Page 1

CallXpress
CallXpress Enterprise
Ericsson MD110 CAS EL7
TCP/IP VM Integration
Integration Technical Note
Page 2

Integration Technical Note
Edition Note
This is the first edition of the Ericsson MD110 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM Integration Technical Note.
Information in this document applies to CallXpress software Version 5.31 or later, or CallXpress Enterprise
software Version 5.31 or later.
This document was produced by the CTI Software Group Technical Communications Department.
Writer: David Leyva
Editor: Brian McCullough
Copyright Notice
Copyright © August 2000 AVT Corporation
All rights reserved
Printed in the United States of America
P/N 081-47504-00
Disclaimer
AVT Corporation reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes from time to time in the
content hereof without obligation of AVT Corporation to notify any person of such revisions or changes.
AVT Corporation exercises care in researching other manufacturers’ specifications but disclaims all
responsibility for their accuracy. All specifications shown here are subject to change without notice.
Trademarks
AVT, the AVT logo, CallServer, CallXpress, and PhoneXpress are registered trademarks of
AVT Corporation.
All other products, brand names, or companies mentioned in this document may be trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective companies.
AVT Corporation
CTI Software Group
P.O. Box 97025
Kirkland, Washington 98083
(425) 820-6000
http://www.avtc.com
ii Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 3

Integration Technical Note
Table of Contents
Overview ..............................................................................................................1
References .................................................................................................................................. 2
Features Supported by This Integration ...................................................................................... 2
Critical Application Considerations .............................................................................................. 4
Installation Requirements ..................................................................................6
Telephone System Requirements ............................................................................................... 6
CallXpress Requirements ............................................................................................................ 7
Programming the Telephone System................................................................8
Initiating the Number Series for the CAS Extensions .................................................................. 8
Programming the Category for CAS Extensions ......................................................................... 8
Initiating the CAS Extensions .................................................................................................... 10
Initiating the Hunt Group............................................................................................................ 10
Programming the NIU Port for Voice Mail ................................................................................. 11
Initiating the Information Computer Function............................................................................. 12
Initiating the Voice Mail Function ............................................................................................... 12
Programming Message Waiting and Call Diversion for Subscriber Telephones....................... 13
Completing the MD110 Programming ....................................................................................... 14
Installing the Aculab Card................................................................................15
Installing the Telephony Server Network Interface........................................16
Configuring CallXpress ....................................................................................17
Switch Protocol .......................................................................................................................... 18
Dialing Template........................................................................................................................ 19
Integrated Lines ......................................................................................................................... 19
Integration.................................................................................................................................. 20
Completing the Integration...............................................................................22
Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN iii
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 4

Integration Technical Note
This page is intentionally left blank.
iv Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 5

Overview
Integration Technical Note
This Integration Technical Note (ITN) is written for dealers who are experienced
with CallXpress
®
and who are familiar with CallXpress procedures and terminology.
It also assumes that you are familiar with the features and programming of the
Ericsson MD110 telephone system.
This document describes how to integrate CallXpress with an Ericsson MD110
telephone system, using an E1 CAS EL7 interface in conjunction with the MD110
Voice Mail TCP/IP integration. This integration is an outband integration. The E1
CAS EL7 interface is a digital 2.048Mb 32-channel interface that can provide up to
30 CAS (channel associated signaling) voice mail ports to CallXpress per E1 link.
The MD110 E1 CAS connection is established at the CallXpress telephony server by
means of an Aculabäplc High Capacity Digital Access card. The Aculab card is the
E1 interface between the MD110 and the Dialogic card(s) in the CallXpress
telephony server. DTMF signaling and voice communications are performed over
the established E1 link between CallXpress and the MD110. The MD110 Voice
Mail interface is an Ethernet network connection that uses the TCP/IP protocol to
communicate between the MD110 and CallXpress. Calling and called party
information is sent to CallXpress via TCP/IP over the network connection at the
same time that a call is sent to a CAS channel. The data is matched with the ringing
channel and CallXpress answers with the appropriate dialog. Message Waiting
Indicator (MWI) operation is also performed via TCP/IP over the
network connection.
Refer to the Ericsson Extra Facility Voice Mail, VM description and the
Interworking Description, CAS extension, EL7 Interface to Voice Mail system for
complete details.
Use this document in conjunction with CallXpress installation guides, administration
guides and online help.
Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN 1
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 6

