Page 1

EPSON
EPSON
EPSON France S.A.
SERVICE MANUAL
LQ-300
PRODUIT
Page 2
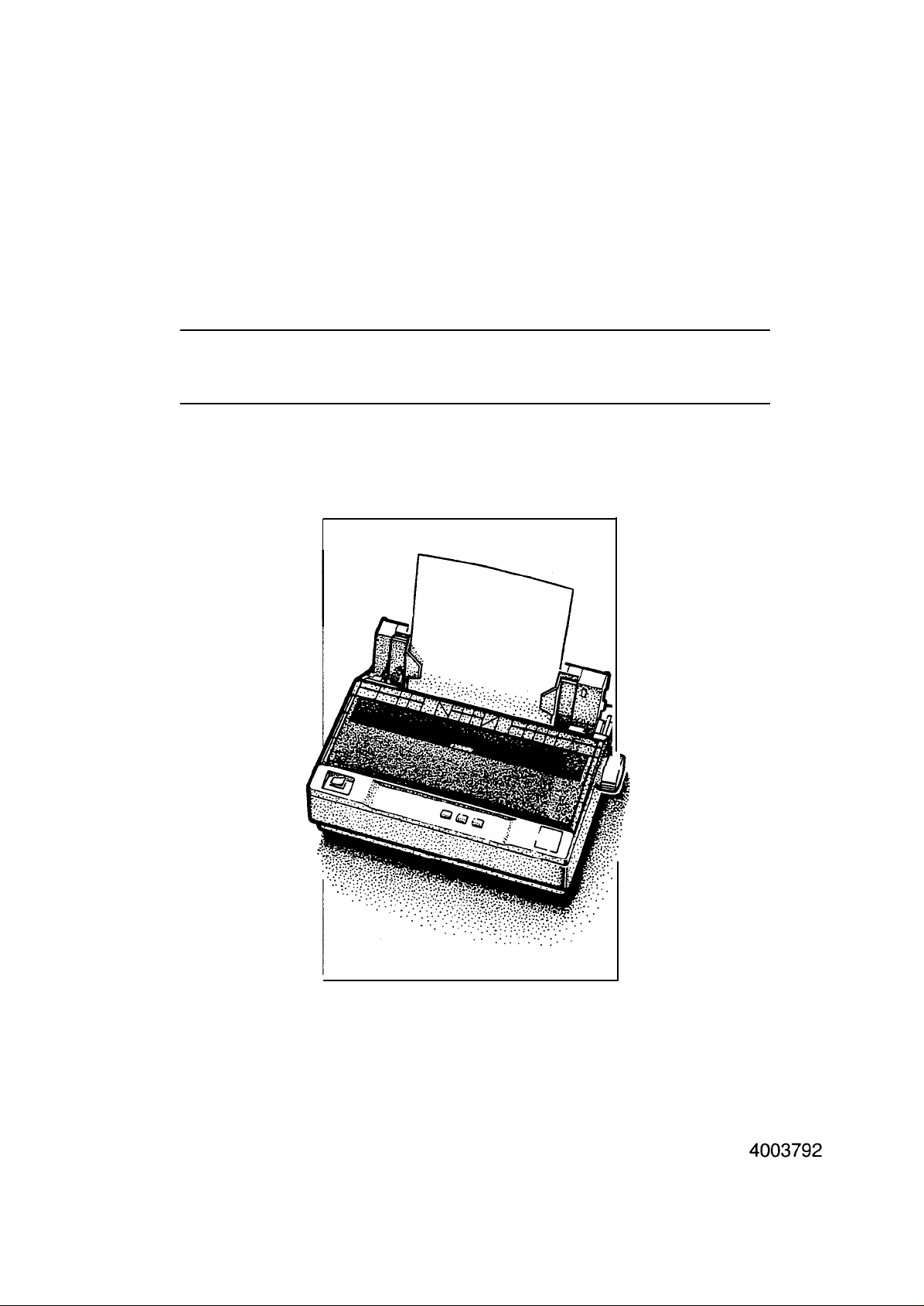
EPSON
TERMINAL
PRINTER
LQ-300
SERVICE MANUAL
EPSON
Page 3

NOTICE
All rights reserved. Reproduction of any part of this manual in any form whatsoever without
SEIKO EPSON’s express written permission is forbidden.
The contents of this manual are subjects to change without notice.
Alleffortshavebeen made toensuretheaccuracy of
thecontentsofthis
manual. However, should
any errors be detected, SEIKO EPSON would greatly appreciate being informed of them.
The above notwithstanding SEIKO EPSON can
assume no
responsibility for any errors in
this
manual or the consequence thereof.
Epson is registered trademark of Seiko Epson Corporation.
General Notice: Other product names used herein are foridentication purposes only and maybe
trademarks of their respective
Copyright @ 1994 by SEIKO EPSON CORPORATION
carnpanies.
-i-
Nagano,
Japan
Page 4

PRECAUTIONS
Precautionary notations throughout the text are categorized relative to 1) personal injury and 2)
damage to equipment.
DANGER
Signals a precaution which, if ignored, could result in serious or fatal personal injury.
Great caution should be exercised in performing procedures preceded by DANGER
Headings.
WARNING
Theprecautionary measures itemized below should alwaysbe observed when performin
Signals a precaution which, if ignored, could result in darnage to equipment.
grepair/
maintenance procedures.
DANGER
1.
ALWAYS DISCONNECT THE PRODUCT FROM BOTH THE POWER SOURCE AND
PERIPHERAL DEVICES PERFORMING ANY MAINTENANCE OR REPAIR PROCEDURE.
2.
NO WORK SHOULD BE PERFORMED ON THE UNIT BY PERSONS
BASIC SAFETY MEASURES AS DICTATED FOR ALL ELECTRONICS TECHNICIANS IN
THEIR LINE OF WORK.
3.
WHEN PERFORMING TESTING AS DICTATED
WITHIN THIS MANUAL, DO NOT
CONNECT THE UNITTOA POWER SOURCE UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. WHEN
THE POWER SUPPLY CABLE MUST BE CONNECTED, USE EXTREME CAUTION IN
WORKING ON POWER SUPPLY AND OTHER ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS.
UNTAMILIARWITH
WARNING
1.
REPAIRS ON EPSON PRODUCT SHOULD BE PERFORMED ONLY BY AN EPSON
CERTIFIED REPAIR TECHNICIAN.
MAKE CERTAIN THAT THE SOURCE VOLTAGE IS THE SAME AS THE RATED VOLT-
2.
AGE, LISTED ON THE SERIAL NUMBER/RATING PLATE. IF
HAS A PRIMARY AC RATING DIFFERENT FROM AVAILABLE POWER SOURCE, DO
NOT CONNECT IT TO THE POWER SOURCE.
3.
ALWAYS VERIFY THAT THE EPSON PRODUCT HAS BEEN DISCONNECTED FROM
THE POWER SOURCE BEFORE REMOVING OR REPLACING PRINTED CIRCUIT
BOARDS AND/OR INDIVIDUAL CHIPS.
4.
IN ORDER TO PROTECT SENSITIVE MICROPROCESSORS AND CIRCUITRY, USE
STATIC DISCHARGE EQUIPMENT, SUCH AS ANTI-STATIC WRIST STRAPS, WHEN
ACCESSING INTERNAL COMPONENTS.
5.
REPLACE MALFUNCTIONING COMPONENTS ONLY WITH THOSE COMPONENTS
BY THE MANUFACTURE; INTRODUCTION OF SECOND-SOURCE
NONAPPROVED COMPONENTS MAY DAMAGE THE PRODUCT AND VOID ANY
APPLICABLE EPSON WARRANTY.
THE
EPSON PRODUCT
Ics
OR OTHER
- ii -
Page 5

PREFACE
This manual describes functions, theory of electrical and mechanical operations, maintenance, and repair
of
LQ-300.
The instructions and procedures included herein are intended for the experience repair technician, and
attention should be given to the precautions on the preceding page. The chapters are organized as
follows:
CHAPTER 1. PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
Provides a
CHAPTER 2. OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Describes the theory of printer operation.
CHAPTER 3. DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
Includes a step-by-step guide for product disassembly and assembly.
CHAPTER 4. ADJUSTMENTS
Includes a step-by-step guide for adjustment.
general product overview, lists specifications, and illustrates the main components of the printer.
CHAPTER 5. TROUBLESHOOTING
Provides Epson-approved techniques for adjustment.
CHAPTER 6. MAINTENANCE
Describes preventive maintenance techniques and lists lubricants and adhesives required to service the equipment.
APPENDIX
Describes connector pin assignments, circuit diagrams, circuit board component layout and exploded diagram.
The contents of this manual are subject to change without notice.
-
iv -
Page 6
REVISION SHEET
f=”:
Revision
Rev. A
Issue Date
September 28, 1994
Revision Page
1st issue
-v-
.-..>
.$...
.,,
.
1
Page 7

TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1.
CHAPTER 2.
CHAPTER 3.
CHAPTER
CHAPTER 5.
CHAPTER 6.
APPENDIX
4.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
OPERATING PRINCIPLES
DISASSEMBLY
AND ASSEMBLY
ADJUSTMENTS
TROUBLESHOOTING
MAINTENANCE
. .
-
vi -
Page 8

CHAPTER 1 Product Description
Table of Contents
1.1 FEATURES
1.2 SPECIFICATIONS
1.2.1 Hardware Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.2.1.1
1.2.1.2
1.2.1.3
1.2.1.4
1.2.1.5
1.2.1.6
1.2.1.7
1.2.1.8
1.2.1.9
Paper Handling Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Paper Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Printable Area... . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ribbon Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electrical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Environmental Conditions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reliability. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Safety Approvals. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Physical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.2.2 FirmwareS pacifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.3 INTERFACE SPECIFICATIONS
1.3.1 Paraliellnterface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.3.1.I Compatible Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.3.1.2 Reverse Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.3.2 Serial Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.3.3 Interface Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.3.4 Preventing the Host from Data TransferTimeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-1
1-2
1-2
1-3
1-4
1-5
.
1-7
1-7
1-7
.
1-11
1-11
1-11
I-13
1-14
1-15
1-15
1-7
1-8
1-8
1-8
1.4 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
1.4.1 Control Panel Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4.2 Self-test Function. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4.3 Hexadecimal Dump Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4.4 Micro Adjustment Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4.5 PrinterStatus Indication.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4.6 Selected Font . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4.7 Printer Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4.7.1 Power-on Initialization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4.7.2 Hardware Initialization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4.7.3 Software Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4.8
PrinterSettings
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4.8.1 Selectable
PrinterSettings
.......:.
. : . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4.8.2 Changing the Default Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.5 MAIN COMPONENTS
1.5.1
C143 MAIN Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.5.2 C130PSB/PSE Board. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.5.3 Printer Mechanism (M-5M1O) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.5.4 Housing Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
.
.
.
.
1-16
1-16
1-17
1-17
1-18
1-18
1-19
1-19
1-19
1-19
1-19
1-20
1-20
1-20
1-24
1-24
1-24
1-25
1-25
Page 9

List of Figures
Figure 1-1. Exterior View of the LQ-300. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure l-2. Pin Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure l-3. PrintableAreafor Cut Sheets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure l-4. PrintableAreafor Envelopes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure l-5.
Figure l-6. Data Transmission Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure
Figure l-8. C143 MAIN Board Component Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure l-9.
Figure 1-10. Printer Mechanism (M-5 M1O). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 1-11. Housing Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PrintableAreafor
1-7.
Control Panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C130
PSB/PSE Board Component Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-24
Continuous Paper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-1
1-2
1-5
1-6
1-6
1-11
1-16
I-24
1-25
1-25
List of Tables
Table l-1. Optional Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table l-2.
Table l-3. Feeding Speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 1-4. Specifications for Cut Sheet Paper (CSF). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 1-5. Specifications for Cut Sheet Paper (Manual Insertion) . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Table
Table
Table
Table
Table
Table
Table
Table
Table
Table
Table
Table
Table
Table
Table
Table
Table
Table l-23. Graphic
Table l-24. Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tablel-25.interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table l-26. Bit Rate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 1-27. Parity Bit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 1-28. Data Length. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PaperThickness
-6. Specifications forEnvelopes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-7. Specifications for Continuous Paper (Single Sheet and Multi-Part) . 1-4
-8. Specifications for Continuous Paper with a Label. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
-9. Electrical Ranges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-lO.
CharacterTables.
-11. Resolution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-12. Printing Speed. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-13. Signal and Connector Pin Assignments forthe Parallel Interface. 1-12
-14. Signal and
-15. Signal and Connector Pin Assignments
-16. Paper Feeding Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-17. Font Selection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-18. Font Lightsand Language Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-19. Default Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-20.
CharacterTables.
-21. Page Length . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-22.
SkiDOver
EX~/ACK/
Perforation/Auto TearOff/AGM/Auto Line Feed
State Reply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ptint
LeverSettings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ConnectorPin
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Direction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Assignments
forthe
forthe Serial Interface . . 1-14
Parallel Interface. 1-13
1-1
1-4
1-4
1-4
1-7
1-8
1-9
1-10
1-17
1-19
1-20
1-21
1-21
1-22
1-22
1-22
1-22
1-22
1-22
1-23
1-23
!!
1-3 -
,’:~\
.,
(:;
f“~.
. .
Page 10
LWOO
Service
Manual
Product Description
1.1 FEATURES
The LQ300 is a small, light-weight, 24pin serial impact dot-matrix color printer suitable for
personal use. The major features of this printer are:
●
Fast printing of
●
Compact design saves precious work space
●
Easy-to-operate panel
● Quiet printing
●
Two built-in 8-bit parallel interfaces and an
●
Printing of up to 66
●
Optional color printing using a color ribbon (black, magenta, cyan, yellow)
●
Detachable tractor (push, pull, and push-pull tractor feed)
lo-cpi
draft characters at 200 cps
kes
on
A4-size
or 62 lines on letter-size paper
EIA-232D
serial interface
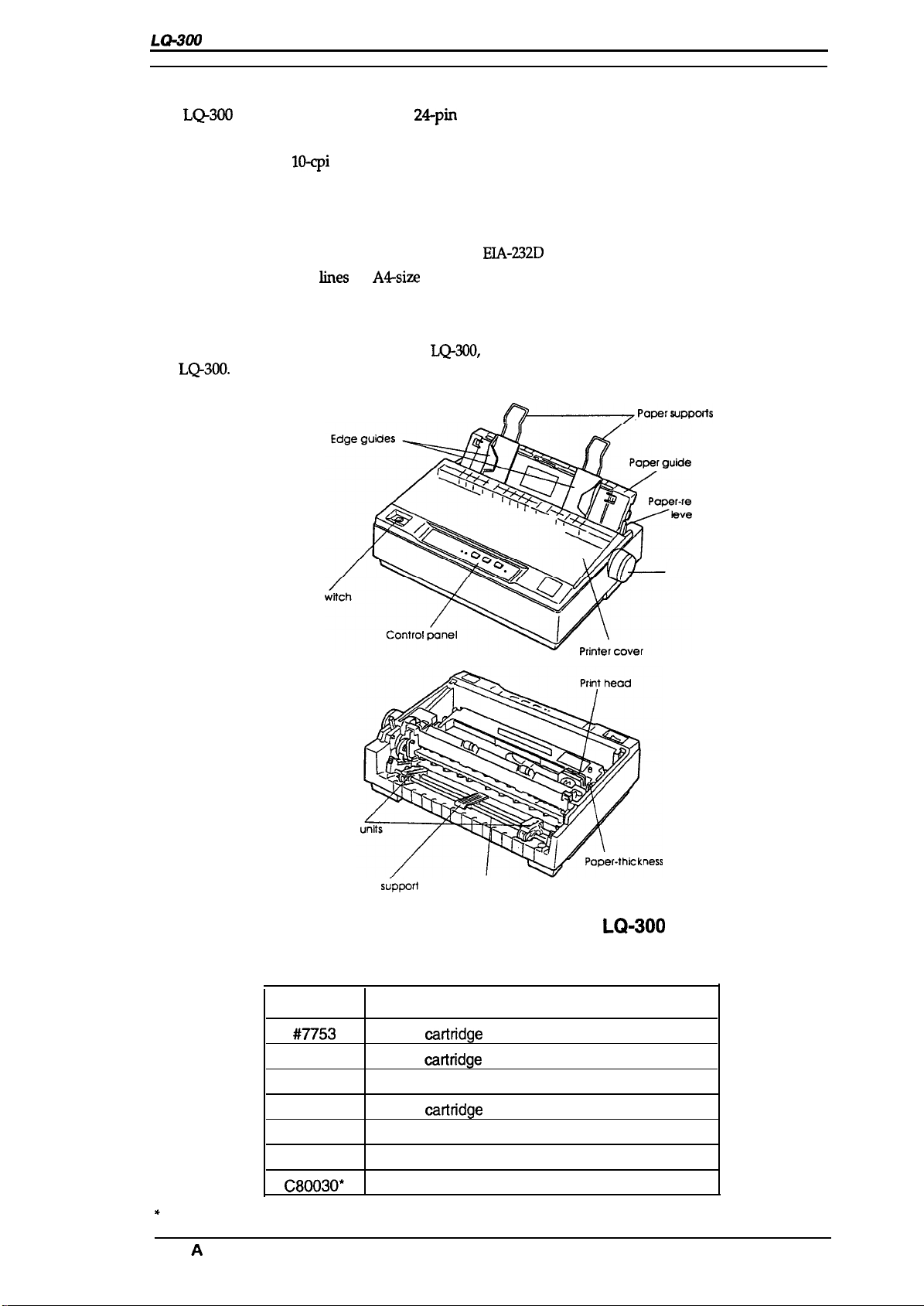
Figure 1-1 shows an exterior view of the
the
LQ-300.
Power
s
LQ-300,
and Table 1-1 lists the optional units available for
~’”pe’”Q@’
lease
r
Knob
Sprocket
Center
support
Tractor unit
Figure 1-1. Exterior View of the LQ-300
Table 1-1. Optional Units
Model
#77!53
#7755
#7768
S015077
C80637*
C83211•
C80030*
*
The number represented by an asterisk varies depending on the country.
Rev. A
Ribbon
Ribbon
oartridge
oartridge
Ribbon cartridge (film)
Ribbon
oartridge
Single-bin cut sheet feeder
Color upgrade kit
Pull tractor unit
Description
(monochrome)
(monochrome, sub-cartridge)
(color)
lever
“l-1
Page 11
Product Description
1.2 SPECIFICATIONS
This
section
1.2.1
provides detailed information about the
Hardware
Specifications
LQ-300.
LQ-300
Service Manual
r
.T,
,$
,’
Printing
Pin arrangement:
Pin diameter:
method:
E
E
In
4
m
m
a
x
‘o
a
.
\
7
5erial
impact dot matrix
12 x 2, staggered
0.20 mm (0.0079 inches)
.
o
m
.
11( )
II
13 ()
15 ()
17<
19()
21 ()
22 ()
L“?”’”
3f
,
5() !
7()
9
( )
)
?
{
!
I
i
-!
I
ij
i(
I
\
(
)
( )
()
10
(
)
16
()
;;:
)22
f
5
L’24
6
8
‘o
{:
.., .-
HEAD CENTER
Printing direction:
Figure 1-2. Pin Configuration
Bidirectional with logic seeking for text and unidirectional for
graphics. (Bidirectional printing of graphics can be selected with a
printer
setdng or software command.)
p
. . . . .
1-2
Rev.
A
Page 12

