Page 1

Technical Manual
SED1520 Series
LCD driver with RAM
Page 2

NOTICE
No parts of this material may be reproduced or duplicated in any form or by any means without the written
permission of Seiko Epson. Seiko Epson reserves the right to make changes to this material without notice.
Seiko Epson does not assume any liability of any kind aristing out of any inaccuracies contained in this
material or due to its application or use in any product or circuit and, further, there is no representation that
this material is applicable to products requiring high level reliability, such as, medical products. Moreover,
no license to any intellectual property rights is granted by implication or otherwise, and there is no
representation or warranty that anything made in accordance with this material will be free from any patent
or copyright infringement of a third party. This material or portions thereof may contain technology or the
subject relating to strategic products under the control of the Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Control
Law of Japan and may require an export licence from teh Ministry of International Trade and Industry or other
approval from another government agency.
© Seiko Epson corporation 1998 All right reserved.
i8088 and i8086 are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation.
Z80 is registered trademark of Zilog Corporation.
V20 and V30 are registered trademarks of Nippon Electric Corporation.
Page 3

CONTENTS
Selection Guide
1. SED1510 Series
2. SED1520 Series
3. SED152A Series
4. SED1526 Series
5. SED1530 Series
6. SED1540 Series
7. SED1560 Series
8. SED1565 Series
9. SED1570 Series
Page 4

SED1500 Series
Selection Guide
Page 5
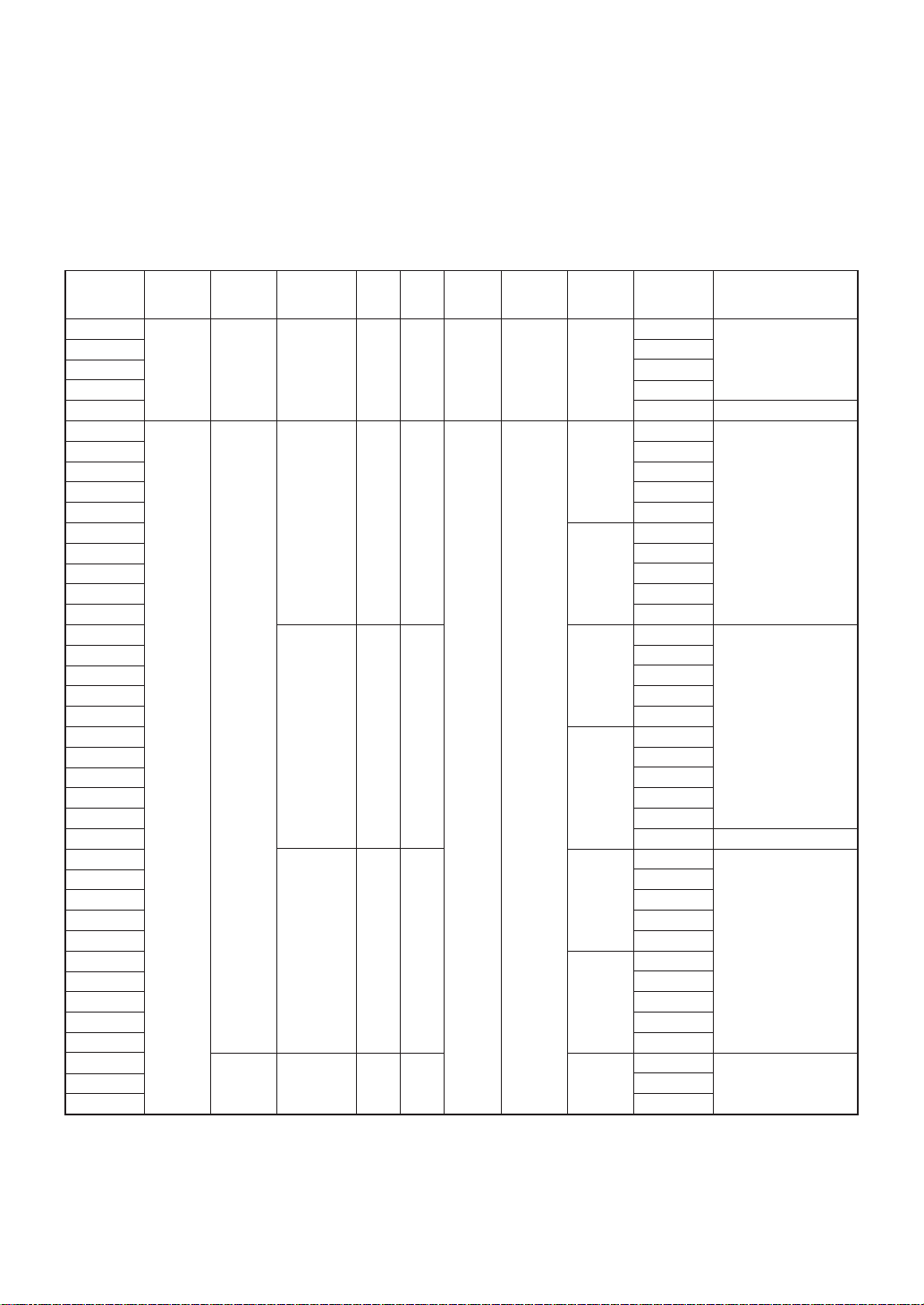
■
LCD drivers with RAM for smalland medium-sized displays
SED1500 series
Ultra-low power consumption and on-chip RAM make this series ideal for compact
LCD-based equipment.
Part number Duty
Supply voltage
range (V)
LCD voltage
range (V)
Segment Common
Display
RAM (bits)
Microprocessor
interface
SED1510D0C
SED1510D0B
SED1510F0C 0.9–6.0 1.8–6.0 1/4 32 4 128 Serial
SED1510F
0E
SED1511D0A
SED1520D0A
SED1520D0B
SED1520F0A
SED1520F0C
SED1520T0A
SED1520D
AA
1/16,1/32 61 16
SED1520DAB
SED1520FAA
SED1520FAC
SED1520TAA
#
SED1521D0A
SED1521D0B
SED1521F0A
SED1521F0C
SED1521T0A
#
SED1521DAA 3.5–13 1/8–1/32 80 –
SED1521D
SED1521F
AB
2.4–7.0
AA
2,560 8-bit parallel
SED1521FAC
SED1521TAA
#
SED152AD0A
SED1522D0A
SED1522D0B
SED1522F0A
SED1522F0C
SED1522T0A
SED1522D
#
AA
1/8,1/16 69 8
SED1522DAB
SED1522FAA
SED1522FAC
SED1522TAA
#
SED1540D0A
SED1540D0B 3.5–11 1/3,1/4 73 3, 4
SED1540F
0A
Frequency
(KHz)
18 (internal)
18
(internal,
external)
2
(external)
18
(external)
2
(external)
18
(internal,
external)
2
(external)
18 (internal)
4 (external)
Package
Application/additional
features
AI pad chip
