Page 1

FAGOR 8025/8030 CNC
Models: M, MG, MS, GP
INSTALLATION MANUAL
Ref. 9707 (in)
Page 2

ABOUT THE INFORMATION IN THIS MANUAL
This manual is addressed to the machine manufacturer.
It includes the necessary information for new users as well as advanced subjects for
those who are already familiar with the 8025 CNC.
It may not be necessary to read this whole manual. Consult the list of "New Features
and Modifications" and the appendix related to the machine parameters. Practically
all of them are cross referenced indicating the chapter and section of the manual
where they are described.
This manual explains all the functions of the 8025 CNC family. Consult the
Comparison Table for the models in order to find the specific ones offered by your
CNC.
To install the CNC onto your machine, we suggest that you consult the appendix
regarding the enclosures required to mount the CNC as well as chapter 1 (CNC
configuration) which indicates the CNC dimensions and details the pin-out of its
connectors.
If your CNC has an integrated PLC (PLCI), the I/O pin-out is different. Therefore,
the PLCI manual must also be consulted.
Chapter 2 (Power and Machine Interface) shows how to connect the CNC to A.C.
power (Mains) and to the electrical cabinet.
To adapt the CNC to the machine, set the CNC machine parameters. Consult chapters
3, 4 and 5 as well as the appendix concerning machine parameters.
There are 2 appendices; one where the parameters are ordered by subject and the
other one where the parameters are in numerical order.
Both appendices offer cross references indicating the section of the manual describing
each parameter.
When explaining each parameter in detail, chapters 3, 4 and 5, they sometimes refer
to chapter 6 (Concepts) where some of them are dealt with in further detail indicating
how to perform various adjustments of the CNC-machine interface.
Once all machine parameters are set, we suggest that you write their settings down
on the charts provided for this purpose in the appendix on "Machine Parameter Setting
Chart".
There is also an appendix on error codes which indicates some of the probable reasons
which could cause each one of them.
Also, if you wish this CNC to communicate with other FAGOR products, you must
use the Fagor Local Area Network (LAN). To do that, refer to the manual on FAGOR
LAN.
Notes
: The information described in this manual may be subject to variations due
to technical modifications.
FAGOR AUTOMATION, S. Coop. Ltda. reserves the right to modify the
contents of this manual without prior notice.
Page 3
INDEX
Section Page
Comparison Table for 8025/8030 CNC models .......................................................ix
New features and modifications ................................................................................xv
INTRODUCTION
Declaration of Conformity ........................................................................................3
Safety Conditions ......................................................................................................4
Warranty Terms .........................................................................................................7
Material Returning Terms .........................................................................................8
Additional Remarks ...................................................................................................9
Fagor Documentation for the 800T CNC ..................................................................11
Manual Contents .......................................................................................................12
Chapter 1 CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
1.1 8025 CNC..................................................................................................................1
1.1.1 Dimensions and installation of the 8025 CNC ........................................................2
1.2 8030 CNC..................................................................................................................3
1.2.1 Central Unit of the 8030 CNC..................................................................................4
1.2.1.1 Keyboard connector ..................................................................................................6
1.2.1.2 Video connector ........................................................................................................8
1.2.2 Monitor/keyboard of the 8030 CNC ........................................................................9
1.2.2.1 Dimensions of the monitor/keyboard ........................................................................9
1.2.2.2 Elements of the monitor/keyboard ...........................................................................10
1.2.2.3 Connectors and monitor/keyboard interface.............................................................11
1.2.3 Operator panel of the 8030 CNC ..............................................................................12
1.3 Connectors and 8025/8030 CNC interface ...............................................................13
1.3.1 Connectors A1, A2, A3, A4.......................................................................................15
1.3.1.1 Dip-switches for connectors A1, A2, A3, A4 ............................................................16
1.3.2 Connector A5 ............................................................................................................17
1.3.2.1 Dip-switches for connector A5..................................................................................18
1.3.3 Connector A6 ............................................................................................................19
1.3.3.1 Machine with "V" axis and handwheel or spindle encoder .....................................20
1.3.3.2 Machine without "V" axis and with electronic handwheel or spindle encoder.......20
1.3.4 RS232C connector ....................................................................................................21
1.3.5 RS485 connector .......................................................................................................24
1.3.5.1 Recommended cable for the RS485..........................................................................24
1.3.6 Connector I/O 1.........................................................................................................25
1.3.6.1 Inputs of connector I/O 1 ..........................................................................................26
1.3.6.2 Outputs of connector I/O 1 .......................................................................................29
1.3.7 Connector I/O 2.........................................................................................................31
1.3.7.1 Outputs of connector I/O 2 .......................................................................................32
Page 4
Section Page
Chapter 2 POWER AND MACHINE INTERFACE
2.1 Power interface......................................................................................................... 1
2.1.1 Internal power supply ............................................................................................... 1
2.2 Machine interface ..................................................................................................... 2
2.2.1 General considerations ............................................................................................. 2
2.2.2 Digital outputs .......................................................................................................... 4
2.2.3 Digital inputs ............................................................................................................ 4
2.2.4 Analog outputs.......................................................................................................... 5
2.2.5 Feedback inputs ........................................................................................................ 5
2.3 Set-up........................................................................................................................ 6
2.3.1 General considerations ............................................................................................. 6
2.3.2 Precautions................................................................................................................ 6
2.3.3 Connection ................................................................................................................ 7
2.3.4 System input/output test ........................................................................................... 8
2.4 Emergency input/output connection......................................................................... 10
Chapter 3 MACHINE PARAMETERS
3.1 Introduction .............................................................................................................. 1
3.2 Operating with parameter tables............................................................................... 3
3.3 General machine parameters .................................................................................... 4
3.3.1 Machine parameters for axis configuration.............................................................. 6
3.3.2 Input/output parameters ............................................................................................ 9
3.3.3 Handwheel parameters.............................................................................................. 14
3.3.4 Touch probe parameters ........................................................................................... 16
3.3.5 Tool parameters ........................................................................................................ 18
3.3.6 Machine parameters for the RS232C serial line....................................................... 22
3.3.7 Jog parameters .......................................................................................................... 24
3.3.8 Parameters related to the emergency subroutine...................................................... 25
3.3.9 Parameters related to operating and programming modes ....................................... 26
Chapter 4 MACHINE PARAMETERS FOR THE AXES
4.1 Parameters related to axis resolution........................................................................ 2
4.2 Parameters related to the analog outputs .................................................................. 5
4.3 Parameters related to travel limits............................................................................ 6
4.4 Feedrate related parameters...................................................................................... 7
4.5 Parameters related to axis control ............................................................................ 10
4.6 Parameters related to machine reference zero.......................................................... 12
4.7 Parameters for acceleration/deceleration of the axes ............................................... 15
4.7.1 Linear acceleration/deceleration ............................................................................... 15
4.7.2 Bell-shaped acceleration/deceleration ...................................................................... 16
4.7.3 Feed-forward gain..................................................................................................... 17
4.8 Parameters for unidirectional approach.................................................................... 18
4.9 Leadscrew related parameters .................................................................................. 19
4.9.1 Leadscrew backlash .................................................................................................. 19
4.9.2 Leadscrew error ........................................................................................................ 20
4.10 Parameters related to cross compensation................................................................ 23
4.10.1 Double cross compensation ...................................................................................... 24
4.11 Pallet related parameters........................................................................................... 25
4.12 Special machine parameters ..................................................................................... 27
Page 5
Section
Chapter 5 SPINDLE MACHINE PARAMETERS
5.1 Parameters related to spindle speed range change ................................................... 2
5.2 Parameters for analog spindle speed output............................................................. 3
5.3 Parameters for spindle speed output in BCD ........................................................... 4
5.4 Parameters used for spindle control ......................................................................... 6
5.5 Parameters related to spindle orientation (M19)...................................................... 7
5.6 Parameters related to rigid tapping (G84R) ............................................................. 10
Chapter 6 CONCEPTS
6.1 Axes and coordinate systems.................................................................................... 1
6.1.1 Nomenclature and selection of the axes................................................................... 1
6.2 Feedback systems ..................................................................................................... 2
6.2.1 Counting frequency limits ........................................................................................ 3
6.3 Axis resolution.......................................................................................................... 4
6.4 Adjustment of the axes............................................................................................. 13
6.4.1 Adjustment of the drift (offset) and maximum feedrate (G00) ................................ 14
6.4.2 Gain adjustment ........................................................................................................ 16
6.4.3 Proportional gain adjustment.................................................................................... 17
6.4.3.1 Calculation of K1, K2 and gain break-point............................................................ 19
6.4.4 Feed-Forward gain adjustment ................................................................................. 21
6.4.4.1 Calculation of feed-forward gain ............................................................................. 21
6.4.5 Leadscrew error compensation ................................................................................. 22
6.5 Reference systems .................................................................................................... 25
6.5.1 Reference points ....................................................................................................... 25
6.5.2 Machine reference (home) search ............................................................................ 26
6.5.2.1 Home search on gantry axes .................................................................................... 27
6.5.3 Adjustment on a system without coded Io ............................................................... 28
6.5.3.1 Machine reference point (home) adjustment............................................................ 28
6.5.3.2 Considerations .......................................................................................................... 29
6.5.4 Adjustment on axis with coded Io............................................................................ 30
6.5.4.1 Scale Offset adjustment............................................................................................ 30
6.5.4.2 Considerations .......................................................................................................... 31
6.5.5 Software travel limits for the axes ........................................................................... 32
6.6 Unidirectional approach ........................................................................................... 33
6.7 Auxiliary functions M, S, T ..................................................................................... 34
6.7.1 Decoded M function table ........................................................................................ 35
6.7.2 M, S, T function transfer .......................................................................................... 37
6.7.3 M, S, T function transfer using the M-done signal.................................................. 38
6.8 Spindle...................................................................................................................... 40
6.9 Spindle speed range change ..................................................................................... 43
6.10 Spindle control.......................................................................................................... 45
6.11 Tools and tool magazine .......................................................................................... 47
6.11.1 Machine without tool magazine ............................................................................... 47
6.11.2 Not-random tool magazine ....................................................................................... 48
6.11.3 Random tool magazine ............................................................................................. 51
6.11.4 Application examples ............................................................................................... 54
6.11.4.1 Not-random magazine with tool changer arm .......................................................... 54
6.11.4.2 Not-random magazine without tool changer arm..................................................... 54
6.12 Pallet work................................................................................................................ 55
Page
Page 6
Section
APPENDICES
A Technical characteristics of the CNC ....................................................................... 2
B Enclosures ................................................................................................................. 5
C Recommended Probe connection diagrams .............................................................. 6
D CNC inputs and outputs ........................................................................................... 7
E 2-digit BCD coded "S" output conversion table ...................................................... 8
F Machine parameter summary chart .......................................................................... 9
G Sequential machine parameter list............................................................................ 15
H Machine parameter setting chart .............................................................................. 24
I Decoded "M" function setting chart ......................................................................... 26
J Leadscrew error compensation setting chart ............................................................ 27
K Cross compensation setting chart ............................................................................ 29
L Maintenance ............................................................................................................. 30
ERROR CODES
Page
Page 7
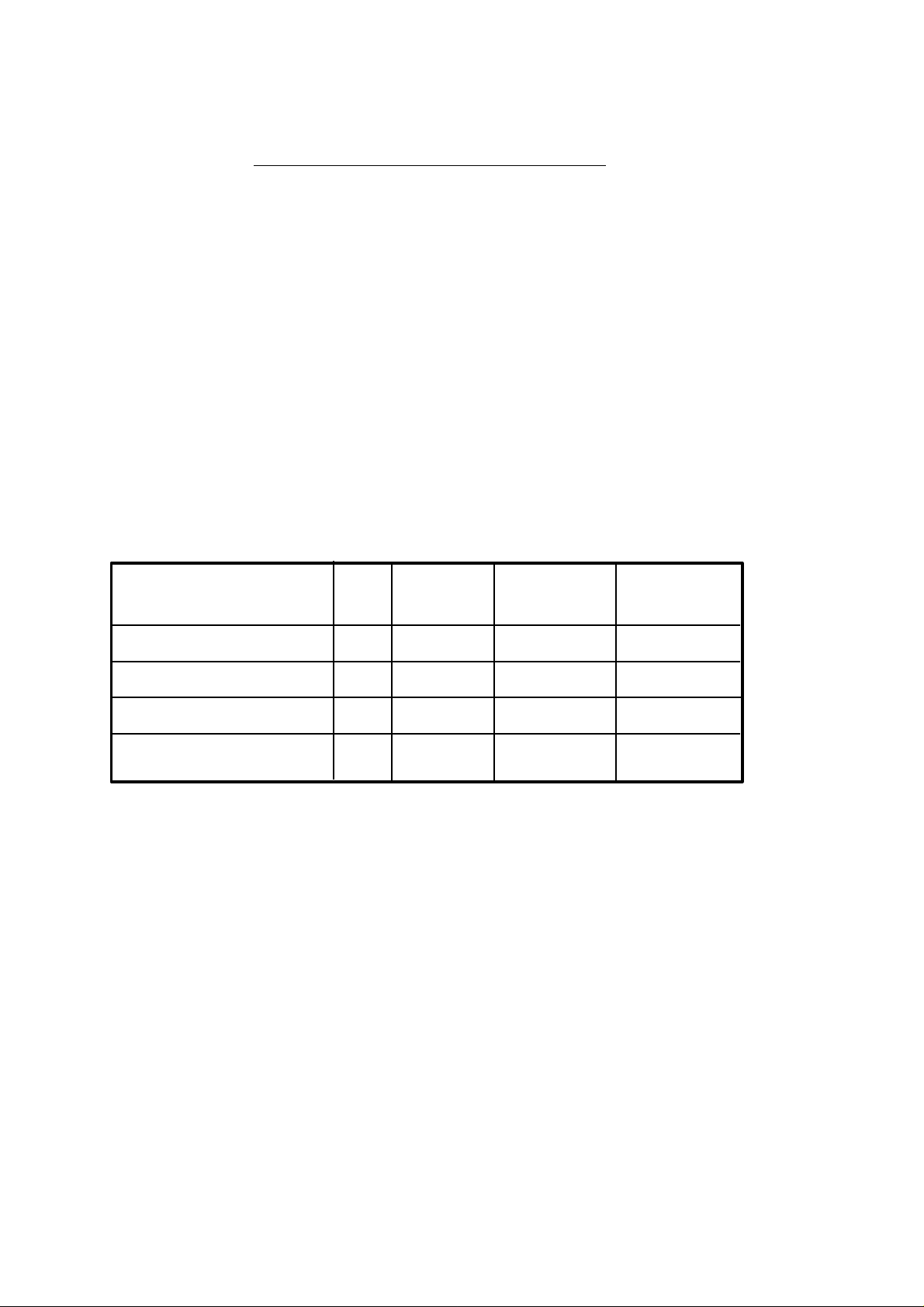
COMPARISON TABLE
FOR MILL MODEL
FAGOR 8025/8030 CNCs
Page 8
8025/8030 MILL MODEL CNCS
Fagor offers the 8025 and 8030 mill type CNCs.
Both types operate the same way and offer similar characteristics. Their basic difference is that
the former is compact and the latter is modular.
Both CNC types offer basic models. Although the differences between the basic models are
detailed later on, each model may be defined as follows:
8025/8030 GP Oriented to General Purpose machines
8025/8030 M Oriented to Milling machines of up to 4 axes.
8025/8030 MG Same as the M model, but with dynamic graphics.
8025/8030 MS Oriented to Machining Centers (up to 5 axes).
When the CNC has an Integrated Programmable Logic Controller (PLCI), the letter "I" is added
to the CNC model denomination: GPI, MI, MGI, MSI.
Also, When the CNC has 512Kb of part-program memory, the letter "K" is added to the CNC
model denomination: GPK, MK, MGK, MSK, GPIK, MIK, MGIK, MSIK.
Basic With PLCI Basic With PLCI
With 512Kb and 512Kb
General Purpose GP GPI GPK GPKI
Mills up to 4 axes M MI MK MIK
Up to 4 axes with graphics MG MGI MGK MGIK
Machining Centers MS MSI MSK MSIK
Page 9
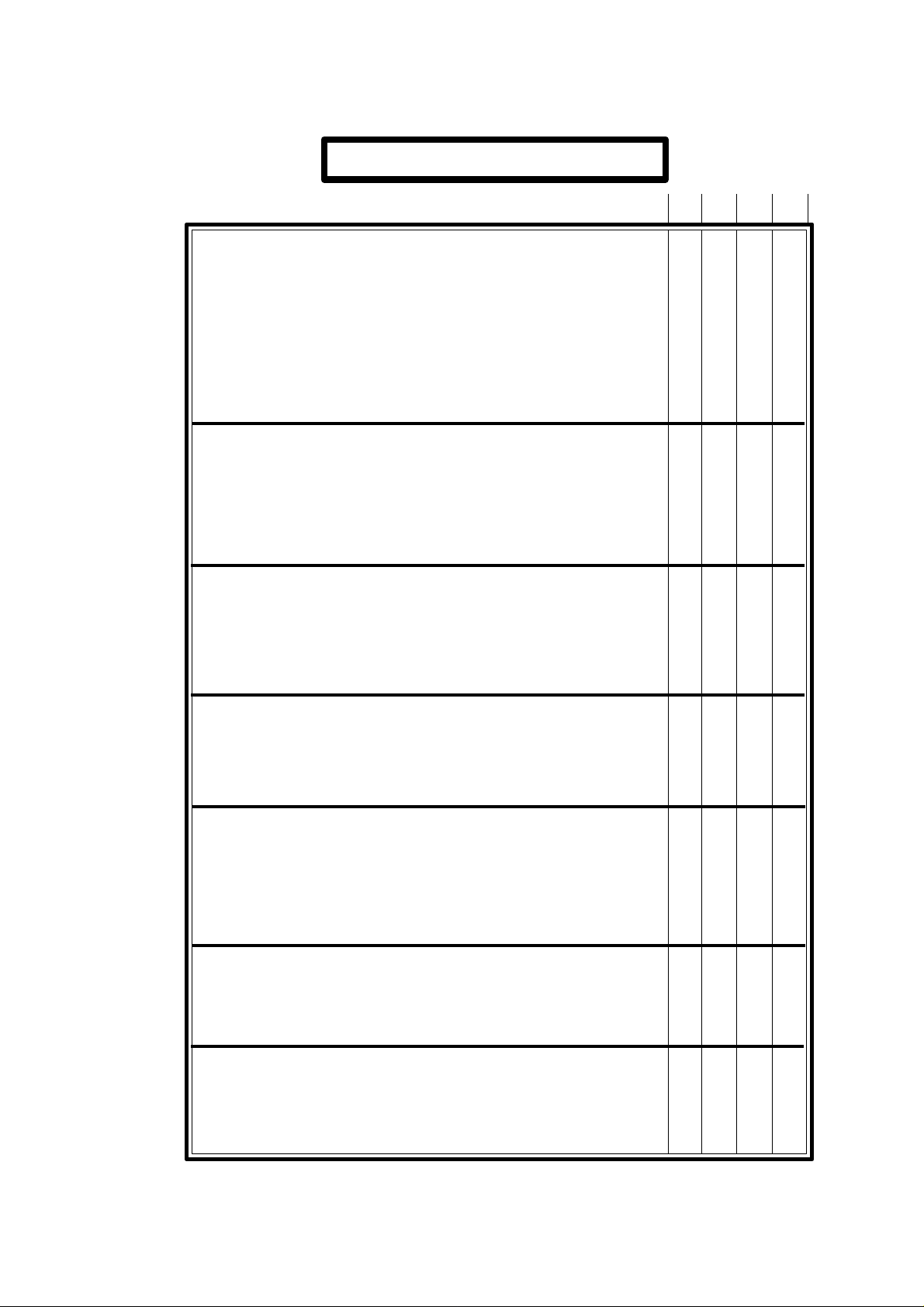
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
GP M MG MS
INPUTS/OUTPUTS
Feedback inputs...................................................................................... 6 6 6 6
Probe input .......................................................................................... x x x x
Square-wave feedback signal multiplying factor, x2/x4........................... x x x x
Sine-wave feedback signal multiplying factor, x2/x4/10/x20 ................... x x x x
Maximum counting resolution 0.001mm/0.001°/0.0001inch ................... x x x x
Analog outputs (±10V) for axis servo drives ........................................... 4 4 4 5
Spindle analog output (±10V)................................................................. 1 1 1 1
AXIS CONTROL
Axes involved in linear interpolations ..................................................... 3 3 3 3
Axes involved in circular interpolations .................................................. 2 2 2 2
Helical interpolation ............................................................................... x x x x
Electronic threading ............................................................................... x x x
Spindle control ....................................................................................... x x x x
Software travel limits.............................................................................. x x x x
Spindle orientation ................................................................................. x x x x
Management of non-servo-controlled Open-Loop motor ......................... x
PROGRAMMING
Part Zero preset by user .......................................................................... x x x x
Absolute/incremental programming ........................................................ x x x x
Programming in cartesian coordinates..................................................... x x x x
Programming in polar coordinates .......................................................... x x x x
Programming in cylindrical coordinates (radius, angle, axis) ................... x x x x
Programming by angle and cartesian coordinate...................................... x x x x
Linear axes ........................................................................ 4 4 4 5
Rotary axes ........................................................................ 2 2 2 2
Spindle encoder ................................................................. 1 1 1 1
Electronic handwheels ....................................................... 1 1 1 1
COMPENSATION
Tool radius compensation ....................................................................... x x x
Tool length compensation....................................................................... x x x x
Leadscrew backlash compensation.......................................................... x x x x
Leadscrew error compensation ............................................................... x x x x
Cross compensation (beam sag) .............................................................. x x x x
DISPLAY
CNC text in Spanish, English, French, German and Italian ...................... x x x x
Display of execution time ....................................................................... x x x x
Piece counter.......................................................................................... x x x x
Graphic movement display and part simulation ....................................... x x
Tool base position display ...................................................................... x x x x
Tool tip position display ......................................................................... x x x x
Geometric programming aide ................................................................. x x x x
COMMUNICATION WITH OTHER DEVICES
Communication vía RS232C................................................................... x x x x
Communication via DNC ....................................................................... x x x x
Communication via RS485 (FAGOR LAN) ............................................ x x x x
ISO program loading from peripherals .................................................... x x x x
OTHERS
Parametric programming ........................................................................ x x x x
Model digitizing ..................................................................................... x x x x
Possibility of an integrated PLC.............................................................. x x x x
Sheetmetal tracing on LASER machines ................................................. x
Jig Grinder .......................................................................................... x
Page 10