LWOO
Service
Manual
1.2.1.1 Paper Handling Specifications
Paper paths
Cut sheet path:
Rear entry (manual insertion or optional
Cannot handle multi-part paper using friction feed
Continuous paper paths:
Rear entry ( push tractor feed using the push tractor unit
or pull tractor feed using the pull tractor unit or push-pull
tractor feed using both tractor units)
Continuous paper parking:
CSF:
Feeding pitch:
Feeding system:
❑
Friction feed
● Set the release lever to the friction position.
Possible, using push tractor unit
Cannot handle envelopes or multi-part paper
% ~~, 1A
$%o
~ch, or Programmable feeding in increments of
inch, minimum
Friction feed or
. Insert the left edge of the sheet at the marked position.
●
Do
not.perform
reverse feed in the area within 0.63 inch (16 mm) from the bottom edge of
the sheet.
Push tractorfeed
● Set the release lever to the tractor position.
●
Install the tractor unit in the rear in the push
●
On the first page (that is, the page immediately after sheet loading) the accuracy of paper
feeding is not guaranteed within the area 0.87 inch (22 mm) from the top edge of the sheet.
●
On the last page, the accuracy of paper feeding is not guaranteed after the paper comes off
the tractor pins.
●
During printing
●
Do
not eject the labels from the rear.
oflabels,
never perform reverse feeding.
&actor
&actor
Product Description
CSF)
(push, pull, and push-pull) feed
position.
❑
Pull tractor feed
● Set the release lever to the tractor position.
. Install the tractor unit in the top in the pull tractor position.
● Do not perform reverse feeding.
● Do not eject them from the rear.
Push pull tractor feed
●
Set the release lever to the tractor position.
●
Install one tractor unit in the rear in the push tractor position and install the other tractor unit
in the top in the pull tractor position.
. Do not perform reverse feeding.
●
Do
not eject the paper from the rear.
Paper thickness
leve~
The adjust lever must be set to proper position for the
paper thickness, as shown below.
Table 1-2. Paper Thickness Lever Settings
Lever Position
o
1
2
3
4
5
Paper-feeding speed:
Paper Thickness
0.065 mm -0.12 mm (0.0026 in. -0.0047 in.)
0.12 mm -0.19 mm (0.0047 in. -0.0075 in.)
0.19 mm -0.26 mm (0.0075 h. -0.01 in.)
0.26 mm -0.32 mm (0.01 in. -0.013 in.)
0.32 mm -0.44 mm (0.013 in. -0.017 in.)
0.44 mm -0.52 mm (0.017 in. -0.02 in.)
See Table 1-3.
Corresponding Paper
Ordinary paper
Multi-part forms (2 sheets)
Multi-part forms (3 sheets)
Multi-part forms (4 sheets)
Envelopes (20 lb.)
Envelopes (24
lb.)
Rev. A
1-3
Page 13
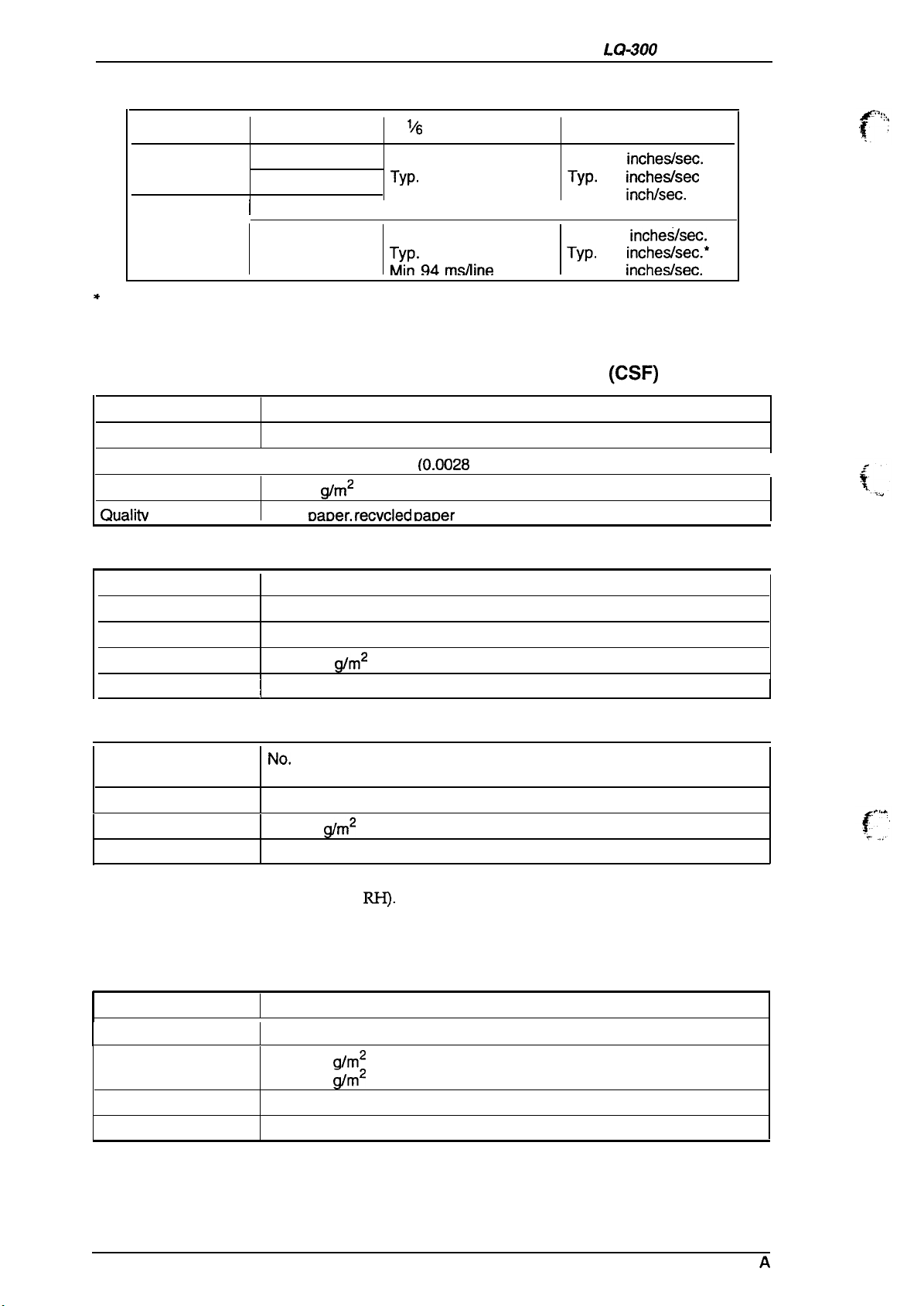
Product Description
LQ-300 Service Manual
Table 1-3. Feeding Speed
Lever Position Feeding
I
Friction
Tractor
Friction
o, 1
2-5
Tractor
*
Feed speed is varies depending on the motor driving voltage.
1/6
inch Line Feed Continuous Feed
Max. 94 ins/line
Typ.
80 ins/line (*)
Min. 75 ins/line Min. 2.8
I I
Max. 106
Typ.
Min 94
redline
104 ins/line (*)
m.s/line
1.2.1.2 Paper Specifications
Table 1-4. Specifications for Cut Sheet Paper
Width
Length
Thickness
Weight
Qualitv
182 mm -216 mm (7.2 in. -8.5 in.)
210 mm -364 mm (8.3 in. -14.3 in.)
10.07
64-90
Plain
mm -0.12 mm (0.0028 in. -0.0047 in.)
g/m2
(18 -24 lb.)
oaDer. recvcled DaDer
Table 1-5. Specifications for Cut Sheet Paper (Manual Insertion)
Max 3.6
Typ.
Max. 2.8
Typ.
Min. 2.2 incheskec.
incheslsec.
3.3 incheshec (*)
inchhec.
incheslsec.
2.5 inche.shec.’
(CSF)
I
Width
Length
Thickness
Weight
Quality
148 mm -257 mm (5.8 in. -10.1 in.)
182 mm -364 mm (7.2 in. -14.3 in.)
0.065 mm -0.14 mm (0.0025 in. -0.0055 in.)
g/m2
52.3-90
I
Plain paper, recycled paper
(14 -24 lb.)
Table 1-6. Specifications for Envelopes
Size
Thickness
Weight
Quality Bond paper (not curled, folded, or crumpled), plain paper, airmail paper
Notes: .
Printing of envelopes is guaranteed only at room temperature and normal humidity (15
No.
No. 10
0.16 mm - 0.52 mm (0.0063 in. - 0.0197 in.)
45- 91
- 25° C (59 - 77° F) ,20- 60%
● Variations in envelope thickness must be less than 0.25 mm (0.0098 in.).
. When inserting envelopes, keep the longer side horizontal.
Width x Length: 166 mm x 92 mm (6.5 in. x 3.6 in.)
6
Width x Length: 240 mm x 104 mm (9.5 in. x 4.1 in.)
g/m2
(12 -24 lb.)
RI-I).
Table 1-7. Specifications for Continuous Paper (Single Sheet and Multi-Part)
Width
Total thickness
Weights
Copies
Quality
101.6 mm - 254 mm (4.0 in. - 10.0 in.)
0.065 mm - 0.32 mm
52.3- 82
40- 58.2
4 sheets (1 original + 3 copies)
Plain paper, recycled paper, carbonless multi-part paper
g/m2
(14 - 22 lb.) — not multi-part
g/m2
(12 - 15 lb.) — multi-part
(0.0025 in. - 0.012 in.)
1-4
Rev.
A
Page 14
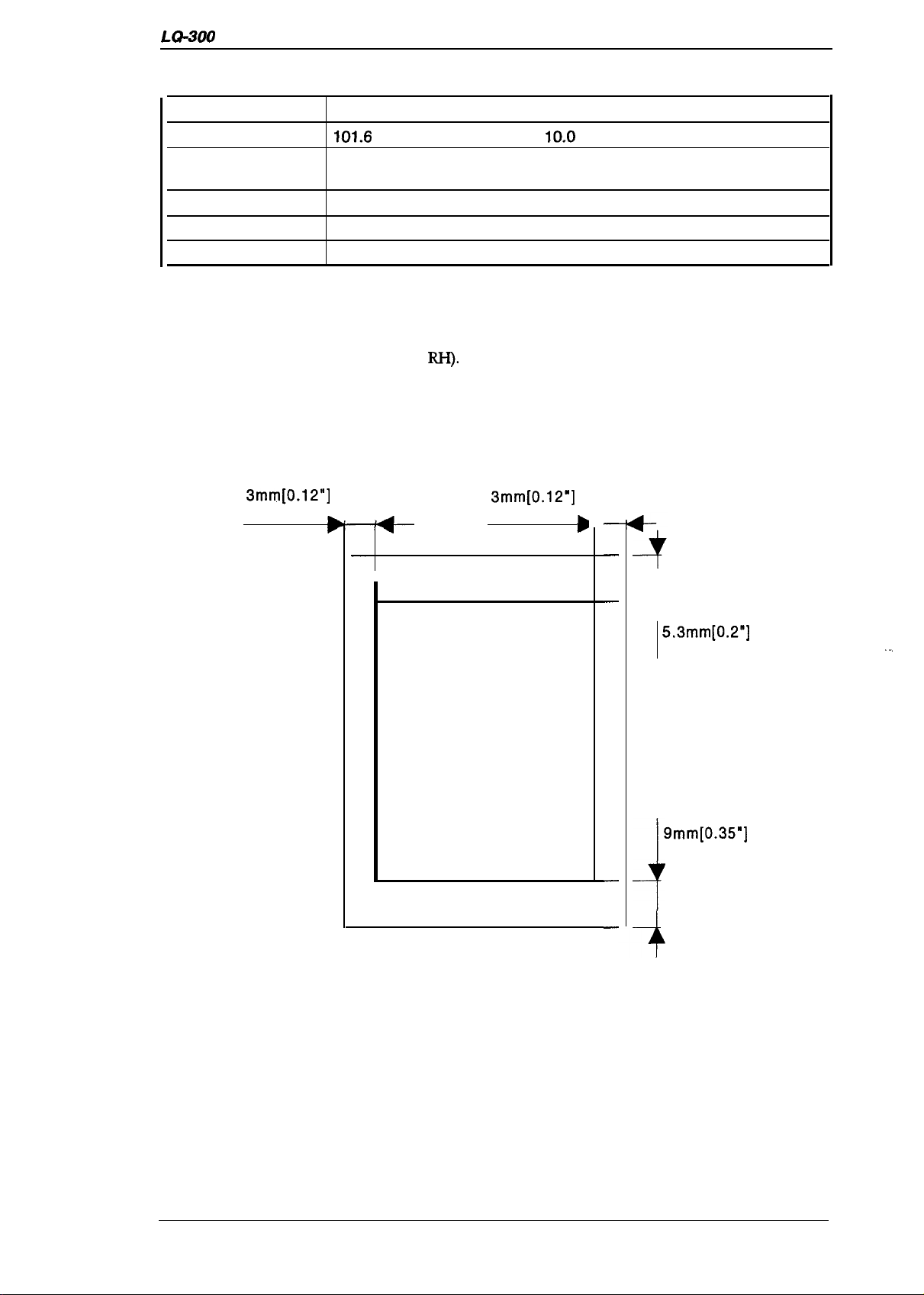
LQ-300 Service Manual
Table 1-8. Specifications for Continuous Paper with a Label
Product Description
Label size (W x L)
Width of base paper
Thickness of base
paper
Total thickness
Weight
Quality
Notes:
1.2.1.3 Printable Area
Cut sheets
●
Use only continuous-type labels and use them only with the tractor.
. Examples of labels
●
Printing of envelopes is guaranteed only at room temperature and normal humidity (15
- 25° C (59 - ’77° F) ,20-
3mm[0.12”]
minimum
63.5 mm (min.) x 23.8 mm (min.) [ 2.5 in. (min.) x 15/16 in. (min.)]
101.6
0.07 mm - 0.09 mm (0.0028 in. - 0.0031 in.)
0.16 mm -0.19 mm (0.0063 in. - 0.0075 in.)
68 g/m2 (17 lb.)
Plain paper
D
mm -254 mm (4.0 in. x
—Avery Continuous Form Labels
—Avery Mini-Line Labels
6(Mo
RI+).
3mm[0.12”]
G-
—
minimum
10,0
in.)
b
—
—
—
4
Printable area
—
4
—
Figure 1-3. Printable Area for Cut Sheets
5,3mm[0.2”]
minimum
9mm[0.35”]
minimum
.. :.,
Rev. A
1-5
Page 15
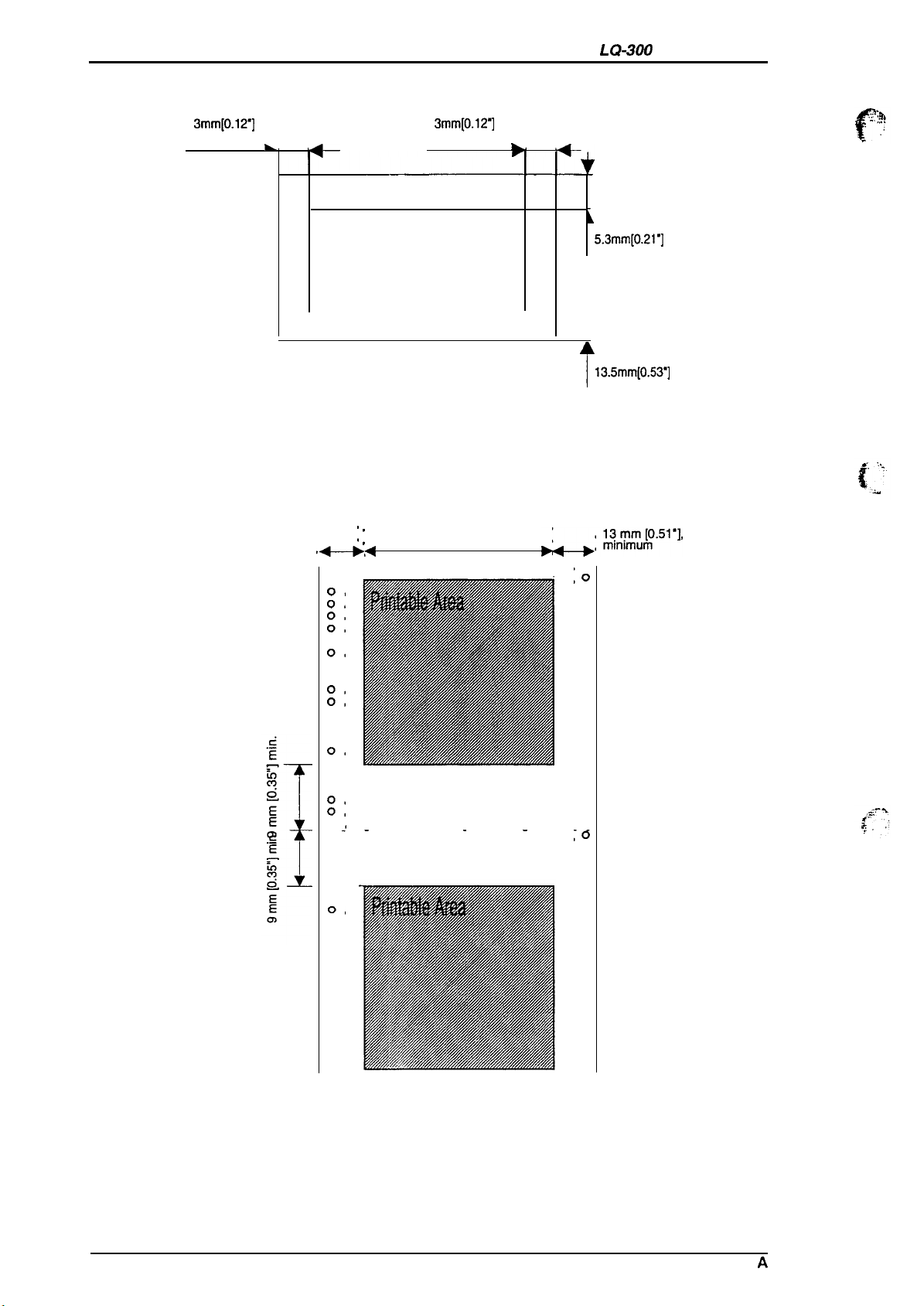
Product Description
Envelopes
LQ-300 Service Manual
3mm[0.12”]
minimum
Continuous paper
3mm[0.12”]
k,
Printable area
minimum
Figure 1-4. Printable Area for
13 mm 10.51 m], ~
minimum
4----++
:
203.2 mm [8”], maximum
0,
0,
06
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
.o---0,
0,
0,
0,
0
.,
. - . . . . . . . - . . . . - .
.
0,
0,
0,
0,
Q-r--
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0
4
0,
0,
0,
=,
A
T
Envelopes
:0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
:6
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
,0
L
5.3mm[0.21”]
minimum
13.5mm[0.53*]
minimum
1-6
Figure 1-5. Printable Area for Continuous Paper
Rev.
A
Page 16
LQ-300 Service Manual
1.2.1.4 Ribbon Specifications
Product Description
Ribbon cartridge (mono):
#7753
#7755 (sub-cartridge)
Ribbon cartridge (film):
Ribbon cartridge (color):
Ribbon color:
Black ribbon life:
Film ribbon life:
#7768
S015077
Black, magenta, cyan, yellow
2 million characters (48 dots/character)
0.2 million characters
(48
dots/character)
Color ribbon life
Black: 1 million characters (48 dots/character)
Magenta:
cyan:
Yellow:
0.7 million characters (48 dots/character)
0.7 million characters (48 dots/character)
0.5 million characters (48 dots/character)
1.2.1.5 Electrical Specifications
Table 1-9. Electrical Ranges
Description 120 V Version 230 V Version
Rated voltage
Input voltage range
Rated frequency range
Input frequency range
Rated current
I
I
I
120
VAC
103.5-132 VAC 198-264
50- 60
49.5- 60.5
1.1 A
t-fz
1
I
220-240
Hz
VAC
VAC
0.6 A
Dielectric strength
1.2.1.6 Environmental Conditions
1000
VAC
ms for 1 minute or
1200 VAC
(between AC line and chassis)
Temperature range:
Operation:
5to35“C (41 to 95 “F)
Operation (film ribbon): 15to35‘C (59 to 95 ‘F)
Operation (envelopes,
labels, or recycled paper): 15to25‘C (59 to
Storage:
–20 to55‘C (-4 to
Humidity (without condensation):
Operation:
Operation (film ribbon):
5 to
10 to
80?40 RH
80Y0 RH
Operation (envelopes,
labels, or recycled paper):
Storage:
20 to
to
5
60Y0 RH
W’/. RH
1.2.1.7 Reliability
rms
for 1 second
77°F)
131
‘F)
1500 VAC
(between AC line and chassis)
rms
for 1 minute
MTBF:
Printhead life:
Rev. A
4000
power on hours
(POH)
200 million strokes/wire (with monochrome ribbon)
100 million strokes/wire (with color and film ribbon)
1-7
Page 17
Product Description
1.2.1.8 Safety Approvals
LQ-300
Service Manual
Safety standards:
U.S. version:
European version: EN 60950
Radio frequency interference:
(RFI)
U.S. version:
European version:
1.2.1.9 Physical Specifications
Dimensions (W x D x H):
Weight without
1.2.2 Firmware
tractoc
Specifications
Control codes:
Input data buffer
Download memory:
Character sets:
Character
tables:
366 x 275x 141 mm (14.4 x 10.8x 5.6 inches) without tractor
4.3 kg (9.5 lb.)
ESC/P2
IBM X24E emulation
EPSON remote
8KB
10KB
14 international character sets and one legal character set
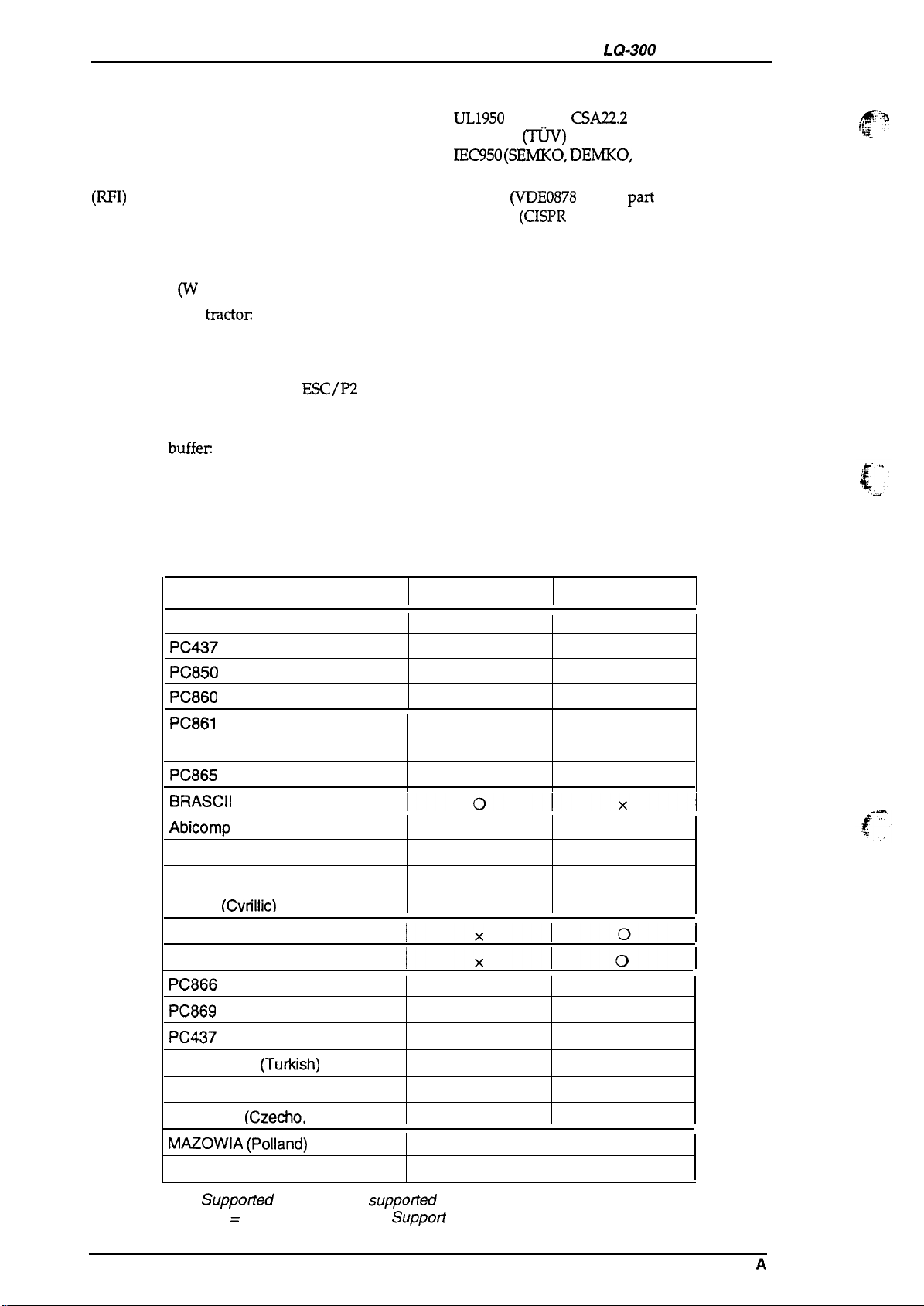
Table 1-10. Character Tables
UL1950
with D3,
CSA22.2
#950 with D3
~)
IEC950 (SEMKO, DEMKO,
NEMKO, SETI)
FCC part 15 subpart B class B
Vfg.243
EN55022
(VDE0878
(CISPR
PUB. 22) class B
part 3,
pati
30)
,ffq
L-.
.,
Character Table Standard Model NLSP* Model
ITALIC
PC437 (US, Standard Europe)
PC850 (Multilingual)
PC860 (Portuguese)
PC861
(Icelandic)
PC863 (Canadian-French)
PC865 (Norwegian)
BRASCII
Abicomp
PC852 (East Europe)
PC853 (Turkish)
PC855
PC857
PC864 (Arabic)
PC866 (Russian)
PC869 (Greek)
PC437 Greek
ISO Latin IT
ISO
Code MJK
MAZOWIA
Bulgaria (Bulgaria)
(Cvrillic)
(Turkish)
8859-7
(TuAish)
(Greek)
(Czecho,
(Polland)
Slovakia)
Iolxl
Ixlol
Ixlol
o 0
o 0
o
o
o
o x
o
o
x o
x
x
x
x
x
x o
x o
x
x o
x
0
x
x
x
x
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
Suppotied
0
‘ NSLP = National Language
1-8 Rev.
x Not
suppofled
Suppori
A
Page 18
LC?-300
Service Manual
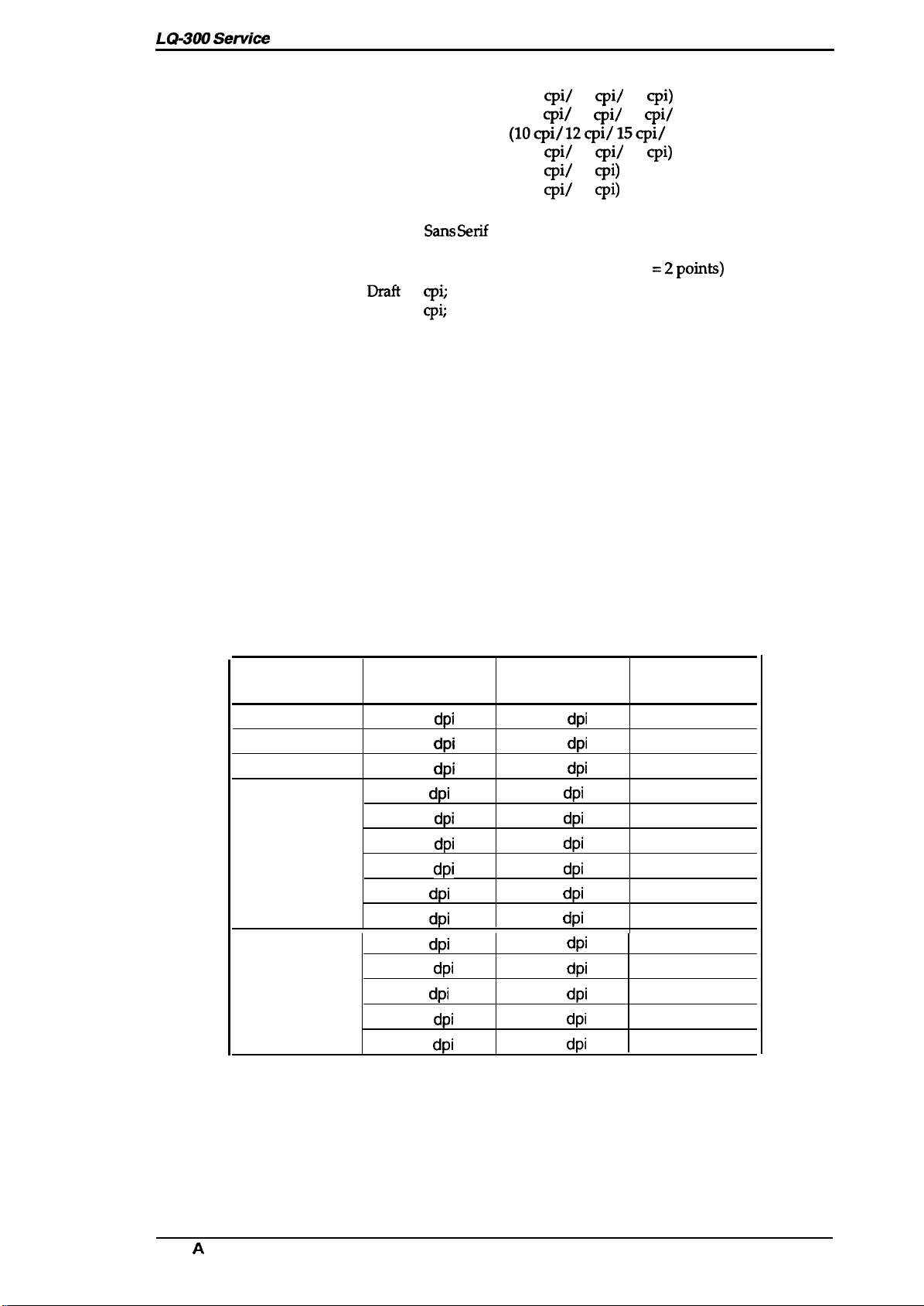
Bitmap fonts:
Scalable fonts:
Character matrix:
Print mode:
Resolution:
Printing speed and
printable columns:
Product Description
(10
cpi/
12
cpi/
15
EPSON Draft
(10
cpi/
12
12
12
12
cpi/
cpi/
cpi)
cpi)
EPSON Roman
EPSON Saris Serif
EPSON Courier
EPSON Prestige
EPSON Script
EPSON Roman
EPSON
!%ns serif
EPSON Roman T
(lOcpi/ 12cpi/ 15cpi/
(10
cpi/
(10
cpi/
(10
cpi/
8-32 points (units= 2 points)
8-32 points (units= 2 points)
8-32 points (units= 2 points)
EPSON Saris Serif H 8- 32points (units
Drailt
10
cpi;
12 horizontal dots, 24 vertical dots
NLQ 10
cpi;
36 horizontal dots, 24 vertical dots
cpi)
15
cpi/
Proportional)
Proportional)
15
cpi)
=2points)
Double-width
Double-height
Condensed
Bold
Double-strike
Italics
Super/subscript
Outline
Shadow
Underline (single, double, single-broken, double-broken)
Strike-through (single, double, single-broken, double-broken)
OverScore (single, double, single-broken, double-broken)
See Table 1-11.
See Table 1-12.
Printing Mode
Draft
Draft condensed
LQ
8-pin bit image
24-pin bit image
Table 1-11. Resolution
Horizontal
Density
dpi
120
240
dpi
360
dpi
60
dpi
dpi
120
dpi
120
240
dpi
80
dpi
dpi
90
dpi
60
dpi
120
dpi
90
dpi
180
dpi
360
Vertical Density
180
dpi
dpi
180
180
dpi
60
dpi
60
dpi
60
dpi
60
dpi
60
dpi
60
dpi
180
dpi
180
dpi
180
dpi
180
dpi
180
dpi
Adjacent Dot
Printed?
No
No
No
Yes
Yes
No
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Rev. A
1-9
Page 19
Product Description
LWOO Service Manual
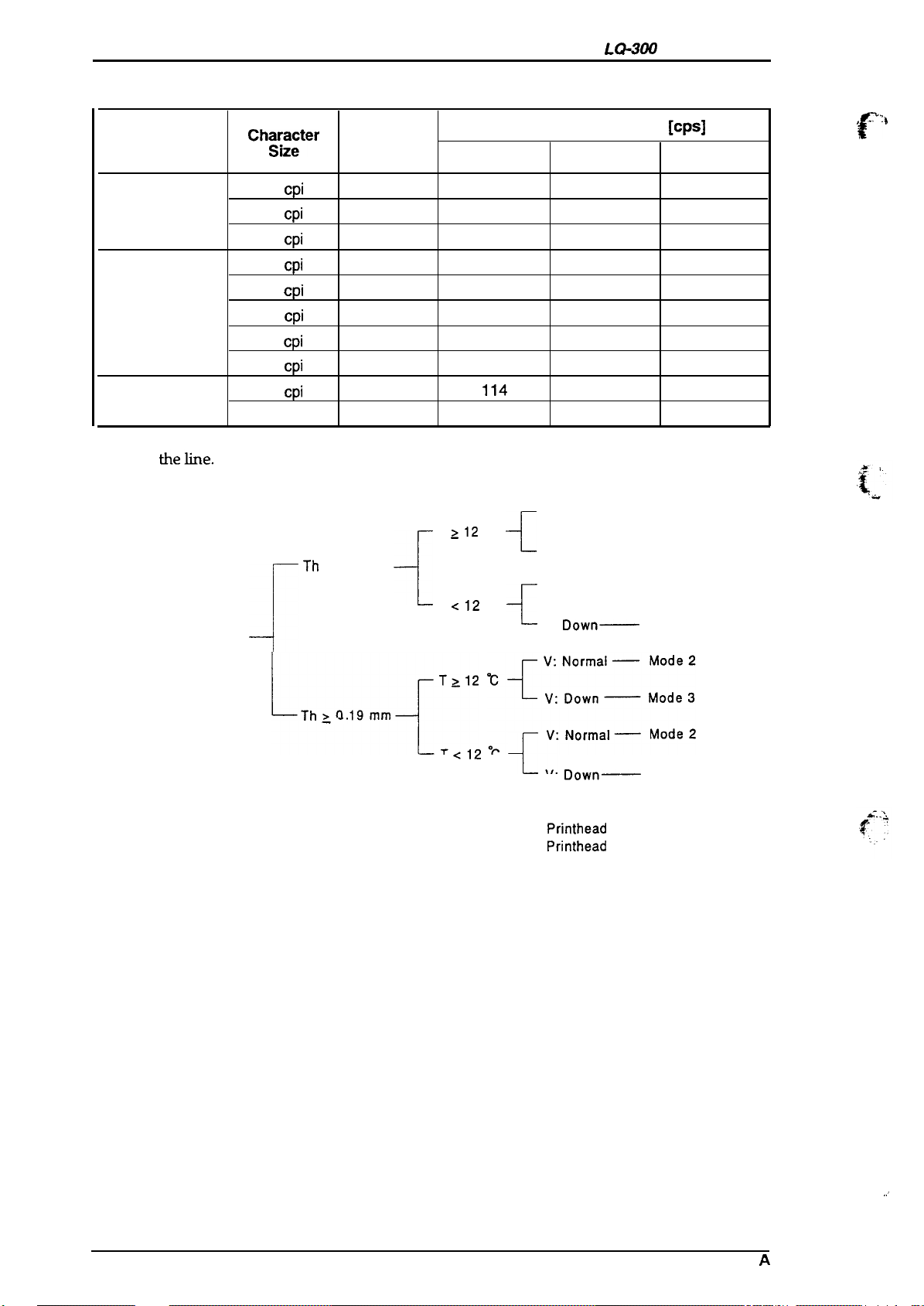
Table 1-12. Printing Speed
Printing Mode
Draft
Draft condensed 17
LQ condensed
Vote:
Each maximum print speed is changeable depending on attributes of characters within
Printing Mode
Chg\;gter Printable
10
12
15
20
10
12
15
17
J
Maximum Print Speed
Columns
cpi
cpi
cpi
cpi
cpi
cpi
cpi
cpi
cpi
20 160
Th
c 0.19 mm
80
96
120
137
160
80
96
120
137
{
~Th>01,mm{T212
Mode 1
200
240
300
171
200
67 50
80
100
114 86
133 100
T
>12
“C
--c
T
<12
“C
+_
.+;:;:;:
V: Normal —
V: Down
V: Normal
V:
Mode 2
133
160
200
114
133
60
75
Down—
Mode 1
—
Mode 3
—
Mode 2
Mode 3
[cps]
Mode 3
.}
F“
100
120
150
86
100
33
40
50
57
67
-.
T
<12
“C
{“
V:
Down—
Th: Paper thickness
T :
Printhead
V :
Printhead
Mode 3
temperature
driving voltage
1-1o
Rev.
,,,
A
Page 20
LQ-300 Service Manual
1.3 INTERFACE SPECIFICATIONS
Product Description
LQ-300
has a
Centronics<ompatible
parallel interface and an
EIA-232D
serial interface, one of
which can be selected in default setting mode. Auto selection is also available.
1.3.1 Parallel Interface
The parallel interface has two modes:
. Compatible mode
● Reverse mode
1.3.1.1 Compatible Mode
Data format:
Synchronization:
Handshaking:
Signal level:
Adaptable comector:
Data transmission timing:
Note:
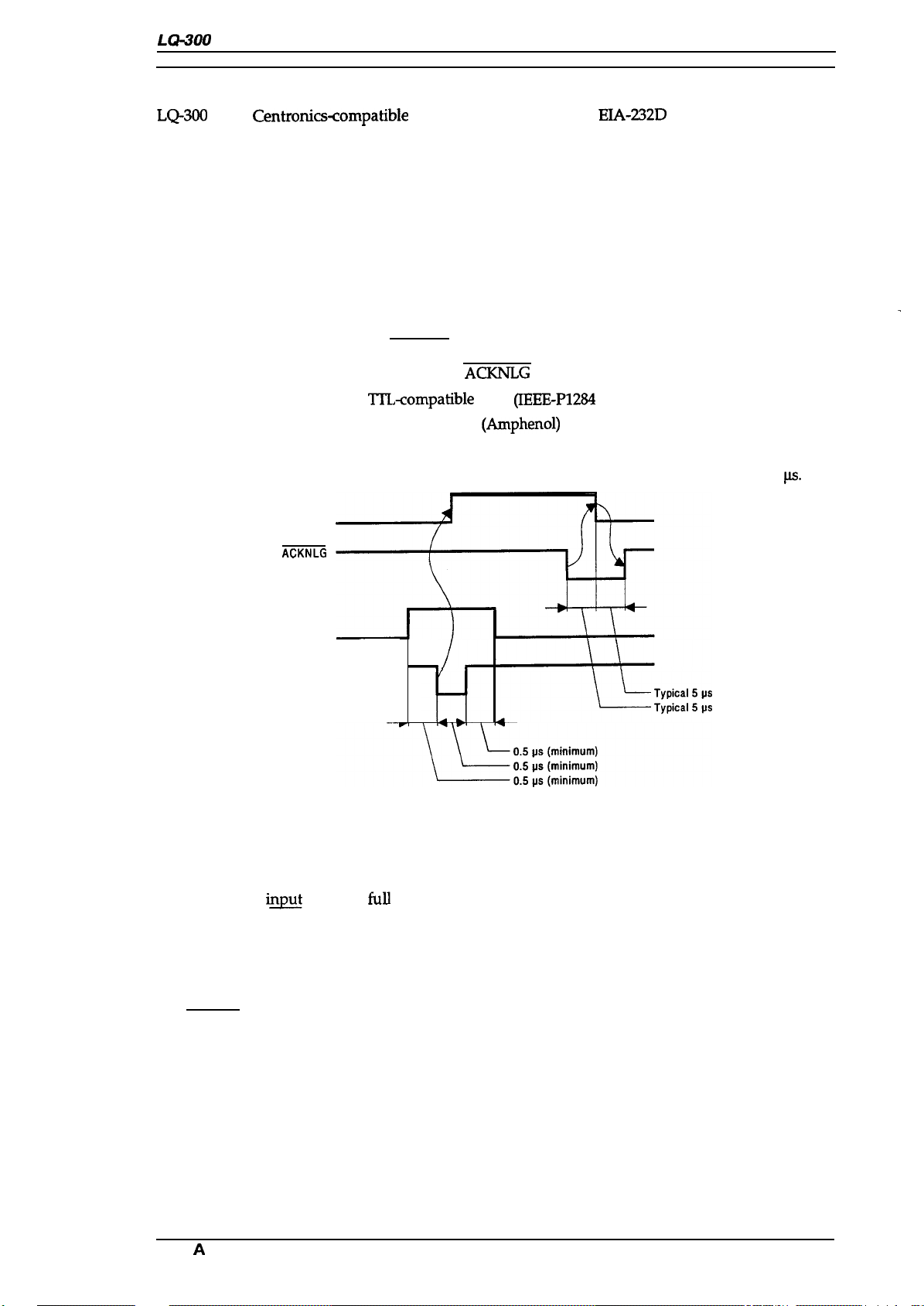
Transition time (rise time and fall time) of every input signal must be less than 0.2
BUSY
ACKNLG
8-bit parallel
By STROBE pulse synchronization
By BUSY and
Tl_’L-compatible
36-pin 57-30360
ACKNLG
level
(IEEE-P1284
(Amphenol)
signals
level 1 device)
or equivalent
See Figure 1-6.
.
ps.
DATA
STROBE
—
~
.
Figure 1-6. Data Transmission Timing
The BUSY signal is active (HIGH) under the following conditions:
. During data reception (See Figure 1-6.)
●
When the
. When the INIT input signal is active
. During a printer error
. During the self-test mode
. During the default setting mode
. When the parallel interface is not selected
The ERROR signal is active (LOW) under the following conditions:
. When a paper-out error occurs
. When a release lever operation error occurs
●
When a fatal error occurs
innt
buffer is
full
The PE signal is active (HIGH) under the following conditions:
●
Rev.
When a
A
paper-out error occurs
1-11
Page 21
Product Description
LQ-300
Service Manual
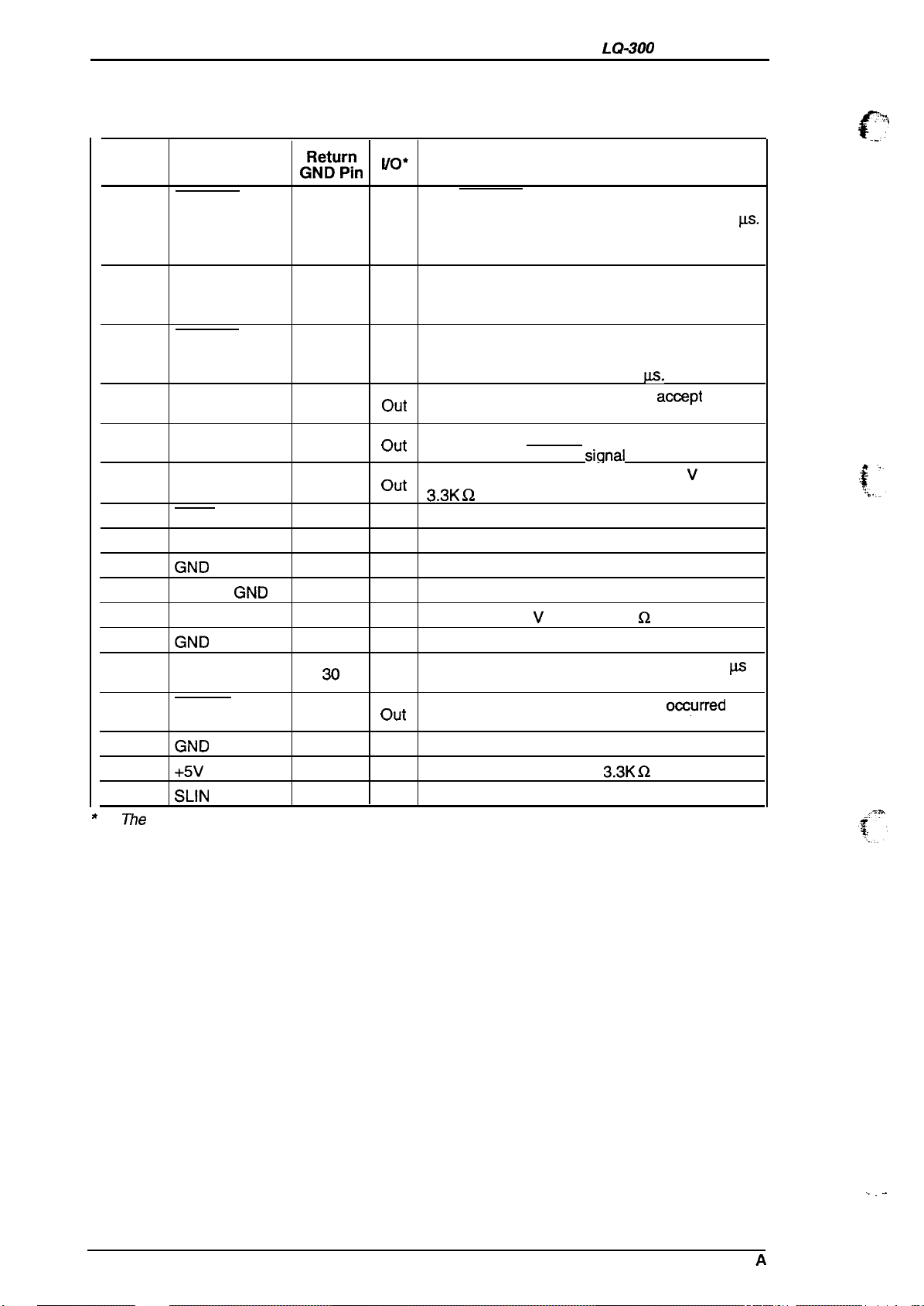
Table 1-13 shows the connector pin assignments and signal functions for the 8-bit parallel interface.
Table 1-13. Signal and Connector Pin Assignments for Parallel Interface
Pin No.
2-9
10
11
12
13
14
15,34
16
17
18
19-30
31
32
33
35
36
*
7%e
1
Signal Name
STROBE
DATAO-DATA7
ACKNLG
BUSY
E
‘
SLCT
AFXT
NC
GND
Chassis
LOGIC-H
GND
INIT
ERROR
GND
+5V
SLIN 30
//0 column indicates the direction of the signal as viewed from the printer.
GND
(!!%”%
19
20-27
28
29
28
28
30
.
—
—
—
. —
30
29
—
—
‘0’
The STROBE pulse is used to read the input
data. The pulse width must be more than 0.5
In
Input data is latched after the falling edge of this
signal.
Parallel input data to the printer.
In
out the printer is ready to accept more data. The
out
out
out
In
—
—
—
out Pulled up to +5
In
out
—
out Pulled up to +5 V through
In
A HIGH level means data 1.
A LOW level means data O.
This pulse indicates data has been received and
pulse width is approximately 12
HIGH indicates the printer cannot acoept more
data.
HIGH indicates paper-out. This signal is effective
only when the ERROR
Always HIGH output. (Pulled up to +5 V through
3.3K Q resistor.)
Not used.
Not connected.
Signal ground.
Chassis ground.
Signal ground.
Input for printer initialization. Pulse width 50
minimum, active LOW.
LOW indicates that some error has
the printer.
Signal ground.
Not used.
Description
U.S.
signal
is LOW.
V
through 3.9K Q resistor.
o=urred
3.3K Q
resistor.
.%
c
ps.
{,,’”.
w
in
-c.-
‘{‘
1-12
. . .
Rev. A
Page 22
LQ-300 Service Manual
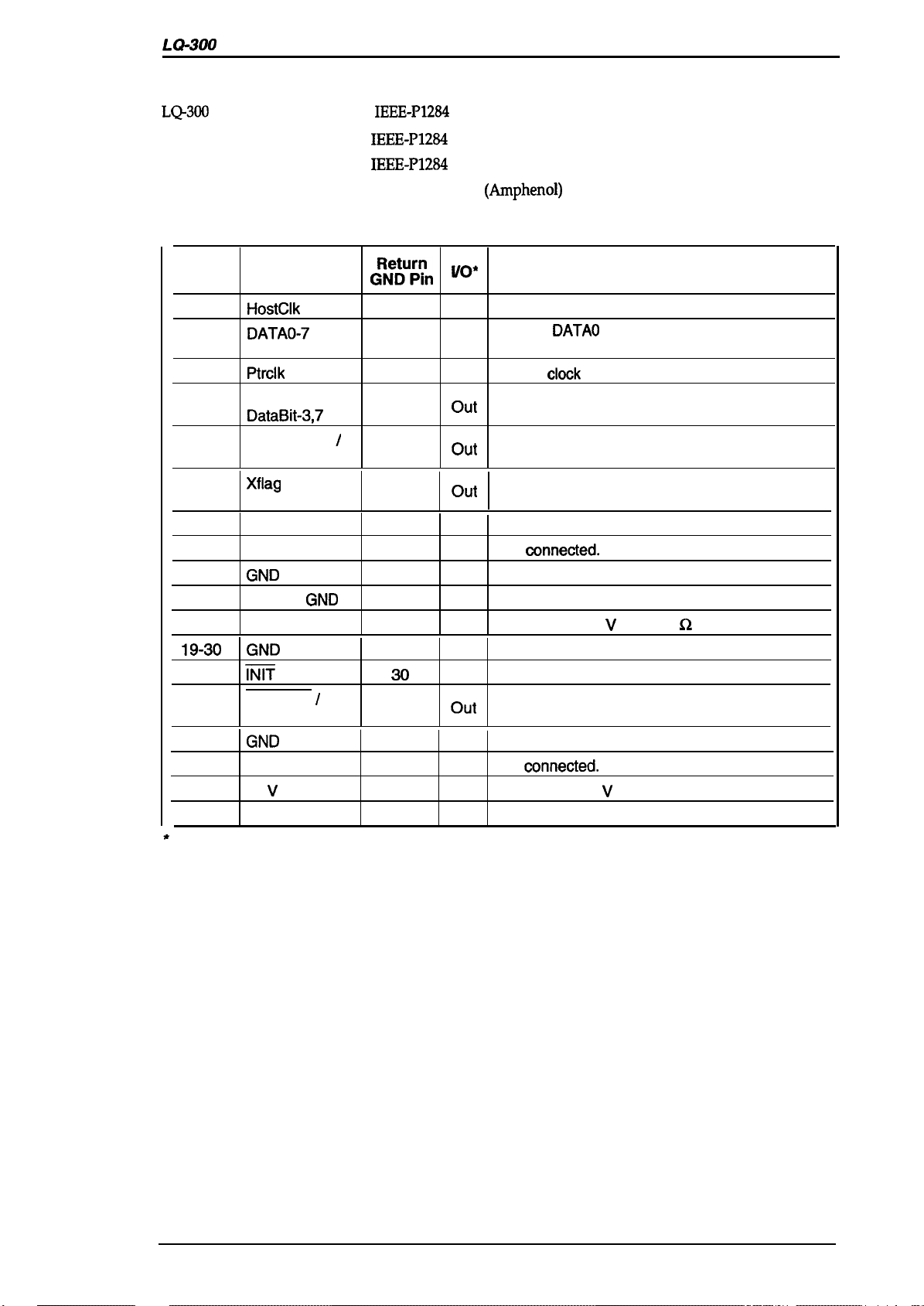
1.3.1.2 Reverse Mode
LQ-300
reverse mode supports
IEEE-P1284
nibble mode, described in this section.
Product Description
Transmission mode: IEEE-P1284
Signal level:
Adaptable connector:
IEEE-P1284
36-pin 57-30360
nibble mode
level 1 device
(Arnphenol)
or equivalent
Table 1-14. Signal and Connector Pin Assignments for Parallel Interface
Pin No. Signal Name
1
2-9
10
11
12
13
14
15 NC
16
17 Chassis
18
19-30
31
32
33
34
35
36
*
The l/O column indicates the direction of the signal as viewed from the printer.
HostClk 19
DATAO-7
Ptrclk
PtrBusy /
DataBit-3,7
AckDataReq
DataBit-2,6
Xflag
I
DataBit-l,5
HostBusy
GND
GND
Logic-H
GND
m
DataAvail
DataBit-0,4
GND
NC
v
+5
1284-Active
/
/
C%%”%
20-27
28
29
28
28
30
—
.
— —
—
—
30
29
— —
—
—
30
‘0’
In
In
out
out
out
out
In
—
—
out
—
In
out
—
out
In
Host clock signal.
Signals
bits O to 7.
Printer
Printer busy signal and reverse channel transfer
data bit 3 or 7.
Acknowledge data request signal and reverse
channel transfer data bit 2 or 6.
X-flag signal and
bit 1 or5.
Host busy signal.
Not oonnected.
Signal ground.
Chassis ground.
Pulled up to +5
Signal ground.
Not used.
Data available signal and reverse channel
transfer bit O or 4.
Signal ground.
Not oonnected.
Pulled up to +5 V via 3.3K S2 resistor.
1284 active signal.
DATAO
clook
Description
through DATA7 represent data
signaL
reverse channel transfer data
V via 3.9K Q resistor.
Rev. A
1-13
Page 23
Product Description
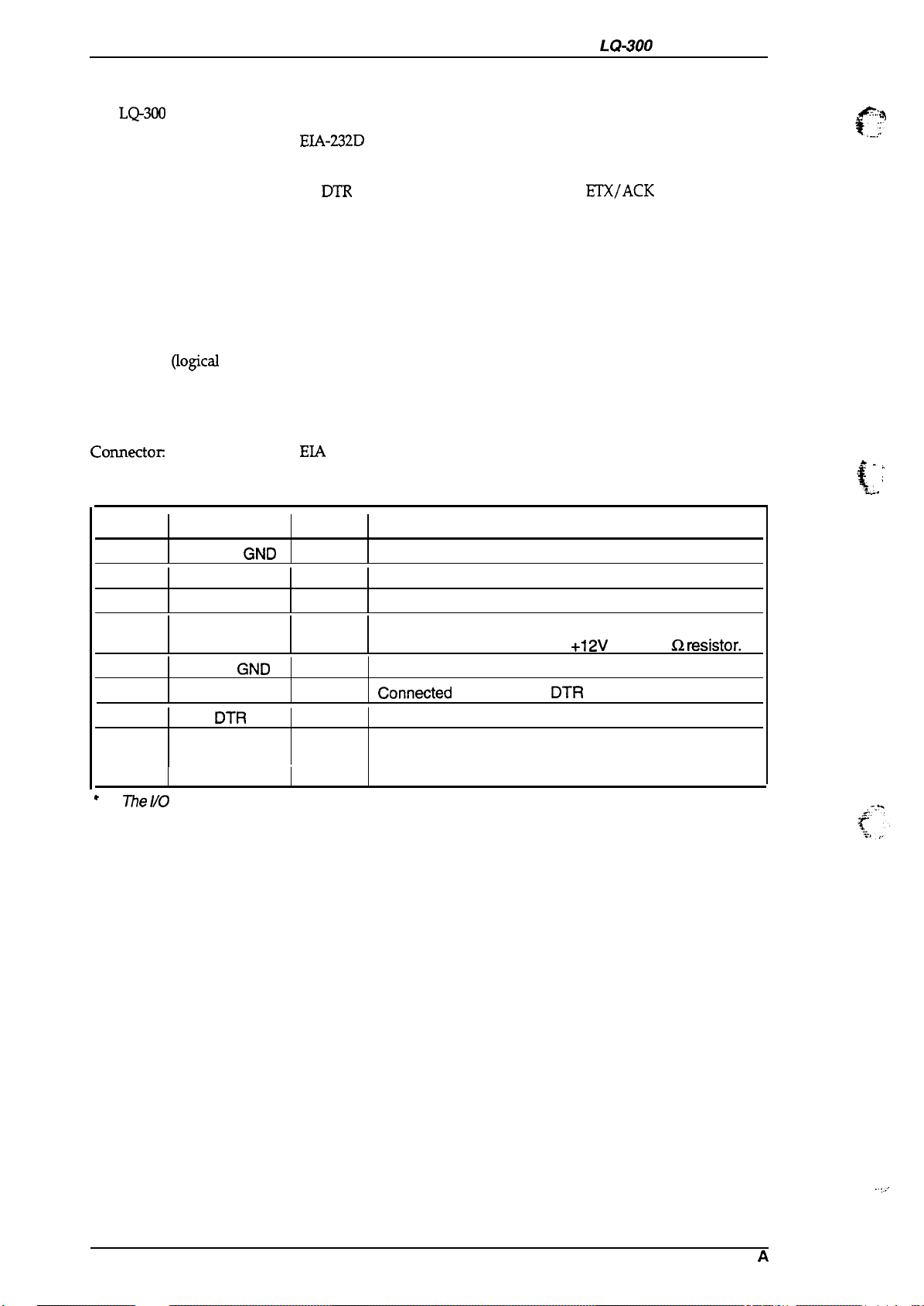
1.3.2 Serial Interface
The
LQ-300
is equipped with an 8-bit serial interface, standard.
LQ-300 Service Manual
Data format:
EIA-232D
serial
Synchronization: Asynchronous
Handshaking:
protocol, X-ON/X-OFF protocol,
ETX/ACK
protocol
By
DTR
Word length
Start bits: 1 bit
Data bits: 7 or 8 bits (selectable)
Parity bit:
Stop bits:
Bit rate:
Odd, even, or none (selectable)
1 bit
300,600,1200,2400,4800, 9600,19200 bps (selectable)
Logic level
MARK
SPACE (logical O):
~OgiCid
1):
–3 V to –25 V
+3 v to +25 v
Parity check:
Connectoc
Odd, even, or no parity bit (selectable)
EIA
standard 25-pin D-SUB female comector
Table 1-15. Signal and Connector Pin Assignments for Serial Interface
Pin No. Signal Name
1
2
3 RXD
4
7
11
20
5,6,8-10,
12-19, NC
21-25
*
l%e
Chassis
Signal
//0
column indicates the direction of the signal as viewed from the printer.
GND
TXD
RTS
GND
REV
DTR
I/o’
—
out
In
out
—
out
out
—
Chassis ground.
Transmit serial data.
Receive serial data.
Request to send. Always SPACE level when the printer
is powered on. Pulled up to
Return path for data and control signals.
Conneoted
Indicates that the printer is ready to receive data or not.
No connection (not used).
directly to the
Description
+12V
DTR
signal.
via 4.7K Q wsistor.
* .
.
.
\ ~
>,
.
1-14
Rev.
,-,...
A
Page 24

