Page 1

INSTALLATIONGUIDE
FLIR
ORYX®
Version 1.0
Revised 10/27/2017
Copyright © 2017 FLIR Integrated Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
Page 2
FCC Compliance
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This
device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesirable operation.
Korean EMCCertification
The KCC symbol indicates that this product complies with Korea’s Electrical Communication Basic Law regarding
EMC testing for electromagnetic interference (EMI) and susceptibility (EMS).
Hardware Warranty
The warranty for the Oryx camera is 3 years. For detailed information on how to repair or replace your camera,
please see the terms and conditions on our website.
Export Control
The ECCN for this product is EAR099.
WEEE
The symbol indicates that this product may not be treated as household waste. Please ensure this
product is properly disposed as inappropriate waste handling of this product may cause potential
hazards to the environment and human health. For more detailed information about recycling of this
product, please contact us.
Trademarks
Names and marks appearing on the products herein are either registered trademarks or trademarks of FLIR
Systems, Inc. and/or its subsidiaries.
Licensing
To view the licenses of open source packages used in this product please see What open source packages does
firmware use?
Copyright © 2017 FLIR Integrated Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
Page 3

Table of Contents
1 Oryx Installation Guide 1
2 Handling Precautions and Camera Care 2
3 Oryx Installation 3
3.1 Preparing for Installation 3
3.2 Installing Your Interface Card and Software 4
3.3 Installing Your Oryx 5
3.4 Powering Your Oryx 6
4 Tools to Control the Oryx 7
4.1 Using the Spinnaker® Software Development Kit 7
4.1.1 SpinView Camera Evaluation Application 7
4.1.2 Custom Applications Built with the Spinnaker API 7
4.2 Using GenICam Applications 8
5 Configuring Oryx Setup 9
5.1 Configuring Camera Driver 9
5.2 Configuring the IP Address 11
5.3 Allocating Bandwidth 11
5.3.1 Determining Bandwidth Requirements 11
5.4 Configuring Other Ethernet Settings 12
5.4.1 Stream Channel Destination Address 12
5.4.2 Heartbeat 13
5.5 Camera Firmware 14
5.5.1 Determining Firmware Version 14
5.5.2 Upgrading Camera Firmware 14
6 Oryx Physical Interface 15
6.1 Oryx Physical Description 15
6.2 Oryx Dimensions 16
6.3 Interface Connector 16
6.3.1 Ethernet Connector 16
6.3.2 Interface Cables 16
6.3.3 Interface Card 17
6.3.4 General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) 17
6.4 Mounting 19
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide i
Page 4

6.5 Case Temperature and Heat Dissipation 19
6.6 Lens Mounting 20
6.6.1 Back Flange Distance 20
6.7 Non-Volatile Flash Memory 21
6.8 Dust Protection 21
6.9 Infrared Cut-Off Filters 22
7 Input/Output Control 23
7.1 General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) 23
7.2 GPIO Electrical Characteristics 25
7.2.1 Output Timing Characteristics 28
7.2.2 Input Timing Characteristics 29
8 Troubleshooting 30
8.1 Support 30
8.2 Status Indicator LED 31
8.2.1 Network Status LEDs 31
Contacting Us 32
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide ii
Page 5
1 Oryx Installation Guide
Welcome to the Oryx camera. We offer a number of resources to assist you with the Oryx.
n Release Notes—information about the current firmware release including feature additions or changes,
bug fixes, and known issues.
n Specifications—information about the camera model as it performs with the current firmware.
n Getting Started—quick start guide for installing the camera and software.
n Installation Guide—information about installing the camera and SDK, the physical interface and
mechanical properties, troubleshooting and how to get help. This document is available as a PDF for
download or as a webpage included in the firmware release package.
n Technical Reference—information about the features supported by the camera model with the current
firmware, including: image format control, acquisition control, sequencing, binning/decimation, and others.
This document is available as a PDF for download or as a webpage included in the firmware release
package.
1 Oryx Installation Guide
n Firmware—programming inserted into the programmable ROM of the camera that can be updated in-field.
New firmware packages are available for download and include both the firmware file and documentation.
n Spinnaker SDK—software development kit that provides GenICam-compliant controls to create
applications for the camera. Spinnaker is available for download. Each installation includes API
documentation for C, C++, and C#.
Our website provides additional information in our Knowledge Base and Technical Application Note library. As
well, the Downloads site is the portal to access documentation and firmware updates.
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 1
Page 6

2 Handling Precautions and Camera Care
2 Handling Precautions and Camera Care
Warning! Do not open the camera housing. Doing so voids the
Hardware Warranty described in the Terms and Conditions on
our website.
Your FLIR digital camera is a precisely manufactured device and should be handled with care. Here are some tips
on how to care for the device.
n Avoid electrostatic charging.
n When handling the camera unit, avoid touching the lenses. Fingerprints will affect the quality of the image
produced by the device.
n To clean the lenses, use a standard camera lens cleaning kit or a clean dry cotton cloth. Do not apply
excessive force.
n Extended exposure to bright sunlight, rain, dusty environments, etc. may cause problems with the
electronics and the optics of the system.
n Avoid excessive shaking, dropping or any kind of mishandling of the device.
Related Knowledge Base Articles
Title Article
Cleaning the imaging surface of your
camera
Knowledge Base Article
10243
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 2
Page 7

