Instruction Manual
ICC
INDUSTRIAL CONTROL COMMUNICATIONS, INC.
OPC-F1-ETH
Multiprotocol Ethernet Interface
Thank you for purchasing the OPC-F1-ETH Multiprotocol Ethernet Interface.
• This product is designed to connect the FRENIC-Eco series of inverters to Ethernet
communication networks. Please read this instruction manual thoroughly in order to become
familiar with the proper interface handling, installation and usage procedures.
• Improper handling may inhibit correct operation or cause premature interface failure.
• Please deliver this instruction manual to the end user of the interface, and retain it in an
accessible location.
• For inverter usage instructions, please refer to the applicable FRENIC-Eco inverter instruction
manual.
September 2011
ICC #10764-1.100-001 © 2011 Industrial Control Communications, Inc.

ICC
Industrial Control Communications, Inc. reserves the right to make changes and improvements to its
INDUSTRIAL CONTROL COMMUNICATIONS, INC.’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE
AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS. Life-support devices or
systems are devices or systems intended to sustain life, and whose failure to perform, when properly
used in accordance with instructions for use provided in the labeling and user's manual, can be
reasonably expected to result in significant injury.
No complex software or hardware system is perfect. Bugs may always be present in a system of any
size. In order to prevent danger to life or property, it is the responsibility of the system designer to
incorporate redundant protective mechanisms appropriate to the risk involved.
OPC-F1-ETH Multiprotocol Ethernet Interface Instruction Manual
Part Number 10764-1.100-001
Printed in U.S.A.
©2011 Industrial Control Communications, Inc.
All rights reserved
products without providing notice.
Notice to Users
1

ICC
Preface
Thank you for purchasing the OPC-F1-ETH Multiprotocol Ethernet Interface. This instruction manual
has been prepared to help you connect your FRENIC-Eco inverter to a variety of Ethernet control
networks.
This instruction manual does not contain inverter usage instructions. Please refer to this instruction
manual in conjunction with the FRENIC-Eco Instruction Manual (INR-SI47-1225-E) in order to become
familiar with the proper handling, installation and operation of this product. Improper handling or
installation procedures may result in incorrect operation or premature product failure.
Please keep this instruction manual in a safe place.
Related Publications
Listed below are publications that are recommended for reference in conjunction with this instruction
manual.
• RS-485 Communication User's Manual ........... (MEH448)
• FRENIC-Eco Instruction Manual ...................... (INR-SI47-1225-E)
These documents are subject to change without notice. Please be sure to refer to the most recent
available versions.
Safety precautions
Please read this instruction manual thoroughly prior to pro ceeding w ith installation, connections,
operation, or maintenance and inspection. Additionally, ensure that all aspects of the system are fully
understood, and familiarize yourself with all safety information and precautions before operating the
inverter.
Safety precautions in this instruction manual are classified into the following two categories:
Failure to heed the information indicated by this symbol may lead
to dangerous conditions, possibly resulting in death or serious
bodily injuries.
Failure to heed the information indicated by this symbol may lead
to dangerous conditions, possibly resulting in minor or light bodily
injuries and/or substantial property damage.
Failure to heed the information contained under the CAUTION title can also result in serious
consequences. These safety precautions are of utmost importance and must be observed at all times.
2

ICC
Installation and wiring
• To avoid electrical shock, remove all power from the inverter and wait at least five minutes prior to
starting installation. Additionally, confirm that the DC link bus voltage as measured between the
P (+) and N (-) terminals is less than 25 VDC.
• Installation should be performed only by qualified personnel.
• To avoid electrical shock, do not operate the inverter with the front cover or wiring cover removed,
as accidental contact with exposed high-voltage terminals and internal components may occur.
• To prevent explosions or similar damage, ensure that all cables are properly connected to the
correct terminals, and observe all wiring polarity indicators.
• Do not install or operate the interface if it is damaged or has parts missing.
• Prevent conductive items such as screws and metal fragments, or flammable substances such as
oil, lint, paper fibers and sawdust from entering the inverter and interface card enclosure.
• Incorrect handling during installation or removal may cause equipment failure.
• Do not subject the cables to scratches, excessive stress, heavy loads or pinching.
• To prevent damage due to electrostatic discharge, always touch a grounded piece of metal prior
to touching any equipment.
• Do not stand on or rest heavy objects on the equipment.
• To prevent burns from hot components, do not touch the inverter while power is on, or for some
time after power is removed.
• Electrical noise may be emitted from the inverter, motor and wires. Always implement
appropriate countermeasures to prevent nearby sensors and devices from malfunctioning due to
such noise.
Operation
• To avoid electrical shock, do not open the front cover of the inverter while power is on or while the
inverter is running.
• To avoid electrical shock, do not operate switches with wet hands.
• If the inverter’s function codes are incorrectly configured, or configured without adequate
understanding of the FRENIC-Eco Instruction Manual (INR-SI47-1225-E) and FRENIC-Eco
User's Manual (MEH532), the motor may rotate with a torque or at a speed not permitted for the
machine. Confirm the settings of all function codes prior to running the inverter.
3
ICC
Maintenance, inspection, and parts replacement
• To avoid electrical shock, remove all power from the inverter and wait at least five minutes prior to
starting inspection. Additionally, confirm that the DC link bus voltage as measured between the P
(+) and N (-) terminals is less than 25 VDC.
• Maintenance, inspection, and parts replacement should be performed only by qualified personnel.
• Remove all watches, rings and other metallic objects prior to starting work.
• To avoid electrical shock or other injuries, always use insulated tools.
Disposal
• Contact the local or state environmental agency in your area for details on the disposal of
electrical components and packaging.
Other
• Do not attempt to modify the equipment: doing so may cause electrical shock or injuries.
• For clarity purposes, illustrations in this manual may be drawn with covers or safety guards
removed. Ensure all covers and safety guards are properly installed prior to starting operation.
• Do not perform hi-pot tests on the equipment.
• Performing a data initialization (function code H03) may reset all inverter function codes to their
factory default settings. After performing this operation, remember to reenter any custom function
code values prior to starting operation.
Icons
The following icons are used throughout this manual:
Indicates information which, if not heeded, can result in the product not operating to full
efficiency, as well as information concerning incorrect operations and settings which may
result in accidents.
Indicates information that can prove handy when performing certain settings or operations.
Indicates a reference to more detailed information.
4

ICC
− TABLE OF CONTENTS −
1 PRE-OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS ............................................................. 8
1.1 Product Overview .................................................................................................... 8
1.2 Unpacking and Product Confirmation ................................................................ 10
1.2.1 Shipment Confirmation ..................................................................................................... 10
1.2.2 Component Overview....................................................................................................... 11
1.3 LED Indicators ....................................................................................................... 12
1.3.1 Network Status LED ......................................................................................................... 12
1.3.2 Module Status LED .......................................................................................................... 12
1.3.3 Ethernet Link LED ............................................................................................................ 12
1.3.4 Ethernet Activity LED ....................................................................................................... 12
1.4 Environmental Specifications .............................................................................. 12
2 INSTALLATION .......................................................................................... 13
2.1 Pre-Installation Instructions ................................................................................. 13
2.2 Installation Procedure .......................................................................................... 14
3 INVERTER FUNCTION CODE SETTINGS ................................................ 16
3.1 RS-485 Communication Settings ......................................................................... 17
3.2 Inverter Control-Related Settings ........................................................................ 18
4 FINDER APPLICATION .............................................................................. 19
4.1 Overview ................................................................................................................ 19
4.2 Configuring the IP Address .................................................................................. 20
4.2.1 Via the Finder Utility ......................................................................................................... 20
4.2.2 Via the Web Page ............................................................................................................ 20
5 EMBEDDED WEB SERVER ....................................................................... 21
5.1 Overview ................................................................................................................ 21
5.2 Authentication ....................................................................................................... 22
5.3 Page Select Tabs ................................................................................................... 22
5.4 Monitor Tab ............................................................................................................ 22
5.4.1 Information Window ......................................................................................................... 22
5.4.2 Function Code Group Selection List ................................................................................. 23
5.4.3 Function Code List ........................................................................................................... 23
5.4.4 Function Code List Filter .................................................................................................. 24
5.4.5 Non-Scanned Function Code Refresh .............................................................................. 25
5.4.6 Radix Selection ................................................................................................................ 25
5.5 PROFI NET Tab ....................................................................................................... 26
5.5.1 Information Window ......................................................................................................... 26
5.5.2 Device Identification and Configurati on ............................................................................ 26
5.5.3 I/O Data Configuration Arrays .......................................................................................... 27
5.5.4 Submitting Changes ......................................................................................................... 27
5.6 BACnet Tab ............................................................................................................ 28
5.6.1 Information Window ......................................................................................................... 28
5.6.2 Device Identifiers ............................................................................................................. 28
5.6.3 Submitting Changes ......................................................................................................... 29
5.7 Con fig Tab.............................................................................................................. 30
5