Integration Technical Note
References
More current information may be available from the following sources:
• AVT BBS (Bulletin Board System)—Download files by calling
(425) 820-4069 using a modem (1200 baud to 28.8K baud).
• OTIS (AVT’s Online Technical Information Service)—Fax AVT documents to
yourself by calling (425) 820-4056 from a fax machine. To request an index of
all documents, select option 1 at the initial voice menu.
• World Wide Web—AVT certified technicians can view or download documents
and program files from AVT’s web site, http://www.avtc.com.
The following print documents are available for your reference:
• Installing CallXpress P/N 081–47495-XX
• Administering CallXpress P/N 081–47295-XX
• Aculab E1 Interface ISA Card Installation and Replacement Spare Parts
Document P/N 081-47844-XX
• Aculab E1 Interface PCI Card Installation and Replacement Spare Parts
Document P/N 081-47800-XX
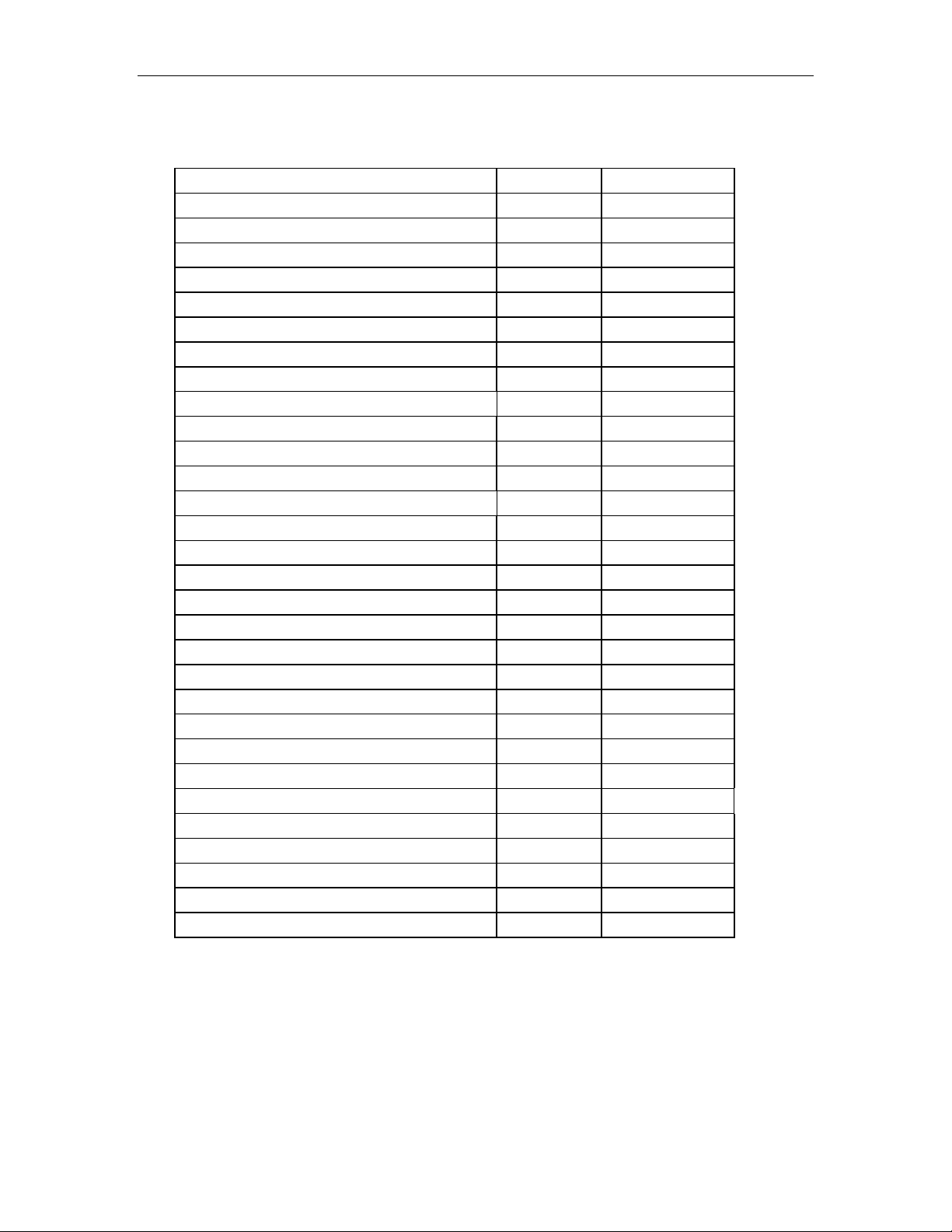
Features Supported by This Integration
Tables 1 and 2 list the features supported using the Ericsson MD110 CAS EL7
TCP/IP VM integration.
Table 1. Call forward to personal greeting for these call types
Divert on... To CallXpress
No Answer Yes
Busy Yes
Forward All Yes
Follow Me Yes
Do Not Disturb No
2 Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 7
Integration Technical Note
Table 2. Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS TCP/IP integration features supported
Feature Supported Notes
Automatic subscriber logon Yes
ANI/CLI Yes
Announce busy greeting on forwarded calls Yes
Call screening Yes
Caller queuing Yes
Daily message reminder Yes
DNIS No
End-to-end DTMF, attendant console Yes
End-to-end DTMF, proprietary telephones Yes
Faxmail Yes See note 1
Faxtext Yes See note 1
Immediate message notification-external Yes
Immediate message notification internal Yes
Internal calling party ID for reply Yes
Live record No See note 2
Live reply to sender Yes
MWI, multiple ports N/A
MWI, refresh on daily maintenance Yes
MWI, set on every message Yes
MWI, clear Yes
MWI, set Yes
Overflow from CallXpress to attendant Yes
Overflow to CallXpress from attendant Yes
PBX-provided disconnect signaling Yes
Revert to operator from personal greeting Yes
Transfers, blind Yes See note 3
Transfers, fully supervised Yes
Transfers, monitored Yes
Trunk ID No
Voice mail networking Yes
Notes:
1. Requires separate Scbus digital fax cards.
2. Third-party conferences are not allowed on an integrated VM port. To use this feature,
you must have a separate non-integrated port.
3. Not compatible when using a restricted traffic matrix for voice mail ports.
Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN 3
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 8