Au bump chip
QFP12-48pin
Small segment-type LCD
display. Command and data
interface
QFP6-60pin
AI pad chip
Small segment-type LCD dislays. Data only
interface
AI pad chip
Au bump chip
QFP5-100pin
QFP15-100pin
TCP
AI pad chip
Dot-matrix LCD displays
Extension driver is the
SED1521.
Au bump chip
QFP5-100pin
QFP15-100pin
TCP
AI pad chip
Au bump chip
QFP5-100pin
QFP15-100pin
TCP
AI pad chip
Extension driver for the
SED1520 and SED1522
Au bump chip
QFP5-100pin
QFP15-100pin
TCP
Al pad chip
P-substrate version of SED1521
AI pad chip
Au bump chip
QFP5-100pin
QFP15-100pin
TCP
AI pad chip
Dot-matrix LCD displays
Extension driver is the
SED1521.
Au bump chip
QFP5-100pin
QFP15-100pin
TCP
AI pad chip
Au bump chip
Segment-type displays
QFP5-100pin
# : Planning TCP : Tape Carrier Package
Page 6
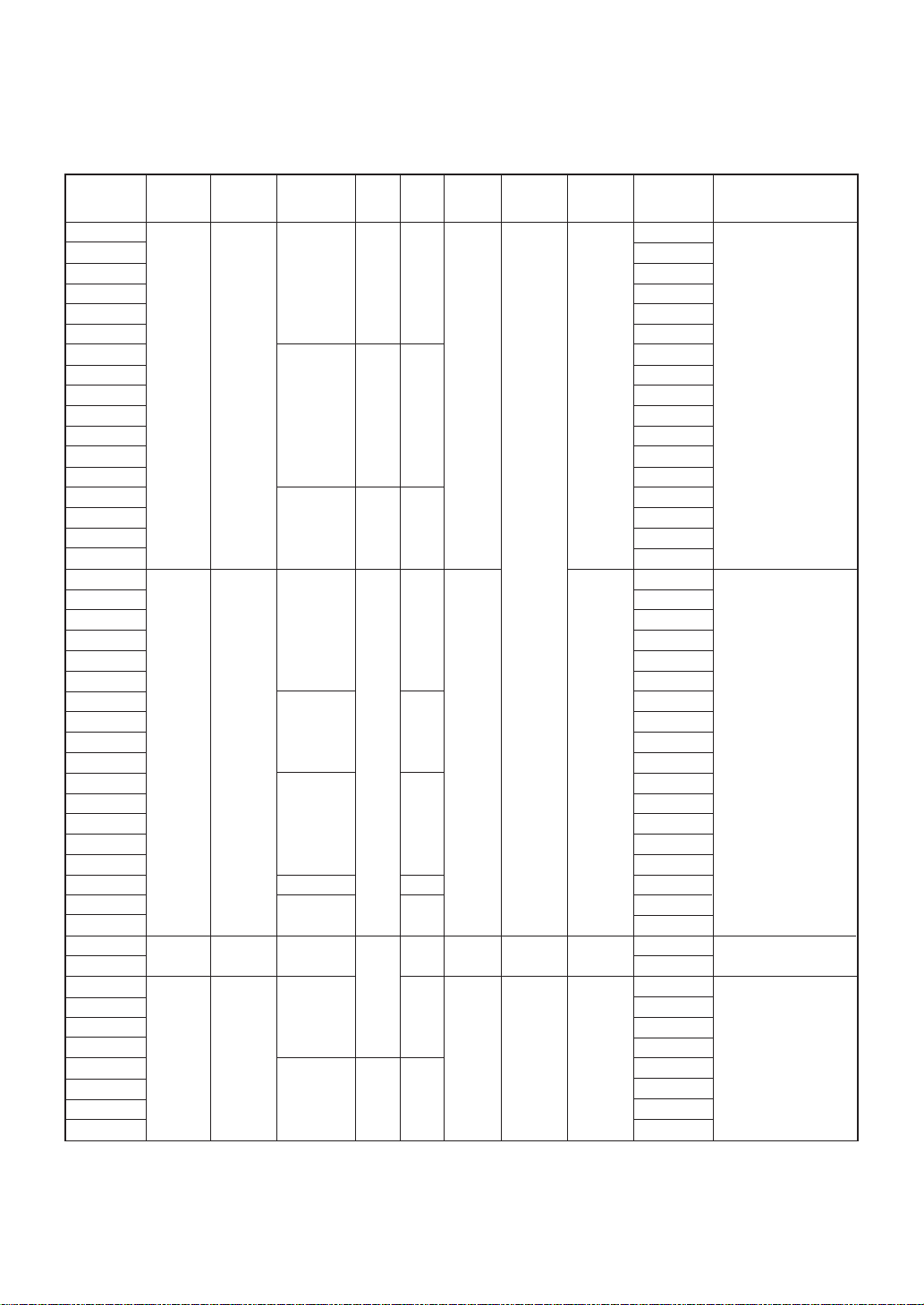
Part number Duty
Supply voltage
range (V)
LCD voltage
range (V)
Segment
Common
Display
RAM (bits)
SED1560D0A
SED1560DAA
SED1560D0B 1/48, 1/49
SED1560D
AB 1/64, 1/65
SED1560T
0B
102 65
SED1560TQA
SED1561D0A
SED1561DAA 166×65
SED1561D
0B 2.4–6.0 6.0–16.0
SED1561D
AB
0B
SED1561T
1/24, 1/25
1/32, 1/33
134 33
bits
SED1561TAB
SED1561TQA
SED1562D0A
SED1562D0B 1/16, 1/17
SED1562T
0B (1/5bias)
SED1562T
QA 8-bit parallel
SED1565D
0B or Serial
SED1565D
1B*
SED1565D
2B 1/65
SED1565T
0A (1/7, 1/9 bias)
SED1565T
0B
150 17
65
SED1565T0C
SED1566D0B
SED1566D1B* 1/49
SED1566D
2B 1.8–5.5 4.5–16.0 (1/6, 1/8 bias)
SED1566T
0A
49 132×65
132 bits
SED1567D0B
SED1567D1B*
SED1567D
2B
0B
SED1567T
1/33
(1/5, 1/6 bias)
33
SED1567T0C
SED1568D0B
0B 1/53
SED1569D
SED1569T
** (1/6, 1/8 bias)
SED1570D
0A
2.7–5.5 8.0–20.0 1/64–1/200 –
0B bits
SED1570D
SED1526D
*A
*B 1/8, 1/9
SED1526D
SED1526F
*A
*A
SED1526T
SED1528D
SED1528D
SED1528F
2.4–6.0 Supply
*A ×3 bits or Serial
*B
*A
voltage
1/55 (1/6, 1/8 bias)
3.5–
80
1/16, 1/17
1/32, 1/33 64 33
55
53
200×80
17
80×33 8-bit parallel
SED1528T*A
Microprocessor
interface
Frequency
4-bit parallel
(KHz)
18
33
–
20
Package
Al pad chip
Al pad chip
Au bump chip
Au bump chip
TCP
QTCP
Al pad chip
Al pad chip
Au bump chip
Au bump chip
TCP
TCP
QTCP
Al pad chip
Au bump chip
TCP
QTCP
Au bump chip
Au bump chip
Au bump chip
TCP
TCP
TCP
Au bump chip
Au bump chip
Au bump chip
TCP
Au bump chip
Au bump chip
Au bump chip
TCP
TCP
Au bump chip
Au bump chip
TCP
Al pad chip
Au bump chip
Al pad chip
Au bump chip
QFP5-128pin
TCP
Al pad chip
Au bump chip
QFP5-128pin
TCP
Application/additional
features
Built-in power circuit for LCD
(voltage tripler)
SED1560✽
0B (1/9 bias)
SED1560✽
AB (1/7 bias)
SED1561✽
0B (1/7 bias)
SED1561✽
AB (1/5 bias)
Built-in power circuit for LCD
(DC/DC×4)
Built-in self-refreshing function
Built-in power circuit for LCD
(voltage tripler)
SED1526✽
0✽
(VREG)
SED1526✽
E✽
(no VREG)
A✽
SED1526✽
(redistribution of COMS)
0✽
SED1528✽
(VREG)
E✽
SED1528✽
(no VREG)
Page 7