ICC
5.7.1 Information Window ......................................................................................................... 30
5.7.2 Authentication Configuration ............................................................................................ 30
5.7.3 IP Address Configuration ................................................................................................. 31
5.7.4 MAC Address Configuration ............................................................................................. 31
5.7.5 Timeout Configuration ...................................................................................................... 31
5.7.6 Submitting Changes ......................................................................................................... 32
5.8 EtherNet/IP Tab ..................................................................................................... 33
5.8.1 Information Window ......................................................................................................... 33
5.8.2 Device Identification ......................................................................................................... 33
5.8.3 Run/Idle Flag Behavior ..................................................................................................... 34
5.8.4 Class 1 (I/O) Data Configuration Arrays ........................................................................... 34
5.8.5 Submitting Changes ......................................................................................................... 35
5.9 Alarm Tab ............................................................................................................... 36
5.9.1 Information Window ......................................................................................................... 36
5.9.2 Email Configuration .......................................................................................................... 37
5.9.3 Alarm Configuration ......................................................................................................... 38
5.9.4 Submitting Changes ......................................................................................................... 39
5.10 Modbus Tab ........................................................................................................... 40
5.10.1 Information Window ......................................................................................................... 40
5.10.2 Supervisory Timer Selection ............................................................................................ 40
5.10.3 Register Remap Configuration ......................................................................................... 41
5.10.4 Submitting Changes ......................................................................................................... 42
5.11 Dashboard Tab ...................................................................................................... 43
5.11.1 Information Window ......................................................................................................... 43
5.11.2 Virtual Keypad.................................................................................................................. 44
5.11.3 Gauge Window Navigation ............................................................................................... 45
5.11.4 Gauge Window Configuration .......................................................................................... 45
5.11.5 Submitting Changes ......................................................................................................... 48
6 FUNCTION CODE NUMBERING AND BEHAVIOR ................................... 49
6.1 Register Numbers ................................................................................................. 49
6.2 Scanned and Non-Scanned Registers ................................................................ 50
7 FILESYSTEM & FIRMWARE ..................................................................... 52
7.1 Overview ................................................................................................................ 52
7.2 Initia ting FTP via the Finder Utility ...................................................................... 53
7.3 Using FTP with Windows Explorer ...................................................................... 53
7.4 Using FTP with a Windows Command Prompt .................................................. 55
7.5 Using FTP with Core FTP LE ................................................................................ 56
7.6 Load ing New Application Firmware .................................................................... 57
8 PROTOCOL-SPECIFIC INFORMA TION .................................................... 58
8.1 Modbus/TCP .......................................................................................................... 58
8.1.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................... 58
8.1.2 Coil & Discrete Input Mappings ........................................................................................ 59
8.2 EtherNet/IP ............................................................................................................. 60
8.2.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................... 60
8.2.2 ODVA AC/DC Drive Profile .............................................................................................. 61
8.2.3 ControlLogix Examples: Setup ......................................................................................... 63
8.2.4 ControlLogix Example: I/O Messaging ............................................................................. 64
8.2.5 ControlLogix Example: Generic Default I/O Add-On Ins truction ....................................... 67
6

ICC
8.2.6 ControlLogix Example: AC/DC Drive Profile Add-On Instruction ...................................... 69
8.2.7 Explicit Messaging Tag Reference ................................................................................... 71
8.2.8 ControlLogix Explicit Messaging Example: Read a Register Block................................... 72
8.2.9 ControlLogix Explicit Messaging Example: Read a Single Register ................................. 77
8.2.10 ControlLogix Explicit Messaging Example: Multiple MSG Instructions ............................. 77
8.2.11 ControlLogix Explicit Messaging Example: Reading and Writing ...................................... 78
8.3 Allen Bradley CSP ................................................................................................. 79
8.3.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................... 79
8.3.2 Tag Reference ................................................................................................................. 79
8.3.3 SLC-5/05 Example: Read a Register Block ...................................................................... 81
8.3.4 SLC-5/05 Example: Read a Single Register ..................................................................... 84
8.3.5 SLC-5/05 Example: Multiple MSG Instructions ................................................................. 85
8.3.6 SLC-5/05 Example: Reading and Writing ......................................................................... 86
8.4 BACnet/IP ............................................................................................................... 87
8.4.1 Protocol Implementation Conformance Statement ........................................................... 87
8.4.2 Supported Objects ........................................................................................................... 9 0
8.4.3 Supported Object Details ................................................................................................. 92
8.5 PROFINET IO ......................................................................................................... 93
8.5.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................... 93
8.5.2 PROFIdrive Profile ........................................................................................................... 93
9 TROUBLESHOOTING ................................................................................ 95
7
ICC
1 PRE-OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS
1.1 Product Overview
The OPC-F1-ETH Ethernet multiprotocol communication interface allows information to be transferred
seamlessly between a FRENIC-Eco inverter and several different Ethernet-based fieldbus networks with
minimal configuration requirements. The interface installs directly onto the inverter, and presents a
standard 10/100BaseT Ethernet port for connection to the Ethernet network. In addition to the
supported fieldbus protocols, the interface also hosts an embedded web server, which provides access
to inverter information via a standard web browser for remote monitoring, configuration and control.
Before using the interface, please familiarize yourself with the product and be sure to thoroughly read
the instructions and precautions contained in this manual. In addition, please make sure that this
instruction manual is delivered to the end user of the interface, and keep this instruction manual in a safe
place for future reference or unit inspection.
Note that different interface firmware versions may provide varying levels of support for the various
protocols. When using this manual, therefore, always keep in mind that the firmware version running on
your interface must match this manual’s respective revi sion in order for all documented aspects to apply.
The primary features of the OPC-F1-ETH are as follows:
Ethernet Port
IEEE 802.3 10/100BaseT Ethernet compliant. Shielded RJ45 connector accepts standard CAT5-type 8conductor unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) patch cable s. Supports multiple simultaneous protocols.
Supported Protocols
The interface currently provides server support for the following fieldbus protocols:
• Modbus/TCP
• EtherNet/IP
• Allen Bradley CSP (also known as “PCCC” and “AB Ethernet”)
• BACnet/IP
• PROFINET IO
Note that use of PROFINET IO is mutually exclusive of the other supported protocols. In order to use
PROFINET IO, a separate application firmware file must be loaded into the interface (refer to section
7.6).
Adobe® Flash-Enabled Embedded Web Server
Interface configuration and real-time inverter register monitoring & control are provided via an embedded
web server. The interface’s web server feature provides direct data access and control via standard
web browsers such as Microsoft Internet Explorer and Mozilla Firefox. The latest version of Adobe
Flash Player browser plug-in is required. Refer to section 5.
XML Configuration File Upload/Download
All interface configuration files are stored in the unit’s internal filesystem in XML format. These files can
be transferred to/from a PC via the FTP protocol, which provides the capability for PC-based file backup
and easy configuration copying to multiple units. Configuration files can also be viewed and edited via
standard text editors, XML editors and web browsers. Refer to section 7.
Email-Based Alarm Notifications
Up to 20 configurable alarm conditions can be programmed into the interface. Value, logical comparison
and time-based conditions can be provided for the interface to autonomously monitor any available
inverter register. When an alarm condition is triggered, a notification email can be sent to up to four
destination email addresses. Refer to section 5.9.
Dashboard GUI
A dashboard tab on the embedded web server provides 10 gauge windows, each of which can be
configured to display any available scanned inverter register in a variety of meter, graph and gauge
formats. A virtual keypad interface is also provided. Refer to section 5.11.
8

ICC
Network Timeout Action
A configurable network timeout action can be programmed that allows registers to have their own unique
"fail-safe" conditions in the event of a network interruption. Refer to section 5.7.5.
Field-Upgradeable
As new firmware becomes available, the interface can be upgraded in the field by the end-user. Refer to
section 7.6 for more information.
EtherNet/IP Data Access Options
The EtherNet/IP protocol provides access to inverter data via explicit messaging, user-defined I/O
assembly instances, and the ODVA AC/DC drive profile. Refer to section 8.2 for more information.
PROFINET Data Access Options
The PROFINET protocol provides access to inverter data via acyclic services, user-defined cyclic I/O
modules, and the PROFIdrive profile. Refer to section 8.5 for more information.
9