LQ-300 Service Manual
1.3.3 Interface Selection
Product Description
The printer has 2 interfaces: parallel and serial.
These interfaces can be selected manually in
default-setting mode or selected automatically.
●
Manual selection
One of the two interfaces can be selected in default-setting mode.
. Automatic selection
When automatic interface selection is enabled in default-setting mode, the printer is
initialized to idle state scanning, in which an interface receives data when it is powered
on, and the interface that receives data first is selected. When the host stops data transfer,
and the printer is in the standby state for 10 or 30 seconds (time selectable in the
default-setting mode), the printer returns to the idle state. As long as the host sends data
to the printer interface in the BUSY state, the currently selected interface remains the
same.
. Interface state and interface selection
When the parallel interface is not selected, the interface is in the BUSY state. When the
serial interface is not selected, the interface sends X-OFF and sets the
When the printer is initialized or returned to the idle state, the parallel interface is in a
READY state, the serial interface sends X-ON and sets the
that the interrupt signal such as a INIT signal on the parallel interface is not effective
while that interface is not selected.
1.3.4 Preventing the Host from Data Transfer Timeout
DTR
signal MARK.
DTR
signal SPACE. Notice
Hosts abandon attempts at data transfers to peripherals when a peripheral is in BUSY state for
dozens of seconds continuously. To prevent hosts from this
ldnd
of timeout, the printer receives
data very slowly, several bytes per minute, even if the printer is in BUSY state. This slowdown is
started when the rest of
the
input buffer becomes several hundreds of bytes. Finally, when the
input buffer is full, the printer goes into the BUSY state continuously.
Rev. A
1-15
Page 25
Product Description
LQ-300
Service Manual
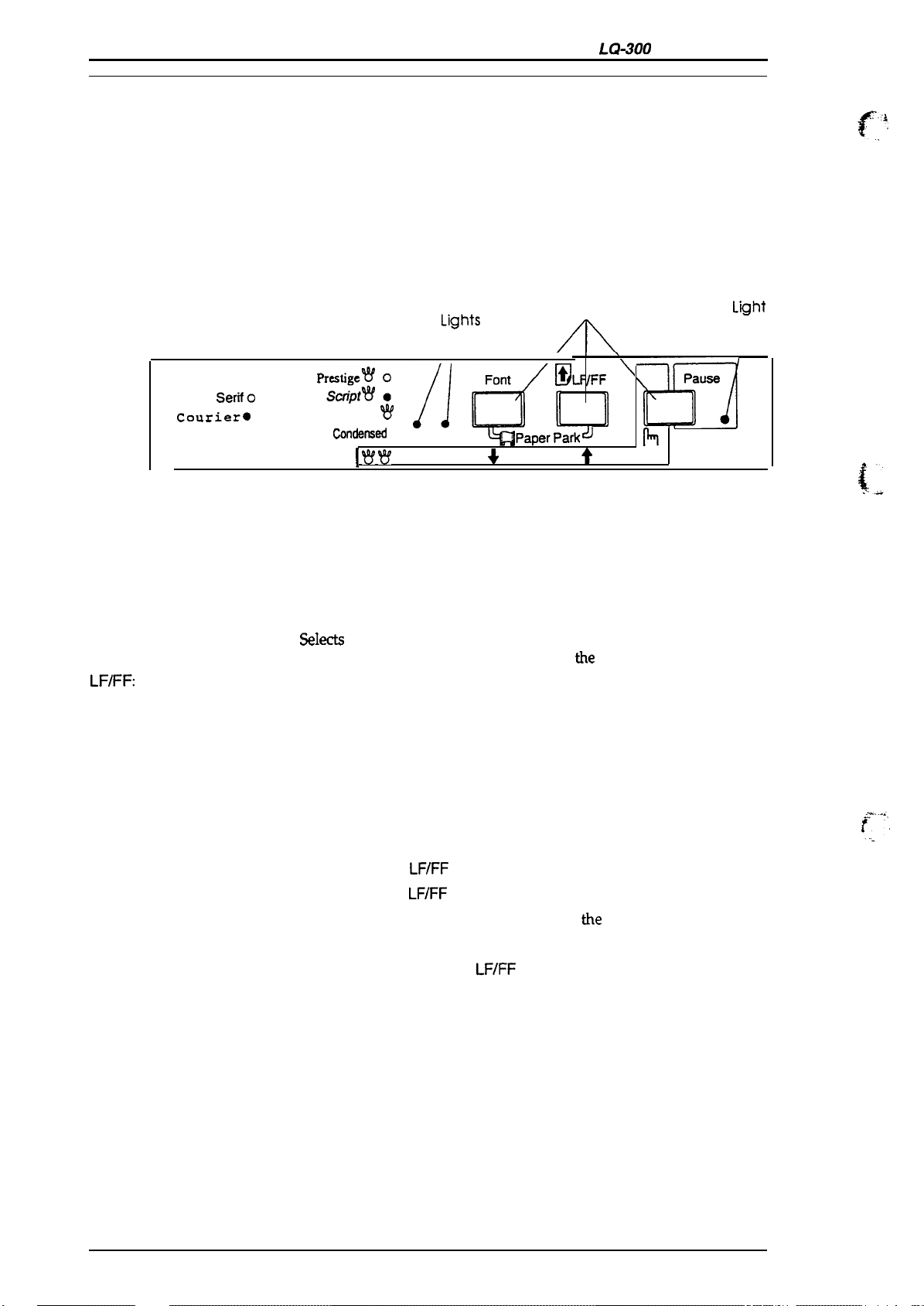
1.4 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
This section describes control panel operation functions, self-test, hexadecimal dump, paper feed,
micro adjustment, and printer initialization methods.
1.4.1 Control Panel Operation
The printer control panel contains three non-lock-type push buttons and three LED indicators for
easy operation of the various printer functions.
Buttons
Pause:
Font:
LFIFF:
Indicators
Roman
Saris
Courier*
Seriio
O 0
●
O
I.ight
Draft
Py:li!: :
Draft O
Condensad
I W ~
W
//
● ● I 2
Micro Adjust
Lights
A
Font
~1’[1
Paper
Buttons
&
Parkd
/FF
1’
Pause
$!!d
h
3sec
Figure 1-7. Control Panel
Switches printer status between printing and no printing, if there is
print data in the input buffer. When the printer is out of paper, the
light flashes and the beeper sounds three times.
S&c&
one of the available fonts. When you hold down this button
while you turn on the printer, you enter
When you press this button, the printer feeds paper line by line.
Hold it down to load a single sheet, or to advance continuous paper
to next top-of-form position.
the
printer setting mode.
Pause (Orange):
Font 1 and 2 (Green):
Special Mode
Self-test mode:
Hex dump mode:
Default-setting mode:
Micro adjustment mode:
Paper park mode:
Lights when the printer in pause mode.
Indicates the currently selected font.
Hold down the
Hold down the
Hold down the
Hold down the
Hold down the
LF/FF button
LF/FF
and Font
Font
buttons and turn on
Pause
Font and
and turn on the printer.
buttons and turn on the printer.
button or
LF/FF
buttons together.
Font
the
button.
printer.
1-16
Rev. A
Page 26
LC?-300
Service Manual
Product Description
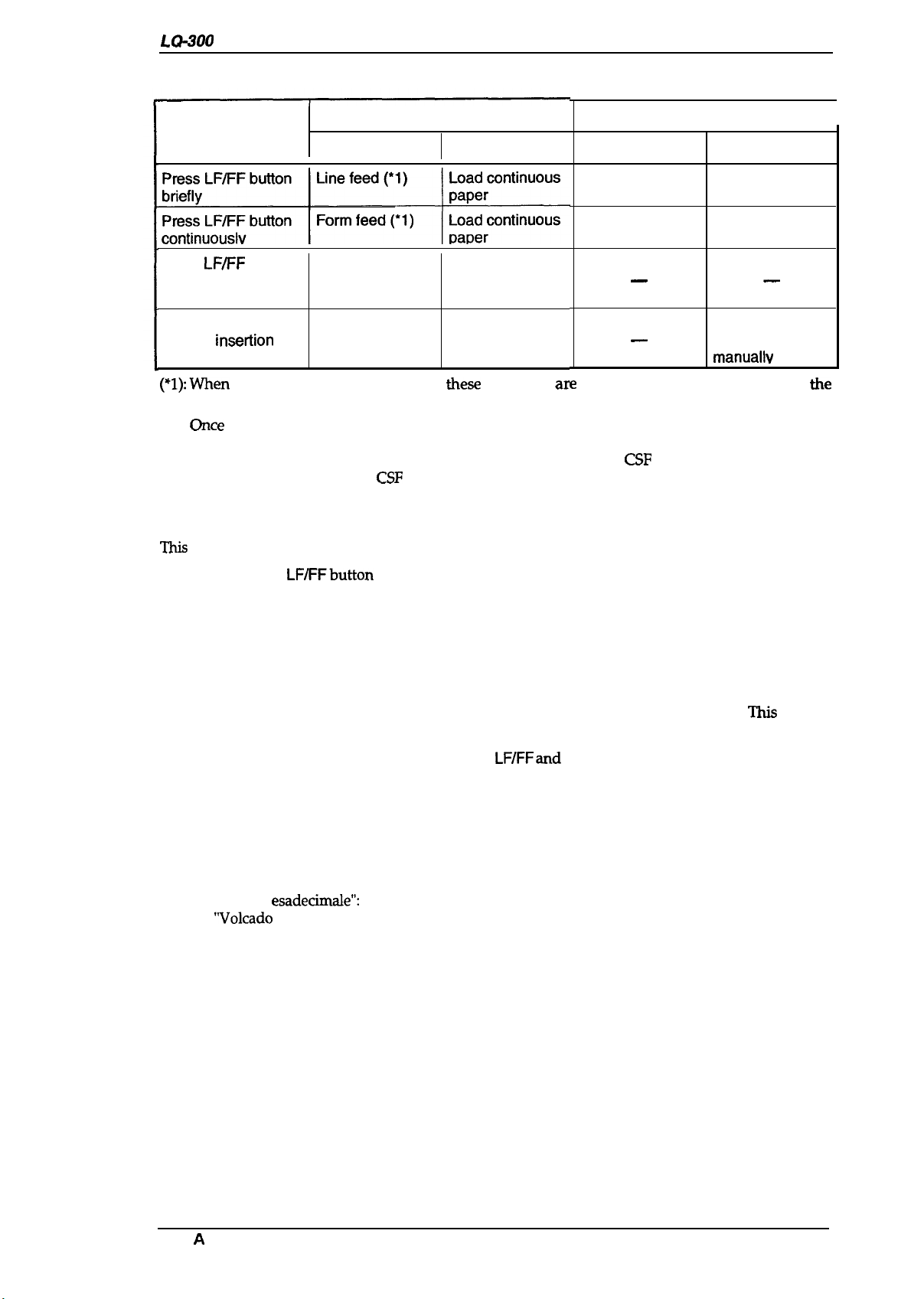
Table 1-16. Paper Feeding Functions
Tractor Feed
Operations
Not Paper Out Paper Out State
Press
LF/FF
and
Font buttons at the
same time
Insert a sheet to the
manual insetiion slot
(*l):~@n
the printer is in tear-off state,
Paper park (*1)
— —
—
the.w
functions a~ performed after returning from
tear-off position.
(*2)
Gce
a manually inserted sheet is loaded, the printer enters manual insertion mode. After
that, even if data remains
in the buffer, the printer goes into a paper out error state at the end
of every a sheet and waits for insertion of the next sheet. The
loading operation from the
CSF
or by
initialization.
1.4.2 Self-test Function
W
section explains how to run the self-test.
Friction Feed
Not Paper Out
Line feed
Eject
—
—
CSF
is enabled again by sheet
Paper Out State
Load a sheet (*2)
Load a sheet (*2)
—
After 2 seconds
load the sheet
manuallv
(*2)
the
I
1. Hold down the
LF/FFbutton
and turn on the printer to start the self-test.
2. If paper is not loaded, the printer attempts to load it.
3. The printer prints alphanumeric characters continuously.
5. Quit self-test mode printing bypressingthe
Pause
button and turning the printer off.
1.4.3 Hexadecimal Dump Function
The hexadecimal dump is a useful tool for troubleshooting data control problems.
describes how to run a hex dump.
1.
Turn on the printer while holding down the
2.
If paper is not loaded, the printer attempts to load it (either single sheet or continuous paper).
3.
If the printer cannot Ioad the paper, it indicates a paper-out error. In this case, insert paper
again, and press the
4.
The printer waits for data after printing the message “Hex dump(*).”
“Hex Dump”:
“Codes Hexadecirnaux”:
“Dump
“Volcado
5.
Received data is printed as both hexadecimal codes and ASCII characters. If a corresponding
esadecimale”:
hex”:
Pause
button.
English or German is selected
French is selected
Italian is selected
Spanish is selected
LF/FF and Font
buttons.
printable character does not exist, the printer outputs a period (.).
6.
Quit hexadecimal dump printing by pressing the PAUSE button and turning the printer off.
Note:
In
hex dump mode, the character table depends on the default setting, and 10 cpi draft is
selected automatically.
This
section
Rev.
A
1-17
Page 27

