Page 1
10" Professional
RS830
Radial Arm Saw
Professionnelle de
254 mm (10 po)
Scie à bras radial
Profesional de
254 mm (10 pulg.)
Sierra de brazo
radial.
A18640 - 4-17-08 Rev. A
Copyright © 2006, 2008 Delta Machinery
Instruction Manual
Manuel d’Utilisation
Manual de Instrucciones
FRANÇAIS (30) ESPAÑOL (58)
www.deltaportercable.com
(800) 223-7278 - US
(800) 463-3582 - CANADA
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS ........................ 2
SAFETY GUIDELINES - DEFINITIONS ......................... 2
GENERAL SAFETY RULES ........................................... 3
ADDITIONAL SPECIFIC SAFETY RULES .................... 6
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION .......................................7
CARTON CONTENTS ...................................................8
ASSEMBLY ..................................................................... 9
OPERATION ................................................................... 18
TROUBLESHOOTING .................................................... 26
MAINTENANCE .............................................................. 26
SERVICE ......................................................................... 28
ACCESSORIES ............................................................... 28
WARRANTY .................................................................... 28
FRANÇAIS ...................................................................... 30
ESPAÑOL ........................................................................ 58
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
Read all warnings and operating instructions before using any tool or equipment. When
using tools or equipment, basic safety precautions should always be followed to reduce the risk of
personal injury. Improper operation, maintenance or modification of tools or equipment could result in
serious injury and property damage. There are certain applications for which tools and equipment are
designed. Delta Machinery strongly recommends that this product NOT be modified and/or used for any application
other than for which it was designed.
If you have any questions relative to its application DO NOT use the product until you have written Delta Machinery and
we have advised you. Contact us online at www.deltaportercable.com or by mail at Technical Service Manager, Delta
Machinery, 4825 Highway 45 North, Jackson, TN 38305. In Canada,125 Mural St. Suite 300, Richmond Hill, ON, L4B 1M4)
Information regarding the safe and proper operation of this tool is available from the following sources:
• PowerToolInstitute,1300 Sumner Avenue, Cleveland, OH 44115-2851or online at www.powertoolinstitute.org
• NationalSafetyCouncil, 1121 Spring Lake Drive, Itasca, IL 60143-3201
• AmericanNationalStandardsInstitute, 25 West 43rd Street, 4 floor, New York, NY 10036 www.ansi.org - ANSI 01.1
Safety Requirements for Woodworking Machines
• U.S.DepartmentofLabor regulations www.osha.gov
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS!
SAFETY GUIDELINES - DEFINITIONS
It is important for you to read and understand this manual. The information it contains relates to protecting YOUR SAFETY
and PREVENTING PROBLEMS. The symbols below are used to help you recognize this information.
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious
injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious
injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or moderate
injury.
Used without the safety alert symbol indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
may result in property damage.
Some dust created by power sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling, and other construction activities
contains chemicals known to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm.
Some examples of these chemicals are:
• leadfromlead-basedpaints,
• crystallinesilicafrombricksandcementandothermasonryproducts,and
• arsenicandchromiumfromchemically-treatedlumber.
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending on how often you do this type of work. To reduce your
exposure to these chemicals: work in a well ventilated area, and work with approved safety equipment, al ways
wear NIOSH/OSHA approved, properly fit ting face mask or res pi ra tor when us ing such tools.
2
Page 3
GENERAL SAFETY RULES
To reduce the risk of injury, read, understand, and follow the instruction manual before using any tool
or equipment. When using tools or equipment, basic safety precautions should always be followed to reduce the risk
of personal injury. Improper operation, maintenance, or modification of tools or equipment could result in serious
injury and property damage. There are certain applications for which tools and equipment are designed. There are
specific limitations and special hazards associated with each tool. Do not modify and/or use for any application other
than for which it was designed.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS!
GROUNDING INSTRUCTIONS
FOLLOW ALL WIRING CODES and recommended electrical connections to prevent shock or
electrocution.
If the saw is of grounded construction, read the following instructions.
SHOCK HAZARD. THIS MACHINE MUST BE GROUNDED WHILE IN USE. SERIOUS INJURY COULD
RESULT.
ALL GROUNDED, CORD-CONNECTED MACHINES
In the event of a malfunction or breakdown, grounding provides a path of least resistance for electric current to reduce
the risk of electric shock. This machine is equipped with an electric cord having an equipment-grounding conductor and
a grounding plug. The plug must be plugged into a matching outlet that is properly installed and grounded in accordance
with all local codes and ordinances. Do not modify the plug provided - if it will not fit the outlet, have the proper outlet
installed by a qualified electrician. Improper connection of the equipment-grounding conductor can result in risk of
electric shock. The conductor with insulation having an outer surface that is green with or without yellow stripes is the
equipment-grounding conductor. If repair or replacement of the electric cord or plug is necessary, do not connect the
equipment-grounding conductor to a live terminal. Check with a qualified electrician or service personnel if the grounding
instructions are not completely understood, or if in doubt as to whether the machine is properly grounded. Use only
three-wire extension cords that have three-prong grounding type plugs and matching three-conductor receptacles that
accept the machine's plug, as shown in Fig. A. Repair or replace damaged or worn cord immediately.
GROUNDED, CORD-CONNECTED MACHINES INTENDED FOR USE ON A SUPPLY CIRCUIT HAVING A NOMINAL
RATING LESS THAN 150 VOLTS
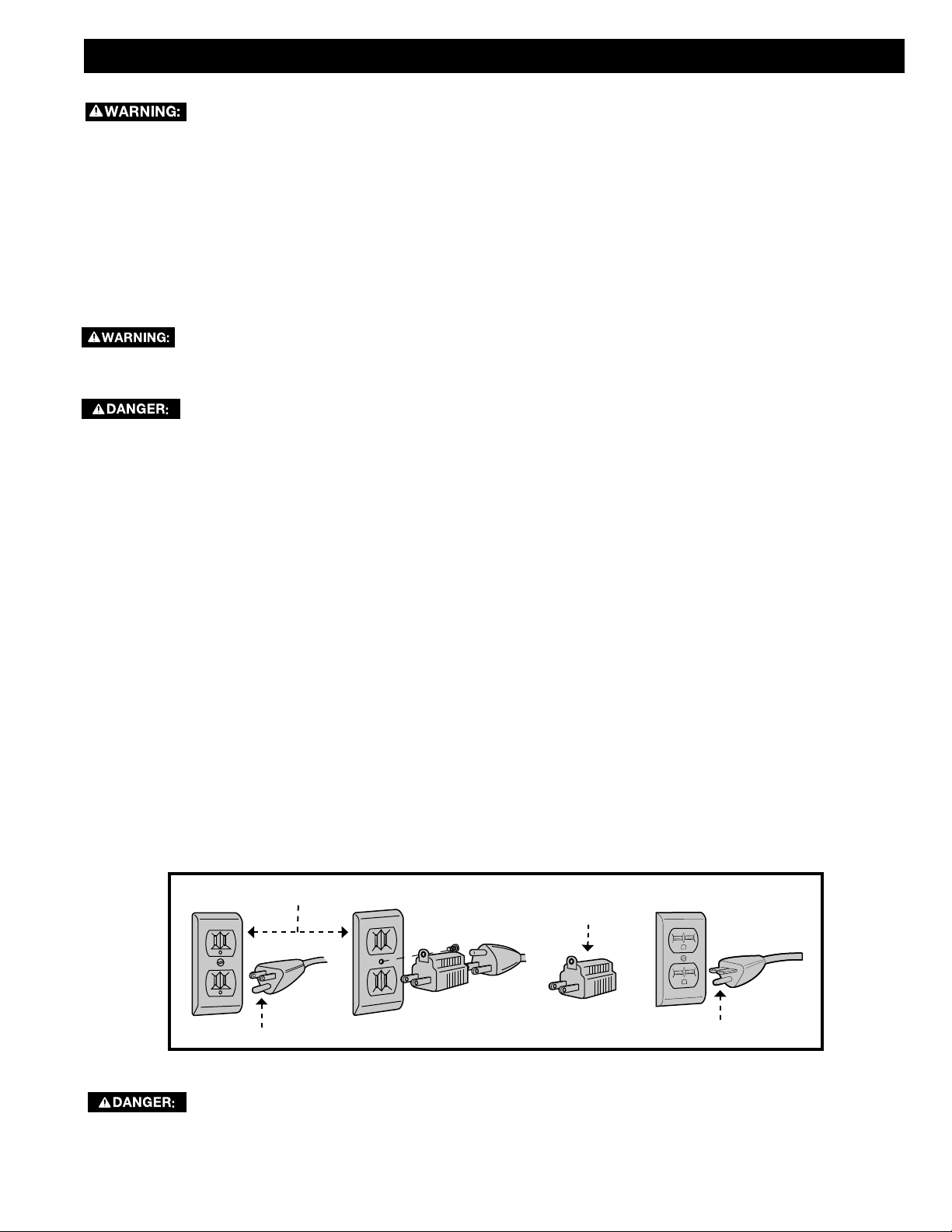
If the machine is intended for use on a circuit that has an outlet that looks like the one illustrated in Fig. A, the machine
will have a grounding plug that looks like the plug illustrated in Fig. A. A temporary adaptor, which looks like the adapter
illustrated in Fig. B may be used to connect this plug to a matching two-conductor receptacle as shown in Fig. B if a
properly grounded outlet is not available. The temporary adapter should be used only until a properly grounded outlet
can be installed by a qualified electrician. The green-colored rigid ear, lug, and the like, extending from the adapter must
be connected to a permanent ground such as a properly grounded outlet box. Whenever the adapter is used, it must
be held in place with a metal screw.
A B
Grounded Outlet
Grounding Pin
Box
C
Grounding
Means
Adapter
D
Grounding Pin
IN ALL CASES, MAKE CERTAIN THAT THE RECEPTACLE IN QUESTION IS PROPERLY GROUNDED.
iF YOU ARE NOT SURE, HAVE A QUALIFIED ELECTRICIAN CHECK THE RECEPTACLE.
3
Page 4
240 VOLT SINGLE PHASE OPERATION
The 120/240 volt, dual-voltage motor supplied with your
machine was shipped prepared for 120 volt operation. It
can be converted for 240 volt operation.
Use the following instructions to convert your saw to 240
volts.
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and
disconnect machine from power source before installing
and removing accessories, before adjusting or changing
set-ups or when making repairs. An accidental start-up
can cause injury.
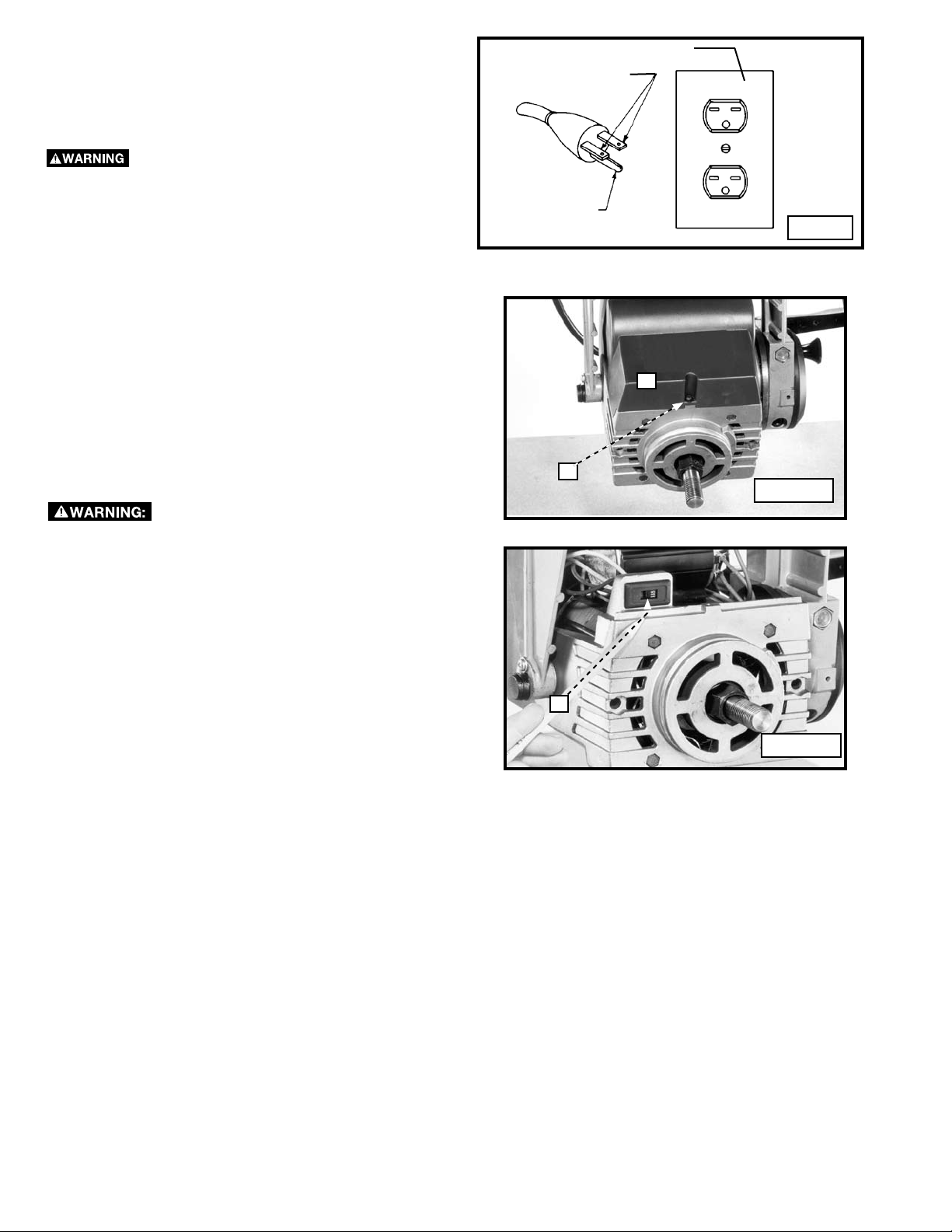
1. Remove the screw (A) Fig. D and remove the plastic
cover (B).
2. Carefully slide the switch (C) Fig. E in the motor
junction box to read 240 volts. Replace the plastic
cover and screw that were removed in STEP 1.
3. You must also replace the 120 volt plug with a UL/CSA
listed plug suitable for 240 volts and the rated current
of the saw.
Either use a qualified electrician to do the conversion, or
take the machine to an Authorized Delta Service Center.
The machine must conform to the National Electric Code
and all local codes and ordinances.
Use the 240 volt plug ONLY in an outlet that has the same
configuration as the plug illustrated in Fig. C. DO NOT use
an adapter with the 240 volt plug.
In all cases, make certain that the
receptacle in question is properly grounded. If you
are not sure, have a qualified electrician check the
receptacle.
GROUNDED OUTLET BOX
CURRENT
CARRYING
PRONGS
GROUNDING BLADE
IS LONGEST OF THE 3 BLADES.
B
A
Fig. C
Fig. D
C
Fig. E
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
1. TO REDUCE THE RISK OF KICKBACK AND OTHER INJURIES, KEEP GUARDS IN PLACE, and in working order.
2. REMOVE ADJUSTING KEYS AND WRENCHES. Form habit of checking to see that keys and adjusting wrenches are
removed from spindle before turning tool on. Tools, scrap pieces, and other debris can be thrown at high speed, causing
injury.
3. KEEP WORK AREA CLEAN. Cluttered areas and benches invite accidents.
4. DO NOT USE THE MACHINE IN A DANGEROUS ENVIRONMENT. The use of power tools in damp or wet locations
or in rain can cause shock or electrocution. Keep your work area well-lit to avoid tripping or placing arms, hands, and
fingers in danger.
4
Page 5

5. KEEP CHILDREN AWAY. All visitors should be kept at a safe distance from work area. Your shop is a potentially
dangerous environment.
6. MAKE WORKSHOP CHILDPROOF with padlocks, master switches, or by removing starter keys. The unauthorized
start-up of a machine by a child or visitor may result in injury.
7. DO NOT FORCE TOOL. It will do the job better and be safer at the rate for which it was designed.
8. USE RIGHT TOOL. Don't force tool or attachment to do a job for which it was not designed. Using the incorrect tool or
attachment may result in personal injury.
9. USE PROPER EXTENSION CORD. Make sure that your extension cord is in good condition. If your product is equipped
a cord set, use only three-wire extension cords that have three-prong grounding-type plugs, and three-pole receptacles
that accept the tool's plug. When using an extension cord, be sure to use one heavy enough to carry the current your
product will draw. An undersized cord will cause a drop in line voltage, resulting in loss of power and overheating. The
following table shows the correct size to use depending on cord length and nameplate ampere rating. If in doubt, use
the next heavier gauge. The smaller the gauge number, the heavier the cord.
MINIMUM GAUGE FOR CORD SETS
Volts Total Length of Cord in Feet
120V
240V
0-25
0-50
26-50
51-100
51-100
101-200
101-150
201-300
Ampere Rating
More
Than
Not More
Than
0 - 6
6 - 10
10 - 12
12 - 16
18
18
16
14
AWG
16
16
16
12
16
14
14
Not Recommended
14
12
12
10. WEAR PROPER APPAREL. No loose clothing, gloves, neckties, rings, bracelets, or other jewelry to get caught in
moving parts. Non-slip footwear is recommended. Wear protective hair covering to contain long hair. Air vents may
cover moving parts and should also be avoided.
11. ALWAYS USE SAFETY GLASSES. Everyday glasses are NOT safety glasses. Also use face or dust mask if cutting
operation is dusty. ALWAYS wear certified safety equipment:
l ANSI A87.1 eye protection (CAN/CSA Z94.3)
l ANSI S12.6 (S3.19) hearing protection
l NIOSH/OSHA respiratory protection
12. DO NOT OVERREACH. Keep proper footing and balance at all times. Loss of balance may cause personal injury.
13. MAINTAIN TOOLS WITH CARE. Keep blades sharp and clean for best and safest performance. Follow instructions
for lubricating and changing accessories. Poorly maintained blades and machines can further damage the blade or
machine and/or cause injury.
14. TURN THE MACHINE "OFF" AND DISCONNECT THE MACHINE FROM THE POWER SOURCE before installing or
removing accessories, before adjusting or changing set-ups, when making repairs or changing locations. Do not touch
the plug's metal prongs when unplugging or plugging in the cord. An accidental start-up can cause injury.
15. REDUCE THE RISK OF UNINTENTIONAL STARTING. Make sure that the switch is in the "OFF" position before
plugging in the power cord. In the event of a power failure, move the switch to the "OFF" position. An accidental startup can cause injury.
16 USE RECOMMENDED ACCESSORIES. Use only accessories that are recommended by the manufacturer for
your model. Accessories that may be suitable for one tool may be hazardous when used on another tool. Consult
the instruction manual for recommended accessories. The use of improper accessories may cause risk of injury to
persons.
17. NEVER STAND ON THE TOOL. Serious injury could occur if the tool is tipped or if the cutting tool is unintentionally
contacted.
18. CHECK FOR DAMAGED PARTS. Before further use of the tool, a guard or other part that is damaged should be
carefully checked to determine that it will operate properly and perform its intended function. Check for alignment
of moving parts, binding of moving parts, breakage of parts, mounting, and any other conditions that may affect its
operation. A guard or other part that is damaged should be properly repaired or replaced. Do not use tool if switch does
not turn it on and off. Damaged parts can cause further damage to the machine and/or personal injury.
19. DIRECTION OF FEED. Feed work into a blade or cutter against the direction of rotation of the blade or cutter only.
20. NEVER LEAVE THE TOOL RUNNING UNATTENDED. TURN THE POWER OFF. Don't leave tool until it comes to a
complete stop. Serious injury can result.
21. DO NOT OPERATE ELECTRIC TOOLS NEAR FLAMMABLE LIQUIDS OR IN GASEOUS OR EXPLOSIVE
ATMOSPHERES. Motors and switches in these tools may spark and ignite fumes.
22. STAY ALERT, WATCH WHAT YOU ARE DOING, AND USE COMMON SENSE. DO NOT USE THE MACHINE WHEN
YOU ARE TIRED OR UNDER THE INFLUENCE OF DRUGS, ALCOHOL, OR MEDICATION. A moment of inattention
while operating power tools may result in serious injury.
23. DO NOT ALLOW FAMILIARITY (gained from frequent use of your saw) TO REPLACE SAFETY RULES. Always
remember that a careless fraction of a second is sufficient to inflict severe injury.
5
Page 6

ADDITIONAL SPECIFIC SAFETY RULES
Failure to follow these rules may result in serious personal injury.
1. ALWAYS USE SAFETY GLASSES. Everyday glasses are NOT safety glasses. Also use face or dust mask if cutting
operation is dusty. ALWAYS wear certified safety equipment:
l ANSI A87.1 eye protection (CAN/CSA Z94.3)
l ANSI S12.6 (S3.19) hearing protection
l NIOSH/OSHA respiratory protection
2. AVOID AWKWARD POSITIONS where a sudden slip could cause a hand to move into a saw blade or other cutting
tool.
3. KEEP ARMS, HANDS, AND FINGERS AWAY from the blade to prevent serious injury.
4. USE A PUSH STICK OR PUSH BLOCK THAT IS APPROPRIATE TO THE APPLICATION TO PUSH WORKPIECES
THROUGH THE SAW. A push stick is a wooden or non-metallic stick, usually homemade that should be used whenever
the size or shape of the workpiece would cause you to place your hands within six inches of the blade.
5. DO NOT PERFORM RIPPING, CROSSCUTTING, OR ANY OTHER OPERATION FREEHAND.
6. NEVER reach around or over the saw blade.
7. STABILITY. Make sure that the radial arm saw is firmly mounted to a secure surface before use and does not move. If
the mobility kit is installed, raise the moveable caster(s) so that the saw is in its stationary position.
8. NEVER CUT FERROUS METALS (those with iron or steel content) or masonry. Damage to the saw and personal injury
may result.
9. USE THE CORRECT SAW BLADE FOR THE INTENDED OPERATION. Follow instructions in operation section of the
manual for proper procedure for any kind of cut. Always tighten the blade arbor nut securely. Before use, inspect the
blade for cracks or missing teeth. Do not use a damaged blade.
10. NEVER ATTEMPT TO FREE A STALLED SAW BLADE WITHOUT FIRST TURNING THE MACHINE OFF. If a
workpiece or cut-off piece becomes trapped inside the guard, turn the saw off, disconnect the machine from the power
source and wait for the blade to stop before lifting the guard and removing the piece.
11. NEVER START THE MACHINE with the workpiece against the blade to reduce the risk of a thrown workpiece and
personal injury.
12. NEVER run the workpiece between the fence and a molding cutterhead to reduce the risk of a thrown workpiece and
personal injury.
13. AVOID AWKWARD OPERATIONS AND HAND POSITIONS where a sudden slip could cause a hand to move into the
blade.
14. NEVER HAVE ANY PART OF YOUR BODY IN LINE WITH THE PATH OF THE SAW BLADE. Personal injury may
occur.
15. NEVER PERFORM LAYOUT, ASSEMBLY, OR SET-UP WORK on the table/work area when the machine is running. A
sudden slip could cause a hand to move into the blade. Severe injury can result.
16. CLEAN THE TABLE/WORK AREA BEFORE LEAVING THE MACHINE. Lock the switch in the "OFF" position to
prevent unauthorized use.
17. DO NOT LEAVE A LONG BOARD (OR OTHER WORKPIECE) UNSUPPORTED SO THE SPRING OF THE BOARD
CAUSES IT TO SHIFT ON THE TABLE RESULTING IN LOSS OF CONTROL AND POSSIBLE INJURY. Provide proper
support for the workpiece, based on its size and the type of operation to be performed. Hold the work firmly against
the fence and down against the table surface. If supports are attached to the saw, be certain that the saw will not tip
under the load.
18. DO NOT OPERATE THIS MACHINE until it is completely assembled and installed according to the instructions. A
machine incorrectly assembled can cause serious injury.
19. OBTAIN ADVICE from your supervisor, instructor, or another qualified person if you are not thoroughly familiar with the
operation of this machine. Knowledge is safety.
20. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION regarding the safe and proper operation of power tools (i.e. a safety video) is available
from the Power Tool Institute, 1300 Sunmer Avenue, Cleveland, OH 44115-2581 (www.powertoolinstitute.com).
Information is also available from the National Safety Council, 1121 Spring Lake Drive, Itasca, IL 60143-3201. Please
refer to the American National Standards Institute ANSI 01.1 Safety Requirements for Woodworking Machines and the
U.S. Department of Labor OSHA 1910.213 Regulations.
The lower retractable blade guard provides operator protection along the sides of the sawblade. To
reduce the risk of potential hazards, use the following rules:
a, KEEP YOUR HANDS AWAY FROM THE GUARD. As the blade cuts, the guard will lift and leave part of the blade
exposed.
b. TURN THE UNIT OFF AND DISCONNECT THE MACHINE FROM THE POWER SOURCE BEFORE FREEING A
JAMMED LOWER GUARD. The guard can get jammed in previous kerfs in the table or fence. Always anticipate the path
of the guard.
c. USE CAUTION when making bevel cuts to be sure that the lower guard is never pinched toward the blade.
d. THE LOWER GUARD CAN JAM AGAINST THE FENCE DURING NARROW IN-RIPS. Should the guard jam against the
fence, disconnect the saw from the power, wait for the blade to stop, then lift the blade guard and rest it on top of the
fence.
6
Page 7

