Page 1
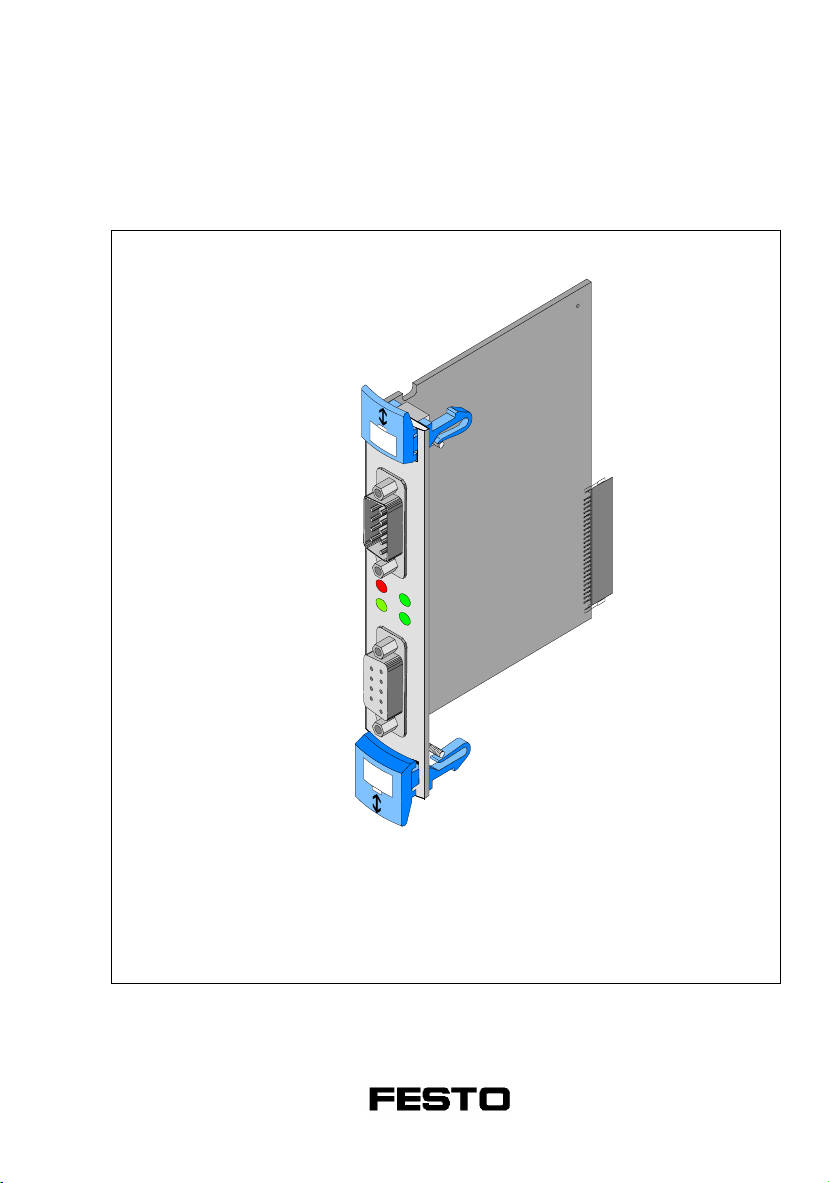
Smart Positioning Controller SPC200
Fieldbus module
INTERBUS
Typ SPC200-COM-IBS
Manual 0503a 188 891 GB
Page 2

Page 3

Author: S. Breuer, E. Klotz
Translation: Douglas Smith
Editors: H.-J. Drung, M. Holder
Layout: Festo AG & Co., Dept. KI-TD
Type setting: KI-TD
Printed on 100 % recycled paper
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Edition: 0503a
©
(Festo AG & Co., D-73726 Esslingen,
Federal Republic of Germany, 1999)
The copying, distribution and utilization of this document as well as the communication of its contents to
others without expressed authorization is prohibited. Offenders will be held liable for the payment of damages.
All rights reserved, in particular the right to carry out
patent, utility model or ornamental design registration.
I
Page 4

Order no.: 188 891
Description: Manual
Designation: P.BE-SPC200-COM-IBS-GB
II
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 5

Contents
Designated use. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . V
Target group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . VI
Important user instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . VI
Danger categories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . VI
Notes on this manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . VIII
Product-specific terms and abbreviations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . IX
1. System summary
1.1 System structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
1.2 Connecting and display elements on the INTERBUS module . 1-4
1.3 Basic structure for operation on the INTERBUS . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
1.4 Operating modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
2. Fitting
2.1 Fitting and removing the field bus module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
3. Installation
3.1 General instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
3.2 Connecting the INTERBUS interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
4. Commissioning
4.1 Procedure for commissioning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
4.1.1 Additional instructions on commissioning with WinPISA . . . . . . . 4-4
4.1.2 Commissioning the field bus (summary) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
4.1.3 Configuring the I/O range for INTERBUS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
4.2 Basic principles of configuration and addressing. . . . . . . . . . . . 4-12
4.2.1 General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-12
4.2.2 Number of configurable inputs and outputs on the
SPC200-COM-IBS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-13
4.2.3 Addressing variants on the INTERBUS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-14
4.3 Bus configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-15
4.3.1 Bus configuration with CMD software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-15
4.3.2 Bus configuration without CMD software. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-22
4.3.3 Switching on the power supplies on the INTERBUS. . . . . . . . . 4-24
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
III
Page 6

4.4 Addressing the SPC200 on the INTERBUS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-25
4.4.1 General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-25
4.4.2 Summary of the I/O addresses of the SPC200-COM-IBS. . . . 4-28
4.4.3 Entering process data via the CMD software . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-30
4.4.4 Preprocessing and periphery errors (PF). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-33
4.5 Programming examples for an S5.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-34
4.5.1 Basic principles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-34
4.5.2 Handshake bits. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-36
4.5.3 Record select . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-39
5. Diagnosis and error treatment
5.1 General instructions on diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
5.2 On-the-spot diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
5.3 Diagnosis via WinPISA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
5.4 Interruption in field bus connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
A. Technical appendix
A.1 Technical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-3
A.2 Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-5
IV
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 7

Designated use
The field bus module type SPC200-COM-IBS has been
designed for connecting the SPC200 to the INTERBUS.
With this field bus module the SPC200 can be operated
as a slave on the remote bus.
The basic components and modules for the SPC200
are described in the User Manual type P.BE-SPC200-...
You must observe at all costs the safety precautions
described therein as well as the designated use of the
individual components and modules. Please observe
also the notes on safety in the operating instructions for
the pneumatic components used. The SPC200 as well
as the modules and cables to be connected may only
be used as follows:
– as intended
– in their original state
– without any modifications
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
– in perfect technical condition
If used with additional commercially-available components, such as sensors and actuators, the specified
limits for pressures, temperatures, electrical specifications, torques, etc. must be observed. Local and national technical regulations must also be observed.
V
Page 8
Target group
This manual is directed exclusively at technicians
trained in control and automation technology and who
have experience in installing, commissioning, programming and diagnosing INTERBUS slaves.
Important user instructions
This manual contains instructions on possible dangers
which can occur if the SPC200 is not used correctly.
These instructions are printed in italics, are placed in a
frame and also marked with a pictogram.
Danger categories
A distinction is made beween the following:
WARNING: This means that considerable injury to
people and/or damage to property can occur if these
instructions are not observed.
VI
CAUTION: This means that injury to people and/or
damage to property can occur if these instructions
are not observed.
PLEASE NOTE: This means that damage to
property can occur if these instructions are not
observed.
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 9
Pictograms
Pictograms and symbols supplement the danger instructions and draw attention to the nature and consequences of dangers.
The following pictograms are used:
Uncontrolled movements of loose tubing
Unintentional movements of the connected actuators
High electric voltage or undefined switching status of
the electronic components which consequently affects
connected circuits.
Electrostatically vulnerable components which will be
damaged if the contacts are touched.
Recommendations and tips are marked with this pictogram.
Te x t
markings
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
•
This point marks activities which can be carried out
in any order.
1. Numbers denote activites which must be carried out
in the sequence listed.
– Hyphens denote general activities.
VII
Page 10
Notes on this manual
This manual contains general basic information on fitting as well as installing and commissioning the
SPC200 as an INTERBUS slave. Reference is made to
the SPC200 Smart Positioning Controller with operating
system version V 3.x and with WinPISA as from version
3.x.
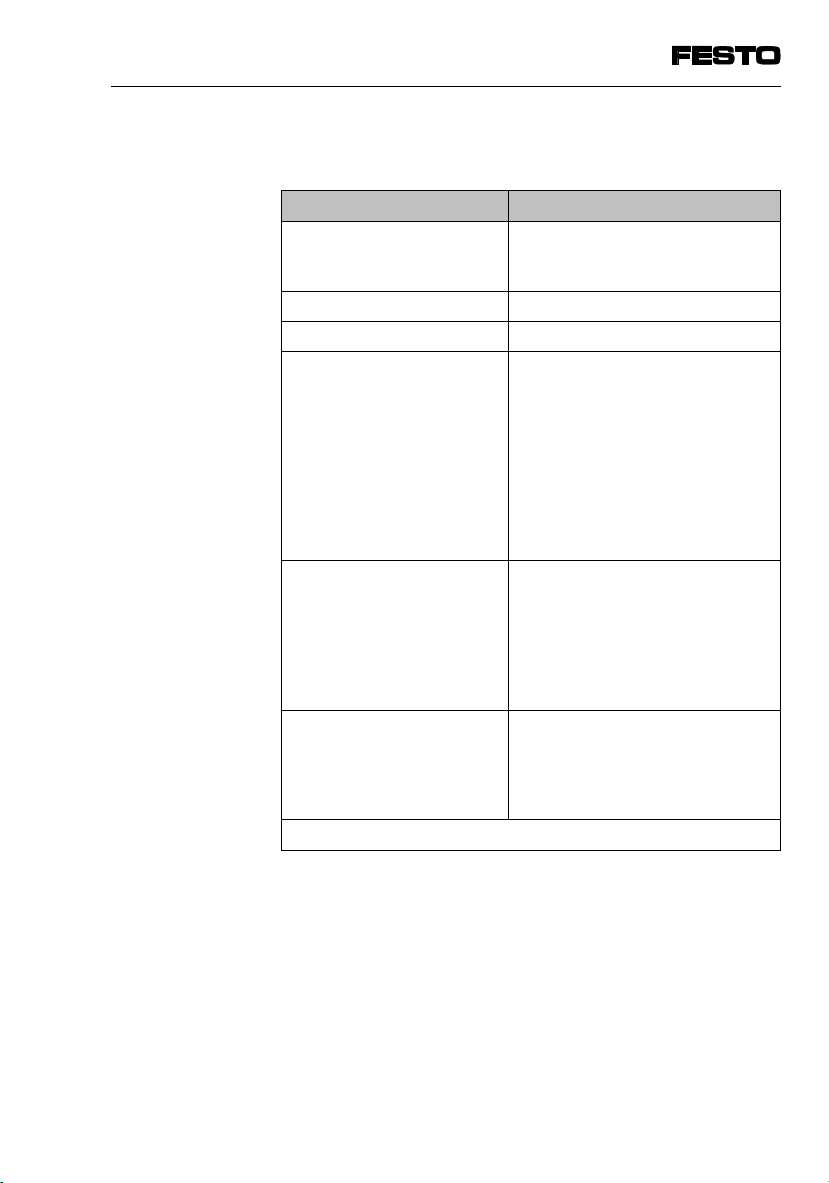
Manuals on the SPC200 Smart Positioning Controller
Type Name Contents
System
manual
Software
manual
Help system Help system for WinPISA
Manuals Field bus module type
SPC200 Smart Positioning
Controller, manual
type P.BE-SPC200-GB
Software package
WinPISA
type P.SW-WIN-PISA-GB
(contained in WinPISA)
P.BE-SPC200-COM-...
Stepping motor indexer
module type
P.BE-SPC200-SMX-...
Installation, commissioning and
diagnosis with the SPC200; standard
components and modules
Functions of the WinPISA software
package
WinPISA help system
Installation, commissioning and
diagnosis of the relevant field bus module
Installation, commissioning and
diagnosis when using a stepping motor
VIII
Special information on commissioning, programming
and diagnosing the SPC200 with the WinPISA software
package can be found in the relevant manual for WinPISA. Information on the electric axes, drive packages
and sensors can be found in the documentation supplied with the product.
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 11
Product-specific terms and abbreviations
The following product-specific terms and abbreviations
are used in this manual:
Term /
abbreviation
Modules Cards which are plugged into the rack of the SPC200 I/Os
I Digital input
IBS INTERBUS (remote bus)
Q Digital output
PLC/IPC Programmable logic controller / industrial PC
Meaning
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
IX
Page 12