Product Description
LQ-300
Service Manual
1.4.4 Micro Adjustment Function
To enter adjustment mode, press the Pause button for three seconds, until the printer beeps once
and the
Pause
lights
bhnk
to indicate that the adjustment
operation is available. If the printer state
is not one of the conditions shown below, this operation is ignored.
● TOF position adjustment:
The position can be adjusted just after the paper is loaded.
● Tear-off position adjustment:
The position can be adjusted when paper is actually located at the tear-off position.
. . .
‘~
f
.,
.
.
In the adjustment mode, press the
paper backward. You can cancel adjustment mode by pressing the
LF/FF button
to feed paper forward and the
Pause
Font
button or inputting a
button to feed
print coremand. The adjusted position is stored in non-volatile memory.
1.4.5 Printer Status Indication
This section describes how the printer indicates status and error conditions using LEDs and the
beeper.
The symbols below describe the frequency of beeper sounds.
(.):
The beeper sounds for 100 rns with an interval of 100 ma between beeps.
(—): The beeper sounds for500rns.
While initialize
signal is active:
During initialization:
Standby or printing state:
Pause state:
Micro adjustment mode:
Tear-off:
Paper-out error
state(”l)
Operating error (~), fatal error (*3):
Notes:
Pause light is on.
Pause light blinks
Pause
light is off
Pause light is on
Beeper sounds (
(light
on:off
Pause light blinks (light
ratio=
●
)
and
Pause light blinks.
1:1)
on:off
ratio=
1:6)
Beeper sounds (.. . ) and Pause light blinks
(light
on:off
ratio=
Beeper sounds (—
6:1)
) and Pause light is on.
(*1):
(*2):
(*3):
A paper-out error occurs with any of the following conditions:
●
Paper is not loaded after loading is attempted.
●
A full sheet finishes printing after single sheet loading by manual insertion.
●
The end of
condrmous
paper is reached.
When a paper-out error occurs, the printer stops printing and enters the pause state. After
that, when a sheet is loaded, the PAUSE light stops blinking and the light stays on, but
the printer remains in the pause state. Press the PAUSE button to start printing.
An operating error occurs for any of the following conditions:
●
The release lever is set to the TRACTOR position without ejecting cut sheets.
●
The release lever is set the FRICTION position without ejecting continuous paper.
A fatal error occurs with any of the following conditions:
●
Power supply voltage is abnormal.
●
Printhead temperature is abnormal.
1-18
.,
Rev. A
Page 28
LQ-300 Service Manual
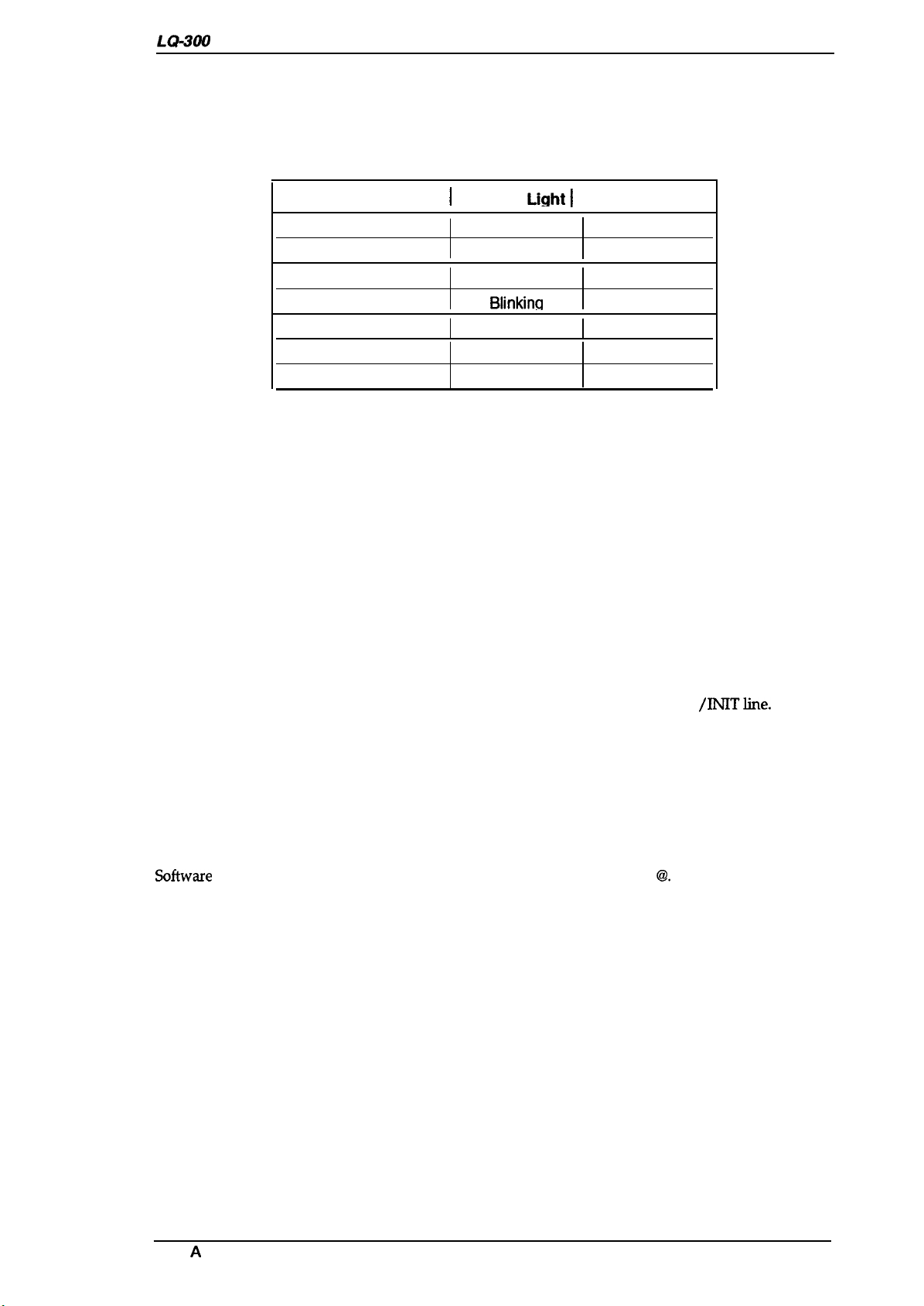
1.4.6 Selected Font
Product Description
The combination of two
To choose one of the seven internal fonts listed on the control panel, press the
Font
LEDs (1 and2) is used to indicate the selected font.
Font
button.
Table 1-17. Font Selection
Selected Font\ Font 1
Roman
Saris Serif
Courier
Prestiae
script
Draft
Draft condensed
Light I
On
On
off
Blinkina
Blinking
On
off
Font2 Light
On
off
On
On
off
Blinking
off
1.4.7 Printer Initialization
There are three types of initialization:
software initialization.
power-on initialization, hardware initialization, and
1.4.7.1 Power-on Initialization
The power-on initialization is performed by turning the printer powered on. When the power-on
initialization is performed:
. The printer mechanism is initialized.
●
The
hardware initialization is performed.
1.4.7.2 Hardware Initialization
Hardware initialization is performed by:
. Turning on the printer.
. The falling edge of a negative pulse ora low signal on theparallel interface
/INITline.
When hardware initialization is performed:
●
Print data in the input buffer is cleared.
. Download character definitions are cleared.
. The printer’s settings areretumed to the defaults.
●
The
printer is set to the standby condition, if no fatal error occurs.
1.4.7.3
Softwme
Software
initialization is performed upon receipt of the control code ESC
Initialization
62.
When software
initialization is performed:
●
Print characters in the buffer are not cleared.
. The printer setting is changed to the default, but download character definition is not cleared.
Rev. A
1-19
Page 29