3 Oryx Installation
3.1 Preparing for Installation
What system configuration is recommended?
3 Oryx Installation
Recommended
System
Configuration
Operating
System
Windows7,
Windows8, or
Windows10
(32- or 64-bit)
CPU RAM Ports
Intel i5
8 GB
(dual
channel
memory)
FLIRACC-01-1101—
NBASE-T Ethernet
PCI Express 2.0 x4,
1 port, Tehuti TN4010
Software to run /
compile example code
Microsoft Visual Studio 2010,
Visual Studio 2013, or
Visual Studio 2015
Do you have all the parts you need?
To install your camera you will need the following components:
n Ethernet cable (see Interface Cables)
n GPIOcable (see General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO))
n C-mount Lens (see Lens Mounting )
n Interface card (see Interface Card)
FLIR sells a number of the additional parts required for installation. To purchase, visit our Accessories page.
Do you have a downloads account?
Our downloads page has many resources to help you operate your camera effectively, including:
n Spinnaker SDKsoftware, including drivers (required for installation)
n Firmware updates and release notes
n Dimensional drawings and CADmodels
n Documentation
To access the software and firmware downloads you must have a downloads account.
1. Go to the FLIR website.
2. In the upper right corner, click Register.
3. Complete the form, then click Register.
After you submit your registration, you will receive an email with instructions on how to activate your account.
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 3
Page 8
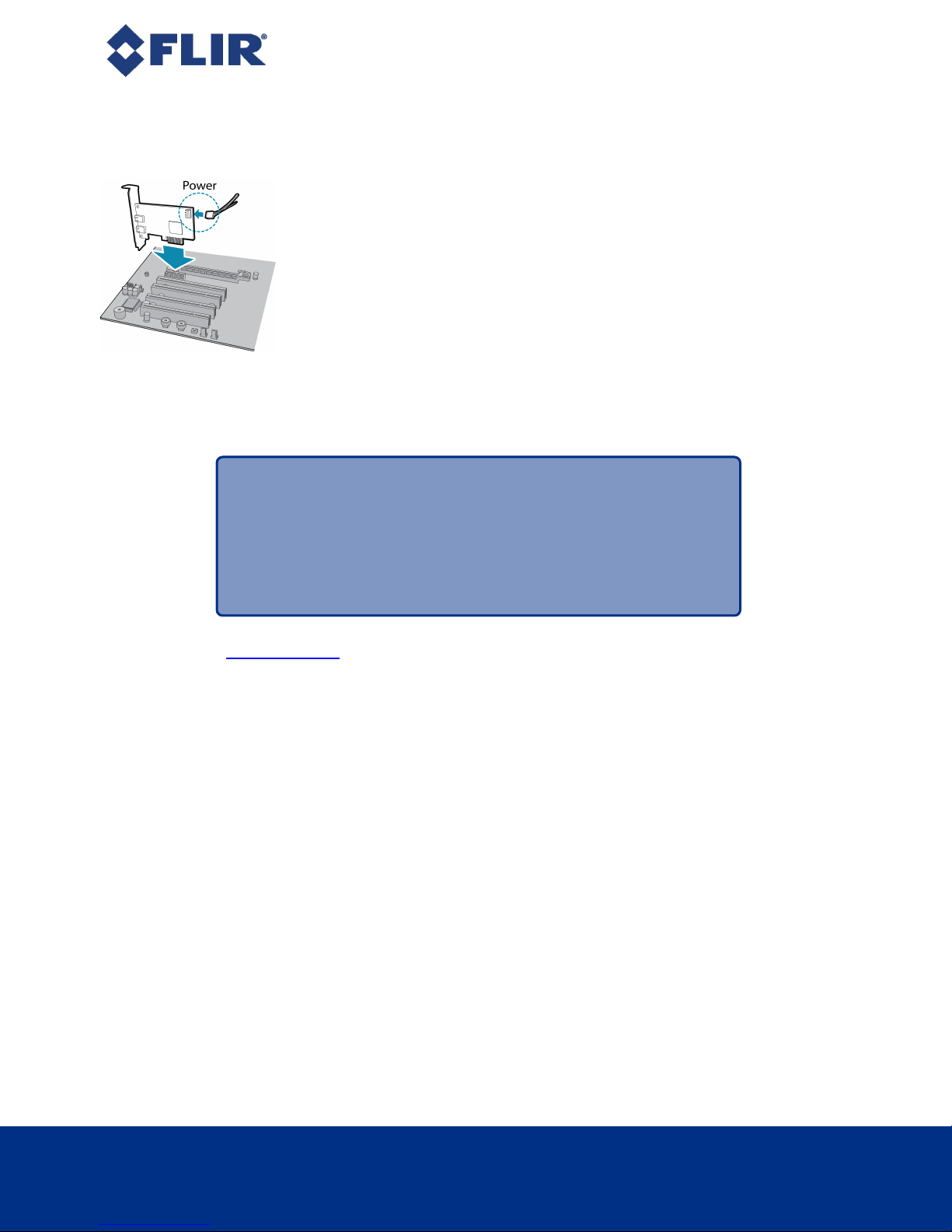
3.2 Installing Your Interface Card and Software
1. Install your Interface Card
Ensure the card is installed per the manufacturer's instructions.
Connect the internal IDE or SATApower connector on the card to the computer power
supply.
Alternatively, use your PC's built-in host controller, if equipped.
Open the Windows Device Manager. Ensure the card is properly installed. Ethernet cards appear under Network
Adapters. An exclamation point (!) next to the card indicates the driver has not yet been installed.
2. Install the Spinnaker® Software
Note: For existing users who already have Spinnaker installed,
we recommend ensuring you have the latest version for optimal
performance of your camera. If you do not need to install
Spinnaker, use SpinView to install and enable drivers for your
card.
3 Oryx Installation
a. Login to the Downloads page.
b. Select your Product Family, Camera Model and Operating System from the drop-down lists.
c. Click on the Software search results to expand the list.
d. Click the appropriate link to begin the download and installation.
After the download is complete, the Spinnaker setup wizard begins. If the wizard does not start automatically,
double-click the .exe file to open it. Follow the steps in each setup dialog.
3. For Ethernet cards: Enable jumbo frames
a. In Start->All Programs-> Point Grey Spinnaker SDK->SpinView, right click on the Network Adapter
and select Adapter Configuration, then select IP Configuration.
b. Click Open Network Connections.
c. Click Change Settings.
d. Click on the Advanced tab and from the Settings list select Jumbo Packet.
e. Set the Value to 9014 Bytes and click OK.
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 4
Page 9
3.3 Installing Your Oryx
1. Attach a Lens
Unscrew the dust cap from the lens holder to install a lens.
2. Connect the interface Card and Cable to the Camera
Plug the interface cable into the host controller card and the camera. The cable jack
screws can be used for a secure connection.
When the camera is first connected, the operating system automatically installs the camera driver. Camera
drivers are available with the Spinnaker SDK installation.
3. Plug in the GPIO connector
GPIOis used for power, trigger, and strobe.
4. Configure IPSettings
By default, a dynamic IPaddress is assigned to the camera according to the DHCP protocol. If DHCP addressing
fails, a link-local address is assigned. If necessary, change the IPaddress of the camera to be on the same subnet
as the NIC.
3 Oryx Installation
5. Confirm Successful Installation
Run the SpinView application: Start->All Programs-> Point Grey Spinnaker->SpinView
The SpinView application can be used to test the camera's image acquisition capabilities.
Changes to your camera's installation configuration can be made using the SpinView application.
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 5
Page 10