X
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 13

1. System summary
Chapter 1
System summary
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
1-1
Page 14

1. System summary
Contents
1. System summary
1.1 System structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
1.2 Connecting and display elements on the INTERBUS module 1-4
1.3 Basic structure for operation on the INTERBUS . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
1.4 Operating modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
1-2
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 15
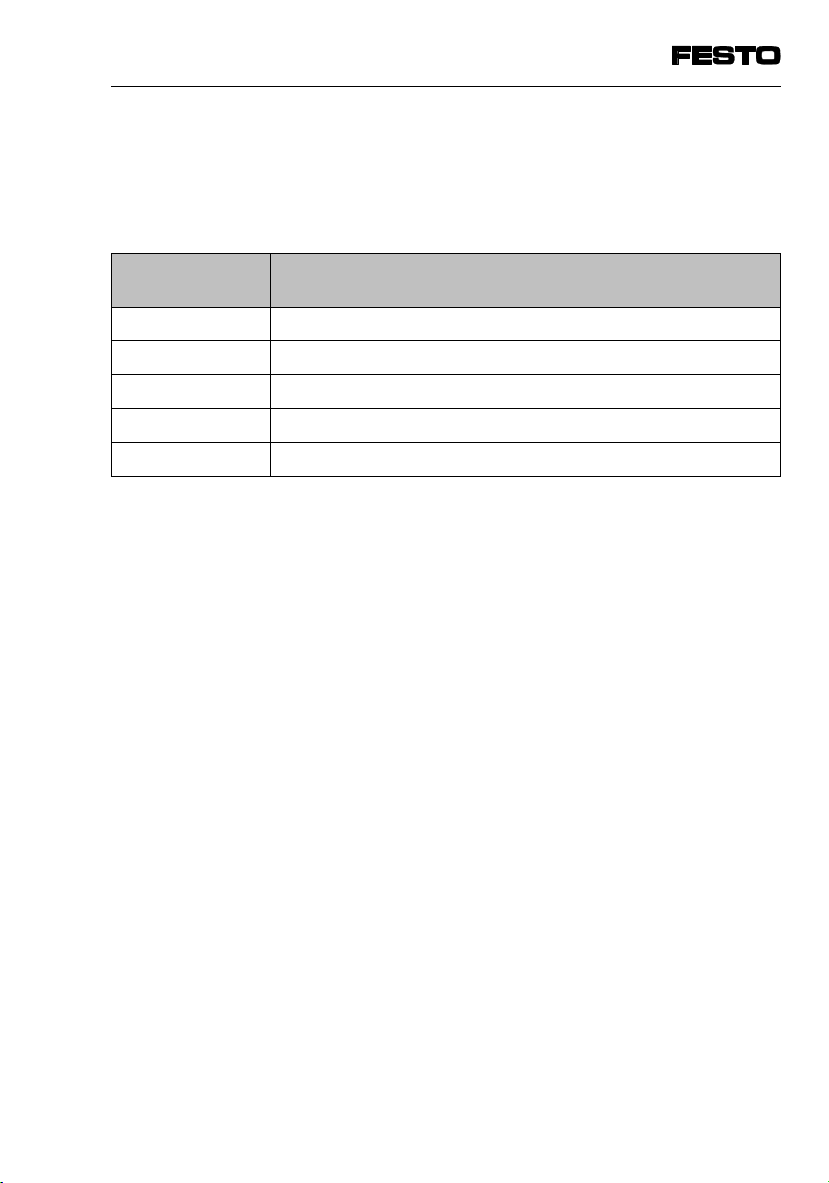
1. System summary
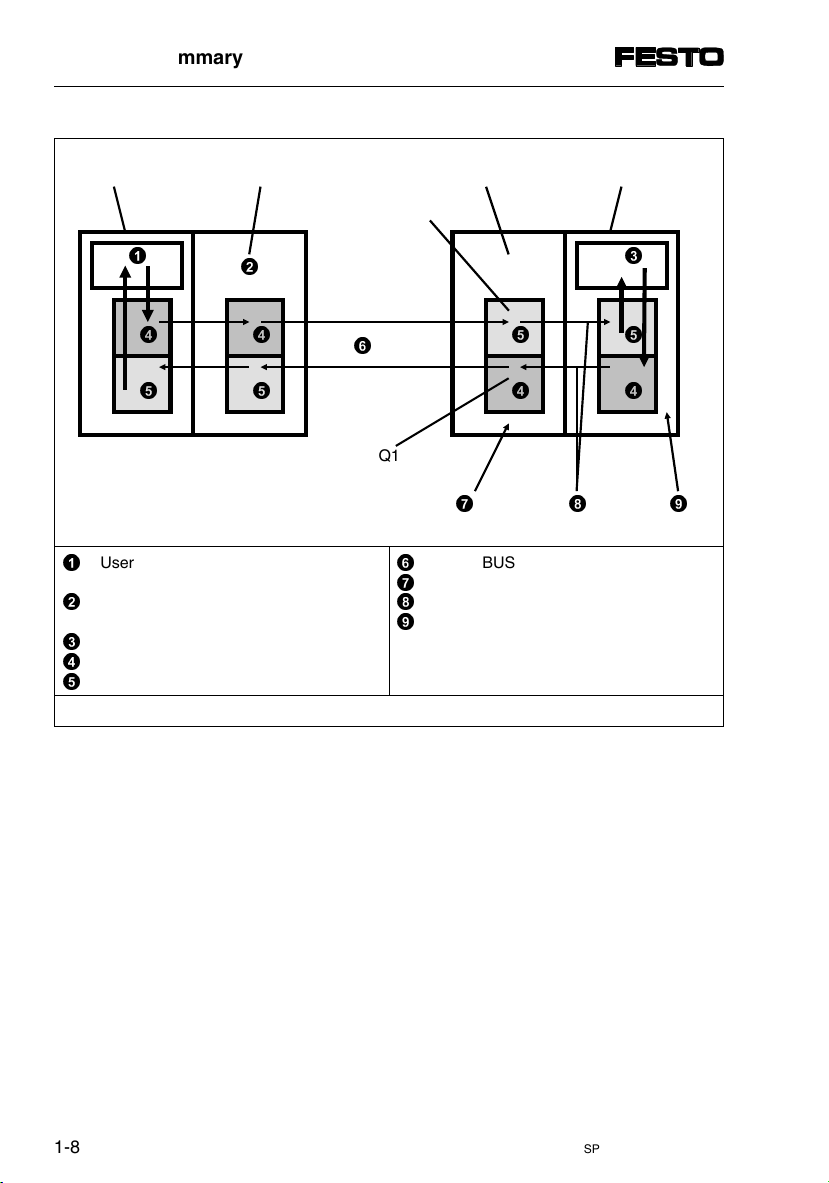
1.1 System structure
Special field bus modules are available for connecting
the SPC200 to field bus systems. Field bus module
type SPC200-COM-IBS enables the SPC200 to be connected to the INTERBUS. With this module the
SPC200 can be operated on the remote bus.
©
PC with suitable software for:
©
- the INTERBUS configuration (CMD-SW)
- programming the IBS master
- configuring the SPC200 (WinPISA)
ª
INTERBUS
Controller/IPC with IBS module
ª
SPC200 as INTERBUS slave
«
Valve terminal on the INTERBUS
¬
(example)
Further slaves on the INTERBUS
ª
«
¬
Fig. 1/1: System summary of SPC200 on the INTERBUS (example)
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
1-3
Page 16
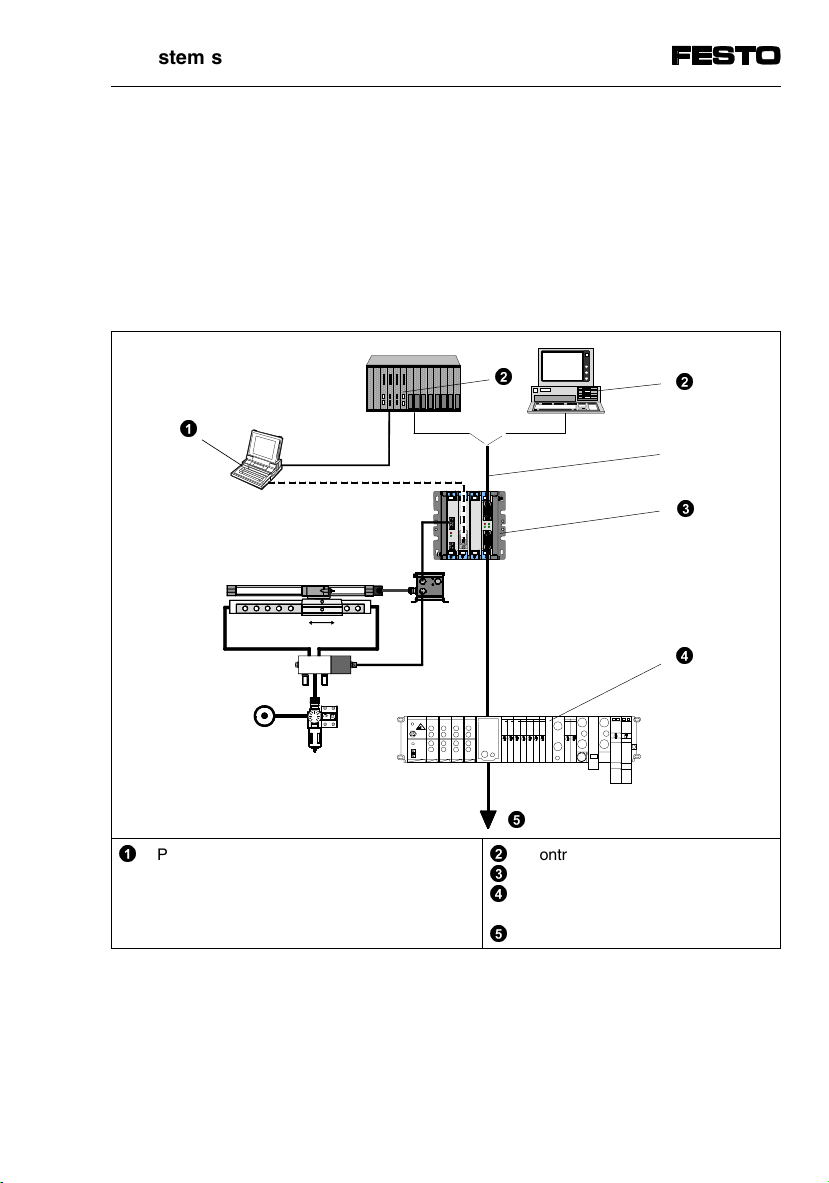
1. System summary
1.2 Connecting and display elements on the INTERBUS module
The diagram below shows the connecting and display
elements on field bus module type SPC200-COM-IBS.
©
ª
«
INTERBUS incoming
©
RD LED (red)
ª
TR LED (green)
«
RC LED (green)
¬
BA LED (green)
INTERBUS continuing
®
Fig. 1/2: Connecting and display elements
¬
®
1-4
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 17
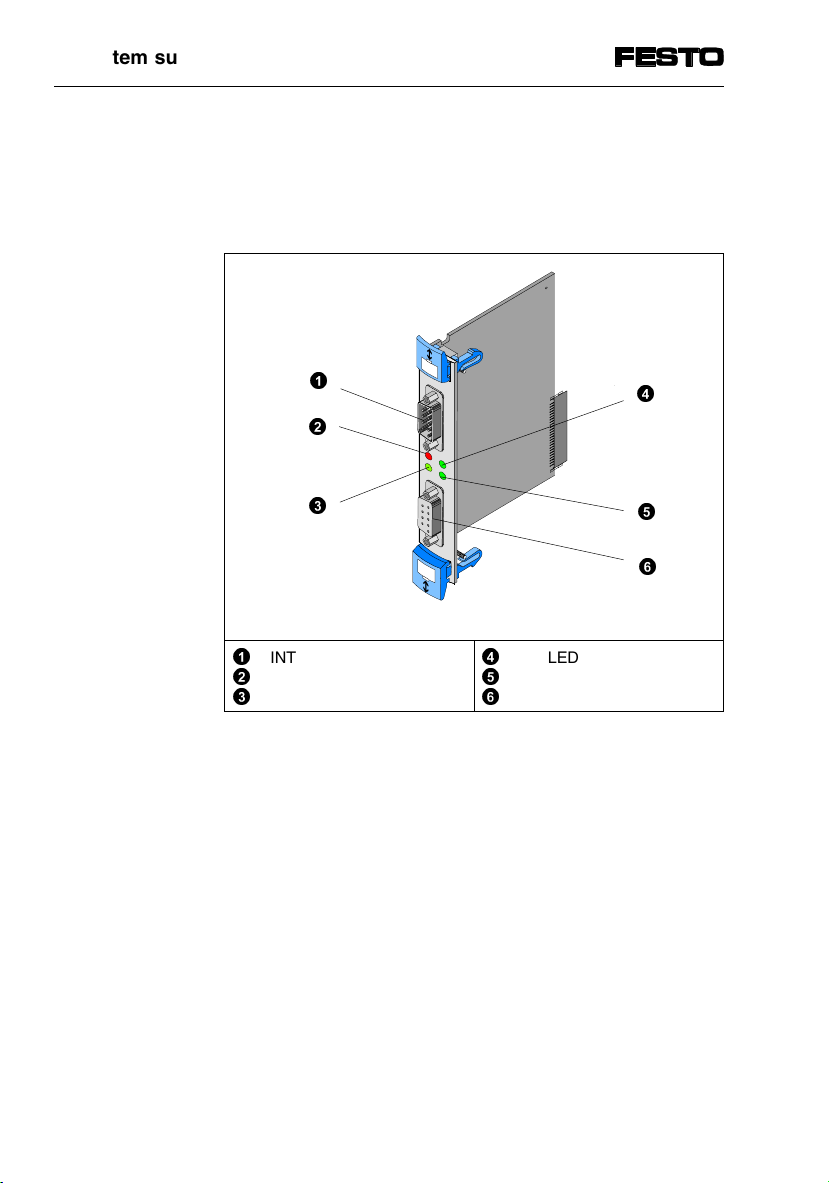
1. System summary
1.3 Basic structure for operation on the INTERBUS
Basic structure for INTERBUS
The SPC200 can function as a remote bus slave with
just the following modules.
©
Power supply module
©
Diagnostic module
ª
Field bus module for INTERBUS
«
ª
Fig. 1/3: Basic structure for INTERBUS
Module Description
Power supply
module
Diagnostic
module
Field bus
module for
INTERBUS
Enables both the power supply and the axis
interface designed as a field device to be
connected.
Enables the operating panel to be inserted
(optional) and a PC to be connected.
Enables connection and communication via
the field bus.
«
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
1-5
Page 18

1. System summary
A system with the above-mentioned modules offers the
following scope of performance:
•
•
•
The SPC200 can be controlled via the INTERBUS in
the operating modes start/stop or record select. The
field bus module provides the address range required
for this.
control of up to two pneumatic axes.
programming and diagnosis via a PC or an operating
panel.
Coordination with external PLC/IPC via field bus.
With field bus module type SPC200-COM-IBS, the
SPC200 can be connected as a remote bus slave on
the INTERBUS.
1-6
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 19
1. System summary
1.4 Operating modes
Whether for control via an I/O module or via a field bus,
the SPC200 offers the following operating modes for
processing the stored NC programs:
•
start/stop mode
•
record select mode
The desired operating mode can be set with the control
panel or with WinPISA. Detailed information on the
operating modes can be found in the user manual for
the SPC200.
The SPC200 communicates with the INTERBUS master via the internal I/O address ranges (internal
input/output addresses) of the field bus module. Depending on the operating mode used, field bus module
type SPC200-COM-IBS provides the following I/O bits
for communication with the INTERBUS master:
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Operating mode I/O address range of field bus
Start/Stop I10.0 - I13.15
Record select I10.0 - I11.15
*)
Address specification as seen by the SPC200
**)
1-4 process data words can be configured
module type SPC200-COM-IBS
*) **)
Q10.0 - Q13.15*)
Q10.0 - Q10.15
**)
*)
*)
CAUTION
The outputs of the INTERBUS master are mapped
on internal inputs of the field bus module or of the
SPC200.
1-7
Page 20
1. System summary
PLC/IPC INTERBUS INTERFACE SPC200-COM-IBS SPC200
I10.0 ... I13.15
1)
ª
®
Q10.0 ... Q13.15
1)
¯
User program in the higher-order
©
PLC/IPC
Communication module/bus module
ª
(IBS master)
User program in the SPC200
«
Outputs
¬
Inputs
1)
Maximum address range; Address specification as seen by the SPC200
INTERBUS (remote bus)
®
Internal I/Os of the field bus module
¯
Time for cyclic data exchange
°
Internal I/Os of the SPC200
±
Fig. 1/4: Internal I/O address range
Due to the large I/O address range, considerably more
NC records can be accessed in record select mode via
the field bus, than via the I/O module.
«©
¬¬
¬¬
° ±
1-8
With the field bus module, 10 bits are available for
selecting the NC record number in record select mode.
The maximum permitted number of NC records (up to
1000) of the determined starting programs can therefore be accessed.
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 21
1. System summary
When a field bus module is used:
•
•
The address assignment when a field bus module is
used is shown in the table below.
the address ranges 0.0 ... 0.15 remain unused.
These address ranges, which serve without field bus
module for controlling the SPC200, are not available.
maximum 3 I/O modules can be inserted. These provide exclusively freely programmable I/Os in the
operating mode start/stop.
Module Maximum address range
1)
-
I/O modules on first
axis interface string
First I/O module I2.0 ... I2.9 Q2.0 ... Q2.7
I/O modules on second
axis interface string
Second I/O module I4.0 ... I4.9 Q4.0 ... Q4.7
Third I/O module I5.0 ... I5.9 Q5.0 ... Q5.7
Field bus module I10.0 ... I13.15 Q10.0 ... Q13.15
1) Address range 0.0 ... 0.15 is not available if a field bus module
is used
I0.0 ...I0.9
I1.0 ... I1.15 Q1.0 ... Q1.15
I3.0 ... I3.15 Q3.0 ... Q3.15
1)
Q0.0 ... Q0.7
1)
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
The functions of the internal input and output bits of the
field bus module, as well as the permitted NC
commands, depend on the operating mode set.
Detailed information on this can be found in the user
manual for the SPC200.
1-9
Page 22

