Page 1

DOT MATRIX PRINTER
LC-7211
TECHNICAL MANUAL
[ THIRD EDITION ]
Page 2

NOTICE
• All rights reserved. Reproduction of any part of this manual in any
form whatsoever, without STAR’s express permission is forbidden.
• The contents of this manual are subject to change without notice.
• All efforts have been made to ensure the accuracy of the contents
of this manual at the time of going to press. However, should any
errors be detected, STAR would greatly appreciate being informed of them.
• The above notwithstanding, STAR can assume no responsibility
for any errors in this manual.
© Copyright 1996 Star Micronics Co.,Ltd.
Page 3

INTRODUCTION
This manual is an introduction to the LC-7211.
It is designed for use as a reference for periodic inspections and maintenance procedures to be executed by
service personnel. It is not intended for the general user. Users of this manual should have a basic knowledge
and understanding of the English language.
• This manual is divided into the following sections:
Chapter 1 General Specifications
Chapter 2 Theory of Operation
Chapter 3 Adjustments
Chapter 4 Parts Replacement
Chapter 5 Maintenance and Lubrication
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting
Chapter 7 Parts List
1
2
3
4
• First edition : Dec. 1995
Second edition : Aug. 1996
Third edition : Aug. 1997
5
6
7
Page 4

Page 5

CHAPTER 1
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
1. General Specifications..........................................................................................3
2. External Appearance and Composition ..............................................................5
3. Control Panel .........................................................................................................7
3-1. Switch Combination Functions ............................................................................. 7
3-2. EDS Mode Settings................................................................................................. 8
4. Parallel Interface....................................................................................................9
4-1. General Specifications ........................................................................................... 9
4-2. Connector Signals .................................................................................................. 9
5. Serial Interface (optional) ...................................................................................10
1
5-1. General Specifications ......................................................................................... 10
5-2. Connector Signals and Functional Descriptions............................................... 10
5-3. DIP Switch Settings .............................................................................................. 11
6. EE-PROM Mode ...................................................................................................12
6-1. Outline ................................................................................................................... 12
6-2. Explanation of Special Control Codes................................................................ 12
6-3. EE-PROM MAP ...................................................................................................... 13
6-4. Rewriting the EE-PROM ....................................................................................... 16
Page 6

