Evga X299 Ftw-k User Manual

EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
User Guide
EVGA X299 FTW-K
Specs and Initial Installation
- 1 -
EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Table of Contents
User Guide ............................................................................................................... |
- 1 - |
EVGA X299 FTW-K ................................................................................................. |
- 1 - |
Specs and Initial Installation..................................................................................... |
- 1 - |
Before You Begin… ................................................................................................. |
- 4 - |
Parts NOT in the Kit ............................................................................................................. |
- 5 - |
Intentions of the Kit .............................................................................................................. |
- 5 - |
Motherboard Specifications.................................................................................................. |
- 6 - |
Unpacking and Parts Descriptions ........................................................................................ |
- 8 - |
Intel X299 FTW-K Motherboard LED reference ................................................................. |
- 9 - |
Intel X299 FTW-K Motherboard Component Legend ....................................................... |
- 12 - |
PCI-E Slot Breakdown ....................................................................................................... |
- 24 - |
M.2 and U.2 Slot Breakdown ............................................................................................. |
- 25 - |
Installing the CPU .................................................................................................. |
- 26 - |
Installing the CPU Cooling Device .................................................................................... |
- 27 - |
Installing System Memory.................................................................................................. |
- 28 - |
Installing the I/O Shield and I/O Cover .............................................................................. |
- 29 - |
Installing the Motherboard...................................................................................... |
- 29 - |
Securing the Motherboard into a System Case ................................................................... |
- 30 - |
Installing M.2 devices......................................................................................................... |
- 32 - |
Tested CPU......................................................................................................................... |
- 35 - |
Tested U.2........................................................................................................................... |
- 35 - |
Tested M.2 Key-M ............................................................................................................. |
- 36 - |
Tested M.2 Key-E............................................................................................................... |
- 36 - |
Connecting Cables .............................................................................................................. |
- 37 - |
Onboard Buttons................................................................................................................. |
- 47 - |
First Boot ................................................................................................................ |
- 48 - |
M.2 SSD, PCI-E SSD, and NVMe SSD Installation steps ................................................. |
- 50 - |
- 2 -
EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Internal RAID Controller ......................................................................................... |
- 52 - |
Fan Header DC and PWM setup ........................................................................... |
- 87 - |
Setting Up SLI and PhysX...................................................................................... |
- 91 - |
Realtek HD Audio Manager ............................................................................................... |
- 95 - |
Configuration of the Killer NIC Software .............................................................. |
- 113 - |
Installing Drivers and Software ............................................................................ |
- 131 - |
Windows 10 Driver Installation........................................................................................ |
- 131 - |
Warranty and Overclocking.............................................................................................. |
- 132 - |
Troubleshooting ................................................................................................... |
- 133 - |
Replacing a BIOS chip ..................................................................................................... |
- 133 - |
SSD / HDD is not detected ............................................................................................... |
- 136 - |
System does not POST, and POST code indicator reads “C”........................................... |
- 138 - |
System does not POST, and POST code indicator reads “55” ......................................... |
- 139 - |
System does not POST, and POST code indicator reads “d7” ......................................... |
- 139 - |
Have a question not covered above, or want some online resources? .............................. |
- 140 - |
POST Beep codes ............................................................................................................. |
- 141 - |
POST Port Debug LED .................................................................................................... |
- 142 - |
POST Codes ........................................................................................................ |
- 143 - |
EVGA Glossary of Terms ................................................................................................ |
- 148 - |
Compliance Information ....................................................................................... |
- 151 - |
- 3 -
EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Before You Begin…
EVGA welcomes you to the next generation of Intel Enthusiast performance: the X299 FTW-K! The X299 platform supports the newest Skylake-X and Kaby Lake-X processors. EVGA X299 motherboards further refine highperformance with multiple options for all the latest SSD options with support for U.2, M.2 and PCI-E drives and is Intel® Optane™ Memory Ready – a revolutionary higher-density memory interface, based on 3D XPoint Technology, delivers a new generation of SSDs designed to obliterate loading times for gamers. However, the X299 platform also supports all the features you’ve come to expect from EVGA, including up to 128GBs of Quad-Channel DDR4 memory at maximum memory speeds of up to 4000MHz+for Skylake- X, and 4133MHz+ for Kaby Lake-X (OC), Gigabit-NIC support, USB 3.0 and USB 3.1 Type-A and Type-C support, an updated UEFI\BIOS GUI, PWM fan control and a variety of SATA options to fit everyone’s needs. The X299 FTW- K is built with a 8-layer PCB, featuring a CPU socket with 150% higher Gold content powered by an Advanced 14-phase Digital VRM (10 Phase VCore, 4 Phase Memory PWM), providing industry-leading stability for all your applications.
Furthermore, this board is designed not ONLY for overclockers, but also for gamers with NVIDIA® 3-Way SLI + PhysX Support without the need for PLX chips, blazing-fast networking featuring the Killer E2500 NIC and an Intel i219, Dual M.2 Key-M, Dual U.2, 8 SATA 3/6g and much more!
Lastly, a motherboard is only as good as its BIOS, and the EVGA X299 FTW- K features an updated UEFI\BIOS GUI with a focus on overclocking and functionality in a lean, straight-forward package. You won’t need to be an expert to configure your motherboard, but if you are, you’ll find features unavailable anywhere else.
Combining the best of current technology with the latest innovations, EVGA is further refining motherboard performance!
- 4 -

EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Parts NOT in the Kit
This kit contains all the hardware necessary to install and connect your new EVGA X299 FTW-K Motherboard. However, it does NOT contain the following items, which must be purchased separately in order to make the system fully-functional and install an Operating System:
Intel Socket 2066 Processor
DDR4 System Memory
CPU Cooling Device
PCI Express Graphics Card
Power Supply
Hard Drive or SSD
Keyboard / Mouse
Monitor
(Optional) Optical Drive
EVGA assumes you have purchased all the necessary parts needed to allow for proper system functionality. For a full list of supported CPUs on this motherboard, please visit www.evga.com/support/motherboard
Intentions of the Kit
When replacing a different model motherboard in a PC case, you may need to reinstall your operating system, even though the current HDD/SSD may already have one installed. Keep in mind, however, you may sometimes also need to reinstall your OS after a RMA even if your motherboard remains the same due to issues that occurred prior to replacing the motherboard.
- 5 -

EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Motherboard Specifications
Size:
EATX form-factor of 12 inches x 10.375 inches (304.8x276.7mm)
Microprocessor support:
Intel Socket 2066 Processor
Operating Systems:
Supports Windows 10 64bit only
System Memory support:
Supports Quad Channel DDR4 up to 4000MHz+ Skylake-X, and 4133MHz+ Kaby Lake-X (OC).
Supports up to 128GB of DDR4 memory.
USB 2.0 Ports:
4x from Intel X299 PCH – 4x internal via 2 FP headers
Supports transfer speeds up to 480 Mbps with full backwards compatibility
USB 3.0 Ports:
8x from Intel X299 PCH – 6x external, 2x internal via 1 FP headers Supports transfer speeds up to 5Gbps with full backwards compatibility
USB 3.1 Ports:
2x from ASMedia ASM2142 – 2x external, 1x Type-C, 1x Type-A Supports transfer speeds up to 10Gbps with full backwards compatibility *Type-C will require a Type-A adapter for backwards compatibility
SATA Ports:
Intel X299 PCH Controller
8x SATA 3/6G (600 MB/s) data transfer rate
-Support for RAID0, RAID1, RAID5, AND RAID10
-Supports hot plug
Onboard LAN:
1x Intel i219v Gigabit (10/100/1000) Ethernet
1x Killer E2500 Gigabit (10/100/1000) Ethernet MAC+PHY Ethernet Teaming NOT Supported
Killer Doubleshot Pro supported with Killer Wireless AC 1535 or 1525 * Killer Wireless AC is NOT included and must be purchased separately
- 6 -
EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Onboard Audio:
Realtek Audio (ALC1150)
Supports 8-channel (7.1) audio with Optical S/PDIF Out
Power Functions:
Supports ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface)
Supports S0 (normal), S3 (suspend to RAM), S4 (Suspend to disk - depends on OS), and S5 (soft - off)
PCI-Express Expansion Slots:
4x PCI-E x16 slot 2x16, 2x8*
1x PCI-E x4 slot
1x PCI-E x1 slot
*LANES PER SLOT CAN VARY BASED OFF OF CPU, PLEASE SEE PAGE 24 FOR LANE BREAKDOWN BASED OFF OF CPU.
PCI-E 3.0 Support:
Low power consumption and power management features
SLI and Crossfire Support:
3-Way SLI
3-Way Crossfire
Additional Expansion Slots:
1x M.2 Key-M 110mm slot PCI-E/NVMe
1x M.2 Key-M 80mm slot PCI-E/NVMe & SATA/Optane Key-M 80mm Supports Intel Optane
1x M.2 Key-E slot (via vertical adapter)
2x U.2 slot
RGB LED Header:
4x 4-pin RGB LED header (For included RBG lit covers ONLY)
VROC Header:
1x 4-pin VROC header
Fan Headers:
2x 4-pin PWM controlled headers
5x 4-pin DC\PWM headers
-3pin(DC)\4pin(PWM) modes are selected and static RPM set in BIOS
ALL FAN HEADERS HAVE A MAXIMUM POWER OF
1 AMP @ 12 VOLTS (12 WATTS) EXCEDING THIS LIMIT WILL CAUSE THE BOARD IRREPARABLE DAMAGE.
- 7 -

EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Unpacking and Parts Descriptions
The following accessories are included with the EVGA X299 FTW-K
Motherboard:
- 8 -

EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Intel X299 FTW-K Motherboard LED reference
The EVGA X299 FTW-K Motherboard has several LEDs indicating power, connectivity, and activity. Below is the location of the LEDs and their function.
LED Legend
1. |
Power Button |
7. |
CATERR |
13. |
CC_LED |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
Reset Button |
8. |
VSM |
14. |
PE2 Status/Mode |
3. |
POSTCODE Indicator |
9. |
VCC |
15. |
PE3 Status/Mode |
4. |
Removable BIOS LED 1 |
10. |
5VSB |
16. |
PE4 Status/Mode |
5. |
Non-Removable BIOS LED 2 |
11. |
SKX Detect |
17. |
PE5 Status/Mode |
6. |
FIVR |
12. |
KBX Detect |
|
|
- 9 -
EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
1.Power Button
a.RED: System is on
b.GREEN (blinking): System in Sleep mode
2.Reset Button
a.WHITE: blinks with storage access
3.POST Code indicator
a.After bootup, this will display the CPU temp.
b.During boot it will cycle many different hexadecimal post codes with a range of 00-FF and this indicates what aspect of the Power On Self Test (POST) is currently running.
i. *For list of POST Codes, please see Page 142.
4.Removable BIOS LED
a.RED: Active BIOS Chip (only 1 will be lit at a time)
b.This LED indicates the removable BIOS chip is active
5.Non-Removable BIOS LED
a.RED: Active BIOS Chip (only 1 will be lit at a time)
b.This LED indicates the non-removable BIOS chip is active
6.FIVR
a.RED: Indicates CPU integrated voltage regulation failure.
b.OFF: No issues detected on FIVR
7.CATERR
a.CATERR stands for Catastrophic Error on the processor.
b.RED: Processor error has occurred.
c.Off: No error state detected in the CPU.
8.VSM
a.YELLOW: Voltage detected (Does not mean PSU is
outputting in-spec, only that this specific voltage is detected)
9.VCC
a. RED: Voltage detected (Does not mean PSU is outputting in-
spec, only that this specific voltage is detected)
10.5VSB
a. WHITE: Voltage detected (Does not mean PSU is outputting
in-spec, only that this specific voltage is detected)
11.SKX LED
a.YELLOW: Indicates a SkyLake-X processor is installed into the socket.
12.KBX LED
a.WHITE: Indicates a Kaby Lake-X processor is installed into the socket.
- 10 -
EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
13.CC_LED
a.USB 3.1 Type-C detection.
b.RED: Indicates device is attached and detected to USB Type-C.
c.OFF: No device detected.
14.PCI-Express LED for PE2. The LED will remain off when this PCI-E slot is disabled or unpopulated.
a.GREEN: Operating at PCI-Express Gen1 speed
b.YELLOW: Operating at PCI-Express Gen2 speed
c.RED: Operating at PCI-Express Gen3 speed
15.PCI-Express LED for PE3. The LED will remain off when this PCI-E slot is disabled or unpopulated.
a.GREEN: Operating at PCI-Express Gen1 speed
b.YELLOW: Operating at PCI-Express Gen2 speed
c.RED: Operating at PCI-Express Gen3 speed
16.PCI-Express LED for PE4. The LED will remain off when this PCI-E slot is disabled or unpopulated.
a.GREEN: Operating at PCI-Express Gen1 speed
b.YELLOW: Operating at PCI-Express Gen2 speed
c.RED: Operating at PCI-Express Gen3 speed
17.PCI-Express LED for PE5. The LED will remain off when this PCI-E slot is disabled or unpopulated.
a.GREEN: Operating at PCI-Express Gen1 speed
b.YELLOW: Operating at PCI-Express Gen2 speed
c.RED: Operating at PCI-Express Gen3 speed
- 11 -
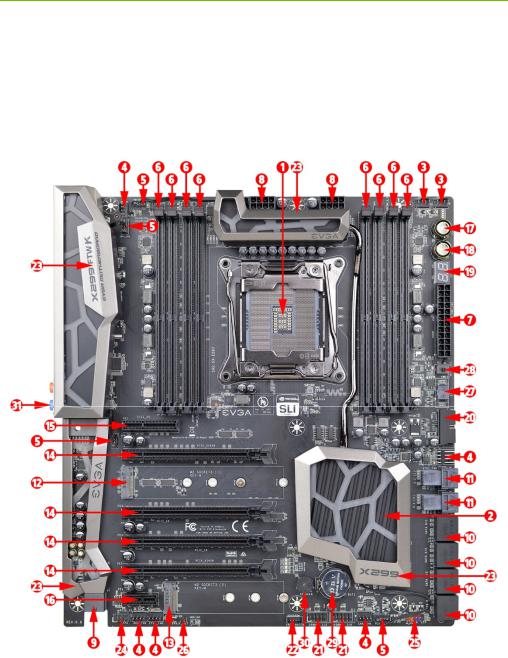
EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Intel X299 FTW-K Motherboard Component
Legend
The EVGA X299 FTW-K Motherboard with the Intel X299 and PCH Chipset. Figure 1 shows the motherboard and Figure 2 shows the back panel connectors
FIGURE 1. X299 FTW-K Motherboard Layout
- 12 -

EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Component Legend
1. |
CPU Socket 2066 |
12. |
M.2 Socket 3 Key-M 110mm |
23. |
RGB Backlit Component Covers |
2. |
Intel X299 PCH (Southbridge) |
13. |
M.2 Socket 3 Key-M 80mm |
24. |
Front Panel Audio Connector |
3. |
CPU Fan Headers (1 amp PWM) |
14. |
PCI-E Slot 16x/8x |
25. |
Front Panel Connectors |
4. |
Fan Headers (1 amp DC/PWM) |
15. |
PCI-E Slot 4x |
26. |
S/PDIF Out |
5. |
RBG LED Controller Header |
16. |
PCI-E Slot 1x |
27. |
Removable BIOS Chip |
6. |
DDR4 Memory DIMM Slots 1-8 |
17. |
Power Button |
28. |
BIOS Selector Switch |
7. |
24-pin ATX power connector |
18. |
Reset Button |
29. |
CMOS Battery |
8. |
8 pin EPS Connector |
19. |
Debug LED / CPU Temp Monitor |
30. |
PC Speaker |
9. |
Supplimental PCI-E 6 pin power |
20. |
USB 3.0 Headers |
31. |
Rear Panel Connectors (Figure 2) |
10. |
Intel Sata 6G RAID Ports |
21. |
USB 2.0 Headers |
|
|
11. |
U.2 (SFF-8639) Port |
22. |
VROC Header |
|
|
**For a FULL description of the above legend, please see Page 15.
- 13 -

EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Figure 2. Chassis Rear Panel Connectors
I/O Hub
1. |
USB 3.0 |
4. |
BIOS/CMOS Reset |
7. |
M.2 Key-E Vertical Header |
2. |
USB 3.1 type A |
5. |
Killer E-2500 NIC |
8. |
Optical Out |
3. |
USB 3.1 type C |
6. |
Intel I 219 NIC |
9. |
Analog Audio Jacks |
3.5mm Audio Jack Legend
Analog Audio |
2/2.1 Channel |
4.0/4.1 Channel |
5.1 (6 Channel) |
7.1 (8 Channel) |
|
Port Breakdown |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Blue |
Line in |
Line In |
Line in |
* Rear Speaker Out |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Green |
Front Speaker Out/ |
Front Speaker Out/ |
Front Speaker |
Front Speaker Out |
|
Front Speaker + Sub |
Front Speaker + Sub |
Out |
|||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pink |
Mic In |
Mic In |
Mic In |
Mic In |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Black |
|
Side Speaker Out |
Side Speaker Out |
Side Speaker Out |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Orange |
|
|
Center/Sub Out |
Center/Sub Out |
|
|
|
|
|
|
* 7.1 output is enabled via Realtek Software from within Windows. (Page 95)
- 14 -
EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Component Legend Descriptions
1. CPU Socket 2066
This is the interface for the Central Processing Unit (CPU), and supports Core i7 models compatible with the Intel 2066 Socket Skylake-X and Kaby Lake-X architecture.
2. Intel X299 PCH (Southbridge)
The Platform Controller Hub (PCH) handles the role that was previously held by the South Bridge. The PCH has 4 PCI-E Gen 3 lanes and allocates bandwidth to smaller PCI-E slots, M.2 Key-E, USB, audio, etc. In simplified terms, the PCH works as a hub for peripherals that are less bandwidthintensive.
3. CPU Fan Headers (PWM)
4-pin fan headers that control the fan speed based on a configurable curve or static percentage. PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) works by pulsing power to the fan at a constant rate and sending the RPM signal to the fan’s controller via a Sense cable, rather than adjusting fan speed by increasing and decreasing voltage. This method is preferable because it eliminates voltage-based fan stall points. Please see Page 87 for more in-depth PWM breakdown and PWM controls within BIOS/UEFI.
4. Fan Headers DC/PWM
These ports are simply toggled between DC and PWM to be compatible with 3 pin and 4 pin fans. The fans will be set to a static percentage set in BIOS.
5. RGB Header
The RBG header is a 4 pin header that allows a software based control within windows for RGB devices via ELEET-X. Please see Page 42 for control specifics.
6. DDR4 Memory Slots
The memory slots support up to four 288-pin DDR4 DIMMs in Quad-Channel mode with Skylake-X processors; and supports up to two 288-pin DDR4 DIMMs in Dual-Channel mode with Kaby Lake-X processors.
Skylake-X processors are certified for Quad-Channel mode, and will be enabled only upon using four sticks of supported memory, according to the installation guide on Page 28. Skylake-X supports up to 128GB (8x16GB) up to 4000MHz+, 32GB modules are *NOT* supported on this platform. Some
- 15 -
EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Dual-Channel kits *may* work; however Skylake-X is certified for QuadChannel operation, not Dual-Channel. Dual-Channel configurations will substantially reduce the potential memory bandwidth of the Skylake-X processor.
Kaby Lake-X processors are certified for Dual-Channel mode, and will be enabled only upon using two sticks of supported memory, according to the installation guide on Page 28. Kaby Lake-X supports up to 64GB (4x16GB) up to 4133MHz+. 32GB modules are *NOT* supported on this platform. Some Quad-Channel kits *may* work, however Kaby Lake-X is not certified for Quad-Channel operation, only Dual-Channel, and will gain no benefit from Quad-Channel over Dual-Channel.
Using an odd number of DIMMs (1,3,5,7) will lower the board to SingleChannel mode, which may significantly lower performance depending on the application.
The speeds listed above cannot be guaranteed as Intel® only certifies the speed of the memory controller up to 2666/2400MHz for Kaby Lake-X and Skylake- X platforms respectively, and all speeds above the speeds certified by Intel® require overclocking.
7. 24-pin ATX power connector
The main power for the motherboard is located on the right side of the board and perpendicular to the PCB; this is also described as a “Vertical” connector (See Page 38 for more specifics to the connector itself, and associated wiring/pinouts). The 24-pin connector IS directional and the connector needs the tab on the socket to line up with the release clip located on the 24-pin connector from the power supply. This connector pulls the bulk of the power for all components; other connectors, such as EPS, PCI-E (video card AND motherboard sides), have been added to reduce the load and increase longevity due to wiring and trace limitations.
8. 8-pin EPS Connector
The EPS is dedicated power for the CPU (See Page 39 for more specifics to the connector itself, and associated wiring/pinouts). Carefully choose the correct power cable by consulting with the installation manual for your power supply. This connector is designed only to work with an EPS or CPU cable. System builders may make the mistake of plugging in a PCI-E 8-pin or 6+2-pin connector, which will prevent the board from POSTing and possibly damage the board; although the cables appear similar, they are wired differently and attaching a PCI-E cable to an EPS connector may cause damage to the motherboard.
- 16 -
EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Alternatively, if no power cable is connected or detected, the system will not POST and will hang at POST code “C.”
9. Supplemental PCI-E 6-pin Power Connector
There is a 6-pin PCI-E connector at the bottom of the motherboard (See page 38 for more specifics to the connector itself, and associated wiring/pinouts). This connector provides dedicated power to the PCI-E x16 slots, augmenting the power provided by the 24-pin and the GPU directly.
This is optional for a single card solution, and is recommended for SLI, CFX, and dual processor video cards.
10. Intel SATA 3/6G Ports
The Intel X299 PCH has a 8-port SATA 3/6G controller (See Page 46 for specifics on the connectors). This controller is backwards-compatible with SATA and SATA 2 devices, and supports SSDs, HDDs and various types of optical devices (CDROM, DVDROM, BD-ROM, etc). The controller also supports NCQ, TRIM, hot swap capability (provided the proper HDD/SSD bays/racks are installed), and RAID levels 0/1/5/10.
11. U.2 Port (SFF-8639)
U.2, originally known as SFF-8639, is a high bandwidth connection specifically engineered for next generation SSD’s. U.2 brings PCI-E x4 (Gen3) NVMe performance to a 2.5” SSD form factor and provides a solution to potential heating problems that may be present in some M.2 solutions.
12. M.2 Socket 3 Key-M 110mm
M.2 is a SSD standard, which uses up to four PCI-E lanes and utilizes Gen3 speeds. Most popularly paired with NVMe SSDs, this standard offers substantially faster transfer speeds and seek time than SATA interface standards. All M.2 devices are designed to connect via a card-bus style connector and be bolted into place and powered by the connector, rather than by a dedicated data cable and power cable.
This socket will support Key-M devices of 110mm, 80mm, 60mm, and 42mm length.
This connector can utilize either a PCI-E/NVMe based M.2 SSD or SATA M.2.
13. M.2 Socket 3 Key-M 80mm
M.2 is a SSD standard, which uses up to four PCI-E lanes and utilizes Gen3 speeds. Most popularly paired with NVMe SSDs, this standard offers substantially faster transfer speeds and seek time than SATA interface standards. All M.2 devices are designed to connect via a card-bus style
- 17 -
EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
connector and be bolted into place and powered by the connector, rather than by a dedicated data cable and power cable.
This socket will support Key-M devices of 80mm, 60mm, and 42mm length. This connector can utilize either a PCI-E/NVMe based M.2 SSD, SATA M.2, or Intel Optane devices.
14. PCI-E Slot x16/x8*
PCI-E x16/x8 slots are primarily for video cards. These full-length slots will provide 8 or 16 lanes of bandwidth to a full-size card, and are backwardscompatible with x8, x4, and x1-length cards.
Skyake-X Socket 2066 processors have 44 or 28 PCI-E lanes available for routing, whereas Kaby Lake-X has 16 PCI-E lanes.
15. PCI-E Slot x4*
PCI-E x4 slot uses up to 4 Gen 3 lanes from the PCH. This slot is typically used for sound cards, WiFi, USB, or other peripheral cards.
Because this slot uses PCH bandwidth, this will have *NO EFFECT* on the bandwidth or throughput of the x16 slots used for SLI.
16. PCI-E Slot x1*
PCI-E 1x is the smallest form-factor PCI-E card slot. They are all one lane and are used for low-bandwidth products. This slot uses 1 lane from the PCH.
17. Power Button
This is an onboard power button, and may be used in place of, or in conjunction with, a front panel power button wired to the board. Benching systems, or test benches before final assembly, are best served by