Part number Duty
SED1530D
Supply voltage
range (V)
0A
LCD voltage
range (V)
Segment
Common
SED1530DAA
SED1530D0B 1/32, 1/33 100 33
SED1530D
AB
SED1530TAA
SED1531D0A
SED1531D0B 132 –
SED1531T
0A 2.4–6.0 4.5–16.0
SED1532D
0A
SED1532DBA 1/64, 1/65
SED1532D
SED1532D
0B
BA
100 33
SED1532T0A
SED1532TBA
SED1535D0B* 1/35 98 35
Display
RAM (bits)
Microprocessor
interface
132×65 8-bit parallel
bits or Serial
Frequency
(KHz)
–
Package
Al pad chip
Al pad chip
Au bump chip
Au bump chip
TCP
Al pad chip
Au bump chip
TCP
Al pad chip
Al pad chip
Au bump chip
Au bump chip
TCP
TCP
Au bump chip
Application/additional
features
Built-in power circuit for LCD
(voltage quadrupler)
SED153✽✽
0✽
(Common: Right side)
SED153✽✽
A✽
(Common: Both side)
SED153✽✽
B✽
(Common: Left side)
SED153✽✽
F✽
(no VREG)
TCP : Tape Carrier Package
Page 8

2. SED1520 Series
Page 9

SED1520 Series
Contents
OVERVIEW ..........................................................................................................................................................2-1
FEATURES...........................................................................................................................................................2-1
BLOCK DIAGRAM ................................................................................................................................................2-2
PACKAGE OUTLINE ............................................................................................................................................2-3
PAD ......................................................................................................................................................................2-4
Pad Arrangement.........................................................................................................................................2-4
PAD ARRANGEMENT .........................................................................................................................................2-5
PIN DESCRIPTION ..............................................................................................................................................2-6
(1) Power Pins .............................................................................................................................................2-6
(2) System Bus Connection Pins .................................................................................................................2-6
(3) LCD Drive Circuit Signals .......................................................................................................................2-7
BLOCK DESCRIPTION ........................................................................................................................................2-8
System Bus..................................................................................................................................................2-8
Display Start Line and Line Count Registers ...............................................................................................2-9
Column Address Counter.............................................................................................................................2-9
Page Register ..............................................................................................................................................2-9
Display Data RAM........................................................................................................................................2-9
Common Timing Generator Circuit ............................................................................................................2-10
Display Data Latch Circuit..........................................................................................................................2-10
LCD Driver Circuit ......................................................................................................................................2-10
Display Timing Generator ..........................................................................................................................2-10
Oscillator Circuit (SED1520*0A Only) ........................................................................................................2-11
Reset Circuit ..............................................................................................................................................2-11
COMMANDS ......................................................................................................................................................2-14
Summary....................................................................................................................................................2-14
Command Description ...............................................................................................................................2-15
SPECIFICATIONS ..............................................................................................................................................2-20
Absolute Maximum Ratings .......................................................................................................................2-20
Electrical Specifications .............................................................................................................................2-20
APPLICATION NOTES.......................................................................................................................................2-26
MPU Interface Configuration......................................................................................................................2-26
LCD Drive Interface Configuration .............................................................................................................2-27
LCD Panel Wiring Example .......................................................................................................................2-29
Package Dimensions .................................................................................................................................2-30
Series
SED1520
– i –
Page 10

SED1520 Series
OVERVIEW
The SED1520 family of dot matrix LCD drivers are
designed for the display of characters and graphics. The
drivers generate LCD drive signals derived from bit
mapped data stored in an internal RAM.
The drivers are available in two configurations
The SED1520 family drivers incorporate innovative
circuit design strategies to achieve very low power
dissipation at a wide range of operating voltages.
These features give the designer a flexible means of
implementing small to medium size LCD displays for
compact, low power systems.
• The SED1520 which is able to drive two lines of
twelve characters each.
• The SED1521 which is able to drive 80 segments for
extention.
• The SED1522 which is able to drive one line of
thirteen characters each.
Line-up
Product
Name
SED1520
SED1521
SED1522
SED1520
SED1521
SED1522
Clock Frequency
On-Chip External
0
18 kHz 18 kHz SED1520
*
*
0
*
0
*
A
*
A
*
A
*
— 18 kHz SED1520
*
18 kHz 18 kHz SED1522
*
— 2 kHz SED1520
*
— 2 kHz SED1520
*
— 2 kHz SED1522
*
Applicable Driver of SEG of CMOS Duty
FEATURES
• Fast 8-bit MPU interface compatible with 80- and 68family microcomputers
• Many command set
• Total 80 (segment + common) drive sets
• Low power — 30 µW at 2 kHz external clock
• Wide range of supply voltages
DD – VSS: –2.4 to –7.0 V
V
DD – V5: –3.5 to –13.0 V
V
• Low-power CMOS
Number Number
Drivers Drivers
0
, SED1521
*
*
0
, SED1522
*
*
0
, SED1521
*
*
A
, SED1521
*
*
A
, SED1522
*
*
A
, SED1521
*
*
0
*
*
0
*
*
0
*
*
A
*
*
A
*
*
A
*
*
61 16 1/16, 1/32
80 0 1/8 to 1/32
69 8 1/8, 1/16
61 16 1/16, 1/32
80 0 1/8 to 1/32
69 8 1/8, 1/16
Series
SED1520
• Package code (For example SED1520)
SED1520T
SED1520F
SED1520D
: PKG SED1520F
**
: Chip SED1520D
**
SED1520F
SED1520D
A (QFP5-100pin)
*
C (QFP15-100pin)
*
A (Al-pad)
*
B (Au-bump)
*
EPSON 2–1
Page 11

SED1520 Series
BLOCK DIAGRAM
An example of SED1520*AA:
5
,V
4
,V
3
,V
2
,V
1
V
15
to COM
0
COM
60
to SEG
0
SEG
SS
DD
V
V
LCD drive circuit
Common counter
Display data latch circuit
Display data RAM
(2560-bit)
Line counter
Display start line register
Line address decoder
I/O buffer
Column address decoder
CL
FR
Display
timing
generator
Column address counter
circuit
Column address register
register
Low-address
Command
decoder
MPU interface
7
~D
,CS
0
0
A
D
2–2 EPSON
RD,WR
(E,R/W)
Status
M/S
RES
Bus
holder
Page 12

PACKAGE OUTLINE
QFP5
SEG21
SEG20
SEG19
SEG18
SEG17
SEG16
SEG15
SEG14
SEG13
SEG12
SEG11
SEG10
SEG9
SEG8
SEG7
SEG6
SEG5
SEG4
SEG3
SEG2
SEG1
SEG0A0CS(OSC1)
CL(OSC2)
E(RD)
R/W(WR)
VSSCS0
SED1520 Series
CS1
QFP15
CS2
CS3
CS4
CS5
CS6
CS7
V
RES
M/S
COM0
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4
55
60
65
70
75
85
DD
F2
V5
V1
V2
V4
V1
90
Index
95
100
5
10
15
20
COM5
COM6
COM7
COM8
COM9
COM10
R/W(WR)
75
SS
V
DD
46
80
46
85
90
95
1
COM11
COM12
COM13
70
Index
5
SEG60
COM14
COM15
SEG59
SEG58
65
10
SEG57
SEG56
SEG55
15
SEG54
SEG53
SEG52
60
SEG51
SEG50
55
20
SEG49
25
SEG48
SEG47
SEG46
50
45
40
35
30
25
45
40
35
SEG45
SEG44
SEG43
SEG42
SEG20V
SEG21D30
SEG22D31
SEG23D32
SEG24D33
SEG25D34
SEG26D35
SEG27D36
SEG28D37
SEG29
SEG30RES
SEG31F R
SEG32V5
SEG33V3
SEG34V2
SEG35M/S
SEG36V4
SEG37V1
SEG38COM 0
SEG39COM 1
SEG40COM 2
SEG41COM 3
SEG42COM 4
SEG43COM 5
SEG44COM 6
SEG22
SEG23
SEG24
SEG25
SEG26
SEG27
SEG28
SEG29
SEG30
SEG31
SEG32
SEG33
SEG34
SEG35
SEG36
SEG37
SEG38
SEG39
SEG40
SEG41
Series
SED1520
SEG46 SEG18
COM 7
COM 8 E (RD)
COM 9 CL (OSC2)
COM10 CS (OSC1)
COM11 AQ
COM12 SEG0
COM13 SEG1
COM14 SEG2
SEG60 SEG4
COM15 SEG3
SEG59 SEG5
SEG58 SEG6
SEG57 SEG7
SEG56 SEG8
SEG55 SEG9
SEG54 SEG10
SEG53 SEG11
SEG52 SEG12
SEG51 SEG13
SEG50 SEG14
SEG49 SEG15
SEG48 SEG16
SEG47 SEG17
SEG45 SEG19
Note: This is an example of SED1520F pin assignment. The modified pin names are given below.
Product Pin/Pad Number
Name 74 75 96 to 100, 1 to 11 93 94 95
SED1520F
SED1521F
SED1522F
SED1520F
SED1521F
SED1522F
0A OSC1 OSC2 COM0 to COM15* M/S V4 V1
0A CS CL SEG76 to SEG61 SEG79 SEG78 SEG77
0A OSC1 OSC2 COM0 to 7, SEG68 to 61 M/S V4 V1
AA CS CL COM0 to COM15* M/S V4 V1
AA CS CL SEG76 to SEG61 SEG79 SEG78 SEG77
AA CS CL COM0 to 7, SEG68 to 61 M/S V4 V1
SED1520: Common outputs COM0 to COM15 of the master LSI correspond to COM31 to COM16 of the
slave LSI.
SED1522: Common outputs COM0 to COM15 of the master LSI correspond to COM15 to COM8 of the
slave LSI.
EPSON 2–3
Page 13

SED1520 Series
PAD
Pad Arrangement
Chip specifications of AL pad package
Chip size: 4.80×7.04×0.400 mm
Pad pitch: 100×100 µm
100 95 90 85
1
Chip specifications of gold bump package
Chip size: 4.80×7.04×0.525 mm
Bump pitch: 199 µm (Min.)
Bump height: 22.5 µm (Typ.)
Bump size: 132×111 µm (±20 µm) for mushroom
model
116×92 µm (±4 µm) for vertical model
80
5
10
15
20
25
30
Note: An example of SED1520D
package.
75
Y
(0, 0)
AA
D1520D *
35 40 45 50
4.80 mm
AA die numbers is given. These numbers are the same as the bump
X
70
7.04 mm
65
60
55
2–4 EPSON
Page 14