Page 7

1. General Specifications
Printing System Serial Impact Dot-Matrix
Printing Speed Pitch Draft(cps/dpi) NLQ(cps/dpi)
Pice (10cpi) 225/120H 56/240H
Elite (12cpi) 270/120H 67/240H
Condensed pica (17cpi) 191/240H 95/240H
Condensed elite (20cpi) 225/240H 112/240H
H:half-dot
Print Direction Draft: Bi-directional logic seeking
NLQ: Uni-directional/bi-directional logic seeking (selectable)
Bit-Image: Uni-directional/bi-directional logic seeking (selectable)
Print Head Number of pins: 9
Life: 200 million dots/pin (adjustment lever position 1 to 3)
100 million dots/pin (adjustment lever position 4 to 8)
Line Spacing 1/6", 1/8"
7/72", n/72", n/216": software
Character Matrix Pitch Draft NLQ
Pica (10cpi) 9×11 18×23
Elite (12cpi) 9×918×19
Condensed Pica (17cpi) 9×11 18×12
Coodensed elite (20cpi) 9×918×10
Environment Operating temperature: 41°F to 95°F (5°C to 35°C)
Storage temperature: –22°F to 149°F (–30°C to 65°C)
Operating humidity: 30% to 80% (noncondensing)
Storage humidity: 20% to 90% (noncondensing)
Paper Cut-sheet
Paper width: 5.5" to 12" / 140 to 305mm
Paper length: 5.5" to 11"/ 140 to 280mm
Paper weight (1-ply): 14 to 42 lbs / 52 to 156 g/m2 / 45 to 135 kg
Multi-part: 11 to 14 lbs / 40 to 52 g/m2 / 34 to 45 kg; pressure
sensitive paper
Total thickness: 0.020" / 0.5mm
Copies: Original + 6
Fanfold
Paper width: 4.5" to 12" / 114 to 305mm
Paper weight (1-ply): 14 to 22 lbs / 52 to 81 g/m2 / 45 to 70 kg
Multi-part: 11 to 14 lbs / 40 to 52 g/m2 / 34 to 45 kg; pressure
sensitive paper
Total thickness: 0.02" / 0.5mm
Copies: Original + 6
– 3 –
Page 8
Labels
Backing sheet: 4.5" to 12" / 114 to 305mm
Thickness:
Backing sheet 0.0028" to 0.0035" / 0.07 to 0.09mm
Total thickness 0.0075" / 0.19mm max.
Envelope
#10 9.4 × 4.1 / 240 × 104mm
Emulation Standard Mode: EPSON ESC/P (9-pin)
IBM Mode: Proprinter III
Interface Standard: Centronics parallel
Option: RS-232C serial
Ribbon Type On-carriage, dedicated
Fabric monochrome ribbon (Black only)
Z9HD: Standard type
LZ9: Long life type (option)
Ribbon Life Z9HD: 2 million characters (ASCII draft)
LZ9: 4 million characters (ASCII draft)
Power Supply 120V AC +10%/–17%, 230V AC +14%/–13%; 50/60Hz (depending on country of
purchase)
Power Consumption 10W during stand-by
31W during ASCII draft printing
Options SPC-8K Serial-To-Parallel Converter
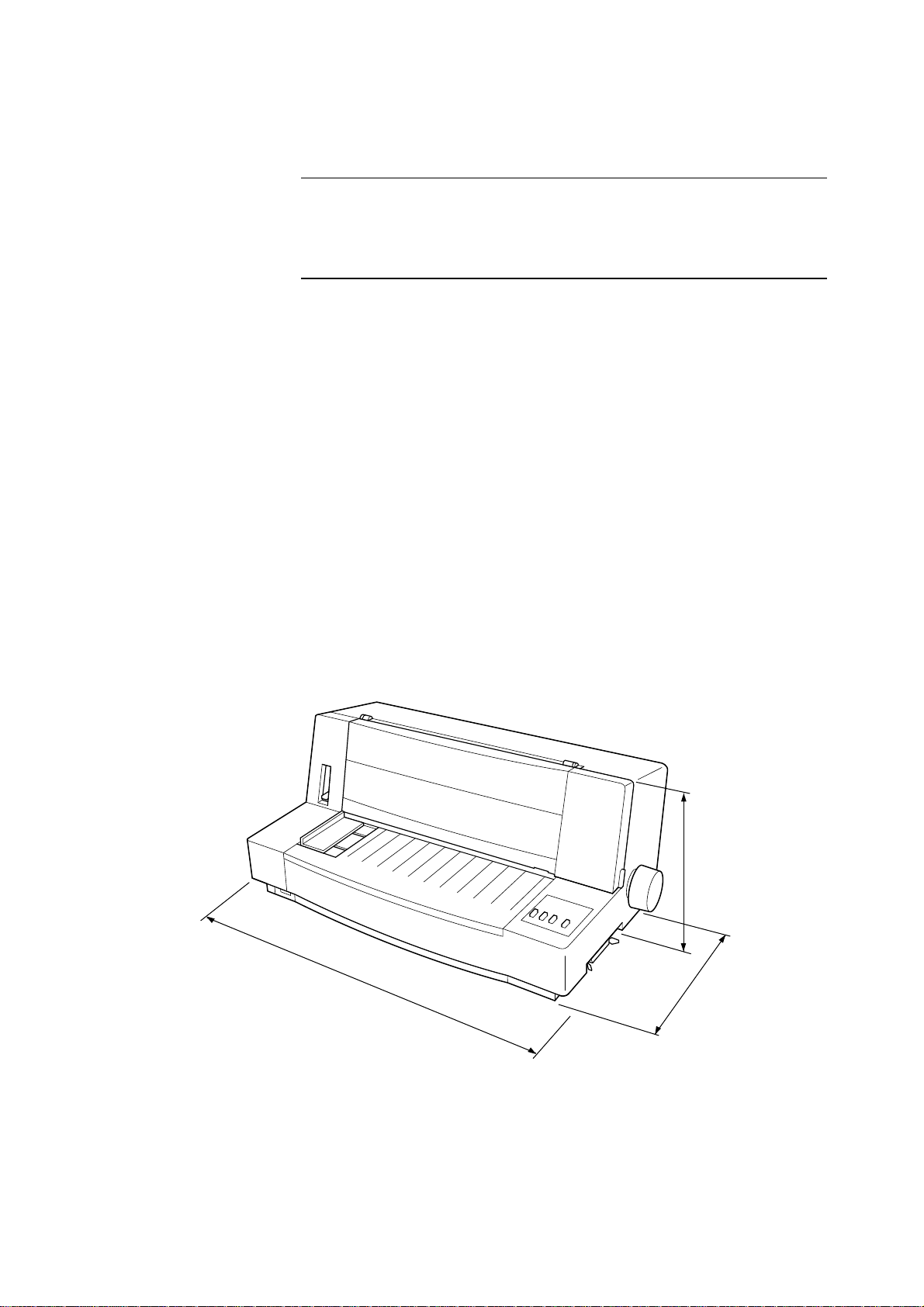
Weight 16.1lbs/7.3kg
525mm
20.67”
Fig. 1-1 External dimensions
– 4 –
230mm
370mm
14.57”
9.06”
Page 9
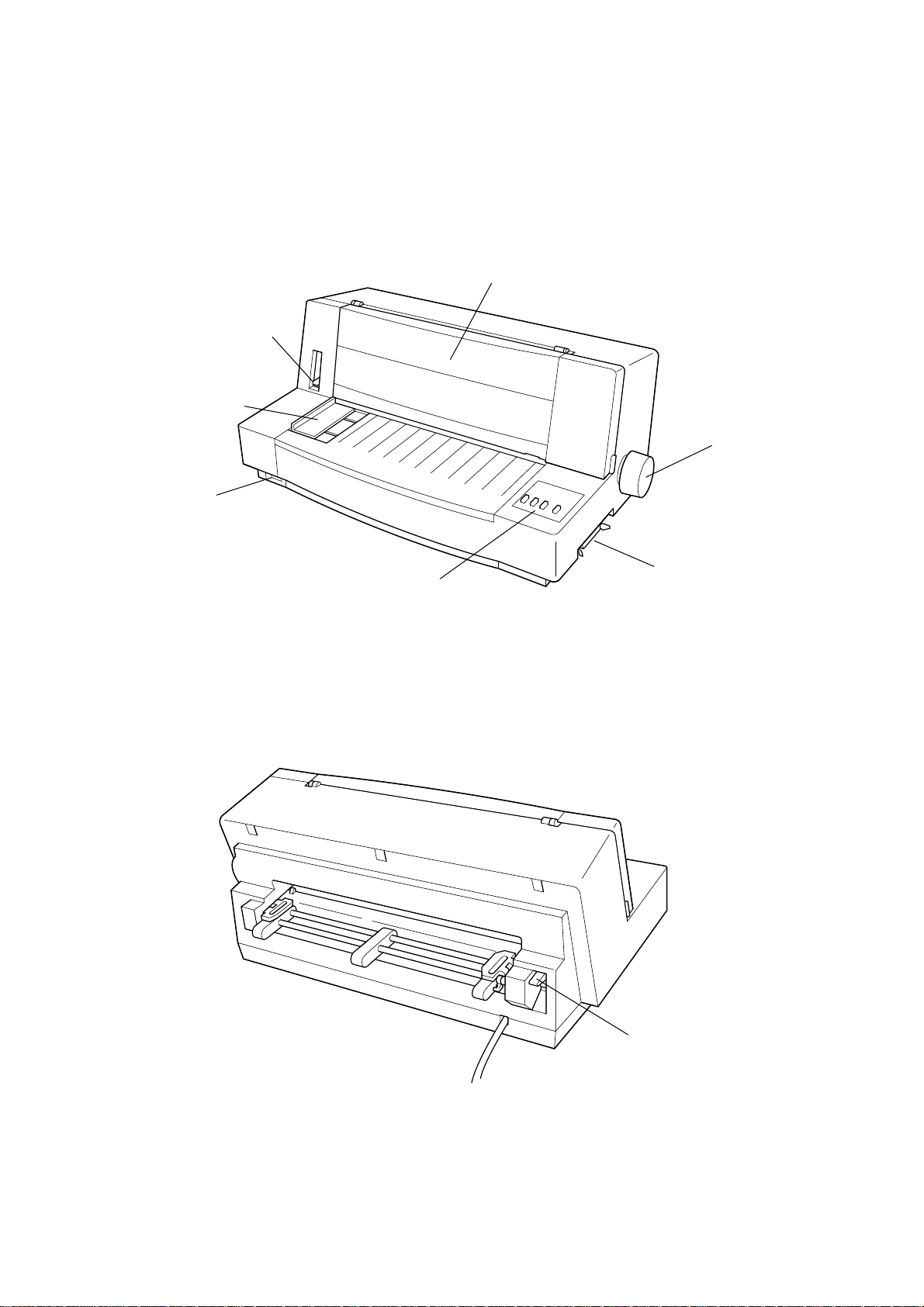
2. External Appearance and Composition
Adjustment lever
Paper guide
Power switch
Front cover
Platen knob
Control panel
Fig. 1-2 Front view of the Printer
Interface connector
Fig. 1-3 Rear view of the Printer
– 5 –
Release laber
Page 10
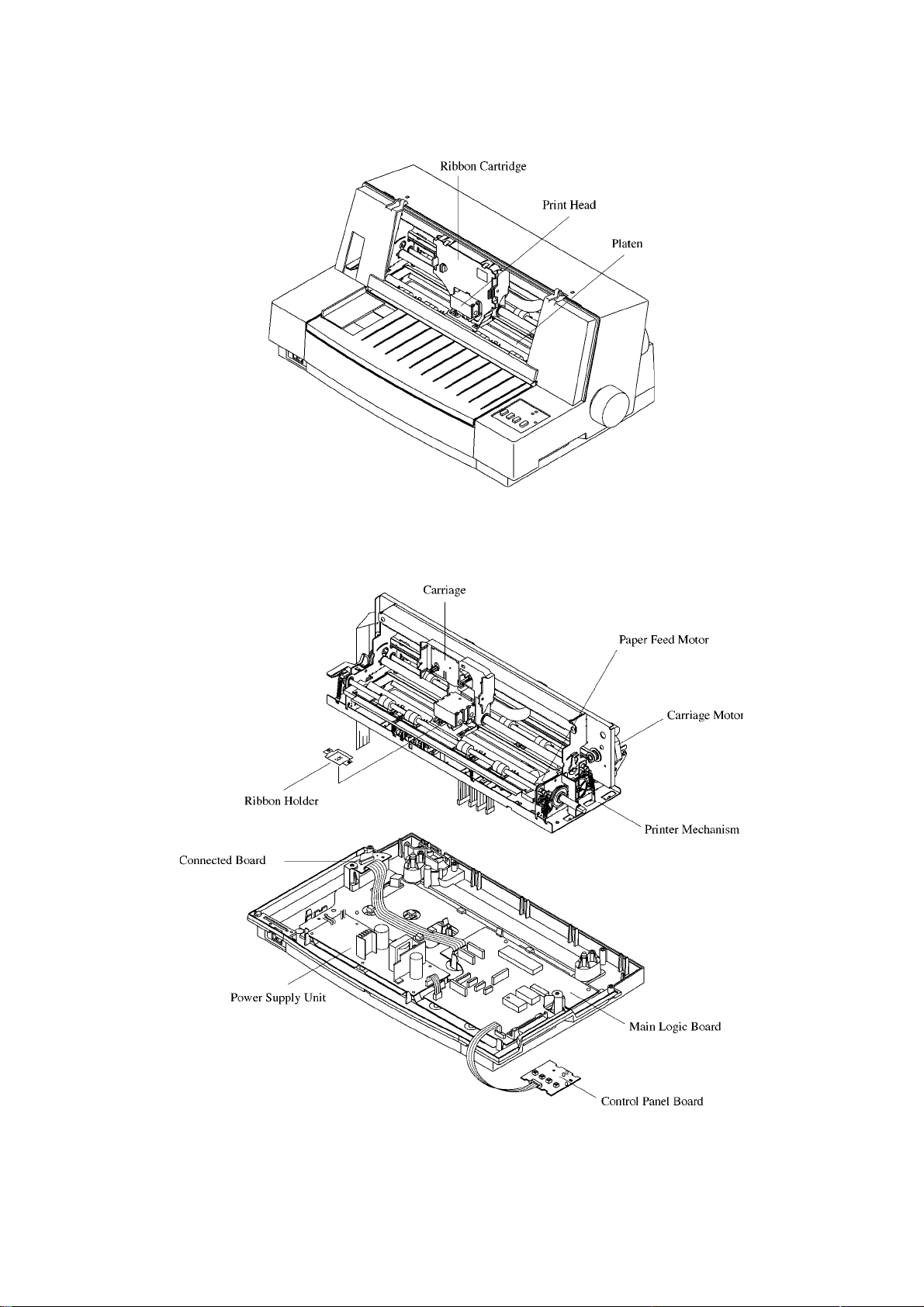
Fig. 1-4 Front cover removed
Fig. 1-5 Diagram of internal layout
– 6 –
Page 11
3. Control Panel
3-1. Switch Combination Functions
BANK SW
A1
ROMAN
B2
SANSERIF
C3
COURIER
D4
PRESTIGE
E5
ORATOR
F
QUIET
FONT MODE LF ON LINE
Hex-Dump Long test Short test 1
MICRO FEED
Short test 2
EDS mode
POWER
DRAFT
QUIET
6
FF
Dot-adjust mode
= Push
= Hold
EDS mode
Aging mode
Tear off Set/Eject/Park Off-LineQuiet
Mode LF/Set On-LineFont
Panel macro Form feed
Backward Forward Micro feed
Set TOF
Buffer clear and All reset
Auto loading position change mode
Bank Switch On/Off Exit
Print
Left Right Next Exit
POWER-ON
ON-LINE
OFF-LINE
EDS MODE
DOT ADJUSTMENT MODE
Paper
Loading
Backward Foward Cancel
Set
Save
Factory settings
AUTO LOADING POSITION CHANGE MODE
– 7 –
Page 12
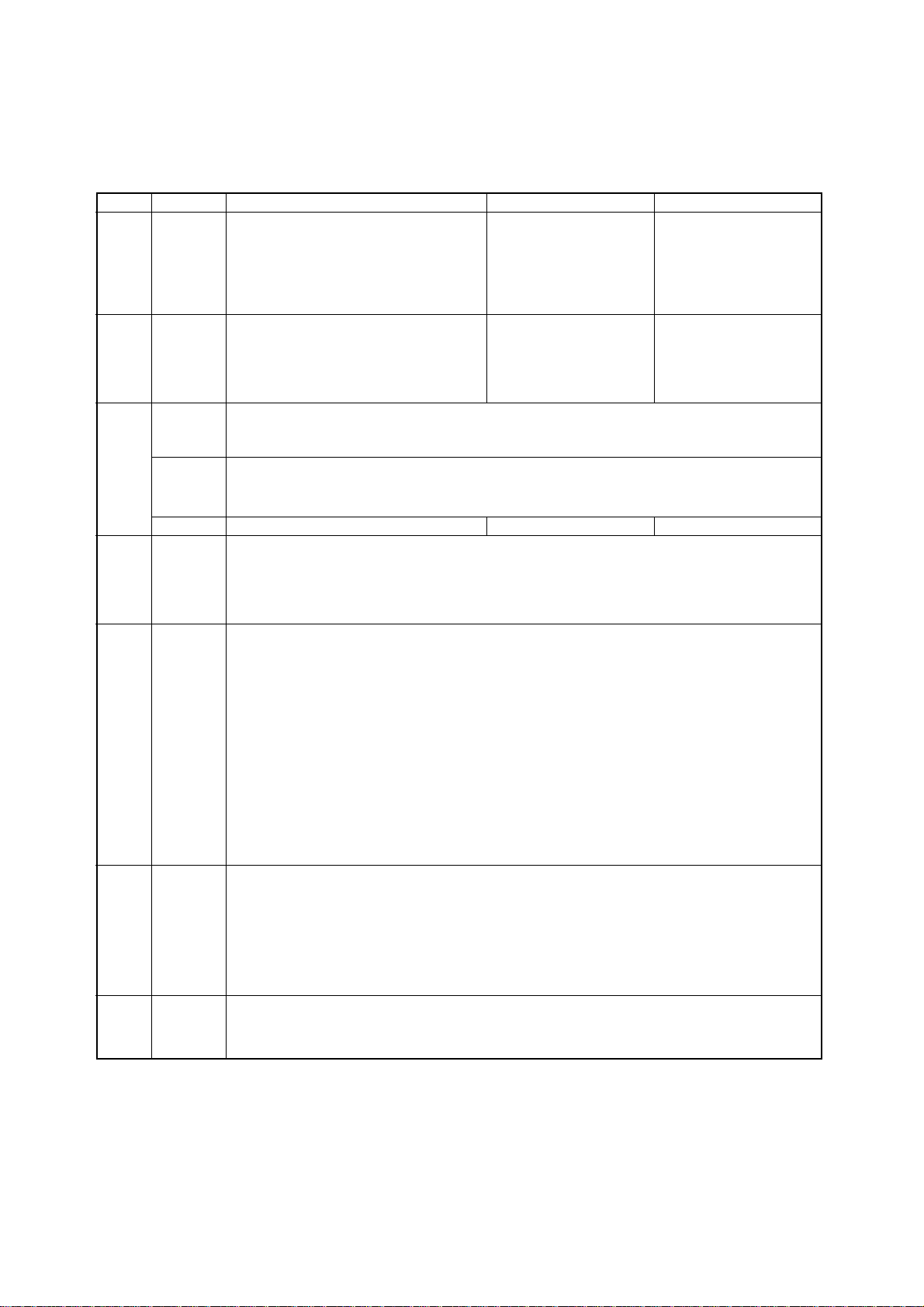
3-2. EDS Mode Settings
Bank Switch Function ON OFF
A 1 Emulation Standard / EPSON IBM
B 1 Graphics Direction Bi-directional Uni-directional
C 1, 2 Print Mode
D 1,2,3,4 Page Length
E 1,2,3,4,5 Code Page (CT=Graphics, IBM #1, #2)
F 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 LQ Font Selection
2 Character Table (CT) Standard / EPSON mode Graphics Italics
IBM mode IBM #2 IBM #1
3 RAM Usage Input Buffer Download Buffer
4 (Not used)
5 Paper Out Detector Enabled Disabled
6 (Not used)
2 Auto Tear-off (Long) Disabled Enabled
3 Line Spacing 1/6" 1/8"
4 Auto LF with CR Disabled Enabled
5 Zero Style Normal Slashed
6 Strobe Timing Normal Reverse
Draft ON ON NLQ ON OFF
(Not used) OFF ON (Not used) OFF OFF
3,4,5 Print Pitch
10cpi ON ON ON 20cpi OFF OFF ON
12cpi OFF ON ON Proportional ON ON OFF
17cpi ON OFF ON
6 Quiet Disabled Enabled
11"/Letter ON ON ON ON 14"/Legal OFF ON OFF ON
8" OFF ON ON ON 10.5"/Executive ON OFF OFF ON
11.7"/A4 ON OFF ON ON 7.25"/Executive OFF OFF OFF ON
12" OFF OFF ON ON 3.5" ON ON ON OFF