using the onboard power because it removes the need to wire a Power/Reset button or cross posts with a screwdriver, which is a semi-common practice. This button provides a safer and easier option than jumpering the Power posts.
18. Reset Button
This is an onboard system reset button, and may be used in place of, or in conjunction with, a front panel system reset button wired to the board. Benching systems, or test benches before final assembly, are best served by using the onboard power because it removes the need to wire a Power/Reset button or cross posts with a screwdriver, which is a semi-common practice. This button provides a safer and easier option than jumpering the Power posts.
19. Debug LED / CPU Temp
This is a two-digit POST code reader, displaying in hexadecimal, which means the characters available (when working as intended) are 0-9, A-F and has a cap of 255 characters. The POST codes are listed in the troubleshooting section on
- 18 -
EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Page 142. After the system boots, it will display the temperature in Celsius. This temperature is specifically for the CPU socket, which will typically read slightly higher than a given CPU core. To read this temp in Fahrenheit, take the value in Celsius, multiply by 9/5 (or 1.8) and add 32.
20. USB 3.0 Headers
The USB3.0 headers are used to connect additional USB interface plugs to the motherboard; these headers are most often used to connect the motherboard to the chassis to enable the USB3.0 ports on the chassis. These will function the same as the USB3 ports found on the motherboard’s hardwired I/O hub, but these can be used to attach to front panel USB, auxiliary ports that mount in the card slots, and also some devices that directly connect to the header.
USB 3.0 standard is 900ma @ 5V for unpowered devices. If your USB device requires more power than this, it is recommended to attach a powered USB Hub.
USB 3.1 Type-A (found on the I/O Hub) shares the power limit of USB 3.0 at 900ma @ 5V. Whereas USB 3.1 Type-C (also found on the IO Hub) has a power limit of 3000ma (3A) @ 5V.
21. USB 2.0 Headers
The USB2.0 header is used to connect additional USB interface plugs to the motherboard; these headers are most often used to connect the motherboard to the chassis to enable the USB2.0 ports on the chassis. These will function the same as the USB2 ports found on the motherboard’s hardwired I/O hub, but these can be used to attach to front panel USB, auxiliary ports that mount in the card slots, and also some devices that directly connect to the header.
USB 2.0 standard is 500ma @ 5V per port (header total is 1000ma) for unpowered devices. If your USB device requires more power than this, it is recommended to attach a powered USB Hub.
22. VROC Header
VROC stands for Virtual RAID On CPU, the VROC headers works in conjunction with the upcoming VROC cards. VROC cards are 4 device M.2 Key-M cards for PCI-E that allow RAID functions on the card. The Header is for an Intel hardware key that will unlock advanced RAID functions, which in VROC’s case is anything other than RAID0.
Important note, as of the time this manual was written, VROC will work with many SSD’s but is only bootable with Intel SSD’s. Also VROC is only compatible with Skylake-X CPUs
- 19 -
EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
23. RGB Backlit Panels
These panels sit on top of other components, such as heatsink, and provide RGB LED lighting. These panels connect to the RGB Headers (component #5) and provide stylized backlighting which can be controlled in EVGA ELEET-X.
These RBG Headers are ONLY to be used for the included/preattached RBG covers, not a 3rd party RGB device.
24. Front Panel Audio Connector
This is a motherboard header, which is used to plug in the audio cable originating from most PC chassis to allow audio to be recorded from or played through the audio connectors on the chassis. This header has a connector that looks similar to USB2 and will use the standard “HD Audio” jack. Some cases may have two headers on one cable strand: one labeled HD Audio, and one labeled AC’97 – this header is not compatible with AC’97.
25. Front Panel Connectors
The Front panel connectors are the four main chassis connections. These include the Power Switch, Power LED, Reset Switch, and HDD LED. The Power and Reset switches are both designed to use “Momentary Switches,” rather than “Latching Switches,” which means the connection between the two posts needs to be made just briefly for it to work, as opposed to being held in place. This is why the Power and Reset switches can be triggered with a screw driver by simultaneously touching the + and - posts.
Power LED will power on with the system, indicating the system is on and can blink with CPU activity.
HDD LED will blink during access to the SATA ports, U.2 port, and/or the M.2 Key-M SSD’s.
26. S/PDIF Out
S/PDIF is used for audio pass-through, which is used on some older video cards, video capture cards, and some older generation devices. This port is not widely used now, but is here in case a legacy item requires the connector. Most of the audio data is pushed through the bus now, and does not require an external cable. NOTE: This is a S/PDIF Out connector, and cannot operate to record data from an external device.
27. Removable BIOS Chip
The ability to remove and replace the BIOS chip without requiring special tools is a key feature on many of our boards, by adding a level of protection against BIOS failures, bad BIOS flashes, BIOS corruption, etc. This feature also allows EVGA to work with end-users if something happens to render the BIOS chip unusable or a BIOS update is needed for CPU compatibility; rather than
- 20 -
EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
replacing the whole board, Customer Support can send a pre-flashed BIOS chip to get you up and running without requiring the end-user to send in the motherboard. Please see the walkthrough on Page 132 for further information.
28. BIOS Selector Switch
This switch toggles between physical BIOS chips. This board has a BIOS chip as a permanent fixture, and the other is a replaceable chip listed above. Each chip holds profiles and all settings that have been saved to the BIOS. This allows you to swap between two physically different BIOS chips. This also makes it substantially easier to hotflash a BIOS if needed. If instructions are needed for hotflashing a BIOS, please EVGA Customer Service (Page 139 for contact info).
29. CMOS Battery
The CMOS battery backup provides uninterruptable power to the BIOS/UEFI to keep all of the settings; otherwise, each boot would behave like you just reset the BIOS. These batteries typically last several years and rarely need to be replaced.
30. PC Speaker
This is a small mono low-fidelity speaker permanently attached to the motherboard used mainly for debugging purposes. A POST beep may indicate a successful POST, various tones for USB initialization, and other beeps to indicate an issue during the post process. Please see Page 140 for more details.
31. Rear Panel Connectors (Figure 2)
This is the section referred to as the I/O Hub. This panel contains the hardwired USB, Sound, and Ethernet connections. Please see Page 14 for a component level breakdown.
CMOS Reset Button (On IO Panel)
This button has two main uses: the first is standard practice to clear BIOS and power on before updating the BIOS, and the second is standard practice when troubleshooting instances when the motherboard fails to POST, such as after upgrading RAM or CPU, installing new hardware, a failed overclock, etc. This button provides a much faster means of resetting than the previous method of removing power from the board, removing the CMOS battery, and discharging power to the board. In rare occasions the older method can help; pressing the clear CMOS button will normally allow you and your system back into the default BIOS.
- 21 -
EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
M.2 Socket 1 Key-E 32mm Vertical Adapter (On IO Panel)
M.2 Key-E is largely used for WiFi and Bluetooth cards. Key-E and Key-M connectors are different, meaning that devices are not interchangeable between sockets.
This variant is also on a vertical mount, which has an adapter that is slid into card-bus slot and bolted to the motherboard, then the M.2 Key-E mounts to the vertical adapter.
* There are two numeric references for PCI-Express: one is mechanical, which is the actual slot-length footprint, and the second is electrical, which is a reference of how many PCI-E lanes are routed to the slot.
As PCI Express is designed to be a universal architecture, you can install x1 cards, such as sound cards or USB controllers into an x16 slot. Many types of cards can use different amounts of PCI-E lanes, while some applications use only certain parts of a card, such as compute apps that allow a card to run off of a single PCI-E lane. This is why there are x16 mechanical slots with x1 electrical PCI-E lane. Using the entire length of a PCI-E slot is not necessary, nor does it cause an adverse effect to use a shorter form-factor bus card in a slot that physically can hold a larger form-factor bus card.
- 22 -

EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Card Slots
The X299 FTW-K features four x16 PCI-E slots, one x4 PCI-E slot, one x1 PCI-E slot, one Socket 3 Key-M M.2 110mm (backwards compatible with Key-M 80mm, 60mm, and 42mm), and one Socket 3 Key-M M.2 80mm (backwards compatible with Key-M 60mm and 42mm).
- 23 -

EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
PCI-E Slot Breakdown
PCI-E Lane Distribution (44 Lane SKX CPU’s)
PE1 – x4 (Gen3, x4 lanes from PCH)
PE2 – x16 (Gen3, x16 lanes from CPU, x8 shared with PE3)
PE3 – x16 (Gen3, x8 lanes from CPU, shares 8 of PE2’s 16 lanes)
PE4 – x16 (Gen3, x8 lanes from CPU, shares 8 of PE5’s 16 lanes)
PE5 – x16 (Gen3, x16 lanes from CPU, x8 shared with PE4)
PE6 – x1 (Gen3, x1 lane from PCH)
PCI-E Lane Distribution (28 Lane SKX CPU’s)
PE1 – x4 (Gen3, x4 lanes from PCH)
PE2 – x16 (Gen3, x16 lanes from CPU, x8 shared with PE3)
PE3 – x16 (Gen3, x8 lanes from CPU, shares 8 of PE2’s 16 lanes)
PE4 – x16 (Not functional with a 28 lane processor.)
PE5 – x16 (Gen3, x8 lanes from CPU)
PE6 – x1 (Gen3, x1 lane from PCH)
PCI-E Lane Distribution (16 Lane KBX CPU’s)
PE1 – x4 (Gen3, x4 lanes from PCH)
PE2 – x16 (Gen3, x8 lanes from CPU)
PE3 – x16 (Not functional with a 16 lane processor.)
PE4 – x16 (Not functional with a 16 lane processor.)
PE5 – x16 (Gen3, x8 lanes from CPU, disabled if 110mm M.2 is used)
PE6 – x1 (Gen3, x1 lane from PCH)
- 24 -

EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
M.2 and U.2 Slot Breakdown
PCI-E Lane Distribution (44 Lane SKX CPU’s)
U.2 1 – Gen3, x4 lanes from CPU (No Shared Lanes)
U.2 2 – Gen3, x4 lanes from CPU (No Shared Lanes)
M.2 Key-M (110mm) – x4 CPU lanes (No Shared Lanes)
M.2 Key-M (80mm) – x4 PCH lanes (No Shared Lanes) (*)
M.2 Key-E (32mm) – x1 PCH lane (No Shared Lanes)
PCI-E Lane Distribution (28 Lane SKX CPU’s)
U.2 1 – Not functional with a 28/16 lane processor.
U.2 2 – Not functional with a 28/16 lane processor.
M.2 Key-M (110mm) – x4 CPU lanes (No Shared Lanes)
M.2 Key-M (80mm) – x4 PCH lanes (No Shared Lanes) (*)
M.2 Key-E (32mm) – x1 PCH lane (No Shared Lanes)
PCI-E Lane Distribution (16 Lane KBX CPU’s)
U.2 1 – Not functional with a 28/16 lane processor.
U.2 2 – Not functional with a 28/16 lane processor.
M.2 Key-M (110mm) – x4 CPU lanes (Gen3, x4 shared with PE5)
M.2 Key-M (80mm) – x4 PCH lanes (*)
M.2 Key-E (32mm) – x1 PCH lane
•All M.2 Key-M slots on this board support PCI-E, NVMe, and SATA M.2 standards.
O(*) If a SATA M.2 drive is used in the 80mm M.2 the SATA 0/1 will be disabled.
•This motherboard does NOT have any lane replication via PLX; all lanes are native and derived from CPU or PCH. This also allows for improved backwards compatibility for Gen 2 devices.
- 25 -

EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Installing the CPU
Note: Use extreme caution when working with the CPU to not damage any pins in the CPU socket on the motherboard!
Note: After removing the CPU socket cover, it is recommended to store it in case you ever need to transport your motherboard. If you ever remove the CPU, it is highly recommended to reinstall the socket cover.
Use the following procedure to install the CPU onto the motherboard:
1.Remove the plastic protective socket cover by pulling it straight up. Be sure not to damage any of the pins inside the socket.
2.Unhook the left socket lever by pushing down and away from the socket.
3.Unhook the right socket lever, this will release the load plate
4.Pull the socket lever back and the load plate will lift.
5.Open the load plate and make sure not to damage any of the pins inside the socket.
- 26 -

EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
6.Align the notches on the CPU to the notches in the socket.
7.Lower the processor straight down into the socket.
Note: Make sure the CPU is fully seated and level in the socket before lowering the load plate.
8.Lower the load plate so it is resting on the CPU.
9.Carefully lock the lever back into place.
Installing the CPU Cooling Device
There are many different cooling devices that can be used with this motherboard. Follow the instructions that come with your cooling assembly.
- 27 -

EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Installing System Memory
Your X299 FTW-K has (8) 288-pin slots for DDR4 memory. These slots support 4GB, 8GB and 16GB DDR4 DIMMs. There must be at least one memory slot populated for the board to boot and operate.
The Intel X299 chipset supports Quad-Channel DDR4 memory, a maximum of 128GB and up to 4000MHz+for Skylake-X, and 4133MHz+ for Kaby Lake-X (OC)+. It is recommended to always use a 4 DIMM Quad Channel kit for
SkyLake-X, and 2 DIMM Dual |
|
|
Skylake-X RAM Slot Fill Order |
|
|
|||||
Channel kit for Kaby Lake-X; in |
|
Slot 1 |
Slot 2 |
Slot 3 |
Slot 4 |
Slot 5 |
Slot 6 |
Slot 7 |
Slot 8 |
|
the event you cannot please fill |
1 DIMM |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the memory slots in the |
2 DIMM |
X |
|
|
X |
|
|
|
|
|
3 DIMM |
X |
|
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
|
|
following order: 1,3,5,7,2,4,6,8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 DIMM |
X |
|
|
X |
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
(5,7,6,8 for KBX). See chart to |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
5 DIMM |
X |
|
X |
X |
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
the right: Use the following |
|
|
|
|
||||||
6 DIMM |
X |
|
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
X |
|
|
procedure to install memory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 DIMM |
X |
|
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
DIMMs. Note that there is an |
8 DIMM |
X |
|
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
off-center gap near the center of |
|
Kaby Lake-X RAM Slot Fill Order |
|
|
||||||
the DIMM slots. This matches |
|
Slot 1 |
Slot 2 |
Slot 3 |
Slot 4 |
Slot 5 |
Slot 6 |
Slot 7 |
Slot 8 |
|
the gap on a DDR4 DIMM to |
1 DIMM |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
X |
|
|
|
|
ensure the memory is installed |
2 DIMM |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
X |
|
|
X |
|
3 DIMM |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
X |
X |
|
X |
|
|
properly, and to prevent the |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 DIMM |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
X |
X |
|
X |
X |
|
incorrect installation of memory. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 DIMM |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
N/A |
N/A |
|
1. Unlock a DIMM slot by |
6 DIMM |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
N/A |
N/A |
pressing the top-side |
7 DIMM |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
N/A |
N/A |
8 DIMM |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
N/A |
N/A |
|
module clips outward. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.Align the memory module to the DIMM slot, and insert the module perpendicular to the DIMM slot, pressing straight down to seat the module. The plastic clips at top side of the DIMM slot automatically lock the DIMM into the connector.
Note: The memory controller on most Skylake-X and Kaby Lake-X CPUs runs at a default frequency of 2400/2666MHz. Achieving memory speeds above 2666MHz+ may require manual setting of the memory timings, frequency and voltages and/or overclocking of the CPU.
Refer to the memory manufacturer specifications for the recommended memory timings.
- 28 -

EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Installing the I/O Shield and I/O Cover
The motherboard kit comes with an I/O shield that is used to block internal components from dust and foreign objects, while also promoting correct airflow within the chassis.
Before installing the motherboard, install the I/O shield from the inside of the chassis. Press the I/O shield into place and make sure it fits securely.
The X299 FTW-K also includes an I/O cover. This I/O cover adds a unique appearance to the I/O area of the motherboard and is completely optional. If you wish to use the cover, please place it over the I/O area and install the chassis screws. These screws will secure the I/O cover to the motherboard.
Installing the Motherboard
Installing the motherboard into a system case depends on several factors: whether you are replacing an existing motherboard, whether you are building a new PC, and the type of chassis that will house your PC components. You must first determine if it would be easier to secure the motherboard to the chassis or if it would be easier to install other components prior to this step. It is normally easier to secure the motherboard first.
Note: Be sure that the CPU fan assembly has enough clearance for the system case covers to lock into place and for expansion cards. Also, make sure the CPU Fan assembly is aligned with the vents on the covers; this is to allow the airflow to properly exhaust from the chassis. The CPU Fan assembly orientation will depend on the system case being used.
- 29 -

EVGA X299 FTW - K (142-SX-E297)
Securing the Motherboard into a System Case
Most system cases require installation of standoffs into the chassis to allow the motherboard to be mounted to the chassis and prevent short circuits. If there are studs that do not align with a mounting hole on the motherboard, it is recommended that you remove that standoff to prevent the possibility of a short circuit; also ensure that all needed standoffs are fully tightened before attaching the motherboard to the chassis. Please review the installation manual included with your chassis for the proper installation of the motherboard standoffs.
1.Carefully place the motherboard onto the standoffs located inside the chassis.
2.Align the mounting holes with the standoffs.
3.Align the connectors to the I/O shield and/or I/O cover.
4.Ensure that the fan assembly is aligned with the chassis vents according to the fan assembly instruction.
5.Secure the motherboard with ten (10) screws (See next page for mount hole location). Ensure that each screw is lined up with and screwing into the corresponding standoff under the board. Double-check alignment to make sure nothing gets cross-threaded.
Tip: If you have difficulty with getting some of the screws fastened, especially near the I/O hub, first try to loosely fasten all other screws on the motherboard, but don’t completely tighten the screws. This may help to hold the board in place, allowing you to thread and fasten the remaining screws. Once all screws are properly threaded, remember to go back and tighten the rest of the screws.
6.See the picture below for a zoomed-in view of a hole to place over a standoff, as well as the locations of standoff holes for the X299 FTW-K.
- 30 -
 Loading...
Loading...