the icon list of the Control Panel. The panel
3. Select "Scanner Utility for Microsoft Windows" from the "Install/Uninstall" list.
4. Click on the [Add/Remove] button. When the confirmation dialog is displayed, click on
5. When uninstallation is completed, click on [OK.]
Note
Figure Fujitsu TWAIN group
displayed.
of properties of [Add/Remove Programs] is displayed.
[OK] if you are ready to uninstall.
Image files that have been scanned and saved will not be deleted.
If other TWAIN-compliant applications and drivers have been installed and you are asked
whether or not to delete files shared with them such as the TWAIN Manager, select [NO]
to avoid deleting them.
7
Page 14

4. Using the Driver
4.1 Selecting the Driver
To use this driver from the TWAIN application, select "FUJITSU TWAIN32" from the TWAIN
data source (driver) selection screen. For general application, the data source selection screen is
displayed by selecting the [Select Scanner] or [Acquire ...] menu. Refer to the instruction
manual for the application used for details.
8
Page 15

4.2 Screen Configuration
Figure Main Dialog
The following pages contain the explanation and operation description for each part.
9
Page 16

4.3 Displaying Driver Information
♦
Image scanner name
The model name, option port name, and capacity of internal scanner memory (in units of
megabytes) of the connected image scanner are displayed.
If no image scanner is connected, this field is blank.
To change the selected scanner, click the [Select ...] button to display a list of connected
scanners and select a scanner from the list.
The type of IPC option board is displayed if an image-processing option board is installed in
the scanner.
IPC-3/3D may not be detected normally, as it is affected by the version number of the
machine type and device. In this case, "IPC2" is displayed.
♦
Preview window
The preview window is used to display the temporary image of read data and for setting the
"Scanning Area."
For settings, see "Scanning Area" later in this manual. Also see the description of the
[Preview] button later in this manual.
♦
Ruler
The large divisions are labeled as "Unit". The scale also varies with the selected scanner.
♦
Message line
The message line is the bottom line of the dialog in which a brief explanation of an input
item or a setting item is displayed when the mouse cursor is moved over the item.
10
Page 17

♦
Data size
The approximate amount of data per image when data is scanned in the present option.
Note
This value is the amount of uncompressed data. The size of the stored file will differ from
this value and is usually smaller if image compression is chosen and the image is
compressed.
4.4 Setting Information on Image Scanning
♦
Current side
When a scanner that allows duplex scanning is used, specifies the page which sets the image
scanning information.
To scan using the same settings as those for "Front side" and "Back side," clear the checks in
the "Individual Setting" checkbox on the "Front" and "Back" tabs. A single "Duplex" tab
will be displayed at the left so that the same image scanning information can be set for
"Front side" and "Back side."
To scan using different settings for "Front side" and "Back side," check the "Individual
Setting" checkbox on the "Front" and "Back" tabs. Two tabs, "Front" and "Back," will be
displayed at the left. Select each tab and enter the desired settings.
This is only effective when ADF (Duplex) is selected for the method of paper feed. For
scanner types which permit duplex scanning, see "Relevant Image Scanner Specification" in
the Appendix.
♦
Resolution
Specifies the number of pixels (dots) per inch.
Select a fixed resolution from the list or [Custom].
High resolution requires more memory.
The supported resolution depends on the type of scanner and the options installed. See
"Relevant Image Scanner Specification" in the Appendix.
11
Page 18

♦
Paper Size
Selects a paper size corresponding to the size of the document to be scanned.
Select a standard paper size from the list or [Custom]. If [Custom] is selected, the "Custom
Paper Size Setting" dialog appears. Enter the size of the document to be scanned.
Some paper sizes may not be accepted by your device. See "Relevant Image Scanner
Specification" in Appendix.
Figure Custom paper size setting dialog
To specify a custom paper size, use the slider or enter the paper size directly. The applicable
unit here is the unit specified under [Option]-[Generic]-[Unit/Scaling].
♦
Scanning Area
Specifies the start position, width and length for the image scan. The maximum allowable
size is the paper size selected previously.
In addition, the minimum size is 1.000 inch, 26 millimeters, or pixels (number of dots per
inch) according to the unit that has been set.
"Left": The left end of the scan area on the scanned document (X coordinate)
"Top": The top end of the scan area or the scanned document (Y coordinate)
"Width": The width of the scan area
"Length": The length of the scan area
These values are related to one another in the following way:
0 ≤ left end coordinate < (paper width - minimum scan area size)
0 ≤ top end coordinate < (paper length - minimum scan area size)
Minimum value ≤ width ≤ (paper width - left end coordinate)
Minimum value ≤ length ≤ (paper length - top end coordinate)
12
Page 19

♦
Scan Type
Selects the feeding device.
The image scanner uses a document bed called the flat bed as well as an automatic document
feeder (ADF) for feeding scanned document. The ADF usually enables the documents to be
scanned only once. The flat bed allows scanning the same documents repeatedly.
♦
Flatbed
Reads a document placed on the flat bed of the device.
♦
ADF (Simplex)
Reads the document on the device's automatic document feeder (ADF). Here, only one side
is read.
♦
ADF (Duplex)
To scan both the front and the back of a page, select this option.
If this option is selected, the document is scanned in the "front to back to front to back ..."
order.
This option can be used only for scanner models that support duplex scanning.
The "Duplex Function" requires that the calling application supports "continuous scan." If
the application does not support "continuous scan," only the data for the front side of the
page is passed to the application.
Some scanner models do not support this option. See "Relevant Image Scanner
Specification" in the Appendix.
♦
Long page (front)
To scan the entire side of a long page whose length exceeds the vertical size of an A3 sheet,
select this option.
The front side and back side can be specified using the same method used for ADF.
If this option is selected, the "Paper Size Setting" dialog box opens. Specify the size of the
document to be scanned.
In this mode, however, the preview window cannot be displayed and the scanning area
cannot be specified.
Scanner models that do not support this option do not display the "Scan Type" selection item.
13
Page 20

♦
Long page (front and backside)
In the same case as that for scanning the front of a long page, this option is selected in order
to scan the entire side of a long page whose length exceeds the vertical size of an A3 sheet.
If this option is selected, the document is scanned in the "front to back to front to back…"
order.
Paper feeding method that is to be supported varies with the type of scanner. See "Relevant
Image Scanner Specification" in the Appendix.
Note
To specify duplex scanning, the number of copies designated should be based on the
number of pages, not the number of paper sheets . In other words, one original with a
front and back is regarded as two pages.
♦
Image Mode
Selects an image mode for scanning the image.
Select a corresponding image mode from the list.
Black & White
Scans data by using the fixed threshold binary, black-and-white. Distinguishes black
from white by the setting in the "Threshold" of "Scanning Parameter." This scanning
mode is suitable for scanning line drawings and text documents.
Halftone (Dither)
Scans data using the halftone processing, with dithering or error diffusion. Uses the
patterns set in "Halftone" to simulate data in black-and-white. Selection of built-in
dithered patterns or error diffusion (not supported by some device models) is allowed.
This scanning mode is suitable for scanning images containing light and shadow such as
a photograph.
Gray scale
Scans data using 256-level monochrome gray scale. Light and shade in photographs can
be represented with greater fidelity. This scanning mode employs far more memory
than the Black & White mode.
Some versions of the scanner do not support this scanning mode. For details contact the
retail store where the device was purchased.
Color
Scans data using 24 bits color. This mode is suitable for scanning color photograph and
employs far more memory that Gray scale mode.
Some versions of the scanner do not support this scanning mode. For details contact the
retail store where the device was purchased.
Automatic separation
14
Page 21

This option specifies whether to distinguish line drawing from photograph image during
scanning.
If this option is selected, the line drawing part is scanned using "Black & White," and
the photograph part is scanned using "halftone". This information is most suitable for
documents containing both photographs, and line drawings or text.
SEE (Selectable edge enhancement)
Line drawing and photograph image are scanned using "halftone." Then, only line
drawing part is highlighted.
This scanning mode is suitable for emphasizing only characters in the documents that
consists of characters and photographs.
Depending on the model of the scanner, this function may not be supported. For details,
refer to "Relevant Image Scanner Specification" in Section 9, Appendix.
♦
Black & White
Specifies the processing method when "Black & White" is specified in "Image Mode".
Simple Slice
Executes simple binary processing based on the "Threshold" setting.
Auto (IPC, DTC)
To enable the auto binary function of the image scanner, specify this option.
If this option is selected, the "Threshold" setting will be disabled.
In addition, auto binary has two modes: "IPC Mode" and "DTC Mode." These modes
can be set using the "Advance" dialog box.
"DTC Mode", however, is limited to the image processing options. Therefore, only
scanner models that have image processing options support "DTC Mode." See
"Relevant Image Scanner Specification" in the Appendix.
♦
Halftone
Selects the halftone pattern for halftone scanning from the built- in pattern list.
Select the desired halftone pattern for displaying the obtained image. This setting is
effective when "Halftone" or "Automatic Separation" are selected in "Image Mode".
Dither Pattern 0
Executes pattern processing that is suitable for scanning a dark photograph.
Dither Pattern 1
Executes pattern processing that is suitable for scanning a dark-colored document
containing both text and photographs.
15
Page 22

Dither Pattern 2
Executes pattern processing that is suitable for scanning a light photograph.
Dither Pattern 3
Executes pattern processing that is suitable for scanning a light-colored document
containing both text and photographs.
Download Pattern
Executes processing using the dithered download pattern specified in the dithered
download file (described later). Some scanner models do not support this function. See
"Image Scanner Specification" in Appendix.
Error Diffusion
Error Diffusion minimizes the difference between the pixel density of the scanned image
and the pixel density of the printed image to create better reproduction of a scanned
photograph.
Some scanner models do not support this function. See "Relevant Image Scanner
Specification" in Appendix.
♦
Scanning Parameters
For fine scan adjustments.
Since there is no fixed set of values, set by trial and error.
♦
Brightness:
Sets the brightness of the overall image.
Specify the brightness with a number in the range of 1 (bright) to 255 (dark).
To brighten the overall image, decrease the value of the setting. To darken the overall
image, increase the value.
This parameter can be set if "Halftone" or "Automatic Separation" is selected for "Image
Mode."
♦
Threshold:
Sets the threshold value by which the black and the white of black-and-white images are
distinguished. Specify a number in the range of 1 (bright) to 255 (dark). This parameter
can be set only if "Black & White" is specified for "Image Mode."
In addition, if "Auto Binary" is selected, the scanner will automatically use the
appropriate threshold value. As a result, the set value cannot be changed.
16
Page 23

In addition, if "Auto Binary" is selected, the scanner will automatically use the
appropriate threshold value. As a result, the set value cannot be changed.
If the light color in the scanned document is read as white, increase the threshold value.
To eliminate light- colored areas in the scanned document, decrease this value.
17
Page 24