3.4 Powering Your Oryx
Power is provided externally through the GPIO interface: 12 - 24 V. Power consumption is 15W maximum, 11 W
nominal.
The camera does not transmit images for the first 100 ms after power-up. The auto-exposure and auto-white
balance algorithms do not run while the camera is powered down. It may therefore take several images to get a
satisfactory image.
When the camera is power cycled (power disengaged then re-engaged), the camera reverts to its default factory
settings, or if applicable, a saved user set.
3 Oryx Installation
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 6
Page 11

4 Tools to Control the Oryx
4 Tools to Control the Oryx
The Oryx's features can be accessed using various controls, including:
n Spinnaker SDK including API examples
n SpinView camera evaluation application, included in the Spinnaker SDK installation
n Third-party GenICam applications
4.1 Using the Spinnaker®Software Development Kit
You can monitor or control features of the camera through Spinnaker API examples provided in the Spinnaker SDK,
or through the SpinView camera evaluation application. A Programmer's Guide and API Reference is included in
the installation.
4.1.1 SpinView Camera Evaluation Application
The SpinView application is a generic, easy-to-use streaming image viewer included with the Spinnaker SDK that
can be used to test many of the capabilities of your camera. It allows you to view a live video stream from the
camera, save individual images, adjust the various attributes, frame rates, features and settings of the camera. It
includes tools for updating firmware, managing drivers, IP addressing, and activity logging.
4.1.2 Custom Applications Built with the Spinnaker API
The Spinnaker SDK includes a full Application Programming Interface that allows you to create custom
applications to control your camera. Included with the SDK are a number of source code examples to help you get
started.
Spinnaker API examples are provided for C, C++, C#, and VB.NET languages. These examples are precompiled
for your convenience.
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 7
Page 12

