fagor 8070 Installation Manual

CNC
8070
Installation manual
(Ref: 1309)

MACHINE SAFETY
It is up to the machine manufacturer to make sure that the safety of the machine
is enabled in order to prevent personal injury and damage to the CNC or to the
products connected to it. On start-up and while validating CNC parameters, it
checks the status of the following safety elements. If any of them is disabled, the
CNC shows a warning message.
• Feedback alarm for analog axes.
• Software limits for analog and sercos linear axes.
• Following error monitoring for analog and sercos axes (except the spindle)
both at the CNC and at the drives.
• Tendency test on analog axes.
FAGOR AUTOMATION shall not be held responsible for any personal injuries or
physical damage caused or suffered by the CNC resulting from any of the safety
elements being disabled.
HARDWARE EXPANSIONS
FAGOR AUTOMATION shall not be held responsible for any personal injuries or
physical damage caused or suffered by the CNC resulting from any hardware
manipulation by personnel unauthorized by Fagor Automation.
If the CNC hardware is modified by personnel unauthorized by Fagor Automation,
it will no longer be under warranty.
COMPUTER VIRUSES
FAGOR AUTOMATION guarantees that the software installed contains no
computer viruses. It is up to the user to keep the unit virus free in order to
guarantee its proper operation.
Computer viruses at the CNC may cause it to malfunction. An antivirus software
is highly recommended if the CNC is connected directly to another PC, it is part
of a computer network or floppy disks or other computer media is used to transmit
data.
FAGOR AUTOMATION shall not be held responsible for any personal injuries or
physical damage caused or suffered by the CNC due a computer virus in the
system.
If a computer virus is found in the system, the unit will no longer be under warranty.
All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be transmitted,
transcribed, stored in a backup device or translated into another language
without Fagor Automation’s consent. Unauthorized copying or distributing of this
software is prohibited.
The information described in this manual may be changed due to technical
modifications. Fagor Automation reserves the right to make any changes to the
contents of this manual without prior notice.
All the trade marks appearing in the manual belong to the corresponding owners.
The use of these marks by third parties for their own purpose could violate the
rights of the owners.
It is possible that CNC can execute more functions than those described in its
associated documentation; however, Fagor Automation does not guarantee the
validity of those applications. Therefore, except under the express permission
from Fagor Automation, any CNC application that is not described in the
documentation must be considered as "impossible". In any case, Fagor
Automation shall not be held responsible for any personal injuries or physical
damage caused or suffered by the CNC if it is used in any way other than as
explained in the related documentation.
The content of this manual and its validity for the product described here has been
verified. Even so, involuntary errors are possible, thus no absolute match is
guaranteed. Anyway, the contents of the manual is periodically checked making
and including the necessary corrections in a future edition. We appreciate your
suggestions for improvement.
The examples described in this manual are for learning purposes. Before using
them in industrial applications, they must be properly adapted making sure that
the safety regulations are fully met.
Installation manual
INDEX
About the product ......................................................................................................................... 7
Declaration of conformity.............................................................................................................. 9
Version history............................................................................................................................ 11
Safety conditions ........................................................................................................................ 21
Warranty terms ........................................................................................................................... 25
Material returning terms.............................................................................................................. 27
CNC maintenance ...................................................................................................................... 29
CHAPTER 1 SOFTWARE INSTALLATION.
1.1 Software installation at the CNC. ................................................................................... 31
1.1.1 Work modes and software protection at the CNC...................................................... 33
1.2 Software installation at the PC (simulator)..................................................................... 35
1.3 Updating the software version. ...................................................................................... 37
1.3.1 Software update since previous versions................................................................... 38
1.4 Requirements before and after CNC setup.................................................................... 41
1.5 Installing third-party software. ........................................................................................ 42
1.6 Software configuration. .................................................................................................. 43
1.6.1 MTB (Machine Tool Builder) folder. ........................................................................... 44
1.6.2 USERS folder............................................................................................................. 45
CHAPTER 2 MACHINE PARAMETERS.
2.1 Parameter matching between the CNC and the Sercos drive. ...................................... 49
2.2 Parameters to verify before the startup.......................................................................... 51
2.3 General machine parameters. ....................................................................................... 53
2.4 General machine parameters. Execution channels. ...................................................... 82
2.5 Machine parameters for the axes and spindles. .......................................................... 104
2.6 Machine parameters for the axes. Work sets. ............................................................. 136
2.7 Machine parameters for JOG mode............................................................................. 171
2.7.1 Example of how to set the handwheels and jog keys. ............................................. 176
2.8 Machine parameters for the M function table............................................................... 180
2.9 Machine parameters for kinetics. ................................................................................. 182
2.9.1 Kinematics configuration.......................................................................................... 182
2.9.2 Definition of the spindle kinetics (types 1 through 8)................................................ 186
2.9.3 Definition of the table kinetics (Types 9 through 12). ............................................... 190
2.9.4 Definition of the kinematics of the spindle - table (Types 13 through 16). ............... 194
2.9.5 Definition of the spindle kinetics (types 17 through 24)............................................ 198
2.9.6 Definition of the –C– axis kinematics (Types 41 through 42)................................... 202
2.9.7 Definition of the –C– axis kinematics (Type 43) ...................................................... 204
2.9.8 Definition of the OEM kinematics (Types 100 through 105)..................................... 205
2.9.9 Configuration of angular transformations................................................................. 206
2.10 Machine parameters for the magazine. ....................................................................... 208
2.10.1 Types of tool magazine. ........................................................................................... 211
2.11 Machine parameters for HMI (Interface). ..................................................................... 213
2.12 OEM machine parameters. .......................................................................................... 219
CHAPTER 3 INTRODUCTION TO THE PLC.
3.1 PLC program................................................................................................................ 224
3.2 Modular structure of the PLC program......................................................................... 225
3.3 PLC program execution. .............................................................................................. 226
3.4 PLC resources. ............................................................................................................ 227
3.4.1 Numbering of the physical inputs and outputs. ........................................................ 230
3.5 Operation of a timer. .................................................................................................... 232
3.5.1 Monostable mode. TG1 input................................................................................... 234
3.5.2 Delayed activation mode. TG2 input. ....................................................................... 236
3.5.3 Delayed deactivation mode. TG3 input. ................................................................... 238
3.5.4 Signal limiting mode. TG4 Input............................................................................... 240
3.6 Operation of a counter. ................................................................................................ 242
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
CHAPTER 4 PLC PROGRAMMING.
4.1 Directing instructions.................................................................................................... 247
·3·