8.5"/Letter ON ON OFF ON 5.5" OFF OFF ON OFF
#437 ON ON ON ON ON #1001 ON ON ON ON OFF
#850 OFF ON ON ON ON #737 OFF ON ON ON OFF
#860 ON OFF ON ON ON #851 ON OFF ON ON OFF
#861 OFF OFF ON ON ON #869 OFF OFF ON ON OFF
#863 ON ON OFF ON ON #928 ON ON OFF ON OFF
#865 OFF ON OFF ON ON #2001 OFF ON OFF ON OFF
#866 ON OFF OFF ON ON #772 ON OFF OFF ON OFF
#3840 OFF OFF OFF ON ON #774 OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
#3841 ON ON ON OFF ON #3001 ON ON ON OFF OFF
#3843 OFF ON ON OFF ON #3002 OFF ON ON OFF OFF
#3844 ON OFF ON OFF ON #3011 ON OFF ON OFF OFF
#3845 OFF OFF ON OFF ON #3012 OFF OFF ON OFF OFF
#3846 ON ON OFF OFF ON #3021 ON ON OFF OFF OFF
#3847 OFF ON OFF OFF ON #3031 OFF ON OFF OFF OFF
#3848 ON OFF OFF OFF ON #3041 ON OFF OFF OFF OFF
#852 OFF OFF OFF OFF ON
International Character Set (CT=Italics)
U.S.A. ON ON ON ON ON Japan ON ON ON OFF ON
France OFF ON ON ON ON Norway OFF ON ON OFF ON
Germany ON OFF ON ON ON Denmark-2 ON OFF ON OFF ON
England OFF OFF ON ON ON Spain-2 OFF OFF ON OFF ON
Denmark-1 ON ON OFF ON ON Latin America ON ON OFF OFF ON
Sweden OFF ON OFF ON ON Korea OFF ON OFF OFF ON
Italy ON OFF OFF ON ON Ireland ON OFF OFF OFF ON
Spain-1 OFF OFF OFF ON ON Legal OFF OFF OFF OFF ON
Roman ON ON ON ON ON Prestige OFF OFF ON ON ON
Sanserif OFF ON ON ON ON Orator OFF OFF OFF ON ON
Courier ON OFF ON ON ON
– 8 –
Page 13
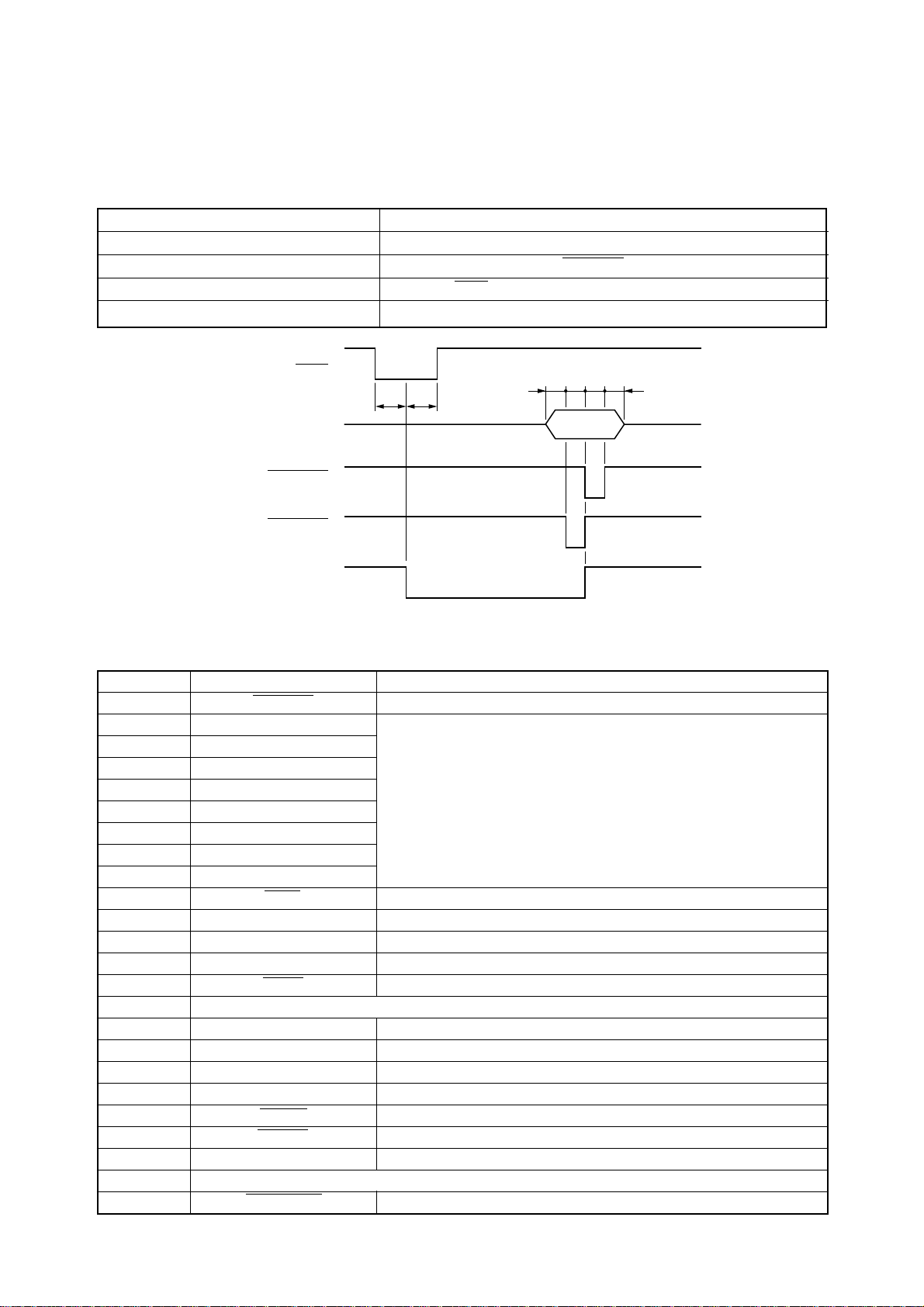
4. Parallel Interface
4-1. General Specifications
Item Specifications
Interface Centronics-compatible
Synchronization System Via externally supplied STROBE pulse
I/F Protocol Using ACK and BUSY signals
Logic Level Compatible with TTL level
ACK
Data
STROBE
(EDS B-6 : ON)
STROBE
(EDS B-6 : OFF)
BUSY
4.1µs
4.1µs
tttt
t : More than 0.5µs
Fig. 1-6 Timing Charts for Parallel Interface
4-2. Connector Signals
Pin Name Function
1 STROBE Goes low for ≥ 0.5µs when active.
2 DATA0
3 DATA1
4 DATA2
5 DATA3
6 DATA4
7 DATA5
8 DATA6
9 DATA7
10 ACK 10µs low to acknowledge receipt of data.
11 BUSY Printer sets line low when ready to receive data.
12 PAPER High when paper runs out.
13 SELECT High when printer is on-line.
14 AFXT Printer ignores this signal.
15 Not used.
16 SIGNAL GND Signal ground
17 CHASSIS Chassis ground (isolated from signal ground)
18 +5V +5V DC output from printer
19~30 GND Twisted pair ground return
31 RESET Printer is reset when this signal goes low.
32 ERROR Low when printing cannot continue due to error.
33 EXT GND External ground
34~35 Not used
36 SELECT IN Printer ignores this signal.
These signals represent information for the 1st through 8th bit of
parallel data, respectively. Each signal is HIGH when data is logical 1,
and LOW when logical 0.
– 9 –
Page 14
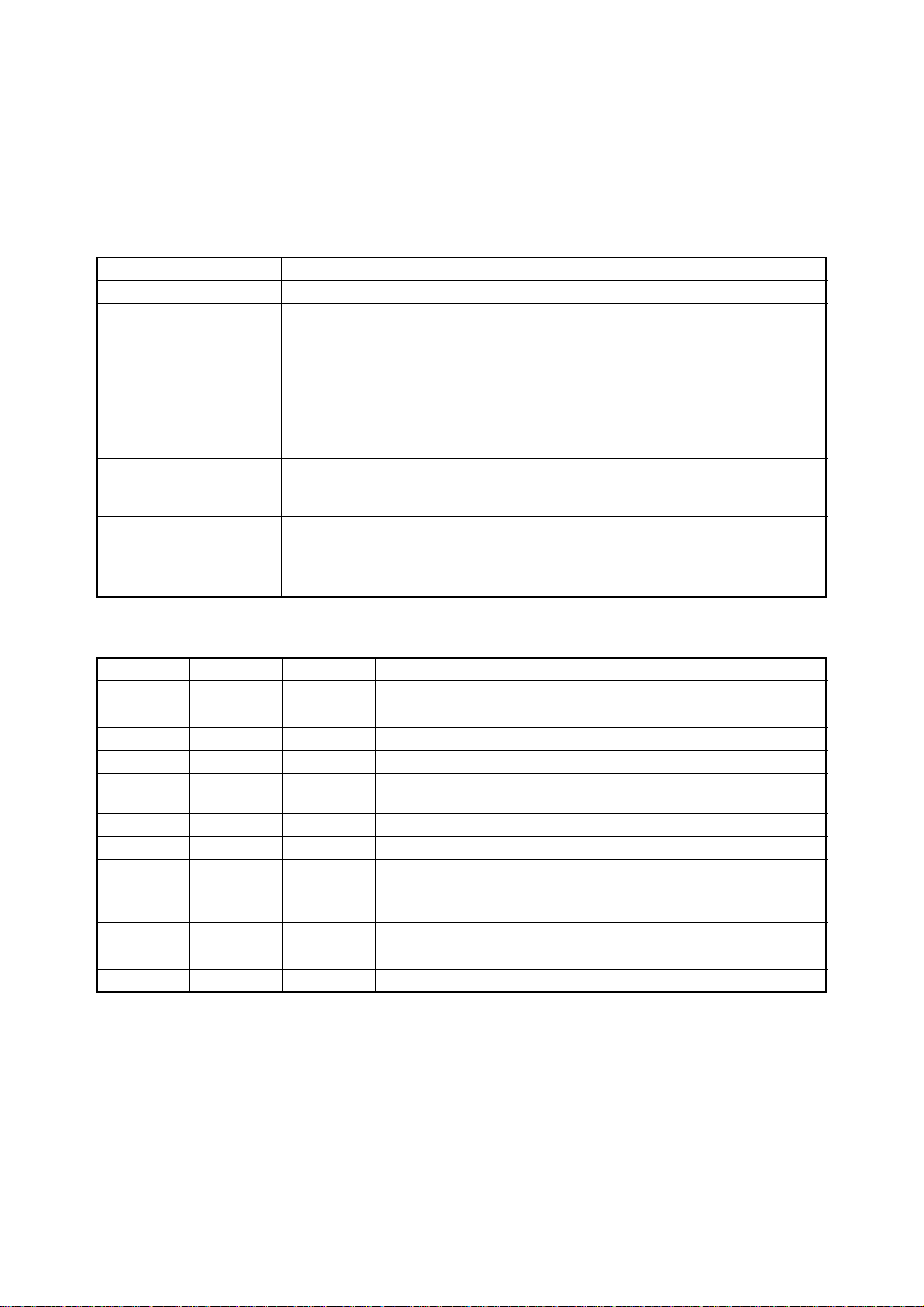
5 Serial Interface (optional)
When using the serial interface, the optional Serial-Parallel Converter must be connected to the printer.
5-1. General Specifications
Item Specifications
Interface RS-232C level
Synchronization System Asynchronous
Baud rate 150 - 19,200 bits per second (BPS) [selectable]
150, 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200 BPS
Word length
Start bit: 1 bit
Data bit: 7 or 8 bits (selectable)
Parity bit: Odd, Even or None (selectable)
Stop bit: More then 1bit length
Signal polarity
Mark: Logic “1” (–3V to –15V)
Space: Logic “0” (+3V to +15V)
Handshaking DTR
XON/XOFF
ETX/ACK
Data buffer 8KB (standard)
5-2. Connector Signal and Functional Descriptions
Pin No. Signal name Direction Function
1 GND —
2 TXD OUT
3 RXD IN
4 RTS OUT
5 CTS —
6NC
7 GND —
8~10 NC
11 RCH OUT
12~19 NC
20 DTR OUT
21~25 NC
Printer chassis ground.
This pin carries data from the printer.
This pin carries data to the printer.
Always space.
This signal is space when the computer is ready to send data.
The printer does not check this pin.
Unused.
Signal ground.
Unused.
The printer sets this signal to space when it is ready to receive data.
This line carries the same signal as pin 20.
Unused.
The printer sets this signal to space when it is ready to receive data.
Unused.
– 10 –
Page 15
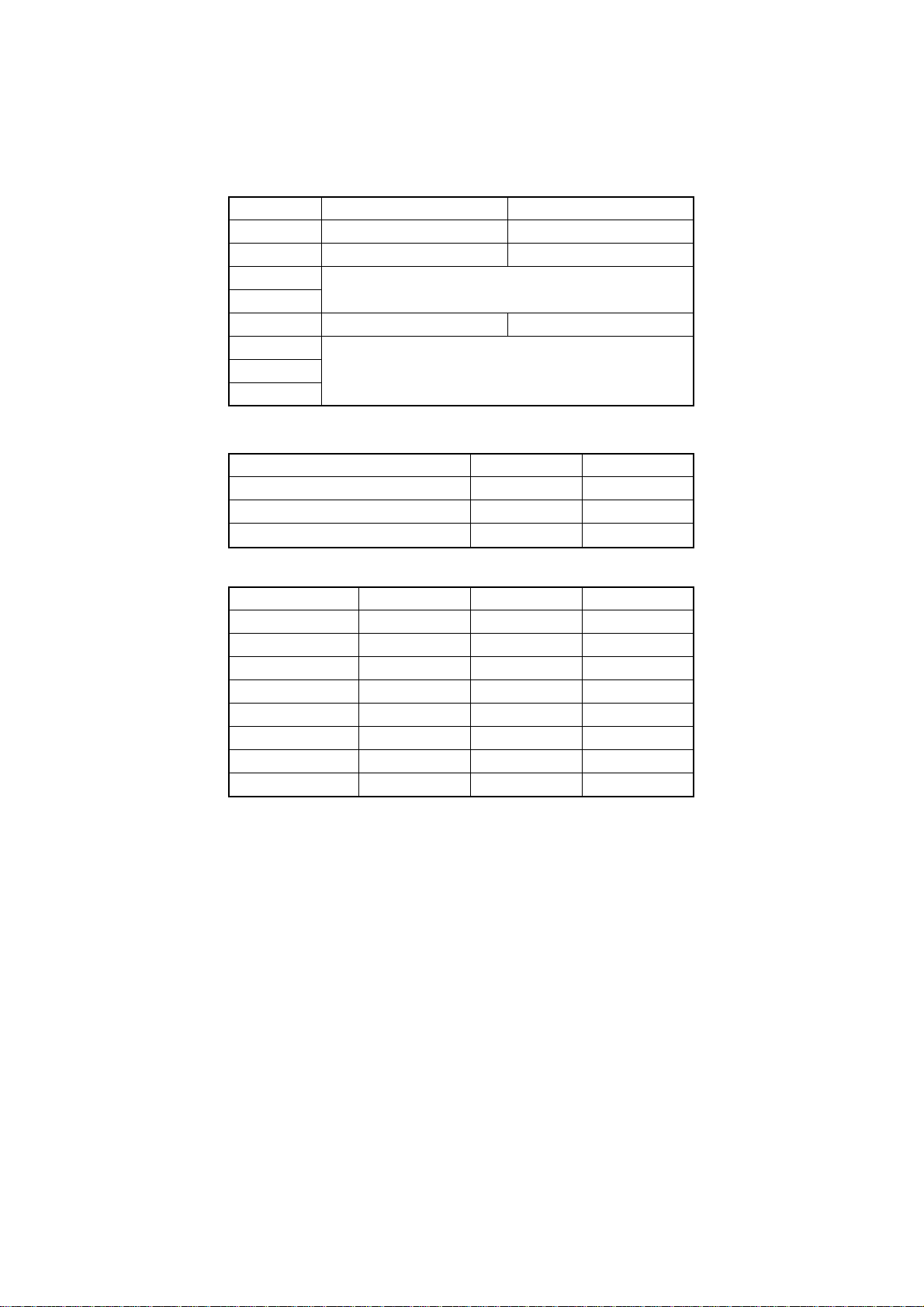
5-3. DIP Switch Settings
Switch ON OFF
All switches are set to ON before the printer leaves the factory.
Baud rate Switch 6 Switch 7 Switch 8
1 8 data bits 7 data bits
2 No parity Parity checked
3
4
5 Odd parity Even parity
6
7 Data transfer rate – see table below
8
150 OFF OFF OFF
300 OFF OFF ON
600 OFF ON OFF
1200 OFF ON ON
2400 ON OFF OFF
4800 ON OFF ON
9600 ON ON OFF
19200 ON ON ON
Handshaking protocols – see table below
Protocol Switch 3 Switch 4
DTR mode ON ON
XON/XOFF mode ON OFF
ETX/ACK mode OFF ON
– 11 –
Page 16