1. System summary
1-10
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 23

2. Fitting
Chapter 2
Fitting
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
2-1
Page 24

2. Fitting
Contens
2. Fitting
2.1 Fitting and removing the field bus module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
2-2
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 25
2. Fitting
WARNING
Before starting the fitting work, switch off the following in the sequence specified here:
1. the compressed air supply
2. the load voltage and operating voltage
supplies on the SPC200 and, if applicable,
on the axis interface string.
You thereby avoid:
– undesired movements of the connected actuators
– uncontrolled movements of loose tubing
– undefined switching states
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
2-3
Page 26
2. Fitting
2.1 Fitting and removing the field bus module
CAUTION
Incorrect handling can damage the modules.
Do not, therefore, touch the contacts on the modules.
Please observe the regulations for handling electrostatically vulnerable components.
Before fitting or removing modules, discharge yourself
electrostatically, in order to protect the modules from
discharges of static electricity.
The slots are numbered 1 to 6 from left to right. Slot 1
is reserved for the power supply module (type SPC200-PWR-AIF). The field bus module can be fitted as
desired in slots 2 to 6. If the field bus module is fitted
next to the diagnostic module, a control panel cannot
be plugged in because of the field bus cable.
2-4
Individual identification of all the modules fitted is carried out automatically.
Only 1 field bus module may
be fitted.
The modules are fixed onto the rack with the aid of a
safety catch. A tool is not therefore required for fitting or
removing the modules.
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 27
2. Fitting
WARNING
Actuators can be activated unintentionally and the
SPC200 can be damaged if modules are added or
removed while the power supply is switched on.
Before undertaking installation and/or maintenance
work, switch off the following in the sequence
specified here:
1. the compressed air supply
2. the load voltage and the operating voltage
supplies for the SPC200 and, if applicable, the
load voltage supply for the axis interface string.
Fitting
modules
When fitting the modules into the rack, proceed as
follows:
1. Switch off the compressed air supply and the operating voltage supply.
2. If applicable, remove the blind plate.
3. Hold the module by the front plate and push it into
the guide rail. Make sure that the modules are not
tilted when they are pushed in and that no components on the printed circuit board are damaged.
4. Make sure that the plugs of the terminal strips are
correctly aligned. Using light pressure, push the module in completely. The safety catches will then lock
automatically (see Fig. 2/1).
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
2-5
Page 28
2. Fitting
©
ª
«
¬
«
modules
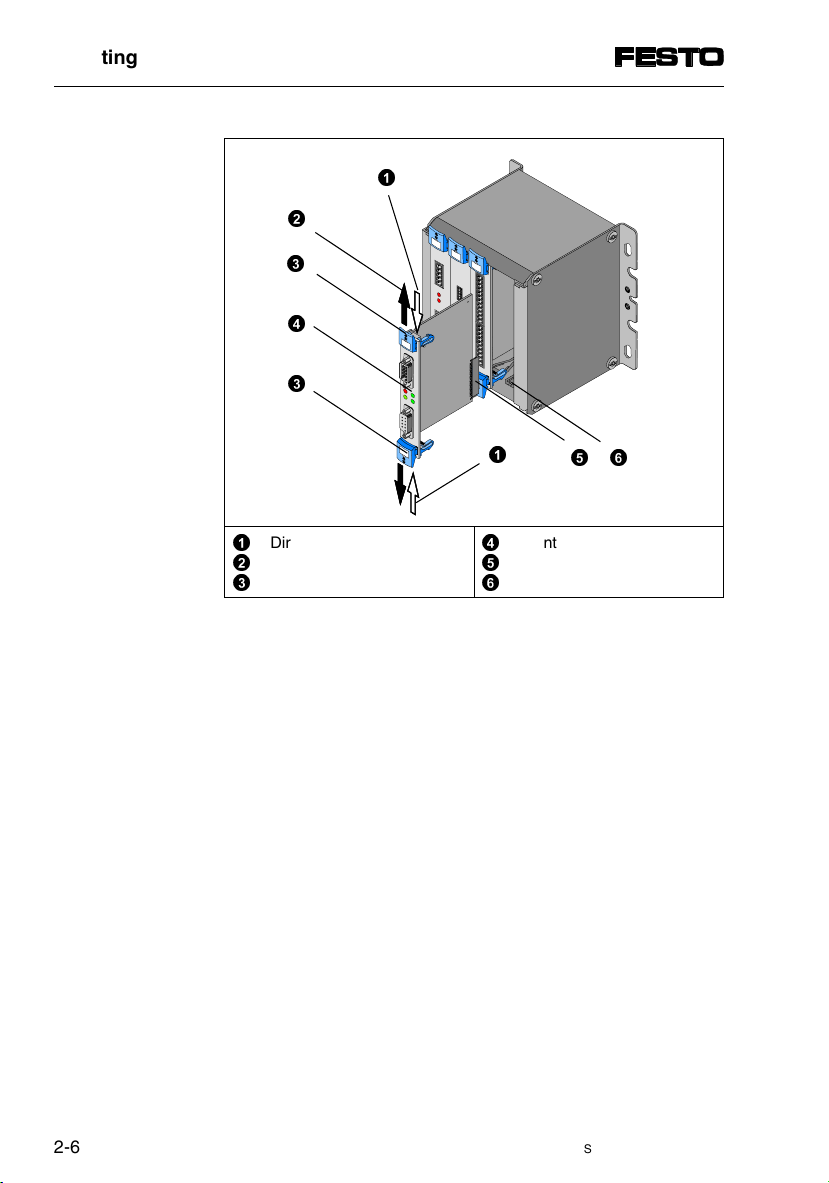
Direction for unlocking
©
Locks automatically
ª
Safety catch
«
©
Front plate of module
¬
Terminal strip
Guide rail
®
®
Fig. 2/1: Fitting the modules
When removing a module, proceed as follows: Removing
1. Switch off the operating voltage and the compressed
air supply.
2. Disconnect and remove the cable on the front of the
module.
3. Unlock both safety catches (see Fig. 2/1) and carefully remove the module.
4. If necessary, seal unused slots with blanking plates.
2-6
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 29

3. Installation
Chapter 3
Installation
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
3-1
Page 30

3. Installation
Contens
3. Installation
3.1 General instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
3.2 Connecting the INTERBUS interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
3-2
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 31
3. Installation
3.1 General instructions
WARNING
Before undertaking installation and/or maintenance
work, switch off the following in the sequence
specified here:
1. the compressed air supply
2. – the load voltage supply for field devices and
proportional directional control valves
(plug X2, pin 1)
– the load voltage supply for the outputs
(plug X6/X8, pin 8)
– if applicable, the load voltage supply for the
axis interface string
– the operating voltage supply for internal
electronics of the SPC200 and field devices
(plug X2, pin 2).
You thereby avoid:
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
– undesired movements of the connected actuators
– uncontrolled movements of loose tubing
– undefined switching states
3-3
Page 32

3. Installation
3.2 Connecting the INTERBUS interface
CAUTION
Observe the basic instructions for setting up and
installing an INTERBUS in the relevant manuals for
your IBS module/master or in the INTERBUS
installation manual from Phoenix Contact.
Phoenix Contact installation manual:
Article:IBS SYS INST UM
Order no. 27 54 28 6
There are two Sub-D plugs on the field bus module to
enable the SPC200 to be connected to the INTERBUS.
These serve for the incoming cable (plug) and for the
continuing INTERBUS cable (socket).
Recommendation:
Use the cables from Phoenix Contact. These are the
correct standard cable type with suitable 9-pin SUB-D
plugs/sockets, e.g.:
IBS RBC/1/1/length in m
*)
*)
3-4
*)
Obtainable from:
Phoenix Contact GmbH & Co.
Postfach 1341
D-32 819 Blomberg, Germany
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 33
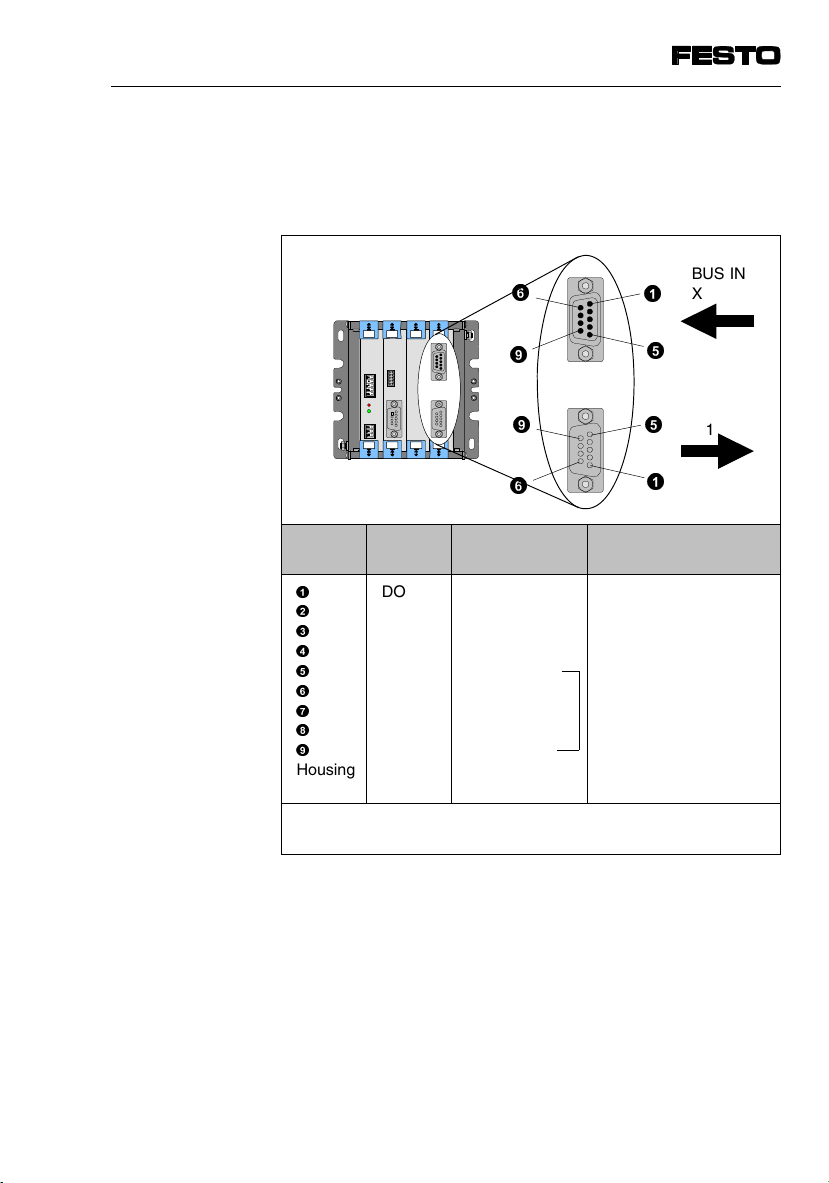
3. Installation
If you wish to use other cables and plugs/sockets,
observe the following pin assignments and installation
instructions.
BUS IN
®
©
X20
±
±
®
Pin Signal
©
ª
«
¬
®
¯
°
±
Housing
1)
Create bridge to pin 5
2)
This bridge/connection serves for recognizing a continuing slave
BUS IN
DO
DI
Mass
n.c.
n.c.
/DO
/DI
n.c.
n.c.
Screening
/shield
Signal
BUS OUT
DO
DI
Mass
n.c.
Vcc Bus +5V
/DO
/DI
n.c.
1)
RBST
Screening/shield
BUS OUT
X21
©
Meaning
Data out
Data in
Reference conductor
Not connected
Recognize slave
Data out inverse
Data in inverse
Not connected
Recognize slave
Screening/shield
Fig. 3/1: Pin assignment of INTERBUS interface
2)
2)
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
3-5
Page 34

3. Installation
General installation instructions and earthing
•
Connect the SPC200 as a remote bus slave to the
INTERBUS. The SPC200 cannot be used as an installation remote bus.
•
The SPC200 must be connected non-floating to the
INTERBUS.
- With ready-to-use cables make sure that
there is a contact via the plug connectors
(metal plugs) used.
- If necessary, connect the screening of the
incoming and of the continuing INTERBUS cables
directly to the housing of the metal plug.
•
Use low-impedance earthing or, if necessary, potential equalization cables.
3-6
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 35

4. Commissioning
Chapter 4
Commissioning
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
4-1
Page 36

4. Commissioning
Contents
4. Commissioning
4.1 Procedure for commissioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
4.1.1 Additional instructions on commissioning with WinPISA . . . . . . 4-4
4.1.2 Commissioning the field bus (summary) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
4.1.3 Configuring the I/O range for INTERBUS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
4.2 Basic principles of configuration and addressing. . . . . . . . . . . 4-12
4.2.1 General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-12
4.2.2 Number of configurable inputs and outputs on the
SPC200-COM-IBS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-13
4.2.3 Addressing variants on the INTERBUS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-14
4.3 Bus configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-15
4.3.1 Bus configuration with CMD software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-15
4.3.2 Bus configuration without CMD software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-22
4.3.3 Switching on the power supplies on the INTERBUS . . . . . . . . 4-24
4.4 Addressing the SPC200 on the INTERBUS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-25
4.4.1 General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-25
4.4.2 Summary of the I/O addresses of the SPC200-COM-IBS. . . . 4-28
4.4.3 Entering process data via the CMD software . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-30
4.4.4 Preprocessing and periphery errors (PF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-33
4.5 Programming examples for an S5.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-34
4.5.1 Basic principles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-34
4.5.2 Handshake bits. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-36
4.5.3 Record select . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-39
4-2
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 37

