Page 1

525A
®
Temperature/Pressure Calibrator
Service Manual
PN 1644492
March 2002
© 2002 Fluke Corporation. All rights reserved. Printed in USA
All product names are trademarks of their respective companies.
Page 2

LIMITED WARRANTY AND LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
Each Fluke product is warranted to be free from defects in material and workmanship under
normal use and service. The warranty period is one year and begins on the date of shipment.
Parts, product repairs, and services are warranted for 90 days. This warranty extends only to the
original buyer or end-user customer of a Fluke authorized reseller, and does not apply to fuses,
disposable batteries, or to any product which, in Fluke’s opinion, has been misused, altered,
neglected, contaminated, or damaged by accident or abnormal conditions of operation or
handling. Fluke warrants that software will operate substantially in accordance with its functional
specifications for 90 days and that it has been properly recorded on non-defective media. Fluke
does not warrant that software will be error free or operate without interruption.
Fluke authorized resellers shall extend this warranty on new and unused products to end-user
customers only but have no authority to extend a greater or different warranty on behalf of Fluke.
Warranty support is available only if product is purchased through a Fluke authorized sales outlet
or Buyer has paid the applicable international price. Fluke reserves the right to invoice Buyer for
importation costs of repair/replacement parts when product purchased in one country is submitted
for repair in another country.
Fluke’s warranty obligation is limited, at Fluke’s option, to refund of the purchase price, free of
charge repair, or replacement of a defective product which is returned to a Fluke authorized
service center within the warranty period.
To obtain warranty service, contact your nearest Fluke authorized service center to obtain return
authorization information, then send the product to that service center, with a description of the
difficulty, postage and insurance prepaid (FOB Destination). Fluke assumes no risk for damage in
transit. Following warranty repair, the product will be returned to Buyer, transportation prepaid
(FOB Destination). If Fluke determines that failure was caused by neglect, misuse, contamination,
alteration, accident, or abnormal condition of operation or handling, including overvoltage failures
caused by use outside the product’s specified rating, or normal wear and tear of mechanical
components, Fluke will provide an estimate of repair costs and obtain authorization before
commencing the work. Following repair, the product will be returned to the Buyer transportation
prepaid and the Buyer will be billed for the repair and return transportation charges (FOB
Shipping Point).
THIS WARRANTY IS BUYER'S SOLE AND EXCLUSIVE REMEDY AND IS IN LIEU OF ALL
OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY
IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
FLUKE SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OR LOSSES, INCLUDING LOSS OF DATA, ARISING FROM
ANY CAUSE OR THEORY.
Since some countries or states do not allow limitation of the term of an implied warranty, or
exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, the limitations and exclusions of
this warranty may not apply to every buyer. If any provision of this Warranty is held invalid or
unenforceable by a court or other decision-maker of competent jurisdiction, such holding will not
affect the validity or enforceability of any other provision.
Fluke Corporation
P.O. Box 9090
Everett, WA 98206-9090
U.S.A.
11/99
Fluke Europe B.V.
P.O. Box 1186
5602 BD Eindhoven
The Netherlands
To register your product online, visit register.fluke.com
Page 3

Table of Contents
Title Page
Introduction....................................................................................................... 1
Contacting Fluke ............................................................................................... 1
Safety Information............................................................................................. 1
Calibrator Specifications ................................................................................... 3
General Specifications .................................................................................. 3
DC Voltage Specifications, Output............................................................... 4
DC Current Specifications, Output............................................................... 4
Resistance Specifications, Output................................................................. 5
Resistance Specifications, Input.................................................................... 5
Thermocouple Specification, Output and Input............................................ 6
TC mV Specifications, Input and Output...................................................... 7
RTD and Thermistor Specification, Output.................................................. 8
RTD and Thermistor Specification, Input..................................................... 9
Pressure Measurement .................................................................................. 11
Theory of Operation.......................................................................................... 11
Micro-Controller Section.............................................................................. 11
Analog Section.............................................................................................. 12
Basic Maintenance............................................................................................. 12
Cleaning the Calibrator................................................................................. 12
Replacing a Line Fuse................................................................................... 12
To Check or Replace a Fuse.......................................................................... 13
Changing Line Voltage................................................................................. 13
Modular-Level Maintenance............................................................................. 14
Disassembly.................................................................................................. 15
Reassembly ................................................................................................... 15
Output Block Subassembly Connections.................................................. 17
Keypad to Main PCB................................................................................ 19
Display Assembly to Main PCB............................................................... 19
Opto RS232 to Main PCA........................................................................ 20
Reinstalling the Circuit Boards................................................................. 21
Connecting the Power Module ................................................................. 21
Final Assembly and Inspection..................................................................... 22
Performance Tests............................................................................................. 23
Required Equipment List.............................................................................. 23
Testing DC Voltage....................................................................................... 24
i
Page 4

525A
Service Manual
Testing DC Current....................................................................................... 25
Testing Thermocouple Output...................................................................... 26
Testing CJC (Cold Junction Compensation)............................................. 27
CJC (Cold Junction Compensation) Calibration....................................... 27
Testing Thermocouple Input......................................................................... 28
Testing Ohms Output.................................................................................... 29
Testing Ohms Input....................................................................................... 30
Testing Pressure Modules............................................................................. 32
Calibration Adjustment ..................................................................................... 32
Initiating Communication............................................................................. 32
Starting Adjustment Mode............................................................................ 32
Adjustment Sequence.................................................................................... 33
14: Calibrate DAC, Digital to Analog Converter Adjustment.................. 34
1: 100 mV Source to 4: 100 V Source, Adjusting DC Source.................. 34
5: 100 mA Source, Adjusting DC Current Source.................................... 35
6: Hi Ohms Source, Adjusting High Resistance Source........................... 37
7: Low Ohms, Adjusting Low Ohms Source............................................ 38
8: Hi Ohms, Adjusting High Resistance Measure.................................... 38
9: Low Ohms, Adjusting Low Resistance Measure.................................. 40
10: SPRT 25, Adjusting SPRT Low Resistance Measure ........................ 41
11: TC SOURCE, Adjusting TC mVolt Source....................................... 43
12: TC Read, Adjusting TC mVolt Measure............................................ 43
Customer Replaceable Parts.............................................................................. 45
ii
Page 5

List of Tables
Table Title Page
1. Symbols Used on the Calibrator............................................................................ 2
2. Replacement Fuses ................................................................................................ 13
3. Front Panel Wire Color Assignments.................................................................... 16
4. Rear Panel Wire Color Assignments ..................................................................... 16
5. Output Block to Main PCA Connections............................................................... 17
6. TC PCA to Main PCA Connections...................................................................... 18
7. Opto RS232 to Main PCA Connections................................................................ 20
8. Power Module to Main PCA Connections............................................................. 21
9. Power Connections................................................................................................ 22
10. Required Equipment.............................................................................................. 23
11. Testing DC Voltage............................................................................................... 24
13. TC Temperatures ................................................................................................... 26
14. Ohms Output Ranges............................................................................................. 29
15. Ohms Ratio Table.................................................................................................. 31
16. Calibration Dependencies...................................................................................... 33
17. List of Equipment for Voltage Calibration Adjustments....................................... 34
18. List of Equipment for Current Calibration Adjustments ....................................... 35
19. List of Equipment for High Ohms Measure Calibration Adjustments .................. 38
20. List of Equipment for High Ohms Measure Calibration Adjustments .................. 40
21. List of Equipment for Low Ohms Measure Calibration Adjustments................... 41
22. List of Test Equipment for Adjusting TC Source.................................................. 43
23. List of Test Equipment for Adjusting TC Read..................................................... 43
24. List of Test Equipment for Adjusting TC CJC...................................................... 45
25. Replacement Parts.................................................................................................. 47
26. Accessories............................................................................................................ 48
iii
Page 6

525A
Service Manual
iv
Page 7

List of Figures
Figure Title Page
1. Accessing the Fuse................................................................................................. 14
2. Wiring Connections............................................................................................... 17
3. Solder Connections for the TC PCA...................................................................... 18
4. Keypad PCA Connections..................................................................................... 19
5. Connections for the Opto RS232 PCA.................................................................. 20
6. Power Module Connections................................................................................... 22
7. Measuring DC Current........................................................................................... 25
8. Testing TC Output................................................................................................. 26
9. Connections for CJC Calibration........................................................................... 27
10. Connections for Measuring TC Input.................................................................... 28
11. Connection for Measuring Resistance Output....................................................... 29
12. 1281 Connection Diagram..................................................................................... 30
13. Connection for Measuring Ohms........................................................................... 31
14. Exploded View of the 525A .................................................................................. 46
v
Page 8