6. EE-PROM mode
6-1. Outline
These settings can be changed in the EE-PROM mode by writing data directly to the EE-PROM on the main logic board:
Setting EE-PROM mode
• Send <ESC><SUB>(09)H command.
Canceling EE-PROM mode
• Initialize the printer by sending <ESC>@
6-2. Explanation of special control codes
<ESC>@ Exits printer from EE-PROM mode and initializes the printer.
<ESC>M@ Returns all data in the EE-PROM to the factory settings. After the buffer is cleared, the buzzer sounds. If
the printer is powered off before the buzzer sounds, all data in the buffer is not cleared.
If all data is not cleared from the buffer, operation is not guaranteed. Be sure to allow the buzzer
to sound before you turn the printer off!
<ESC>MWn
Code Function Address Capacity
<ESC>MW0 <data> Stores data into entire area of EE-PROM. 00H-7FH 128bytes
<ESC>MW1nm Stores data (m) into the address (n) nH 1 byte
<ESC>MW2<data> Stores auto-start software data into 2CH-54H 41bytes
EE-PROM. 55H-7DH 41bytes
• The data (m) used in the commands above are stored in the specified address in order (n).
• When the data to be stored exceeds the specified capacity, subsequent data are ignored.
• Data are stored in the EE-PROM according to the memory map. (See section 3. EDS mode setting and
6-3. EE-PROM Map.)
• After all data are stored, a beep indicates the completion of storage.
• If the printer is powered off during data storage, data stored before power off are valid, but subsequent
operation of the printer is not guaranteed.
Do not power off the printer while data is being stored!
<ESC>MR Dumps all data in the EE-PROM to a hard copy.
For an example of using these control codes, see section 6-4. For the corresponding EE-PROM addresses, see the
EE-PROM memory map in section 3-2. EDS mode setting and 6-3 EE-PROM Map.
– 12 –
Page 17
6-3. EE-PROM MP
Address Function Factory data
00H EDS setting FFH
Bit Function 1 0
b0 Emulation
Character Table
b1 Standard / EPSON mode Graphics Italics
IBM mode IBM #2 IBM #1
b2 RAM Usage Input Buffer
b3 (Not used) — —
b4 Paper out Detector Enabled Disabled
b5 (Not used) — —
01H EDS setting FFH
Bit Function 1 0
b0 Graphics Direction Bi-directional Uni-directional
b1 Tear-off Disabled Enabled
b2 Line Spacing 1/6" 1/8"
b3 Auto LF with CR Disabled Enabled
b4 Zero Style Normal Slashed
b5 Strobe Timing Normal Reverse
STANDARD/EPSON
IBM
Download Buffer
02H EDS setting FFH
Print Mode Print Pitch
Function b0 b1 Function b2 b3 b4
Draft 1 1 10cpi 1 1 1
NLQ 1 0 12cpi 0 1 1
17cpi 1 0 1
20cpi 0 0 1
Proportional 1 1 0
Bit Function 1 0
b5 Quiet Disabled Enabled
03H EDS setting FFH
Page Length
Function b0 b1 b2 b3 Function b0 b1 b2 b3
11"/Letter 1 1 1 1 14"/Legal 0101
8" 0 1 1 1 10.5"/Executive 1001
11.7"/A4 1 0 1 1 7.25"/Executive 0001
12" 0 0 1 1 3.5" 1110
8.5"/Letter 1 1 0 1 5.5" 0110
– 13 –
Page 18
Address Function Factory data
04H EDS setting FFH
IBM Code Page (Character Table=Graphics, IBM#1, #2)
Function b0 b1 b2 b3 b4 Function b0 b1 b2 b3 b4
#437 11111 #3841 1 1 1 0 1
#850 01111 #3843 0 1 1 0 1
#860 10111 #3844 1 0 1 0 1
#861 00111 #3845 0 0 1 0 1
#863 11011 #3846 1 1 0 0 1
#864 01011 #3847 0 1 0 0 1
#866 10011 #3848 1 0 0 0 1
#3840 00011 #852 0 0 0 0 1
International Character Set (Character Table=Italics)
Function b0 b1 b2 b3 b4 Function b0 b1 b2 b3 b4
U.S.A. 11111 Japan 1 1 1 0 1
France 01111 Norway 0 1 1 0 1
Germany 10111 Denmark-2 1 0 1 0 1
England 00111 Spain-2 0 0 1 0 1
Denmark-1 11011
Sweden 01011 Korea 0 1 0 0 1
Italy 10011 Ireland 1 0 0 0 1
Spain-1 00011 Legal 0 0 0 0 1
Latin America
11001
05H EDS setting FFH
NLQ Font Selection
Function b0 b1 b2 b3 b4 Function b0 b1 b2 b3 b4
Roman 11111 Prestige 0 0 1 1 1
Sanserif 01111 Orator 0 0 0 1 1
Courier 10111
06H Misalignment correction 60 DPI (F) 80H
07H Misalignment correction 72 DPI (F) 80H
08H Misalignment correction 80 DPI (F) 80H
09H Misalignment correction 90 DPI (F) 80H
0AH Misalignment correction 120 DPI (H) Text 80H
0BH Misalignment correction 120 DPI (H) Bit-image 80H
0CH Misalignment correction 120 DPI (F) 80H
0DH Misalignment correction 144 DPI (H) 80H
0EH Misalignment correction 240 DPI (H) Text 80H
0FH Misalignment correction 240 DPI (H) Bit-image 80H
10H Misalignment correction Multi-part Mode 60 DPI (F) 80H
11H Misalignment correction Multi-part Mode 72 DPI (F) 80H
12H Misalignment correction Multi-part Mode 80 DPI (F) 80H
13H Misalignment correction Multi-part Mode 90 DPI (F) 80H
14H Misalignment correction Multi-part Mode 120 DPI (H) Text 80H
15H Misalignment correction Multi-part Mode 120 DPI (H) Bit-image 80H
16H Misalignment correction Multi-part Mode 120 DPI (F) 80H
17H Misalignment correction Multi-part Mode 144 DPI (H) 80H
18H Misalignment correction Multi-part Mode 240 DPI (H) Text 80H
19H Misalignment correction Multi-part Mode 240 DPI (H) Bit-image 80H
– 14 –
Page 19
Address Function Factory data
1AH, 1BH Top Margin in Auto-loading Tractor 48H
00H
1CH, 1DH Top Margin in Auto-loading Friction 48H
00H
1EH~21H Macro Set EPSON 00H
00H
22H~25H Macro Set IBM 00H
00H
26H, 27H TEAR OFF (Short) 00H
80H
28H, 29H TEAR OFF (Long) 00H
80H
2AH, 2BH Initial Condition Area FFH
FFH
2CH~54H Auto Start Area EPSON (41 byte) 00H
00H
55H~70H Auto Start Area IBM (41 byte) 00H
00H
7EH FF Control Code (Space 00H / Null 0FH) 00H
7FH EE-PROM Check Code 01H
– 15 –
Page 20

6-4. Rewriting the EE-PROM
Follow this procedure to rewrite the EE-PROM.
(1) Turn the printer on.
(2) Load a BASIC disk in the computer.
(3) Turn the computer on.
(4) Set a sheet of paper in the printer, and press the ON LINE switch.
(5) Enter the program listed below and run the program.
10 LPRINT CHR$(27);CHR$(26);CHR$(&H09)
20 LPRINT CHR$(27);”MW1";CHR$(&H01);CHR$(&HFB)
30 LPRINT CHR$(27);”MR”
BASIC Program Code What It Does
10 LPRINT CHR$(27);CHR$(26);CHR$(&H09) Enters the EE-PROM mode.
20 LPRINT CHR$(27);”MW1"; Starts rewriting the EE-PROM.
CHR$(&H01); Address data from &H01 will show
EDS mode from the EE-PROM memory
map.
CHR$(&HFB) Data from &HFB will change the Line
spacing from 1/6" to 1/8".
30 LPRINT CHR$(27);”MR” Dumps all EE-PROM data to hexadeci-
mal.
(6) To complete the setting, turn the printer off.
– 16 –
Page 21

CHAPTER 2
THEORY OF OPERATION
1. Block Diagram (Main logic Board).....................................................................19
2. Main Logic Board ................................................................................................20
2-1. General Flow Chart............................................................................................... 20
3. Power Supply Circuit ..........................................................................................21
4. Mechanisms.........................................................................................................22
4-1. Print Head Mechanism ......................................................................................... 22
4-2. Print Head Carrying Mechanism ......................................................................... 23
4-3. Ink Ribbon Feed Mechanism ............................................................................... 24
2
4-4. Paper Feed Mechanism........................................................................................ 25
4-5. Detectors ............................................................................................................... 26
Page 22