PREPARATORY FUNCTIONS
GP M MG MS
AXES AND COORDINATE SYSTEMS
XY (G17) plane selection ....................................................................... x x x x
XZ and YZ plane selection (G18,G19).................................................... x x x x
Part measuring units. Millimeters or inches (G70,G71) ........................... x x x x
Absolute/incremental programming (G90,G91) ...................................... x x x x
Independent axis (G65) .......................................................................... x x x x
REFERENCE SYSTEMS
Machine reference (home) search (G74) ................................................. x x x x
Coordinate preset (G92) ......................................................................... x x x x
Zero offsets (G53...G59)......................................................................... x x x x
Polar origin preset (G93) ........................................................................ x x x x
Store current part zero (G31) .................................................................. x x x x
Recover stored part zero (G32) .............................................................. x x x x
PREPARATORY FUNCTIONS
Feedrate F .......................................................................................... x x x x
Feedrate in mm/min. or inches/minute (G94) .......................................... x x x x
Feedrate in mm/revolution or inches/revolution (G95) ............................ x x x x
Constant surface speed (G96) ................................................................. x x x x
Constant tool center speed (G97) ............................................................ x x x x
Programmable feedrate override (G49) ................................................... x x x x
Spindle speed (S).................................................................................... x x x x
S value limit (G92) ................................................................................. x x x x
Tool and tool offset selection (T) ............................................................ x x x x
AUXILIARY FUNCTIONS
Program stop (M00) ............................................................................... x x x x
Conditional program stop (M01)............................................................. x x x x
End of program (M02)............................................................................ x x x x
End of program with return to first block (M30)...................................... x x x x
Clockwise spindle start (M03) ................................................................ x x x x
Counter-clockwise spindle start (M04).................................................... x x x x
Spindle stop (M05)................................................................................. x x x x
Tool change in machining centers (M06) ................................................ x x x x
Spindle orientation (M19)....................................................................... x x x x
Spindle speed range change (M41, M42, M43, M44) .............................. x x x x
Functions associated with pallets (M22, M23, M24, M25) ...................... x x x
PATH CONTROL
Rapid traverse (G00) ............................................................................ x x x x
Linear interpolation (G01) ....................................................................x x x x
Circular interpolation (G02,G03) ..........................................................x x x x
Circular interpolation with absolute center coordinates (G06)................x x x x
Circular path tangent to previous path (G08).........................................x x x x
Arc defined by three points (G09)......................................................... x x x x
Tangential entry at beginning of a machining operation (G37) .............x x x x
Tangential exit at the end of a machining operation (G38).....................x x x x
Controlled radius blend (G36) ..............................................................x x x x
Chamfer (G39) .....................................................................................x x x x
Electronic threading (G33) ..................................................................... x x x
ADDITIONAL PREPARATORY FUNCTIONS
Dwell (G04 K) .....................................................................................x x x x
Round and square corner (G05, G07).................................................... x x x x
Mirror image (G10,G11,G12) ............................................................... x x x x
Mirror image along the Z axis (G13).....................................................x x x x
Scaling factor (G72) .............................................................................x x x x
Pattern rotation (G73)...........................................................................x x x x
Slaving/unslaving of axes (G77, G78)...................................................x x x x
Single block treatment (G47, G48)........................................................x x x x
User error display (G30) .......................................................................x x x x
Automatic block generation (G76) .......................................................... x
Communication with FAGOR Local Area Network (G52) ....................x x x x
Page 11
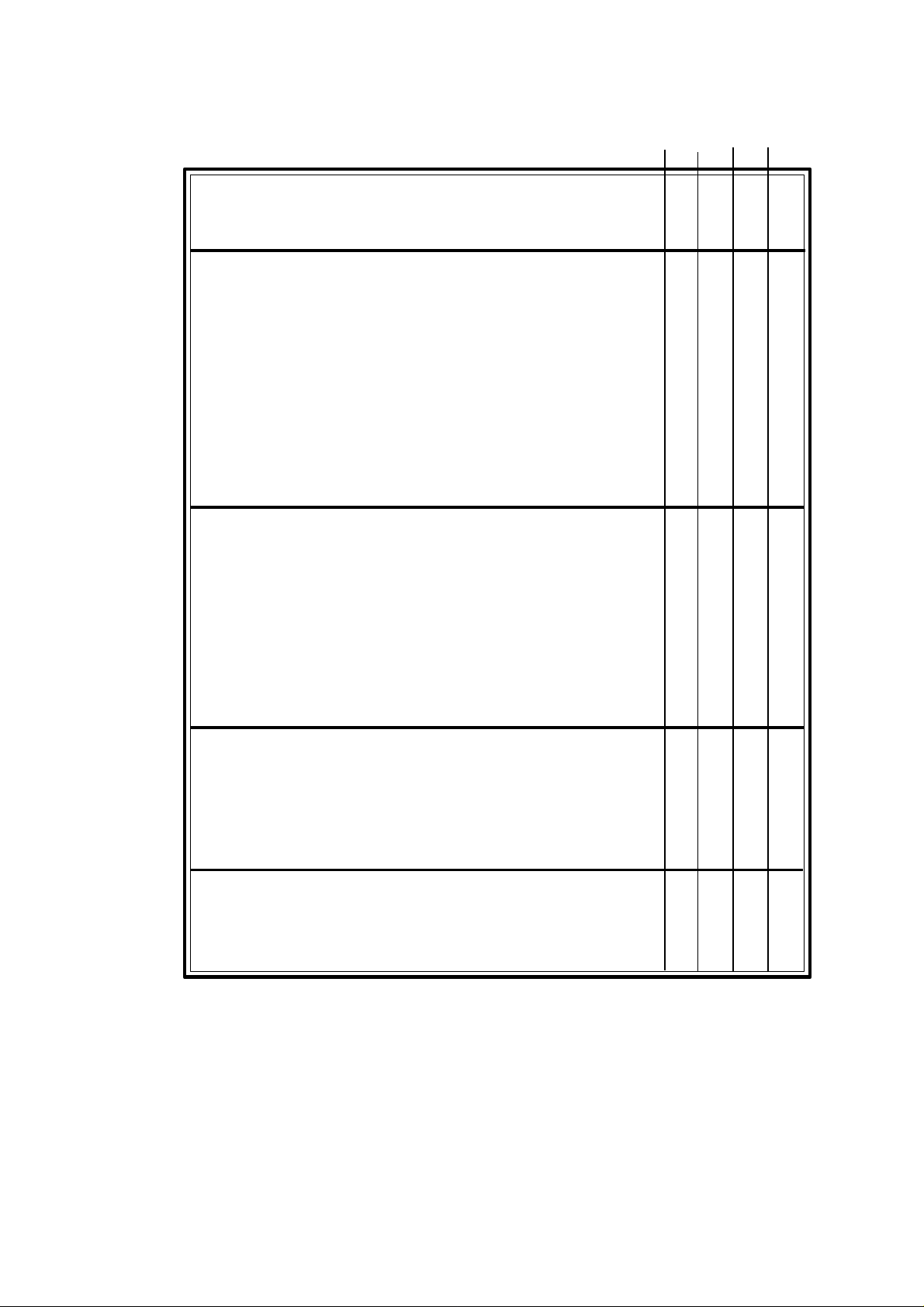
GP M MG MS
COMPENSATION
Tool radius compensation (G40,G41,G42) ............................................. x x x
Tool length compensation (G43,G44) .................................................... x x x x
Loading of tool dimensions into internal tool table (G50) ....................... x x x x
CANNED CYCLES
Multiple arc-pattern machining (G64) .................................................... x x x
User defined canned cycle (G79) ........................................................... x x x x
Drilling cycle (G81) .............................................................................. x x x
Drilling cycle with dwell (G82) ............................................................. x x x
Deep hole drilling cycle (G83)............................................................... x x x
Tapping cycle (G84).............................................................................. x x x
Rigid tapping cycle (G84R) ................................................................... x x x
Reaming cycle (G85)............................................................................. x x x
Boring cycle with withdrawal in G00 (G86)........................................... x x x
Rectangular pocket milling cycle (G87) ................................................. x x x
Circular pocket milling cycle (G88) ....................................................... x x x
Boring cycle with withdrawal in G01 (G89)........................................... x x x
Canned cycle cancellation (G80)............................................................ x x x x
Return to starting point (G98) ................................................................ x x x
Return to reference plane (G99) ............................................................. x x x
PROBING
Probing (G75) ....................................................................................... x x x x
Tool length calibration canned cycle (G75N0) ....................................... x
Probe calibration canned cycle (G75N1) ................................................ x
Surface measuring canned cycle (G75N2).............................................. x
Surface measuring canned cycle with tool offset (G75N3)...................... x
Outside edge measuring canned cycle (G75N4) ..................................... x
Inside edge measuring canned cycle (G75N5) ........................................ x
Angle measuring canned cycle (G75N6) ................................................ x
Outside edge and angle measuring canned cycle (G75N7)...................... x
Hole centering canned cycle (G75N8).................................................... x
Boss centering canned cycle (G75N9).................................................... x
Hole measuring canned cycle (G75N10) ................................................ x
Boss measuring canned cycle (G75N11) ................................................ x
SUBROUTINES
Number of standard subroutines............................................................. 99 99 99 99
Definition of standard subroutine (G22) ................................................. x x x x
Call to a standard subroutine (G20)........................................................ x x x x
Number of parametric subroutines ......................................................... 99 99 99 99
Definition of parametric subroutine (G23) ............................................. x x x x
Call to a parametric subroutine (G21) ................................................... x x x x
End of standard or parametric subroutine (G24) ..................................... x x x x
JUMP OR CALL FUNCTIONS
Unconditional jump/call (G25) .............................................................. x x x x
Jump or call if zero (G26) ...................................................................... x x x x
Jump or call if not zero (G27) ................................................................ x x x x
Jump or call if smaller (G28) ................................................................. x x x x
Jump or call if equal or greater (G29)..................................................... x x x x
Page 12

NEW FEATURES
AND
MODIFICATIONS
Date: February 1991 Software version: 2.1 and newer
FEATURE MODIFIED MANUAL AND SECTION
Error 65 is not issued while probing (G75) Installation Manual Section 3.3.4
It is possible to select the home searching Installation Manual Section 4.6
direction for each axis
New 1, 2, 5, 10 resolution values for Installation Manual Section 4.1
sine-wave feedback signals of each axis
PLCI register access from the CNC Programming Manual G52
Sheetmetal tracing on laser machines Applications Manual
Jig Grinder Applications Manual
Date: June 1991 Software version: 3.1 and newer
FEATURE MODIFIED MANUAL AND SECTION
Repetitive emergency subroutine Installation Manual Section 3.3.8
New function F29. It takes the value of the Programming Manual Chapter 13
selected tool
Function M06 does not execute M19 Installation Manual Section 3.3.5
Greater speed when executing several
parametric blocks in a row.
xv
Page 13
Date: March 1992 Software version: 4.1 and newer
FEATURE MODIFIED MANUAL AND SECTION
Bell-shape acceleration/deceleration control Installation Manual Section 4.7
Expansion of cross compensation Installation Manual Section 4.10
Rigid Tapping G84 R Programming Manual G84
Possibility to enter the sign of the leadscrew Installation Manual Section 4.9
backlash for each axis
Independent execution of an axis Programming Manual G65
Date: July 1993 Software version: 5.1 and newer
FEATURE MODIFIED MANUAL AND SECTION
Double cross compensation Installation Manual Section 4.10
Linear and bell-shaped acc./dec. ramp Installation Manual Section 4.7
combination for the axes
Acceleration/deceleration control for the Installation Manual Section 5.
the spindle
Multiple arc pattern machining Programming Manual G64
Tool tip position display Installation Manual Section 3.3.5
The associated subroutine is executed before Installation Manual Section 3.3.5
the T function
The additional circular sections of a Installation Manual Section 3.3.8
compensated path are executed in G05 or G07
VGA monitor 8030 CNC. Installation Manual Chapter 1
xvi
Page 14
Date: March 1995 Software version: 5.3 and newer
FEATURE MODIFIED MANUAL AND SECTION
Management of feedback with coded Io Installation Manual Section 4.6 & 6.5
Spindle inhibit by PLC Installation Manual Section 3.3.9
Handwheel management by PLC Installation Manual Section 3.3.3
Rapid (JOG) key simulation via PLC PLCI Manual
Non-servo-controlled open-loop motors Applications Manual
Function G64, multiple machining in an arc. Installation Manual Section 3.3.9
To be selected by machine parameter.
Initialization of machine parameters after
memory loss.
Date: September 1995 Software version: 6.0 and newer
FEATURE MODIFIED MANUAL AND SECTION
512 Kb of part-program memory Operating Manual Section 3.6
When conditional input (block skip) active
while in JOG mode, the
key is ignored Installation Manual Section 1.3.6
xvii
Page 15
Atention:
INTRODUCTION
Before starting up the CNC, carefully read the instructions of Chapter
2 in the Installation Manual.
The CNC must not be powered-on until verifying that the machine
complies with the "89/392/CEE" Directive.
Introduction - 1
Page 16
DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
Manufacturer: Fagor Automation, S. Coop.
Barrio de San Andrés s/n, C.P. 20500, Mondragón -Guipúzcoa- (ESPAÑA)
We hereby declare, under our responsibility that the product:
Fagor 8025 M CNC
meets the following directives:
SAFETY:
EN 60204-1 Machine safety. Electrical equipment of the machines.
ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY:
EN 50081-2 Emission
EN 55011 Radiated. Class A, Group 1.
EN 55011 Conducted. Class A, Group 1.
EN 50082-2 Immunity
EN 61000-4-2 Electrostatic Discharges.
EN 61000-4-4 Bursts and fast transients.
EN 61000-4-11Voltage fluctuations and Outages.
ENV 50140 Radiofrequency Radiated Electromagnetic Fields.
ENV 50141 Conducted disturbance induced by radio frequency fields.
As instructed by the European Community Directives on Low Voltage: 73/23/EEC,
on Machine Safety 89/392/EEC and 89/336/EEC on Electromagnetic Compatibility.
In Mondragón, on January 2nd, 1997
Introduction - 3
Page 17

SAFETY CONDITIONS
Read the following safety measures in order to prevent damage to personnel, to
this product and to those products connected to it.
This unit must only be repaired by personnel authorized by Fagor Automation.
Fagor Automation shall not be held responsible for any physical or material
damage derived from the violation of these basic safety regulations.
Precautions against personal damage
Module interconnection
Use the cables supplied with the unit.
Use proper Mains AC power cables
To avoid risks, use only the Mains AC cables recommended for this unit.
Avoid electrical overloads
In order to avoid electrical discharges and fire hazards, do not apply electrical voltage
outside the range selected on the rear panel of the Central Unit.
Ground connection
In order to avoid electrical discharges, connect the ground terminals of all the
modules to the main ground terminal. Before connecting the inputs and outputs of this
unit, make sure that all the grounding connections are properly made.
Before powering the unit up, make sure that it is connected to ground
In order to avoid electrical discharges, make sure that all the grounding connections
are properly made.
Do not work in humid environments
In order to avoid electrical discharges, always work under 90% of relative humidity
(non-condensing) and 45º C (113º F).
Do not work in explosive environments
In order to avoid risks, damage, do not work in explosive environments.
Precautions against product damage
Working environment
This unit is ready to be used in Industrial Environments complying with the directives
and regulations effective in the European Community
Fagor Automation shall not be held responsible for any damage suffered or caused
when installed in other environments (residential or homes).
Install the unit in the right place
Introduction - 4
It is recommended, whenever possible, to instal the CNC away from coolants,
chemical product, blows, etc. that could damage it.
Page 18