PAD ARRANGEMENT
An example of SED1520DA* pin names is given. The
asterisk (
bump package.
SED1520DAB Pad Center Coordinates
) can be A for AL pad package or B for gold
*
SED1520 Series
Pad Pin
No. Name No. Name No. Name
XY
1 COM5 159 6507
2 COM6 159 6308
3 COM7 159 6108
4 COM8 159 5909
5 COM9 159 5709
6 COM10 159 5510
7 COM11 159 5310
8 COM12 159 5111
9 COM13 159 4911
10 COM14 159 4712
11 COM15 159 4512
12 SEG60 159 4169
13 SEG59 159 3969
14 SEG58 159 3770
15 SEG57 159 3570
16 SEG56 159 3371
17 SEG55 159 3075
18 SEG54 159 2876
19 SEG53 159 2676
20 SEG52 159 2477
21 SEG51 159 2277
22 SEG50 159 2078
23 SEG49 159 1878
24 SEG48 159 1679
25 SEG47 159 1479
26 SEG46 159 1280
27 SEG45 159 1080
28 SEG44 159 881
29 SEG43 159 681
30 SEG42 159 482
31 SEG41 504 159
32 SEG40 704 159
33 SEG39 903 159
34 SEG38 1103 159
Pad Pin
XY
35 SEG37 1302 159
36 SEG36 1502 159
37 SEG35 1701 159
38 SEG34 1901 159
39 SEG33 2100 159
40 SEG32 2300 159
41 SEG31 2499 159
42 SEG30 2699 159
43 SEG29 2898 159
44 SEG28 3098 159
45 SEG27 3297 159
46 SEG26 3497 159
47 SEG25 3696 159
48 SEG24 3896 159
49 SEG23 4095 159
50 SEG22 4295 159
51 SEG21 4641 482
52 SEG20 4641 681
53 SEG19 4641 881
54 SEG18 4641 1080
55 SEG17 4641 1280
56 SEG16 4641 1479
57 SEG15 4641 1679
58 SEG14 4641 1878
59 SEG13 4641 2078
60 SEG12 4641 2277
61 SEG11 4641 2477
62 SEG10 4641 2676
63 SEG9 4641 2876
64 SEG8 4641 3075
65 SEG7 4641 3275
66 SEG6 4641 3474
67 SEG5 4641 3674
68 SEG4 4641 3948
Pad Pin
69 SEG3 4641 4148
70 SEG2 4641 4347
71 SEG1 4641 4547
72 SEG0 4641 4789
73 A0 4641 5048
74 CS 4641 5247
75 CL 4641 5447
76 E (RD) 4641 5646
R/W (WR)
77
78 V
SS 4641 6107
79 DB0 4641 6307
80 DB1 4641 6506
81 DB2 4295 6884
82 DB3 4095 6884
83 DB4 3896 6884
84 DB5 3696 6884
85 DB6 3497 6884
86 DB7 3297 6884
87 V
DD 3098 6884
88 RES 2898 6884
89 FR 2699 6884
90 V
91 V
5 2499 6884
3 2300 6884
92 V2 2100 6884
93 M/S 1901 6884
94 V
4 1701 6884
95 V1 1502 6884
96 COM0 1302 6884
97 COM1 1103 6884
98 COM2 903 6884
99 COM3 704 6884
100 COM4 504 6884
XY
4641 5846
Series
SED1520
The other SED1520 series packages have the different pin names as shown.
Package/Pad No. 74 75 96 to 100, 1 to 11 93 94 95
SED1520D
0* OSC1 OSC2 COM0 to COM15 * M/S V4 V1
SED1522D0* OSC1 OSC2 COM0 to 7, SEG68 to 61 M/S V4 V1
SED1522DA* OSC1 OSC2 COM0 to 7, SEG68 to 61 M/S V4 V1
SED1521D0* CS CL SEG76 to SEG61 SEG79 SEG78 SEG77
SED1521D
A* CS CL SEG76 to SEG61 SEG79 SEG78 SEG77
EPSON 2–5
Page 15

SED1520 Series
PIN DESCRIPTION
(1) Power Pins
Name Description
DD Connected to the +5Vdc power. Common to the VCC MPU power pin.
V
V
SS 0 Vdc pin connected to the system ground.
1, V2, V3, V4, V5 Multi-level power supplies for LCD driving. The voltage determined for each liquid
V
(2) System Bus Connection Pins
crystal cell is divided by resistance or it is converted in impedance by the op amp,
and supplied. These voltages must satisfy the following:
DD ≥ V1 ≥ V2 ≥ V3 ≥ V4 ≥ V5
V
D7 to D0 Three-state I/O.
The 8-bit bidirectional data buses to be connected to the 8- or 16-bit standard MPU
data buses.
A0 Input.
Usually connected to the low-order bit of the MPU address bus and used to identify
the data or a command.
A0=0: D0 to D7 are display control data.
A0=1: D0 to D7 are display data.
RES Input.
When the RES signal goes the 68-series MPU is initialized, and when it
goes , the 80-series MPU is initialized. The system is reset during edge
sense of the RES signal. The interface type to the 68-series or 80-series MPU is
selected by the level input as follows:
High level: 68-series MPU interface
Low level: 80-series MPU interface
CS Input. Active low. Effective for an external clock operation model only.
An address bus signal is usually decoded by use of chip select signal, and it is
entered. If the system has a built-in oscillator, this is used as an input pin to the
oscillator amp and an Rf oscillator resistor is connected to it. In such case, the RD,
WR and E signals must be ORed with the CS signals and entered.
E (RD) •
If the 68-series MPU is connected:
Input. Active high.
Used as an enable clock input of the 68-series MPU.
If the 80-series MPU is connected:
•
Input. Active low.
The RD signal of the 80-series MPU is entered in this pin. When this signal is
kept low, the SED1520 data bus is in the output status.
R/W (WR) •
If the 68-series MPU is connected:
Input.
Used as an input pin of read control signals (if R/W is high) or write control
signals (if low).
If the 80-series MPU is connected:
•
Input. Active low.
The WR signal of the 80-series MPU is entered in this pin. A signal on the data
bus is fetched at the rising edge of WR signal.
2–6 EPSON
Page 16

(3) LCD Drive Circuit Signals
10
1010
VV1V5 V4
DD
FR signal
Counter output
Output level
Name Description
SED1520 Series
CL Input. Effective for an external clock operation model only.
This is a display data latch signal to count up the line counter and common counter
at each signal falling and rising edges. If the system has a built-in oscillator, this is
used as an output pin of the oscillator amp and an Rf oscillator resistor is connected to it.
FR Input/output.
This is an I/P pin of LCD AC signals, and connected to the M terminal of common
driver.
I/O selection
• Common oscillator built-in model: Output if M/S is 1;
Input if M/S is 0.
• Dedicate segment model: Input
SEGn Output.
The output pin for LCD column (segment) driving. A single level of V
5 is selected by the combination of display RAM contents and RF signal.
V
FR signal
Data
Output level
10
1010
VV2V5V3
DD
COMn Output.
The output pin for LCD common (low) driving. A single level of VDD, V1, V4 and V5
is selected by the combination of common counter output and RF signal. The
slave LSI has the reverse common output scan sequence than the master LSI.
DD, V2, V3 and
Series
SED1520
M/S Input.
The master or slave LSI operation select pin for the SED1520 or SED1522.
Connected to V
slave LSI operation mode).
When this M/S pin is set, the functions of FR, COM0 to COM15, OSC1 (CS), and
OSC2 (CL) pins are changed.
SED1520F
SED1522F
* The slave driver has the reverse common output scan sequence than the master
driver.
DD (to select the master LSI operation mode) or VSS (to select the
M/S FR COM output OSC1 OSC2
0A VDD Output COM0 to COM15 Input Output
V
SS Input COM31 to COM16 NC Input
0A VDD Output COM0 to COM7 Input Output
V
SS Input COM15 to COM8 NC Input
EPSON 2–7
Page 17