TERMS: The following terms will be used throughout the manual and you should become familiar with them.
• Through-sawing refers to any cut that completely severs the work piece.
• Push Stick refers to a wooden stick, usually homemade, that is used to push small work piece through the saw and keeps
the operator’s hands clear of the blade.
• Kickback occurs when the saw blade binds in the cut and violently thrusts the work piece back toward the operator.
• Freehand refers to cutting without the use of a miter gauge or rip fence or any other means of guiding or holding the work
piece other than the operator’s hand.
SAW BLADE GUARD AND SPLITTER
Your radial arm saw is equipped with a blade guard, splitter and anti-kickback fingers. The splitter fits into the cut made by
the saw blade when ripping and effectively fights kickback by lessening the tendency of the blade to bind in the cut. Use the
spreader and blade guard for all cuts. Two anti-kickback pawls are located on the sides of the splitter that allow the wood to
pass through the blade in the cutting direction, but lock if the wood tries to move backward toward the operator.
KICKBACKS
How to avoid them and protect yourself from possible injury.
a. Be certain that the rip fence is parallel to the saw blade.
b. Do not rip by applying the feed force to the section of the workpiece that will become the cut-off (free) piece. Feed force
when ripping should always be applied between the saw blade and the fence. Use a push stick for short work, 6" (152
mm) wide or less.
c. Keep saw blade guard, splitter, and anti-kickback teeth in place and operating properly. Keep teeth sharp. If teeth are not
operational, return your unit to the nearest authorized Delta service center for repair. The splitter must be in alignment
with the saw blade and the teeth must stop a kickback once it has started. Check their action before ripping by pushing
the wood under the anti-kickback teeth. The teeth must prevent the wood from being pulled toward the front of the
saw.
d. Plastic and composition (like hardboard) materials may be cut on your saw. However, since these are usually quite hard
and slippery, the anti-kickback pawls may not stop a kickback. Therefore, be especially attentive to following proper
set-up and cutting procedures for ripping.
e. Use saw blade guard for every operation for which it can be used, including all through-sawing.
f. Push the workpiece past the saw blade prior to release when ripping.
g. NEVER rip a workpiece that is twisted or warped, or does not have a straight edge to guid along the fence.
h. NEVER saw a large workpiece that cannot be controlled.
i. NEVER saw a workpiece with loose knots, flaws, nails, or other foreign objects.
j. NEVER rip a workpiece shorter than 10".
k. Always use anti-kickback fingers when ripping. Lower the guard on the infeed end and adjust the anti-kickback
attachment properly.
Some dust created by power sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling, and other construction activities contains
chemicals know to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive harm. Some examples of
these are:
l Lead from Lead-based paints,
l Crystalline silica from bricks and cement and other masonry products, and
l arsenic and chromium from chemically-treated lumber (CCA).
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending on how often you do this type of work. To reduce your exposure to these
chemicals: work in a well-ventilated area, and work with approved safety equipment, such as those dust masks that are
specially designed to filter out microscopic particles.
l Avoid prolonged contact with dust from power sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling, and other construction activities.
Wear protective clothing and wash exposed areas with soap and water. Allowing dust to get into your mouth, eyes,
or lay on the skin may promote absorption of harmful chemicals.
Use of this tool can generate and/or disburse dust, which may cause serious and permanent respiratory or
other injury. Always use NIOSH/OSHA approved respiratory protection appropriate for the dust exposure. Direct particles
away from face and body. Always operated tool in a well-ventilated area and provide for proper dust removal. Use dust
collection system wherever possible.
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
FOREWORD
The Delta Model RS830 is a 10" (254mm) Professional Radial Arm Saw with a maximum cutting capacity of 16" (406mm)
crosscut, 2-3/4" (70mm) depth at 90°, and 2-1/2" (64mm) depth at 45° bevel. This tool has positive bevel stops at 0°, 45° and
90°, and positive miter stops at 0° and 45°, both right and left. The unit includes a 1-1/2 HP, 120/240V motor, an automatic
blade brake, a saw blade, wrenches, a steel stand, a cast-iron track, and an extra-large table.
NOTICE: The image on the manual cover illustrates the current production model. All other illustrations contained in the
manual are representative only and may not depict the actual labeling or accessories included. These are intended to illustrate
technique only.
7
Page 8
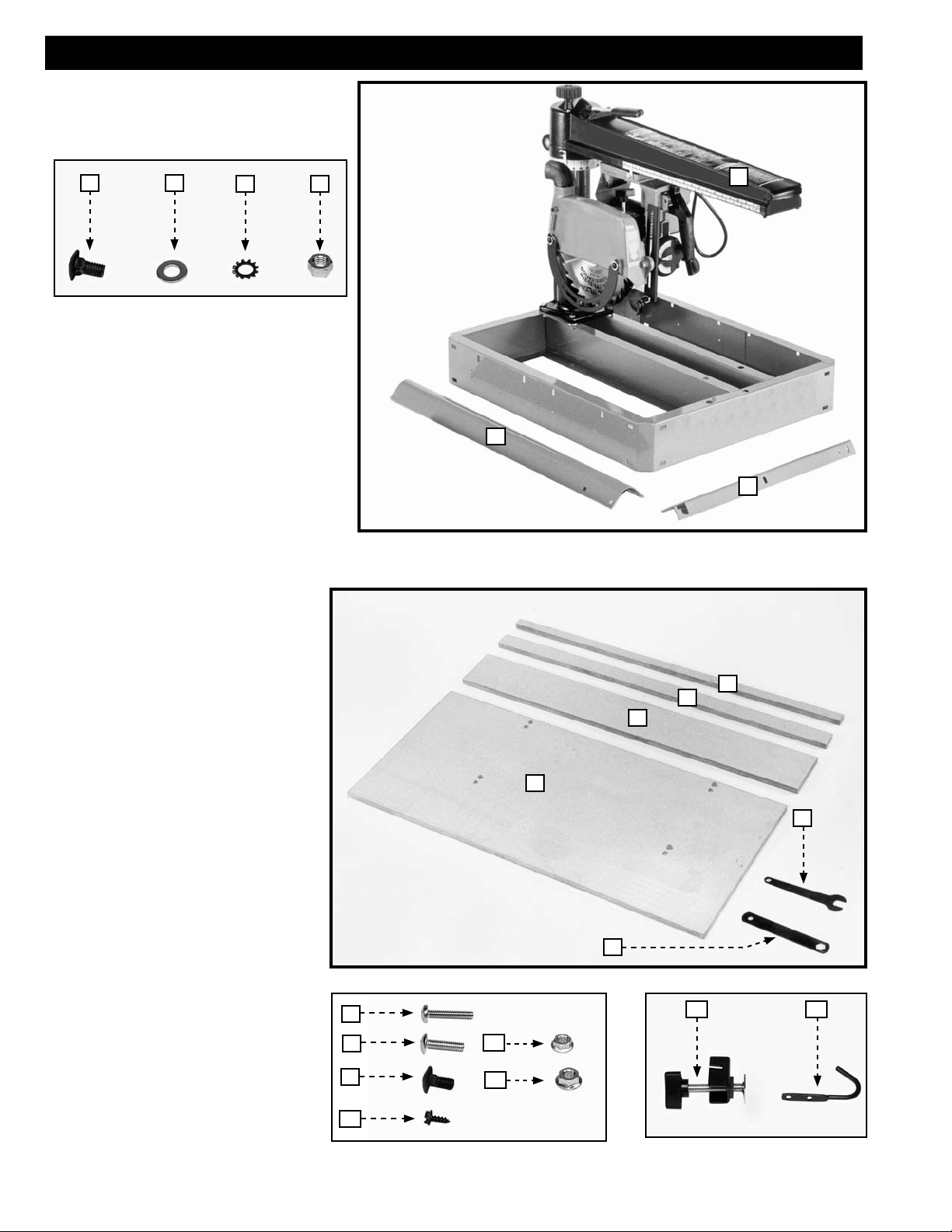
RADIAL ARM SAW PARTS
CARTON CONTENTS
4 5
1. Radial Arm Saw
2. Legs (4)
3. Table Supports (2)
4. 5/16-18x5/8" Carriage Head Screws (16)
5. 5/16" Flat Washers (16)
6. 5/16" External Tooth Lockwashers (16)
7. 5/16-18 Hex Nuts (16)
6 7
TABLE BOARD PARTS
1. Fence Board
1
2
3
2. Middle Table Board
3. Rear Table Board
4. Front Table Board
5. 7/8" Open End - 1/2" Box Wrench
6. 7/8" x 1/2" Box Wrench
7. 1/4-20x1¼" Round Head Screw (4)
8. 1/4-20x1" Round Head Screw (4)
9. 5/16-18x5/8" Carriage Head Screw
(6)
10. #10x1/2" Sheet Metal Screw (2)
11. 1/4-20 Flange Hex Nut (4)
12. 5/16-18 Flange Hex Nut (6)
13. Table Board Clamp (2)
14. Wrench Hook
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
12
13 14
10
8
Page 9
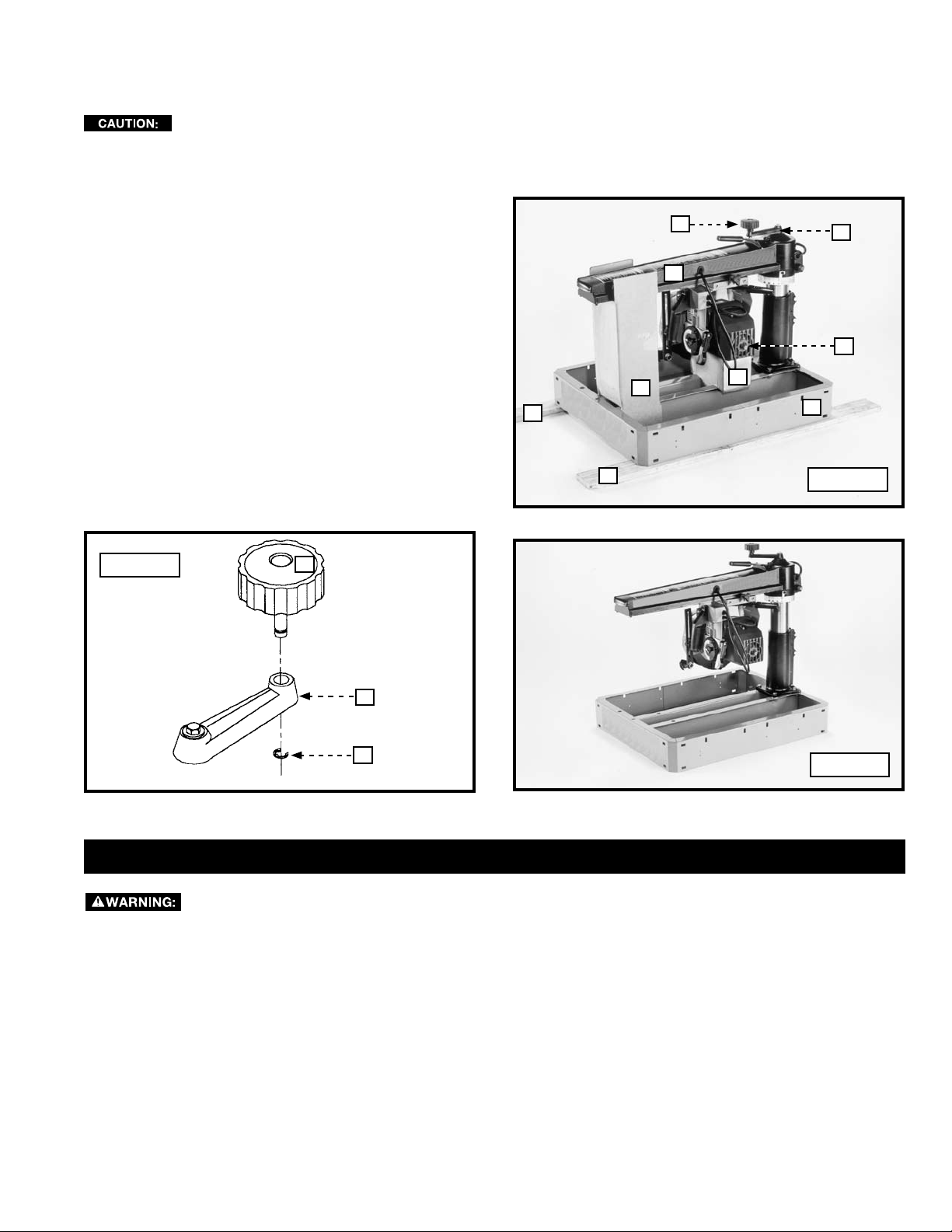
UNPACKING AND CLEANING
Carefully unpack the machine and all loose items from the shipping container(s). Remove the rust-preventative oil from
unpainted surfaces using a soft cloth moistened with mineral spirits, paint thinner or denatured alcohol.
Do not use highly volatile solvents such as gasoline, naphtha, acetone or lacquer thinner for cleaning your
machine.
After cleaning, cover the unpainted surfaces with a good quality household floor paste wax.
1. The saw was packed at the factory with support blocks
(A) Fig. A1 under the cutter-head (B) and the track arm
(C). Shipping boards (D) Fig. A1 were fastened to saw
base (G). To prevent damage during shipment, the
track arm elevating knob (H) was removed from the
lever (E). Insert the post of the knob (H) Fig. A2 through
the hole in the lever (E). Attach the E-ring (K) to the slot
in the post.
2. You can remove the support blocks (A) Fig. A1 by rotating
the track arm elevating knob (H) clockwise. Remove the
shipping boards (D) by taking out the hold-down screws
(not shown), located inside the saw base. Discard the
support blocks (A) and the shipping boards (D).
3 The saw with the support blocks and shipping boards
removed is illustrated in Fig. A3.
D
H
E
C
B
A
A
G
D
Fig. A2
H
E
K
ASSEMBLY
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and disconnect it from power source before installing and remov-
ing accessories, before adjusting or when making repairs. An accidental start-up can cause injury.
Fig. A1
Fig. A3
ASSEMBLY TOOLS REQUIRED
7/8" Open End - 1/2" Box Wrench (included)
7/8" x 1/2" Box Wrench (included)
1/2” and 3/8” Wrenches, Open End or Socket
Flathead Screwdriver
ASSEMBLY TIME ESTIMATE
Assembly for this machine takes approximately 2-3 hours.
9
Page 10
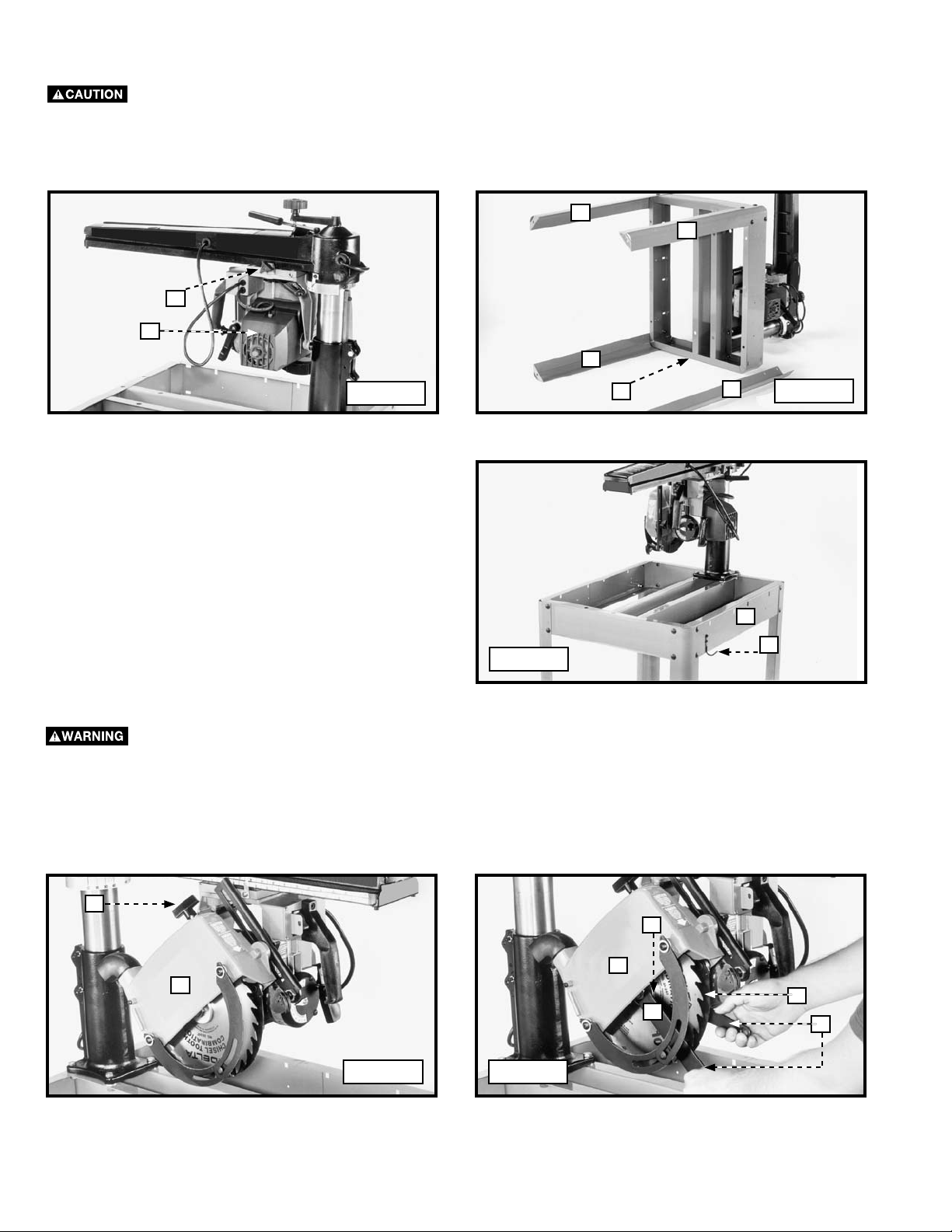
ATTACHING THE LEGS TO THE SAW BASE
1. Loosen the lock knob (A) Fig. 1, and move the cutting-head (B) to the rear position. Tighten the knob (A).
Clamp the cuttinghead at the back of the track arm securely.
2. Place the radial arm saw on its back. Use sixteen 5/16-18 x 5/8" carriage head screws to attach the legs (C) Fig. 2 (three of
which are shown attached) to each corner of saw base (D). Place the screws through the stand, then use a flat washer, a
lock washer, and a nut to secure them. Hand tighten the nuts.
3. Stand the saw in the upright position and securely tighten all stand hardware.
C
C
A
B
C
Fig. 1
D
C
Fig. 2
ATTACHING THE WRENCH HOOK
Attach the wrench hook (K) Fig. 3 to the front
right or back left side of saw base (D), using two
#10 x 1/2" sheet metal screws.
D
K
Fig. 3
REMOVING THE BLADE AND BLADE GUARD FROM THE SAW
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and disconnect machine from power source before installing and
removing accessories, before adjusting or changing set-ups or when making repairs. An accidental start-up can cause
injury.
1. Loosen the blade guard clamp knob (A) Fig. 4 and rotate the blade guard (B) to the position shown.
2. Use the wrenches (C) Fig. 5 to loosen the arbor nut (D).
NOTE: Arbor nut has left-hand threads.
A
F
B
B
G
D
C
Fig. 4
10
Fig. 5
Page 11
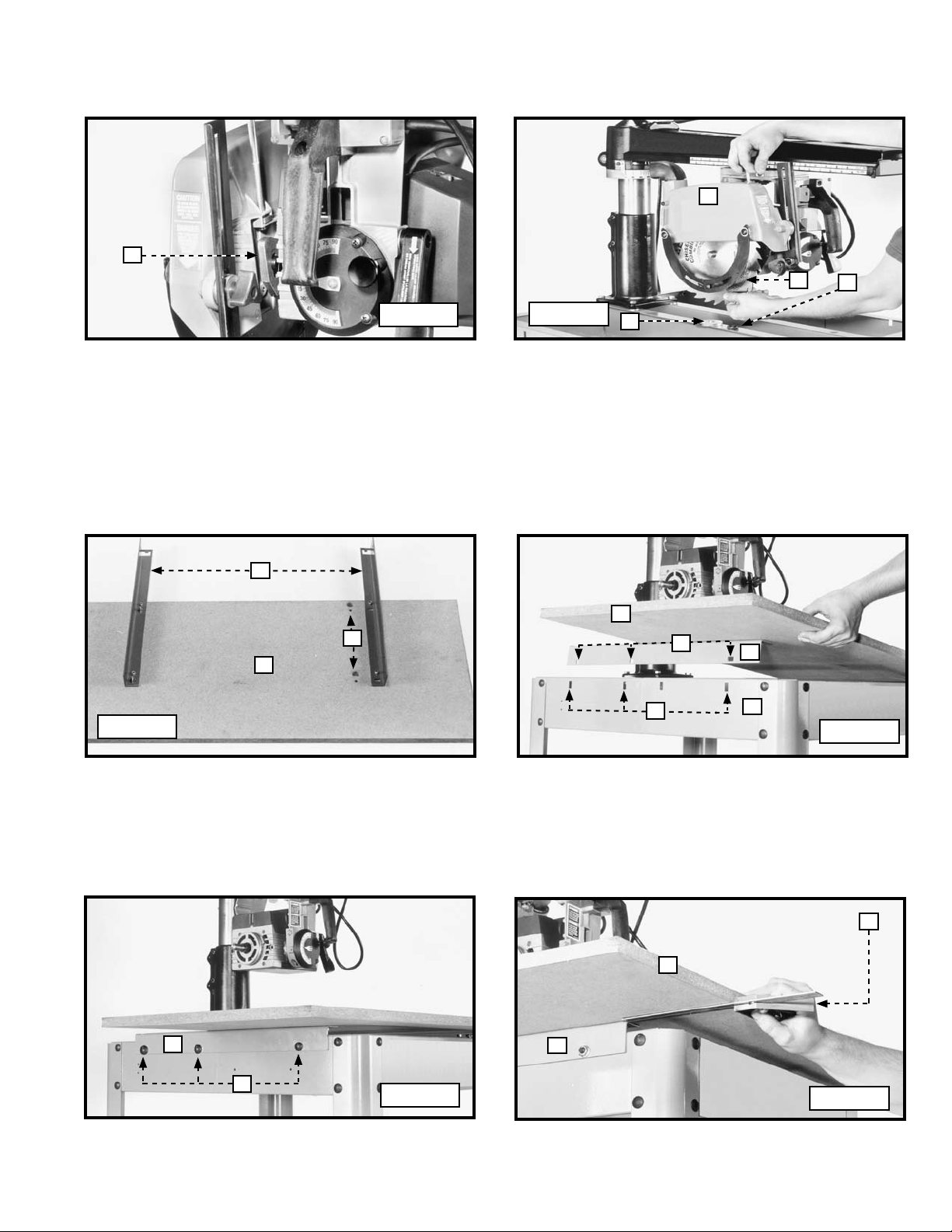
3. Lift the cam (E) Fig. 6 that holds the blade guard (B) Fig. 5 in position. Move the blade guard (B), the outer blade flange
(F), and the blade (G) out.
4. Lift the blade guard (B) Fig. 7. Remove the arbor nut (D), the outer blade flange (F), and the blade (G).
5. Remove the blade guard (B).
B
E
G
D
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
F
TABLE SUPPORTS
1. Place the front table board (A) Fig. 8 on a stable surface (counter-bored holes down) with one side of the board off the
edge of the surface to expose the counter-bored holes. Insert a 1/4-20 x 1" round head screw up through one of the
holes and a table support. Secure loosely with a 1/4-20 hex nut. Do the same with the other hole.
2. Follow the same procedure to attach the other table support.
3. Place the front table board (A) Fig. 9 on the saw base (G) so that table supports (B) straddle the outside of the saw base
(G) and three holes (H) in each table support (B) align with the three slots (J) in each side of saw base (G).
B
A
D
A
Fig. 8
H
J
B
G
Fig. 9
4. Secure the table supports (one of which is shown at(B) Fig. 10) to each side of the saw base using six 5/16-18 x 5/8"
carriage head screws (L) and six 5/16-18 flanged hex nuts. Loosely tighten the nuts for further adjustment.
IMPORTANT: Insert the screws through the table supports and the saw base from the outside.
5. Use a combination square (M) Fig. 11 to check the left and right front edge of table board (A). Both sides should be the
same distance from the edge of the table supports (B) Fig. 11.
M
A
B
L
Fig. 10
11
B
Fig. 11
Page 12
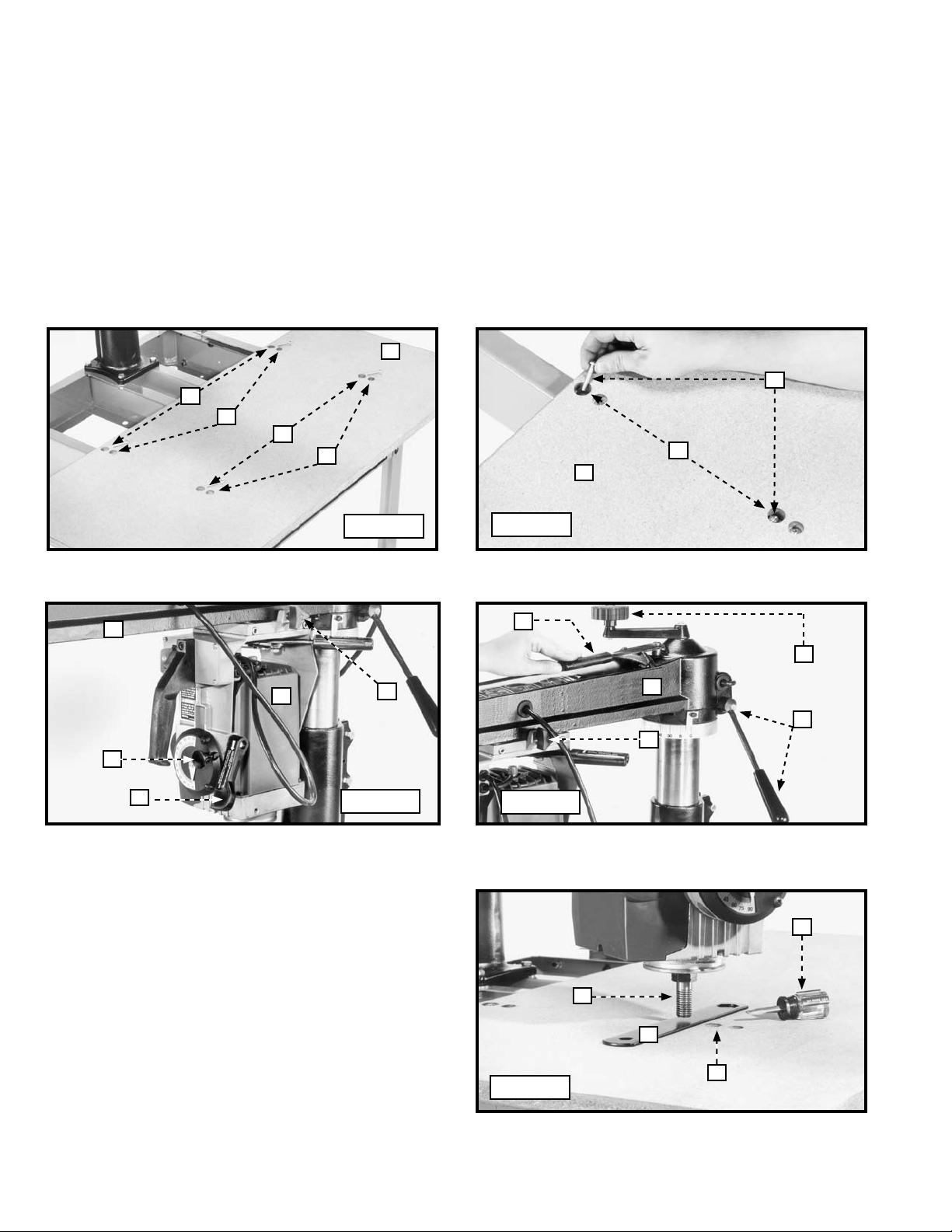
6. After adjusting, tighten the four screws located in holes (N) Fig. 12 of the front table board (A).
7. Insert four 1/4-20 x 1-1/4" round-head screws (P) Fig. 12 in the holes (R) Figs. 11 and 12 of the table board. Tighten
each of the screws until each corner of the table board raises approximately 1/8".
8. Loosen the bevel clamp lever (S) Fig. 14, pull out the bevel index knob (T), and rotate the motor (V) to the vertical
position until the bevel index engages. Tighten the bevel clamp lever (S).
NOTE: If the motor shaft contacts the table board before the motor is fully rotated, raise the track arm (X) Fig. 15 by turning the
elevating handle (C).
9. Loosen the cuttinghead clamp knob (W) Fig. 15. Move the cuttinghead to the front of the track arm (X). Tighten the
cuttinghead clamp knob (W).
10. Loosen the track arm clamp handle (Y) Fig. 15.
NOTE: The track arm clamp handle (Y) Fig. 15 has left-handed threads. Press down on the indexing release handle (Z) Fig.
15, and pivot the track arm (X) to the left until the motor shaft (B) Fig. 16 is near the front left adjustment screw (P) Fig. 13 of
table board (C) Fig. 13. Tighten the track arm clamp handle (Y) Fig. 15.
C
P
R
N
R
N
R
C
Fig. 12
X
V
W
T
S
11. Place an arbor wrench (D) Fig.16 between the table
board (A) and the motor shaft (B). Lower the track arm
(X) Fig. 15 by turning the elevating handle (C) counterclockwise until the motor shaft (B) Fig. 16 touches the
arbor wrench.
Fig. 14
Fig. 13
Z
C
X
Y
W
Fig. 15
A
B
D
12
P
Fig. 16
Page 13
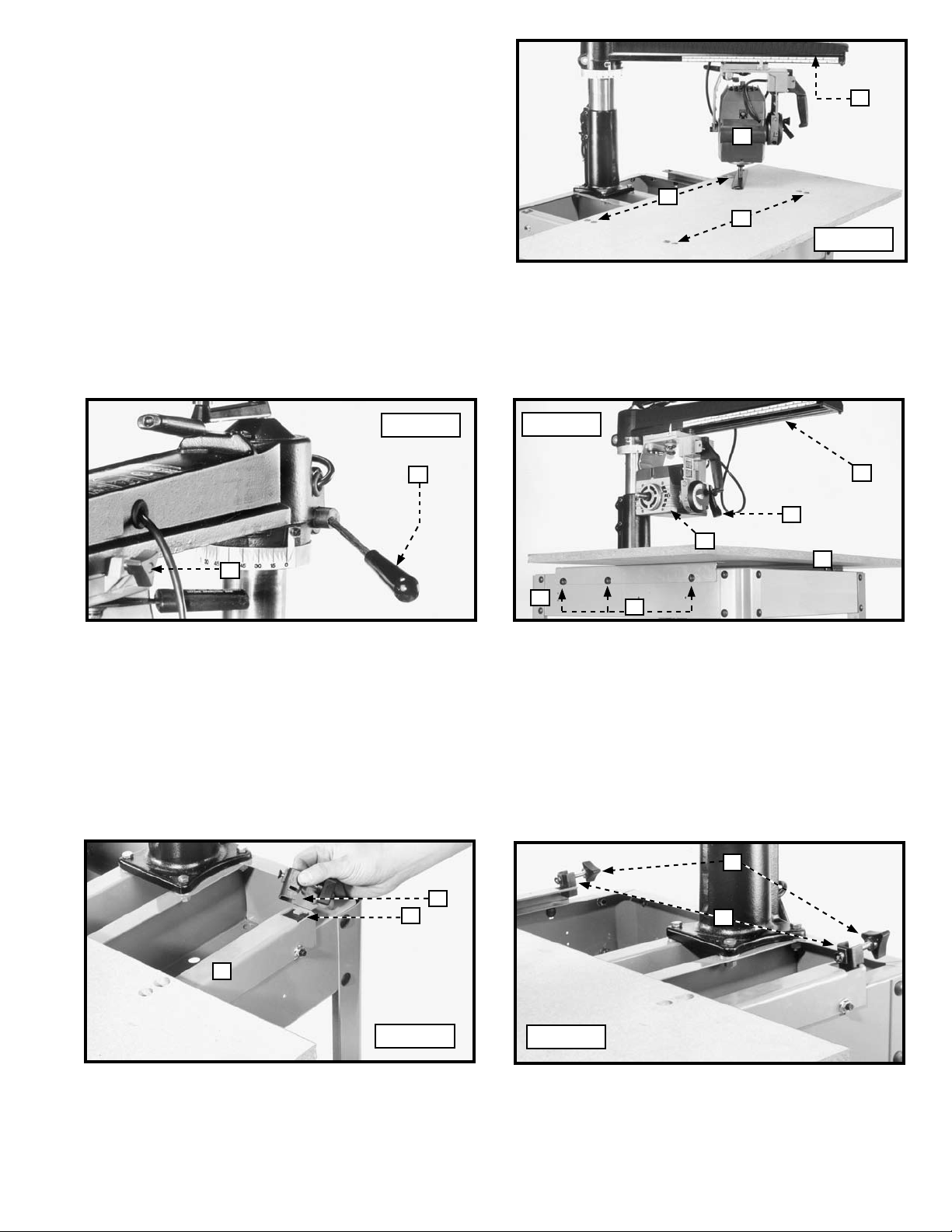
12. Check the height of the table board above the other
three table board adjustment screws (E) Fig. 17 by
repositioning the track arm (X), and the cuttinghead
assembly (V) until you determine the highest point of the
table.
NOTE: Make certain that the cuttinghead clamp knob
(W) Fig. 18 and the track arm clamp handle shaft (Y) are
located above each of the adjustment screws. Do not
change the height of the track arm (X) Fig. 17 until you
determine the highest screw and have adjusted all four
corners of the table board.
13. Position the motor shaft over the three lower corners of the table board. Adjust the table adjustment screws (E) Fig. 17
until the arbor wrench fits between the arbor shaft and table board in each location.
14. Tighten the three screws (G) Fig. 19 on each side of saw base (H). Return the track arm (X) and the motor (V) to the 90°
position. Tighten the bevel clamp lever (S) and the track arm clamp handle (Y) Fig. 18.
E
V
E
X
Fig. 17
Fig. 18
Y
Fig. 19
X
S
V
W
H
G
A
TABLE BOARD CLAMPS AND TABLE BOARDS
1. Locate the table board clamps (A) Fig. 20. Insert one clamp into each of the slotted holes (B) located at the rear of each
table support bracket (C) Fig. 20.
2. Turn the adjusting screw (D) Fig. 21 counter-clockwise, so that the knobs (A) are in the rear position.
D
A
B
A
C
Fig. 20
13
Fig. 21
Page 14
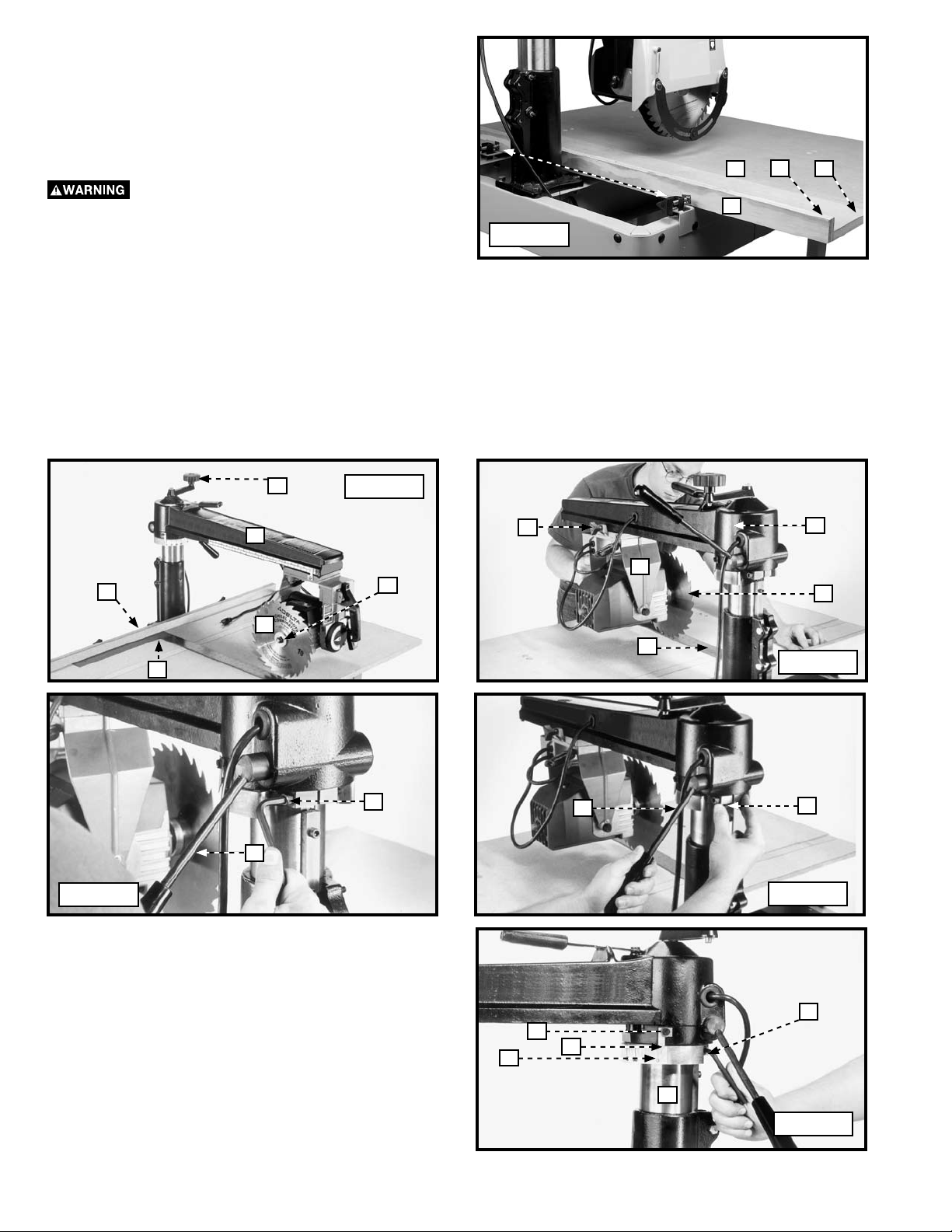
3. Place a 1-1/4" wide board (E) Fig. 22 against the front
of the table board (G), and a 5-3/4" wide board (J)
against the 1-1/4" wide board (E). Place the 1-3/4"
wide board (H) in the upright position against the
5-3/4" wide board (J). Tighten the knobs (D) until the
table boards are securely clamped.
ADJUSTING AND CHECKING
THE SAW BLADE TRAVEL
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and
disconnect machine from power source before installing
and removing accessories, before adjusting or changing
set-ups or when making repairs. An accidental start-up
can cause injury.
1. Raise the track arm (A) Fig. 23 by turning the elevating handle (B) until you can attach the blade (C) on the motor shaft.
Tighten the arbor nut (D) using the supplied wrenches.
2. Place a framing square (E) Fig. 23 against the fence (H). Lower the track arm (A) Fig. 23 until the blade clears the table
surface.
3. Loosen the cuttinghead clamp knob (S) Fig. 24. Slide the cuttinghead (T) the entire length of track arm (A) to determine if
the blade (C) travels parallel to the square (E).
4. To adjust, loosen the index-ring locking screw (J) Fig. 25, and the track arm clamp handle (K).
5. Rotate the track arm (A) Fig. 24 until the blade (C) travels parallel to the square (E). Tighten the track arm clamp
handle (K) Fig. 26.
6. With the track arm clamp handle (K) Fig. 26 tightened, rotate the index ring (L) counter-clockwise until it stops. Tighten
the index ring locking screw (J) Fig. 27.
Fig. 22
H
J
G E
H
Fig. 25
B
A
Fig. 23
S
A
T
D
C
C
E
E
J
K
Fig. 24
L
K
Fig. 26
7. Two miter index pointers are on this machine, one of
which is shown at (M) Fig. 27. To adjust, loosen the
screw (N) and move the pointer (M) until it aligns with
the “zero” mark on the miter scale (P). Tighten the
screw (N). Adjust the miter index pointer located on the
other side of column (R) in the same manner.
14
J
N
P
M
R
Fig. 27
Page 15
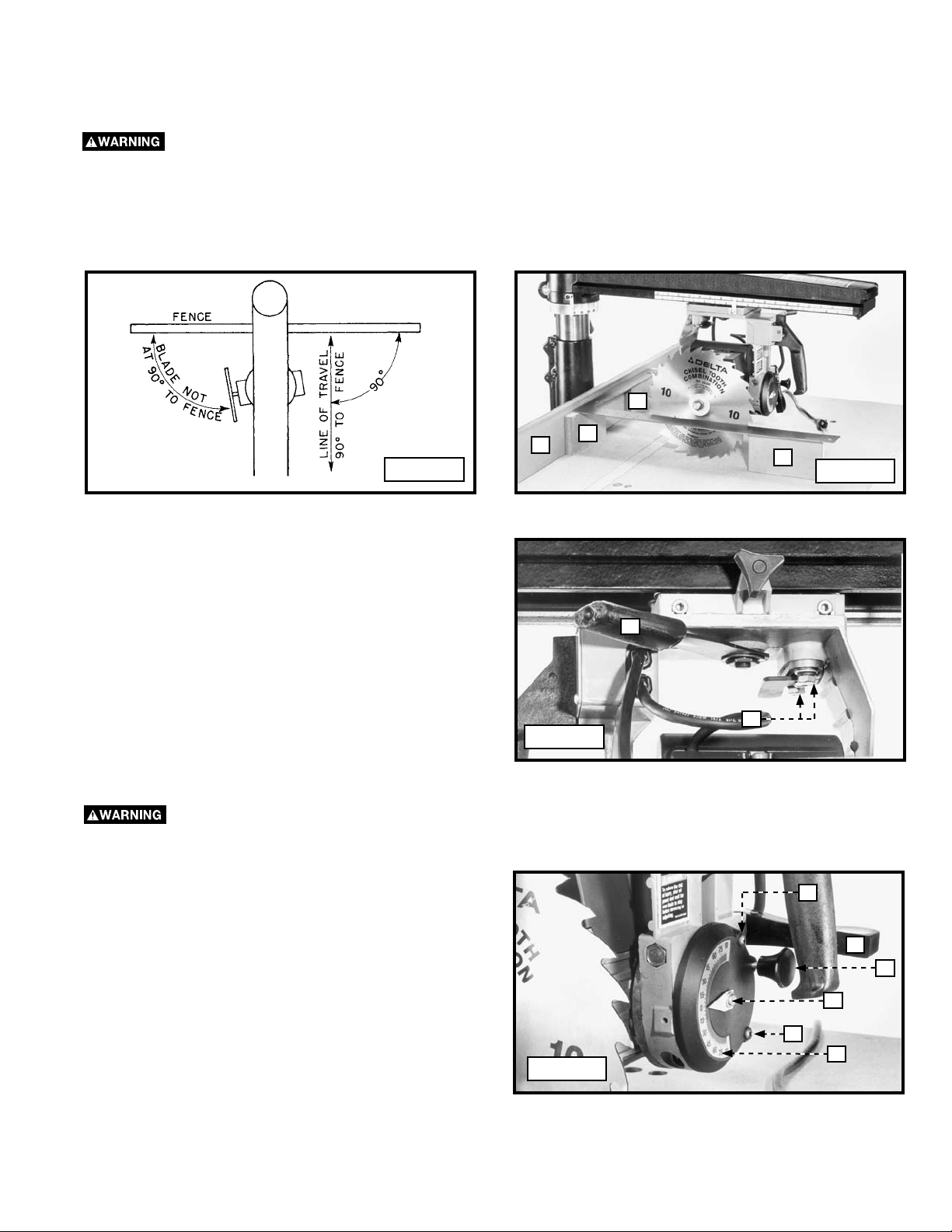
REMOVING “HEELING”
Even though the cuttinghead travel may be perfectly aligned at 90° to the fence, the blade itself may not be 90° or square
with the fence (Fig. 28). This condition is known as “heeling.”
To check and adjust:
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and disconnect machine from power source before installing and
removing accessories, before adjusting or changing set-ups or when making repairs. An accidental start-up can cause
injury.
1. Install saw blade without the guard.
2. Replace the fence with a flat piece of 3/4" wood (A) Fig. 29 that is at least 5" high. Tighten the table board clamps.
3. Place three identical pieces of wood (B) Fig. 29 on the table. Lay a framing square on them so that the short arm is flush
against the fence and the long arm is against the blade. Be sure that the square is between the teeth of the blade.
B
A
Fig. 28
4. Release the yoke clamp handle (C) Fig. 30 and slightly
loosen the two hex screws (D). Swivel the yoke until
the blade is parallel with the square. Tighten the yoke
clamp handle (C). Tighten the two hex screws (D).
B
B
Fig. 29
C
D
Fig. 30
SQUARING THE SAWBLADE TO THE TABLE
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and disconnect machine from power source before installing and
removing accessories, before adjusting or changing set-ups or when making repairs. An accidental start-up can cause
injury.
1. Attach the inner blade flange, saw blade, outer blade
flange, and arbor nut on the saw arbor.
F
2. Place the cuttinghead in a cross-cut position (Fig. 29).
Lower the track arm until the saw blade is clear of the
table. Slide the cuttinghead forward until it is positioned
over the front table board. Clamp the cuttinghead in
position.
3. Engage the bevel index knob (A) Fig. 31. Check to see
that the motor is in a horizontal position. Tighten the
bevel clamp handle (C).
C
A
E
F
B
Fig. 31
15
Page 16
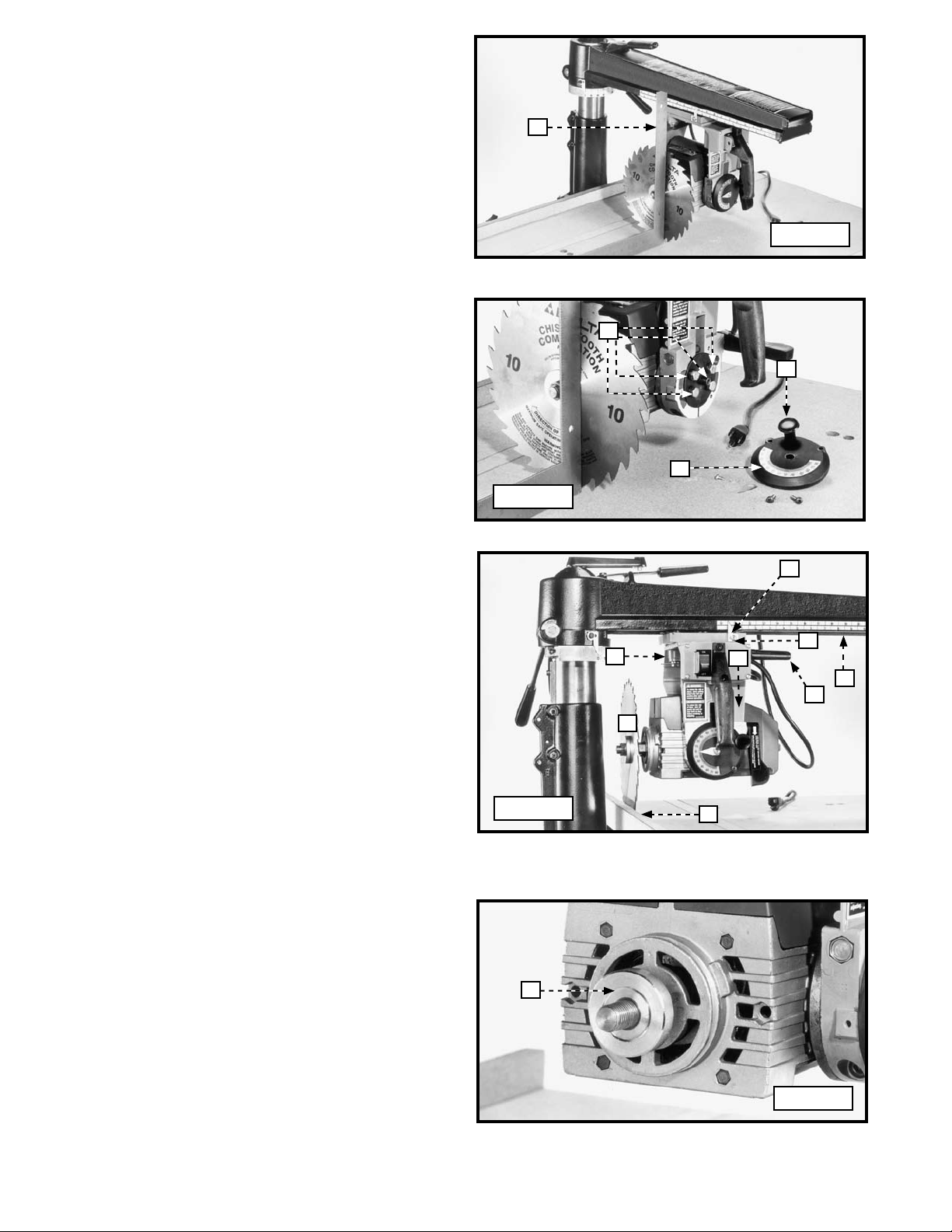
4. Place a square (D) Fig. 32 on the table and against the
saw blade. See if the blade is square with the table.
NOTE: The square should rest between two teeth of the
saw blade.
5. To adjust, tighten the bevel clamp lever (C) Fig. 31.
6. Remove the screw, flat washer, and pointer (E) Fig. 31.
7. Remove the two screws (F) Fig. 31 and the bevel scale
plate (H) Fig. 32 with the index knob (A).
8. Loosen the four hex screws (G) Fig. 33. Tilt the motor
until the saw blade is flush with the square. Tighten the
four hex screws (G).
9. Replace the bevel scale plate (H) Fig. 33 with the bevel
index release knob (A), two screws, and pointer that
were removed earlier.
NOTE: Adjust the pointer to “zero” on the bevel index scale.
D
Fig. 32
G
A
H
ADJUSTING IN/OUT RIP SCALE
1. Loosen the yoke clamp handle (A) Fig. 34. Release
the yoke index by pressing the release lever (B) up or
down. Rotate the cuttinghead (C) to the in-rip position
(Fig. 34). Tighten yoke clamp handle (A).
2. Position the fence (D) Fig. 34 at the rear of the table.
3. Loosen the cuttinghead clamp knob (C) Fig. 34. Slide
the cuttinghead to the rear of the track arm until the
saw blade (F) is flush against the fence (D).
4. Tighten the cuttinghead clamp knob. Adjust the pointer
(H) Fig. 34 to the “zero” mark on the lower scale (J)
by loosening the screw (K). Tighten the screw when
finished.
ATTACHING THE BLADE AND BLADE GUARD
NOTE: Use only 10" blades with 5/8" arbor holes and
rated for 5000 rpm or higher.
Fig. 33
Fig. 34
H
K
B
C
J
A
F
D
1. Attach the inside (thick) arbor flange (A) Fig. 35 to the
arbor shaft with the recessed side of flange (A) facing
out.
A
Fig. 35
16
Page 17
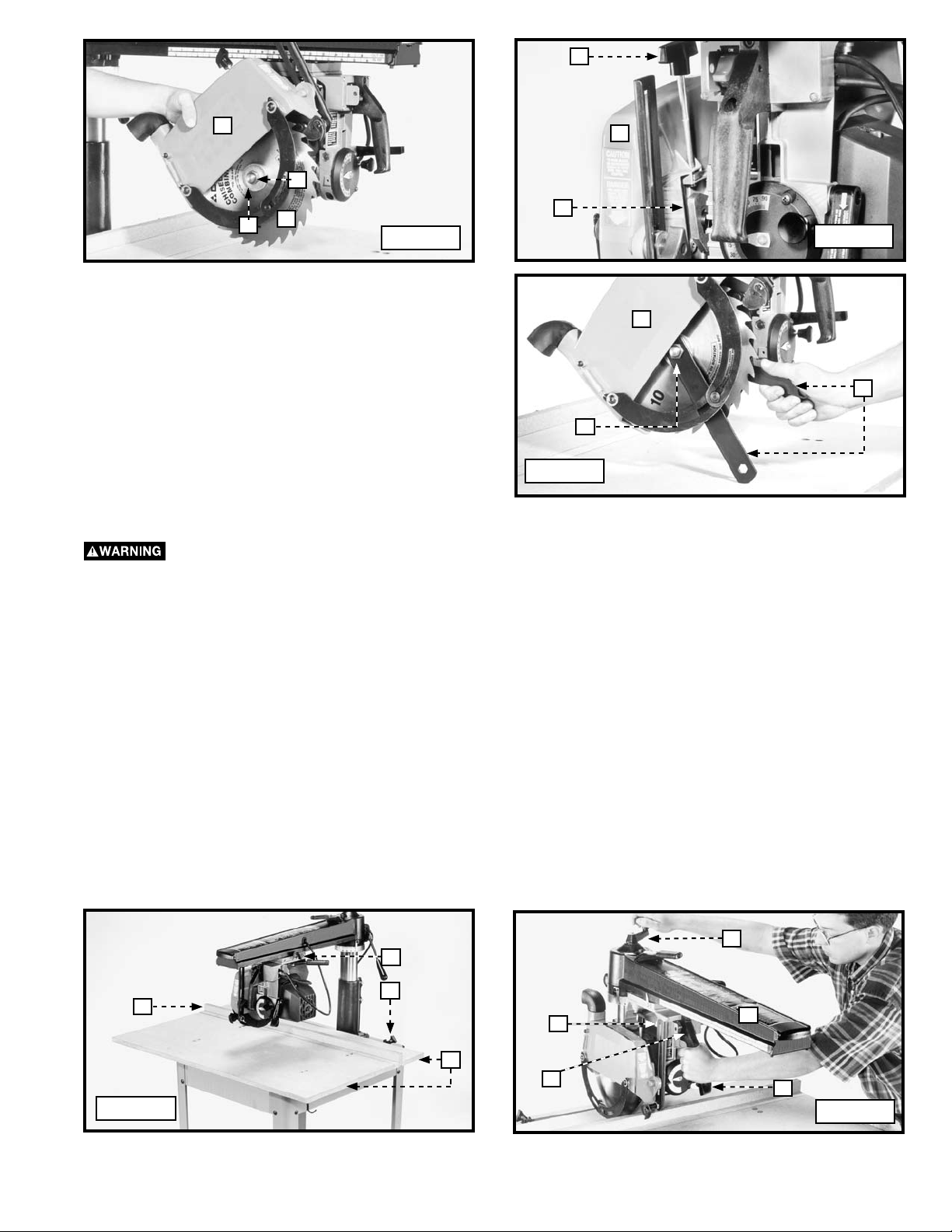
H
B
B
E
C
D
Fig. 36
2. With the blade guard (B) Fig. 32 in the left hand, insert
the saw blade (C) into the blade guard (B) and on the
arbor shaft.
3. Atttach the outside (thin) blade flange (D) Fig. 36 to the
recessed side of the flange (D) facing in. Place the arbor
nut (E) on the arbor shaft.
NOTE: The arbor nut (E) Fig. 36 has a left-hand thread.
4. Lift the cam (F) Fig. 37. Attach the blade guard (B) to the
cuttinghead assembly.
NOTE: Seat the tongue of the guard in the groove of the
cuttinghead.
5. Pull back on blade guard (B) Fig. 38, so that it rotates to
the rear. Use the 7/8" box wrench around the arbor nut
(E), and the 7/8" open-end wrench on the flat of the arbor to hold it in place.
6. Rotate the blade guard (B) Fig. 38 to the horizontal position and tighten the clamp knob (H) Fig. 37.
Tighten the clamp knob (H) FIG. 37 and secure the blade guard before operating the machine.
The lower retractable blade guard provides operator protection along the sides of the sawblade. To reduce the risk of
potential hazards, use the following rules:
A) KEEP YOUR HANDS AWAY FROM THE GUARD. As the blade cuts, the guard will lift and leave part of the blade
exposed.
B) SHUT OFF THE POWER BEFORE FREEING A JAMMED LOWER GUARD. The guard can get jammed in previous
kerfs in the table or fence. Always anticipate the path of the guard.
C) USE CAUTION when making bevel cuts to ensure that the lower guard is never pinched toward the blade.
D) THE LOWER GUARD CAN JAM AGAINST THE FENCE DURING NARROW IN-RIPS. Should the guard jam against
the fence, disconnect the saw from the power, wait for the blade to stop, then lift the blade guard and rest it on
top of the fence.
F
Fig. 37
B
G
E
Fig. 38
CUTTING INTO THE TABLE BOARDS
1. Attach the table boards (A) Fig. 38 and the fence (B). Secure the boards in place with table clamps, one of which is
shown at (C).
2. Return the cuttinghead (D) Fig. 39 to the rear of the track arm (E). Tighten the cuttinghead clamp knob (G) Fig. 37.
Check to see that the switch (H) Fig. 39 is in the “OFF” position and connect the saw to the power source.
3. While holding cuttinghead handle (L) Fig. 39 firmly, turn the switch (H) “ON”. Lower the track arm (E) by turning the
elevating handle (K). Lower the saw blade until it cuts into the table surface approximately 1/16” deep.
K
G
C
B
D
A
H
Fig. 39
17
E
L
Fig. 40
Page 18
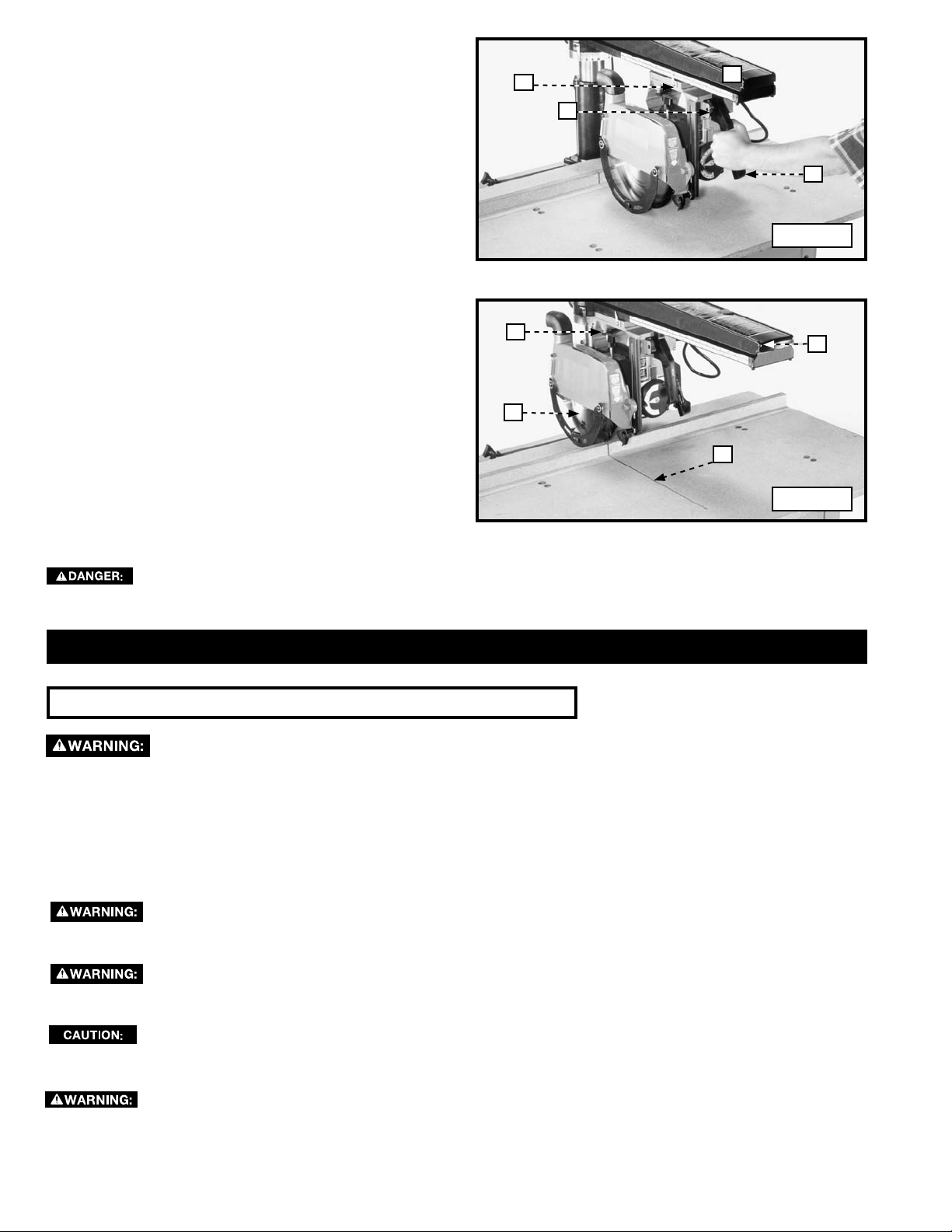
D
E
4. While still holding the cuttinghead handle (L) Fig. 41
firmly, loosen the cuttinghead clamp knob, and slowly
pull the cuttinghead (D) Fig. 41 toward the front of the
track arm (E) until the travel stops. Turn the switch (H)
“OFF”.
5. Wait for the saw blade (M) Fig. 42 to stop, then return
the cuttinghead (D) to the rear of the track arm (E). Note
the saw kerf (N) Fig. 42 in the table boards.
IMPORTANT: Raise the track arm (E) Fig. 42 before
attempting to rotate it. Perform the procedure “CUTTING
INTO THE TABLE BOARDS” for each separate angle cut.
M
H
L
Fig. 41
D
E
N
Fig. 42
If, during operation, the saw has a tendency to tip over, slide, or walk on the supporting surface, secure the
saw to the floor surface through the holes provided on the bottom of each leg.
OPERATION
OPERATIONAL CONTROLS AND ADJUSTMENTS
Before using the saw, verify the following each and every time:
1. ALWAYS wear proper eye, hearing, and respiratory equipment.
2. Blade is tight.
3. Bevel angle and height lock knobs are tight.
4. If ripping, ensure fence lock lever is tight and fence is parallel to the blade.
5. The blade guard is properly attached and the anti-kick teeth are functioning.
6. ALWAYS inspect the guard and splitter for proper alignment operation and clearance with saw blade.
Failure to adhere to these common safety rules can greatly increase the likelihood of injury.
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and disconnect machine from power source before installing
and removing accessories, before adjusting or changing set-ups, or when making repairs. An accidental
start-up can cause injury.
Before connecting the radial arm saw to the power source or operating the saw, always inspect the
guard and splitter for proper operation alignment and clearance with saw blade. Personal injury may
result.
If your saw makes an unfamiliar noise, or if it vibrates excessively, cease operating immmediately until the
source has been located and the problem corrected.
STARTING AND STOPPING
Make sure that the switch is in the “OFF” position before plugging cord into outlet. Do not touch the
plug’s metal prongs when unplugging or plugging in the cord.
The on/off switch (A) Fig. 43 is located at the front of the cuttinghead. To turn the saw “ON”, move the switch (A) up to the
“ON” position. To turn the saw “OFF”, move the switch down to the “OFF” position.
18
Page 19
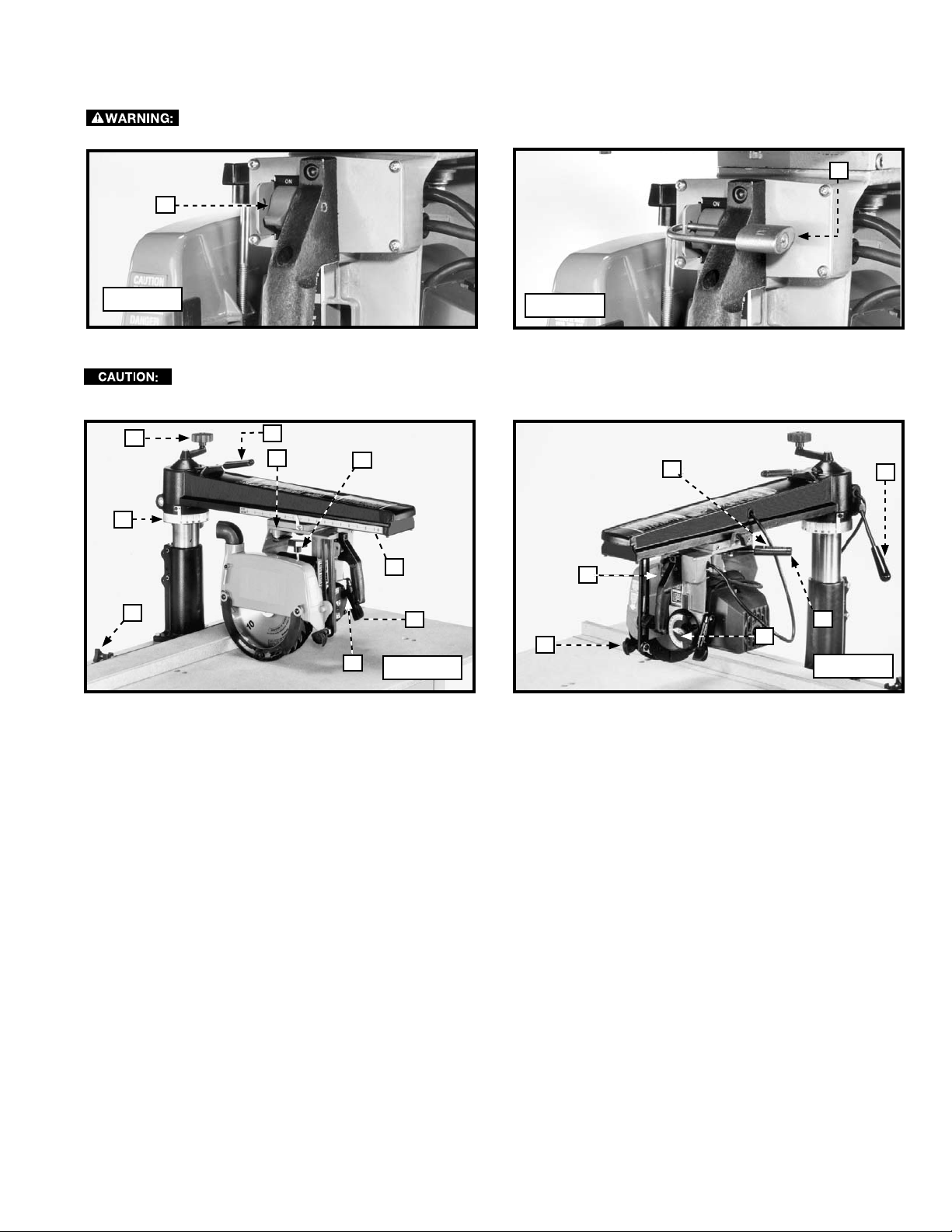
LOCKING THE SWITCH IN THE "OFF" POSITION
IMPORTANT: When the machine is not in use, lock the switch in the “OFF” position to prevent unauthorized use, using a
padlock (D) Fig. 44 with a 3/16" diameter shackle
In the event of a power outage (such as a breaker or fuse trip), always move the switch to the “OFF”
position until the main power is restored.
D
A
Fig. 43
Fig. 44
GUIDE TO CONTROLS
Study the following terms and explanations carefully to familiarize yourself with the controls before turning on
the power. Doing otherwise may cause damage to the saw or personal injury (Figs. E and F).
C
D
A
A. THE TABLE CLAMP KNOBS allow you to quickly set
the desired fence position (Fig. G).
B. THE TRACK ARM INDEXING RELEASE HANDLE
releases the indexing pin from the 0° and 45° positions
to allow the arm to rotate. Depress the handle to release
the index pin (Fig. G).
C. THE TRACK ARM ELEVATING HANDLE controls the
depth-of-cut in all operations. Turn the handle clockwise
to raise, or counter-clockwise to lower the track arm
(Fig. G).
D. THE MITER SCALE indicates the degrees left and right
for setting track arm to desired miter angle (Fig. G).
F. THE RIP SCALE indicates the in and out rip positions of
the cutterhead (Fig. E).
G. THE BLADE GUARD CLAMP KNOB clamps the blade
guard at rotated positions for ripping (Fig.G.
H. THE BEVEL CLAMP HANDLE controls the tilt of
the motor for bevel cutting operations. It also locks
the motor at any desired angle on the bevel scale.
Lift the handle to loosen, and push it down to lock
(Fig. G).
J. THE BEVEL INDEX RELEASE KNOB allows the motor to
position in the 0°, 45°, and 90° bevel settings. To tilt the
motor for bevel cutting, loosen the bevel clamp handle.
To release the index, pull out the release knob (Fig. G).
K. THE YOKE INDEXING RELEASE LEVER allows the
saw to achieve a 90° position for ripping or cross-cutting
operations. Loosen the yoke clamp handle to rotate the
yoke. Push the release lever either up or down to release
the indexing pin (Fig. G).
B
K
G
F
N
P
H
M
J
Fig. G
L. THE YOKE CLAMP HANDLE must be loose when
rotating the yoke between the rip and cross-cutting
position. Pull the handle to release and push it to lock
(Fig. H).
M. THE ANTI-KICKBACK DEVICE helps to prevent injury
or damage caused by kickback. When ripping, position
and clamp the yoke so that the blade is parallel to the
fence. Rotate the rear of the blade guard until it almost
touches the workpiece. Lower the anti-kickback rod so
that the fingers catch and hold the workpiece. Never
rip from the anti-kickback end of the blade guard
(Fig. H).
N. THE ON-OFF SWITCH is conveniently located, and can be
turned on or off in an instant for added operation protection.
You can also lock this switch in the "OFF" position to
prevent unauthorized use using an accessory padlock
(Fig. H).
P. THE CUTTING-HEAD CLAMP KNOB locks the
cutting-head at any position on the track arm. Tighten
the clamp knob (Fig. H).
R. THE BEVEL SCALE indicates the degree of rotation
for setting motor bevel positions (Fig. H).
S. THE TRACK ARM CLAMP HANDLE controls the
rotation of the track arm for all miter cutting operations.
It locks the track arm at any miter angle position. To
rotate the track arm to the right, loosen the clamp
handle and rotate the arm. The arm will stop at
45°. To rotate past 45°, depress the indexing release
handle and rotate. The arm will rotate an additional 5°.
To rotate to the left, the operation is the same except
that you must depress the indexing release handle to
19
start the rotation (Fig. H).
S
L
R
Fig. H
Page 20
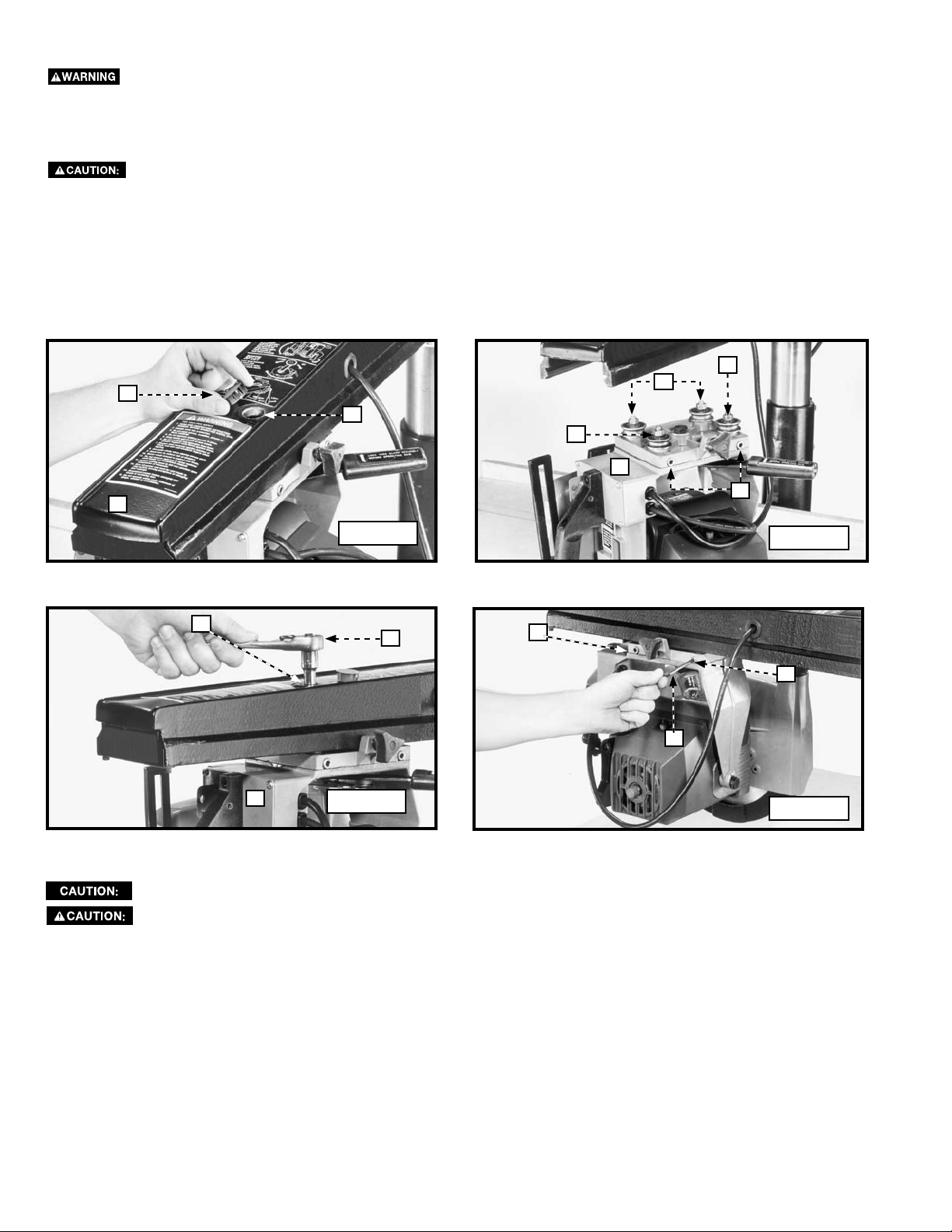
ADJUSTING THE BALL BEARINGS AGAINST THE TRACK
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and disconnect machine from power source before installing and
removing accessories, before adjusting or changing set-ups or when making repairs. An accidental start-up can cause injury.
The cuttinghead (C) Fig. 46 is suspended from four pre-loaded, lubricated, shielded ball bearings, two of which are on fixed
shafts at (A), and two on adjustable shafts at (B).
The cuttinghead (C) Fig. 46 was removed from the track arm for illustration purposes. DO NOT remove the
cuttinghead from the track arm.
After extended use, wear may develop in the track arm, causing “play” between the ball bearings and the track. The ball
bearings must ride smoothly and evenly in the channels of the track arm. To adjust the ball bearings:
1. Remove the plastic plug (D) Fig. 45 from the top of track arm (E).
2. Slide the cuttinghead (C) Fig. 46 until one of the adjustable bearings (B) Fig. 46 is visible through the hole (G) Fig. 46.
3. Use a 1/2" socket, extension, and ratchet (H) Fig. 47 through the hole (G) in the track arm to slightly loosen the hex nut
on the adjustable shaft (G) Fig. 47 approximately 1/8 turn. Repeat the procedure for the other bearing.
B
D
A
G
B
C
K
E
Fig. 45
G
H
K
Fig. 46
K
J
C
4. Use a 3/16" hex wrench (J) Fig. 48 to turn the adjustment screws (K) Fig. 48 to remove all “play.”
Do not overtighten the adjustment screws (K). This can damage the bearings.
Do not loosen the adjustment screws (K) more than 1/2 turn. The cuttinghead may fall from the track arm.
5. Tighten the two hex nuts loosened in STEP 3. Check the cuttinghead travel for any “play”. Ensure that it moves freely and
smoothly.
6. Replace the plastic plug that was removed in STEP 1.
Fig. 47
Fig. 48
20
Page 21
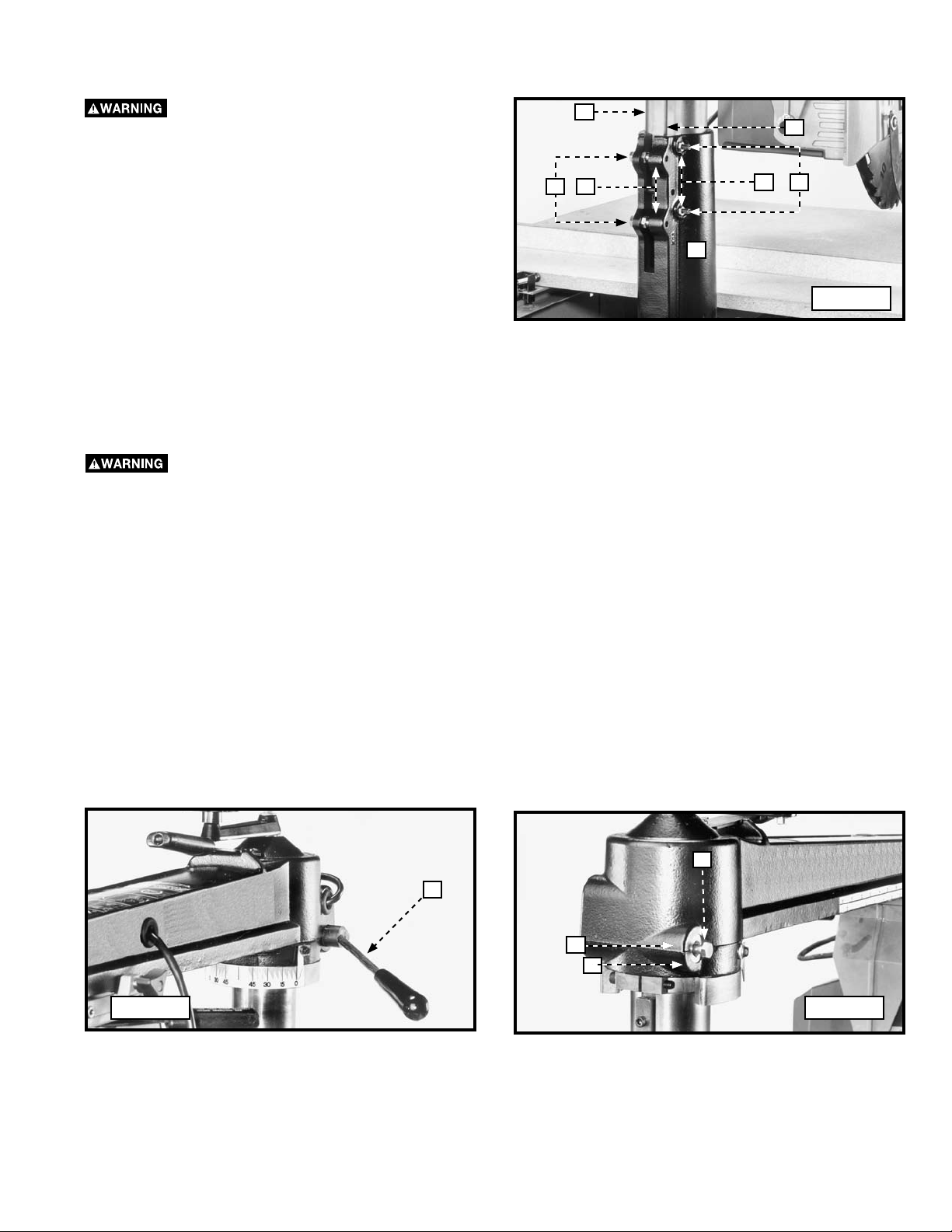
ADJUSTING THE TENSION ON THE ELEVATING COLUMN
Elevating column tension is preset at the factory. “Play” may develop after extended use. To adjust:
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and
disconnect machine from power source before installing
and removing accessories, before adjusting or changing
set-ups or when making repairs. An accidental start-up can
cause injury.
1. Loosen the hex nuts (A) Fig. 49 and the gib adjustment
screws (C).
2. Loosen the hex nuts (D) and turn the screws (E) until the
column base wraps around the column securely and can
be raised or lowered without binding. Tighten the hex
nuts (D) against the column base.
3. Tighten the gib and adjustment screws (C) against the
gib (H) until all side-to-side play is removed. Tighten
the hex nuts (A) against column base.
NOTE: After adjusting column tension, refer to “ADJUSTING SAW BLADE TRAVEL SQUARE WITH FENCE” to determine
if saw blade travel was affected.
F
H
A
E
D
C
B
Fig. 49
CHANGING THE POSITION OF THE TRACK ARM CLAMPING HANDLE
To reposition the track arm clamping handle (A) Fig. 50 when it does not lock in a convenient position:
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and disconnect machine from power source before installing and
removing accessories, before adjusting or changing set-ups or when making repairs. An accidental start-up can cause injury.
1. Loosen and remove the track arm clamping lever (A) Fig. 50. Push the hex bolt (B) Fig. 51 back through the hole until the
head of the bolt is out of the recessed bushing (C).
NOTE: The track arm clamping lever has a left-hand thread.
2. Rotate hex bolt (B) Fig. 51 in the desired direction.
3. Push the hex bolt (B) Fig. 51 back through hole. Check to see if the head of hex bolt is seated properly in the recessed
bushing (C). Attach the track arm clamping lever.
NOTE: If the track arm clamping lever (A) Fig. 49 tightens before approximately four turns, the clamping bushings (one of which
is shown at (C) Fig. 51 may have rotated. These bushings should seat completely inside the track (D). If they do not, slightly loosen
the clamping lever (A) Fig. 50 and rotate the clamping bushing (C) Fig. 51 until it seats. Check to see if you need to rotate the
bushing on the clamp lever side also.
NOTE: The flats on the clamping bushings should face the front of the saw.
NOTE: The clamp lever (A) Fig. 50 will thread at one of two positions. If, after making the adjustment, the clamp lever (A)
tightens 180° from where desired, slowly unscrew clamp lever (A) while holding in on the hex bolt (B). When the clamp lever (A)
comes off of the hex bolt (B), rotate the clamp lever (A) 180°. Thread the clamp lever.
Fig. 50
B
A
D
C
Fig. 51
21
Page 22