Product Description
LQ-300
Service Manual
1.4.8 Printer Settings
1.4.8.1 Selectable Printer Settings
The following printer settings can be changed by users in default-setting mode:
Character table (Standard):
Character table
(NLSP):
Page length:
l-inch skip-over-perforation:
Auto tear off:
Graphic print direction:
Software
AGM:
Auto line feed:
Interface:
Bit rate (serial I/F):
Parity bit (serial I/F):
Data length (serial):
ETX/ACK
(serial):
State reply
Note:
Underlines show factory setting.
PC437/850/860/861
PC437/437 Greek/850 /852/853/855/857/864/866/869
IT
/1S0
8859-7/Code
/863/865
/BRASCII/Abicomp
MJK/Ma.zowia/Bulgaria
/1S0
Latin
11 /12/ 8.5/ 70/6 inches (A4)
on/Qff
on/mf
Unidirectional / Bidirectional
ESC/P2
on/
/ IBM
Q.tl
X24E
on/Qf
Auto selection (10 second wait) / Auto selection (30 second wait)/
Parallel / Serial
300 / 600/ 1200/ 2400/ 4800/
!26Q!2
/
19200
bps
None / Odd/ Even
7bits / 8 bits
on/Qll
on/Qff
1.4.8.2 Changing the Default
Settings
You can change some parameters that the printer refers to at printer initialization.
1. To enter the default setting mode, turn on the printer while holding down the
Font
button,
The printer prints out the firmware version. Ifpaperisnot loaded, insert a sheet of paper.
2. The printer automatically loads paper and prints a table of languages to choose from: English,
French, German, Italian, and Spanish. The
Font
lights indicate the currently selected language,
as shown in the table below.
Table 1-18. Font Lights and Language Selection
Font 2 Light
ON
Blinks
OFF German
ON
Blinks
3. Press the
Font
4. Press the Font
Font 1 Light
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
button to change the language, and press the
button
again after selecting a language. The printer prints help text to guide
you in setting defaults. The printed instructions include submenu tables listing all the settings
you can change and showing you how the control panel lights appear for each selection.
5. To change the settings, press the Font button to move down and press the
move up in the menu of options shown below. The printer beeps once each time you press the
these buttons while you are in this menu.
Language
English
French
Italian
Spanish
LF/FF
button to select.
\
I
LF/FF
button to
<-’
.,
1-20
., .,
Rev. A
Page 30
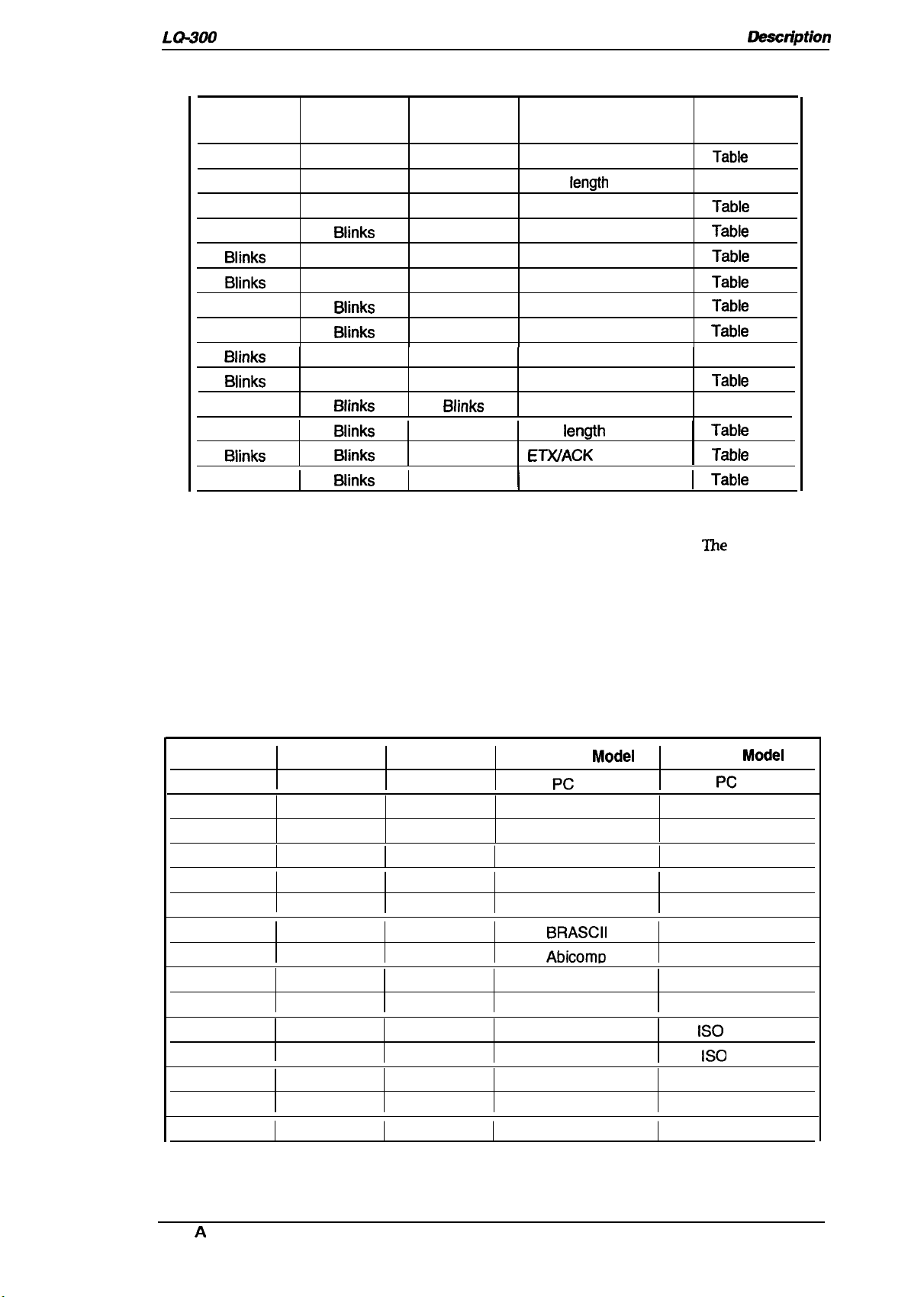
LQ-300 Service Manual
Table 1-19. Default Options
Product
Deacfiption
Font 1 Light Font 2 Light Pause Light
6.
Blinks
Blinks
OFF
ON
Biinks
Biinks
OFF
ON
Biinks
Biinks
OFF
ON
Biinks Biinks Blinks
Blinks
you reach the setting you want to change, press the
When
OFF OFF
ON
Blinks
Biinks
OFF
ON ON
Biinks
Biinks
OFF
ON
Biinks Blinks
Biinks
Biinks OFF
Setting
Character table
Page
OFF
OFF
OFF Auto tear-off
ON
ON
ON
Blinks
Blinks Bit rate
Blinks
I
State reply
iength
Skip over perforation
Graphic print direction
Software
AGM
Auto line feed
interface
Parity bit
Data
iength
ETWACK
Pause
button once. The printer
Go to
Submenu
Tabie
Table 1-21
Tabie 1-22
Tabie
Tabie 1-23
Tabie 1-24
Tabie
Tabie
Table 1-25
Tabie
Table 1-27
Tabie 1-28
Tabie
,
Tabie
1-20
1-22
1-22
1-22
1-26
1-22
1-22
automatically enters the submenu for that setting.
7.
Press the
twice each time you press the
8.
When the lights match your desired setting, press the Pause button to make your selection.
Font
button to move the through the settings in the submenu.
Font
button while in a submenu.
The
printer beeps
The printer saves the new setting and returns to the menu shown above.
Repeat steps 5 through 8 for each additional setting you want to change, or skip to step 10 to
9.
exit the printer’s default setting mode.
10.
When you are finished, turn the printer off. Any settings you have made remain in effect until
you change them
again.
Font 1 Light
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
Blinks
Table 1-20. Character Tables
Font 2 Light Pause Light
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
ON ON
ON
OFF Blinks
OFF
ON
ON
Blinks Blinks
Blinks Blinks
Blinks Blinks
OFF
OFF
OFF Pc 860
OFF PC 863
ON
ON
ON
Blinks
Blinks
Blinks
Standard
Pc
437
PC 850
PC 865
Pc 861
BRASCII
AbicomD
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
Modei
NLSP
Modei
Pc
437
Pc 650
PC 864
PC 437 Greek
Pc 652
PC 853
PC 855
PC 857
Pc 866
PC 869
iSO
Latin IT
ISO
8859-7
Code MJK
Mazowia
Bulgaria
Rev. A
1-21
Page 31

Product Description
LQ-300
Service Manual
Table 1-21. Page Length
Font 1 Light
OFF OFF
ON
OFF
ON
Font 2 Light Pause Light
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
Setting
11
inches
12 inches
8.5 inches
i’0/6
inches
Table 1-22. Skip Over Perforation / Auto Tear Off/ AGM / Auto Line Feed/
ETWACK / State Reply
. . . .
..:.
~
f
. .
Font 1 Light
OFF OFF
ON
Font 2 Light
ON
Table 1-23. Graphic Print Direction
Font 1 Light
OFF
ON ON ON
Font 2 Light
OFF
Table 1-24. Software
Font 1 Light Font 2 Light
OFF
ON ON
OFF
Table 1-25. Interface
Font 1 Light
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
Font 2 Light
OFF
OFF OFF
ON
ON
Table 1-26. Bit Rate
Pause Light
OFF off
ON On
Pause Light
OFF
Pause Light
OFF
ON
Pause Light
OFF
OFF
OFF Serial
Auto selection (10 ms wait)
Auto selection (30 ms wait)
Setting
Setting
Uni-D
Bi-D
Setting
ESC/P2
IBM X24E
Setting
Parallel
gT’-
.,
.,,.
Font 1 Light
OFF
ON
OFF
ON ON
OFF
ON
OFF
1-22 Rev. A
Font 2 Light Pause Light
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF 300 bps
OFF 600 bps
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
Setting
1200 bps
2400 bps
4800 bps
9600 bps
19200 bps
Page 32

LQ-300 Service Manual
Product Description
Table 1-27. Parity Bit
Font 1 Light Font 2 Light Pause Light
OFF
ON
OFF
I
OFF OFF
OFF OFF
ON
OFF
Table 1-28. Data Length
Font 1 Light
OFF
ON ON
I
Font 2 Light Pause Light
OFF OFF
ON
Setting
None
Even
Setting
7 bits
8 bits
I
1
J
Rev.
A
1-23
Page 33

Product Description
1.5 MAIN COMPONENTS
LQ-300
Service Manual
The main components of the
components are:
■
C143
MAIN board: control board
■
C130 PSB/PSE
■
M-5M1O: Printer mechanism
■
Housing
(120 V/230 V) board:
1.5.1 C143 MAIN Board
The
C143
MAIN
PS-RAM,
SLA7022M
(CR Motor Driver) /
an
PROM
(Program /
4-2
SC5060
(PF Motor Driver)
board consists of the
EEPROM,
etc.
PSRAM256K
CG)
\
[
boll n
0
_
/
LQ-300
TMP90C041
00
is
designed for easy removal and repair. The main
power supply board
(CPU), an
TM P90C041 (CPU)
EEPROM
a a
I
E05B02(GA),
o o’/
a
program/CG
E05B02(GA)
6-STA475A
(Printhead Driver)
UPC78M05AHF
(Regulator
ROM, a
IC)
2-M51955B
(Reset
IC)
\ (Color Option)
C143
Figure 1-8.
1.5.2
The power supply boards are the same as those for the LX-300. The boards have two ratings for
input AC voltages:
transformer, switching
+5 VDC and +35
C130 PSB/PSE
120 VAC
VDC
for the main board and printer mechanism.
Transformer
Board
FETs,
regulator
Switching FET
(j
“n=.
MAIN Board Component Layout
(C130 PSB)
II
and 230 VAC
IC,
diode bridge, etc. The power supply board provides
yu
❑
n nnnn
lu~uuul
--
(C130 PSE),
Diode Bridge
—1
~
m
l/--
Both boards consist of a
Power Switch
I
1-----
\
Figure 1-9.
1-24 Rev. A
C130 PSB/PSE
\
Reaulator
IC
Board Component Layout
/
Page 34

LQ-300 Service Manual
1.5.3 Printer Mechanism (M-5M1O)
Product Description
The printer mechanism consists of 24-pin impact dot head, PF motor, RF motor, PE sensor,
~
sensor, PG sensor, release lever sensor, etc.
Figure 1-10. Printer Mechanism
1.5.4. Housing Assembly
This consists of printer cover assembly, edge guide assembly, upper housing, lower housing
assembly, etc.
-=
Edge Guide Assembly
Printer Cover Assembly
per Housing Assembly
Rev.
r Housing Assembly
Figure 1-11. Housing
A
Assembly
1-25
Page 35

;“+
:
c
-
,.. .
!:,
,,-,
f
~.
’,,,..
Page 36

CHAPTER 2 Operating Principles
Table of Contents
2.1 PRINTER MECHANISM OPERATION
2.1.1 Printing Mechanism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1.2 Carriage Movement Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
2.1.3 Paper Handling Mechanism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
2.1.3.1 Paper Feed Mechanisms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
2.1.3.2
2.1.4 Ribbon Advance Mechanism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
2.1.5 Ribbon Shift Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
2.1.6 Platen GapAdjustment Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
2.2 POWER SUPPLY OPERATION
2.2.1
Power Supply Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
2.2.2 Power Supply Circuit Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.3 CONTROL CIRCUIT
2.3.1 Control
2.3.2
2.3.3
2.3.4
2.3.5
2.3.6
2.3.7
2.3.8
2.3.9
2.3.10 Interface Circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.3.11
2.3.12
2.3.13 Color Ribbon
2.3.14 Platen GapSensorCircuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power On Reset’Circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power OffSensorCircuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Home Position Sensor Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Paper End
Release Lever Position Sensor Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Carriage
Paper Feed
Printhead
EEPROM
CS
PaperAdvance
CircuitODeration
SensorCircuit
MotorDriveCircuit
MotorDriveCircuit
Drive Circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-16
Control Circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
Motor Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
SensorCircuit
Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
overvie w . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-16
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-19
2“1
2-1
2-1o
2-11
2-12
2-12
.
2-13
.
2-13
2-17
.
2-19
Page 37

List of Figures
Figure 2-1.
Printhead
Operation Principles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-1
Figure 2-2. Carriage Movement Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Figure 2-3. Friction Advance Mechanism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Figure 2-4. Push Tractor Paper Advance Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
Figure 2-5. Pull Tractor Paper Advance Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Figure 2-6. Push-Pull Tractor Paper Advance Mechanism. . ...............2-6
Figure 2-7. Paper Path. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. .2-6
Figure 2-8. Ribbon Advance Gear Linkage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Figure 2-9. Color Shift Mechanism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . z-g
Figure 2-10. Platen Gap Adjustment Mechanism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-11.
Figure 2-12. Control Circuit Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-13. Power On Reset Circuit Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Z-13
Figure 2-14.
Figure 2-15.
Power
Supply
Circuit Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-11
Power Off Sensor Circuit Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Z-13
Home Position Sensor Circuit Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Figure 2-16. Paper End Sensor Circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
z-g
2-12
2-14
Figure 2-17. Release Lever Position Sensor Circuit Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Figure 2-18. Carriage Motor Driver Circuit Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-19. Paper Feed Motor Driver Circuit Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-20.
Printhead
Figure 2-21. Parallel Interface
Figure 2-22. Serial Interface Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-23. EEPROM Control Circuit Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-24.
Figure 2-25. Color Ribbon Sensor Circuit Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure
2-26.
CS
Platen Gap Sensor Circuit Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-19
Driver Circuit Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-17
Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Motor Assembly Circuit Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-16
2-17
2-18
2-18
Z-18
2-19
2-15
[;?
,s. -.
1
~,
..
List of Tables
Table 2-1. CR Motor Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Table 2-2. PF Motor Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
Table 2-3. Ribbon Advance Gear Linkage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Table 2-4. CS Motor Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .............2-8
Table 2-5. Coloring Sequences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
Table 2-6. Power Supply Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-7. Power Supply Output Voltages and Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-8. Functions of the Main [C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .....2-12
Table 2-9. Carriage Motor Drive Modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
2-10
2-10
Page 38

LQ400
Service Manual
2.1 PRINTER MECHANISM OPERATION
This
section
2.1.1 Printing Mechanism
describes the printer mechanism and explains how it works.
Operating Principles
The printing mechanism is composed of the
is a 24pin head for impact dot printing. Each wire has own drive coil, which causes the wire to
move in and out of the
driving wires work.
A drive signal transmitted from the control arcuit to the
1.
the proper
then causes the iron core to become magnetized.
The magnetic force draws the actuating plate toward the core, and the dot wire, which is
2.
connected to the core, rushes toward the platen.
When the dot wire impacts the platen, pressing against the ribbon and paper, it prints a dot.
3.
4.
When the driving voltage stops energizing the coil, the magnetic force from the iron core
vanishes. The actuating plate returns to its original position
energized) with spring action. The dot wire also returns to its original position.
This is the sequence used to print a single dot.
The mechanism is equipped with a built-in thermistor for head temperature detection. The
temperature detected by the thermistor is converted to an electric signal and fed back to the control
circuit.
printhead
printhead
driving voltage, which energizes a corresponding coil. The energized coil
Wire Resettin S rin
to print each dot.
Stopper
prirdhead,
Dot Wire
ink ribbon, and ribbon mask.
The four steps below describe how these
printhead
drive arcuit is converted to
(the
position before coil was
.
The printhead
Yn7YY2
77
r
Actuating Spring
Figure 2-1.
\
Printhead Operation Principles
Rev.A
2-1
Page 39

Operating Principles
LQ-300
Service Manual
2.1.2 Carriage Movement Mechanism
The carriage movement mechanism consists of the carnage assembly, CR motor, timing belt, driven
pulley, HP sensor, etc. The CR motor drives the
the timing belt, which is moved by the CR motor.
mechanism.
tirnkigbelt.
Figure 2-2 shows the carriage movement
The carnage assembly is connected to
The printer detects
determin”mg
position. The sensor is ON, when the carriage is pushed to the right or left. The striker on the
carriage
the carriage home position.
actives
tie
carriage home position with the HI? sensor. This sensor is the basis for
The HP sensor informs the CPU of the carriage home
the sensor to indicate the carriage home position, which toggles the sensor to OFF.
Table 2-1. CR Motor Assembly Specifications
I
Type
Drive
I
Coil Resistance
Drive Pulse Frequency
Excitation Method
Category
Voltaae
I
4-phase, 96-pole,
31.5 -38.5 VDC
I 19.6
Normal Mode Draft
Color Mode LQ
Constant-voltage 2-2 phase excitation
Q *
Requirement
HB-type
8%
(Der Dhase, at25° C,770 F) I
1-2 phase excitation
stepping motor
2400
PPS
1600
DDS
I
I
Figure 2-2. Carriage Movement Mechanism
-1
F ~~
-.. ,.
2-2
Rev.A
Page 40

LQ-300 Service Manual Oparating Principles
2.1.3 Paper Handling Mechanism
During
normal
operation, paper is fed to the printer, advanced to the specified position, and
ejected from the printer. These functions are performed by various paper handling mechanisms,
such as the
&actors,
rollers, and gears. This section describes the paper handling mechanism for
this printer.
2.1.3.1 Paper Feed Mechanisms
Cut sheets are fed by friction. Continuous paper is fed by a tractor. There are three ways to feed
with tractors: the push tractor method, the pull tractor method, and the push-pull tractor method.
During normal operation, the printer is set up with only one tractor, which functions as either a
push or a pull tractor, depending on where it is attached on the printer. To use the push-pull .
tractor feed method, an optional tractor must be attached.
There are two ways to insert paper into the printer. Cut sheets use the top entrance and continuous
paper uses rear insertion.
2.1.3.2 Paper Advance Mechanism
This section describes how the friction and tractor advance mechanisms feed paper through the
printer. The paper advance mechanism consists of the
driven roller cover, tractor assembly, knob,
both forward and in
Friction Advance Method
reveme.
PF
gear train, etc. The PF motor can drive the platen
Paper is held by the platen, the PF driven roller, and the eject roller assembly. Turning in the
direction of the black arrows, the PF motor pinion gear drives the paper advance reduction gear.
The paper advance reduction gear turns the platen gear, PF driven roller, and the platen. The
platen drives the driven roller cover; then the driven roller cover drives to eject the paper. The
paper advances in the direction of white arrows.
when the paper is fed through the top paper entrance.
PF
motor, platen, driven roller assembly,
Figure 2-3 shows the friction advance method
.
Driven Roller Cover
Driven PF Roller
Rev.A
Figure 2-3. Friction Advance Mechanism
2-3
Page 41

Operating Principles
Table 2-2. PF Motor Specifications
LQ-300
Service Manual
Category
Type
Drive Voltage
Coil Resistance
Drive Pulse Frequency
Excitation Method
4-phase, 48-pole, PM-type stepping motor
31.5 -38.5 VDC
58.5 Q * 5% (per phase, at 25°C,
800,900, 1000, 1200, 1300
Constant-voltage 1-2 phase excitation
Requirement
77°F)
ppS
Push Tractor Method
When the push
&actor
method is used with
the
rear entrance, the torque generated by the PF motor
is transmitted to the push tractor gear through the PF motor pinion gear, the paper advance
reduction gear, and the tractor transmission gear.
When the PF motor pinion gear turns in the
direction of the black arrows, the tractor gear rotates in the direction of the black arrow and thus
feeds the paper into the printer. The paper is advanced by the platen, which is also driven by the
PF
motor through the gear train.
Continuous Paper
push Tractor
/
PE
\
\&@
Sensor
Platen
Driven Roller Cover
Platen Gear
Pinion Gear
/
w-
P&
5
~P
‘b
d
-0
Figure 2-4. Push Tractor Paper Advance Mechanism
o
-1. .
I ractor
/
Transmission Gear
Tractor Gear
~
Reduction Gear
/
‘aperAdvance
\
PF Motor
Page 42

L
WOO
Service Manual
Pull Tractor Method
The pull tractor advances paper in basically the same way as the push tractor. When the push
tractor is installed at the paper exit instead of paper entrance, the tractor functions as a Pull tractor
instead of a push tractor, pulling the paper out of the printer mechanism.
tractor advance mechanism.
Continuous Paper
Operating Principles
Figure 2-5
sho-ws
the pull
/hk/
PI
,
. .
(/
(3”
Platen Gear
~d
Pinion Gear “
Figure 2-5. Pull Tractor Paper Advance Mechanism
Tractor
PF Motor
0
-
ear
Rev.A
2-5
Page 43

operating
Push - Pull Tractor Method
The push-pull tractor method is a combination of the push method, using the standard tractor, and
the pull method, using an optional tractor. The two tractors operate simultaneously to push and
pull the paper through the printer mechanism. Figure 2-6 shows push-pull &actor operation when
the paper is fed through the rear paper entrance.
Principles
LQ-300
Service Manual
..’.%
t
.
-.,. .
- .,,
b
.,,
Figure 2-6. Push-Pull Tractor Paper Advance Mechanism
Disengage Lever
The disengage lever switches whether or not the printer transmits the torque of the PF motor to the
tractor transmission gear. (See Figures 2-5 and 2-6.)
The paper path is different from friction feed and tractor feed. The PF driven roller is not in the
tractor feed paper path, so continuous paper is not advanced by this roller. Figure 2-7 shows the
paper path.
,>
Sheet
Platen
QY
\
/
PF Driven Roller
Guide
<&Tractor
PE Sensor Assembly
Cut Sheet
.
Continuous paper
2-6
Figure 2-7. Paper Path
Rev.A
Page 44