SED1520 Series
BLOCK DESCRIPTION
System Bus
MPU interface
1. Selecting an interface type
The SED1520 series transfers data via 8-bit bidirectional data buses (D0 to D7). As its Reset pin has the
MPU interface select function, the 80-series MPU or
the 68-series MPU can directly be connected to the
MPU bus by the selection of high or low RES signal
Table 1
RES signal input level MPU type A0 E R/W CS D0 to D7
Active low 68-series ↑↑↑↑↑
Active high 80-series ↑ RD WR ↑↑
Data transfer
The SED1520 and SED1521 drivers use the A0, E (or
RD) and R/W (or WR) signals to transfer data between
the system MPU and internal registers. The combinations used are given in the table blow.
In order to match the timing requirements of the MPU
with those of the display data RAM and control registers
all data is latched into and out of the driver. This
introduces a one cycle delay between a read request for
data and the data arriving. For example when the MPU
level after reset (see Table 1).
When the CS signal is high, the SED1520 series is
disconnected from the MPU bus and set to stand by.
However, the reset signal is entered regardless of the
internal setup status.
executes a read cycle to access display RAM the current
contents of the latch are placed on the system data bus
while the desired contents of the display RAM are moved
into the latch.
This means that a dummy read cycle has to be executed
at the start of every series of reads. See Figure 1.
No dummy cycle is required at the start of a series of
writes as data is transferred automatically from the input
latch to its destination.
Common 68 MPU 80 MPU
A0 R/W RD WR
1 1 0 1 Read display data
1 0 1 0 Write display data
0 1 0 1 Read status
0 0 1 0 Write to internal register (command)
Function
2–8 EPSON
Page 18

WRITE
MPU
WR
DATA
SED1520 Series
N
N + 1
N + 2
N + 3
Internal
timing
READ
MPU
Internal
timing
Bus
hold
WR
WR
RD
DATA
WR
RD
Column
address
Bus
hold
N
Address set
at N
N n n + 1
Dummy read Data read
N N + 1
N + 1
N n n + 1N
Figure 1 Bus Buffer Delay
at N
N + 2
Data read
at N + 1
N + 2
N + 3
n + 2
Series
SED1520
Busy flag
When the Busy flag is logical 1, the SED1520 series is
executing its internal operations. Any command other
than Status Read is rejected during this time. The Busy
flag is output at pin D7 by the Status Read command. If
an appropriate cycle time (tcyc) is given, this flag needs
not be checked at the beginning of each command and,
therefore, the MPU processing capacity can greatly be
enhanced.
Display Start Line and Line Count
Registers
The contents of this register form a pointer to a line of
data in display data RAM corresponding to the first line
of the display (COM0), and are set by the Display Start
Line command. See section 3.
The contents of the display start line register are copied
into the line count register at the start of every frame, that
is on each edge of FR. The line count register is
incremented by the CL clock once for every display line,
thus generating a pointer to the current line of data, in
display data RAM, being transferred to the segment
driver circuits.
Column Address Counter
The column address counter is a 7-bit presettable counter
that supplies the column address for MPU access to the
display data RAM. See Figure 2. The counter is
incremented by one every time the driver receives a Read
or Write Display Data command. Addresses above 50H
are invalid, and the counter will not increment past this
value. The contents of the column address counter are set
with the Set Column Address command.
Page Register
The page resiter is a 2-bit register that supplies the page
address for MPU access to the display data RAM. See
Figure 2. The contents of the page register are set by the
Set Page Register command.
Display Data RAM
The display data RAM stores the LCD display data, on a
1-bit per pixel basis. The relation-ship between display
data, display address and the display is shown in Figure
2.
EPSON 2–9
Page 19

SED1520 Series
Common Timing Generator Circuit
Generates common timing signals and FR frame signals
from the CL basic clock. The 1/16 or 1/32 duty (for
SED1520) or 1/8 or 1/16 duty (for SED1522) can be
selected by the Duty Select command. If the 1/32 duty is
selected for the SED1520 and 1/16 duty is selected for the
SED1522, the 1/32 and 1/16 duties are provided by two
chips consisting of the master and slave chips in the
common multi-chip mode.
SED1520
FR signal
(Master output)
Master Common
Slave Common
012 1415 01 15
SED1522
FR signal
(Master output)
Master Common
Slave Common
012 67 01 7
Display Data Latch Circuit
This latch stores one line of display data for use by the
LCD driver interface circuitry. The output of this latch
is controlled by the Display ON/OFF and Static Drive
ON/OFF commands.
LCD Driver Circuit
The LCD driver circuitry generates the 80 4-level signals
used to drive the LCD panel, using output from the
display data latch and the common timing generator
circuitry.
16 17 30 31
8 9 14 15
16 17 31
89 15
Display Timing Generator
This circuit generates the internal display timing signal
using the basic clock, CL, and the frame signals, FR.
FR is used to generate the dual frame AC-drive waveform (type B drive) and to lock the line counter and
common timing generator to the system frame rate.
CL is used to lock the line counter to the system line scan
rate. If a system uses both SED1520s or SED1522 and
SED1521s they must have the same CL frequency rating.
2–10 EPSON
Page 20

SED1520 Series
Oscillator Circuit (SED1520
0A Only)
*
A low power-consumption CR oscillator for adjusting
the oscillation frequency using Rf oscillation resistor
only. This circuit generates a display timing signal.
Some of SED1520 and SED1522 series models have a
built-in oscillator and others use an external clock. This
difference must be checked before use.
Connect the Rf oscillation resistor as follows. To suppress the built-in oscillator circuit and drive the MPU
using an external clock, enter the clock having the same
phase as the OSC2 of mater chip into OSC2 of the slave
chip.
• MPU having a built-in oscillator
V
DD
M/S M/S
Master chip Slave chip
(CS) (CL) (CS) (CL)
OSC1 OSC2 OSC1 OSC2
Rf
*2
*1
V
SS
Open
*1 If the parasitic capacitance of this section increases, the oscillation frequency may shift to the lower
frequency. Therefore, the Rf oscillation frequency must be reduced below the specified level.
*2 A CMOS buffer is required if the oscillation circuit is connected to two or more slave MPU chips.
Series
SED1520
• MPU driven with an external clock
Y driver
CL2
Reset Circuit
Detects a rising or falling edge of an RES input and
initializes the MPU during power-on.
• Initialization status
1. Display is off.
2. Display start line register is set to line 1.
3. Static drive is turned off.
4. Column address counter is set to address 0.
5. Page address register is set to page 3.
6. 1/32 duty (SED1520) or 1/16 duty (SED1522) is
selected.
7. Forward ADC is selected (ADC command D0 is
1 and ADC status flag is 1).
8. Read-modify-write is turned off.
SED1521F
AA
CL
The input signal level at RES pin is sensed, and an
MPU interface mode is selected as shown on Table 1.
For the 80-series MPU, the RES input is passed
through the inverter and the active high reset signal
must be entered. For the 68-series MPU, the active
low reset signal must be entered.
As shown for the MPU interface (reference example),
the RES pin must be connected to the Reset pin and
reset at the same time as the MPU initialization.
If the MPU is not initialized by the use of RES pin
during power-on, an unrecoverable MPU failure may
occur.
When the Reset command is issued, initialization
EPSON 2–11
Page 21

SED1520 Series
Column address
ADC
SEG pin
D
0
= "1"
D
0
= "0"
SEG 0 4F H00
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
4E
4D
4C
4B
4A
49
48
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
D
1
1,1
D
D0D
D
D
D
D
D
D
6
7
H
3
4
5
Page 3
7
1
2
1,0
D
D0D
D
D
D
D
D
6
3
4
5
Page 2
7
1
2
0,1
D0D
D
D
D
D
D
6
5
4
Page 1
1
2
3
,D
2
= 0,0
D
D
D
D
D
6
7
5
3
4
Page 0
Page address
DATA
D0D
D
1
2
77
78
79
4E
01
00
4F
1E
1F
COM 30
COM 31
1B
1C
1D
COM 27
COM 28
COM 29
19
1A
COM 25
COM 26
17
18
1/16
COM 22
COM 23
COM 24
16
13
14
15
COM 19
COM 20
COM 21
12
COM 18
4D
02
Figure 2 Display Data RAM Addressing
2–12 EPSON
0E
0F
10
11
Display area
COM 14
COM 15
COM 16
COM 17
0B
0C
0D
COM 11
COM 12
COM 13
09
0A
COM 9
COM 10
06
07
08
Start
COM 6
COM 7
COM 8
04
05
COM 4
COM 5
01
02
03
COM 1
COM 2
COM 3
Line
address
00
H
Response
COM 0
Common
output
Start line
(Example)
Page 22

1/5 bias, 1/16 duty
1/6 bias, 1/32 duty
COM0
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4
COM5
COM6
COM7
COM8
COM9
COM10
COM11
COM12
COM13
COM14
COM15
SEG0
SEG1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
FR
COM0
COM1
COM2
SEG0
SEG1
COM0—SEG0
COM0—SEG1
0123 150
3
0012
31
11223
SED1520 Series
3
15
31
DD
V
SS
V
DD
V
V1
V2
V3
V4
Series
SED1520
V5
V
DD
V1
V2
V3
V4
V5
V
DD
V1
V2
V3
V4
V5
V
DD
V1
V2
V3
V4
V5
V
DD
V1
V2
V3
V4
V5
V5
V4
V3
V2
V1
V
DD
-V1
-V2
-V3
-V4
-V5
V5
V4
V3
V2
V1
V
DD
-V1
-V2
-V3
-V4
-V5
Figure 4 LCD drive waveforms example
EPSON 2–13
Page 23