This unit complies with the European directives on electromagnetic compatibility.
Nevertheless, it is recommended to keep it away from sources of electromagnetic
disturbance such as.
- Powerful loads connected to the same AC power line as this equipment.
- Nearby portable transmitters (Radio-telephones, Ham radio transmitters).
- Nearby radio / TC transmitters.
- Nearby arc welding machines
- Nearby High Voltage power lines
- Etc.
Enclosures
The manufacturer is responsible of assuring that the enclosure involving the equipment
meets all the currently effective directives of the European Community.
Avoid disturbances coming from the machine tool
The machine-tool must have all the interference generating elements (relay coils,
contactors, motors, etc.) uncoupled.
Use the proper power supply
Use an external regulated 24 Vdc power supply for the inputs and outputs.
Grounding of the power supply
The zero volt point of the external power supply must be connected to the main ground
point of the machine.
Analog inputs and outputs connection
It is recommended to connect them using shielded cables and connecting their shields
(mesh) to the corresponding pin (See chapter 2).
Ambient conditions
The working temperature must be between +5° C and +45° C (41ºF and 113º F)
The storage temperature must be between -25° C and 70° C. (-13º F and 158º F)
Monitor enclosure
Assure that the Monitor is installed at the distances indicated in chapter 1 from the
walls of the enclosure.
Use a DC fan to improve enclosure ventilation.
Main AC Power Switch
This switch must be easy to access and at a distance between 0.7 m (27.5 inches) and
1.7 m (5.6 ft) off the floor.
Protections of the unit itself
It carries two fast fuses of 3.15 Amp./ 250V. to protect the mains AC input.
All the digital inputs and outputs have galvanic isolation via optocouplers between
the CNC circuitry and the outside.
They are protected by an external fast fuse (F) of 3.15 Amp./ 250V. against over
voltage and reverse connection of the power supply.
The type of fuse depends on the type of monitor. See the identification label of the
unit.
Introduction - 5
Page 19
Precautions during repair
Do not manipulate the inside of the unit
Only personnel authorized by Fagor Automation may manipulate the
inside of this unit.
Do not manipulate the connectors with the unit connected to AC
power.
Before manipulating the connectors (inputs/outputs, feedback, etc.)
make sure that the unit is not connected to AC power.
Safety symbols
Symbols which may appear on the manual
WARNING. symbol
It has an associated text indicating those actions or operations may hurt
people or damage products.
Symbols that may be carried on the product
WARNING. symbol
It has an associated text indicating those actions or operations may hurt
people or damage products.
"Electrical Shock" symbol
It indicates that point may be under electrical voltage
"Ground Protection" symbol
It indicates that point must be connected to the main ground point of the
machine as protection for people and units.
Introduction - 6
Page 20

WARRANTY
All products manufactured or marketed by Fagor Automation has a warranty period
of 12 months from the day they are shipped out of our warehouses.
The mentioned warranty covers repair material and labor costs, at FAGOR facilities,
incurred in the repair of the products.
Within the warranty period, Fagor will repair or replace the products verified as being
defective.
FAGOR is committed to repairing or replacing its products from the time when the
first such product was launched up to 8 years after such product has disappeared from
the product catalog.
It is entirely up to FAGOR to determine whether a repair is to be considered under
warranty.
WARRANTY TERMS
EXCLUDING CLAUSES
The repair will take place at our facilities. Therefore, all shipping expenses as well
as travelling expenses incurred by technical personnel are NOT under warranty even
when the unit is under warranty.
This warranty will be applied so long as the equipment has been installed according
to the instructions, it has not been mistreated or damaged by accident or negligence
and has been manipulated by personnel authorized by FAGOR.
If once the service call or repair has been completed, the cause of the failure is not to
be blamed the FAGOR product, the customer must cover all generated expenses
according to current fees.
No other implicit or explicit warranty is covered and FAGOR AUTOMATION shall
not be held responsible, under any circumstances, of the damage which could be
originated.
SERVICE CONTRACTS
Service and Maintenance Contracts are available for the customer within the
warranty period as well as outside of it.
Introduction - 7
Page 21

MATERIAL RETURNING TERMS
When returning the CNC, pack it in its original package and with its original packaging
material. If not available, pack it as follows:
1.- Get a cardboard box whose three inside dimensions are at least 15 cm (6 inches) larger
than those of the unit. The cardboard being used to make the box must have a
resistance of 170 Kg (375 lb.).
2.- When sending it to a Fagor Automation office for repair, attach a label indicating the
owner of the unit, person to contact, type of unit, serial number, symptom and a brief
description of the problem.
3.- Wrap the unit in a polyethylene roll or similar material to protect it.
When sending the monitor, especially protect the CRT glass.
4.- Pad the unit inside the cardboard box with poly-utherane foam on all sides.
5.- Seal the cardboard box with packing tape or industrial staples.
Introduction - 8
Page 22
ADDITIONAL REMARKS
* Mount the CNC away from coolants, chemical products, blows, etc. which could
damage it.
* Before turning the unit on, verify that the ground connections have been properly
made. See Section 2.2 of this manual.
* To prevent electrical shock at the Central Unit, use the proper mains AC connector at
the Power Supply Module. Use 3-wire power cables (one for ground connection)
* To prevent electrical shock at the Monitor, use the proper mains AC connector at the
Power Supply Module. Use 3-wire power cables (one for ground connection)
* Before turning the unit on, verify that the external AC line fuse, of each unit, is the right
one.
Central Unit
Must be 2 fast fuses (F) of 3.15 Amp./ 250V.
Introduction - 9
Page 23
Monitor
Depends on the type of monitor. See identification label of the unit itself.
* In case of a malfunction or failure, disconnect it and call the technical service. Do not
manipulate inside the unit.
Introduction - 10
Page 24

FAGOR DOCUMENTATION
FOR THE 8025/30 M CNC
8025 M CNC OEM Manual Is directed to the machine builder or person in charge of installing and starting
up the CNC.
It contains 2 manuals:
Installation Manual describing how to isntall and set-up the CNC.
LAN Manual describing how to instal the CNC in the Local
Sometimes, it may contain an additional manual describing New Software
Features recently implemented.
8025 M CNC USER Manual Is directed to the end user or CNC operator.
It contains 3 manuals:
Operating Manual describing how to operate the CNC.
Programming Manual describing how to program the CNC.
Applications Manual describing other applications for this CNC
Sometimes, it may contain an additional manual describing New Software
Features recently implemented.
DNC 25/30 Software Manual Is directed to people using the optional DNC communications software.
Area Network.
non-specific of Milling machines
DNC 25/30 Protocol Manual Is directed to people wishing to design their own DNC communications
software to communicate with the 800 without using the DNC25/30 software..
PLCI Manual To be used when the CNC has an integrated PLC.
Is directed to the machine builder or person in charge of installing and starting
up the PLCI.
DNC-PLC Manual Is directed to people using the optional communications software: DNC-PLC.
FLOPPY DISK Manual Is directed to people using the Fagor Floppy Disk Unit and it shows how to use
it.
Introduction - 11
Page 25

MANUAL CONTENTS
The installation manual consists of the following chapters:
Index
Comparison table of FAGOR models: 8025 M CNCs
New Features and modifications.
Introduction Warning sheet prior to start-up:
Declaration of Conformity.
Safety conditions.
Warranty terms.
Material returning conditions.
Additional remarks.
FAGOR documentation for the 8025 M CNC.
Manual contents.
Chapter 1 CNC configuration.
Indicates the possible compositions: modular and compact.
Description and dimensions of the Central Unit.
Description and dimensions of the Monitor.
Description and dimensions of the Operator Panel.
Detailed description of all the connectors.
Chapter 2 Machine and Power connection
Chapter 3 Machine parameters.
Chapter 4 Machine parameters for the axes.
Chapter 5 Machine Parameters for the spindle.
Chapter 6 Concepts.
Indicates how to connect the main AC power
The ground connection.
The characteristics of the digital inputs and outputs.
The characteristics of the analog output.
The characteristics of the feedback inputs.
CNC set-up and start-up.
System input/output test.
Emergency input and output connection.
How to operate with the machine parameters.
How to set the machine parameters.
Detail description of the general machine parameters.
Detail description of the machine parameters for the axes.
Detail description of the machine parameters for the spindle.
Axes and coordinate systems. Nomenclature and selection.
Feedback systems, resolution.
Axis and gain adjustment.
Reference systems; Reference points, search and adjustment.
Software axis travel limits.
Acceleration / deceleration.
Unidirectional approach.
Spindle: speed control, range change.
Tools and tool magazine.
Treatment of the «Feed-hold» and «M-done» signals.
M, S, T auxiliary function transfer.
Pallet work.
Appendix Technical characteristics of the CNC. Enclosures.
Error codes.
Introduction - 12
Recommended probe connection circuits.
CNC inputs and outputs.
2-digit BCD spindle output conversion table.
Machine parameters. Summary chart, sequential list and setting chart.
Auxiliary «M» functions. Setting chart.
Leadscrew error compensation and cross compensation tables.
Maintenance.
Page 26
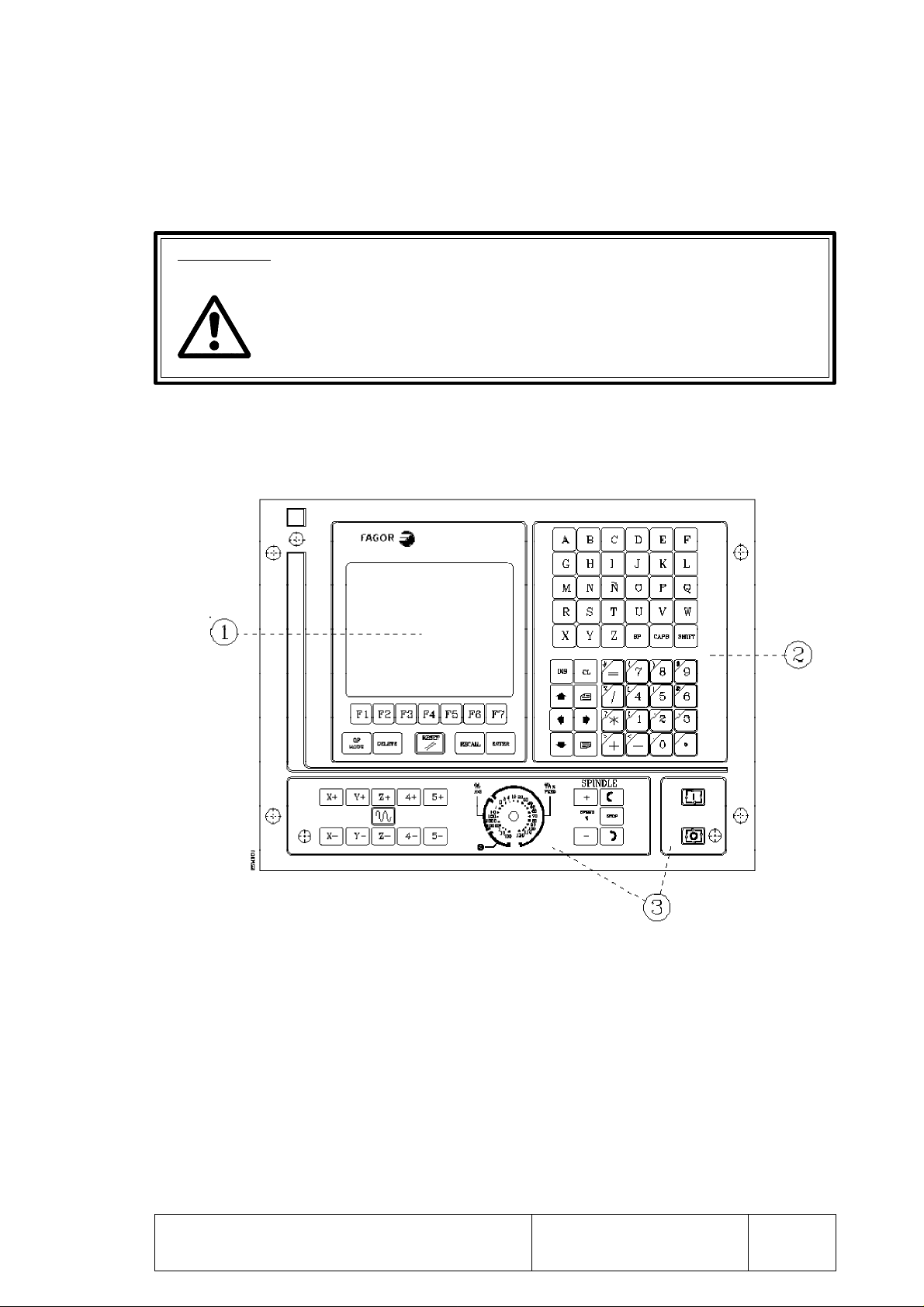
1. CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
Atention:
The CNC is prepared to be used in Industrial Environments, especially on
milling machines, lathes, etc. It can control machine movements and devices.
It can control machine movements and devices.
1.1 8025 CNC
The 8025 CNC is an enclosed compact module whose front view offers:
1. An 8" monochrome amber monitor or CRT screen used to display the required system
information.
2. A keyboard which permits communications with the CNC; being possible to request
information or change the CNC status by generating new instructions.
3. An operator panel containing the necessary keys to work in JOG mode as well as the
Cycle Start/Stop keys.
PageChapter: 1 Section:
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
8025 CNC
1
Page 27
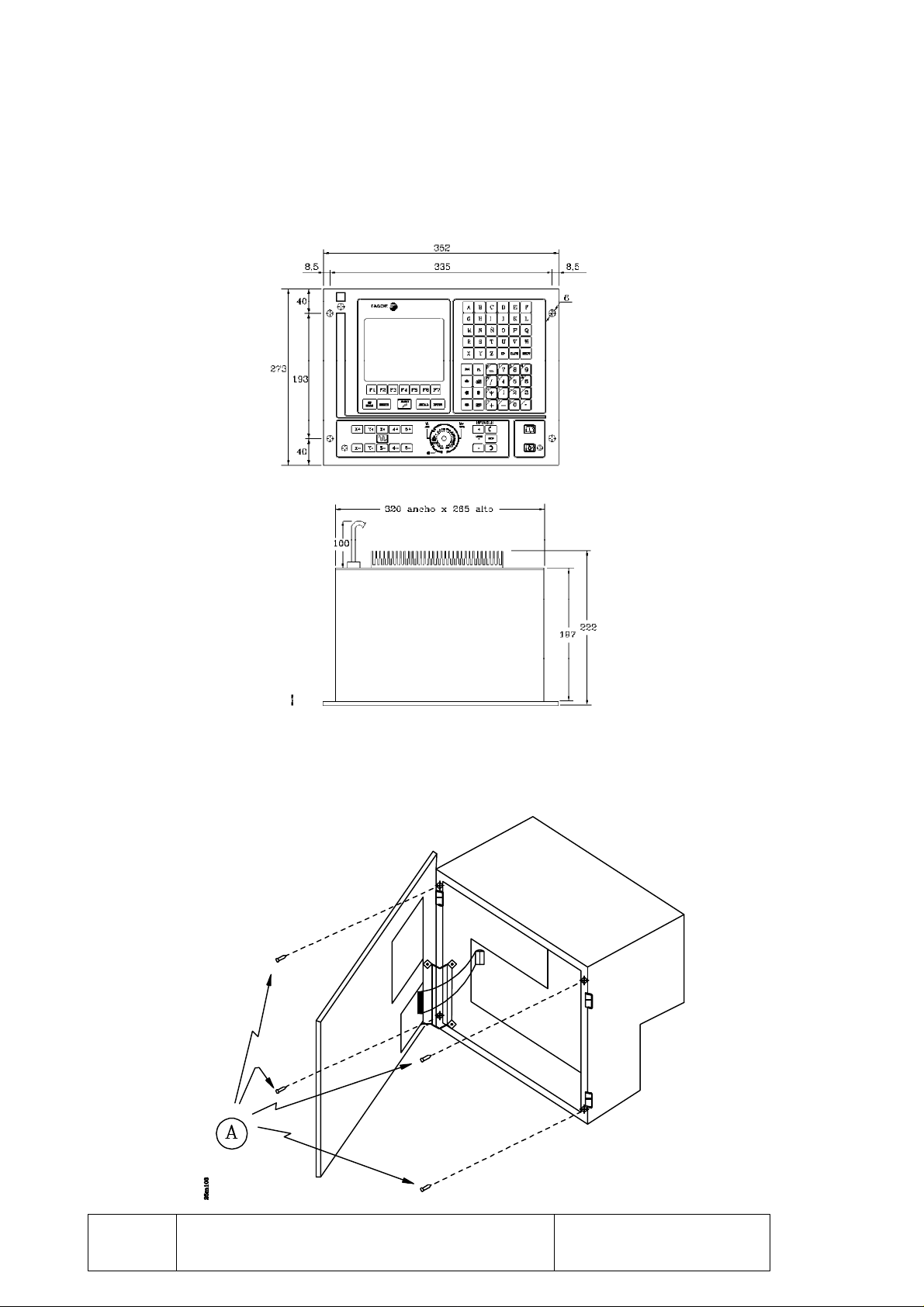
1.1.1 DIMENSIONS AND INSTALLATION OF THE 8025 CNC
This CNC, usually mounted on the machine pendant, has 4 mounting holes.
When installing it, leave enough room to swing the FRONT PANEL open in order to allow
future access to its interior.
To open it, undo the 4 allen-screws located next to the CNC mounting holes.
Page
2
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
Section:Chapter: 1
8025 CNC
Page 28
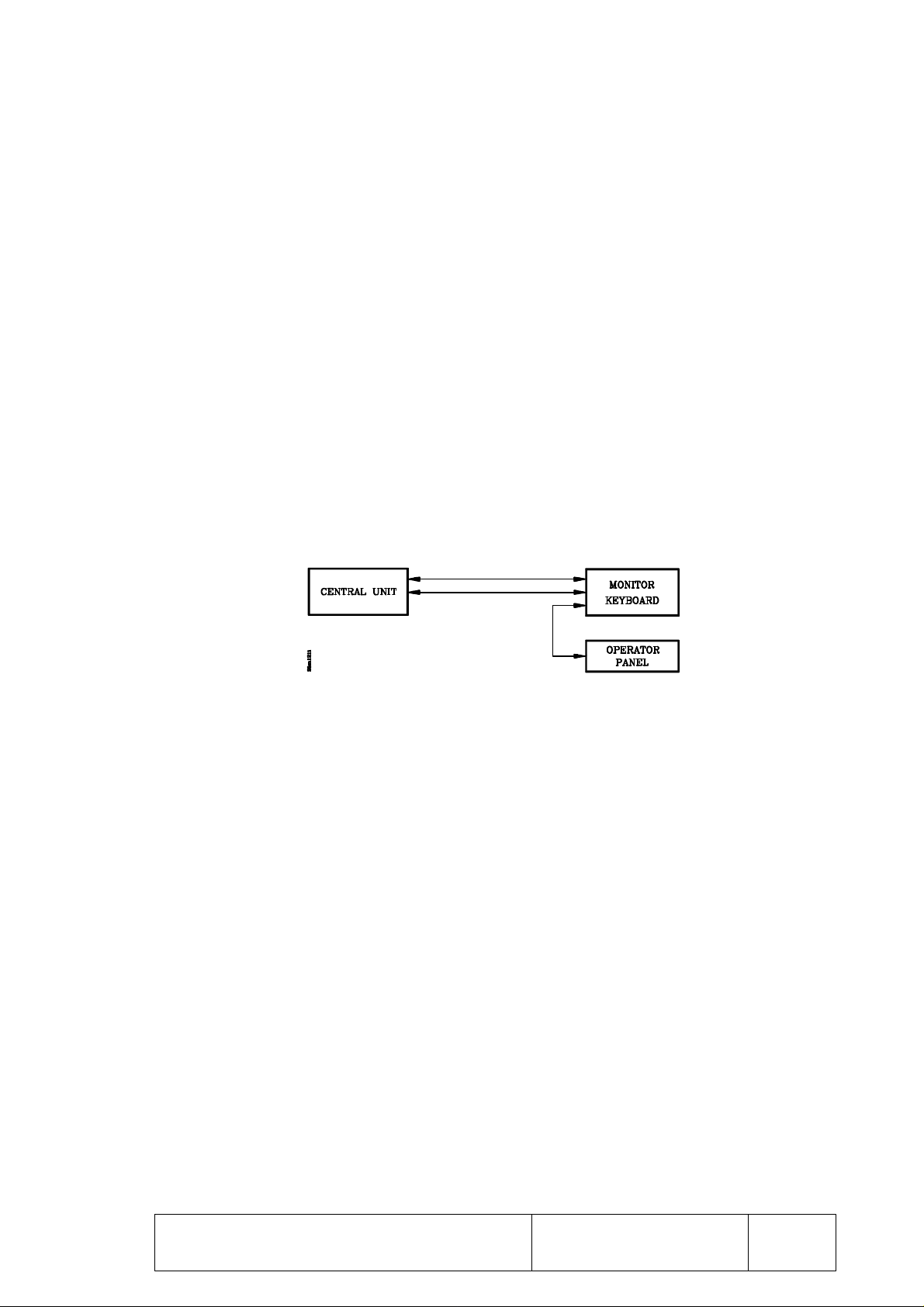
1.2 8030 CNC
This model CNC consists of 3 independent interconnected modules. These modules can be
mounted on different locations and they are:
- CENTRAL UNIT
- MONITOR/KEYBOARD
- OPERATOR PANEL
The OPERATOR PANEL module is connected to the MONITOR/KEYBOARD module
via a cable supplied with that module.
These two modules will be placed next to each other and must be connected with the
CENTRAL UNIT module which could be located somewhere else. The two cables used
to connect them together are also supplied with these modules. Their maximum length is 25
meters (82 feet) and they are referred to as:
- Video cable.
- Keyboard cable.
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
8030 CNC
PageChapter: 1 Section:
3
Page 29
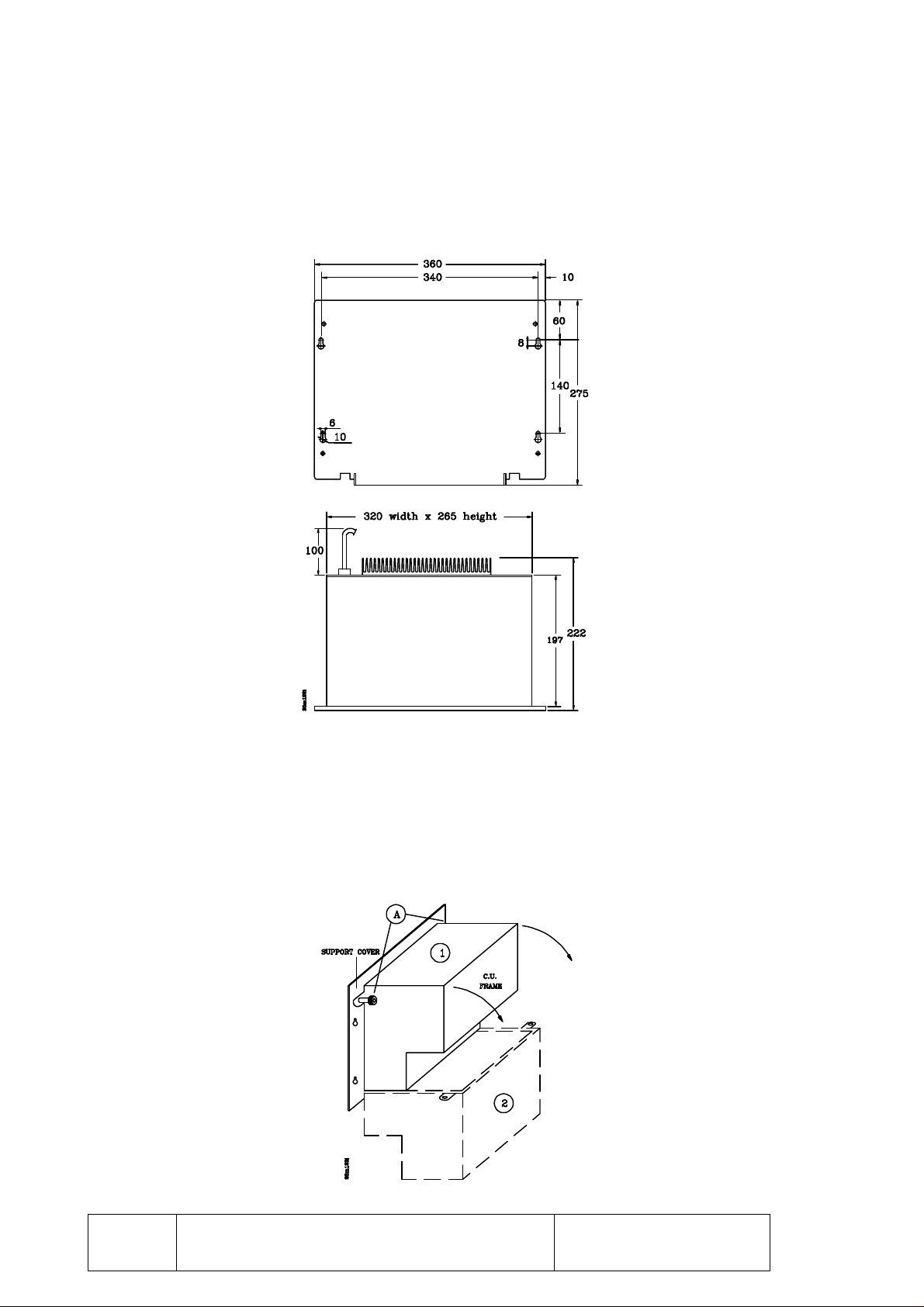
1.2.1 CENTRAL UNIT OF THE 8030 CNC
The CENTRAL UNIT is usually mounted in the electrical cabinet (machine enclosure) and
it is secured by means of the mounting holes located on the support cover.
When installing it, observe enough clearance to swing the CENTRAL UNIT open in case
of future inside manipulation.
To swing it open, once the support cover is secured on the machine enclosure, undo the two
knurled nuts on top and swing it open while holding the body of the CENTRAL UNIT.
Page
4
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
Section:Chapter: 1
CENTRAL UNIT
8030 CNC
Page 30
The CENTRAL UNIT has two connectors to connect it with the MONITOR/KEYBOARD
module by means of the video and keyboard signal cables.
1.- 15-pin SUB-D type female connector for for video signals.
2.- 25-pin SUB-D type female connector for keyboard signals.
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
CENTRAL UNIT
8030 CNC
PageChapter: 1 Section:
5
Page 31