525A
Service Manual
vi
Page 9

Introduction
This manual provides user-service information for the 525A Temperature/Pressure
Calibrator (hereafter referred to as "the Calibrator"). Details regarding verification of the
Calibrator’s functionality and calibration, basic maintenance, contacting Fluke service
centers, and important safety information are also contained within this manual.
Contacting Fluke
To contact Fluke, order accessories, or locate the nearest Fluke Service Center or
distributor, call:
• USA: 1-888-99-FLUKE (1-888-993-5853)
• Canada: 1-800-36-FLUKE (1-800-363-5853)
• Europe: +31-402-678-200
• Japan: +81-3-3434-0181
• Singapore: +65-738-5655
• Anywhere in the world: +1-425-446-5500
525A
Or, visit Fluke’s Web site at www.fluke.com.
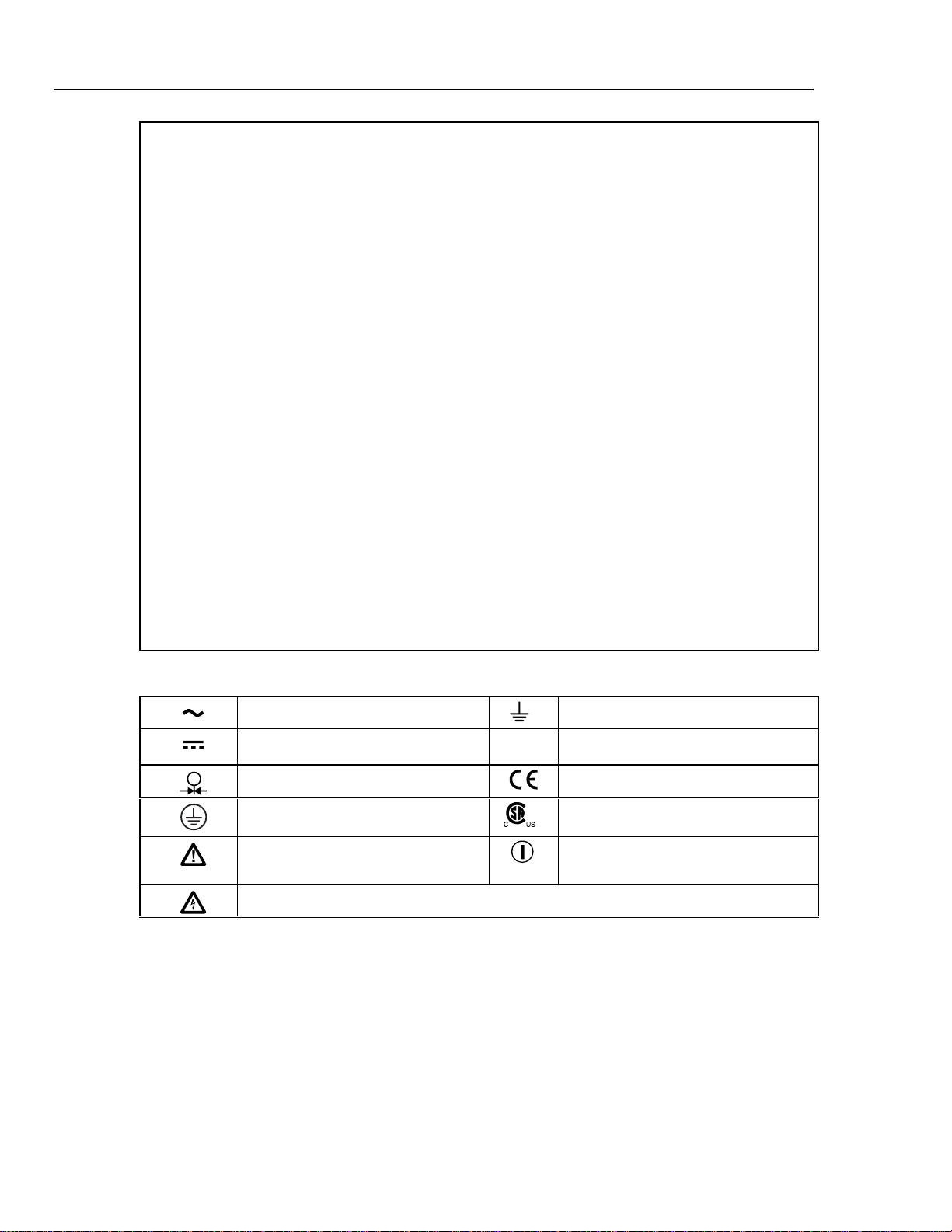
Safety Information
The Calibrator complies with EN 61010, ANSI/ISA-S82.01-1994, and CAN/CSA-C22.2
No. 1010.1-92. Use the Calibrator only as specified in this manual, otherwise the
protection provided by the Calibrator may be impaired.
CAT II equipment is designed to protect against transients from energy-consuming
equipment supplied from a fixed installation, such as televisions, personal computers,
portable tools, and other household appliances.
A “WWarning” statement identifie s hazardous conditions and actions that could cause
bodily harm or death.
A “WCaution” statement identifies conditions and actions that could damage the
Calibrator or the equipment under test.
International symbols used on the Calibrator and in this manual are explained in Table 1.
1
Page 10
525A
Service Manual
WWarning
To avoid possible electric shock or personal injury, follow these guidelines:
Use the Calibrator only as specified in this manual or the protection provided by the
•
Calibrator might be impaired.
Inspect the Calibrator before use. Do not use the Calibrator if it appears damaged.
•
Look for cracks or missing plastic. Pay particular attention to the insulation around
the connectors.
Have the Calibrator serviced only by qualified service personnel.
•
Do not apply more than the rated voltage between the terminals, as marked on the
•
Calibrator, or between any terminal and earth ground.
Always use the power cord and connector appropriate for the voltage and outlet of
•
the country or location in which you are working.
Never operate the Calibrator with the cover removed or the case open.
•
Never remove the cover or open the case of the Calibrator without first removing the
•
power source.
Use caution when working with voltages above 30 V ac rms, 42 V ac peak, or
•
60 V dc. These voltages pose a shock hazard.
Use only the replacement fuse(s) specified in this manual.
•
Use the proper terminals, function, and range for your measurements.
•
Do not operate the Calibrator around explosive gas, vapor, or dust.
•
• When servicing the Calibrator, use only specified replacement parts.
Table 1. Symbols Used on the Calibrator
AC (Alternating Current)
DC (Direct Current)
Pressure
Chassis protective ground
Important Information. Refer to the
manual.
Caution, risk of electric shock
Ω
Earth ground
Resistance
Conforms to European Union directives
Canadian Standards Association,
NRTL
International ON/OFF symbol.
2
Page 11
Calibrator Specifications
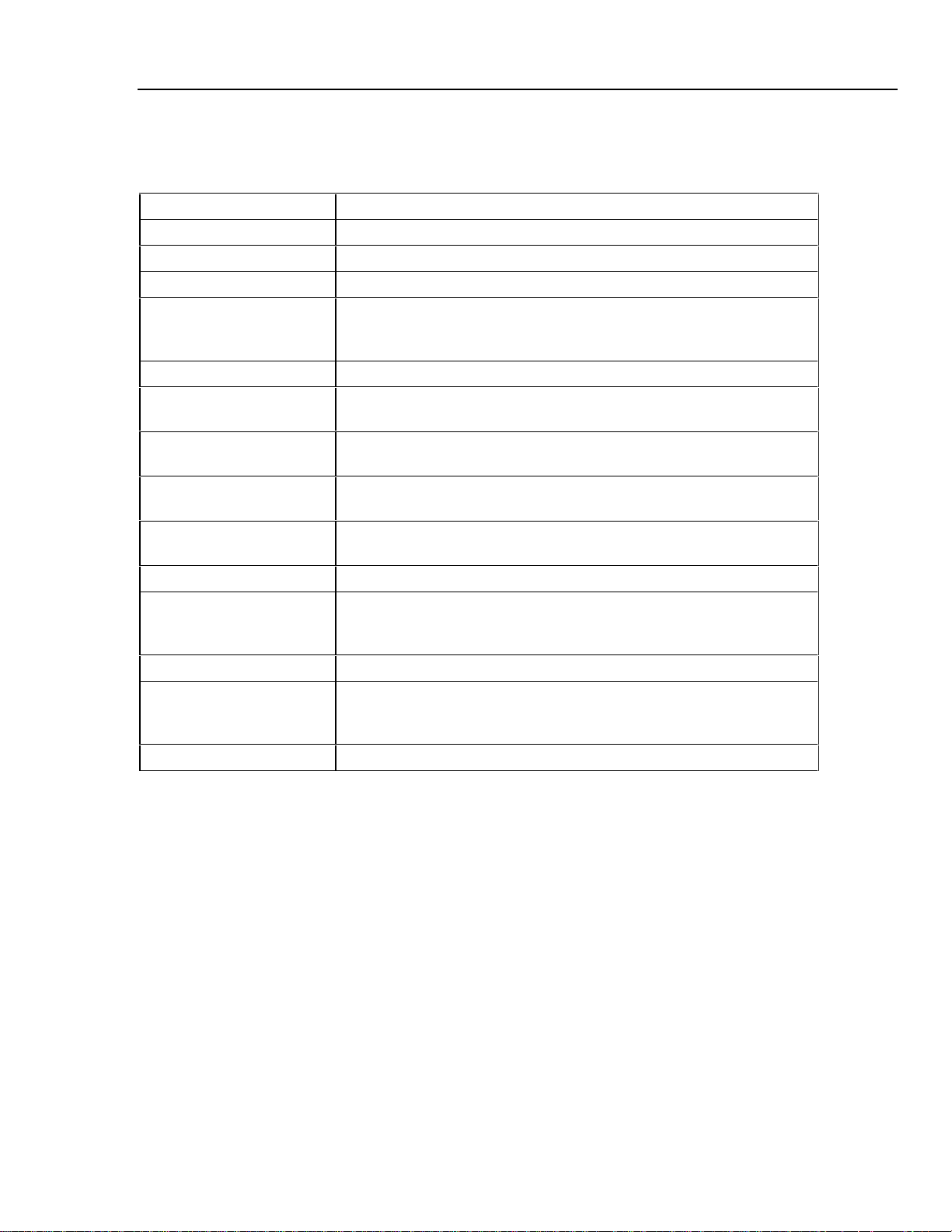
General Specifications
Warm up time Twice the time since last warmed up, to a maximum of 30 minutes
Settling time Less than 5 seconds for all functions and ranges except as noted
Standard interface RS-232
Optional interface IEEE-488 (GPIB)
Temperature performance
Electromagnetic compatibility CE: Conforms to EN61326
Temperature coefficient Temperature coefficient for temperatures outside tcal ±5 °C is
Relative humidity
Altitude Operating 3,050 m (10,000 ft) maximum
Safety
Analog low isolation 20 V
Line power Line Voltage (selectable) 100 V/120 V or 220 V/240 V
Power consumption 15 VA maximum
Dimensions Height 13.3 cm (5.25 in) plus 1.5 cm (0.6 in) four feet on bottom
Weight (without options) 4 kg (9 lb)
Operating 0 °C to 50 °C
Calibration (tcal) 18 °C to 28 °C
Storage -20 °C to 70 °C
10 % of the 90 day specification (or 1 year if applicable) per °C
Operating < 80 % to 30 °C, < 70 % to 40 °C, < 40 % to 50 °C
Storage < 95 % noncondensing
Nonoperating 12,200 m (40,000 ft) maximum
EN 61010 Second, ANSI/ISA-S82.01-1994,
CAN/CSA-C22.2 No. 1010.1-92, NRTL
Line Frequency 47 to 63 Hz
Line Voltage Variation ±10 % about line voltage setting
Width ¾ standard rack width
Depth 47.3 cm (18.6 in) overall
525A
Calibrator Specification s
3
Page 12
525A
Service Manual
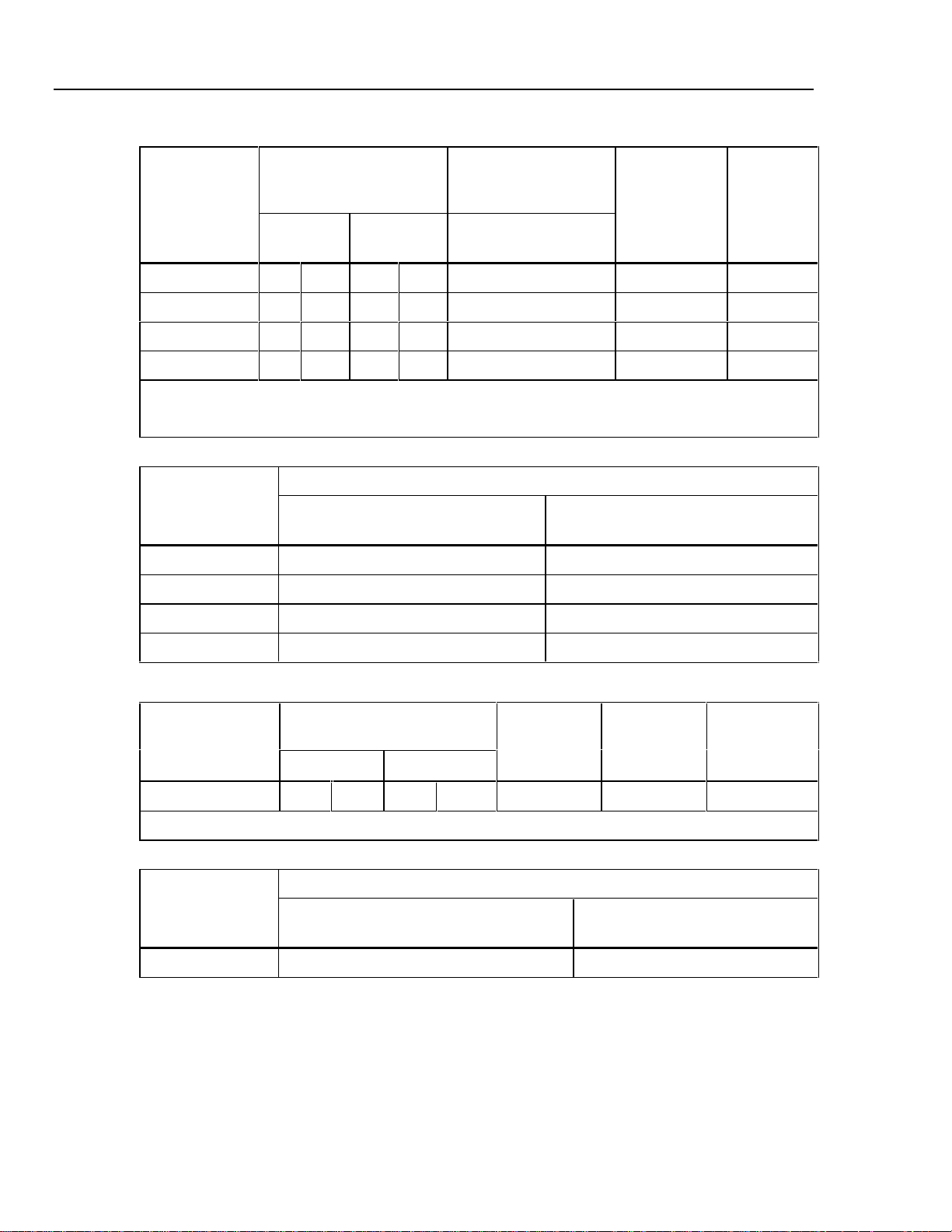
DC Voltage Specifications, Output
Absolute Uncertainty,
tcal ±5 °C
± (ppm of output +µV) Stability
Maximum
Burden
Ranges
1
90 days 1 year
± (ppm of output +µV)
Resolution
24 hours, ±1 °C
0 to 100.000 mV 25 3 30 3 5 +2 1 µV 10 mA
0 to 1.00000 V 25 20 30 20 4 +20 10 µV 10 mA
0 to 10.0000 V 25 200 30 200 4 +200 100 µV 10 mA
0 to 100.000 V 25 2 mV 30 2 mV 5 +1 mV 1 mV 1 mA
1. All outputs are positive only.
2. Remote sensing is not provided. Output resistance is < 1Ω.
Noise
Ranges
Bandwidth 0.1 to 10 Hz
(ppm of output +µV p-p)
Bandwidth10 Hz to 10 kHz
(µV rms)
0 to 100.000 mV 1 µV6 µV
0 to 1.00000 V 10 µV 60 µV
0 to 10.0000 V 100 µV 600 µV
0 to 100.000 V 10 ppm+1 mV 20 mV
2
DC Current Specifications, Output
Ranges
Absolute Uncertainty,
tcal ±5 °C
1
90 days 1 year
± (ppm of output +µA)
Resolution
Maximum
Compliance
Voltage
0 to 100.000 mA 85 2 100 2 1 µA 10 V 100 µH
1. All outputs are positive only.
Noise
Ranges
Bandwidth
0.1 to 10 Hz p-p
Bandwidth
10 Hz to 10 kHz rms
0 to 100.000 mA 2000 nA 20 µA
Maximum
Inductive
Load
4
Page 13
Calibrator Specification s
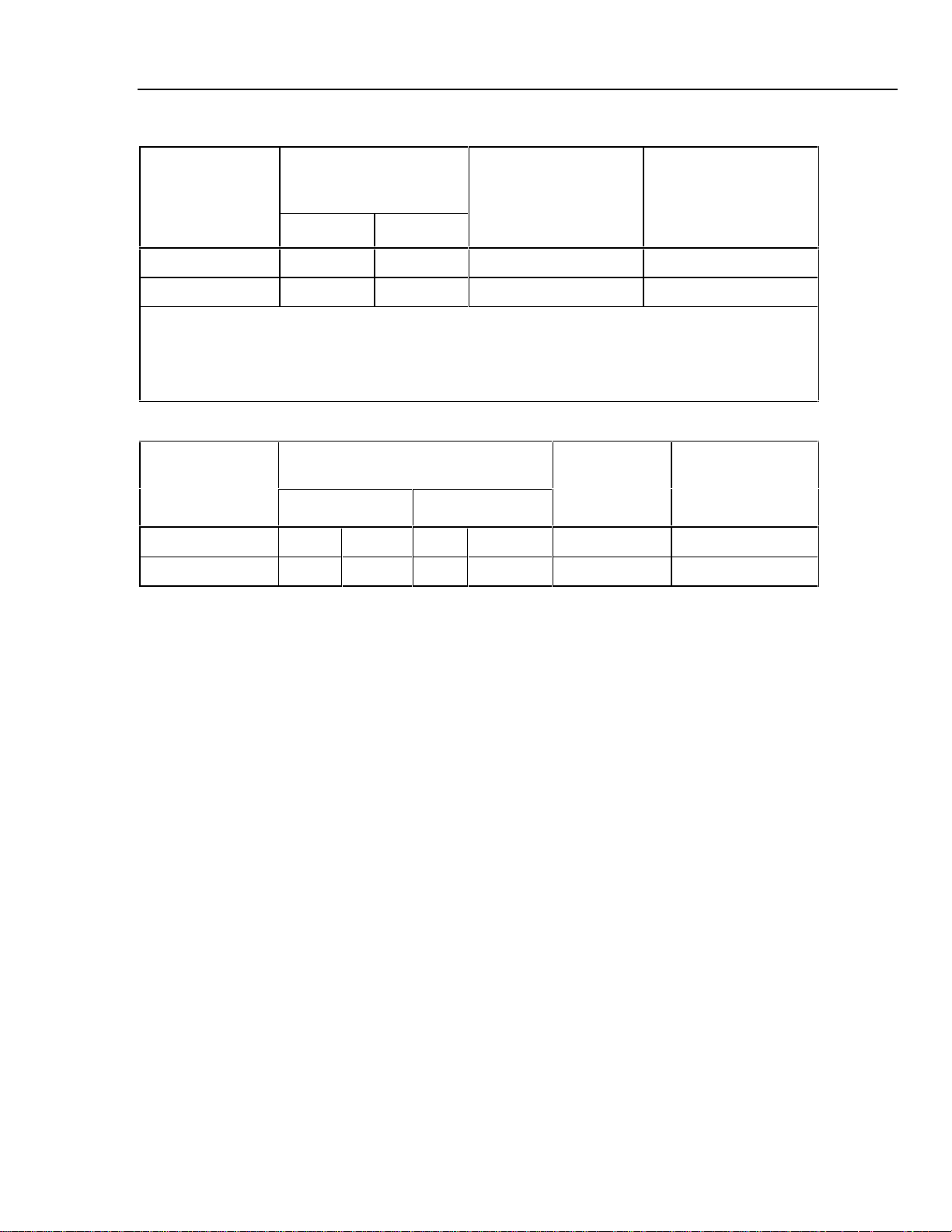
Resistance Specifications, Output
Absolute Uncertainty,
tcal ±5 °C,
Ranges
1
5 to 400.00 Ω 0.025 0.03 0.01 Ω 1 to 10 mA
5 to 4.0000 kΩ 0.25 0.3 0.1 Ω 250 µA to 1 mA
1. Continuously variable from 0 to 4 kΩ.
±(ppm of output ± Ω)
Resolution Allowable Current
90 days 1 year
525A
2
2. For currents lower than shown, the floor adder increases by Floor
(new)
= Floor
(old)
x I
min/Iactual
For example, a 500 µA stimulus measuring 100 Ω has a floor uncertainty of 0.025 Ω x 1 mA/500 µA =
0.05 Ω.
Resistance Specifications, Input
Absolute Uncertainty,
tcal ±5 °C, ±(ppm of output ± Ω)
Ranges
0 to 400.00 Ω 35 0.003 40 0.003 0.001 Ω 1 mA
401 to 4001.00 Ω 35 0.03 40 0.03 0.01 Ω 0.1 mA