ICC
1.2 Unpacking and Product Confirmation
1.2.1 Shipment Confirmation
Check the enclosed items. Confirm that the correct quantity of each item was received, and that no
damage occurred during shipment.
• OPC-F1-ETH interface board (see Figure 1).
• Four nylon standoffs (see Figure 2).
Figure 2: Nylon Standoffs
Figure 1: OPC-F1-ETH Interface Board
10
ICC
1.2.2 Component Overview
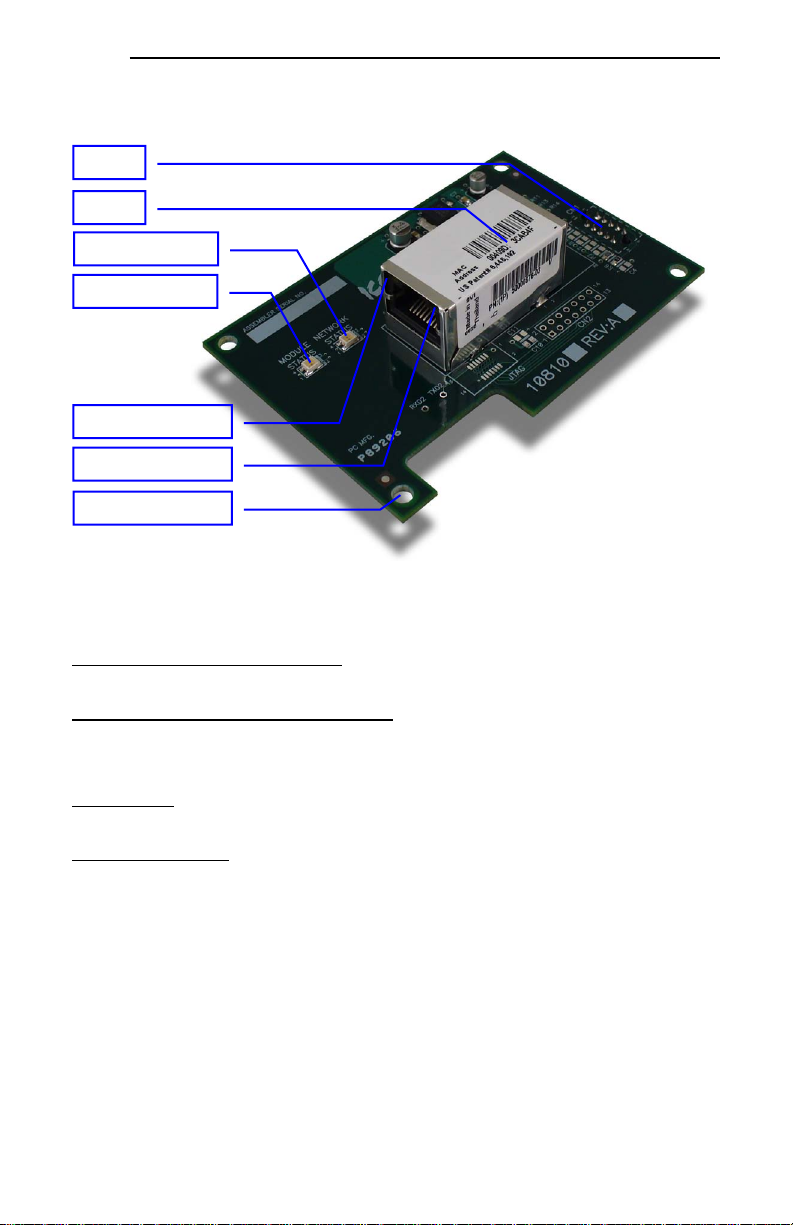
Figure 3 shows an overview of the important interface card components.
CN1
MAC ID
Network status LED
Module status LED
Ethernet link LED
Ethernet activity LED
Standoff hole (4 total)
Figure 3: OPC-F1-ETH Component Overview
Network Status and Module Status LEDs
These LEDs indicate the current status of the interface card and protocols in use. Refer to section 1.3.
Ethernet Jack with Embedded LEDs and MAC ID
The Ethernet network is connected here, and the embedded LEDs provide insight into the Ethernet
network’s status and activity. Refer to section 1.3. The unique MAC ID for the interface card is also
located on a barcode sticker on top of the Ethernet jack.
Connector CN1
Connects to the “Port A” connector on the inverter’s control board. Refer to section 2.2.
Standoff Holes (4 Total)
Receive the ends of the four nylon standoffs used to mount the interface card to the inverter’s control
board.
11
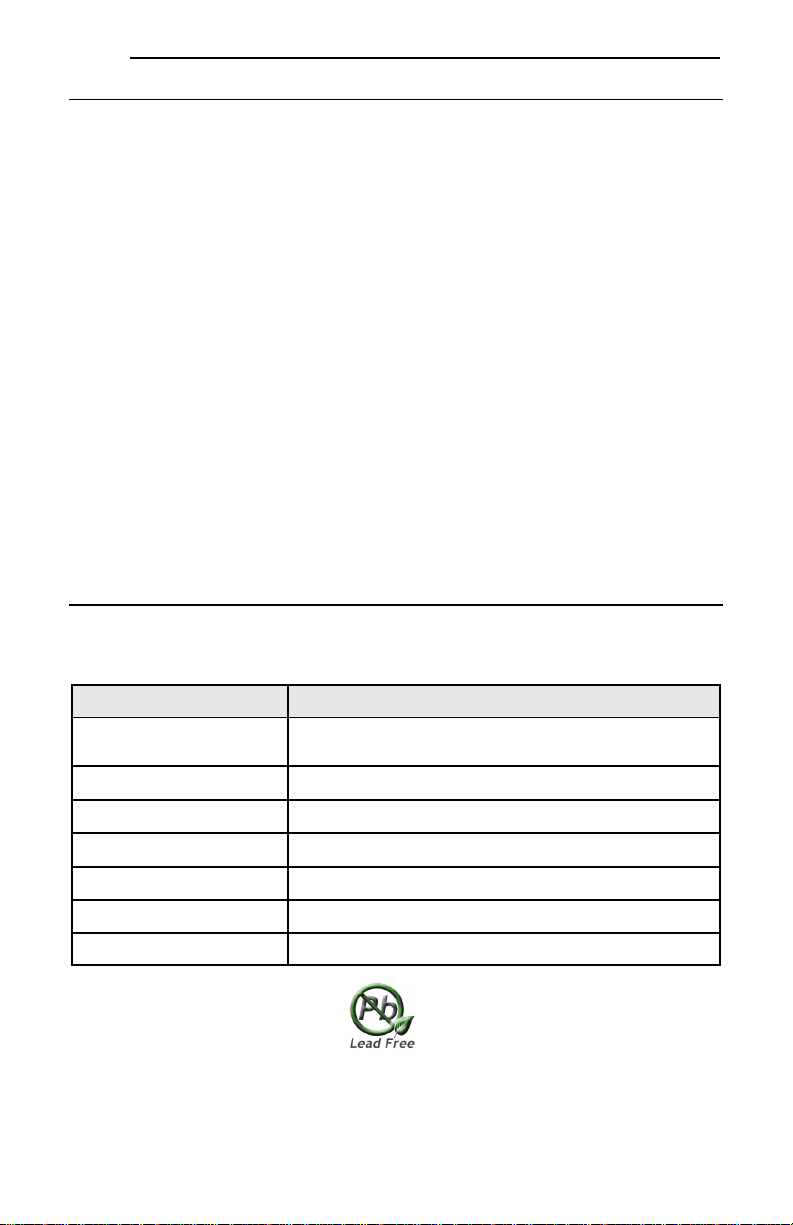
ICC
∼
∼
∼
1.3 LED Indicators
1.3.1 Network Status LED
• When the multiprotocol firmware image (with EtherNet/IP support) is loaded, this LED conforms to
the prescribed “network status LED” behavior as dictated in the EtherNet/IP specification, Volume 2,
Chapter 9.
• When the PROFINET IO firmware image is loaded, this LED is on solid green when the controller
has established a link with the interface board and is communicating with it.
1.3.2 Module Status LED
• When the multiprotocol firmware image (with EtherNet/IP support) is loaded, this LED conforms to
the prescribed “module status LED” behavior as dictated in the EtherNet/IP specification, Volume 2,
Chapter 9.
• When the PROFINET IO firmware image is loaded, this LED is always off.
• Contact ICC technical support if a blinking red error code is observed.
1.3.3 Ethernet Link LED
• This amber LED (embedded in the upper-left corner of the Ethernet jack) is lit whenever a viable
Ethernet network is connected to the port.
1.3.4 Ethernet Activity LED
• This green LED blinks briefly when network packets are sent or received.
1.4 Environmental Specifications
The interface’s environmental specifications are detailed in Table 1.
Table 1: Environmental Specifications
Item Specification
Operating Environment
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature
Relative Humidity
Vibration
Cooling Method Self-cooled
Communication Speed 10/100BaseT auto sensing
This device is lead-free / RoHS-compliant.
Indoors, less than 1000m above sea level, do not expose to direct
sunlight or corrosive / explosive gasses
+50°C (+14 ∼ +122°F)
-10
+85°C (-40 ∼ +185°F)
-40
20%
90% (without condensation)
2
(0.6G) or less (10 ∼ 55Hz)
5.9m/s
12