Integration Technical Note
Critical Application Considerations
Known limitations or conditions within the telephone system and CallXpress that
affect the integration performance are listed here. General recommendations are
provided when ways to avoid these limitations exist.
• The MD110 voice mail port number of each CAS EL7 extension must be assigned
correctly to each integrated CallXpress port. The integration will not function if
these entries are incorrect. The voice mail port numbers and format (POFMT)
are programmable parameters and are defined during the initiation of the voice
mail port of the MD110.
• Program the instrument category (ICAT) of the CAS EL7 extensions that will
serve CallXpress for enhanced global tones and assign them as voice mail ports.
• The MD110 requires a static TCP/IP address. It cannot be assigned a lease
through a DHCP server. If the customer site is using a DHCP server, a
reservation must be made for the MD110.
• Set the traffic matrix (TCMAP) and TRAF parameter of the extension category
to restrict voice mail ports from calling other voice mail ports. This allows a Ttype supervised transfer to take place for call screening applications without
having to remove diversion programming from the subscriber telephone.
• The use of traffic restricted voice mail ports is not compatible with blind
transfers. We recommend that you use the monitor transfer type unless the
application requires a t-type supervised transfer..
• If the malicious call trace feature of the MD110 is enabled on the voice mail
ports, no disconnect packet will be sent to CallXpress from the NIU port of the
MD110.
• When using reason code diversions from subscriber telephones, diverted calls
will always go to the common diversion position. If CallXpress is chosen as the
common diversion position (CDCOI), calls will always be diverted there, even if
individual diversions (CDINI) have been programmed to divert calls elsewhere.
• Station numbers cannot have a 0 as the leading digit. Non-numeric
DTMF tones cannot be used as any character in a station number. The
maximum length of a station number is six digits.
4 Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 9