90 days 1 year
Resolution Stimulus Current
.
5
Page 14
525A
Service Manual
Thermocouple Specification, Output and Input
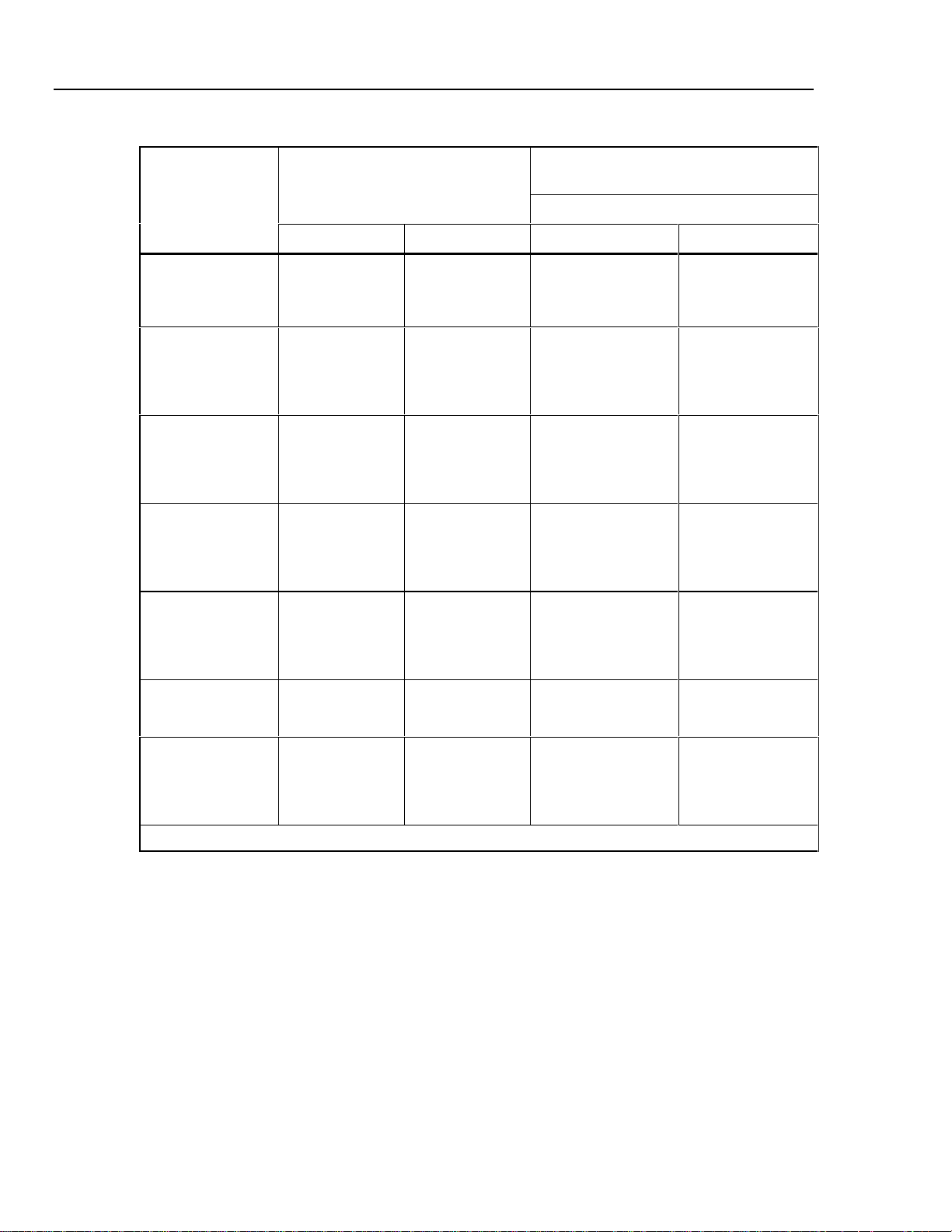
Range (°C)
TC Type
B 600 °C
C0 °C
E -250 °C
J -210 °C
K -200 °C
L -200 °C
N -200 °C
1. Does not include thermocouple wire error.
Minimum Maximum 90 days 1 year
800 °C
1000 °C
1550 °C
150 °C
650 °C
1000 °C
1800 °C
-100 °C
-25 °C
350 °C
650 °C
-100 °C
-30 °C
150 °C
760 °C
-100 °C
-25 °C
120 °C
1000 °C
-100 °C
800 °C
-100 °C
-25 °C
120 °C
410 °C
800 °C
1000 °C
1550 °C
1820 °C
150 °C
650 °C
1000 °C
1800 °C
2316 °C
-100 °C
-25 °C
350 °C
650 °C
1000 °C
-100 °C
-30 °C
150 °C
760 °C
1200 °C
-100 °C
-25 °C
120 °C
1000 °C
1372 °C
-100 °C
800 °C
900 °C
-100 °C
-25 °C
120 °C
410 °C
1300 °C
Absolute Uncertainty,
tcal ±5 °C, ±(°C)
Output/Input
0.42 °C
0.39 °C
0.40 °C
0.44 °C
0.25 °C
0.21 °C
0.23 °C
0.38 °C
0.63 °C
0.38 °C
0.16 °C
0.14 °C
0.14 °C
0.16 °C
0.20 °C
0.18 °C
0.14 °C
0.14 °C
0.18 °C
0.25 °C
0.19 °C
0.14 °C
0.19 °C
0.30 °C
0.37 °C
0.26 °C
0.17 °C
0.33 °C
0.20 °C
0.16 °C
0.14 °C
0.21 °C
1
0.46 °C
0.39 °C
0.40 °C
0.45 °C
0.30 °C
0.26 °C
0.31 °C
0.50 °C
0.84 °C
0.50 °C
0.18 °C
0.15 °C
0.16 °C
0.21 °C
0.27 °C
0.20 °C
0.16 °C
0.17 °C
0.23 °C
0.33 °C
0.22 °C
0.16 °C
0.26 °C
0.40 °C
0.37 °C
0.26 °C
0.17 °C
0.40 °C
0.24 °C
0.19 °C
0.18 °C
0.27 °C
6
Page 15
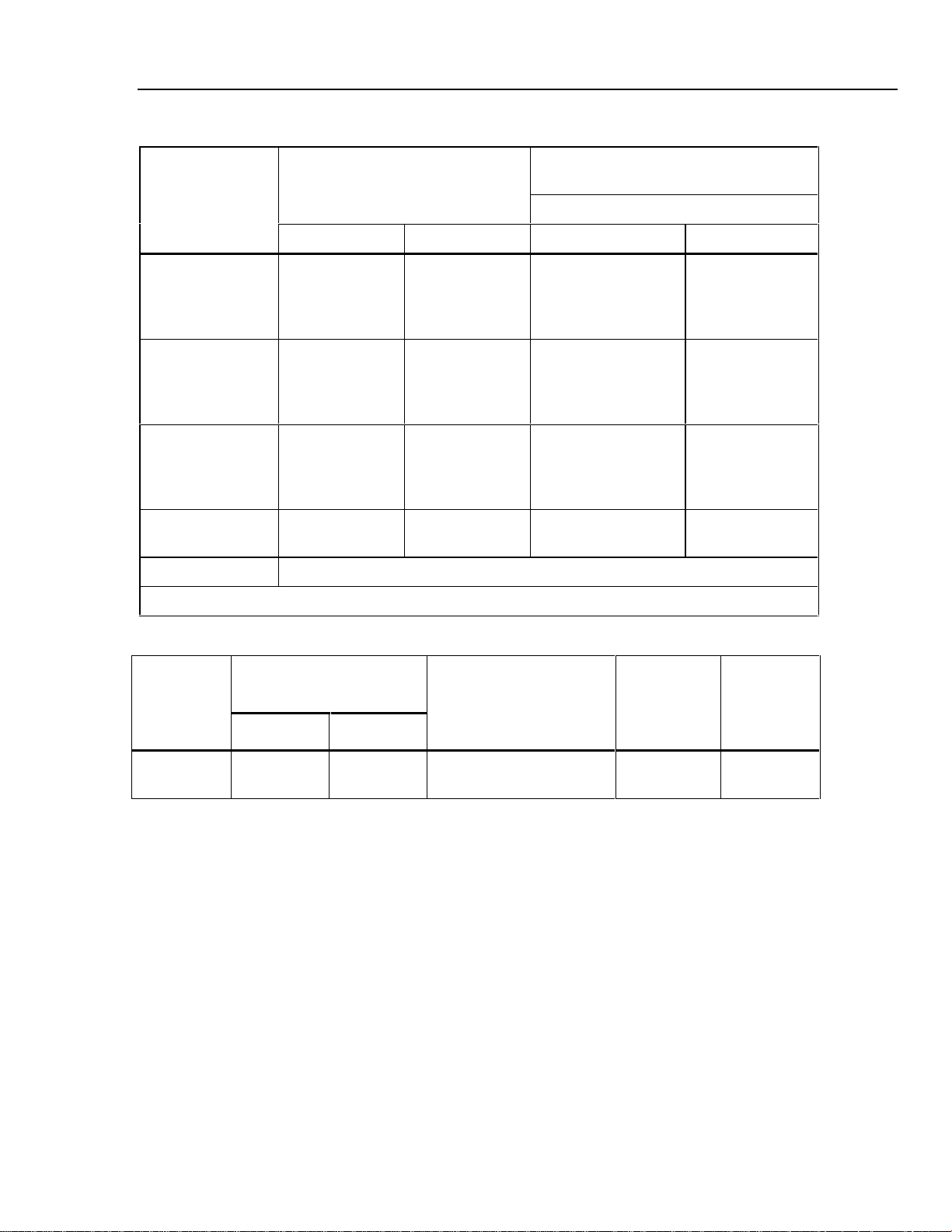
Thermocouple Specification, Output and Input (continued)
525A
Calibrator Specification s
Range (°C)
TC Type
R0 °C
S0 °C
T -250 °C
U -200 °C
mV -10 to 75.000 mV
1. Does not include thermocouple wire error.
Minimum Maximum 90 days 1 year
250 °C
400 °C
1000 °C
250 °C
1000 °C
1400 °C
-150 °C
0 °C
120 °C
0 °C
250 °C
400 °C
1000 °C
1750 °C
250 °C
1000 °C
1400 °C
1750 °C
-150 °C
0 °C
120 °C
400 °C
0 °C
600 °C
Absolute Uncertainty,
tcal ±5 °C, ±(°C)
Output/Input
0.58 °C
0.34 °C
0.31 °C
0.30 °C
0.56 °C
0.36 °C
0.30 °C
0.35 °C
0.51 °C
0.18 °C
0.13 °C
0.12 °C
0.56 °C
0.27 °C
1
0.58 °C
0.35 °C
0.33 °C
0.40 °C
0.56 °C
0.36 °C
0.37 °C
0.46 °C
0.63 °C
0.24 °C
0.16 °C
0.14 °C
0.56 °C
0.27 °C
TC mV Specifications, Input and Output
Absolute Uncertainty,
tcal +/-5 °C
+/-( ppm of output + µV)
Range
(mV)
-10 to
75.000
90 Days 1 Year
25 + 3µV 30 + 3µV5 + 2µV1µV 10 Ohms
+/- ( ppm of output + µV) Resolution
Stability
24 Hours +/-1°C
Maximum
Burden
7
Page 16
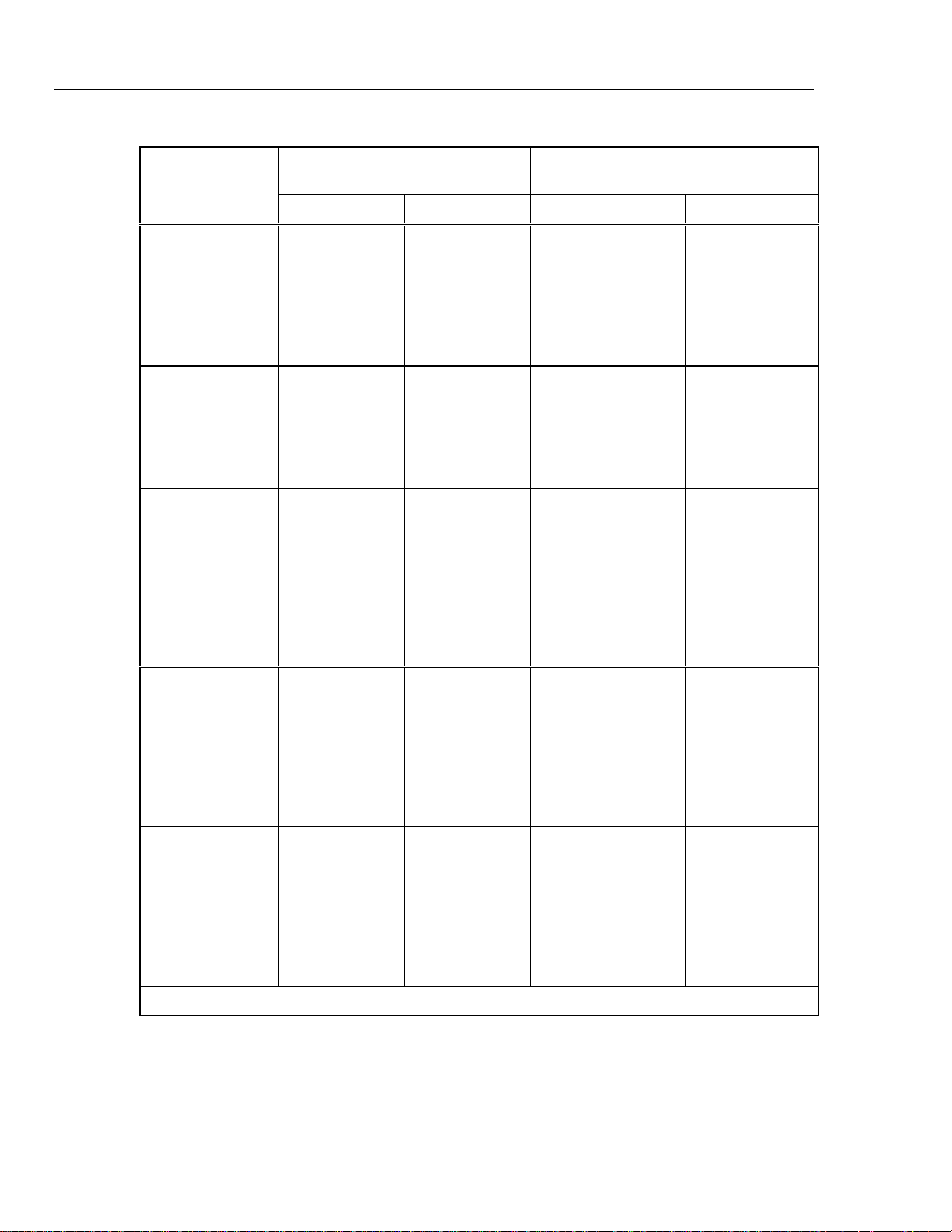
525A
Service Manual
RTD and Thermistor Specification, Output
RTD Type
Pt 385, 100 Ω -200 °C
Pt 3926, 100 Ω -200 °C
Pt 3916, 100 Ω -200 °C
Minimum Maximum 90 days 1 year
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
300 °C
400 °C
630 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
300 °C
400 °C
-190 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
260 °C
300 °C
400 °C
600 °C
Range (°C)
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
300 °C
400 °C
630 °C
800 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
300 °C
400 °C
630 °C
-190 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
260 °C
300 °C
400 °C
600 °C
630 °C
Absolute Uncertainty
tcal ±5 °C, ±(°C)
0.06 °C
0.08 °C
0.08 °C
0.07 °C
0.07 °C
0.08 °C
0.08 °C
0.06 °C
0.06 °C
0.06 °C
0.07 °C
0.07 °C
0.08 °C
0.06 °C
0.06 °C
0.06 °C
0.06 °C
0.07 °C
0.07 °C
0.07 °C
0.08 °C
0.08 °C
1
0.07 °C
0.10 °C
0.10 °C
0.09 °C
0.09 °C
0.09 °C
0.10 °C
0.07 °C
0.07 °C
0.08 °C
0.08 °C
0.09 °C
0.09 °C
0.07 °C
0.08 °C
0.08 °C
0.08 °C
0.08 °C
0.08 °C
0.09 °C
0.09 °C
0.09 °C
Pt 385, 200 Ω -200 °C
Pt 385, 500 Ω -200 °C
1. 2-wire output
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
260 °C
300 °C
400 °C
600 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
260 °C
300 °C
400 °C
600 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
260 °C
300 °C
400 °C
600 °C
630 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
260 °C
300 °C
400 °C
600 °C
630 °C
0.31 °C
0.32 °C
0.33 °C
0.33 °C
0.36 °C
0.36 °C
0.42 °C
0.42 °C
0.13 °C
0.13 °C
0.13 °C
0.14 °C
0.14 °C
0.15 °C
0.16 °C
0.16 °C
0.38 °C
0.38 °C
0.39 °C
0.39 °C
0.43 °C
0.43 °C
0.50 °C
0.50 °C
0.15 °C
0.15 °C
0.16 °C
0.17 °C
0.17 °C
0.18 °C
0.19 °C
0.19 °C
8
Page 17
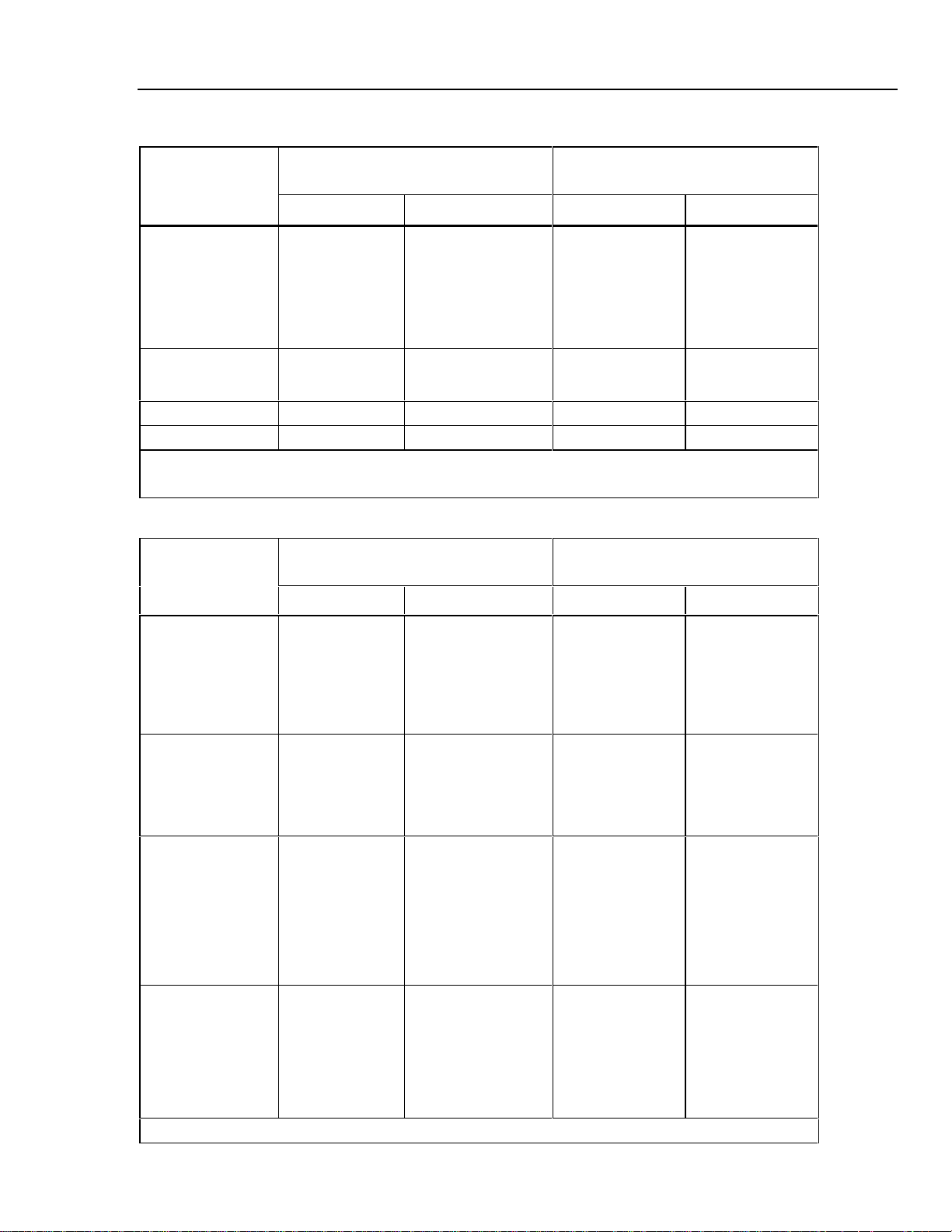
RTD and Thermistor Specification, Output (continued)
525A
Calibrator Specification s
Absolute Uncertainty
RTD Type
Minimum Maximum 90 days 1 year
Pt 385, 1000 Ω -200 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
260 °C
300 °C
400 °C
600 °C
PtNi 385, 120 Ω
(Ni 120)
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
Cu 427, 10 Ω
2
-100 °C 260 °C 0.63 °C 0.75 °C
Range (°C)
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
260 °C
300 °C
400 °C
600 °C
630 °C
0 °C
100 °C
260 °C
0.06 °C
0.06 °C
0.07 °C
0.07 °C
0.07 °C
0.07 °C
0.08 °C
0.08 °C
0.04 °C
0.04 °C
0.03 °C
tcal ±5 °C, ±(°C)
YSI 400 15 °C 50 °C 0.005 °C 0.007 °C
1. 2-wire output
2. Based on MINCO Application Aid No. 18.
RTD and Thermistor Specification, Input
Absolute Uncertainty,
RTD Type
Range (°C)
Minimum Maximum 90 days 1 year
tcal ±5 °C, ±(°C)
1
0.07 °C
0.08 °C
0.08 °C
0.08 °C
0.09 °C
0.09 °C
0.09 °C
0.09 °C
0.05 °C
0.04 °C
0.03 °C
1
Pt 385, 100 Ω -200 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
300 °C
400 °C
630 °C
Pt 3926, 100 Ω -200 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
300 °C
400 °C
Pt 3916, 100 Ω -200 °C
-190 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
260 °C
300 °C
400 °C
600 °C
Pt 385, 200 Ω
-200 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
260 °C
300 °C
400 °C
600 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
300 °C
400 °C
630 °C
800 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
300 °C
400 °C
630 °C
-190 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
260 °C
300 °C
400 °C
600 °C
630 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
260 °C
300 °C
400 °C
600 °C
630 °C
1. 4-wire mode. Uncertainties listed do not include probe uncertainties.
0.031 °C
0.018 °C
0.018 °C
0.027 °C
0.031 °C
0.042 °C
0.050 °C
0.031 °C
0.014 °C
0.018 °C
0.026 °C
0.031 °C
0.041 °C
0.026 °C
0.011 °C
0.014 °C
0.018 °C
0.025 °C
0.026 °C
0.031 °C
0.040 °C
0.042 °C
0.071 °C
0.075 °C
0.079 °C
0.082 °C
0.090 °C
0.093 °C
0.100 °C
0.101 °C
0.012 °C
0.020 °C
0.020 °C
0.030 °C
0.035 °C
0.047 °C
0.057 °C
0.031 °C
0.015 °C
0.019 °C
0.029 °C
0.034 °C
0.046 °C
0.028 °C
0.012 °C
0.015 °C
0.019 °C
0.028 °C
0.029 °C
0.034 °C
0.045 °C
0.047 °C
0.072 °C
0.076 °C
0.081 °C
0.085 °C
0.093 °C
0.097 °C
0.105 °C
0.106 °C
9
Page 18