SED1520 Series
COMMANDS
Summary
Command
Display On/OFF 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0/1
Display start line 0 1 0 1 1 0 Display start address (0 to 31)
Set page address 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 Page (0 to 3)
Set column
(segment) address
Read status 0 0 1 Busy ADC ON/OFF Reset 0 0 0 0
Write display data 1 1 0 Write data
Read display data 1 0 1 Read data
Select ADC 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0/1
Statis drive
ON/OFF
Select duty 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0/1
Read-Modify-Write 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
End 0101 1 1 0111 0
Reset 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0
A0
RD WR
0 1 0 0 Column address (0 to 79)
0101 0 1 00100/1
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Code
Function
Turns display on or off.
1: ON, 0: OFF
Specifies RAM line corresponding to top line
of display.
Sets display RAM page in page address
register.
Sets display RAM column address in
column address register.
Reads the following status:
BUSY 1: Busy
0: Ready
ADC 1: CW output
0: CCW output
ON/OFF 1: Display off
0: Display on
RESET 1: Being reset
0: Normal
Writes data from data bus into display RAM.
Reads data from display RAM onto data
bus.
0: CW output, 1: CCW output
Selects static driving operation.
1: Static drive, 0: Normal driving
Selets LCD duty cycle
1: 1/32, 0: 1/16
Read-modify-write ON
Read-modify-write OFF
Software reset
2–14 EPSON
Page 24

SED1520 Series
Command Description
Table 3 is the command table. The SED1520 series identifies a data bus using a combination of A0 and R/W (RD or WR)
signals. As the MPU translates a command in the internal timing only (independent from the external clock), its speed
is very high. The busy check is usually not required.
Display ON/OFF
0 RD WR D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
A
0101010111DAEH, AFH
This command turns the display on and off.
• D=1: Display ON
• D=0: Display OFF
Display Start Line
This command specifies the line address shown in Figure 3 and indicates the display line that corresponds to COM0. The
display area begins at the specified line address and continues in the line address increment direction. This area having
the number of lines of the specified display duty is displayed. If the line address is changed dynamically by this command,
the vertical smooth scrolling and paging can be used.
R/W
R/W
0 RD WR D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
A
010110A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 C0H to DFH
This command loads the display start line register.
A
4 A3 A2 A1 A0 Line Address
00000 0
00001 1
::
::
11111 31
Series
SED1520
See Figure 2.
Set Page Address
This command specifies the page address that corresponds to the low address of the display data RAM when it is accessed
by the MPU. Any bit of the display data RAM can be accessed when its page address and column address are specified.
The display status is not changed even when the page address is changed.
R/W
0 RD WR D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
A
010101110A1 A0 B8H to BBH
This command loads the page address register.
A1 A0 Page
00 0
01 1
10 2
11 3
See Figure 2.
EPSON 2–15
Page 25

SED1520 Series
Set Column Address
This command specifies a column address of the display data RAM. When the display data RAM is accessed by the MPU
continuously, the column address is incremented by 1 each time it is accessed from the set address. Therefore, the MPU
can access to data continuously. The column address stops to be incremented at address 80, and the page address is not
changed continuously.
R/W
0 RD WR D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
A
0100A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 00H to 4FH
This command loads the column address register.
A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 Column Address
0000000 0
0000001 1
1001111 79
Read Status
::
::
0 RD WR D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
A
0 0 1 BUSY ADC ON/OFF RESET 0000
Reading the command I/O register (A0=0) yields system status information.
• The busy bit indicates whether the driver will accept a command or not.
Busy=1: The driver is currently executing a command or is resetting. No new command will be accepted.
Busy=0: The driver will accept a new command.
• The ADC bit indicates the way column addresses are assigned to segment drivers.
ADC=1: Normal. Column address n → segment driver n.
ADC=0: Inverted. Column address 79-u → segment driver u.
• The ON/OFF bit indicates the current status of the display.
It is the inverse of the polarity of the display ON/OFF command.
ON/OFF=1: Display OFF
ON/OFF=0: Display ON
• The RESET bit indicates whether the driver is executing a hardware or software reset or if it is in normal operating mode.
RESET=1: Currently executing reset command.
RESET=0: Normal operation
Write Display Data
R/W
R/W
0 RD WR D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
A
1 1 0 Write data
Writes 8-bits of data into the display data RAM, at a location specified by the contents of the column address and page
address registers and then increments the column address register by one.
2–16 EPSON
Page 26

SED1520 Series
Read Display Data
R/W
0 RD WR D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
A
1 0 1 Read data
Reads 8-bits of data from the data I/O latch, updates the contents of the I/O latch with display data from the display data
RAM location specified by the contents of the column address and page address registers and then increments the column
address register.
After loading a new address into the column address register one dummy read is required before valid data is obtained.
Select ADC
0 RD WR D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
A
0101010000DA0H, A1H
This command selects the relationship between display data RAM column addresses and segment drivers.
D=1: SEG0 ← column address 4FH, … (inverted)
D=0: SEG0 ← column address 00H, … (normal)
This command is provided to reduce restrictions on the placement of driver ICs and routing of traces during printed circuit
board design. See Figure 2 for a table of segments and column addresses for the two values of D.
Static Drive ON/OFF
R/W
Series
SED1520
0 RD WR D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
A
0101010010DA4H, A5H
Forces display on and all common outputs to be selected.
D=1: Static drive on
D=0: Static drive off
Select Duty
R/W
R/W
0 RD WR D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
A
0101010100DA8H, A9H
This command sets the duty cycle of the LCD drive and is only valid for the SED1520F and SED1522F. It is invalid for
the SED1521F which performs passive operation. The duty cycle of the SED1521F is determined by the externally
generated FR signal.
SED1520 SED1522
D=1: 1/32 duty cycle 1/16 duty cycle
D=0: 1/16 duty cycle 1/8 duty cycle
When using the SED1520F
0A, SED1522F0A (having a built-in oscillator) and the SED1521F0A continuously, set the duty
as follows:
SED1521F0A
SED1520F0A 1/32 1/32
1/16 1/16
SED1522F
0A 1/16 1/32
1/8 1/16
EPSON 2–17
Page 27

SED1520 Series
Read-Modify-Write
R/W
0 RD WR D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
A
01011100000E0H
This command defeats column address register auto-increment after data reads. The current conetents of the column
address register are saved. This mode remains active until an End command is received.
• Operation sequence during cursor display
When the End command is entered, the column address is returned to the one used during input of Read-Modify-Write
command. This function can reduce the load of MPU when data change is repeated at a specific display area (such as cursor
blinking).
* Any command other than Data Read or Write can be used in the Read-Modify-Write mode. However, the Column
Address Set command cannot be used.
Set Page Address
Set Column Address
Read-Modify-Write
Dummy Read
Read Data
Write Data
No
Completed?
Yes
End
End
R/W
0 RD WR D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
A
01011101110EEH
This command cancels read-modify-write mode and restores the contents of the column address register to their value prior
to the receipt of the Read-Modify-Write command.
Return
Column address
N N+1 N+2 N+3 N+m N
Read-Modify-Write mode is selected. End
2–18 EPSON
Page 28

Reset
SED1520 Series
0 RD WR D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
A
01011100010E2H
This command clears
• the display start line register.
• and set page address register to 3 page.
It does not affect the contents of the display data RAM.
When the power supply is turned on, a Reset signal is entered in the RES pin. The Reset command cannot be used instead
of this Reset signal.
Power Save (Combination command)
The Power Save mode is selected if the static drive is turned ON when the display is OFF. The current consumption can
be reduced to almost the static current level. In the Power Save mode:
R/W
(a) The LCD drive is stopped, and the segment and common driver outputs are set to the V
DD level.
(b) The external oscillation clock input is inhibited, and the OSC2 is set to the floating mode.
(c) The display and operation modes are kept.
The Power Save mode is released when the display is turned ON or when the static drive is turned OFF. If the LCD drive
voltage is supplied from an external resistance divider circuit, the current passing through this resistor must be cut by the
Power Save signal.
V
DD
V
DD
V
1
V
2
V
3
SED1520
SED1522
Series
SED1520
V
4
V
5
Power Save signal
V
SSH
If the LCD drive power is generated by resistance division, the resistance and capacitance are determined by the LCD panel
size. After the panel size has been determined, reduce the resistance to the level where the display quality is not affected
and reduce the power consumption using the divider resistor.
EPSON 2–19
Page 29