4.2 Using GenICam Applications
GigE Vision is an interface standard that allows for fast image transfer over Ethernet networks. All cameras
supporting GigE Vision interact the same way with software also supporting GigE Vision.
For more information on the standard, visit visiononline.org.
The standard defines required elements for camera identification, control, and output. It uses GenICam, a
programming interface for camera attribute control. GenICam allows camera vendors to define features and
attributes in an XML file stored inside the camera. The file is parsed by the host application when the camera is
initially discovered. One of the key benefits of GenICam is the ability for camera vendors to introduce new
camera-specific features without needing to update the host application.
Each camera attribute, such as exposure time, is controlled by a specific GenICam feature. The camera includes
an XML device description file for interfacing with third-party GenICam-compliant APIs.
For more information on GenICam, visit emva.org.
Getting Started with Third-Party Applications Resources
Title Article
Getting Started with OpenCV
4 Tools to Control the Oryx
Technical Application Note
10861
Getting Started with MATLAB
Getting Started with MVTec HALCON
Getting Started with Cognex VisionPro
Getting Started with Adaptive Vision
Getting Started with Matrox Imaging Library
Getting Started with Matrox Design Assistant
Getting Started with NI-MAX and LabVIEW
Getting Started with NI Vision Builder for Automatic Inspection
Technical Application Note
10898
Technical Application Note
10793
Technical Application Note
10794
Technical Application Note
10865
Technical Application Note
10790
Technical Application Note
10862
Technical Application Note
10791
Technical Application Note
10875
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 8
Page 13

5 Configuring Oryx Setup
After successful installation of your camera and interface card, you can make changes to the setup. Use the tools
described below to change the IP Address or the driver for your interface card.
For information on updating your camera's firmware post installation, see Camera Firmware.
5.1 Configuring Camera Driver
For the Oryx camera, ensure that PGRLWF driver version 2.7.3.92 or above is installed.
The PGRLWF driver should already be installed automatically using the Spinnaker SDK installer when the Camera
Evaluation option is selected. Or in the case of Application Development option, the driver is installed if you select
the GigE Driver checkbox.
Alternatively, you can manually install the driver. The PGRLWF files are located in:
C:\Program Files\Point Grey Research\Spinnaker\driver64
To verify your driver:
5 Configuring Oryx Setup
1. Launch SpinView:
Start-->All Programs-->Point Grey-->Spinnaker SDK-->SpinView
2. Select the camera.
3. In the Feature tree search box, enter "driver". The Device Driver Version feature is highlighted.
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 9
Page 14

5 Configuring Oryx Setup
4. If you need to update the driver, right-click on the device and select Filter Driver Configuration.
5. In the Filter Driver Configuration window, ensure the driver is installed and enabled. Click Refresh if making
changes.
Note: If the filter driver is not installed, a caution icon appears
next to the device. Right-click on the device and select
GigEFilter driver is not installed-->Install filter driver to resolve.
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 10
Page 15

5.2 Configuring the IP Address
When a new GigE camera is first powered and initialized, a dynamic IP address is assigned to the camera
according to the DHCP protocol. If DHCP addressing fails, a link-local address is assigned. You can configure the
IP address using the GenICam Features Transport Layer Control.
Alternatively, SpinView is a tool included with the Spinnaker SDK that allows you to set the internet protocol (IP)
configuration for any GigE interface cards or FLIR GigE Vision cameras connected to your system. Using
SpinView, you can:
n Set the IP address for the current connection.
n Program a persistent IP address for the camera.
n Configure the default IP addressing behavior of the camera on startup using a persistent IP, DHCP or LLA.
n Enable Jumbo Frames on the GigE NIC.
Both your camera and host adapter must have an IP address on the same subnet. This can be assigned in three
ways:
n Persistent—The camera has a fixed IP address that does not change. Generally the address is within a
closed network range of 192.168.X.X.
5 Configuring Oryx Setup
n Dynamic (DHCP)—The camera is set to automatically obtain an IP address. This means that the IP
address may change (within a range) every time the camera or computer is restarted. It may take up to one
minute for the IP address to resolve and the camera to enumerate.
n Default (LLA)—The camera uses an IP address from the link-local address block 169.254.x.x.
The camera assigns its current IP address in the following sequence:
1. Persistent—Uses the defined IP address. If not available, then;
2. DHCP—Attempts to find a dynamic IP address. If not available, then;
3. LLA—Uses an LLA IP address.
SpinView can automatically force an IP address refresh. This detects the IP address of the Network Interface card
and automatically sets the camera’s IP address relative to the card.
To open SpinView:
Start Menu > All Programs > Point Grey Spinnaker SDK > SpinView
5.3 Allocating Bandwidth
The User Datagram Protocol (UDP) used by the GigE Vision standard provides no guaranteed transmission or
fixed timing mechanism. Therefore, bandwidth must be managed by the Device Throughput Limit, based on
desired resolution and frame rate.
5.3.1 Determining Bandwidth Requirements
The maximum bandwidth available is 1.25 GB. This includes image data, control data and image resends, which
occur when frames are being dropped. Each image and each packet has a certain amount of overhead that will
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 11
Page 16