4. Commissioning
4.1 Procedure for commissioning
In order to commission an SPC200 mit integrated field
bus module, you will require the WinPISA software
package as from version 3.X.
Recommendation
Proceed with commissioning as follows:
1. Create and save the desired hardware configuration
(incl. field bus module).
2. First commission the individual axes with the aid of
WinPISA, but without using the field bus interface.
After reading this chapter, refer to the WinPISA
manual.
3. Then start commissioning the field bus.
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
4-3
Page 38
4. Commissioning
4.1.1 Additional instructions on commissioning with WinPISA
Proceed first of all as described in the WinPISA manual
(see Chapter 4 in the WinPISA manual).
With some of the commissioning steps, the signals
ENABLE, START and STOP are required for controlling
the axes, e.g. with the steps:
– movement test
– identification travel
– test and start program
If a field bus module is installed, you can generate
these control signals in the test mode when commissioning. Commissioning can then be carried out independently of the INTERBUS master.
Activating the test mode
4-4
CAUTION
You can specify input signals in test mode. The input
signals actually present will be ignored.
Activate the test mode only:
– when the SPC200 is
not
connected to the field
bus or when it is not online or
– when you are aware of the effects produced by
the signals.
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 39
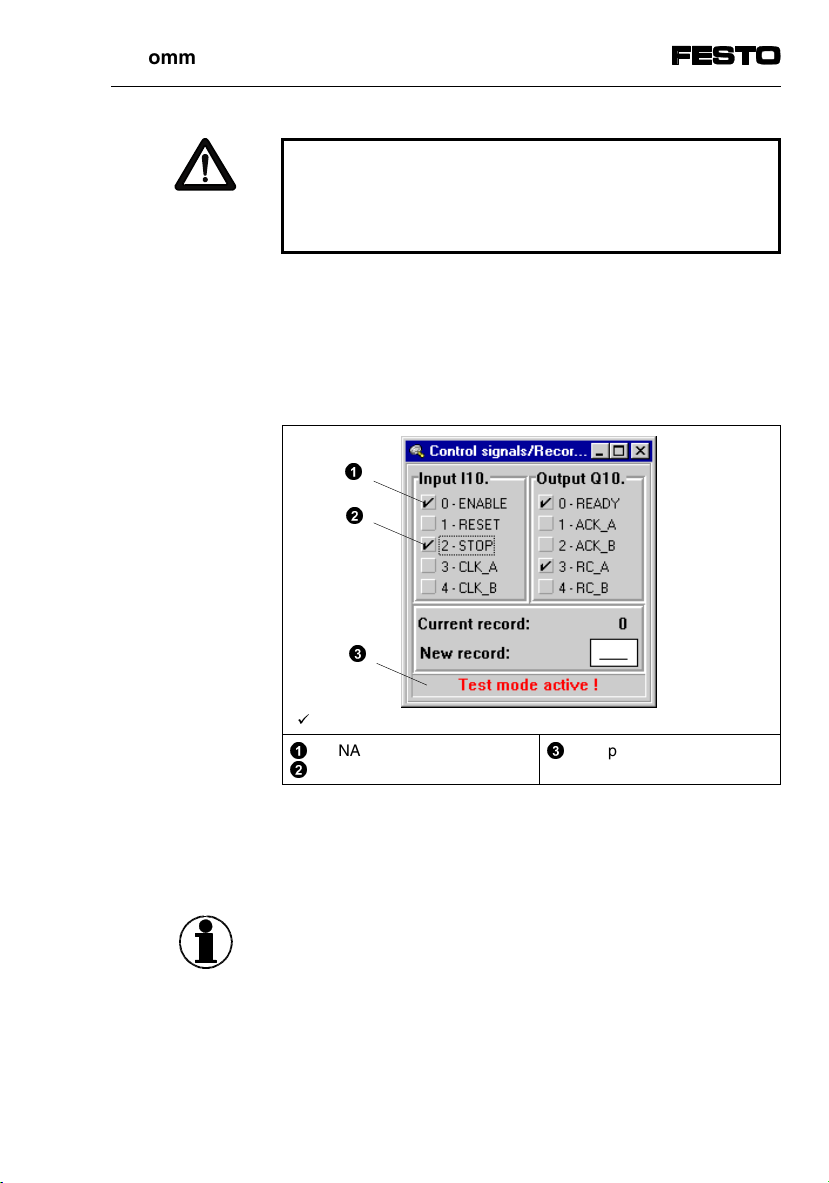
4. Commissioning
WARNING
Make sure that nobody can place his/her hand in the
positioning range of the moving mass and that no
objects lie in this path.
In order to generate control signals in test mode, first
activate the command [Online] [Observe] [Selection]
[Control signals]. Then switch on the test mode, e.g.
with function key F5. The contents of the window [Control signals] depends on the operating mode set.
©
ª
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
«
= 1-signal
'
©
ª
ENABLE
Stop signal
Display for test mode
«
Fig. 4/1: Control signals for commissioning (example)
Especially the signals ENABLE and STOP are important for commmissioning.
Now refer to the WinPISA manual for information on
carrying out commissioning.
4-5
Page 40
4. Commissioning
I/O control signals (summary)
Detailed explanations of the I/O control signals can be
found in the manual for the SPC200. A detailed summary of the I/O assignment is shown in section 4.4.2.
Start/stop mode
Address *) Control signal Description
I10.0 ENABLE Enable controller (1=controller enabled)
I10.1 START/RESET Start/continue programs or
reset (RESET in conjunction with STOP=0)
I10.2 STOP Stop program run (0=stopped)
I10.3/I10.4 SYNC_A/B Synchronization input for M00
Q10.0 READY System ready
Q10.1/Q10.2 SYNC_OA/B Synchronization output for M00
Q10.3/Q10.4 MC_A/B MC output for program A/B (motion complete)
*) Address specifications as seen by SPC200
Record select mode
Address *) Control signal Description
I10.0 ENABLE Enable controller
I10.1 RESET Reset programs
(in conjunction with STOP=0)
I10.2 STOP Stop positioning task (0=stopped)
I10.3/I10.4 CLK_A/B Start NC record from program A/B
I11.0 ... I11.15 RECBIT1...10 Bits for NC record number (RECBIT1 for 2
Q10.0 READY System ready
Q10.1/Q10.2 ACK_A/B Task accepted for program A/B
Q10.3/Q10.4 RC_A/B NC record concluded by program A/B
*) Address specifications as seen by SPC200
0
etc.)
4-6
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 41
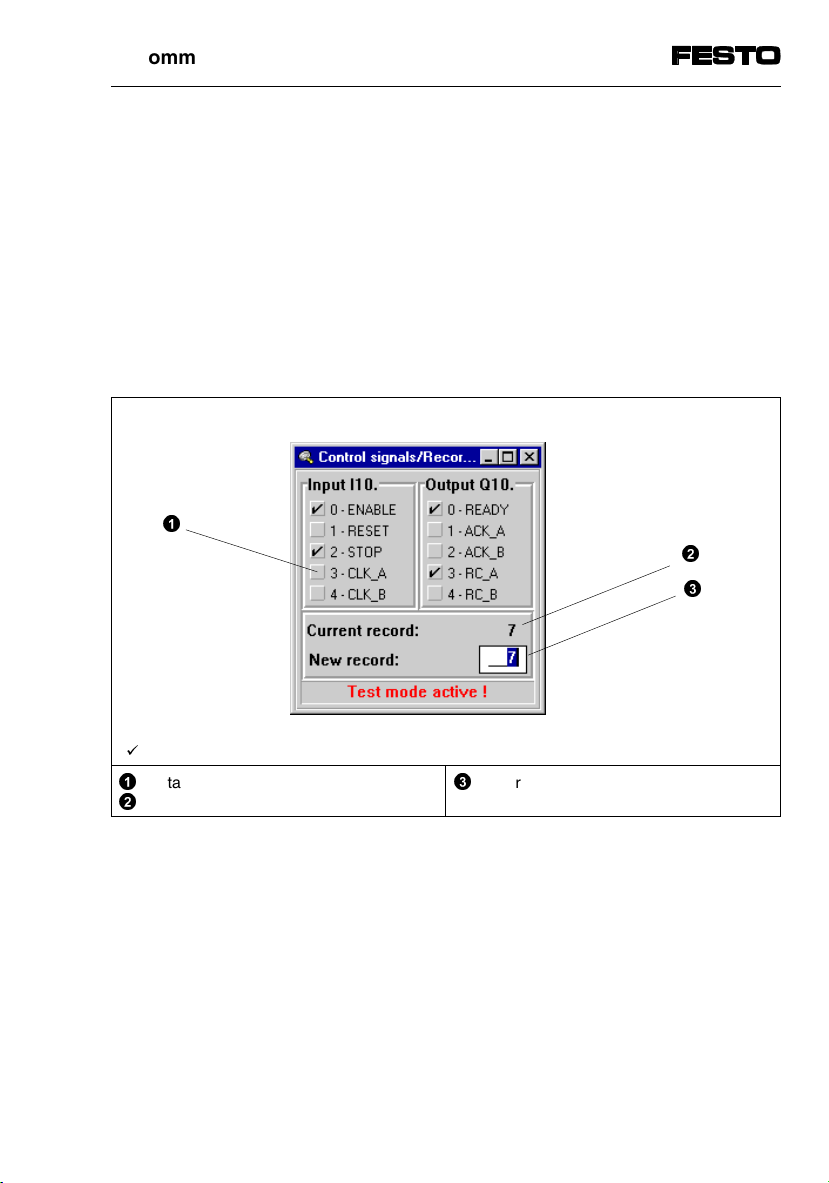
4. Commissioning
Program test in record select mode
In record select mode, the window "Control signals"
enables the direct selection of an NC record number.
This NC record number corresponds to the actual NC
record number in the NC program.
Please note that when loading a program with
WinPISA, the programmed record numbers are stored
beginning with N000 and with step size 1.
Example 1: Start NC record from line N007 of program A
©
ª
«
'
= 1-signal
Start NC record with CLK_A signal
©
Current NC record number (here 7)
ª
Entry field for NC record number
«
(conclude entry with ENTER)
Fig. 4/2: Selecting an NC record in record select mode (example)
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
4-7
Page 42

4. Commissioning
4.1.2 Commissioning the field bus (summary)
Proceed as follows when commissioning the SPC200
as a field bus slave:
1. Make sure that the field bus module is installed in
the SPC200 system and that the I/O range is configured correctly for INTERBUS with the aid of WinPISA (see Chapter 4.1.3).
2. Install INTERBUS completely with all relevant slaves
and prepare all slaves for commissioning.
3. Configure INTERBUS with the appropriate configuration software (e.g. with CMD software).
4. Switch on the power supply to the INTERBUS and
start the complete commissioning of all the slaves.
Further details can be found in the sections which follow.
4-8
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 43
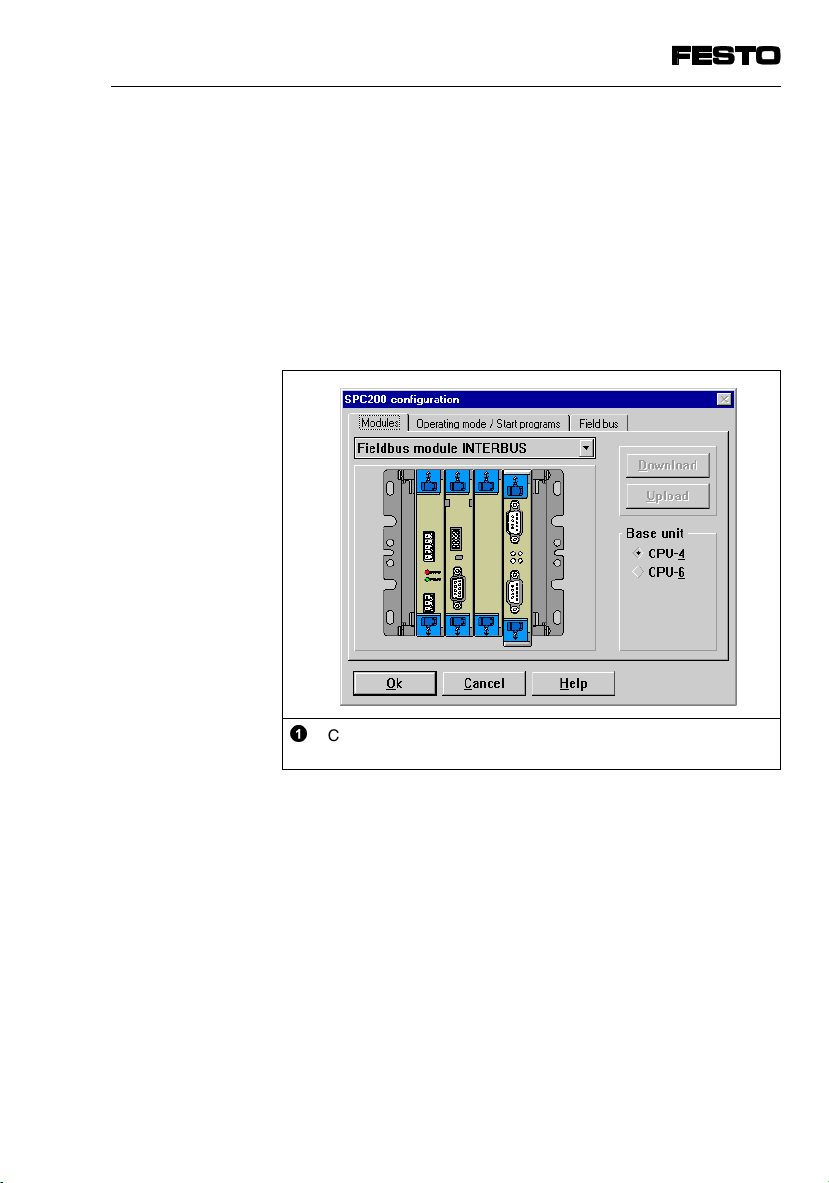
4. Commissioning
4.1.3 Configuring the I/O range for INTERBUS
An I/O range must be configured in the field bus module for communication on the INTERBUS. The size of
the I/O range to be set depends on the selected operating mode of the SPC200. Proceed here as follows:
•
Open the dialogue window “SPC200 configuration”
•
Select SPC200-COM-IBS by clicking
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Configuring field bus module SPC200-COM-IBS for
©
INTERBUS
Fig. 4/3: Dialogue window for SPC200 configuration
4-9
Page 44
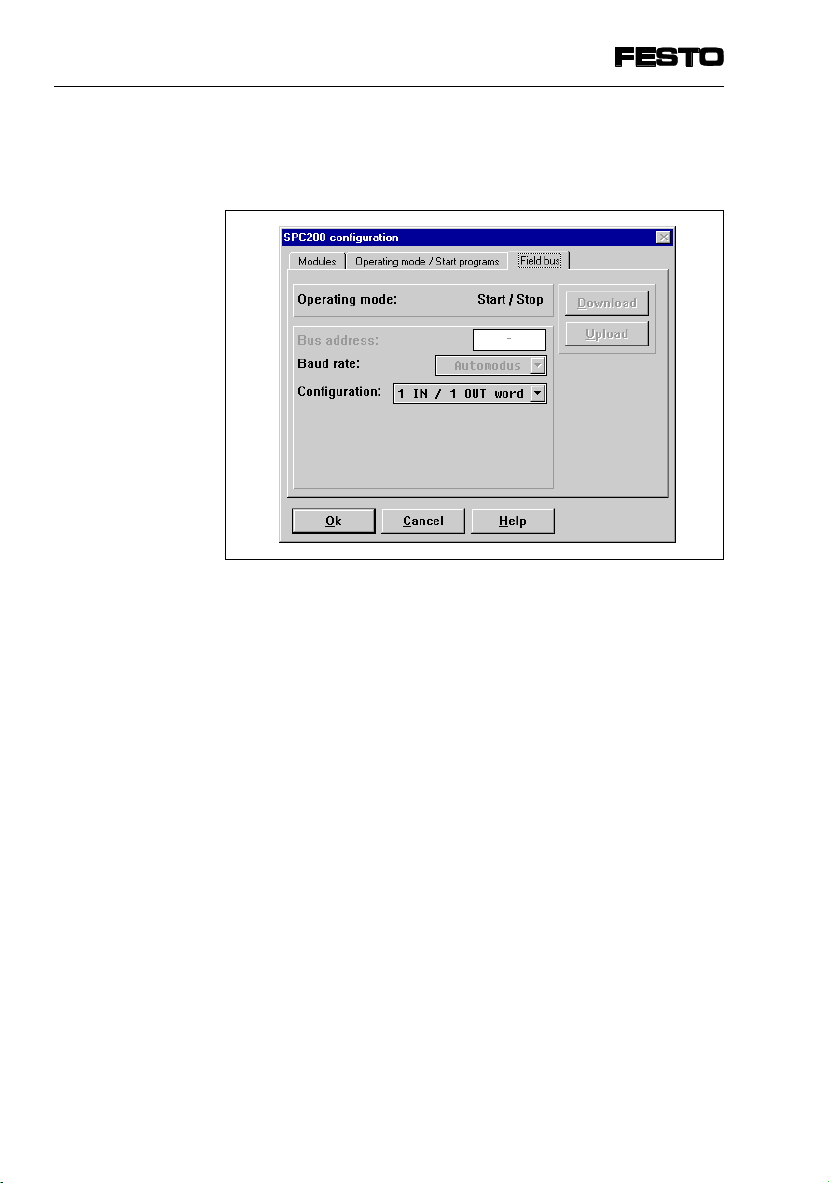
4. Commissioning
•
Actuate the register tab “Field bus”. The following
dialogue window will appear:
Fig. 4/4: Dialogue window INTERBUS configuration
The following specifications are required here depending on the operating mode selected:
4-10
•
the baud rate:
In “Auto mode”, the field bus module sets itself automatically to the INTERBUS baud rate of 500 kB.
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 45