CHANGING THE POSITION OF THE BEVEL CLAMP HANDLE
To reposition the bevel clamp handle:
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and disconnect machine from power source before installing and
removing accessories, before adjusting or changing set-ups or when making repairs. An accidental start-up can cause injury.
1. Loosen the bevel clamp handle (A) Fig. 52, release the
bevel index release knob (B), and turn the motor (C) to
the vertical position.
NOTE: If the blade guard contacts the table surface, raise
the track arm.
2. Loosen the bevel clamp handle (A) Fig. 52 several
turns until the hex head of the screw (D) can be
pushed out of hex-shaped recess in yoke.
3. Turn the screw (D) Fig. 52 one or two flats of the hex
head in the direction the handle needs to be turned.
Push it back into hex-shaped recess in yoke.
4. Tighten the bevel clamp handle (A) Fig. 52.
NOTE: The screw is left-hand thread - turn the clamp
handle counter-clockwise to tighten.
D
B
C
A
Fig. 52
CHANGING THE POSITION OF THE YOKE CLAMP HANDLE
To reposition the yoke clamp handle (A) Fig. 53:
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and
disconnect machine from power source before installing
and removing accessories, before adjusting or changing
set-ups or when making repairs. An accidental start-up can
cause injury.
1 Remove retaining ring (B) Fig. 53.
2. Reposition yoke clamp handle (A) Fig. 53 on hex clamp
nut.
3. Replace retaining ring (B) Fig. 53
A
B
Fig. 53
POSITIVE STOP YOKE INDEX
The yoke index lever (A) Fig. 54 activates a positive stop that positions the cuttinghead in the cross-cut or rip position. To rotate
the cuttinghead, release the yoke clamp handle, press up or down on yoke index lever (A) to release the positive stop, and
rotate the cuttinghead to either the #1 in-rip or #2 out-rip or #3 cross-cut positions. Release the yoke index lever (A) Fig. 53 and
the cuttinghead will automatically index at each of the three positions.
POSITIVE STOP BEVEL INDEX
The bevel index knob (A) Fig. 55 provides a positive stop when positioning the saw blade at 0°, 45°, and 90° left, and 90° right
on the bevel scale (C). To change the angle of the saw blade, loosen the bevel clamp handle (B), pull out bevel index knob (A),
and tilt the saw blade and motor. For the 0°, 45°, and 90° left, and 90° right positions, release the bevel index knob (A) and the
saw blade will index at each of these positions. Tighten the bevel clamp handle (B). For saw blade angles between positive
stops, set the blade at the desired angle on bevel scale (C) and tighten the bevel clamp handle (B) Fig. 55.
B
A
A
Fig. 54
22
C
Fig. 55
Page 23
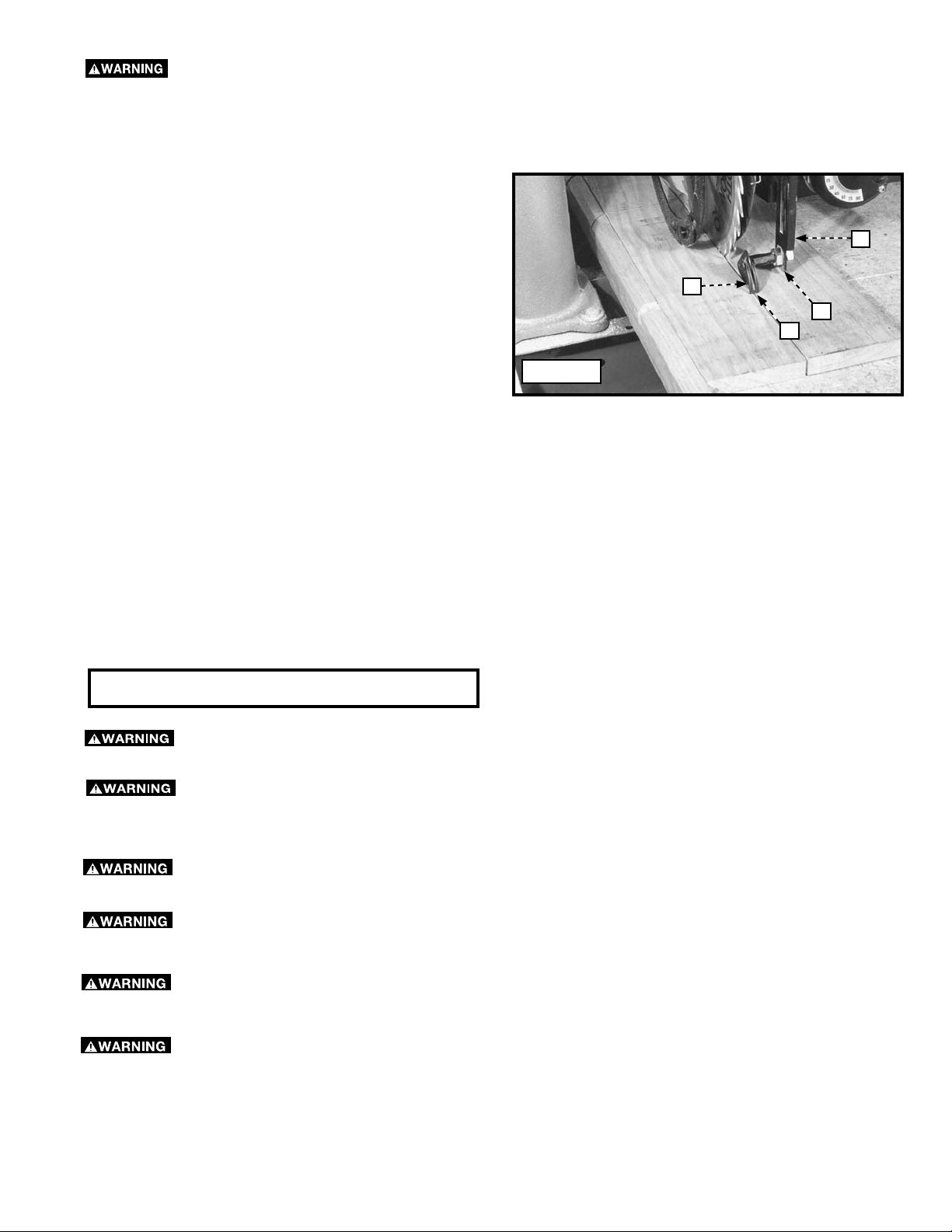
ADJUSTING THE SPLITTER AND ANTI-KICKBACK FINGERS
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and disconnect machine from power source before installing and
removing accessories, before adjusting or changing set-ups or when making repairs. An accidental start-up can cause injury.
During ripping operations, the splitter (A) Fig. 56 must ride in the saw kerf and the anti-kickback fingers (B) should touch the
workpiece to prevent kickback.
1. Set the saw up in the ripping position with the blade guard lowered on the in-feed side to act as a holddown.
2. Start a piece of material through the saw (Fig. 56).
3. Shut the saw off, and disconnect it from the power
source.
4. Adjust the arm (C) Fig. 56 so that it is vertical and the
splitter (A) is in the saw kerf.
5. If the splitter (A) Fig. 56 does not align with the saw
kerf, loosen the hex nuts (D), and position the splitter
(A) into the saw kerf. Tighten the hex nuts (D) against
the arm (C). The straight side of the splitter should
be toward the blade (Fig. 56), and the anti-kickback
fingers should rest on the workpiece.
NOTE: The clamp knob for arm (C) must be tight. Move
arm (C) front to back while tightening clamp knob with
other hand to be sure clamp is firmly seated and tight.
6. Pull backward on the workpiece to determine if the
anti-kickback fingers bite into the material and prevent
further backward movement. If necessary, readjust the height of the arm (C) Fig. 56.
Fig. 56
A
B
C
D
AUXILIARY TABLE BOARD FACING
To prevent repeated cutting into the table surface which will eventually cause the table to sag, you can cut an auxiliary table
board facing and fit it to the table. Make it from 1/4" plywood or particle board. Cut it to a size that will cover all of the table
boards in front of the fence. Place the auxiliary table board facing flat on the table and butt it against the table fence. Fasten
it to the table with a small brad or finish nail in each corner.
USING A TABLE EXTENSION
When a table extension more than 24" long is attached to the saw, use a sturdy outrigger support or secure the stand or
bench to the floor.
MACHINE USE
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and disconnect the machine from the power source before
installing and removing accessories, before adjusting or changing set-ups, or when making repairs. An
accidental start-up can cause injury.
Before connecting the radial arm saw to the power source or operating the saw, always inspect the guard and
splitter for proper operation alignment and clearance with the saw blade. Personal injury may result.
CROSS-CUTTING
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and disconnect the machine from the power source before
installing and removing accessories, before adjusting or changing set-ups, or when making repairs. An
accidental start-up can cause injury.
NEVER touch the "free end" of the workpiece or a "free Piece" that is cut off while the power is "ON"
and/or the saw blade is rotating. The piece may contact the blade resulting in a thrown workpiece and
possible injury.
NEVER use a length stop on the free end of the workpiece when crosscutting. In short, the cut-off piece
in any through-sawing (cutting completely through the workpiece) operation must never be confined
- it must be allowed to move away from the saw blade to prevent contact with the blade resulting in a
thrown workpiece and possibly injury.
Use caution when starting the cut to prevent binding of the guard against the workpiece resulting in
damage to the saw and possible injury.
23
Page 24
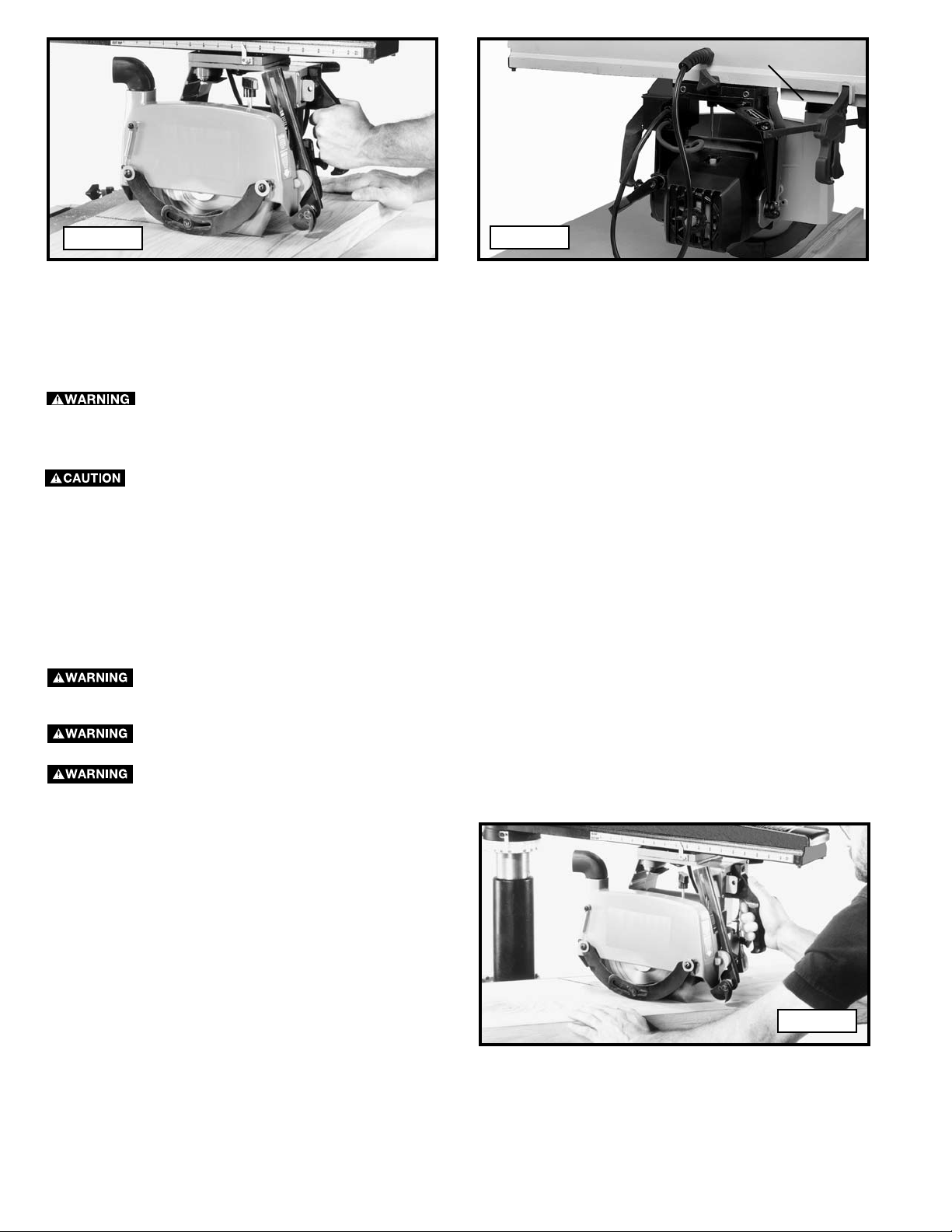
B
Fig. 57
To cross-cut, support the workpiece against the fence and pull the saw blade through the material at right angles to it. (Fig. 57)
When cross-cutting, set the track arm at “0” and tighten the track arm clamp handle. Clamp the fence between the table
boards. Make sure that the saw blade is on the left and behind the fence. Place the workpiece on the table and butt it against
the fence. Make sure that the saw blade is clear of the fence and the table when the machine is turned "ON". Lower the saw
blade until it lightly cuts into the table surface. Position your body a little to the left of the machine for better visibility. Pull the
saw blade across the work, just far enough to complete the cut, then return the saw blade to its starting position. Turn the
machine off, and wait for the blade to stop before touching the cut-off piece.
Always be conscious of your hand position. Make sure that your hands are clear of the blade and that
you are holding the workpiece firmly.
Additionally, you can turn the anti-kickback rod upside down and lock it in place so that the rod just clears the workpiece.
The rod can act as a guard from the exposed teeth of the blade.
Always return the cutterhead carriage to the full rear position after each cross-cut operation.
NOTE: When cross-cutting material more than 1" thick, position the fence immediately behind the fixed front table board.
Fig. 58
CROSS-CUT STOP
A block of wood (B) Fig. 58 clamped to the track arm will prevent unnecessary travel of the cutting-head on the track arm,
especially useful when performing repetitive operations. Clamp the block of wood to the right side of the track arm at a
position which will stop the cuttinghead travel as soon as the saw blade cuts through the workpiece.
MITER CUTTING
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and disconnect the machine from the power source before
installing and removing accessories, before adjusting or changing set-ups, or when making repairs. An accidental
start-up can cause injury.
Use caution when starting the cut to prevent binding of the guard against the workpiece resulting in
damage to the saw and possible personal injury.
Before connecting the radial arm saw to the power source or operating the saw, always inspect the guard
and splitter for proper operation alignment and clearance with the saw blade. Check the alignment after each change
of bevel angle.
Miter cutting is similar to cross-cutting except the workpiece
is cut at an angle (up to 45° right or left). Perform the settings
and operation in the same manner as cross-cutting except
first position the track arm to the desired angle on the miter
scale before you clamp it in place. Position your hand that
holds the workpiece on the opposite side of the direction of
the miter so that the blade is pulled through the workpiece
and away from your hand. Fig. 59 shows a typical miter
cutting operation on the radial saw.
Fig. 59
24
Page 25

COMPOUND MITER CUTTING
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and disconnect the machine from the power source before
installing and removing accessories, before adjusting or changing set-ups, or when making repairs. An accidental
start-up can cause injury.
Use caution when starting the cut to
prevent binding of the guard against the workpiece
resulting in damage to the saw and possible personal
injury.
Before connecting the radial arm saw to
the power source or operating the saw, always inspect
the guard and splitter for proper operation alignment
and clearance with the saw blade. Check the alignment
after each change of bevel angle.
Compound miter cutting is performed the same as miter
cutting except that the saw blade is tilted to the desired
angle on the bevel scale and clamped for a bevel cut. See
Fig. 60 for an illustration of the compound miter cut.
Fig. 60
RIPPING
To reduce the risk of injury, the workpiece must never be fed into the outfeed end of the blade guard
or personal injury may result.
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and disconnect the machine from the power source before
installing and removing accessories, before adjusting or changing set-ups, or when making repairs. An accidental
start-up can cause injury.
NEVER touch the "free end" of the workpiece or a "free Piece" that is cut off while the power is "ON"
and/or the saw blade is rotating. The piece may contact the blade resulting in a thrown workpiece and possible injury.
Keep the saw blade guard, splitter, and anti-kickback teeth in place and operating properly. Keep teeth
sharp. If teeth are not operational, return your unit to the nearest authorized Delta service center for repair. The splitter
must be in alignment with the saw blade and the teeth must stop a kickback once it has started. Check their action
before ripping by pushing the wood under the anti-kickback teeth. The teeth must prevent the wood from being pulled
toward the front of the saw.
A rip fence should ALWAYS be used for ripping operations to prevent loss of control and personal injury.
NEVER perform a ripping operation freehand. ALWAYS be sure the fence is locked down.
IMPORTANT: In certain applications, you may need to use two push sticks, and/or featherboards.
Keep all push sticks, featherboards, etc. handy
so that you can reach them without having to get near the
blade.
Ripping involves making a lengthwise cut through a board
along the grain. Clamp the track arm at “0” on the miter scale.
Position and clamp the yoke so that the blade is parallel to the
fence in either the in-rip or out-rip position. When feeding the
workpiece, make sure that one edge rides against the fence
with the flat side resting on the table. Lower the guard
on the in-feed side until it almost touches the workpiece
(Fig. 61) to act as a holddown. Adjust the splitter and antikickback fingers (A) Fig. 61 as described under the section
“ADJUSTING THE SPLITTER AND ANTI-KICKBACK
FINGERS” in this manual. Keep your hands well away from,
and to the side of the blade. When ripping narrow work, always use a push stick (Fig. 62) to push the work between the fence
and blade.
The workpiece must have one straight edge to follow the fence. If the board is bowed, place the hollow side down.
Securely tighten the cuttinghead clamp knob for all ripping operations.
Never feed the workpiece into the outfeed end of the blade guard.
Fig. 61
A
25
Page 26

OUT-RIPPING
Out-ripping is generally the same as ripping except that you
clamp the yoke at a right angle to the track arm with the
blade guard facing the FRONT of the machine. Position the
cuttinghead on the out-rip scale to the desired setting and
clamp it in position. Feed the workpiece from the left side of
the saw. A typical out-ripping operation is illustrated in Fig.
61.
IN-RIPPING
In-ripping is generally the same as ripping except that you
clamp the yoke at a right angle to the track arm with the
blade guard facing the REAR of the machine. Position the
cuttinghead on the in-rip scale to the desired setting and
clamp it in position. Feed the workpiece from the right side
of the saw. A typical in-ripping operation is illustrated in Fig.
62.
When ripping a workpiece less than 6" wide, use a push stick to complete the feed (Fig. 62).
PUSH-STICKS
In order to operate your radial arm saw safely, you must use a push-stick whenever the size or shape of the workpiece would
cause your hands to be within 6" (152mm) of the saw blade or other cutter.
No special wood is needed to make a push-stick as long as it's sturdy and long enough. A length of 12" (305mm) is
recommended with a notch that fits against the edge of the workpiece to prevent slipping. It's a good idea to have several
push-sticks of the same length [12" (305 mm) with different size notches for different workpiece thicknesses.
See the next page for an illustration of a push-stick. The shape can vary to suit your own needs as long as it performs its
intended function of keeping your hands away from the blade.
Fig. 62
TROUBLESHOOTING
For assistance with your machine, visit our website at www.deltaportercable.com for a list of service centers or call the
DELTA Machinery help line at 1-800-223-7278 (In Canada call 1-800-463-3582).
MAINTENANCE
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and disconnect it from power source before installing and removing
accessories, before adjusting or when making repairs. An accidental start-up can cause injury.
KEEP MACHINE CLEAN
Periodically blow out all air passages with dry compressed air. All plastic parts should be cleaned with a soft damp
cloth. NEVER use solvents to clean plastic parts. They could possibly dissolve or otherwise damage the material.
FAILURE TO START
Should your machine fail to start, check to make sure the prongs on the cord plug are making good contact in the
outlet. Also, check for blown fuses or open circuit breakers in the line.
LUBRICATION & RUST PROTECTION
Apply household floor paste wax to the machine table, extension table or other work surface weekly. Or use a commercially
available protective product designed for this purpose. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for use and safety.
To clean cast iron tables of rust, you will need the following materials: a sheet of medium Scotch-Brite™ Blending Hand
Pad, a can of WD-40® and a can of degreaser. Apply the WD-40 and polish the table surface with the Scotch-Brite pad.
Degrease the table, then apply the protective product as described above.
OVERLOAD PROTECTION
Wear certified safety equipment for eye, hearing and respiratory protection while using compressed air.
The motor on your saw is equipped with an overload
relay (A) Fig. 63. If the motor shuts off or fails to start
due to overloading, or low voltage, turn the switch to the
“OFF” position, let the motor cool three to five minutes
then push the reset button (A). The motor can then be
turned on again in the usual manner. Some conditions
that may cause overloading are; cutting stock too fast,
using a dull blade, using the saw beyond its capacity, etc.
A
Fig. 63
26
Page 27
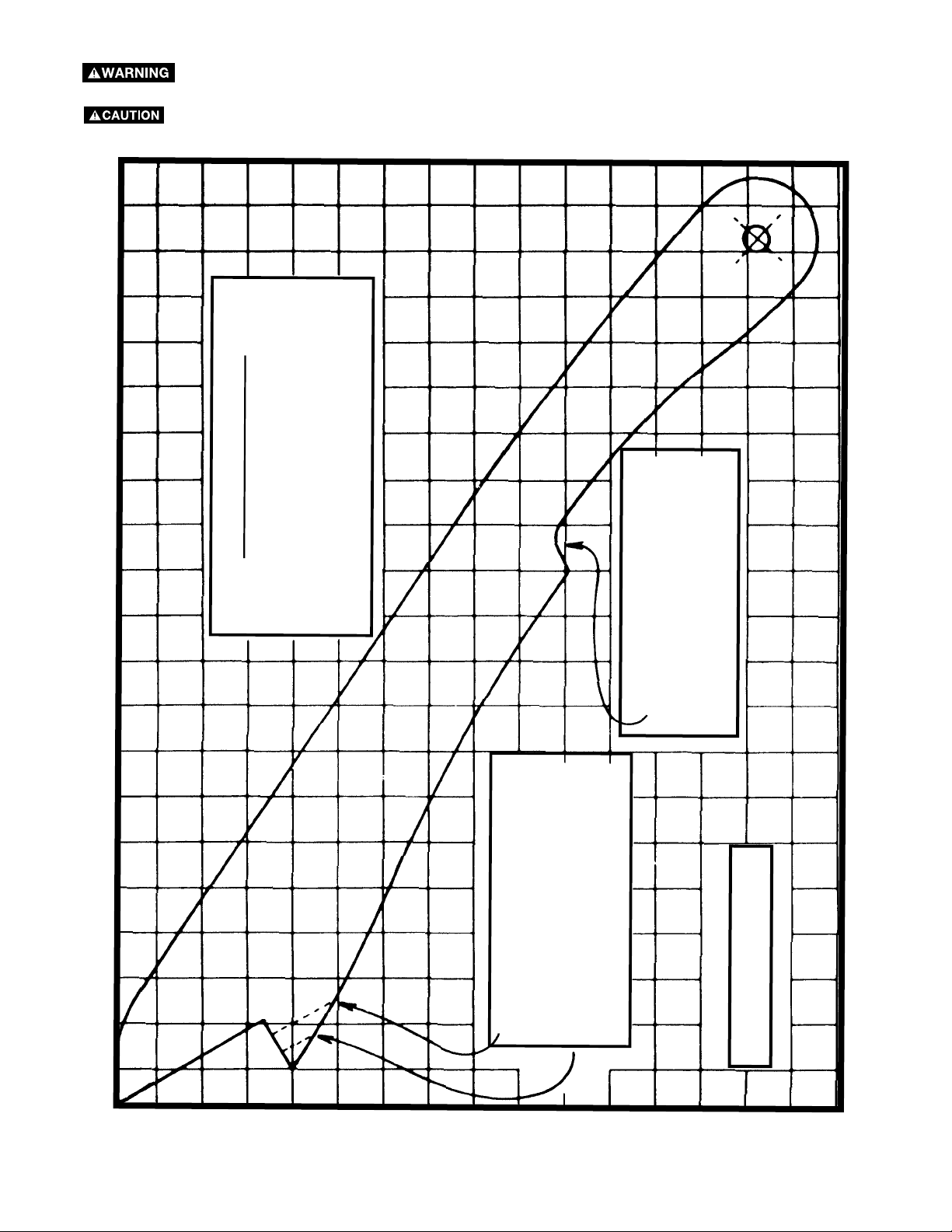
CONSTRUCTING A PUSH STICK
When ripping work less than 6" wide, a push-stick should be used to complete the feed and could easily be
made from scrap material by following the pattern shown in Fig. 83.
Make a push-stick from plywood or softwood, equal to or less than the width of the material to be cut.
PUSH STICK
thickness less than
width of material to be cut.
Make from 1/2" OR 3/4" WOOD or
prevent hand
Notch to help
from slipping.
27
Cut here to push 1/4" wood.
Cut here to push 1/2" wood.
1/2" Squares
Page 28

SERVICE
REPLACEMENT PARTS
Use only identical replacement parts. For a parts list or to order parts, visit our website at
You can also order parts from your nearest factory-owned branch, or by calling our Customer Care Center at 1-800-223-7278 to
receive personalized support from highly-trained technicians.
www.deltaportercableservicenet.com.
SERVICE AND REPAIRS
All quality tools will eventually require servicing and/or replacement of parts. For information about Delta Machinery, its factoryowned branches, or an Authorized Warranty Service Center, visit our website at www.deltaportercable.com or call our Customer
Care Center at 1-800-223-7278. All repairs made by our service centers are fully guaranteed against defective material and
workmanship. We cannot guarantee repairs made or attempted by others.
You can also write to us for information at Delta Machinery, 4825 Highway 45 North, Jackson, Tennessee 38305 - Attention:
Product Service. Be sure to include all of the information shown on the nameplate of your tool (model number, type, serial number,
etc.)
ACCESSORIES
Since accessories other than those offered by Delta have not been tested with this product, use
of such accessories could be hazardous. For safest operation, only Delta recommended accessories should be
used with this product.
A complete line of accessories is available from your Delta Supplier, Porter-Cable • Delta Factory Service Centers, and
Delta Authorized Service Stations. Please visit our Web Site www.deltaportercable.com for a catalog or for the name
of your nearest supplier.
WARRANTY
To register your tool for warranty service visit our website at www.deltaportercable.com.
Two Year Limited New Product Warranty
Delta will repair or replace, at its expense and at its option, any new Delta machine, machine part, or machine accessory which in normal
use has proven to be defective in workmanship or material, provided that the customer returns the product prepaid to a Delta factory service
center or authorized service station with proof of purchase of the product within two years and provides Delta with reasonable opportunity
to verify the alleged defect by inspection. For all refurbished Delta product, the warranty period is 180 days. Delta may require that electric
motors be returned prepaid to a motor manufacturer’s authorized station for inspection and repair or replacement. Delta will not be responsible
for any asserted defect which has resulted from normal wear, misuse, abuse or repair or alteration made or specifically authorized by anyone
other than an authorized Delta service facility or representative. Under no circumstances will Delta be liable for incidental or consequential
damages resulting from defective products. This warranty is Delta’s sole warranty and sets forth the customer’s exclusive remedy, with respect
to defective products; all other warranties, express or implied, whether of merchantability, fitness for purpose, or otherwise, are expressly
disclaimed by Delta.
LATIN AMERICA: This warranty does not apply to products sold in Latin America. For products sold in Latin America, see coun-
try specific warranty information contained in the packaging, call the local company or see website for warranty information.
28
Page 29

RIP
LOCK
Cutterhead
must be clamped
before performing
ripping operations.
YOKE
PIVOT
Pull handle toward
front of machine.
Pull plunger pin.
Pivot head to
desired position.
Push handle
back to lock.
BEVEL
ANGLE
Pull handle
toward
operator.
Pull plunger pin.
Set head to
desired bevel
angle. Push
handle to lock
head securely.
DEPTH
OF CUT
Lock head securely
on track arm.
Turn crank to raise
or lower blade depth.
MITER
ANGLE
Pull locking
arm to up
position. Depress
plunger and
move arm to
desired angle.
Push locking
arm back to
engage.
DOWN UP
DOWN
UNLOCK
LOCK
TO REDUCE
THE RISK OF
INJURY RETURN CUTTING HEAD TO FULL REAR
POSITION AFTER EACH CROSSCUT OPERATION.
SHUT OFF POWER AND WAIT FOR BLADE TO
STOP BEFORE SERVICING OR ADJUSTING.
PARA REDUCIR EL RIESGO DE LESIONES
COLOQUE NUEVAMENTE EL CABEZAL DE
CORTE EN SU POSICIÓN TRASERA MÁXIMA
DESPUÉS DE CADA CORTE TRANSVERSAL.
DESCONECTE LA ENERGÍA Y ESPERE A QUE LA
HOJA SE DETENGA ANTES DE REALIZAR
TAREAS DE MANTENIMIENTO O AJUSTES.
POUR RÉDUIRE LE RISQUE DE BLESSURES,
RAMENER LA TÊTE DE COUPE COMPLÈTEMENT
À L’ARRIÈRE APRÈS CHAQUE COUPE
TRANSVERSALE. COUPER L’ALIMENTATION
ET ATTENDRE L’ARRÊT DE LA LAME AVANT
DE RÉPARER OU DE RÉGLER LA SCIE.
TO AVOID INJURY NO
ADJUSTMENTS SHOULD
BE MADE UNTIL TOOL
HAS STOPPED.
FOR YOUR OWN SAFETY
DO NOT FEED MATERIAL
INTO CUTTING TOOL
FROM THIS END.
PARA EVITAR LESIONES,
NO DEBE REALIZARSE
NINGÚN AJUSTE HASTA
QUE LA HERRAMIENTA SE
HAYA DETENIDO.
POR SU PROPIA
SEGURIDAD, NO
INTRODUZCA MATERIAL
EN LA HERRAMIENTA DE
CORTE POR ESTE
EXTREMO.
TO REDUCE THE RISK OF
INJURY READ
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
BEFORE OPERATING RADIAL
SA W. ALWAYS WEAR EYE PROTECTION. DO NOT WEAR
GLOVES, NECKTIES, JEWELRY OR LOOSE CLOTHING.
DO NOT OPERATE WITHOUT GUARDS IN PLACE.
KEEEP HANDS OUT OF PATH OF SAW BLADE. DO
NOT PERFORM ANY OPERATING FREE-HAND.
ALWAYS SUPPORT WORK FIRMLY AGAINST FENCE.
ALWAYS FEED MATERIAL AGAINST ROTATION OF
BLADE AND USE ANTI-KICKBACK FINGERS WHEN
RIPPING. USE PUSH STICKS WHEN RIPPING NARROW
WORK. KNOW HOW TO REDUCE RISK OF KICKBACK. NEVER
REACH AROUND OR BEHIND SAW BLADE. DO NOT REMOVE JAMMED
OR SCRAP MATERIAL UNTIL BLADE HAS COMPLETELY STOPPED. RETURN CUTTING
HEAD TO FULL REAR POSITION UPON COMPLETION OF CROSSCUTS. SHUT OFF
POWER AND WAIT FOR SAW BLADE TO STOP BEFORE MOVING WORKPIECE OR
CHANGING TOOL SETTINGS. DISCONNECT POWER BEFORE CHANGING SAW BLADE
OR SERVICING TOOL. DO NOT EXPOSE TO RAIN OR USE IN DAMP LOCATIONS.
PARA REDUCIR EL RIESGO DE LESIONES
LEA EL MANUAL DE INSTRUCCIONES ANTES
DE OPERAR LA SIERRA RADIAL. UTILICE SIEMPRE PROTECCIÓN ADECUADA PARA
LOS OJOS. NO UTILICE GUANTES, CORBATAS, ALHAJAS NI ROPA HOLGADA. NO
OPERE LA SIERRA SI LOS PROTECTORES NO ESTÁN ADECUADAMENTE INSTALADOS.
MANTENGA LAS MANOS ALEJADAS DEL TRAYECTO DE LA HOJA DE LA SIERRA. NO
REALICE NINGUNA OPERACIÓN SIN UTILIZAR LAS MANOS. SIEMPRE SOSTENGA EL
TRABAJO FIRMEMENTE CONTRA LA GUÍA. SIEMPRE INTRODUZCA EL MATERIAL EN
SENTIDO CONTRARIO AL GIRO DE LA HOJA Y UTILICE DEDOS DE ANTIRETROCESO
CUANDO REALICE CORTES LONGITUDINALES. UTILICE VARAS DE EMPUJE AL
REALIZAR CORTES LONGITUDINALES EN PIEZAS DE TRABAJO ANGOSTAS. SEPA
CÓMO EVITAR EL RIESGO DE RETROCESOS. NUNCA INTENTE ALCANZAR OBJETOS
ALREDEDOR O DETRÁS DE LA HOJA DE LA SIERRA. NO RETIRE EL MATERIAL
ATASCADO O DE DESCARTE HASTA QUE LA HOJA NO SE HAYA DETENIDO
COMPLETAMENTE. COLOQUE NUEVAMENTE EL CABEZAL DE CORTE EN LA POSICIÓN
TRASERA MÁXIMA LUEGO DE REALIZAR CORTES TRANSVERSALES. DESCONECTE LA
ENERGÍA Y ESPERE A QUE LA HOJA SE DETENGA ANTES DE MOVER LA PIEZA DE
TRABAJO O CAMBIAR LA CONFIGURACIÓN DE LA HERRAMIENTA. DESCONECTE LA
ENERGÍA ANTES DE CAMBIAR LA HOJA DE LA SIERRA O REALIZAR TAREAS DE
MANTENIMIENTO. NO EXPONGA A LA LLUVIA NI UTILICE EN LUGARES HÚMEDOS
POUR RÉDUIRE LE RISQUE DE
BLESSURES, LIRE LE MODE D’EMPLOI
AVANT L’UTILISATION DE LA SCIE RADIALE. TOUJOURS PORTER UNE PROTECTION
OCULAIRE ADÉQUATE. NE PAS PORTER DE GANTS, NI CRAVATES, BIJOUX OU
VÊTEMENTS AMPLES. NE PAS UTILISER LA SCIE SANS QUE LES PROTÈGE-LAME NE
SOIENT EN PLACE. GARDER LES MAINS HORS DE LA TRAJECTOIRE DE LA LAME DE
LA SCIE. EFFECTUER TOUTE OPÉRATION EN TENANT L’OUTIL DES DEUX MAINS.
TOUJOURS APPUYER LA PIÈCE CONTRE LE GUIDE. TOUJOURS AVANCER LE MATÉRIEL
À CONTRE-COURANT DE LA ROTATION DE LA LAME ET UTILISER LES DOIGTS
ANTI-EFFET DE REBOND LORS DE SCIAGE EN LONG. UTILISER DES POUSSOIRS POUR
SCIER EN LONG UNE PIÈCE ÉTROITE. CONNAÎTRE LES TECHNIQUES POUR RÉDUIRE
LE RISQUE ASSOCIÉ À L’EFFET DE REBOND. NE PAS PASSER LES MAINS AUTOUR DE
LA LAME OU DERRIÈRE CELLE-CI. NE PAS RETIRER LA PIÈCE COINCÉE OU LA PIÈCE
DE CHUTE AVANT L’ARRÊT COMPLET DE LA LAME. RAMENER LA TÊTE DE COUPE
COMPLÈTEMENT À L’ARRIÈRE APRÈS DES COUPES TRANSVERSALES. COUPER
L’ALIMENTATION ET ATTENDRE L’ARRÊT COMPLET DE LA LAME DE LA SCIE AVANT
DE DÉPLACER LA PIÈCE OU DE MODIFIER LES RÉGLAGES. DÉBRANCHER LA SCIE
AVANT DE REMPLACER LA LAME OU D’EFFECTUER DES RÉPARATIONS. PROTÉGER
DE LA PLUIE ET NE PAS UTILISER DANS DES ENDROITS HUMIDES.
angle. Push
handle to lock
head securely.
DEPTH
OF CUT
Lock head securely
on track arm.
Turn crank to raise
or lower blade depth.
MITER
ANGLE
Pull locking
arm to up
position. Depress
plunger and
move arm to
desired angle.
Push locking
arm back to
engage.
DOWN UP
DOWN
UNLOCK
LOCK
POUR EMPÊCHER DES
BLESSURES, ATTENDRE
L’ARRÊT COMPLET DE
L’OUTIL AVANT D’EFFECTUER
TOUS RÉGLAGES.
POUR VOTRE PROPRE
SÉCURITÉ, NE PAS
INTRODUIRE DE MATÉRIAU
À PARTIR DE CETTE
EXTRÉMITÉ DE CET OUTIL.
TO AVOID INJURY NO
ADJUSTMENTS SHOULD
BE MADE UNTIL TOOL
HAS STOPPED.
FOR YOUR OWN SAFETY
DO NOT FEED MATERIAL
INTO CUTTING TOOL
FROM THIS END.
PARA EVITAR LESIONES,
NO DEBE REALIZARSE
NINGÚN AJUSTE HASTA
QUE LA HERRAMIENTA SE
HAYA DETENIDO.
POR SU PROPIA
SEGURIDAD, NO
INTRODUZCA MATERIAL
EN LA HERRAMIENTA DE
CORTE POR ESTE
EXTREMO.
FREE WARNING LABEL REPLACEMENT
If your warning labels become illegible or are missing, call
1-800-223-7278
for a free replacement.
29
Page 30