5 Configuring Oryx Setup
use some bandwidth. Therefore, when calculating your bandwidth requirements, you should not attempt to use
the full maximum of 1.25 GB. The default bandwidth is 850 MB.
Note: If the packet size and packet delay combination exceeds
the available bandwidth, frames will be dropped.
To calculate your bandwidth requirements:
Determine your required resolution, frame rate, and pixel format (bytes per pixel)
(Height x Width x Frame Rate x Bytes per Pixel)/1000000 = Bandwidth in MB
For example, for an image that is 4K resolution, 60 FPS, Mono8:
3840 (H) x 2160 (W) x 60 (FPS) x 1 (BPP) = ~497 MB
Once you have calculated your required bandwidth, you can allocate an amount to each camera by adjusting the
packet size and packet delay. Allocating a specific amount to each camera helps to avoid dropped packets due to
a data burst. You would do this in a set up with multiple cameras, or in a situation where the system bandwidth
might be limited or shared due to hardware architecture.
Bandwidth Requirements for Multiple Cameras
Multiple cameras can be set up in two ways: 1) Each camera is connected directly to a single Ethernet port; or, 2)
multiple cameras are connected to a single port through an Ethernet switch.
If using the first method, each camera has the full bandwidth allocation available to it. If using the second method,
the combination of all cameras on a switch cannot exceed the available bandwidth.
Related Knowledge Base Articles
Title Article
Setting Up Multiple GigECameras
Technical Application Note 10351
5.4 Configuring Other Ethernet Settings
5.4.1 Stream Channel Destination Address
The stream channel destination address (SCDA) register is used to specify the streaming destination IP address.
The default SCDA is the IPaddress of the network or computer to which the camera is connected. It can be set
within a range so that the camera sends data as a multicast. As long as switches in the path between the sender
and receivers support and are configured for multicasting, multiple receivers can listen to the data stream from the
camera.
Multicast addresses are between 224.0.0.0 and 239.255.255.255.
Note: For more information on multicast address assignments,
see http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3171
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 12
Page 17

To control SCDA use:
n GenICam—GevSCDA in the Transport Layer Control
5.4.2 Heartbeat
The heartbeat is a mandatory GigE Vision feature to monitor the connection between an application and the
camera. The application must continually reset the heartbeat timer, or the camera assumes an error has occurred
and shuts down the connection.
In general, the Spinnaker API manages the heartbeat at a low level; however the following two features are
controllable: Heartbeat Timeout and Heartbeat Disable.
Heartbeat Timeout
Heartbeat timeout is the time, in milliseconds, that the camera waits before closing the connection. Heartbeat
timeout can be set between 500 ms and 10 seconds. The default setting is 3000 ms (3 seconds). If there is no
communication between the camera and the application for longer than the timeout value, the connection is shut
down.
To control Heartbeat Timeout use:
n GenICam—Under Transport Layer Control, GevHeartbeatTimeout.
5 Configuring Oryx Setup
n Spinnaker API—The Spinnaker SDK supports configuring heartbeat timeout.
Heartbeat Disable
The heartbeat is enabled by default.
To disable Heartbeat use:
n GenICam—Under Transport Layer Control GevGVCPHeartbeatDisable.
n Spinnaker API—The Spinnaker SDK supports disabling heartbeat.
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 13
Page 18

5.5 Camera Firmware
Firmware is programming that is inserted into the programmable read-only memory (programmable ROM) of
most FLIR cameras. Firmware is created and tested like software. When ready, it can be distributed like other
software and installed in the programmable read-only memory by the user.
The latest firmware versions often include significant bug fixes and feature enhancements. To determine the
changes made in a specific firmware version, consult the Release Notes.
Firmware is identified by a version number, a build date, and a description.
5.5.1 Determining Firmware Version
To determine the firmware version number of your camera:
n Query the GenICam Device Control feature DeviceFirmwareVersion.
5.5.2 Upgrading Camera Firmware
Camera firmware can be upgraded or downgraded to later or earlier versions using SpinView, part of the Spinnaker
SDK available from the Downloads page.
5 Configuring Oryx Setup
Before upgrading firmware:
n Install the Spinnaker SDK, available from the Downloads page.
n Download the firmware file from the Downloads page.
To upgrade the firmware:
1.
Start Menu-->All Programs-->Point Grey Spinnaker SDK-->SpinView
2. From the Device list, right click the camera and select Update Device Firmware.
If you get a Device is Active warning, close the Display pane or click the Disconnect button and right click
the camera again.
3. Browse to select the firmware file and click Open.
4. Click Yes to continue.
Warning! Do not disconnect the camera during the firmware
update process.
Related Knowledge Base Articles
Title Article
FLIR software and firmware version numbering scheme/standards
Knowledge Base Article 10310
Determining the firmware version used by my camera
Should I upgrade my camera firmware or software?
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
Knowledge Base Article 10312
Knowledge Base Article 10216
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 14
Page 19