4. Commissioning
•
the configuration of the process data channel in
record select mode: 2I / 2O words
In the record select operating mode the field bus
module communicates fixed with 4 input and 4 output
*)
bytes
bits.
•
the configuration of the process data channel in
start/stop mode: 1I/O ... 4 I/O words (
process data channel comprises 32
. The
default 1 I/O)
In the start/stop operating mode further freely
programmable inputs/outputs can be configured, in
addition to the I/O word for the control signals
*)
. The
process data channel then comprises 16, 32, 48
or 64 bits.
*)
The meaning of the I/O bytes is explained in more
.
detail in Chapter 4.2.2.
Downloading the field bus parameters
– The parameters of the field bus module are always
loaded into the SPC200 within the complete project.
A system reset then takes place. A separate
download of the field bus parameters is not possible.
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
– The field bus module is ready for operation on the
INTERBUS when the LED “RD” lights up (the
initialization phase of the SPC200 is then concluded).
Control panel
Configuration of the process data channel can also be
carried out with the control panel of the SPC200. To do
this switch to the menu "CONFIG.SYSTEM" and select
"FIELDBUS" therein.
4-11
Page 46

4. Commissioning
4.2 Basic principles of configuration and addressing
This chapter deals with the configuration and addressing of an SPC200 on the remote bus for an INTERBUS
master or compatible master.
4.2.1 General information
Before commissioning or programming, you should
compile a configuration list of all the connected field
bus slaves. On the basis of this list you can:
– compare the SET and ACTUAL configurations in
order to detect connection faults.
– access these specifications during addressing and
during a syntax check, in order to avoid addressing
errors.
Please observe the specifications in the following sections. When you have completed the configuration and
addressing of all the slaves, you can switch on the
power supply and start to commission the INTERBUS.
4-12
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 47
4. Commissioning
4.2.2 Number of configurable inputs and outputs on the
SPC200-COM-IBS
The SPC200 communicates with the INTERBUS module/master via internal I/O address ranges of field bus
module SPC200-COM-IBS.
PLEASE NOTE
– Field bus module SPC200-COM-IBS occupies
different inputs and outputs, depending
on the operating mode of the SPC200 and
on the I/O configuration set with WinPISA.
The Ident-code is always 3
–
The table below gives a summary of the control signals
in the I/O address range of the field bus module. The
exact position of the control signals can be found in the
tables in Chapter 4.1.1.
Field bus module type SPC200-COM-IBS
Operating
mode
Start/stop
Record select
*)
Designation scheme/address specifications as seen by the SPC200
**)
The higher number (inputs/outputs) is decisive for configuration of the process data.
Function of the inputs/outputs Process data
I10.0 - I10.15
I11.0 - I13.15
Q10.0...Q10.15
Q11.0 - Q13.15
I10.0 - I10.15
I11.0 - I11.15
Q10.0 - Q10.15
Q11.0 - Q11.15
*)
Control signals and freely
programmable inputs
*)
(optional) for freely
programmable inputs
*)
Control signals and freely
programmable outputs
*)
(optional) for freely
programmable outputs
*)
Control signals
*)
Record numbers
*)
Control signals
*)
reserved/unused
**)
/ 03H.
D
channel
16 bits
(optional)
32, 48 or 64 bits
32 bits
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
4-13
Page 48
4. Commissioning
4.2.3 Addressing variants on the INTERBUS
The SPC200 with field bus module SPC200-COM-IBS
supports the following addressing variants, depending
on the INTERBUS module and PLC used:
– configuration via CMD software (Chapter 4.3.1)
– logical addressing (Chapter 4.3.2)
– physical addressing (Chapter 4.3.2)
PLEASE NOTE
The I/O addresses for the bus slaves are set on the
INTERBUS module by switch or by software.
Address settings on the field bus module of the
SPC200 are not necessary.
4-14
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 49
4. Commissioning
4.3 Bus configuration
4.3.1 Bus configuration with CMD software
This chapter describes, as an example, the main steps
within the CMD software for inserting an SPC200 in
your project. A general and comprehensive description
can be found in the relevant manual for the CMD software. It is assumed here that the user is already familiar with the contents of the CMD manual.
PLEASE NOTE
– The software packages are subject to modifications
which are not taken into account in this manual.
– The examples used here for the screen displays
are taken from the CMD software version 4.
Note that the dialogue windows may be slightly
different, depending on your Windows version
(3.1, 95, NT etc.).
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
– Further and current information can be found in
the manuals for your CMD software and your
control system.
4-15
Page 50
4. Commissioning
Inserting with the Ident-code
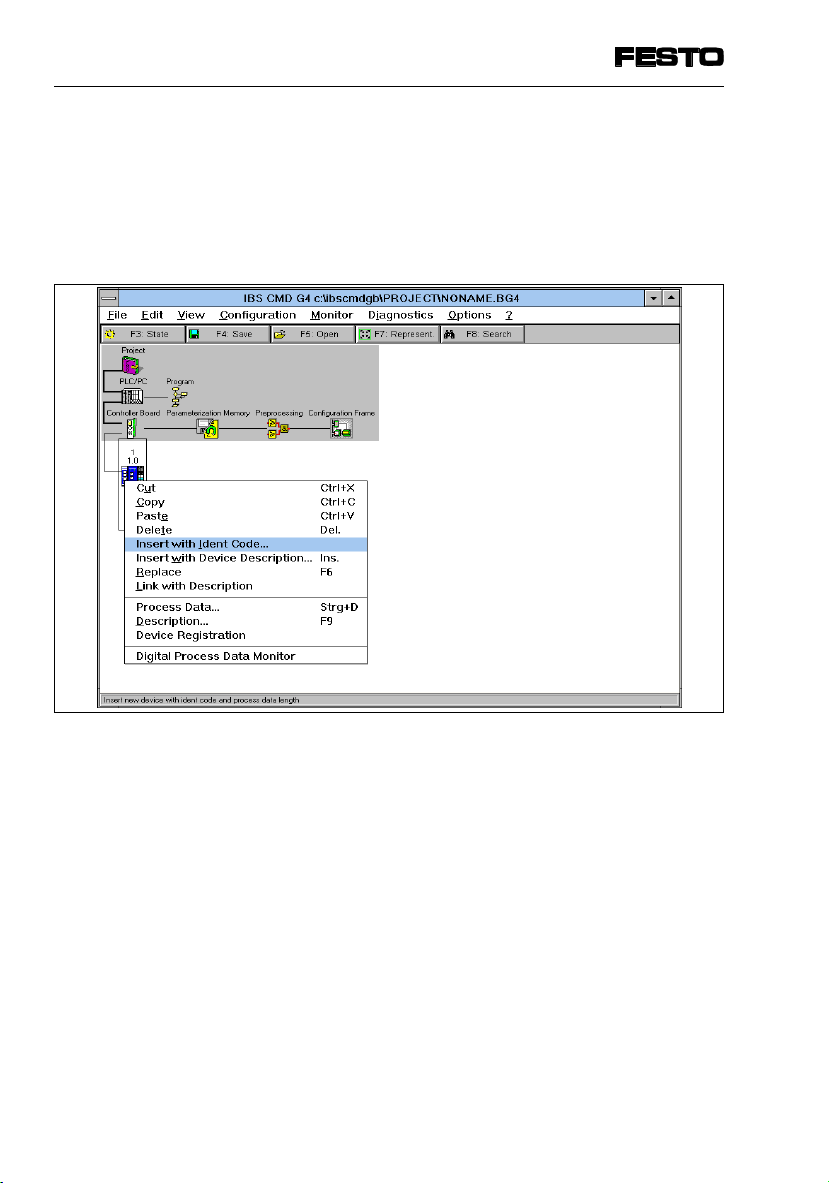
•
Open the dialogue window of the INTERBUS
module.
•
Select the option “Inserting with Ident Code...”
Fig. 4/5: Inserting with Ident Code...
4-16
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 51
4. Commissioning
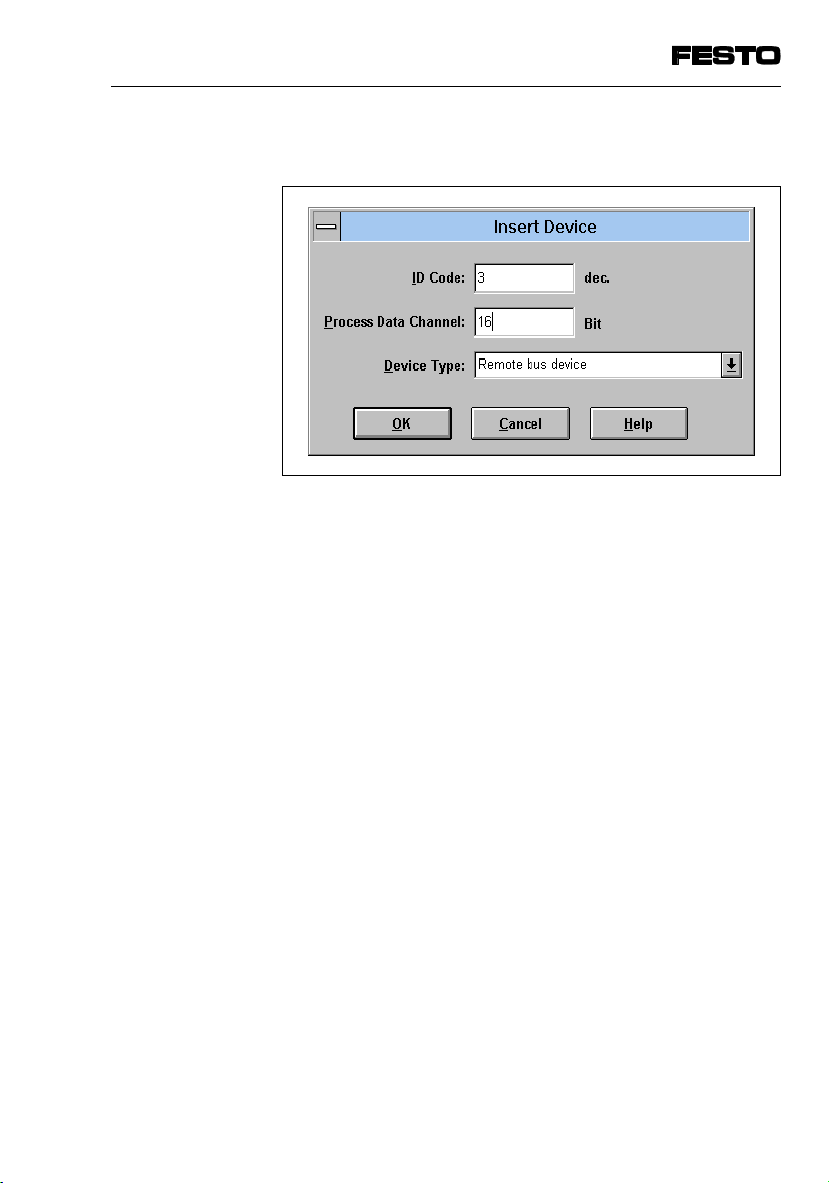
The following dialogue window will then appear:
Fig. 4/6: Dialogue window “Insert Device"
Enter the following in the dialogue window:
•
ID Code
Enter Ident-code 3 for the SPC200.
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
•
Process Data Channel
Enter here the appropriate number of bits, depending
on the operating mode of the SPC200 and on the I/O
configuration set with WinPISA (see Chapters 4.2.2
and 4.1.3).
•
Device Type
Enter here the default entry “Remote bus device.”
•
Save these entries by pressing the OK button.
4-17
Page 52
4. Commissioning
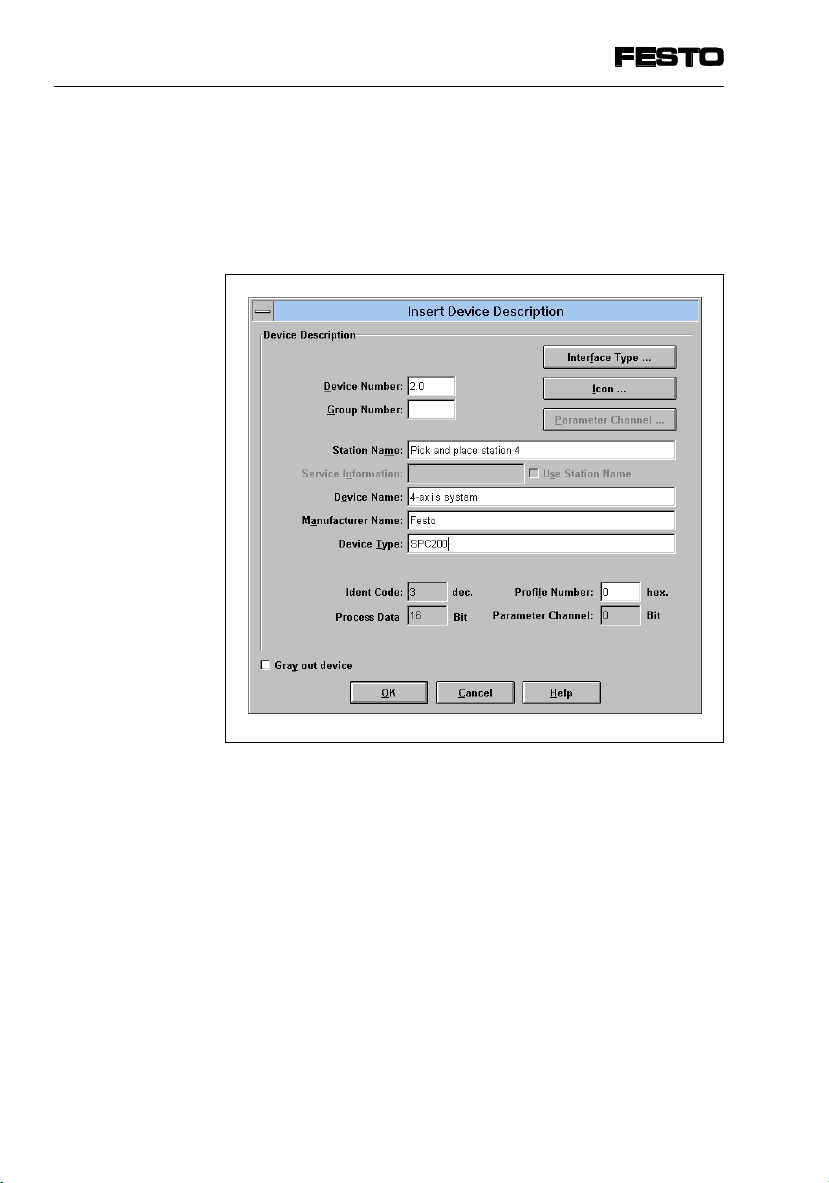
Insert Device Description
You can describe the slave and enter specific information about the SPC200, e.g. station name and slave
picture, in the mask below.
4-18
Fig. 4/7: Dialogue window “Insert Device Description"
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 53
4. Commissioning
Possible entries
•
Profile number
The default value can be used. Profile numbers cannot be used in the current version of the SPC200.
•
Interface type
The default entry “Interface type universal” can be
used. Alternatively you can select the type “Remote
bus.”
•
Icon
Open the dialogue window “Icon”, if you wish to use
a specific icon for the SPC200.
PLEASE NOTE
– The specific icons for the Festo products
can be found on the enclosed CD ROM.
– If necessary, read the file “Readme.txt” on the
CD ROM for a quick summary of the
contents of the CD ROM.
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
– Copy the file “Festo.ICL” into the
CMD directory (Folder) \PICTURE\.
4-19
Page 54
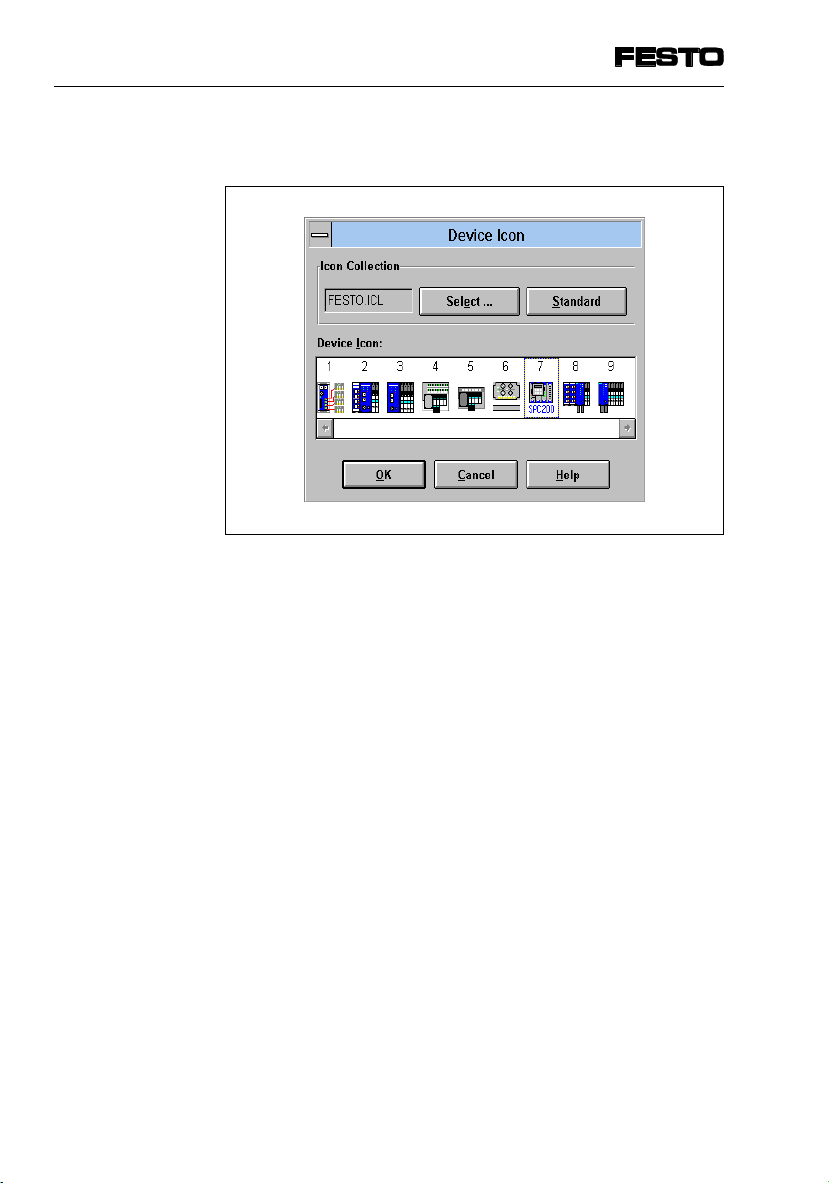
4. Commissioning
The following dialogue window will then appear:
Fig. 4/8: Dialogue window “Device Icon” for selecting
an icon
Proceed as follows:
4-20
•
Use the box “Select...” to select the file Festo.ICL.
•
Mark the icon which corresponds to your SPC200.
•
Accept the icon with OK.
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 55
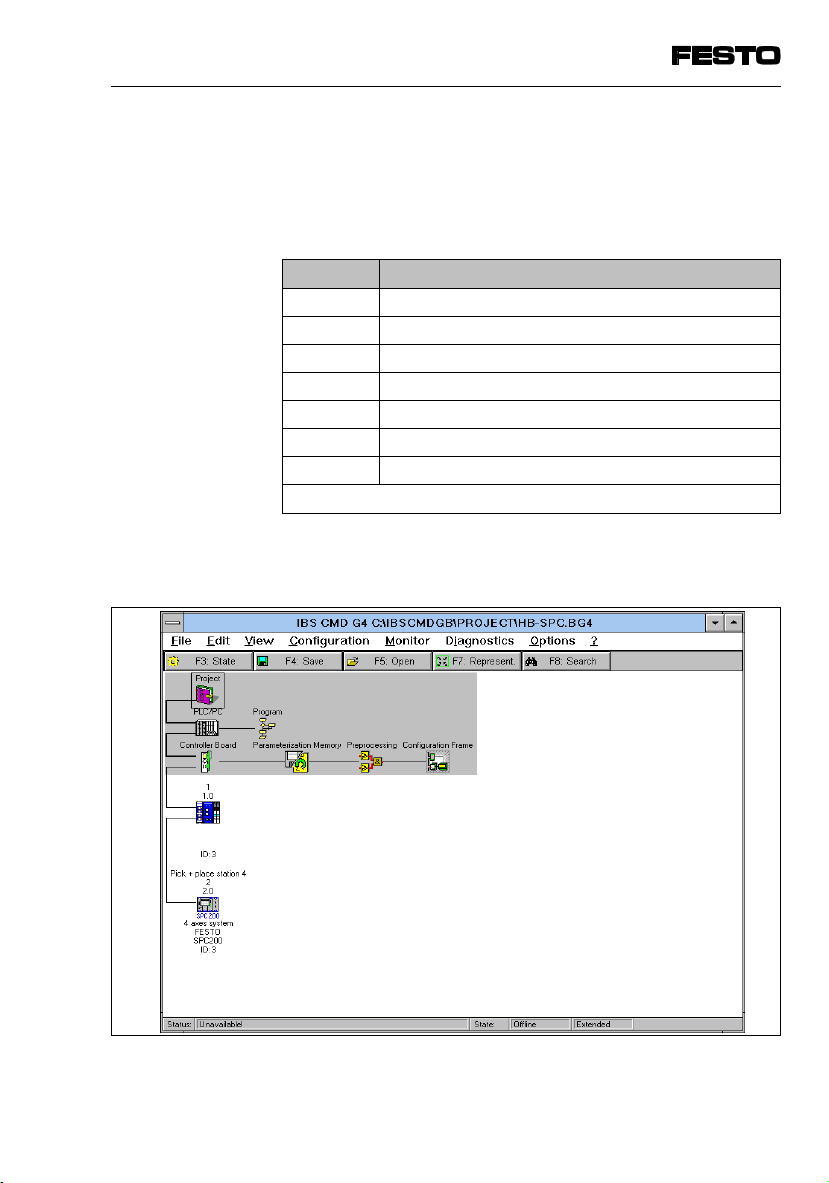
4. Commissioning
The icons are numbered. The table below shows the
correlation between the number of the icon and the
Festo products (Valve terminals types 02...10, positioning system SPC...):
Icon no. Festo products
1 Type 10 with four strings
2 Types 03-05 with inputs and outputs
3 Types 03-05 only with valves and/or outputs
4 Type 02 with inputs and outputs
5 Type 02 only with valve terminals
6 Type 10 CPV for INTERBUS loop
7 SPC200 with field bus module for INTERBUS
*)
Remote bus slave
*)
*)
*)
*)
*)
*)
When you have completed all the entries, the SPC200
is integrated into your bus system as follows (example).
Fig. 4/9: Example - Inserted valve terminal type 03 and SPC200
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
4-21
Page 56