1.2.1.1KEYBOARD CONNECTOR
It is a 25-pin SUB-D type female connector to connect the CENTRAL UNIT module to
the MONITOR/KEYBOARD module.
FAGOR AUTOMATION provides the cable required for this connection. It comes with
a 25-pin SUB-D type male connector at each end.
Both connectors have a latching system UNC4.40 by means of two screws.
PIN SIGNAL
1 GND
2 C9
3 C11
4 C13
5 C15
6 C1
7 C3
8 C5
9 C7
10 D1
11 D3
12 D5
13 D7
14 C8
15 C10
16 C12
17 C14
18 C0
19 C2
20 C4
21 C6
22 D0
23 D2
24 D4
25 D6
Metal hood Shield
The supplied cable has 25 wires (25 x 0.14mm²) with overall shield and acrylic cover. Its
maximum length must be 25 meters (82 feet).
Page
6
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
Section:Chapter: 1
CENTRAL UNIT
8030 CNC
Page 32

The cable shield is soldered to the metal hoods (housings) of both connectors and connected
to pin 1 at both the CENTRAL UNIT and the MONITOR/KEYBOARD connectors.
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
CENTRAL UNIT
8030 CNC
PageChapter: 1 Section:
7
Page 33

1.2.1.2VIDEO CONNECTOR
It is a 15-pin SUB-D type female connector used to interconnect the CENTRAL UNIT
module and the MONITOR/KEYBOARD module.
FAGOR AUTOMATION provides the cable required for this connection. It comes with
a 15-pin SUB-D type male connector at one end and a 15-pin SUB-D type female connector
at the other.
Both connectors have a latching system UNC4.40 by means of two screws.
PIN SIGNAL
1 GND
2 H
3 V
4 I
5 R
6 G
7 B
8 not connected
9 not connected
10 H
11 V
12 I
13 R
14 G
15 B
Metal hood shield
The supplied cable has 6 twisted-pairs of wires (6 x 2 x 0.34mm²) with overall shield and
acrylic cover. It has a specific impedance of 120 Ohm. Its maximum length must be 25
meters (82 feet).
The cable shield is soldered to the metal hoods (housings) of both connectors and connected
to pin 1 at both the CENTRAL UNIT and MONITOR/KEYBOARD connectors.
Page
8
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
Section:Chapter: 1
CENTRAL UNIT
8030 CNC
Page 34

1.2.2 MONITOR/KEYBOARD OF THE 8030 CNC
This module can be mounted on the machine pendant and it lets the operator get the
necessary information at the MONITOR as well as operate the CNC by means of its
KEYBOARD and OPERATOR PANEL.
This module has the connectors to connect it with the CENTRAL UNIT module.
1.2.2.1 DIMENSIONS OF THE MONITOR/KEYBOARD
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
MONITOR/KEYBOARD
8030 CNC
PageChapter: 1 Section:
9
Page 35

1.2.2.2 ELEMENTS OF THE MONITOR/KEYBOARD
X1 25-pin SUB-D type female connector for keyboard signals.
X2 15-pin SUB-D type male connector for video signals.
X3 15-pin SUB-D type female connector to connect the MONITOR/KEYBOARD
module to the OPERATOR PANEL module.
1.- A.C. power plug. Use the plug supplied with the unit to connect it to A.C. power and
ground.
2.- Ground terminal. Used for general machine ground connection. Metric 6 screw.
3.- Buzzer
Atention:
Do not manipulate inside this unit
Only personnel authorized by Fagor Automatin may manipulate inside
this module.
Do not manipulate the connectors with the unit connected to main AC
power
Before manipulating these connectors, make sure that the unit is not
connected to main AC power.
Page
10
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
Section:Chapter: 1
MONITOR/KEYBOARD
8030 CNC
Page 36

1.2.2.3 CONNECTORS AND MONITOR/KEYBOARD INTERFACE
Connectors X1, X2
They are described in the chapter corresponding to the CENTRAL UNIT.
Connector X3
It is a 15-pin SUB-D type female connector used to connect the MONITOR/
KEYBOARD with the OPERATOR PANEL.
FAGOR AUTOMATION supplies the cable required for this connection. It is a
250mm-long 15-wire ribbon cable.
To obtain a greater distance between the Monitor/Keyboard and the Operator
Panel, replace this cable with a round 15-conductor cable (15 x 0.14 mm²) with
overall shield and acrylic rubber cover. The length of this cable plus the length of
the one used between the Central Unit and the Keyboard (X1) must not exceed 25
meters (82 feet).
PIN SIGNAL
1
2 uC13
3 uC12
4 jC11
5 jC10
6 jC9
7 D7
8 D6
9 D5
10 D4
11 D3
12 D2
13 D1
14 D0
15 C14
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
MONITOR/KEYBOARD
8030 CNC
PageChapter: 1 Section:
11
Page 37

1.2.3 OPERATOR PANEL OF THE 8030 CNC
This module is connected to the MONITOR/KEYBOARD module via a ribbon cable and
it contains the JOG keys, Feedrate Override knob, Cycle Start and Stop keys, spindle keys
as well as an Emergency-stop push-button (mushroom) or an optional electronic handwheel.
X1 15-pin SUB-D type female connector to connect the MONITOR/KEYBOARD
module to the OPERATOR PANEL module.
It is described in the chapter corresponding to the MONITOR/KEYBOARD.
1.- Not being used at this time.
2.- Optional mounting location for the E-Stop button or Electronic handwheel.
Page
12
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
OPERATOR PANEL
Section:Chapter: 1
8030 CNC
Page 38

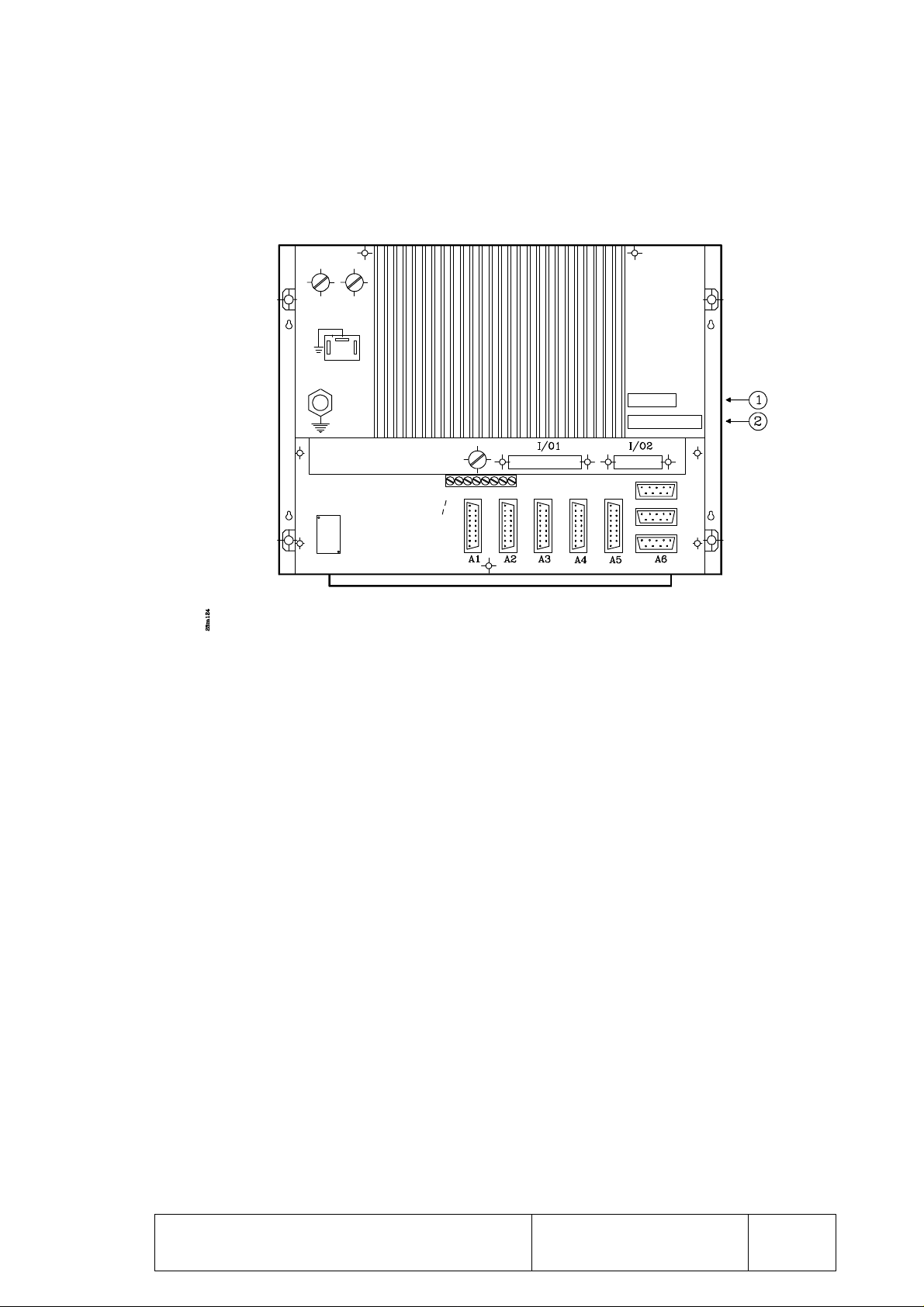
1.3 CONNECTORS AND 8025/8030 INTERFACE
A1 15-pin SUB-D type female connector to connect the X axis feedback system. It
accepts sine-wave signal.
A2 15-pin SUB-D type female connector to connect the Y axis feedback system. It
accepts sine-wave signal.
A3 15-pin SUB-D type female connector to connect the Z axis feedback system. It
accepts sine-wave signal.
A4 15-pin SUB-D type female connector to connect the W axis feedback system. It
accepts sine-wave signal.
A5 15-pin SUB-D type female connector to connect the 5th axis (V) feedback system.
It does not accept sine-wave signal.
When using the spindle encoder and an electronic handwheel, the CNC will only
control up to 4 axes. This connector will then be used for the spindle encoder or the
electronic handwheel (the other device will be connected to A6).
A6 9-pin SUB-D type female connector to connect the spindle encoder or an electronic
handwheel and a touch probe. It does not accept sine-wave signal.
RS485 9-pin SUB-D type female connector to connect the RS485 serial line.
RS232C 9-pin SUB-D type female connector to connect the RS232C serial line.
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
CONNECTORS AND
INTERFACE
PageChapter: 1 Section:
13
Page 39

I/O1 37-pin SUB-D type female connector to interface with the electrical cabinet
offering 10 digital inputs, 16 digital outputs and 4 analog outputs for servo drives
(range: ±10 V.).
I/O2 25-pin SUB-D type female connector to interface with the electrical cabinet
offering 16 digital outputs and 2 analog outputs for servo drives (range: ±10V.).
1- Main AC fuse. It has two 3.15Amp./250V. fast fuses (F), one per AC line, to protect
the main AC input.
2- AC power connector To power the CNC. It must be connected to the power
transformer and to ground.
3- Ground terminal. It must be connected to the general machine ground point. Metric
6.
4- Fuse. 3.15Amp./250V fast fuse (F) to protect the internal I/O circuitry of the CNC.
5- Lithium battery. Maintains the RAM data when the system's power disappears.
6- Adjustment potentiometers for the analog outputs. ONLY TO BE USED BY
THE TECHNICAL SERVICE DEPARTMENT.
7- 10 dip-switches. There are 2 under each feedback connector (A1 thru A5) and they are
utilized to set the CNC according to the type of feedback signal being used.
8 CRT brightness adjustment potentiometer
9 Heat-sink.
Atention:
Do not manipulate the connectors with the unit connected to main AC
power
Before manipulating these connectors, make sure that the unit is not
connected to main AC power.
Page
14
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
Section:Chapter: 1
CONNECTORS AND
INTERFACE
Page 40

1.3.1 CONNECTORS A1, A2, A3, A4
They are 15-pin SUB-D type female connectors used to connect the feedback signals.
* Connector A1 for X axis feedback signals.
* Connector A2 for Y axis feedback signals.
* Connector A3 for Z axis feedback signals.
* Connector A4 for W axis feedback signals.
The cable must have overall shield. The rest of the specifications depend on the feedback
system utilized and the cable length required.
It is highly recommended to run these cables as far as possible from the power cables of the
machine.
PIN SIGNAL AND FUNCTION
1 A
2 A Differential square-wave feedback signals
3 B
4 B
Atention:
When using square-wave rotary encoders, their signals must be TTL compatible.
5 Io Machine Reference Signals (marker pulses)
6 Io
7 Ac Sine-wave feedback signals
8 Bc
9 +5V. Power to feedback system.
10 Not connected.
11 0V. Power to feedback system.
12 Not connected.
13 -5V. Power to feedback system.
14 Not connected.
15 CHASSIS Shield
Encoders with open collector outputs MUST NOT be used.
Do not manipulate the connectors with the unit connected to main AC
power
Before manipulating these connectors, make sure that the unit is not
connected to main AC power.
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
CONNECTORS
A1, A2, A3 & A4
PageChapter: 1 Section:
15
Page 41

1.3.1.1 DIP-SWITCHES FOR CONNECTORS A1, A2, A3, A4
There are 2 dip-switches below each feedback input connector (A1 thru A4) to set the CNC
according to the type of feedback signal being used.
Switch 1 indicates whether the feedback signal is sine-wave or square-wave and switch 2
indicates whether the feedback signal is single- or double-ended (differential).
The possible types of feedback signals to be used at connectors A1 thru A4 are:
* Sine-wave (Ac, Bc, Io)
* Single-ended square-wave (A, B, Io)
* Double-ended (differential) square-wave (A, A, B, B, Io, Io)
To select the type of signal for each axis, use the switch combinations below:
Dip-switch SIGNAL AND FUNCTION
1 2
ON ON Single-ended sine-wave signal (Ac,Bc,Io)
ON OFF Double-ended sine-wave signal "Not allowed"
OFF ON Single-ended square-wave signal (A,B,Io)
OFF OFF Double-ended square-wave (A, A,B, B, Io, Io)
There is a label next to each dip-switch pair indicating the meaning of each switch.
Page
16
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
Section:Chapter: 1
CONNECTORS
A1, A2, A3 & A4
Page 42