ICC
2 INSTALLATION
2.1 Pre-Installation Instructions
• To avoid electrical shock, remove all power from the inverter and wait at least five minutes prior to
starting installation. Additionally, confirm that the DC link bus voltage as measured between the
P (+) and N (-) terminals is less than 25 VDC.
• Installation should be performed only by qualified personnel.
• To avoid electrical shock, do not operate the inverter with the front cover or wiring cover removed,
as accidental contact with exposed high-voltage terminals and internal components may occur.
• To prevent explosions or similar damage, ensure that all cables are properly connected to the
correct terminals, and observe all wiring polarity indicators.
13
ICC
2.2 Installation Procedure
Before installing the interface card, perform all wiring for the main circuit terminals and
control circuit terminals.
1. Remove the covers from the inverter to expose the control board.
Note: For inverters with capacities of 37kW and above, also open the keypad enclosure.
For removal instructions, refer to the FRENIC-Eco Instruction Manual (INR-SI47-1225-E),
Chapter 2, Section 2.3 "Wiring."
2. Insert the four nylon standoffs into the four holes located on the inverter’s control board. Ensure
that the standoffs are fully seated into the circuit board.
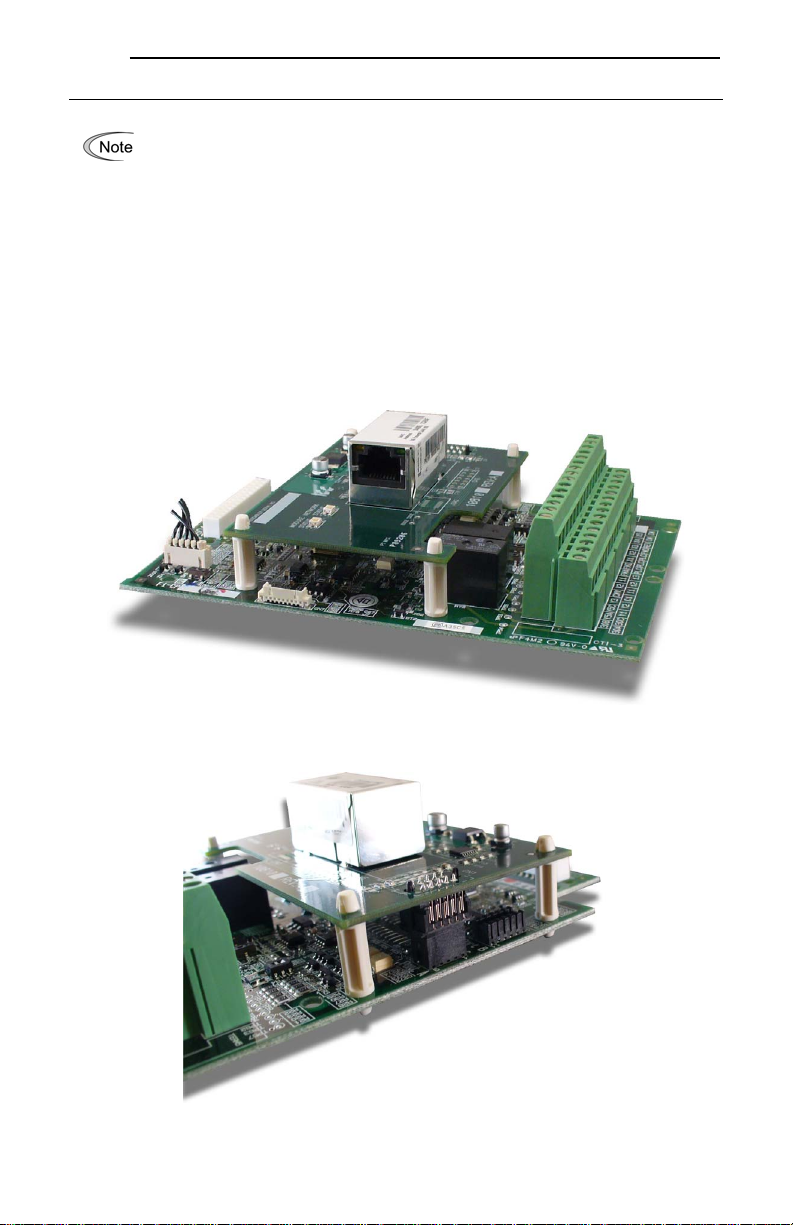
3. Press the interface board onto the tops of the four nylon standoffs, while simultaneously aligning
connector CN1 on the back of the interface board with the “Port A” connector on the inverter’s
control board. Ensure that the retention tabs on the standoffs protrude fully through the holes on
the interface board, and that the CN1 and Port A connectors are fully seated. Refer to Figure 4
and Figure 5.
Figure 4: Interface Board Installation Complete
Figure 5: CN1 and “Port A” Connectors Properly Seated
14

ICC
4. Insert the Ethernet cable into the Ethernet jack, making sure that it is fully seated. Route the cable
to the left of the control terminal block and out through the opening at the bottom of the inverter.
Make sure that the cable is routed in such a way that it will not be pinched and is not located near
any power-carrying wiring, such as the input power or motor wires. Refer to Figure 6.
Due to available spacing and the 90-degree downward turn required on small capacity
inverters, it may be helpful to use Ethernet cables without large or rigid strain relief collars,
as they allow a more gradual bending radius to be implemented.
Figure 6: Example Ethernet Cable Routing
5. Reinstall all covers removed in step 1. Take a moment to confirm that the Ethernet cable is not
being pinched and is not routed near any power-carrying wiring.
Note: For inverters with capacities of 37kW and above, also close the keypad enclosure.
For reinstallation instructions, refer to the FRENIC-Eco Instruction Manual (INR-SI47-1225-
15
E), Chapter 2, Section 2.3 "Wiring."
ICC
3 INVERTER FUNCTION CODE SETTINGS
The inverter function codes listed in Table 2 are critical for overall operation of the end-to-end
communication system. Some of these function codes must be set to specific values, and some may
have multiple allowable settings depending on the desired operation of the overall application. Although
there may be many other function codes that will require configuration for your specific applic ation, it is
important to understand the manner in which the following function codes will impact successful
communications with, and control of, the inverter.
For further details regarding these function codes, please refer to the FRENIC-Eco
Instruction Manual (INR-SI47-1225-E), Chapter 5 "FUNCTION CODES", FRENIC-Eco
User’s Manual, “y codes: Link Functions”, and RS-485 Communication User's Manual
(MEH448), Chapter 5, Section 5.2 "Data Formats."
Table 2: Function Code Settings Overview
Code Name
H30
y11 RS-485 Station Address 1 to 255 1 1
y12 RS-485 Communications Error Processing 0 to 3 0 2 or 3
y13 RS-485 Communications Error Timer 0.0 to 60.0 2.0
y14 RS-485 Baud Rate 0 to 4 3 4
y16 RS-485 Parity 0 to 2 0 0
y18 RS-485 No-Response Error Detection Time 0, 1 to 60 0 N/A
y19 RS-485 Response Delay
y20 RS-485 Protocol Selection 0, 3, 4 0 0
Y98 Bus Link Function (Mode Selection) 0 to 3 0 N/A
Communications Link Function (Mode
Selection)
Setting
Range
0 to 8 0 N/A
0.00 to
1.00
Default
Value
0.01
Required
Value
60.0 (if
y12=2)
0.00 or
0.01
16