525A
Service Manual
RTD and Thermistor Specification, Input (continued)
RTD Type
Minimum Maximum 90 days 1 year
Pt 385, 500 Ω -200 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
260 °C
300 °C
400 °C
600 °C
Pt 385, 1000 Ω -200 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
260 °C
300 °C
400 °C
600 °C
PtNi 385, 120 Ω
(Ni120)
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
Cu 427, 10 Ω
2
-100 °C 260 °C 0.300 °C 0.069 °C
Range (°C)
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
260 °C
300 °C
400 °C
600 °C
630 °C
-80 °C
0 °C
100 °C
260 °C
300 °C
400 °C
600 °C
630 °C
0 °C
100 °C
260 °C
Absolute Uncertainty,
tcal ±5 °C, ±(°C)
0.046 °C
0.049 °C
0.043 °C
0.030 °C
0.032 °C
0.037 °C
0.047 °C
0.048 °C
0.031 °C
0.034 °C
0.039 °C
0.025 °C
0.027 °C
0.030 °C
0.041 °C
0.042 °C
0.209 °C
0.210 °C
0.211 °C
1
0.047 °C
0.050 °C
0.045 °C
0.033 °C
0.035 °C
0.041 °C
0.052 °C
0.076 °C
0.032 °C
0.035 °C
0.040 °C
0.028 °C
0.030 °C
0.034 °C
0.045 °C
0.047 °C
0.210 °C
0.211 °C
0.212 °C
YSI 400 15 °C 50 °C 0.005 °C 0.304 °C
SPRT, 25 Ω User Defined User Defined 0.05 °C 0.06 °C
1. 4-wire mode. Uncertainties listed do not include probe uncertainties.
2. Based on MINCO Application Aid No. 18.
10
Page 19

Pressure Measurement
The Calibrator can accept either the Fluke 700 or 6100 series pressure modules. Pressure
modules plug directly into the front panel Lemo connector. The Calibrator firmware
automatically detects the type and value of the module you are attaching, and recognizes
the following units of measurement:
• PSI
(pounds per square inch)
• inH2O4°C
(inches of water at 4 degrees Celsius)
• inH2O20C
(inches of water at 20 degrees Celsius)
• cmH2O4°C
(centimeters of water at 4 degrees Celsius)
• cmH2O20C
(centimeters of water at 20 degrees Celsius)
• BAR
(bars)
525A
Theory of Operation
• mBAR
(millibars)
• KPAL
(kilopascals)
• inHG 0°C
(inches of mercury at 0 degrees Celsius)
• mmHG 0°C
(millimeters of mercury at 0 degrees
Celsius)
• Kg/cm2
(kilograms per square centimeter)
Theory of Operation
The Calibrator serves as an accurate laboratory device for calibrating thermocouples,
RTDs, pressure devices, and low-level dc voltages and currents. The main PCB
assembly, and several subassemblies, work together to provide high-reliability and easy
maintenance.
Micro-Controller Section
The Atmel ATmega 103 micro-controller is the heart of the 525A. It contains all of the
program memory, nv-ram, FlashROM, static RAM, and EEProm. The micro-controller
allows a minimal amount of external glue logic. The main external digital ICs are the RS232 driver, relay drivers, LCD controller, and the digitally controlled analog switches.
Many of the ICs are interfaced through the micro-controller’s three-wire SPI bus
minimizing interconnecting lines. Inputs or outputs begin with instructions entered
through the keypad or through remote communications (serial or IEEE-488) into the
micro-controller. The micro-controller processes the commands and sets conditions that
are appropriate for the command.
11
Page 20