1.3.2 CONNECTOR A5
It is a 15-pin SUB-D type female connector for the 5th axis (V) feedback signal.
It does not accept sine-wave signals.
When using the spindle encoder and an electronic handwheel, the CNC will only control
up to 4 axes. This connector will then be used for the spindle encoder or the electronic
handwheel (the other device will be connected to A6).
The cable must have overall shield. The rest of the specifications depend on the feedback
system utilized and the cable length required.
It is highly recommended to run these cables as far as possible from the power cables of the
machine.
PIN SIGNAL AND FUNCTION
1 A
2 A Double-ended square-wave signal.
3 B
4 B
5 Io Machine Reference signals (marker pulse)
6 Io
Atention:
7 Micro Io "V" axis home switch input.
8 0V. "V" axis home switch 0V input. (elec.cabinet)
9 +5V. Power to feedback system.
10 Not connected.
11 0V. Power to feedback system.
12 Not connected.
13 -5V. Power to feedback system.
14 Not connected.
15 CHASSIS Shield.
When using square-wave rotary encoders, their signals must be TTL compatible.
Encoders with open collector outputs MUST NOT be used.
Do not manipulate the connectors with the unit connected to main AC
power
Before manipulating these connectors, make sure that the unit is not
connected to main AC power.
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
CONNECTOR A5
PageChapter: 1 Section:
17
Page 43

1.3.2.1 DIP-SWITCHES FOR CONNECTOR A5
There are 2 dip-switches below this feedback input connector to set the CNC according to
the type of feedback signal being used.
Switch 1 indicates whether the feedback signal is sine-wave or square-wave and switch 2
indicates whether the feedback signal is single- or double-ended (differential).
The possible types of feedback signals to be used at connector A5 are:
* Single-ended square-wave (A, B, Io)
* Double-ended (differential) square-wave (A, A, B, B,Io, Io)
To select the type of signal for each axis, use the switch combinations below:
Dip-switch SIGNAL AND FUNCTION
1 2
ON ON Single-ended sine-wave signal "Not allowed"
ON OFF Double-ended sine-wave signal "Not allowed"
OFF ON Single-ended square-wave signal (A,B,Io)
OFF OFF Double-ended square-wave (A, A,B, B, Io, Io)
There is a label next to each dip-switch pair indicating the meaning of each switch.
Page
18
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
Section:Chapter: 1
CONNECTOR A5
Page 44

1.3.3 CONNECTOR A6
It is a 9-pin SUB-D type female connector to connect the spindle encoder or the electronic
handwheel and a touch probe. It does not take sine-wave signals.
The cable must have overall shield. The rest of the specifications depend on the feedback
system utilized and the cable length required.
It is highly recommended to run these cables as far as possible from the power cables of the
machine.
There are two probe inputs (5V and 24V) and the 0V of the external power supply must be
connected to the "probe 0V input" (pin 8).
The appendix of the manual includes information about these probe inputs as well as
recommended probe connection diagrams.
All cable shields must be connected to ground ONLY at the CNC end through the connector
leaving the other end of the cable not connected. The wires of a shielded cable must not be
unshielded (sticking out) for more than 75mm (about 3 inches).
PIN SIGNAL AND FUNCTION
Atention:
When using square-wave rotary encoders, their signals must be TTL compatible.
Encoders with open collector outputs MUST NOT be used.
When using a FAGOR 100P handwheel, the axis selector signal must be
connected to pin 3.
1 A Square-wave signals from the spindle
2 B encoder or from the electronic handwheel
3 Io Home marker pulse (Machine Reference)
4 +5V. Power to spindle encoder or handwheel
5 0V.
6 PROB 5 Probe input: 5 V. TTL
7 PROB 24 Probe input: 24 Vcc
8 0 PROB Probe input: 0 V.
9 CHASSIS Shield.
Do not manipulate the connectors with the unit connected to main AC
power
Before manipulating these connectors, make sure that the unit is not
connected to main AC power.
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
CONNECTOR A6
PageChapter: 1 Section:
19
Page 45

1.3.3.1 MACHINE WITH "V" AXIS" AND HANDWHEEL OR SPINDLE
ENCODER
When using a "V" axis, machine parameter P616(4) must be set to "1". In this case, it is
possible to use connector A6 to connect the electronic handwheel or the spindle encoder;
but not both at the same time.
A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6
X Y Z W V S
X Y Z W V Handwheel
Machine parameter P800 must also be set with the corresponding value to indicate which
one of them is being connected.
1.3.3.2 WITHOUT "V AXIS" AND WITH ELECTRONIC HANDWHEEL
OR SPINDLE ENCODER
When the machine does not have a "V" axis, machine parameter P616(4) must be set to "0".
In this case, it is possible to connect the electronic handwheel or the spindle encoder or both
at the same time.
It is also possible to select the connector (A5 or A6) where each device is being
connected.
A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6
X Y Z W Handwheel S
X Y Z W S Handwheel
Page
20
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
Section:Chapter: 1
CONNECTOR A6
Page 46

1.3.4 RS232C CONNECTOR
9-pin SUB-D type female connector to connect the RS 232 C serial port.
The cable shield must be soldered to pin 1 at the CNC end and to the metallic housing at
the peripheral end.
PIN SIGNAL FUNCTION
1 FG Shield
2 TxD Transmit Data
3 RxD Receive Data
4 RTS Request To Send
5 CTS Clear To Send
6 DSR Data Send Ready
7 GND Ground
8 —- Not connected
9 DTR Data Terminal Ready
SUGGESTIONS FOR THE RS232C INTERFACE
* Connect/disconnect peripheral.
The CNC must be powered off when connecting or disconnecting any
peripheral through this connector.
* Cable length. EIA RS232C standards specify that the capacitance of the cable must
not exceed 2500pF; therefore, since average cables have a capacitance between 130pF
and 170pF per meter, the maximum length of the cable should not be greater than 15m
(49ft).
For greater distances, it is suggested to intercalate RS232C-to-RS422A signal converters
(and vice-versa). Contact the corresponding distributor.
Shielded cable with twisted-pair wires should be used to avoid communication
interference when using long cables.
Use shielded 7-conductor cable of 7*0.14mm² section.
* Transmission speed (baudrate). The baudrate normally used with peripherals is 9600
baud.
All unused wires should be grounded to avoid erroneous control and data signals.
* Ground connection. It is suggested to reference all control and data signals to the same
ground cable (pin 7 GND) thus, avoiding reference points at different voltages
especially in long cables.
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
RS232C CONNECTOR
PageChapter: 1 Section:
21
Page 47

RECOMMENDED CONNECTIONS FOR THE RS232C INTERFACE
* Complete connection
* Simplified connection
To be used when the peripheral or the computer meets one of the following requirements:
- It does not have the RTS signal.
- It is connected via DNC.
- The receiver can receive data at the selected baudrate.
Nevertheless, it is suggested to refer to the technical manuals of the peripheral
equipment in case there should be any discrepancy.
Page
22
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
RS232C CONNECTOR
Section:Chapter: 1
Page 48

CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
RS232C CONNECTOR
PageChapter: 1 Section:
23
Page 49

1.3.5 RS485 CONNECTOR
---
Not connected
Impedance
107± 5% Ohm at 1 MHz.
It is a 9-pin SUB-D type female connector to connect the RS485 serial line.
This serial line is used to integrate the CNC into the FAGOR LOCAL AREA
NETWORK (LAN) in order to communicate with other FAGOR CNCs and PLCs
(FAGOR PLC 64).
PIN SIGNAL FUNCTION
1 --2 --3 TxD Transmit Data
4 --5 --6 --7 --8 TxD Transmit Data
9
Not connected
Not connected
Not connected
Not connected
Not connected
Not connected
Atention:
Do not manipulate the connectors with the unit connected to main AC
power
Before manipulating these connectors, make sure that the unit is not
connected to main AC power.
For better immunity of the RS485 serial line against conducted electromagnetic
disturbances, it is recommended to solder the cable mesh to the metal hood
of the connector.
1.3.5.1 RECOMMENDED CABLE FOR THE RS485
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
CABLE “TWINAXIAL”
SPECIFICATIONS
Conductor
Insulator
Shields
Covering
Type:
Material:
Resistance:
Material: Teflon
Material
Type
Cover
Resistance
Material:
Outside diameter
Capacitance
02 AWG twisted 7x28
Copper (only one stained wire)
Max 11 L per every 305m. (1000 ft)
Stained copper
Braid 34 AWG. 8 ends / 16 carriers
Minimum 95%
Maximum 3L per every 305m. (1000 ft)
Teflon
Nominal 7mm. (0.257inches)
Maximum 53,1 pF/m (16.2 pF/ft)
Page
24
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
Section:Chapter: 1
RS485 CONNECTOR
Page 50

1.3.6 CONNECTOR I/O 1
It is a 37-pin SUB-D type female connector to interface with the electrical cabinet.
Pin SIGNAL AND FUNCTION
1 0V. Input from external power supply
2 T Strobe Output. The BCD outputs represent a tool code.
3 S Strobe Output. The BCD outputs represent a spindle speed code.
4 M Strobe Output. The BCD outputs represent an M code.
5 Emergency Output.
6 W Enable Output.
Threading ON
7 Z Enable Output.
8 Y Enable Output.
9 X Enable Output.
10 X home switch Input from machine reference switch.
11 Y home switch Input from machine reference switch.
12 Z home switch Input from machine reference switch.
13 W home switch Input from machine reference switch.
14 Emergency Stop Input.
15 Feed Hold Input.
Transfer inhibit
M-done
16 Stop Input.
Emergency subrout.
17 Start Input
Rapid JOG
Enter in Play-back
18 Block Skip Conditional Input
19 DRO Input. The CNC acts as a DRO
20 MST80 BCD coded output, weight: 80
21 MST40 BCD coded output, weight: 40
22 MST20 BCD coded output, weight: 20
23 MST10 BCD coded output, weight: 10
24 MST08 BCD coded output, weight: 8
25 MST04 BCD coded output, weight: 4
26 MST02 BCD coded output, weight: 2
27 MST01 BCD coded output, weight: 1
28 CHASSIS Connect all cable shields to this pin.
29 24V. Input from external power supply.
30 ±10V Analog output for X axis servo drive.
31 0V. Analog output for X axis servo drive.
32 ±10V Analog output for Y axis servo drive.
33 0V. Analog output for Y axis servo drive.
34 ±10V Analog output for Z axis servo drive.
35 0V. Analog output for Z axis servo drive.
36 ±10V Analog output for the spindle drive.
37 0V. Analog output for the spindle drive.
Atention:
The machine manufacturer must comply with the EN 60204-1 (IEC-204-1)
regulation regarding the protection against electrical shock derived from
defective input/output connection with the external power supply when this
connector is not connected before turning the power supply on.
Do not manipulate the connectors with the unit connected to main AC power
Before manipulating these connectors, make sure that the unit is not
connected to main AC power.
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
CONNECTOR I/O1
PageChapter: 1 Section:
25
Page 51

1.3.6.1 INPUTS OF CONNECTOR I/O 1
0 V. Pin 1
INPUT from external power supply.
X AXIS HOME SWITCH Pin 10
This INPUT must be high (24V) as long as the machine reference switch for the X axis
is pressed.
Y AXIS HOME SWITCH Pin 11
This INPUT must be high (24V) as long as the machine reference switch for the Y axis
is pressed.
Z AXIS HOME SWITCH Pin 12
This INPUT must be high (24V) as long as the machine reference switch for the Z axis
is pressed.
W AXIS HOME SWITCH Pin 13
This INPUT must be high (24V) as long as the machine reference switch for the W axis
is pressed.
EMERGENCY STOP Pin 14
This INPUT must be normally high (24V).
When set low (0V), the CNC deactivates the axis enables and analog voltages, it
interrupts the part program execution and it displays ERROR 64 on the CRT.
It does not imply an emergency output (pin 5 of this connector).
Page
26
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
Section:Chapter: 1
CONNECTOR I/O1
(inputs)
Page 52

FEED HOLD / TRANSFER INHIBIT / M-DONE Pin 15
This INPUT must be normally high (24V) and its meaning depends on the type of block
or function being executed at the time.
* If while moving the axes this signal (FEED-HOLD) is set low (0V), the CNC
maintains the spindle turning and stops the axes bringing their analog voltages to 0V
while maintaining their enables active.
When this input is brought back high (24V), the axes will resume their
movements.
* If while executing a motionless block this signal (TRANSFER INHIBIT) is set low
(0V), the CNC interrupts the program execution at the end of the block currently
in execution.
When this signal is brought back high, the CNC resumes program execution.
* The "M-DONE" signal is used when machine parameter P605(5) is set to "1".
The CNC waits for the electrical cabinet to execute the requested miscellaneous
M function. In other words, it waits for the "M-done" input to be set high (24V).
STOP/ EMERGENCY SUBROUTINE Pin 16
This INPUT must be normally high (24V) and its meaning depends on the setting of
machine parameter "P727".
* P727= 0. There is no emergency subroutine.
When this input is set low (0V), the CNC interrupts the program execution just
as if the key were pressed at the OPERATOR PANEL.
To resume program execution, it is necessary to bring this input back high
(24V) and press the key at the OPERATOR PANEL.
* P727 other than "0". There is an emergency subroutine.
When a down-flank (trailing edge or high-to-low transition) of this signal
(EMERGENCY SUBROUTINE) is detected, the CNC interrupts the execution of
the current program and "jumps" to execute the subroutine whose number is
indicated by machine parameter P727.
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
CONNECTOR I/O1
(inputs)
PageChapter: 1 Section:
27
Page 53

START / RAPID TRAVERSE / ENTER Pin 17
This INPUT must be normally low (0V) and its meaning depends on the type of
operation selected.
* If an up-flank (leading edge or low-to-high transition) of this signal (START)
is detected while in Automatic, Single Block or Dry-Run mode, the CNC
considers that the external CYCLE START key is pressed and it behaves as if
the key were pressed at the OPERATOR PANEL.
However, to disable the key of the OPERATOR PANEL in order to
only use this input, set machine parameter P618(1) to "1".
* When machine parameter P609(7) has been set to "1" and this input (RAPID
TRAVERSE) is high (24V), the CNC acts as if the key were pressed.
The CNC will perform all G01, G02 and G03 movements at 200% of the
programmed feedrate F. If the resulting feedrate is greater than the maximum
established by machine parameter P708, the CNC will issue the corresponding error
message.
Also, in the JOG mode and while this input is maintained high (24V), all movements
will be carried out in rapid (G00).
* If while in PLAY BACK mode and being machine parameter P610(3) set to "1",
the CNC detects an up-flank (leading edge or low-to-high transition) at this input,
it acts as if the [ENTER] key were pressed.
While inactive, this input must be connected to 0V through a 10KOhm resistor.
BLOCK SKIP (Conditional input)Pin 18
Every time the CNC executes the miscellaneous function M01 (conditional stop), it
analyzes the status of this input. If high (24V), the CNC will interrupt the execution of
the program.
By the same token, every time the CNC must execute a conditional block, it will analyze
the status of this input and it will execute the block if this input is high (24V).
When the JOG mode is selected, the CNC analyzes the status of this input. If active,
(high) the CNC ignores the
key.
DRO (DRO mode) Pin 19
If this input is set high (24V) while in the JOG mode, the CNC acts as a DRO.
Page
28
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
Section:Chapter: 1
CONNECTOR I/O1
(inputs)
Page 54

1.3.6.2 OUTPUTS OF CONNECTOR I/O 1
T Strobe Pin 2
The CNC sets this output high (24V) whenever it sends a tool code (T function) via the
BCD outputs (pins 20 thru 27).
S Strobe Pin 3
The CNC sets this output high (24V) whenever it sends a spindle speed code (S
function) via the BCD outputs (pins 20 thru 27).
M Strobe Pin 4
The CNC sets this output high (24V) whenever it sends an M function code via the
BCD outputs (pins 20 thru 27).
EMERGENCY Pin 5
The CNC activates this output whenever it detects an alarm condition or internal
emergency.
This output is normally high (24V) or low (0V) depending on the setting of machine
parameter P605(8).
W AXIS ENABLE / THREADING ON Pin 6
The function of this OUTPUT depends on the axes controlled by the CNC.
When the W axis is used, the CNC sets this output (W ENABLE) high (24V) whenever
the W axis drive must be enabled.
When the W axis is not used (3-axis machine, machine parameter P11=0), the CNC sets
this output (THREADING ON) high (24V) whenever an electronic threading block
(G33) is being executed.
Z AXIS ENABLE Pin 7
The CNC sets this output high (24V) to enable the Z axis servo drive.
Y AXIS ENABLE Pin 8
The CNC sets this output high (24V) to enable the Y axis servo drive.
X AXIS ENABLE Pin 9
The CNC sets this output high (24V) to enable the X axis servo drive.
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
CONNECTOR I/O1
(outputs)
PageChapter: 1 Section:
29
Page 55

MST80 Pin 20
MST40 Pin 21
MST20 Pin 22
MST10 Pin 23
MST08 Pin 24
MST04 Pin 25
MST02 Pin 26
MST01 Pin 27
The CNC uses these outputs to indicate to the electrical cabinet the M, S or T function
that has been selected.
This information is BCD coded and the significance (weight) of each output is
expressed by the corresponding mnemonic.
For example, to select the first spindle speed range, the CNC sends the M41 code out
to the electrical cabinet.
MST80 MST40 MST20 MST10 MST08 MST04 MST02 MST01
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1
Together with these signals, the CNC will activate the "M Strobe", "T Strobe" or "S
Strobe" output to indicate the type of function being selected.
CHASSIS Pin 28
This pin must be used to connect all cable shields to it.
Analog voltage for X ±10V. Pin 30
Analog voltage for X 0V. Pin 31
These outputs provide the analog voltage for the X axis servo drive. The cable used for
this connection must be shielded.
Analog voltage for Y ±10V. Pin 32
Analog voltage for Y 0V. Pin 33
These outputs provide the analog voltage for the Y axis servo drive. The cable used for
this connection must be shielded.
Analog voltage for Z ±10V. Pin 34
Analog voltage for Z 0V. Pin 35
These outputs provide the analog voltage for the Z axis servo drive. The cable used for
this connection must be shielded.
Spindle analog voltage ±10V. Pin 36
Spindle analog voltage 0V. Pin 37
These outputs provide the analog voltage for the spindle drive. The cable used for this
connection must be shielded.
Page
30
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
Section:Chapter: 1
CONNECTOR I/O1
(outputs)
Page 56

1.3.7 CONNECTOR I/O 2
It is a 25-pin SUB-D type female connector to interface with the electrical cabinet.
PIN SIGNAL AND FUNCTION
1 0V. Input from external power supply.
2 0V. Input from external power supply.
3 Output M1 Value of bit 1 of the decoded M function table.
4 Output M2 Value of bit 2 of the decoded M function table.
5 Output M3 Value of bit 3 of the decoded M function table.
6 Output M4 Value of bit 4 of the decoded M function table.
7 Output M5 Value of bit 5 of the decoded M function table.
8 Output M6 Value of bit 6 of the decoded M function table.
9 Output M7 Value of bit 7 of the decoded M function table.
10 Output M8 Value of bit 8 of the decoded M function table.
11 Output M9 Value of bit 9 of the decoded M function table.
12 Output M10 Value of bit 10 of the decoded M function table.
V Enable
13 Output M11 Value of bit 11 of the decoded M function table.
Addit. data
14 0V Analog voltage output for V axis servo drive.
15 ±10V. Analog voltage output for V axis servo drive.
16 CHASSIS Connect all cable shields to this pin.
17 0V Analog voltage output for W axis servo drive.
18 ±10V. Analog voltage output for W axis servo drive.
19 24V. Input from external power supply.
20 24V. Input from external power supply.
21 JOG Output. JOG mode is selected.
22 Output M15 Value of bit 15 of the decoded M function table.
Magaz. Rot.
23 Output M14 Value of bit 14 of the decoded M function table.
Reset
24 Output M13 Value of bit 13 of the decoded M function table.
Cycle On
Automatic
G00
25 Output M12 Value of bit 12 of the decoded M function table.
Vertical axis
Atention:
The machine manufacturer must comply with the EN 60204-1 (IEC-204-
1) regulation regarding the protection against electrical shock derived from
defective input/output connection with the external power supply when this
connector is not connected before turning the power supply on.
Do not manipulate the connectors with the unit connected to main AC
power
Before manipulating these connectors, make sure that the unit is not
connected to main AC power.
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
CONNECTOR I/O2
PageChapter: 1 Section:
31
Page 57