6 Oryx Physical Interface
6.1 Oryx Physical Description
6 Oryx Physical Interface
1. Lens holder (C-mount)
See Lens Mounting
2. Glass/IR filter system
See Dust Protection and Infrared Cut- Off
Filters
3. M4.OXO.7 mounting holes (x16)
SeeMounting
4. General purpose I/O connector
See General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
5. Status LED
See Status Indicator LED
6. Interface connector
See Interface Connector
7. Camera label
Contains camera information such as model
name, serial number and required
compliance.
8. 1/4-20 mounting hole
SeeMounting
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 15
Page 20

6.2 Oryx Dimensions
Note: To obtain 3D models, go to our Downloads page or
contact Support.
6 Oryx Physical Interface
6.3 Interface Connector
6.3.1 Ethernet Connector
The 8-pin RJ- 45 Ethernet jack is equipped with two (2) M2 screwholes for secure connection. Pin assignments
conform to the Ethernet standard.
6.3.2 Interface Cables
To purchase a recommended cable from FLIR, visit the Products Accessories page.
Category 5e cables up to 40 meters in length can be used with 10 GigE. For cable lengths greater than 40 meters,
Category 6a cables should be used. FLIR sells Category 5e cables.
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
Oryx Dimensional Drawing
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 16
Page 21

Note: For optimal ESD protection, we recommend using a
shielded Ethernet cable or connecting the camera housing to
chassis ground (earth).
6.3.3 Interface Card
The camera must connect to an interface card. This is sometimes called a host adapter, a bus controller, or a
network interface card (NIC).
A 10G BASE-T NIC is recommended for streaming images on the Ethernet network between the camera and host
system.
FLIR sells a compatible card (PN: ACC-01-1101) available from our Products Accessories page.
6.3.4 General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
The camera has an 12-pin GPIO connector on the back of the case; refer to the diagram below for wire colorcoding.
6 Oryx Physical Interface
Color Pin Line Function Description
Black
White
Red
Green
Orange
Blue
White with black
stripes
Red with black
stripes
Green with black
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
1 N/A GND DCcamera power ground
2 N/A POWER DCcamera power
Line
3
1
Line
4
4
Line
5
0
Line
6
3
Line
7
2
Line
8
5
9 N/A GND DC camera power ground
GPIO_OPT_OUT1 Opto-isolated output (GPO1)
GPIO_OPT_OUT2 Opto-isolated output (GPO2)
GPIO_OPT_IN1 Opto-isolated input (GPI1)
GPIO_OPT_IN2 Opto-isolated input (GPI2)
GPIO_TTL_IO3 TTL input/output 3
GPIO_TTL_IO4 TTL input/output 4
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 17
Page 22

Color Pin Line Function Description
stripes
6 Oryx Physical Interface
Orange with
black stripes
Blue with black
stripes
Black with white
stripes
10 N/A POWER DC camera power
Line
11
3.3 VOUTPUT
6
12 N/A OPTO_GND
+3.3 V output, current 120 mA (nominal) - firmware
enabled
Ground for opto-isolated I/O, not connected to camera
ground
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 18
Page 23

6.4 Mounting
The case is equipped with the following mounting holes:
n Four (4) M4.0 x 0.7 mounting holes on each side of the case
n One (1) 1/4-20 UNC mounting hole on the bottom of the case
6.5 Case Temperature and Heat Dissipation
You must provide sufficient heat dissipation to control the internal operating temperature of the camera.
The camera is equipped with an on-board temperature sensor. It allows you to obtain the temperature of the
camera board-level components. The sensor measures the ambient temperature within the case.
As a result of packing the camera electronics into a small space, the outer case of the camera
can become hot to the touch when running. This is expected behavior and will not damage the
camera electronics.
To reduce heat, use a cooling fan to set up a positive air flow around the camera, taking into consideration the
following precautions:
6 Oryx Physical Interface
n Mount the camera on a heat sink, such as a camera mounting bracket, made out of a heat-conductive
material like aluminum.
n Make sure the flow of heat from the camera case to the bracket is not blocked by a non-conductive
material like plastic.
n Make sure the camera has enough open space around it to facilitate the free flow of air.
To access temperature information:
n Query the GenICam Device Control feature DeviceTemperature.
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 19
Page 24

6.6 Lens Mounting
Lenses are not included with individual cameras.
Related Knowledge Base Articles
Title Article
Selecting a lens for your
camera
The lens mount is compatible with C-mount lenses. Correct focus cannot be achieved using a CS-mount lens on a
C-mount camera.
6.6.1 Back Flange Distance
The Back Flange Distance (BFD) is offset due to the presence of both a 1 mm infrared cutoff (IRC) filter and a 0.5
mm sensor package window. These two pieces of glass fit between the lens and the sensor image plane. The IRC
filter is installed on color cameras. In monochrome cameras, it is a transparent piece of glass. The sensor
package window is installed by the sensor manufacturer. Both components cause refraction, which requires
some offset in flange back distance to correct.
The resulting C-mount BFDis 17.99 mm.
6 Oryx Physical Interface
Knowledge Base Article 10694
For more information about the IRC filter, see Infrared Cut-Off Filters.
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 20
Page 25