525A
Service Manual
Analog Section
The Calibrator can source DC voltage to 100 V, DC current to 100 mA, resistances from 5 to
4000 Ω, and thermocouples and RTDs. The main components of the analog circuit consist of a
precision 2.5-volt temperature compensated reference, 20-bit DAC and a 24-bit ADC. Precision
metal foil resistor networks and several chopper-stabilized OP-AMPS are the most critical analog
components.
When sourcing, the micro-controller, using stored calibration constants, adjusts the D/A to
generate an output based on the function and range selected. To achieve high accuracy, a low drift
24-bit A/D converter is used as a feedback element near the output of the D/A converter. The
scaled output DAC_CK is routed to the A/D converter.
In the input mode, the A/D is used directly to measure either the T/C or the resistance (RTD)
inputs. The A/D features an internal self-calibration function that continually nulls out zero drift
due to temperature changes. A programmable gain stage in the A/D is adjusted by the microcontroller to allow direct T/C and RTD inputs without requiring external amplification. In the
RTD mode, a constant current source is used to excite the RTD and the voltage developed across
the RTD is measured by the A/D, then the resistance can be calculated.
Basic Maintenance
To avoid personal injury or damage to the Calibrator, use only
the specified replacement parts and do not allow water into the
case.
Cleaning the Calibrator
To avoid damaging the case, do not use solvents or abrasive
cleaners.
Clean the Calibrator and pressure modules with a soft cloth dampened with water or mild
soap and water.
Replacing a Line Fuse
To avoid electrical shock, disconnect line power before opening
the case or line voltage selector.
The line power fuses and line voltage selector switch are located in a compartment above
the power switch on the right rear of the Calibrator. The fuse-rating label on the rear
panel shows the correct replacement fuse for each line voltage setting.
W Warning
WCaution
W Warning
12
Table 2 lists the fuse part numbers for each line voltage setting. Figure 1 shows how to
remove the fuse compartment cover.
Page 21

To Check or Replace a Fuse
1. Disconnect line power.
2. Using a flat-blade screwdriver, pry the tab at the base of the line fuse compartment.
The compartment cover will pop part way out.
3. Remove the compartment cover. The fuses come out with the compartment cover and
can easily be checked or replaced.
4. To reinstall the fuse, push the compartment cover back into the compartment until the
tab locks in place.
Note
When changing the line voltage setting, make sure to verif y that the
appropriate line fuse is installed in the Calibrator. Replace the fuse as
required.
Table 2. Replacement Fuses
Part Number Fuse Description Line Voltage Setting
1645311 W Fuse, 0.25 A fast fuse 120 V (90 V to 132 V)
525A
Basic Maintenance
1645327 W Fuse, 0.125 A fast fuse 240 V (198 V to 264 V)
Changing Line Voltage
The Calibrator arrives from the factory configured for the line voltage appropriate for the
country of purchase or as specified when it is ordered. To verify the line voltage setting,
check the line voltage indicator on the line power fuse compartment cover.
Note
Confirm that the line voltage selection is set for 120 V for line voltages
between 90 V and 132 V or that the selector is set to 240 V for line voltages
between 198 V and 264 V.
To change the line voltage:
1. Disconnect line power.
2. Using a flat-blade screwdriver, pry the tab at the base of the line fuse compartment.
The compartment cover will pop part way out.
3. Remove the compartment cover.
4. Remove the line voltage selector assembly by gripping the line voltage indicator tab
with pliers and pulling it straight out of the compartment.
5. Rotate the line voltage selector assembly to the desired voltage and reinsert.
6. Verify the appropriate fuse is being used for the selected line voltage (see Table 2)
and reinstall the fuse compartment by pushing it in unt il the tab lock s in place.
13
Page 22

525A
Service Manual
Line voltage
indicator
Changing
line fuse
Line fuse
compartment
(SB)
0V
Figure 1. Accessing the Fuse
Modular-Level Maintenance
XWarning
Do not attempt to complete the following procedures unless
qualified to do so. This information is for use by qualified
personnel only.
When making solder connections, use "no clean" solder.
120
Changing line
voltage
WCaution
240V
120V
Rotate to change
line voltage indicator
ajr12f.eps
14
At some point in time, it may be necessary to perform modular-level maintenance or
troubleshooting of the Calibrator.
Page 23

Evaluation of most problems can be made after the top cover is removed. Inside the
chassis are six circuit boards. They are connected to one another with point to point
wiring. The six circuit boards are the Main PCA, Keypad PCA, TC PCA, Lemo PCA,
Opto RS232 PCA, and the Display PCA.
Most of the Calibrator circuitry is located on the Main PCA. The Display PCA, Keypad
PCA, and Lemo PCA are mounted to the front of the chassis. The TC PCA is mounted in
the Output Block, and the Opto RS232 PCA is mounted on the rear of the chassis.
If the Main PCA needs repair, it is recommended that all other circuit boards be removed
from the chassis still assembled. Repair of the other circuit boards can be accomplished
while leaving them inside the cha ssis.
Disassembly
To open the Calibrator case, remove the six screws from each end and lift off the top
cover.
To remove all of the circuit boards while still assembled, do the following:
1. Stand the chassis on the front handles.
2. Remove the four nylon screws that attach the Display PCA to the front.
525A
Modular-Level Maintenance
3. Remove the six screws that attach the Keypad PCA to the front.
4. Remove the five nuts that attach the Output Block to the front.
5. Remove the standoff nuts from the 9-pin D connector on the Opto RS232 PCA, if
present.
6. Stand the 525A back on its feet.
7. Remove the screws attaching the Opto RS232 PCA to the back, if present.
8. Remove the four screws through the transformer.
9. Remove the six screws that attach the Main PCA to the chassis base.
10. Carefully lift all of the attached circuit boards out of the chassis.
Reassembly
It is easier to solder the wires interconnecting the circuit boards before placing the
assemblies back into the chassis. The procedures in this section will explain how to
reconnect each of the circuit boards.
There are two wire sets available from Fluke. These wire sets are used to connect the
circuit boards. One set is for the front connections and the other set is for the rea r panel
connections. Refer to Figure 2 for wire locations and Tables 3 and 4 for the detailed list
of front and rear panel connections.
15
Page 24

525A
Service Manual
Table 3. Front Panel Wire Color Assignments
Wire Number Color
J5 Red 24 g Wire
J7 Black 24 g Wire
J16 Purple 20 g Wire *
J 17 Grey 20 g Wire *
J18 (1st 6 inches) Red 20 g Wire *
J19 Black 20 g Wire *
J20 Blue 20 g Wire *
J21 Yellow 20 g Wire *
J22 (2nd six inches) Red 20 g Wire *
J33 White/Red 20 g Wire *
J34 Green 20 g Wire *
(all lengths are 6 inches)
Gage
J35 White 20 g Wire *
J36 Black/Red 20 g Wire *
* Connect With Terminal Lug
Table 4. Rear Panel Wire Color Assignments
Wire Number Color
AC3 Red 20 g Wire*
AC4 White 20 g Wire*
AC7 Red 20 g Wire *
AC8 Green 20 g Wire *
AC9 Black 20 g Wire *
AC10 White 20 g Wire *
* Connect With Spade Lug
(all lengths are 6 inches)
Gage
16
Page 25

Ribbon wire
525A
Modular-Level Maintenance
Purple wire
Yellow wire
Blue wire
Red wire
Yellow
wire
Blue
wire
Figure 2. Wiring Connections
Grey
wire
Purple
wire
Red
wires
Output Block Subassembly Connections
Table 5 lists the connections to be made when connecting the Output Block to the Main
PCA. Use 8-32 low thermal nuts and 8-32 low thermal washers for these connections.
Table 5. Output Block to Main PCA Connections
Wire Color Connect From Connect To
Blue J20 RTD HI
Green wire
aby01f.eps
Yellow J21 RTD LO
Purple J16 mA HI
Grey J17 mA LO
Green J34 4 W RTD Sense HI
White J35 4 W RTD Sense LO
Red (2 wires) J18 & J22 one leg of the 0.1 µF Cap Volts Hi
Black J19 the other leg of the 0.1 µF Cap Volts LO
Black with red stripe J33 4 W RTD HI
White with red stripe J36 4 W RTD LO
17
Page 26

525A
Service Manual
The TC PCA needs to be connected to the Main PCA. Use the wire connections listed in
Table 6. These connections require soldering. Refer to Figure 3.
Table 6. TC PCA to Main PCA Connections
Solder From TC PCA
Wire Color
Red 1st wire pad J23
Black 2nd wire pad J24
Blue 3rd wire pad J25
Yellow 4th wire pad J26
White 5th wire pad J27
Purple 6th wire pad J28
(from left to right) Solder To Main PCA
Blue wire
Yellow wire
Purple wire
Red wire
Ribbon
cable
Figure 3. Solder Connections for the TC PCA
aby02f.eps
18
Page 27

Keypad PCA to Main PCA
To connect the Keypad PCA to the Main PCA, solder the following connections (refer to
Figure 4):
1. Solder the 12-conductor cable to the back of the Keypad PCA with pin 1 on the cable
aligned with pin 1 on the Keypad PCA.
2. Solder the Keypad ribbon cable to J11 with pin 1 lined up with the square hole in
J11.
525A
Modular-Level Maintenance
Figure 4. Keypad PCA Connections
Display Assembly to Main PCA
To attach the Display Assembly to the Main PCA, make the following connections:
1. Solder a red wire from J5 on the Main PCA to the "A" hole in the Display PCA.
2. Solder a black wire from J7 on the Main PCA to the "K" hole in the Display PCA.
3. Solder the 14-connector cable to the back of the Display PCA with pin 1 on the cable
aligned with pin 1 on the Display PCA.
4. Solder the 14-conductor ribbon cable to the LCD Display (J4) position on the right
side of the Main PCA with pin 1 in the square hole in J4.
Ribbon
cables
aby03f.eps
19
Page 28

525A
Service Manual
Opto RS232 PCA to Main PCA
Use 4 wires to connect the Opto RS232 PCA to the Main PCA. Refer to Table 7 and
Figure 5.
Table 7. Opto RS232 to Main PCA Connections
Main PCA Opto RS232
J38, pin 2 J1, pin 2
J38, pin 3 J1, pin 3
J38, pin 5 J1, pin 5
J63 J1, pin 4
After completing this task, the circuit board assembly is ready to reinstall into the chassis.
Red wire
Figure 5. Connections for the Opto RS232 PCA
aby04f.eps
20
Page 29

Reinstalling the Circuit Boards
1. Place the Main PCA with all its attachments into the chassis base.
2. Put the Output Block into place in the front of the chassis.
3. Use five nylock nuts to secure the Output Block to the Chassis Base.
4. Lay the Main PCA down so that it is in place.
5. Use the (6) 6-32 5/8" screws and (6) lock washers to secure the Main PCA to the
chassis base.
6. Use the (4) 6-32 X-former screws and (4) #6 nylon washers to secure the transformer
to the chassis.
7. Using the (2) jack standoffs, attach the Opto RS232 PCA to the rear of the chassis.
8. Stand the unit on its front handles.
9. Insert the keypad into the front of the chassis.
10. Use (6) 6-32 x 3/8" screws to attach the Keypad PCA to the chassis base.
11. Remove the protective plastic from the LCD and put it over the lens on the front label
(outside).
12. Use the (4) 6-32 nylon screws and the 4 nylon washers to attach the Display PCA to
the chassis. The washers go between the Display PCA and the chassis base.
525A
Modular-Level Maintenance
Connecting the Power Module
To attach the Power Module to the Main PCA, make the connections listed in Table 8.
Refer to Figure 6.
Table 8. Power Module to Main PCA Connections
Wire Color From To
Red AC3 Terminal 3 on Power Module
White AC4 Terminal 4 on Power Module
Red AC7 Terminal 7 on Power Module
Green AC8 Terminal 8 on Power Module
Black AC9 Terminal 9 on Power Module
White AC10 Terminal 10 on Power Module
21
Page 30

525A
Service Manual
Red
wires
Green wire
Top view
Red wires
Green wire
Figure 6. Power Module Connections
Final Assembly and Inspection
To complete final assembly and inspection, use a digital multimeter and verify the
continuity of the connections listed in Table 9.
Table 9. Power Connections
Wire Color Position B Position on Main PCA
Red Power Module Pin 3 AC3
White Power Module Pin 4 AC4
Red Power Module Pin 7 AC7
Green Power Module Pin 8 AC8
Black Power Module Pin 9 AC9
White Power Module Pin 10 AC10
Red J5 LCD J2 A
Black J7 LCD J2 K
aby05f.eps
22
White J62 Opto Pin 4
N/A J52 Inside Chassis Base (no connection)
Install tie wraps around the AC wires, the Output Block wires, the LCD backlight wires,
the 5-conductor cable, and the Opto-RS232 wires.
Page 31

Performance Tests
The following performance tests are used to verify the functionality of the Calibrator. If
the Calibrator fails any part of the performance tests, calibration adjustment or repair by a
Fluke Service Center is in order. For a list of service centers, refer to "Contacting Fluke"
earlier in this manual.
Required Equipment List
To complete the performance tests and calibration adjustment, the equipment listed in
Table 10 is necessary. If the equipment listed is not available, equipment with the same
or better specifications can be substituted.
Table 10. Required Equipment
Manufacturer Model Equipment Purpose
Fluke Fluke- 525A/Leads Test Lead Set All Functions
525A
Performance Tests
Fluke 742A-10 Resistance
Standard, 10 Ω
Fluke 742A-100 Resistance
Standard, 100 Ω
Fluke 742A-10K Resistance
Standard, 10K Ω
Fluke 5520A Calibrator Low Ohms Measure and SPRT
Wavetek 1281 DMM All functions except CJC
_ _ Ohms Shorting
Block
_ _ RTD Probe TC CJC Calibration
Hart Scientific 1521 Precision
Thermometer
Omega J Thermocouple
Probe
_ _ Lag Bath TC CJC Calibration
100 mA source calibration
Low Ohms Measure and SPRT
Calibration.
Hi Ohms Measure Calibration
Calibration. Hi Ohms Measure
Calibration.
Low Ohms Measure and SPRT
Calibration. Hi Ohms Measure
Calibration.
TC CJC Calibration
TC CJC Calibration
__
__
Dewar Flask with
lid
Banana Jack to
Copper TC MiniConnector Cable
TC tests
TC tests
23
Page 32