♦
Contrast:
Sets the contrast of light and shadow in a scanned image.
Specify the contrast with a number in the range of 1 (low [soft]) to 255 (high [sharp]).
The contrast can be set if "Gray Scale" is selected in "Image Mode."
If this value is increased, the dark part of the image is shown darker and the light part is
shown lighter.
Some scanner models do not support this function. See "Relevant Image Scanner
Specification" in Appendix.
4.5 Specifying Driver Operation
♦
[Preview]
Reads in a preliminary image based on set values, and displays the image in the preview
window.
Before actual scanning, the preview function can be used to display the entire document for
specifying the desired scan area.
This function is available only on devices that support the use of a flat bed. Some models do
not support this function. See "Relevant Image Scanner Specification".
♦
[Scan]
Scans the specified scan range based on set values.
The following "progress indicator" is displayed during scanning to show the progress of the
scan operation. To stop scanning, click the [Cancel] button.
The character string indicates the data transfer mode used between the driver and the
application.
18
Page 25

Progress indicator
♦
[Close] / [OK]
Closes the dialog box without scanning.
If a setting is changed, the changed setting is saved in the initial value file.
♦
[Reset]
Restores the current setting values to the status immediately after the window is opened.
♦
[Help]
Displays online help. When the [F1] key is pressed, help information regarding the item on
which the cursor is placed is displayed.
Note
Depending on the application used help information may not be displayable with the [F1]
key. This is because the driver operation is controlled through the application and the [F1]
key may be used differently in each application program.
Help information can be displayed by pressing the [F1] key while holding down the [Ctrl]
or [Shift] key.
♦
[Option]
Displays the "option dialog" for setting device-specific functions. See Section 4.7, "Setting
Option" described later.
19
Page 26

♦
[Advance]
Displays the "advance dialog " for settings related to color variance and image processing.
♦
[Config]
Displays the "basic scan dialog" for managing the settings file and for setting simple scan
dialog switching.
♦
[About]
Express the version of this driver by clicking this button.
4.6 Setting "Scanning Area"
Specify the scan area in the preview window as follows:
Setting:
1. Press the left mouse button to specify the origin (top left corner) of the scanning area.
(The cursor appears as a "+".)
2. Drag the mouse to show the outline of the scanning area. (As the cursor moves, a range
frame is shown.)
3. Release the left mouse button again to set the range (bottom right corner) of the scanning
area.
Movement:
1. Move the cursor into the range frame. (The cursor appears as a hand.)
2. Press the left mouse button. (The cursor changes to a fist.)
3. Drag the mouse to move the range frame.
4. Release the left mouse button to set the current range.
Cancellation:
The range frame can be canceled by either of the following ways:
−
Click the left mouse button outside the range frame (inside the scan document).
−
Select other paper types.
20
Page 27

4.7 Setting Options
The "option dialog" is used to set device-specific functions and the items that differ depending
on whether the scanner used supports them.
The option specification is divided into "Rotation", "Job/Cache", "Generic", and "Endorser".
The supported options depend on the scanner. See "Relevant Image Scanner Specification" in
the Appendix. ( is displayed for options that cannot be used.)
The option dialog in this driver is explained below.
The commonly used buttons are explained first.
♦
[OK]
Enables the new setting, and terminates the option dialog box.
♦
[Cancel]
Disables the new setting, returns the setting to the previous value, and terminates the
processing.
♦
[Help]
Displays online help.
21
Page 28

The options are described below:
Figure Option dialog (Rotation)
♦
Flip Side Rotation
Specifies the binding of the document when both sides are scanned using ADF.
Book
Outputs the scanned image for both sides as is.
Select this option to scan documents bound on the left or right side.
Fanfold
Scans only the back side and outputs the scanned image rotated 180 degrees.
Select this option to scan documents bound on the top or bottom.
22
Page 29

♦
Rotation Degree
Outputs the scanned image rotated to the right or left 90 degrees.
0.0 degree
Outputs the scanned image as is.
90.0 degree
Outputs the scanned image rotated 90 degrees to the right (clockwise).
-90.0 degree
Outputs the scanned image rotated 90 degrees to the left (counterclockwise).
180.0 degree
Outputs the scanned image rotated 180 degrees (top and bottom reversed).
♦
Auto Deskew
When ADF is used for scanning, this option detects skew of the document being fed and
automatically corrects skewing.
Check the checkbox to enable this option.
This option may not be supported for some scanners. See "Relevant Image Scanner
Specification" in the Appendix.
23
Page 30

Figure Option dialog (Job/Cache)
♦
Caching
Specifies whether to preread (cache) when a document is scanned. This option enables
faster scanning.
If processing of the application being used slows down and scanning stops, this option can
be used to prevent degradation of the scanning speed. (The effect, however, depends on the
environment being used.)
None
Caching is not performed.
Read ahead
One document page is scanned, and the data is preread and stored in PC memory (main
memory of the personal computer).
24
Page 31

Ram cache
Prereads the allowable amount based on the allocated memory size and stores the data in
PC memory.
A memory size between 1 and 200 MB can be set.
Use Memory on Scanner
Prereads using the memory installed in the scanner (displayed only if supported by the
scanner).
♦
Batch Detection
The application can detect documents on a specific type of form (special paper). The
application must support this function.
None
No detection. Scanning is done without change.
Include and Continue
After the special paper is detected, scanning continues. The data on the special paper is
also valid.
Include and Stop
After the special paper is detected, scanning stops. The data on the special paper is also
valid.
Exclude and Continue
After the special paper is detected, scanning continues. The data on the special paper is
excluded and will not be transferred to the application.
Exclude and Stop
After the special paper is detected, scanning stops. The data on the special paper is
excluded and will not be transferred to the application.
25
Page 32

♦
Double Feed Detection
This option detects a double feed (occurs when two or more documents are sent) based on
the set condition.
If a double feed is detected when this setting has been turned on, the device will stop and an
error message output.
None
Double feed detection is not performed.
Hardware Setting
A double feed is detected based on the device setting.
Check thickness
The thickness of the transmitted document is checked by the sensor in the device. A
double feed is detected by detecting changes in the thickness when more than one
document is sent.
Check length
The length of the transmitted document is checked by the sensor in the device. A double
feed is detected by detecting changes in the length when more than one document is sent.
Check thickness and length
The thickness and length of the transmitted document are checked.
The detection accuracy can be improved by using [Check thickness] for continuous scanning
of forms that have different lengths and [Check length] for scanning of forms that have
different thicknesses.
♦
Blank page skip
This option skips blank pages (blank pages or completely black pages) during ADF
continuous scanning.
For blank pages, use the [White Dots Ratio] slider to set the skip condition. For black pages,
use the [Black Dots Ratio] slider to set the skip condition.
The value displayed to the right of the slider displays the garbage ratio(*1). If a scanned
document is below this value, it is recognized as a blank page. The setting range is OFF(- -)
and 0.2% to 3.0% (in increments of 0.2%).
<If blank page skip does not operate properly>
−
If a blank page is scanned, increase the value set.
−
If scanning is skipped up to the required document, decrease the value set.
26
Page 33

This option is valid only when the cache setting is set to [Use Memory on Scanner]. In
addition, this option cannot be used unless it is supported by the scanner.
*1: Ratio of black dots included in the scanning area (for blank pages)
Figure Option dialog (Generic)
♦
Unit/Scaling
This option selects the unit for the scanning area and preview window. One inch is
calculated as 25.4 millimeters. When inches are converted to millimeters, values are
rounded off.
27
Page 34

Note
The TWAIN specifications require that the data width be arranged in units of 32 bits. As a
result, a difference of up to 31 dots can be included, depending on the value set.
Figure Option dialog (Endorser)
♦
Enable Endorser
Specifies enabling or disabling the endorsement function of the device.
When the option is selected and scanning has been completed, the scanned originals are
printed or a stamp is imprinted according to the instructions below. This applies only to
stamp or endorser options. Therefore, the function is supported only in devices in which the
stamp or endorser option can be installed. See "Relevant Image Scanner Specification"
described in the Appendix.
♦
Y Offset (Printing)
Specifies Y Offset from the edge of the original for the placement of printing. See "Relevant
Image Scanner Specification" in the Appendix because the standard value specified here
depends on the device.
28
Page 35

♦
Direction (Printing)
Specifies the direction of endorsement strings. When the direction is perpendicular to the
direction of scanning, designate "Up to bottom". Only this version of the device permits the
direction to be specified.
♦
Surface (Printing)
Designates the side for printing or stamp imprinting. If the side is opposite the scanned
surface, select "Back." Select "Front" for the scanned surface. If both sides are scanned, the
side scanned first is considered to be the "Front."
See "Relevant Image Scanner Specification" in the Appendix, because the available options
depend on the device.
♦
Initial Count (Counter)
Designates the initial count when the endorsement string is set, including a counter value.
Programmable values range from 0 to +65535.
♦
Counter Step (Counter)
Designates the counter increment of the set counter values. In other words, this value is
added to or subtracted from the counter each time one original is scanned.
An increment of 0, 1, or 2 may be specified. Usually, 1 is designated for a single-sided
original, and 2 for a double- sided original.
♦
Counter (Counter)
Designates whether to increase or decrease the specified step value.
29
Page 36

♦
Endorsement String
Specifies the endorsement string. The following definitions can be used. They may also be
selected from the menu, which is displayed by clicking on ">".
%YYYY: The year is printed in four digits using the Western calendar.
%YYY: The year is printed using the two digits of the Japanese calendar (current, or Heisei
era).
%YY: The year is printed in the last two digits of the Western calendar.
%MMM: An English abbreviation of the month is printed; for example, JAN for January
and FEB for February.
%MM: The month is printed in two digits; for example, 01 for January and 12 for
December.
%M: The month is printed using one or two digits; for example, 1 for January and 12
for December.
%DD: The day is printed using two digits; for example, 03 for the 3rd day of the month
and 26 for the 26th day of the month.
%D: The day is printed using one or two digits; for example, 3 for the 3rd day of the
month and 26 for the 26th day of the month.
%HH: The hour is printed using two digits of the 24-hour clock; for example, 08 for 8:00
a.m. and 14 for 2:00 p.m.
%H: The hour is printed using one or two digits of the 24-hour clock; for example, 8 for
8:00 a.m. and 14 for 2:00 p.m.
%NN: The minute is printed using two digits; for example, 02 for 8:02 a.m. and 48 for
2:48 p.m.
%N: The minute is printed using one or two digits; for example, 2 for 8:02 a.m. and 48
for 2:48 p.m.
%05ud: A counter value is printed which increases or decreases with each page.
The initial counter and the methods of increasing and decreasing values can be specified as
explained above under the heading "Counter."
This specification is only permitted at the end of an endorsement string.
♦
Sample
Displays printed examples of the endorsement string designated above.
Note
The printed counter, date, and time do not always look like the sample because the
scanning option takes precedence.
30
Page 37