6.7 Non-Volatile Flash Memory
The camera has 4 MB non-volatile memory for users to store data.
Related Knowledge Base Articles
Title Article
Storing data in on-camera flash memory
6.8 Dust Protection
The camera housing is designed to prevent dust from falling directly onto the sensor's protective glass surface.
This is achieved by placing a piece of clear glass (monochrome camera models) or an IR cut-off filter (color
models) that sits above the surface of the sensor's glass. A removable plastic retainer keeps this glass/filter
system in place. By increasing the distance between the imaging surface and the location of the potential dust
particles, the likelihood of interference from the dust (assuming non-collimated light) and the possibility of damage
to the sensor during cleaning is reduced.
6 Oryx Physical Interface
Knowledge
Base
Article
10370
Warning! Cameras are sealed when they are shipped. To avoid
contamination, seals should not be broken until cameras are
ready for assembly on site.
Warning! Use caution when removing the protective glass or
filter. Damage to any component of the optical path voids the
Hardware Warranty. Removing the protective glass or filter alters
the optical path of the camera, and may result in problems
obtaining proper focus with your lens.
Related Knowledge Base Articles
Title Article
Removing the IR filter from a color camera
Selecting a lens for your camera
Knowledge
Base
Article
10080
Technical
Application
Note
10694
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 21
Page 26

6.9 Infrared Cut-Off Filters
FLIR color camera models are equipped with an additional infrared (IR) cut- off filter. This filter can reduce
sensitivity in the near infrared spectrum and help prevent smearing. The properties of this filter are illustrated in the
results below.
IR filter transmittance graph
6 Oryx Physical Interface
Transmission Wavelength
T=50%
T>80%
T>85%
T average 1%
T<3%
680 nm ±10 nm
400 nm - 420 nm
420 nm - 650 nm
750 nm - 1100 nm
750 nm - 1100 nm
In monochrome models, the IR filter is replaced with a transparent piece of glass.
The following are the properties of the IR filter/protective glass:
Type
Material
Dimensions
Thickness
Anti-reflective
Schott B270
15.5 ±0.08 x 18 ±0.08
mm
1 ±0.07 mm
For more information, see Dust Protection.
Related Knowledge Base Articles
Title Article
Removing the IR filter from a color camera
Knowledge Base Article 10080
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 22
Page 27

7 Input/Output Control
7.1 General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
The camera has an 12-pin GPIO connector on the back of the case; refer to the diagram below for wire colorcoding.
GPIO pin assignments (as shown looking at rear of camera)
7 Input/Output Control
Color Pin Line Function Description
Black
White
Red
Green
Orange
Blue
White with black
stripes
Red with black
stripes
Green with black
stripes
Orange with
black stripes
1 N/A GND DCcamera power ground
2 N/A POWER DCcamera power
Line
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 N/A GND DC camera power ground
10 N/A POWER DC camera power
GPIO_OPT_OUT1 Opto-isolated output (GPO1)
1
Line
GPIO_OPT_OUT2 Opto-isolated output (GPO2)
4
Line
Line
Line
Line
GPIO_OPT_IN1 Opto-isolated input (GPI1)
0
GPIO_OPT_IN2 Opto-isolated input (GPI2)
3
GPIO_TTL_IO3 TTL input/output 3
2
GPIO_TTL_IO4 TTL input/output 4
5
Blue with black
stripes
Black with white
stripes
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
Line
11
6
12 N/A OPTO_GND
3.3 VOUTPUT
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 23
+3.3 V output, current 120 mA (nominal) - firmware
enabled
Ground for opto-isolated I/O, not connected to camera
ground
Page 28

For details on GPIO circuits, see GPIO Electrical Characteristics.
7 Input/Output Control
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 24
Page 29

7.2 GPIO Electrical Characteristics
Both the opto-isolated input and output have over current protection.
The output is open collector and thus requires a pull-up resistor to operate. The rise time and bias current will be
determined by the resistor value chosen. If the camera is generating an output signal that approaches the rise time
plus the fall time of the opto-isolated circuit, care must be taken to optimize the pull-up resistor chosen to minimize
the rise time while still remaining within the current limits of the output circuit.
The opto-isolated specifications listed below are applicable when power to the camera is provided through the
interface and not through the GPIO.
Warning! To avoid damage, connect the OPTO_GND pin first
before applying voltage to the GPIO line.
Warning! Prolonged use of the camera outside of the Operating
Range described below may lead to unexpected behavior and
should be avoided.
7 Input/Output Control
Operating Range
Description Minimum Maximum
Non-opto-isolated Voltage 0 V 24 V
Opto-isolated Input Voltage 0 V 30 V
Opto-isolated Output Voltage 0 V 24 V
Non-opto-isolated Sinking Current 25 mA
Opto-isolated Output Current 25 mA
3.3 V Output Curr ent 200 mA
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Description Minimum Maximum
Non-opto-isolated Voltage -24 V 42 V
Opto-isolated Input Voltage -70 V 40 V
Opto-isolated Output Voltage -24 V 24 V
External Voltage Resistor Combinations at 90 FPS
External
Voltage
3.3 V 200 Ω 1.44 V 3.29 V 8.2 mA
5.0 V 1.0 kΩ 0.88 V 4.94 V 3.8 mA
External
Resistor
OPTO_OUT
Low Voltage
OPTO_OUT
High Voltage
Output Current
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 25
Page 30