525A
Service Manual
Testing DC Voltage
The DC voltage amplitude accuracy test verifi es the accu racy of DC volt age at the 525A
calibrator front panel Volts Source output. See Table 11.
Table 11. Testing DC Voltage
Range
100 mV
1.0 V
10.0 V
100.0 V
Nominal
Value (V)
0 0.000003 0.000003
0.025 3.63E-06 3.75E-06
0.075 4.88E-06 5.25E-06
0.1 5.5E-06 0.000006
0 0.00002 0.00002
0.25 2.63E-05 2.75E-05
0.75 3.88E-05 4.25E-05
1 0.000045 0.00005
0 0.0002 0.0002
2.5 0.000263 0.000275
7.5 0.000388 0.000425
10 0.00045 0.0005
0 0.002 0.002
25 0.002625 0.00275
Measured
Value Deviation %
90 Day Spec.
(V)
One Year
Spec. (V)
75 0.003875 0.00425
100 0.0045 0.005
24
Page 33

Testing DC Current
Use the Wavetek 1281 and the precision shunt to measure the 525A output as shown in
Figure 7. Take the Voltage reading from the Wavetek 1281 and divide it by the 742A-1
actual value. See Table 12.
525A
Performance Tests
Current Shunt
CE
OUTPUT
100V MA X
VOLTS
20V PK
MAX
INPUT
20V PK
MAX
TEMPERATURE / PRESSURE CALIBRATOR
525A
RTD
mA
100mA MAX
HI
HI
LO
LO
4W RTD
HI
SENSE
LO
INPUT/OUTPUT
20V PK
525A
TC
RTD
INPUTOUTPUT
ZERO
8
CJCSETUP
C / F
56
AUTOSET
2
LOCAL EXP
0
TYPE
UNITS
SHIFT
9
3
ENTER
•
VOLTS
STBY
OPR
TC
MAX
mA
7
4
SET RECALL
1
RNG LOCK
/
mA
Output
Terminals
Figure 7. Measuring DC Current
Table 12. Measuring DC Current
742A-1
100 mA
Output (A) Volt
Current
(I=E/R)
Shunt
Value 90 Day (A) 1 Year (A)
0.000 Direct Into
1281 Input
1281 DCV Function
ajr25f.eps
0.000002 0.000002
0.025 0.0000041 0.0000045
0.075 0.0000083 0.0000095
0.100 0.0000105 0.000012
25
Page 34

525A
Service Manual
Testing Thermocouple Output
For this test the TC mV specifications will be used. When this test is combined with the
CJC test, all functions of the TC output will have been checked. Typically, the cable
needs to connect the 525A to the 1281 and will need to be fabricated. The TC miniconnector will need to be copper - copper (white). Using copper wire, connect the TC
mini-connector to standard banana jacks. See Figure 8 for a connection diagram.
For this test, the CJC (cold junction compensation) must be turned off. Press I 5 to
turn off the CJC. XCJC on the display indicates that the CJC is turned off. Select TC, and
Output. Press Euntil mV/°C is shown on the display. Output the mV values listed in
Table 13.
525A
TEMPERATURE / PRESSURE CALIBRATOR
525A
4W RTD
RTD
mA
100mA MAX
HI
HI
LO
LO
HI
SENSE
LO
TC
INPUT/OUTPUT
20V PK
MAX
VOLTS
STBY
OPR
mA
OUTPUT
7
4
SET RECALL
1
RNG LOCK
/
TC
RTD
INPUT
ZERO
8
9
CJCSETUP
C / F
56
AUTOSET
2
3
LOCAL EX P
•
0
TYPE
UNITS
SHIFT
ENTER
CE
OUTPUT
100V M AX
20V PK
INPUT
20V PK
VOLTS
MAX
MAX
1281
Figure 8. Testing TC Output
Table 13. TC Temperatures
Nominal Voltage (mV) 90 Day Spec. (mV) 1 Year Spec. (mV)
-5.000 0.003125 0.00315
15.00 0.003375 0.00345
30.00 0.00375 0.0039
50.00 0.00425 0.0045
70.00 0.00475 0.0051
ajr26f.eps
26
Page 35

Testing CJC (Cold Junction Compensation)
Connect a Type-J thermocouple to the TC terminal on the 525A. Immerse the
thermocouple and a precision thermometer into a mineral oil lag bath. The test set-up is
shown in Figure 9.
Verify that the readings of the 525A and the precision thermometer are within the Type-J
specifications:
• The 90 day spec is 0.14 °C
• The 1 year spec is 0.16 °C
Note
Typical Type-J thermocouples Do not have specifications accurate enough
to be used as a standard. To maintain a good Test Uncertainty Ratio (TUR)
a characterized Type-J thermocouple may need to be used.
CJC (Cold Junction Compensation) Calibration
Connect a Type-J thermocouple to the TC terminals on the Calibrator, and immerse the
thermocouple and a precision thermometer in a mineral oil lag bath. The test setup is
shown in Figure 9. Verify that the readings of the thermometer and the Calibrator are
within the thermocouple specifications listed in the Specifications section.
525A
Performance Tests
OUTPUT
100V M AX
20V PK
INPUT
20V PK
VOLTS
MAX
MAX
TEMPERATURE / PRESSURE CALIBRATOR
525A
RTD
mA
100mA MAX
HI
HI
LO
LO
4W RTD
HI
SENSE
LO
Thermocouple
TC
INPUT/OUTPUT
20V PK
MAX
J type
525A
TC
RTD
INPUT
ZERO
8
CJCSETUP
C / F
56
AUTOSET
2
LOCAL EXP
0
TYPE
UNITS
SHIFT
9
3
ENTER
•
CE
VOLTS
STBY
OPR
mA
OUTPUT
7
4
SET RECALL
1
RNG LOCK
/
Mineral Oil
Lag Bath
Figure 9. Connections for CJC Calibration
Mercury
Thermometer
Dewar Flask
and Cap
ajr22f.eps
27
Page 36

525A
Service Manual
Testing Thermocouple Input
Set the 525A to TC input by pressing I then 7. All other 525A conditions will be
the same as the thermocouple output test, CJC off, mV/°C mode.
Connect the 525A to the 5520A as shown in Figure 10. Set the 5520A to output the mV
values in Table 13.
525A
TEMPERATURE / PRESSURE CALIBRATOR
525A
4W RTD
RTD
mA
100mA MAX
HI
HI
LO
HI
SENSE
LO
TC
LO
INPUT/OUTPUT
20V PK
MAX
VOLTS
STBY
OPR
mA
OUTPUT
7
4
SET RECALL
1
RNG LOCK
/
TC
RTD
INPUT
ZERO
8
CJCSETUP
C / F
56
AUTOSET
2
LOCAL EXP
0
TYPE
UNITS
SHIFT
9
3
ENTER
•
CE
5520A Normal Output
DC Volts
Function
OUTPUT
100V M AX
VOLTS
20V PK
MAX
INPUT
20V PK
MAX
Figure 10. Connections for Measuring TC Input
ajr24f.eps
28
Page 37

Testing Ohms Output
Use the precision digital multimeter (DMM) to measure the resistance output. Figure 11
shows the four-wire connections. See Table 14.
The Wavetek 1281 must be in the “loI” (low current mode) when measuring
Ω
in the 4 kΩ range or an overload will occur.
5
525A
TEMPERATURE / PRESSURE CALIBRATOR
525A
4W RTD
RTD
mA
100mA MAX
HI
HI
LO
HI
SENSE
LO
TC
LO
INPUT/OUTPUT
20V PK
MAX
OUTPUT
100V M AX
20V PK
20V PK
VOLTS
MAX
INPUT
MAX
525A
Performance Tests
Note
VOLTS
STBY
OPR
mA
OUTPUT
7
4
SET RECALL
1
RNG LOCK
/
TC
RTD
INPUT
ZERO
8
CJCSETUP
C / F
56
AUTOSET
2
LOCAL EXP
0
TYPE
UNITS
SHIFT
9
3
ENTER
•
CE
1281 Ohms
4-wire Function
Figure 11. Connection for Measuring Resistance Output
Table 14. Ohms Output Ranges
Range (Ω) Output (Ω) 1 Year (Ω)
400
50.03
100
200 0.03
300 0.03
400 0.03
4000
50.3
1000
2000 0.3
3000 0.3
4000 0.3
ajr23f.eps
29
Page 38

525A
Service Manual
Testing Ohms Input
Before measuring ohms input, the ohms output of a 5520A must be “characterized”. To
achieve the needed accuracy, the Wavetek 1281 is used as a transfer standa rd an d the
742A is used as the reference standard. To find the true value of the 5520A output, the
ratio-input function of the Wavetek 1281 is used. The ratio function of the 1281 is located
on the rear panel and is designated as Channel A and Channel B. Connect Channel A to
the 742A and connect the 5520A to Channel B, both using four-wire measure.
See Figure 12 for a connection diagram.
1281
Chan A
Pin Pin
Hi I I Lo
742
31 28 23 21 31 28 23 21
+
-
Figure 12. 1281 Connection Diagram
Rear inputs
+
Hi I I Lo
-
Chan B
5520A
ajr28f.eps
For the 400 Ω range use the 742A-1K and for the 4 kΩ range use the 742A-10K. For
more information on the correct usage of ratio mode refer to the 1281 Operators Manua l.
Use Table 15 to note the ratio indication on the 1281. Ignore the 0 Ω value. Use the
formula (742A actual value/ratio indication * 100 = actual 5520A value) and enter that
ohm value into the 5520A actual value column.
30
Page 39

Table 15. Ohms Ratio Table
525A
Performance Tests
5520A
Range
(Ω)
742A
Value
(Ω)Ratio
Actual
Value
(Ω)
525A
Reading Specification
90 Day
Specification
400
0 0.002 0.003 0.003
100 0.006 0.0065 0.007
200 0.01 0.010 0.011
300 0.014 0.0135 0.015
400 0.018 0.017 0.019
4000
0 0.02 0.03 0.03
1000 0.06 0.065 0.07
2000 0.1 0.10 0.11
3000 0.14 0.135 0.15
4000 0.18 0.17 0.19
First apply a four wire short to the 525A 4W RTD Ohm input. Set the 525A to the 400 Ω
range. Note the reading. Set the 525A to the 4000 Ω range. Note the reading. Move the
525A 4W RTD Ohm input to the output of the 5520A. Output the same nominal values
and note the 525A readings in the 525A reading column. Subtract the actual 5520A value
from the 525A reading and ensure that it is within the specified tolerance.
1 Year
Specification
OUTPUT
100V MA X
VOLTS
20V PK
MAX
INPUT
20V PK
MAX
TEMPERATURE / PRESSURE CALIBRATOR
525A
RTD
mA
100mA MAX
HI
HI
LO
LO
4W RTD
HI
SENSE
LO
INPUT/OUTPUT
20V PK
525A
TC
RTD
INPUT
ZERO
8
CJCSETUP
C / F
56
AUTOSET
2
LOCAL EXP
0
TYPE
UNITS
SHIFT
9
3
ENTER
•
CE
5520A 4
Function
ajr27f.eps
VOLTS
STBY
OPR
TC
MAX
mA
OUTPUT
7
4
SET REC ALL
1
RNG LOCK
/
Figure 13. Connection for Measuring Ohms
31
Page 40

525A
Service Manual
Testing Pressure Modules
Calibration Adjustment
Initiating Communication
The Fluke 700 series pressure modules are calibrated separately from the 525A. The
calibration follows the pressure module, so only a performance test is needed. Connect
any of the Fluke 700 series pressure modules to the pressure module connector. Verify
that the Calibrator reads pressure.
Adjusting the Calibrator requires no mechanical adjustment. All adjustments are
performed electronically. The calibration is performed via serial communications port.
The adjustments take place over the normal RS232 interface. Refer to Table 6 for a list of
required equipment for performing the following procedures. Note that the adjustment for
the Resistance Measure was designed to be especially flexible, allowing for the use of
fixed resistors.
Terminals can be set up using terminal communications software on a personal computer
(PC). Connect a 9-pin null modem cable to the RS232 connector on the back of the
Calibrator. Connect the other end of the cable to the PC/PC serial port. An adapter may
be needed for terminals that use 25 pin D serial connectors. A terminal program such as
Window HyperTerminal may be used in the PC.
The terminal settings need to be set as follows:
Bits per second: 9600
Data bits: 8
Parity: None
Stop bits: 1
Flow control: None
Local echo: on
Starting Adjustment Mode
The Calibrator needs to warm up for at least 30 minutes before performing these
procedures. This will allow any thermal changes in the Calibrator to stabilize. If the unit
has been repaired or is new, it should be given 24 hours to burn in. To initiate the
calibration mode, use the PC to send the CAL_START command. The following will be
displayed on the PC:
Calibration is password protected
Enter Password:
32
Page 41

Calibration Adjustment
The password is 525. Enter the password through the PC keyboard and the following is
displayed on the PC monitor:
Calibration Menu:
1: 100 mV Source
2: 1 V Source
3: 10 V Source
4: 100 V Source
5: 100 mA Source
6: Hi Ohms Source
7: Low Ohms Source
8: Hi Ohms Measure
9: Low Ohms Measure
10: SPRT 25
11: TC SOURCE
12: TC READ
13: TC CJC
14: Calibrate DAC
Enter Selection:
525A
Adjustment Sequence
Manual calibration of the Calibrator is a menu driven process. The menu consists of 14
different menu selections for calibration of the different operating modes.
Certain functions must be calibrated before others. Table 16 lists the calibration
dependencies and tells which functions are dependent on others being calibrated first. An
X in a row indicates that the step in that column must be before the step in that row can
be completed. These dependencies are only related to calibration adjustment. They are
not intended to show the relationship between normal functionality and calibration.
Table 16. Calibration Dependencies
1234567891011121314
1N/A X
2N/A X
3N/A X
4N/A X
5N/A X
6N/A
7N/A
8N/A
9N/A
10 N/A
11 N/A X
12 XN/A X
13 XXN/AX
14 N/A
33
Page 42