LES INSTRUCTIONS IMPORTANTES DE SURETE
Lire toutes instructions d'avertissements et opération avant d'utiliser n'importe
quel outil ou n'importe quel équipement. En utilisant les outils ou l'équipement, les précautions de
sûreté fondamentales toujours devraient être suivies pour réduire le risque de blessure personnelle.
L'opération déplacée, l'entretien ou la modification d'outils ou d'équipement ont pour résultat la
blessure sérieux et les dommages de propriété. Il y a de certaines applications pour lequel outils et l'équipement
sont conçus. La Delta Machinery recommande avec force que ce produit n'ait pas modifié et/ou utilisé pour
l'application autrement que pour lequel il a été conçu.
Si vous avez n'importe quelles questions relatives à son application n'utilisent pas le produit jusqu'à ce que vous
avez écrit Delta Machinery et nous vous avons conseillé. La forme en ligne de contact à www.deltaportercable.com
Courrier Postal: Technical Service Manager, Delta Machinery, 4825 Highway 45 North, Jackson, TN 38305.
125 Mural St. Suite 300, Richmond Hill, ON, L4B 1M4.
Information en ce qui concerne l'opération sûre et correcte de cet outil est disponible des sources suivantes:
• Power Tool Institute, 1300 Sumner Avenue, Cleveland, OH 44115-2851 ou en ligne www.powertoolinstitute.org
• National Safety Council, 1121 Spring Lake Drive, Itasca, IL 60143-3201
• American National Standards Institute, 25 West 43rd Street, 4 floor, New York, NY 10036 www.ansi.org - ANSI
01.1 Safety Requirements for Woodworking Machines
• U.S. Department of Labor: www.osha.gov
Dans Canada,
MESURES DE SÉCURITÉ - DÉFINITIONS
Ce guide contient des renseignements importants que vous deviez bien saisir. Cette information porte sur VOTRE SÉCURITÉ
et sur LA PRÉVENTION DE PROBLÈMES D’ÉQUIPEMENT. Afin de vous aider à identifier cette information, nous avons
utilisé les symboles ci-dessous. Veuillez lire attentivement ce guide en portant une attention particulière à ces sections.
Indique une situation dangereuse imminente qui, si elle n’est pas évitée, causera la mort ou des blessures
graves.
Indique une situation potentiellement dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas évitée, pourrait se solder par un décès
ou des blessures graves.
Indique une situation potentiellement dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas évitée pourrait se solder par des bles-
sures mineures ou modérées.
Utilisé sans le symbole d’alerte à la sécurité, indique une situation potentiellement dangereuse qui, si elle n'est
pas évitée pourrait se solder par des dommages à la propriété.
Certaines poussières produites par les travaux de ponçage, de sciage, de meulage,
de perçage et par toute autre activité de construction contiennent des produits chimiques reconnus par l’État
de la Californie comme pouvant causer le cancer, des anomalies congénitales ou d’autres problèmes liés aux
fonctions reproductrices. Voici quelques exemples de ces produits chimiques :
• leplombdespeinturesàbasedeplomb,
• lasilicecristallineprovenantdesbriques,ducimentetd’autresproduitsdemaçonnerieainsique,et
• l’arsenicetlechromeissusduboistraitéchimiquement.
Les risques reliés à l’exposition à ces produits chimiques varient selon la fréquence à laquelle l’utilisateur
effectue ce type de travail. Pour réduire l’exposition à ces produits chimiques : travailler dans un endroit
bien ventilé et porter un équipement de sécurité approuvé, notamment un masque antipoussières conçu
spécialement pour filtrer les particules microscopiques.
30
Page 31

RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ GÉNÉRALES
des risques de choc électrique, d’incendie et/ou de blessure grave.
lire toutes les directives avant d’utiliser le produit. Tout manquement aux directives suivantes pose
CONSERVER CES DIRECTIVES
DIRECTIVES RELATIVES À LA MISE À LA TERRE
tout choc électrique ou électrocution.
Si la scie est mise à la terre (intégré), lire les directives suivantes
RISQUE D’ÉLECTROCUTION. LE PRÉSENT APPAREIL DOIT ÊTRE MIS À LA TERRE LORS DE SON UTILISATION.
DE GRAVES BLESSURES PEUVENT SURVENIR.
POUR TOUS LES APPAREILS MIS À LA TERRE, BRANCHÉS À UN CORDON D’ALIMENTATION :
En cas de défaillance ou de panne, la mise à la terre permet un cheminement de moindre résistance pour le courant électrique
afin de réduire le risque de choc électrique. Cet appareil est muni d’un cordon d’alimentation doté d’un conducteur de mise à
la terre d’équipement et d’une fiche de mise à la terre. La fiche doit être branchée sur une prise de courant correspondante qui
est installée et mise à la terre conformément à tous les codes et à toutes les ordonnances à l’échelle locale. Ne pas modifier la
fiche fournie; si elle ne s’insère pas dans la prise de courant, faire installer une prise appropriée par un électricien professionnel. Si le conducteur de mise à la terre d’équipement n’est pas correctement connecté, ceci peut provoquer un choc électrique.
Le conducteur de mise à la terre d’équipement est le conducteur avec isolation qui a une surface extérieure verte avec ou
sans rayures jaunes. S’il est nécessaire de faire réparer ou remplacer le cordon électrique ou la fiche, ne pas connecter le
conducteur de mise à la terre d’équipement à une borne sous tension. Vérifier auprès d’un électricien ou d’un personnel de
réparation professionnel si les directives de mise à la terre ne sont pas parfaitement comprises ou en cas de doute sur le fait
que l’appareil soit correctement mis à la terre ou non. Utiliser uniquement une rallonge à 3 fils pourvue d’une fiche de mise à
la terre à 3 lames et une prise à 3 conducteurs correspondant à la fiche de l’appareil comme le montre la fig. A. Réparer ou
remplacer immédiatement le cordon s’il est endommagé ou usé.
SUIVRE TOUS LES CODES DE CÂBLAGE et les branchements électriques recommandés afin d’éviter
POUR LES APPAREILS MIS À LA TERRE ET BRANCHÉS À UN CORDON D’ALIMENTATION UTILISÉ
SUR UN CIRCUIT D’ALIMENTATION DE RÉGIME NOMINAL INFÉRIEUR À 150 V :
Si l’appareil est utilisé sur un circuit dont la prise de courant ressemble à celle de la fig. A, il aura alors une fiche de mise
à la terre semblable à celle de la fig. A. Un adaptateur temporaire, qui ressemble à celui de la fig. B, peut être utilisé pour
connecter cette fiche à une prise à 2 conducteurs, comme le montre la fig. B, s’il n’existe aucune prise de courant correctement mise à la terre. L’adaptateur temporaire ne doit être utilisé que jusqu’à ce qu’un électricien qualifié puisse installer une
prise électrique correctement mise à la terre. La patte rigide verte, la cosse et tout élément semblable sortant de l’adaptateur
doivent être correctement branchés à une masse permanente comme une boîte de sortie mise à la terre. Chaque fois que
l’adaptateur est utilisé, il doit être maintenu en place par une vis métallique.
A B
REMARQUE : Au Canada, l’utilisation d’un adaptateur temporaire n’est pas autorisée par le Code électrique canadien.
BOÎTE DE SORTIE
DE
MISE À LA TERRE
GOUPILLE DE MISE À
LA TERRE
C
MOYENS DE MISE À
LA TERRE
ADAPTATEUR
D
GOUPILLE DE MISE À
LA TERRE
À LA TERRE. EN CAS DE DOUTE, DEMANDER À UN ÉLECTRICIEN PROFESSIONNEL DE VÉRIFIER LA PRISE.
DANS TOUS LES CAS, S’ASSURER QUE LA PRISE DE COURANT EN QUESTION EST CORRECTEMENT MISE
31
Page 32
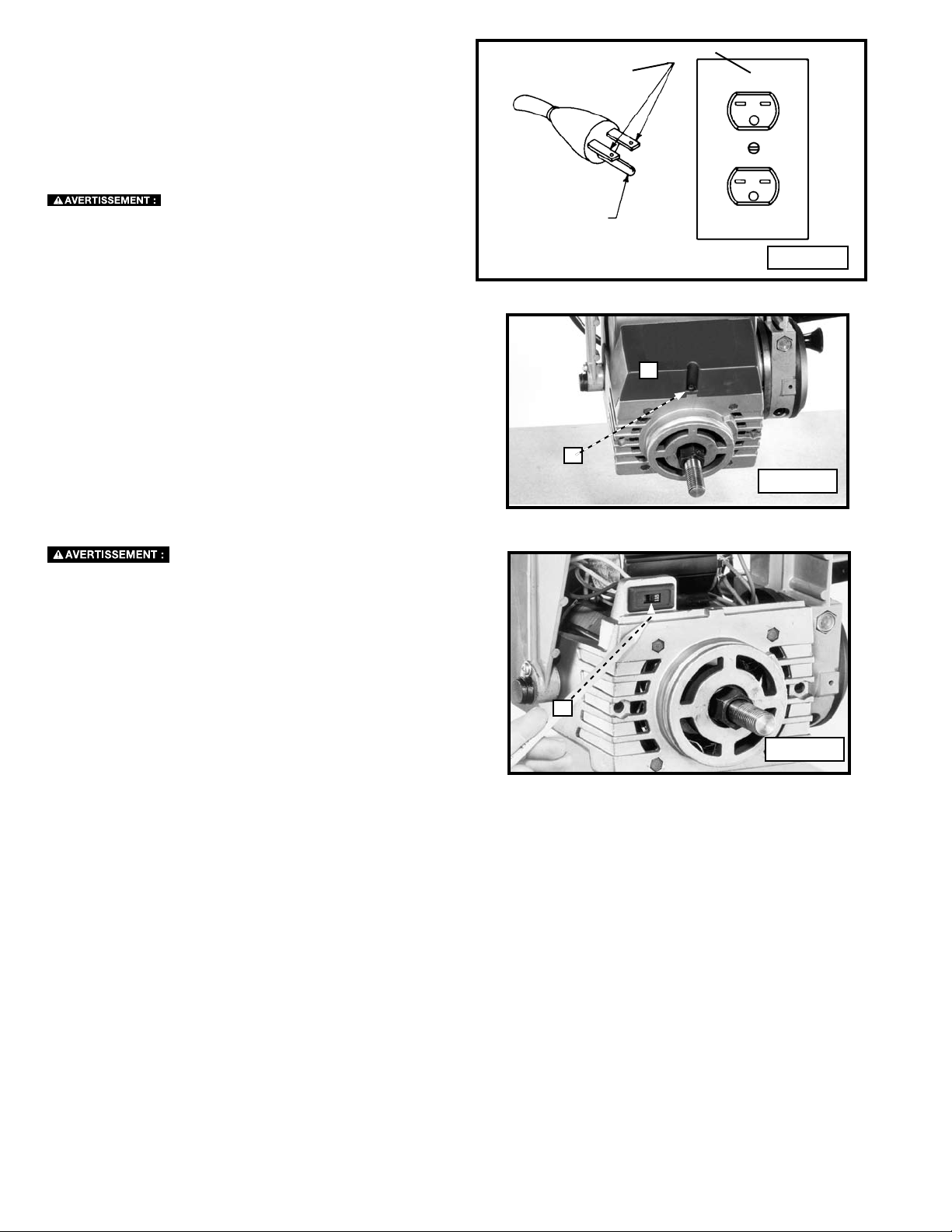
240 OPERATION DE PHASE DE SEUL DE VOLT
Le moteur double tension 120/240 vol ts fourni avec
votre appareil a été préparé à sa sortie d’usine pour une
utilisation sous 120 volts. Toutefois, il peut être converti au
fonctionnement sous 240 volts.
Utiliser les instructions suivantes pour convertir votre scie à
240 volts.
Pour réduire le risque de blessures corporelles graves, éteindre l’outil et le débrancher avant
d’installer et de retirer tout accessoire, avant d'ajuster ou de
modifier les réglages ou lors de réparations. Un démarrage
accidentel peut provoquer des blessures.
1. Enlever la vis (A) Figure D et enlever le cache de la plaque
signalétique (B).
2. Faire glisser avec précaution l’interrupteur (C) Figure E
dans la boîte de jonction du moteur de façon à ce que
240 volts soit affiché. Replacer le cache de la plaque
signalétique et revisser la vis enlevée à l’ÉTAPE1.
3. Vous devez également remplacer la fiche de 120 volts par
une fiche convenable pour du 240 volts, homologuée UL/
CSA, prévue pour le courant nominal de la scie.
Faire appel à un électricien qualifié pour faire la conversion
ou utiliser les services d’un centre de réparations agréé Delta.
L’appareil doit être conforme au Code électrique national et à
tous les codes et à toutes les ordonnances à l’échelle locale.
Utiliser la fiche de 240 volts UNIQUEMENT dans une prise qui
a la même configuration que la fiche de la figure C. NE PAS
utiliser d’adaptateur pour la fiche de 240 volts.
BOÎTE DE SORTIE MISE À LA TERRE
LAMES
CONDUCTRICES
LA LAME DE MISE À LA TERRE
EST LA PLUS LONGUE DES
TROIS LAMES
B
A
Fig. C
Fig. D
QUE LA FICHE EN QUESTION EST MISE À LA TERRE
DANS TOUS LES CAS, S’ASSURER
ADÉQUATEMENT. EN CAS DE DOUTES, DEMANDER À UN
ÉLECTRICIEN PROFESSIONNEL DE VÉRIFIER LA PRISE.
C
Fig. E
DIRECTIVES DE SÉCURITÉ IMPORTANTES
1. POUR RÉDUIRE LE RISQUE D’EFFET DE REBOND, CONSERVER LES DISPOSITIFS DE PROTECTION EN PLACE et en bon
état de fonctionnement.
2. RETIRER LES CLÉS À MOLETTE ET LES CLÉS DE RÉGLAGE. S’habituer à vérifier si les clés à molette et les clés de réglage
sont retirées de la broche avant de mettre l’outil sous tension. Des outils, chutes, et autres débris peuvent être projetés à grande
vitesse, provoquant des blessures.
3. GARDER LA ZONE DE TRAVAIL PROPRE. Les zones et établis encombrés sont souvent des causes d’accidents.
4. NE PAS UTILISER LE PRÉSENT APPAREIL DANS UN ENVIRONNEMENT DANGEREUX. L’utilisation d’outils électriques dans
un endroit humide ou mouillé ou sous la pluie peut provoquer un choc électrique ou une électrocution. Tenir la zone de travail bien
éclairée pour éviter de trébucher ou de mettre vos bras, mains et doigts en danger.
32
Page 33

5. TENIR LES ENFANTS À L’ÉCART. Tous les visiteurs doivent se trouver à une distance sûre de la zone de travail. L’atelier représente
un environnement potentiellement dangereux.
6. S’ASSURER QUE L’ATELIER NE PRÉSENTE PAS DE DANGER POUR LES ENFANTS en utilisant des cadenas, des interrupt-
eurs principaux ou en retirant les clés de démarrage. Le démarrage non autorisé d’un appareil par un enfant ou un visiteur pourrait
se solder par des blessures.
7. NE PAS FORCER L’OUTIL. Le travail sera mieux accompli et sera moins dangereux au rythme prévu pour l’appareil.
8. UTILISER L’OUTIL APPROPRIÉ. Ne pas forcer un outil ou un accessoire à accomplir un travail pour lequel il n’a pas été conçu.
L’utilisation de l’outil ou de l’accessoire de façon incorrecte pourrait se solder par des blessures corporelles.
9. UTILISER LA RALLONGE APPROPRIÉE. S’assurer que la rallonge est en bon état. Si le produit est doté d’un cordon d’alimentation,
utiliser uniquement une rallonge à 3 fils pourvue d’une fiche de mise à la terre à 3 lames et une prise à 3 fentes correspondant à la
fiche de l’outil. Lorsque qu’une rallonge électrique est utilisée, s’assurer d’en utiliser une de calibre suffisamment élevé pour assurer
le transport du courant nécessaire au fonctionnement de l’appareil. Un cordon de calibre inférieur causera une chute de tension de
ligne et donc une perte de puissance et une surchauffe. Le tableau suivant indique le calibre approprié à utiliser selon la longueur
du cordon et l’intensité nominale de la plaque signalétique. En cas de doute, utiliser le calibre suivant le plus gros. Plus le numéro
de calibre est petit, plus le cordon est lourd.
CALIBRE MINIMUM POUR RALLONGE
Volts Longueur totale de la rallonge en pieds
120 V 0-25 26-50 51-100 101-150
240 V 0-50 51-100 101-200 201-300
Intensité nominale
Plus Pas plus AWG
de de
0 - 6 18 16 16 14
6 - 10 18 16 14 12
10 - 12 16 16 14 12
12 - 16 14 12 Non recommandé
10. PORTER LES VÊTEMENTS APPROPRIÉS. Ne pas porter ni vêtement ample, ni gant, ni cravate, ni bague, ni bracelet, ni autre
bijou, car ces derniers pourraient s’enchevêtrer dans des pièces mobiles. Des souliers antidérapants sont recommandés. Se couvrir
les cheveux s’ils sont longs. Se tenir éloigné des évents, car ces derniers pourraient camoufler des pièces mobiles.
11. TOUJOURS PORTER DES LUNETTES DE SÉCURITÉ. Les lunettes de vue ne constituent PAS des lunettes de sécurité. Utiliser
également un masque facial ou anti-poussière si l’opération de découpe génère de la poussière. TOUJOURS porter un équipement
de protection homologué :
• protectionoculaireconformeàlanormeANSIZ87.1(CAN/CSAZ94.3);
• protectionauditiveANSIS12.6(S3.19)et;
• protectiondesvoiesrespiratoiresconformesauxnormesNIOSH/OSHA/MSHA.
12. NE PAS TROP TENDRE LES BRAS. Conserver son équilibre en tout temps. Une perte d’équilibre risquerait d’entraîner une bles-
sure corporelle.
13. PRENDRE SOIN DES OUTILS. S’assurer que les lames sont aiguisées et propres afin d’optimiser sécurité et performance.
Suivre les consignes de graissage et de changement d’accessoires. Les lames et les appareils mal entretenus peuvent
s’endommager davantage et/ou provoquer des blessures.
14. ÉTEINDRE L’APPAREIL ET COUPER LE COURANT avant d’installer ou de retirer des accessoires, avant tout réglages ou modifi-
cations de celles-ci, lors de réparation ou de déplacements de l’appareil. Lors du branchement/débranchement de la fiche, prendre
garde de ne pas toucher à ses lames métalliques. Un démarrage accidentel peut provoquer des blessures.
15. RÉDUIRE LE RISQUE DE DÉMARRAGE ACCIDENTEL. S’assurer que l’interrupteur se trouve sur la position d’arrêt avant de
brancher le cordon d’alimentation. En cas de panne de courant, mettre l’interrupteur sur la position d’arrêt. Un démarrage accidentel peut provoquer des blessures.
16. UTILISATION DES ACCESSOIRES RECOMMANDÉS. N’utiliser que les accessoires conseillés par le fabricant pour le modèle de
votre outil. Des accessoires qui conviennent à un outil pourraient être dangereux lorsqu’ils sont utilisés avec un autre outil. Une liste
des accessoires recommandés se trouve dans le mode d’emploi. L’utilisation d’accessoires inappropriés peut entraîner un risque
de blessure corporelle.
17. NE JAMAIS SE TENIR SUR L’OUTIL. Une blessure grave pourrait se produire en cas de basculement de l’outil ou de démarrage
accidentel de l’outil de découpe.
18. VÉRIFIER QUE LES PIÈCES NE SONT PAS ENDOMMAGÉES. Avant toute utilisation ultérieure de l’outil, un protège-lame (ou
une autre pièce) endommagé doit être soigneusement examiné afin de déterminer s’il fonctionnera correctement et s’il remplira
sa fonction prévue – vérifier l’alignement des pièces mobiles, la présence de grippage des pièces mobiles, la rupture de pièces,
la fixation et tout problème pouvant nuire au fonctionnement de l’outil. Un protège-lame (ou toute autre pièce) endommagé doit
être réparé et remplacé adéquatement. Ne pas utiliser l’outil si l’interrupteur ne fonctionne pas. Les pièces endommagées peuvent
contribuer à endommager davantage l’appareil et/ou provoquer des blessures corporelles.
19. DIRECTION DE L’AVANCEMENT DE LA PIÈCE. Acheminer la pièce dans une lame ou un couteau uniquement à contre-courant
de la rotation de la lame ou du couteau.
20. NE JAMAIS LAISSER L’OUTIL FONCTIONNER SANS SURVEILLANCE. ÉTEINDRE L’APPAREIL. Ne pas laisser l’outil tant qu’il
n’est pas complètement arrêté. De graves blessures pourraient survenir.
21. NE PAS UTILISER D’OUTILS ÉLECTRIQUES À PROXIMITÉ DE LIQUIDES INFLAMMABLES OU DANS UNE ATMOSPHÈRE
GAZEUSE OU EXPLOSIVE. Les moteurs et interrupteurs des outils pourraient provoquer des étincelles et enflammer des
vapeurs.
22. ÊTRE VIGILANT, SURVEILLER LE TRAVAIL EFFECTUÉ, ET FAIRE PREUVE DE JUGEMENT. NE PAS UTILISER L’APPAREIL
EN CAS DE FATIGUE OU SOUS L’INFLUENCE DE DROGUES, D’ALCOOL, OU DE MÉDICAMENTS. Un moment d’inattention,
durant l’utilisation d’un outil électrique, peut se solder par des blessures corporelles graves.
23. NE PAS LAISSER UNE BONNE CONNAISSANCE DE L’OUTIL (ACQUISE PAR L’UTILISATION FRÉQUENTE DE LA SCIE)
PRENDRE PRÉCÉDENCE SUR LES RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ. Toujours se souvenir qu’une fraction de seconde d’imprudence est
suffisante pour infliger de graves blessures.
33
Page 34

RÈGLES SPÉCIFIQUES ADDITIONNELLES DE SÛRETÉ
L’inobservation de ces règles peut conduire à des blessures graves.
TOUJOURS PORTER DES LUNETTES DE SÉCURITÉ. Les lunettes de vue ne constituent PAS des lunettes de sécurité. Utiliser
1.
également un masque facial ou anti-poussière si l’opération de découpe génère de la poussière. Tous les utilisateurs et les personnes à proximité DOIVENT TOUJOURS utiliser un équipement de sécurité homologué :
• protectionoculaireconformeàlanormeANSIZ87.1(CAN/CSAZ94.3),
• protectionauditiveconformeàlanormeANSIS12.6(S3.19)et
• protectiondesvoiesrespiratoiresconformesauxnormesNIOSH/OSHA/MSHA.
2. ÉVITER de placer les mains à un endroit où un glissement soudain pourrait amener la main sur la lame de la scie.
3. GARDER LES BRAS, LES MAINS, ET LES DOIGTS ÉLOIGNÉS de la lame afin d’éviter des blessures graves.
4. UTILISER UN POUSSOIR OU UN BLOC-POUSSOIR ADÉQUAT POUR L’APPLICATION EN COURS, QUI PERMET
D’AVANCER LES PIÈCES SUR LA LAME. Un poussoir est un petit bâton de bois ou d’une matière non métallique,
normalement fait maison, qui s’utilise pour éviter d’approcher vos mains à près de15,2 cm (6 po) de la lame à chaque fois que la
taille ou la forme de la pièce l’exige.
5. NE PAS SCIER EN LONG, EXÉCUTER DES TRONÇONNAGES OU TOUTE AUTRE OPÉRATION DE COUPE À MAINS
LIBRES.
6. NE JAMAIS s’incliner près ou au-dessus de la lame de scie.
7. STABILITÉ. S’assurer que le banc de scie soit fermement fixé à une surface solide et qu’il ne bouge pas avant de l’utiliser.
8. NE JAMAIS COUPER DE MÉTAUX FERREUX (métaux contenant du fer ou de l’acier), PANNEAU DE CIMENT OU
MAÇONNERIE. Certaines matières artificielles comportent des directives spécifiques pour la coupe sur des bancs de scie.
Suivre les recommandations du fabricant en tout temps. Il sera ainsi possible de prévenir des dommages à la scie ou des
blessures corporelles.
9. UTILISER LA LAME DE SCIE APPROPRIÉE POUR L’UTILISATION PRÉVUE. Respecter les directives décrites sous la
rubrique Fonctionnement du mode d’emploi pour connaître la bonne procédure pour tout type de coupe. Toujours serrer
solidement l’écrou d’axe de la lame. Avant l’utilisation, inspecter la lame pour toutes traces de fissures ou de dents manquantes.
Ne pas utiliser de lame endommagée.
10. NE JAMAIS TENTER DE DÉBLOQUER UNE LAME COINCÉE SANS AVOIR MIS L’APPAREIL HORS FONCTION AU
PRÉALABLE. Si une pièce ou un morceau de bois se coince dans le protège-lame, arrêter la scie, débrancher l’appareil et
attendre l’immobilisation complète de la lame avant de relever le protège-lame et de retirer la pièce.
11. NE JAMAIS DÉMARRER L’APPAREIL avec la pièce contre la lame afin de réduire le risque de projection de la pièce et de
blessures corporelles.
12. NE JAMAIS avancer la pièce entre le guide longitudinal et une tête de coupe pour moulure pour réduire le risque de projection de
la pièce et de blessures corporelles.
13. ÉVITER LES OPÉRATIONS MALADROITES ET ÉVITER D’AVOIR LES MAINS MAL PLACÉES : en glissant soudainement, une
main pourrait percuter la lame.
14. AUCUNE PARTIE DU CORPS NE DOIT SE TROUVER DANS LA TRAJECTOIRE DE LA LAME DE LA SCIE. Sinon, il y aurait
risque de blessures.
15. NE JAMAIS EFFECTUER D’OPÉRATIONS DE TRAÇAGE, D’ASSEMBLAGE, OU DE RÉGLAGE sur la table/l’espace de travail
lorsque l’appareil est en marche. Un glissement soudain de la pièce pourrait entraîner votre main vers la lame. Des blessures
graves pourraient survenir.
16. NETTOYER LA TABLE/ESPACE DE TRAVAIL AVANT DE LAISSER L’APPAREIL. Verrouiller l’interrupteur en position d’arrêt
et débrancher l’appareil pour empêcher toute utilisation non autorisée
17. NE PAS LAISSER une planche longue (ou une autre pièce) sans appui de sorte que l’élasticité de la planche provoque un
déplacement sur la table de la scie. Un tel déplacement pourrait se solder par une perte de maîtrise et une blessure éventuelle. Bien
soutenir la pièce en fonction de sa taille et du type d’opération à exécuter. Tenir la pièce fermement contre le guide et la surface
de la table.
18. NE PAS UTILISER L’APPAREIL avant qu’il ne soit entièrement assemblé et installé conformément aux directives. Un appareil mal
assemblé peut provoquer des blessures graves.
19. DEMANDER CONSEIL CONSEIL à un superviseur, instructeur ou toute autre personne qualifiée si l’on ne maîtrise pas parfaitement
l’utilisation de cet appareil. La connaissance est synonyme de sécurité
20. DES INFORMATIONS SUPPLÉMENTAIRES (c.-à-d., une vidéo sur la sécurité), indiquant comment utiliser des outils électriques
correctement et en toute sécurité, sont disponibles auprès du Power Tool Institute, 1300 Sumner Avenue, Cleveland, OH
44115-2851, États-Unis (www.powertoolinstitute.com). Des renseignements sont également disponibles auprès du National Safety
Council, 1121 Spring Lake Drive, Itasca, IL 60143-3201 É.-U. Se reporter à la norme ANSI 01,1 de l’American National Standards
Institute concernant les machines de travail du bois, ainsi qu’à la réglementation OSHA 1910.213. du ministère américain du
travail.
réduire les risques potentiels, voici les règles à respecter:
a. GARDER LES MAINS LOIN DU PROTÈGE-LAME. Lorsque la lame coupe, le protège-lame se soulève et une partie de la lame
est exposée.
b. ÉTEINDRE L'APPAREIL ET LE DÉBRANCHER AVANT DE LIBÉRER UN PROTÈGE-LAME INFÉRIEUR COINCÉ. Le protège-
lame peut se coincer à cause de traits de scie sur le banc ou le guide. Toujours prévoir le chemin emprunté par le protègelame.
c. PRENDRE GARDE lors des coupes en biseau : s'assurer que le protège-lame inférieur n'est jamais coincé dans la lame.
d. LE PROTÈGE-LAME INFÉRIEUR PEUT SE COINCER CONTRE LE GUIDE PENDANT LES SCIAGES ÉTROITS VERS
L'INTÉRIEUR. Si le protège-lame se coince contre le guide, débrancher la scie, attendre que la lame s'immobilise, puis soulever
le protège-lame et le poser sur le dessus du guide.
Le protège-lame rétractable inférieur protège l’utilisateur sur les côtés de la lame de la scie. Pour
34
Page 35

TERMINOLOGIE : Les termes suivants seront utilisés dans le manuel et vous devriez vous familiariser avec ceux-ci.
• DÉBITAGE COMPLET : définit une coupe de part en autre de la pièce.
• POUSSOIR : est un petit bâton de bois, normalement fait maison, qui s’utilise pour pousser la pièce et éviter d’approcher les
mains près de la lame à chaque fois que la taille ou la forme de la pièce l’exige.
• EFFET DE REBOND : se produit lorsque la lame de la scie se coince dans le trait de scie et projette violemment la pièce en
direction de l’opérateur.
• COUPE À MAINS LIBRES : définit une coupe sans l’utilisation d’un guide d’onglet ou longitudinal ou tout autre mode de guidage
ou de soutien de la pièce autre que les mains de l’opérateur.
PROTÈGE-LAME ET COUTEAU SÉPARATEUR
La scie à bras radial est dotée d’un protège-lame, d’un couteau séparateur et de linguets antireculs. Le couteau séparateur s’insère
dans le trait de coupe formé par la lame de la scie lors de sciage en long et protège effectivement contre les rebonds en diminuant
la tendance de la lame à se coincer dans le trait de scie. Pour tous les types de coupes, toujours utiliser le couteau séparateur et le
protège-lame adéquatement positionné. Deux cliquets antireculs sont logés sur les côtés du couteau séparateur. Ils permettent à la
pièce d’avancer sur la lame, mais se bloquent si la pièce recule en direction de l’opérateur.
EFFETS DE REBOND
Comment les éviter et se protéger de blessures éventuelles.
a. S’assurer que le guide longitudinal est parallèle à la lame de la scie.
b. Ne pas exécuter un sciage en long en appliquant la force sur la portion fixe qui deviendra la pièce coupée. Au cours du sciage
en long, la force doit toujours être appliquée entre la lame de la scie et le guide. Utiliser un poussoir pour les pièces courtes, soit
celles de 152 mm (6 po) de largeur ou moins.
c. Maintenir le protège-lame, le couteau séparateur et les dents antireculs en position et en bon état de fonctionnement. Maintenir
les dents affûtées. Si les dents ne fonctionnent pas, retourner l’appareil au centre de réparation Delta autorisé le plus près pour
une réparation. Le couteau séparateur doit être aligné avec la lame de la scie et les dents doivent arrêter un effet de rebond une
fois l’appareil amorcé. Vérifier le fonctionnement des ensembles avant le sciage en long en avançant une pièce de bois sous les
dents antireculs. Les dents doivent empêcher la projection de la pièce de bois vers l’avant de la lame de la scie.
d. Il est possible de couper des matières plastiques et du composé (comme des panneaux pressés) avec la scie. Toutefois, puisque
ces matières sont normalement très dures et glissantes, il est possible que les cliquets antireculs ne puissent pas contenir un
effet de rebond. On doit donc suivre attentivement les procédures de montage et de coupe lors de sciages en long.
e. Utiliser un protège-lame pour toutes les opérations demandant son utilisation, y compris tout débitage complet.
f. Lors de sciage en long, pousser la pièce au-delà de la lame de scie avant de relâcher la pièce.
g. Ne JAMAIS scier en long une pièce qui est tordue ou voilée ou qui n’a pas de bord droit pour glisser le long du guide.
h. Ne JAMAIS scier une grande pièce qui ne peut pas être contrôlée.
i. Ne JAMAIS scier une pièce à nœuds instables, avec défauts, clous ou tout autre corps étranger.
j. Ne JAMAIS débiter une pièce plus courte que 254 mm (10 po).
k. Toujours utiliser des linguets antireculs pour les coupes longitudinales. Abaisser le protège-lame sur l’extrémité de l’alimentation
et régler correctement l’accessoire antirecul.
tiennent des produits chimiques reconnus par l’État de la Californie comme pouvant causer le cancer, des anomalies congénitales ou d’autres problèmes liés aux fonctions reproductrices. Voici quelques exemples de ces produits chimiques
• leplombcontenudanslespeinturesàbasedeplomb,
• lasilicecristallinedelabrique,ducimentetd’autresproduitsdemaçonnerie,et
• l’arsenicetlechromeprovenantduboistraitéchimiquement.
Les risques reliés à l’exposition à ces poussières varient selon la fréquence à laquelle l’utilisateur travaille avec ce type de matériaux. Pour réduire l’exposition à ces produits chimiques : travailler dans un endroit bien ventilé et porter un équipement de sécurité
approuvé comme un masque antipoussières conçu spécialement pour filtrer les particules microscopiques.
• Éviter le contact prolongé avec les poussières produites par les activités de ponçage, sciage, meulage, perçage et autres
activités de construction. Porter des vêtements de protection et laver les parties du corps exposées avec une solution
d’eau et de savon. Laisser la poussière pénétrer dans la bouche et les yeux ou la laisser reposer sur la peau, pourrait promouvoir
l’absorption de produits chimiques nocifs.
ratoires graves et permanents et d’autres blessures. Toujours porter un appareil respiratoire approuvé par la NIOSH/OSHA pour se
protéger de la poussière. Diriger les particules loin du visage et du corps. Toujours utiliser l’outil dans des endroits bien aérés et veiller
à dépoussiérer correctement la zone de travail. Utiliser un système de dépoussiérage lorsque c’est possible.
certaines poussières produites par les travaux de ponçage, sciage, meulage, perçage et autres con-
l’utilisation de cet outil peut produire de la poussière et/ou la disperser, ce qui peut causer des troubles respi-
DESCRIPTION FONCTIONNELLE
AVANT-PROPOS
Le modèle Delta RS830 est une scie à bras radial professionnelle de 254 mm (10 po) avec une capacité de coupe maximum de 406,4
mm (16 po), une profondeur de 70 mm (2-3/4 po) à un angle de 90° et une profondeur de 64 mm (2-1/2 po à un angle de 45°. Cet outil
possède une butée de biseau positive à 0°, 45° et 90° et une butée d’onglet positive à 0° et 45°, à droite et à gauche. L’unité inclut un
moteur 120/240V de 1,5 HP, un frein de lame automatique, une lame, des clés, un socle en acier, un rail en fonte et une table extra large.
REMARQUE : La illustration de la couverture du mode d’emploi illustre le modèle de production actuel. Les autres illustrations de ce
mode d’emploi ne sont présentes qu’à titre indicatif et il est possible que les étiquettes et accessoires actuels diffèrent des caractéristiques réelles de ce modèle. Ces illustrations ont uniquement pour but d’illustrer la technique.
35
Page 36
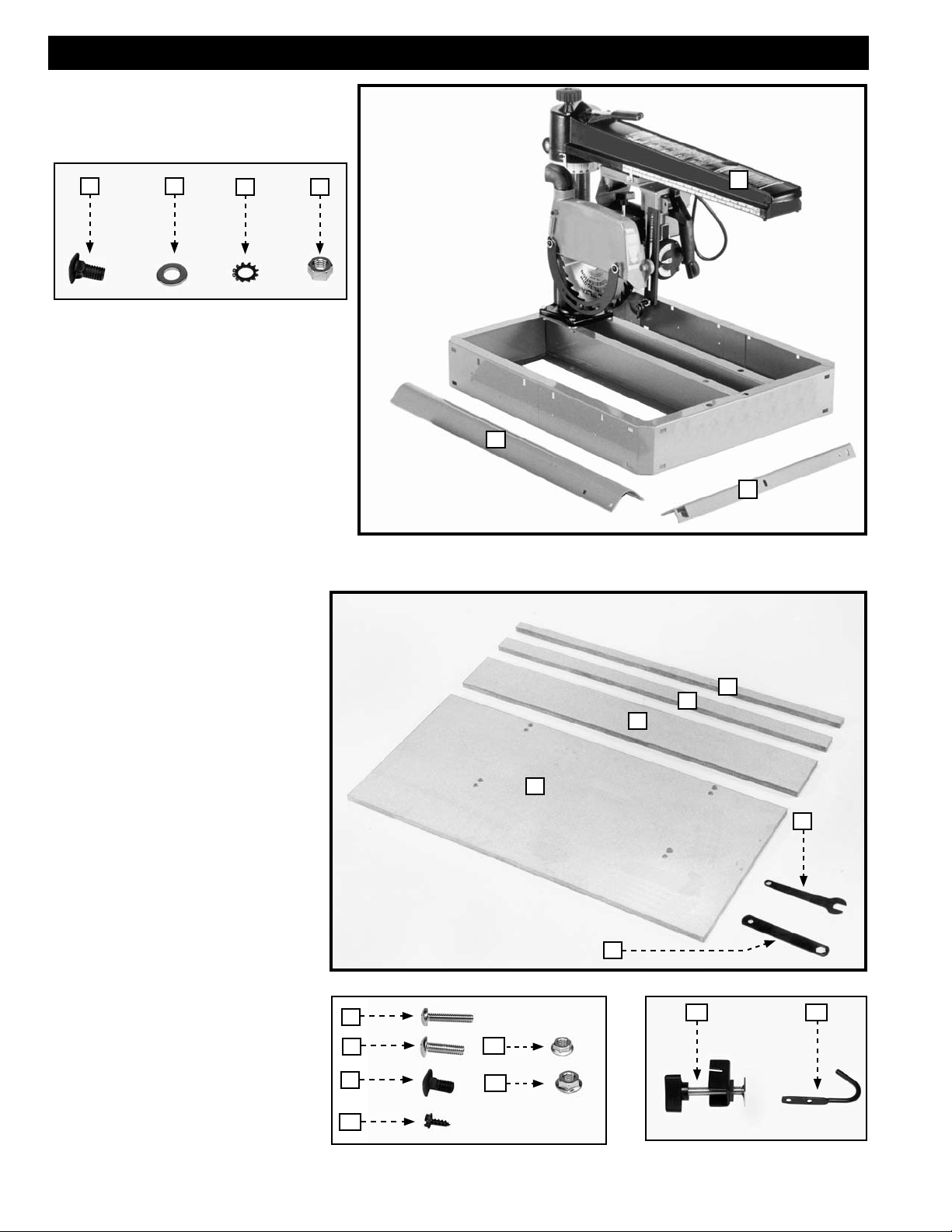
CONTENUS DE BOITE
PIÈCES DE LA SCIE À BRAS RADIAL
4 5
1. Scie à bras radial
2. (4) pattes
3. Supports de banc (2)
4. Vis de chariot de 7,9 mm -18 x 15,9 mm
(5/16 - 18 x 5/8 po) (16)
5. Rondelles plates de 7,9 mm (5/16 po) (16)
6. Rondelles de blocage dentées de 7,9 mm
(5/16 po) (16)
7. Écrous hexagonaux de 7,9 mm (5/16 po)
-18 (16)
6 7
PIÈCES DE LA PLANCHE DE BANC
1. Planche du guide
2. Planche du milieu du banc
3. Planche arrière du banc
4. Planche avant du banc
5. Clé à fourche de 22,2 mm (7/8 po) -
Clé polygonale de 12,7 mm (1/2 po)
6. Clé polygonale de 22,2 mm x 12,7
mm (7/8 po x 1/2 po)
7. Vis à tête ronde de 6,3 mm - 20 x
31,7 mm (1/4 po - 20 x 1 1/4 po) (4)
8. Vis à tête ronde de 6,3 mm - 20 x
25,4 mm 1/4 po - 20 x 1 po) (4)
9. Vis de chariot de 7,9 mm -18 x 15,9
mm (5/16 po - 18 x 5/8 po) (6)
10. Vis à tôle n° 10 x 12,7 mm (10 x 1/2
po) (2)
11. Écrous hexagonaux à embase de 6,3
mm (1/4 po) - 20 (4)
12. Écrous hexagonaux à embase de 7,9
mm (5/16 po) -18 (6)
13. Serres pour planche de banc (2)
14. Crochet pour clé
7
8
9
1
2
3
1
2
3
4
5
6
13 14
11
12
10
36
Page 37

DÉSEMBALLAGE ET NETTOYAGE
Désemballer soigneusement la machine et toutes les pièces de ou des emballage(s) d’expédition. Retirer l’huile anticorrosion
des surfaces non peintes à l’aide d’un chiffon doux humidifié avec de l’alcool, du diluant à peinture ou de l’alcool dénaturé.
N’utiliser pas de solvants hautement volatils tel l’essence, le naphte, l’acétone ou du diluant à laque
pour nettoyer.
Après nettoyage, couvrir les surfaces non peintes d’une cire à parquets d’usage domestique de bonne qualité.
1. La scie a été emballée en usine avec des cales de
soutien (A) Figure A1 sous la tête de coupe (B) et le
bras (C). Des planches (D) Figure A1 ont été attachées
à la base de la scie (G) pour l’expédition. Pour éviter les
dommages pendant l’expédition, le bouton d’élévation
du bras (H) a été enlevé du levier (E). Insérer le montant
du bouton (H) Figure A2 dans le trou du levier (E).
Attacher l’anneau de retenue en forme de E (K) dans le
guide du montant.
2. Vous pouvez enlever les cales de soutien (A) Figure
A1 en tournant le bouton d’élévation du bras (H) dans
le sens des aiguilles d’une montre. Vous pouvez alors
enlever les planches d’expédition (D) en retirant les
vis de fixation (non illustrées) situées dans la base de
la scie. Jeter les cales de soutien (A) et les planches
d’expédition (D).
3. La scie sans les cales de soutien et les planches
d’expédition est illustrée sur la (Fig. A3).
Fig. A2
H
H
E
C
B
A
D
D
A
G
Fig. A1
E
K
Fig. A3
37
Page 38
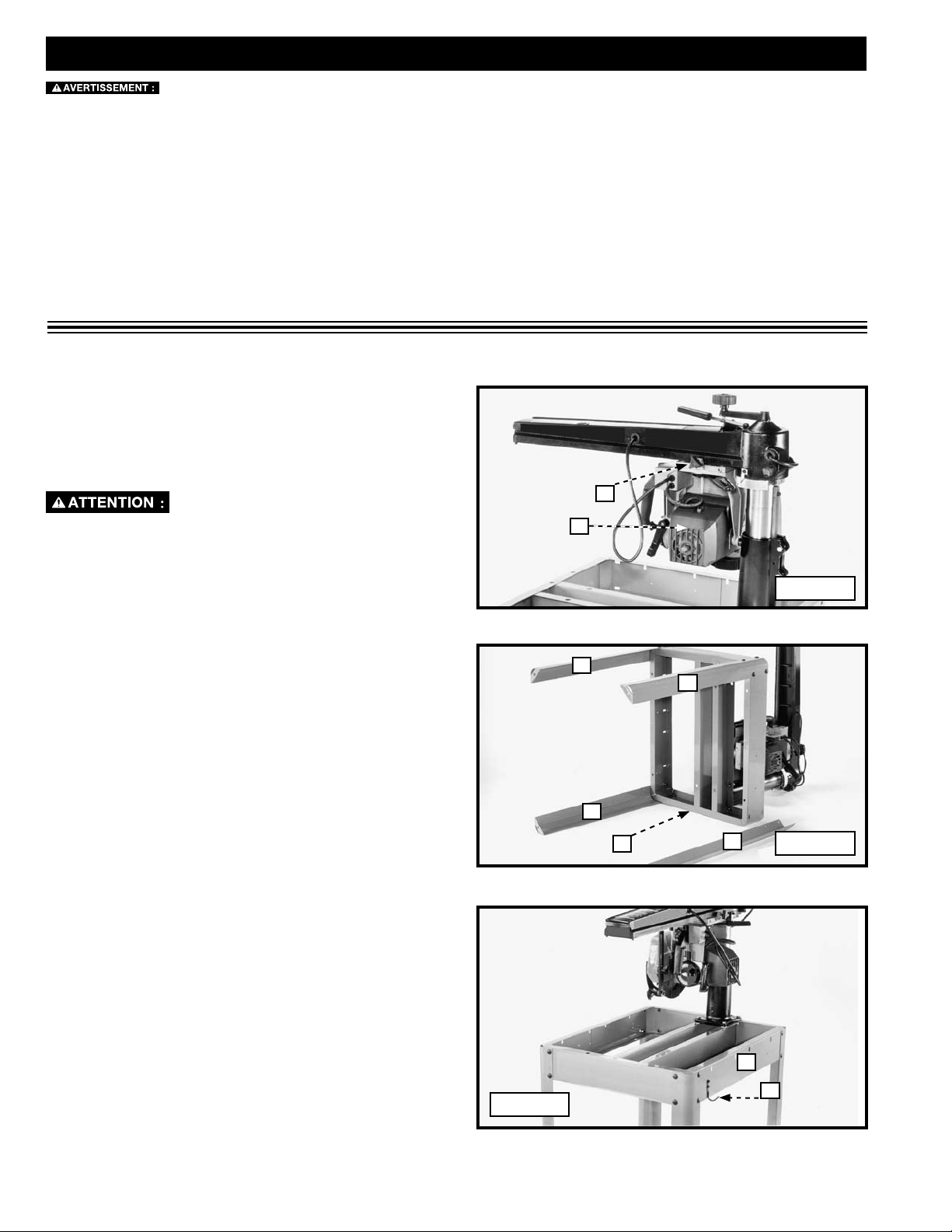
ASSEMBLAGE
Pour réduire le risque de blessures corporelles graves, éteindre l’outil et le débrancher avant
d’installer et de retirer tout accessoire, avant d'ajuster ou de modifier les réglages ou lors de réparations. Un démar-
rage accidentel peut provoquer des blessures.
OUTILS NÉCESSAIRES POUR L’ASSEMBLEE
Clé à fourche de 22,2 mm (7/8 po) - Clé polygonale de 12,7 mm (1/2 po) (comprise)
Clé polygonale de 22,2 mm (7/8 po) x 12,7 mm (1/2 po) (comprise)
Clés de 12,7 mm (1/2 po) et 9,5 mm (3/8 po), à fourche ou à douille
Tournevis à lame plate
L'ESTIMATION DE TEMPS D'ASSEMBLEE
L’Assemblée pour cette machine prend deux à trois heures.
ATTACHER LES PATTES AU SOCLE DE LA SCIE
1. Desserrer le bouton de verrouillage (A) Figure 1 et
déplacer la tête de coupe (B) en position arrière. Serrer
le bouton (A).
Brider la tête de coupe à l’arrière du
bras.
A
B
3. Placer la scie à bras radial sur le dos. Utiliser les vis de
chariot de 7,9 mm (5/16 po) - 18 x 15,9 mm (5/8 po) pour
attacher les pattes (C) Figure 2 (trois sont illustrées) à
chaque coin du socle de la scie (D). Passer les vis dans
le socle, puis utiliser une rondelle plate, une rondelle de
blocage et un écrou pour les sécuriser. Bien serrer les
écrous.
4. Tenir la scie dans la position debout et resserrer
assurément tout matériel de position.
ATTACHER LE CROCHET POUR CLÉ
Attacher le crochet pour clé (K) Figure 3 sur le côté avant droit
(comme illustré) ou arrière gauche du socle de la scie (D), en
utilisant deux vis à tôle n° 10 x 12,7 mm (1/2 po).
Fig. 1
C
C
C
D
C
Fig. 2
Fig. 9
38
D
K
Fig. 3
Fig. 10
Page 39