4.2 Consulting instructions................................................................................................. 251
4.2.1 Simple consulting instructions.................................................................................. 251
4.2.2 Flank detection instructions. .................................................................................... 252
4.2.3 Comparing instructions. ........................................................................................... 253
4.3 Operators and symbols................................................................................................ 254
4.4 Action instructions........................................................................................................ 255
4.4.1 Assignment binary instructions. ............................................................................... 256
4.4.2 Conditional binary instructions. ................................................................................ 257
4.4.3 Sequence breaking action instructions. ................................................................... 258
4.4.4 Arithmetic action instructions. .................................................................................. 259
4.4.5 Logic action instructions........................................................................................... 261
4.4.6 Specific action instructions....................................................................................... 263
4.4.7 Action instruction of the electronic cam. ................................................................. 266
4.4.8 Instructions for independent move: positioning. ...................................................... 268
4.4.9 Instructions for independent move: synchronization. .............................................. 270
4.4.10 Instructions for coordinate latching using a probe or digital input. ........................... 272
4.5 Summary programming commands............................................................................. 276
CHAPTER 5 CNC-PLC COMMUNICATION.
5.1 Auxiliary –M– functions................................................................................................ 280
5.1.1 Special considerations with the multi-spindle option and channels. ........................ 281
5.2 Auxiliary –H– functions. ............................................................................................... 282
5.2.1 Special considerations with the multi-spindle option and channels. ........................ 283
5.3 Auxiliary –S– function. ................................................................................................. 284
5.3.1 Special considerations with the multi-spindle option and channels. ........................ 285
5.4 Transferring auxiliary functions -M-, -H-, -S-................................................................ 286
5.4.1 Synchronized transfer. ............................................................................................. 287
5.4.2 Non-synchronized transfer....................................................................................... 288
5.5 Displaying PLC errors and messages. ........................................................................ 289
Installation manual
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
CHAPTER 6 LOGIC CNC INPUTS AND OUTPUTS.
6.1 General consulting signals........................................................................................... 292
6.2 Consulting signals for axes and spindles..................................................................... 302
6.3 Consulting signals for the spindle. ............................................................................... 308
6.4 Consultation signals of the independent interpolator................................................... 310
6.5 Tool manager consulting signals. ................................................................................ 312
6.6 Keystroke consulting signals. ...................................................................................... 314
6.7 General modifiable signals. ........................................................................................ 318
6.8 Modifiable signals for axes and spindles. .................................................................... 327
6.9 Spindle modifiable signals. .......................................................................................... 331
6.10 Modifiable signals of the independent interpolator. ..................................................... 335
6.11 Tool manager modifiable signals. ................................................................................ 336
6.12 Keystroke modifiable signals. ...................................................................................... 339
CHAPTER 7 TOOL AND MAGAZINE MANAGEMENT.
7.1 Types of tool magazine................................................................................................ 347
7.2 Tool table, active tool table and tool magazine table ................................................... 349
7.3 Communication between manager and PLC. .............................................................. 350
7.3.1 Manager --> PLC communication. ........................................................................... 351
7.3.2 PLC --> Manager communication. ........................................................................... 352
7.3.3 Manager Emergency................................................................................................ 354
7.3.4 Tool monitoring. ....................................................................................................... 355
7.4 Variables related to tool magazine management. ....................................................... 356
7.5 Tool loading and unloading from the magazines. ........................................................ 357
7.6 Magazine-less system. ................................................................................................ 358
7.6.1 Valid operations and marks activated by the PLC with each one of them. .............. 359
7.6.2 Detailed description of the operations of the magazine. .......................................... 360
7.6.3 Basic PLC programming. ......................................................................................... 361
7.7 Turret type magazine................................................................................................... 362
7.7.1 Valid operations and marks activated by the PLC with each one of them. .............. 363
7.7.2 Detailed description of the operations of the magazine. .......................................... 365
7.7.3 Communication between the PLC and the M06 subroutine..................................... 367
7.7.4 Program of the M06 subroutine. .............................................................................. 368
7.7.5 Basic PLC programming. ......................................................................................... 371
7.8 Synchronous magazine without changer arm.............................................................. 372
7.8.1 Valid operations and marks activated by the PLC with each one of them. .............. 373
7.8.2 Detailed description of the operations of the magazine. .......................................... 375
7.8.3 Communication between the PLC and the M06 subroutine..................................... 378
7.8.4 Program of the M06 subroutine. .............................................................................. 379
7.8.5 Basic PLC programming. ......................................................................................... 383
·4·
Installation manual
7.9 Synchronous magazine with changer arm and 1 claw................................................. 385
7.9.1 Valid operations and marks activated by the PLC with each one of them. .............. 386
7.9.2 Detailed description of the operations of the magazine. .......................................... 388
7.9.3 Communication between the PLC and the M06 subroutine..................................... 391
7.9.4 Program of the M06 subroutine................................................................................ 392
7.9.5 Basic PLC programming. ......................................................................................... 397
7.10 Synchronous magazine with changer arm and 2 claws............................................... 399
7.10.1 Valid operations and marks activated by the PLC with each one of them. .............. 400
7.10.2 Detailed description of the operations of the magazine. .......................................... 402
7.10.3 Communication between the PLC and the M06 subroutine..................................... 405
7.10.4 Program of the M06 subroutine................................................................................ 406
7.10.5 Basic PLC programming. ......................................................................................... 411
7.11 Asynchronous magazine with changer arm. ................................................................ 413
7.11.1 Valid operations and marks activated by the PLC with each one of them. .............. 414
7.11.2 Detailed description of the operations of the magazine. .......................................... 416
7.11.3 Communication between the PLC and the M06 subroutine..................................... 419
7.11.4 Program of the M06 subroutine................................................................................ 420
7.11.5 Basic PLC programming. ......................................................................................... 426
CHAPTER 8 KEY CODES.
8.1 Example for simulating the keyboard from the PLC..................................................... 432
8.2 Assigning codes for a Spanish keyboard..................................................................... 434
CHAPTER 9 CONCEPTS.
9.1 Configure the name and number of axes and spindles. .............................................. 437
9.1.1 Configure the number of axes and spindles of the system. ..................................... 438
9.1.2 Configure the number of axes and spindles of the channels. .................................. 439
9.1.3 Configuration examples. .......................................................................................... 440
9.2 Configure an axis as rotary axis................................................................................... 450
9.3 Configure two axes as a tandem axis. ......................................................................... 453
9.3.1 Tandem axis configuration. Machine parameters. ................................................... 454
9.3.2 Effect of the preload................................................................................................. 456
9.3.3 Tandem axis configuration. Block diagram. ............................................................. 458
9.3.4 Tandem related variables......................................................................................... 460
9.3.5 Tandem adjustment procedure. ............................................................................... 461
9.4 Analog axes. ................................................................................................................ 462
9.4.1 Configure the number of the analog output and of the feedback input. ................... 462
9.4.2 Configure 2 axes with the same feedback input and analog output......................... 464
9.5 Multi-axis management................................................................................................ 465
9.5.1 Configuration of a multi-axis group. Machine parameters........................................ 467
9.5.2 Configuration of a multi-axis group. The PLC program generates an error. ............ 470
9.5.3 Changing the set and the gear at the CNC and at the drive. ................................... 471
9.5.4 Configuration examples. .......................................................................................... 472
9.6 Home search................................................................................................................ 474
9.6.1 Home search (axes and spindles)............................................................................ 476
9.6.2 Home search (gantry axes)...................................................................................... 479
9.7 Software limits of the axes. .......................................................................................... 481
9.7.1 How to set the software travel limits......................................................................... 483
9.7.2 Set the tolerance for an axis located at the software travel limits. ........................... 485
9.8 Configure a handwheel as "feed handwheel". ............................................................. 486
9.9 Configuration of the HSC mode (High Speed Cutting). ............................................... 488
9.9.1 Configuration of the HSC mode. .............................................................................. 489
9.9.2 Influence of the type of acceleration and of the filters in HSC mode. ...................... 492
9.9.3 Procedure for analysis and adjustment of the HSC. ................................................ 493
9.9.4 Summary of the useful variables to analyze the HSC.............................................. 496
9.9.5 The loops and the variables. ................................................................................... 501
9.10 Calculation of the kinematics dimensions. ................................................................... 502
9.10.1 Swivel (angular) spindle. Calculation of the dimensions using a probe. .................. 503
9.10.2 Swivel (angular) spindle. Calculation of the dimensions using a dial indicator. ....... 509
9.10.3 Rotary table. Calculation of the dimensions using a probe...................................... 513
9.11 Management of several keyboards. ............................................................................ 517
9.11.1 How to configure the feature. ................................................................................... 517
9.11.2 Operation of the jog panels. ..................................................................................... 522
9.12 Remote OpenPCS. ...................................................................................................... 523
9.13 Assigning a help text to the graphic softkeys and to the CNC status icon................... 525
9.14 Remote module RCS-S. .............................................................................................. 526
9.14.1 Configure the module like as a node of the Sercos bus........................................... 527
9.14.2 Configure the analog outputs. .................................................................................. 527
9.14.3 Configuration of the feedback inputs........................................................................ 528
9.14.4 Configure the feedback input for a handwheel......................................................... 528
9.14.5 Parameter setting example. ..................................................................................... 529
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
·5·