ICC
3.1 RS-485 Communication Settings
Because the interface card communicates with the inverter via the Modbus RTU protocol on the control
board’s “Port A” connector, certain RS-485 -related inverter function codes must be set appropriately in
order to allow the interface card to successfully exchange data with the inverter. If any of these function
codes are not correctly configured, the interface card may not be able to communicate with the inverter.
RS-485 Station Address (y11)
Must be set to a value of “1” in order to allow the interface card to communicate with the inverter.
RS-485 Communications Error Processing (y12)
If operation command or frequency command is not configured to be from “RS-485 option card” (the
interface card), then the setting of y12 is not relevant, as all error occurrences will be disregarded. On
the other hand, if either operation command or frequency command is configured to be from “RS-485
option card”, then y12 settings of 0 (trip immediately when an error is detected) and 1 (trip after y13 time
setting when an error is detected) are not recommended. This is due to the fact that interface card
communications to the inverter (the transmission of request packets) is performed asynchronously to
other threads in the interface card’s internal operating system. Some of these other threads are able to
reboot the interface card under certain circumstances (when commanded by the user via the Finder
program, or after configuration changes are submitted via the web browser, for example). It is possible
that the interface card may be in the middle of transmitting a request packet to the inverter when one of
these asynchronous reboots is issued, thereby resulting in a single incomplete packet being received by
the inverter. If the inverter is running at the time such an incomplete packet is received, then it will trip
(either immediately if y12 is set to 0 or after the time set in y13 if y12 is set to 1). To eliminate the
possibility of such “nuisance” trips, therefore, do not configure y12 with a value of 0 or 1.
If it is desired to trip the inverter when the inverter is controlled from the interface card, is currently
running, and there is a “real” communication problem between the interface card and the inverter, then
y12 can be set to a value of 2 (attempt recovery within the time set by y13). In such a scenario,
however, it is also recommended to set y13 to a value of 60 (60 seconds). A retry time of 60 seconds
will allow sufficient time for the interface card to successfully re-establish communications with the
inverter when the outage is recoverable (when the interface card reboots after a new configuration is
submitted via the web page, for example). This would also allow the inverter to trip after 60 seconds
when an actual unrecoverable problem occurs.
If it is desired to ignore any communi cation errors between the interface card and the inverter, then set
y12 to a value of 3 (continue to run).
RS-485 Communications Error Timer (y13)
As mentioned in the discussion of y12 above, the value of y13 is only relevant when y12 is set to 2
(attempt recovery within the time set by y13). The recommended value of y13 in this scenario is 60. If
y12 is set to a value of 3 (continue to run), then y13 is not relevant and can be disregarded.
RS-485 Baud Rate (y14)
Determines the data rate at which the interface card will communicate to the inverter, and must be set to
a value of “4” (38.4kbaud).
RS-485 Data Length (y15) and RS-485 Stop Bits (y17)
These function codes are not relevant and therefore can be disregarded.
RS-485 Parity (y16)
Determines the parity of the communication packets, and must be set to a value of “0” (no parity).
RS-485 No-Response Error Detection Time (y18)
Related to the discussion of function codes y12 and y13 above, the value of y18 will only be relevant
when y12 is set to 2 (attempt recovery within the time set by y13). In this scenario, y18 works in
conjunction with y13 to differentiate recoverable communication issues between the interface card and
17
ICC
the inverter from those that are unrecoverable. When y13 is set to its recommended value of 60
seconds, the setting of y18 will only determine the speed with which the inverter will react to an
unrecoverable communication fault. For example, if y18 is set to 2 seconds, then a timeout error will be
triggered within 2 seconds of a communication interruption. If the caus e of such an interruption was
recoverable (the interface card had simply been rebooted, for example), then the 60-second “grace
period” set by y13 will allow a normal recovery to take place, and the inverter will not trip as a result of
the error. If, on the other hand, the cause of the interruption was unrecoverable, then the inverter will
trip 62 seconds after the initial communication gap (2 seconds for the error to be signaled due to y18,
and an additional 60 seconds due to y13 before the error is converted to an inverter trip).
RS-485 Response Delay (y19)
Sets a delay time that is added to the inverter’s internal processing time before it will send a response
packet to the interface card. While the factory default value of 0.01 (10ms) is acceptable, optimal
performance can be achieved by setting y19 to 0.00. A setting of 0.00 will allow the inverter to response
to interface card requests immediately after it has completed its internal processing.
RS-485 Protocol Selection (y20)
Determines the RS-485 port protocol, and must be set to a value of “0” (Modbus RTU).
3.2 Inverter Control-Related Settings
The following function codes relate to whether or not the inverter is to be controlled (command word
and/or frequency command) from the network, or whether the inverter will be locally-controlled, and only
monitored and/or configured via the network.
Communications Link Function (Mode Selection) (H30)
If the inverter is to be controlled from the network (both command word and frequency command), then
set the value of H30 to 8. Otherwise, set the value of H30 as appropriate for the chosen command and
frequency command input sources.
Bus Link Function (Mode Selection) (y98)
If the inverter is to be controlled from the network, then set the value of y98 to 0 (follow H30 data). A
setting of 0 for y98 may also be appropriate even if H30 is configured for an alternate (local) control
scheme.
18
ICC
4 FINDER APPLICATION
4.1 Overview
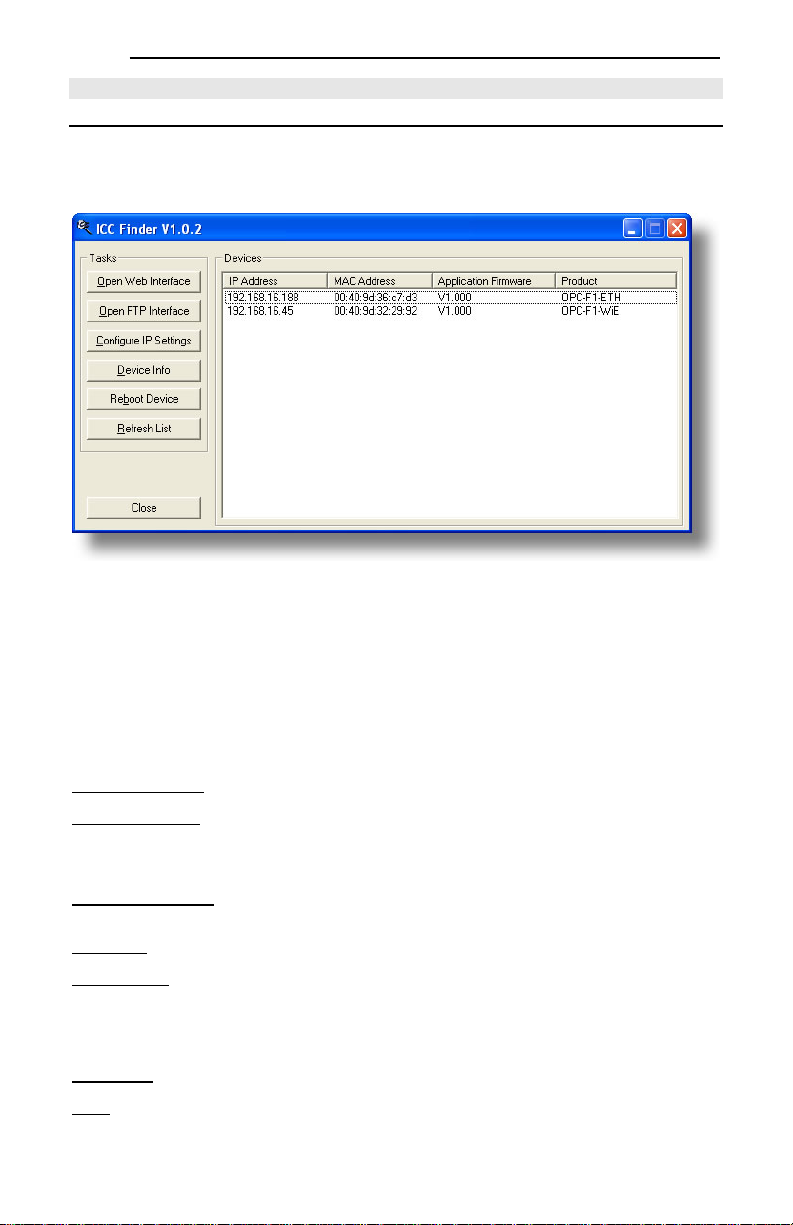
The “ICC Finder” application is a simple Windows PC program (just a single .exe file, no installations,
DLL’s etc.), which when executed discovers all ICC communication interfaces on the current Ethernet
subnet, regardless of whether or not their network parameters are currently compatible with the subnet
upon which they reside. Refer to Figure 7.
Figure 7: ICC Finder Discovery Utility
In order for the Finder application to discover devices, certain UDP Ethernet traffic must be allowed in
and out of the computer, and firewall applications (such as Windows Firewall) are often configured to
block such traffic by default. If the Finder is unable to discover any devices on the current subnet, be
sure to check the computer’s firewall settings during troubleshooting, and add an exception to the
firewall configuration if necessary.
All discovered devices can be organized in ascending or descending order by clicking on the desired
sort header (IP Address, MAC Address, Application Firmware or Product). The buttons on the left side
of the window perform the following actions:
Open Web Interface: Opens a web browser page of the selected device. Refer to section 5.
Open FTP Interface: Opens the computer’s default FTP application, which could be either Windows
Explorer, a web browser, or a 3rd-party FTP program (whatever the computer/operating system is
configured for by default). This allows you to interact directly with the unit’s on-board flash filesystem,
enabling you to drag and drop files to/from the unit and upload new firmware. Refer to section 7.
Configure IP Settings: Allows configuration of whether the device will use static IP parameters or will
obtain its IP parameters via DHCP. Refer to section 4.2 for more information.
Device Info: Opens a dialog box containing relevant device information.
Reboot Device: Opens a dialog box which prompts for a password to reboot the interface. Enter the
case-sensitive system password (default is “icc”), then click Reboot. The reboot cycle has completed
when the displayed status changes from “Rebooting” to “Ready” (note that this may require 30s or more
to complete.) Clicking Close will then close the dialog box and cause the discovery utility to
automatically rescan the network.
Refresh List: Causes the discovery utility to rescan the network.
Close: Closes the discovery utility.
19