Page 23
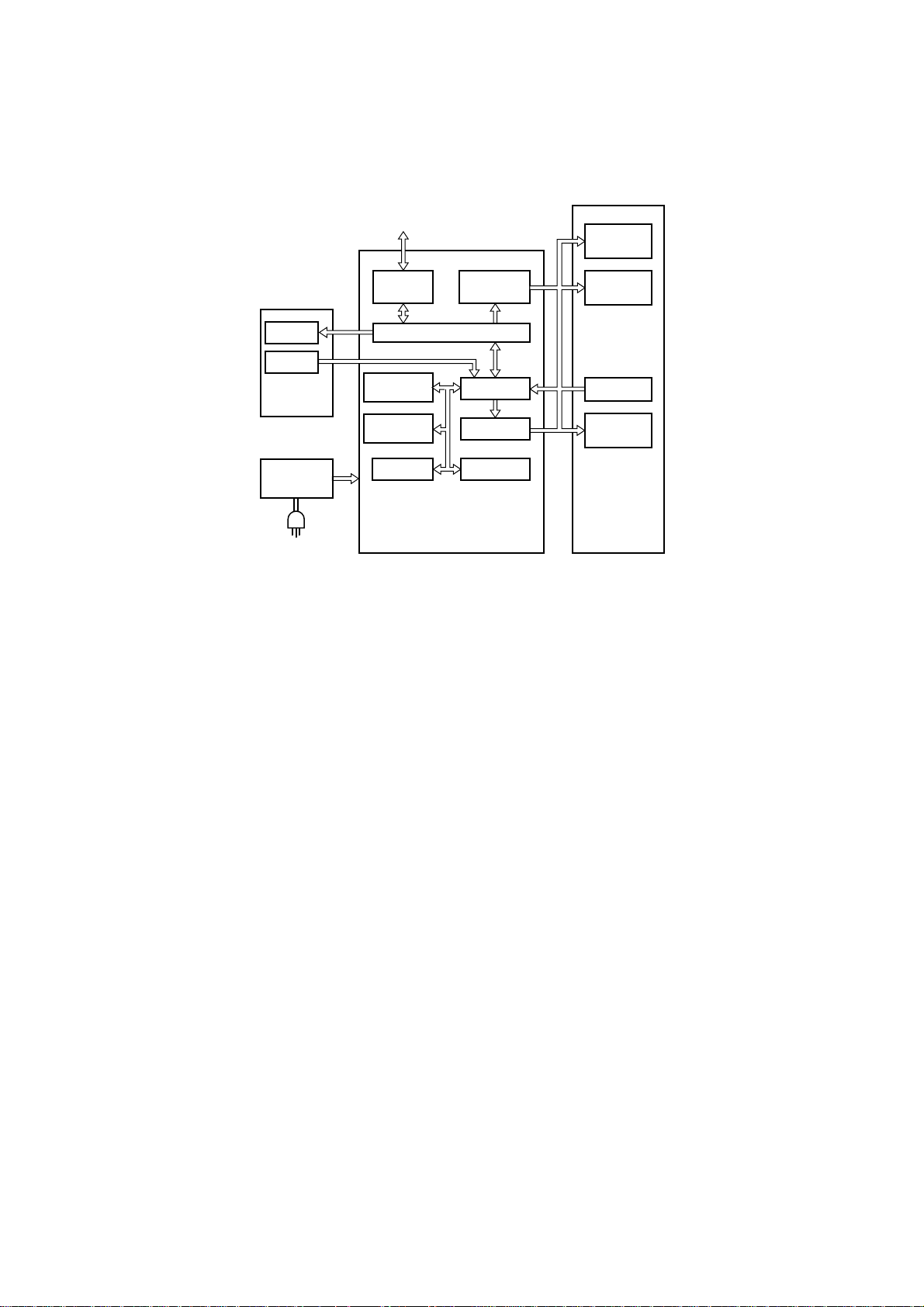
1. Block Diagram (Main logic Board)
The block diagram of this printer is shown in Fig. 2-1.
Data (From Host Computer)
Print head
LED
Switch
Control
panel board
Power
supply unit
AC Power
Parallel
interface
Masked ROM
2M
UVE-PROM
512K
EE-PROM
Main logic board
Driver
Gate array
CPU
Driver
RAM
Carriage
motor
Detectors
Paper feed
motor
Printer
mechanism
Fig. 2-1 Block Diagram
(1) Main Logic Board
This board receives data from the host computer and stores it in the RAM in the order it arrives. The CPU on this
board reads the data from the RAM, and edits it according to the program stored in the ROM.
When editing is completed, various drive signals from the CPU are sent to the printer mechanism to perform
printing.
Explanation
• CPU TMP90C041
Controls this printer.
• UVE-PROM 27512 512K bit
Contains the program which executes control of the printer. UVE-PROM is not provided with some versions of the
software.
• Masked ROM 2M bit
Contains the character font and the program.
• EE-PROM KM93C46 64 × 16 bits
Contains the data (EDS data and so on) in the memory switch.
• RAM 256K bytes
Used as a stack area, work area and data buffer of the CPU.
• Parallel interface
• Gate array (custom IC)
Inputs/outputs several signals.
• Driver
The data edited by the CPU and gate array are sent to the printer mechanism after conversion to the signal for the
print head drive and motor drives.
(2) Control panel board
Panel circuit for manual control of the printer.
(3) Printer Mechanism
Consists of a print head, carriage motor, paper feed motor, and detectors.
(4) Power Supply Unit
Converts AC power to 33VDC and 5VDC.
– 19 –
Page 24
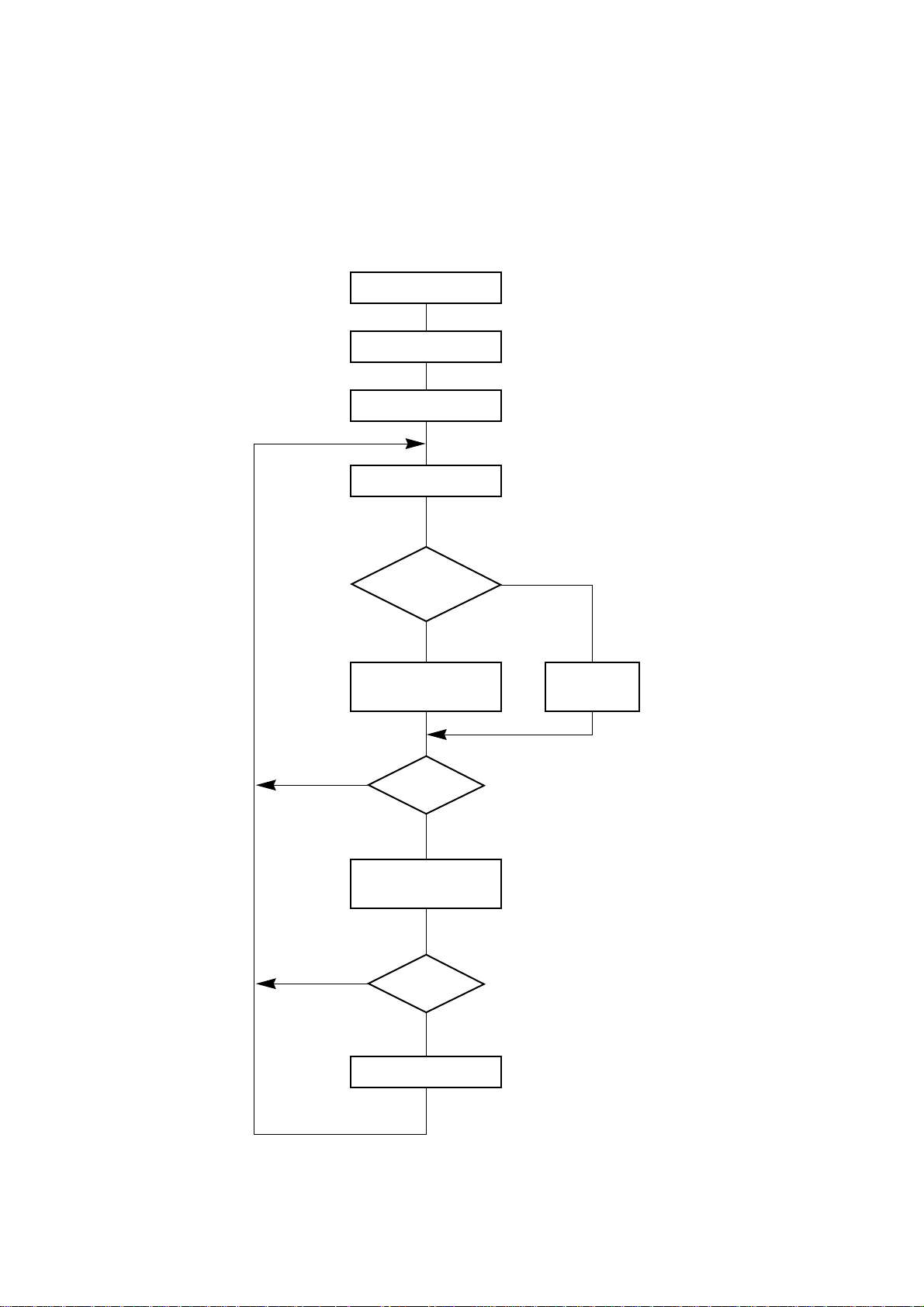
2. Main Logic Board
2-1. General Flow Chart
The flow chart below shows you the general flow of editing and printing operations.
POWER ON
Initialization
Ready state
Read data
Control
code?
No
Control code
NO
Data processing
NO
Return action
YES
processing
Print?
YES
or printing
Return?
YES
Data
storage
(Line buffer determination)
(Print out of data)
Fig. 2-2 General Flow Chart of Editing and Printing
– 20 –
Page 25
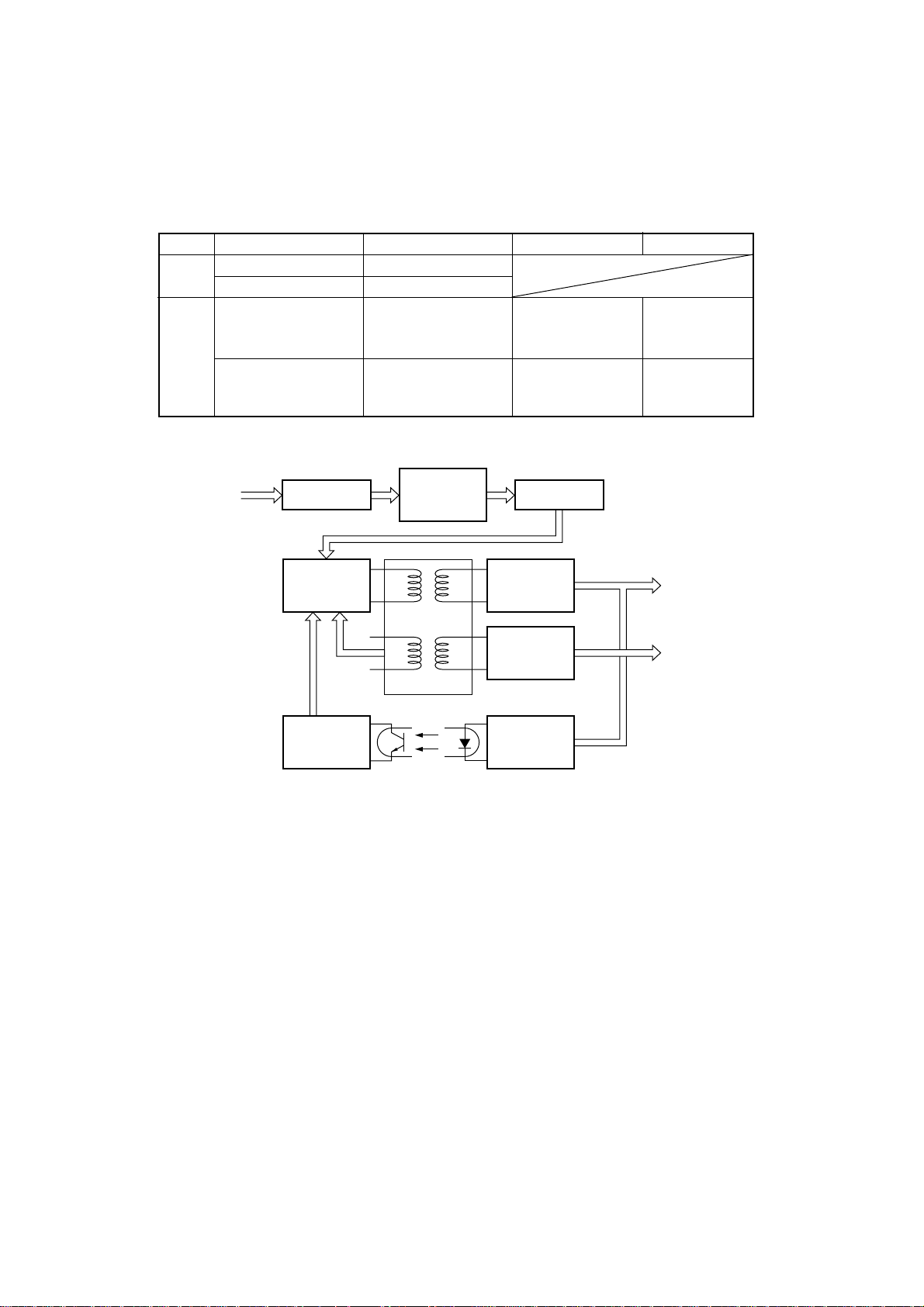
3. Power Supply Circuit
A ringing choke converter type circuit is used with a dropper type circuit in the power supply unit, fulfilling the input and
output conditions described in the chart below.
Voltage Range Max. Current Output Service Circuit Type
Input
Output
110VAC, 120VAC 1.0 A
220VAC to 240VAC 0.6 A
5 VDC ±5% 0.4 A Dropper
For logic circuit
drive, for motor
holding.
33 VDC ±5% 1.25A Ringing choke
For print head
drive, for motor
converter.
drive.
Input
110VAC
120VAC
220VAC
230VAC
240VAC
Noise filter
circuit
Switching
section
(Transistor Q1)
Control
circuit
In rush current
protection
circuit
Transformer T1
PC1
Photo-Coupler
Fig. 2-3 Power Supply unit block diagram
Rectifier
circuit
Ringing
choke
converter
Dropper
circuit
Voltage
reference
Output
33V DC
Output
5V DC
– 21 –
Page 26
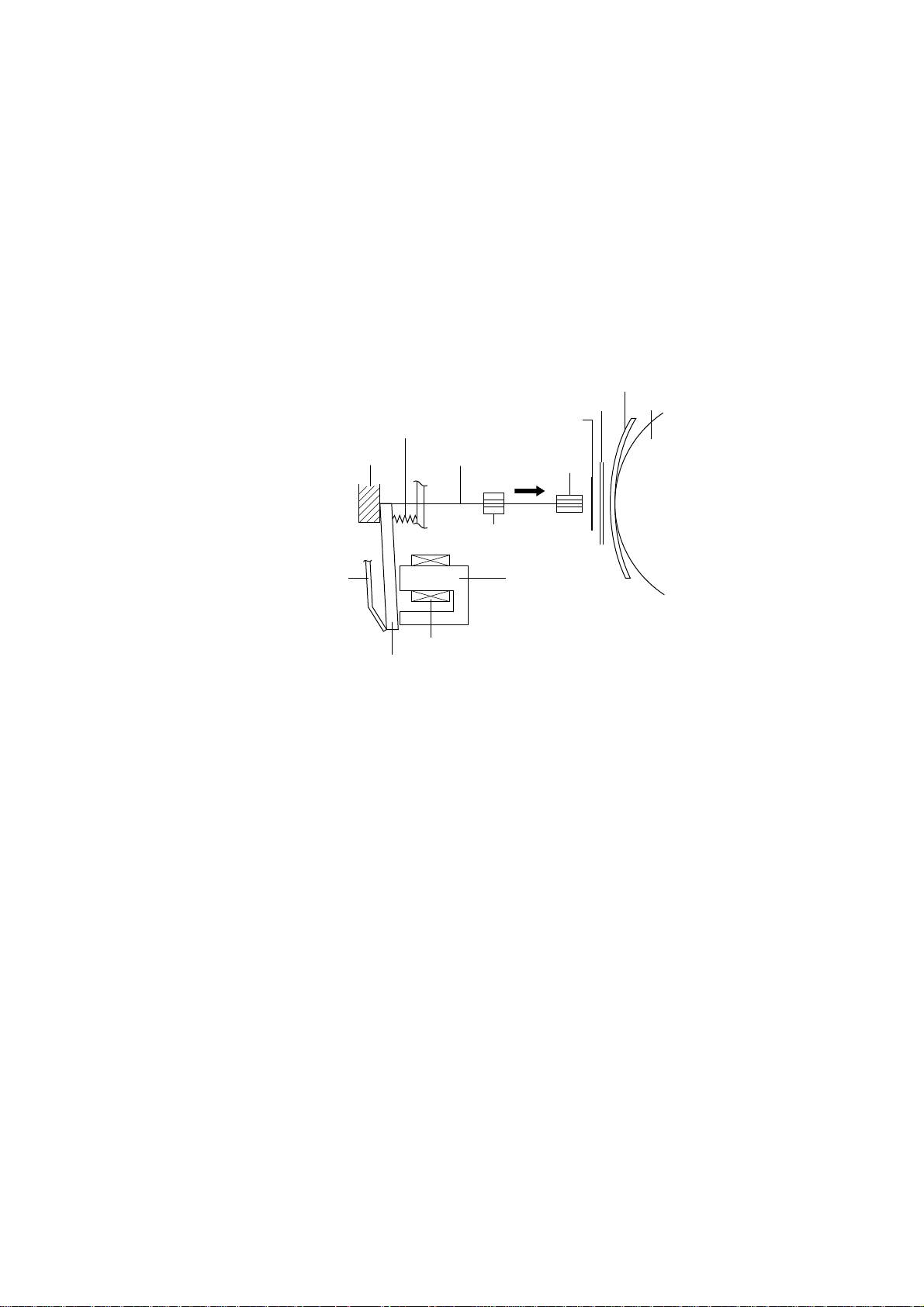
4. Mechanism
4-1. Print Head Mechanism
The print head consists of 9 needle wires and 9 print solenoids.
The following explains how each needle wire operates during printing.
(1) When the print solenoid is energized, the clapper is attracted by the iron core and the needle wire is driven toward
the platen.
(2) This needle wire hits the platen via the ink ribbon and paper. A single dot is printed on the paper.
(3) When the print solenoid is de-energized, the needle wire is returned to its original position by rebound energy and
spring and clapper holder (leaf spring) force.
Paper
Platen
Spring
Paper guide
Ink ribbon
Clapper holder
Stopper
Clapper
Needle wire
Print solenoid
Guide
Subguide
Iron core
Fig. 2-4 Outline of Print Head Mechanism
– 22 –
Page 27
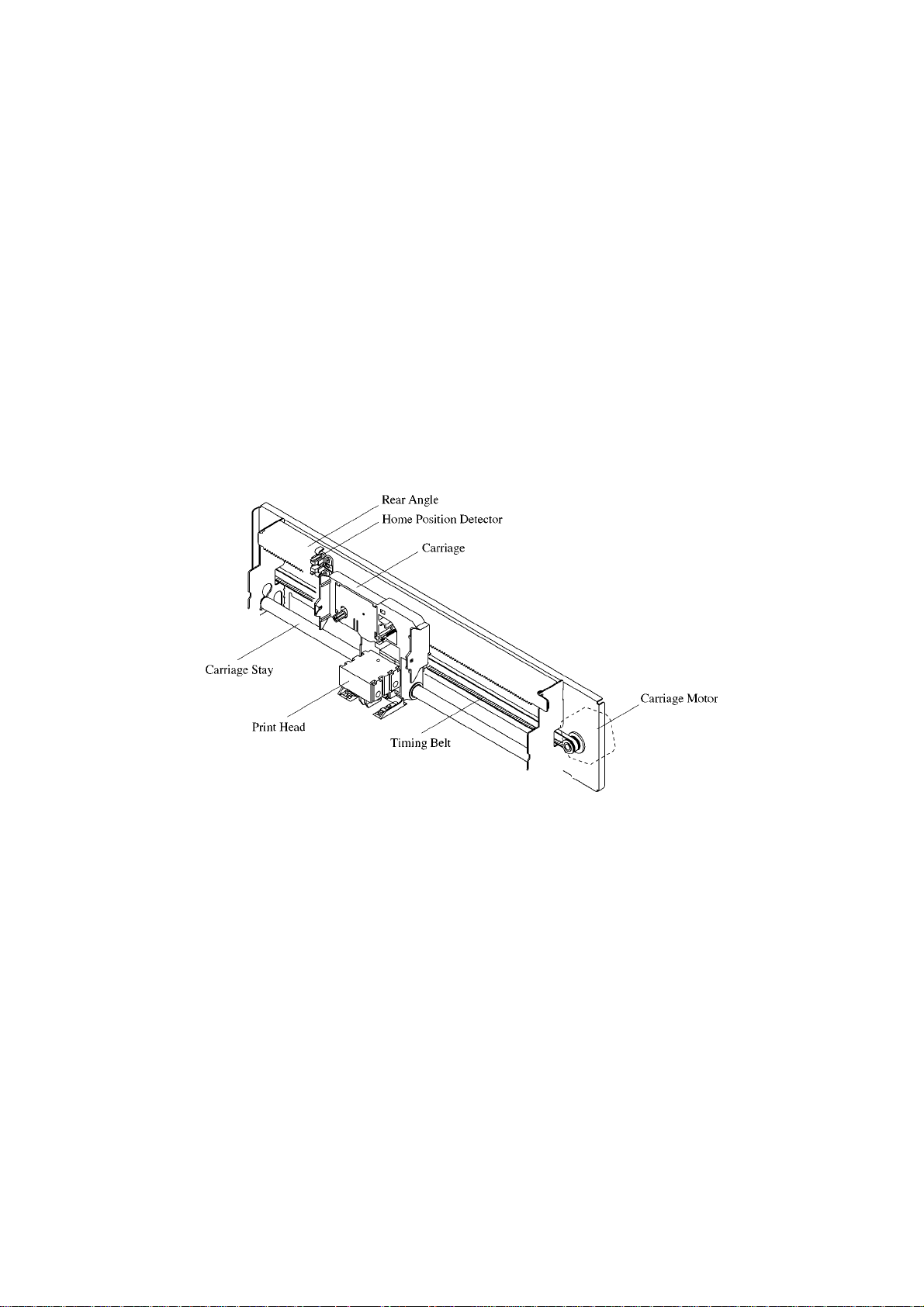
4-2. Print Head Carrying Mechanism
The print head carrying mechanism consists of a carriage, timing belt, carriage motor, and home position detector.
Carriage
The carriage is supported horizontally by the carriage stay and rear angle. The carriage moves from side to side with
the print head mounted above it. A timing belt is clamped to the base of the carriage and a shield plate is mounted
at the base for home position detection.
Timing Belt
The timing belt is suspended between the timing pulley of the carriage motor and the timing pulley of the tension
lever. The timing belt maintains a constant tension.
The timing belt is also clamped to the base of the carriage so that it can move the carriage accurately with driving
force from the carriage motor.
Carriage Motor
The carriage motor is a HB (Hybrid)type, 4-phase, 192-pole pulse motor driven by pulse signals from the control
circuit. The rotational rate depends on the number of pulses per unit time. By varying this rotational rate (carriage
carrying rate), the size of the horizontal letters can be changed in each print mode.
Fig. 2-5 Print Head Carrying Mechanism
– 23 –
Page 28
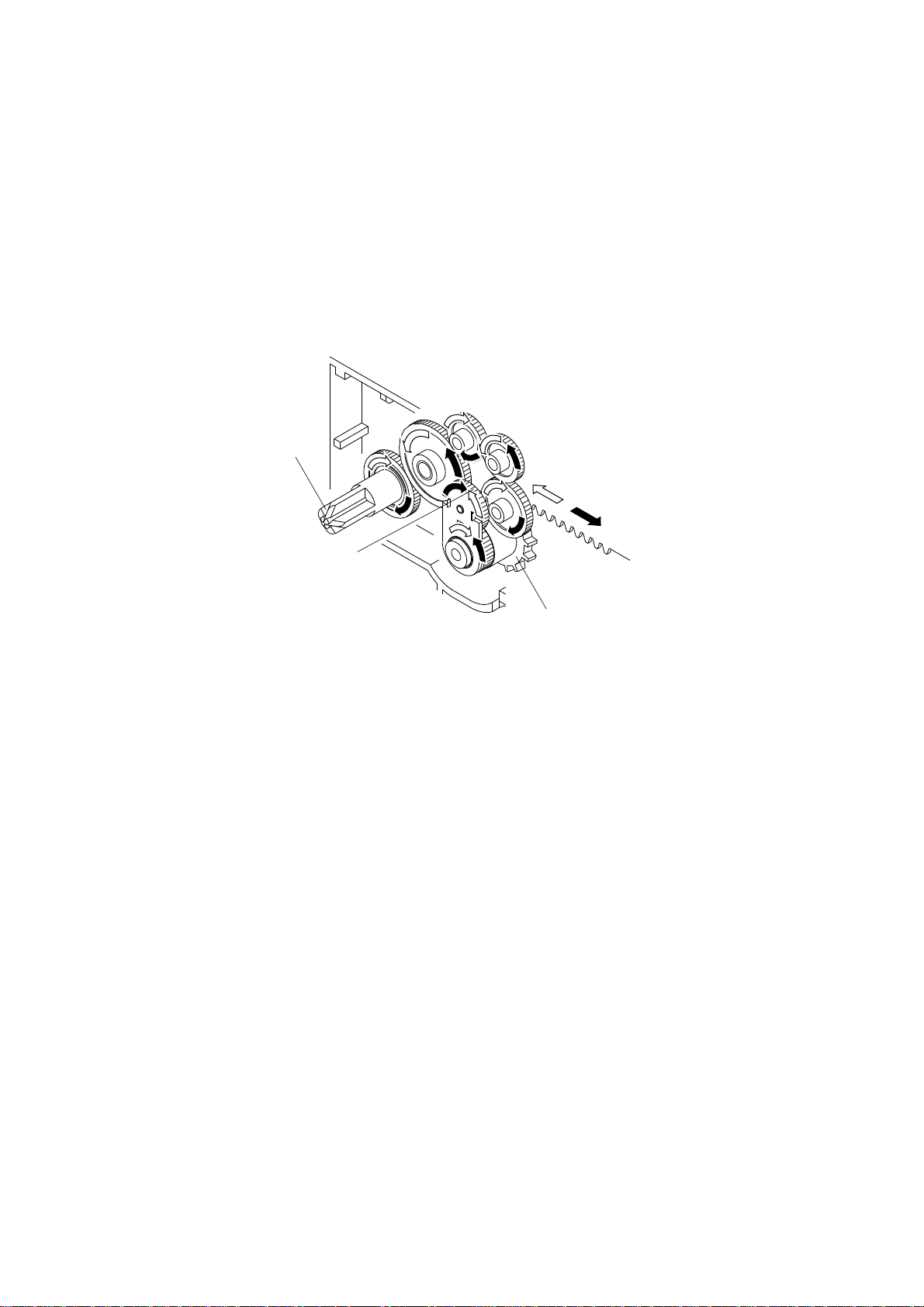
4-3. Ink ribbon feed mechanism
The ink ribbon feed mechanism is linked to the print head carrying mechanism so the ink ribbon always winds
automatically in the same direction while the carriage moves left and right.
The movement of the carriage along the serrated edge of the rear angle of the printer mechanism drives the idler gear. The
rotation of the idler gear is conveyed sequentially to the gears that work and wind the ribbon. The carriage has a clutch
lever that keeps the direction of the cassette gear rotation constant, regardless of the direction of the idler gear rotation
as the carriage moves left and right.
Cassette Gear
Gear of The Clutch Lever
Idler Gear
Fig. 2-6 Ribbon feed mechanism
– 24 –
Page 29
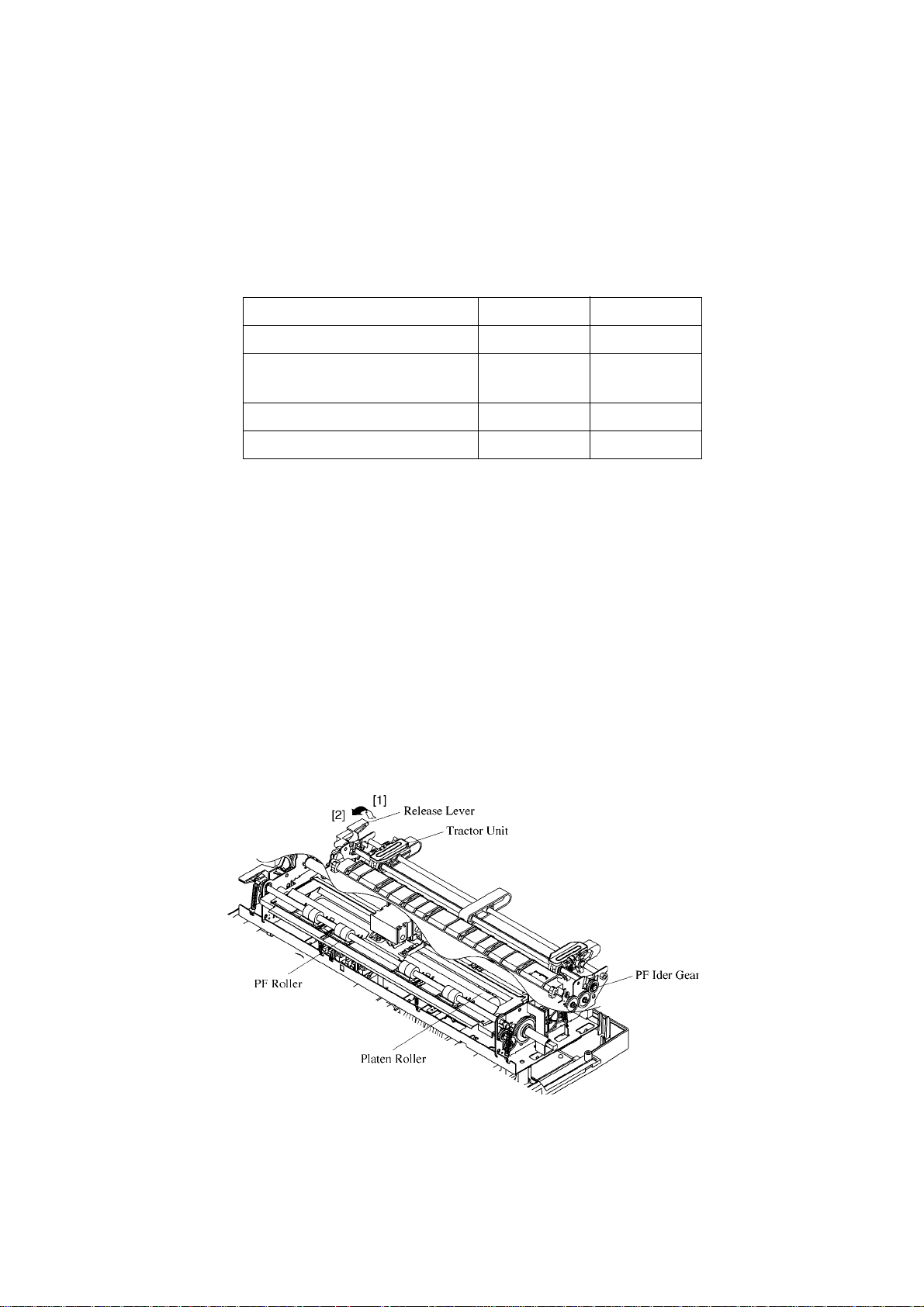
4-4. Paper Feed Mechanism
The paper feed mechanism consists of a paper feed motor, an idler gear, a platen and a traction unit.
The paper feed motor is a PM (Permanent Magnet) 4-phase and 48 pulse motor.
There are two ways of feeding paper into the printer: the friction method and the tractor method. You can select the
method you want to use by setting the release lever on the optional push tractor unit.
Position of release lever [1] [2]
Engaement of the PF idler gear Not linked Linked
Status of the PF roller and
PF roller
Release lever position detector Open Closed
Paper feeding method Friction Tractor
• Friction Method
Friction method is selected when the release lever is position [1].
With this method, paper is pressed between the platen roller and the holder roller therefore, paper is fed as the rollers
turn.
As the paper feed motor is driven, the motor gear, through the idler gear, turns the platen gear in the paper feeding
direction. However, since the tractor gear and the tractor clutch are not linked at this time, the tractor unit will not
be driven.
• Tractor Method
Tractor method is selected when the release lever is position [2].
Paper feeding is facilitated by rotation of the sprocket pin of the tractor unit. When the tractor method is selected,
the PF idler gear is linked to the PF idler gear, enabling the drive force generated by the paper feed motor to be
transferred to the tractor unit via the idler gear.
Pressed Not
Fig. 2-7 Paper Feed Mechanism
– 25 –
Page 30
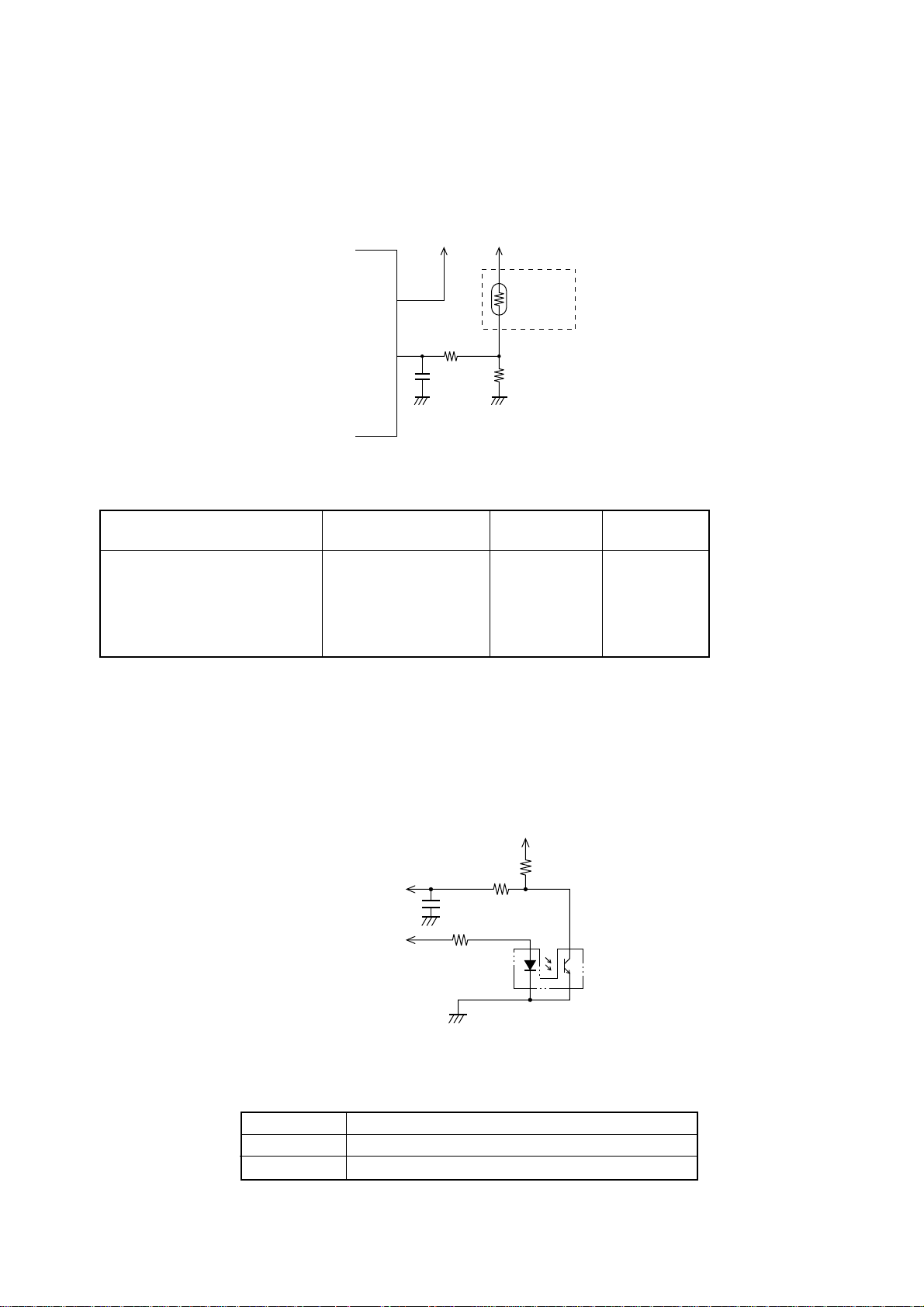
4-5. Detectors
(1) Print head temperature detectors
The A/D converter in the CPU detects the print head temperature at power on and before each line begins to print.
+5V +5V
Printer head
ref
V
Thermistor
AN0
CPU
R1
R2
Fig. 2-8 Printer head temperature detector circuit
Control Method
Print
A/D Conversion Value
POINT
AN Voltage
V
Temperature
°C
Error stop (thermistor open) 0-5 0.00 Normal print 6-213 0.00-4.35 ~120
Unidirectional print 214-221 4.35-4.48 120-130
Print stop 222-251 4.48-4.83 Over 130
Error stop (thermistor closed) 252-255 Over 5.00 -
(2) Home Position Detector
A photo-interrupter is used in the home detector on the printer.
ON/OFF signals are generated according to the position of the carriage. (Shield plate mounted at the base of the
carriage.) The printing position is determined by these signals.
Detecting
signal
+5V
C1
R3
Fig. 2-9 Carriage home position detector circuit
Control Method
Output (V) Decision
5 in home position (with shield plate)
0 not in home position (without shield plate)
– 26 –
R1
+5V
R2
Page 31