LQ-300 Service Manual
Operating Principles
2.1.4 Ribbon Advance Mechanism
The ribbon is held between the ribbon advance roller (ribbon driven gear) and the ribbon pressure
roIler.
When the carriage moves on the CR guide shaft from
left
to right and vice versa, the timing
belt turns the belt driven pulley. Then the torque is transmitted to the ribbon driving gear through
the gear trains. The ribbon driving gear rotates counterclockwise no matter what direction the
carriage moves, because a planetary gear is used in the gear linkage.
Table 2-3. Ribbon Advance Gear Linkage
)
Direction of Carriage Movement
I
1
Gear Linkage
Left to right
(indicated by the black arrow)
Right to light
irtdioated by the white arrow)
Belt driven pulley + Gear(1)+ Gear (2) -+
Ribbon driving gear
Belt driven pulley
Gear (4) + Ribbon driving gear
+
Gear(1)+ Gear (3)+
The ribbon brake spring, attached to the exit of the cartridge case, prevents slack in the ribbon and
keeps the ribbon tension at an appropriate level.
The ribbon mask prevents the ribbon from
brushing against the paper.
Ribbon Advance Roller
Ribbon
Pressure
\
&
Ink Ribbon
Mask
/
Rev.A
R
D
Ribbon Brake
Carriage
Spring
Figure 2-8. Ribbon Advance Gear Linkage
2-7
Page 45

Operating Principles
2.1.5 Ribbon Shift Mechanism
LQ-300 Service Manual
This printer can be equipped
printing unidirectionally.
with
a color upgrade kit to print in color. The printer performs color
The
option is composed of the color ribbon shift mechanism. The color
ribbon feed mechanism is shared in common with black ribbon feed mechanism, and the shift
mechanism shifts the ribbon cartridge up and down.
Table 2-2 shows the CS motor specifications. The motor control system is open-loop, so that when
the color is being changed, the positioning is controlled by stepping pulse.
Table 2-4. CS Motor Specifications
Category
Type 4-phase, 48-pole, PM-type stepping motor
Drive Voltage
Coil Resistance
Drive Pulse
Excitation Method
Freauencv
35 VDC + 10%
150 Q * 5% (per phase, at 25° C or 77°
Color shift 500 DDS
I
Constant-voltage 2-2 phase excitation
The ribbon shift mechanism consists of the color ribbon and color upgrade kit. The color upgrade
kit is composed of the
CS
motor, ribbon
shift
gear/cam, motor driver
The 1-inch-wide color ribbon is separated into four equal-width bands of different colors. The
ribbon shift mechanism shifts the ribbon cartridge up and down.
When the color ribbon cartridge is loaded, it is possible to print in up to seven colors. One of the
four colors on the ribbon is selected by the color ribbon
the plastic posts into the slots in the printer mechanism as a fulcrum.
shift mechanism. The mechanism
shifts
the
ribbon cartridge by converting the gear rotation to
liner motion (up and down) of the color ribbon cartridge, using color shift cam gear.
Requirement
cartxidge
motion, which inserts a portion of
I
F)
1
IC,
and color ribbon sensor.
Figure 2-9 illustrates the color
-’$
c’
. . . .
.;.
.
Any color band can be selected by rotation of the CS motor, using the color home position (the
position of the black color band) as a starting point and reference position. Home position is
recognized by the
CS
motor stepping pulse. When printer is powered on, the CS motor is first
exated at any phase position. Next, the CS motor is turned 235 steps ( black + yellow). Then, the
motor returns one step
steps
(yellow+ black) and stops. This position is home position.
Table 2-5 gives coloring sequences.
(yellow+ black), and the motor is stopped. Finally, the motor returns 223
For halftones, as shown in the table, a color is created by
printing one color on top of another.
Table 2-5. Coloring Sequences
Print Ribbon
Print Color
First Printing Second Printing
—
—
—
Cyan
Magenta
Cvan
I
Note:
Black Black
Magenta
Cyan Cyan
I Yellow
Green
Orange
Violet
I
The printer prints the brighter
I
I
wlor
Magenta
Yellow
Yellow
Yellow
l–l
Ma~enta I
first to prevent the ribbon from being stained,
,*,
f
‘
-c
.,
2-8
Rev.A
Page 46

LQ-300
Service
CS
Manual
Lever
Fulcrum Color Ribbon Cartridge
1/
//
Black
Cyan
Magenta
Yellow
:
~>
Color Cartridge Holder
Operating Principiea
CS Motor Assembly
Color
/
\
CS Cam Gear
Shift
Cam
Pinion
Color Shift Cam Follower
Figure 2-9. Color Shift Mechanism
2.1.6 Platen Gap Adjustment Mechanism
The
platen gap (the gap between the platen and the printhead) can be adjusted to allow the printer
to use paper of different weights or thicknesses. When the gap adjust lever is moved forward or
badcward,
the platen and changes the platen gap.
the CR guide shaft rotates. This rotation moves the carriage either toward or away from
lhe
correct platen gap is 0.45 & 0.02 mm, with the gap
adjust lever set to position O.
Gap Adjust Lever Motion
PG
Gap Adjust Lever
Rev.A
—..4
—..
Platen
‘\
CR Guide Shaft
Figure 2-10. Platen Gap Adjustment Mechanism
2-9
Page 47

Operating Principles
L(?-300
Service Manual
2.2 POWER SUPPLY OPERATION
The printer can be powered by either of two power supply boards: the
C130 PSE
(230 V) power supply. These boards are the same as the LX-300’S power supplies. The
two boards function identically, except for a difference in primary circuitry. The power supply
board outputs the DC current necessary to drive the printer control circuits and drive mechanism.
Table 2-6 shows the input voltages and fuse ratings for these boards.
Table 2-6. Power Supply Board
C130 PSB
(120 V) or the
,’
‘%
c
Board
C130 PSB
C130 PSE
Input Voltage
100.5-132
198-264
VAC
VAC
Fuse F1 Rating
2.5A 1125 V, 250 V
1.25 A 1250 V
2.2.1 Power Supply Overview
The power supply board has two power outputs for use in the various control circuits and drive
mechanisms. Table 2-7 lists the circuitry and the units that are driven by the two DC output supply
voltages.
Table 2-7. Power Supply Output Voltages and Applications
output supply
Voltage (DC)
+35 v (VP)
+9
V (VL)
CR motor drivers
PF motor drivers
Printhead drivers
CS motor drivers
Main board assembly logic circuitry
Various sensors
Control panel LED
PF motor/ CS motor hold
Applications
f
..;
.
..-
~.,
‘
2-10
Rev.A
Page 48

LQ-300 Service Manual
2.2.2 Power Supply Circuit Operation
Figure 2-11 shows a block diagram of the power supply circuitry. When AC power is supplied to
the printer from an external power source, a filter
undergoes full-wave rectification and is smoothed to produce the direct current supply voltage.
This voltage is fed through a switching circuit and secondary smoothing circuit to produce the
stepped down +35
to the switching circuit. This feedback control arrangement ensures that the +35
kept stabilized.
A +9
VDC
supply is created by putting the +35
cimuit.
This circuit further steps down the +35
+9
VDC
output is stabilized to +5
There are several circuits to protect the supply
VDC
supply. A +35 V line voltage detector
VDC
using the regulator on the
cinmit
removes the noise. The AC voltage then
(ZD51
and
VDC
line through the +9
VDC
voltage and outputs a stabilized supply. The
C130
arcuits
and avoid danger.
Operating Principle
PC1)
circuit is connected
VDC
supply is
VDC
power supply
MAIN board assembly.
The +9
protection circuit
It stops switching
The +35
protection circuit ( ZD52,
It stops switching circuit operation, which stops the output from the +35
Full-Wave
Rectification
Circuit
Filter Circuit
VDC
line contains a voltage overload protection circuit. The +9 V voltage overload
(ZD53, Q82,
arcuit
VDC
line has a voltage overload protection circuit. The +35
Smoothing
—
Circuit
and
PC1)
cuts the supply if the voltage reaches or exceeds
operation, which stops the output from the +35
Q82,
and
PC1
) cuts the supply if the voltage reaches or exceeds +36
Switching
Circuit
4
Smoothing
Circuit
VDC
VDC
VDC
T
AC Line
-Ez!t
+11 VDC.
line.
voltage overload
line.
~
+35
VDC
-+9 VDC
(VL)
VDC.
(VP)
c1
— Over-voltage
Figure 2-11. Power Supply Circuit
+9
VDC
Line
Over-voltage
Protection
Circuit
I
+35
VDC
Linel
Protection
I
Circuit
Block Diagram
t
I
Rev.A
2-11
Page 49

Operating Principles
2.3 CONTROL CIRCUIT
LQ-300 Service Manual
The control circuit consists of the C143 MAIN board assembly. This section
desuibes
the major
components and explains how the board works.
2.3.1 Control Circuit Operation Overview
The printer has a CPU
PS-RAM (256K-bit),
(TMP90C041)
a ROM (4 or
that runs at 9.8304 MHz, a gate array (E05B02-type), a
8M-bit),
etc. It oversees control of all the components in the
printer. The printer uses the E05B02 gate array to control memory management, parallel
communications, PF motor drive signals, etc. Table 2-8 shows functions of
2-12 shows the control circuits in
bl&k diagram form.
Table 2-8. Functions of the Main
Ic
CPU
+
EEPROM
R----R-
I
Location
ICI
I
IC2
IC3
Function
Receives data from the host computer and sends it to the input buffer
in RAM (under interrupt processing control). Extends the input data
held in the buffer to create image data. Loads this image data to the
image buffer in RAM. Transfers the image data to the
drive circuit. Also controls various parts of the printer mechanism,
such as
Controls the functions below:
An electrically
information as the TOF position and bidirectional adjustment value.
Driver / receiver
Hardware reset function
Power off detection
Contains the program that runs the CPU and holds the character
design (also called the charaoter generator).
Input buffer
PF motor control and color select motor control.
● Input/Output Control
● Memory Management
. Bit Manipulation
● Interface Control
. Expanded Parallel Port
Printhead
.
● Motor Control
Control
writable
and erasable ROM used to hold such
IC
ICS
and circuits. Figure
Printhead
-.,
f
,., .-
Panel
SWILED
Parallel l/F
Serial l/F
2-12
I Printhead
I
~
DRV.
A
Gate Array
1
&kiiEl
Figure 2-12. Control Circuit Block Diagram
Printhead
Sensor
I
L
EEPROM RESET
Color Ribbon Sensor
Temp.
1
I
Power Off Sensor
1
I
v
+35 V Sensor
PE Sensor
‘p”
<
4
Y
*
1
4 Release Lever Sensor
D
A
. . .
Rev.A
Page 50

LWOO Service Manual Operating Principles
2.3.2 Power On Reset Circuit
When
the
power supply is turned on and immediately the VL (+9 V) goes up to +7.5 V (typical), the
reset IC
level signal from the reset
(IC6)
outputs the system RESET signal (LOW). The CPU and gate array receive this LOW
IC
and reset themselves.
XRST
GATE ARRAY
(IC2)
67
A
VL
4
b
3
(
)
2
(IC6)
IN
Vcc
~
16
i
RESET
CPU
(ICI)
3
4
GND
z+
Fgiure 2-13. Power On Reset Circuit Diagram
2.3.3 Power Off Sensor Circuit
When the power supply is turned off and the VP
the reset IC
from the reset IC and resets itself.
(IC7)
outputs the system
RFSETsignal
15
1
(+35V)
(LOW). The
+5
4
Power Off
Sensor IC
4
L
Vcc
+i’-
OUT
6
L
immediately goes down to
CPUreceives
(IC7)
2
IN
this LOW
VP
t
I
7+7
+25
V (typical),
Ievelsignal
Figure 2-14. Power Off Sensor Circuit Diagram
Rev.A
2-13
Page 51

Operating Principles
2.3.4 Home Position Sensor Circuit
This printer has a connector switch to sense the carriage home position. The CPU receives a signal
from the HP sensor and recognizes the carriage home position when the printer is turned on. The
comector
the carriage is out of home position.
switch is open (OFF) when the carriage is in the home position and is closed (ON) when
+5 v
LQ-300
Service Manual
CPU (ICI)
P551AN5
Figure 2-15. Home Position Sensor Circuit Diagram
2.3.5
Paper End Sensor Circuit
This printer has a
connector switch and
no paper on the platen and is open (OFF) when paper is present.
comector
reco~es
CPU (ICI)
P52JAN2
2
switch for sensing the paper end. The CPU receives a signal from the
a paper end. The connector switch is closed (ON) when there is
. .
63
+5
1
Home Position
Sensor
4
)
v
t
“
PE Sensor
(..;
E
Figure 2-16. Paper End Sensor Circuit
2.3.6 Release Lever Position Sensor Circuit
This printer has a connector switch to detect the type of paper handling. The CPU receives a signal
from the connector switch to indicate whether the paper is fed using friction or
connector switch is closed (OFF) when friction feed is selected and is open (ON) when tractor feed
is selected.
CPU (lCl)
Release Lever
1
P53/AN3
Position Sensor
hactor
feed. The
2-14
Figure 2-17. Release Lever Position Sensor Circuit Diagram
Rev.A
Page 52

L WOO Service Manual
2.3.7 Carriage Motor Driver Circuit
Operating Principles
Figure 2-18 shows the carriage motor driver circuit. The carriage motor driver uses an
constant-current chopping drive arrangement. The motor is driven with 2-2 phase excitation and
1-2 phase excitation.
The MOO-3 (pins 3-6) on the CPU are used to control the phases of stepping motor. The carriage
motor driver IC
current. The amount of current flowing in the coils varies, depending on the speed of the carriage
motor. The amount of the
on the CPU.
Driver
3 x speed
2 X speed
X
3/2
1 X speed
3/4 x
1/2 x speed
GATE ARRAY
(IC8)
ODENO-1
Mode
speed
speed
ODEN1
OPH1
ODENO
OPHO
detects the amount of current in
cument
and
OPHO-1
Table 2-9. Carriage Motor Drive Modes
Excitation Type
2-2 phase
2-2 phase 1600
2-2 phase
1-2 phase
1-2 phase
1-2 phase
is set by the gate array
on the CPU control the stepping motor.
Drive Frequency Type
2400
1200
1600
1200
800
+5V +5V
IC2)
H
the
carnage motor
(IC2).
PPS
PPS
pps
ppS
pps
PPS
CR Motor
Driver IC (
OA
O-A
00
o-B
Signals are sent to the
Draft Mode
Draft Copy Mode
Bit Image Mode
LQ Mode
LQ
LQ
coils
and regulates the
Standard Print Character
Copy Mode
Speed Down Mode
;8)
.
10
15
open-Ioop,
ODO-0D2
CR MOTOR
CRA
CR_A
CRB
CR_B
OD2
OD1
ODO
46
72
B2
Vx
3
T
‘IIIJ
n
Jr
Figure 2-18. Carriage Motor Driver Circuit Diagram
Vx
t-
CRCOM
Rev.A
2-15
Page 53

Operating Principles
2.3.8 Paper Feed Motor Driver Circuit
Figure 2-19 shows the paper feed motor driver circuit, an open-loop, constant-voltage drive with
1-2 phase excitation.
The ports (pins 7-lo) on the CPU are used to control the stepping motor. The pulse signal from the
IC1
controls four
600, 1000, 1200, and 1300 pps, to correspond to the idling voltage, the paper handling condition,
and the volume of paper feeding.
PFCOM
voltage is changed VX
tmmsistors
and the stepping motor. The motor is driven at six speeds, 300,500,
The
CPU controls motor driving speed. At the holding time, the
(+35
V) into VL (+5 V) via Q1
and
Q6 by the gate array.
LC&300
Service Manual
.,
c
\
Gate Array
143
CPU (ICI)
E
I
~-
Figure 2-19. Paper Feed Motor Driver Circuit Diagram
2.3.9
Figure 2-20 shows the
image
Port
sampling the +35
possible to maintain the energy supplied to
+35 V line is HIGH,
ICI lengthens the output pulse.
Printhead Driver Circuit
printhead
data
is split by the
AN6
(pin 66) of
VDC
CPU
CPU
and transferred to the
IC1
samples
line voltage and deterrninin
ICI
shortens
Gate Array
DATA
BUS
driver
circuit block diagram. Print data, already expanded into
the
voltage of the +35
the
output
puke.
●
●
●
-vW-
●
●
●
b
●
PF Motor Drive
Transistors
!37
M13
!W
M12
139
Mll
140
MIO
==%
+5V
latch
g the length of the head drive signal, it is
the
head at a constant level. If the voltage from the
If the voltage from
QM1 -6
Q2
Q3
Q4
Q5
A4 &
k---wTpFcOM
‘
J
VL
1
Vx
circuit in the gate array in the system.
VDC line
VP
●
●
9
●
●
●
PF-~
PF_A
PF~
P FA
via the A/D converter. By
the
+35
VDC
line is LOW,
#l
,
●
y
●
●
● :
+
!
●
●
,
#24
., .
.,
c
--h
i
,-,,
f
.,
‘
2-16
ANI
62
Id
Figure 2-20.
+5 v VP
-1-
d
Printhead
A=
Driver Circuit Diagram
Rev.A
Page 54

LQ-300 Service Manual
Operating Principles
2.3.10 Interface Circuit
Figure 2-21 shows the parallel interface arcuit block diagram. Data from the host computer is
latched within the gate array by STROBE signal. The gate array outputs XBUSY signal
automatically to stop the host computer from sending further data. The gate array reads the data
latched periodically with generating an interrupt.
The parallel I/F conforms to bidirectional parallel I/F
Parallel l/F
127-134
~
4
4
4
4
IEEE-P1284
Gate
39
Array
DINO-7
-----: XSTROB
13
12
14
15
4
L
;
XB”SY
----
‘
~
------ XPE
------ XERR
------ XSLCT
---”-
‘
level 1 nibble mode.
XSLIN
Figure 2-21. Parallel Interface Block Diagram
Fim.ue
2-22 shows
E&232D. RXD
driver/receiver
when a CR code is received or when the input buffer is filled.
the serial
interface circuit block diagram. The serial interface conforms to
is data received by the serial 1/0 of th~CPU block from the host computer via
IC4.
Data is transmitted to an input buffer in
IC1l
(IC2)
from the CPU. Printing starts
Serial
TXD
DTR
RXD
CTS
RST
+5V
IIF
4
4
Driver/Receiver
(IC4)
.,
.
D1OUT
D20UT
F
RIIN
+
R21N
DIIN
D21N
R1OUT
R20UT
t
?
~
53
52
50
54
CPU (lCl)
P33
P32
P30
P34
Figure 2-22. Serial Interface Block Diagram
Rev.A
2-17
Page 55

Operating Principles
2.3.11 EEPROM Control Circuit
LQ-300
Service Manual
Figure 2-23 shows the
information as the top-of-form position. The
not lost if the printer is powered off. Since the
converts 8-bit data into serial data.
EEPROM
CPU (lCl)
control circuit block diagram. The
EEPROM
is non-volatile memory, so information is
EEPROM
is a serial I/O-type device, the CPU
EEPROM (IC3)
EEPROM (IC6)
+5
v
contains such
A
05
06
07
17
3
38
::5
‘
Cs
2
CK
3
DI
4
DO
’
Vcc
GND
L
}
)
+’7-
Figure 2-23.
2.3.12 CS Motor Circuit
Figure 2-24 shows a block diagram of the CS motor circuit in the optional color upgrade kit. The
CS motor is a permanent magnet (PM) stepping motor, driven with 2-2 phase
proportion to the desired rotational speed. This motor can be rotated in either direction and
stopped at any position. Four phase signals are directly output from the system
through a
tcansistorarray.
The drive voltage is constant (i.e., +35
EEPROM
Control Circuit Diagram
VDC
from the VP line).
exatation
IC
and pass
in
Source Voltage
Current Consumption
GATE ARRAY
-
35 VDc * 10
245
mA
(IC2)
9
MT3
49
MT2
4a
MT1
47
MTO
( peak)
?40
I
I
1
i
Q1
CS
MOTOR
CS-B
CS-A
CS
B
CS A
I=%z
CS-HOLD
04
*
Printer
Figure 2-24. CS
I
Motor Circuit
Color Upgrade Kit
2-18
. .-
Rev.A
Page 56

LQ-300 Service Manual
Operating
PrinciMes
2.3.13 Color Ribbon Sensor Circuit
The printer’s color ribbon circuitry is shown in the figure below. The CPU receives signals (HIGH
or LOW) from the mechanical switch. The signal is HIGH (ON) when a color ribbon is installed
and is LOW (OFF) otherwise.
+5
v
CPU (Cl)
tl
1
51
P31
Printer
Figure 2-25. Color Ribbon
2.3.14 Platen Gap
This printer has a connector switch to sense the
receives a signal from the
switch is
close(ON)
decrease in copy mode.
open(OFF)
when the printer is in normal
Sensor Circuit
PG
sensor and recognizes the PG adjust lever position. The comector
when the printer is in copy
mode(PG
adjust lever position:-l-+l). The printing speed
]
Color
I
I
;
Color Upgrade Kit
I
Sensor Circuit Diagram
PG(Platen
mode(PG
Ribbon
Gap) adjust lever position. The CPU
adjust lever position:2-6) and is
Sensor
+5V
CPU (ICI)
P54
1
t
Figure 2-26. Platen Gap Sensor Circuit Diagram
Rev.A 2-19
Page 57
4?
CHAPTER 3 Disassembly and Assembly
Table of Contents
3.1 OVERVIEW
3.1.1 Disassembly Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.1.2 Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
.
. . . . - - .”.-...””
““”.””””””””
3-1
3-1
3-1
3.1.3 Service ChecksAfterRepair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
3.1.4 Specifications
forScreWs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. ... ...
3.2 DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
3.2.1 Removing the Printhead . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ........””””-””.
...”O”” ....”.”
3-3
3-4
““.” 3-5
3.2.2 Removing the Upper Housing Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
3.2.3
3.2.2.1
Removingthe MAIN and
Removinq
the
Eject
Roller Assembly
“.””” .s
PSB/PSE BoardAssembfies
s””””””” o
-”” -”
3-6
—
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
3.2.3.1 Removing the MAIN Board Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
PSB/PSE Board Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
PF
Motor
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. -------
3-10
3-11
.””. “ -.. “ 3-12
3-13
3-14
3-14
3-15
3-16
3-17
3-18
$19
3-20
3-20
3-20
3-20
3.2.4
3.2.5
3.2.6
3.2.7
3.2.3.2 Removing the
Removing the Printer Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . “ . . . “ “ “ - 3-9
3.2.4.1 Removing the
3.2.4.2 Removing the CR Motor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2.4.3 Removing the Platen. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2.4.4 Removing the PE Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2.4.5 Removing the HP Sensor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2.4.6 Removing the Release Lever Position Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2.4.7 Removing the Carriage Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2.4.8 Removing the Ribbon Drive Gear Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2.4.9 Removing the PG Sensor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removing the Interface Board Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removing the Driven Roller Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembling and Assembling the Color Upgrade Kit. . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2.7.1 Removing the Ribbon Motor Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2.7.2 Removing the CS Cam. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . “
3.2.7.3 Removing the Color Sensor Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 58