ICC
4.2 Configuring the IP Address
Before you can access the interface from your web browser or begin using it as a part of your
automation network, you must know its IP address. The interface comes from the factory configured to
obtain an IP address dynamically (DHCP/BOOTP). You can determine the interface’s current IP address
using the ICC Finder application included on the CD provided with the interface, or available from the
ICC website at http://www.iccdesigns.com.
4.2.1 Via the Finder Utility
To configure the interface to use a static IP address:
1. Connect the interface to your network and apply power to the inverter. When the interface boots
up, it will attempt to obtain an IP address from a DHCP server or, failing that, will fallback to either
the last static IP address assigned, or a default stati c IP address of 192.168.16.102 if no static IP
address has yet been assigned.
2. To determine the initial IP address of your interface, start the ICC FINDER.EXE discovery utility.
3. The discovery utility scans the network for ICC devices and then lists each device’s IP Address,
MAC Address, Firmware Version and Pr oduct Name . Refer to Figure 7 on page 19. Identify
your device by its unique MAC address (printed on a label on the top of the Ethernet network jack).
4. To change the IP address, select the device in the list of detected devices and click the Configure
IP Settings button.
5. In the dialog that appears, select Manually configure network settings.
6. Enter the desired IP Address, Subnet Mask and Default Gateway in the appropriate boxes, and
then click Apply.
7. Enter the case-sensitive system password (default is “icc”) in the Authentication dialog box, then
click Submit.
8. A popup dialog box will prompt you to reboot. Click Reboot. Rebooting may require 30s or more
to complete. When the device status indicates “Ready”, click Close.
9. The discovery utility will automatically rescan the network. Confirm that the new IP address has
been accepted by the device.
4.2.2 Via the Web Page
Once an initial IP address has been assigned to the device and the configuration web page can be
accessed, the IP address-related parameters can also be modified via the web page. Refer to section
5.7.3.
20
ICC
5 EMBEDDED WEB SERVER
5.1 Overview
The interface contains an embedded web server (also known as an HTTP server), which allows users to
access the inverter’s internal data in a graphical manner with web browsers such as Microsoft Internet
Explorer or Mozilla Firefox. In this way, the inverter can be monitored, configured and controlled from
across the room or from across the globe.
In order to view the interface’s web page, the free Adobe (formerly Macromedia) Flash Player browser
plug-in is required. If the plug-in is not already installed on your computer, then your browser will
automatically be redirected to the appropriate Adobe download web site when you initially attempt to
access the interface’s web page. Alternatively, the plug-in can be downloaded directly by going to
http://www.adobe.com, and choosing the “get Adobe Flash Player” link. Always ensure that you have
the latest version of the Flash Player installed: if some aspect of the web page does not appear to be
displayed properly, installing the latest Flash Player update usually resolves the problem.
To access an interface’s embedded web server, either use the finder application (refer to section 4) and
select the “Open Web Interface” button when the target unit is highlighted, or just directly enter the target
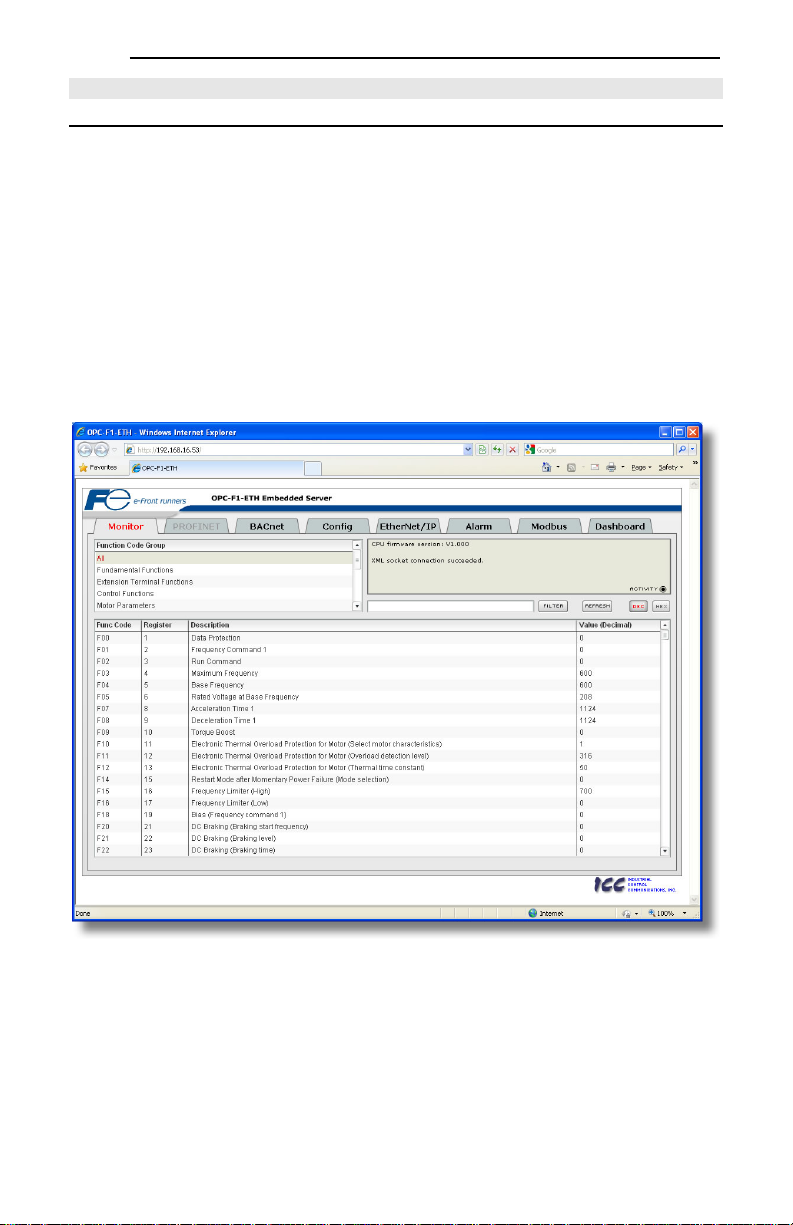
unit’s IP address into the address (URL) field of your web browser. Refer to Figure 8 for a
representative screenshot of the web server interface.
Figure 8: Embedded Web Server
In order to access the web server and view the function code values, destinat ion TCP ports 80 and 2000
must be accessible from the client computer. If an “XML socket connection failed” error message is
displayed in the information window, and no function code values are shown, this is typically indicative of
port 2000 being blocked by a firewall or Ethernet router situated between the client computer and the
interface card.
21

ICC
5.2 Authentication
For security, the interface requires valid user
authentication whenever the web page is accessed.
The authentication request will appear as a browser
popup box that will request entry of a user name and
password. Refer to Figure 9.
The factory-default user name is “root”, and the
password is “icc”. Note that the username and
password are case-sensitive, and that once
authenticated, the authentication will remain in effect
from that point until all browser windows are closed.
The authentication credentials can also be changed
from their default settings (refer to section 5.7.2.)
5.3 Page Select Tabs
The web interface is subdivided into several different “tabs” of associated information, much the same as
how folders in a filing cabinet are arranged. Refer to Figure 10. To change tabs, just click on the tab
you wish to view. The title of the currently-selected tab is red. Note that because different protocols are
supported by the interface with different firmware images, not all tabs may be accessible with the
firmware image currently loaded. The titles of tabs that are not accessible are grayed-out, and clicking
them has no effect.
Figure 9: Web Server Authentication
Figure 10: Page Select Tabs
5.4 Monitor Tab
5.4.1 Information Window
Figure 11 shows the Information Window, which is located in the upper-right hand corner of the monitor
tab. This window displays various informational messages regarding the status of the interface card or
web browser session. There is also an “activity” indicator located in the lower-right hand corner of the
Information Window, which blinks periodically to show the status of data communication between the
web browser and the interface card. If you do not observe the activity indicator blink at all for several
seconds or more, it is possible that the web browser may have lost contact to the web server due to an
inverter power cycle or a network problem: to reestablish communications, select “refresh” on your web
browser.
Figure 11: Monitor Tab Information Window
22