(3) Paper end Detector
The paper end Detector is located in the paper chute unit. The A/D converter in the CPU detects the presence or
absence of paper.
+5V
+5V
Detecting
signal
Detecting
signal
Detecting
signal
R1
R3
R6
R2
R4
R7
R5
R8
R9
Fig. 2-10Paper end detector circuit
Control Method
Output
(V)
Detection
0 No paper
5 Paper present
Friction
Skew
Tractor
(4) Release lever switch and lever switch Adjustment
Detecting
signal
R1
Fig. 2-11 Release lever switch circuit and Adjustment lever switch circuit
Control Method
Output Release Adjustment
(V)
Lever SW Lever SW
0 Tractor Normal mode
5 Friction Multi-part mode
+5V
R2
Leaf switch
– 27 –
Page 32

Page 33

CHAPTER 3
ADJUSTMENTS
This printer has undergone various adjustments so that it will attain a given standard of performance.
In this chapter, a brief explanation is given of the methods for making adjustments.
Follow the instructions when performing maintenance inspections or when replacing parts to correct
malfunctions.
1. Adjustment of Gap Between Print Head and Platen ........................................31
2. Adjustment of Timing Belt Tension...................................................................32
3
Page 34

Page 35

1. Adjustment of Gap Between Print Head and Platen
(1) Remove the front case unit ,rear angle and ribbon holder [1] according to the procedures described in chapter 4.
(Fig. 3-1)
(2) Install rear angle [2].
(3) Set adjusting lever [3] to the second position from the bottom. (Fig. 3-1)
(4) Position the center of the carriage unit [4] 55 mm from the left end of the platen assy [5]. (Fig. 3-2)
(5) Measure the gap between platen [5] and head [6] using a gauge [7] . (Fig. 3-3)
(6) Use adjusting bushing L [8] to adjust the gap to between 0.34 and 0.40 mm. (Fig. 3-4)
(7) Position the center of the carriage unit [4] 55 mm from the right end of the platen assy [5], then measure the gap
and adjust it in the same way.
(8) Repeat steps (4) to (6) to measuring the gap and readjusting as necessary.
(9) Remove the rear angle [2].
(10) Install the ribbon holder [1], rear angle [2] and front case.
[
]
4
LR
[
]
55mm 55mm
5
Fig. 3-1 Mechanism Fig. 3-2 Positioning the carriage unit
gap
[
]
6
]
[
7
[5]
+–
( L )
[8]
gap
–+
( R )
Fig. 3-3 Gap measurement Fig. 3-4 Adjusting bushing
– 31 –
Page 36

2. Adjustment of Timing Belt Tension
(1) Remove the front case unit according to the procedures described in chapter 4.
(2) Move the carriage unit [1] up to the extreme right position.
(3) Move the screw [3] fixing tension lever assembly [2] approximately 1mm to loosen the tension, then tighten the
screw.
The timing belt tension [4] is determined by the spring [5].
Fig 3-5 Adjustment of timing belt tension
– 32 –
Page 37

CHAPTER 4
PARTS REPLACEMENT
This chapter explains disassembly and reassembly of the printer. Note the following regarding disassembly
and reassembly.
1. Disconnect the printer from the wall outlet before servicing it.
2. Assy is the reverse of disassembly unless otherwise specified.
3. After reassembly, coat the screw heads with locking sealant.
4. Lubrication information is not provided in this chapter. Refer to section 2 in chapter 5.
1. Front Case Unit....................................................................................................35
2. Rear Case Unit.....................................................................................................35
3. Ribbon Holder......................................................................................................36
4. Printer Mechanism ..............................................................................................36
5. Main Logic Board Unit ........................................................................................37
6. Power Supply Unit...............................................................................................37
7. Print Head ............................................................................................................38
8. Fuse ......................................................................................................................39
9. Tractor Unit..........................................................................................................39
10. Carriage Motor Assy ...........................................................................................40
11. Carriage Unit........................................................................................................40
4
12. Paper Feed Roller A ............................................................................................41
13. Frame Holder .......................................................................................................41
14. Paper Guide Assy................................................................................................42
15. Platen Assembly..................................................................................................42
16. Paper Feed Motor Assy ......................................................................................43
17. Paper Path Change Plate....................................................................................43
18. Detector................................................................................................................44
– 33 –
Page 38

Page 39

1. Front Case Unit
(1) Turn off the power switch.
(2) Remove the power cord from the AC output socket.
(3) Remove
• Platen knob unit [1]
• Front case unit [2]
Detach the five hooks marked A using the tool
shown below.
• Control board [3]
Detach the two hooks.
2. Rear Case Unit
(1) Remove
• Front case unit as described above 1.
• Four screws [1]
• Rear case unit [2]
– 35 –
Page 40

3. Ribbon Holder
(1) Remove
• Front case unit as described in section 1.
• Two screws [1]
• Rear angle [2]
• Ribbon holder [3]
Center the carriage unit, tile it, then remove the
ribbon holder.
4. Printer Mechanism
(1) Remove
• Four screws [1]
• Four connectors [2]
• Cable [3]
• Printer mechanism [4]
– 36 –
Page 41

5. Main Logic Board Unit
(1) Remove
• Printer mechanism as described in section 4.
• Three screws [1]
• Connector [2]
• Main logic board [3]
6. Power Supply Unit
(1) Remove
• Printer mechanism as described in section 4.
• Seven screws [1]
• Screw [2]
• Switch holder [3]
• Power cord holder [4]
• Power supply unit [5]
– 37 –
Page 42

7. Print Head
(1) Remove
• Front case unit as described in section 1.
• Two screws [1]
• Cable [2]
• Print head [3]
WARNING
The print head gets hot after printing.
Do not touch it until it cools.
(2) Adjust
• Gap between print head and platen. Refer to
section 1 of Chapter 3.
Note:
Fold the head cables according to the dimensions shown below.
163±1
19±1
10±1
Cat size (Double-sided tape)
90°±1
108.5±1
0.5±0.5
85±0.5
— Double-sided tape
468±1
90°±1
21±1
– 38 –
: mm
Page 43

8. Fuse
(1) Remove
• Front case unit as described in section 1.
(2) Inspect
• Fuse F1 [1]
Defective → Replace fuse as follows:
AC voltage Fuse Type
110/120V 5TT2A-250V
220V/240V 215-1A-250V
New fuse blown → Inspect circuit
9. Tractor Unit
(1) Remove
• Rear case unit as described in section 2.
• Two hexagonal nuts [1]
• Stop ring [2]
• Release lever [3]
• Tractor unit [5]
Push tractor bushing [4] with a screwdriver and
lift tractor unit [5].
B
Note:
Align the “∆” mark on the release lever [3] with
the “∆” mark on the paper path change plate [6].
– 39 –
Page 44

10. Carriage Motor Assy
(1) Remove
• Rear case unit as described in section 2.
• Screw [1]
• Spring [2]
Set tension lever assy [3] in the unlocked position.
• Two screws [4]
• Carriage motor unit [5]
Note:
When assembling the carriage motor assy, the
tension lever assy [3] must be secured with the
screw [1] when the spring [2] is in place.
11. Carriage Unit
(1) Remove
• Ribbon holder as described in section 3.
• Print head as described in section 8.
• Head cable [1]
• Ground spring [2]
• Stop ring [3]
• Adjusting gear [4]
• Adjusting bushings L, R [5] [6]
Adjusting bushings L/R can be removed by turning them.
• Carriage unit [7]
Center the carriage unit.
Note:
Move the carriage unit to the center position, then
align the “∆” mark of adjusting gear [4] with the
“∆” mark of adjusting lever [8].
– 40 –
Page 45

12. Paper Feed Roller Assy
(1) Remove
• Carriage unit as described in section 11
• Four springs [1], [2], [6]
• Four stop rings[7]
• Two gears [3]
• Two plain washer [4]
• Tow paper feed roller Assy [5]
13. Frame Holder
(1) Remove
• Rear angle [1]
• Carriage motor unit [2] as described in section 8
• Home position detector [3]
• Four roll pins [4]
• Frame holder [5]
Note:
Roll pins [4] should not be used again once they
have been removed. Always use new ones.
– 41 –
Page 46

14. Paper Guide Assy
(1) Remove
• Paper feed roller Assy as described in section 12.
• Three screws [1]
• Frame support (R) [2]
• Stop ring [3]
• Platen gear [4]
• Gear [5]
• Frame holder as described in section 13.
• Four screws [6]
• Two screws [7]
• Two washers [8]
• Paper guide assy [9]
Note:
Gears [4],[5] should not be used again once it has
been removed. Always use a new one.
15. Platen Assy
(1) Remove
Paper guide assy as described in section 14.
• Two stop rings [1]
• Platen assy [2]
– 42 –
Page 47

16. Paper Feed Motor Assy
(1) Remove
Platen assy as described in section 15.
• Two screws [1]
• Paper feed motor assy [2]
17. Paper Path Change Plate
(1) Remove
• Paper feed roller A as described in section 12.
• Right stop ring [1]
• Right release shaft [2]
Push inwards.
• Left release shaft [2]
Pull the shaft outwards until the slot is exposed.
• Paper path change plate [3]
Note:
Align the “∆” mark on the paper path change plate
with the “∆” mark on the release gear.
– 43 –
Page 48

18. Detector
[1]
(1) Remove
• Paper guide assy as described in section 14.
• Four detectors [1]
Note:
Secure the lead wires at one point using fasteners
[2] .
[1]
[2]
[1]
Solder side
– 44 –
Page 49

CHAPTER 5
MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION
1. Maintenance......................................................................................................... 47
1-1. Cleaning ................................................................................................................ 47
1-2. Checks ................................................................................................................... 47
2. Lubrication........................................................................................................... 48
2-1. Lubricant ............................................................................................................... 48
2-2. Lubricating Method .............................................................................................. 48
2-3 Lubricated Areas .................................................................................................. 48
5
Page 50

Page 51

1. Maintenance
In order to maintain the optimum performance of this printer and to prevent trouble, maintenance must be carried out
according to the following items.
1-1. Cleaning
(1) Removal of dirt
Wipe off dirt with a soft cloth soaked in alcohol or benzine.
*Note: Do not use thinner, trichlene or ketone solvents because they may damage plastic parts. Also during
cleaning, be careful not to moisten or damage electronic parts, wiring, or mechanical parts.
(2) Removal of dust, pile, etc.
Vacuum cleaning (with an electric cleaner) is preferred. Remove all dust, etc., inside the printer.
*Note: After cleaning, check the oil level. If it is not adequate due to cleaning, replenish it.
1-2. Checks
Checks must be carried out at two levels: a “daily check” which the operator can easily carry out during operation, and
a “periodic check” which an expert should carry out.
(1) Daily check
When the printer is used on a daily basis, check that the printer is used properly. Make sure that the printer is
operating under the best conditions.
• Is any paper stuck in the paper box or printer case?
• Is the cartridge ribbon set at the right position?
• Is there any foreign matter inside the printer? (Remove if any.)
• Is the print head getting excessively dirty?
(2) Periodic check
After 6 months or printing 1 million lines, the periodic check and lubrication must be carried out.
• Check for deformation of springs.
• Check the gap between the platen and the print head.
• Remove dust, dirt, etc., around the detectors.
– 47 –
Page 52

2. Lubrication
Lubrication is very important to maintain optimum performance and to prevent trouble.
2-1. Lubricant
The type of lubricant greatly affects the performance and durability of the printer, especially in a low temperature
environment. We recommend use of the grease and lubrication oils listed below for this printer
Type of oil Product name Maker
Grease MOLYKOTE EM-30L DOW CORNING ASIA LTD
Lubricant Mobil 1 Mobil oil
2-2. Lubricating Method
When lubrication is carried out in assembly and disassembly, wash parts well to remove dust and dirt before lubrication.
Lubrication must be carried out regularly once every 6 months or after 1 million lines have been printed. Lubrication is
necessary irrespective of the regular lubrication whenever lubricant becomes deficient after cleaning or whenever parts
have been disassembled or replaced.
2-3. Lubricated Areas
NO. LubricationProduct Name
[1] Rubbing surfaces of pully bushing B,Timing pulley and Shaft EM-30L
[2] Rubbing surfaces of Release lever and Frame EM-30L
[3] Rubbing surfaces of Release lever spring and Frame EM-30L
[4] Rubbing surfaces of Adjusting lever and Frame EM-30L
[5] Rubbing surfaces of Springs and Paper feed roller B EM-30L
[6] Rubbing surfaces of Carrige stay Mobil 1
[7] Rubbing surfaces of Gear 32x0.5 and Shaft EM-30L
[8] Rubbing surfaces of Idler gear 16x72x0.5 and Shaft EM-30L
[9] Rubbing surfaces of PF roller assy and Roller holder L.R EM-30L
[10] Rubbing surfaces of Paper feed loller B and Roller holder L.R EM-30L
[11] Rubbing surfaces of Platen washer and Stopring EM-30L
[12] Rubbing surfaces of Gear cover and Shaft EM-30L
[13] Rubbing surfaces of Idler assy and Gear cover EM-30L
[14] Rubbing surfaces of Ribbon cassette gear and Gear cover EM-30L
[15] Rubbing surfaces of Gear,idler and Shaft EM-30L
[16] Rubbing surfaces of Rear loller and Shaft EM-30L
[17] Rubbing surfaces of Tractor shaft and Release lever EM-30L
[18] Rubbing surfaces of Tractor shaft EM-30L
[19] Rubbing surfaces of Gear and Shaft EM-30L
– 48 –
Page 53

Fig. 5-1 Lubricated Areas (printer mechanism)
– 49 –
Page 54

[17]
[18]
20
mm
10
Fig. 5-2 Lubricated Areas (Carriage unit )
mm
Fig. 5-3 Lubricated Areas (tractor unit)
– 50 –
[18]
10
mm
10
mm
Page 55

Fig. 5-4 Lubricated Areas (Frame R unit)
– 51 –
Page 56

Page 57

CHAPTER 6
TROUBLESHOOTING
1. Troubleshooting Procedures ............................................................................. 55
2. Unit Replacement Priority Chart ........................................................................ 56
3. Repair by Unit Replacement............................................................................... 57
4. Repair by Parts Replacement............................................................................. 63
4-1. Does not Operate at All with Power on............................................................... 63
4-2. Power Supply Circuit Abnormal.......................................................................... 64
4-3. Defective Motor Operation................................................................................... 65
4-4. Defective Print Head Operation........................................................................... 66
4-5. Defective Interface Operation.............................................................................. 67
6
Page 58

Page 59

1. Troubleshooting Procedures
Troubleshooting is never easy because various problems arise depending upon the particular location of the breakdown.
The following procedures should be taken in making repairs.
(1) The first method is to make repairs through unit replacements. The two display codes appearing in the flow chart
are defined as follows: 1) indicates main logic board replacement; and 2) indicates printer mechanism replacement,
to be carried out if the problem has not been corrected.
1) Main Logic Board Replacement
2) Printer Mechanism Replacement
Check again at this time whether the replaced unit is malfunctioning. (This is done to rule out trouble caused by improper
contact of connectors.)
Replaceable units consist of the following:
• Power supply unit
• Main logic board
• Printer mechanism
• Control panel board
In replacing these units, always refer to the unit replacement priority chart.
(2) The second method is to make repairs by parts replacement to replace defective elements inside a particular unit.
(Note 1) Before starting to repair, be sure to check visually the contact of the connector and the mounting of the IC in
the IC socket.
(Note 2) Always turn off power source and remove power plug before replacing any units or parts.
(Note 3) All check items shown in the flow chart must be checked. Otherwise, newly mounted parts or units may become
damaged.
(Note 4) If, in the process of making repairs, there is any confusion about proper procedures, restart the job from the
beginning.
(Note 5) Be careful to avoid injury from static electricity when handling ICs and main logic board.
– 55 –
Page 60

2. Unit Replacement Priority Chart
Category Remarks
Operation related
Motor related
related
Print head
related
Detector
Problem
Details
Specific display
lamp only will
not glow
Specific switch
only cannot be
input
Buzzer does not
sound (sound
volume
inadequate)
Strange sounds
during operation
No motor
holding power
(power very
weak)
Dots skipped
Print is too light
Ink ribbon
entanglement
(wire sticks out)
Absence of paper
not detected
Lever position
not detected
Incorrect printing
Ink ribbon not
forwarded
No operation at
EDS setting
Power
supply unit
2
Unit Exchange Sequence
Main
logic board
2
2
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
Printer
mechanism
2
2
1
1
1
1
2
1
Control
panel board
1
1
Replace ink ribbon
Check I/F cable
Faulty operation
when power is
turned on/off
Abnormal motor
operating speed
(slow)
Interface related and others
Fuse blown
during operation
Error detection of
head temperature
Carriage motor
error
Paper handling error
S. W. I error
EE-PROM &
Error indication
RAM error
Watch dog timer
error
Note: The figures 1, 2 and 3 mean the priority of replacement.
3
1
1
1
2
2
2
1
1
1
– 56 –
2
2
1
1
1
ROMAN lamp blink
COURIER lamp blink
ORATOR lamp blink
POWER lamp light
DRAFT lamp blink
POWER lamp light
Page 61

3. Repair by Unit Replacement
START
* Turn power off.
* Remove I/F cable.
* Mount ink ribbon.
* Set paper.
* Move carriage to center.
Turn power on.
A
Carriage
Moves?
YES
Carriage operates
normally?
YES
Carriage
stops at home
position?
(left side)
NO
NO
NO
B
Carriage motor
operating waveform is
normal? *1
YES
Replace printer mechanism.
A
*1 See (6) and waveform in
item 7 of Chapter 7.
NO
1) Replace main logic
board.
2) Replace printer
mechanism.
YES
1
Home position
switch signal is
normal?
YES
Replace main logic board.
A
NO
1) Replace main logic
board.
2) Replace printer
mechanism.
– 57 –
Page 62

1
On line lamp light?
YES
Press on line switch to take
off line.
On line lamp is out?
YES
Press paper feed switch.
Paper feed switch
operation is normal?
YES
Turn power off.
NO
NO
NO
On line lamp
signal is normal?
YES
Replace control panel board.
A
E
Paper feed
motor drive waveform
is normal? *2
YES
NO
Replace main logic board.
*2 See (7) and (8) waveform in
item 7 of Chapter 7.
NO
1) Replace main logic board.
2) Replace printer mechanism.
Holding paper feed switch,
turn power on.
Carriage operates
normally?
YES
2
Self
printing:
NO
Replace printer mechanism.
A
Carriage motor
drive waveform is
normal? *1
YES
Replace printer mechanism.
A
*1 See (6) and waveform in
item7 of Chapter 7.
NO
1) Replace main logic board.
2) Replace printer mechanism.
– 58 –
Page 63

2
Printing operation
is normal?
YES
Paper feed
operation is
normal?
YES
Ribbon feed
operation is
normal?
NO
NO
NO
Print head
drive signal waveform is
normal? *3
YES
Replace printer mechanism.
A
motor drive waveform is
*3 See (4) and (5) waveform in
item 7 of Chapter 7.
NO
1) Replace main logic board.
2) Replace printer mechanism.
*2 See (7) and (8) waveform in
item 7 of Chapter 7.
Paper feed
NO
normal? *2
YES
NO
1) Replace main logic board.
2) Replace printer mechanism.
YES
Terminates self printing.
Check host computer
connection.
Turn power off and check
I/F cable.
Turn power on.
Send print program from host
computer.
3
1) Replace ink ribbon.
2) Replace printer mechanism.
A
Replace printer mechanism.
A
C
– 59 –
Page 64