CNC 8070
Installation manual
CHAPTER 10 CNC VARIABLES.
10.1 Understanding how variables work.............................................................................. 531
10.1.1 Accessing numeric variables from the PLC. ............................................................ 533
10.2 Variables in a single-channel system. ......................................................................... 534
10.3 Variables in a multi-channel system. ........................................................................... 537
10.4 Variables related to general machine parameters. ...................................................... 540
10.5 Variables related to the machine parameters of the channels..................................... 561
10.6 Variables related to axis and spindle machine parameters. ........................................ 582
10.7 Variables related to the sets of machine parameters. ................................................. 619
10.8 Variables related to machine parameters for JOG mode. ........................................... 672
10.9 Variables related to machine parameters for M functions. .......................................... 676
10.10 Variables related to kinematic machine parameters.................................................... 678
10.11 Variables related to machine parameters for the tool magazine. ................................ 682
10.12 Variables related to OEM machine parameters........................................................... 685
10.13 Variables associated with the status and resources of the PLC.................................. 687
10.14 PLC consulting logic signals; general. ......................................................................... 691
10.15 PLC consulting logic signals; axes and spindles. ........................................................ 702
10.16 PLC consulting logic signals; spindles......................................................................... 707
10.17 PLC consulting logic signals; independent interpolator. .............................................. 709
10.18 PLC consulting logic signals; tool manager. ................................................................ 711
10.19 PLC consulting logic signals; keys............................................................................... 714
10.20 PLC modifiable logic signals; general.......................................................................... 715
10.21 PLC modifiable logic signals; axes and spindles. ........................................................ 723
10.22 PLC modifiable logic signals; spindles......................................................................... 729
10.23 PLC modifiable logic signals; independent interpolator. .............................................. 731
10.24 PLC modifiable logic signals; tool manager................................................................. 732
10.25 PLC modifiable logic signals; keys. ............................................................................. 737
10.26 Variables related to the machine configuration............................................................ 738
10.27 Variables related to volumetric compensation. ............................................................ 746
10.28 Variables associated with the Mechatrolink bus. ........................................................ 747
10.29 Variables related to synchronized switching................................................................ 749
10.30 PWM related variables................................................................................................. 750
10.31 Variables related to cycle time..................................................................................... 752
10.32 Variables associated with the feedback inputs for analog axes. ................................. 754
10.33 Variables associated with the analog inputs and outputs. ........................................... 756
10.34 Variables associated with the velocity command and the feedback of the drive. ........ 757
10.35 Variables related to the change of gear and set of the Sercos drive. .......................... 759
10.36 Variables related to loop adjustment. .......................................................................... 760
10.37 Variables related to the loop of the axis or of the tandem spindle. .............................. 768
10.38 Variables related to user tables (zero offset table). ..................................................... 770
10.39 Variables related to user tables (fixture table). ............................................................ 775
10.40 Variables related to user tables (arithmetic parameters table). ................................... 777
10.41 Variables related to the position of the axes................................................................ 781
10.42 Variables related to spindle position. ........................................................................... 787
10.43 Feedrate related variables. .......................................................................................... 789
10.44 Variables associated with acceleration and jerk on the tool path. ............................... 794
10.45 Variables related to managing the feedrate in HSC mode. ......................................... 795
10.46 Variables related to spindle speed............................................................................... 798
10.47 Variables associated with the tool manager. ............................................................... 806
10.48 Variables related to managing the tool magazine and the tool changer arm............... 808
10.49 Variables related to the active tool and to the next one............................................... 810
10.50 Variables associated with any tool............................................................................... 822
10.51 Variables associated with the tool being prepared. ..................................................... 831
10.52 Variables related to jog mode. ..................................................................................... 839
10.53 Variables related to the programmed functions. .......................................................... 845
10.54 Variables related to the electronic cam........................................................................ 872
10.55 Variables related to the independent axes. ................................................................. 874
10.56 Variables associated with the virtual tool axis. ............................................................ 881
10.57 Variables defined by the user. ..................................................................................... 882
10.58 General variables of the CNC...................................................................................... 883
10.59 Variables related to CNC status. ................................................................................. 886
10.60 Variables associated with the part-program being executed. ...................................... 891
10.61 Interface related variables. .......................................................................................... 895
(REF: 1309)
·6·
Installation manual
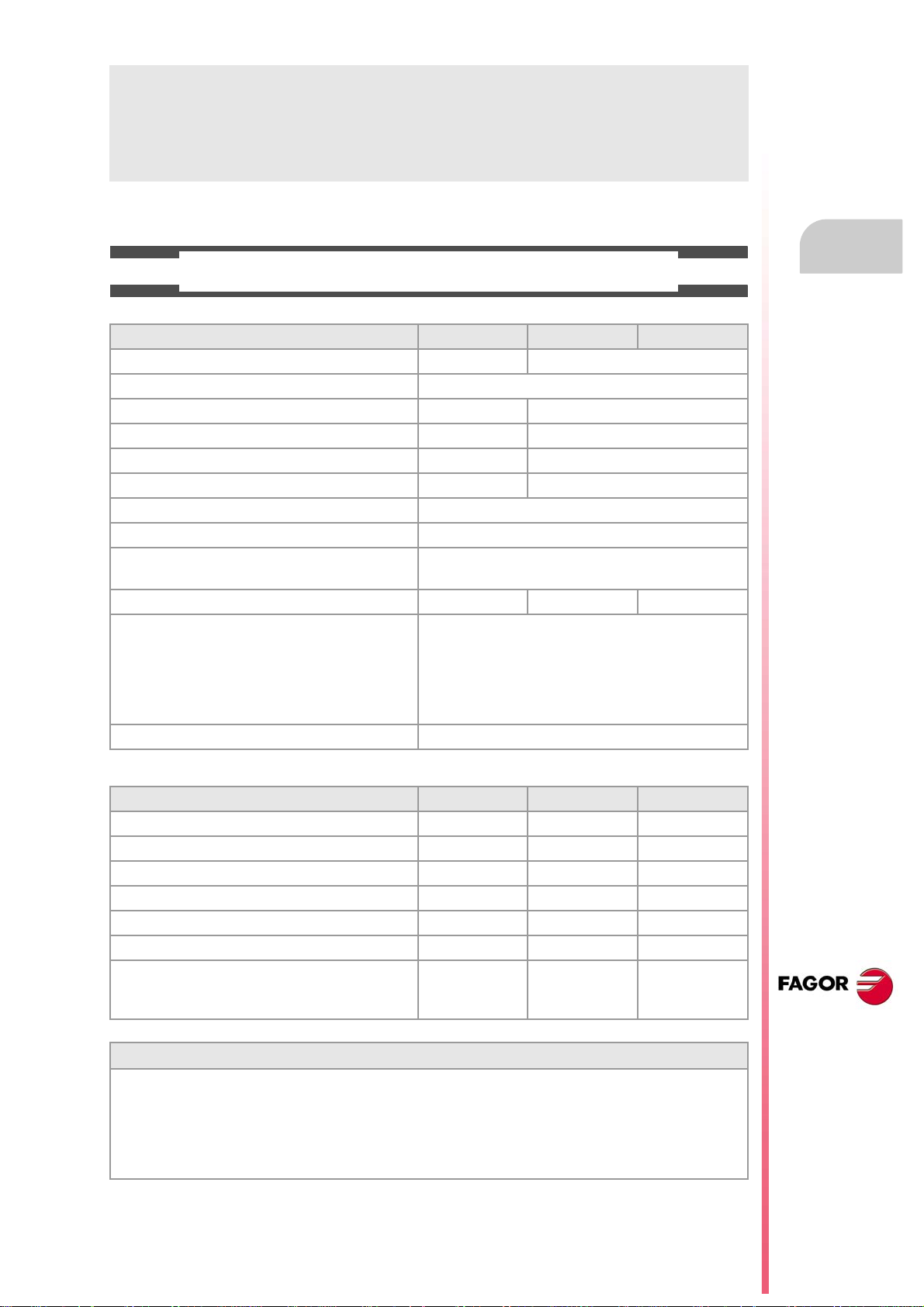
ABOUT THE PRODUCT
BASIC CHARACTERISTICS.
Basic characteristics. ·BL· ·OL· ·M· / ·T·
PC-based system. Closed system Open system
Operating system. Windows XP
Number of axes. 3 to 7 3 to 28
Number of spindles. 1 1 to 4
Number of tool magazines. 1 1 to 4
Number of execution channels. 1 1 to 4
Number of handwheels. 1 to 12
Type of servo system. Analog / Digital Sercos / Digital Mechatrolink
Communications. RS485 / RS422 / RS232
Ethernet
PCI expansion. No Option No
Integrated PLC.
PLC execution time.
Digital inputs / Digital outputs.
Marks / Registers.
Timers / Counters.
Symbols.
Block processing time. < 1 ms
< 1ms/K
1024 / 1024
8192 / 1024
512 / 256
Unlimited
Remote modules. RIOW RIO5 RIO70
Communication with the remote modules. CANopen CANopen CANfagor
Digital inputs per module. 8 16 or 32 16
Digital outputs per module. 8 24 or 48 16
Analog inputs per module. 4 4 8
Analog outputs per module. 4 4 4
Inputs for PT100 temperature sensors. 2 2 - - -
Feedback inputs. - - - - - - 4
Differential TTL
Sinusoidal 1 Vpp
Customizing.
PC-based open system, fully customizable.
INI configuration files.
FGUIM visual configuration tool.
Visual Basic®, Visual C++®, etc.
Internal databases in Microsoft® Access.
OPC compatible interface
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
·7·
Installation manual
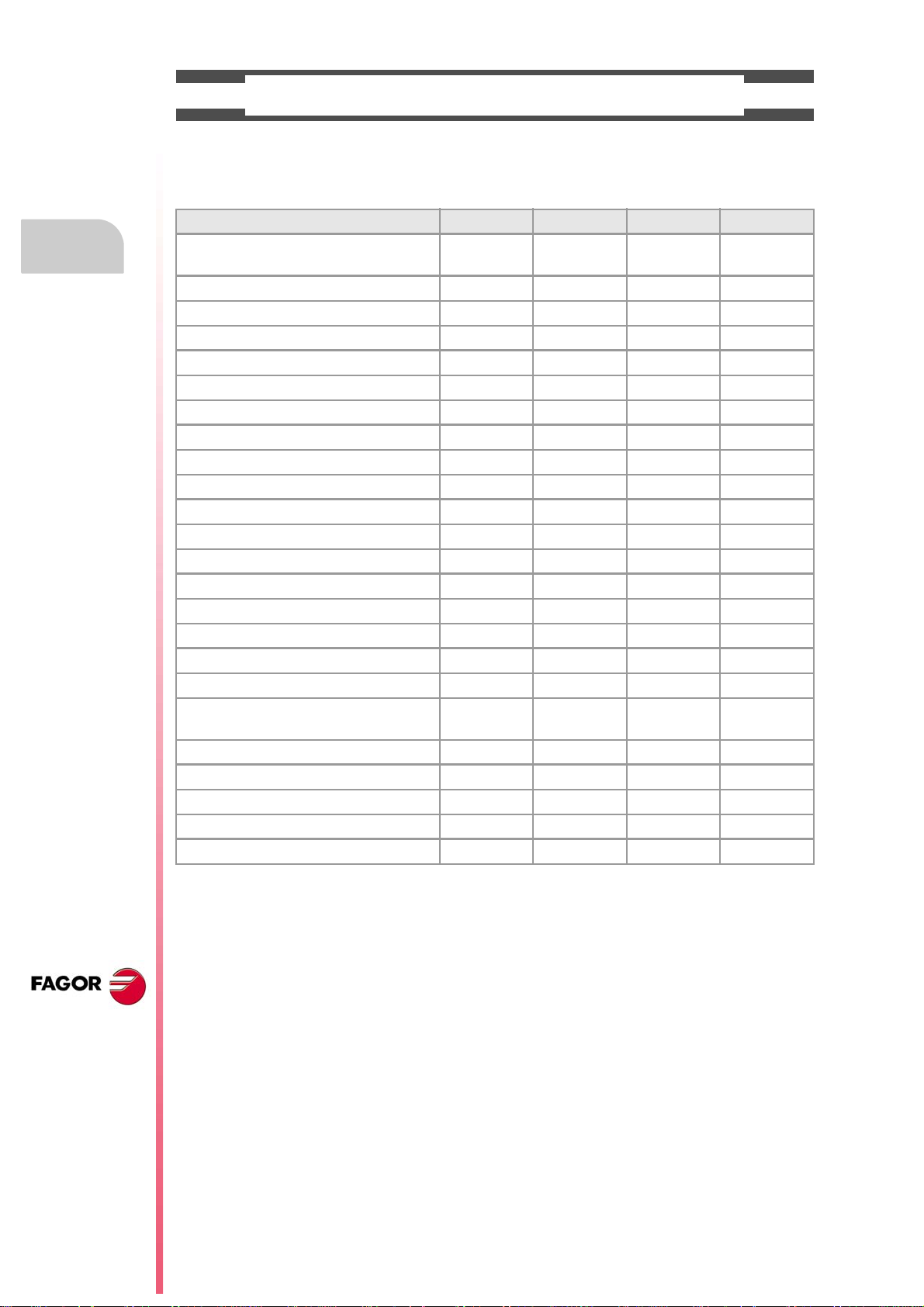
SOFTWARE OPTIONS.
Bear in mind that some of the features described in this manual depend on the software options that are
installed. The information of the following table is informative only; when purchasing the software options,
only the information provided in the ordering handbook is valid.
-BL- model -OL- model -M- model -T- model
Open system.
Access to the administrator mode.
Editing and simulation environment. - - - Standard Standard Standard
Number of execution channels 1 1 to 4 1 to 4 1 to 4
Number of axes 3 to 7 3 to 28 3 to 28 3 to 28
Number of spindles 1 1 to 4 1 to 4 1 to 4
Number of tool magazines 1 1 to 4 1 to 4 1 to 4
Number of interpolated axes (maximum) 4 28 - - - - - -
Limited to 4 interpolated axes Option Option Option Option
IEC 61131 language Option Option - - - - - -
HD graphics - - - Option Option Option
Conversational IIP - - - - - - Option Option
Non-Fagor digital drive Option Option - - - - - -
Tool radius compensation Option Option Standard Standard
"C" axis Option Option Standard Standard
Dynamic RTCP Option Option - - - Option
HSSA machining system. Option Option Standard Standard
Probing canned cycles - - - - - - Option Standard
Profile editor - - - - - - Standard Standard
Drilling ISO cycles for the OL model.
(G80, G81, G82, G83).
Tandem axes - - - Option - - - Option
Synchronism and cams Option Option - - - - - -
Tangential control Option Option - - - Standard
Volumetric compensation (up to 10 m³). Option Option Option Option
Volumetric compensation (more than 10 m³). Option Option Option Option
- - - Option - - - - - -
- - - Option - - - - - -
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
·8·
Installation manual
DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
The manufacturer:
Fagor Automation S. Coop.
Barrio de San Andrés Nº 19, C.P.20500, Mondragón -Guipúzcoa- (Spain).
Declares:
The manufacturer declares under their exclusive responsibility the conformity of the product:
8070 CNC
Consisting of the following modules and accessories:
8070-BL-ICU, 8070-OL-ICU
8070-BL-MCU, 8070-OL-MCU , 8070-OL-MCU-PCI
MONITOR-LCD-10K, MONITOR-LCD-15, MONITOR-SVGA-15
HORIZONTAL-KEYB, VERTICAL-KEYB, OP-PANEL
BATTERY, MOUSE UNIT
Remote Modules RIOW, RIO5, RIO70, RCS-S.
Note.Some additional characters may follow the model references indicated above. They all comply with the
directives listed here. However, compliance may be verified on the label of the unit itself.
Referred to by this declaration with following directives:
Low-voltage regulations.
IEC 60204-1:2005/A1:2008 Electrical equipment on machines. Part1. General requirements.
Regulation on electromagnetic compatibility.
EN 61131-2: 2007 PLC. Part 2. Equipment requirements and tests.
According to the European Community Directives 2006/95/EC on Low Voltage and 2004/108/EC
on Electromagnetic Compatibility and their updates.
In Mondragón, September 1st, 2013.
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
·9·