1.3.7.1 OUTPUTS OF CONNECTOR I/O 2
"Decoded M" outputs Pins 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 22, 23, 24, 25
These OUTPUTS provide the values indicated at the table corresponding to the
selected M function.
For example: If the table corresponding to function M41 has been set as follows:
M41 100100100100100 (outputs to be activated)
00100100100100100 (outputs to be deactivated)
Every time this M41 function is executed, the CNC will act as follows:
M01 M02 M03 M04 M05 M06 M07 M08 M09 M10 M11 M12 M13 M14 M15
Pin I/O2
at 24V
at 0V
Not
modified
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 25 24 23 22
x x x x x
x x x x x
x x x x x
Outputs M10 / V axis Enable Pin 12
This output provides the value of bit 10 of the decoded table corresponding to the
selected M function.
When the V axis is being used, this output will be utilized as Enable signal for this axis.
Therefore, When having a V axis, be careful not to set the bit of the decoded M table
which corresponds to this M10 output since the CNC will activate it in both cases.
Outputs M11 / Additional data Pin 13
This output provides the value of bit 11 of the decoded table corresponding to the
selected M function.
When operating with M06 and RANDOM tool magazine, the CNC will set this output
high (24V) whenever a SPECIAL TOOL is selected.
If the tool magazine being used is NOT RANDOM and the M06 function requires a
special treatment (prior tool positioning, etc.), machine parameter P603(2) must be set
to "1" and the CNC will set this output high (24V) every time M06 is selected.
Care must be taken when having one of these options not use the bit of the decoded M
table corresponding to this output M11 since the CNC will activate it in both cases.
Page
32
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
Section:Chapter: 1
CONNECTOR I/O2
Page 58

V axis analog voltage ±10V. Pin 15
V axis analog voltage 0V. Pin 14
These outputs provide the analog voltage for the V axis servo drive. The cable used for
this connection must be shielded.
W axis analog voltage ±10V. Pin 18
W axis analog voltage 0V. Pin 17
These outputs provide the analog voltage for the W axis servo drive. The cable used for
this connection must be shielded.
JOG Pin 21
The CNC sets this OUTPUT high (24V) whenever the JOG mode is selected.
Outputs M15 / Tool magazine rotating direction Pin 22
This OUTPUT provides the value of bit 15 of the decoded M table corresponding to
the selected M function.
If machine parameter P605(7) is set so the tool magazine rotates in the quickest
direction, this output will indicate the rotating direction. If the tool magazine is turning
in the positive direction (counting up), this output will be set low (0V) and if it is turning
in the negative direction (counting down), this output will be set high (24V).
Care must be taken, when having this option, not to use the bit of the decoded M table
corresponding to this output M15 since the CNC will activate it in both cases.
Outputs M14 / RESET Pin 23
This OUTPUT provides the value of bit 14 of the decoded M table corresponding to
the selected M function.
If machine parameter P609(3) is set to "1" to provide a RESET pulse, this positive reset
pulse will be output every time the CNC executes a RESET.
Care must be taken, when having this option, not to use the bit of the decoded M table
corresponding to this output M14 since the CNC will activate it in both cases.
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
CONNECTOR I/O2
PageChapter: 1 Section:
33
Page 59

Outputs M13 / CYCLE ON / AUTOMATIC / G00 Pin 24
This OUTPUT provides the value of bit 13 of the decoded M table corresponding to
the selected M function.
If machine parameter P611(1) is set to "1" so the CNC provides the status of the
CYCLE ON signal, this OUTPUT will be set high (24V) every time a part-program
block is being executed.
If machine parameter P611(6) is set to "1" so the CNC provides the status of the
AUTOMATIC signal, this OUTPUT will be set high (24V) whenever the
AUTOMATIC mode of operation is selected.
If machine parameter P613(4) is set to "1" so the CNC provides the status of the G00
signal, this OUTPUT will be set high (24V) whenever the CNC is executing a rapid
positioning move (G00).
Care must be taken, when having one of these options, not to use the bit of the decoded
M table corresponding to this output M13 since the CNC will activate it in both cases.
Outputs M12 / Vertical axis movement Pin 25
This OUTPUT provides the value of bit 12 of the decoded M table corresponding to
the selected M function.
If machine parameter P613(2) is set to "1" in order for the CNC to provide the status
of the vertical axis movement, this output will indicate the direction of that movement.
If the axis is moving in the positive direction (counting up), this output will be set low
(0V) and it will be set high (24V) if moving in the negative direction (counting down).
Care must be taken, when having this option, not to use the bit of the decoded M table
corresponding to this output M12 since the CNC will activate it in both cases.
Page
34
CONFIGURATION OF THE CNC
Section:Chapter: 1
CONNECTOR I/O2
Page 60

2. POWER AND MACHINE INTERFACE
Atention:
Power switch
This power switch must be mounted in such a way that it is esaily
accessed and at a distance between 0.7 meters (27.5 inches) and 1.7
meters (5.5 ft) off the floor.
Intall this unit in the proper place
It is recommended to install the CNC away from coolants, chemical
products, possible blows etc. which could damage it.
2.1 POWER INTERFACE
The rear of the 8025 CNC has a three-prong connector for AC and ground connection.
This connection must be done through an independent shielded 110VA transformer
with an AC output voltage between 100V and 240V +10% -15%.
The power outlet to connect the equipment must be near it and easily accessible.
In case of overload or overvoltage, it is recommended to wait for 3 minutes before
powering the unit back up in order to prevent any possible damage to the power
supply.
2.1.1 INTERNAL POWER SUPPLY
Inside the 8025 CNC there is a power supply providing the required voltages.
Besides the 2 outside AC power fuses (one per line), it has a 5 Amp. fuse inside to
protect it against overcurrent.
POWER AND MACHINE INTERFACE
POWER INTERFACE
PageChapter: 2 Section:
1
Page 61

2.2 MACHINE INTERFACE
2.2.1 GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS
The machine tool must have decoupled all those elements capable of generating
interference (relay coils, contactors, motors, etc.).
* D.C. Relay coils.
Diode type 1N4000.
* A.C. relay coils
RC connected as close as possible to the coils. Their approximate values should
be:
R 220 Ohms/1W
C 0,2 µF/600V
* A.C. motors.
RC connected between phases with values:
R 300 Ohms/6W
C 0,47µF/600V
Ground connection.
It is imperative to carry out a proper ground connection in order to achieve:
* Protection of anybody against electrical shocks caused by a malfunction.
* Protection of the electronic equipment against interference generated by the
proper machine or by other electronic equipment near by which could cause
erratic equipment behavior.
Therefore, it is crucial to install one or two ground points where the above
mentioned elements must be connected.
Use large section cables for this purpose in order to obtain low impedance and
efficiently avoid any interference. This way, all parts of the installation will have
the same voltage reference.
Even when a proper ground connection reduces the effects of electrical
interference (noise), the signal cables require additional protection.
This is generally achieved by using twisted-pair cables which are also covered
with anti-static shielding mesh-wire. This shield must be connected to a specific
point avoiding ground loops that could cause undesired effects. This connection
is usually done at one of the CNC's ground points.
Page
2
POWER AND MACHINE INTERFACE
Section:Chapter: 2
MACHINE INTERFACE
Page 62

Each element of the machine-tool/CNC interface must be connected to ground
via the established main points. These points will be conveniently set close to
the machine-tool and properly connected to the general ground (of the building).
When a second point is necessary, it is recommended to join both points with a
cable whose section is not smaller than 8 mm².
Verify that the impedance between the central point of each connector housing
and the main ground point is less than 1 Ohm.
Ground connection diagram
Chassis
Ground
Ground (for safety)
POWER AND MACHINE INTERFACE
MACHINE INTERFACE
PageChapter: 2 Section:
3
Page 63

2.2.2 DIGITAL OUTPUTS.
The CNC has several optocoupled digital outputs which may be used to activate
relays, deacons, etc.
These digital outputs, with galvanic isolation by optocouplers, can commutate D.C.
voltages supplied by the electrical cabinet of the machine.
The electrical characteristics of these outputs are:
Nominal voltage value +24 V D.C.
Maximum voltage value +30 V D.C.
Minimum voltage value +18 V D.C.
Output voltage Vcc.- 2V
Maximum output current 100 mA.
All outputs are protected by means of:
Galvanic isolation by optocouplers.
External 3A fuse for protection against output overload (greater than 125mA),
external power supply overvoltage (over 33V DC) and against reverse connection
of the external power supply.
2.2.3 DIGITAL INPUTS.
The digital inputs of the CNC are to used to "read" external devices.
All of them are galvanically isolated from the outside world by optocouplers.
The electrical characteristics of these inputs are:
Nominal voltage value +24 V DC
Maximum voltage value +30 V.
Minimum voltage value +18 V.
High threshold voltage (logic state 1) over +18V.
Low threshold voltage (logic state 0) under +5V.
Typical input consumption 5 mA.
Maximum consumption per input 7 mA.
All inputs are protected by means of:
Galvanic isolation by optocouplers.
Protection against reverse connection of the power supply up to -30V.
Atention:
The external 24V power supply used for the digital inputs and outputs
must be regulated.
Page
4
The 0V point of this power supply must be connected to the main ground
point of the electrical cabinet.
Section:Chapter: 2
POWER AND MACHINE INTERFACE
DIGITAL INPUTS/OUTPUTS
Page 64

2.2.4 ANALOG OUTPUTS.
The CNC has 6 analog outputs which could be used to command servo drives, spindle
drives and other devices.
The electrical characteristics of these outputs are:
Analog voltage range: ±10V.
Minimum impedance of the connected drive: 10 KOhm.
Maximum cable length without shield: 75 mm.
It is highly recommended to use the shielded cable connecting the shield to the
corresponding pin of the connector.
Atention:
It is recommended to adjust the servo drives so their maximum feedrate
(G00) is obtained at ±9.5 V.
2.2.5 FEEDBACK INPUTS
The feedback inputs are used to receive sine-wave, single-ended and double-ended
square-wave signals coming from linear or rotary transducers (encoders).
Connector A1 is used for the X axis feedback signals and it accepts sine-wave and
double-ended (differential) square-wave signals.
Connector A2 is used for the Y axis feedback signals and it accepts sine-wave and
double-ended (differential) square-wave signals.
Connector A3 is used for the Z axis feedback signals and it accepts sine-wave and
double-ended (differential) square-wave signals.
Connector A4 is used for the W axis feedback signals and it accepts sine-wave and
double-ended (differential) square-wave signals.
Connector A5 is used for the 5th axis (V) feedback signals and it accepts doubleended (differential) square-wave signals.
Connector A6 is used for the spindle encoder or for the electronic handwheel and it
accepts single-ended (not differential) square-wave signals.
The electrical characteristics of these inputs are:
Sine-wave signals Supply voltage ±5V.±5%
Maximum counting frequency 25KHz.
Square-wave signals Supply voltage ±5V.±5%
Maximum counting frequency 200KHz.
It is recommended to use shielded cables for their connection connecting the shield
to the corresponding pin of the connector.
PageChapter: 2 Section:
POWER AND MACHINE INTERFACE
ANALOG OUTPUTS
FEEDBACK INPUTS
5
Page 65

2.3 SET-UP
2.3.1 GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS
Inspect the whole electrical cabinet verifying the ground connections BEFORE
powering it up.
This ground connection must be done at a single machine point (Main Ground Point)
and all other ground points must be connected to this point.
Verify that the 24V external power supply used for the digital inputs and outputs is
REGULATED and that its 0V are connected to the Main Ground Point.
Verify the connection of the feedback system cables to the CNC.
DO NOT connect or disconnect these cables to/from the CNC when the CNC is on.
Look for short-circuits in all connectors (inputs, outputs, axes, feedback, etc.) BEFORE
supplying power to them.
2.3.2 PRECAUTIONS
It is recommended to reduce the axis travel installing the limit switches closer to
each other or detaching the motor from the axis until they are under control.
Verify that there is no power going from the servo drives to the motors.
Verify that the connectors for the digital inputs and outputs are disconnected.
Verify that the feedback dip-switches for each axis are set according to the type of
feedback signal being used.
Verify that the E-STOP button is pressed.
Page
6
POWER AND MACHINE INTERFACE
Section:Chapter: 2
SET-UP
Page 66

2.3.3 CONNECTION
Verify that the AC power is correct.
Being the CNC disconnected, power the electrical cabinet and verify that it responds
properly.
Verify that there is proper voltage between the pins corresponding to 0V and 24V
of the connectors for the digital inputs and outputs.
Apply 24V to each one of the terminals of the electrical cabinet being used that
correspond to the digital outputs of the CNC and verify their correct performance.
With the motors being decoupled from the axes, verify that the system consisting of
drive, motor and tacho is operating properly.
Connect the AC power to the CNC. The CRT will show the model number and the
available software (for example: CNC8025-MS).
After a self-test, the CNC will show the message: "GENERAL TEST PASSED". If
there is any problem, the CNC will display the corresponding error message.
POWER AND MACHINE INTERFACE
SET-UP
PageChapter: 2 Section:
7
Page 67

2.3.4 SYSTEM INPUT/OUTPUT TEST
This CNC offers a work mode which allows the possibility to activate or deactivate
each one of the logic inputs and outputs of the CNC.
To do this, press the following keystroke sequence:
[OP MODE]
[9] (SPECIAL MODES)
[0] (TEST)
After the self-test, the CNC will show at the bottom of the screen a series of options
which may be selected by means of the corresponding softkey.
By pressing the [IN/OUT] softkey, it will show the status of the logic inputs and it
will be possible to change the status of the logic outputs.
Logic inputs
INPUT PIN FUNCTION
A 17 (I/O 1) START
B 16 (I/O 1) STOP
C 15 (I/O 1) FEEDHOLD
D 14 (I/O 1) EMERGENCY STOP
E 13 (I/O 1) W axis home switch
F 12 (I/O 1) Z axis home switch
G 11 (I/O 1) Y axis home switch
H 10 (I/O 1) X axis home switch
I 19 (I/O 1) DRO mode
J 18 (I/O 1) Block skip (conditional stop)
K To be used only by the technical service
L To be used only by the technical service
M To be used only by the technical service
N To be used only by the technical service
The CNC will show at all times and dynamically the status of all these inputs.
To check a specific one, just actuate on the external push-button or switch
observing its behavior on the CRT.
The value of "1" on the screen indicates that the corresponding input is receiving
24V DC and a "0" indicates that it doesn't.
Page
8
POWER AND MACHINE INTERFACE
Section:Chapter: 2
SET-UP
Page 68

Logic outputs
ROW 1 ROW 2
OUTPUT PIN/FUNCTION PIN/FUNCTION
A (2 I/O 1) T Strobe (3 I/O 2) Output 1, decoded M
B (3 I/O 1) S Strobe (4 I/O 2) Output 2, decoded M
D (5 I/O 1) Emergency (6 I/O 2) Output 4, decoded M
E (6 I/O 1) W Enable (7 I/O 2) Output 5, decoded M
F (7 I/O 1) Z Enable (8 I/O 2) Output 6, decoded M
G (8 I/O 1) Y Enable (9 I/O 2) Output 7, decoded M
H (9 I/O 1) X Enable (10 I/O 2) Output 8, decoded M
I (27 I/O 1) MST01 (11 I/O 2) Output 9, decoded M
J (26 I/O 1) MST02 (12 I/O 2) Output 10, decoded M
K (25 I/O 1) MST04 (13 I/O 2) Output 11, decoded M
L (24 I/O 1) MST08 (25 I/O 2) Output 12, decoded M
M (23 I/O 1) MST10 (24 I/O 2) Output 13, decoded M
N (22 I/O 1) MST20 (23 I/O 2) Output 14, decoded M
O (21 I/O 1) MST40 (22 I/O 2) Output 15, decoded M
P (20 I/O 1) MST80 (21 I/O 2) CNC in JOG mode
To check one of these outputs, select it with the cursor which may be moved by
means of the right and left arrow keys.
Once the desired output is selected, press "1" to activate it and "0" to deactivate
it. The CRT will show the status change.
It is possible to have several outputs active at the same time providing 24V at
their corresponding pins.
Once the INPUT/OUTPUT test is completed, disconnect the electrical cabinet and,
then, connect the input/output connectors as well as the feedback systems of the
axes to the CNC.
Then, connect the electrical cabinet and the CNC to AC power and activate the servo
drives.
POWER AND MACHINE INTERFACE
SET-UP
PageChapter: 2 Section:
9
Page 69

2.4 EMERGENCY INPUT/OUTPUT CONNECTION
The Emergency Input of the CNC is called EMERGENCY STOP (E-STOP) and
corresponds to pin 14 of connector I/O1. This input must normally have 24V DC.
The CNC processes this signal directly, therefore, whenever these 24V disappear, it
will issue EXTERNAL EMERGENCY ERROR (Error 64), it will deactivate the
axes enables and cancel the analog voltages for all the axes and the spindle.
It does NOT imply the emergency output (pin5).
The electrical cabinet interface must take into account all the external elements that
could cause this error.
For example, some of these elements may be:
* The E-Stop button has been pressed.
* An axis travel limit switch has been pressed.
* An axis servo drive is not ready.
On the other hand, whenever a CNC detects an internal emergency error, it will
activate the EMERGENCY OUTPUT at pin 5 of connector I/O1.
This output will be normally high or low depending on the setting of machine parameter
P605(8).
There are some of the internal causes that can activate this output:
* An excessive axis following error has occurred.
* An axis feedback error has occurred.
* There is erroneous data on the machine parameter table.
Page
10
POWER AND MACHINE INTERFACE
Section:Chapter: 2
EMERGENCY I/O
CONNECTION
Page 70

The recommended connection when P605(8)= 1 (output normally HIGH) is:
European Style:
USA Style:
POWER AND MACHINE INTERFACE
EMERGENCY I/O
CONNECTION
PageChapter: 2 Section:
11
Page 71

The recommended connection when P605(8)= 0 (output normally LOW) is:
European Style:
USA Style:
Page
12
POWER AND MACHINE INTERFACE
Section:Chapter: 2
EMERGENCY I/O
CONNECTION
Page 72

3. MACHINE PARAMETERS
Atention:
All unused machine parameters must be set to "0" to guarantee the proper
functioning of this CNC.
It is recommended to save the machine parameters of the CNC at a
peripheral device or computer in order to be able to recover them after
their accidental loss.
Please note that some of the machine parameters mentioned here are
described in greater detail in the chapter on "CONCEPTS" in this manual.
3.1 INTRODUCTION
On power-up, the CNC performs a system hardware test. When completed, it displays
the model name and the message "GENERAL TEST PASSED" when successful and
the corresponding error message if otherwise.
In order for the machine-tool to be able to properly execute the programmed
instructions and recognize the interconnected elements, the CNC must "know" the
specific data for the machine such as feedrates, acceleration ramps, feedback devices,
etc.
This data is determined by the machine manufacturer and may be input via keyboard
or via the RS232C serial line by setting the machine parameters.
To lock or unlock access to machine parameters, decoded "M" function table and to
the leadscrew error compensation tables, proceed as follows:
* Press the [OP MODE] key.
* Press [6] to select the Editing mode.
* Press the softkey for [LOCK/UNLOCK]. The screen will show the word: "CODE:"
(password).
* Key in "PKJIY" and press [ENTER] to lock the access or key in "PKJIN" and
press [ENTER] to unlock the access.
When access to machine parameters is locked, only
communications via RS232C may be changed.
CAUTION when using a CNC with an integrated PLC (CNC+PLCI)
When using this access locking code, the machine parameters, the decoded "M"
function table and the leadscrew error compensation tables are stored in EEPROM
memory.
those regarding serial line
MACHINE PARAMETERS
INTRODUCTION
PageChapter: 3 Section:
1
Page 73