4. Commissioning
4.3.2 Bus configuration without CMD software
Logical addressing
One or several configuration lists have been created in
the SPC or in the INTERBUS module for logical
addressing. These lists contain at least the following
entries:
– the ID codes of all the slaves
– the logical addresses of all the slaves
– the number of inputs
– the number of outputs
These specifications must be known or ascertained for
every slave. To do this proceed as follows with the
SPC200:
4-22
•
Assign the ID code 3
•
Assign a logical number to each SPC200.
•
Assign a logical IN and OUT address to each
to each SPC200.
D
SPC200. Depending on the operating mode of the
SPC200 and on the I/O configuration set with
WinPISA, the field bus module of the SPC200 occupies the appropriate number of bits (inputs/outputs,
see Chapters 4.2.2 and 4.1.3).
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 57
4. Commissioning
Physical addressing
PLEASE NOTE
Use the logical addressing or the bus configuration
via the CMD software, providing your INTERBUS
module permits this.
In this way you can avoid input and output addresses being shifted during later extensions.
The first bus slave is addressed with the basis address
(BA) of the INTERBUS module. The address of the
next bus slave is obtained by adding the relevant number of bits of the process data channel of all the previous slaves to the basis address. The procedure must
be carried out separately for inputs and outputs.
Example of physical addressing:
1st.
terminal
Process data
channel bits
Physical
address
*)
The field bus module of the SPC200 occupies the appropriate number of bits
depending on the operating mode of the SPC200 and on the I/O configuration set with
WinPISA (inputs/outputs, see Chapters 4.2.2 and 4.1.3).
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
32 64
BA BA+32 BA+32+64 BA+32+64+48BA+32+64+
2nd.
SPC200
*)
3rd.
SPC200
*)
48
4th.
terminal
32 16
5th.
terminal ...
48+32+....
4-23
Page 58
4. Commissioning
4.3.3 Switching on the power supplies on the INTERBUS
PLEASE NOTE
Observe also the switching-on instructions in the
PLC manual for your controller.
When you switch the controller on, it will automatically
carry out a comparison of the SET and ACTUAL
configurations. for this comparison it is important that
the specifications on the configuration are complete and
correct.
Please observe the following points when switching on
the power supply:
– Common supply: If there is a common supply for the
control system and all the field bus slaves, switch the
power supply on via a central power unit or switch.
– Separate supply: If there is a separate supply for the
control system and the field bus slaves, the supplies
should be switched on in the following order:
4-24
1. The power supply for all the field bus slaves.
2. The power supply for the control system.
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 59
4. Commissioning
4.4 Addressing the SPC200 on the INTERBUS
4.4.1 General information
Further information on addressing can be found in the
manuals for your controller and the INTERBUS module.
The address assignment (process data assignment) of
the inputs and outputs of an SPC200 on the
INTERBUS or on systems compatible thereto depends
primarily on the INTERBUS module and on the control
system used.
CAUTION
There are different address assignments on the
INTERBUS. The reason for this is the assignment of
the process data within the INTERBUS module and
not within the SPC200.
– Note with the assignment of the addresses the
position of the high and low bytes, as on some
control systems the position of these bytes may
be swapped.
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
You can thereby avoid errors when addressing the
SPC200.
4-25
Page 60