Installation manual
VERSION HISTORY
Here is a list of the features added to each manual reference. Each manual reference is valid for the
indicated software version and newer versions.
Ref. 0201
Software V01.00
First version. Milling model.
Ref. 0212
Software V01.10
Set the numbering of the digital I/O. • Machine parameters:
Probe management from the digital inputs; it is not possible to manage remote
feedback inputs ("Counter" module).
Tabletop probe configuration. • Machine parameters:
Define the repositioning feedrate after tool inspection. • Machine parameter: REPOSFEED.
New treatment of the JOG keys. Different keys to select the axis and the
direction.
Kinematics for rotary tables (TYPE9 to TYPE12). • Kinematics TYPE9 through TYPE12.
Know the dimensions of the kinematics on an axis. • Variable: (V.)A.HEADOF.xn
Keyboard simulation from the PLC. • Variable: (V.)G.KEY
Knowing which is the active probe. • Variable: (V.)G.ACTIVPROBE
Know the active general scaling factor. • Variable: (V.)G.SCALE
Park and unpark Sercos axes from the PLC. • PLC command: PARK, UNPARK.
NDIMOD, DIMODADRR, DIMOD,
NDOMOD, DOMODADRR, DOMOD.
• Machine parameters:
PRBDI1, PRBDI2, PRBPULSE1, PRBPULSE2.
PROBE, PRB1MIN...PRB3MIN,
PRB1MAX...PRB3MAX.
• Machine parameter: JOGKEYDEF.
Ref. 0501
Software V02.01
Windows XP operating system.
Emergency shutdown with battery (central unit PC104).
Multi-channel system, up to 4 channels. Swapping of axes and spindles,
communication and synchronization between channels, common arithmetic
parameters, access variables by channel, etc.
Multi-spindle system, up to 4 spindles.
Tool management with up to 4 magazines.
Parameter matching between the CNC and the Sercos drive. • Parameter matching.
New main operating mode for the drive; velocity Sercos. • Machine parameter: OPMODEP.
New kinematics table-spindle (TYPE13 to TYPE16). • Kinematics TYPE13 through TYPE16.
New kinematics for C axis (TYPE41 to TYPE43). • Kinematics TYPE41 through TYPE43.
New languages (Basque and Portuguese). • Machine parameter: LANGUAGE.
Placing the vertical softkeys on the left or on the right. • Machine parameter: VMENU.
Tandem axes. • Machien parameters:
Gantry axis. Maximum difference allowed between the following errors of both
axes before issuing a warning.
Apply cross compensation to either theoretical or real coordinates. • Machine parameter: TYPCROSS.
Apply leadscrew compensation to either theoretical or real coordinates. • Machine parameter: TYPLSCRW.
Tool radius compensation mode (G136/G137) by default • Machine parameter: IRCOMP.
Defining the type of reference pulse. • Machine parameter: REFPULSE.
Memory sharing between applications. • Machine parameter: PLCDATASIZE.
OEM generic machine parameters. • Machine parameter: MTBPAR.
Reading Sercos variables from the CNC. • Machine parameter: DRIVEVAR.
Electronic-cam editor. • Machine parameter: CAM.
Backlash peak compensation. • Machine parameter:
New behavior for rotary axes. • Machine parameters:
Sercos transmission at 8 MHz and 16 MHz. • Machine parameter: SERBRATE.
TANDEM, TMASTERAXIS, TSLAVEAXIS,
TORQDIST, PRELOAD, PRELFITI, TPROGAIN,
TINTTIME, TCOMPLIM.
• Machine parameter: WARNCOUPE.
BAKANOUT, BAKTIME, ACTBAKAN.
AXISMODE, UNIDIR, SHORTESTWAY.
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
·11·

Installation manual
Software V02.01
Define the anticipation time for the axes to be considered to be in position. • Machine parameters: ANTIME.
PLC. The TMOPERATION may take the values 13 and 14. • PLC mark: TMOPERATION.
PLC. Detect when the operating system locks up. • PLC marks: MMCWDG.
PLC. Disable the cross compensation tables. • PLC marks: DISCROSS.
PLC. Correct the parallelism on Gantry axes. • PLC marks: DIFFCOMP.
PLC. Execute CNC blocks. • PLC command: CNCEX.
PLC. Reading arithmetic parameters and OEM parameters with CNCRD
returns the value multiplied by 10000 (reading in float mode).
PLC. Define external symbols. • PLC command: PDEF.
PLC. The RESETIN mark is not necessary to park/unpark axes or spindles
from the PLC.
The "(V.).TM.MZWAIT " variable is not necessary in the subroutine associated
with M06.
Apply filters to eliminate the resonance of the spindle when it works as C axis
or during rigid tapping.
Optimize the reading and writing of variables from the PLC. Only the access
to the following variables will be asynchronous.
• The tool variables will be read asynchronously when the tool is neither
the active one nor in the magazine.
• The tool variables will be written asynchronously whether the tool is the
active one or not.
• The variables referred to local arithmetic parameters of the active levels
will be read and written asynchronously.
Spindle parking and unparking. • PLC marks: PARK, UNPARK.
Know the software version. • Variable: (V.)G.SOFTWARE
Variables related to loop adjustment. Gain setting via PLC. • Variables:
Variables related to loop adjustment. Position increment and sampling period. • Variables:
Variables related to loop adjustment. Fine adjustment of feedrate,
acceleration and jerk.
Variables related to the feedback inputs. • Variables:
• PLC marks: ADVINPOS.
• PLC marks: FREE.
• PLC command: CNCRD.
• PLC marks: RESETIN, PARK, UNPARK.
• Subroutine associated with M6.
• Variable: (V.).TM.MZWAIT
• Frequency filters. "C" axis. Rigid tapping.
• Reading and writing of variables from the PLC.
• Instructions #PARK, #UNPARK.
(V.)A.PLCFFGAIN.xn (V.)A.PLCACFGAIN.xn
(V.)A.PLCPROGAIN.xn
(V.)A.POSINC.xn (V.)A.TPOSINC.xn
(V.)A.PREVPOSINC.xn
• Variables:
(V.)A.FEED.xn (V.)A.TFEED.xn
(V.)A.ACCEL.xn (V.)A.TACCEL.xn
(V.)A.JERK.xn (V.)A.TJERK.xn
(V.)A.COUNTER.xn (V.)A.COUNTERST.xn
(V.)A.ASINUS.xn (V.)A.BSINUS.xn
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
Ref. 0504
Software V02.03
New values of Sercos optic power for the "Sercos II" board. • Machine parameters: SERPOWSE.
Electronic cam programming commands (real coordinates). • PLC command: CAM.
Independent axis movement programming commands. • PLC command: MOVE.
Programming commands for axis synchronization (real coordinates). • PLC command: FOLLOW.
New signals that may be consulted and changed for the independent
interpolator (electronic cam and independent movement)
The simulated axes are ignored regarding the validation code.
When matching parameters, it does not send parameters G00FEED and
MAXVOLT to the drive.
Function G112 changes the drive gear set. • G112 function.
Ref. 0509
Software V03.00
Lathe model. Machining canned cycles, lathe tool calibration, variables to
consult the geometry of lathe tools, etc.
Incline axis. • Machine parameter:
CAN bus type selection (CANopen/CANfagor). • Machine parameter: CANMODE.
Function G95 being active, allow setting the feed per turn in jog mode. • Machine parameter: FPRMAN.
Lathe model. Select graphics configuration. • Machine parameter: GRAPHTYPE.
Lathe model. Select axis configuration. • Machine parameter: GEOCONFIG.
Set of parameters of the master axis or spindle for synchronization. • Machine parameter: SYNCSET.
The CNC can keep the C axis active after executing M02, M30 or after an
emergency or reset.
Improved definition of kinematics for the C axis.
Magazine-less system. • Machine parameter: NTOOLMZ.
Ground tools for a turret magazine. The TMOPERATION register may take
the values 3, 4, 9 and 10.
Commands CNCRD and CNCWR. The channel number and the indexes may
be defined in the variables using an integer, a register or a symbol.
Spindle synchronization.
NANG, ANGTR, ANGAXNA, ORTAXNA,
ANGANTR, OFFANGAX.
• Machine parameter: PERCAX.
• PLC register: TMOPERATION.
• PLC commands: CNCRD and CNCWR.
·12·