ENLEVER LA LAME ET LE PROTÈGE-LAME DE LA SCIE
Pour réduire le risque de blessures corporelles graves, éteindre l’outil et le débrancher avant
d’installer et de retirer tout accessoire, avant d'ajuster ou de modifier les réglages ou lors de réparations. Un démar-
rage accidentel peut provoquer des blessures.
1. Desserrer le bouton de serrage du protège-lame (A) Figure 4 et tourner le protège-lame (B) dans la position indiquée.
2. Utiliser les clés (C) Figure 5 pour desserrer l’écrou d’arbre (D).
REMARQUE : L’écrou d’arbre est fileté à gauche.
3. Lever la came (E) Figure 6 qui maintient le protège-lame (B) Figure 5 en position. Enlever le protège-lame (B), la bride
extérieure de la lame (F) et la lame (G).
4. Soulever le protège-lame (B) Figure 7. Enlever l’écrou d’arbre (D), la bride extérieure de la lame (F) et la lame (G).
5. Enlever le protège-lame (B).
A
F
B
B
G
D
C
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
B
E
G
Fig. 6
SUPPORTS DU BANC
1. Placer la planche avant du banc (A) Figure 8 sur une surface stable avec les trous percés vers le bas.
2. Attacher les supports droit et gauche du banc (B) Figure 8 au bas de la planche avant du banc (A) en insérant quatre vis
à tête ronde de 6,3 mm (1/4 po) - 20 x 25,4 mm (1 po) dans les trous percés (D) dans la planche (A) et les supports du
banc (B). Les sécuriser une fois en place en utilisant quatre écrous hexagonaux de 6,3 mm (1/4 po) - 20. Ne pas trop
serrer les vis pour un réglage futur.
3. Placer la planche avant du banc (A) Figure 9 sur le socle de la scie (G) de façon à ce que les supports du banc (B) soient
écartés du socle (G) et que les trois trous (H) dans
Fig. 7
F
D
Fig. 8
B
A
D
H
B
A
J
G
Fig. 9
39
Page 40
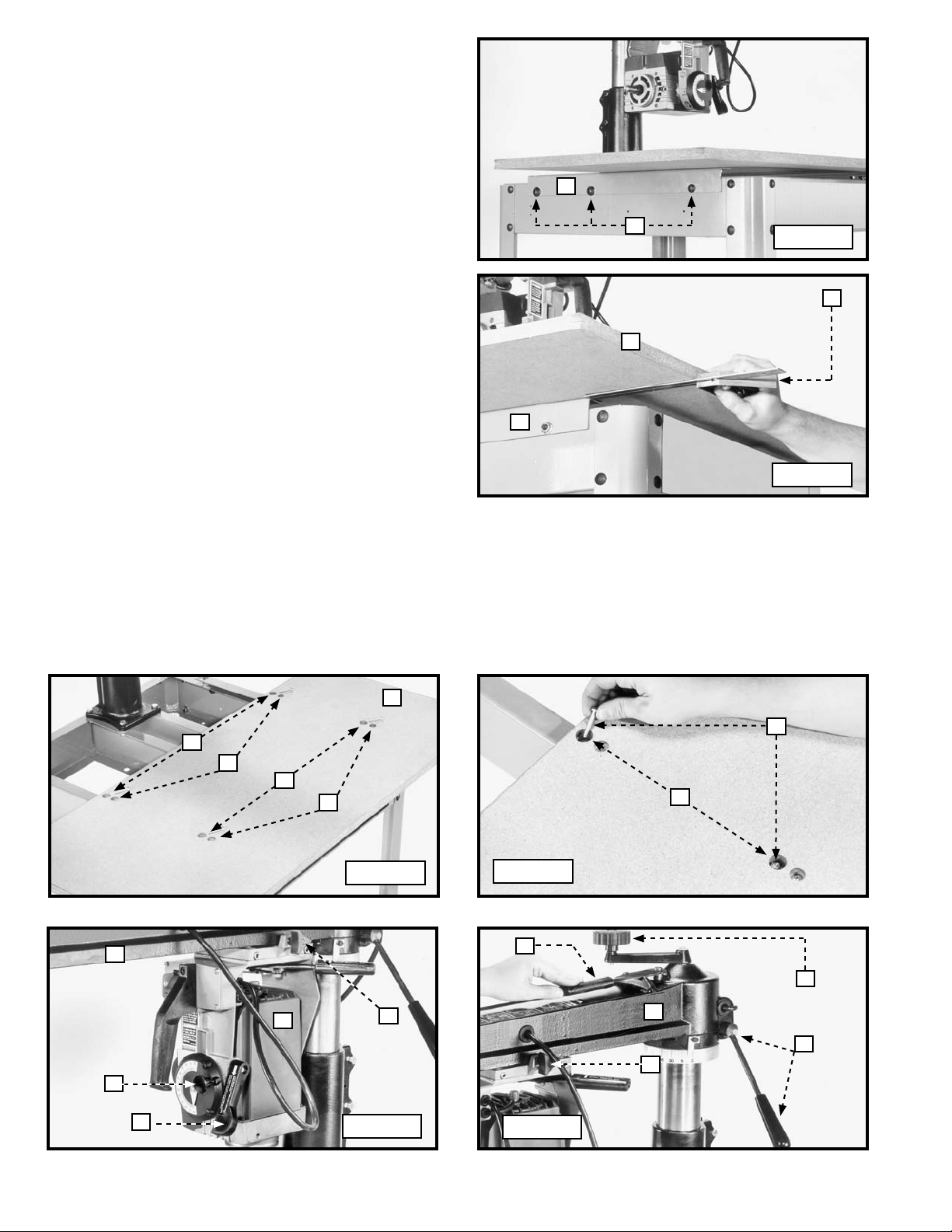
4. Sécuriser les supports du banc (comme illustré pour
l’un d’entre eux en (B) sur la Figure 10) de chaque côté
du socle de la scie en utilisant six vis de chariot de 7,9
mm (5/16 po) - 18 x 15,9 mm (5/8 po) (L) et six écrous
hexagonaux de 7,9 mm (5/16 po) - 18. Ne pas trop
serrer les vis pour un réglage futur.
IMPORTANT : Insérer les vis dans les supports du banc et
dans le socle de la scie depuis l’extérieur.
5. Utiliser une équerre combinée (A) Figure 11 pour
vérifier les bords avant droit et gauche de la planche
du banc (A). Les deux côtés doivent être à la même
distance que le bord des supports du banc (B) Figure
11.
B
L
Fig. 10
6. Après l’ajustement, serrer les quatre vis situées dans
les trous (N) Figure 12 de la planche avant du banc (A).
7. Insérer quatre vis à tête ronde de 6,3 mm (1/4 po) - 20
x 31,7 mm (1-1/4 po) (P) Figure 12 dans les trous (R)
Figures 11 et 12 de la planche du banc. Serrer chaque
vis jusqu’à ce que chaque coin de la planche du banc
s’élève d’environ 3,2 mm (1/8 po).
8. Desserrer le levier de fixation de biseau (S) Figure
14, tirer le bouton d’index de biseau (T) et tourner le
moteur (V) en position verticale jusqu’à ce que l’index
de biseau s’engage. Serrer le levier de fixation de
biseau (S).
REMARQUE : Si l’arbre du moteur entre en contact avec la planche de banc avant que le moteur ne soit en rotation totale,
lever le bras (X) Figure 14 en tournant la poignée d’élévation (C).
9. Desserrer le bouton de serrage de la tête de coupe (W) Figure 14. Déplacer la tête de coupe à l’avant du bras (X). Serrer
le bouton de serrage de la tête de coupe (W).
10. Desserrer la poignée de fixation du bras (Y) Figure 15.
REMARQUE : La poignée de fixation du bras (Y) Figure 13 est filetée à gauche. Appuyer sur la poignée de dégagement de
l’indexation (Z) Figure 15, et faire pivoter le bras (X) vers la gauche jusqu’à ce que l’arbre du moteur (B) Figure 16 soit près
de la vis d’ajustement avant gauche (P) Figure 13 de la planche du banc (A) Figure 13. Serrer la poignée de fixation du bras
(Y) Figure 15.
B
A
Fig. 11
C
P
R
N
R
M
N
R
Fig. 12
X
Fig. 13
Z
C
V
W
X
Y
W
T
S
Fig. 14
Fig. 15
40
Page 41

11. Placer une clé pour arbre (D) Figure 16 entre la planche du banc (A) et l’arbre du moteur (B). Abaisser le bras (X) Figure
16 en tournant la poignée d’élévation (C) dans le sens inverse des aiguilles d’une montre jusqu’à ce que l’arbre du
moteur (B) Figure 16 touche presque la clé pour arbre.
12. Vérifier le poids de la planche du banc au-dessus des vis d’ajustement des trois autres planches de banc (E) Figure 17
en repositionnant le bras (X) et la tête de coupe (V) jusqu’à ce que le plus haut point du banc soit identifié.
REMARQUE : S’assurer que le bouton de serrage de la tête de coupe (W) Figure 18 et l’axe de la poignée de fixation du
bras (Y) sont situés au-dessus de chacune des vis d’ajustement. Ne pas changer la hauteur du bras (X) Figure 17 avant
d’avoir identifié la plus haute vis et ajusté tous les coins de la planche de banc.
13. Positionner l’arbre du moteur sur les trois coins les plus bas de la planche du banc. Ajuster les vis d’ajustement du banc
(E) Figure 17 jusqu’à ce que la clé pour arbre puisse passer entre l’arbre et la planche du banc à chaque endroit.
14. Serrer les trois vis (G) Figure 19 de chaque côté du socle de la scie (H). Ramener le bras (X) et le moteur (V) en position à
90°. Serrer le levier de fixation de biseau (S) et la poignée de fixation du bras (Y) Figure 18.
A
X
B
D
P
Fig. 16
Fig. 18
Y
W
BRIDES POUR PLANCHE DE BANC ET PLANCHES DE BANC
Fig. 19
H
V
E
E
Fig. 17
X
S
V
A
G
1. Localiser les brides pour planche de banc (A) Figure 20. Insérer une bride dans chacune des fentes (B) situées à l’arrière
de chaque fixation de support de banc (C) Figure 20.
2. Tourner la vis d’ajustement (D) Figure 21 dans le sens inverse des aiguilles d’une montre de façon à ce que les boutons
(A) soient en position arrière.
D
A
B
A
C
Fig. 20
41
Fig. 21
Page 42

3. Placer une planche de 31,7 mm (1-1/4 po) de largeur
(E) Figure 22 contre la planche avant du banc (G) et
une planche de 146,5 mm (5-3/4 po) de largeur (J)
contre la planche de 31,7 mm (1-1/4 po) de largeur (E).
Placer la planche de 44,4 mm (1-3/4 po) de largeur (H)
en position levée contre la planche de 146,5 mm (5-3/4
po) de largeur (J). Serrer les boutons (D) jusqu’à ce que
les planches du banc soient correctement bridées.
J
G E
AJUSTER ET VÉRIFIER LA COURSE DE LA LAME
Pour réduire le risque de blessures cor-
H
porelles graves, éteindre l’outil et le débrancher avant
d’installer et de retirer tout accessoire, avant d'ajuster
Fig. 22
ou de modifier les réglages ou lors de réparations. Un
démarrage accidentel peut provoquer des blessures.
1. Lever le bras (A) Figure 23 en tournant la poignée d’élévation (B) jusqu’à ce qu’il soit possible d’attacher la lame (C) sur
l’arbre du moteur. Serrer l’écrou d’arbre (D) en utilisant les clés fournies.
2. Placer une équerre de charpentier (E) Figure 23 contre le guide (H). Abaisser le bras (A) Figure 23 jusqu’à ce que la lame
ne soit plus en contact avec la surface du banc.
3. Desserrer le bouton de serrage de la tête de coupe (S) Figure 24. Faire glisser la tête de coupe (T) sur toute la longueur
du bras (A) pour déterminer si la lame (C) se déplace parallèlement à l’équerre (E).
4. Pour ajuster, desserrer la vis de verrouillage de l’anneau d’index (J) Figure 25 et la poignée de fixation du bras (K).
5. Faire pivoter le bras (A) Figure 24 jusqu’à ce que la lame (C) se déplace parallèlement à l’équerre (E). Serrer la poignée
de fixation du bras (K) Figure 26.
6. Avec la poignée de fixation du bras (K) Figure 26 serrée, faire tourner l’anneau d’index (L) dans le sens inverse des
aiguilles d’une montre jusqu’à ce qu’il s’arrête. Serrer la vis de verrouillage de l’anneau d’index (J) Figure 27.
H
Fig. 23
Fig. 25
B
A
S
A
T
D
C
E
E
C
Fig. 24
J
K
L
K
Fig. 26
7. Deux pointeurs d’index d’onglet existent sur cet
appareil, dont l’un est indiqué (M) sur la Figure 27. Pour
l’ajuster, desserrer la vis (N) et déplacer le pointeur
(M) jusqu’à ce qu’il soit aligné avec la marque « zéro
» sur l’échelle à onglets (P). Serrer la vis (N). Ajuster le
pointeur de l’index d’onglet situé de l’autre côté de la
colonne (R) de la même manière.
42
J
N
P
M
R
Fig. 27
Page 43

ÉLIMINER LE « TALONNEMENT »
Bien que la course de la tête de coupe puisse être parfaitement alignée à 90° avec le guide, la lame elle-même peut ne pas
être à 90° ou ajustée avec le guide (Figure 26). Cette condition est appelée « talonnement ». Vérification et réglage :
Pour réduire le risque de blessures corporelles graves, éteindre l’outil et le débrancher avant
d’installer et de retirer tout accessoire, avant d'ajuster ou de modifier les réglages ou lors de réparations. Un démar-
rage accidentel peut provoquer des blessures.
1. Installer la lame de coupe sans le protège-lame.
2. Remplacer le guide par une pièce de bois plate de 19 mm (3/4 po) (A) Figure 29 épaisse d’au moins 127 mm (5 po).
Serrer les brides pour planche de banc.
3. Placer trois pièces de bois identiques (B) Figure 29 sur le banc. Déposer une équerre de charpentier sur celles-ci de
façon à ce que le bras court soit au même niveau contre le guide et le bras long contre la lame. S’assurer que l’équerre
est entre les dents de la scie.
B
A
Fig. 28
4. Si la lame n’est pas parallèle à l’équerre, ajuster. Libérer
la poignée de fixation de la fourche (C) Figure 30 et
desserrer légèrement les deux vis hexagonales (D).
Faire pivoter la fourche jusqu’à ce que la lame soit
parallèle avec l’équerre. Serrer la poignée de fixation
de la fourche (C). Serrer les deux vis hexagonales (D)
B
B
Fig. 29
C
D
Fig. 30
ALIGNER LA LAME DE LA SCIE AVEC LE BANC
Pour réduire le risque de blessures corporelles graves, éteindre l’outil et le débrancher avant
d’installer et de retirer tout accessoire, avant d'ajuster ou de modifier les réglages ou lors de réparations. Un démar-
rage accidentel peut provoquer des blessures.
1. Attacher la bride intérieure de la lame, la lame, la bride
extérieure de la lame et l’écrou sur l’arbre de la scie.
2. Placer la tête de coupe en position transversale (Figure
29). Abaisser le bras jusqu’à ce que la lame de coupe
ne soit plus en contact avec le banc. Faire glisser la
tête vers l’avant jusqu’à ce qu’elle soit positionnée audessus de la planche avant du banc. Brider la tête de
coupe dans cette position.
3. Engager le bouton d’index de biseau (A) Figure 31.
Vérifier que le moteur est en position horizontale. Serrer
la poignée de fixation de biseau (C).
F
C
A
E
F
B
Fig. 31
43
Page 44

4. Placer une équerre (A) Figure 32 sur le banc et contre
la lame. Vérifier si la lame est d’équerre avec le banc.
REMARQUE : L’équerre doit reposer entre deux dents de
la lame.
5. Pour ajuster, serrer le levier de fixation de biseau (C)
Figure 31.
6. Enlever la vis, la rondelle plate et le pointeur (C) Figure
31.
7. Enlever les deux vis (F) fig. 31 et la plaque d’échelle de
biseau (H) Figure 32 avec le bouton d’index (A).
8. Desserrer les quatre vis hexagonales (G) Figure 33.
Incliner le moteur jusqu’à ce que la lame soit de niveau
avec l’équerre. Serrer les quatre vis hexagonales (G).
9. Replacer la plaque d’échelle de biseau (H) Figure 331
avec le bouton de dégagement d’index de biseau (A),
les deux vis et le pointeur enlevés précédemment.
REMARQUE : Ajuster le pointeur sur « zéro » sur l’échelle
d’index de biseau.
D
Fig. 32
G
A
H
RÉGLER L’ÉCHELLE DE SCIAGE À L’INTÉRIEUR/À
L’EXTÉRIEUR
1. Desserrer la poignée de fixation de la fourche (A)
Figure 34. Dégager l’index de la fourche en appuyant
sur ou en abaissant le levier de dégagement (B). Faire
tourner la tête de coupe (C) en position de sciage vers
l’intérieur (Figure 34). Serrer la poignée de fixation de la
fourche (A).
2. Positionner le guide (D) Figure 34 à l’arrière de la table.
3. Desserrer le bouton de serrage de la tête de coupe (S)
Figure 34. Faire glisser la tête de coupe (C) Figure 32
vers l’arrière du bras jusqu’à ce que la lame (F) soit au
même niveau que le guide (D).
4. Desserrer le bouton de serrage de la tête de coupe.
Régler le pointeur (H) Figure 34 sur la marque « zéro »
sur l’échelle la plus basse (J) en desserrant la vis (K).
Resserrer la vis lorsque c’est terminé.
ATTACHER LA LAME ET LE PROTÈGE-LAME
REMARQUE : Utiliser seulement des lames de 254 mm
(10 po) avec des trous d’axe de 15,9 mm (5/8 po) et
homologuées pour 5 000 tr/min ou plus.
Fig. 33
Fig. 34
H
K
B
C
J
A
F
D
1. Attacher la bride d’axe interne (épaisse) (A) Figure 33
à l’axe avec le côté enfoncé de la bride (A) orienté vers
l’extérieur.
A
Fig. 35
44
Page 45

H
B
B
E
C
D
Fig. 36
2. En maintenant le protège-lame (B) Figure 32 dans la
main gauche, insérer la lame (C) dans le protège-lame
(B) et sur l’axe.
3. Attacher la bride externe de la lame (mince) (D) Figure
36 du côté enfoncé de la bride (D) orientée vers
l’intérieur. Placer l’écrou (E) dans l’axe.
REMARQUE : L’écrou (E) Figure 32 est fileté à gauche.
4. Lever la came (E) Figure 375. Attacher le protège-lame
(B) à la tête de coupe.
REMARQUE : Poser la languette du protège-lame dans la
rainure de la tête de coupe.
5. Tirer sur le protège-lame (B) Figure 38 de façon à ce
qu’il tourne vers l’arrière. Utiliser la clé polygonale
de 22,2 mm (7/8 po) sur l’écrou d’arbre (E) et la clé à fourche de 22,2 mm (7/8 po) sur la partie plate de l’arbre pour le
maintenir en place.
6. Faire pivoter le protège-lame (B) Figure 34 en position horizontale et serrer le bouton de serrage (H) Figure 37.
Serrer le bouton de serrage (H) FIG. 37 et sécuriser le protège-lame avant de faire fonctionner l’appareil.
Le protège-lame rétractable inférieur protège l’utilisateur sur les côtés de la lame de la scie. Pour réduire les risques
potentiels, voici les règles à respecter :
F
Fig. 37
B
G
E
Fig. 38
A) GARDER LES MAINS LOIN DU PROTÈGE-LAME. Lorsque la lame coupe, le protège-lame se soulève et exposer
une partie de la lame.
B) COUPER LE COURANT AVANT DE DÉGAGER UN PROTÈGE-LAME INFÉRIEUR COINCÉ. Le protège-lame peut
se coincer à cause de traits de scie sur le banc ou le guide. Toujours anticiper le chemin du protège-lame.
C) PRENDRE GARDE lors des coupes en biseau et s’assurer que le protège-lame inférieur n’est jamais pincé dans la
lame.
D) LE PROTÈGE-LAME INFÉRIEUR PEUT SE BLOQUER CONTRE LE GUIDE PENDANT LES SCIAGES ÉTROITS
VERS L’INTÉRIEUR. Si le protège-lame se bloque contre le guide, débrancher la scie, attendre que la lame s’arrête,
puis soulever le protège-lame et le poser sur le guide.
COUPER DANS LES PLANCHES DU BANC
1. Attacher les planches du banc (A) Figure 38 et le guide (B). Sécuriser les planches avec les brides de fixation, dont l’une
est illustrée en (C).
2. Faire revenir la tête de coupe (D) Figure 40 à l’arrière du bras (E). Desserrer le bouton de serrage de la tête de coupe (G)
Figure 37. Vérifier que l’interrupteur (H) Figure 40 est en position « ARRÊT » et brancher la scie au secteur.
3. En tenant fermement la poignée de la tête de coupe (L) Figure 40, faire basculer l’interrupteur (H) en position « MARCHE
». Abaisser le bras (E) en tournant la poignée d’élévation (K). Abaisser la lame de la scie jusqu’à ce qu’elle coupe dans
la surface de la table à environ 1,5 mm (1/16 po) de profondeur.
K
G
C
B
D
E
Fig. 39
A
H
L
Fig. 40
45
Page 46

4. En tenant toujours fermement la poignée de la tête de
coupe (L) Figure 41, desserrer le bouton de serrage de
la tête de coupe et tirer doucement la tête de coupe
(D) Figure 41 vers l’avant du bras (E) jusqu’à ce qu’elle
s’arrête. Éteindre l’outil.
D
E
H
5. Attendre que la lame de la scie (M) Figure 42 s’arrête,
puis faire revenir la tête de coupe à l’arrière du bras (E).
Remarquer les traits de scie (N) Figure 42 sur le banc.
IMPORTANT : Soulever le bras (E) Figure 42 avant d’essayer
de le faire tourner. Effectuer la procédure de découpe dans
les planches du banc pour chaque coupe d’angle séparée.
Si, pendant une utilisation, la scie a tendance
à s’incliner, à glisser ou à accrocher la surface de support,
sécuriser la scie au sol en utilisant les trous fournis en bas
de chaque patte.
Fig. 41
D
M
L
E
N
Fig. 42
FONCTIONNEMENT
L'OPERATION CONTROLE DE LE ET LES AJUSTEMENTS
avant chaque utilisation de la scie, vérifier les points suivants.
1. TOUJOURS utiliser une protection oculaire, auditive et un appareil de protection des voies respiratoires.
2. La lame est bien serrée.
3. Les poignées de verrouillage de l’angle du biseau et de la hauteur sont bien serrées.
4. S’assurer que la poignée de blocage du guide longitudinal est bien serrée et que le guide longitudinal est parallèle à la lame
en cas de sciage en long.
5. Le protège-lame est correctement attaché et les dents anti-effet de rebond fonctionnent.
6. TOUJOURS inspecter le bon alignement et le dégagement du protège-lame et du couteau séparateur. Ces derniers ne
devraient pas toucher la lame de scie en cours de fonctionnement.
Le non-respect de ces consignes de sécurité de base augmente grandement la possibilité de blessures.
Pour réduire le risque de blessures, éteindre l’appareil et le débrancher avant d’installer ou de
retirer tout accessoire, avant d’ajuster ou de modifier les réglages, ou lors de réparations. Un
démarrage accidentel peut provoquer desblessures..
Avant de connecter le banc de scie à la source d’alimentation ou de le mettre en marche,
toujours vérifier l’alignement et le dégagement corrects duprotège-lame et du couteau
séparateur en cours de fonctionnement. Il peut en résulter des blessures corporelles.
Si la scie produit un bruit étrange ou vibre excessivement, suspendre immédiatement son utilisation
jusqu’à ce que la cause soit repérée et le problème, corrigé.
DÉMARRAGE ET ARRÊT DE SCIE
S’assurer que l’interrupteur se trouve sur la position d’arrêt avant de brancher le cordon
d’alimentation dans la prise. Ne pas toucher aux lames métalliques de la fiche lors du branchement ou débranchement du cordon.
L’interrupteur MARCHE/ARRÊT est situé sous un écran de protection (A) fig 43. Pour mettre la scie en marche, mettre le levier
de l’interrupteur (B) en position élevée.
VERROUILLER L’INTERRUPTEUR EN POSITION D’ARRÊT
IMPORTANT : Lorsque la machine n’est pas utilisée, l’interrupteur doit être verrouillé en position d’arrêt (OFF) pour empêch-
er toute utilisation non autorisée en utilisant un cadenas (figure 44) avec une boucle (D) de 4,76 mm (3/16 po).
En cas de panne d'electricite (telle un disjoncteur desarme ou un fusible grille) toujours deplacer
l'interrupteur in position d'arret (OFF) jusqu'a ce que l'alimentation soit retablie.
46
Page 47

D
A
Fig. 43
Fig. 44
GUIDE DES PIÈCES
Lire attentivement les termes et explications suivants pour vous familiariser avec les commandes avant d’allumer
la scie. Le non respect de cette consigne pourrait entraîner des dommages à la scie ou des blessures (Figures 5B et 5C).
C
D
A
A. LES BOUTONS DE SERRAGE DU BANC permettent
à l’utilisateur de régler rapidement la position du guide
(Figure G).
B. LA POIGNÉE DE DÉGAGEMENT DU BRAS relâche
l’aiguille d’indexation des positions à 0° et 45° pour
permettre au bras de pivoter. Appuyer sur la poignée
pour relâcher l’aiguille d’indexation (Figure G).
C. LA POIGNÉE D’ÉLÉVATION DU BRAS commande
la profondeur de coupe dans toutes les opérations.
Tourner la poignée dans le sens des aiguilles d’une
montre pour lever le bras ou dans le sens inverse des
aiguilles d’une montre pour l’abaisser (Figure G).
D. L’ÉCHELLE À ONGLETS indique les degrés à droite
et à gauche pour régler le bras à l’angle d’onglet désiré
(Figure G).
F. L’ÉCHELLE DE SCIAGE indique les positions d’entrée
et de sortie du porte-lame (Figure G).
G LE BOUTON DE SERRAGE DU PROTÈGE-LAME fixe
le protège-lame aux différentes positions pour le sciage
(Figure G).
H. LA POIGNÉE DE FIXATION DE BISEAU contrôle
l’inclinaison du moteur pour les coupes en biseau.
Il verrouille également le moteur à l’angle désiré sur
l’échelle du biseau. Soulever la poignée pour desserrer
et appuyer dessus pour la verrouiller (Figure G).
J. LE BOUTON DE DÉGAGEMENT DE L’INDEX DE
BISEAU permet de positionner le moteur aux réglages
de biseau 0°, 45° et 90°. Pour incliner le moteur pour
les coupes en biseau, commencer par desserrer la
poignée de fixation de biseau. Pour libérer l’index, tirer
sur le bouton de dégagement (Figure G).
K. LE LEVIER DE DÉGAGEMENT DE L’INDEXATION
DE LA FOURCHE permet à la scie d’atteindre une
position à 90° pour les opérations de sciage ou de
tronçonnage. Pour faire pivoter la fourche, commencer
par desserrer la poignée de fixation. Pousser le levier
de dégagement vers le haut ou vers le bas pour libérer
l’aiguille d’indexation (Figure G).
L. LA POIGNÉE DE FIXATION DE LA FOURCHE doit
être desserrée pour la rotation de la fourche entre
B
K
G
Fig. G
P
N
F
H
M
J
Fig. H
la position de sciage et la position de tronçonnage.
Tirer la poignée pour libérer et appuyer dessus pour
verrouiller (Figure H).
M. LE DISPOSITIF ANTI-EFFET DE REBOND aide à
empêcher les blessures ou les dommages causés par
les rebonds. Lors du sciage, positionner et brider la
fourche de sorte que la lame soit parallèle au guide.
Faire pivoter l’arrière du protège-lame jusqu’à ce qu’il
touche presque la pièce de bois. Abaisser la tige antieffet de rebond de façon à ce que les doigts attrapent
et tiennent la pièce de bois. Ne jamais scier depuis
l’extrémité anti-effet de rebond du protège-lame (Figure
H).
N. L’INTERRUPTEUR MARCHE/ARRÊT est idéalement
situé et peut être activé en un instant pour une
protection supplémentaire. Vous pouvez également
verrouiller cet interrupteur en position « ARRÊT » pour
éviter une utilisation non autorisée en utilisant un
cadenas accessoire (Figure H).
P. LE BOUTON DE SERRAGE DE LA TÊTE DE COUPE
verrouille la tête de coupe sur n’importe quelle position
sur le bras. Lors du sciage, s’assurer que le bouton de
serrage est bien serré (Figure H).
R. L’ÉCHELLE DE BISEAU indique le degré de rotation
pour les réglages de la position en biseau du moteur
(Figure H).
S. LA POIGNÉE DE FIXATION DU BRAS commande la
rotation du bras pour toutes les opérations de coupe à
onglet. Elle verrouille le bras dans un angle de position
d’onglet. Pour tourner le bras vers la droite, desserrer la
poignée de fixation et tourner le bras. Le bras s’arrêtera
à 45°. Pour le tourner à plus de 45°, appuyer sur la
poignée de dégagement d’indexation et tourner. Le
bras tournera de 5° supplémentaires. Pour le tourner
vers la gauche, la marche à suivre est la même sauf
qu’il faut appuyer sur la poignée de dégagement de
l’indexation pour commencer à tourner (Figure H).
R
S
L
47
Page 48
AJUSTEMENT DES ROULEMENTS À BILLES SUR LA VOIE
La tête de coupe (C) Figure 46 est suspendue par quatre roulements à billes préchargés, lubrifiés et blindés, dont deux sont
situés sur les axes fixes en (A) et deux sur des axes réglables en (B).
La tête de coupe (C) Figure 46 a été enlevée du bras pour les besoins de l’illustration. NE PAS enlever la tête de
coupe du bras.
Après une utilisation prolongée, de l’usure peut se développer au niveau du bras, causant du jeu entre les roulements à
billes et la voie. Les roulements à billes doivent rouler sans à-coup et de manière uniforme dans les canaux du bras. Pour
ajuster les roulements à billes :
de retirer tout accessoire, avant d'ajuster ou de modifier les réglages ou lors de réparations. Un démarrage accidentel peut
provoquer des blessures.
1. Enlever le cache en plastique (D) Figure 45 à partir du haut du bras (E).
2. Faire glisser la tête de coupe (C) Figure 46 jusqu’à ce qu’un des roulements à billes (B) Figure 46 soit visible par le trou
(G) Figure 43.
3. Utiliser une douille de 12,7 mm (1/2 po), une rallonge et un cliquet (H) Figure 47 à travers le trou (G) dans le bras pour
desserrer légèrement l’écrou hexagonal sur l’axe ajustable (B) Figure 44 d’environ 1/8 de tour. Répéter l’opération pour
les autres roulements à billes.
Pour réduire le risque de blessures corporelles graves, éteindre l’outil et le débrancher avant d’installer et
B
D
A
G
B
C
K
E
Fig. 45
G
H
K
Fig. 46
K
J
C
4. Utiliser une clé hexagonale de 4,8 mm (3/16 po) (J) Figure 48 pour tourner les vis de réglage (K) Figure 48 afin de retirer
tout jeu éventuel.
Ne pas trop serrer les vis de réglage (K). Cela pourrait endommager les roulements à billes.
Ne pas desserrer les vis d’ajustement (K) de plus d’1/2 tour. La tête de coupe pourrait tomber du bras.
5. Serrer les deux écrous hexagonaux desserrés à l’ÉTAPE 3. Vérifier que la course de la tête de coupe n’a pas de jeu.
S’assurer qu’elle se déplace librement et sans à-coup.
6. Replacer le cache retiré à l’ÉTAPE 1.
AJUSTER LA TENSION DE LA COLONNE ÉLÉVATRICE
La tension de la colonne élévatrice est préréglée en usine.
Du jeu peut se développer après une utilisation prolongée.
Pour effectuer le réglage, procéder comme suit :
1. Desserrer les écrous hexagonaux (A) Figure 49 et les
vis de réglage de contre-clavette (C).
2. Desserrer les écrous hexagonaux (D) et tourner les vis (E)
jusqu’à ce que la base de la colonne s’enveloppe autours
de la colonne et puisse être levée ou abaissée librement.
Serrer les écrous hexagonaux (D) contre la base de la
colonne.
3. Serrer les vis de réglage de contre-clavette (C) contre
la contre-clavette (H) jusqu’à ce qu’il n’y ait plus de
jeu. Serrer les écrous hexagonaux (A) contre la base
de la colonne. nuts (A) against column base.
Fig. 47
48
Fig. 48
F
H
A
E
D
C
B
Fig. 48
Page 49
REMARQUE : Après le réglage de la tension de la colonne, se reporter à la section « RÉGLER LA COURSE DE LA LAME
AVEC LE GUIDE » pour déterminer si la course de la lame de la scie a été affectée par ce changement.
CHANGER LA POSITION DE LA POIGNÉE DE FIXATION DU BRAS
de retirer tout accessoire, avant d'ajuster ou de modifier les réglages ou lors de réparations. Un démarrage accidentel peut
provoquer des blessures.
Pour repositionner la poignée de fixation du bras (A) Figure 50 quand il ne se verrouille pas dans une position adéquate :
1. Desserrer et enlever le levier de fixation du bras (A) Figure 50. Appuyer sur le boulon hexagonal (B) Figure 51 pour la
sortie du trou jusqu’à ce que la tête du boulon soit sortie de la douille enfoncée (C).
REMARQUE : Le levier de fixation du bras est fileté à gauche.
2. Faire tourner le boulon hexagonal (B) Figure 51 dans la position désirée.
3. Appuyer sur le boulon hexagonal (B) Figure 51 pour le sortir du trou. Vérifier que la tête du boulon hexagonal est posée
correctement dans la douille enfoncée (C). Attacher le levier de fixation du bras.
REMARQUE : Si le levier de fixation du bras (A) Figure 49 devient difficile à tourner avant environ quatre tours, les douilles
de fixation (dont l’une est illustrée en (C) sur la figure 51) peuvent avoir tourné. Ces douilles de fixation doivent être posées
complètement à l’intérieur de la voie (D). Si elles ne le sont pas, desserrer légèrement le levier de fixation (A) Figure 48 et
faire tourner les douilles de fixation (C) Figure 51 jusqu’à ce qu’elles soient en place. Vérifier s’il est nécessaire de faire
tourner les douilles du côté du levier de fixation également.
REMARQUE : Les facettes sur les douilles de fixation doivent être orientées vers l’avant de la scie.
REMARQUE : Le levier de fixation (A) Figure 50 va fileter à l’une position parmi deux. Si, après un réglage, le levier de
fixation (A) se bloque à 180° de la position désirée, dévisser doucement le levier de fixation (A) tout en tenant le boulon
hexagonal (B). Quand le levier de fixation (A) se détache du boulon hexagonal (B), faire tourner le levier de fixation (A) de
180°. Fileter le levier de fixation.
Pour réduire le risque de blessures corporelles graves, éteindre l’outil et le débrancher avant d’installer et
B
A
D
C
Fig. 50
CHANGER LA POSITION DE LA POIGNÉE DE FIXATION DE BISEAU
Pour réduire le risque de blessures corporelles graves, éteindre l’outil et le débrancher avant d’installer et
de retirer tout accessoire, avant d'ajuster ou de modifier les réglages ou lors de réparations. Un démarrage accidentel peut
provoquer des blessures.
Pour repositionner la poignée de fixation de biseau :
1. Desserrer la poignée de fixation de biseau (A) Figure
52, libérer le bouton de dégagement de l’index de
biseau (B), puis tourner le moteur (C) en position
verticale.
REMARQUE : Si le protège-lame entre en contact avec la
surface du banc, soulever le bras.
2. Desserrer la poignée de fixation de biseau (A) Figure 52
de plusieurs tours jusqu’à ce que la tête hexagonale
de la vis (D) puisse être poussée en dehors de la
cavité en forme hexagonale de la fourche.
3. Tourner la vis (D) Figure 52 d’un ou deux plats de la
tête hexagonale dans la direction dans laquelle la
poignée doit être tournée. La pousser dans la cavité à
forme hexagonale de la fourche.
4. Resserrer la poignée de fixation de biseau (A) Figure
50.
REMARQUE : La vis est filetée à gauche - tourner la
poignée de fixation dans le sens inverse des aiguilles
d’une montre pour la serrer.
D
C
Fig. 51
B
A
Fig. 52
49
Page 50
CHANGER LA POSITION DE LA POIGNÉE DE FIXATION
DE LA FOURCHE
Pour repositionner la poignée de fixation de la fourche (A)
Figure 53.
Pour réduire le risque de blessures
corporelles graves, éteindre l’outil et le débrancher avant
d’installer et de retirer tout accessoire, avant d'ajuster ou
de modifier les réglages ou lors de réparations. Un démar-
rage accidentel peut provoquer des blessures.
1 Enlever l’anneau de retenue (B) Figure 53.
2. Repositionner la poignée de fixation de la fourche (A)
Figure 53 sur l’écrou de fixation hexagonal.
3. Remplacer l’anneau de retenue (B) Figure 53.
INDEX DE FOURCHE - BUTÉE POSITIVE
Le levier d’index de la fourche (A) Figure 54 active une butée positive qui met en place la tête de coupe en position transversale
ou de sciage. Pour faire tourner la tête de coupe, relâcher la poignée de fixation de la fourche, appuyer ou relever le levier
d’index de la fourche (A) pour relâcher la butée positive, puis faire tourner la tête de coupe en position de sciage vers l’intérieur
(1), de sciage vers l’extérieur (2) ou de coupe transversale (3). Libérer le levier d’index de la fourche (A) Figure 53 et la tête de
coupe s’indexera automatiquement à chacune des trois positions.
INDEX DE BISEAU - BUTÉE POSITIVE
Le bouton d’index de biseau (A) Figure 53 fournit une butée positive quand le positionnement de la lame de la scie est à
0°, 45° et 90° à gauche et à 90° à droite sur l’échelle de biseau (C). Pour changer l’angle de la lame de la scie, desserrer la
poignée de fixation de biseau (B), tirer sur le bouton d’index de biseau (A) puis incliner la lame de la scie et le moteur. Pour les
positions à 0°, 45° et 90° à gauche et 90° à droite, relâcher le bouton d’index de biseau (A) et la lame de la scie s’indexera à
chacune de ces positions. Serrer la poignée de fixation du biseau (B). Pour les angles de la lame de la scie entre les butées
positives, régler la lame à l’angle désiré sur l’échelle de biseau (C) et serrer la poignée de fixation de biseau (B) Figure 55.
A
B
Fig. 53
Fig. 51
B
A
Fig. 54
AJUSTEMENT DU SÉPARATEUR ET DU DOIGT ANTI-EFFET DE REBOND
Pour réduire le risque de blessures corporelles graves, éteindre l’outil et le débrancher avant d’installer et
de retirer tout accessoire, avant d'ajuster ou de modifier les réglages ou lors de réparations. Un démarrage accidentel peut
provoquer des blessures.
Pendant les opérations de sciage, le séparateur (A) Figure 56 doit suivre le trait de scie et les doigts anti-effet de rebond (B)
doivent toucher la pièce de bois pour empêcher les rebonds.
1. Régler la scie en position de sciage avec le protège-lame de la scie abaissé du côté de l’alimentation pour servir de
retenue.
2. Commencer à travailler une pièce de bois avec la scie
(Figure 54).
3. Éteindre la scie et la débrancher.
4. Régler le bras (C) fig. 56 de façon à ce qu’il soit vertical
et que le séparateur (A) soit dans le trait de la scie.
5. Si le séparateur (A) Figure 56 n’est pas aligné avec le
trait de la scie, desserrer les écrous hexagonaux (D)
et positionner le séparateur (A) dans le trait de la scie.
Serrer les écrous hexagonaux (D) contre le bras. Le
côté serré du séparateur devrait être contre la lame
(Figure 56), et les doigts anti-effet de rebond doivent
rester sur la pièce de bois.
REMARQUE : Le bouton de serrage pour le bras (C) doit
être serré. Déplacer le bras (C) d’avant en arrière en
serrant le bouton de serrage avec l’autre main pour
être sûr que la bride est fermement posée et serrée.
6. Tirer la pièce de bois vers l’arrière pour déterminer si les doigts anti-effet de rebond ont fait des traces dans le bois et
empêché d’autres mouvements de recul. Si nécessaire, réajuster la hauteur du bras (C) Figure 56.
50
Fig. 56
C
A
A
Fig. 55
C
D
B
Page 51
REVÊTEMENT AUXILIAIRE DES PLANCHES DU BANC
Pour empêcher des coupes répétées dans la surface du banc qui finiront par causer son fléchissement, vous pouvez
couper un revêtement auxiliaire pour les planches du banc et le placer sur le banc. Utiliser une plaque de contreplaqué ou
un panneau de particules de 6,3 mm d’épaisseur. Couper à une taille qui couvrira toutes les planches du banc devant le
guide. Placer le revêtement auxiliaire à plat sur le banc et l’abouter contre le guide. L’attacher au banc en utilisant un petit
clou à tête perdue ou un clou de finition dans chaque coin.
UTILISER UNE RALLONGE
Si une rallonge de plus de 610 mm (24 po) de longueur est attachée à la scie, utiliser un support solide ou sécuriser le
support au plancher.
UTILISATION DE LA MACHINE
pour réduire le risque de blessures, éteindre l’appareil et le débrancher avant d’installer ou de retirer tout
accessoire, avant d’ajuster ou de modifier les réglages ou lors de réparations. Un démarrage accidentel pourrait provoquer des
blessures.
avant de connecter la scie à bras radial à la source d’alimentation ou de la mettre en marche, toujours
vérifier que l’alignement du protège-lame et du couteau séparateur et leur dégagement par rapport à la lame de la scie sont
appropriés. Une telle pratique peut entraîner des blessures corporelles.
TRONÇONNAGE
pour réduire le risque de blessures, éteindre l’appareil et le débrancher avant d’installer ou de retirer
tout accessoire, avant d’ajuster ou de modifier les réglages ou lors de réparations. Un démarrage accidentel pourrait
provoquer des blessures.
NE JAMAIS toucher l’« extrémité libre » de la pièce ou une « pièce libre » qui est coupée alors que
l’appareil est en marche et/ou que la lame de la scie tourne toujours. La pièce pourrait toucher la lame et être projetée
pouvant ainsi vous blesser.
NE JAMAIS utiliser un butoir à l’extrémité libre de la pièce lors du tronçonnage. En résumé, une
pièce qui sera débitée au complet (coupe de part et d’autre de la pièce) ne doit jamais être coincée. Elle doit pouvoir
s’éloigner de la lame de scie pour empêcher un contact avec la lame. En effet, ce contact pourrait projeter la pièce et
vous blesser.
être prudent lors de l’amorce d’une coupe pour empêcher un coincement du protège-lame avec la
pièce. Un tel coincement risque d’endommager la scie ou de vous blesser.
Pour tronçonner, placer la pièce de bois contre le guide et tirer la lame de la scie à angle droit vers le matériau. (Fig. 57)
Lors du tronçonnage, régler le bras sur « 0 » et serrer la
poignée de fixation du bras. Fixer le guide entre les planches
du banc. S’assurer que la lame de la scie est sur la gauche et
derrière le guide. Placer la pièce sur la table et l’ébouter contre
le guide. S’assurer qu’il n’y a pas d’obstacle entre la lame,
le guide et le banc lorsque l’appareil est allumé. Abaisser la
lame de la scie jusqu’à ce qu’elle coupe légèrement la surface
de la table. Se positionner un peu sur la gauche de l’appareil
pour une meilleure visibilité. Tirer la lame de la scie en travers
de l’ouvrage, juste assez pour réaliser la coupe, puis faire
revenir la lame de la scie dans sa position de départ. Éteindre
l’appareil et attendre que la lame s’immobilise avant de toucher
la pièce de bois coupée.
soyez toujours attentif à la position de
vos mains. S’assurer que les mains ne sont pas sur la trajectoire de la lame et que la pièce est tenue fermement.
De plus, la tige antirecul peut être positionnée et verrouillée dans cette position afin qu’elle soit juste au niveau de la pièce.
La tige peut agir comme une protection contre les dents exposées de la lame.
toujours remettre le chariot de la tête de coupe en position arrière après chaque tronçonnage.
REMARQUE : pour tronçonner un matériau de plus de 25 mm (1 po) d’épaisseur, positionner le guide immédiatement derrière la
planche fixe avant de la table.
Fig. 57
51
Page 52
BUTÉE POUR LE TRONÇONNAGE
Un bloc de bois (B), fig. 58, fixé sur le bras évitera les
courses inutiles de la lame sur le rail, ce qui est très utile
pour les coupes répétitives. Fixer le bloc de bois du côté
droit du bras sur rail dans une position qui arrêtera la
course de la tête de coupe dès que la lame de la scie aura
entièrement coupé la pièce.
DÉCOUPE À ONGLET
pour réduire le risque de blessures,
éteindre l’appareil et le débrancher avant d’installer ou
de retirer tout accessoire, avant d’ajuster ou de modifier
les réglages ou lors de réparations. Un démarrage
accidentel pourrait provoquer des blessures.
être prudent lors de l’amorce d’une
coupe pour empêcher un coincement du protège-lame
avec la pièce. Un tel coincement risque d’endommager
la scie et de vous blesser.
avant de connecter la scie à bras
radial à la source d’alimentation ou de la mettre en
marche, toujours vérifier que l’alignement du protègelame et du couteau séparateur et leur dégagement par
rapport à la lame de la scie sont appropriés. Vérifier
l’alignement après chaque changement d’angle de
biseau.
La coupe à onglet est similaire au tronçonnage sauf que
l’ouvrage est coupé en angle (jusqu’à 45° à droite ou à
gauche). Effectuer les réglages et procéder de la même
manière que pour le tronçonnage, mais en positionnant tout
d’abord le bras à l’angle désiré sur l’échelle à onglets avant
de le fixer. Positionner la main qui tient la pièce du côté
opposé à la direction de l’onglet de sorte que la lame soit
tirée de part et d’autre de la pièce et à l’écart de la main. La
figure 59 illustre une opération de coupe à onglet sur la scie
radiale.
B
Fig. 58
Fig. 59
DÉCOUPE À ONGLET MIXTE
pour réduire le risque de blessures,
éteindre l’appareil et le débrancher avant d’installer ou
de retirer tout accessoire, avant d’ajuster ou de modifier
les réglages ou lors de réparations. Un démarrage
accidentel pourrait provoquer des blessures.
être prudent lors de l’amorce d’une coupe pour empêcher un coincement du protège-lame avec la
pièce. Un tel coincement risque d’endommager la scie et de vous blesser.
avant de connecter la scie à bras radial à la source d’alimentation ou de la mettre en marche,
toujours vérifier que l’alignement du protège-lame et du couteau séparateur et leur dégagement par rapport à la lame
de la scie sont appropriés. Vérifier l’alignement après chaque changement d’angle de biseau.
La découpe à onglet mixte est effectuée de la même manière que la coupe à onglet sauf que la lame de la scie est inclinée à
l’angle désiré sur l’échelle de biseau et fixée pour une coupe en biseau. Consulter la figure 60 pour une illustration de la coupe
à onglet mixte.
Fig. 60
SCIAGE EN LONG
pour réduire le risque de blessure, la pièce ne doit jamais être acheminée par l’extrémité de sortie du
protège-lame sinon il y aura danger de blessures.
pour réduire le risque de blessures, éteindre l’appareil et le débrancher avant d’installer ou de retirer
tout accessoire, avant d’ajuster ou de modifier les réglages ou lors de réparations. Un démarrage accidentel pourrait
provoquer des blessures.
NE JAMAIS toucher l’« extrémité libre » de la pièce ou une « pièce libre » qui est coupée alors que
l’appareil est en marche et/ou que la lame de la scie tourne toujours. La pièce pourrait toucher la lame et être projetée
pouvant ainsi vous blesser.
maintenir le protège-lame, le couteau séparateur et les dents antireculs en position et en bon
état de fonctionnement. Maintenir les dents affûtées. Si les dents ne fonctionnent pas, retourner l’appareil au centre
de réparation Delta autorisé le plus près pour une réparation. Le couteau séparateur doit être aligné avec la lame
de la scie et les dents doivent arrêter un effet de rebond une fois la coupe amorcée. Vérifier le fonctionnement
des ensembles avant le sciage en long en avançant une pièce de bois sous les dents antireculs. Les dents doivent
empêcher la projection de la pièce de bois vers l’avant de la scie.
52
Page 53