4.8 Setting Advance Options
The "advance dialog" is used to set items related to image processing. The settings apply to
device-specific functions and items that differ according to whether the scanner used supports
them.
The advance option specification is divided into "Color Variance", "Image Processing", and
"Auto Binary".
The supported options depend on the scanner. See "Relevant Image Scanner Specification" in
the Appendix. ( is displayed for options that cannot be used.)
The option dialog for this driver is explained below.
The commonly used buttons are explained first.
♦
[OK]
Makes the new setting valid and closes the option dialog box.
♦
[Cancel]
Makes the new setting invalid, returns the setting to the previous value, and terminates
processing.
♦
[Help]
Displays online help.
31
Page 38

The options are described below:
Figure Advance dialog (density correction)
♦
Gamma Pattern
This option corrects distortions from nonlinear image representation. Scanner sensors are
generally designed to generate output linear to the density of the light reflected from the
document. However, most output terminals do not produce output that has the desired linear
relation to the input, and the resulting distortion must be corrected.
One of the following can be selected as a correction pattern: "Normal", "Soft", "Sharp",
"Download Pattern", or "Custom".
32
Page 39

When "Download Pattern" is selected, the above dialog box opens.
Select the gamma pattern download file to be used from the list of file names. Then, press
the [OK] button. Correction will then be executed using the selected gamma pattern.
If the gamma pattern download file has not been registered in the list of file names, use the
[Add] button to register the file.
See "Download Pattern File" for information about how to specify the file.
When "Custom" is selected, a custom specification can be entered.
Entering an arbitrary value between 0.1 and 10.0 enables a gamma pattern corresponding to
the entered value to be specified.
♦
White Level Follower
Select this option to scan a document whose background color is not white, such as a
newspaper.
Select "Auto", "Enable", or "Disable".
When "Enable" is selected, the document is scanned using background follow-up (for line
drawings). When "Disable" is selected, the document is scanned using the standard basic
white background (for photographs). When "Auto" is selected, the option automatically
switches to the optimal setting based on the specified "Image Mode".
"White Level Follower" is used to adjust the density of the white background of a document
and correct variations in the background color by compensating the pixels of scanned images
individually.
For ordinary use, set "White Level Follower" to off. Use of "White Level Follower" often
increases the background noise because IPC-3/3D is very sensitive.
This option is not available if "Gray Scale" is selected for "Image Mode".
In addition, some scanner models do not support this option. See "Relevant Image Scanner
Specification" in the Appendix.
33
Page 40

♦
Dropout Color
This option enables scanning excluding the selected color information of green, red, or blue
(the three primary colors of light). For example, to scan black characters framed in red,
selecting red for scanning will scan only the black characters.
♦
Reverse
This option specifies whether to reverse the black and white of a scanned image.
If this option is selected, black and white are reversed by reversing the black and white
pixels. If this option is not selected, the black and white values of the reproduced image
corresponds to the original image.
Some applications do not permit normal operation. If this occurs, contact the manufacturer
of the application.
Figure Advance dialog (image processing)
34
Page 41

♦
Edge Processing
This option specifies the sharpness of a scanned image.
Select "None", "Edge Extract", or "Smoothing (Background Removal)".
None
Edge processing is not performed.
Edge Extract
This option outputs an image with the edge extracted.
If this option is selected, the boundary between the black part and white part in a closed
area is traced and the edge extracted.
"DTC Variance" and "Edge Extract" are mutually exclusive.
Smoothing
This option smoothes the curves in an image by removing zigzag lines.
Emphasis
This option outputs an image with the edge emphasized.
"Emphasis High", "Emphasis Mid", or "Emphasis Low" can be selected.
If "Emphasis High" is selected, the image becomes sharper. If "Emphasis Low" is
selected, the image appears less distinct.
♦
Mirror
This option specifies whether to flip the scanned image over the scanning axis.
If this option is selected, a mirror image of the original image is obtained.
♦
Variance (Simple auto binary)
This option specifies the value for adjusting the dynamic threshold of an image based on the
brightness of the image.
A value is specified using the slider. The smaller the value, the lower the variance becomes.
The higher the value, the higher the variance becomes. To specify the value, drag the tab of
the slider to the desired setting position. The current setting is displayed on the right. This
option is mainly used for optical character recognition (OCR). It enables dark and bright
images in a document to be scanned effectively.
35
Page 42

This option is valid only when "Simple auto binary" is set.
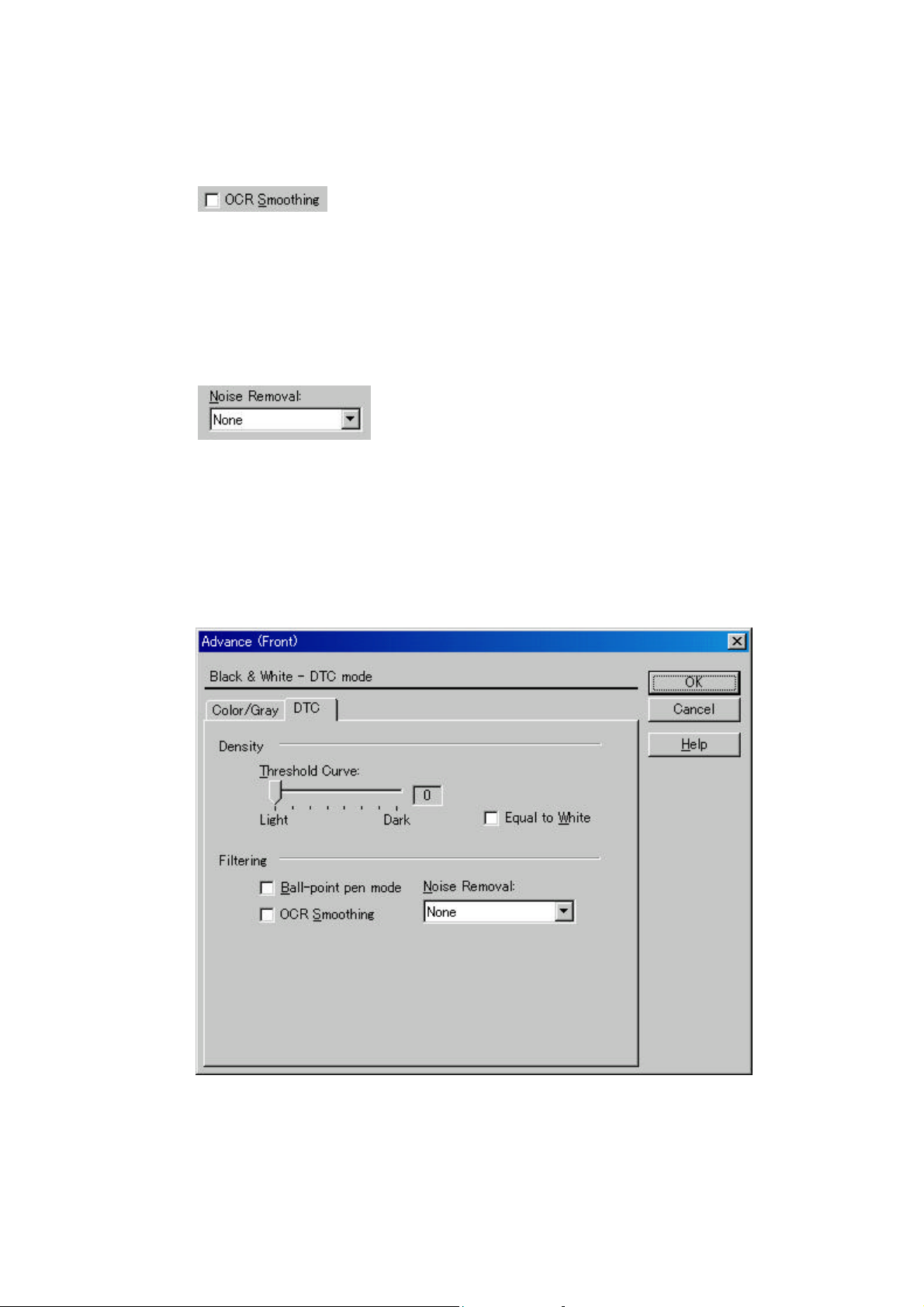
Figure Advance dialog (DTC Mode)
♦
Scan mode
This option selects one of the following two scan modes:
[for OCR]: This mode is for text recognition applications where irregularity in the image is
undesirable.
[for Image]: This mode is for image scanning applications that scan images without prior
smoothing.
The specification changes the specifiable items and members for "Threshold Curve" and
"Gamma Curve".
The selection screens for "for OCR" and "for Image" are not displayed if IPC-3/3D and IPC4D are installed.
36
Page 43

♦
Density curve
This option specifies the relationship between the threshold value and the maximum density.
This specification method depends on the [Scan mode] setting.
In [for OCR] mode, use the slider to set the inclination and density level. To specify the
value, drag the tab of the slider to the desired setting position. The current setting value is
displayed on the right. (figure on the left)
In [for Image] mode, select [Normal] or [Lightest]. (figure on the right)
If IPC-3/3D and IPC-4D have been installed, there is no difference between [for OCR] and
[for Image]. The slider is used to set the inclination and density level. (The figure on the
right is not displayed.)
♦
Gamma Curve
This option specifies the gamma correction curve pattern.
The available choices depend on the [Scan mode] setting.
In [for OCR] mode, select [OCR1] or [OCR2].
In [for Image] mode, select [Dark Image] or [Even].
For IPC-3/3D and IPC-4D, the gamma curve need not be specified because the contrast is
adjusted automatically. ([Gamma Curve] is not displayed.)
♦
Equal to White
At conversion to binary, this option specifies whether to set the data to black or white when
the threshold value and the value of the scanned data are equal.
When using IPC-4D, this option cannot be selected.
♦
Ball-Point Pen Mode
When an image made with a pencil or ball-point pen is scanned, the light reflected from the
pencil lead or ink is not uniform. As a result, part of the image may be missing. If the [BallPoint Pen] checkbox is checked, filtering is applied to offset the bright area in the document
and compensate for disconnected or faint lines.
37
Page 44
♦
OCR Smoothing
This option specifies whether to enable the function that modifies the zigzag lines in the line
drawing to smooth curves.
If this option is selected, the smoothing function is enabled.
For IPC-3/3D, either [Noise Removal] or [Smoothing] can be selected.
♦
Noise Removal
This option automatically removes spots that appear as black stains in a white area and spots
that appear as white stains in a black area.
This option uses an algorithm that removes particles from 2 x 2 to 5 x 5 dot matrixes. The
size of one dot depends on the resolution setting, and is equivalent to 1/400 inch for 400 dpi.
Particles are distinguished from the text by whether they are connected to other dots within
the specified number of pixels.
[Noise Removal] and [Smoothing] are valid only for IPC-3/3D.
Figure Advance dialog (DTC Mode) <IPC-3/3D and IPC-4D installed>
38
Page 45