Installation manual
Software V03.00
Variable to read the accumulated PLC offset. • Variable: (V.)[ch].A.ACTPLCOF.xn
Variable to obtain a linear estimation of the following error. • Variable: (V.)[ch].A.FLWEST.xn
Variables to read the instant value of feed-forward or AC-forward. • Variables:
Variable to know the line number of the file being executed. • Variable: (V.)[ch].G.LINEN
Variable to know what kind of cycle is active. • Variable: (V.)[ch].G.CYCLETYPEON
Variable to know the tool orientation. • Variable: (V.)[ch].G.TOOLDIR
Variable to know the theoretical feedrate on 3D path. • Variable: (V.)[ch].G.F3D
Variable to know the number of the warning being displayed. • Variable: (V.)[ch].G.CNCWARNING
The variable (V.)G.CNCERR is now per channel. • Variable: (V.)G.CNCERR
Improved coordinate transformation.
• Keep the part zero when deactivating the transformation.
• Working with 45º spindles. Select between the two choices.
• Keep the rotation of the plane axes with MODE 6.
Function G112 is not valid for the spindle. • G112 function.
New criteria when assuming a new master spindle in the channel.
(V.)[ch].A.ACTFFW.xn (V.)[ch].A.ACTACF.xn
•
Ref. 0601
Software V03.01
Screen test on power-up, if any element is missing, it restores the relevant
backup.
CAN bus. Transmission speed for cable lengths of 110, 120 and 130 m. • Machine parameter: CANLENGTH.
The CNC can keep axes slaved (coupled to each other) after executing M02,
M30 or after an emergency or reset.
Configure the way the CNC cancels tool radius compensation. • Machine parameter: COMPCANCEL.
Dual-feedback (internal + external) system, they may be swapped via PLC. • Machine parameters:
The PLC informs that a position synchronization has begun. • PLC mark: SYNCRONP.
The PLC informs about the status of the Sercos ring. • PLC mark: SERCOSRDY.
Parameter matching sends parameter MODUPLIM.
Variables. Geometry of the lathe tools.
Variables. Number of the tool in the claws of the changer arm. • Variables:
• Machine parameter: LINKCANCEL.
FBACKSRC, FBACKDIFF.
• PLC marks:
FBACKSEL(axis), ACTBACK(axis).
(V.)TM.TOOLCH1[mz]
(V.)TM.TOOLCH2[mz]
Ref. 0606
Software V03.10
New home searching method for spindles with home switch. The spindle goes
through the home switch twice.
New FAGOR low passing filters.
Maximum machining feedrate. • Machine parameter: MAXFEED.
Default machining feedrate when none has been programmed. • Machine parameter: DEFAULTFEED.
The user keys may be configured as jog keys. • Machine parameter: USERKEYDEF.
The CNC allows changing the spindle override during electronic threading
(G33) and in the threading canned cycles of the ·T· model (G86, G87 and their
equivalent of the cycle editor).
CANopen protocol. • Machine parameter: CANMODE.
The CNC may have several general handwheels. • Machine parameter: MPGAXIS.
A general handwheel can move several axes at the same time. • Machine parameter: MPGAXIS.
New parameter to set whether or not the CNC sends the M, H, S functions to
the PLC during block search.
M function table. New field to define whether the function is sent out to the PLC
or not during block search.
M function table. Each M function may have a different describing comment
associated with it.
On a handwheel with button, it is possible to configure the button from the PLC
to select sequentially the axis to be jogged with the handwheel.
Dead axis. Handling the blending of (transition between) blocks. • PLC mark: DEAD(axis)
Disabling a keyboard or jog panel integrated into the CAN bus. • PLC mark: PANELOFF.
Aborting CNCEX commands launched from the PLC. • PLC mark: PLCABORT.
In automatic and jog modes, the CNC shows the status of the _FEEDHOL
mark.
In automatic and jog modes, the CNC shows the status of the INHIBIT mark
of the axes and spindle.
OEM machine parameters.
• Range of parameters that can be written from the part-program, from the
PLC or from the interface.
• Range of parameters affected by the change of units.
• Each parameter may have a different describing comment associated
with it.
The CNC displays the warnings generated at the drive.
Configuring 2 axes with the same feedback input and analog output.
Up to 8 axes can now get involved in a kinematics (before just 5).
• Machine parameters:
THREADOVR, OVRFILTER.
• Machine parameter: FUNPLC.
• Field: MPLC.
• Field: COMMENT.
• PLC mark: NEXTMPGAXIS.
• PLC mark: _FEEDHOL.
• PLC mark: INHIBIT.
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
·13·

Installation manual
Software V03.10
Kinematics type 41/42. Angular offset for the rotary axis. • Kinematics TYPE41 and TYPE42.
Kinematics type 41/42. Tool misalignment with the C axis. • Kinematics TYPE41 and TYPE42.
Kinematics type 43. Angular offset for the rotary axis. • Kinematics TYPE43.
New kinematics; type 100 to 105. Integrating OEM kinematics through
machine parameters.
Programming help files for OEM and global subroutines.
Help file with the list of available subroutines.
"Retrace" function. • Machine parameter:
Tangential control. • PLC marks:
Canceling the preset turning direction of a tool. • Variable: (V.)G.SPDLTURDIR
Change the maximum feedrate allowed in the channel from the PLC. • Variable: (V.)[ch].PLC.PLCG00FEED
Show the status of the emergency relay. • Variable: (V.)G.ERELAYST
• Kinematics TYPE100 to TYPE105.
RETRACAC, NRETBLK, RETMFUNC.
• PLC marks:
RETRAEND, RETRACE.
TANGACTIV, TANGACT(axis).
• Variables: (V.)A.TANGAN.xn
(V.)G.TANGFEED
(V.)[ch].A.TGCTRLST.xn
(V.)[ch].G.TGCTRLST
Ref. 0608
Software V03.11
Simulator Possibility to use the dongle (hardware key) in a network.
The default value of some machine parameters is different for the CNC and
for the simulator installed on a PC.
"Retrace" function. Improvements to the retrace function.
Abort the execution of the program and resume it somewhere else. • PLC mark: PRGABORT.
CNC 8070
Ref. 0610
Software V03.12
In parameter matching, the CNC sends parameters it sends REFSHIFT and
FBMIXTIME.
Time constant for combined feedback. • Machine parameter: FBMIXTIME.
When the axes are position-Sercos; during parameter matching, the CNC
sends the value of parameter REFSHIFT to the drive so it takes it into account;
this way the CNC coordinate and that of the drive will be the same.
Ref. 0704 / Ref. 0706
Software V03.13
Sign criteria for tool offsets (dimensions) and tool wear. • Machine parameter: TOOLOFSG.
Variables V.TM.TOOLCH1[mz] / V.TM.TOOLCH2[mz] may be written from
the PLC.
Software V03.14
MCU and ICU central unit. battery powered RAM. Connecting handwheels to
the central unit. local I/O. Local feedback inputs. Loca probes.
The handwheels may be connected to the central unit. • Machine parameters:
Local feedback inputs. • Machine parameters:
Management of local I/O. • Machine parameters:
Number of non-volatile PLC registers. • Machine parameter: BKUPREG.
Number of non-volatile PLC counters. • Machine parameter: BKUPCOUN.
Number of common non-volatile arithmetic parameters. • Machine parameter: BKUPCUP.
Connect the probes to the central unit (local probes). • Machine parameters:
Define whether the spindle is homed automatically with the first movement or
not.
• Variables:
(V.)TM.TOOLCH1[mz]
(V.)TM.TOOLCH2[mz]
COUNTERTYPE, COUNTERID.
COUNTERTYPE, COUNTERID.
NLOCOUT, EXPSCHK.
PRBDI1, PROBETYPE1,
PRBDI2, PROBETYPE2.
• Machine parameter: REFINI.
(REF: 1309)
·14·
Ref. 0707
Software V03.15
In parameter matching, the CNC sends parameter ABSOFF when using
absolute feedback.
On rotary axes or spindles working in velocity-Sercos, the CNC calculates the
module of the coordinate. In parameter matching, drive parameter PP76(7) is
set to 0.
Variable to know the type of hardware. • Variable: (V.)G.HARDTYPE
Variable to know the theoretical tool feedrate along the path. • Variable: (V.)[ch].G.PATHFEED