4. Commissioning
The following examples give basic instructions on the
different address assignments and the position of the
low byte (n) and the high byte (n+1). A distinction is
made here between the:
– Siemens mode and the
– Standard mode
Example:
– In the
Siemens mode
the lower-value output byte
(byte n) is mapped on outputs 0 - 7 of the field bus
module of the SPC200; byte n+1 on the next outputs
(8 - 15).
– In the
Standard mode
the lower-value output byte
(byte n) is mapped on outputs 8 - 15 of the field bus
module of the SPC200; byte n+1 on outputs 0-7.
These different assignments can be corrected with the
CMD software if the byte assignment is swapped (“Byte
swap”).
4-26
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 61
4. Commissioning
Example of Siemens mode
The assignment of the inputs and outputs of the field
bus module of the SPC200 to the addresses in the
Siemens mode is shown in the table below (example
for SPC200 start/stop mode).
Start/stop operating mode in the Siemens mode
Byte n+1 Byte n
7654321076543210
SPC200-COM-IBS
Freely programmable inputs Control signals
10.15 10.14 10.13 10.12 10.11 10.10 10.9 10.8 10.7 10.6 10.5 SYNC_BSYNC_AStop Start Enable
Fig. 4/10: Example of Siemens mode for SPC200 operating mode
start/stop
Example of standard mode
The assignment of the inputs and outputs of the field
bus module of the SPC200 to the addresses in the
standard mode is shown in the table below.
Start/stop operating mode in the standard mode
Byte n+1 Byte n
7654321076543210
SPC200-COM-IBS
Inputs Control signals Freely programmable inputs
10.7 10.6 10.5 SYNC_BSYNC_AStop Start En-
10.15 10.14 10.13 10.12 10.11 10.10 10.9 10.8
able
Fig. 4/11: Example of standard mode for SPC200 operating mode
start/stop
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
4-27
Page 62
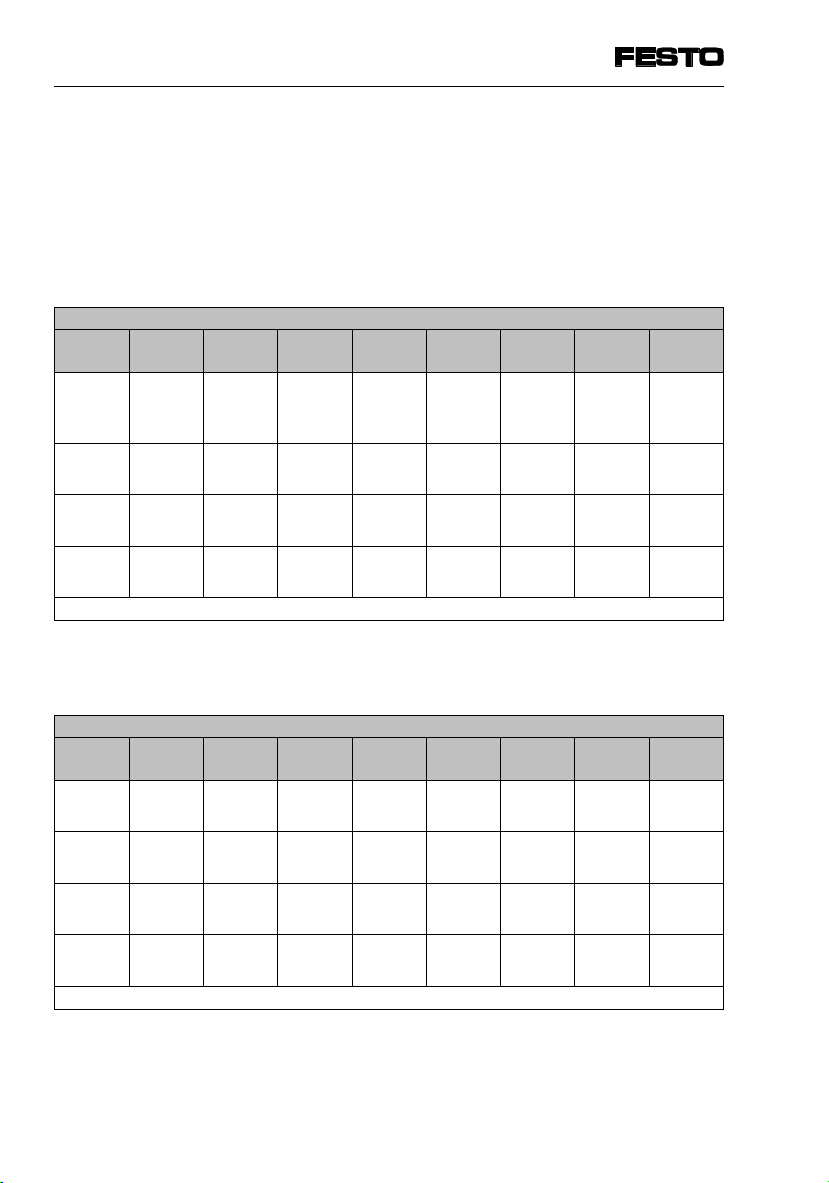
4. Commissioning
4.4.2 Summary of the I/O addresses of the SPC200-COM-IBS
Internal I/O addresses in start/stop mode
The configured outputs of the master are mapped on
the input bits.
Bit 6
Bit 14
1)
Bit 5
Bit 13
I10.5
I10.13
I11.5
I11.13
I12.5
I12.13
I13.5
I13.13
Input bits (I10.0 ... I13.15)
Byte Bit 7
n
n+1
n+2
n+3
n+4
n+5
n+6
n+7
1)
Address assignment as seen by the SPC200
Bit 15
I10.7
I10.15
I11.7
I11.15
I12.7
I12.15
I13.7
I13.15
I10.6
I10.14
I11.6
I11.14
I12.6
I12.14
I13.6
I13.14
The internal outputs of the field bus module are
mapped on the configured inputs of the master.
Output bits (Q10.0 ... Q13.15)
Byte Bit 7
n
n+1
n+2
n+3
n+4
n+5
n+6
n+7
1)
Address assignment as seen by the SPC200
Bit 15
Q10.7
Q10.15
Q11.7
Q11.15
Q12.7
Q12.15
Q13.7
Q13.15
Bit 6
Bit 14
Q10.6
Q10.14
Q11.6
Q11.14
Q12.6
Q12.14
Q13.6
Q13.14
1)
Bit 5
Bit 13
Q10.5
Q10.13
Q11.5
Q11.13
Q12.5
Q12.13
Q13.5
Q13.13
Bit 4
Bit 12
Sync_IB
I10.12
I11.4
I11.12
I12.4
I12.12
I13.4
I13.12
Bit 4
Bit 12
MC_B
Q10.12
Q11.4
Q11.12
Q12.4
Q12.12
Q13.4
Q13.12
Bit 3
Bit 11
Sync_IA
I10.11
I11.3
I11.11
I12.3
I12.11
I13.3
I13.11
Bit 3
Bit 11
MC_A
Q10.11
Q11.3
Q11.11
Q12.3
Q12.11
Q13.3
Q13.11
Bit 2
Bit 10
Stop
I10.10
I11.2
I11.10
I12.2
I12.10
I13.2
I13.10
Bit 2
Bit 10
Sync_OB
Q10.10
Q11.2
Q11.10
Q12.2
Q12.10
Q13.2
Q13.10
Bit 1
Bit 9
Start/
Reset
I10.9
I11.1
I11.9
I12.1
I12.9
I13.1
I13.9
Bit 1
Bit 9
Sync_OA
Q10.9
Q11.1
Q11.9
Q12.1
Q12.9
Q13.1
Q13.9
Bit 0
Bit 8
Enable
I10.8
I11.0
I11.8
I12.0
I12.8
I13.0
I13.8
Bit 0
Bit 8
Ready
Q10.8
Q11.0
Q11.8
Q12.0
Q12.8
Q13.0
Q13.8
4-28
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 63
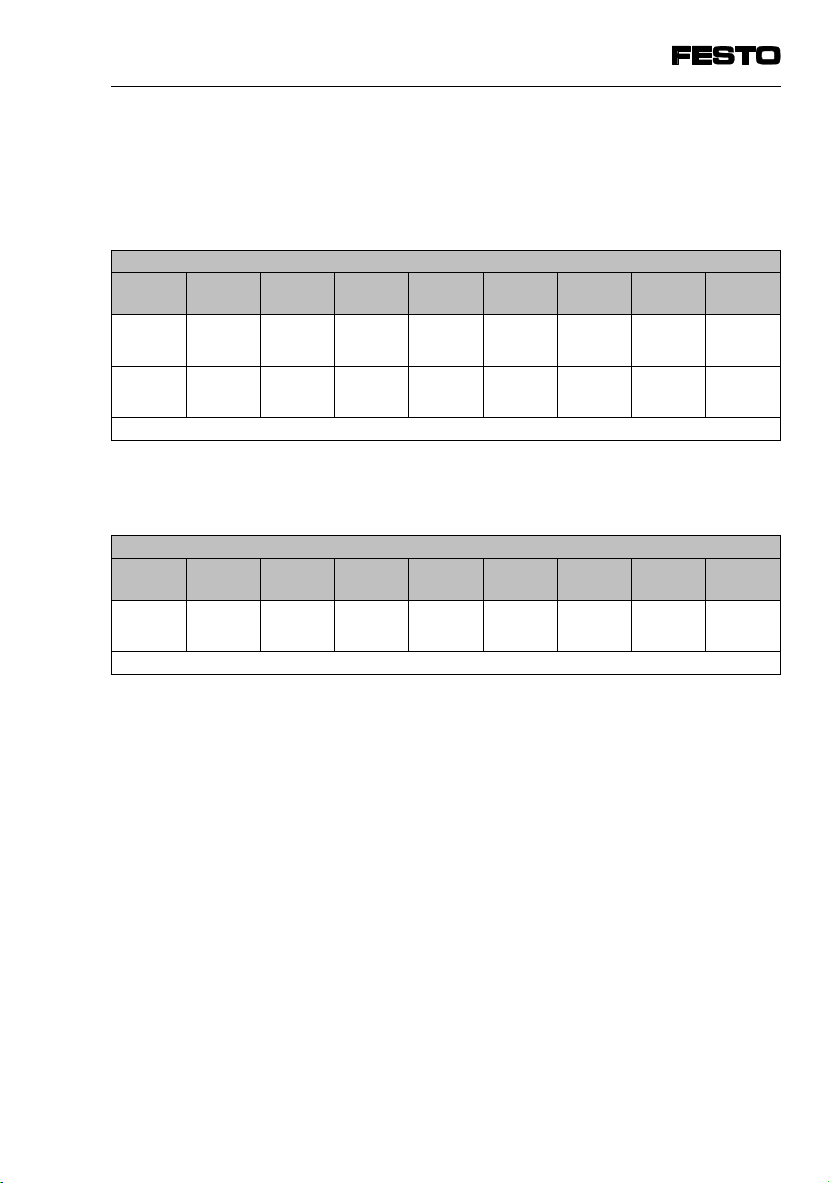
4. Commissioning
Internal I/O addresses in record select mode
The configured outputs of the master are mapped on
the input bits (I10.0 ... I13.15).
Bit 6
Bit 14
-
-
1)
Bit 5
Bit 13
-
-
Input bits (I10.0 ... I11.15)
Byte Bit 7
n
n+1
n+2
n+3
1)
Address assignment as seen by the SPC200
Bit 15
-
-
Recbit8-Recbit7-Recbit6-Recbit5-Recbit4-Recbit3
The internal outputs of the field bus module are
mapped on the configured inputs of the master.
Output bits (Q10.0 ... Q10.15)
Byte Bit 7
n
n+1
1)
Address assignment as seen by the SPC200
Bit 15
-
-
Bit 6
Bit 14
-
-
1)
Bit 5
Bit 13
-
-
Bit 4
Bit 12
CLK_B-CLK_A-Stop
Bit 4
Bit 12
RC_B-RC_A-ACK_B-ACK_A-Ready
Bit 3
Bit 11
Bit 3
Bit 11
Bit 2
Bit 10
-
Bit 2
Bit 10
Bit 1
Bit 9
Reset-Enable
Recbit10
Recbit2
Bit 1
Bit 9
Bit 0
Bit 8
-
Recbit9
Recbit1
Bit 0
Bit 8
-
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
4-29
Page 64
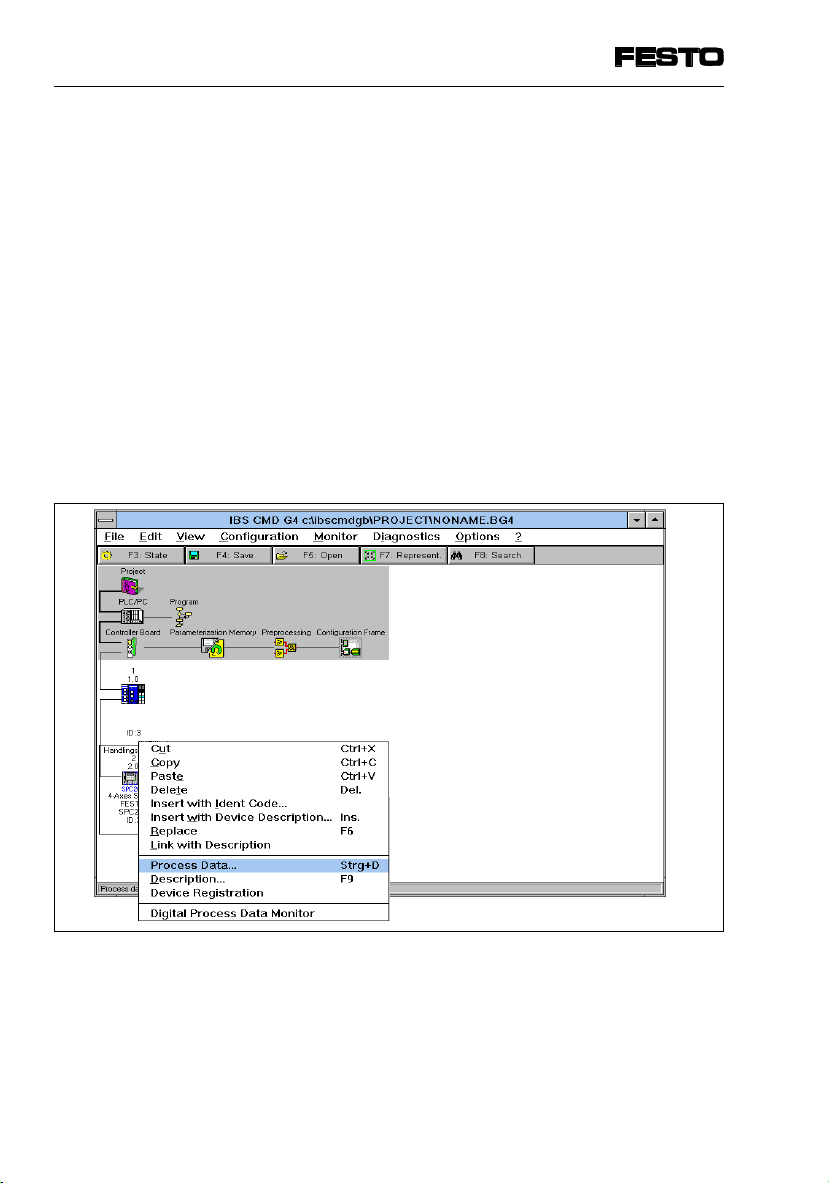
4. Commissioning
4.4.3 Entering process data via the CMD software
The CMD software offers as from version 4.x the possibility of assigning any output of the PLC/IPC to each
input or output of the field bus module of the SPC200,
within the configured address range. In order to do this,
proceed as follows:
•
Add the SPC200 to your bus structure (necessary
steps see section 4.3.1, “Bus configuration with CMD
software”).
•
Use the right-hand mouse button to open the dialogue window of the inserted SPC200.
•
Select the option “Process data”.
Fig. 4/12: Option for entering the process data
4-30
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 65
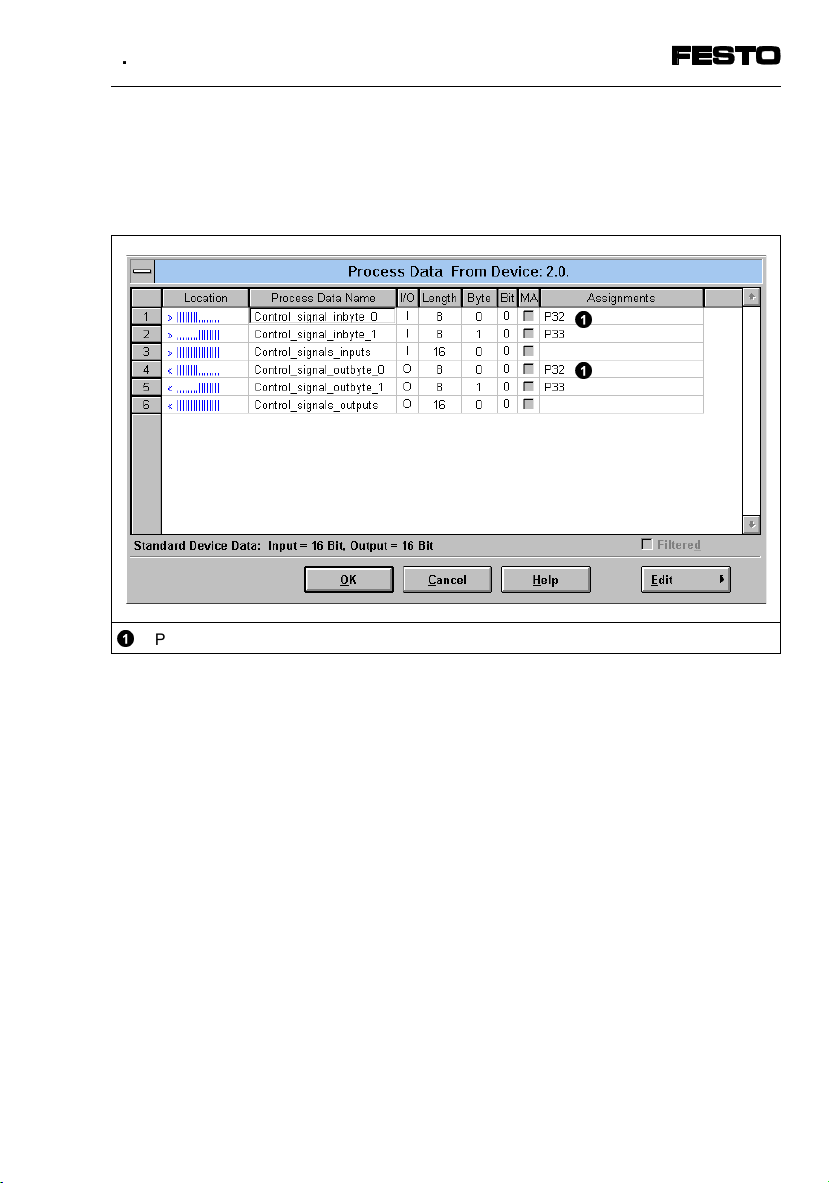
4. Commissioning
You can determine the I/O addresses in the following
menu (example: Siemens mode, byte-by-byte assignment for an S5).
©
©
P32 = Inbyte_0
©
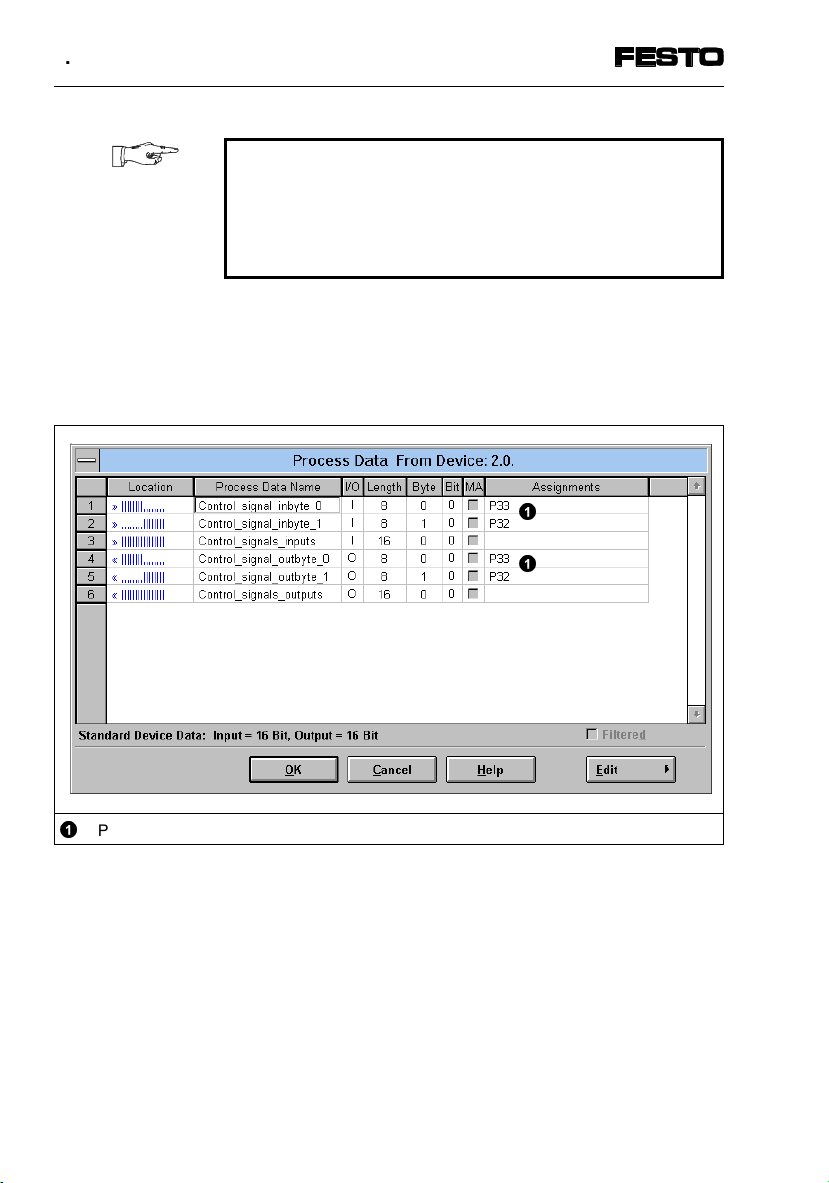
Fig. 4/13: Entering process data – example for Siemens mode
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
4-31
Page 66
4. Commissioning
PLEASE NOTE
In order to correct the byte swap, it will suffice if you
swap the assignment of the two bytes.
Individual I/O assignment at bit level is only necessary in a few cases.
The following dialogue window shows the entries
necessary for swapping/correcting the assignment of
the high and low bytes (example: byte swap for standard mode).
©
©
P33 = Inbyte_0 (Byte swap)
©
Fig. 4/14: Byte swap correction – example for standard mode
4-32
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 67
4. Commissioning
4.4.4 Preprocessing and periphery errors (PF)
Preprocessing
Under preprocessing we understand the logical linking
of process data within the INTERBUS module (formerly
called "Event programming" or "Receive bit manipulation").
PLEASE NOTE
All the inputs and outputs of the SPC200-COM-IBS
can be preprocessed.
Periphery errors (PF)
Field bus module type SPC200-COM-IBS does not
generate any periphery errors in the current version.
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
4-33
Page 68
4. Commissioning
4.5 Programming examples for an S5.
The following section contains programming examples
which should help you in programming your field bus
master. You must adapt position specifications and I/O
addresses to suit your application.
4.5.1 Basic principles
The examples are based on the following symbolic reference. The inputs of the SPC200 can be addressed
with the PLC output bytes 20 to 27; the outputs of the
SPC200 can be addressed with the PLC input bytes 20
to 27.
Inputs Outputs
E 20.0 #READY A 20.0 #ENABLE
E 20.1 #SYNCOA A 20.1 #START
E 20.2 #SYNCO A 20.2 #STOP
E 20.3 #MCA A 20.3 #SYNCI_A
E 20.4 #MCB A 20.4 #SYNCI_B
4-34
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 69