Integration Technical Note
Critical Application Considerations (continued)
• Aculab does not provide BNC connectors on their PCI type boards. These boards
are supplied with RJ45 connectors only.
• Mixing like kinds of ISA and PCI cards in the same telephony server platform
requires a separate system interrupt (IRQ) for each type board used. This practice
is not recommended or supported.
• Mixing unlike kinds of ISA and PCI type Aculab or Dialogic boards in the same
telephony server platform require an SCbus to H.100 bus (CTbus) cable adapter.
ISA boards have SCbus connectors and use SCbus ribbon cables for connection;
PCI boards have CTbus connectors and use CTbus or H.100 bus ribbon cables
for connection. SCbus signaling is done over the H.100/CTbus interface.
Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN 5
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 10

Integration Technical Note
Installation Requirements
Review the following information before performing any of the procedures in this
document. To successfully install this integration, you must meet the installation
requirements for both the telephone system and CallXpress.
Telephone System Requirements
These are the software and hardware requirements for the MD110:
• Ericsson MD110 PABX with system software Version BC10 or later. The
following Version BC10 patches are required for TCP/IP integration: 87804,
87997, 87998, 88383 and 88407. The following Version BC10 patches are
required for ANI/CLI information to the GICI port: 86363, 86376, 86377, 86444
and 88445.
• NIU port to provide the TCP/IP network connection. The TCP/IP address of this
network interface port must be a static network address.
• TSR 902 0240/XXXX cable for the network connection between the NIU board
and the Ethernet network.
• One TLU76/3 E1 CAS card will provide up to 30 CAS EL7 voice ports
• TSR 902 0267/XXXX cable for the RJ45 high impedance connection between
the TLU76/3 card and the E1 Aculab card, or a TSR 901 0301/XXXX cable for
the BNC low impedance connection between the TLU76/3 board on the MD110
and the E1 Aculab card.
6 Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 11

Integration Technical Note
CallXpress Requirements
These are the requirements for CallXpress:
• Properly configured Windows NT Server 4.0 telephony server platform with an
Ethernet network adapter card
• CallXpress software Version 5.31 or later. Consult the AVT BBS, OTIS, or the
AVT web site for current service packs and software levels. (See “References”
earlier in this document)
• Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS TCP/IP VM Switch Integration Module (SIM 34)
enabled on the AVT software key diskette
• Aculab Rev.5 ISA single port cards will support 30 CallXpress ports
• Aculab Rev.5 PCI single port cards will support 30 CallXpress ports
• Aculab Rev.5 PCI dual port cards will support 60 CallXpress ports
• One digital Dialogic port for each CallXpress voice port to be integrated. Use
Dialogic ISA D/80, D/160, D/320 SCbus cards or, Dialogic PCI D/80, D/320
SCbus cards.
• Uninterruptible power supply (UPS) and surge protection device (recommended)
Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN 7
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 12

Integration Technical Note
Programming the Telephone System
Follow the recommendations and programming examples in this section to program
the MD110 for integration with CallXpress. Programming examples show
commands and parameters of Version BC10 that are necessary for integration, but
they do not represent PBX programming in its entirety.
The installing technician should be familiar with programming the telephone system.
For detailed programming information on this software version or other MD110
software versions, refer to the appropriate ASB Basic Exchange and Extra Facility
documentation and the Ericsson MD110 OEM country-specific documentation.
Initiating the Number Series for the CAS Extensions
Initiate extension numbers in Number Analysis for the CallXpress extensions. Use
EX as the NUMTYP. Choose directory numbers that are appropriate for your
numbering plan.
For example:
NANSI:NUMSE=4001&&4030,NUMTYP=EX;
Verify your work with the command: NADAP;
Programming the Category for CAS Extensions
Set the Extension Category code for the CallXpress ports and configure the traffic
matrix to restrict one voice mail port from calling another voice mail port. Use a
separate category for the CallXpress ports.
1. Set the CAT for CallXpress ports with the TRAF parameter that uses the defined
TCMAP table.
For example:
EXCCS: CAT=1,TRAF=03151501,SERV=00001000,
CDIV=000060000,ROC=000000;
Verify your work with the command: EXCCP:CAT=1;
8 Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 13