Figure Advance dialog (Color) <Image Mode : Color selected>
♦
Shadow/Highlight
Shadow : The highlight allows the darkest part of the document to be controlled. The higher
the shadow value, the darker the image.
Highlight : The highlight allows the brightest part of the document to be controlled. The
higher the highlight value, the lighter the image.
Any levels on the document outside these settings are flooded (all 0 or 255), while the
interval between the shadow and highlight settings is equally divided into 255 levels, which
are used to create the output images. This means that if the shadow and highlight settings are
close to each other, the contrast for that interval in the scanned document will be very strong
(but with all other areas maximizing high or low).
♦
Contrast/Brightness
Contrast : Sets the contrast of light and shadow in a scanned image. Specify the contrast
with a number in the range of 1 (low [soft]) to 255 (high [sharp]). If this value is
39
Page 46

increased, the dark part of the image is shown darker and the light part is shown
lighter.
Some scanner models do not support this function. See "Relevant Image Scanner
Specification" in Appendix.
Brightness : Sets the brightness of the overall image. Specify the brightness with a number
in the range of 1 (bright) to 255 (dark). To brighten the overall image, decrease
the value of the setting. To darken the overall image, increase the value.
♦
Gamma
This option corrects distortions from nonlinear image representation. Scanner sensors are
generally designed to generate output linear to the density of the light reflected from the
document. However, most output terminals do not produce output that has the desired linear
relation to the input, and the resulting distortion must be corrected.
An arbitrary range is between 0.1 and 10.0.
♦
Color select
It is possible to select independent value on each color
40
Page 47

Figure Advance dialog (Quality) <Image Mode : Color selected>
♦
Image Emphasis
This option specifies the sharpness of a scanned image.
Select "None", "De-Screen" or "Emphasis".
None
Edge processing is not performed.
Emphasis
This option outputs an image with the edge emphasized.
"Emphasis High", "Emphasis Mid", or "Emphasis Low" can be selected.
If "Emphasis High" is selected, the image becomes sharper. If "Emphasis Low" is
selected, the image appears less distinct.
41
Page 48

De-Screen
"De-Screen Level 1", "De-Screen Level 2", "De-Screen Level 3", or "De-Screen Level
4" can be selected.
This option eliminate moirés patterns. To eliminate more effectively, higher level is
selected.
♦
White Level Follower
Select this option to scan a document whose background color is not white, such as a
newspaper.
Select "Auto", "Enable", or "Disable".
When "Enable" is selected, the document is scanned using background follow-up (for line
drawings). When "Disable" is selected, the document is scanned using the standard basic
white background (for photographs). When "Auto" is selected, the option automatically
switches to the optimal setting based on the specified "Image Mode".
"White Level Follower" is used to adjust the density of the white background of a document
and correct variations in the background color by compensating the pixels of scanned images
individually.
♦
Reverse
This option specifies whether to reverse the black and white of a scanned image.
If this option is selected, color data is reversed. If this option is not selected, the color values
of the reproduced image corresponds to the original image.
Some applications do not permit normal operation. If this occurs, contact the manufacturer
of the application.
42
Page 49

4.9 Setting the Configuration Options
These options are used to manage the setting files, and switch the basic scan dialog display.
Press the [Config] button of the main dialog to open the [Configuration] dialog box shown below.
Figure Option dialog box (simplified DTC)
♦
Setting Files
The setting information of the scan conditions can be saved in a “Setting file.”
Scan condition settings that have been set in advance in this dialog can be selected from the
list of setting files. This enables selection of all settings at the same time without having to
enter the scan conditions one at a time. Press the button to open the list of setting files.
Subsequent scanning operations can be performed effectively by registering several types of
scan conditions that are frequently used.
43
Page 50

♦
FTS File Information
The information of the setting file selected in [Setting Files] is displayed.
♦
[Show this dialog next open] checkbox
If this checkbox is checked, [Basic Scan Dialog] will be activated the next time the driver is
activated.
♦
[OK] button
Makes the new setting valid, closes this dialog box, and returns to the main dialog.
♦
[Add] button
Adds the setting of the current driver to a setting file.
Pressing the [Add] button opens the [File addition] dialog.
Enter the [Description] and [Filename] as shown in the example above. Then, press the
[OK] button to add the new setting file. To cancel, press the [Cancel] button.
Description: Enter a character string to be displayed in the selection frame of the [Setting
Files].
44
Page 51

Filename: Specify the name of the file used to save the settings.
♦
[Delete] button
Deletes unnecessary setting files.
Select the setting file to be deleted and then press the [Delete] button. A confirmation dialog
will be displayed. Press the [OK] button to delete the setting file. To cancel, press the
[Cancel] button.
♦
[Help] button
Displays online help.
45
Page 52

4.10 Basic Scan Dialog
The basic scan dialog contains only the minimum functions required for scanning. The detailed
setting functions of the main dialog have been omitted.
Scanning can be easily performed by selecting a registered setting file.
The basic scan dialog is also useful for avoiding incorrect operations when standard work is
performed.
By checking the [Show this dialog next open] checkbox of the [Configuration] dialog, the basic
scan dialog box will be opened instead of the main dialog box at the next activation.
<Scan Procedure>
1. Select the file to be used from the list of setting files.
2. Press the [Scan] button.
→ Scanning is performed based on the settings of the setting file information.
<Configuration>
♦
Setting Files
A list of setting files is displayed. When the desired file is selected, the setting information
saved in the file will be read and reflected during scanning.
46
Page 53

♦
FTS File Information
The contents of the selected file are displayed.
♦
[Scan] button
Executes scanning based on the contents of the setting file.
♦
[OK] button
Terminates without performing the scan operation.
♦
[Adjust] button
Switches from the basic scan dialog to the main dialog.
♦
[Help] button
Displays online help.
♦
[Show this dialog next open] checkbox
If this checkbox is checked, the [Basic Scan Dialog] will be opened at the next startup. If
this checkbox is not checked, the main dialog will be opened at the next startup.
47
Page 54

4.11 Download Pattern File
The "download pattern file" of this driver is a file that defines the patterns to be used by the
scanner to execute various image processing. This file is available in the following two versions.
Each version can be selected using the [Download Selection Dialog] that opens when
[Download] is selected.
The file is a text file that conforms to the following rules. Use an appropriate text editing
program (for example, "Note Pad" in the operating system) to edit the file.
♦
Dithered download pattern file
Any user defined dithered pattern can be used to scan an image by downloading the pattern
from the dithered download file to the scanner. The defined pattern becomes effective when
[Download Pattern] is selected for [Halftone].
Some models do not support this file. See "Relevant Image Scanner Specification" in
Appendix.
Although the standard extension of the file name is ".DTH," there may be exceptions.
Coding configuration:
(n, size in the X direction),(m, size in the Y direction),
(pattern value for the X1/Y1 coordinates),
(pattern value for the X1/Y2 coordinates),
(pattern value for the X1/Y2 coordinates),........
(pattern value for the Xn/Ym-2 coordinates),
(pattern value for the Xn/Ym-1 coordinates),
(pattern value for the Xn/Ym coordinates)
Meaning of each element:
(n, size in the X direction) indicates the size of the matrix in the X direction. Specify 8
for the scanner supported by this driver.
(m, size in the Y direction) indicates the size of the matrix in the Y direction. Specify 8
for the scanner supported by this driver.
(Pattern value for the Xx/Yy coordinates) contains a values in the range of 0 (bright) to
255 (dark) that specifies the brightness of the X coordinate, x, and the Y coordinate, y.
Note
Use a delimiter other than a number to delimit elements. For most cases, use a
comma (,).
48
Page 55

Example
8, 8,
128, 128, 128, 128, 128, 128, 128, 128,
255, 128, 128, 128, 128, 128, 128, 128,
255, 255, 128, 128, 128, 128, 128, 128,
255, 255, 255, 128, 128, 128, 128, 128,
255, 255, 255, 255, 128, 128, 128, 128,
255, 255, 255, 255, 255, 128, 128, 128,
255, 255, 255, 255, 255, 255, 128, 128,
255, 255, 255, 255, 255, 255, 255, 128,
49
Page 56

♦
Gamma download pattern file
Any user defined gamma correction processing can be performed by downloading the
pattern from the gamma download file to the scanner. The defined pattern becomes
effective when [Download Pattern] is selected for [Gamma Pattern].
Some models do not support this file. See "Relevant Image Scanner Specification" in
Appendix.
Although the standard extension of the file name is ".GMA," there may be exceptions
Creation of a gamma download pattern file can be facilitated using the following utilities for
editing the gamma correction pattern:
Coding configuration:
(gray-scale in the X direction),(gray-scale in the Y direction),
(X0 output value),(X1 output value),(X2 output value),........
(X253 output value),(X254 output value),(X255 output value)
Meaning of each element:
(gray-scale in the X direction) indicates the size and the gray scale of the input value.
(In this driver, this value is fixed at 256.)
(gray-scale in the Y direction) indicates the size and the gray scale of the output value.
(In this driver, this value is fixed at 256.)
(Xx output value) indicates the output value, in the range of 0 (bright) to 255 (dark), for
an input value x.
Note
Use a delimiter other than a number to delimit elements. For most cases, use a
comma (,).
50
Page 57

Example
256, 256,
255, 254, 253, 252, 251, 250, 249, 248, 247, 246, 245, 244, 243,
242, 241, 240, 239, 238, 237, 236, 235, 234, 233, 232, 231, 230,
229, 228, 227, 226, 225, 224, 223, 222, 221, 220, 219, 218, 217,
216, 215, 214, 213, 212, 211, 210, 209, 208, 207, 206, 205, 204,
203, 202, 201, 200, 199, 198, 197, 196, 195, 194, 193, 192, 191,
190, 189, 188, 187, 186, 185, 184, 183, 182, 181, 180, 179, 178,
177, 176, 175, 174, 173, 172, 171, 170, 169, 168, 167, 166, 165,
164, 163, 162, 161, 160, 159, 158, 157, 156, 155, 154, 153, 152,
151, 150, 149, 148, 147, 146, 145, 144, 143, 142, 141, 140, 139,
138, 137, 136, 135, 134, 133, 132, 131, 130, 129, 128, 127, 126,
125, 124, 123, 122, 121, 120, 119, 118, 117, 116, 115, 114, 113,
112, 111, 110, 109, 108, 107, 106, 105, 104, 103, 102, 101, 100,
99, 98, 97, 96, 95, 94, 93, 92, 91, 90, 89, 88, 87, 86, 85, 84,
83, 82, 81, 80, 79, 78, 77, 76, 75, 74, 73, 72, 71, 70, 69, 68,
67, 66, 65, 64, 63, 62, 61, 60, 59, 58, 57, 56, 55, 54, 53, 52,
51, 50, 49, 48, 47, 46, 45, 44, 43, 42, 41, 40, 39, 38, 37, 36,
35, 34, 33, 32, 31, 30, 29, 28, 27, 26, 25, 24, 23, 22, 21, 20,
19, 18, 17, 16, 15, 14, 13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0
51
Page 58

5. Using the Gamma Pattern Editor
5.1 Start-up
Click on "Start" and select "Download Pattern Editor" from "Scanner Utility for Microsoft
Windows" under "Programs." The following menu is displayed:
Figure Gamma Pattern Editor Tool start-up menu
52
Page 59