Installation manual
Software V03.15
Managing an analog axis through the analog output and the second feedback
of a Sercos drive.
PLC errors may have an additional data file associated with them, same as
PLC messages.
The CNC shows a warning when a channel is expecting a tool that is being
used in another channel.
Ref. 0709
Software V03.16
Tandem spindles.
The CNC uses the combined feedback to calculate the velocity command, but
it uses the direct feedback to calculate the compensations, circularity test, etc.
The CNC does not assume any kinematics on power-up. • Machine parameters: KINID
The CNC allows modifying the spindle override while threading if it detects that
the feed forward (parameter FFWTYPE) is not active in a gear of the axes
involved or if the active feed forward is lower than 90%
• Machine parameters:
THREADOVR, OVRFILTER.
Ref. 0712
Software V03.17
On rotary axes with module and spindle working in velocity-Sercos mode, with
a whole gear ratio and with drive parameter PP76(7)=1, the parameter
matching does not redefine parameter PP76(7)=1; the CNC shows a warning
so the user recalculates the value of drive parameter PP4 (GC6 command).
In a tandem system, the master axis or spindle must have external feedback
and the slave internal feedback.
Keep C axis active after executing M02, M30 or after an emergency or reset. • Machine parameter: PERCAX.
Ref. 0801
Software V03.20
The CNC has a different MTB folder for each type of software installed; MTB_T
for lathe, MTB_M for mill and MTB_MC for motion control.
The CNC allows setting the maximum position difference between the two
axes of a gantry axis in order to correct it.
Configure the analog inputs for temperature sensors PT100. • Machine parameters: NPT100, PT100.
By default, the feedback alarms of the analog axes are activated. • Machine parameter: FBACKAL.
At the lathe model, the orientation of the axes in the profile editor is defined
by parameter GRAPHTYPE.
Kinematics type 17 to 24. 3-axis orthogonal spindles. • Kinematics TYPE17 through TYPE24.
When a feedback alarm occurs on the analog axes, the CNC deactivates the
REFPOIN(axis) mark.
Set change. For the CNC to assume the new parameter set, it must wait for
the PLC to receive the confirmation of one of the marks GEAR1 to GEAR4.
The CNC concludes the gear change when the PLC receives the confirmation
signal AUXEND.
The PLC informs that there is an OEM password. • PLC mark: PSWSET.
Gear change on a Sercos spindle. The set change only affects the drive when
it implies a change of gear ratio.
The CNC lets change the set of the slave axis or spindle of a tandem.
The PLC informs that, for the spindle, the parameter set selected at the CNC
does not match that of the PLC.
The PLC can Initiate the CNC shut-down sequence. • PLC mark: CNCOFF.
Park and unpark the main axes. • PLC marks: PARK, UNPARK.
Coordinate latching with the help of a probe or a digital input. • PLC command: TOUCHPROBE
Dynamic distribution of the machining operations between channels. During
the roughing operation of the cycle, the CNC channel activates these marks
to indicate which channel has the cycle been programmed in and which are
the channels involved in the distribution of the passes.
Electronic cam programming commands (theoretical coordinates). • PLC command: TCAM.
There is no need to use the partition character "\" in the PLC program to divide
a logic expression in two lines.
PLC. The PLC program can have several mnemonic files (extension "plc").
PLC. Grouping the additional information text files in a single file.
Check the status of the probes. • Variables:
Axis synchronization. Managing a rotary axis as an infinite axis making it
possible to increase the feedback count of the axis indefinitely (wihout limits)
regardless of the value of the module.
Interface related variables.
• Machine parameters: MAXDIFF.
• Machine parameter: GRAPHTYPE.
• PLC mark: REFPOIN(axis).
• PLC mark: GEAR1 to GEAR4.
• PLC mark: AUXEND.
• PLC mark: GEAROK.
• PLC marks:
PROBE1ACTIVE, PROBE2ACTIVE,
LATCH1ACTIVE(axis), LATCH2ACTIVE(axis),
LATCH1DONE(axis), LATCH2DONE(axis).
• Variables:
(V.)[ch].A.LATCH1.xn (V.)[ch].A.LATCH2.xn
• PLC marks:
DINDISTC1, DINDISTC2, DINDISTC3,
DINDISTC4.
(V.)G.PRBST1
(V.)G.PRBST2.
• Variable: (V.)[ch].A.ACCUDIST.xn
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
·15·

Installation manual
Software V03.20
When defining each PLC error, it is possible to select whether it opens the
emergency relay or not.
Machine parameters tables. Import and export leadscrew compensation
tables.
CNC errors between 10000 and 20000 are reserved for the OEM so he can
create his own warning or error texts in different languages.
The CNC allows modifying the percentage of acceleration and jek of the
spindles via part-program or in MDI/MDA mode
• Functions G130 and G132.
Ref. 0809
Software V04.00 (it does not include the features of version V03.21)
Unicode.
New language (Chinese). • Machine parameter: LANGUAGE.
When the CNC is installed as a simulator at a PC, the drive may be a simulated
type or a Sercos type.
In the machine parameter table, an icon indicates which parameters are
involved in parameter matching.
There can now be up to 12 handwheels. • Machine parameter: NMPG.
The CNC applies module compensation throughout the entire revolution of the
axis.
HSC mode. Eliminate the first resonance frequency of the machine when
generating the velocity command.
Home search moving the axis to the reference point. • Machine parameter: POSINREF.
Delay estimate at the drive. • Machine parameter: AXDELAY.
Transfer inhibit for the independent axes. • Machine parameter: XFITOIND.
Status of the axis position loop. • PLC mark: LOPEN(axis).
Positioning a turret magazine whether there is a tool in the indicated position
or not (TMOPERATION=15).
Detect overtemperature at the CNC. • PLC mark: OVRTEMP.
There can now be up to 1024 PLC messages. • PLC resources: MSG.
There can now be up to 1024 PLC errors. • PLC resources: ERR.
Inhibit the handwheels of the system. • PLC mark: INHIBITMPG1/INHIBITMPG12.
Cancel spindle synchronization after executing M02, M30 or after an error or
a reset.
A channel can maintain its master spindle after executing M02, M30 or after
an emergency or a reset or restarting the CNC.
Force the change of gears and/or of the parameter set of a Sercos drive • PLC mark: SERPLCAC.
Set a machine coordinate. • PLC mark: REFPOIN(axis).
Axis synchronization. Managing a rotary axis as an infinite axis making it
possible to increase the feedback count of the axis indefinitely (wihout limits)
regardless of the value of the module.
The variable (V.)[ch].E.PROGSELECT can be written via part-program, PLC
and interface. This variable can only be written with the value of ·0·
The following variables are valid for the spindle. • Variables:
Number of pulses sent by the handwheel since the system was started up. Variable: (V.)G.HANDP[hw]
The general handwheels can move axes with an associated individual
handwheel.
Feed handwheel.
• Machine parameter: DRIVETYPE.
• Machine parameter: MODCOMP.
• Machine parameter: FREQRES.
• PLC mark: _XFERINH and _XFERINH(axis).
• PLC mark: TMOPERATION.
• Machine parameter: SYNCCANCEL.
• Machine parameter: MASTERSPDL.
• Variable: (V.)A.SETGE.xn
• G174 function.
• Variables: (V.)[ch].A.PREVACCUDIST.xn
• Variables: (V.)[ch].E.PROGSELECT
(V.)[ch].A.MEAS.sn
(V.)[ch].A.ATIPMEAS.sn
(V.)[ch].A.MEASOF.sn
(V.)[ch].A.MEASOK.sn
(V.)[ch].A.MEASIN.sn
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
·16·
Ref. 0811
Software V03.21 (features not included in version V04.00)
There can now be up to 1024 PLC messages. • PLC resources: MSG.
There can now be up to 1024 PLC errors. • PLC resources: ERR.
Ref. 0907
Software V04.01
The CNC turns the internal fan on and off as necessary. The CNC turns the
fan on when the temperature exceeds 50 ºC (122 ºF) and turns it off when it
gets under 45 ºC (113 ºF).
Communication with servos (axis and spindle) and inverters (spindle) through
the Mechatrolink bus, in Mlink-I (17 bytes) and Mlink-II (17 or 32 bytes) mode.
Multi-axis management. Controlling several Sercos axes or spindles with a
single drive.
Kinematics (types 1 through 8). Spindle position referred to the machine
reference point.
• Machine parameter: MLINK.
• Machine parameter: MULTIAXIS.
• PLC mark: SWITCH(axis).
• Kinematics TYPE1 through TYPE8.

Installation manual
Software V04.01
Define the maximum acceleration and jerk allowed on the tool path. • Machine parameters:
New behavior of parameter "PREPFREQ". • Machine parameter: PREPFREQ
Variable to know the following error (lag) when feedback combination is active. • Variables:
Variable to know the position value of the first feedback when feedback
combination is active.
MAXACCEL, MAXJERK.
• Variables:
(V.)[ch].G.MAXACCEL (V.)[ch].G.MAXJERK
(V.)[ch].A.FLWE.xn (V.)[ch].A.FLWACT.xn
• Variable: (V.)[ch].A.POSMOTOR.xn
Ref. 1007
Software V04.10 (it does not include the features of version V04.02)
New languages (Russian and Czech). • Machine parameter: LANGUAGE.
Volumetric compensation. • Machine parameter: VOLCOMP.
• PLC mark: VOLCOMP1/VOLCOMP4.
• Variable: (V.)[ch].A.COMPVOL.xn
(V.)[ch].A.PIVOT.xn
Remote OpenPCS.
Cancel the inclined plane on start-up. • Machine parameter: CSCANCEL.
Handwheels. Setting a negative resolution reverses the axis moving direction. • Machine parameter: MPGRESOL.
Activate the rapid traverse for the automatic mode while executing a program. • Machine parameters: RAPIDEN, FRAPIDEN.
Maximum axis machining feedrate. • Machine parameter: MAXFEED.
Management of several keyboards. • Machine parameter: NKEYBD.
Configure the serial line as RS232, RS422 or RS485. • Machine parameter: RSTYPE.
Enable the HBLS handwheel. • Machine parameter: HBLS.
Selecting the type of PLC (IEC61131 or Fagor). • Machine parameter: PLCTYPE
Set the feedback system units. • Machine parameter: POSUNITS.
Cancel the name change for axes and spindles (#RENAME) after executing
M02 or M30, after a reset or at the beginning of a new part-program in the same
channel.
Connection with ACSD Sercos drives
RTCP. On tilting tables, rotate the part coordinate system when rotating the
table.
PLC. There are now 512 PLC timers. • PLC resources: Timers.
PLC. Management of spindle M functions (M3, M4 and M5) from the PLC. • PLC marks: PLCM3, PLCM4 and PLCM5.
PLC. Disable the alphanumeric keyboards. • PLC marks: QWERTYOFF
PLC. When the keyboard and the operator panel make up a single unit, the
PANELOFF mark only disables the jog panel.
PLC. Unslave the tandem axis temporarily. • PLC marks: TANDEMOFF(axis).
PLC. The CNC allows eliminating certain errors by pressing the [ESC] key
without having to do a reset.
M functions with an associated subroutine.
Detailed CNC status in jog mode. • Variable: (V.)[ch].G.CNCMANSTATUS
Detailed CNC status in automatic mode. • Variable: (V.)[ch].G.CNCAUTSTATUS
Know the axes selected for home search, repositioning, coordinate preset or
movement to a coordinate.
Know the current position of the main rotary axes of the kinematics (third axis). • Variable: (V.)[ch].G.POSROTT
Know the target position of the main rotary axes of the kinematics (third axis). • Variable: (V.)[ch].G.TOOLORIT1
• PLC mark: EXRAPID.
• Machine parameter: RENAMECANCEL.
• #RENAME instruction.
• Kinematics TYPE9 through TYPE12.
• PLC marks: PANELOFF
• Variable: (V.)[ch].G.SELECTEDAXIS
(V.)[ch].G.TOOLORIT2
Ref. 1010
Software V04.02 (features not included in version V04.10)
New language (Russian). • Machine parameter: LANGUAGE.
Activate the rapid traverse for the automatic mode while executing a program. • Machine parameters: RAPIDEN, FRAPIDEN.
Maximum axis machining feedrate. • Machine parameter: MAXFEED.
Management of several keyboards. • Machine parameter: NKEYBD.
Configure the serial line as RS232, RS422 or RS485. • Machine parameter: RSTYPE.
Set the feedback system units. • Machine parameter: POSUNITS.
Runaway protection and tendency test.
Synchronize spindles without forcing a set change. • Machine parameter: SYNCSET.
Mechatrolink. Activate the drive options. • Machine parameter: OPTION.
Cancel the name change for axes and spindles (#RENAME) after executing
M02 or M30, after a reset or at the beginning of a new part-program in the same
channel.
Connection with ACSD Sercos drives
RTCP. On tilting tables, rotate the part coordinate system when rotating the
table.
PLC. Disable the alphanumeric keyboards. • PLC marks: QWERTYOFF
PLC. When the keyboard and the operator panel make up a single unit, the
PANELOFF mark only disables the jog panel.
Load a file cam from the PLC. • PLC command: CAM SELECT, CAM
Detailed CNC status in jog mode. • Variable: (V.)[ch].G.CNCMANSTATUS
• PLC mark: EXRAPID.
• Machine parameters: TENDENCY, TENDTIME.
• Machine parameter: RENAMECANCEL.
• #RENAME instruction.
• Kinematics TYPE9 through TYPE12.
• PLC marks: PANELOFF
DESELECT
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
·17·

CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
Installation manual
Software V04.02 (features not included in version V04.10)
Detailed CNC status in automatic mode. • Variable: (V.)[ch].G.CNCAUTSTATUS
Know the axes selected for home search, repositioning, coordinate preset or
movement to a coordinate.
Know the current position of the main rotary axes of the kinematics (third axis). • Variable: (V.)[ch].G.POSROTT
Know the target position of the main rotary axes of the kinematics (third axis). • Variable: (V.)[ch].G.TOOLORIT1
Know the status of a cam. • Variable: (V.)G.CAMST[cam]
Modify the range of the slave axis when activating the cam. • Variable: (V.)G.CAM[cam][index]
Set 0% feedrate override via PLC. • Variable: (V.)[ch].PLC.FRO
• Variable: (V.)[ch].G.SELECTEDAXIS
(V.)[ch].G.TOOLORIT2
Ref. 1107
Software V04.11
Synchronized switching. • Machine parameters:
CANopen bus. Configuring CNC baudrate. • Machine parameter: CANOPENFREQ.
SWTOUTPUT, SWTDELAY.
• Variables:
(V.)G.TON (V.)G.TOF
(V.)G.PON (V.)G.POF
Ref. 1304
Software V04.20
Runaway protection and tendency test.
Synchronize spindles without forcing a set change. • Machine parameter: SYNCSET.
Mechatrolink. Activate the drive options. • Machine parameter: OPTION.
Load a file cam from the PLC. • PLC command:
Interruption subroutines per channel. • Machine parameters:
Set specific acceleration and jerk for G00 movements. • Machine parameters: G0ACDCJERK,
There may be up to 30 OEM subroutines per channel now (G180-G189 /
G380-G399).
Configure how to operate the CNC. Access work modes using hotkeys or from
the softkey menu.
Configure how to use the softkey menu, either using menus and submenus
(there are different softkey levels within a work mode) or using popup menus
(there is only 1 softkey menu, without submenus).
Maximum safety limit for feedrate. • Machine parameter: FLIMIT.
Maximum safety speed limit. • Machine parameter: SLIMIT.
Know the status of a cam. • Variable: (V.)G.CAMST[cam]
Modify the range of the slave axis when activating the cam. • Variable: (V.)G.CAM[cam][index]
Set 0% feedrate override via PLC. • Variable: (V.)[ch].PLC.FRO
Detailed CNC status in automatic mode. New values. • Variable: (V.)[ch].G.CNCAUTSTATUS
Active zero offset. • Variable: (V.)[ch].G.EXTORG
Assign a help text to the graphic softkeys.
Assign a help text to the icons that show the CNC status, at the top of the screen
Software V04.21
New model LCD-10K. • Machine parameters:
Software V04.22
Set the zero offsets with a coarse part and a fine part. • Machine parameter:
Cancel mirror image (G11/G12/G13/G14) after M30 and reset. • Machine parameter:
Set the feedrate displaying format (integers and decimals). • Machine parameter:
Set the spindle speed displaying format (integers and decimals). • Machine parameter:
• Machine parameters: TENDENCY, TENDTIME.
CAM SELECT, CAM DESELECT
INT1SUB - INT4SUB, SUBINTSTOP.
• PLC commands: INT1 - INT4.
LACC1G0, LACC2G0, LFEEDG0, ACCELG0,
DECELG0, ACCJERKG0, DECJERKG0
• Machine parameters:
OEMSUB (G380) - OEMSUB (G399)
• Machine parameter: HMITYPE.
• Machine parameter: SFTYPE.
• PLC commands: FLIMITAC, FLIMITACCH.
• PLC commands: SLIMITAC, SLIMITACSPDL.
JOGKEYDEF n
USERKEYDEF n
• Variables:
(V.)MPMAN.JOGKEYDEF[jk]
(V.)MPMAN.USERKEYDEF[uk]
FINEORG
• Variables:
(V.)[ch].A.ADDORG.xn
(V.)[ch].A.COARSEORG.xn
(V.)[ch].A.FINEORG.xn
(V.)[ch].A.COARSEORGT[nb].xn
(V.)[ch].A.FINEORGT[nb].xn
MIRRORCANCEL
FFORMAT
SFORMAT
·18·
Installation manual
Backlash peak cuttoff distance. • Machine parameter:
Hysteresis for applying the additional command pulse in movement reversals. • Machine parameter:
Software V04.24
Additional negative command pulse for analog axes. • Machine parameters:
The SPDLEREV mark also reverses the spindle turning direction in M19. • Machine parameters:
The default format for displaying the feedrate is 5.2. • Machine parameter:
The feedrate display format accepts 0.0. • Machine parameter:
The spindle speed display format accepts 0.0. • Machine parameter:
Dynamic distribution of the machining operations between channels. Both
options use the same PLC marks.
Leadscrew error compensation tables. The machine reference point, whose
position is indicated in parameter REFVALUE, may have any value.
Software V04.25
Synchronized switching. • Variables:
Error programmed in HSC mode. • Variable:
The HSC FAST mode may be used to adjust the chordal error (parameter E). • Statement: #HSC
The CNC will load into RAM memory the subroutines having the extension .fst.
If function G95 is active and the spindle does not have an encoder, the CNC
will use the programmed theoretical rpm to calculate the feedrate.
PEAKDISP
REVEHYST
BAKANOUT
M19SPDLEREV
• PLC signal:
SPDLEREV
FFORMAT
FFORMAT
SFORMAT
• PLC signal:
DINDISTC1, DINDISTC2,
DINDISTC3, DINDISTC4
(V.)G.TON (V.)G.TOF
(V.)G.PON (V.)G.POF
• Statement: #SWTOUT
(V.)[ch].G.CONTERROR
• Function G95.
Ref. 1305
Software V04.26
New model LCD-10K.
New model LCD-15.
New keyboard VERTICAL-KEYB.
New keyboard HORIZONTAL-KEYB.
New operator panel OP-PANEL.
Keep the longitudinal axis when changing planes (G17/G18/G19). • Machine parameter:
Show the softkey for toggling the display format between mm and inches. • Machine parameter:
Parameter REFSHIFT is only valid for linear and rotary axes. • Machine parameter:
PLC mark to indicate that the CNC has not corrected the position (coordinate)
difference between the master axis and the slave axis of a gantry axis.
• Machine parameters:
JOGKEYDEF n
USERKEYDEF n
• Variables:
(V.)MPMAN.JOGKEYDEF[jk]
(V.)MPMAN.USERKEYDEF[uk]
LCOMPTYP.
MMINCHSOFTKEY.
REFSHIFT.
• PLC signal: MAXDIFF(axis).
Ref. 1308
Software V04.26.10
The CNC checks every minute the unit temperature; if in three samples in a
row the temperature exceeds 60 ºC (140 ºF), the CNC activates the
OVERTEMP mark.
When the CPU has a fan, during regular operation of the CNC, it monitors and
verifies that the fan is running. This test is run every minute, same as the
temperature watch.
Every time [START] is pressed, the CNC checks that the room temperature
does not exceed 65 ºC (149 ºF) and, if it does, the CNC does not let run the
program and issues the corresponding error message.
• PLC signal: OVERTEMP.
Ref. 1309
Software V04.27
Hardware.
• The model LCD-10K (front mounting) is removed.
• The model LCD-15 (front mounting) is removed.
• The module OP-PANEL-H/E is removed.
• The module JOG-PANEL is removed.
• The module KB-PANEL-H is removed.
The _EMERGEN signal activates the _ALARM mark. • PLC signal: _ALARM.
New language (Korean). • Machine parameter: LANGUAGE.
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
·19·