ICC
5.4.2 Function Code Group Selection List
The Function Code Group
Selection List is located in the
upper-left hand corner of the
Monitor Tab. Refer to Figure 12.
Individual groups can be
selected by clicking on the group
name. Multiple groups may also
be selected by holding down the
CTRL key while clicking on the
group names, or a range of
groups can be selected by first
selecting the starting group, and then holding down the SHIFT key while selecting the last group in the
range. When a function code group is selected, the function codes contained in that group are displayed
in the Function Code List (refer to section 5.4.3). The following function code groups are available:
All: All function codes/registers are available.
Fundamental Functions: F function codes are available.
Extension Terminal Functions: E function codes are available.
Control Functions: C function codes are available.
Motor Parameters: P function codes are available.
High Performance Functions: H function codes are available.
Command Data: S function codes are available.
Monitor Data 1: M function codes are available.
Application Functions: J function codes are available.
Link Functions: Y function codes are available.
Monitor Data 2: W function codes are available.
Alarm Data 1: X function codes are available.
Alarm Data 2: Z function codes are available.
Note that only the Command Data (S), Monitor Data 1 (M) and Monitor Data 2 (W) function code groups
are scanned, and that all others are non-scanned. The values of non-scanned function codes are not
continuously updated from the inverter. For more information regarding scanned vs. non-scanned
function codes, refer to sections 5.4.5 and 6.2.
5.4.3 Function Code List
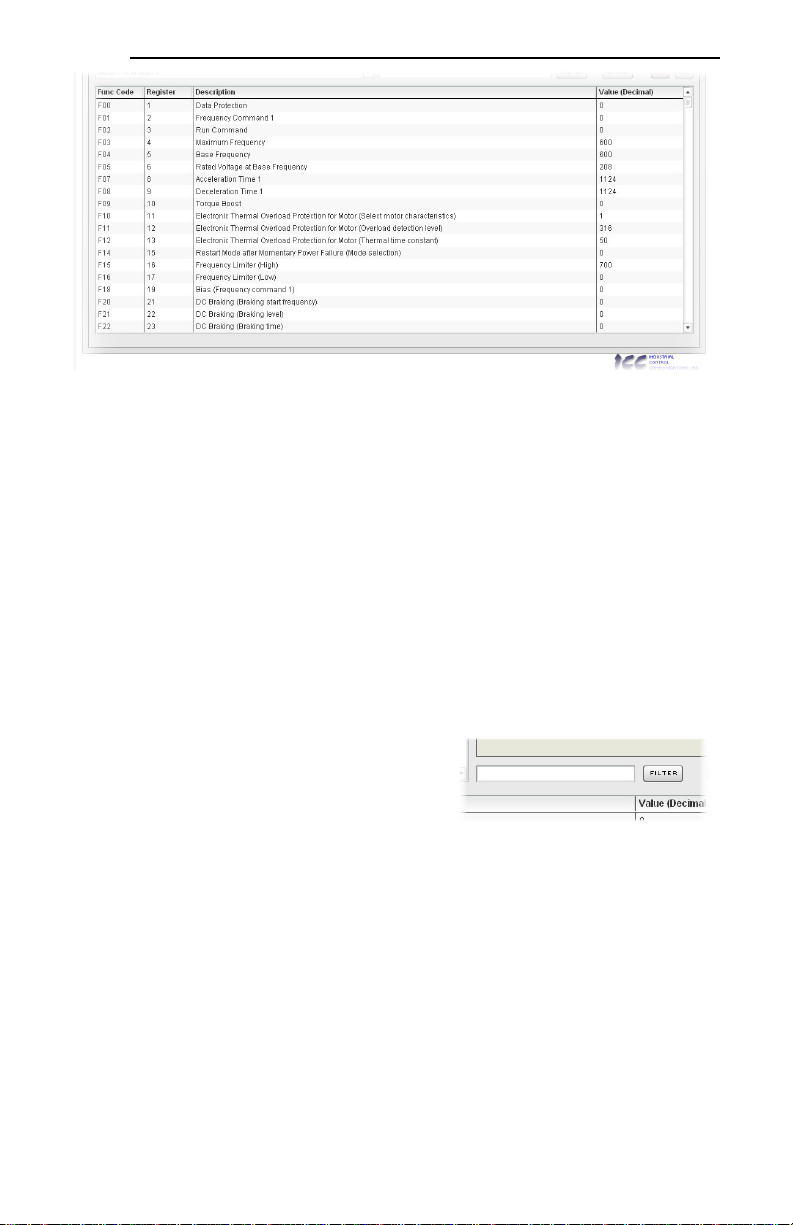
The bottom half of the Monitor tab contains the function code list (refer to Figure 13). The function
codes that are displayed in the list at any given time depend on the function code groups that are
currently selected (refer to section 5.4.2), as well as whether or not any filters have been applied (refer
to section 5.4.4).
The first column of the Function Code List shows the inverter function code designation that is normally
used when accessing a given function code via the inverter’s keypad. Note that this column is for user
convenience and inverter user’s manual cross-reference only: function codes are not referenced through
the interface card by their function code designations, but by their register numbers.
The second column of the Function Code List shows the register number that provides network access
to each function code (refer to section 6). The third column contains the function code descriptions,
which are used by the filter function. The last column performs two functions: it displays the current
value of the function code, and (for writable function codes) also allows changing the function code’s
value by clicking on the number in the value column and entering the new value.
Figure 12: Function Code Group Selection List
23
ICC
Figure 13: Function Code List
Some items to keep in mind when interacting with the Function Code List are:
• When entering new function code values, be sure that the number being entered is appropriate for
the currently-selected radix (refer to section 5.4.6): for example, an entered value of “1000” in
hexadecimal is equal to 4096 in decimal.
• If desired, the column widths can be changed by dragging the vertical bars that separate the header
row’s cells to a different position.
• If you begin changing a function code value and then decide to abandon the change, pressing the
ESC key on your keyboard will abandon the change and redisplay the current function code value.
• When editing a function code value, clicking someplace off the entry cell is equivalent to hitting the
ENTER key.
• The values of all non-scanned function codes are only read from the inverter by the web browser
when the “refresh” button is clicked (refer to section 5.4.5). Values of non-scanned function codes
are immediately written down to the inverter when they are changed, however.
5.4.4 Function Code List Filter
A filter function provides Function Code List search
capabilities. To use the filter function, simply type a word
or portion of a word into the filter entry box and then click
the “filter” button. Refer to Figure 14.
The filter will then display only those function codes
currently available in the Function Code List that satisfy
the search criteria. For example, to find all monitor data
1 function codes that contain some derivative of the word
“volt” (such as “voltage” or “volts”), select the “Monitor Data 1” group, enter “volt” in the filter entry box,
and then click the “filter” button.
Once a filter has been entered, it will continue to be applied to all information normally displayed in the
Function Code List for as long as the filter term is left in the filter entry box. Continuing the previous
example where we filtered on the root term “volt” in the monitor data 1 group, we can then easily apply
this filter to all available function codes simply by selecting the “All” func tion code group. The Function
Code List will now display all command, monitor, configuration etc. function codes that contain the root
term “volt”.
To remove the filter, delete any characters contained in the filter entry box and then click the “filter”
button.
Figure 14: Function Code List Filter
24
ICC
5.4.5 Non-Scanned Function Code Refresh
The values of all non-scanned function codes are only read from the
inverter when the “refresh” button (shown in Figure 15) is clicked.
Once clicked, the interface card will display the message “refreshing
values…” in the Information Window (refer to section 5.4.1), and will
begin to retrieve the values of all non-scanned function codes from
the inverter. This process may require 5s-10s to complete. When
completed, the current values of all non-scanned function codes will
be updated in the Function Code List, and the Information Window
will display the message “refresh completed.” For further detail s regarding scanned v s. non-scan ned
function codes, refer to section 6.2.
5.4.6 Radix Selection
Figure 16 shows the radix selection buttons. These selection
buttons allow changing the Function Code List “value” column data
display and entry radix between decimal and hexadecimal formats.
When “DEC” is selected, the “value” column heading will be “Value
(Decimal)”, current function code values will be displayed in decimal,
and values to be written to function codes must be entered in
decimal format. For example, to change the inverter’s frequency command to 40.00Hz, enter the
decimal value 4000.
Similarly, when “HEX” is selected, the “value” column heading will be “Value (Hexadecimal)”, current
function code values will be displayed in hexadecimal, and values to be written to function codes must
be entered in hexadecimal format. For example, to turn on bit #10 in the inverter’s operation command