When using the access unlocking code, it recovers these previously stored tables
from the EEPROM memory.
Therefore, one must be careful and lock these tables before
unlocking them.
Otherwise, the factory set values or other prelocked values, may be restored overwriting
the ones the manufacturer entered but did not lock.
To access the machine parameter table via keyboard, press the following keystroke
sequence:
[OP MODE] Shows the various operating modes
[9] Special modes
[1] General parameters
Page
2
MACHINE PARAMETERS
Section:Chapter: 3
INTRODUCTION
Page 74

3.2 OPERATING WITH PARAMETER TABLES
Once the machine parameter table has been selected, the operator may view the
following or previous pages by means of the up and down arrow keys.
To view a particular parameter, key in the desired parameter number and press
[RECALL]. The CNC will display the page corresponding to that parameter.
To EDIT a parameter, key in the desired number, press [=] and key in the value to
be assigned to that parameter.
Depending on the type of machine parameter selected, it could be assigned one of
the following types of values:
* A number P111 = 30000
* A group of 8 bits P602 = 00001111
* A character P105 = Y
Once the value of the parameter has been keyed in, press [ENTER] so it is entered
on the table.
If when pressing [=], the parameter being edited disappears from the screen, it means
that the machine parmeters are locked, therefore protected against modifications.
Every time a parameter bit is mentioned while describing the different machine
parameters, refer to this nomenclature:
P602 = 00 0 0 1 1 1 1
Bit 1
Bit 2
Bit 3
Bit 4
Bit 5
Bit 6
Bit 7
Bit 8
MACHINE PARAMETERS
OPERATING WITH
PARAMETER TABLES
PageChapter: 3 Section:
3
Page 75

3.3 GENERAL MACHINE PARAMETERS
P5 AC frequency
Possible values: 50 Hz. and 60 Hz.
P99 Language
Determines the language used by the CNC to show texts and messages on the
screen.
0 = Spanish.
1 = German.
2 = English.
3 = French.
4 = Italian.
P13 Measuring units (mm/inches)
It determines the measuring units assumed by the CNC for machine parameters,
tool tables and work units at power-up, after executing M02 or M30 and after
RESET.
0 = Millimeters (G71).
1 = Inches (G70).
P6 Theoretical or Real display
It determines whether the CNC will display the real axis position or the theoretical
position.
0 (REAL)= The CNC displays the real position values (coordinates).
1 (THEO)= The CNC displays the theoretical position values (ignoring the
following error).
P802 Protected program
It indicates the number of the program to be protected against being read or
edited.
It is given by an integer between 0 and 9999. If "0" is assigned, the CNC will
interpret that no program is to be protected.
It is recommended to use this parameter to protect a program which contains the
subroutines associated with functions M06, M22, M23, M24, M25 and G74, as
well as those which should remain unseen by the operator.
The protected program will not be listed on the program directory and when
requesting a subroutine defined in this program, the CNC will show the text:
“P????”.
Page
4
MACHINE PARAMETERS
Section:Chapter: 3
GENERAL
Page 76

P619(1), P619(2) Monitor display color combination
These parameters are used by the CNC to select the color combination on a color
monitor. The possible values are:
P619(2) P619(1) Display color
0 0 Monochrome
0 1 Combination 1
1 0 Combination 2
MACHINE PARAMETERS
GENERAL
PageChapter: 3 Section:
5
Page 77

3.3.1 MACHINE PARAMETERS FOR AXIS CONFIGURATION
This CNC has 6 feedback inputs, A1 through A6, and the parameters indicated below
can be used to set the CNC for the type of machine being installed.
The possible axis combinations offered by this CNC are:
A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6
X Y Z W V S
X Y Z W V Handwheel
X Y Z W S Handwheel
X Y Z W Handwheel S
The "S" letter indicates that the feedback input is used to control the spindle. However,
it is possible to control the spindle without having to use that feedback device since
the CNC provides the corresponding analog voltage output at pins 36 and 37 of
connector I/O1.
P11 Number of axes controlled by the CNC
This CNC can interpolate up to 3 axes simultaneously; therefore, the W axis will
be incompatible the X, Y or Z axis as selected by this parameter.
0 = The CNC does not control the W axis.
X = The CNC controls the W axis making it incompatible with the X axis
Y = The CNC controls the W axis making it incompatible with the Y axis
Z = The CNC controls the W axis making it incompatible with the Z axis
P600(4) Machine type (mill or boring mill)
Depending on the type of machine available, the CNC assumes the Z or Y axis
as the vertical axis of the machine.
0 = Milling machine. Z as vertical axis.
1 = Boring mill. Y as vertical axis.
P616(4) The CNC controls the V axis
0 = The CNC does not control the V axis.
1 = The CNC controls the V axis.
P612(1) Connector A6. Electronic handwheel or spindle
It indicates whether the handwheel or the spindle encoder is connected to connector
A6. When not having a fifth axis "V" (4-axis machine), connector A5 may be
used to connect the other device.
Page
6
0 = Spindle encoder connected to A5 and Electronic handwheel to A6.
1 = Spindle encoder connected to A6 and Electronic handwheel to A5.
Section:Chapter: 3
MACHINE PARAMETERS
FOR AXIS CONFIGURATION
Page 78

P617(5), P605(6), P617(4), P611(4), P617(3) The X, Y, Z, W, V axis is a DRO axis.
It indicates whether the corresponding axis is treated as a normal axis (controlled
by the CNC) or a DRO axis (moved externally).
0 = Normal axis.
1 = DRO axis.
P618(6), P618(5), P618(4), P618(3), P618(7) Display of the X, Y, Z, W, V axis
It indicates whether the corresponding axis is displayed on the CRT or not.
0 = It is displayed.
1 = It is not displayed.
P600(3), P616(3) W, V axis, normal or positioning-only
It determines the type of axis being used. Normal or positioning-only.
A positioning-only axis does not admit circular interpolation nor tool radius
compensation.
0 = Normal axis.
1 = Positioning-only axis.
P600(1), P616(1) W, V axis, linear or rotary
It determines whether the axis is linear or rotary.
The position of a rotary axis is shown in degrees, thus not being affected by the
mm/inch unit conversion. It does not admit tool radius compensation nor circular
interpolation.
0 = Linear axis.
1 = Rotary axis.
Note: Parameter P604(1) for W and P616(7) for V indicating feedback pulse
units must be set to "0" (mm) when rotary axis.
P600(2), P616(2) W, V rotary HIRTH axis
It determines whether it is a rotary axis with HIRTH toothing or not.
A HIRTH axis must be set as rotary (P600(1)= 1, P616(1)= 1) and it will only
admit whole degree movements between 0° and 360°.
0 = It is not a HIRTH axis.
1 = It is a HIRTH axis.
The feedback resolution for a HIRTH axis must be in thousandths of a degree.
MACHINE PARAMETERS
FOR AXIS CONFIGURATION
PageChapter: 3 Section:
7
Page 79

P606(1) W axis rotary ROLLOVER
This parameter is used when the W axis is rotary (P600(1) = 1) and its displayed
position value is wanted to reset to 0° every time it reaches 360°.
0 = It is not ROLLOVER.
1 = It is ROLLOVER. Position value rolls over from 359° to 0° and vice
versa.
P619(8), P620(6) W, V axis rotary ROLLOVER positioning via shortest path
These parameters will be used when the corresponding axis is rotary ROLLOVER
(P600(1)=1, P606(1)=1 and P616(1)= 1 respectively) and their programmed moves
are to be carried out in the shortest direction.
0 = The moves are not carried out in the quickest direction.
1 = The moves are carried out in the quickest direction.
P617(7) GANTRY axis
It determines whether the machine has a GANTRY axis or not.
0 = There is no GANTRY axis.
1 = There is a GANTRY axis.
With this CNC it is possible to have a pair of GANTRY axes:
* On 5-axis machines, it will consist of the V axis and its associated axis which
will be indicated by machine parameter P11.
* On 4-axis machines, it will consist of the W axis and its associated axis which
will be indicated by machine parameter P11.
When having a GANTRY axis, the CNC will not display the V or W axis and it
will not be possible to program it.
Also, when programming a movement of the main axis, the one set by parameter
P11, the CNC will apply the same move to both the main and the GANTRY
axes.
P805 Maximum coupling (slaving) following error for GANTRY axes.
It sets the maximum position difference tolerated between two GANTRY axes
as well as between two axes slaved by program (G77).
It is expressed in microns regardless of the type of work units being used.
Possible value: 0 thru 9999 microns
Page
8
MACHINE PARAMETERS
Section:Chapter: 3
FOR AXIS CONFIGURATION
Page 80

3.3.2 INPUT/OUTPUT PARAMETERS
P605(8) Normal status of the Emergency output (pin 5 connector I/O 1)
It determines whether the emergency output is normally low or high.
0 = Normally low (0V). An emergency situation will set this output high (24V)
1 = Normally high (24V). An emergency situation will set this output low
(0V)
P609(7) Pin 17 of connector I/O 1 as RAPID TRAVERSE (fast feed)
It determines whether the signal input at pin 17 of connector I/O1 is treated as
EXTERNAL CYCLE START or RAPID TRAVERSE.
0 = It is treated as EXTERNAL CYCLE START.
1 = It is treated as RAPID TRAVERSE.
If set as Rapid Traverse and while this input is active, the CNC will carry out all
G01, G02 and G03 moves at 200% of the programmed feedrate F.
By the same token, in the JOG mode and while this input is kept active, the CNC
will jog the axes in rapid G00.
P610(3) Pin 17 of connector I/O 1 as ENTER in PLAY-BACK mode
It determines whether or not the signal input at pin 17 of connector I/O1 is treated
as the ENTER key while in the PLAY-BACK mode.
0 = It is not treated as the ENTER key.
1 = It is treated as the ENTER key.
P605(7) Pin 22 of connector I/O 2 as "tool magazine turning direction"
It indicates, on machines with automatic tool changer, whether or not pin 22 of
connector I/O2 is used to indicate the turning direction of the tool magazine.
0 = It is not used as indicator of tool magazine turning direction.
1 = It is used as indicator of tool magazine turning direction.
If this parameter is set to "1", the output will go low (0V) to indicate the positive
turning direction (count-up) and it will go high (24V) to indicate the negative
turning direction (count-down).
It must be borne in mind that this pin is also used as output 15 of the decoded
M functions; therefore, it should not be set on the decoded M function table
when this parameter is set to indicate tool magazine turning direction (set to
"1").
MACHINE PARAMETERS
I/O PARAMETERS
PageChapter: 3 Section:
9
Page 81

P609(3) Pin 23 of connector I/O 2 as RESET output
Indicates whether there is or not a RESET output via pin 23 of connector I/O2.
0 = It is not used as RESET output.
1 = It is used as RESET output.
It must be borne in mind that this pin is also used as output 14 of the decoded
M functions; therefore, it should not be set on the decoded M function table
when this parameter is set to output a RESET signal (set to "1").
P611(1) Pin 24 of connector I/O 2 as CYCLE ON
P611(6) Pin 24 of connector I/O 2 as AUTOMATIC
P613(4) Pin 24 of connector I/O 2 as G00
They indicate whether there is or not a CYCLE ON, AUTOMATIC or G00
indicating output via pin 24 of connector I/O2.
The CYCLE ON signal will be active whenever the CNC is executing a block.
The AUTOMATIC signal will be active as long as the AUTOMATIC mode of
operation is selected.
The G00 signal will be active as long as the CNC is moving an axis in rapid
(G00).
It must be borne in mind that this pin is also used as output 13 of the decoded
M functions; therefore, it should not be set on the decoded M function table
when this parameter is set for the output to indicate CYCLE ON, AUTOMATIC
or G00. (set to "1").
0 = Used as output 13 of decoded M functions.
1 = Used as output indicating CYCLE ON, AUTOMATIC or G00, and output
13 of decoded M functions.
When setting two or three of these parameters to "1", the CNC will only output
one of them "CYCLE ON" having the highest priority and "G00" the lowest.
CYCLE ON -> AUTOMATIC -> G00
P613(2) Pin 25 of connector I/O 2 as "Vertical axis movement" indicator
output
It determines whether or not pin 25 of connector I/O2 is used to indicate the
direction of the vertical axis movement. This output will be low (0V) for positive
direction (count-up) or high (24V) for negative direction (count-down).
0 = It is not used as vertical axis moving direction indicator output.
1 = It is used as vertical axis moving direction indicator output.
It must be borne in mind that this pin is also used as output 12 of the decoded
M functions; therefore, it should not be set on the decoded M function table
when this parameter is set for the output to be used as vertical axis moving direction
indicator (set to "1").
Page
10
MACHINE PARAMETERS
Section:Chapter: 3
I/O PARAMETERS
Page 82

P617(8) M functions output in BCD or BINARY code
It determines whether the M function is output in BCD or Binary code via pins
20 thru 27 of connector I/O1.
0 = M function output in BCD code
1 = M function output in BINARY code
The significance or weight of each pin in both cases is as follows:
Pin M in BCD M in BINARY
WEIGHT WEIGHT
27 1 1
26 2 2
25 4 4
24 8 8
23 10 16
22 20 32
21 40 64
20 80 128
For example: Depending on the type of code selected, the CNC will output the
M41 as follows:
Pin 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
BCD 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1
Binary 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1
MACHINE PARAMETERS
I/O PARAMETERS
PageChapter: 3 Section:
11
Page 83

P605(5)The CNC waits for the down flank (trailing edge) at M-DONE input
It indicates whether it is necessary or not to wait for the down flank (24V-to-0V
transition) of the M-DONE signal (at pin 15 of connector I/O 1) in response to
an "S STROBE", "T STROBE" or "M STROBE" so the CNC resumes the
execution of such functions.
“P605(5)=0”
The CNC will send out to the electrical cabinet the BCD signals corresponding
to the M, S or T code for a period of 200 milliseconds. Then, if the "M-DONE"
signal is low (0V), it will wait for it to be set high (24V) in order to consider
the M, S or T function done (completed).
“P605(5)=1”
50 milliseconds after having sent the M, S or T BCD signals out to the electrical
cabinet, it sends out the corresponding "Strobe" signal.
Then, if the "M-DONE" signal is high (24V), the CNC waits for it to be set
low (0V).
Once the "M-done" signal is set low, the CNC continues maintaining the
"Strobe" signal active for another 100 milliseconds.
After deactivating the Strobe signal, the M, S T BCD code signals are kept
active for another 50 milliseconds.
After that time and if the "M-DONE signal is low, the CNC will wait until it
becomes high so it can consider the auxiliary function M, S or T completed.
Page
12
MACHINE PARAMETERS
Section:Chapter: 3
I/O PARAMETERS
Page 84

P609(5) Decoded M function code NOT output in BCD or BINARY.
When executing an M function which is decoded on the table, the CNC activates
the decoded outputs of connector I/O2.
This parameter determines whether or not the CNC activates the M-BCD outputs
of connector I/O1 (pins 20 thru 27) besides the decoded M outputs of connector
I/O2.
0 = It also outputs the M function in BCD or BINARY code.
1 = It does not output the M function in BCD or BINARY code.
P602(8), P602(7), P602(6), P602(5), P603(1)Feedback alarm cancellation of the
X, Y, Z, W and 5th axis respectively
The CNC will show the axis feedback alarm when not receiving all its
corresponding feedback signals or when any of them is not within the permitted
levels.
This parameter indicates whether this feedback alarm is to be cancelled or not.
0 = The feedback alarm for the corresponding axis is not cancelled.
1 = The feedback alarm for the corresponding axis is cancelled.
If the feedback system being used only utilizes 3 square-wave signals (A, B and
Io), the corresponding parameter must be set to "1" (feedback alarm for that axis
cancelled).
It must be borne in mind that the 5th axis might be the V axis or the Spindle.
MACHINE PARAMETERS
I/O PARAMETERS
PageChapter: 3 Section:
13
Page 85

3.3.3 HANDWHEEL PARAMETERS
P613(1) Electronic handwheel FAGOR 100P
It indicates whether the electronic handwheel being used is a FAGOR 100P model
with axis selector button.
0 = It is not a FAGOR 100P model.
1 = It is a FAGOR 100P model.
P612(2) Counting direction of the electronic handwheel
It indicates the counting direction of the electronic handwheel. If correct, leave
it as is and change it if otherwise.
Possible values: “1” and “0”.
P612(3) Feedback units of the electronic handwheel
It indicates whether the pulses received from the electronic handwheel are
considered to be in millimeters or inches.
0 = Millimeters.
1 = Inches.
P612(4), P612(5) Feedback resolution of the electronic handwheel
They indicate the counting resolution of the electronic handwheel.
Possible values with square-wave signals:
1 = Resolution of 0.001 mm, 0.0001 inch or 0.001°.
2 = Resolution of 0.002 mm, 0.0002 inch or 0.002°.
5 = Resolution of 0.005 mm, 0.0005 inch or 0.005°.
10 = Resolution of 0.010 mm, 0.0010 inch or 0.010°.
The units being used depend on the setting of parameter P612(3) and on whether
it is a linear or rotary axis.
To set the type of resolution, use the following chart:
P612(5) P612(4) Resolution
0 0 1
0 1 2
1 0 5
1 1 10
Page
14
MACHINE PARAMETERS
Section:Chapter: 3
HANDWHEEL
PARAMETERS
Page 86

P612(6) Multiplying factor for Electronic handwheel signals
It indicates the "x2" or "x4" multiplying factor to be applied to the feedback
signals provided by the electronic handhweel.
0 = "x4" factor being applied.
1 = "x2" factor being applied.
Example:
If the electronic handwheel has been set as follows:
P612(3) = 0 Millimeters
P612(4) = 0 y P612(5) = 0 Resolution 0.001 mm.
P612(6) = 0 Multiplying factor of "x4"
And the Feedrate Override Switch is positioned at "x100".
The selected axis will move 0.001mm x4 x100 = 0.4mm per pulse received.
P625(7) Electronic handwheel managed by the PLC
It indicates whether the CNC assumes the handwheel positions of the manual
feedrate override switch or the PLCI outputs O45 and O46 or Marks M13, M14
of the PLC64 when jogging the axes with the handwheel.
0 = Assumes the Manual Feedrate Override Switch positions.
1= Assumes the setting of PLCI outputs O45 and O46 or Marks M13 and
M14 of the PLC64.
O45 O46
M13 M14
0 0 Assumes MFO switch settings
1 0 Equivalent to x1 of MFO switch
0 1 Equivalent to x10 of MFO switch
1 1 Equivalent to x100 of MFO switch
MACHINE PARAMETERS
HANDWHEEL
PARAMETERS
PageChapter: 3 Section:
15
Page 87