4. Commissioning
Generating a starting edge
L KH 1D00 Enable,Stop, set SYNCIA and SYNCIB
T AW 20
U -READY Wait until SPC200 is ready
S -START Generate start of both subsystems
BE
Quitting an M00 in subsystem A
U M 20.1 Step 1
U -SYNCOA and M00 applies
R -SYNCIA Quit M00
R M 20.1 in next step
S M 20.2
U M 20.2 Step 2
UN -SYNCOA and SPC200 has quitted M00
R M 20.2 in next step
S M 20.1
BE
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
4-35
Page 70

4. Commissioning
4.5.2 Handshake bits
Moving to different positions
– Program in SPC200, moves to three different posi-
tions
N0000 #TI11.0 20 Jump distributor for three positions
N0005 #TI11.1 30
N0010 #TI11.2 40
N0015 M30
N0020 G00 X200
N0025 M30
N0030 G00 X300
N0035 M30
N0040 G00 X400
N0045 M30
– Program in the S5
U E 0.0 When position 200 is selected
U -MCA and axis stands still
= A 22.0
U E 0.1 When position 300 is selected
U -MCA and axis stands still
= A 22.1
U E 0.2 When position 400 is selected
U -MCA and axis stands still
= A 22.2
BE
4-36
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 71

4. Commissioning
Setting outputs
– Complicated method! Program in SPC200
N0000 #TI11.0 30 Set or reset an output
N0010 #RQ1.0
N0020 E05 40
N0030 #SQ1.0
N0040...
– Program in the S5
U E 0.0 When input is actuated on PLC
= A 22.0 Set SPC200 handshake bit
BE
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
4-37
Page 72

4. Commissioning
Interrogating inputs
– Complicated method! Program in SPC200
N0000 #TI1.0 30 Status message of an input to the PLC
N0010 #RQ11.0
N0020 E05 40
N0030 #SQ11.0
N0040...
– Program in the S5
U E 22.0 When input on SPC200 is actuated
= A 0.0 Set PLC output
BE
4-38
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 73

4. Commissioning
4.5.3 Record select
Record 3 of subsystem A is started with this S5 program..
L KH 0003 Record number
T AW 22
UN -CLKA When PLC is in starting position
UN -ACKA and SPC200 is ready
U -RCA
S -CLKA Start record
U -CLKA When task is placed
U -ACKA and accepted
UN -RCA
R -CLKA Return to starting position
BE
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
4-39
Page 74

4. Commissioning
4-40
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 75

5. Diagnosis and error treatment
Chapter 5
Diagnosis and error treatment
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
5-1
Page 76

5. Diagnosis and error treatment
Contents
5. Diagnosis and error treatment
5.1 General instructions on diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
5.2 On-the-spot diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
5.3 Diagnosis via WinPISA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
5.4 Interruption in field bus connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
5-2
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 77

5. Diagnosis and error treatment
5.1 General instructions on diagnosis
Information on general diagnosis and error treatment
can be found in the user manual for the SPC200 order
no. P.BE-SPC200-GB. This chapter contains information on diagnosing the field bus module as well as diagnosis and error treatment with the INTERBUS.
Summary of diagnostic possibilities
The SPC200 offers the following possibilities of diagnosis and error treatment:
– The LEDs on the SPC200 and on the connected field
devices show directly configuration errors, hardware
errors, string errors, bus errors, etc.
– The control panel shows detailed error messages
coded in the form of an 8-figure hexadecimal number. In online mode WinPISA shows the 8-figure
error messages as well as a description of the error
in clear text.
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
– Several error messages and statistics on the bus
connection can be read out on the INTERBUS via
the module (see manual for the CMD software or the
IBS plug-in module).
– The output bit READY (Q10.0) shows the basic sys-
tem readiness by means of the internal I/Os of the
field bus module.
5-3
Page 78
5. Diagnosis and error treatment
5.2 On-the-spot diagnosis
The four LEDs on the field bus module permit a
speedy on-the-spot diagnosis of the communication
status. Note also the LEDs on the other modules of the
SPC200 and their description in the user manual for the
SPC200.
LED displays on the field bus module type
SPC200-COM-IBS
RD LED RC LED BA LED Operating status
out out out No voltage
flashes
slowly
flashes
fast
on out out Field bus card ready for bus operation, but still no
on on out Connection to the INTERBUS but still no data
out on out Connection to the INTERBUS but no data exchange
out on on INTERBUS active, normal operating status
– = Status of the LED is not relevant
– – Field bus module waits for parameter data of the
SPC200
– – Parameter error. Operating mode, process data size
incorrectly set or not yet parametrized.
physical connection to the INTERBUS.
exchange (bus inactive).
(bus inactive)
Fig. 5/1: Meaning of the LEDs on field bus module type SPC200-COM-IBS
5-4
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 79

5. Diagnosis and error treatment
5.3 Diagnosis via WinPISA
In WinPISA you can read out the set parameters of the
field bus module as well as further status information as
follows [Register: Field bus]:
Fig. 5/2: Status display of the field bus module in
WinPISA
Status of Message/meaning
Connection
Bus address No significance with INTERBUS
Baud rate Current baud rate (up till now fixed at 500 kBit/s, later extension
I/O assignment The process data of the field bus module on the INTERBUS
Software version Current version of the field bus module SPC200-COM-IBS
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Offline
(no physical connection to the INTERBUS)
or
Bus inactive
or
Bus active
possible)
parametrized via WinPISA.
(there is a connection, but no data exchange)
(data exchange takes place with the field bus master)
5-5
Page 80

5. Diagnosis and error treatment
5.4 Interruption in field bus connection
If there is an interruption in the field bus connection
(INTERBUS) during operation, the module type
SPC200-COM-IBS will react as follows:
– the control bit "STOP" will be reset
– the other control bits will be frozen
– the SPC200 will enter a safe status.
5-6
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 81

A. Technical appendix
Appendix A
Technical appendix
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
A-1
Page 82

A. Technical appendix
Contents
A. Technical appendix
A.1 Technical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-3
A.2 Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-5
A-2
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 83
A. Technical appendix
A.1 Technical specifications
Type SPC200-COM-IBS
Temperature range:
-operation
- storage/transport
Weight 80 g
Relative humidity 95 % non condensing
Field bus
-design
- transmission type
-protocol
- baud rate
- cable length (between
two remote bus slave)
- cable length of complete
system
Electromagnetic
compatibility
- Interference emitted
- Immunity against
interference
o
C ... + 50 oC
-5
o
-20
C ... + 70 oC
RS 422, floating
serial asynchronous, full-duplex
INTERBUS
500 kbaud automatic
baud rate recognition
max. 400 m
up to 12.8 km
Tested as per
DIN EN 61000-6-4 (industry)
1)
Tested as per
DIN EN 61000-6-2 (industry)
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Oscillation and shock
- oscillation
- shock
1)
The component is intended for industrial use.
tested as per DIN/IEC 68
part 2-6–6 severity 1
tested as per DIN/IEC 68
part 2- 27–27 severity 2
A-3
Page 84

A. Technical appendix
A-4
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 85

A. Technical appendix
A.2 Index
A
Addressing the SPC200 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-25
B
Basic principles of configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-12
Basic structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
Baud rate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-10
Bus configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-15
Byte swap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-26, 4-32
C
CD ROM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-19
CMD software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-15, 4-30
Commissioning
Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-11
Control panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-11
field bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
with WinPISA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
D
Diagnosis
field bus connection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
LED displays on the field bus module. . . . . . . . . 5-4
WinPISA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
Display elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Download . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-11
A-5
Page 86

A. Technical appendix
E
Entering process data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-30
F
Field bus cable
Fitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
I
I/O addresses
I/O control signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
Icon. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-19
Ident-code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-16
Important user instructions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . VI
Installation instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
INTERBUS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3, 1-5, 4-9, 4-25
INTERBUS interface
Interruption in field bus connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-28
addressing variants . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-14
bus configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-15
connecting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
pin assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
A-6
L
LEDs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
Page 87

A. Technical appendix
O
Operating modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7, 4-13
P
Periphery errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-33
Preprocessing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-33
Process data assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-25
Process data channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-11, 4-17
Programming examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-34
R
Record select mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7, 4-29
Register tab
Remote bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
I/O address range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
program test. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
field bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-10
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
S
Siemens mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-26 - 4-27, 4-31
Slave
description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-18
SPC200
addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-25
SPC200 configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
Standard mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-26 - 4-27, 4-32
Start/stop mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-28
Switching on. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-24
System structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
A-7
Page 88

A. Technical appendix
T
Technical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-3
Test mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
W
WinPISA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-13
A-8
SPC200-COM-IBS 0503a
 Loading...
Loading...