Integration Technical Note
2. Configure the Traffic Matrix (TCMAP) to restrict voice mail ports from
connecting to other voice mail ports. Allow all other extensions to connect to
voice mail ports and allow voice mail ports to connect to all other extensions.
Table 3 is an example of the restricted traffic matrix.
For example:
TCMAR:A=1,B=1,CON=T;
TCMAS:A=1,B=2&&14,CON=T;
TCMAS:B=1,A=2&&14,CON=T;
Verify your work with the command: TCMAP;
Table 3. Sample traffic group matrix
Traffic Group Matrix Data CON=T
B
A0123456789101112131415
00000000000000001
10011111111111111
20100000000000001
30100000000000001
40100000000000001
50100000000000001
60100000000000001
70100000000000001
80100000000000001
90100000000000001
100100000000000001
110100000000000001
120100000000000001
130100000000000001
140100000000000001
151111111111111111
Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN 9
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 14

Integration Technical Note
Initiating the CAS Extensions
1. Initiate the CAS EL7 extensions, assign the equipment, the category, and the
instrument category. ICAT=0086 assigns enhanced global tones for call progress
and enables the CAS ports as voice mail ports.
For example:
EXTEI:DIR=4001&&4015,EQU=2-1-30-01,TYPE=EL7,CAT=1,ICAT=0086;
EXTEI:DIR=4016&&4030,EQU=2-1-30-17,TYPE=EL7,CAT=1,ICAT=0086;
Verify your work with EXDDP:DIR=4001&&4030;
Initiating the Hunt Group
1. Initiate a hunt group and assign the CallXpress extensions to the group. Specify
the type as LONGEST FREE HUNTING and set Queuing to 10. Define the SEL
parameter to allow overflow diversion when all ports are busy, if desired.
For example:
GHGRI:GRP=4000,LIM=2,SERV=1000,TRAF=15,SEL=110,QUE=10;
Verify your work with the command: GHDAP:GRP=4000;
2. Assign the CallXpress Directory numbers to the hunt group.
For example:
GHGMI:GRP=4000,DIR=4001&&4030;
Verify your work with the command: GHDAP:GRP=4000;
3. You may want to program the CallXpress ports to divert when they are
unavailable. For instance, the following programming example would divert calls
intended for CallXpress, to the attendant, if all ports were busy or RNA.
For example:
CDINI:GRP=4000,DIV=00; (00=operator)
Verify your work with the command: CDIDP:GRP=4000;
10 Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 15

Integration Technical Note
Programming the NIU Port for Voice Mail
1. Initiate the NIU board position (BPOS) for the network port.
Name the NODE “CALLXPRESS”.
For example:
IOBPI:NODE=CALLXPRESS,BPOS=2-1-40;
Verify your work with the command: IODDP;
2. Initiate the I/O Equipment Position for the network port. Assign a name to the
I/O device, assign the TYPE as NETWORK and the USAGE as OUT.
For example:
IOEQI:IODEV=CALLXPRESS,EQU=2-1-40-4,
TYPE=NETWORK,USAGE=OUT;
Verify your work with the command: IODDP;
3. Initiate the I/O Network Connection. Assign the USER as GICI-1, the RPORT as
2555, and the TCP/IP address that was pre-determined by the
network system administrator.
For example:
IONCI:IODEV=CALLXPRESS,USER=GICI-1,
RPORT=2555,IP=195.100.102.105;
Verify your work with the command: IONCP;
Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN 11
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 16