525A
Service Manual
14: Calibrate DAC, Digital to Analog Converter Adjustment
1: 100 mV Source to 4: 100 V Source, Adjusting DC Source
If all of the functions that are affected by the digital to analog converter (DAC)
adjustment are going to be adjusted, start with step 14 which adjusts the DAC. Do not
adjust the DAC unless all of the ranges affected are going to be readjusted. During
normal calibration adjustment, it is necessary to adjust the DAC. However, for example,
if a mistake were made in the 100 V range, the user would not want to readjust the DAC.
If it were readjusted, the user would have to readjust everything that depends on that
range.
To adjust the calibration of the DAC from the menu, type 14 and then press the Enter key
on the PC keyboard. No external connection is necessary. The DAC adjust will execute,
save the calibration constants, then display the Calibration Menu on the PC.
Adjusting the voltage output breaks down into four distinct ranges; each can be adjusted
separately using menu selections 1-4. The adjustments are done in 2 parts. The first part
sets the 0 and span values. The second part is to fine adjust the zero, span, and adjusts the
linearity. The example below is for the 1 V range. The other ranges use the same steps
with different voltage values. Refer to Table 17 for a list of equipment used in this
section.
Table 17. List of Equipment for Voltage Calibration Adjustments
Manufacturer Model Equipment
Fluke FLUKE-525A/LEADS Test Lead Set
Wavetek 1281 DMM
1. Connect the calibrator VOLTS HI and LO to the DMM input.
2. Set the DMM to DC Volts.
3. Type 2 and push the Enter key on the PC. The following is displayed on the PC:
First Calibration Point. Enter the Volts displayed:
4. When the reading on the DMM stabilizes, type the reading value on the PC and press
Enter. After the value has been entered, the following is displayed on the PC:
Second Calibration Point. Enter the Volts displayed:
5. When the reading on the DMM stabilizes, type the reading value on the PC and press
Enter. After the value has been entered, the following is displayed on the PC:
Second Calibration Point. Enter the Volts displayed:
Adjust the 0 Percent of Scale, 8 for up 2 for down, Press Enter When Stable
34
The second part of the calibration adjustment follows. In the 10 key section of the PC
keyboard, use the 8 (up arrow) to increase the output voltage displayed or 2 (down arrow)
to decrease the output voltage displayed. Keep in mind the lag time between a change in
output voltage to a stable display on the DMM. Make small changes then wait for a stable
reading. Adjust the output so that you get a good, stable 0 V reading. When satisfied with
the reading, press the Enter key.
Page 43

Calibration Adjustment
The PC display shows:
Please Wait…
25755
Adjust to 25 Percent of Scale, 8 for up 2 for down, Press Enter When Stable
The value is the raw A/D counts for this calibration point, followed by a prompt to adjust
the 25 % of scale value. Use the 8 (up) and 2 (down) key on the PC to adjust the output to
get a reading very close to 25 % of the range full scale.
• For the 100 mV range, 25 % is 25 mV
• For the 1 V range, 25 % is 250 mV
• For the 10 V range, 25 % is 2.5 V
• For the 100 V range, 25 % is 25 V
When satisfied with the reading, press Enter and the PC shows:
Please Wait…
2083980
525A
Adjust to 50 Percent of Scale, 8 for up 2 for down, Press Enter When Stable
The value is the raw A/D counts for this calibration point followed by a prompt to adjust
the 50 % of scale value. Use the 8 (up) and 2 (down) key on the PC to adjust the output to
get a reading very close to 50 % of the range full scale.
• For the 100 mV range, 50 % is 50 mV
• For the 1 V range, 50 % is 500 mV
• For the 10 V range, 50 % is 5.0 V
• For the 100 V range, 50 % is 50 V
This process continues until the user goes through the 100 % range. Use the same
procedures for those ranges.
After the raw A/D counts are displayed, this calibration step is complete. The calibration
constants for the range have been saved. Press Enter to return to the Calibration menu.
5: 100 mA Source, Adjusting DC Current Source
Adjusting the DC current output is similar to the voltage source calibration adjustment.
Just like the voltage calibration adjustment, this adjustment is executed in 2 parts. Part 1
sets the 0 and span values. Part 2 is to fine adjust the zero, span, and adjusts the linearity.
Refer to Table 18 for a list of equipment used in this section.
Table 18. List of Equipment for Current Calibration Adjustments
Manufacturer Model Equipment
Fluke FLUKE-525A/LEADS Test Lead Set
Fluke 742A-10 Resistance Standard, 10 Ω
Wavetek 1281 DMM
35
Page 44

525A
Service Manual
The voltage is measured across a 10 Ω shunt resistor instead of measuring current
directly.
Readings taken from the DMM need to be converted to mA (multiplied by 100) before
they can be entered in at the PC.
1. Set the DMM to read DC Volts.
2. Use the test leads for the following connections:
a. Connect the mA HI jack of the Calibrator to the high side of the current input of
the 742A.
b. Connect the mA LO jack of the calibrator to the low side of the current input of
the 742A.
c. Connect the high side of the sense output of the 742A to the high side of the
voltage input of the DMM.
d. Connect the low side of the sense output of the 742A to the low side of the
voltage into the DMM.
3. Type 5 and then press the Enter key on the PC. The following will be displayed on
the PC:
First Calibration Point. Enter the mAmps displayed:
4. When the reading on the DMM stabilizes, calculate the mA (multiply the voltage
reading by 100) and type the mA on the PC then press the Enter key. After the value
has been entered, the following shows on the PC:
Second Calibration Point. Enter the mAmps displayed:
5. When the reading on the DMM stabilizes, calculate the mA (multiply the voltage
reading by 100) and type the mA on the PC then press the Enter key. After the value
has been entered, the following shows on the PC:
Second Calibration Point. Enter the volts displayed
Adjust the 0 Percent of Scale, 8 for up 2 for down, Press Enter When Stable
The second part of the calibration adjustment follows. In the 10 key section of the PC
keyboard, use the 8 (up arrow) to increase the output voltage displayed or 2 (down arrow)
to decrease the output voltage displayed. Keep in mind the lag time between a change in
output voltage to a stable display on the DMM. Make small changes then wait for a stable
reading. Adjust the output so that you get a good, stable 0 V reading. When satisfied with
the reading, press the Enter key.
The PC display shows:
Please Wait…
111260
36
Adjust to 25 Percent of Scale, 8 for up 2 for down, Press Enter When Stable
The value is the raw A/D counts for this calibration point, followed by a prompt to adjust
the 25 % of scale value. Use the 8 (up) and 2 (down) key on the PC to adjust the output to
get a reading very close to 25 % of the range full scale.
• For the 100 mA range, 25 % is 250 mV
When satisfied with the reading, press Enter and the PC shows:
Page 45

Please Wait…
2147203
Adjust to 50 Percent of Scale, 8 for up 2 for down, Press Enter When Stable
The value is the raw A/D counts for this calibration point followed by a prompt to adjust
the 50 % of scale value. Use the 8 (up) and 2 (down) key on the PC to adjust the output to
get a reading very close to 50 % of the range full scale.
• For the 100 mA range, 50 % is 500 mV
Repeat this process until the user goes through the 100 % range. Use the same procedures
for those ranges.
• For the 100 mA range, 75 % is 750 mV
• For the 100 mA range, 100 % is 1 V
After the raw A/D counts are displayed, this calibration step is complete. The calibration
constants for the range have been saved. Press Enter to return to the Calibration menu.
6: Hi Ohms Source, Adjusting High Resistance Source
When calibrating the 5-4000 Ω output range (High Ohms Source), the calibrator outputs
two calibration points. After the output becomes stable, the values are entered at the PC.
525A
Calibration Adjustment
1. Use the same test equipment listed in Table 16.
2. Make the following connections:
a. Connect the HI RTD Ω jack of the Calibrator to the high side of the Ohms
measure sense jacks on the DMM.
b. Connect the LO RTD Ω jack of the Calibrator to the low side of the Ohms
measure sense jacks on the DMM.
c. Connect the HI RTD Ω jack of the Calibrator to the high side of the Ohms
measure current source jacks on the DMM.
d. Connect the LO RTD Ω jack of the Calibrator to the low side of the Ohms
measure current source jacks on the DMM. It is important that the sense leads be
on the bottom of the stack on the Calibrator Ohms source jacks.
3. Set the DMM to measure 4-wire ohms.
4. Type 6, then the Enter key on the PC. The PC will display:
First Calibration Point. Enter the Ohms displayed:
5. When the reading dis pla yed on the DMM stabi lizes, type the reading value on the PC
and press the Enter key. After the value has been entered, the PC displays the
following:
Second Calibration Point. Enter the Ohms displayed:
6. When the reading dis pla yed on the DMM stabi lizes, type the reading value on the PC
and press the Enter key. After the second value has been entered, the Calibrator will
return to the calibration menu.
37
Page 46

525A
Service Manual
7: Low Ohms, Adjusting Low Ohms Source
When calibrating the 5-400 Ω output range (High Ohms Source), the calibrator outputs
two calibration points. After the output becomes stable, the values are entered at the PC.
1. Use the same test equipment listed in Table 16.
2. Use the same connections as in 6: Adjusting High Resistance Source.
3. Set the DMM to measure 4-wire ohms.
4. Type 7, then press the Enter key on the PC. The PC will display:
First Calibration Point. Enter the Ohms displayed:
5. When the reading dis pla yed on the DMM stabi lizes, type the reading value on the PC
and press the Enter key. After the value has been entered, the PC displays the
following:
Second Calibration Point. Enter the Ohms displayed:
6. When the reading dis pla yed on the DMM stabi lizes, type the reading value on the PC
and press the Enter key. After the second value has been entered, the Calibrator will
return to the calibration menu.
8: Hi Ohms, Adjusting High Resistance Measure
When adjusting the calibration for the 5-4000 Ohms Measure range (High Ohms
Measure), the Calibrator will first measure a short and then two resistances. Refer to
Table 19 for a list of equipment used in this section.
Table 19. List of Equipment for High Ohms Measure Calibration Adjustments
Manufacturer Model Equipment
Fluke FLUKE-525A/LEADS Test Lead Set
Fluke 742A-10K Resistance Standard, 10K Ω
Fluke 5520A Calibrator
Wavetek 1281 DMM
1. Insert a 4-wire short into the 525A 4W RTD Ω jacks.
2. Type 8 then press the Enter key on the PC. The following will show on the PC:
Input 0 Ohms, Press Enter When Stable
3. Allow a few seconds for stabilization, then press the Enter key. In a few moments the
following appears on the PC:
38
Input ~2000 Ohms, Enter the actual value when stable:
The ~2000 indicates that the desired resistance is about 2000 Ω. The actual resistance is
not as important as the accuracy with which the value is known. The method described
below uses the 1281 to establish a ratio between the 5520A output and the 742 to
improve the accuracy with which the 5520A’s output resistance is known.
Page 47

1. Connect channel A of the 1281 to the resistance standard as follows:
a. Connect I+ of the DMM to the high side of the current input of the resistance
standard.
b. Connect I- of the DMM to the low side of the current input of the resistance
standard.
c. Connect the high side (HI) of the DMM sense input to the high side of the sense
output of the resistance standard.
d. Connect the low side (LO) of the DMM sense input to the low side of the sense
output of the resistance standard.
2. Connect channel B of the 1281 to the 5520A as follows:
a. Connect I+ of the DMM to the high side of the current input of the 5520A.
b. Connect I- of the DMM to the low side of the current input of the 5520A.
c. Connect the high side (HI) of the DMM sense input to the high side of the sense
output of the 5520A.
d. Connect the low side (LO) of the DMM sense input to the high side of the sense
output of the 5520A.
525A
Calibration Adjustment
3. Connect the 525A to the 5520A as follows:
a. Connect the HI INPUT 4W RTD Ω jack of the Calibrator to the high side of the
current input of the 5520A.
b. Connect the LO INPUT 4W RTD Ω jack of the Calibrator to the low side of the
current input of the 5520A.
c. Connect the HI SENSE 4W RTD Ω jack of the Calibrator to high side of the
sense output of the 5520A.
d. Connect the LO SENSE 4W RTD Ω jack of the Calibrator to the low side of the
sense output of the 5520A.
4. Set the 5520A to source 2000 Ω.
5. Using the 2 channels on the DMM, calculate the actual value of the 5520A’s output.
This is done by using the ratio of a known standard to the output of the 5520A. The
1281 can be used to calculate the ratio or proceed as follows:
Ratio = A/B
RA = RS/Ratio
Where:
A = The reading from channel A of the DMM
B = The reading from channel B on the DMM
RS = The value of the resistance standard (in this case 10K)
RA = The actual output of the 5520A
After the actual output value, the PC displays the following:
Input ~4000 Ohms, Enter the actual value when stable
1. Set the 5520A to source 4000 Ω (nominal) and enter the actual value calculated
as described above.
After the value is entered, the calibration constants will be saved and the display returns
to the main Calibration Menu.
39
Page 48

525A
Service Manual
9: Low Ohms, Adjusting Low Resistance Measure
When adjusting the calibration for the 5-400 Ohms Measure range (Low Ohms Measure),
the Calibrator will measure 3 resistances. Refer to Table 20 for a list of equipment used
in this section.
Table 20. List of Equipment for High Ohms Measure Calibration Adjustments
Manufacturer Model Equipment
Fluke FLUKE-525A/LEADS Test Lead Set
Fluke 742A-100 Resistance Standard, 100 Ω
Fluke 5520A Calibrator
Wavetek 1281 DMM
The method described below uses the 1281 to establish a ratio between the 5520A output
and the 742 to improve the accuracy with which the 5520A’s output resistance is known.
1. Connect channel A of the 1281 to the Resistance Standard as follows:
a. Connect I+ of the DMM to the high side of the current input of the Resistance
Standard.
b. Connect I- of the DMM to the low side of the current input of the Resistance
Standard.
c. Connect the high side (HI) of the DMM sense input to the high side of the sense
output of the resistance standard.
d. Connect the low side (LO) of the DMM sense input to the low side of the sense
output of the resistance standard.
2. Connect channel B of the 1281 to the 5520A as follows:
a. Connect I+ of the DMM to the high side of the current input of the 5520A.
b. Connect I- of the DMM to the low side of the current input of the 5520A.
c. Connect the high side (HI) of the DMM sense input to the high side of the sense
output of the 5520A.
d. Connect the low side (LO) of the DMM sense input to the low side of the sense
output of the 5520A.
3. Connect 525A to the 5520A as follows:
a. Connect HI INPUT 4W RTD Ω jack of the 525A to the high side of the current
input of the 5520A.
b. Connect LO INPUT 4W RTD Ω jack of the 525A to the low side of the current
input of the 5520A.
40
c. Connect the HI SENSE 4W RTD Ω jack of the 525A to the high side of the sense
output of the 5520A.
d. Connect the LO SENSE 4W RTD Ω jack of the 525A sense input to the low side
of the sense output of the 5520A.
4. Type 9 {enter} on the PC. The following will be displayed on the PC.
Input ~100 Ohms, Enter the actual value when stable:
Page 49