3.3.4 TOUCH PROBE PARAMETERS
P612(7) Pulse type of the touch probe
It indicates whether the probe functions of the CNC are active high (positive
pulse) or low (negative pulse) with the probe signal received at connector A6.
0 = Negative pulse (0V.).
1 = Positive pulse (5V. or 24V.).
P720 M function associated with the probing movement (G75)
It indicates the M function that is executed when a probing move is carried out
(G75).
It is defined by an integer between 0 and 99. If set to "0", no miscellaneous M
function will be executed.
The CNC executes the selected M function before starting the execution of G75.
The selected M function may be used, for example, to activate an infrared-based
probe.
P804 Probing feedrate in JOG mode
It indicates the probing feedrate used when calibrating and loading the tool length
by means of a touch probe in JOG mode.
Possible values: 1 thru 65.535 mm./minute (degrees/minute).
1 thru 25.800 tenths-of-inch/minute.
P910 Minimum X coordinate of the touch probe
P911 Maximum X coordinate of the touch probe
P912 Minimum Y coordinate of the touch probe
P913 Maximum Y coordinate of the touch probe
P914 Minimum Z coordinate of the touch probe
P915 Maximum Z coordinate of the touch probe
They determine the position the table-top probe occupies for tool calibration.
These coordinates are absolute and referred to Machine Reference Zero.
Possible values: ± 8388.607 millimeters.
± 330.2599 inches.
Page
16
MACHINE PARAMETERS
Section:Chapter: 3
PROBE PARAMETERS
Page 88

P621(6) No error is issued when probing (G75)
It indicates whether the CNC issues "error 65" or not when the probe reaches the
target position without sending the signal to the CNC during a probing move
(G75).
The CNC interrupts the program whenever error 65 is issued.
0 = Error 65 is issued interrupting the program.
1 = Error 65 is not issued and it does not interrupt the program.
MACHINE PARAMETERS
PROBE PARAMETERS
PageChapter: 3 Section:
17
Page 89

3.3.5 TOOL PARAMETERS
The section on "tools and tool magazine" in the chapter on "concepts" of this
manual describes how these parameters may be used.
P701 Number of tool positions in the tool magazine
It indicates the number of tool positions in the tool magazine.
It is given by an integer between 0 and 98.
When the machine does not have an automatic tool changer, this parameter must
be set to "98".
P743 Subroutine associated with the T function
It indicates the standard subroutine (not parametric) that will be executed when
the block in execution contains a T function. In other words, every time a tool
is selected in the part-program.
It is defined by an integer between 0 and 99. If set to "0", no subroutine will be
executed.
This way, it will be possible to define the corresponding standard subroutine to
select the desired tool.
P625(4) The associated subroutine is executed before the T function
It determines whether the subroutine associated with the T function is executed
before or after the T function.
0 = It is executed after the T function.
1 = It is executed before the T function.
When setting this parameter to "1", the following considerations must be observed:
* The T function must be programmed alone in a block.
* When executing the T function in the Teach-in mode, the CNC will not execute
the associated subroutine.
P626(1) The CNC displays the tool tip or tool base position
It indicates whether the CNC displays the tool base or tool tip position when
working with tool length compensation (G43).
0 = It displays the tool base position.
1 = It displays the tool tip position.
Atention:
Page
18
When not working with tool length compensation (G44), the CNC always
displays the tool base position.
Section:Chapter: 3
MACHINE PARAMETERS
TOOL PARAMETERS
Page 90

P601(5) Machining Center
It indicates whether it is a MACHINING CENTER or not.
0 = It is not a Machining Center.
1 = It is a Machining Center.
When it is a machining center, the CNC selects, in the tool magazine, the tool
indicated by the T function and it will, then, be necessary to execute an "M06"
to perform the tool change.
P601(1) RANDOM tool magazine
It indicates whether the tool magazine is or not RANDOM.
0 = The tool magazine is not RANDOM.
1 = The tool magazine is RANDOM.
If this parameter is set as RANDOM, the CNC will consider it to be a machining
center regardless of the setting of parameter "P601(5)" (machining center).
P709 Subroutine associated with function M06
It indicates the standard subroutine (not parametric) that will be executed when
executing an M06 function.
It is defined by an integer between 0 and 99. If set to "0", no subroutine will be
executed.
This way, it will be possible to define the corresponding standard subroutine to
carry out the desired tool change
P618(2) M06 executed before or after the subroutine
It determines whether the CNC outputs the M06 before or after executing its
associated subroutine (parameter P709).
0 = M06 output before associated subroutine.
1 = M06 output after associated subroutine.
P601(8) Function M06 interrupts program execution
It indicates whether function M06 interrupts the program or not.
0 = It does not interrupt program execution.
1 = It interrupts program execution.
MACHINE PARAMETERS
TOOL PARAMETERS
PageChapter: 3 Section:
19
Page 91

P702 First axis to move when executing function M06
P703 Second axis to move when executing function M06
P704 Third axis to move when executing function M06
P705 Fourth axis to move when executing function M06
These parameters indicate the order the axes will move when executing an M06
function.
It is set by an integer between 0 and 5.
0 = No axis moves.
1 = X axis.
2 = Y axis.
3 = Z axis.
4 = W axis.
5 = V axis.
If parameter "P702" is set to "0", no axis will move regardless of the setting of
the other three parameters.
P900 Tool change position of the first axis when executing M06
P901 Tool change position of the second axis when executing M06
P902 Tool change position of the third axis when executing M06
P903 Tool change position of the fourth axis when executing M06
These parameters indicate the tool change position of the axes when executing
an M06. The order of their movements are established by parameters “P702,
P703, P704 and P705”.
These coordinates are absolute and referred to Machine Reference Zero of the
corresponding axis.
Possible values: ± 8388.607 millimeters.
± 330.2599 inches.
P621(7) Function M06 implies M19 execution
Indicates whether the CNC executes or not function M19 when executing an
M06.
0 = M06 implies M19 execution.
1 = M06 does not imply M19 execution.
Function M19 consists in two stages: Home search on the spindle and spindle
orient to the position indicated by machine parameter "P916".
Page
20
MACHINE PARAMETERS
Section:Chapter: 3
TOOL PARAMETERS
Page 92

P615(8) In M06, the M19 is executed while moving the axis.
This parameter is used when a tool change involves the movement of the axes
and spindle orientation (M19) and the spindle takes a long time to be homed
(first stage of M19 execution).
By means of this parameter, it is possible to select that the movement of the first
axis and the homing of the spindle are carried out simultaneously.
0 = The first axis does not move until function M19 is completed.
1 = The first axis move and the spindle homing are performed at the same
time.
P603(2) Special sequence with M06
This parameter is used when the tool magazine is NOT RANDOM and the M06
requires special treatment (such as previous tool magazine positioning, etc.).
It indicates whether the CNC executes a normal or special sequence when executing
an M06.
0 = Normal sequence with M06.
1 = Special sequence with M06.
The special M06 sequence is carried out as follows:
* The CNC activates the output at pin 13 of connector I/O2 when executing
M06.
* Without waiting for the up-flank (leading edge or 0V-to-24V transition) at
the M-DONE input (pin 15 of connector I/O1), the CNC outputs a T function
indicating the tool pocket number where the tool which was at the spindle
must be deposited.
* Once the execution of this T function is ended, the M-DONE input must be
set high (24V).
The CNC will consider the SPECIAL M06 SEQUENCE completed when it detects
this up-flank at the M-DONE input.
MACHINE PARAMETERS
TOOL PARAMETERS
PageChapter: 3 Section:
21
Page 93

3.3.6 MACHINE PARAMETERS FOR THE RS232C SERIAL LINE
P0 Transmission speed (baudrate)
It determines the transmission baudrate used in communications between the CNC
and the peripheral devices.
It is given by an integer (9600 maximum) and in baud units.
Typical values:
110, 150, 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600
P1 Data bits per transmitted character
It determines the number of data bits used in each transmitted character.
Possible values:
7 = Only the 7 least significant bits (out of 8) are used. Assign this value when
transmitting standard ASCII characters.
8 = All 8 bits of the transmitted character are used. Assign this value when
transmitting special characters (ASCII code over 127).
P2 Parity
It determines the type of parity check used in the transmission.
Possible values:
0 = None.
1 = ODD parity.
2 = EVEN parity.
P3 Stop bits
It determines the number of stop bits used at the end of the transmitted word.
Possible values:
1 = 1 stop bit.
2 = 2 stop bits.
P607(3) DNC
It indicates whether the CNC can work with the DNC protocol or not.
0 = DNC function not available.
1 = DNC function available.
Page
22
MACHINE PARAMETERS
Section:Chapter: 3
RS232C SERIAL LINE
Page 94

P607(4) Type of communication, FAGOR Floppy Disk Unit or Cassette
P607(4) =1 Communication with a FAGOR Floppy Disk Unit. The CNC uses
the settings of machine parameters P0, P1, P2 and P3.
P607(4)=0 Communication with a FAGOR Cassette reader reader/recorder.
The CNC ignores the setting of parameters P0, P1, P2 and P3 and
it uses the following internal setting for the FAGOR Cassette
reader/recorder:
Baudrate = 13,714 Baud
Number of data bits = 7 bits
Parity = Even
Stop bits = 1
P607(5) DNC protocol active on power-up
It indicates whether the DNC protocol is active on CNC power-up or not.
0 = DNC not active on power-up.
1 = DNC active on power-up.
P607(6) The CNC does not abort DNC communication (program debugging)
The CNC offers a safety system that aborts DNC communications whenever:
* More than 30 seconds elapse without receiving a character while in the reception
mode.
* More than 3 incorrect acknowledgments or non-acknowledgments occur in a row
while in transmission mode.
This parameter can be used in order to be able to debug a user communications
program without the CNC aborting the communication.
0 = The CNC aborts communications.
1 = The CNC does not abort communications (Debug mode).
P607(7) Status report by interruption
It indicates whether the "status report by interruption" is active or not while in DNC
mode.
0 = It is not active.
1 = It is active.
A more detailed explanation on this function can be found in the "DNC
COMMUNICATIONS PROTOCOL FOR THE 8025 CNC" manual.
MACHINE PARAMETERS
RS232C SERIAL LINE
PageChapter: 3 Section:
23
Page 95

3.3.7 JOG PARAMETERS
P606(3) M30 when switching to JOG mode
It indicates whether the CNC must generate an M30 automatically or not when
switching to the JOG mode.
0 = M30 is not generated.
1 = M30 is generated.
P803 Axis feedrate when selecting the JOG mode
It defines the feedrate F assumed by the CNC when in JOG mode. This feedrate
will be the same for all the axes.
Possible values: 1 thru 9.999 mm./minute (degrees/minute).
1 thru 3.936 tenths-of-inch/minute.
If this parameter is set to "0", the feedrate for each axis will be the maximum
one established by machine parameters P110, P210, P310, P410 and P510.
P12 Continuous or pulsating axis jog
It indicates whether the axes are jogged while their corresponding jog keys are
pressed (pulsating) or their movements are maintained until the CYCLE STOP
key or another jog key is pressed (continuous).
Y = Pulsating mode. The axis is jogged as long as its corresponding jog key
is maintained pressed.
N = Continuous mode. The axis starts moving when its corresponding jog
key is pressed and it stops when the CYCLE STOP key or another jog
key is pressed. In this latter case, the CNC will move the new selected
axis in the chosen direction until the CYCLE STOP key or another jog
key is pressed.
P609(6) Maximum incremental JOG move
It indicates the maximum distance the axes can be jogged when selecting one of
the JOG positions of the Feedrate Override Switch on the operator panel (positions
1, 10, 100, 1000, 10000).
0 = Limited to 10 mm. or 1 inch.
1 = Limited to 1 mm. or 0.1 inch.
Page
24
MACHINE PARAMETERS
Section:Chapter: 3
JOG PARAMETERS
Page 96

3.3.8 PARAMETERS RELATED TO THE EMERGENCY SUBROUTINE
P727 EMERGENCY subroutine
It indicates the number of the standard subroutine (not parametric) that will be
executed when activating the EMERGENCY SUBROUTINE input (pin 16 of
connector I/O1).
It is defined by an integer between 0 and 99. If set to "0", no emergency subroutine
will be executed.
P621(3) Repetitive EMERGENCY subroutine
This parameter will be taken into account if the Emergency subroutine input
(pin 16 of connector I/O1) is activated while the Emergency subroutine (P727)
was already being executed.
It indicates whether the Emergency subroutine must be restarted every time the
emergency subroutine input is activated or the status of the emergency subroutine
input is ignored while the emergency subroutine is being executed.
0 = The status of the emergency subroutine input is ignored while the
emergency subroutine is being executed.
1 = The Emergency subroutine is restarted every time the emergency
subroutine input is activated.
P619(5) The Emergency subroutine executes M00
It indicates whether the CNC must execute an M00 after the Emergency subroutine
or not.
Function M00 interrupts program execution and is not output.
0 = M00 is executed.
1 = M00 is not executed.
P619(4) Coordinate assignment to arithmetic parameter in Emergency
subroutine
It indicates the coordinates to be assigned to an arithmetic parameter when
executing a "P0=X" type block in the emergency subroutine.
0 = It assigns the coordinates of the beginning point of the block interrupted
by the emergency.
1 = It assigns the coordinates of the point where the emergency input was
activated.
If at the beginning of the emergency subroutine we program the block: “P0=X
P1=Y P2=Z”, and after performing all the emergency operations we program,
inside the emergency subroutine, a block with movement to point "XP0 YP1
ZP2", the tool will return to the point of program interruption or to the beginning
point of the interrupted block.
MACHINE PARAMETERS
RELATED TO EMERGENCY
SUBROUTINE
PageChapter: 3 Section:
25
Page 97

3.3.9 PARAMETERS RELATED TO OPERATING AND
PROGRAMMING MODES
P609(8) Graphic representation of coordinate system
Mill model Boring Mill model
P605(4) XZ plane representation
P611(3) Z axis represented as Z + W axes
It indicates whether the Z axis graphic representation corresponds only to Z axis
movements or to the combined movements of the Z and the W axes.
0 = Normal representation. The Z axis graphic representation corresponds only
to Z axis movements
1 = Special representation. The Z axis graphic representation corresponds to
the combined movements of the Z and the W axes.
In order to use the special representation, the W axis must be set as linear
“P601(1)=0” and incompatible with the Z axis “P11=Z”.
P618(1) Disabling the CYCLE START key
It indicates whether the CYCLE START key of the operator panel is cancelled
(ignored by the CNC) or not.
0 = The CYCLE START key is not disabled.
1 = The CYCLE START key is disabled (ignored by the CNC).
P625(6) Spindle inhibit via PLC.
To stop the spindle via PLC, it is possible to:
* Cancel (disable) the drive enable.
* Send the M05 code out to the CNC.
* Use the O44 signal of the PLCI or the M12 signal of the PLC64 to disable
or re-enable the Spindle.
Page
26
MACHINE PARAMETERS
Section:Chapter: 3
OPERAT./PROGRAMMING
PARAMETERS
Page 98

This machine parameter, P625(6), indicates whether or not O44 (at the PLCI) or
M12 (at the PLC64) are used to enable or disable the spindle.
0 = They are not used.
1 = They are used.
When the CNC receives the spindle inhibiting signal, (O44 =1) or (M12=1), it
outputs an analog voltage of 0V; but it does not change the current spindle
conditions such as selected gear, rotating direction, etc.
When the spindle is re-enabled, (O44 =0) or (M12=0), the CNC outputs the
corresponding spindle analog voltage again.
P606(2) Maximum value of the Manual Feedrate Override
It indicates the maximum feedrate override value to be selected by the Manual
Feedrate Override Switch at the operator panel.
0 = Possible up to 120%.
1 = Limited to 100% even when selecting the 110% and 120% switch positions.
P4 The Manual Feedrate Override switch active in G00
It indicates whether it is possible or not to override the axis feedrate by this
switch when moving in G00 (rapid positioning).
NO The feedrate override switch is ignored when in G00.
YES The feedrate override switch is active (not ignored) when in G00 applying
a range from 0% to 100% of the maximum feedrate set by machine
parameters P111, P211, P311, P411 and P511 even at 110% and 120%
positions.
P610(2) Vectored G00
It indicates whether the G00 moves (rapid positioning) are vectored (interpolatedall axes reaching the final position at the same time-) or not.
0 = G00 not vectored (not interpolated). Each axis moves at its fastest feedrate
reaching the target point at different times.
1 = Vectored G00 (interpolated). All the axes involved in the move reach
the target point at the same time. Their calculated feedrates are based
on the maximum feedrate of the slowest axis.
P613(5) G05 or G07 active on power up
It indicates whether the CNC assumes function G05 (round corner) or G07 (square
corner) on power-up, after M02, M30, EMERGENCY or RESET.
0 = G07 (square corner).
1 = G05 (round corner).
MACHINE PARAMETERS
OPERAT./PROGRAMMING
PARAMETERS
PageChapter: 3 Section:
27
Page 99

P715 Dwell between blocks in G07 (square corner)
It defines the dwell applied to motion blocks in G07.
It is given by an integer between 0 and 255.
Value 0 = No dwell.
Value 1 = 10 msec.
Value 10 = 100 msec.
Value 255 = 2550 msec.
P611(5) Feedrate units in G94
It determines the F programming units when function G94 is active.
0 = 1 mm./minute or 0.1 inch/minute.
1 = 0.1 mm./minute or 0.01 inches/minute.
If parameter "P611(5)=1", it is working in mm and F0.1 is programmed, the
applied feedrate will be F0.01 mm/min.
It must be borne in mind that the machine parameters corresponding to the
maximum programmable feedrate F0 (P110/210/310/410/510), the maximum
feedrate in G00 (P111/211/311/411/511), the home searching feedrate (P112/
212/312/412/512) and the unidirectional approach feedrate (P801) are not
affected by this parameter. They are expressed in 1 mm/min or 0.1 inch/min
units.
P607(8) G53 zero offset applied on RESET
It determines whether the CNC applies the G53 zero offset (selected on the zero
offset table) when executing a RESET.
0 = G53 is not applied.
1 = G53 is applied.
P619(7) G59 as additive zero offset
It determines if function G59 is applied as regular zero offset or as an additive
zero offset which will be added to the one currently selected. It does not affect
G53.
0 = G59 acts as a regular zero offset.
1 = G59 acts as an additive zero offset.
If "P619(7)=1" and one of functions G54, G55, G56, G57 or G58 is executed,
the CNC will apply a zero offset equal to the sum of their corresponding table
values plus that of G59.
P607(2) The spindle turning reversal in G84 generates M05
It determines whether the CNC generates an M05 (stops the spindle) when
reversing the spindle turning direction in the tapping canned cycle (G84).
Page
28
0 = G84 with M05.
1 = G84 without M05.
MACHINE PARAMETERS
Section:Chapter: 3
OPERAT./PROGRAMMING
PARAMETERS
Page 100

P610(1) FEED-HOLD in G84 and G47
It indicates whether the CNC stops the movement of the axes while the FEEDHOLD input is active during the tapping cycle (G84) and during G47 (single
block treatment).
0 = The FEED-HOLD input does not stop the axes.
1 = The FEED-HOLD input stops the axes.
P613(8) Arithmetic parameters P150 thru P254 read-only
It indicates whether arithmetic parameters P150 thru P254 are read/write or readonly when the machine parameters are locked (code: PKJIY).
0 = They are always read/write.
1 = When the machine parameters are locked, these arithmetic parameters
are read-only; otherwise, they are read/write.
P618(8) Function P1=0X takes into account work units
It indicates whether or not the work units (mm or inches) are taken into account
or ignored when executing a "P1=0X" type block.
0 = The work units are ignored. The axis position with respect to the machine
reference zero is always taken in millimeters.
1 = The work units are not ignored. The axis position with respect to the
machine reference zero is taken in the work units currently active (mm
or inches).
P625(5) Type of compensation in sections programmed in G07
The CNC takes this parameter into account when tool radius compensation (G41
or G42) must be applied on a section programmed in G07 (square corner) which
requires an additional circular section.
When the profile has been programmed in G05 (round corner), the whole
compensated path will be done in G05.
MACHINE PARAMETERS
OPERAT./PROGRAMMING
PARAMETERS
PageChapter: 3 Section:
29
 Loading...
Loading...