3
Printing begins?
YES
Printing
operation normal?
YES
Stop print program.
END
B
Carriage moves
with hand?
YES
NO
NO
NO
D
1) Replace I/F cable.
2) Replace main logic board.
3) Check host computer.
C
Replace printer mechanism.
Output
(+33V, +5V)
of power supply unit is
normal? *4
NO
Turn power off.
Fuse blows out?
YES
Replace fuse.
Remove connector CN6 from
main logic board.
Turn power on.
4
YES
1) Replace main logic board.
2) Replace printer mechanism.
3) Replace control panel
board.
NO
Replace power supply unit.
A
*4 Power Supply Unit
VH (33V) Line +33V ± 5% Between Pin 4 and Pin 3 of CN101
VL (5V) Line +5V ± 5% Between Pin 1 and Pin 2 of CN101
– 60 –
Page 65

4
Output of
power supply unit is
normal? *4
YES
Turn power off.
Connect connector CN6
from main logic board.
Turn power on.
Fuse blows out?
YES
Replace fuse.
1) Replace main logic board.
2) Replace printer mechanism.
3) Replace control panel board.
NO
Replace power supply unit.
NO
A
*4 Power Supply Unit
VH (33V) Line +33V ± 5% Between Pin 4 and Pin 3 of CN101
VL (5V) Line +5V ± 5% Between Pin 1 and Pin 2 of CN101
– 61 –
Page 66

D
*5 See (9) waveform in
item 7 of Chapter 7.
I/F signal is
normal? *5
NO
Ready condition?
YES
There is data
transmission?
NO
Check hardware or host
computer print program.
C
YES
NO
YES
I/F mode set
up properly?
NO
Change I/F mode.
YES
1) Replace I/F cable.
2) I/F cartridge
3) Replace main logic board.
A
E
On line switch
goes ON/OFF?
YES
On line lamp
drive signal is
normal?
YES
Replace control panel board.
A
NO
NO
Replace main logic board.
1) Replace control panel board.
2) Replace main logic board.
– 62 –
Page 67

4. Repair by Parts Replacement
4-1. Does not Operate at All with Power on
START
+33V, +5V
are
supplied? *1
YES
RESET
signal becomes
HIGH? *2
YES
Crystal
waveform is
normal? *3
YES
ROM OE
signals become
LOW?
YES
Carriage motor abnormal.
NO
NO
NO
NO
DC Power abnormal.
Check RESET circuit;
replace parts.
Check crystal circuit;
replace parts.
1) Replace CPU or ROM.
2) Check relevant circuit.
See 4-2. Power Supply
Circuit Abnormal.
Check operation.
END
*1
VH (33V) Line +33V ± 5% Between Pin 4 and Pin 3 of CN101
VL (5V) Line +5V ± 5% Between Pin 1 and Pin 2 of CN101
*2 See (2) waveform in item 7 of Chapter 7.
*3 See (1) waveform in item 7 of Chapter 7.
– 63 –
Page 68

4-2. Power Supply Circuit Abnormal
(1) Remove connector CN101 from power supply unit.
START
Fuse F1
is blown?
NO
YES
Replace Fuse F1
Fuse is
blown again?
NO
The no load voltages are below:
VH (33V) Line +33V ± 5% Between Pin 4 and Pin 3 of CN101
VL (5V) Line +5V ± 5% Between Pin 1 and Pin 2 of CN101
YES
Replace
1) Power supply unit
Check the 5V line of the
main logic board.
END
– 64 –
Page 69

4-3. Defective Motor Operation
START
LF-CMN
signal is normal?
*4
YES
LF-ø1,
ø2, ø3, ø4 are
normal? *5
YES
Paper Feed Motor Carriage Motor
NO
Check and replace
1) TR6
2) TR7
3) Gate array
NO
Check and replace
1) TA1
2) CPU
START
CR-ø1,
ø2, ø3, ø4 are
normal? *6
YES
Replace
CR motor
Check operation
END
NO
Check and replace
1) TA 2
2) Gate array
Replace
LF motor
Check operation
END
*4 See (7) waveform in item 7 of Chapter 7.
*5 See (8) waveform in item 7 of Chapter 7.
*6 See (6) waveform in item 7 of Chapter 7.
– 65 –
Page 70

4-4. Defective Print Head Operation
START
Does not
print at all?
+33V line
is supplied?
Check and replace
1) TR11
2) TR8 ~ TR10
3) Gate array
Head
energizing control
signal is normal?
*7
YES
YES
NO
NO
Check and replace
1) Power supply unit
(Refer to item 4-2.)
NO
A specific
pin does not
work?
NO
Print is light
as whole?
NO
YES
Check and replace
• TA3 (HD1, 2, 4, 6)
• TA4 (HD3, 7, 8, 9)
YES
Adjust gap
(Refer to Chapter 3.)
Check and replace
1) Print head
END
YES
Check and replace
1) Gate array
2) CPU
*7 See (4) waveform in item 7 of Chapter 7.
– 66 –
Page 71

4-5. Defective Interface Operation
START
Press on line switch to
take on line.
Send print program
from host computer.
Is I/F
signal normal? *8
YES
NO
*8 See (9) waveform in
item 7 of Chapter 7.
Incorrect print
generated?
NO
Check operation
END
YES
Check I/F cable.
Check and replace
1) IC 6
2) Gate array
3) CPU
– 67 –
Page 72

Page 73

CHAPTER 7
PARTS LIST
HOW TO USE PARTS LIST
(1) DRWG. NO.
This column shows the drawing number of the illustration.
(2) REVISED EDITION MARK
This column shows a revision number.
Part that have been added in the revised edition are indicated with “#”.
Part that have been abolished in the revised edition are indicated with “*”.
#1 : First edition → Second edition *1 : First edition → Second edition
(3) PARRTS NO.
Parts numbers must be notified when ordering replacement parts. Parts described as “NPN” have no parts number
and are not in stock, i.e., unavailable.
(4) PARTS NAME
Parts names must be notified when ordering replacement parts.
(5) Q’TY
This column shows the number of the part used as indicated in the figure.
(6) REMARKS
When there are differences in the specifications of the fuse, destinations, etc., the differences are described in words
or indicated by two letters.
US .....U.S.A. EC ..... EC(with Germany) UK..... United Kingdom HK..... Hong Kong
AS .....Australia LA..... Latin America SU ..... Russia
(7) RANK
Parts marked “S” are service parts. Service parts are recommended to be in stock for maintenance.
1. Printer Assembly ................................70
1-1. Disassembly Drawing ....................... 70
1-2. Parts List............................................ 71
2. Printer Mechanism ............................. 72
2-1. Disassembly Drawing ....................... 72
2-2. Parts List............................................ 73
3. Sub-Assembly .................................... 75
3-1. Lower Case Unit ................................ 75
3-2. Front Case Unit ................................. 76
3-3. Serial-Parallel Converter (Option) ... 77
3-4. Tractor Unit........................................ 78
3-5. Carriage Unit ..................................... 79
3-6. Frame Base Assy .............................. 80
3-7. Frame L Unit ...................................... 81
3-8. Frame R Unit ..................................... 82
4. Wiring Scheme of Printer .................. 83
5. Electrical Parts ................................... 84
5-1. Main Logic Board .............................. 84
5-1-1. Circuit Diagram ....................... 84
5-1-2. Component Layout ................. 86
5-1-3. Parts List.................................. 88
5-2. Control Panel Board ......................... 91
5-2-1. Circuit Diagram ....................... 91
5-2-2. Component Layout ................. 91
5-2-3. Parts List.................................. 91
5-3. Connected Board .............................. 92
5-3-1. Component Layout ................. 92
5-3-2. Parts List .................................. 92
5-4. Power Supply Unit ............................ 93
5-4-1. Circuit Diagram ....................... 93
5-4-2. Component Layout ................. 94
5-4-3. Parts List .................................. 95
6. Serial-Parallel Converter Board
( Option ) .............................................
6-1. Wiring Scheme .................................. 97
6-2. I/F Board ............................................ 98
6-2-1. Circuit Diagram ....................... 98
6-2-2. Component Layout ................. 98
6-2-3. Parts List .................................. 98
6-3. CPU Board ......................................... 99
6-3-1. Circuit Diagram ....................... 99
6-3-2. Component Layout ............... 100
6-3-3. Parts List ................................ 100
97
7. Waveform with Oscilloscope ........... 101
7
Page 74

1. Printer Assembly
1-1. Disassembly Drawing
– 70 –
Page 75

1-2. Parts List
Printer Assembly
DRWG.NO. REV. PARTS NO. PARTS NAME Q’TY REMARKS RANK
1 89430050 MECHANISM WITH HEAD DP701E (D) 1 S
2 87814610 POWER SPLY BD UNIT HA-15 US(D) 1 FOR US S
87814620 POWER SPLY BD UNIT HA-15 EC(D) 1 FOR EC,LA,RU S
87814630 POWER SPLY BD UNIT HA-15 UK(D) 1 FOR UK S
87814640 POWER SPLY BD UNIT HA-15 AS(D) 1 FOR AS S
87814650 POWER SPLY BD UNIT HA-15 HK(D) 1 FOR HK S
3 *2 87822080 MAIN LOGIC BD UNIT HF-12H(D) 1 S
#2 87822081 MAIN LOGIC BD UNIT HF-12H 1 EXCEPT FOR RU S
#2 86822281 MAIN LOGIC BD UNIT HF-12H RU 1 FOR RU S
4 *2 87821080 LOWER CASE UNIT HBF-12(D) 1 S
#2 87821081 LOWER CASE UNIT HBF-12(D) 1 S
5 *2 87820640 SUB-GUIDE B ASSY HF-12(D) 1 INCLUDED DRWG.NO.11 S
#2 80910461 SUB-GUIDE B WITH TAPE HF-12 1 INCLUDED DRWG.NO.11 S
6 87820180 PRINTER COVER UNIT HF-12H(D) 1 S
7 87820160 FRONT CASE UNIT HF-12H(D) 1 S
8 87816300 PLATEN KNOB UNIT QBF-10(D) 1 S
9 NPN POWER CORD HOLDER HF-12 1
10 NPN SWITCH HOLDER HF-12 1
11 87820450 REAR CASE ASSY HF-12(D) 1 S
12 82902600 RIBBON HOLDER 701C 1 S
13 01914036 SCREW TR 4-5 WS 1 S
14 01914031 SCREW TAT 4-12 PT-FL 8 S
15 01903038 SCREW TAT 3-10 PT-FL 10 S
16 00930803 SCREW TAT 3-8 PT 1 S
17 89595010 S-P CONVERTER SPC-8K UPC 1 FOR US,LA :OPTION
89595020 S-P CONVERTER SPC-8K JAN 1 EXCEPT FOR US,LA:OPT
18 89510230 RIBBON CASSETTE JAN Z9HD 1 EXCEPT FOR US,LA S
89510240 RIBBON CASSETTE UPC Z9HD 1 FOR US,LA S
89510260 RIBBON CASSETTE JAN LZ9 1 EXCEPT FOR US,LA:OPT
89510270 RIBBON CASSETTE UPC LZ9 1 FOR US,LA :OPTION
– 71 –
Page 76

2. Printer Mechanism
2-1. Disassembly Drawing
– 72 –
Page 77

2-2. Parts List
Printer Mechanism
DRWG.NO. REV. PARTS NO. PARTS NAME Q’TY REMARKS RANK
1 *2 89137060 PRINT HEAD DP7001E (D) 1 S
#2 89137061 PRINT HEAD DP7001E (D) 1 S
2 86436010 TRACTOR UNIT 701C 1
3 *2 86432010 CARRIAGE UNIT 701C 1 S
#2 86432011 CARRIAGE UNIT 701C 1 S
4 86431310 HEAD CABLE ASSY 701C 1 S
5 NPN FRAME BASE ASSY 791C 1
6 86430420 PF ROLLER ASSY 701C 2 S
6-1 83200881 HOLDER ROLLER 102 8 INCLUDED DRWG.NO.6
6-2 81361150 PF ROLLER SHAFT 701C 1 INCLUDED DRWG.NO.6
6-3 04020014 STOP RING SE6.0 8 INCLUDED DRWG.NO.6
7 86430390 CARRIAGE MOTOR ASSY 701C 1 S
8 86430350 PLATEN ASSY 701C 1 S
9 86430050 FRAME R UNIT 701E 1
10 86430040 PAPER GUIDE UNIT 701C 1 S
11 86430020 FRAME L UNIT 701C 1
12 86037381 TENSION LEVER ASSY 981 1
13 *2 83904520 PICK-UP LEVER 791C 1
#2 83904521 PICK-UP LEVER 791C 1
14 83904470 ROLLER HOLDER L 701C 2
15 83904460 ROLLER HOLDER R 701C 2
16 *2 83401341 PE DETECTOR LEVER 701C 2
#2 83401342 PE DETECTOR LEVER 701C 2
17 83401331 ADJUSTING LEVER 701C 1 S
18 83401320 RELEASE LEVER 701C 1 S
19 83201100 ADJUSTING BUSHING L 701C 1 S
20 83201090 ADJUSTING BUSHING R 701C 1 S
21 83201080 BUSHING F10X14X5.5 701C 1
22 83200222 PULLEY CAP 868 1
23 83120570 TIMING PULLEY B 102 1
24 83101910 RELEASE GEAR 701C 2 S
25 83101900 ADJUSTING GEAR 701C 1 S
26 83101890 GEAR 30X0.5 701C 2 S
27 83101880 GEAR 15X1 701C 4 S
28 83101820 PLATEN GEAR 721 1 S
29 83101240 GEAR 32X0.5 941 1 S
30 83100520 IDLER GEAR 16X72X0.5 1 S
31 83010090 PAPER PATH CHANGE PLATE 701C 1
32 NPN FRAME SUPPORT L 701C 1
33 NPN FRAME SUPPORT R 701C 1
34 82210200 WAVE WASHER 701C 1 S
35 82210120 WAVE WASHER 905 1 S
36 NPN FRAME HOLDER 701C 1
37 82091610 REAR ANGLE 701C 1
38 81361040 RELEASE SHAFT 701C 1
39 NPN CARRIAGE STAY 701C 1
40 80531110 RELEASE LEVER SPRING 701C 1 S
41 80531090 GROUND SPRING 701C 1
42 80511170 SPRING E050-035-0236-B 1 S
43 80511161 SPRING E040-018-0146 3 S
44 80510670 SPRING E040-023-0137 1 S
45 80510590 SPRING E050-040-0263 2 S
46 80510220 SPRING E050-060-0183 1 S
47 80201270 PAPER FEED ROLLER B 701C 2 S
48 04020018 STOP RING SE8.0 3 S
49 04020017 STOP RING SE5.0 9 S
– 73 –
Page 78

Printer Mechanism
DRWG.NO. REV. PARTS NO. PARTS NAME Q’TY REMARKS RANK
50 04020016 STOP RING SE4.0 2 S
51 04020015 STOP RING SE3.0 4 S
52 04012501 ROLL PIN SP2.5X10 8 S
53 02440401 WAVE WASHER WW4X8X0.2X1.5H 2 S
54 02210001 PLAIN WASHER WF10X18X1.6 1 S
55 02206002 PLAIN WASHER WF6X13X1.0 3 S
56 02020401 HEXAGON NUT NH4-2 2 S
57 01903073 SCREW TR 3-6 FL SPECIAL 1 S
58 01903038 SCREW TAT 3-10 PT-FL 2 S
59 01903031 SCREW TR 3-6 FL 2 S
60 00630404 SCREW TR 3-4 14 S
61 #2 03870405 BEARING L-940ZZR 1 S
– 74 –
Page 79

3. Sub - Assembly
3-1. Lower Case Unit
DRWG.NO. REV. PARTS NO. PARTS NAME Q’TY REMARKS RANK
4-1 *2 83026071 LOWER CASE HF-12 1 S
#2 83026072 LOWER CASE HF-12 1 S
4-2 NPN LOWER CASE CHASSIS HF-12 1
4-3 NPN RUBBER FOOT 15X15 QBS-10 2
4-4 02010401 HEXAGON NUT NH4-1 1
4-5 00930803 SCREW TAT 3-8 PT 1
– 75 –
Page 80

3-2. Front Case Unit
DRWG.NO. REV. PARTS NO. PARTS NAME Q’TY REMARKS RANK
7-1 87820430 BLIND BRUSH ASSY HF-12(D) 2
7-2 *1 83904512 PAPER ADJUSTER HF-12 1 :NOTE1
#1 83904780 PAPER ADJUSTER HBF-12 1 :NOTE1
7-3 83026062 FRONT CASE HF-12 1 S
7-4 NPN SHEET 3 HF-12 1
7-5 NPN SHEET 2 HF-12 1
7-6 NPN RUBBER CUSHION B HF-12 1
7-7 NPN RUBBER CUSHION A HF-12 1
7-8 80910451 SUB-GUIDE A HF-12 1 S
7-9 80088210 OPERATION SHEET HF-12H 1 EXCEPT FOR RU
*2 80088350 OPERATION SHEET HF-12H SU 1 FOR RU
#2 80088210 OPERATION SHEET HF-12H 1 FOR RU
7-10 83904770 ADJUSTER HOLDER HF-12H 1 :NOTE1
7-11 83912390 KEY-TOP HBF-12 1
NOTE 1: An adjuster holder (7-10) has been installed in
Pin
7-2 (PAPER ADJUSTER)
printers manufactured after the first lot. For
installation, insert the pins on the paper adjuster
into the holes in the adjuster holder, then use
7-3
(FRONT CASE)
7-10 (ADJUSTER HOLDER)
plastic adhesive to glue together the paper adjuster and adjuster holder.
– 76 –
Page 81