5.2 [File] menu
♦
[Load]
This menu is used to read the Gamma Download file and display the graph and gradations.
The name of the open file is displayed above the graph area.
♦
[Save]
The gamma pattern currently being edited is saved in the file whose name is displayed above
the graph area. If no filename is displayed, the pattern is named and saved in that file.
♦
[Save As]
The gamma pattern currently being edited is named and saved in that file. The saved
filename is then displayed above the graph area.
♦
[Close]
Select this to exit the editing program.
53
Page 60

5.3 [Help] menu
♦
[About]
Information related to this editor and its version number is displayed.
54
Page 61

5.4 Gamma Pattern Editing
♦
Graph Area
The graph area is a 256-dot × 256-dot white square area bordered by black lines, where the
relationship between the input values of 0 to 255 (x axis) and output values of 0 to 255 (y
axis) is indicated in blue lines. Each graph dot represents one division (unit).
♦
Gradation
The input is displayed in black and white in 256 single-dot steps from 0 at the left border to
255 at the right border. The gama function of the scanner is displayed. After saving it, the
displayed (gray scale) gama function is fixed and constant. The output values are displayed
in single dots in relation to the input values and the brightness of the output equipment is
displayed. To ensure accurate display, the display must be set for "True-Color" or greater.
♦
Gamma
Calculation of the output values is based on the value γ entered in the edit box; the graph and
the gradation are then displayed. The values that can be input are integers greater than 0 or
fractions.
<<Formula>> Output = (input ÷ 255)γ × 255 (Input = 0 - 255)
♦
Free Edit
Designates whether to enable editing of the graph area directly using the mouse cursor.
If this box is checked, the gamma pattern input edit box cannot be used and only editing
using the mouse cursor is supported.
♦
Smooth
Designates whether to smooth edited curves. This setting is only valid when Free Edit is
selected. In this setting, the curved lines drawn by the mouse are automatically smoothed.
This is reflected in the graph and gradation display.
♦
Reverse
Designates whether to reverse black and white. When this box is checked, the current output
values are converted to (255 - output values).
55
Page 62

6. How to Use the FUJITSU Scanner Control Center
6.1 Outline
This software that is resident in the system continuously monitors the scanner connected and
starts the target application in response to an instruction from the operation panel in the scanner.
(Pressing the start button on the scanner starts the application that has been set in advance.)
For applicable models, see "Relevant Image Scanner Specification" in the Appendix.
6.2 How to Start the FUJITSU Scanner Control Center
Select as follows: [Start] - [Program] - [Scanner Utility for Microsoft Windows], then
[FUJITSU Scanner Control Center]
If this application is started, it is stationed in the system, then an icon is displayed on the task
tray.
An icon indication changes to show how the scanner is connected as follows:
1. The scanner can be used:
2. The scanner power is turned off and not connected:
56
Page 63

Right-clicking the icon displays the following pop-up menu.
Left-clicking the icon displays the scanner being connected as shown below.
The scanner that has been monitored by this application is indicated with a check mark.
6.3 Pop-up Menu
♦
[Rescan Scanner]
Rescans the scanner that is currently connected.
A scanner that is not recognized by the OS cannot be found even though it is rescanned.
♦
[Option]
Sets up the application to be started when the start button of the scanner is pressed.
57
Page 64

♦
[Path]
Specifies a file name of the application to be started with its absolute pathname.
A file can be also selected directly by using the […] button.
♦
[Argument]
Specifies an argument to be passed when starting the specified application. (This item can
be omitted.)
♦
[Start in]
Specifies a default folder for starting the application.
A default folder can be also selected by using the […] button.
(This parameter can be omitted.)
♦
[Run]
Specifies the display size of the application to be started.
58
Page 65

♦
[Use Plug-In]
Checking this check box specifies a plug-in.
(A plug-in is an additional program for adding a new function to the application.)
♦
[Setting]
Sets a plug-in in accordance with the following procedure:
•
Pressing the [Setting] button after selecting a target plug-in name in the plug-in list
displayed displays the plug-in setting screen.
•
Pressing the [OK] button after setting each item reflects the settings for the application
to be started.
♦
[Install]
A new plug-in can be installed.
Press the [Install] button and specify a file of the plug-in to be installed. A new plug-in is
registered in the list.
* Up to 50 plug-ins can be registered.
<<Setting the Start button>>
If the scanner being monitored has function keys, it is necessary to assign a function key to the
start button in advance.
If no function key has been assigned to the start button, a dialog box for determining whether to
set the start button is displayed when the dialog box is displayed after selecting [Option] on the
pop-up menu.
59
Page 66

Selecting "Yes" displays a dialog box below.
(If "No" is selected, the function to start any application when the start button in this application
is pressed is disabled.)
Pressing the [OK] button after selecting one of function keys from F1 to F3 enables assigning a
function key to the start button. If the [Cancel] button is pressed, the function key is not
assigned to the start button.
(If the [Cancel] button is pressed, the function to start any application when the start button in
this application is pressed is disabled.)
♦
[Select Scanner]
When multiple scanners are connected, select a scanner to be monitored.
With this application, only one scanner can be monitored at a time. If multiple scanners are
connected, scanner switching is required to monitor the individual scanners.
Select a scanner to be monitored in the list of scanners to be connected. (The list is given
below.)
60
Page 67

Left-clicking the task tray icon displays connected scanner names on the pop-up menu. It is
also possible to select a scanner on this menu.
♦
[Help]
Displays help information concerning to this application.
♦
[About]
Displays version information concerning to this application.
♦
[Exit]
Terminates this application.
61
Page 68

7. Troubleshooting
7.1 Error Messages
7.1.1 Messages from the TWAIN Driver
•
The input value is outside the range.
Cause: A value exceeding the range allowed for an input item was input.
User response: Input a value inside the allowed range. Refer to the input item or the
image scanner specification for the range.
•
The input value is not acceptable.
Cause: A value exceeding the range allowed for an input item was input.
User response: Input a value inside the allowed range. Refer to [Help] of the item or
the User's Guide for the correct range.
•
This file cannot be removed because it is specified in other side.
Cause: An attempt was made to remove a file using the dither pattern or
gamma download pattern file setting dialog. However, the file is
being used for the other side (front side if back side or back side if
front side).
User response: Before removing the file, change the setting of the other side and then
remove.
•
The initial value data file contains an invalid value. The standard value is set.
Cause: A value outside the specified range, or invalid text was found in the
initial-value data file (the specific item involved is indicated by
Entry=XXXXX). If the file has been modified, the setting value for
the item may be wrong. If the file has not been rewritten, the file may
have been damaged.
User response: The value is set to a standard value. Be sure to check the hard disk
(chkdsk/scandsk) and check for computer viruses regularly.
•
The value is higher than the maximum scanning size. Either the resolution value or the
scanning area has to be reduced.
Cause: A value exceeding the data capacity of the scanner was specified. As
the resolution is increased, the amount of data to be scanned also
increases.
User response: Decrease the resolution or reduce the size of the scan area.
62
Page 69

•
The value for custom paper is higher than the maximum scan size. Width needs to equal 279
mm or less and length needs to equal 420 mm or less.
•
The value for custom paper is higher than the maximum scan size. Width needs to equal 11
inch or less and length needs to equal 16.53 inch or less.
•
The value for custom paper is higher than the maximum scan size. Width needs to equal xxx
pixel or less and length needs to equal xxx pixel or less.
Cause: A value exceeding the limit applicable to the scan area of the scanner
was specified.
User response: To specify a custom paper size, specify the value that is smaller than
the value applicable to the device.
•
The resolution must be less or equal to xxx dpi when scanning in Gray Scale.
Cause: A value exceeding the limit of resolution for gray-scale scan was
specified.
User response: Specify a resolution value that is below the indicated xxx dpi.
•
Cannot specify Gray Scale with Custom resolution.
Cause: Custom resolution was designated when multi-tone (gray scale) was
designated.
User response: Designate a resolution value other than Custom.
•
Cannot specify Individual Setting with Gray Scale.
Cause: Gray scale was specified in the settings for the front side or back side
was set as the object to be set.
User response: Specify Gray Scale only when making the settings for both sides.
•
Dither pattern file not found.
Cause: File download has been specified, but a file has not been selected.
User response: Use the [File…] button to specify a file.
•
Gamma pattern file not found.
Cause: File download has been specified, but a file has not been selected.
User response: Use the [File…] button to specify a file.
•
Selected file could not delete.
Cause: If the selected setting file is write-protected, it cannot be deleted.
User response: Use Explorer to delete the file later.
63
Page 70

•
Description not specified.
Cause: The description of the setting file has not been specified.
User response: Enter the description of the setting file in the description field. Then,
try scanning again.
•
Filename not specified.
Cause: The filename of the setting file has not been specified.
User response: Enter the filename of the setting file. Then, try scanning again.
•
Specified string is too long.
Cause: The specified string is too long. Up to 128 en-size characters and up
to 64 em-size characters can be specified.
User response: User response: Reduce the number of characters in the string so that
they do not exceed 128 en-size characters. Then, try scanning again.
•
Cannot specify next words for filename. \:;?”<> |.
Cause: The specified filename contains one or more of the following
characters: \:;?”<> |.
User response: Enter a file name that does not contain the above characters. Then,
make the settings again.
•
The image scanner cannot be found.
Cause: Possible causes include the following: an image scanner that is not
supported by this driver has been connected, no image scanner has
been connected, or the cable is not connected.
Otherwise, the initial values of the image scanner were overwritten
while the driver was open.
User response: Check the connection of the image scanner. Also be sure to close the
driver before using the initial value adjustment utility in the image
scanner.
•
The specified image scanner is being used.
Cause: The image scanner may be already in use by another application, or
the TWAIN driver may have been started twice.
User response: User response: After all applications are terminated, restart the image
scanner for scanning.
64
Page 71

•
An input-output error occurred in the image scanner.
Cause: A fault occured during the scan operation of the image scanner. There
may be a fault in the image scanner itself.
User response: Turn off the power of all devices, then turn on the power of the
computer before turning on the scanner and retry scanning. If the
error still occurs, contact the retail store where the image scanner was
purchased, or the nearest service center.
•
Paper jammed in the ADF
Cause: A paper jam occurred in the device.
User response: Turn off the power of the device, then remove the paper from inside
the device. Removing the paper by using excessive force will result
in device failure, so be careful.
•
The hopper tray is open. Reinsert the document and close the tray.
Cause: The document tray is open.
User response: For double-sided scan, close the document tray.
•
No paper in the ADF
Cause: Although ADF was selected as the paper feeding method, no paper is
found in the document tray.
User response: Select another paper feeding method or set the document in the
document tray.
•
The hopper tray is open, or No paper in the ADF.
Cause: The hopper tray cover is open, or there is no paper in the ADF.
User response: Close the hopper tray cover, or load paper.
•
Insufficient buffer memory size of scanner device for current scanning parameters. Please
reduce the scanning area or the resolution, or install additional memory in the scanner.
Cause: A memory option has not been installed in the image scanner.
Otherwise, a large area or resolution that is not supported by the
image scanner has been specified.
User response: Reduce the scanning area or resolution. Otherwise, install the
memory option. Refer to the User's Guide of the image scanner for
more information.
65
Page 72