TOUJOURS utiliser un guide
longitudinal pour les sciages en long pour bien maîtriser
la pièce et prévenir les blessures. Ne JAMAIS effectuer
d’opération de sciage en long à mains libres. TOUJOURS
verrouiller le guide longitudinal sur la barre de guidage.
IMPORTANT : pour certaines utilisations, vous aurez besoin
de deux poussoirs et/ou de planches en éventail.
garder tous les poussoirs, planches en
éventail, etc. à portée de main de façon à pouvoir les
prendre sans devoir passer près de la lame.
Le sciage en long implique de faire une coupe en longueur
dans une planche en suivant le fil du bois. Fixer le bras à « 0 »
sur l’échelle à onglets. Positionner et fixer la fourche de sorte
que la lame soit parallèle au guide en position de sciage vers
l’intérieur ou l’extérieur. Lors de l’acheminement de la pièce,
s’assurer qu’un bord est appuyé contre le guide avec le côté
plat appuyé sur la table. Abaisser le protège-lame du côté
de l’alimentation jusqu’à ce qu’il touche presque la pièce
(fig. 61) de sorte qu’il fonctionne comme retenue. Régler
le couteau séparateur et les linguets antireculs (A), fig. 61,
comme décrit sous la rubrique « RÉGLAGE DU COUTEAU
SÉPARATEUR ET DES LINGUETS ANTIRECULS » du
présent mode d’emploi. Garder les mains bien éloignées et
sur le côté de la lame. Pour découper une pièce étroite en
long, toujours utiliser un poussoir (fig. 62) pour acheminer la
pièce entre le guide et la lame.
La pièce doit avoir un bord droit pour suivre le guide. Si le
bord est voilé, placer le côté creux vers le bas.
Serrer solidement la poignée de la serre de la tête de coupe pour toutes les opérations de sciage en long.
ne jamais faire avancer la pièce par l’extrémité de sortie du protège-lame.
Fig. 61
Fig. 62
A
SCIAGE VERS L’EXTÉRIEUR
Un sciage vers l’extérieur est généralement le même qu’un sciage en long sauf qu’il s’agit de fixer la fourche à angle droit par
rapport au bras sur rail avec le protège-lame dirigé vers L’AVANT de l’appareil. Positionner la tête de coupe sur l’échelle de
sciage vers l’extérieur au réglage désiré et la fixer dans cette position. Faire avancer la pièce par le côté gauche de la scie. Une
opération courante de sciage vers l’extérieur est illustrée à la fig. 61.
SCIAGE VERS L’INTÉRIEUR
Un sciage vers l’intérieur est généralement le même qu’un sciage en long sauf qu’il s’agit de fixer la fourche à angle droit par
rapport au bras sur rail avec le protège-lame dirigé vers L’ARRIÈRE de l’appareil. Positionner la tête de coupe sur l’échelle de
sciage vers l’intérieur au réglage désiré et la fixer dans cette position. Faire avancer la pièce par le côté droit de la scie. Une
opération courante de sciage vers l’intérieur est illustrée à la fig. 62.
pour scier une pièce de moins de 15 cm (6 po) de largeur, utiliser un poussoir pour terminer la
coupe (fig. 62).
POUSSOIRS
Pour utiliser la scie à bras radial en toute sécurité, utiliser un poussoir pour éviter d’approcher les mains à moins de 15 cm
(6 po) de la lame de la scie, ou d’autre organe de coupe, à chaque fois que la taille ou la forme de la pièce l’exige.
Il n’est pas obligatoire d’utiliser un bois particulier pour fabriquer des poussoirs pourvu qu’ils soient solides et suffisamment
longs. On recommande une longueur de 30 cm (12 po) avec une encoche qui s’adapte contre le bord de la pièce pour prévenir
tout glissement. Il est pratique d’avoir sous la main plusieurs poussoirs de 30 cm (12 po) de long avec des encoches de
différentes tailles pour s’adapter à différentes épaisseurs de pièce.
Consulter l’illustration de la page suivante pour visualiser un poussoir. La forme du poussoir peut varier pour répondre à vos
besoins à condition qu’il éloigne effectivement les mains de la lame.
53
Page 54

FABRICATION D'UN POUSSOIR
Pour scier en long une pièce de moins de 6 po de large, utiliser un poussoir pour terminer la
coupe. Il est facile de fabriquer un poussoir avec des déchets de découpe.
Fabriquer le poussoir à partir de contreplaqué ou de bois tendre de la même largeur ou un peu
moins large que la pièce à couper.
POUSSOIR
largeur de la pièce à couper.
d'une épaisseur inférieure à la
Le fabriquer à partir de BOIS d'une
épaisseur de 1/2 po OU de 3/4 po ou
Encoche qui permet
bois de 1/4 po.
bois de 1/2 po.
.
main.
d'éviter le glissement de la
Couper ici pour un poussoir en
54
Couper ici pour un poussoir en
Carrés de 1/2 po
Page 55

DEPANNAGE
Pour l'assistance avec votre outil, visiter notre site web à www.deltaportercable.com pour une liste de centres de
maintenance ou appeler la ligne d'aide de Delta Machinery à
1-800-223-7278. (Canada: 1-800-463-3582).
ENTRETIEN
Pour réduire le risque de blessures corporelles graves, éteindre l’outil et le débrancher avant
d’installer et de retirer tout accessoire, avant d'ajuster ou de modifier les réglages ou lors de réparations. Un démar-
rage accidentel peut provoquer des blessures.
GARDER LA MACHINE PROPRE
Porter des protections oculaire et auditive homologuées et utiliser un appareil respiratoire lors
de l’utilisation d’air comprimé.
Dégager régulièrement toutes les conduites d’air avec de l’air comprimé sec. Toutes les pièces en plastique doivent être nettoyées à l’aide d’un chiffon doux humide. NE JAMAIS utiliser de solvants pour nettoyer les pièces en plastique. Les solvants
peuvent dissoudre ou endommager le matériel.
DÉMARRAGE IMPOSSIBLE
Si la machine ne démarre pas, s’assurer que les lames de la fiche du cordon d’alimentation sont bien enfoncées dans la prise
de courant. Vérifier également que les fusibles ne sont pas grillés ou que le disjoncteur ne s’est pas déclenché.
LUBRIFICATION ET PROTECTION CONTRE LA ROUILLE
Appliquer chaque semaine une cire à parquets d’usage domestique sur la table de la machine, sur la rallonge de table ou
toute autre surface de travail. Ou utiliser un produit protecteur commercial conçu à cet effet. Suivre les directives du fabricant
pour l’utilisation et la sécurité.
Pour nettoyer les tables en fonte contre la rouille, utiliser le matériel suivant : une feuille de papier à poncer Scotch-Brite™
medium, une boîte de WD-40® et une boîte de dégraissant. Appliquer le WD-40 et polir la surface de la table avec le papier
à poncer Scotch-Brite. Dégraisser la table puis appliquer le produit protecteur comme décrit ci-dessus.
PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES
Le moteur de votre scie est équipé d’un relais de surcharge
(A) Figure 61. Si le moteur s’éteint ou ne s’allume pas à
cause d’une surcharge, ou d’une basse tension, basculer
l’interrupteur en position « ARRÊT», laisser le moteur
se refroidir pendant trois à cinq minutes, puis appuyer
sur le bouton de réinitialisation (A). Le moteur peut alors
redémarrer normalement. Les utilisations qui peuvent
causer une surcharge sont : une découpe trop rapide,
l’utilisation d’une lame émoussée, l’utilisation de la scie
au-delà de ses capacités, etc.
Fig. 63
A
SERVICE
PIÈCES DE RECHANGE
Utiliser seulement des pièces de rechange identiques. Pour obtenir une liste des pièces de rechange ou pour en commander,
consulter notre site Web au www.deltaportercableservicenet.com. Commander aussi des pièces auprès d’une succursale
d’usine ou composer le 1-800-223-7278 pour le service à la clientèle et recevoir ainsi une assistance personnalisée de
techniciens bien formés.
ENTRETIEN ET RÉPARATION
Tous les outils de qualité finissent par demander un entretien ou un changement de pièce. Pour de plus amples renseignements
à propos de Delta Machinery, ses succursales d’usine ou un centre de réparation sous garantie autorisé, consulter notre site
Web au www.deltaportercable.com ou composer le 1-800-223-7278 pour le service à la clientèle. Toutes les réparations
effectuées dans nos centres de réparation sont entièrement garanties contre les défauts de matériaux et de main-d’oeuvre.
Nous ne pouvons garantir les réparations effectuées en partie ou totalement par d’autres.
Pour de plus amples renseignements par courrier, écrire à Delta Machinery, 4825 Highway 45 North, Jackson, Tennessee
38305, É.-U. – à l’attention de : Product Service. S’assurer d’indiquer toutes les informations figurant sur la plaque signalétique
de l’outil (numéro du modèle, type, numéro de série, etc.).
55
Page 56
RIP
LOCK
Cutterhead
must be clamped
before performing
ripping operations.
YOKE
PIVOT
Pull handle toward
front of machine.
Pull plunger pin.
Pivot head to
desired position.
Push handle
back to lock.
BEVEL
ANGLE
Pull handle
toward
operator.
Pull plunger pin.
Set head to
desired bevel
angle. Push
handle to lock
head securely.
DEPTH
OF CUT
Lock head securely
on track arm.
Turn crank to raise
or lower blade depth.
MITER
ANGLE
Pull locking
arm to up
position. Depress
plunger and
move arm to
desired angle.
Push locking
arm back to
engage.
DOWN UP
DOWN
UNLOCK
LOCK
TO REDUCE
THE RISK OF
INJURY RETURN CUTTING HEAD TO FULL REAR
POSITION AFTER EACH CROSSCUT OPERATION.
SHUT OFF POWER AND WAIT FOR BLADE TO
STOP BEFORE SERVICING OR ADJUSTING.
PARA REDUCIR EL RIESGO DE LESIONES
COLOQUE NUEVAMENTE EL CABEZAL DE
CORTE EN SU POSICIÓN TRASERA MÁXIMA
DESPUÉS DE CADA CORTE TRANSVERSAL.
DESCONECTE LA ENERGÍA Y ESPERE A QUE LA
HOJA SE DETENGA ANTES DE REALIZAR
TAREAS DE MANTENIMIENTO O AJUSTES.
POUR RÉDUIRE LE RISQUE DE BLESSURES,
RAMENER LA TÊTE DE COUPE COMPLÈTEMENT
À L’ARRIÈRE APRÈS CHAQUE COUPE
TRANSVERSALE. COUPER L’ALIMENTATION
ET ATTENDRE L’ARRÊT DE LA LAME AVANT
DE RÉPARER OU DE RÉGLER LA SCIE.
TO AVOID INJURY NO
ADJUSTMENTS SHOULD
BE MADE UNTIL TOOL
HAS STOPPED.
FOR YOUR OWN SAFETY
DO NOT FEED MATERIAL
INTO CUTTING TOOL
FROM THIS END.
PARA EVITAR LESIONES,
NO DEBE REALIZARSE
NINGÚN AJUSTE HASTA
QUE LA HERRAMIENTA SE
HAYA DETENIDO.
POR SU PROPIA
SEGURIDAD, NO
INTRODUZCA MATERIAL
EN LA HERRAMIENTA DE
CORTE POR ESTE
EXTREMO.
TO REDUCE THE RISK OF
INJURY READ
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
BEFORE OPERATING RADIAL
SA W. ALWAYS WEAR EYE PROTECTION. DO NOT WEAR
GLOVES, NECKTIES, JEWELRY OR LOOSE CLOTHING.
DO NOT OPERATE WITHOUT GUARDS IN PLACE.
KEEEP HANDS OUT OF PATH OF SAW BLADE. DO
NOT PERFORM ANY OPERATING FREE-HAND.
ALWAYS SUPPORT WORK FIRMLY AGAINST FENCE.
ALWAYS FEED MATERIAL AGAINST ROTATION OF
BLADE AND USE ANTI-KICKBACK FINGERS WHEN
RIPPING. USE PUSH STICKS WHEN RIPPING NARROW
WORK. KNOW HOW TO REDUCE RISK OF KICKBACK. NEVER
REACH AROUND OR BEHIND SAW BLADE. DO NOT REMOVE JAMMED
OR SCRAP MATERIAL UNTIL BLADE HAS COMPLETELY STOPPED. RETURN CUTTING
HEAD TO FULL REAR POSITION UPON COMPLETION OF CROSSCUTS. SHUT OFF
POWER AND WAIT FOR SAW BLADE TO STOP BEFORE MOVING WORKPIECE OR
CHANGING TOOL SETTINGS. DISCONNECT POWER BEFORE CHANGING SAW BLADE
OR SERVICING TOOL. DO NOT EXPOSE TO RAIN OR USE IN DAMP LOCATIONS.
PARA REDUCIR EL RIESGO DE LESIONES
LEA EL MANUAL DE INSTRUCCIONES ANTES
DE OPERAR LA SIERRA RADIAL. UTILICE SIEMPRE PROTECCIÓN ADECUADA PARA
LOS OJOS. NO UTILICE GUANTES, CORBATAS, ALHAJAS NI ROPA HOLGADA. NO
OPERE LA SIERRA SI LOS PROTECTORES NO ESTÁN ADECUADAMENTE INSTALADOS.
MANTENGA LAS MANOS ALEJADAS DEL TRAYECTO DE LA HOJA DE LA SIERRA. NO
REALICE NINGUNA OPERACIÓN SIN UTILIZAR LAS MANOS. SIEMPRE SOSTENGA EL
TRABAJO FIRMEMENTE CONTRA LA GUÍA. SIEMPRE INTRODUZCA EL MATERIAL EN
SENTIDO CONTRARIO AL GIRO DE LA HOJA Y UTILICE DEDOS DE ANTIRETROCESO
CUANDO REALICE CORTES LONGITUDINALES. UTILICE VARAS DE EMPUJE AL
REALIZAR CORTES LONGITUDINALES EN PIEZAS DE TRABAJO ANGOSTAS. SEPA
CÓMO EVITAR EL RIESGO DE RETROCESOS. NUNCA INTENTE ALCANZAR OBJETOS
ALREDEDOR O DETRÁS DE LA HOJA DE LA SIERRA. NO RETIRE EL MATERIAL
ATASCADO O DE DESCARTE HASTA QUE LA HOJA NO SE HAYA DETENIDO
COMPLETAMENTE. COLOQUE NUEVAMENTE EL CABEZAL DE CORTE EN LA POSICIÓN
TRASERA MÁXIMA LUEGO DE REALIZAR CORTES TRANSVERSALES. DESCONECTE LA
ENERGÍA Y ESPERE A QUE LA HOJA SE DETENGA ANTES DE MOVER LA PIEZA DE
TRABAJO O CAMBIAR LA CONFIGURACIÓN DE LA HERRAMIENTA. DESCONECTE LA
ENERGÍA ANTES DE CAMBIAR LA HOJA DE LA SIERRA O REALIZAR TAREAS DE
MANTENIMIENTO. NO EXPONGA A LA LLUVIA NI UTILICE EN LUGARES HÚMEDOS
POUR RÉDUIRE LE RISQUE DE
BLESSURES, LIRE LE MODE D’EMPLOI
AVANT L’UTILISATION DE LA SCIE RADIALE. TOUJOURS PORTER UNE PROTECTION
OCULAIRE ADÉQUATE. NE PAS PORTER DE GANTS, NI CRAVATES, BIJOUX OU
VÊTEMENTS AMPLES. NE PAS UTILISER LA SCIE SANS QUE LES PROTÈGE-LAME NE
SOIENT EN PLACE. GARDER LES MAINS HORS DE LA TRAJECTOIRE DE LA LAME DE
LA SCIE. EFFECTUER TOUTE OPÉRATION EN TENANT L’OUTIL DES DEUX MAINS.
TOUJOURS APPUYER LA PIÈCE CONTRE LE GUIDE. TOUJOURS AVANCER LE MATÉRIEL
À CONTRE-COURANT DE LA ROTATION DE LA LAME ET UTILISER LES DOIGTS
ANTI-EFFET DE REBOND LORS DE SCIAGE EN LONG. UTILISER DES POUSSOIRS POUR
SCIER EN LONG UNE PIÈCE ÉTROITE. CONNAÎTRE LES TECHNIQUES POUR RÉDUIRE
LE RISQUE ASSOCIÉ À L’EFFET DE REBOND. NE PAS PASSER LES MAINS AUTOUR DE
LA LAME OU DERRIÈRE CELLE-CI. NE PAS RETIRER LA PIÈCE COINCÉE OU LA PIÈCE
DE CHUTE AVANT L’ARRÊT COMPLET DE LA LAME. RAMENER LA TÊTE DE COUPE
COMPLÈTEMENT À L’ARRIÈRE APRÈS DES COUPES TRANSVERSALES. COUPER
L’ALIMENTATION ET ATTENDRE L’ARRÊT COMPLET DE LA LAME DE LA SCIE AVANT
DE DÉPLACER LA PIÈCE OU DE MODIFIER LES RÉGLAGES. DÉBRANCHER LA SCIE
AVANT DE REMPLACER LA LAME OU D’EFFECTUER DES RÉPARATIONS. PROTÉGER
DE LA PLUIE ET NE PAS UTILISER DANS DES ENDROITS HUMIDES.
angle. Push
handle to lock
head securely.
DEPTH
OF CUT
Lock head securely
on track arm.
Turn crank to raise
or lower blade depth.
MITER
ANGLE
Pull locking
arm to up
position. Depress
plunger and
move arm to
desired angle.
Push locking
arm back to
engage.
DOWN UP
DOWN
UNLOCK
LOCK
POUR EMPÊCHER DES
BLESSURES, ATTENDRE
L’ARRÊT COMPLET DE
L’OUTIL AVANT D’EFFECTUER
TOUS RÉGLAGES.
POUR VOTRE PROPRE
SÉCURITÉ, NE PAS
INTRODUIRE DE MATÉRIAU
À PARTIR DE CETTE
EXTRÉMITÉ DE CET OUTIL.
TO AVOID INJURY NO
ADJUSTMENTS SHOULD
BE MADE UNTIL TOOL
HAS STOPPED.
FOR YOUR OWN SAFETY
DO NOT FEED MATERIAL
INTO CUTTING TOOL
FROM THIS END.
PARA EVITAR LESIONES,
NO DEBE REALIZARSE
NINGÚN AJUSTE HASTA
QUE LA HERRAMIENTA SE
HAYA DETENIDO.
POR SU PROPIA
SEGURIDAD, NO
INTRODUZCA MATERIAL
EN LA HERRAMIENTA DE
CORTE POR ESTE
EXTREMO.
REMPLACEMENT GRATUIT DE L'ÉTIQUETTE
Si vos étiquettes d'avertissement deviennent illisibles ou sont manquantes, composez le 1-800-223-7278 pour obtenir
une étiquette de remplacement gratuite.
56
Page 57
ACCESSOIRIES
Depuis des accessoiresautreque ceux offertsparPorter-Cable•Deltan'ont pas été testés
avec ce produit, utilisation de tels accessoires a pu être dangereux. Pour l'exploitation sûre, seulement Porter-
Cable•Deltaarecommandédesaccessoiresdevraitêtreutiliséavecceproduit.
Une ligne complète des accessoires est fournie des centres commerciaux d'usine de par votre de Porter-Cable•Delta
fournisseur, de Porter-Cable•Delta, et des stations service autorisées par Porter-Cable. Veuillez visiter notre site Web
www.deltaportercable.com pour un catalogue ou pour le nom de votre fournisseur plus proche.
GARANTIE
Pour enregistrer votre outil pour la garantie service la visite notre site Web à www.deltaportercable.com.
Garantie limitée de deux ans
Delta réparera ou remplacera, à ses frais et à sa discrétion, toute nouvelle machine Delta, pièce de rechange ou tout accessoire qui,
dans des circonstances d'utilisation normale, s'est avéré défectueux en raison de défauts de matériau ou de fabrication, à condition
que le client retourne le produit (transport payé d'avance) au centre de réparation de l'usine Delta ou à un centre de réparation autorisé
accompagné d'une preuve d'achat et dans les deux ans de la date d'achat du produit, et fournisse à Delta une opportunité raisonnable de
vérifier le défaut présumé par une inspection. La période de garantie des produits Delta réusinés est de 180 jours. Delta peut demander
que les moteurs électriques soient retournés (transport payé d'avance) à un centre de réparation autorisé du fabricant du moteur en vue
d'une inspection, d'une réparation ou d'un remplacement. Delta ne peut être tenu pour responsable des défauts résultants de l'usure
normale, de la mauvaise utilisation, de l'abus, de la réparation ou de la modification du produit, sauf en cas d'autorisation spécifique
d'un centre de réparation ou d'un représentant Delta autorisé. En aucune circonstance Delta ne peut être tenu pour responsable des
dommages accidentels ou indirects résultant d'un produit défectueux. Cette garantie constitue la seule garantie de Delta et le recours
exclusif des clients en ce qui concerne les produits défectueux ; toutes les autres garanties, expresses ou implicites, de qualité
marchande, d'adéquation à un usage particulier, ou autre, sont expressément déclinées par Delta.
AMÉRIQUE LATINE : Cette garantie ne s’applique aux produits vendus en Amérique latine. Pour ceux-ci, veuillez consulter les informations
relatives à la garantie spécifique présente dans l’emballage, appeler l’entreprise locale ou consulter le site Web pour les informations relatives
à cette garantie.
57
Page 58

INSTRUCCIONES DE SEGURIDAD IMPORTANTES
Lea a todas advertencias y las instrucciones operadoras antes de utilizar
cualquier instrumento o el equipo. Cuando se usa instrumentos o equipo, las precauciones básicas
de la seguridad siempre se deben seguir para reducir el riesgo de la herida personal. La operación
impropia, la conservación o la modificación de instrumentos o equipo podrían tener como resultado el
daño grave de la herida y la propiedad. Hay ciertas aplicaciones para que equipaas con herramienta y el equipo
se diseña. La Delta Machinery recomienda totalmente que este producto no sea modificado y/o utilizado para
ninguna aplicación de otra manera que para que se diseñó.
Si usted tiene cualquiera pregunta el pariente a su aplicación no utiliza el producto hasta que usted haya escrito Delta
Machinery y nosotros lo hemos aconsejado. La forma en línea del contacto en www. deltaportercable. com o por
correoTechnical Service Manager, Delta Machinery, 4825 Highway 45 North, Jackson, TN 38305. En Canada, 125 Mural St.
Suite 300, Richmond Hill, ON, L4B 1M4
Información con respecto a la operación segura y apropiada de este instrumento está disponible
de las fuentes siguientes:
•
Power Tool Institute, 1300 Sumner Avenue, Cleveland, OH 44115-2851 o en línea ww.powertoolinstitute.org
•
National Safety Council, 1121 Spring Lake Drive, Itasca, IL 60143-3201
•
American National Standards Institute, 25 West 43rd Street, 4 floor, New York, NY 10036 www.ansi.org - ANSI 01.1
Safety Requirements for Woodworking Machines
•
U.S. Department of Labor: www.osha.gov
GUARDE ESTAS INSTRUCCIONES!
PAUTAS DE SEGURIDAD/DEFINICIONES
Es importante para usted leer y entender este manual. La información que lo contiene relaciona a proteger SU
SEGURIDAD y PREVENIR los PROBLEMAS. Los símbolos debajo de son utilizados para ayudarlo a reconocer esta
información.
Indica una situación de peligro inminente que, si no se evita,
Indica una situación de peligro potencial que, si no se evita,
Indica una situación de peligro potencial que, si no se evita,
Utilizado sin el símbolo de alerta de seguridad indica una situación de peligro potencial que, si no se evita,
puede provocar
Parte del polvo producido por las herramientas eléctricas al lijar, aserrar, esmerilar, taladrar y
realizar otras actividades de construcción contiene productos químicos reconocidos por el Estado de California
como causantes de cáncer, defectos de nacimiento u otros problemas reproductivos. Algunos ejemplos de
estos productos químicos son:
• elplomodelaspinturasdebaseplomo,
• lasílicecristalinadelosladrillos,elcementoyotrosproductosdemampostería,y
• elarsénicoyelcromodelamaderacontratamientoquímico.
El riesgo derivado de la exposición a estos productos químicos varía según la frecuencia con la que se realice
este tipo de trabajo. Para reducir su exposición, trabaje en áreas bien ventiladas y use equipos de seguridad
aprobados, como las máscaras para polvo especialmente diseñadas para filtrar las partículas microscópicas.
daños en la
propiedad.
provocará
podría
puede
provocar la
provocar
la
muerte o lesiones graves.
muerte o lesiones graves.
lesiones leves o moderadas.
58
Page 59

NORMAS GENERALES DE SEGURIDAD
Lea todas las instrucciones antes de operar el producto. El incumplimiento de todas y cada una de las
instrucciones enumeradas a continuación puede provocar una descarga eléctrica, un incendio y/o lesiones graves.
CONSERVE ESTAS INSTRUCCIONES!
INSTRUCCIONES DE CONEXIÓN A TIERRA
RESPETE TODOS LOS CÓDIGOS DE CABLEADO y las conexiones eléctricas recomendadas para
prevenir los riesgos de descargas eléctricas o electrocución.
Para realizar la conexión a tierra de la sierra, lea las siguientes instrucciones.
Riesgo de descarga eléctrica. Esta máquina debe estar conectada a tierra mientras esté en uso. De lo
contrario, puede causar lesiones graves.
TODAS LAS MÁQUINAS ESTÁN PUESTAS A TIERRA Y CONECTADAS A TRAVÉS DE UN CABLE
En caso de un mal funcionamiento o falla, la conexión a tierra proporciona un trayecto de la menor resistencia posible para
reducir el riesgo de que la corriente ocasione una descarga eléctrica. Esta máquina está equipada con un cable eléctrico que
tiene un conductor y un enchufe para poner el equipo a tierra. El enchufe se debe utilizar con un tomacorriente adecuado que
haya sido instalado correctamente y conectado a tierra de acuerdo con todos los códigos y las ordenanzas locales. No cambie el enchufe suministrado; si no se adapta apropiadamente al tomacorriente, solicite a un electricista calificado que instale
el tomacorriente correcto. Como consecuencia de una conexión inadecuada del conductor a tierra del equipo se puede generar un riesgo de descarga eléctrica. El conductor a tierra del equipo es el que tiene un aislante de color verde en la superficie
externa, con o sin bandas amarillas. Si fuera necesario reparar o reemplazar el cable eléctrico, no conecte el conductor a tierra
del equipo a una terminal de baja tensión. Llame a un electricista calificado o al personal del servicio para que verifique las
conexiones si no comprende completamente las instrucciones de conexión a tierra o si duda de que la máquina esté conectada a tierra correctamente. Utilice solamente cables prolongadores de 3 conductores que tengan enchufes a tierra de 3 patas
y tomacorrientes de 3 conductores que se adapten al enchufe de la máquina, como se muestra en la Figura A. Repare o
reemplace los cables dañados o gastados inmediatamente.
MÁQUINAS PUESTAS A TIERRA, CONECTADAS A TRAVÉS DE UN CABLE Y DISEÑADAS PARA SER UTILIZADAS EN
UN CIRCUITO DE SUMINISTRO CON UN ÍNDICE NOMINAL MENOR A 150 VOLTIOS
Si la máquina está diseñada para utilizarse en un circuito que tiene un tomacorriente, similar al que ilustra la Figura A, tendrá
un enchufe a tierra parecido al que ilustra la Figura A. Si no dispone de un tomacorriente correctamente conectado a tierra,
puede usar un adaptador provisional, similar al que ilustra la Figura B, para conectar este enchufe a un tomacorriente para
dos patas correspondiente, como el que se muestra en la Figura B. El adaptador provisional únicamente debe usarse hasta
que un electricista calificado instale un tomacorriente correctamente conectado a tierra. La oreja, la lengüeta, o algo semejante, de color verde que sale del adaptador debe estar conectada a tierra en forma permanente por medio de una caja de
tomacorriente conectado a tierra correctamente. Cuando se utilice el adaptador, debe estar fijo con un tornillo de metal.
A B
TOMACORRIENTE A
TIERRA
PATA A TIERRA
C
MEDIOS DE PUESTA A
TIERRA
ADAPTADOR
D
PATA A TIERRA
NOTA: en Canadá, el Código de Electricidad Canadiense no permite el uso de adaptadores provisionales.
En todos los casos, asegúrese de que el receptáculo en cuestión esté conectado a tierra
adecuadamente. Si no está seguro, haga que un electricista calificado compruebe el receptáculo.
59
Page 60

OPERACIÓN DE UNA SOLA FASE CON 240 VOLTIOS
El motor provisto con su máquina es de doble voltaje, es
decir de 120/140 voltios. Viene listo para su funcionamiento
en operaciones de 120 voltios. Sin embargo, se puede
convertir para operaciones de 240 voltios.
Siga las siguientes instrucciones para cambiar su sierra
para que opere con 240 voltios.
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones personales graves, apague la herramienta y desconéctela de
la fuente de alimentación antes de instalar y retirar accesorios, ajustar o cambiar configuraciones o realizar reparaciones. Un arranque accidental podría causar lesiones.
1. Retire el tornillo (A) Figura D y retire la cubierta de la
placa con inscripción (B).
2. Deslice cuidadosamente el interruptor (C) Figura E en
la caja de empalmes del motor para que indique 240
voltios. Vuelva a colocar el cobertor de la placa con
inscripción y el tornillo que retiró en el PASO 1.
3. También debe reemplazar el enchufe de 120 voltios con
un enchufe listado por UL/CSA como adecuado para el
funcionamiento a 240 voltios y la corriente nominal
para la sierra.
GROUNDED OUTLET BOX
CURRENT
CARRYING
PRONGS
Fig. C
GROUNDING BLADE
IS LONGEST OF THE 3 BLADES.
B
Contrate a un electricista calificado para hacer el cambio
o lleve la máquina a un Centro de Servicio Autorizado de
A
Fig. D
Delta. La máquina debe cumplir con el Código Eléctrico
Nacional, y con todos los códigos y ordenanzas locales.
SÓLO use en enchufe de 240 voltios en una toma que
tenga la misma configuración que el enchufe ilustrado en
la figura C. NO use un adaptador para el enchufe de 240
voltios.
En todos los casos, asegúrese de
que el receptáculo en uso esté conectado a tierra
correctamente. Si no está seguro, contrate a un
electricista calificado para que verifique el receptáculo.
C
Fig. E
INSTRUCCIONES DE SEGURIDAD IMPORTANTES
1. PARA REDUCIR EL RIESGO DE RETROCESO Y OTRAS LESIONES, MANTENGA LOS PROTECTORES INSTALADOS
ADECUADAMENTE y en funcionamiento en todo momento.
2. RETIRE LAS LLAVES DE AJUSTE Y LLAVES DE TUERCAS. Acostúmbrese averificar que se hayan retirado del eje las
llaves de ajuste y las llaves de tuercas antes de encender la herramienta. Las herramientas, las piezas de descarte y otro
tipo de desechos pueden salir despedidos a alta velocidad y provocar lesiones.
3. MANTENGA LIMPIA EL ÁREA DE TRABAJO. Los espacios y los bancos de trabajo abarrotados propician accidentes.
4. NO UTILICE LA MÁQUINA EN LUGARES PELIGROSOS. El uso de herramientas eléctricas en lugares húmedos o mojados
o bajo la lluvia puede provocar descargas eléctricas o electrocución. Mantenga su área de trabajo bien iluminada para evitar
tropezones o poner en peligro brazos, manos y dedos.
60
Page 61

5. MANTENGA A LOS NIÑOS ALEJADOS. Los visitantes deben mantenerse a una distancia segura del área de trabajo. Su taller
es un lugar potencialmente peligroso.
6. PROCURE QUE SU TALLER SEA INACCESIBLE PARA LOS NIÑOS instale candados e interruptores maestros, o retire las llaves
que accionan las herramientas. Si un niño o un visitante enciende una máquina sin autorización, podría producirle lesiones.
7. NO FUERCE LA HERRAMIENTA. Funcionará mejor y será más segura si la utiliza a la velocidad para la que fue diseñada.
8. UTILICE LA HERRAMIENTA ADECUADA. No fuerce la herramienta o el accesorio para realizar tareas para las que no fueron
diseñados. Usar la herramienta o el accesorio incorrecto puede causar lesiones personales.
9. UTILICE EL CABLE PROLONGADOR APROPIADO. Asegúrese de que el cable prolongador esté en buenas condiciones. Si
su herramienta está equipada con un juego de cables, utilice solamente cables prolongadores de 3 conductores que tengan
enchufes a tierra de 3 patas y tomacorrientes tripolares que se adapten al enchufe de la herramienta. Cuando utilice un cable
prolongador, asegúrese de que tenga la capacidad para conducir la corriente que su producto exige. Un cable de menorcapacidad
provocará una disminución en el voltaje de la línea, lo cual producirá una pérdida de potencia y sobrecalentamiento. La siguiente
tabla muestra la medida correcta que debe utilizar según la longitud del cable y la capacidad nominal en amperios indicada en
la placa. En caso de duda, utilice el calibre inmediatamente superior. Cuanto menor es el número de calibre, más grueso es el
cable.
CALIBRE MÍNIMO PARA LOS JUEGOS DE CABLES
Voltios Largo total del cable en pies
120 V 0-25 26-50 51-100 101-150
240 V 0-50 51-100 101-200 201-300
Capacidad nominal en amperios
Más No más AWG
que que
0 - 6 18 16 16 14
6 - 10 18 16 14 12
10 - 12 16 16 14 12
12 - 16 14 12 No recomendado
10. UTILICE INDUMENTARIA ADECUADA. No utilice ropa holgada, guantes, corbatas, anillos, pulseras u otras alhajas que
puedan quedar atrapadas entre las piezas móviles. Se recomienda el uso de calzado antideslizante. Recójase y cubra el
cabello largo. Los orificios de ventilación pueden cubrir piezas en movimiento, por lo que también se deben evitar.
11. SIEMPRE USE LENTES DE SEGURIDAD. Everyday eyeglasses are NOT safety glasses. Also use face or dust mask if cutting
opLos anteojos de uso diario NO son lentes de seguridad. Utilice también máscaras faciales o para polvo si el corte produce
polvillo. Utilice SIEMPRE equipos de seguridad ificados:
• ProtecciónparalosojossegúnlanormaANSIZ87.1(CAN/CSAZ94.3)
• ProtecciónauditivasegúnlanormaANSIS12.6(S3.19)
• ProtecciónrespiratoriasegúnlasnormasNIOSH/OSHA/MSHA.
12. NO SE ESTIRE. Conserve el equilibrio y párese adecuadamente en todo momento. La pérdida de equilibrio podría provocar
lesiones personales.
13. CONSERVE LAS HERRAMIENTAS ADECUADAMENTE. Mantenga las hojas afiladas y limpias para obtener un rendimiento
óptimo y seguro. Siga las instrucciones para lubricar y cambiar los accesorios. Las máquinas y las hojas que carecen de un
mantenimiento adecuado pueden dañar aún más la máquina o la hoja o causar lesiones.
14. APAGUE LA MÁQUINA Y DESCONÉCTELA DE LA FUENTE DE ALIMENTACIÓN las configuraciones o cuando haga
reparaciones. No toque las patas de metal del enchufe al enchufar o desenchufar el cable. Un arranque accidental
podría causar lesiones
15. REDUZCA EL RIESGO DE ENCENDIDO ACCIDENTAL. Asegúrese de que el interruptor esté en la posición “OFF” (de
apagado) antes de enchufar el cable de alimentación. En caso de un corte de corriente, mueva el interruptor a la posición de
“OFF” (de apagado). Un arranque accidental podría causar lesiones.
16 UTILICE ACCESORIOS RECOMENDADOS. Utilice sólo accesorios recomendados por el fabricante para el modelo que
posee. Los accesorios que pueden ser aptos para una herramienta, pueden convertirse en un factor de riesgo cuando
se utilizan en otra herramienta. Consulte el manual de instrucciones para obtener información acerca de los accesorios
recomendados. La utilización de accesorios inadecuados puede ocasionar lesiones personales.
17. NUNCA SE PARE SOBRE LA HERRAMIENTA. Si la herramienta se cae o alguien toca accidentalmente el elemento cortante,
podrían producirse lesiones graves.
18. VERIFIQUE QUE NO HAYA PIEZAS DAÑADAS. Antes de volver a utilizar la herramienta, se deben controlar cuidadosamente
los protectores o cualquier otra pieza dañada para asegurar el funcionamiento y el rendimiento apropiados de la herramienta
en la aplicación deseada. Verifique la unidad para comprobar la alineación de las piezas móviles, si hay piezas dañadas,
bloqueos o cualquier otra situación que pueda afectar el funcionamiento de la herramienta. Los protectores u otras piezas
dañadas deben ser correctamente reparados o reemplazados. No utilice la herramienta si no puede encenderla o apagarla
con el interruptor. Las piezas dañadas pueden deteriorar la máquina aún más o causar lesiones.
19. DIRECCIÓN DE ALIMENTACIÓN. Introduzca la pieza de trabajo solamente en dirección contraria a la rotación de la hoja o
cortadora
20. NUNCA DEJE LA HERRAMIENTA EN FUNCIONAMIENTO Y SIN ATENCIÓN. DESCONECTE LA ENERGÍA. No suelte la
herramienta hasta que no se haya detenido por completo. Puede causar lesiones grave
21. NO OPERE HERRAMIENTAS ELÉCTRICAS CERCA DE LÍQUIDOS INFLAMABLES O EN ATMÓSFERAS GASEOSAS O
EXPLOSIVAS. Los motores e interruptores de estas herramientas originan chispas que pueden encender los vapores.
22. MANTÉNGASE ALERTA, PONGA ATENCIÓN EN LO QUE ESTÁ HACIENDO Y USE EL SENTIDO COMÚN. NO UTILICE
LA MÁQUINA SI ESTÁ CANSADO O BAJO EL EFECTO DE DROGAS, ALCOHOL O MEDICAMENTOS. Un momento de
descuido mientras se opera una herramienta eléctrica puede provocar daños graves
23. NO IGNORE LAS REGLAS DE SEGURIDAD POR ESTAR FAMILIARIZADO CON LA HERRAMIENTA (debido al uso
frecuente de su sierra). Recuerde siempre que un descuido de una fracción de segundo es suficiente para causar lesiones
graves.
61
Page 62

NORMAS ESPECÍFICAS ADICIONALES DE SEGURIDAD
Si no se siguen estas normas, el resultado podría ser lesiones graves.
1. USE SIEMPRE LENTES DE SEGURIDAD. Everyday eyeglasses are NOT safety glasses. Also use face or dust mask if cutting
operatLos anteojos de uso diario NO son lentes de seguridad. Utilice también máscaras faciales o para polvo si el corte produce
polvillo. Todos los usuarios y espectadores SIEMPRE DEBEN utilizar equipo de protección certificado:
• ProtecciónparalosojosANSIZ87.1(CAN/CSAZ94.3),
• protecciónauditivaANSIS12.6(S3.19),
• ProtecciónrespiratoriasegúnlasnormasNIOSH/OSHA/MSHA.
2. EVITE POSICIONES COMPLICADAS, donde un desliz repentino podría provocar que la mano se desplace hacia la hoja.
3. MANTENGA LOS BRAZOS, LAS MANOS Y LOS DEDOS LEJOS de la hoja para prevenir lesiones graves.
4. USE UNA VARA DE EMPUJE O UN BLOQUE DE EMPUJE ADECUADO PARA LA APLICACIÓN PARA EMPUJAR LA PIEZA
DE TRABAJO A TRAVÉS DE LA SIERRA. Una vara de empuje es una vara de madera u otro material que no sea metal, por lo
general de confección casera, que se debe usar siempre que el tamaño o la forma de la pieza de trabajo lo obligue a poner sus
manos a menos de 152 mm (6 pulgadas) de la hoja. Utilice patrones, plantillas sujetadoras, tablas de canto biselado u otras formas
de sujeción para dirigir y controlar la pieza de trabajo cuando no pueda utilizar el protector. Utilice el conjunto protector de la hoja
y hendedor en todas las operaciones en las que se pueda usar, incluidos todos los cortes pasantes.
5. NO REALICE A PULSO CORTES LONGITUDINALES O TRANSVERSALES NI NINGUNA OTRA OPERACIÓN.
6. NUNCA se extienda alrededor o por detrás de la hoja de la sierra.
7. ESTABILIDAD. Antes de usar la sierra de banco, confirme que esté firmemente montada en una superficie segura y que no se
mueva
8. NUNCA CORTE METALES FERROSOS (que contengan hierro o acero), TABLAS DE CEMENTO O MAMPOSTERÍA. Para cortar
ciertos materiales sintéticos con las sierras de banco se deben seguir instrucciones especiales. Siga las recomendaciones del
fabricante en todo momento. De lo contrario, la sierra se puede dañar o se pueden producir lesiones personales
9. UTILICE LA HOJA DE SIERRA ADECUADA PARA LA OPERACIÓN QUE REALIZARÁ. Siga las instrucciones de la sección
Operación del manual para realizar el procedimiento adecuado para cualquier tipo de corte. Ajuste siempre la tuerca de eje de la
hoja en forma segura. Antes de usar, inspeccione la hoja para detectar grietas o dientes faltantes. No utilice hojas dañadas.
10. NUNCA TRATE DE EXTRAER UNA HOJA DE LA SIERRA ATASCADA SIN APAGAR LA MÁQUINA PRIMERO. Si una pieza de
trabajo o de corte queda atrapada en el protector, apague la sierra, desconecte la máquina de la fuente de alimentación y espere
hasta que la hoja se detenga antes de levantar el protector y retirar la pieza.
11. NUNCA ENCIENDA LA MÁQUINA con la pieza de trabajo contra la hoja para reducir el riesgo de que la pieza de trabajo salga
despedida y ocasione lesiones personales.
12. NUNCA se ubique de modo que alguna parte del cuerpo quede en la misma línea que el trayecto de la hoja de la sierra. Se
producirán lesiones graves.
13. EVITE OPERACIONES COMPLICADAS Y POSICIONES DE LAS MANOS donde un desliz repentino podría provocar que la
mano se desplace hacia la hoja.
14. NUNCA SE UBIQUE DE MODO QUE ALGUNA PARTE DEL CUERPO QUEDE EN LA MISMA LÍNEA QUE EL TRAYECTO
DE LA HOJA DE LA SIERRA. Puede ocasionar lesiones personales.
15. NUNCA REALICE TRABAJOS DE TRAZADO, ARMADO O INSTALACIÓN en el banco o el área de trabajo cuando la máquina
esté en funcionamiento. Un deslizamiento repentino podría llevar la mano hacia la hoja. Esto puede causar lesiones graves.
16. LIMPIE EL BANCO Y EL ÁREA DE TRABAJO ANTES DE ABANDONARLOS. Bloquee el interruptor en la posición “OFF” (de
apagado) y desconecte la herramienta de la fuente de alimentación para evitar el uso no autorizado.
17. NO DEJE UNA TABLA LARGA l(ni otra pieza de trabajo) sin apoyo ya que el rebote de la tabla ocasiona su desplazamiento lateral
sobre el banco, lo que a su vez ocasiona la pérdida de control y posibles lesiones. Teniendo en cuenta el tamaño de la pieza de
trabajo y el tipo de operación que realizará, suministre el apoyo adecuado a la pieza de trabajo. Sostenga el trabajo firmemente
contra la guía y hacia abajo contra la superficie del banco.
18. NO OPERE ESTA MÁQUINA hasta que no esté armada e instalada completamente, según las instrucciones. Una máquina
montada de manera incorrecta puede provocar lesiones graves.
19. SOLICITE EL ASESORAMIENTO de su supervisor, instructor o alguna persona calificada si no está familiarizado con el
funcionamiento de esta máquina. El conocimiento garantiza la seguridad.
20. Encontrará INFORMACIÓN ADICIONAL disponible acerca de la operación correcta y segura de herramientas eléctricas (por
ejemplo: un vídeo de seguridad) en el Instituto de Herramientas Eléctricas (Power Tool Institute), 1300 Sumner Avenue, Cleveland,
OH 44115-2851 (www.powertoolinstitute.com). Además, encontrará información disponible en el Consejo Nacional de Seguridad
(National Safety Council), 1121 Spring Lake Drive, Itasca, IL 60143-3201. Remítase a los Requisitos de Seguridad 01.1 para las
máquinas de carpintería del Instituto Estadounidense de Normas Nacionales (American National Standards Institute - ANSI) y a
las Normas OSHA 1910.213 del Ministerio de Trabajo de los Estados Unidos.
Para reducir el riesgo de peligros potenciales, siga las siguientes reglas:
a. MANTENGA LAS MANOS ALEJADAS DEL PROTECTOR. A medida que la hoja realiza el corte, el protector se levantará y
dejará expuesta parte de la hoja.
b. ANTES DE LIBERAR UN PROTECTOR INFERIOR ATASCADO, APAGUE LA UNIDAD Y DESCONECTE LA MÁQUINA DE LA
FUENTE DE ALIMENTACIÓN. El protector puede atascarse en cortes previos en el banco o la guía. Prevea siempre el trayecto
del protector.
c. Al realizar cortes biselados, TENGA CUIDADO y asegúrese de que el protector inferior nunca esté contraído hacia la hoja.
d. EL PROTECTOR INFERIOR PUEDE ATASCARSE CONTRA LA GUÍA DURANTE LOS CORTES LONGITUDINALES
INTERNOS ESTRECHOS. Si el protector se atasca contra la guía, desconecte la sierra de la fuente, espere que la hoja se
detenga y luego levante el protector de la hoja y apóyelo sobre la guía.
El protector inferior retráctil de la hoja protege al operador a lo largo de los lados de la hoja de la sierra.
62
Page 63

TÉRMINOS: Los siguientes términos se usarán a lo largo del manual y usted deberá familiarizarse con ellos.
• Corte pasante: se refiere a cualquier corte que secciona la pieza de trabajo por completo.
• Vara de empuje: se refiere a una vara de madera, por lo general de confección casera, que se usa para empujar piezas de trabajo
pequeñas a través de la sierra y mantiene las manos del operador fuera del alcance de la hoja.
• Retroceso: ocurre cuando la hoja se atasca durante el corte y despide con violencia la pieza de trabajo hacia atrás, en dirección
al operador.
• A pulso: se refiere al corte de una pieza de trabajo sin un calibrador de inglete, una guía de corte longitudinal o cualquier otro medio
de guía o sujeción que la mano del operador.
PROTECTOR DE LA HOJA Y HENDEDOR
Su sierra de brazo radial está equipada con un protector de la hoja, un hendedor y dedos de antirretroceso. El hendedor se ajusta al
corte longitudinal que realiza la hoja y reduce la posibilidad de retroceso con eficacia al disminuir la tendencia de la hoja de atascarse
durante el corte. Utilice el separador y el protector de la hoja para todos los cortes. El hendedor posee dos seguros antirretroceso
que permiten que la hoja atraviese la madera en la dirección de corte, pero que la bloquean si trata de retroceder en dirección al
operador.
RETROCESOS
Cómo evitarlos y protegerse contra lesiones personales.
a. Asegúrese de que la guía de corte longitudinal esté paralela a la hoja de la sierra.
b. Al realizar cortes longitudinales, no aplique la fuerza de alimentación sobre la sección de la pieza de trabajo que corresponderá
a la pieza cortada (libre). Al realizar cortes longitudinales, la fuerza de la presión se debe aplicar siempre entre la hoja de la
sierra y la guía. Utilice una vara de empuje para las piezas de trabajo cortas, de 152 mm (6") o menos.
c. Mantenga el protector de la hoja, el hendedor y los dientes antirretroceso instalados correctamente y en funcionamiento.
Mantenga los dientes afilados. Si los dientes no están en condiciones operativas, devuelva la unidad al centro de mantenimiento
autorizado Delta más cercano para su reparación. El hendedor debe estar alineado con la hoja y los dientes deben detener
un retroceso una vez que ha comenzado. Para controlar la acción de los dientes antirretroceso, antes de realizar cortes
longitudinales, empuje la madera debajo de éstos. Los dientes deben evitar que la madera salga despedida hacia el frente de
la hoja de la sierra.
d. Su sierra también puede cortar plástico y materiales compuestos, como madera aglomerada. Sin embargo, como estos
materiales suelen ser bastante duros y resbaladizos, es posible que los seguros antirretroceso no detengan un retroceso. Por
lo tanto, cuando realice cortes longitudinales, sea especialmente cuidadoso y siga los siguientes procedimientos de instalación
y corte.
e. Utilice el protector de la hoja en todas las operaciones en las que se pueda usar, incluidos todos los cortes pasantes.
f. Al realizar cortes longitudinales, antes de soltar la pieza de trabajo, empújela hasta que pase la hoja de la sierra.
g. NUNCA realice un corte longitudinal en una pieza de trabajo que esté torcida o deformada o sin un borde recto que sirva de
guía.
h. NUNCA corte una pieza de trabajo grande que no pueda controlar.
i. NUNCA corte una pieza de trabajo que tenga nudos sueltos, defectos, clavos u otros objetos extraños.
j. NUNCA realice un corte longitudinal en una pieza de trabajo que mida menos de 254 mm (10").
k. Siempre utilice dedos de antirretroceso cuando realice cortes longitudinales. Baje el protector del extremo de avance de
entrada y ajuste el accesorio antirretroceso correctamente.
ción contienen productos químicos reconocidos por el Estado de California como causantes de cáncer, defectos congénitos
u otros problemas reproductivos. Algunos ejemplos de estos productos químicos son:
• elplomodelaspinturasdebaseplomo,
• lasílicecristalinadeladrillos,elcementoyotrosproductosdemampostería,y
• elarsénicoyelcromodelamaderacontratamientoquímico(CCA).
El riesgo derivado de estas exposiciones varía según la frecuencia con la que se realice este tipo de trabajo. Para reducir la
exposición a estos productos químicos, se recomienda trabajar en áreas bien ventiladas y usar equipos de seguridad aprobados,
como las máscaras para polvo especialmente diseñadas para filtrar las partículas microscópicas.
• Evite el contacto prolongado con las partículas de polvo originadas al lijar, aserrar, esmerilar, taladrar y realizar demás
actividades de la construcción. Use indumentaria protectora y lave las áreas expuestas con agua y jabón. Evite que el polvo
entre en la boca y en los ojos o se deposite en la piel, para impedir la absorción de productos químicos nocivos.
graves y permanentes u otras lesiones. Use siempre protección respiratoria apropiada para la exposición al polvo aprobada
por el Instituto Nacional de Salud y Seguridad Ocupacional de EE.UU. y la Administración de Salud y Seguridad Ocupacional
de EE.UU. (NIOSH y OSHA respectivamente, por sus siglas en inglés). Aleje la cara y el cuerpo del contacto con las partículas.
Siempre opere la herramienta en áreas con buena ventilación y procure eliminar el polvo adecuadamente. Utilice un sistema de
recolección de polvo, donde sea posible.
Algunas partículas originadas al lijar, aserrar, esmerilar, taladrar y realizar otras actividades de construc-
El uso de esta herramienta puede generar o dispersar polvo. Esto puede provocar problemas respiratorios
DESCRIPCIÓN FUNCIONAL
PROLOGO
El Modelo Delta RS830 es una Sierra de brazo radial profesional de 10 pulg. (254 mm) con una capacidad máxima de corte
transversal de 16 pulg. (406 mm), una profundidad de 2-3/4 pulg. (70 mm) en una profundidad de 90°, y de 2-1/2 pulg. (64 mm)
a 45°. Esta herramienta cuenta con paradas biseladas positivas en 0°, 45° y 90°, y paradas positivas de los ingletes en 0° y 45°,
tanto derecho como izquierdo. La unidad incluye un motor de 1-1/2 fuerzas de caballo de 120/240 voltios, un freno automático de
la hoja, una hoja de sierra, llaves, una base de acero, un riel de hierro forjado y una mesa extra grande.
NOTA: La foto del cubierta del manual illustra el modelo de production actual. Todas las demas ilustraciones son solamente
representativas y es posible que no muestren el color, el etiquetado y los accesorios reales.
63
Page 64