Integration Technical Note
Initiating the Information Computer Function
Initiate the Information Computer Function for the Voice Mail Port. Name the I/O
Device “CallXpress” and specify the USER as GICI-1. Set the directory format
length (DFMT) to match the directory number length of the extensions, set the
update function (UPDFCN) to YES, and set the FILLER to 32 (space).
For example:
ICFUI:IFCIND=1,IODEV=CALLXPRESS,USER=GICI-1,
DFMT=4,UPDFCN=YES,FILLER=32;
Verify your work with the command: ICFUP;
Initiate the Message Waiting data for the voice mail port. Define the system ID
(SID) of the PBX, the DTXT, and group number (DIG) to be called when
subscribers press the message-waiting button (MWC) to retrieve messages.
For example:
ICMWC:SID=01,DTXT=4000,DIG=4000,KFCN=MWC;
Verify With ICMWP:SID=01;
Initiating the Voice Mail Function
Initiate the Voice Mail Function for the NIU port. Set the port format (POFMT) to 3.
Set the Voice Mail Functionality (VMF) to EXTN3 if ANI/CLI services will be used.
If ANI/CLI services are not required, set VMF to EXTN2.
For example:
VMFUI:IFCIND=1,VMF=EXTN3,POFMT=3;
Verify your work with the command: VMFUP;
Initiate the Voice Mail Port and identify the starting PORT number. Add the
CallXpress directory numbers and the hunt group number to the Voice Mail Port.
For example:
VMPOI:IFCIND=1,DIR=4001&&4030,PORT=001;
VMPOI:IFCIND=1,GRP=4000;
Verify your work with the command: VMPOP;
12 Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 17

Integration Technical Note
Programming Message Waiting and Call Diversion for
Subscriber Telephones
Digital subscriber telephones can have an MWI key assigned in addition to the
“Message Waiting” display on their LCD telephones. Subscribers can press the lit
MWI key to retrieve messages from CallXpress. Use the Key System Function Key
Change command to assign an MWI key appearance on each subscriber telephone.
For example:
KSFKC:DIR=2001&&2299,KEY=2,FCN=MEW;
Verify your work with the command: KSFKP:DIR=2001&&2299;
Analog subscriber telephones can receive a pling ring for MWI or a special dial
tone. Use the ASPAC command to set either pling ring or special dial tone.
For example:
ASPAC:PARNUM=88,PARVAL=1;
(PARVAL=1 sets special dial tone and PARVAL=0 sets pling ring.)
NOTE When PARVAL=0 the “Message Waiting” text message on digital set
displays is not available.
Program the time interval between pling rings when pling is used for message
notification. The following example sets the pling interval to fifteen minutes.
For example:
ASPAC:PARNUM=45,PARVAL=900
Verify your work with the command: ASPAP;
Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN 13
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 18

Integration Technical Note
Assign the CallXpress hunt group as the diversion point for subscribers. Use the
CDCOI command to create a common diversion to voice mail for subscribers or use
the CDINI command to create individual diversions.
For example:
CDINI: DIR=2001&&2299, DIV=4000;
Verify your work with the command: CDIDP:DIR=2001&&2299;
If Call Diversion is not programmed, subscribers must use the FOLLOW ME feature
to divert calls to CallXpress.
NOTE If CallXpress is chosen as the common diversion position (CDCOI), then
ICS calls will always be diverted to this position, even if CDINI has been
programmed to divert calls elsewhere. In other words, reason code diversion will
always go to the common diversion position. Refer to the VIM online book for more
information on programming reason code diversions.
Completing the MD110 Programming
Verify your work and that the programming is correct by using the print command
related to each executable command.
Make sure that the following program units have been installed in the MD110 in
accordance with the Line Interface Module (LIM) disposition table, as follows:
• DIR
• MWP
• DIM
• IHAH
• ILP
• IDP
• IHH
14 Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 19