•
The current parameter(s) is (are) not allowed. Please use (an)other parameter(s) and try
scanning again.
Cause: An incorrect value has been specified for the image scanner. The
problem may be due to an illegal combination with the specification
value from the application.
User response: Change the specification values. Then, try scanning again.
•
The scanner is in an irregular status; fuse is broken, etc. Please check the scanner status.
Cause: A scanner fault such as a blown fuse or foreign matter in the scanning
section has occurred.
User response: Check the scanner status. If a fuse has blown, replace the fuse. If
there is foreign matter in the scanning section, remove the foreign
matter. If the error persists, contact the retail store where the image
scanner was purchased or the nearest maintenance and service center.
•
Memory is insufficient.
Cause: Insufficient memory for scanning. The memory available may be
insufficient because an application consuming much GDI memory is
operating, too many other programs operate at the same time, or there
are too many registered device drivers. The user may mistakenly
think that adding more memory will solve this problem. However, in
most cases, memory shortage is due to insufficient conventional
memory (called the main memory within 640 kilobytes). Checking
CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT may be a better solution.
User response: Cancel the registration of device drivers that are irrelevant and make
sure that only the absolutely necessary programs are operating. Use
the memory optimization tool to allocate as much conventional
memory as possible.
•
An error occurred in the temporary file.
Cause: Accessing the internal temporary file of the scanned image is causing
the error. The disk space may be insufficient, the temporary file may
be damaged, or other programs may be affecting disk access.
User response: Increase the free space of the disk. Check the hard disk (chkdsk and
scandsk). Make sure that no other program is accessing the disk. If
the error message persists, contact the retail store where the product
was purchased or the nearest service center.
•
Download file not found.
Cause: A file specified as a dither pattern or gamma pattern cannot be found.
User response: Check that the download file is in the specified directory. Otherwise,
use the file selection dialog to specify an available file.
66
Page 73

•
Illegal format or data in download file.
Cause: The format of the specified download file is illegal or the data is
incorrect.
User response: User response: Use an editor to check file format and data.
•
ASPI manager not found.
Cause: The ASPI manager may not have been installed, or may have been
deleted.
User response: Reinstall the products, including the ASPI manager attached to the
SCSI board. Then reboot the PC.
•
Scanner DLL file not found.
Cause: An image scanner was selected, but the DLL file of the selected image
scanner has not been installed in the directory in which this driver is
installed.
User response: Perform the setup again.
•
A parameter error has occurred (internally)
•
The calling procedure is invalid (internally).
•
The area is specified incorrectly (internally).
•
The calculation result exceeded the value that can be expressed (internally).
•
User definition is not registered (internally).
Cause: This is a program error that occurs during command exchange
between the driver and the image scanner.
User response: Try again by rebooting the machine. If the error persists, contact the
retail store where the product was purchased or the nearest service
center.
•
A general fault of the MSG_XXXXX response (internally).
Cause: This is a program error that usually occurs during internal message
transfer. This message involves the sub-messages described later.
User response: Contact the retail store where the product was purchased or the
nearest service center.
•
A general fault of the DAT_XXXXX response (internally).
Cause: This is a program error that usually occurs during internal data
transfer. This message involves the sub-messages described later.
67
Page 74

User response: Contact the retail store where the product was purchased or the
nearest maintenance service center.
•
A general fault of the DAT_XXXXX, MSG_SET, and unsupported type response.
(Internally)
Cause: This is a program error that usually occurs while making the internal
data settings.
User response: Contact the place of purchase or your nearest maintenance and service
center.
•
An undefined error occurred
•
Processing cannot be continued because of insufficient memory.
•
The data source cannot be found.
•
The driver is connected to a maximum number of applications supported.
•
An operation error occurred.
•
An invalid function is specified.
•
Unpermitted combination of MSG DG DAT.
•
An invalid value is specified.
•
An invalid procedure of DG DAT MSG is specified.
Cause: These sub-messages are added to the error messages "General
MSG_XXXXX response violation (internal)" and "General
DAT_XXXXX violation (internal)." These sub- messages indicate
details about the programming errors that occur during message and
data processing.
User response: Contact the retail store where the product was purchased or the
nearest service center.
68
Page 75

7.1.2 Error messages relating to gamma correction pattern editing
•
Enter a positive decimal value.
Cause: A value other than a number has been entered as the gamma
correction value.
Alternatively, 0 or a negative value has been entered.
User response: Reenter a valid value.
•
The file could not be created.
Cause: The file for saving could not be created. There is insufficient space to
save the file or the disk to which the file was to be saved is corrupted.
Alternatively, writing to the directory in which the file was to be
saved may not be allowed or other programs relating to disk access
may be affecting performance.
User response: Increase the amount of available space on the disk.
Use a utility such as chkdsk or scandisk to check the hard disk.
Ensure that any background programs that access the disk are not
operating
If this error message continues to be displayed, contact the place of
purchase or your nearest maintenance and service center.
•
The file cannot be opened.
Cause: The file could not be opened.
The specified file name may be incorrect or the disk from which it is
being read may be corrupted. Alternatively, the specified file may be
a write-only file or other programs relating to disk access may be
affecting performance.
User response: If the specified filename is correct, use a utility such as chkdsk or
scandisk to check the hard disk. Ensure that no background programs
that access the disk are operating.
If this error message continues to be displayed, contact the place of
purchase or your nearest maintenance and service center.
•
There is a file formatting error.
Cause: There is an error in the format of the specified file. Either an incorrect
file has been specified or the content of the specified file is incorrect.
User response: After checking the users' manual, check that the content of the
specified file is correct.
69
Page 76

7.1.3 Messages concerning to FUJITSU Scanner Control Center
•
Failed to start-up the application. Check the setting of FUJITSU Scanner Control Center.
•
The setting of the path is blank. Check the setting of FUJITSU Scanner Control Center.
•
Can not find the specified file. Check if the specified path and file name is correct.
•
Can not find the specified work folder. Check if the specified path is correct.
Cause: The setting of the application may be inadequate.
User response: Check setting items of [General] in [Application Dialog] and make
sure settings are correct and there is no omission. If you find any
incorrect setting or omission, correct it.
•
The same Plug-in has been installed already. Specified Plug-in can not install.
Cause: An attempt was made to install the same plug-in that has been already
installed.
User response: Two or more plug-ins assigned to the same name cannot be installed.
•
The specified file is not the effective plug-in.Specified file can not install.
•
Can not find the entry point of the specified plug-in. Specified file can not install.
Cause: The specified file may not be the effective plug-in.
User response: Check whether the specified file is the effective plug-in and retry.
•
Exceeded the number of plug-in to be supported. Can not install the new plug-in.
Cause: The number of plug-ins to be supported was exceeded.
User response: The maximum number of plug-ins that can be supported is 50. Delete
unnecessary plug-ins in the folder where FUJITSU Scanner Control
Center has been installed, then install another plug-in.
•
The plug-in has not been installed.
Cause: The check box "Use a Plug-In" was checked but no plug-in has been
installed.
User response: To use a plug-in, install a plug-in, then check the check box "Use a
Plug-In."
•
Can not find the application for the Plug-in use.Can not use the specified plug-in
Cause: The application to be used for the plug-in may not have been installed.
User response: Verify that the application to be used for the plug-in has been
installed. If no application is found, install it.
70
Page 77

•
Scanner could not find although it searched again. Check the connection of the scanner and
retry again
Cause: The scanner power may not have been turned on or the cable may
have been connected incorrectly. Otherwise, the OS may not
recognize the scanner.
User response: Make sure that the scanner power has been turned on and the cable
has been connected correctly, then retry rescanning. Or, check if the
OS recognizes the scanner. If the OS does not recognize it, let it
recognize the scanner, then retry.
•
Can not rescan the scanner.Close the application using the driver and retry again
Cause: An attempt was made to rescan while the driver was in use.
User response: It is impossible to rescan while the driver is in use. Close the
application that uses the driver and retry.
•
Can not get the EEPROM data. The setting of the function key can not change. Check the
connection of the scanner
•
Can not change the setting of the function key.Check the connection of the scanner and try
the operation again
Cause: While the scanner with function keys are being monitored, the scanner
power may be turned off or the cable may be connected incorrectly.
User response: Make sure that the scanner power has been turned on and the cable
has been connected correctly.
•
It is not authorized to write into the folder which is installed FUJITSU Scanner Control
Center. Can not change the function of the function key. Check the Access Authority of the
folder which is installed FUJITSU Scanner Control Center.
Cause: While the scanner with function keys are being monitored, Access
Authority may not have been set to the folder where the FUJITSU
scanner Control Center has been installed.
User response: To change the setting of the function key, Access Authority of the
folder where FUJITSU scanner Control Center has been installed is
required. Set Access Authority to the folder where FUJITSU scanner
Control Center has been installed, or execute it with Administrator
Authority.
•
Scanner is not selected. Please select a scanner
Cause: The OK button was pressed without selecting the scanner in the
scanner select dialog.
User response: Press the OK button after selecting the scanner to be monitored.
71
Page 78

8. Appendix
8.1 Relevant Image Scanner Specification
Product: M3093GX 1 (device name: fi-4320S)
Type: Desktop
Image sensor: Reduced optical system
Operating method: Document fixed, scanner unit moving (flat bed),
Automatic Document Feeder (ADF)
Light source: Xe discharge tube (Green)
Basic resolution: Horizontal scanning: 400 dpi
Vertical scanning:400, 300, 240, 200 dpi
Output resolution: Standard: 400, 300, 240, 200 dpi
With image processing option: 50 dpi to 800 dpi (at steps of 1 dpi)
Grayscale levels (internal): 8 bit 256 levels
Grayscale output: Enabled (8 bits)
Halftone Patterns: Dither matrix (can be downloaded), Error diffusion
Scanning speed: 1.6 sec or less (A4, 200 dpi)
ADF scanning speed 2: 27 pages/minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
ADF stacker capacity: Maximum 50 sheets, ream weight: 55kg, A4
Document size 3: Maximum 216 mm × 356 mm Legal size paper
Supported regular paper: A4, A5/A5 Landscape, A6/A6 Landscape, B5, B6/B6 Landscape,
Letter, Legal, US Executive
Isolation specification: Specified (one location)
Background compensation: Enabled
Contrast setting: 256 steps
Gamma pattern: 3 internal types (can be downloaded)
Image processing function: Image processing circuit II required,
Outline emphasis, Outline extraction, Automatic separation,
Mirror image, Reverse image, Automatic binarization, Smoothing,
Filtering, Noise removal
Interface: SCSI-II
Job control: Enabled
Use of FUJITSU Scanner Control Center: Disabled
1. Use of this scanner requires that the image compression option board (CMP-2) be installed in the scanner.
2. This speed is only specified for the scanner itself. The actual reading speed may vary depending on the
system configuration.
3. Not all sizes of paper can be used in all devices. For details, refer to the users' manual for the device.
For other paper sizes, the customer settings can be used.
72
Page 79