SED1520 Series
SPECIFICATIONS
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Symbol Rating Unit
Supply voltage (1) V
Supply voltage (2) V
Supply voltage (3) V
Input voltage V
Output voltage V
Power dissipation P
Operating temperature T
Storage temperature T
Soldering temperature time at lead T
Notes: 1. All voltages are specified relative to V
2. The following relation must be always hold
DD ≥ V1 ≥ V2 ≥ V3 ≥ V4 ≥ V5
V
3. Exceeding the absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. Functional
operation under these conditions is not implied.
4. Moisture resistance of flat packages can be reduced by the soldering process, so care should be taken to
avoid thermally stressing the package during board assembly.
1, V4, V2, V3 V5 to +0.3 V
DD = 0 V.
SS –8.0 to +0.3 V
5 –16.5 to +0.3 V
IN VSS–0.3 to +0.3 V
O VSS–0.3 to +0.3 V
D 250 mW
opr –40 to +85 deg. C
stg –65 to +150 deg. C
sol 260, 10 deg. C, sec
Electrical Specifications
DC Characteristics
Ta = –20 to 75 deg. C, V
Parameter Symbol Condition Unit Applicable Pin
Operating Recommended –5.5 –5.0 –4.5
voltage (1) V
See note 1. Allowable –7.0 — –2.4
Recommended –13.0 — –3.5 V5
Operating Allowable –13.0 — — See note 10.
voltage (2) Allowable V1, V2 0.6×V5 —VDD VV1, V2
Allowable V3, V4 V5 — 0.4×V5 VV3, V4
High-level input voltage
Low-level input voltage
High-level output voltage
2–20 EPSON
DD = 0 V unless stated otherwise
Rating
Min. Typ. Max.
SS VVSS
V5 V
VIHT VSS+2.0 — VDD
IHC 0.2×VSS —VDD
V
IHT VSS = –3 V 0.2×VSS —VDD
V
IHC VSS = –3 V 0.2×VSS —VDD
V
ILT VSS VSS+0.8
V
ILC VSS 0.8×VSS
V
ILT VSS = –3 V VSS 0.85×VSS
V
ILC VSS = –3 V VSS 0.8×VSS
V
VOHT IOH = –3.0 mA VSS+2.4 — —
OHC1 IOH = –2.0 mA VSS+2.4 — — V
V
OHC2 IOH = –120 µA 0.2×VSS ——
V
OHT VSS = –3 V IOH = –2 mA 0.2×VSS
V
OHC1 VSS = –3 V IOH = –2 mA 0.2×VSS V
V
OHC2 VSS = –3 V IOH = –50 µA 0.2×VSS
V
See note 2 & 3.
See note 2 & 3.
V
See note 2 & 3.
See note 2 & 3.
OSC2
See note 4 & 5.
See note 4 & 5.
OSC2
(continued)
Page 30

SED1520 Series
DC Characteristics (Cont’d)
Ta = –20 to 75 deg. C, V
Parameter Symbol Condition Unit Applicable Pin
Low-level output voltage
Input leakage current ILI –1.0 — 1.0 µA See note 6.
Output leakage current I
LCD driver ON resistance R
DD = 0 V unless stated otherwise
Rating
Min. Typ. Max.
OLT IOL = 3.0 mA — — VSS+0.4
V
OLC1 IOL = 2.0 mA — — VSS+0.4 V
V
OLC2 IOL = 120 µA — — 0.8×VSS
V
OLT VSS = –3 V IOL = 2 mA 0.8×VSS
V
OLC1 VSS = –3 V IOL = 2 mA 0.8×VSS V
V
OLC2 VSS = –3 V IOL = 50 µA 0.8×VSS
V
LO –3.0 — 3.0 µA See note 7.
V5 = –5.0 V — 5.0 7.5 SEG0 to 79,
ON Ta = 25 deg. C kΩ COM0 to 15,
V
5 = –3.5 V — 10.0 50.0 See note 11
OSC2
See note 4 & 5.
See note 4 & 5.
OSC2
Series
SED1520
Static current dissipation IDDQ
I
Dynamic current dissipation V5 = –5 V µA
DD (1)
CS
= CL = VDD — 0.05 1.0 µAVDD
During display
5 = –5.0 V
V
During display f
SS = –3 V Rf = 1 MΩ 6.0 12.0
V
fCL = 2 kHz — 2.0 5.0 VDD
f = 1 MΩ — 9.5 15.0 µA See note 12,
R
CL = 18 kHz — 5.0 10.0 13 & 14.
f
CL = 2 kHz 1.5 4.5
DD
V
See note 12 & 13.
During access tcyc = 200 kHz — 300 500
I
DD (2) VSS = –3V, µA See note 8.
cyc = 200 kHz
15 18 21
11 16 21
Input pin capacitance C
Oscillation frequency f
During access t
IN Ta = 25 deg. C, f = 1 MHz — 5.0 8.0 pF All input pins
R
f = 1.0 MΩ ±2%,
SS = –5.0 V
V
OSC kHz See note 9.
f = 1.0 MΩ ±2%,
R
SS = –3.0 V
V
Reset time tR 1.0 — µS
150 300
RES
See note 15.
Notes: 1. Operation over the specified voltage range is guaranteed, except where the supply voltage changes
suddenly during CPU access.
2. A0, D0 to D7, E (or RD), R/W (or WR) and CS
3. CL, FR, M/S and RES
4. D0 to D7
5. FR
6. A0, E (or RD), R/W (or WR), CS, CL, M/S and RES
7. When D0 to D7 and FR are high impedance.
8. During continual write acess at a frequency of t
cyc. Current consumption during access is effectively
proportional to the access frequency.
9. See figure below for details
10. See figure below for details
11. For a voltage differential of 0.1 V between input (V
1, …, V4) and output (COM, SEG) pins. All voltages
within specified operating voltage range.
A
12. SED1520
stray and panel capacitances.
13. SED1520
capacitances.
14. SED1521
R (Reset time) represents the time from the RES signal edge to the completion of reset of the internal
15. t
and SED1521
*
*
0
and SED1522
*
*
0
only. Does not include transient currents due to stray and panel capacitances.
*
*
A
and SED1522
*
*
0
only. Does not include transient currents due to stray and panel
*
*
A
only. Does not include transient currents due to
*
*
circuit. Therefore, the SED1520 series enters the normal operation status after this tR.
EPSON 2–21
Page 31

SED1520 Series
Relationship between fOSC, fFR and Rf, and operating bounds on VSS and V5
*9 • Relationship between oscillation frequency, frames and Rf
(SED1520F0A), (SED1522F0A)
OSC1
Rf
OSC2
40
Ta=25°C V =-5V
SS
200
Same for 1/16 and 1/32 duties
Ta=25°C V =-5V
SS
30
[kHz]fosc
20
10
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
V =-3V
SS
V =-5V
SS
Rf [M ]Ω
Figure 5 (a) Figure 5 (b)
• Relationship between external clocks (f
(SED1520F
AA) , (SED1522FAA)
200
[Hz]Frame
100
0123
CL) and frames
f CL [kHz]
Figure 5 (c)
[Hz]Frame
100
SED1520
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
SED1522
[M ]ΩRf
duty1/32
duty1/16
duty1/8
*10 • Operating voltage range of V
SS and V5 systems
–15
–10
(V)
Operating voltage
5
–5
V
0 –2–4–6–8
V
SS
Figure 6
2–22 EPSON
range
(V)
Page 32

AC Characteristics
• MPU Bus Read/Write I (80-family MPU)
A0,CS
t
WR,RD
D0 to D7
(WRITE)
D0 to D7
(READ)
AW8
t
f
t
ACC8
t
t
CYC8
CC
t
DS8
Ta = –20 to 75 deg. C, VSS = –5.0 V ±10% unless stated otherwise
SED1520 Series
t
AH8
t
r
t
DH8
t
OH8
Series
SED1520
Parameter Symbol Condition Unit Signal
Rating
Min. Max.
Address hold time tAH8 10 — ns
Address setup time t
System cycle time t
Control pulsewidth t
Data setup time t
Data hold time t
RD access time t
Output disable time t
Rise and fall time t
SS = –2.7 to –4.5 V, Ta = –20 to +75°C)
(V
Parameter Symbol Condition Unit Signal
Address hold time t
Address setup time t
System cycle time t
Control pulse width t
Data setup time t
Data hold time t
RD access time t
Output disable time t
Rise and fall time t
AW8 20 — ns
CYC8 1000 — ns
CC 200 — ns
DS8 80 — ns
DH8 10 — ns
ACC8 —90ns
CH8 10 60 ns
r, tf — — 15 ns —
L = 100 pF
C
Rating
Min. Max.
AH8 20 — ns
AW8 40 — ns
CYC8 2000 — ns
CC 400 — ns
DS8 160 — ns
DH8 20 — ns
ACC8 — 180 ns
CH8 20 120 ns
r, tf — — 15 ns —
— A0, CS
— WR, RD
—
L = 100 pF
C
A0, CS
WR, RD
D0 to D7
D0 to D7
EPSON 2–23
Page 33