CHAPTER 3 Disassembly and Assembly
Table of Contents
3.1 OVERVIEW
3.1.1 Disassembly Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.1.2
ToOIS
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.1.3 Service ChecksAfterRepair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
3.1.4
Specificationsfor
3.2 DISASSEMBLY
Screws. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
AND ASSEMBLY
3.2.1 Removing the Printhead . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
3.2.2
Removing the Upper Housing Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
3.2.2.1 Removing the Eject Roller Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
3.2.3
3.2.4
Removing the MAIN and
3.2.3.1 Removing the
3.2.3.2 Removing the
Removing the Printer Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
PSB/PSE Board Assemblies. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
MAIN
Board Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
PSB/PSE Board Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
3.2.4.1 Removing the PF Motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2.4.2 Removing the CR Motor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2.4.3 Removing the Platen. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-12
3.2.4.4 Removing the
3.2.4.5 Removing the HP Sensor. ., . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-14
PE Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2.4.6 Removing the Release Lever Position Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-14
3.2.4.7 Removing the Carriage Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-15
3.2.4.8 Removing the Ribbon Drive Gear Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-16
3.2.4.9 Removing the PG Sensor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-17
3.2.5
3.2.6
3.2.7
Removing the Interface Board Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-18
Removing the Driven Roller Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Disassembling and Assembling the Color Upgrade Kit. . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-20
3.2.7.1 Removing the Ribbon Motor Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-20
3.2.7.2 Removing the CS Cam. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2.7.3 Removing the Color Sensor Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-20
3-1
3-1
3-1
3-4
3-10
3-11
3-13
3-19
3-20
Page 59

LQ-300 Service Manual
3.1 OVERVIEW
Disassembly and Assembly
This section describes various points to
note when
disassembling and assembling the printer.
3.1.1 Disassembly Precautions
Follow the precautions below when disassembling the printer.
Before disassembling, assembling, or adjusting the printer, disconnect the power
cablefiom
To maintain
●
Use
●
Use only the recommended
.
Adjust the
3.1.2
the
AC
power socket. Failure to do so
efi”cient
printer operation:
can
cause personal
only the recommended tools for maintenance work.
Tools
pn”nter
lubn”cants
only in the manner described in this manual.
and adhesives
(see
Chapter
injuy.
6).
supply
Tables 3-1 and 3-2 list the tools recommended for disassembling, assembling, or adjusting the
printer. Use only tools that meet these specifications.
Table 3-1. Recommended Tools
Note:
Note:
Tool
Round-nose pliers
Nippers
Tweezers
Soldering iron
E-ring holder #2.5
Phillips screwdriver No.2
Normal screwdriver
Thickness gauge
All tools are commercially available.
Table 3-2. Equipment Required for Maintenance
Description
Multimeter
Oscilloscope
An
oscilloswpe
is required only for servicers who repair to the component level.
Specification
50
MHz
Part No.
6740400100
B7405OO1OO
6741000100
B7402OO1OO
6740800400
6743800200
6743000100
6776702201
Rev.A
3-1
Page 60

Disassembly and Assembly
LQ-300 Service Manual
3.1.3 Service Checks After Repair
Before returning the printer after service, use the checklist in Table 3-3, which provides a record to
make servicing and shipping more effiaent.
Table 3-3. Inspection Check list for Repaired Printer
Category Component
Printer
units
Adjustment Printhead Is the platen gap adjusted correctly?
System ROM ROM version
upgrade
Printhead Are any wires broken?
Are any wires worn out?
Carriage Does the
❑
mechanism
Paper
advance
mechanism
Paper path Is the
Ribbon Is the ribbon mask free of distortion?
mask
Self-print
test
On-line test Was the on-line test successful?
printing
Default Have user-ohangeable settings been
setting
version
Shipment
Movement noisy Q Mechanism dirty
❑
Mechanism oily
Is the CR motor at the
oorrect temperature (not overheating)
Is paper advancing smoothly?
❑
Movement
❑
Mechanism
Is the
at the correct temperature (not
overheating)
feeding smoothly?
Is the tractor feeding the paper
correctly?
Is the paper path clear of all
obstructions?
Is the platen
Was the self-print successful?
Is the bidirectional print position
adjusted
reset to the default value?
Has the ribbon been removed?
Have all relevant parts been included
in the shipment?
Item to
oarriage move smoothly?
paper
advanoe
&oe
of paper in the printer
free of damage?
oorreotly?
Check
noisya
oily
Mechanism dirty
motor running
Is Check Required?
❑
Checked ❑ Not necessary
❑ Checkeda Not
❑ Checked D Not
neoessary
neoessary
❑ Checked UNot necessary
❑ Checkedn Not
❑
Checked ❑ Not
❑
Checked ❑ Not
❑ Checkedn Not
❑
Checked ❑ Not
❑
Checked ❑ Not
neoessary
neoessary
neoessary
neoessary
neoessary
neoessaty
❑ Checkedn Not necessary
❑
Checked ❑ Not necessary
❑
Checked ❑ Not necessary
❑
Checked ❑ Not necessary
❑
Checked D Not necessary
❑
Checked ❑ Not necessary
❑
Checked ❑ Not necessary
❑
Checked ❑ Not necessary
❑
Checked ❑ Not necessary
.
3-2
Rev.A
Page 61

LQ-300 Service Manual
3.1.4 Specifications for Screws
Disassembly and Assembly
Table 3-4 lists the abbreviations used in the following sections for small parts, such as
screws
washers.
Table 3-4. Screw Abbreviations
Abbreviation Part
CP
CPB Cross-recessed pan head B-tight screw
CBB
CBS Cross-recessed bind head S-tight screw
CBC
CB(0) Cross-recessed bind head with outside toothed lock washer
CFP Cross-recessed flat head P-tight screw
Cross-recessed pan
Cross-recessed bind head B-tight screw
Cross-recessed bind head
head screw
C-Lamitite
Name
screw
and
Rev.A
3-3
Page 62

Disassembly and Assembly
LQ+?O Service Manual
3.2 DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
This section describes the procedures for disassembling and assembling the main components of
the printer. When the procedure for installing a component is simply the reverse of the procedure
for removing the component, no description of the installation is given. Any points of special
concern follow the description of the procedure.
●
Before disassembling any part of the printer, note the warnings in Section 3.1.
●
Before disassembling any part of the printer, remove the paper and the ink
Disassembly includes the following seven procedures:
1.
Removing the printhead.
2.
Removing the upper housing assembly.
Removing the MAIN and
3.
4.
Removing the printer mechanism.
Removing the interface board assembly.
5.
Disassembling the driven roller assembly.
6.
Disassembling the color upgrade kit
7.
PSB/PSE
board assemblies.
Refer to the diagrams in the appendix to see how components fit together.
rt”bbon.
,’
START
I
1
I
Unplug the power cable and the
interface cable from h
I
3.2.2.1
Rem-wing the Upper Housing Assembly
Removing the MAIN and
E&
prfntart
I
1
PSB/
PSE
Boerd
I
I
3-9
!echsnism
3.2.4.1
Removing the PF Motor
3.2.4.3
Removing the Platen
3.2.4.5
Removmg
the Carnage Assembly
Assemblies
I
i
13-12
I
Removing the Driven Roller
Rerswing
the
Ejecl
Removirw the CR Motor
Renwma
the PE Sensor
Removing the Release Lever Position Sensor
3.2.4.8
Rernowng
the
Rtbb@
Roller
AexmMy
Drive Gear
Aawmbly
1
] 3-16
Aaeembly
I
3.2.4.9
Removing
3.2.5
Removing the Interface Board Assembly
I 3-18
Figure 3-1. Procedure for Disassembling the Printer
3-4
the
PG Sensor
3-17
I
I
I
Rev.A
Page 63

LQ-300 Service Manual
Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.1 Removing the
Remove the printer cover assembly, edge guide assembly, ribbon cartridge, tractor assembly,
1.
Printhead
platen knob, and color upgrade kit.
2. Remove
3. Remove the
4. Remove the head cables
the
CPB (M3 x 14) screw attaching the
printhead.
(FFCS)
from the
printhead.
Printhead
printhead
to the carnage assembly.
FC
Fgiure
3-2. Removing the Printhead
Rev.A
3-5
Page 64

Disassembly and Assembly
LQ-300 Service Manual
3.2.2 Removing the Upper Housing Assembly
1. Remove the printer cover assembly, edge guide assembly, ribbon cartridge, tractor assembly,
platen knob, and optional color upgrade kit.
2. Remove 4
assembly.
3. Lift off the upper housing assembly.
CPB (M4
x
12) screws
attaching the upper housing assembly to the lower housing
Upper Housing Assembly
Housing Assembly
Figure 3-3. Removing the Upper Housing Assembly
3.2.2.1 Removing the Eject
1.
Remove the upper housing assembly ( see Section 3.221).
2. Lift the eject roller assembly up and atan angle from theupperhousing assembly.
Note:
User care
when removing the eject
Roller Assembly
ro//erassemb/y,
v
or the 500 g spring may pop out.
=
500g Spring
Upper Housing Assembly
~
Eject Roller Assembly
‘N
3-6
Figure 3-4. Removing the Eject Roller Assembly
Rev.A
Page 65

LC?-300
Service Manual
Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.3 Removing the MAIN and
Remove the printer cover assembly, edge guide assembly, ribbon cartridge, tractor assembly,
1.
PSB/PSE
Board Assemblies
platen knob, and optional color upgrade kit.
Remove the upper housing assembly (see Section 3.2.2).
2.
Disconnect 4 flexible flat cables
3.
(FFCS)
and 7 connectors from the MAIN and
PSB/PSE
board
assemblies.
4.
Remove 4
assemblies, the
CBB (M3
CBB (M3
x 8) screws attaching the shield plate to the MAIN and
x 8) screw attaching the CS board, and the
PSB/PSE
CB(0) (M4
board
x 8) screw
attaching the ground wire of the power cable.
Disengage the shield plate and W and
5.
PSB/PSE
board assemblies from the grounding
plate.
CBB(M3X8)
MA
PSB/PSE
/
Board
Shield Plate
AssemblY
M4x8)
CBB(
Grounding Plate
Figure 3-5. Removing
the Shield Plate
round
Wire
er Cable
Rev.A
3-7
Page 66

Disassembly and Assembly
LQ-300 Service Manual
3.2.3.1
1. Remove the
2. Remove the
Removing the
PSB/PSEboard
CBC
(M3x8)screwand the3CBUSCAC
MAIN Board Assembly
assembly
FFC fromconnector CN20fthe
(M3
MAIN board assembly.
x8).
3. Remove the MAIN board assembly.
3.2.3.2 Removing the
1.
Remove the
FFC
PSB/PSE
for the
PSB/F’SE
Board Assembly
board assembly from connector CN2 on the MAIN board
assembly.
2. Remove he CB
3. Remove the
●
When replacing the MAIN board assembly, bend the LED lead wires parallel to the MAIN
board assembly
●
The shield plate is easily bent; be
MAW
and
CBUSCA
USCA
C
(M3
PSB/PSEboard
(see
Figure 3-7).
PSBIPSE
board assemblies.
C(M3X1O)
x 10) screw and 2 CB
assembly.
carefil
when tightening the screws that attach it to the
CBUSCA C(M3X8)
USCA
C
(M3
x 8) screws.
CBUSCA C(M3X8)
CBC(M3X8)
\
\,
\@
*A
\f\/’#J@?y
FFc shield
/
.
,1,
.
Plate
<’
/
PSB/PSE Board Assembly
~~Q
MAIN Board Assembly
Figure 3-6. Removing MAIN and PSB/PSE Board Assemblies
CBUSCAC(M3X8)
$
~’
u
3-8
MAIN Board Assembly
\
Figure 3-7. Bending the LED Lead Wires
Rev.A
Page 67

LQ-300 Service Manual
Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.4 Removing the Printer Mechanism
1.
Remove
tie Pfiter cover
assemblies, edge guide assemblies, ribbon cartridge, tractor
assemblies, platen knob, and optional color upgrade kit.
2.
Remove the upper housing assembly (see Section 3.2.2).
Remove the connectors and
3.
4.
Remove the 3 lower housing shafts (1018296).
Remove the other lower housing shaft (1015457). (Note that this shaft is different from the
5.
FFCS
from the MAIN board assembly.
three described in the previous step.)
Remove the printer mechanism.
6
Lower Housing
Shaft (1015457)
Lower Housing Assembly
Lower Housing
Shaft
(101 8296)
n
Rev.A
Figure 3-8. Removing the Printer Mechanism
3-9
Page 68

Disassembly and Assembly
LQ-300 Service Manual
3.2.4.1 Removing the PF Motor
1. Remove the printer mechanism (see Section 3.2.4).
2. Remove the platen grounding spring
3. Remove the CBB (M3 x8) screw attaching the
thatsecures theplatenshaft
PFmotorto the
nghtframe.
(see Section 3.2.4.3).
4. Release the clip holding the PF motor assembly from the right frame.
5. Remove the PF motor from the right frame.
Figure 3-9. Removing the PF Motor
PF
Motor “
3-1o
Rev.A
Page 69

LQ-300 Service Manual
Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.4.2
1.
Removing the CR Motor
Remove the printer mechanism (see Section 3.2.4).
2. Remove the extension spring from the hook on the CR motor and the hook on the base frame.
3. Remove the timing belt from the pulley drive.
4. Remove the E-ring, pulley washer, belt pulley flange, and pulley drive from the CR motor.
5. Rotate the CR motor counterclockwise and remove it.
Timing Belt
Extension Spring
Right Frame
Figure 3-10. Removing the CR Motor
Rev.A
3-11
Page 70

Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.4.3 Removing the Platen
1. Remove the printer mechanism (see Section 3.2.4).
2. Remove the platen
3. Remove the 25 mm gear from the right frame.
4. Disengage the teeth of the 211 mm bushings and rotate them.
5. Rotate the platen and
fir
i’-’~
gmundingspring
&move
I
lrnm
Busing
that secures the platen shaft.
it.
Platen
‘@(!!?=-”mmGear
<
-++(I
Am’
LQ+OO
Service Manual
piaten Grounding
*
Spring
Right ‘Frame
Figure 3-11. Removing the Platen
25mrn Gear
3-12
Rev.A
Page 71