Calibration Adjustment
The ~100 indicates that the desired resistance is about 100 Ω. The actual resistance
is not as important as the accuracy with which the value is known.
5. Set the 5520A to source 100 Ω.
6. Using the two channels on the DMM, calculate the actual value of the 5520A’s
output. This is done by using the ratio of a known standard to the output of the
5520A. You can use the 1281 to calculate the ratio or proceed as follows.
Ratio = A/B
RA = RS/Ratio
Where:
A = The reading taken from channel A on the DMM.
B = The reading taken from channel B on the DMM.
RS = The value of the resistance standard (in this case 100 Ω).
RA = The actual output of the 5520A.
After the actual output value is entered, the PC displays the following:
Input ~200 Ohms, Enter the actual value when stable:
525A
7. Set the 5520A to source 200 Ω (nominal) and enter the actual value calculated as
described above.
Set Input ~400 Ohms, Enter the actual value when stable:
8. Set the 5520A to source 400 Ω (nominal) and enter the actual value calculated as
described above.
After the value is entered, the calibration constants will be saved and the display will
return to the main Calibration Menu.
10: SPRT 25, Adjusting SPRT Low Resistance Measure
The SPRT 25 range is used for measuring SPRTs (typically 25 Ohm R0) and Ohms from
0 to 100 Ohms in the 0-400 Ohms range. The 525A will measure a short, and 2
resistances. Refer to Table 21 for a list of equipment used in this section.
Table 21. List of Equipment for Low Ohms Measure Calibration Adjustments
Manufacturer Model Equipment
Fluke FLUKE-525A/LEADS Test lead set
Fluke 742A-100 Resistance Standard, 100 Ω
Fluke 5520A Calibrator
Wavetek 1281 DMM
1. Insert a good 4-wire short into the 525A 4W RTD Ω jacks.
2. Type 10 and press the Enter key on the PC. The following is displayed on the PC.
Input 0 Ohms, Press Enter When Stable
41
Page 50

525A
Service Manual
3. Allow a few seconds for everything to stabilize, then press the Enter key. In a few
moments the following is displayed on the PC:
Input ~50 Ohms, Enter the actual value when stable:
The ~50 indicates that the desired resistance is about 50 Ω. The actual resistance is
not as important as the accuracy with which the value is known. The method
described below uses the 1281 to establish a ratio between the 5520A output and the
742 to improve the accuracy with which 5520As output resistance is known.
4. Connect channel A of the 1281 to the Resistance Standard as follows:
1. Connect I+ of the DMM to the high side of the current input of the Resistance
Standard.
2. Connect I- of the DMM to the low side of the current input of the Resistance
Standard.
3. Connect the high side (HI) of the DMM sense input to the high side of the sense
output of the resistance standard.
4. Connect the low side (LO) of the DMM sense input to the low side of the sense
output of the resistance standard.
5. Connect channel B of the 1281 to the 5520A as follows:
a. Connect I+ of the DMM to the high side of the current input of the 5520A.
b. Connect I- of the DMM to the low side of the current input of the 5520A.
c. Connect the high side (HI) of the DMM sense input to the high side of the sense
output of the 5520A.
d. Connect the low side (LO) of the DMM sense input to the low side of the sense
output of the 5520A.
6. Connect 525A to the 5520A as follows:
a. Connect HI INPUT 4W RTD Ω jack of the 525A to the high side of the current
input of the 5520A.
b. Connect LO INPUT 4W RTD Ω jack of the 525A to the low side of the current
input of the 5520A.
c. Connect the HI SENSE 4W RTD Ω jack of the 525A to the high side of the sense
output of the 5520A.
d. Connect the LO SENSE 4W RTD Ω jack of the 525A sense input to the low side
of the sense output of the 5520A.
7. Set the 5520A to source 50 Ω.
8. Using the two channels on the DMM, calculate the actual value of the 5520A’s
output. This is done by using the ratio of a known standard to the output of the
5520A. The 1281 can be used to calculate the ratio or proceed as follows.
42
Ratio = A/B
RA = RS/Ratio
Where:
A = The reading taken from channel A on the DMM.
B = The reading taken from channel B on the DMM.
RS = The value of the resistance standard (in this case 10K).
Page 51

RA = The actual output of the 5520A.
9. After the actual output value is entered, the PC displays the following:
Input ~100 Ohms, Enter the actual value when stable:
10. Set the 5520A to source 100 Ω (nominal) and enter the actual value calculated as
described above.
After entering the value, the calibration constants will be saved and the display returns to
the main Calibration Menu.
11: TC SOURCE, Adjusting TC mVolt Source
The adjust of the TC Source output range is similar to the first part of the voltage source
calibration, the 525A outputs two Adjust points, after the output becomes stable the
values can be entered at the PC. Refer to Table 22 for a list of equipment used in this
section.
Table 22. List of Test Equipment for Adjusting TC Source
Manufacturer Model Equipment
525A
Calibration Adjustment
Fluke FLUKE-525A/LEADS Test lead set
Wavetek 1281 DMM
1. Use a copper TC mini-plug cable with low thermal EMF jacks on the other end to
connect the Calibrator to the DMM. Make certain the polarity is correct. Set the
DMM to read DC Volts.
2. Type 11 and press the Enter key on the PC. The following is displayed on the PC:
First Calibration Point. Enter the Volts displayed:
3. When the reading dis pla yed on the DMM stabi lizes, type the reading value on the PC
and press the Enter key. After the value has been entered, the following is displayed
on the PC.
Second Calibration Point. Enter the Volts displayed:
4. When the reading dis pla yed on the DMM stabi lizes, type the reading value on the PC
and press the Enter key.
After the calibration constants are saved, the Calibration Menu is displayed on the PC.
12: TC Read, Adjusting TC mVolt Measure
The adjust of the TC Source output range is similar to the first part of the voltage source
calibration, the Calibrator outputs 2 adjustment points, after the output stabilizes, the
values can be entered from PC. Refer to Table 23 for a list of equipment used in this
section.
Table 23. List of Test Equipment for Adjusting TC Read
Manufacturer Model Equipment
Fluke FLUKE-525A/LEADS Test lead set
Wavetek 1281 DMM
43
Page 52

525A
Service Manual
Use a copper TC mini-plug cable with low thermal EMF jacks on the other end to
connect the 525A to the DMM. Make certain the polarity is correct.
1. Set the DMM to read DC Volts.
2. Type 12 and press the Enter key on the PC. The following is displayed on the PC:
Adjust to -10 mV, 8 for up 2 for down, Press Enter When Stable
3. In the 10 key section of the PC keyboard, use the 8 (up arrow) to increase the output
voltage displayed or 2 (down arrow) to decrease the output voltage displayed. Keep
in mind the lag time between a change in output voltage to a stable display on the
DMM and make small changes. Wait for the reading to stabilize.
4. Adjust the output so that there is a stable -10 mV reading. When satisfied with the
reading, press the Enter key on the PC. The PC display will show:
Please Wait...
-1073806
Adjust to 15 mV, 8 for up 2 for down, Press Enter When Stable
5. The value is the raw A/D counts for this calibration point, followed by a prompt to
adjust for 15 mV. Use the 8 (up) and 2 (down) key on the PC to adjust the output so
that a reading very close to 15 mV is obtained.
6. When satisfied with the reading, press the Enter key. The PC display shows:
Please Wait...
1610975
Adjust to 40 mV, 8 for up 2 for down, Press Enter When Stable
7. The value is the raw A/D counts for this calibration point, followed by a prompt to
adjust for 40 mV. Use the 8 (up) and 2 (down) key on the PC to adjust the output so
that a reading very close to 40 mV is obtained.
8. When satisfied with the reading, press the Enter key. The PC display shows:
Please Wait...
4295762
Adjust to 65 mV, 8 for up 2 for down, Press Enter When Stable
9. The value is the raw A/D counts for this calibration point, followed by a prompt to
adjust for 65 mV. Use the 8 (up) and 2 (down) key on the PC to adjust the output so
that a reading very close to 65 mV is obtained.
10. When satisfied with the reading, press {enter}. The PC display will show:
44
Please Wait...
6980475
Adjust to 75 mV, 8 for up 2 for down, Press Enter When Stable
11. The value is the raw A/D counts for this calibration point, followed by a prompt to
adjust for 75 mV. Use the 8 (up) and 2 (down) key on the PC to adjust the output so
Page 53

Customer Replaceable Parts
that a reading very close to 75 mV is obtained. When satisfied with the reading,
press the Enter key. The PC display will show:
Please Wait...
8054372
12. After the raw A/D counts are displayed, the calibration step is complete. The
calibration constants for the range have been saved. Press the Enter key to return to
the Calibration Menu.
13: TC CJC, Adjusting TC Cold Junction Temperature
The Calibration of the TC CJC (cold junction compensation) is a critical part of the
calibration adjustment process. It is important that the thermocouple junction be allowed
to completely stabilize. Refer to Table 24 for a list of equipment used in this section.
Table 24. List of Test Equipment for Adjusting TC CJC
Manufacturer Model Equipment
Hart Scientific 1521 Precision Thermometer
Omega J Thermocouple Probe
525A
_ _ Lag Bath
__RTD Probe
The precision thermometer’s probe should already be in the lag bath along with the J
thermocouple probe.
1. Plug the mini-plug on the J thermocouple probe into the TC jack on the Calibrator.
2. Type 12 and press the Enter key on the PC. The following is displayed on the PC:
Input a Type J Thermocouple. Enter temperature when stable.
3. Allow about three minutes for all of the thermal junctions to stabilize.
4. Enter the temperature from the temperature reference. The final display should look
like the following.
Input a Type J Thermocouple. Enter temperature when stable. 377376 26.699269
1103.936911
1124.668121
0.000000
-20.731080
26.698029
5. Press the Enter key to return to the Calibration Menu.
Customer Replaceable Parts
Replacement parts are shown in Figure 14. Table 25 provides a description and part
number of each replacement part. Table 26 lists optional accessories.
45
Page 54

525A
Service Manual
32
31
9
2
29
24
7
3
22
12
21
15
16
4
28
26
30
25
20
27
5
19
23
18
5
13
14
17
33
8
1
11
10
6
46
Figure 14. Exploded View of the 525A
ajr20f.eps
Page 55

Customer Replaceable Parts
Table 25. Replacement Parts
Part
Item #
1 1601576 525A Front Panel Decal Front Of Top Chassis 1
2 1617918 Fuse Drawer Power Module 1
W3 1645311 Fuse, (1/4A), FB For 1x0 VAC Fuse Drawer 2
W4 1645327 Fuse, (1/8A), FB For 2x0 VAC Fuse Drawer 2
5 1601601 525A Output Block Front Plate 1
6 295105 Allen Head Screw Handles To Case 20
7 320093 Flathead Screw Top Cover 10
8 1601583 525A Chassis Base 1
9 1601590 525A Instrument Top Cover 1
10 886341 Chassis Handles Front/Rear Chassis 4
11 868786 Plastic Feet Bottom of Chassis 4
Number Description Location Quantity
525A
12 1601078 Programming Door Back of Chassis Base 1
13 886382 Red 5-Way Binding Post Output Block 5
14 886379 Black 5-Way Binding Post Output Block 5
15 859939 #8 Washer, Low Thermal Output Block 10
16 850334 8-32 Nut, Low Thermal Output Block 10
17 942714 Pressure Conn, Circ, 5 Socket Output Block 1
18 1601565 525A Keypad Front Of Top Chassis 1
20 1618591 Main PCA 1
20* 1642173 PEP Main PCA 1
22 1617941 Display PCA 1
23 1618617 Keypad PCA 1
24 1640190 6-32 X 3/8" Screw, Nylon, Pan, Display To Chassis 4
25 1640305 Nylock Nut 6-32 Block To Chassis 5
25 1640305 Nylock Nut 6-32 Power Module to Chassis 2
26 494641 5-20 X .312, Screw TC PCA To Output Block 2
27 110338 #6, Int Tooth Lock Washer Main PCA To Chassis 6
27 152181 6-32 X 5/8’’ Screw, Round Main PCA To Chassis 6
28 1640225 6-32 X 2-1/2" Screw, Ph Transformer To Chassis 4
29 1640202 #6 Nylon Washer Display PCA To Chassis 4
29 1640202 #6 Nylon Washer Transformer 4
30 1618600 TC PCA 1
47
Page 56

525A
Service Manual
Table 25. Replacement Parts (continued)
Part
Item #
31 1617929 Power Module Back Of Chassis 1
32 1617907 Voltage Selector Power Module 1
33 1638939 Opto RS232 PCA Back of Chassis 1
Not shown 271973 .1uf/250V Cap., Polyester Output Block 1
Not shown 1617866 14 Cond Ribbon Cable J4 To Display 1
Not shown 1617882 5 Cond Ribbon Cable Lemo PCA To Main PCA 1
Not shown 1627364 12 Cond Ribbon Cable J11 To Keypad PCA 1
34 1640331 Pressure-Lemo PCB Lemo Connector 1
Not shown 172080 Cable Tie, 4’’ 4
Not shown 1618621 Line Cord, 3 COND 1
Not shown 110338 #6, Int Tooth Lock Washer Keypad PCA to Chassis 5
Number Description Location Quantity
Not shown 152165 #6 X 3/8" Screw, PH Keypad PCA to Chassis 5
Not shown 152165 #6 X 3/8" Screw, PH Power Module to Chassis 2
Not shown 152165 #6 X 3/8" Screw, PH Program Door to Chassis 1
Not shown 721266 Lug, Closed, Round, #8 Stud Output Block 11
Not shown 110619 1/4"-28 Nut Ground Lug Stud 2
Not shown 448092 Jack Screw RS232 Conn 9 Pin D-Sub 1
Not shown 110338 1/4" Int Tooth Lock Washer Binding Post Stud 2
Not shown 102889 Binding Head Thumbscrew Binding Post Stud 1
Not shown 102707 Binding Post Jack Chassis Back 1
Not shown 1601541 525A Getting Started Guide 1
Not shown 1601552 525A User Manual (on CD) 1
W For safety, use exact replacement only.
* PEP is an exchange of a repairable assembly for a factory repaired one.
Table 26. Accessories
Description Part Number
Fluke 525A/LEAD, Lead wire set 1616018
48
Fluke Y525 Rack Mount Kit 1622027
RS43, RS232 Null Modem Cable 946470
525A Service Manual 1644492
 Loading...
Loading...