7 Input/Output Control
External
Voltage
12 V 2.0 kΩ 1.1 V 11.93 V 5.1 mA
12 V 2.4 kΩ 0.98 V 11.93 V 4.2 mA
24 V 4.7 kΩ 0.75 V 23.75 V 4.5 mA
30 V 4.7 kΩ 0.88 V 29.81 V 5.7 mA
Values are for reference only
External
Resistor
OPTO_OUT
Low Voltage
OPTO_OUT
High Voltage
Output Current
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
Opto-isolated input circuit
Opto-isolated output circuit
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 26
Page 31

7 Input/Output Control
Input/Output circuit
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 27
Page 32

7.2.1 Output Timing Characteristics
Note: Timing specifications are preliminary and subject to
change.
7 Input/Output Control
Output Timing Characteristics
Opto-isolated Output Performance at (measured at Vcc = 5 V, Rext = 1 kΩ)
Parameter Symbol Opto-isolated at 1 FPS Opto-isolated at 90 FPS
Output Low Voltage V
Output High Voltage V
Output Threshold High Voltage V
Output Threshold Low Voltage V
Cycle Rise Time t
Cycle Fall Time t
Opto Current 3.8 mA 3.8 mA
Opto Isolator Delay(High to Low) 2.92 µs 2.92 µs
Opto Isolator Delay(Low to High) 24.2 µs 24.2 µs
L
H
THH
THL
R
F
0.84 V 0.83 V
4.98 V 4.98 V
4.56 V 4.56 V
1.25 V 1.24 V
7.9 µs 7.8 µs
2.1 µs 1.44 µs
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 28
Page 33

7.2.2 Input Timing Characteristics
Note: Timing specifications are preliminary and subject to
change.
7 Input/Output Control
Input Timing Characteristics (Vcc = 5 V pk-pk)
Parameter Symbol Opto-isolated at 5 FPS
Input Low Voltage V
Input High Voltage V
Propagation Delay Low to High t
Propagation Delay High to Low t
Minimum PositivePulse Width t
Minimum Negative Pulse Width t
MPPW
MNPW
IL
IH
PDLH
PDHL
≤0.825 V
≥2.325 V
7.7 µs
16.2 µs
0.772 ms
32.56 ms
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 29
Page 34

8 Troubleshooting
8.1 Support
FLIR endeavors to provide the highest level of technical support possible to you. Most support resources can be
accessed through our Product Support page.
Creating a Customer Login Account
The first step in accessing our technical support resources is to obtain a Customer Login Account. This requires a
valid name and e-mail address. To apply for a Customer Login Account go to our website, and from the upper right
corner, click Register. Complete the form and then click Register. After you submit your registration, you will
receive an email with instructions on how to activate your account.
Knowledge Base
Our Knowledge Base contains answers to some of the most common support questions. It is constantly updated,
expanded, and refined to ensure that our customers have access to the latest information.
Learning Center
8 Troubleshooting
Our Learning Center contains links to many resources including videos, case studies, popular topics, application
notes, and information on sensor technology.
Product Downloads
With a Customer Login Account you can access the latest software and firmware for their cameras from our
Product Downloads page. We encourage you to keep your software and firmware up-to-date by downloading and
installing the latest versions.
Contacting Technical Support
Before contacting Technical Support, have you:
1. Read the product documentation?
2. Searched the Knowledge Base?
3. Downloaded and installed the latest version of software and/or firmware?
If you have done all the above and still can’t find an answer to your question, contact our Technical Support team.
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 30
Page 35

8.2 Status Indicator LED
LED GigE
No Light
8 Troubleshooting
No power
or LED is in inactive state
or LED is in error status state with no error
Blinking Green (1 blink)
Blinking Green (2 blinks)
Blinking Green (3 blinks)
Solid Green
Rapid Flashing Green
Flashing Green and Red
8.2.1 Network Status LEDs
No Light
Left and Right Bright Green
Left Dim and Right Bright Green
Left and/or Right Blinking Green
Persistent IPAddress
DHCPIPAddress
Link-Local Address (LLA)
Acquisition Started
Firmware update in progress
General Error
No network connection
10 GigE connection
1 GigE connection
Data transfer in progress
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 31
Page 36

Contacting Us
For any questions, concerns or comments please contact us via the following methods:
Contacting Us
Email
Knowledge Base
Downloads
Contact Information
General questions
Technical support (existing customers only)
Find answers to commonly asked questions in our
Knowledge Base
Download the latest documents and software
Contact Us on our website
10/27/2017
©2017 FLIR Integrated
Imaging Solutions Inc.
Allrights reserved.
FLIROryx®Installation Guide 32
 Loading...
Loading...