CONTENIDO DE CARTON
PIEZAS DE LA SIERRA DE BRAZO RADIAL
4 5
1. Sierra de brazo radial
2. Patas (4)
3. Soportes de mesa (2)
4. Tornillos de cabeza de hongo de 5/1618x5/8 pulgadas (16)
5. Arandelas planas de 11,11 mm (5/16 pulg.)
(16)
6. Arandelas de cierre de dientes externos de
5/16 pulg. (16)
7. Tuercas hexagonales de 5/16-18 pulg. (16)
6 7
PIEZAS DE LA TABLA DE MESA
1. Tabla de la guía
2. Tabla de mesa intermedia
3. Tabla de mesa posterior
4. Tabla de mesa delantera
5. Llave plana de 7/8 pulg. - Llave de
estría de 1/2 pulg.
6. Llave de estría de 7/8 pulg. x 1/2
pulg.
7. Tornillo de cabeza redonda de 1/420x31,75 mm (1¼") (4)
8. Tornillo de cabeza redonda de 1/420x1 pulg. (4)
9. Tornillos de cabeza de hongo de
7,93 mm (5/16)-18 x 5/8 pulg. (42)
10. Tornillo de chapa de #10x1/2 pulg.
(2)
11. Tuerca hexagonal de pestaña de
1/4-20 (4)
12. Tuerca hexagonal de pestaña de
9,52 mm (5/16)-18 (6)
13. Abrazadera de las tablas de la
mesa (2)
14. Gancho para llave
9
1
2
3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
11
12
13 14
10
64
Page 65
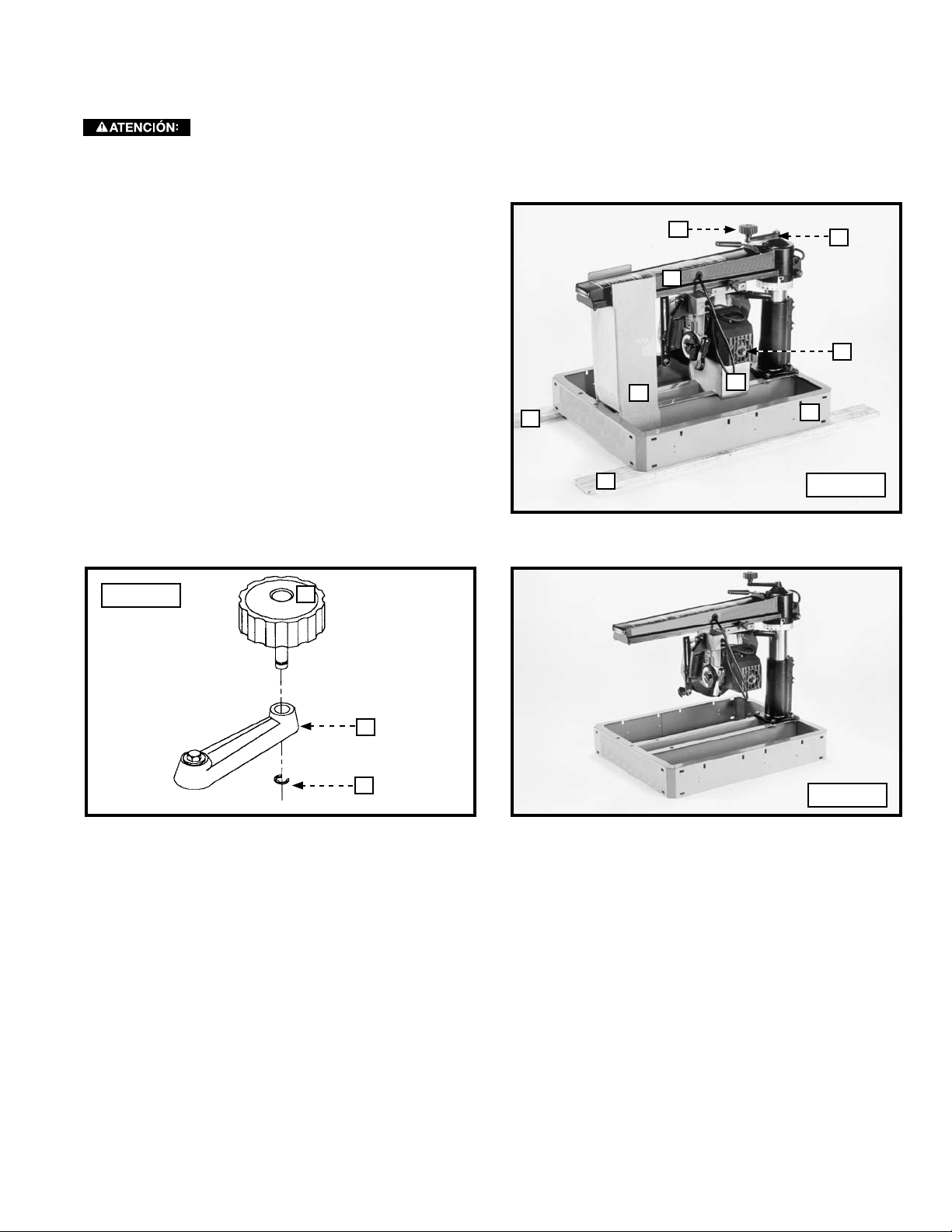
DESEMPAQUETADO Y LIMPIEZA
Desembale cuidadosamente la máquina y todos los elementos sueltos del o los contenedores de envío. Retire el aceite
anticorrosivo de las superficies sin pintura con un paño suave humedecido con alcohol mineral, solvente o alcohol
desnaturalizado.
No use solventes volátiles como gasolina, nafta, acetona o solvente de barniz para limpiar la máquina.
Luego de limpiar, cubra las superficies sin pintura con cera en pasta de buena calidad que se utiliza para los pisos del
hogar.
1. La sierra fue empacada en la fábrica con bloques de
apoyo (A) figura A1 bajo el cabezal de corte (B) y bajo
el brazo guía (C). Tablas de embarque (D) figura A1
fueron sujetados a la base de la sierra (G). Para evitar
el daño durante el embarque, la perilla de elevación del
brazo guía (H) fue removida de la palanca (E). Inserte el
poste de la perilla (H) figura A2 a través del agujero en
la palanca (E). Coloque el aro E (K) entro de la ranura
del poste.
2. Puede retirar los bloques de apoyo (A) figura A1 al
girar la perilla de elevación de la brazo guía (H) en el
sentido de las agujas del reloj. Puede retirar las tablas
de embarque (D) al sacar los tornillos de sujeción (no
están mostrados), situados dentro de la base de la
sierra. Deseche los bloques de apoyo (A) y las tablas
de embarque (D).
3. La sierra, sin los bloques de soporte y las tablas de
embarque se muestra en la figura A3.
D
D
H
E
C
B
A
A
G
Fig. A1
Fig. A2
H
E
K
Fig. A3
65
Page 66

ASSEMBLY
fuente de alimentación antes de instalar y retirar accesorios, ajustar o cambiar configuraciones o realizar reparaciones. Un
arranque accidental podría causar lesiones.
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones personales graves, apague la herramienta y desconéctela de la
HERRAMIENTAS DE ENSAMBLAJE REQUERIDAS
Llave plana de 7/8" - Llave de estría de 1/2" (incluidas)
Llave de estría de 7/8" x 1/2" (incluida)
Llaves planas o tubulares de 1/2” y 3/8 pulgadas
Desatornillador de cabeza plana
ESTIMACIÓN DEL TIEMPO DE ENSAMBLAJE
La asamblea para esta máquina es más o menos 2-3 horas
PARA ENSAMBLAR LAS PATAS A LA BASE DE LA SIERRA
1. Afloje la pernilla de cierre (A) Fig. 1, y mueva el cabezal
de corte (B) a la posición posterior. Apriete la pernilla
(A).
posterior del brazo de guía firmemente.
Sujete el cabezal de corte a la parte
A
B
2. Coloque la sierra de brazo radial de espaldas. Utilice
dieciséis tornillos de cabeza de hongo de 7,93-7,1 mm
(5/16-18") x 15,87 mm (5/8") para montar las patas (C)
Fig. 2 (tres de los cuales se muestran colocados) en cada
esquina de la base de la sierra (D). Coloque los tornillos
a través de la base, luego utilice una arandela plana, una
arandela de cierre y una tuerca para asegurarlos. Apriete
las tuercas manualmente.
3. Párese el vio en la posición vertical y aprieta
seguramente todo hardware del soporte.
PARA ENSAMBLAR EL GANCHO DE LLAVES
Monte el gancho de llave (K) Fig. 3 al lado delantero derecho
(como se muestra), o al lado posterior izquierdo de la base
de la sierra (D), utilizando dos tornillos de chapa #10 x 1/2 de
pulgada.
Fig. 1
C
C
C
D
C
Fig. 2
66
Fig. 3
D
K
Page 67
PARA RETIRAR LA HOJA Y EL PROTECTOR DE LA HOJA DE LA SIERRA
fuente de alimentación antes de instalar y retirar accesorios, ajustar o cambiar configuraciones o realizar reparaciones. Un
arranque accidental podría causar lesiones.
1. Afloje la perilla de sujeción del protector de la hoja (A) Fig. 4 y gire el protector de la hoja (B) hacia la posición ilustrada.
2. Utilice las llaves (C) Fig. 5 para aflojar la tuerca de árbol (D).
NOTA: La tuerca de árbol está enroscada a la izquierda.
3. Levante la leva (E) Fig. 6 que sostiene el protector de la hoja (B) Fig. 5 en posición. Saque el protector de la hoja (B), la
pestaña exterior de la hoja (F), y la hoja (G).
4. Levante el protector de la hoja (B) Fig. 7. Retire la tuerca de árbol (D), la pestaña exterior de la hoja (F), y la hoja (G).
5. Extraiga el protector de la hoja
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones personales graves, apague la herramienta y desconéctela de la
A
F
B
B
G
D
C
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
B
E
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
G
F
D
67
Page 68

SOPORTES DE LA MESA
1. Coloque la tabla de mesa delantera (A) Fig. 8 sobre una superficie estable con los agujeros rebajados apuntando hacia
abajo.
2. Sujete el soporte derecho e izquierdo de la mesa (B) Fig. 8 a la parte inferior de la tabla de mesa (A) al insertar cuatro
tornillos de cabeza redonda de 1/4-20 x 1" hacia arriba a través de los agujeros rebajados (D) en la tabla de mesa (A) y
los soportes de mesa (B). Sujételos en su lugar utilizando cuatro tuercas hexagonales con pestaña de 1/4-20 Apriete las
tuercas levemente para su ajuste posterior.
3. Coloque la tabla de mesa delantera (A) Fig. 9 sobre la base de la sierra (G) para que los soportes de la mesa (B) monten
a horcajadas la parte externa de la base de la sierra (G) y los tres agujeros (H) en cada soporte de mesa (B) se aliñen con
las tres ranuras (J) en cada lado de la base de la sierra (G).
B
A
D
H
B
A
Fig. 8
4. Sujete los soportes de la mesa (una de cada una se
muestra en (B) Fig. 10) a cada lado de la base de la sierra
usando seis tornillos de cabeza de hongo de 5/16-18 x
5/8 pulg.. (L) y seis tuercas hexagonales con pestaña de
5/16-18 pulg. Apriete las tuercas levemente para su ajuste
posterior.
IMPORTANTE: Inserte los tornillos a través de los soportes
de la mesa y la bases de la sierra desde el exterior.
5. Utilice una escuadra de combinación (M) Fig. 11 para
revisar el borde delantero izquierdo y derecho de la
tabla de mesa (A). Ambos lados deben tener la misma
distancia del borde de cada soporte de mesa (B) Fig.
11.
6. Luego de ajustar, apriete los cuatro tornillos ubicados
en los agujeros (N) Fig. 12 de la tabla de mesa
delantera (A).
7. Inserte cuatro tornillos de cabeza redonda de
1/4-20x1-1/4 pulg. (P) Fig. 13, en los agujeros (R)
Figuras 11 y 12 de la tabla de mesa. Apriete cada uno
de los tornillos hasta que cada esquina de la tabla de
mesa se eleve aproximadamente 1/8".
8. Afloje la palanca de la abrazadera de bisel (S) figura 14,
retire el perno de índice de bisel (T), y gire el motor (V)
a la posición vertical hasta que el índice de bisel quede
engranado. Apriete la palanca de la abrazadera de
bisel (S).
AVISO: Si el eje del motor entra en contacto con la tabla de
mesa antes de que el motor haya girado completamente,
levante el brazo guía (X) figura 15 al girar el mango de elevación (C).
J
G
Fig. 9
B
L
Fig. 10
M
A
B
Fig. 11
9. Afloje la perilla de la abrazadera del cabezal de corte (W) figura 15. Mueva el cabezal de corte al frente del brazo guía
(X). Apriete la perilla de la abrazadera del cabezal de corte (W).
10. Afloje el mango de la abrazadera del brazo guía (Y) figura 15.
AVISO: El mango de la abrazadera del brazo guía (Y) figura 15 tiene un enroscado hacia la izquierda. Presione la palanca de
liberación de índice hacia abajo (Z) figura 15, y gire el brazo guía (X) hacia la izquierda hasta que el eje del motor (B) figura
16 esté cerca del tornillo de ajuste delantero izquierdo (P) figura 13 de la tabla de mesa (A) figura 13. Apriete el mango de la
abrazadera del brazo guía (Y) figura 15.
68
Page 69
C
P
R
N
R
N
R
Fig. 12
X
Fig. 13
Z
C
V
W
X
Y
W
T
S
11. Coloque la llave de árbol (D) figura 16, entre la tabla de mesa (A) y el eje del motor (B). Baje el brazo guía (X) figura 16 al
girar el mango de elevación (C) en sentido contrario a las agujas del reloj hasta que el eje del motor (B) figura 16 apenas
toque la llave del árbol.
12. Revise la altura de la tabla de mesa sobre los otros tres tornillos de ajuste de la tabla de mesa (E) figura 17, al volver a
posicionar el brazo guía (X), y el montaje del cabezal de corte (V) hasta que establezca el punto más alto de la mesa.
AVISO: Asegúrese que la perilla de sujeción del cabezal de corte (W) figura 18 y el eje del mango de la abrazadera del brazo
guía (Y) estén situados sobre cada uno de los tornillos de ajuste. No cambie la altura del brazo guía (X) figura 17 hasta
establecer el tornillo más alto y haber ajustado las cuatro esquinas de la tabla de mesa.
13. Posicione el eje del motor sobre las tres esquinas inferiores de la tabla de mesa. Ajuste los tornillos de ajuste de la mesa
(E) figura 17 hasta que la llave del árbol se ajuste entre el eje del árbol y la tabla de mesa en cada ubicación.
14. Apriete los tres tornillos (G) figura 19 en cada lado de la base de la sierra (H). Vuelva a colocar el brazo guía (X) y el motor
(V) a la posición de 90° . Apriete la palanca de la abrazadera de bisel (S) y el mango de la abrazadera del brazo guía (Y)
figura 18.
Fig. 14
Fig. 15
Fig. 16
A
X
B
V
D
E
P
E
Fig. 17
Fig. 18
Y
Fig. 19
X
S
V
A
W
H
69
G
Page 70
ABRAZADERAS DE LA TABLA DE MESA Y LAS TABLAS DE MESA
1. Localice las abrazaderas de la tabla de mesa (A) figura 20. Inserte una abrazadera dentro de cada uno de los agujeros
con ranuras (B) ubicados en la parte posterior de cada soporte de la mesa (C) figura 30.
2. Gire el tornillo de ajuste (D) figura 21 en el sentido contrario al de las agujas del reloj, para que las perillas (A) estén en la
posición posterior.
D
A
B
C
A
Fig. 20
3. Coloque una tabla de 1-1/4" (E) figura 22, contra
la tabla de mesa delantera, (G), y una tabla de un
ancho de 5-3/4" (J) contra una tabla de un ancho de
1-1/4" (E). Coloque la tabla de 1-3/4" de ancho (H) en
posición vertical contra la tabla de 5-3/4" de ancho (J).
Apriete las perillas (D) hasta que las tablas de mesa
estén bien sujetas.
PARA AJUSTAR Y VERIFICAR EL RECORRIDO
DE LA HOJA DE LA SIERRA
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones personales graves, apague la herramienta y desconéctela de
la fuente de alimentación antes de instalar y retirar accesorios, ajustar o cambiar configuraciones o realizar reparaciones. Un arranque accidental podría causar lesiones.
1. Levante el brazo guía (A) figura 21 girando el mango de elevación (B) hasta que la hoja (C) se pueda ensamblar sobre el
eje del motor. Apriete la tuerca del árbol (D) utilizando las llaves provistas.
2. Coloque una escuadra de enmarcar (E) figura 22 contra la guía (H). Baje el brazo guía (A) figura 22 hasta que la hoja
quede justo por encima de la superficie de la mesa.
3. Afloje la perilla de sujeción del cabezal de corte (S) figura 22. Deslice el cabezal de corte (T) a lo largo del brazo guía (A)
para establecer si el recorrido de la hoja (C) es paralelo a la escuadra (E).
4. Para ajustar, afloje el tornillo de cierre del anillo índice (J) figura 23, y el mango de la abrazadera del brazo guía (K).
5. Gire el brazo guía (A) figura 22 hasta que la hoja (C) tenga un recorrido paralelo a la escuadra (E). Apriete el mango de la
abrazadera del brazo guía (K) figura 24.
6. Con el mango de la abrazadera del brazo guía (K) figura 24 apretada, gire el anillo índice (L) en sentido contrario a las
agujas del reloj hasta que se detenga. Apriete el tornillo de cierre del anillo índice (J) figura 23.
Fig. 21
Fig. 22
J
G E
H
H
Fig. 23
B
A
S
A
T
D
C
E
E
C
Fig. 24
70
Page 71
J
K
L
K
Fig. 25
7. En la máquina hay dos indicadores de índice de
ingletes, uno de los cuales se muestra en (M) figura 25.
Para ajustar, afloje el tornillo (N) y mueva el indicador
(M) hasta que esté alineado con la marca "cero" en la
escala de ingletes (P). Apriete el tornillo (N). Ajuste el
indicador del índice de ingletes ubicado en el otro lado
de la columna (R), de la misma forma.
N
P
M
Fig. 26
J
R
Fig. 27
PARA ELIMINAR LA INCLINACIÓN ANGULAR (HEELING)
Aunque el recorrido del cabezal de corte podría estar perfectamente alineado a 90° con la guía, la hoja misma podría no
estar a 90° ni cuadrada con la guía (figura 28). Esta condición se conoce como inclinación angular o “heeling.”
Para verificar y ajustar:
fuente de alimentación antes de instalar y retirar accesorios, ajustar o cambiar configuraciones o realizar reparaciones. Un
arranque accidental podría causar lesiones.
1. Instale la hoja de la sierra sin protector.
2. Sustituya la guía con una pieza plana de madera de 3/4 de pulgada (A) figura 29 que sea de por lo menos 5" de alto.
Apriete las abrazaderas de la tabla de mesa.
3. Coloque tres piezas idénticas de madera (B) figura 29 sobre la mesa. Coloque una escuadra de enmarcar sobre éstas de
manera que el brazo corto esté al ras contra la guía y el brazo largo contra la hoja. Asegúrese que la escuadra esté entre
los dientes de la hoja.
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones personales graves, apague la herramienta y desconéctela de la
Fig. 28
71
B
A
B
B
Fig. 29
Page 72
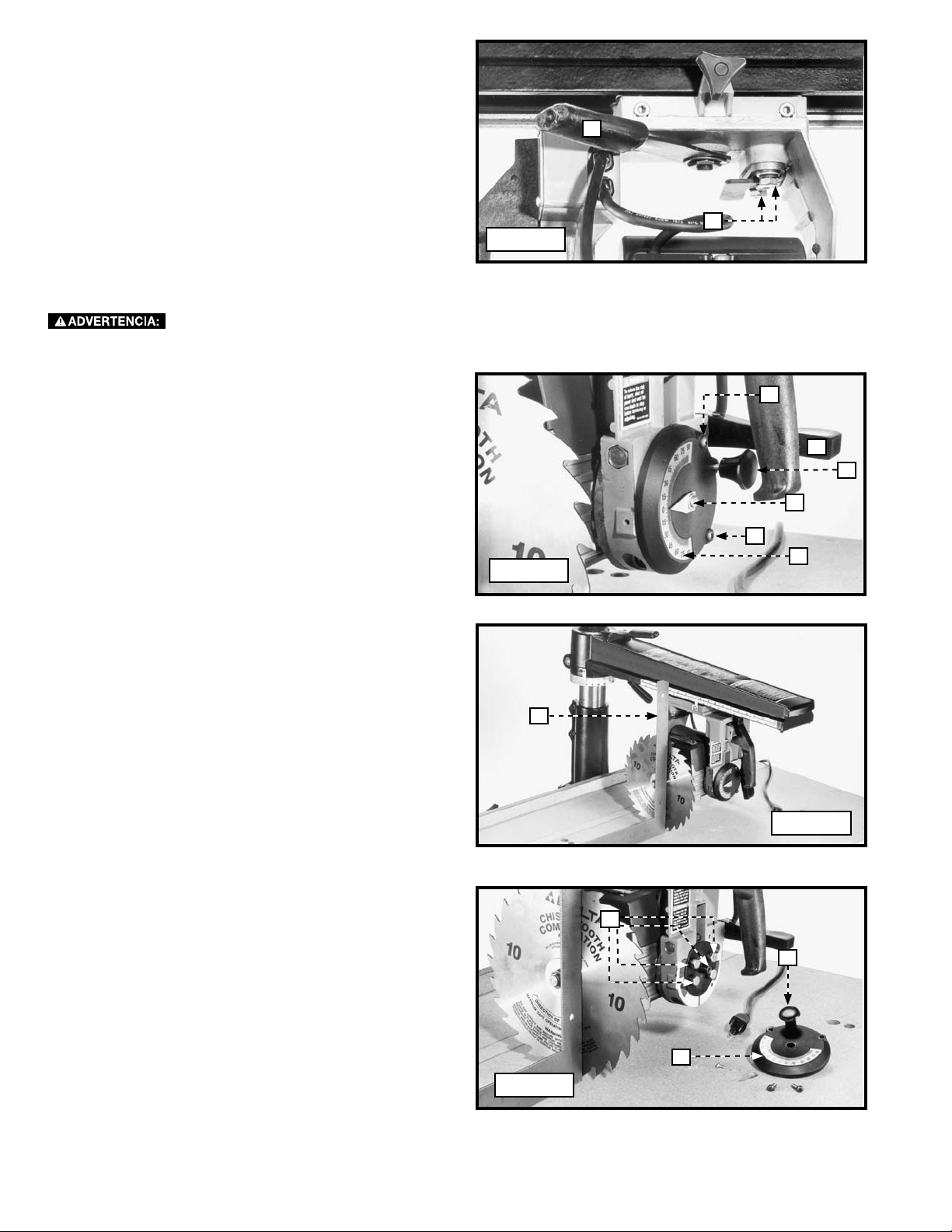
4. Si la hoja no está paralela a la escuadra, realice un
ajuste. Libere el mango de sujeción de la horquilla
(C) figura 30 y afloje los dos tornillos hexagonales (D)
levemente. Gire la horquilla hasta que la hoja esté
paralela con la escuadra. Apriete el mango de sujeción
de la horquilla (C). Apriete los dos tornillos hexagonales
(D).
PARA QUE LA HOJA DE LA SIERRA CUADRE CON LA MESA
¡Desconecte la máquina de la fuente del poder!
1. Adjunte la pestaña de la hoja interior, la hoja de la
sierra, la pestaña exterior de la hoja, y la tuerca del
árbol en el árbol de la sierra.
2. Coloque el cabezal de corte en posición de corte
transversal (figura 29) Baje el brazo guía hasta que
la hoja de la sierra quede justo encima de la mesa.
Deslice el cabezal de corte hacia el frente hasta que
esté posicionado sobre la tabla de mesa delantera.
Sujete el cabezal de corte en posición (figura 30)
3. Engrane la perilla del índice de bisel (A) figura 31.
Verifique que el motor esté en posición horizontal.
Apriete el mango de abrazadera de bisel (B).
C
D
Fig. 30
F
C
A
E
F
B
Fig. 31
4. Coloque una escuadra (D) figura 32 sobre la mesa y
contra la hoja de la sierra. Verifique si la hoja cuadre
con la mesa.
AVISO: La escuadra debe descansar entre dos dientes de
la hoja de la sierra.
5. Para ajustar, apriete la palanca sujetadora de bisel (C)
figura 31.
6. Retire el tornillo, la arandela plana y el indicador (E)
figura 31.
7. Retire los dos tornillos (F) figura 31 y el plato de la
escala de bisel (H) figura 32 con la perilla de índice (A).
8. Afloje los cuatro tornillos hexagonales (G) figura 33.
Incline el motor hasta que la hoja de la sierra esté
al ras con la escuadra. Apriete los cuatro tornillos
hexagonales (G).
9. Vuelva a colocar el plato de la escala de bisel (H)
figura 33 con la perilla de liberación del índice de
bisel (A), dos tornillos, y el indicador que se retiraron
anteriormente.
AVISO: Ajuste el indicador a "cero" en la escala de índice
de bisel.
D
Fig. 32
G
A
H
Fig. 33
72
Page 73
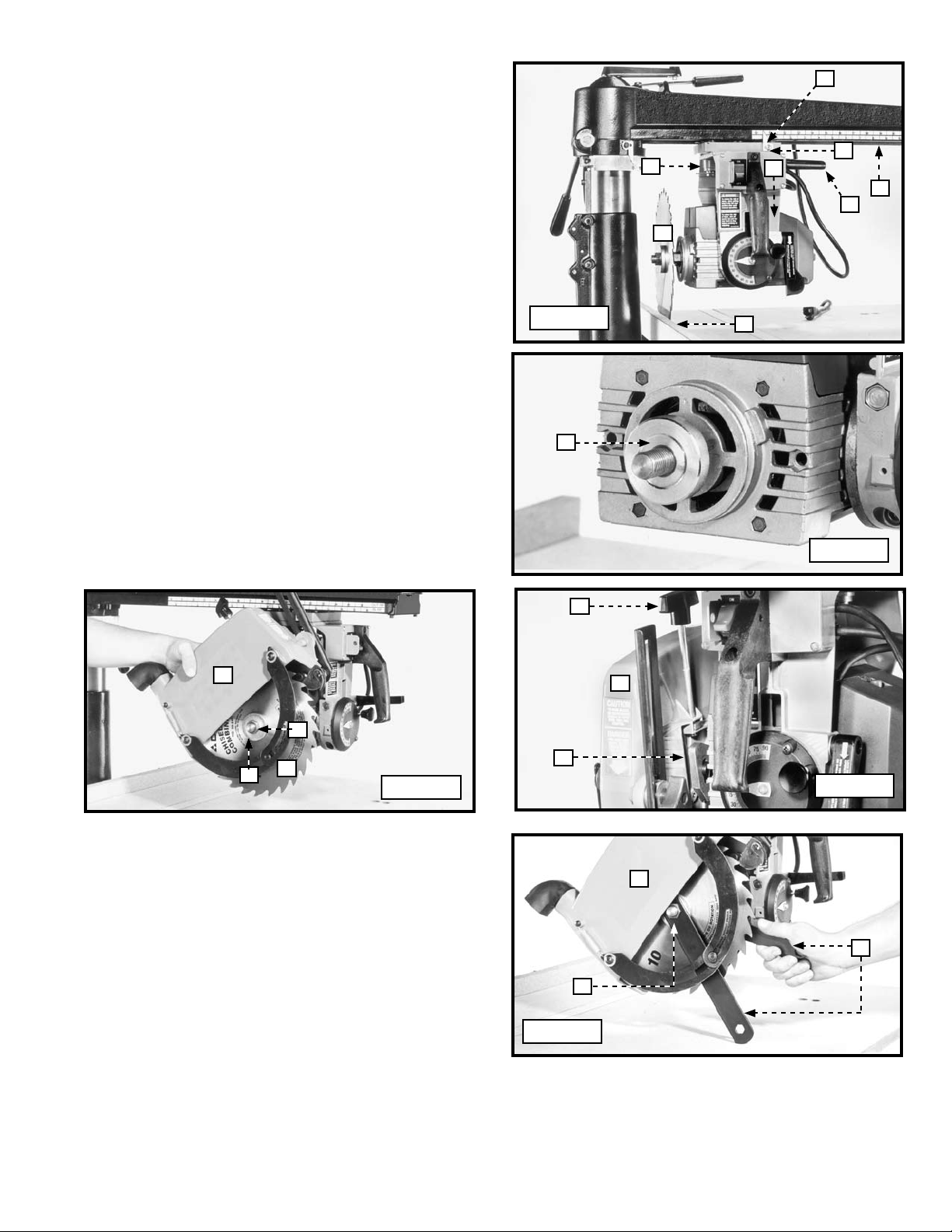
PARA AJUSTAR LA ESCALA DE CORTE LONGITUDINAL INTERIOR/EXTERIOR
1. Afloje el mango de sujeción de la horquilla (A) Fig.
34. Libere el indicador de la horquilla presionando la
palanca de liberación (B) hacia arriba o abajo. Gire el
cabezal de corte (C) hacia la posición de corte interna
(Fig. 34). Ajuste el mango de sujeción de la horquilla
(A).
2. Posicione la guía (D) Fig. 34 en la parte posterior de la
mesa.
3. Afloje la perilla de sujeción del cabezal de corte (G) Fig.
34. Deslice el cabezal de corte (C) figura 32 hacia la
parte posterior del brazo guía hasta que la hoja de la
sierra (F) quede pareja con la guía (D).
4. Apriete la perilla de sujeción del cabezal de corte (G)
Fig. 34. Ajuste el indicador (H) Fig. 34 a la marca “cero”
en una escala más baja (J) aflojando el tornillo (K).
Apriete el tornillo al finalizar.
PARA MONTAR LA HOJA Y EL PROTECTOR DE LA HOJA
AVISO: Sólo utilice hojas de 10 pulg. con agujeros de árbol
de 5/8 pulg. y tasadas para el funcionamiento a 5000 rpm
o más alto.
1. Monte la pestaña interior (gruesa) del árbol (A) Fig.
35sobre el eje del árbol con el lado embutido de la
pestaña (A) apuntando hacia afuera.
Fig. 34
A
H
K
B
C
J
A
F
D
Fig. 35
H
B
B
E
C
D
Fig. 36
2. Con el protector de la hoja (B) Fig. 37 en la mano
izquierda, inserte la hoja de la sierra (C) dentro del
protector de la hoja (B) y sobre el eje del árbol.
3. Monte la pestaña exterior de la hoja (delgada) (D) Fig.
36 sobre el lado embutido de la pestaña que apunta
hacia adentro (D). Coloque la tuerca del árbol (E) en el
eje del árbol.
AVISO: La tuerca del árbol (E) Fig. 36 se enrosca hacia la
izquierda.
4. Levante la leva (F) Fig. 37. Ensamble el protector de la
hoja (B) sobre el ensamblado del cabezal de corte.
AVISO: Asiente la lengüeta del protector en la ranura del
cabezal de corte.
5. Hale el protector de la hoja (B) Fig. 38, de manera
que gire hacia atrás. Use la llave tubular de 7/8 de pulgada alrededor de la tuerca de árbol (E),y la llave plana de 7/8 de
pulgada sobre la parte plana del árbol para sujetarlo en su lugar.
6. Gire el protector de la hoja (B) Fig. 38 a la posición horizontal y apriete la perilla de sujeción (H) Fig. 37.
F
Fig. 37
B
E
Fig. 38
G
73
Page 74

marcha.
El protector inferior retráctil de la hoja protege al operador a lo largo de los lados de la hoja de la sierra. Para reducir el riesgo
de peligros potenciales, siga las siguientes reglas:
A) MANTENGA SUS MANOS ALEJADAS DEL PROTECTOR. Conforme la hoja realice el corte, el protector se
B) APAGUE LA ENERGÍA ANTES DE LIBERAR UN PROTECTOR INFERIOR ATASCADO. El protector puede quedar
C) TOME PRECAUCIONES al realizar cortes de bisel para asegurarse que el protector inferior nunca esté apretado
D) EL PROTECTOR INFERIOR PUEDE ATASCARSE CONTRA LA GUÍA DURANTE CORTES AL HILO INTERIORES
PARA CORTAR ENTRO DE LAS TABLAS DE MESA
1. Monte las tablas de mesa (A) Fig. 38 y el tope de guía (B). Asegure las tablas con las abrazaderas de mesa, una de las
cuales se muestra en (C).
2. Vuelva a girar el cabezal de corte (D) Fig. 39 hacia la parte posterior del brazo guía (E). Ajuste la perilla de sujeción del
cabezal de corte. Verifique que el interruptor (H) Fig. 39 esté en la posición “OFF” (Apagado) y conecte la sierra a la
fuente de energía.
3. Mientras sujeta el mango del cabezal de corte (L) Fig. 40 con firmeza, gire el interruptor hacia la posición (H) “ON”
(Encendido). Baje el brazo guía (E) girando el mango de elevación (K). Baje la hoja de la sierra hasta que haba un corte
sobre la superficie de la mesa de aproximadamente 1,58 mm (1/16”) de profundidad.
Apriete la perilla de sujeción (H) Fig. 37 y asegure el protector de la hoja antes de poner la máquina en
levantará dejando parte de la hoja expuesta.
atascado en las entalladuras anteriores en la mesa o la guía. Anticipe el trayecto del protector en todo momento.
hacia la hoja.
ANGOSTOS. Si el protector se atasca contra la guía, desconecte la sierra de la fuente de energía, espere que la
hoja se detenga completamente y luego levante el protector de la hoja y descánselo sobrela parte superior de la
guía.
K
G
C
B
A
Fig. 39
4. Mientras todavía sostiene el mango del cabezal
de corte (L) Fig. 41 con firmeza, afloje la perilla de
sujeción del cabezal de corte y hale el cabezal de
corte (D) Fig. 41 lentamente hacia el frente del brazo
guía (E) hasta que se detenga el recorrido. Gire el
interruptor hacia la posición (H) “OFF” (Apagado).
5. Espere que la hoja de la sierra (M) Fig. 42 se detenga,
luego gire el cabezal de corte (D) hacia la parte
posterior del brazo guía (E). Advierta la ranura fina de
la sierra (N) Fig. 40 en las tablas de la mesa.
D
H
E
L
Fig. 40
D
E
H
L
Fig. 41
D
E
IMPORTANTE: Levante el brazo guía (E) Fig. 42 antes de tratar
de girarlo. Realice el procedimiento “PARA CORTAR LAS
TABLAS DE MESA” para cada corte en ángulo individual.
Si, durante la operación, la sierra tiende a voltearse, deslizarse o avanzar sobre la superficie de apoyo,
asegure la sierra al piso a través de los orificios provistos en la parte inferior de cada pata.
74
M
N
Fig. 42
Page 75

OPERACIÓN
CONTROLES Y AJUSTES OPERACIONALES
Cada vez que use la sierra, verifique que:
1. El equipo de protección ocular, auditiva y respiratoria que utilice sea SIEMPRE el adecuado.
2. La hoja esté ajustada.
3. El ángulo del bisel y las perillas de bloqueo de altura estén ajustadas.
4. En el caso de los cortes longitudinales, la palanca de bloqueo de la guía esté ajustada y la guía esté paralela a la
hoja.
5. El protector de la hoja esté ajustado adecuadamente y que los dientes antirretroceso funcionen.
6. El conjunto protector de la hoja y hendedor esté SIEMPRE correctamente alineado y a la distancia apropiada de la
hoja.
El incumplimiento de estas normas de seguridad básicas puede aumentar la posibilidad de lesiones.
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones, apague la unidad y desconéctela de la fuente de alimentación
antes de instalar o retirar accesorios, ajustar o cambiar configuraciones o realizar reparaciones. Un arranque accidental
podría causar lesiones.
Antes de conectar la sierra de brazo radial a la fuente de alimentación u operar la sierra, controle
siempre que el conjunto protector de la hoja y hendedor esté correctamente alineado y a la distancia apropiada de la
hoja. Puede causar lesiones personales.
Si su sierra hace ruidos desconocidos o si vibra demasiado, cese el funcionamiento de inmediato hasta
localizar la fuente del problema y solucionarlo.
ARRANCANDO Y DETENIENDO LA SIERRA
Cerciórese que el interruptor está en el “LEJOS” la posición antes de conectar la cuerda del
poder. En caso de un fallo del suministro eléctrico, mueva el interruptor al “LEJOS” la posición. Una compania nueva
accidental puede causar la herida.
El interruptor de ENCENDIDO/APAGADO (A) Fig. 42 está
localizado el frente de la corte-cabeza. Para ENCENDER
la máquina, mueva el interruptor (A) a la posición elevada.
Para APAGAR la máquina, mueva el interruptor (A) a la
posición inferior.
FIJANDO EL INTERRUPTOR EN LA POSICION DE
APAGADO
IMPORTANTE: Cuando la sierra para cortar ingletes no
se esté utilizando, el interruptor debe bloquearse en la
posición de apagado utilizando un candado (D) Fig. 43
con una barra de 3/16” de diámetro para impedir el uso no
autorizado de la sierra.
En el caso de un corte eléctrico (por
ejemplo por un interruptor o fusible quemados) bloquee
siempre el interruptor en la posición de apagado (off)
hasta que se restablezca la energía principal.
A
Fig. 43
D
Fig. 44
75
Page 76

GUÍA SOBRE LAS PIEZAS
Estudie los siguientes términos y explicaciones cuidadosamente para familiarizarse con los controles antes
de encender la herramienta. De lo contrario, se puede dañar la sierra o puede resultar en lesiones (Figuras G y H).
C
B
K
G
D
F
A
H
J
Fig. G
A. LAS PERILLAS DE SUJECIÓN PARA LA MESA le
permiten al operador ajustar rápidamente la posición
deseada de la guía (Fig. G).
B. EL MANGO DE LIBERACIÓN INDICADOR DEL BRAZO
GUÍA libera la clavija indicadora de las posiciones de 0° y
45° para permitir que el brazo gire. Oprima el mango para
liberar la clavija indicadora (Fig. G).
C. EL MANGO DE ELEVACIÓN DEL BRAZO GUÍA controla
la profundidad de corte en todas las operaciones. Gire el
mango en sentido de las agujas del reloj para elevar el
brazo guía o en el sentido opuesto para bajarlo (Fig. G).
D. LA ESCALA DE INGLETE indica los grados hacia la
izquierda y la derecha para ajustar el brazo guía en el
ángulo de inglete deseado (Fig. G).
F. LA ESCALA DE CORTE indica las posiciones de corte
longitudinal internas y externas del cabezal de corte (Fig.
G).
G. LA PERILLA DE SUJECIÓN DEL PROTECTOR DE LA
HOJA sujeta el protector de la hoja en las posiciones de
giro para los cortes al hilo (Fig. G).
H. EL MANGO DE SUJECIÓN DEL BISEL controla la
inclinación del motor para las operaciones de corte de
bisel. También fija el motor en cualquier ángulo deseado
en la escala de bisel. Levante el mango para aflojar, y
empújelo hacia abajo para fijar (Fig. G).
J. LA PERILLA DE LIBERACIÓN DE INDICADOR
DEL BISEL le permite al motor posicionarse en las
configuraciones de 0°, 45°, y 90° del bisel. Cuando incline
el motor para realizar el corte de bisel, primero afloje el
mango de sujeción del bisel. Para liberar el indicador, tire
la perilla de liberación hacia afuera (Fig. G).
K. PALANCA DE LIBERACIÓN DE LA HORQUILLA
INDICADORA le permite a la sierra lograr una posición
de 90° para operaciones de corte longitudinal o corte
transversal. Cuando gire la horquilla, primero afloje el
mango de sujeción de la horquilla. Empuje la palanca de
liberación hacia arriba o hacia abajo para liberar la clavija
indicadora (Fig. G).
Fig. H
P
S
N
L
M
R
L EL MANGO DE SUJECIÓN DE LA HORQUILLA debe
estar flojo al girar la horquilla entre la posición de corte
longitudinal y la posición transversal. Tire del mango
para liberar o empújelo para fijar (Fig. H).
M EL DISPOSITIVO ANTIRETROCESO ayuda a prevenir
las lesiones o daños ocasionados por el retroceso.
Cuando realice un corte longitudinal, posicione y sujete
la horquilla para que la hoja esté paralela al guía. Gire la
parte posterior del protector de la hoja hasta que casi
toque la pieza de trabajo. Baje la varilla antiretroceso
para que los dedos agarren y sujeten la pieza de trabajo.
Nunca corte desde el extremo de antiretroceso del
protector de la hoja (Fig. H).
N EL INTERRUPTOR DE ENCENDIDO Y APAGADO
está convenientemente ubicado y se puede encender y
apagar en un instante para obtener protección adicional
durante la operación. También puede asegurar el
interruptor en la posición "OFF" (Apagado) para evitar el
uso no autorizado utilizando un candado adicional (Fig.
H).
P. LA PERILLA DE SUJECIÓN DEL CABEZAL fija el
cabezal en cualquier posición en el brazo guía. Cuando
realice cortes al hilo, asegúrese que la perilla de sujeción
esté bien ajustada (Fig. H).
R. LA ESCALA DE BISEL indica el grado de rotación para
configurar las posiciones de bisel del motor (Fig. H).
S. EL MANGO DE SUJECIÓN DEL BRAZO GUÍA controla
la rotación del brazo guía para todas las operaciones de
corte de inglete. Fija el brazo guía en cualquier posición
de ángulo de inglete. Para girar el brazo guía hacia la
derecha, afloje el mango de sujeción y gire el brazo.
El brazo se detendrá a 45°. Para girar más allá de 45°,
oprima el mango de liberación índice y gírelo. El brazo
girará unos 5° adicionales. Para girar hacia la izquierda,
la operación es la misma excepto que debe presionar
el mango de liberación indicador para comenzar a girar
(Fig. H).
76
Page 77

PARA AJUSTAR LOS COJINETES CONTRA EL RIEL
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones, apague la unidad y desconéctela de la fuente de alimentación
antes de instalar o retirar accesorios, ajustar o cambiar configuraciones o realizar reparaciones. Un arranque accidental
podría causar lesiones.
El cabezal de corte (C) Fig. 46 está suspendido desde cuatro cojinetes pre-cargados, lubricados y blindados, dos de los
cuales se encuentran sobre ejes fijos en (A), y dos sobre ejes ajustables en (B).
cabezal de corte del brazo guía.
Después del uso prolongado, puede haber cierto desgaste en el brazo guía, ocasionando "holgura" entre los cojinetes y el
riel. Los cojinetes deben desplazarse libre y uniformemente en los canales del brazo guía. Para ajustar los cojinetes:
1. Retire el tapón plástico (D) Fig. 45 de la parte superior del brazo guía (E).
2. Deslice el cabezal de corte (C) Fig. 46 hasta que uno de los cojinetes ajustables (B) Fig. 46 quede visible a través del
agujero (G) Fig. 43.
3. Use un casquillo, una extensión y un trinquete de 1/2 pulgada (H) Fig. 47 a través del agujero (G) en el brazo guía
para aflojar levemente la tuerca hexagonal sobre el eje ajustable (B) Fig. 47 aproximadamente 1/8 de vuelta. Repita el
procedimiento para los demás cojinetes.
El cabezal de corte (C) Fig. 46 fue retirado del brazo guía para propósitos de ilustración. NO retire el
B
D
A
G
B
C
K
E
Fig. 45
G
K
Fig. 46
H
K
J
C
4. Use una llave Allen de 3/16 de pulgada (J) Fig. 48 para girar los tornillos de ajuste (K) Fig. 48 para eliminar la "holgura".
Do not overtighten the adjustment screws (K). This can damage the bearings.
Do not loosen the adjustment screws (K) more than 1/2 turn. The cuttinghead may fall from the track arm.
5. Apriete las tuercas hexagonales que se aflojaron en el PASO 3. Verifique el recorrido del cabezal de corte por si hay alguna
"holgura". Asegúrese de que se mueva en forma libre y uniforme.
6. Reemplace la tapa plástica que retiró en el PASO 1.
Fig. 47
Fig. 48
PARA AJUSTAR LA TENSIÓN EN LA COLUMNA DE ELEVACIÓN
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones, apague la unidad y desconéctela de la fuente de alimentación
antes de instalar o retirar accesorios, ajustar o cambiar configuraciones o realizar reparaciones. Un arranque accidental
podría causar lesiones.
La tensión de la columna de elevación está configurada
anteriormente en la fábrica. Se puede desarrollar "holgura"
después del uso prolongado de la máquina. Para ajustar:
1. Afloje las tuercas hexagonales (A) Fig. 49 y los tornillos de
ajuste de la contra chaveta (C).
2. Afloje las tuercas hexagonales (D) y gire los tornillos (E) hasta
que la base de la columna se enrolle firmemente alrededor de
la columna y se pueda elevar o bajar sin quedar atada. Ajuste
las tuercas hexagonales (D) contra la base de la columna.
3. Ajuste la contra chaveta y los tornillos de ajuste (C) contra la
contra chaveta (H) hasta que se elimine toda la holgura de
lado a lado. Ajuste las tuercas hexagonales (A) contra la base
de la columna.
77
F
H
A
E
D
C
B
Fig. 49
Page 78