Installation manual
Software V04.27
Virtual tool axis. • Machine parameter:
Management of the RCS-S module. • Machine parameter:
Select the type of feedback of the RCS-S module. • Machine parameter:
SSI feedback in the RCS-S module. • Machine parameter:
Modify the simulation speed via PLC. • Variable: (V.)PLC.SIMUSPEED
Correction of the delay inserted by the bus and the drive. • Machine parameter:
PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) • Machine parameter:
VIRTAXISNAME, VIRTAXCANCEL.
• Variables:
(V.)[ch].G.VIRTAXIS
(V.)[ch].G.VIRTAXST
(V.)[ch].A.VIRTAXOF.xn
NSERCOUNT, SERCOUNTID,
FEEDBACKTYPE.
FEEDBACKTYPE.
SSITYPE, SSI.
TRANSDELAY.
PWMOUTPUT, PWMCANCEL.
• PLC signal: PWMON.
• Variables:
(V.)G.PWMON
(V.)G.PWMFREQ
(V.)G.PWMDUTY
(V.)PLC.PWMFREQ
(V.)PLC.PWMDUTY
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
·20·
Installation manual
SAFETY CONDITIONS
Read the following safety measures in order to prevent harming people or damage to this product and those
products connected to it. Fagor Automation shall not be held responsible of any physical damage or
defective unit resulting from not complying with these basic safety regulations.
Before start-up, verify that the machine that integrates this CNC meets the 89/392/CEE Directive.
PRECAUTIONS BEFORE CLEANING THE UNIT
If the CNC does not turn on when actuating the start-up switch, verify the connections.
Do not get into the inside of the unit. Only personnel authorized by Fagor Automation may manipulate the
Do not handle the connectors with the unit
connected to AC power.
inside of this unit.
Before manipulating the connectors (inputs/outputs, feedback, etc.)
make sure that the unit is not connected to AC power.
PRECAUTIONS DURING REPAIR
In case of a malfunction or failure, disconnect it and call the technical service.
Do not get into the inside of the unit. Only personnel authorized by Fagor Automation may manipulate the
inside of this unit.
Do not handle the connectors with the unit
connected to AC power.
Before manipulating the connectors (inputs/outputs, feedback, etc.)
make sure that the unit is not connected to AC power.
PRECAUTIONS AGAINST PERSONAL DAMAGE
Interconnection of modules. Use the connection cables provided with the unit.
Use proper cables. To prevent risks, use the proper cables for mains, Sercos and Bus
CAN recommended for this unit.
In order to avoid electrical shock at the central unit, use the proper
power (mains) cable. Use 3-wire power cables (one for ground
connection).
Avoid electrical overloads. In order to avoid electrical discharges and fire hazards, do not apply
electrical voltage outside the range selected on the rear panel of the
central unit.
Ground connection. In order to avoid electrical discharges, connect the ground terminals
of all the modules to the main ground terminal. Before connecting the
inputs and outputs of this unit, make sure that all the grounding
connections are properly made.
In order to avoid electrical shock, before turning the unit on verify that
the ground connection is properly made.
Do not work in humid environments. In order to avoid electrical discharges, always work under 90% of
relative humidity (non-condensing) and 45 ºC (113 ºF).
Do not work in explosive environments. In order to avoid risks or damages, do no work in explosive
environments.
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
·21·
Installation manual
PRECAUTIONS AGAINST PRODUCT DAMAGE
Working environment. This unit is ready to be used in industr ial environments complying with
the directives and regulations effective in the European Community.
Fagor Automation shall not be held responsible for any damage
suffered or caused by the CNC when installed in other environments
(residential or homes).
Install the unit in the right place. It is recommended, whenever possible, to install the CNC away from
coolants, chemical product, blows, etc. that could damage it.
This unit complies with the European directives on electromagnetic
compatibility. Nevertheless, it is recommended to keep it away from
sources of electromagnetic disturbance such as:
Powerful loads connected to the same AC power line as this
equipment.
Nearby portable transmitters (Radio-telephones, Ham radio
transmitters).
Nearby radio/TV transmitters.
Nearby arc welding machines.
Nearby High Voltage power lines.
Enclosures. The manufacturer is responsible of assuring that the enclosure
involving the equipment meets all the currently effective directives of
the European Community.
Avoid disturbances coming from the
machine.
Use the proper power supply. Use an external regulated 24 Vdc power supply for the keyboard and
Grounding of the power supply. The zero volt point of the external power supply must be connected
Analog inputs and outputs connection. Use shielded cables connecting all their meshes to the corresponding
Ambient conditions. The storage temperature must be between +5 ºC and +45 ºC (41 ºF
Central unit enclosure. Make sure that the needed gap is kept between the central unit and
Main AC power switch. This switch must be easy to access and at a distance between 0.7 and
The machine must have all the interference generating elements
(relay coils, contactors, motors, etc.) uncoupled.
the remote modules.
to the main ground point of the machine.
pin.
and 113 ºF).
The storage temperature must be between -25 ºC and 70 ºC (-13 ºF
and 158 ºF).
each wall of the enclosure.
Use a DC fan to improve enclosure ventilation.
1.7 m (2.3 and 5.6 ft) off the floor.
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
·22·
PROTECTIONS OF THE UNIT ITSELF
Remote modules. All the digital inputs and outputs have galvanic isolation via
optocouplers between the CNC circuitry and the outside.
Installation manual
i
SAFETY SYMBOLS
Symbols that may appear on the manual.
Danger or prohibition symbol.
It indicates actions or operations that may hurt people or damage products.
Warning symbol.
It indicates situations that certain operations could cause and the suggested actions to prevent them.
Obligation symbol.
It indicates actions and operations that must be carried out.
Information symbol.
It indicates notes, warnings and advises.
Symbols that the product may carry.
Ground protection symbol.
It indicates that that point must be under voltage.
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
·23·

Installation manual
WARRANTY TERMS
INITIAL WARRANTY
All products manufactured or marketed by FAGOR carry a 12-month warranty for the end user which could
be controlled by the our service network by means of the warranty control system established by FAGOR
for this purpose.
In order to prevent the possibility of having the time period from the time a product leaves our warehouse
until the end user actually receives it run against this 12-month warranty, FAGOR has set up a warranty
control system based on having the manufacturer or agent inform FAGOR of the destination, identification
and on-machine installation date, by filling out the document accompanying each FAGOR product in the
warranty envelope. This system, besides assuring a full year of warranty to the end user, enables our service
network to know about FAGOR equipment coming from other countries into their area of responsibility.
The warranty starting date will be the one appearing as the installation date on the above mentioned
document. FAGOR offers the manufacturer or agent 12 months to sell and install the product. This means
that the warranty starting date may be up to one year after the product has left our warehouse so long as
the warranty control sheet has been sent back to us. This translates into the extension of warranty period
to two years since the product left our warehouse. If this sheet has not been sent to us, the warranty period
ends 15 months from when the product left our warehouse.
This warranty covers all costs of material and labour involved in repairs at FAGOR carried out to correct
malfunctions in the equipment. FAGOR undertakes to repair or replace their products within the period from
the moment manufacture begins until 8 years after the date on which it disappears from the catalogue.
It is entirely up to FAGOR to determine whether the repair is or not under warranty.
EXCLUDING CLAUSES
Repairs will be carried out on our premises. Therefore, all expenses incurred as a result of trips made by
technical personnel to carry out equipment repairs, despite these being within the above-mentioned period
of warranty, are not covered by the warranty.
Said warranty will be applied whenever the equipment has been installed in accordance with instructions,
has not be mistreated, has not been damaged by accident or by negligence and has not been tampered
with by personnel not authorised by FAGOR. If, once servicing or repairs have been made, the cause of
the malfunction cannot be attributed to said elements, the customer is obliged to cover the expenses
incurred, in accordance with the tariffs in force.
Other warranties, implicit or explicit, are not covered and FAGOR AUTOMATION cannot be held responsible
for other damages which may occur.
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
·25·

Installation manual
WARRANTY ON REPAIRS
In a similar way to the initial warranty, FAGOR offers a warranty on standard repairs according to the
following conditions:
PERIOD 12 months.
CONCEPT Covers parts and labor for repairs (or replacements) at the
network's own facilities.
EXCLUDING CLAUSES The same as those applied regarding the chapter on initial
warranty. If the repair is carried out within the warranty period, the
warranty extension has no effect.
When the customer does not choose the standard repair and just the faulty material has been replaced,
the warranty will cover just the replaced parts or components within 12 months.
For sold parts the warranty is 12 moths length.
SERVICE CONTRACTS
The SERVICE CONTRACT is available for the distributor or manufacturer who buys and installs our CNC
systems.
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
·26·
Installation manual
MATERIAL RETURNING TERMS
When sending the central nit or the remote modules, pack them in its original package and packaging
material. If the original packaging material is not available, pack it as follows:
1 Get a cardboard box whose three inside dimensions are at least 15 cm (6 inches) larger than those
of the unit. The cardboard being used to make the box must have a resistance of 170 Kg (375 lb.).
2 Attach a label indicating the owner of the unit, person to contact, type of unit and serial number. In case
of malfunction also indicate symptom and a brief description of the problem.
3 Wrap the unit in a polyethylene roll or similar material to protect it. When sending a central unit with
monitor, protect especially the screen.
4 Pad the unit inside the cardboard box with poly-utherane foam on all sides.
5 Seal the cardboard box with packing tape or industrial staples.
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
·27·

Installation manual
CNC MAINTENANCE
CLEANING
The accumulated dirt inside the unit may act as a screen preventing the proper dissipation of the heat
generated by the internal circuitry which could result in a harmful overheating of the unit and, consequently,
possible malfunctions. Accumulated dirt can sometimes act as an electrical conductor and short-circuit the
internal circuitry, especially under high humidity conditions.
To clean the operator panel and the monitor, a smooth cloth should be used which has been dipped into
de-ionized water and /or non abrasive dish-washer soap (liquid, never powder) or 75º alcohol. Do not use
highly compressed air to clean the unit because it could generate electrostatic discharges.
The plastics used on the front panel are resistant to grease and mineral oils, bases and bleach, dissolved
detergents and alcohol. Avoid the action of solvents such as chlorine hydrocarbons, venzole, esters and
ether which can damage the plastics used to make the unit’s front panel.
PRECAUTIONS BEFORE CLEANING THE UNIT
Fagor Automation shall not be held responsible for any material or physical damage derived from the
violation of these basic safety requirements.
• Do not handle the connectors with the unit connected to AC power. Before handling these connectors
(I/O, feedback, etc.), make sure that the unit is not connected to main AC power.
• Do not get into the inside of the unit. Only personnel authorized by Fagor Automation may manipulate
the inside of this unit.
• If the CNC does not turn on when actuating the start-up switch, verify the connections.
CNC 8070
(REF: 1309)
·29·

 Loading...
Loading...