word, enter the hexadecimal number 0400.
Figure 15: Refresh Button
Figure 16: Radix Selection
25
ICC
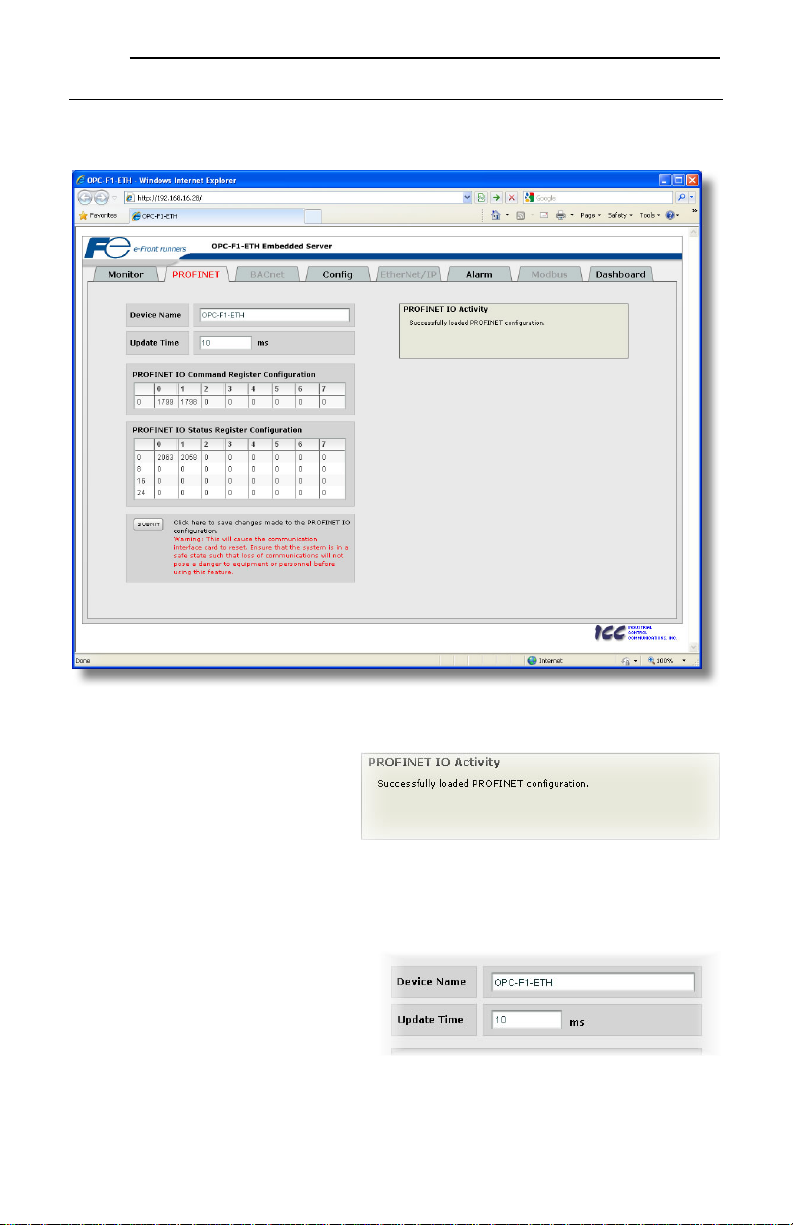
5.5 PROFINET Tab
This section is only applicable when the PROFINET firmware is loaded onto the interface card. The
PROFINET tab provides for the configuration of the device on a PROFINET network. Refer to Figure
17.
Figure 17: PROFINET Tab
5.5.1 Information Window
Figure 18 shows the Information Window,
which is located in the upper-right hand
corner of the PROFINET tab. This window
displays various informational messages
regarding the status of the PROFINET
configuration (loading or submitting).
5.5.2 Device Identification and Configuration
There are several identification and
configuration items available for setting
various characteristics of the PROFINET
device. These items are shown in Figure 19
and are explained in further detail below.
A PROFINET device’s name (station name)
must be unique across the entire PROFINET
network because it is used by controllers to
uniquely identify PROFINET devices. The
Device Name text entry box is used to configure this unique device identifier on every inverter.
Figure 18: PROFINET Tab Information Window
Figure 19: PROFINET Device Identification and
Configuration
26
ICC
The Update Time field is a configuration item which changes the frequency with which command and
status data updates take place internally in the device. This setting is not related to the frequency with
which data communications take place on the Ethernet network. This time setting is a 32-bit value
adjustable in 1ms increments. Typically, this value should not need to be changed from its default value
of 10ms. Please note that this setting is not related and should not be confused with the I/O Cycle
Update Time (in Step 7 or an equivalent hardware configuration tool).
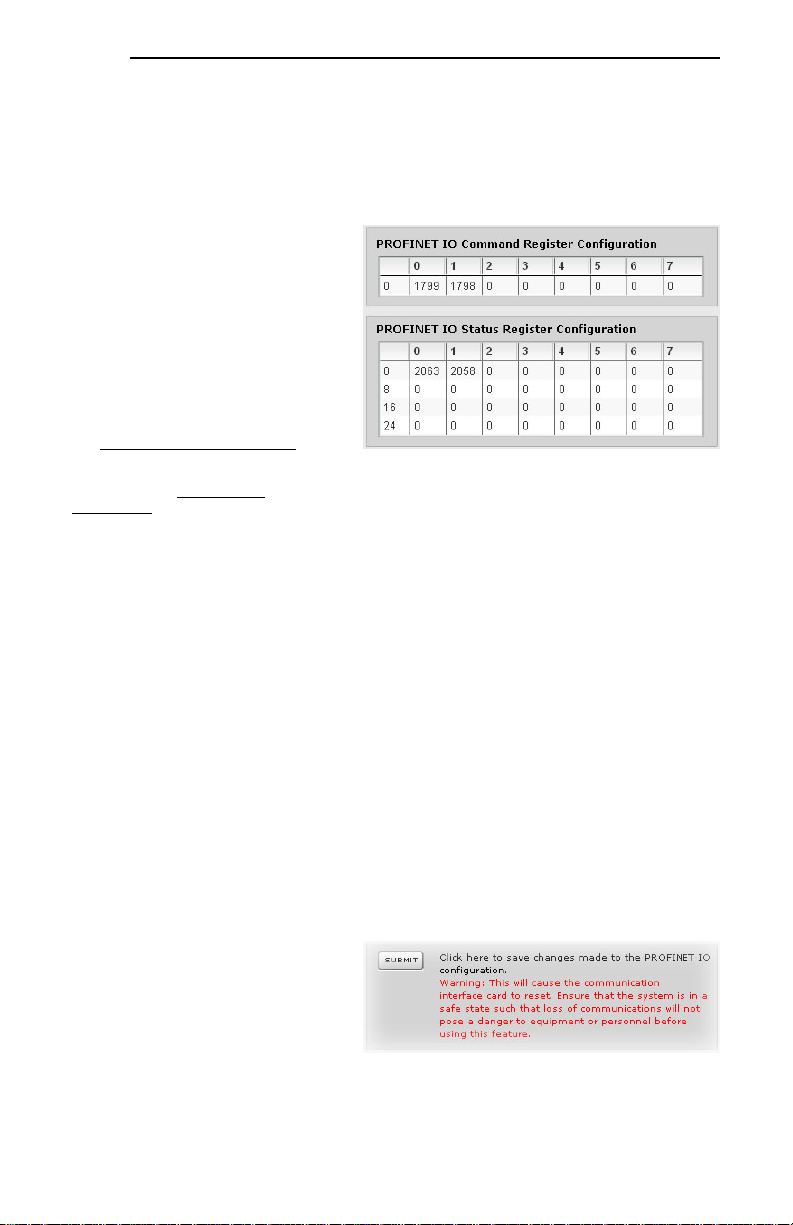
5.5.3 I/O Data Configuration Arrays
The interface card supports two different
types of PROFINET data transfer. One
type is included with the implementation of
the PROFIdrive profile, and requires no
user configuration (refer to section 8. 5 for
more information). The other type,
however, is entirely user-configurable, and
is utilized when a standard “IN: XX,
OUT:YY” I/O module is chosen during
network configuration.
The I/O data configuration arrays consist of
two separate elements (refer to Figure 20.)
The command register configuration
defines the structure of the command data
sent from the PROFINET controller to the
inverter, and the status register
configuration defines the structure of the status data sent from the inverter back to the controller. These
arrays allow the creation of custom-built I/O data. Up to 8 command registers can be sent to the
inverter, and up to 32 status registers can be sent back to the controller. Each box in an array is
capable of containing a register number. Because all inverter registers are 16-bit data elements, each
box therefore represents two bytes of input or output data.
The command register array locations are numbered 0-7, and traverse from left to right. The status
register array locations are numbered 0-31, and traverse from left to right across each row, and then
increment to the left-most position on the next row. Clicking on a box in an array allows the user to enter
a register number that will be referenced at that location when data is either received from or sent to the
controller. Note that only scanned registers may be entered into the register array locations: if an
attempt is made to enter a non-scanned register number, an error dialog box will appear (refer to section
6.2 for an explanation of scanned vs. non-scanned registers.) A value of 0 indicates that no register is
referenced at that location, which will cause corresponding command data to be ignored and status data
to be a default value of 0.
As an example, looking at the default configuration shown in Figure 20, we can see that each array
contains two defined registers. Therefore, up to 4 “meaningful” bytes of data can be both received and
sent (the qualifier “meaningful” is used here because the module currently selected by the controller may
require larger input and/or output data sizes, but all unreferenced command data will be ignored, and all
unreferenced status data will contain dummy “0” values). The first word (two bytes) of command data
will be written to register 1799 (operation command word) and the second word will be written to register
1798 (frequency command). Similarly, the first word of status data will contain the value of register 2063
(operation status word) and the second word will contain the value of register 2058 (output frequency).
5.5.4 Submitting Changes
Whenever any of the PROFINET
configuration elements (I/O array
configuration, Device Name, etc.) have
been changed, the “submit” button located
in the lower left-hand portion of the web
page must be clicked in order to write these
settings to the interface card’s filesy stem.
Note that because these configuration
elements are read from the filesystem only
when the interface card boots up, the act of submitting configuration changes will also reset the interface
card. Please allow 30 seconds for the interface card to reboot, at which time it will then be operating
with the recently-submitted configuration. Refer to Figure 21.
Figure 20: I/O Data Configuration
Figure 21: Submit PROFINET Changes
27
ICC
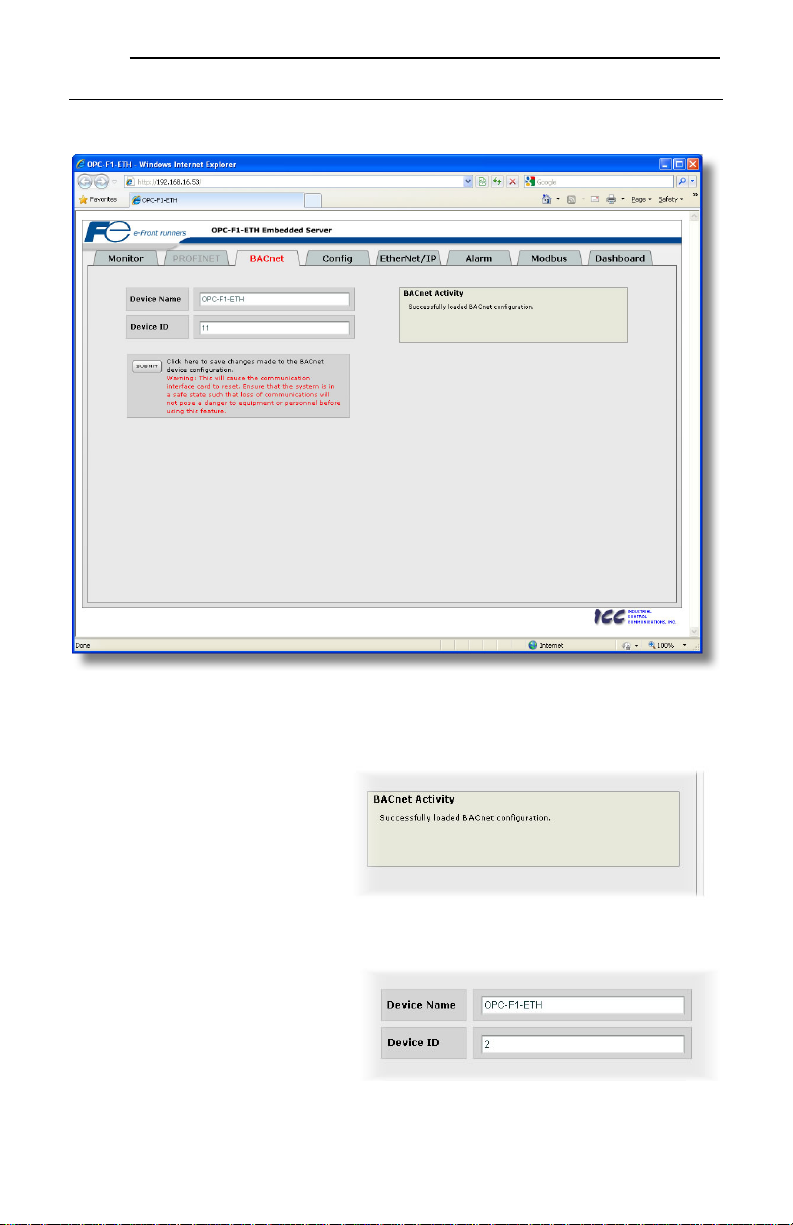
5.6 BACnet Tab
The BACnet tab provides for the configuration of the device on a BACnet/IP network. Refer to Figure
22.
Figure 22: BACnet Tab
5.6.1 Information Window
Figure 23 shows the Information
Window, which is located in the upperright hand corner of the BACnet tab.
This window displays various
informational messages regarding the
status of the BAC ne t configuration
(loading or submitting).
5.6.2 Device Identifiers
A BACnet device’s name and ID (the
Object_Name and Object_Identifier
properties, respectively, of the Device
Object) must be unique across the entire
BACnet network because they are used to
uniquely identify BACnet devices. The text
entry boxes shown in Figure 24 are used to
configure these unique device identifiers on
every inverter.
Figure 23: BACnet Tab Information Window
Figure 24: BACnet Device Identifiers
28

ICC
5.6.3 Submitting Changes
Whenever either of the BACnet
configuration elements (Device Name or
Device ID) has been changed, the
“submit” button located in the left-hand
portion of the web page must be clicked in
order to write these settings to the
interface card’s filesystem.
Note that because these configuration
elements are read from the filesystem
only when the interface card boots up, the
act of submitting configuration changes
will also reset the interface card. Please allow 30 seconds for the interface card to reboot, at which time
it will then be operating with the recently-submitted configuration. Refer to Figure 25.
Figure 25: Submit BACnet Changes
29
 Loading...
Loading...