AVISO: Después de ajustar la tensión de la columna, consulte “PARA AJUSTAR EL DESPLIEGUE DE LA HOJA DE LA
SIERRA CON LA GUÍA” para establecer si el despliegue de la hoja de la sierra se vio afectado.
PARA CAMBIAR LA POSICIÓN DEL MANGO DE SUJECIÓN DEL BRAZO GUÍA
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones, apague la unidad y desconéctela de la fuente de alimentación
antes de instalar o retirar accesorios, ajustar o cambiar configuraciones o realizar reparaciones. Un arranque accidental
podría causar lesiones.
Para volver a posicionar el mango de sujeción del brazo guía (A) Fig. 50 cuando éste no queda fijado (asegurado) en una
posición conveniente:
1. Afloje y retire la palanca de sujeción del brazo guía (A) Fig. 50. Empuje el perno hexagonal (B) Fig. 51 hacia atrás a
través del agujero, hasta que la cabeza del perno salga del buje embutido (C).
AVISO: La palanca de sujeción del brazo guía se enrosca hacia la izquierda.
2. Gire el perno hexagonal (B) Fig. 51 en la dirección deseada.
3. Empuje el perno hexagonal (B) Fig. 49 hacia atrás a través del agujero. Verifique si la cabeza del perno hexagonal está
asentada correctamente en el buje embutido (C). Ensamble la palanca de sujeción del brazo guía.
AVISO: si la palanca de sujeción del brazo guía (A) Fig. 49 se ajusta antes de aproximadamente cuatro giros, los bujes de
sujeción (uno de los cuales se muestra en (C) Fig. 51) pueden haber girado. Estos bujes se deben asentar completamente
dentro de la guía (D). De no hacerlo, afloje levemente la palanca de sujeción (A) Fig. 51 y gire el buje de sujeción (C) Fig. 49
hasta que se asiente. Verifique si también necesita girar el buje del lado de la palanca de sujeción.
AVISO: Los ejes en los bujes de sujeción deben apuntar hacia la parte delantera de la sierra.
AVISO: La palanca de sujeción (A) Fig. 50 se deslizará a una de las dos posiciones. Si, después del ajuste, la palanca de
sujeción (A) se ajusta a 180° de donde se lo desea, lentamente desatornille la palanca de sujeción (A) mientras sujeta el
perno hexagonal (B). Cuando la palanca de sujeción (A) se sale del perno hexagonal (B), gire la palanca de sujeción (A) a
unos 180°. Deslice la palanca de sujeción.
B
A
D
C
Fig. 50
Fig. 51
PARA CAMBIAR LA POSICIÓN DEL MANGO DE SUJECIÓN de bisel
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones, apague la unidad y desconéctela de la fuente de alimentación
antes de instalar o retirar accesorios, ajustar o cambiar configuraciones o realizar reparaciones. Un arranque accidental
podría causar lesiones.
Para volver a posicionar el mango de sujeción de bisel:
1. Afloje el mango de sujeción de la horquilla (A) Fig. 32,
libere el perno de índice de bisel (B), y gire el motor (C)
a la posición vertical.
AVISO: Si el protector de la hoja entra en contacto con la
superficie de la mesa, levante el brazo guía.
2. Afloje el mango de sujeción de la horquilla (A) Fig. 52
dando varias vueltas hasta que la cabeza hexagonal
del tornillo (D) se pueda empujar fuera del espacio
hexagonal en la horquilla.
3. Gire el tornillo (D) Fig. 52 una o dos partes planas de
la cabeza hexagonal en la dirección en que el mango
necesita ser girado. Vuelva a empujarlo dentro del
espacio en forma hexagonal en la horquilla.
4. Apriete el mango de sujeción de bisel (A) Fig. 52.
AVISO: El tornillo se enrosca hacia la izquierda - gire el
mango de sujeción en dirección opuesta a la agujas
del reloj para apretar.
D
B
C
A
Fig. 52
78
Page 79

PARA CAMBIAR LA POSICIÓN DEL MANGO DE SUJECIÓN DE LA HORQUILLA
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones,
apague la unidad y desconéctela de la fuente de
alimentación antes de instalar o retirar accesorios, ajustar
o cambiar configuraciones o realizar reparaciones. Un
arranque accidental podría causar lesiones.
Para volver a posicionar el mango de sujeción de la horquilla
(A) Fig. 53:
1 Retire el anillo de retención (B) Fig. 53.
2. Vuelva a posicionar el mango de sujeción de la
horquilla (A) Fig. 53, sobre la tuerca de abrazadera
hexagonal.
3. Vuelva a colocar el anillo de retención (B) Fig. 53.
ÍNDICE DEL TOPE POSITIVO DE LA HORQUILLA
La palanca indicadora de la horquilla (A) Fig. 54 activa un tope positivo que coloca el cabezal de corte en posición de corte
transversal o longitudinal. Para girar el cabezal de corte, libere el mango de sujeción de la horquilla, presione la palanca
indicadora de la horquilla (A) hacia arriba o abajo para liberar el tope positivo y gire el cabezal de corte hacia las posiciones de
corte longitudinal interno n.º 1 o de corte longitudinal externo n.º 2 o de corte transversal n.º 3. Libere la palanca indicadora de
la horquilla (A) Fig. 53 y el cabezal de corte se ajustará automáticamente a cada una de las tres posiciones.
ÍNDICE DE TOPE POSITIVO DEL BISEL
La perilla indicadora del bisel (A) Fig. 55 proporciona un tope positivo cuando se coloca la hoja de la sierra a 0°, 45°, y 90°
hacia la izquierda y 90° hacia la derecha en la escala de bisel (C). Para cambiar el ángulo de la hoja de la sierra, afloje el
mango de sujeción de bisel (B), tire hacia afuera la perilla indicadora del bisel (A) e incline la hoja de la sierra y el motor. Para
las posiciones de 0°, 45°, y 90° hacia la izquierda y 90° hacia la derecha, libere la perilla indicadora del bisel (A) y la hoja de la
sierra se ajustará a cada una de estas posiciones. Apriete el mango de sujeción del bisel (B). Para los ángulos de la hoja de
sierra entre topes positivos, coloque la hoja en el ángulo deseado en la escala de bisel (C) y apriete el mango de sujeción del
bisel (B) Fig. 55.
A
B
Fig. 53
B
A
Fig. 54
PARA AJUSTAR EL SEPARADOR Y EL DEDO ANTIRETROCESO
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones, apague la unidad y desconéctela de la fuente de alimentación
antes de instalar o retirar accesorios, ajustar o cambiar configuraciones o realizar reparaciones. Un arranque accidental
podría causar lesiones.
Durante las funciones de corte longitudinal, el separador
(A) Fig. 56 debe quedar en la entalladura de la sierra y los
dedos antiretroceso (B) deben tocar la pieza de trabajo
para evitar el retroceso.
1. Coloque la sierra en posición de corte longitudinal con
el protector de la hoja bajado sobre el lado del avance
de entrada para que funcione como un sujetador.
2. Avance un pedazo de material a través de la sierra (Fig.
56).
3. Apague la sierra y desco-néctela de la fuente de
energía.
4. Ajuste el brazo (C) Fig. 56, para que quede en posición
vertical y el separador (A) esté en la entalladura de la
sierra.
5. Si el separador (A) Fig. 56 no queda alineado con la
entalladura de la sierra, afloje las tuercas hexagonales
(D), y la posición del separador (A) dentro de la entalladura de la sierra. Apriete las tuercas hexagonales (D) contra el
brazo. El lado recto del separador debe apuntar hacia la hoja (Fig. 56), y los dedos antiretroceso deben descansar sobre
la pieza de trabajo.
AVISO: El manto de sujeción para el brazo (C) debe estar apretado. Mueva el brazo (C) de adelante hacia atrás para apretar el
mango de sujeción con la otra mano, para asegurarse que la abrazadera esté asentada firmemente y apretada.
6. Tire hacia atrás sobre la pieza de trabajo para establecer si los dedos antiretroceso muerden el material y eviten el
movimiento hacia atrás. Si fuera necesario, vuelva a ajustar la altura del brazo (C) Fig. 56.
Fig. 56
C
A
A
Fig. 55
C
D
B
79
Page 80

EL REVESTIMIENTO AUXILIAR DE LA MESA
Para evitar los cortes repetidos en la superficie de la mesa que finalmente hará que la mesa ceda, puede cortar un
revestimiento de tabla de mesa auxiliar y colocarlo en la mesa. Hágalo de madera contrachapada o tabla de madera
comprimida de 6,35 mm (1/4"). Córtelo de un tamaño que cubra todas las tablas de mesa delante de la guía. Coloque el
revestimiento de tabla de mesa auxiliar en forma horizontal sobre la mesa y ensámblelo contra la guía de la mesa. Fíjelo a la
mesa con una clavadora pequeña o con clavos de acabado en cada esquina.
EL USO DE UNA EXTENSIÓN DE MESA
Cuando se anexa a la sierra una extensión de mesa que es más larga de 60 cm. (24"), use un soporte con balancín firme o
asegure la base o mesa al piso.
UTILIZAR LA MAQUINA
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones, apague la unidad y desconéctela de la fuente de alimentación antes
de instalar o retirar accesorios, ajustar o cambiar configuraciones, o realizar reparaciones. Un arranque accidental puede
causar lesiones.
Antes de conectar la sierra de brazo radial a la fuente de alimentación u operar la sierra, controle
siempre que el protector y hendedor esté correctamente alineado y a la distancia apropiada de la hoja de la sierra. Puede
causar lesiones personales.
CORTE TRANSVERSAL
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones, apague la unidad y desconéctela de la fuente de alimentación
antes de instalar o retirar accesorios, ajustar o cambiar configuraciones, o realizar reparaciones. Un arranque accidental
puede causar lesiones.
NUNCA toque el “extremo libre” de la pieza de trabajo o una “pieza libre” cortada mientras la
herramienta está en la posición "ON" (encendido) o la hoja está girando. La pieza puede entrar en contacto con la hoja
y ser despedida, lo que puede ocasionar una lesión.
NUNCA use un tope longitudinal en el extremo libre de la pieza de trabajo cuando realice cortes
transversales. En resumen, la pieza cortada durante un corte pasante (corte en el que la pieza de trabajo se secciona
por completo) nunca debe ser restringida. Por el contrario, debe permitir que se mueva lejos de la hoja de la sierra,
para evitar que entre en contacto con ésta y sea despedida, lo que puede causar lesiones.
Tenga cuidado cuando comience el corte, para evitar el atascamiento del protector contra la
pieza de trabajo, lo que puede ocasionar daños a la sierra y posibles lesiones.
Para realizar un corte transversal, sujete la pieza de trabajo a la guía y tire la hoja de la sierra a través del material en ángulos
rectos hacia ésta. (Fig. 57)
Cuando realice cortes transversales, configure el brazo guía
a “0” y ajuste el mango de sujeción del brazo guía. Sujete
la guía entre las tablas del banco. Asegúrese de que la hoja
de la sierra esté a la izquierda y detrás de la guía. Coloque
la pieza trabajo en el banco y ensámblela contra la guía.
Asegúrese de que la hoja de la sierra esté alejada de la guía
y del banco cuando se coloque la máquina en la posición
"ON" (encendido). Baje la hoja de la sierra hasta que corte
levemente la superficie del banco. Coloque el cuerpo un
poco hacia la izquierda de la máquina para tener mejor
visibilidad. Tire la hoja de la sierra a través de la pieza de
trabajo, sólo lo suficientemente lejos para realizar el corte,
luego vuelva la hoja de la sierra a su posición inicial. Apague
la máquina y espere a que la hoja se detenga antes de tocar
la pieza cortada.
Fig. 57
Siempre tenga conciencia de la posición de la mano. Asegúrese de que las manos estén
alejadas de la hoja y de que sostengan la pieza de trabajo con firmeza.
Además, puede dar vuelta la varilla antirretroceso y fijarla en su lugar sólo para que despeje la pieza de trabajo. La varilla
puede funcionar como un protector de los dientes expuestos de la hoja.
Siempre vuelva a colocar el soporte del cabezal de corte en su posición trasera después de cada operación
de corte transversal.
NOTA: Cuando realice cortes transversales de material de más de 25 mm (1") de espesor, coloque la guía justo detrás de la
tabla fija delantera del banco.
TOPE DE CORTE TRANSVERSAL
Si coloca una bloque de madera (B) Fig. 58 en el brazo guía evitará el recorrido innecesario del cabezal de corte en el brazo
guía; esto es especialmente útil cuando realiza operaciones que se repiten. Sujete el bloque de madera al lado derecho del
brazo guía en una posición que detendrá el recorrido del cabezal de corte en cuanto la hoja de la sierra corte la pieza de
trabajo.
80
Page 81
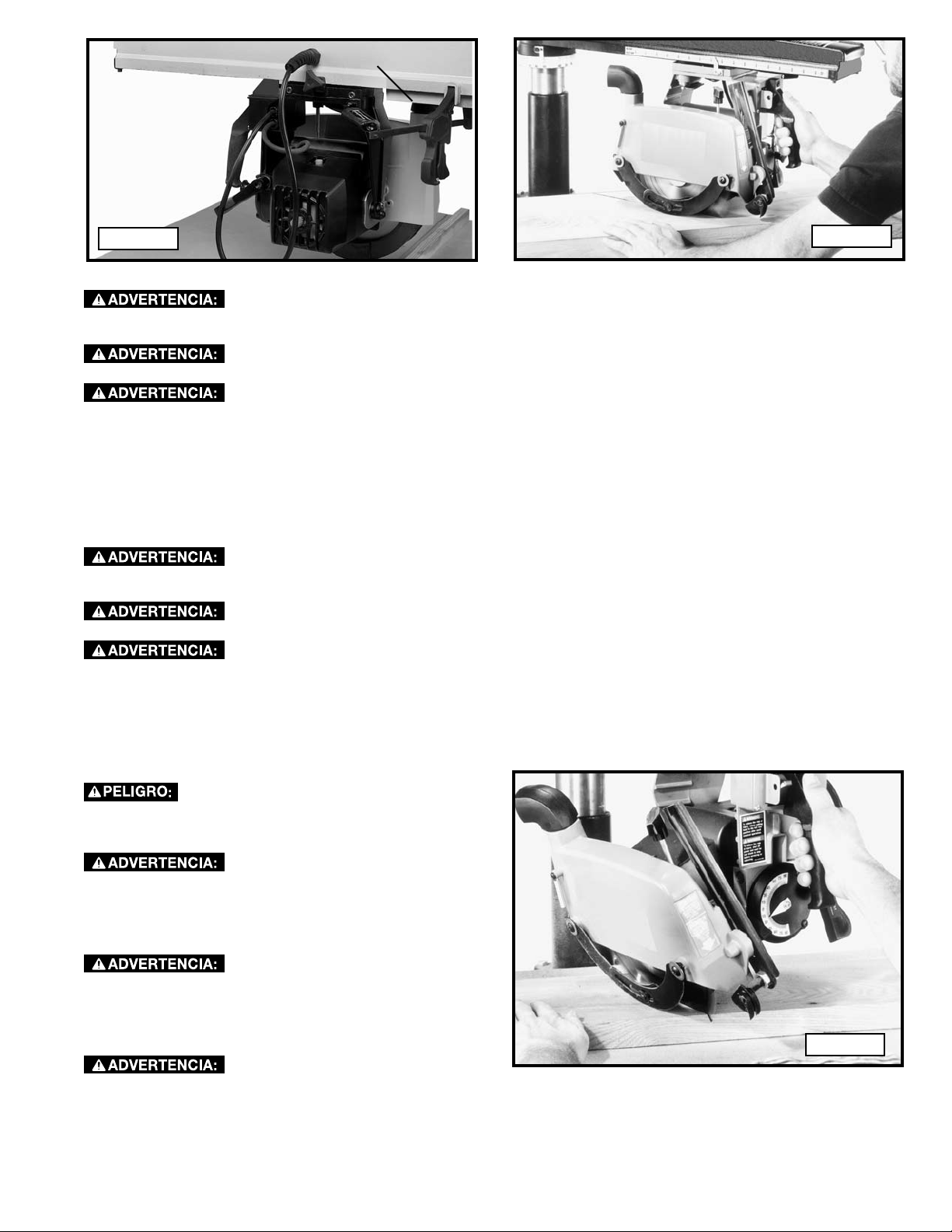
B
Fig. 58
CORTE DE INGLETES
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones, apague la unidad y desconéctela de la fuente de alimentación
antes de instalar o retirar accesorios, ajustar o cambiar configuraciones, o realizar reparaciones. Un arranque accidental
puede causar lesiones.
Tenga cuidado cada vez que comience un corte para evitar el atascamiento del protector contra
la pieza de trabajo, lo que puede ocasionar daños a la sierra y posibles lesiones personales.
Antes de conectar la sierra de brazo radial a la fuente de alimentación u operar la sierra, controle
siempre que el protector y hendedor esté correctamente alineado y a la distancia apropiada de la hoja de la sierra.
Verifique la alineación después de cada cambio de ángulo de bisel.
El corte de inglete es similar al corte transversal excepto que la pieza de trabajo se corta en ángulo (hasta 45° hacia la derecha
o la izquierda). Realice los ajustes y la operación de la misma forma que en el corte transversal excepto que primero debe
colocar el brazo guía en el ángulo deseado en la escala de inglete antes de sujetarlo en su lugar. Coloque la mano que sujeta
la pieza de trabajo del lado opuesto a la dirección del inglete para que la hoja se tire a través de la pieza de trabajo y lejos de la
mano. La figura 59 muestra una típica operación de corte de inglete en la sierra radial.
CORTE DE INGLETES COMPUESTOS
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones, apague la unidad y desconéctela de la fuente de alimentación
antes de instalar o retirar accesorios, ajustar o cambiar configuraciones, o realizar reparaciones. Un arranque accidental
puede causar lesiones.
Tenga cuidado cada vez que comience un corte para evitar el atascamiento del protector contra
la pieza de trabajo, lo que puede ocasionar daños a la sierra y posibles lesiones personales.
Antes de conectar la sierra de brazo radial a la fuente de alimentación u operar la sierra, controle
siempre que el protector y hendedor esté correctamente alineado y a la distancia apropiada de la hoja de la sierra.
Verifique la alineación después de cada cambio de ángulo de bisel.
Fig. 59
El corte de ingletes compuestos se realiza de la misma forma que el corte de inglete excepto que la hoja de la sierra se inclina
hacia el ángulo deseado en la escala de bisel y se sujeta para un corte biselado. Consulte la Fig. 60 para ver una ilustración de
corte de ingletes compuestos.
CORTE LONGITUDINAL
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones, nunca
introduzca la pieza de trabajo en el extremo de avance
de salida del protector de la hoja, ya que podría causar
lesiones personales.
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones,
apague la unidad y desconéctela de la fuente de
alimentación antes de instalar o retirar accesorios,
ajustar o cambiar configuraciones, o realizar
reparaciones. Un arranque accidental puede causar
lesiones.
NUNCA toque el “extremo libre” de
la pieza de trabajo o una “pieza libre” cortada mientras
la herramienta está en la posición "ON" (encendido) o
la hoja está girando. La pieza puede entrar en contacto
con la hoja y ser despedida, lo que puede ocasionar una
lesión.
Mantenga el protector de la hoja,
el hendedor y los dientes antirretroceso instalados correctamente y en funcionamiento. Mantenga los dientes afilados.
Si los dientes no están en condiciones operativas, devuelva la unidad al centro de mantenimiento autorizado Delta más
cercano para su reparación. El hendedor debe estar alineado con la hoja de la sierra y los dientes deben detener un
retroceso una vez que ha comenzado. Para controlar la acción de los dientes antirretroceso, antes de realizar cortes
longitudinales, empuje la madera debajo de éstos. Los dientes deben evitar que la madera salga despedida hacia el
frente de la sierra.
Fig. 60
81
Page 82

SIEMPRE debe usar una guía de
corte longitudinal al realizar cortes longitudinales, para
evitar la pérdida de control y las lesiones personales.
NUNCA realice operaciones de corte longitudinal a
pulso. Ajuste SIEMPRE la guía al riel.
IMPORTANTE: En determinadas aplicaciones, quizá
necesite dos varas de empuje o tablas de canto biselado.
Tenga las varas de empuje, las tablas de
canto biselado, etc. a mano para que pueda tener acceso a
ellas sin tener que acercarse a la hoja.
El corte longitudinal conlleva realizar un corte a lo largo a
través de una tabla siguiendo la veta de la madera. Fije el
brazo guía en “0” en la escala de inglete. Coloque en posición
y sujete la horquilla para que la hoja esté paralela a la guía
en la posición interna o externa de la tabla. Al introducir la
pieza de trabajo, asegúrese de que un borde corra contra
la guía con el lado plano apoyado en el banco. Baje el
protector del lado que introduce la pieza hasta casi tocar
la pieza de trabajo (Fig. 61) para que actúe como sujetador.
Ajuste el hendedor y los dedos de antirretroceso (A),
Fig. 61 como se lo indicó en la sección “AJUSTE DEL
HENDEDOR Y LOS DEDOS DE ANTIRRETROCESO” en
este manual. Mantenga las manos alejadas y del lado de
la hoja. Cuando realice cortes longitudinales en piezas de
trabajo angostas, siempre utilice una vara para empujar
(Fig. 62) la pieza entre la guía y la hoja.
La pieza de trabajo debe tener un borde recto para seguir la guía. Si la tabla está curvada, coloque el lado hueco hacia abajo.
Sujete con firmeza la perilla de sujeción del cabezal de corte para todas las operaciones de corte longitudinal.
Nunca introduzca la pieza de trabajo en el extremo de avance de salida del protector de la hoja.
CORTE LONGITUDINAL EXTERNO
Por lo general, el corte longitudinal externo es el mismo que el corte longitudinal, excepto que sujeta la horquilla en ángulo
recto hacia el brazo guía con el protector de la hoja en dirección hacia el FRENTE de la máquina. Posicione el cabezal de
corte en la escala de corte externo en el ajuste deseado y fíjelo en posición. Introduzca la pieza de trabajo del lado izquierdo
de la sierra. Una típica ilustración de corte longitudinal externo se muestra en la Fig. 61.
CORTE LONGITUDINAL INTERNO
Por lo general, el corte longitudinal interno es el mismo que el corte longitudinal, excepto que sujeta la horquilla en ángulo
recto hacia el brazo guía con el protector de la hoja en dirección hacia la parte TRASERA de la máquina. Posicione el cabezal
de corte en la escala de corte interno en el ajuste deseado y fíjelo en posición. Introduzca la pieza de trabajo del lado derecho
de la sierra. Una ilustración típica de corte longitudinal interno se muestra en la Fig. 62.
Fig. 61
Fig. 62
A
Cuando realice un corte longitudinal en una pieza de trabajo que tiene menos de 152 mm (6")
de ancho, utilice una vara de empuje para terminar de introducir la pieza (Fig. 62).
VARAS DE EMPUJE
Para operar su sierra de brazo radial en forma segura, debe utilizar una vara de empuje cuando el tamaño o la forma de la
pieza de trabajo requiera que coloque las manos a 152 mm (6") o menos de la hoja de la sierra u otra cortadora.
Para fabricar una vara de empuje no se requiere ninguna madera especial, en tanto se trate de un trozo de madera
suficientemente fuerte y largo. Se recomienda utilizar varas de empuje de 305 mm (12") con una muesca que se ajuste contra
el borde de la pieza de trabajo para evitar que se resbale. También se aconseja tener varias varas de empuje del mismo largo
[305 mm (12")] con muescas de diferentes tamaños para utilizar con piezas de trabajo de distintos espesores.
Consulte la página siguiente para ver una ilustración de una vara de empuje. En tanto que cumpla con la función de mantener
las manos alejadas de la hoja, la forma de la vara de empuje puede variar según sus necesidades individuales.
82
Page 83
CONSTRUCCIÓN DE UNA VARA PARA EMPUJAR
Cuando realice un corte longitudinal en una pieza con un ancho menor a 6”, puede utilizar una vara
para empujar el material hacia la hoja. Esta vara se puede hacer fácilmente con material de desecho.
Fabrique varas para empujar de madera contrachapada o madera blanda, cuyo ancho sea igual o menor
que el ancho del material que desea cortar.
material que desea cortar.
VARA PARA EMPUJAR
3/4” o de un espesor menor que el
Constrúyala en MADERA de 1/2” Ó
que la mano se resbale.
Hágale muescas para evitar
madera de 1/4”.
Corte aquí para empujar
madera de 1/2”.
Corte aquí para empujar
83
Cuadrados de 1/2”
Page 84

LOCALIZACION DE FALLAS
Para obtener asistencia para su máquina, visite nuestro sitio Web en www.deltaportercable.com para tener acceso a
una lista de centros de servicio o llame a la línea de ayuda de Delta Machinery al 1-800-223-7278. (En Canadá, llame al
1-800-463-3582.)
MANTENIMIENTO
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones personales graves, apague la herramienta y desconéctela de la
fuente de alimentación antes de instalar y retirar accesorios, ajustar o cambiar configuraciones o realizar reparaciones. Un
arranque accidental podría causar lesiones.
MANTENGA LA MÁQUINA LIMPIA
Utilice equipo de seguridad certificado para proteger sus ojos, oídos y vías respiratorias cuando use
aire comprimido.
Periódicamente sople por todas las entradas de aire con aire comprimido seco. Todas las piezas de plástico deben limpiarse con un paño suave y húmedo. NUNCA utilice solventes para limpiar las piezas de plástico. Podrían derretirse o dañar
el material.
FALLA EN EL ENCENDIDO
Si la máquina no enciende, verifique que las patas del enchufe del cable hagan buen contacto en el tomacorriente. Además,
revise que no hayan fusibles quemados o interruptores automáticos de circuito abierto en la línea.
LUBRICACIÓN Y PROTECCIÓN CONTRA ÓXIDO
Aplique semanalmente cera en pasta para pisos a la mesa de la máquina y a la extensión u otra superficie de trabajo.
También puede usar productos protectores disponibles en comercios y diseñados con este propósito. Siga las instrucciones
del fabricante para su uso y seguridad. Para limpiar el óxido de las mesas de hierro fundido, necesitará los siguientes materiales: 1 hoja de Almohadilla Manual para Matizado mediana Scotch-Brite™ , 1 lata de WD-40® y 1 lata de desgrasador.
Aplique el WD-40 y pula la superficie de la mesa con la almohadilla Scotch-Brite. Desgrase la mesa y luego aplique el producto protector como se muestra más arriba.
PROTECCION CONTRA SOBRECARGAS
El motor en su sierra está equipado con un botón de relé
para sobrecargas (A) Fig. 63. Si el motor se apaga o no
enciende debido a una sobrecarga o voltaje bajo, gire
el interruptor a la posición “APAGADO”(Off), permita
que el motor enfríe durante tres a cinco minutos y luego
em-puje el botón de re-configuración (A). Luego el motor
puede volver a encenderse normalmente. Algunas de las
condiciones que pueden causar la sobrecarga son: el corte
demasiado rápido de troncos, el uso de una hoja no afilada,
el uso de la sierra que sobrepase su capacidad, etc.
Fig. 63
A
SERVICIO
PIEZAS DE REPUESTO
Utilice sólo piezas de repuesto idénticas. Para obtener una lista de piezas o para solicitar piezas, visite nuestro sitio web en
www.deltaportercableservicenet.com. También puede solicitar piezas en nuestro centro más cercano, o llamando a nuestro
Centro de atención al cliente al 1-800-223-7278 para obtener asistencia personalizada de nuestros técnicos capacitados.
MANTENIMIENTO Y REPARACIONES
Con el paso del tiempo, todas las herramientas de calidad requieren mantenimiento o reemplazo de las piezas. Para obtener
información acerca de Delta Machinery, sus sucursales propias o un Centro de mantenimiento con garantía autorizado, visite
nuestro sitio web en www.deltaportercable.com o llame a nuestro Centro de atención al cliente al 1-800-223-7278. Todas
las reparaciones realizadas por nuestros centros de mantenimiento están completamente garantizadas en relación con los
materiales defectuosos y la mano de obra. No podemos otorgar garantías en relación con las reparaciones ni los intentos de
reparación de otras personas.
También puede escribirnos solicitando información a Delta Machinery, 4825 Highway 45 North, Jackson, Tennessee 38305 Mantenimiento de productos. Asegúrese de incluir toda la información mencionada en la placa de la herramienta (número de
modelo, tipo, número de serie, etc.)
84
Page 85
RIP
LOCK
Cutterhead
must be clamped
before performing
ripping operations.
YOKE
PIVOT
Pull handle toward
front of machine.
Pull plunger pin.
Pivot head to
desired position.
Push handle
back to lock.
BEVEL
ANGLE
Pull handle
toward
operator.
Pull plunger pin.
Set head to
desired bevel
angle. Push
handle to lock
head securely.
DEPTH
OF CUT
Lock head securely
on track arm.
Turn crank to raise
or lower blade depth.
MITER
ANGLE
Pull locking
arm to up
position. Depress
plunger and
move arm to
desired angle.
Push locking
arm back to
engage.
DOWN UP
DOWN
UNLOCK
LOCK
TO REDUCE
THE RISK OF
INJURY RETURN CUTTING HEAD TO FULL REAR
POSITION AFTER EACH CROSSCUT OPERATION.
SHUT OFF POWER AND WAIT FOR BLADE TO
STOP BEFORE SERVICING OR ADJUSTING.
PARA REDUCIR EL RIESGO DE LESIONES
COLOQUE NUEVAMENTE EL CABEZAL DE
CORTE EN SU POSICIÓN TRASERA MÁXIMA
DESPUÉS DE CADA CORTE TRANSVERSAL.
DESCONECTE LA ENERGÍA Y ESPERE A QUE LA
HOJA SE DETENGA ANTES DE REALIZAR
TAREAS DE MANTENIMIENTO O AJUSTES.
POUR RÉDUIRE LE RISQUE DE BLESSURES,
RAMENER LA TÊTE DE COUPE COMPLÈTEMENT
À L’ARRIÈRE APRÈS CHAQUE COUPE
TRANSVERSALE. COUPER L’ALIMENTATION
ET ATTENDRE L’ARRÊT DE LA LAME AVANT
DE RÉPARER OU DE RÉGLER LA SCIE.
TO AVOID INJURY NO
ADJUSTMENTS SHOULD
BE MADE UNTIL TOOL
HAS STOPPED.
FOR YOUR OWN SAFETY
DO NOT FEED MATERIAL
INTO CUTTING TOOL
FROM THIS END.
PARA EVITAR LESIONES,
NO DEBE REALIZARSE
NINGÚN AJUSTE HASTA
QUE LA HERRAMIENTA SE
HAYA DETENIDO.
POR SU PROPIA
SEGURIDAD, NO
INTRODUZCA MATERIAL
EN LA HERRAMIENTA DE
CORTE POR ESTE
EXTREMO.
TO REDUCE THE RISK OF
INJURY READ
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
BEFORE OPERATING RADIAL
SA W. ALWAYS WEAR EYE PROTECTION. DO NOT WEAR
GLOVES, NECKTIES, JEWELRY OR LOOSE CLOTHING.
DO NOT OPERATE WITHOUT GUARDS IN PLACE.
KEEEP HANDS OUT OF PATH OF SAW BLADE. DO
NOT PERFORM ANY OPERATING FREE-HAND.
ALWAYS SUPPORT WORK FIRMLY AGAINST FENCE.
ALWAYS FEED MATERIAL AGAINST ROTATION OF
BLADE AND USE ANTI-KICKBACK FINGERS WHEN
RIPPING. USE PUSH STICKS WHEN RIPPING NARROW
WORK. KNOW HOW TO REDUCE RISK OF KICKBACK. NEVER
REACH AROUND OR BEHIND SAW BLADE. DO NOT REMOVE JAMMED
OR SCRAP MATERIAL UNTIL BLADE HAS COMPLETELY STOPPED. RETURN CUTTING
HEAD TO FULL REAR POSITION UPON COMPLETION OF CROSSCUTS. SHUT OFF
POWER AND WAIT FOR SAW BLADE TO STOP BEFORE MOVING WORKPIECE OR
CHANGING TOOL SETTINGS. DISCONNECT POWER BEFORE CHANGING SAW BLADE
OR SERVICING TOOL. DO NOT EXPOSE TO RAIN OR USE IN DAMP LOCATIONS.
PARA REDUCIR EL RIESGO DE LESIONES
LEA EL MANUAL DE INSTRUCCIONES ANTES
DE OPERAR LA SIERRA RADIAL. UTILICE SIEMPRE PROTECCIÓN ADECUADA PARA
LOS OJOS. NO UTILICE GUANTES, CORBATAS, ALHAJAS NI ROPA HOLGADA. NO
OPERE LA SIERRA SI LOS PROTECTORES NO ESTÁN ADECUADAMENTE INSTALADOS.
MANTENGA LAS MANOS ALEJADAS DEL TRAYECTO DE LA HOJA DE LA SIERRA. NO
REALICE NINGUNA OPERACIÓN SIN UTILIZAR LAS MANOS. SIEMPRE SOSTENGA EL
TRABAJO FIRMEMENTE CONTRA LA GUÍA. SIEMPRE INTRODUZCA EL MATERIAL EN
SENTIDO CONTRARIO AL GIRO DE LA HOJA Y UTILICE DEDOS DE ANTIRETROCESO
CUANDO REALICE CORTES LONGITUDINALES. UTILICE VARAS DE EMPUJE AL
REALIZAR CORTES LONGITUDINALES EN PIEZAS DE TRABAJO ANGOSTAS. SEPA
CÓMO EVITAR EL RIESGO DE RETROCESOS. NUNCA INTENTE ALCANZAR OBJETOS
ALREDEDOR O DETRÁS DE LA HOJA DE LA SIERRA. NO RETIRE EL MATERIAL
ATASCADO O DE DESCARTE HASTA QUE LA HOJA NO SE HAYA DETENIDO
COMPLETAMENTE. COLOQUE NUEVAMENTE EL CABEZAL DE CORTE EN LA POSICIÓN
TRASERA MÁXIMA LUEGO DE REALIZAR CORTES TRANSVERSALES. DESCONECTE LA
ENERGÍA Y ESPERE A QUE LA HOJA SE DETENGA ANTES DE MOVER LA PIEZA DE
TRABAJO O CAMBIAR LA CONFIGURACIÓN DE LA HERRAMIENTA. DESCONECTE LA
ENERGÍA ANTES DE CAMBIAR LA HOJA DE LA SIERRA O REALIZAR TAREAS DE
MANTENIMIENTO. NO EXPONGA A LA LLUVIA NI UTILICE EN LUGARES HÚMEDOS
POUR RÉDUIRE LE RISQUE DE
BLESSURES, LIRE LE MODE D’EMPLOI
AVANT L’UTILISATION DE LA SCIE RADIALE. TOUJOURS PORTER UNE PROTECTION
OCULAIRE ADÉQUATE. NE PAS PORTER DE GANTS, NI CRAVATES, BIJOUX OU
VÊTEMENTS AMPLES. NE PAS UTILISER LA SCIE SANS QUE LES PROTÈGE-LAME NE
SOIENT EN PLACE. GARDER LES MAINS HORS DE LA TRAJECTOIRE DE LA LAME DE
LA SCIE. EFFECTUER TOUTE OPÉRATION EN TENANT L’OUTIL DES DEUX MAINS.
TOUJOURS APPUYER LA PIÈCE CONTRE LE GUIDE. TOUJOURS AVANCER LE MATÉRIEL
À CONTRE-COURANT DE LA ROTATION DE LA LAME ET UTILISER LES DOIGTS
ANTI-EFFET DE REBOND LORS DE SCIAGE EN LONG. UTILISER DES POUSSOIRS POUR
SCIER EN LONG UNE PIÈCE ÉTROITE. CONNAÎTRE LES TECHNIQUES POUR RÉDUIRE
LE RISQUE ASSOCIÉ À L’EFFET DE REBOND. NE PAS PASSER LES MAINS AUTOUR DE
LA LAME OU DERRIÈRE CELLE-CI. NE PAS RETIRER LA PIÈCE COINCÉE OU LA PIÈCE
DE CHUTE AVANT L’ARRÊT COMPLET DE LA LAME. RAMENER LA TÊTE DE COUPE
COMPLÈTEMENT À L’ARRIÈRE APRÈS DES COUPES TRANSVERSALES. COUPER
L’ALIMENTATION ET ATTENDRE L’ARRÊT COMPLET DE LA LAME DE LA SCIE AVANT
DE DÉPLACER LA PIÈCE OU DE MODIFIER LES RÉGLAGES. DÉBRANCHER LA SCIE
AVANT DE REMPLACER LA LAME OU D’EFFECTUER DES RÉPARATIONS. PROTÉGER
DE LA PLUIE ET NE PAS UTILISER DANS DES ENDROITS HUMIDES.
angle. Push
handle to lock
head securely.
DEPTH
OF CUT
Lock head securely
on track arm.
Turn crank to raise
or lower blade depth.
MITER
ANGLE
Pull locking
arm to up
position. Depress
plunger and
move arm to
desired angle.
Push locking
arm back to
engage.
DOWN UP
DOWN
UNLOCK
LOCK
POUR EMPÊCHER DES
BLESSURES, ATTENDRE
L’ARRÊT COMPLET DE
L’OUTIL AVANT D’EFFECTUER
TOUS RÉGLAGES.
POUR VOTRE PROPRE
SÉCURITÉ, NE PAS
INTRODUIRE DE MATÉRIAU
À PARTIR DE CETTE
EXTRÉMITÉ DE CET OUTIL.
TO AVOID INJURY NO
ADJUSTMENTS SHOULD
BE MADE UNTIL TOOL
HAS STOPPED.
FOR YOUR OWN SAFETY
DO NOT FEED MATERIAL
INTO CUTTING TOOL
FROM THIS END.
PARA EVITAR LESIONES,
NO DEBE REALIZARSE
NINGÚN AJUSTE HASTA
QUE LA HERRAMIENTA SE
HAYA DETENIDO.
POR SU PROPIA
SEGURIDAD, NO
INTRODUZCA MATERIAL
EN LA HERRAMIENTA DE
CORTE POR ESTE
EXTREMO.
REEMPLAZO GRATUITO DE LAS ETIQUETAS DE ADVERTENCIA
Si las etiquetas de advertencia se tornan eligibles o se pierden, llame al 1-800-223-7278 para reemplazarlas sin costo
alguno.
85
Page 86

ACCESORIOS
Puesto que los accesorios con excepción de ésos ofrecidos por Delta no se han probado con
este producto, el uso de tales accesorios podría ser peligroso. Para la operación más segura, solamente el delta
recomendó los accesorios se debe utilizar con este producto.
Una línea completa de accesorios está disponible de su surtidor de Porter-Cable • Delta, centros de servicio de la fábrica de
Porter-Cable • Delta, y estaciones autorizadas delta. Visite por favor nuestro Web site www.deltaportercable.com para un
catálogo o para el nombre de su surtidor más cercano.
PÓLIZA DE GARANTÍA
IDENTIFICACIÓN DELPRODUCTO:
Sello o firma del Distribuidor.Nombre del producto: _______________________ Mod./Cat.: ________________________Marca: _
______________________________ Núm. de serie:________________________(Datos para ser llenados por el distribuidor)Fecha
de compra y/o entrega del producto: _______________________________________Nombre y domicilio del distribuidor donde
se adquirió el producto:__________________________________________________________________________Este producto está
garantizado por un año a partir de la fecha de entrega, contra cualquierdefecto en su funcionamiento, así como en materiales y
mano de obra empleados para su fab-ricación. Nuestra garantía incluye la reparación o reposición del producto y/o componentes sincargo alguno para el cliente, incluyendo mano de obra, así como los gastos de transportaciónrazonablemente erogados
derivados del cumplimiento de este certificado.Para hacer efectiva esta garantía deberá presentar su herramienta y esta póliza
sellada por elestablecimiento comercial donde se adquirió el producto, de no contar con ésta, bastará la fac-tura de compra.
EXCEPCIONES
Esta garantía no será válida en los siguientes casos:
•Cuandoelproductosehubieseutilizadoencondicionesdistintasalasnormales;
•Cuandoelproductonohubiesesidooperadodeacuerdoconelinstructivodeusoqueseacompaña;
•Cuandoelproductohubiesesidoalteradooreparadoporpersonasdistintasalasenlis-tadasalfinaldeestecertificado.
Anexo encontrará una relación de sucursales de servicio de fábrica, centros de servicio autor-izados y franquiciados en la
República Mexicana, donde podrá hacer efectiva su garantía yadquirir partes, refacciones y accesorios originales.
86
Page 87
PARA REPARACIÓN Y SERVICIO DE SUS
HERRAMIENTAS ELÉCTRICAS, FAVOR DE
DIRIGIRSE AL CENTRO DE SERVICIO MÁS CERCANO
CULIACAN, SIN
Blvd.Emiliano Zapata 5400-1
Poniente Col. San Rafael (667) 7 12 42 11
GUADALAJARA, JAL
Av. La Paz #1779 - Col. Americana Sector Juárez (33) 3825 6978
MEXICO, D.F.
Eje Central Lázaro Cárdenas No. 18
Local D, Col. Obrera (55) 5588 9377
MERIDA, YUC
Calle 63 #459-A - Col. Centro (999) 928 5038
MONTERREY, N.L.
Av. Francisco I. Madero No.831 - Col. Centro (81) 8375 2313
PUEBLA, PUE
17 Norte #205 - Col. Centro (222) 246 3714
QUERETARO, QRO
Av. Madero 139 Pte. - Col. Centro (442) 214 1660
SAN LUIS POTOSI, SLP
Av. Universidad 1525 - Col. San Luis (444) 814 2383
TORREON, COAH
Blvd. Independencia, 96 Pte. - Col. Centro (871) 716 5265
VERACRUZ, VER
Prolongación Díaz Mirón #4280 - Col. Remes (229) 921 7016
VILLAHERMOSA, TAB
Constitución 516-A - Col. Centro (993) 312 5111
PARA OTRAS LOCALIDADES:
Si se encuentra en México, por favor llame al (55) 5326 7100
Si se encuentra en U.S., por favor llame al
(888) 848-5175
ESPECIFICACIONES
MODEL 22-450 / 22-451
Tensión de alimentación: 22-450: 200-220 V / 440 V
22-451: 230 V
Consumo de corriente: 22-450: 12 A @ 220 V
22-451: 25.5 A @ 230 V
Frecuencia de operación: 60 Hz
Rotación sin carga: 4 950 rpm
SOLAMENTE PARA PROPÓSITO DE MÉXICO:
IMPORTADO POR: D
BOSQUES DE CIDROS, ACCESO RADIATAS NO.42
3A. SECCIÓN DE BOSQUES DE LAS LOMAS
DELEGACIÓN CUAJIMALPA,
05120, MÉXICO, D.F.
TEL. (52) 555-326-7100
R.F.C.: BDE810626-1W7
Para servicio y ventas consulte
“HERRAMIENTAS ELECTRICAS”
en la sección amarilla.
eWALT S.A. DE C.V.
GARANTIA
Para registrar la herramienta para obtener el mantenimiento cubierto por la garantía de la herramienta, visite nuestro sitio web
en www.deltaportercable.com.
Garantía limitada de dos años para productos nuevos
Delta reparará o reemplazará, a expensas y opción propias, cualquier máquina nueva, pieza de máquina nueva o accesorio de máquina nuevo
Delta que durante el uso normal haya presentado defectos de fabricación o de material, siempre que el cliente devuelva el producto con el
transporte prepagado a un centro de servicio de fábrica Delta o una estación de servicio autorizado Delta, con un comprobante de compra
del producto, dentro del plazo de dos años y dé a Delta una oportunidad razonable de verificar el supuesto defecto mediante la realización de
una inspección. Para todos los productos Delta reacondicionados, el período de garantía es de 180 días. Delta podrá requerir que los motores
eléctricos sean devueltos con el transporte prepagado a una estación autorizada de un fabricante de motores para ser sometidos a inspección y
reparación o para ser reemplazados. Delta no será responsable de ningún defecto alegado que haya resultado del desgaste normal, uso indebido,
abuso o reparación o alteración realizada o autorizada específicamente por alguien que no sea un centro de servicio autorizado Delta o un
representante autorizado Delta. Delta no será responsable en ninguna circunstancia de los daños incidentales o emergentes que se produzcan
como resultado de productos defectuosos. Esta garantía es la única garantía de Delta y establece el recurso exclusivo del cliente en lo que
respecta a los productos defectuosos; Delta rechaza expresamente todas las demás garantías, expresas o implícitas, tanto de comerciabilidad
como de idoneidad para un propósito o de cualquier otro tipo.
AMÉRICA LATINA: Esta garantía no se aplica a los productos que se venden en América Latina. Para los productos que se
venden en América Latina, debe consultar la información de la garantía específica del país que viene en el empaque, llamar a
la compañía local o visitar el sitio Web a fin de obtener esa información.
87
Page 88
The following are trademarks for one or more Porter-Cable and Delta products: Les marques suivantes sont des marques de commerce se rapportant
à un ou plusieurs produits Porter-Cable ou Delta : Las siguientes son marcas comerciales para uno o más productos de Porter-Cable y Delta:
2 BY 4®, 890™, Air America®, AIRBOSS™, Auto-Set®, B.O.S.S.®, Bammer®, Biesemeyer®, Builders Saw®, Charge Air®, Charge Air Pro®,
CONTRACTOR SUPERDUTY®, Contractor's Saw®, Delta®, DELTA®, Delta Industrial®, DELTA MACHINERY & DESIGN™, Delta Shopmaster
and Design®, Delta X5®, Deltacraft®, DELTAGRAM®, Do It. Feel It.®, DUAL LASERLOC AND DESIGN®, EASY AIR®, EASY AIR TO GO™,
ENDURADIAMOND®, Ex-Cell®, Front Bevel Lock®, Get Yours While the Sun Shines®, Grip to Fit®, GRIPVAC™, GTF®, HICKORY WOODWORKING®,
Homecraft®, HP FRAMER HIGH PRESSURE®, IMPACT SERIES™, Innovation That Works®, Jet-Lock®, Job Boss®, Kickstand®, LASERLOC®,
LONG-LASTING WORK LIFE®, MAX FORCE™, MAX LIFE®, Micro-Set®, Midi-Lathe®, Monsoon®, MONSTER-CARBIDE™, Network®, OLDHAM®,
Omnijig®, PC EDGE®, Performance Crew™, Performance Gear®, Pocket Cutter®, Porta-Band®, Porta-Plane®, Porter Cable®, Porter-Cable
Professional Power Tools®, Powerback®, POZI-STOP™, Pressure Wave®, PRO 4000®, Proair®, Quicksand and Design®, Quickset II®, QUIET
DRIVE TECHNOLOGY™, QUIET DRIVE TECHNOLOGY AND DESIGN™, Quik-Change®, QUIK-TILT®, RAPID-RELEASE™, RAZOR®, Redefining
Performance®, Riptide®, Safe Guard II®, Sand Trap and Design®, Sanding Center®, Saw Boss®, Shop Boss®, Sidekick®, Site Boss®, Speed-Bloc®,
Speedmatic®, Stair Ease®, Steel Driver Series®, SUPERDUTY®, T4 & DESIGN®, THE AMERICAN WOODSHOP®, THE PROFESSIONAL EDGE®,
Thin-Line®, Tiger Saw®, TIGERCLAW®, TIGERCLAW AND DESIGN®, Torq-Buster®, TRU-MATCH®, T-Square®, Twinlaser®, Unifence®, Uniguard®,
UNIRIP®, UNISAW®, UNITED STATES SAW
Whisper Series®, X5®, YOUR ACHIEVEMENT. OUR TOOLS.
Trademarks noted with ® are registered in the United States Patent and Trademark Office and may also be registered in other countries. Other
trademarks may apply. Les marques de commerce suivies du symbole ® sont enregistrées auprès du United States Patent and Trademark Office et
peuvent être enregistrées dans d’autres pays. D’autres marques de commerce peuvent également être applicables. Las marcas comerciales con el
símbolo ® están registradas en la Oficina de patentes y marcas comerciales de Estados Unidos (United States Patent and Trademark Office), y también
pueden estar registradas en otros países. Posiblemente se apliquen otras marcas comerciales registradas.
®,
Veri-Set®, Versa-Feeder®, VIPER®, VT™, VT RAZOR
®
™,
Water Driver®, WATER VROOM®, Waveform®,
Delta Machinery
4825 Highway 45 North
Jackson, TN 38305
(800) 223-7278
www.deltaportercable.com
 Loading...
Loading...