Product: M3093DG (device name: fi-4320)
Type: Desktop
Image sensor: Reduced optical system
Operating method: Document fixed, scanner unit moving (flat bed)
Automatic Document Feeder (ADF)
simultaneous double-sided reading
Light source: Xe discharge tube (Green)
Basic resolution: Horizontal scanning: 400 dpi
Vertical-scanning: 400, 300, 240, 200 dpi
Output resolution: Standard: 6001, 400, 300, 240, 200, 150, 100 dpi
With image processing option: 50 dpi to 800 dpi (at steps of 1 dpi)
Grayscale levels (internal): 8 bit 256 levels
Grayscale output: Enabled (8 bits)
Halftone Patterns: Dither matrix (can be downloaded), Error diffusion
Scanning speed 2: 1.6 sec or less (A4, 200 dpi)
ADF scanning speed: Single-sided: 27 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
Double-sided: 22.5 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
(= 45 screens per minute)
ADF stacker capacity: Maximum 50 sheets, (ream weight: 55kg, A4 [High quality paper,
normal temperature and humidit])
Document size: Maximum 216 mm × 356 mm
Supported regular paper 4: A4, A5/A5 landscape, A6/A6 landscape, B5, B6/B6 landscape,
Letter, Legal, US Executive
Cutout specification: Specified (one location)
Background compensation: Enabled
Contrast setting: 256 steps
Gamma pattern: 3 internal types (can be downloaded)
Image processing function: Automatic binary (simple system)
With image processing option
Outline emphasis, Outline extraction, Automatic separation,
Mirror image, Reverse image, Automatic binarization, Smoothing,
Filtering, Noise removal
Interface: SCSI-II
Job control: Enabled
Use of FUJITSU Scanner Control Center: Disabled
1. An eight-megabyte expanded memory option can be loaded in some models.
2. This speed is only specified in the scanner itself. The actual reading speed may vary depending on the
system
configuration.
4. Not all sizes of paper can be used in all devices. For details, refer to the users' manual for the device.
For other paper sizes, the customer settings can be used.
73
Page 80

Product: M3096GX1 (device name: fi-4620S)
Type: Desktop
Image sensor: Reduced optical system
Operating method: Document fixed, scanner unit moving (flat bed),
Automatic Document Feed (ADF)
Light source: Xe discharge tube (Green)
Basic resolution: Horizontal scanning: 400 dpi
Vertical scanning:400, 300, 240, 200 dpi
Output resolution: Standard: 400, 300, 240, 200 dpi
With image processing option: 50 dpi to 800 dpi (at steps of 1)
Grayscale levels (internal): 8 bit 256 levels
Grayscale output: Enabled (8 bits)
Halftone Patterns: Dither matrix (can be downloaded), Error diffusion
Scanning speed: 2.0 sec or less (A4, 200 dpi)
ADF scanning speed 2: 21 pages/minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
ADF stacker capacity: Maximum 50 sheets, (ream weight: 55 kg, A4 [High quality
paper, Normal temperature and humidity])
Document size: Maximum 297 mm × 432 mm A3 or Double letter sized paper
Supported regular paper 5: A3, A4/A4 Landscape, A5/A5 Landscape, A6/A6 Landscape,B4,
B5/B5 Landscape, B6/B6 Landscape, Letter, Letter Landscape,
Legal, Double letter, US Executive/US Executive Landscape
Isolation specification: Specified (one location)
Background compensation: Enabled
Contrast setting: 256 steps
Gamma patterns: 3 internal types (can be downloaded)
Image processing function: Auto binary (simplified method)
Image processing option installed
Outline emphasis, Outline extraction, Automatic separation,
Mirror image, Reverse image, Automatic binarization, Smoothing,
Filtering, Noise removal
Interface: SCSI-II
Job control: Enabled
Use of FUJITSU Scanner Control Center: Disabled
1. Use of this scanner may require installation of the optional image compression option board (CMP-2) in the
scanner device.
2. This speed is only specified for the scanner itself. The actual reading speed may vary depending on the
system
configuration.
5 Not all paper sizes can be used in all devices. For details, refer to the users' manual for the device.
For other paper sizes, the customer settings can be used.
74
Page 81

Product: M3097G1
Type: Desktop
Image sensor: Reduced optical system
Operating method: Document fixed, scanner unit moving (flat bed),
Automatic Document Feed (ADF)
Light source: Fluorescent tube (Green)
Basic resolution: Horizontal scanning: 400 dpi
Vertical scanning:400, 300, 240, 200 dpi
Output resolution: Standard: 400, 300, 240, 200 dpi
With image processing option: 50 dpi to 1,600 dpi
(at steps of 1)
Grayscale levels (internal): 8 bit 256 levels
Grayscale output: Enabled (8 bits) Some release version of scanner do not support
gray-scale output format
Halftone Patterns: Dither matrix (can be downloaded), Error diffusion
Scanning speed: 1.3 sec or less (A4, 200 dpi)
3.7 sec or less (A3, 400 dpi)
ADF scanning speed 2: 36 pages/minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
ADF stacker capacity: Maximum 100 sheets, (ream weight: 55 kg, A4 [High quality
paper, Normal temperature and humidity])
Document size: Maximum 297 mm × 432 mm
Supported regular paper 6: A3, A4/A4 Landscape, A5/A5 Landscape, A6/A6 Landscape, B4,
B5/B5 Landscape, B6/B6 Landscape, Letter/Letter Landscape,
Double Letter, Legal, US Executive/US Executive Landscape
Isolation specification: Specified (one location)
Background compensation: Enabled
Contrast setting: 256 steps
Gamma pattern: 3 internal types (can be downloaded)
Image processing function: Auto binary (simplified method)
Outline emphasis, Outline extraction, Automatic separation,
Mirror image, Reverse image, Automatic binarization, Smoothing,
Filtering, Noise removal
Interface: SCSI-II
Job control: Enabled
Use of FUJITSU Scanner Control Center: Disabled
1. Use of this scanner may require installation of the optional image compression board (CMP-2).
2. This speed is only specified for the scanner itself. The actual reading speed may vary depending on the
system configuration.
6 Not all paper sizes can be used in all devices. For details, refer to the users' manual for the device.
For other paper sizes, the customer settings can be used.
75
Page 82

Product: M3097DG
Type: Desktop
Image sensor: Reduced optical system
Operating method: Document fixed, scanner unit moving (flat bed),
Automatic Document Feed (ADF)
simultaneous double-sided reading
Light source: Xe discharge tube (Green)
Basic resolution: Horizontal scanning: 400 dpi
Vertical scanning: 400, 300, 240, 200 dpi
Output resolution: Standard: 600, 400, 300, 240, 200, 150, 100 dpi
With image processing option: 50 dpi to 800 dpi
(at steps of 1 dpi)
Grayscale levels (internal): 8 bit 256 levels
Grayscale output: Enabled (8 bits)
Halftone Patterns: Dither matrix (can be downloaded), Error diffusion
Scanning speed: 1.3 seconds or less (A4, 200 dpi)
ADF scanning speed 1: Single sided: 36 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
Double sided: 30 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
(= 60 screens per minute)
ADF sacker capacity: Maximum 100 sheets, (ream weight: 55 kg, A4 [High quality
paper, Normal temperature and humidity])
Documnt size: Maximum 297 mm × 432 mm
Suppored regular paper 2: A3, A4/A4 Landscape, A5/A5 Landscape, A6/A6 Landscape, B4,
B5/B5 Landscape, Double Letter, Letter/Letter landscape, Legal,
US Executive/ US Executive Landscape
Cutoutcification: Specified (one location)
Background compensation: Enabled
Contrast setting: 256 steps
Gamma pattern: 3 internal types (can be downloaded)
Image processing function: Automatic binary (simple system)
With image processing option
Outline emphasis, Outline extraction, Automatic separation,
Mirror image, Reverse image, Automatic binarization, Smoothing,
Filtering, Noise removal.
Interface: SCSI-II
Job control: Enabled
Long page scanning: Enabled (front side and both sides)
1. This speed is only specified for the scanner itself. The actual reading speed may vary depending on the
system configuration.
2 Not all paper sizes can be used in all devices. For details, refer to the users' manual for the device.
For other paper sizes, the customer settings can be used.
76
Page 83

Use of FUJITSU Scanner Control Center: Disabled
Product: M3099G, M3099GX
Type: Desktop
Image sensor: Reduced optical system
Operating method: Automatic Document Feed (ADF), simultaneous double-sided
reading
Light source: Fluorescent tube (Green)
Basic resolution: Horizontal scanning: 200 dpi
Vertical scanning: 400, 300, 240, 200 dpi
Output resolution: Standard: 400, 300, 240, 200, dpi
With image processing option: 50 dpi to 400 dpi (at steps of 1 dpi)
Grayscale levels (internal): 8 bit 256 levels
Grayscale output: Disabled
Halftone Patterns: Dither matrix (can be downloaded), Error diffusion
ADF scanning speed 1: <M3099G>
Single sided: 55 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
Double sided: 50 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
(= 100 screens per minute)
<M3099GX>
Single sided: 60 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
Double sided: 50 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
(= 100 screens per minute)
ADF stacker capacity: <M3099G>
Maximum 500 sheets, ream weight: 55 kg, A4
<M3099GX>
Maximum 1,000 sheets, ream weight: 55 kg, A4
Document size: Maximum 297 mm × 432 mm
Supported regular paper 2: A3, A4/A4 Landscape, A5/A5 Landscape, A6/A6 Landscape, B4,
B5/B5 Landscape, B6/B6 Landscape, Double Letter, Letter/Letter
Landscape, Legal, US Executive/US Executive Landscape
Cutout specification: Specified (one location)
Background compensation: Enabled
Contrast setting: 256 levels
Gamma pattern: 3 internal types (can be downloaded)
Use of FUJITSU Scanner Control Center: Disabled
1. This speed is only specified for the scanner itself. The actual reading speed may vary depending on the
system configuration.
2 Not all paper sizes can be used in all devices. For details, refer to the users' manual for the device.
For other paper sizes, the customer settings can be used.
77
Page 84

Image processing function: Automatic binary (simple system)
With image processing option
Outline emphasis, Outline extraction, Automatic separation,
Mirror image, Reverse image, Automatic binarization, Smoothing,
Filtering, Noise removal
Endorser/stamp: With endorser option
(Reverse side, minimum left margin printing position of 20 mm)2
Maximum number of characters to be printed: 20 characters
Interface: SCSI-II
Job control: Enabled
Use of FUJITSU Scanner Control Center: Disabled
2. If 0 mm is specified as the endorser print position, printing will begin 20 mm from the edge of the page.
78
Page 85