Integration Technical Note
Installing the Aculab Card
This section describes the Aculab plc High Capacity Digital Access card. The
Aculab plc High Capacity Digital Access card is the interface between the MD110
TLU76/3 E1 CAS card and CallXpress. Each single-port Aculab plc High Capacity
Digital Access card supports 30 CAS EL7 channels.
Aculab markets both ISA and PCI type E1 cards. Aculab cards of either bus type
require a separate interrupt and memory address on the telephony server platform.
Multiple Aculab cards share the same IRQ but require a unique memory address.
The Aculab card communicates with the Dialogic card(s) in the telephony server via
an SCbus connection. The Aculab ISA card has an SCbus connector that is cabled to
the SCbus connector of a Dialogic ISA card(s) with an SCbus ribbon cable. The
Aculab PCI card has an H.100 connector that is cabled to the H.100 connector of the
Dialogic PCI cards with an H.100 or CTbus ribbon cable. The signaling type over
the H.100 bus or CTbus is SCbus signaling. H.100/SCbus adapters are required to
satisfy the physical connection requirements of these ribbon cables when mixing
cards of both bus types in the system.
For detailed instructions on the installation of the Aculab card, refer to the AVT
document Aculab E1 ISA Interface Card Installation and Replacement Spare Parts
Document (P/N 081-47844-XX), or Aculab E1 PCI Interface Card Installation and
Replacement Spare Parts Document (P/N 081-47800-XX).
Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN 15
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 20

Integration Technical Note
Installing the Telephony Server
Network Interface
The Ethernet network adapter card and TCP/IP protocol may have been installed
during initial installation of the Windows NT Server operating system. Alternatively,
both the network adapter and the required TCP/IP protocol can be installed now.
Consult the site system administrator for specific information on how to configure
the network environment for the telephony server. Refer to the Microsoft Windows
NT documentation or online help for information on installing network adapter cards
and network protocols.
Once the telephony server’s network environment has been programmed and the
telephony server has joined the same network as the MD110, verify that the
telephony server can communicate with the PBX via TCP/IP. At the telephony
server, open a command prompt window. Type the ping command followed by the
TCP/IP address assigned to the PBX. If the TCP/IP protocol and network interface is
installed properly, the PBX will reply. The following is an example of how to use
the ping command:
C:\>ping 195.100.102.105
Pinging 195.100.102.105 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 195.100.102.105: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 195.100.102.105: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 195.100.102.105: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 157.108.0.31: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
16 Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 21

Integration Technical Note
Configuring CallXpress
Once the telephone system is programmed, you must configure CallXpress for the
integration. During setup, you’ll need to supply the following information, specific
to this integration, to configure CallXpress.
• From the Switch List box of the Switch tab, select Ericsson MD110 CAS TCP/IP
as the telephone system.
• From the Integration Type box of the Switch tab, select the Integration
type as Outband.
• Enable the integration.
• Enable Integrated Call Processing.
The fields related to the telephone system on the Dialing, Environment, Messaging,
Timing, Audio Disconnect, and Switch Protocol tabs are filled in correctly when you
select the correct telephone system during setup. From the Integration tab, the
Integrated Lines and Configuration must be customized to suit the requirements of
each application. Parameters critical to the integration and their fields are shown
here for your information.
By nature, applications vary from one to another and some parameters may need to
be modified. Refer to the reference guide or the online help for more details about
setting up these parameters.
Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN 17
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 22

Integration Technical Note
Switch Protocol
The Switch Protocol tab field values are preset for the Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS
VM TCP/IP integration when you choose the correct telephone system in the
Configuration utility. Table 4 shows them for your information.
Table 4. Switch Protocol configuration for the MD110 E1 CAS TCP/IP VM integration
Function Inband Inband code Outband
Transfer init: Yes FP
Transfer abort: Yes FP
Transfer abort RNA: No
Transfer complete: Yes P
Reject call trans: Yes FP
Set MWI: No Yes
Clear MWI: No Yes
MWI confirmation tone: Ignore Voice to fax transfer type: Blind xfr
First inband SIM DTMF time-out: 0 Subscriber transfer type: Monitor xfr
Next inband SIM DTMF time-out: 0
Integrated disconnect delay: No Offhook before packet: No
Enable integrated call processing: Yes
18 Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 23