SED1520 Series
• MPU Bus Read/Write II (68-family MPU)
E
R/W
A0,CS
D0 to D7
(WRITE)
D0 to D7
(READ)
t
CYC6
t
EW
t
r
t
t
AW6
t
ACC6
DS6
t
f
t
AH6
t
DH6
t
OH6
Ta = –20 to 75 deg. C, VSS = –5 V ±10 unless stated otherwise
Parameter Symbol Condition Unit Signal
System cycle time t
Address setup time t
Address hold time t
Data setup time t
Data hold time t
Output disable time t
Access time t
Enable Read 100 — ns
pulsewidth Write 80 — ns
CYC6 1000 — ns
AW6 20 — ns A0, CS, R/W
AH6 10 — ns
DS6 80 — ns
DH6 10 — ns
OH6 10 60 ns
ACC6 —90ns
L = 100 pF
C
tEW E
Rating
Min. Max.
D0 to D7
Rise and fall time tr, tf — — 15 ns —
SS = –2.7 to – 4.5 V, Ta = –20 to +75°C)
(V
Parameter Symbol Condition Unit Signal
System cycle time
*1
Address setup time t
Address hold time t
Data setup time t
Data hold time t
Output disable time t
Access time t
Enable Read 200 — ns
pulse width Write 160 — ns
tCYC6 — 2000 — ns
AW6 40 — ns A0, CS, R/W
AH6 20 — ns
DS6 160 — ns
DH6 20 — ns
OH6 20 120 ns
ACC6 — 180 ns
—
—
L = 100 pF
C
tEW —E
Rating
Min. Max.
D0 to D7
Rise and fall time tr, tf — — 15 ns —
Notes: 1. t
CYC6 is the cycle time of CS. E = H, not the cycle time of E.
2–24 EPSON
Page 34

• Display Control Signal Timing
SED1520 Series
CL
FR
t
WLCL
t
DFR
t
WHCL
t f
t r
Input
Ta = –20 to 75 deg. C, V
Parameter Symbol Condition Unit Signal
Low-level pulsewidth t
High-level pulsewidth t
Rise time t
Fall time t
FR delay time t
SS = –5.0 V ±10% unless stated otherwise
Rating
Min. Typ. Max.
WLCL 35 — — µs
WHCL 35 — — µs
r — 30 150 ns
f — 30 150 ns
DFR –2.0 0.2 2.0 µsFR
VSS = –2.7 to –4.5 V, Ta = –20 to +75°C
Parameter Symbol Condition Unit Signal
Low-level pulse width t
High-level pulse width t
Rise time t
Fall time t
FR delay time t
Note: The listed input t
WLCL —70——µs
WHCL —70——µs
r — — 60 300 ns
f — — 60 300 ns
DFR — –4.0 0.4 4.0 µsFR
DFR applies to the SED1520 and SED1521 and SED1522 in slave mode.
Rating
Min. Typ. Max.
CL
CL
Series
SED1520
Output
Ta = –20 to 75 deg. C, VSS = –5.0 V ±10% unless stated otherwise
Parameter Symbol Condition Unit Signal
FR delay time t
DFR CL = 100 pF — 0.2 0.4 µsFR
Rating
Min. Typ. Max.
VSS = –2.7 to –4.5 V, Ta = –20 to +75°C
Parameter Symbol Condition Unit Signal
FR delay time t
Notes: 1. The listed output t
DFR CL = 100 pF — 0.4 0.8 µsFR
DFR applies to the SED1520 and SED1522 in master mode.
Rating
Min. Typ. Max.
EPSON 2–25
Page 35

SED1520 Series
APPLICATION NOTES
MPU Interface Configuration
80 Family MPU
V
CC
A0
A1 to A7
D0 to D7
GND
IOQR
RD
WR
RES
MPU
Decoder
RESET
A0
CS
SED1520F
D0 to D7
RD
WR
RES
V
SS
V
DD
AA
V
5
2–26 EPSON
Page 36

LCD Drive Interface Configuration
SED1520F0A–SED1520F0A
SED1522F0A–SED1522F0A
SED1520 Series
To LCD COM
V
DD
M/S
OSC1 OSC2 FR OSC1 OSC2 FR
SED1520FAA–SED1520FAA
SED1522FAA–SED1522FAA
To LCD COM
DD
V
M/S
To LCD SEG
0A
SED1520F
Master Slave
R
f
To LCD SEG
SED1520F
AA
Master
CL FR CL FR
To LCD SEG
SED1520F
To LCD SEG
SED1520F
Slave
0A
M/S
AA
M/S
To LCD COM
V
SS
To LCD COM
V
SS
Series
SED1520
SED1520F0A
SED1522F
0A
External clock
)–SED1521F0A (See note 1)
To LCD SEG
To LCD COM
V
DD
SED1520F
M/S
Master Slave
OSC1 OSC2 FR OSC1 OSC2 FR
Rf
To LCD SEG
0A SED1521F0A
*2
EPSON 2–27
Page 37

SED1520 Series
SED1520FAA–SED1521FAA
To LCD SEG
To LCD COM
DD
V
M/S
SED1520F
AA
CL FR CL FR
External clock
Notes: 1. The duty cycle of the slave must be the same as that for the master.
2. If a system has two or more slave drivers a CMOS buffer will be required.
To LCD SEG
SED1521F
AA
2–28 EPSON
Page 38

SED1520 Series
LCD Panel Wiring Example (The full-dot LCD panel displays a character in 6
1/16 duty:
• 10 characters × 2 lines
1
LCD 16×61
16
161
SEG
SED1520F
LCD 16×141
1/16 duty:
• 23 characters × 2 lines
COM
1
16162 141
16
SEG SEG
COM
SED1520F SED1521F
××
×8 dots.)
××
Series
SED1520
1/32 duty:
• 33 characters × 4 lines
1
16
16162 141 142 202
SEG SEG SEG
COM
SED1520F SED1521F SED1520F
LCD 32×202
*
17
32
COM
* The SED1521F can be omitted (the 32×122-dot display mode is selected).
Note: A combination of AB or AA type chip (that uses internal clocks) and 0B or 0A type chip (that uses external
clocks) is NOT allowed.
EPSON 2–29
Page 39

SED1520 Series
Package Dimensions
• Plastic QFP5–100 pin
Dimensions: inches (mm)
± 0.016
1.008
± 0.4
(25.6
)
± 0.004
± 0.1
(20
0.787
)
80 51
• Plastic QFP15–100 pin
81
Index
100 31
± 0.004
0.026
0.630
0.551
(0.65
± 0.016
± 0.004
± 0.1
)
(16.0
(14.0
± 0.4
± 0.1
30
± 0.004
0.012
± 0.1
(0.30
)
0.110
(2.8)
)
)
51
± 0.002
0.006
)
± 0.05
(0.15
± 0.004
0.106
± 0.1
)
(2.7
1
75
50
± 0.004
0.551
0.059
(1.5
)
± 0.1
(14
± 0.012
± 0.3
± 0.4
± 0.016
0~12°
)
)
(19.6
0.772
Index
1
)
± 0.002
0.005
± 0.05
± 0.004
± 0.1
)
(1.4
0.055
0.020
(0.5
± 0.004
± 0.1
(0.127
± 0.004
0.007
(0.18
)
2–30 EPSON
± 0.1
5076
)
)
± 0.4
± 0.1
(16.0
(14.0
± 0.016
± 0.004
0.630
0.551
26100
25
)
0~12°
± 0.004
0.020
0.039(1.0)
(0.5
± 0.2
)
Page 40

Output terminal pattern shape
SED1520 Series
Specifications
• Base: U-rexS, 75µm
• Copper foil: Electrolytic copper foil, 35µm
• Sn plating
• Product pitch: 81P (28.5mm)
• Solder resist positional tolerance: ±0.3
Series
SED1520
Punching
hole for
(Mold, marking area)
(Mold, marking area)
good
product
EPSON 2–31
 Loading...
Loading...