LQ-300 Service Manual
Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.4.4
1.
2.
3. Release the friction shaft of theupperpaper Wide from the clips on the right and left frame.
4. Remove the upper paper guide from the right and left frame.
Removing the PE Sensor
Remove the printer mechanism (see Section
Remove the platen (see Section3.2.4.3)-
3.2.4).
~J.:,,pD’ve::e:::ier.uide
14.2g Compression
Spring
Left Frame
\
01
1,
<
a~q
~
Ct,
&’&
k?
\
-.
1,
‘i
L
‘\
PE Sensor
Friction Shaft
I
~~~-~gcompression
Figure 3-12. Removing the PE Sensor
5.
Release the 2 clips securing the PE sensor and remove it.
PE Sensor
\
Upper Paper Guide
Figure 3-13. Wiring of the PE Harness
Frame
mess
Rev.A
3-13
Page 72

Disassembly and Assembly
LG?-300
Service Manual
3.2.4.5
1.
2. Release the 2 clips attaching the HP sensor and remove it. The clips
Removing the HP Sensor
Remove theprinter mechanism (see Section 3.2.4).
can
be accessed though 2
holes in the base frame. To release the clips, push each with a pair of tweezers.
Base
Figure 3-14. Removing the HP Sensor
3.2.4.6 Removing the Release
1. Remove the
2. Release the 2 clips that attach the release lever position sensor to the frame of the
assembly.
3. Remove the release lever position sensor from the frame of the PFmotor assembly.
PFmotor
assembly (see Section 3.2.4.1).
Lever Position Sensor
Frame of the
PF Motor
/
Release Lever
Position Sensor
.
PF
Clip
motor
3-14
Figure 3-15. Removing the Release Lever Position Sensor
Rev.A
Page 73

LQ-300 Service Manual
3.2.4.7 Removing the Carriage Assembly
1.
Remove the printer mechanism (see Section 3.2.4).
2. Remove the belt tension spring from the hook on the CR motor (see Section 3.2.4.2), and
remove the carriage assembly timing belt from the drive pulley.
3. Release the hook that attaches the head cable sheet to the base frame. Slide the cable to the left
and remove it.
4. Remove the printhead
5. Remove the CR shaft grounding plate from the left side of the printer mechanism.
6. Rotate both sides of the parallelism adjustment bushing and remove them from the left and
right frame.
7. Remove the CR guide shaft assembly and the carriage assembly.
FFC
from the base frame.
Disassembly and Assembly
CR S
Paralleli
Adjustm
,ase,rame
-’y2y!//Righ’Frame
Cable Head
w
Figure 3-16. Removing the Carriage Assembly
9
Rev.A
3-15
Page 74

Disassembly and AssemblY
LQ-300 Service Manual
3.2.4.8
1. Remove the printer mechanism (see Section 3.2.4).
2. Release the 3 hooks attaching the ribbon drive
3. Remove the RDcover.
4. Remove the belt tension spring between the hook on the CR motor assembly and the hook on
5. Remove the timing belt from the driven pulley.
Removing the Ribbon Drive Gear Assembly
(RD)
cover to the left frame.
the base frame (see Section 3.2.4.2).
Make sure not to put the timing belt between the RD cover and the
RD
Ratchet
RDCover,,o
“No
p
Ribbon Planetary
Gear
Shafi 5.1 ,16.2mm
Combination
G“
Plane Washer>
Spring
4
Gear
Washer”
~2.3m\<17mjn,f3eH
“e.
+Q
&
~
,
,
5,
.WL
/
e
leftj%ame.
pulley
Washer
Belt Pulley Flange
Pulley
Driven Shaft Pulley
1,.zmm Gear
Driven
‘d
\
““’mmGear’
‘ Left Frame
‘:
“%5116.2mm
C“ornbination
Gear
\q
~$<”
Base Frame
q
‘o&
~
&
J’
:h:\
IL
‘:’y-&
1
c
Figure 3-17. Removing the Ribbon Drive Gear Assembly
3-16
Rev.A
Page 75

LQ-300 Service Manual
Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.4.9 Removing the PG Sensor
1.
Remove the printer mechanism (see Section 3.2.4).
2. Release the 2 clips attaching the PG sensor and remove it. The clips can be accessed through 2
holes in the left frame; to release the clips, push each with a pair of tweezers.
/
PG
/
Sensor
Left Frame
Figure 3-18. Removing the PG Sensor
Rev.A
3-17
Page 76

Disassembly and Assembly
LWOO Service Manual
3.2.5 Removing the Interface Board Assembly
1. Remove theprinter mechanism (see Section 3.2.4).
2. Remove the grounding plate connecting the interface shield plate and theshieldplate.
3. Remove the
the lower housing assembly.
4. Remove
assembly.
5. Remove the bottom cover and the interface board assembly.
the
CBB (M3
2
CBB (M3
x 8) screw and the
x 8)
SCreWS attaching
CBB (M3
the
x 10) screw attaching the bottom cover to
interface board assembly to the lower housing
l/F
Board Assembly
Grounding Plate
Lower Housing Assembly
Figure 3-19. Removing the Interface Board Assembly
3-18
Rev.A
Page 77

LQ-300 Service Manual
3.2.6 Removing the Driven Roller Assembly
Remove the printer cover.
1.
2. Remove the
3. Remove the driven roller assembly.
Driven Roller
CFP (M2.6
x 8) screw attaching the driven
CFP(M2.6X8)
roller
Disassembly and Assembly
assembly.
73g Spring
\
1“
Driven Roller Holder /
Ta/A
“ven’o’’ercover
Figure 3-20. Removing the Driven Roller Assembly
“h
I
/
\Kf..w
pfinter~er
,
\~
Rev.A
3-19
Page 78

Disassembly and Assembly
LQ-300 Service Manual
3.2.7 Disassembling and Assembling the Color Upgrade Kit
3.2.7.1 Removing the Ribbon Motor Assembly
1. Remove
the
2
CBB
(h43
x 8) screws attaching the ribbon motor assembly to the CS cover.
2. Release the 2 clips attached to the CS cover.
3. Remove the ribbon motor assembly along with the CS board assembly from the CScover.
3.2.7.2 Remove the CS Cam
1. Remove theribbonmotor assembly (see Section 3.2.7.1).
2. Remove the E-ring3 from the CS frame shaft.
3. Remove the CS cam
3.2.7.3 Removing the Color Sensor Assembly
1. Remove the ribbon motor assembly andthe
2. Remove the 4rnm
E-ringfrom
thecartridge holder shaft.
3. Remove the color cartridge holder from the ribbon motor assembly.
4. Release the clip that attaches the color cartridge holder to
5. Remove the connector of thecolorsensor assembly fromthe
CS Cover
\
-
P
-1 /
CSboardassembly
CS
Board Assembly
(see Section 3.2.7.1).
tie
color sensor assembly.
CSboardassembly.
‘“p
I
p
CS
\
CBS(M3X6)
3mm E-ring
Cam
Color Cartridge Holder
Figure 3-21. Disassembling the Color Upgrade Kit
9
/
CS Lever
3-20
Rev.A
Page 79

CHAPTER
4 Adjustments
Table of Contents
4.1 ADJUSTING THE PRINTER MECHANISM
4.1.1 Platen Gap Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.2 DEFAULTS, MACHINE INFORMATION
BIDIRECTIONAL ADJUSTMENT
4.2’.1 Default Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
4.2.2 Bidirectional Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SEITINGS,
AND
List of Figures
Figure 4-1. The Flowchart of the Platen Gap Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Figure 4-2.
The Bidirectional Pattern Print. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-1
4-1
4-2
A-A
4-4
Page 80

LQ-300 Service Manual
Adjustments
4.1 ADJUSTING THE PRINTER MECHANISM
This section describes the adjustments you may need to make to the printer mechanism.
4.1.1 Platen Gap Adjustment
If
you have rotated or reassembled the CR guide shaft assembly or the parallelism adjustment
bushing, or if printing is abnormal, you must adjust the platen and the
1.
Set the release lever to the friction position.
2.
Remove the upper housing assembly (see Section 3.2.1).
3.
Set the gap adjustment lever to O.
4.
Remove the
5.
Remove the ribbon mask with a pair of tweezers.
6.
Install the
7.
Adjust the platen gap using the flowchart below. The correct platen gap is 0.455 mm
0.015 mm. When measuring the gap, take care to let the gauge fall between the platen and the
printhead
toward the platen using a screwdriver. To reduce the platen gap, turn the parallelism
adjustment bushing away from the platen.
printhead.
printhead.
by gravity only. To
inmease
the platen gap, turn the parallelism adjustment bushing
printhead.
*
START
YES
Is
gap correct on the
right
o
YES
X7
>
the
platen
side?
NO
‘c
L+
ND
Adjust the platen
Adjust the platen
gap on the right
side.
Is the
platen
gap correct on the
left side?
YES
NO
Rev.A
Figure 4-1. Flowchart for Platen Gap Adjustment
4-1
Page 81

Adjustments
LQ-300 Service Manual
4.2 DEFAULTS, MACHINE INFORMATION SEITINGS, AND
BIDIRECTIONAL ADJUSTMENT
4.2.1 Defaults and Machine Information Settings
Perform the procedure below when the main board assembly is replaced.
1.
Connect the printer to a PC.
Turn the printer on.
2.
3.
Load paper into the printer by pressing the
continuous paper.
4.
Load the
Insert a diskette containing the
5.
6.
Load the
When you run the program, the following message appears on the display:
7.
GWBASIC
LQ-300
Adjustment
program onto the PC.
LQ-300
Adjustment Program into the PC’s diskette drive.
Program’’BKMENLJ.BAS”.
LF/FF
button. You can use either cut sheet or
LQ-300
2.
3.
4.
Adjustment Program
1.
EAI, EAI
EDG,
(Latin A), EIS, EIB, EUL, ESP, EHK
EFS
EDG (NLSP)
El-l-
5. END
Do nut input unspecified destination!
Please input each destination No.( 1-4 ) and
Do
not input unspecific destination data!
8.
Press 1-4, then go to adjustment program of each destination
9. The following message appears on the display:
LQ-300
Adjustment Program
Enter
1. Bi-DAdjustment
2. Defaults& Machine Information Settings
3. END
If ready, press 1-3 and the
Enter key. -
Key.
10. The following message
appears on the display:
If you press the Y key, all data stored in the EEPROM on the main board will be initialized to
the factory default settings.
Before proceeding, confirm the following:
1. The printer is comected to the computer correctly.
2. The printer is on.
3. Paper is loaded in the printer.
If ready, press Y and the Enter key. -
4-2
Rev.A
Page 82

LQ-300 Service Manual
11.
Press Y, then Enter. The default setting table appears on the display:
Adjustments
Uo.
1
language
2
Model
3
Character table
4
Page length (Tractor)
Skip-over-perforation
5
6
Auto tear-off
7 Graphic Print Direction
8
Software
9
Auto line feed
10
Interface selection
11
Bit rate
12
Parity bit
13
Date Length
14
ETWACK protocol
15
State Reply
16
Font
17
Model Name
Add Function
ID
SW& Valid
English
PC-437
11 inch
Uni-D
ESC/P2
Auto
Selection(l
19200 bps
None
Roman
LQ-300
STD
OFF
OFF
OFF
8 bit
OFF
OFF
These are the factory defaults programmed into this printer.
0s)
12.
Press Y, then Enter to confirm these settings and return to the initial menu.
13.
Exit the program by pressing 3, then Enter.
14.
The following message appears on the display:
r
Any setting value specified within this program
is not stored in the
EEPROM until
you turn the printer OFF.
Turn the printer OFF now.
15.
Turn the printer off to store the defaults shown above into the
EEPROM
assembly.
Notes:
1. If you have replaced the main board assembly, you must also perform the bidirectional
adjustment procedure after competing this procedure.
2. The
SOi7VVAREand
setting by this program, but we cm only change those settings by operation panel.
INTERFACE settings are not been able to change to Factory
on the main board
Rev.A
4-3
Page 83

Adjustments
4.2.2 Bidirectional Adjustment
This
section describes the adjustment procedure necessary when the
or when parts are reinstalled or replaced.
assembly has been replaced.
This procedure is also necessary if the main board
LQ-300 Service Manual
LQ-300
printer is reassembled
Notes:
1. Connect the printer to a PC.
2. Turn the printer on.
3. Load paper into the pninterbypressing the
4. Load the
5. Insert a diskette containing the LQ-300Adjustment Program into the PC’s diskette drive.
6. Load the
7. When you run the program, the following message
●
When
the
main boadis
procedure first, then perform
●
Theprintercover
notperfonn
. Do
. The optional color upgrade
GWBASIC
LQ-300
LQ-300
1.
2. EDG, EFS
3. EDG
4. El-r
5. END
Do nut input unspecified destination!
Please input each destination
the
program onto the PC.
Adjustment Program’’BKMENU.BAS”.
Adjustment Program
EAI, EAI(Latin
(NLSP)
rep/aced, perform the Defaults& Machine Information Settings
the Bi-D
mustbe installed
Bi-D
Adjustment
kitmustbe
A), EIS, EIB, EUL,
whenyouperfonn
procedure if the input voltage is fluctuating heavily.
No.(
1-4 ) and Enter Key.
Adjustment procedure.
the
Bi-Dadjbstment.
removed when youpefform the
LF/FF
button.
appeam
ESP,
on the display:
EHK
Bi-Da~”ustment.
8.
Press 1-4, then go to adjustment program of each destination
9. When you input
1.
Bi-D
2. Defaults& Machine Information Settings
3. END
If ready, press 1-3 and the
10. Type 1 to select
5 rows of H characters in both draft and LQ modes.
printing, the message
iili’t!
Dra.
LQ
——
-4, the following message
1
LQ-300
Adjustment
Adjustment Program
Enter key. –
Bi-D
Adjustment then press Enter.
“Bi-DTESTPIUIWING”
Ii
ii
It El II II I II II II El II El II El El B II II
appeam
on the display:
After 10 line feeds, the printer prints
When the printer begins bidirectional
appears on the
HI
displ~y.
-
II
4-4
ih:il
II
Figure 4-2. The Bidirectional Pattern Print
II
II
K I Ii Ii Ii Ii Ii II II II B Ii
II
K [
II
Rev.A
Page 84

LQ-300 Service Manual
After printing is complete, the following message appears on the display:
11.
Adjustments
K
From the 5 rows of draft patterns, find the row in which the vertical lines in the H are best
aligned, then enter the value assigned to that row. The following figure is an example of the
Bi-D
printout.
After you enter the value for draft, the following message appears on the display:
12.
m
From the 5 rows of LQ patterns, find
the
row in which the vertical lines in the H are best
aligned, then enter the value assigned to that row.
13.
The printer lets you check your print pattern selection for confirmation following steps 9 and
10 by printing one row of the pattern you selected.
14.
After the printer prints check patterns for confirmation, the following message appears on the
display:
If
Bi-D
is correct, press “Y” and the Enter key, and
d
BI-D M
incorrect, press N and
Enter. –
ET
If your printed pattern is aligned vertically, press Y and Enter to complete the
15.
adjustment. Otherwise, press N to return to step 11 to specify another adjustment
value.8.
Bi-D
Rev.A
4-5
Page 85

Chapter 5 Troubleshooting
Table of Contents
5.1 OVERVIEW
UNIT LEVEL TROUBLESHOOTING
5.2
5.3 REPAIRING THE MAIN BOARD ASSEMBLY
5.4 REPAIRING THE PRINTER MECHANISM
Figure 5-1.
Figure 5-2.
Figure 5-3.
Figure 5-4.
Figure 5-5.
Figure 5-6.
Figure 5-7.
Figure 5-8.
Figure 5-9.
List of
Troubleshooting Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Printhead ConnectorPin Alignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Flowchart Symbols ., . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Flowchart - 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
Flowchart-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Flowchatt
Flowchart -4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Flowchart -5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Flowchart -6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figures
5-1
5-4
5-11
5-13
5-1
5-4
5-6
5-7
5-8
s-g
5-10
List of Tables
Table 5-l,
Table 5-2. MotorDriverTest Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Table 5-3.
Table 5-4. SensorTest Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Table 5-5. Error State Indication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Table 5-6. Symptomsand Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
Table 5-7. Repairing Problems in the Main Board Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-11
Table 5-8. Repairing the Printer Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-13
PrintheadCoil
MotorCoil
ResistanceTest Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-1
Page 86

LQ-300 Service Manual
5.1 OVERVIEW
Follow the procedures in the flowchart below to identify printer problems.
START
Troubleshooting
Note:
Section
T
I
i
1
I
Description
t
Page
*W
( The Fault is Corrected )
Figure 5-1. Troubleshooting Procedures
/f the power supply board assembly is faulty, it must be replaced as a whole unit. No field
repair should be performed on it, except for the replacement of
tise F1.
The following tables provide troubleshooting information.
I
Part
Printhead
Table 5-1.
I
Coil resistance 54.7 Q * 3.9 Q at 25° C (77°
Printhead
Coil Resistance
Specifications
F)
I
Rev.A
5-1
Page 87
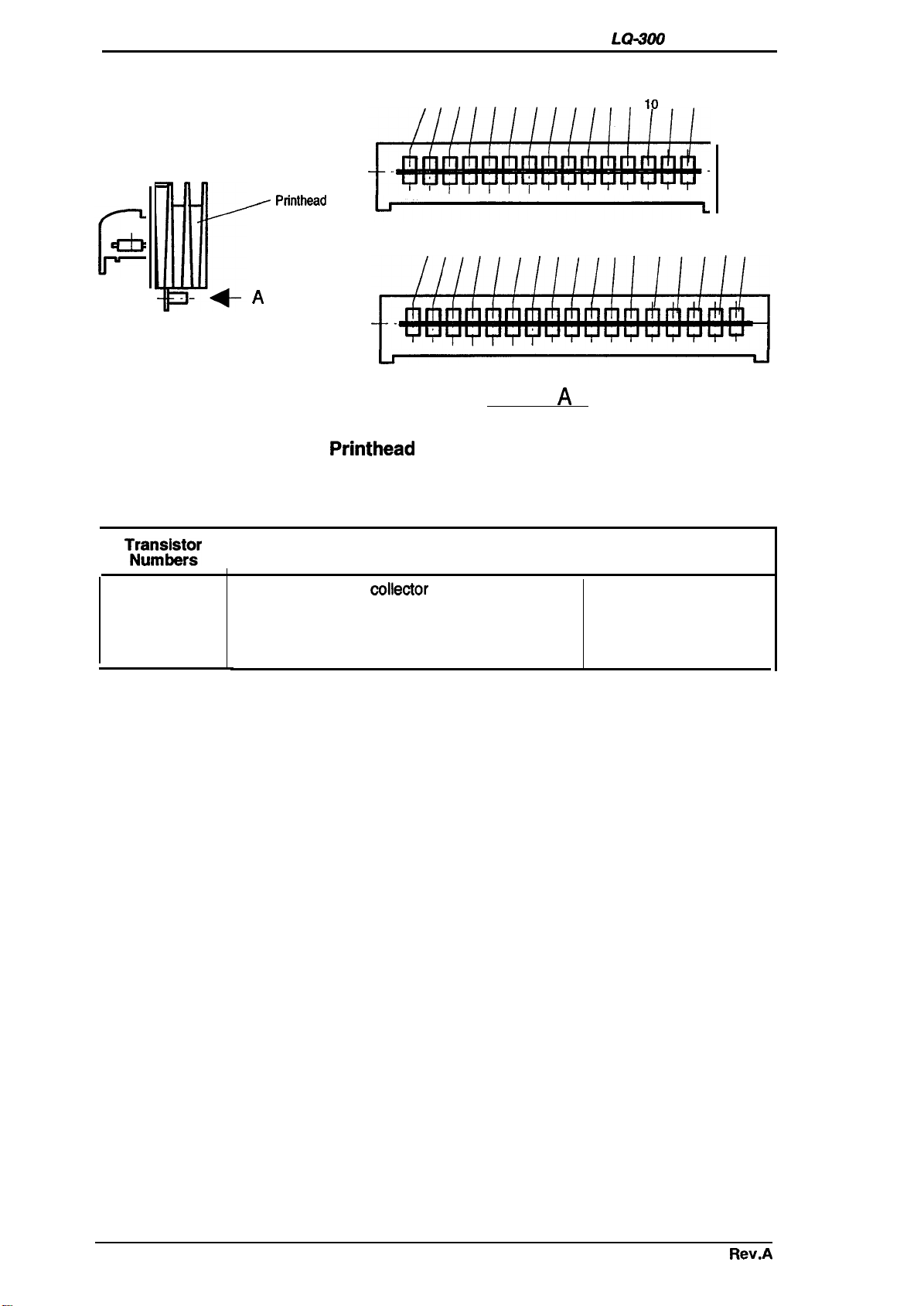
Troubleshooting
~ Printhead
A
LQ-300 Service Manual
Head
Pin No.
311 219 7 C C C 22151823
Head
Pin No.
5 1 13 921 17 C C C 2416 12 8 20 4
View
A
10
14 6
C: COMMON
T
T
T~::sis;:r
I
PF Motor
(Q2, Q3, Q4, Q5
Driver
Figure 5-2.
Printhead
Connector Pin Alignment
Table 5-2. Motor Driver Test Points
(Set Meter to Diodes. Check wfth Power Off.)
I
Cheek from base to ooliector and from base to
emitter.
Reverse leads and test again.
(Emitter and base are marked on the main board
assembly.)
Test Method
Meter Reading
I
The reading should be
neither open nor shorted
from
base to collector or
base to emitter.
5-2
Rev.A
Page 88
LQ-300 Service Manual
Troubleshooting
Table
Motor
Connector
Number
CR Motor
(CN2)
PF Motor
(CN3)
CS Motor
(CS
Board
Assembly)
Sensor Connector
Number
Common
Pin
Number
3
3
5
5-3.
Motor Coil Resistance Test Points
Test
Method
Test
Pin
Number
1,2,4,5
1,2, 4,5
1,2,5,6
(Set Meter
Motor from Main Board and Check it
with Printer Power Off.)
Place one lead on pin 3 and the other
lead on each of the 4 test pins to check
the two motor
Place one lead on pin 3 and the other
lead on each of the 4 test pins to check
the two motor phases.
Place one lead on pin 5 (brown) and the
other lead on each of the 4 test pins to
check the 4 motor phases. (Pin 3 is a
common pin.)
to Ohms. Disconnect
Dhases.
Table 5-4. Sensor Test Points
Set Meter to Ohms. Check Printer witt
Test Method
Power Off.)
Meter Reading
19.6f2
k
8?X0
25° C, 77° F)
58.5Q
+
s~o (at
25° C,
77°
150Q f
25° C, 77° F)
Method Reading
5% (at
(at
F)
HP sensor
PE sensor
Release Lever
Position Sensor
(CN9)
Platen Gap Sensor
(CN1O)
Color Ribbon
Sensor
Assembjy)
The printer beeps
and the PAUSE light
blinks
The printer beeps (---
and the PAUSE light
stays on
(CN8)
(CN7)
(CS
Board
Error Indication
(**o)
Place one lead on pin 1
lead on pin 2. Toggle the sensor position
Plaoe
lead on pin 2. Toggle the
inserting
Place one lead on pin 1 and the other
lead on pin
lever position.
Place one lead on pin 1 and the other
lead on pin 2. Change the paper-release
lever position.
Place one lead on pin 1 and the other
lead on pin
and the other
one lead on pin 1 and the other
sensor by
and removing a sheet of
2.
Change the paper-release
2.
Toggle sensor position.
paper.
Meter should toggle between
oDen
and shott.
Meter should toggle between
open and short. (Open = paper
installed.)
Meter should toggle between
open and short. (Open =
continuous paper.)
Meter should toggle between
open and short. (Open = platen
gap lever position 2 -6)
Meter should toggle between
open and
shott.
Table 5-5. Error State Indication
Error Status
Paper-out Paper is not installed
error.
)
Operating
error. position before the cut sheet is ejected.
Fatal error.
. The release lever is set to the TRACTOR
. The release lever is set to the FRICTION
position before the continuous paper is ejected.
Power supply voltage is abnormal.
Cause
(ODen
= home.)
(Open= active.)
Notes: (*) Theprinterbeeps
The
pfinterbeeps for
(-)
Rev.A
for 1/10 ofa second with a
1/2
of a second with a l/10-second pause.
l/10-secondpause.
5-3
Page 89

Troubleshooting LQ-300 Service Manual
5.2 UNIT LEVEL TROUBLESHOOTING
You may be able to identify the defective unit just from the symptom displayed. The table below
provides the symptoms for a number of failures, so that you can easily identify the problem. Once
the problem has been identified, refer to the flowchart listed in the right-hand column of the table
bel~w
to determin
e the cause of the problem.
Table 5-6. Symptoms and Problems
Symptom
Printer fails
when the power is on.
Abnormal carriage
operation.
Printing is faulty during
self-test, but carriage
oDeration
Abnormal paper feed.
Abnormal control
panel operation.
Data sent by the host
computer is printed
incorrectly.
The repair procedure flowcharts use the following symbols:
to operate
is normal.
● Carriage does not move.
. Control panel indicator
●
Carriage moves away from
. The carriage returns to home position correctly, but the
printer then fails to enter the READY mode.
● No printing at all.
. Faulty printing — some of the dot are not printing.
. The printer prints but paper feeds incorrectly.
. When the LF/FF button is pressed, no paper is fed.
. Carriage operates normally at power up, and self-test
is executed
. Data from the computer is printed
correotly,
Problem
LEDs do not light.
home position at power on.
but data is not printed.
inoorreotly.
See Page
5-5
5-6
5-7
5-8
[
5-9
I
5-1o
o
v
N
v
Figure 5-3. Flowchart Symbols
Decision
Return to the
Start of the item
END
5-4
Rev.A
Page 90

LQ-300 Service Manual
Troubleshooting
1. Printer fails to operate when the power
Is the AC
input voltage normal?
120 V version range is 103.5-132 V
230 V version range is 198-264 V
~“”
Measure the
CN2
2 of
on
PSB/PSE
VP (+35
VDC)
at pins 1 and
Board Assembly.
L
is
on.
‘T
Replace the fuse.
NO
does the new fuse also
Measure the VL
of
CN2
on the
(+9
VDC)
PSB/PSE
at pins 4 and 5
Board Assembly
=’+
Verify each motor’s coil resistance
e’+
Replace the MAIN
Board Assembly.
NO
Replace the PSB/PSE
Board Assembly.
NO
‘-
If any motor is shorted,
be sure to check the driver.
[f the driver is bad, replace
along with the motor.
Rev.A
Figure 5-4. Flowchart -1
5-5
Page 91

Troubleshooting
2. Abnormal carriage operation.
LQ-300 Sarvice Manual
Are connectors CN2 -
CNIO
connecting the MAIN Board Assembly
and the Printer Mechanism
YES
4
YES
4
Check the HP
sensor.
YES
Reinsert connectors
correctly.
NO
See the troubleshooting
items under Printer
*
Mecnanism
(Section 5.4).
NO
YES
motor and drivers with
the same time.
Is the
‘au’tcorrected’
YES
ND
+
YES
corrected7
fault
‘>
Replace the MAIN
Board Assembly
ND
5-6
T
Figure 5-5. Flowchart -2
Rev.A
Page 92

LQ-300 Service Manual
Troubleshooting
3. Printing is faulty during self-test, but carriage operation
Use correct AC input voltage.
120 V version range is 103.5-132 V
0 V version range is 198-264
Hold down the
and turn on the printer to
start printing the self-test.
LF/FF
button
No fluctuation from AC voltage
range is permitted.
Are connectors CN2-
CN1
O from the MAIN Board
is
normal.
T
YES
Verify FFCS are properly inserted
and have
=
tance. If any pins are shorted, be
sure to replace the drivers along
with the r)rinthead.
contlnuky. If they are
w
I
I
Reinsert them
correctly.
YES
I
v
Check all motor resistances
I
I
t
and the drivers for all motors.
If anything is bad or shorted,
ret)lace.
NO
I
Is the fault
corrected?
T
N
v
o
Rev.A
*N*
YES
N
+
Figure 5-6. Flowchart -3
5-7
Page 93

Troubleshooting
4. Abnormal paper feed.
START
T
LQ-3#
Sarvice Manual
I
smoothly
when turned manual
with the power off?
Check the resistance of
the PF motor and check
the PF motor drivers. If
anything is bad, replace.
Is the
fault corrected?
NO
Replace the MAIN
Board Assembly.
+J
YES
NO
N
I YES
N
v
I
*
See the troubleshooting
items for the printer
mechanism ((Section 5.4).
NO
~
Is the
fault corrected?
YES
N
e
5-8
Is the
fault corrected?
YES
91
NO
Figure 5-7. Flowchart -4
Rev.A
Page 94

LQ-300 Service Manual
5. Abnormal control panel operation.
START
T
Troubleshooting
A .
----- .s click ‘‘-
button!
<
Whi
YES
4
Check the switches using a
multimeter.
the upper housing
assemb
IReplace the MAIN Board
If bad, replace
Iv.
YES
.
Replace the upper
?
NO
I
fault corrected?
I
YES
N
9’
Figure 5-8. Flowchart -5
Refer to the other
troubleshooting items.
Rev.A
5-9
Page 95

Troubleshooting
6. Data sent by the host computer is printed incorrectly.
START
Print the self-test.
F
Refer to the other
troubleshooting items.
YES
Check the default settings.
LQ~OO
Service Manual
eNo
YES
4
I
Replace the MAIN
‘F
I
T
NO
YES
ND
+
Increase the the setting of
➤
the paper-thickness lever.
NO
fault corrected?
I
YES
ND
v
I
ND
T7
Adjust the platen gap
(Section 4.1.1).
5-10
Figure 5-9. Flowchart -6
Rev.A
Page 96

LQ-300 Service Manual
Troubleshooting
5.3 REPAIRING THE MAIN BOARD ASSEMBLY
This section provides instructions for repairing a defective main board assembly. It describes
various symptoms, likely causes, and checkpoints.
resistance values, and other values to be checked when evaluating
faulty component. Check these values and take the appropriate
Checkpoints refer to proper waveforms,
the
operation of any potentially
-
a~tion.
Note:
This
section is
required on/y
for semicers who repair to the
component/eve/.
Table 5-7. Repairing Problems in the Main Board Assembly
Rev.A
5-11
Page 97

Troubleshooting
LQ-3OO
Service Manual
Table 5-7. Repairing Problems in the Main Board Assembly (Continued)
5-12
Rev.A
Page 98

LQ-300 Service Manual
5.4 REPAIRING THE PRINTER MECHANISM
Troubleshooting
For detailed procedures for replacing or adjusting parts, refer to Chapter 3,
Assembly,
and Chapter 4,
Adjustments.
If a problem or symptom recurs
Disassembly and
folIowing
repair, refer to Table 5-8 and try to find other potential causes.
Table 5-8. Repairing the Printer Mechanism
Problem
The CR
fails to operate.
The carriage
does not
operate when
turned on
motor
(after the
carriage has
been manually
centered prior
to power on.)
Self-test
printing is not
executed.
Symptom
The CR motor
fails to operate
the timing belt
after power on.
The CR motor The belt
rotates, but
the
oarriage defeotive.
does not move.
The carriage
moves to the movement is moves smoothly when moved
left slightly, not smooth. manually.
then stops.
The carnage
moves to the
left or right
end, then
stops.
The caniage
moves;
does not print. wires are
but
Cause
Foreign
substances
are lodged in
the gears or
elsewhere in
the
mechanism.
The CR motor
is defective.
pulleys are
The
timing
is defective.
The
oarriage Cheek whether the carriage
The HP
sensor is
defective.
The
prirrthead
FFC
common the
disconnected.
The
printhead
is bad.
Manually move the timing belt
to see if the motor can rotate
freely.
Measure the motor coil
resistance. It should be about
19.6
also check the CR motor
drivers on the main board
Check for broken or worn
pulleys.
belt
Ch=k that
inserted correctly into the
bottom of the carriage.
Check for a broken timing belt.
Use a
HP sensor.
Check the common wires for
Measure the
resistance. It should be
approximately 54.7
Printhead
cheek the drivers.
Checkpoint
Q.
If the motor is shorted,
the timing belt
multimeter
printhead FFC.
is shorted, also
to check the
printhead
Q.
is
coil
If the
an attempted
Solution
Remove the
foreign
substances.
Replace the
CR motor (and
drivers, if
necessary).
Replace the
belt pulleys.
Reinsert the
timing
belt.
Replace the
timing
belt.
Clean and
lubricate the
CR guide
shaft. Replace
the CR motor.
Replace the
HP sensor.
Replace the
FFC.
Replace the
printhead
drivers, if
necessary).
(and
Rev.A
5-13
Page 99

Troubleshooting LQ-300 Service Manual
Table 5-8. Repairing the Printer Mechanism (Continued)
Problem
Symptom
Self-test A particular
printing is
abnormal.
Paper feed is
abnormal.
The
ribbon
‘eed is
~bnormal.
dot is missing. is defective.
The printing is The
too light, or the
print
density is
not uniform.
Printing is per- Foreign
formed but the
paper is not are
fed or is not
fed uniformly.
The ribbon is
not turning.
The ribbon
feeds properly gear is
only when the defective.
carriage
moves in one
direction (i.e.,
it fails to feed
when the
carriage
moves in the
other
direction).
Cause
The
printhead
printhead
is defeotive. wires are worn.
The
platen
gap is not the first position, and check the
properly
adjusted.
substances
iodged
the paper path.
The PF motor
is not driving
the gear the gears and that the gears
correctly. are not broken or worn.
The PF motor Measure the coil resistance for
is defective.
The ribbon
cartridge is rotate its ribbon feed knob
defective.
Foreign Cheek whether the RD ratchet Remove any
substances
are caught in
the gears. .
The planetary Move the carriage manually;
Measure the pnnthead
resistance. it should be
approximately 54.7
printhead
check the drivers.
Check to see if the dot wires
are worn.
Check whether the tips of the
Set the gap adjustment lever to
platen gap. The appropriate
value is 0.45 mm.
Perform a visual check of the
paper path.
in
Check that no foreign Remove any
substance is
the PF motor. The approximate
value should be 56 Q. if the
motor is shotied, also check
the drivers.
Remove the ribbon cartridge,
manually, and see if the ribbon
feeds normally.
rotates when the carriage is
moved
check whether the planetary
gear turns in reverse and
engages the gear.
Checkpoint
ooil
Q.
if the
is shorted, also
iodged
between
manuaily. substances.
Soiution
Replaoe
printhead
drivers, if
necessary).
Replace the
printhead.
Replace the
printhead.
Adjust the
gap. Refer to
Section 4.1.1,
Platen Gap
A@Mnent.
Remove any
foreign
substances.
foreign
substances.
Replaoe
PF motor
reduction
gears.
Replace the
paper pickup
gears.
Replace the
PF motor (and
drivers, if
necessary).
Replace the
ribbon
cartridge.
foreign
Replace the
ribbon feed
mechanism.
Replace the
ribbon feed
mechanism.
the
(and
the
.,.
5-14
Rev.A
Page 100

CHAPTER 6 Maintenance
Table of Contents
6.1 PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
6.2 APPLYING LUBRICATION
List of Figures
Figure 6-1.
LQ-300
Lubrication Points. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
List of Tables
Table 6-1. Lubrication
Table 6-2. Lubrication
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Points. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
6-1
6-1
6-1
 Loading...
Loading...