Integration Technical Note
Dialing Template
The callout template fields on the Switch tab are preset for the Ericsson MD110 E1
CAS VM integration when you choose the correct telephone system. They are shown
in Table 5 for your information. The prefix digit may be changed to suit the
application requirements.
Table 5. Dialing Template configuration for the MD110 E1 CAS TCP/IP VM integration
Callout Templates Callout prefix
Extension Calls Template X
Local Calls Template 9X
Long Distance Calls 9X
Integrated Lines
Use the Integration tab to assign the port numbers of individual lines on the system.
The numbers you enter must match the order of voice mail port numbers connected
to the CallXpress ports. Also, enable the Integrated field for each CallXpress port
that will be integrated. Table 6 provides an example of correct port configuration.
IMPORTANT
The integration will not function correctly if port numbers are omitted or incorrect.
Table 6. Lines configuration for the Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS TCP/IP VM integration
Line Extension Type Integrated MWI Callout Open
1 001 Loop start X -- -- X
2 002 Loop start X -- -- X
3 003 Loop start X -- -- X
4 004 Loop start X X X
Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN 19
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 24

Integration Technical Note
Integration
The Integration Configuration field values are shown in Table 7 for your
information. Some of the values are preset for the Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS TCP/IP
VM integration when you choose the correct telephone system. The field values left
unspecified require modification to suit the specific site and application. Consult the
PBX installation manual or the third-party documentation for specifics on the
network port configuration. Consult the PBX installation manual for information on
the network port configuration.
Table 7. Integration configuration parameters for the MD110 E1 CAS TCP/IP VM
integration
Field Comments
PBX switch code Enter the PABX name code.
The default is 1 (MD110).
PBX IP address or Computer
name
TCP/IP port number to use Enter the RPORT number defined on the
Parser filename
MWI initialization mode
Enter the TCP/IP address or name
of the PBX.
MD110. The default is 2555.
MDCASTCP is the default. Do not
change this filename unless advised by
AVT technical staff.
Enter a parameter to determine how
CallXpress initializes all message waiting
indicators when the system is started or
restarted.
3 causes CallXpress to synchronize all
MWIs by issuing an MWI set or clear
command for each subscriber mailbox
that the Set MWI box checked to Yes and
the telephone Primary Type set to Real.
2 causes CallXpress to clear MWIs only
on startup.
1 causes CallXpress to set MWIs only on
startup.
0 results in no MWI initialization at
startup.
The default is 0.
20 Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 25

Integration Technical Note
Table 7 (continued). Integration configuration parameters for the
MD110 E1 CAS TCP/IP VM integration
Field Comments
Pause between MWI Enter the number of milliseconds to wait
between MWI packets. Default is 500.
Voice message system number
Enter the VMS number. Default is 01.
This number is the system ID (SID)
number of the voice mail system of
the MD110.
T-extension length Enter the length of the MD110 directory
(TLEN) number. Default is 4.
D-extension length Enter the length of the MD110 directory
(DLEN) number. Default is 4.
V-extension length Enter the length of the MD110 voice
message port number (VLEN). Default is
3. The number of digits here matches the
number of digits in the parameter
POFMT of the VMFUI command. (See
“Programming the Telephone System”
earlier in this document.)
Optional MWI filler digit Enter the filler digit to be used for short
DNs when setting/clearing MWIs on
mixed DN systems. The default is a blank
space.
Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN 21
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
Page 26

Integration Technical Note
Completing the Integration
Now you are ready to complete the CallXpress installation. See Installing
CallXpress, Administering CallXpress, or the CallXpress online help for
instructions. For general information on integrations, You may also wish to consult
Installing CallXpress for general information on integrations.
22 Ericsson MD110 E1 CAS EL7 TCP/IP VM ITN
© August 2000 AVT Corporation P/N 081-47504-00
 Loading...
Loading...