Product: M3099GH
Type: Desktop
Image sensor: Reduced optical system
Operating method: Automatic Document Feed (ADF), simultaneous double-sided
reading
Light source: Fluorescent tube (Green)
Basic resolution: Horizontal scanning: 200 dpi
Vertical scanning: 400, 300, 240, 200 dpi
Output resolution: Standard: 400, 300, 240, 200, dpi
with image processing option: 50 dpi to 400 dpi (at steps of 1 dpi)
Grayscale levels (internal): 8 bit 256 levels
Grayscale output: Disabled
Halftone Patterns: Dither matrix (can be downloaded), Error diffusion
ADF scanning speed 1: Single sided: 80 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
Double sided: 60 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
(= 120 screens per minute)
ADF stacker capacity: Maximum 1,000 sheets, (ream weight: 55 kg, A4 [High quality
paper, Normal temperature and humidity])
Document size: Maximum 216 mm × 356 mm
Supported regular paper 2: A4/A4 Landscape, A5/A5 Landscape, B5, B6/B6 Landscape,
Letter, Legal, US Executive
Cutout specification: Specified (one location)
White level follower: Enabled
Contrast setting: 256 steps
Gamma pattern: 3 internal types (can be downloaded)
Image processing function: Automatic binary (simple system)
With image processing option
Outline emphasis, Outline extraction, Automatic separation,
Mirror image, Reverse image, Automatic binarization, Smoothing,
Filtering, Noise removal
1. This speed is only specified for the scanner itself. The actual reading speed may vary depending on the
system configuration.
2 Not all paper sizes can be used in all devices. For details, refer to the users' manual for the device.
For other paper sizes, the customer settings can be used.
79
Page 86

Endorser/stamp: With endorser option
(Reverse side, minimum left margin printing position of 20 mm)2
Maximum number of characters to be printed: 20 characters
Interface: SCSI-II
Job control: Enabled
Use of FUJITSU Scanner Control Center: Disabled
2 If 0 mm is specified as the endorser print position, printing will begin 20 mm from the edge of the page.
80
Page 87

Product: M4097D (device name: fi-4750)
Type: Desktop
Image sensor: Reduced optical system
Operating method: Document fixed Flat bed, Automatic Document
Feed(ADF), simultaneous double-sided reading
Long page scanning (297mm x 1387mm)
Light source: Xe discharge tube(Green)
Basic resolution: Horizontal scanning: 400 dpi
Vertical scanning: 800,700,600,500, 400, 300, 240, 200, 150,
100 dpi
Output resolution: Standard: 800,700,600, 500,400, 300, 240, 200,150,100 dpi
With image processing option: 50 dpi to 800 dpi (at steps of 1dpi)
Grayscale levels (internal): 10 bit 1024 levels
Grayscale output: Enabled (8 bits)
Halftone Patterns: Dither matrix (can be downloaded), Error diffusion
Scanning speed: 0.9 sec or less
ADF scanning speed 1: Single sided: 50 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
Double sided: 45 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55kg)
(=90 screens per minute)
ADF stacker capacity: Maximum 100 sheets, ream weight: 55 kg, A4 [High quality
paper, normal temperature and humidity])
Document size: Maximum 297 mm × 432 mm
Supported regular paper 2: A3, A4/A4 Landscape, A5/A5 Landscape, A6/A6 Landscape, B4,
B5/B5 Landscape, B6/B6 Landscape, Letter/Letter Landscape,
Double Letter, Legal, US Executive/US Executive Landscape
Isolation specification: Specified (one location)
Background compensation: Enabled
Contrast setting: 256 steps
Gamma pattern: 3 internal types (can be downloaded)
Image processing function: Automatic binary(simple system)
With image processing option
Outline emphasis, Outline extraction, SEE(Selectable Edge
Enhancement), Reverse image, Automatic binarization,
Smoothing, Filtering, Noise removal
1 This speed is only specified for the scanner itself. The actual reading speed may vary depending on the
system configuration.
2 Not all paper sizes can be used in all devices. For details, refer to the users' manual for the device.
For other paper sizes, the customer settings can be used.
81
Page 88

Interface: SCSI-II
Job control: Enabled
Double feed detection: Enabled
Long page scanning: Enabled (front side and both sides)
Use of FUJITSU Scanner Control Center: Enabled
82
Page 89

Product: fi-4750C
Type: Desktop
Image sensor: LED(RGB) + Reduced optical system
Operating method: Document fixed Flat bed, Automatic Document
Feed(ADF), simultaneous double-sided reading
Long page scanning (297mm×1387mm)
Light source: LED (R, G, B)
Basic resolution: Horizontal scanning: 400 dpi
Vertical scanning: 800,700,600,500, 400, 300, 240, 200, 150,
100 dpi
Output resolution: Standard: 800,700,600, 500,400, 300, 240, 200,150,100 dpi
With image processing option: 50 dpi to 800 dpi (at steps of 1dpi)
Grayscale levels (internal): 10 bit 1024 levels
Grayscale output: Enabled (8 bits)
Halftone Patterns: Dither matrix (can be downloaded), Error diffusion
Color 24bit
Scanning speed: B/W : 0.9 sec or less
Color : 3.1 sec or less
ADF scanning speed 1: B/W
Single sided: 50 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
Double sided: 45 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55kg)
(=90 screens per minute)
Color
Single sided: 12 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
Double sided: 11.5 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55kg)
(=23 screens per minute)
ADF stacker capacity: Maximum 100 sheets, ream weight: 55 kg, A4 [High quality
paper, normal temperature and humidity])
Document size: Maximum 297 mm × 432 mm
Supported regular paper 2: A3, A4/A4 Landscape, A5/A5 Landscape, A6/A6 Landscape, B4,
B5/B5 Landscape, B6/B6 Landscape, Letter/Letter Landscape,
Double Letter, Legal, US Executive/US Executive Landscape
Isolation specification: Specified (one location)
Background compensation: Enabled
Contrast setting: 256 steps
Gamma pattern: 3 internal types (can be downloaded)
1 This speed is only specified for the scanner itself. The actual reading speed may vary depending on the
system configuration.
2 Not all paper sizes can be used in all devices. For details, refer to the users' manual for the device.
For other paper sizes, the customer settings can be used.
83
Page 90

Image processing function: Automatic binary(simple system), Outline emphasis,
Outline extraction, SEE(Selectable Edge Enhancement),
De-Screen, Reverse image,
With image processing option
Automatic binarization, Smoothing, Filtering, Noise removal
Interface: SCSI-II
Job control: Enabled
Double feed detection: Enabled
Long page scanning: Enabled (front side and both sides)
Use of FUJITSU Scanner Control Center: Enabled
84
Page 91

Product: M4099D (device name: fi-4990)
Type: Desktop
Image sensor: Reduced optical system
Operating method: Automatic Document Feed (ADF), simultaneous double-sided
reading Long page scanning (297mm×878mm)
Light source: Fluorescent tube (White)
Basic resolution: Horizontal scanning: 400 dpi
Vertical scanning: 400, 300, 240, 200 dpi
Output resolution: Standard: 400, 300, 240, 200, dpi
With image processing option: 50 dpi to 400 dpi (at steps of 1 dpi)
Grayscale levels (internal): 10 bit 1024 levels
Gray scale (8 bits) output: Enabled (200 dpi only)
Halftone Patterns: Dither matrix (can be downloaded), Error diffusion
ADF scanning speed 1: <Asynchronous Scanning>
Single sided: 90 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
Double sided: 90 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
< Synchronous Scanning >
(= 180 screens per minute)
Single sided: 80 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
Double sided: 60 pages per minute (200 dpi, A4, 55 kg)
(= 120 screens per minute)
ADF stacker capacity: Maximum 1,000 sheets, (ream weight: 55 kg, A4 [High quality
paper, Normal temperature and humidity])
Document size: Maximum 297 mm × 432 mm
Supported regular paper 2: A3, A4/A4 Landscape, A5/A5 Landscape, A6/A6 Landscape, B4,
B5/B5 Landscape, B6/B6 Landscape, Double Letter, Letter/Letter
Landscape, Legal, US Executive/US Executive Landscape
Cutout specification: Specified (one location)
Background compensation: Enabled
Contrast setting: 256 levels
Gamma pattern: 3 internal types (can be downloaded)
Image processing function: Automatic binary (simple system)
With image processing option
Outline emphasis, Outline extraction, Automatic separation,
Mirror image, Reverse image, Automatic binarization, Smoothing,
Filtering, Noise removal
1. This speed is only specified for the scanner itself. The actual reading speed may vary depending on the
system configuration.
2 Not all paper sizes can be used in all devices. For details, refer to the users' manual for the device.
For other paper sizes, the customer settings can be used.
85
Page 92

Endorser/stamp: With endorser option
(Reverse side, minimum left margin printing position of
20 mm) 2
Maximum number of characters to be printed: 30 characters
Interface: SCSI-II
Online offset adjustment: Enabled
Job control: Enabled
Automatic skew compensation: Enabled
Drop out: Enabled
Double feed detection: Enabled
Buffer scan (cache using scanner memory) function: Enabled
Blank page skip: Enabled (only when scanner memory is used)
Use of FUJITSU Scanner Control Center: Enabled
2 If 0 mm is specified as the endorser print position, printing will begin 20 mm from the edge of the page.
86
Page 93

8.2 Maintenance Service
This section explains briefly how you can help us to provide you with high-quality maintenance
service.
Since it is practically impossible for the Fujitsu service staff to be aware of every detail of your
daily scanning operation, please understand that our staff may sometimes be unable to answer
your question immediately. To help us in our effort to provide you with the best maintenance
service possible, we ask you to kindly write down the following items (as many as possible):
•
Serial number, version, and date, etc., of this product
•
Name and product number of the image scanner being used
•
The options installed on the image scanner being used
•
Manufacturer, product name, and type number of the computer being used
•
Manufacturer and version of the Windows OS (whether Windows has been updated)
•
Manufacturer and version of MS-DOS (Whether MS-DOS has been updated)
•
Name and version of the display driver
•
Name and version of the printer driver
•
Resolution (1024 × 768), number of colors, and number of dots (or points) of the screen
•
Product name of the SCSI adapter, and name and version of the SCSI driver
•
Error occurrence processing (the simpler the processing, the easier it is to determine the
cause.)
Also, we would appreciate it very much if you could kindly verify the following items prior to
receiving our maintenance service;
•
Is the power turned on?
•
Is the cable connected correctly?
•
Is the correct image scanner driver selected?
87
Page 94

TWAIN Scanner/Driver Utility
“Scanner Utility for Microsoft® Windows®”
Users Guide
32 bit version
First Edition September 2000
All Rights Reserved, Copyright FUJITSU LIMITED 1998, 2000
• The contents of this document may change for improvements without
prior notice.
• Fujitsu takes no responsibilities for infringements of third parties’ patents
or other rights that may stem from the use of the data in this document.
• Unauthorized reproduction of this document is prohibited
• Missing or misplaced pages are subject to exchange.
88
 Loading...
Loading...