3-3. Serial-Parallel Converter ( Option )
17-3
17-8
17-1
17-7
17-5
17-2
17-4
17-6
17-6
17-6
DRWG.NO. REV. PARTS NO. PARTS NAME Q’TY REMARKS RANK
17-1 NPN UPPER CASE SPC-8K 1
17-2 NPN CPU BOARD UNIT SPC-8K 1
17-3 87590020 IF BOARD UNIT SPC-8K 1
17-4 NPN LOWER CASE UNIT SPC-8K 1
17-5 NPN CORD HOLDER SPC-8K 1
17-6 NPN SCREW TAT 3-12 PT-FL 3
17-7 NPN SCREW TAT 3-8 PT-FL 1
17-8 NPN CORD HOLDER PLATE SPC-8K 1
– NPN FERRITE CORE HF70RU12X5 2
– 77 –
Page 82

3-4. Tractor Unit
DRWG.NO. REV. PARTS NO. PARTS NAME Q’TY REMARKS RANK
2-1 86436330 TRACTOR L ASSY 701C 1 S
2-2 86436320 TRACTOR R ASSY 701C 1 S
2-3 NPN SHEET GUIDE 701C 1
2-4 83200651 TRACTOR BUSHING 891 2 S
2-5 83101690 TRACTOR GEAR 771 1 S
2-6 NPN TRACTOR SHAFT 701C 1
2-7 NPN TRACTOR STAY 701C 1
2-8 80521090 SPRING C090-060-0179 1
2-9 04020017 STOP RING SE5.0 3
2-10 04012002 ROLL PIN SP2.0X10 1
2-11 02307050 POLY-SLIDER WP7X0.5 2
– 78 –
Page 83

3-5. Carriage Unit
DRWG.NO. REV. PARTS NO. PARTS NAME Q’TY REMARKS RANK
3-1 86432320 CLUTCH PLATE UNIT 701C 1 S
3-2 *2 86432310 CARRIAGE ASSY 701C 1
#2 86432311 CARRIAGE ASSY 701C 1
3-3 86060810 IDLER ASSY 921 1
3-4 86032411 GEAR A ASSY 981 1
3-5 83912331 GEAR COVER 701C 1
3-6 83904490 CARD HOLDER 701C 1
3-7 83200990 REAR ROLLER 981 2 S
3-8 83120470 RIBBON CASSETTE GEAR 921 1 S
3-9 83101370 GEAR 48X0.3 965 1 S
3-10 83100721 RF IDLER GEAR 37X0.3 905 2 S
3-11 NPN ROLLER SHAFT 981 1
3-12 NPN ROLLER SHAFT 965 1
3-13 80902220 TIMING BELT HTD102 446X4.8 1
3-14 80511150 SPRING E035-029-0171 1
– 79 –
Page 84

3-6. Frame Base Assy
5-1-2
5-1-3
5-2
a
5-1-3
5-1-2
5-3
5-4
5-3
5-3
c
b
b
5-1-1
a
5-3
5-1-3
c
5-1
5-1-2
DRWG.NO. REV. PARTS NO. PARTS NAME Q’TY REMARKS RANK
5-1 #2 86430630 DETECTOR A UNIT 791C 1 S
5-1-1 *2 87770280 CABLE ASSY A 791C(D) 1 S
#2 80705710 CABLE UNIT A 791C 1
5-1-2 83904500 DETECTOR HOLDER 701C 3
5-1-3 08300152 PHOTO-INTERRUPTER RPI-574 3 S
5-2 NPN FRAME BASE 701C 1
5-3 01903064 SCREW TAT 3-5 CT 4
5-4 NPN WIRE 18UL1007BLK125TT 1
– 80 –
Page 85

3-7. Frame L Unit
11-1-2
11-1-4
11-3
11-3
a
c
b
a
11-1-1
11-1-3
11-1-5
c
11-1
11-1-3
11-1-5
b
11-2
DRWG.NO. REV. PARTS NO. PARTS NAME Q’TY REMARKS RANK
11-1 #2 86430620 DETECTOR B UNIT 701C 1 S
11-1-1 *2 87770210 CABLE ASSY B 701C(D) 1 S
#2 80705650 CABLE UNIT B 701C 1 S
11-1-2 83904500 DETECTOR HOLDER 701C 1
11-1-3 09090039 LEAF SWITCH LSA1119H 2 S
11-1-4 08300152 PHOTO-INTERRUPTER RPI-574 1 S
11-1-5 NPN HEAT-SHRINK TUBE F2-2.0 4
11-2 NPN FRAME L ASSY 701C 1
11-3 00926603 SCREW TAT 2.6-6 CT 2
– 81 –
Page 86

3-8. Frame R Unit
DRWG.NO. REV. PARTS NO. PARTS NAME Q’TY REMARKS RANK
9-1 86430440 PAPER FEED MOTOR ASSY 791C 1 S
9-2 NPN FRAME R ASSY 701C 1
9-3 83100510 GEAR 40X0.5 4 S
9-4 83100110 GEAR 26X0.5 1 S
9-5 04020010 STOP RING SE2.0 1
9-6 01903064 SCREW TAT 3-5 CT 2
– 82 –
Page 87

4. Wiring Scheme of Printer
– 83 –
Page 88

5. Electrical Parts
5-1. Main Logic Board
5-1-1. Circuit Diagram
– 84 –
Page 89

– 85 –
Page 90

5-1-2. Component Layout
– 86 –
Page 91

– 87 –
Page 92

5-1-3. Parts List
Main Logic Board
DRWG.NO. REV. PARTS NO. PARTS NAME Q’TY REMARKS RANK
IC1 08250007 CPU TMP90C041 1 S
IC2 08221044 PSRAM HM65256BLSP-100NS 1 S
IC3 *2 08223300 MASKED ROM 1.0 HF-12H 1 S
#2 08223271 MASKED ROM 2.0 HA-15 1 S
*2 NPN IC SOCKET ICS-32-2T 1
IC4 *2 08222017 EPROM D27C1001D-150NS 1 S
#2 08220116 EPROM 27512-150NS 1 HF12 H *.* S
NPN IC SOCKET ICS-32-2T 1
IC5 08210103 TTL IC 74LS06 1 S
IC6 08240081 GATE ARRAY D65626GF-H09W1 1 S
IC7 08222047 EEPROM KM93C46 1 S
IC8 08200142 IC-RESET PST592D-2* 1 S
IC9 08200091 IC-LIN NJM2903D 1 S
D1 *1 08000087 DIODE 1N4002 1 S
#1 08000084 DIODE 1N4002 1 S
D2-3 *2 08000039 DIODE 1S1588 2
#2 08000096 DIODE 1S2076A*A 2
D4-5 08000040 DIODE DSM1D1 2
D6 NOT MOUNTED
ZD1-2 08020130 ZENER DIODE HZ33-1 2
ZD3 08020099 ZENER DIODE RD30JSB2 1
TA1 07650052 TRANSISTOR ARRAY STA475A 1
TA2 08043001 FET ARRAY UPA1501H 1
TA3-4 07650056 TRANSISTOR ARRAY UPA1428AH 2
TR1-3 07011752 TRANSISTOR 2SA1266* 3
TR4-5 *2 07601002 TRANSISTOR 2SC3198GR* 2
#2 07601004 TRANSISTOR 2SC3199GR* 2
TR6 07113871 TRANSISTOR 2SB1387TZ 1
TR7-8 *2 07601002 TRANSISTOR 2SC3198GR* 2
#2 07601004 TRANSISTOR 2SC3199GR* 2
TR9-10 07018411 TRANSISTOR 2SA1841 2
TR11 07320101 TRANSISTOR 2SD2010 1
TR12 *2 07601002 TRANSISTOR 2SC3198GR* 1
#2 07601004 TRANSISTOR 2SC3199GR* 1
TR13 07011752 TRANSISTOR 2SA1266* 1
C1 NPN CERA. CAPA. 0.01UF 50V 1
C2 NPN CERA. CAPA. 470PF 50V 1
C3 NOT MOUNTED
C4 NPN CERA. CAPA. 0.01UF 250V 1
C5-6 NPN CERA. CAPA. 0.022UF 50V 2
C7-10 NPN CERA. CAPA. 100PF 50V 4
C11-12 NOT MOUNTED
C13-14 NPN CERA. CAPA. 1000PF 50V 2
C15-16 NPN CERA. CAPA. 470PF 50V 2
C17 NPN CERA. CAPA. 0.022UF 50V 1
C18 NOT MOUNTED
C19 NPN CERA. CAPA. 0.022UF 50V 1
C20-21 NPN CERA. CAPA. 0.01UF 50V 2
C22 NPN CERA. CAPA. 100PF 50V 1
C23 NPN CERA. CAPA. 33PF 50V 1
C24-31 NOT USED
C32-34 NPN CERA. CAPA. 0.022UF 50V 3
C35-36 NPN CERA. CAPA. 33PF 50V 2
C37 NPN CERA. CAPA. 0.01UF 50V 1
C38 NPN CERA. CAPA. 0.022UF 50V 1
C39-40 NPN CERA. CAPA. 0.01UF 50V 2
– 88 –
Page 93

Main Logic Board
DRWG.NO. REV. PARTS NO. PARTS NAME Q’TY REMARKS RANK
C41 NPN CERA. CAPA. 0.022UF 50V 1
C42-44 NPN CERA. CAPA. 1000PF 50V 3
C45 NPN CERA. CAPA. 470PF 50V 1
C46 NOT MOUNTED
C47 NPN CERA. CAPA. 0.022UF 50V 1
CA1-3 NPN CAPA. ARRAY 100PF 50V 8EL 3
CA4 NPN CAPA. ARRAY 1000PF 50V 4EL 1
R1 NOT USED
R2 NPN RD RESISTOR 2.2 K-OHM 1/6W 1
R3-10 NPN RD RESISTOR 4.7 K-OHM 1/6W 8
R11 NPN RD RESISTOR 2.2 K-OHM 1/6W 1
R12 NPN RD RESISTOR 100 OHM 1/6W 1
R13-15 NPN RD RESISTOR 4.7 K-OHM 1/6W 3
R16 NPN RD RESISTOR 2.2 K-OHM 1/6W 1
R17 NPN RD RESISTOR 4.7 K-OHM 1/6W 1
R18 NPN RD RESISTOR 2.2 K-OHM 1/6W 1
R19 NPN RD RESISTOR 4.7 K-OHM 1/6W 1
R20 NPN RD RESISTOR 2.2 K-OHM 1/6W 1
R21-22 NPN RD RESISTOR 4.7 K-OHM 1/6W 2
R23 NPN RD RESISTOR 220 OHM 1/6W 1
R24-25 NPN RD RESISTOR 100 OHM 1/6W 2
R26-29 NPN RD RESISTOR 2.2 K-OHM 1/6W 4
R30-33 NOT USED
R34-37 NPN RD RESISTOR 220 OHM 1/6W 4
R38-41 NPN JUMPER WIRE STP122 4 P=5mm
R42 NOT MOUNTED
R43-44 NPN RD RESISTOR 4.7 K-OHM 1/6W 2
R45 NPN RN RESISTOR 5.1 K-OHM 1/6W 1
R46-47 NPN RD RESISTOR 10 K-OHM 1/6W 2
R48 NPN RN RESISTOR 2.2 K-OHM 1/6W 1
R49-50 NPN RD RESISTOR 10 K-OHM 1/6W 2
R51-52 NPN RN RESISTOR 1 OHM 2W 2
R53 NPN RD RESISTOR 2.2 K-OHM 1/6W 1
R54 NPN RD RESISTOR 33 K-OHM 1/6W 1
R55 NPN RD RESISTOR 2.2 K-OHM 1/6W 1
R56 NPN RD RESISTOR 10 K-OHM 1/6W 1
R57-58 NPN RD RESISTOR 2.2 K-OHM 1/6W 2
R59-60 NPN RN RESISTOR 1.5 K-OHM 1W 2
R61-62 NPN RD RESISTOR 220 OHM 1/6W 2
R63-71 NPN RD RESISTOR 2.2 K-OHM 1/6W 9
R72-74 NPN RD RESISTOR 220 OHM 1/6W 3
R75-76 NPN RD RESISTOR 10 K-OHM 1/6W 2
R77 NPN RN RESISTOR 1 K-OHM 1/6W 1% 1
R78 NPN RN RESISTOR 5.1 K-OHM 1/6W 1
R79-81 NPN RD RESISTOR 10 K-OHM 1/6W 3
R82-85 NPN RD RESISTOR 2.2 K-OHM 1/6W 4
R86-88 NPN RD RESISTOR 4.7 K-OHM 1/6W 3
R89-91 NPN RD RESISTOR 33 K-OHM 1/6W 3
R92-94 NPN RD RESISTOR 220 OHM 1/6W 3
R95 NPN RD RESISTOR 33 K-OHM 1/6W 1
R96-98 NPN RD RESISTOR 4.7 K-OHM 1/6W 3
R99 NPN RD RESISTOR 220 OHM 1/6W 1
R100-101 NPN RD RESISTOR 10 K-OHM 1/6W 2
RA1 NPN RESIS. ARRAY 4.7K-OHM 1/8W 8EL 1
RA2 NPN RESIS. ARRAY 2.2K-OHM 1/8W 8EL 1
RA3 NPN RESIS. ARRAY 4.7K-OHM 1/8W 4EL 1
– 89 –
Page 94

Main Logic Board
DRWG.NO. REV. PARTS NO. PARTS NAME Q’TY REMARKS RANK
CN1 09100615 CONNECTOR 57RE4036080BD29A 1
CN2 09100621 CONNECTOR 53253-1210 1
CN3 09100573 CONNECTOR 53253-0610 1
CN4 09100620 CONNECTOR 53253-0810 1
CN5 09100267 CONNECTOR 5483-06A 1
CN6 09100317 CONNECTOR 5483-04A 1
CN8-9 09100624 CONNECTOR 51048-1300 2
CN10 09100622 CONNECTOR 51016-1100 1
CN11 09100623 CONNECTOR 51020-1100 1
JP1 80705570 FLAT CABLE 11X215 HF-12H 1
JP2 80705470 FLAT CABLE 13X298 HF-12 1
JP3 *2 87775070 WIRE 20UL1007BLK180 1
#2 80701900 WIRE 20UL1007BLK180 1
JP4-5 *2 87775080 WIRE 20UL1007BLK085 2
#2 80701910 WIRE 20UL1007BLK085 2
JP6 80700250 WIRE 18UL1007BLK055T 1
J63-JPSW1 #2 80701960 WIRE 28UL1007BLK075 1
X1 09250040 CERA. OSCILLATOR CST12.0MTW 1
L1 *2 09990706 BEADS INDUCTOR B-01AT 1
#2 09990737 BEADS INDUCTOR RH035047AT-Y7 1
L2 *2 09990705 BEADS INDUCTOR B01-RT 1
#2 09990736 BEADS INDUCTOR RH035047RT-Y7 1
L3 *2 09990706 BEADS INDUCTOR B-01AT 1
#2 09990737 BEADS INDUCTOR RH035047AT-Y7 1
L4-5 *2 09990705 BEADS INDUCTOR B01-RT 2
#2 09990736 BEADS INDUCTOR RH035047RT-Y7 2
L6 *2 09990706 BEADS INDUCTOR B-01AT 1
#2 09990737 BEADS INDUCTOR RH035047AT-Y7 1
L7 *2 09990705 BEADS INDUCTOR B01-RT 1
#2 09990736 BEADS INDUCTOR RH035047RT-Y7 1
– 90 –
Page 95

5-2. Control Panel Board
5-2-1. Circuit Diagram
5-2-2. Component Layout
5-2-3. Parts List
DRWG.NO. REV. PARTS NO. PARTS NAME Q’TY REMARKS RANK
SW0-2 09010041 PUSH SWITCH SKHHAL 3
OLSW 09010041 PUSH SWITCH SKHHAL 1
LED0-5,P *2 08300151 LED LTL232 7
#2 08300168 LED GL3EG8 7
Control Panel Board
– 91 –
Page 96

5-3. Connected Board
5-3-1. Component Layout
5-3-2. Parts List
Relay Board
DRWG.NO. REV. PARTS NO. PARTS NAME Q’TY REMARKS RANK
CN7 09100373 CONNECTOR HLEM16S-1 1
J118 NPN JUMPER WIRE STP122 1
– 92 –
Page 97

5-4. Power Supply Unit
5-4-1. Circuit Diagram
– 93 –
Page 98

5-4-2. Component Layout
– 94 –
Page 99

5-4-3. Parts List
Power Supply Unit
DRWG.NO. REV. PARTS NO. PARTS NAME Q’TY REMARKS RANK
R1 NPN CEMENT RESISTOR 5.6 OHM 5W 1 FOR US
NPN CEMENT RESISTOR 10 OHM 5W 1 EXCEPT FOR US
R2 NPN RN RESISTOR 62 K-OHM 3W 1
R3 NPN RD RESISTOR 330 K-OHM 1/4W 1 FOR US
NPN RD RESISTOR 680 K-OHM 1/4W 1 EXCEPT FOR US
R4 NPN RN RESISTOR 100 OHM 3W 1
R5 NPN RN RESISTOR 22 OHM 2W 1 FOR US
NPN RN RESISTOR 39 OHM 2W 1 EXCEPT FOR US
R6 NPN RN RESISTOR 0.15 OHM 2W 1 FOR US
NPN RN RESISTOR 0.36 OHM 2W 1 EXCEPT FOR US
R7 NPN RD RESISTOR 150 OHM 1/4W 1
R8 NPN RD RESISTOR 560 OHM 1/4W 1 FOR US
NPN RD RESISTOR 820 OHM 1/4W 1 EXCEPT FOR US
R9 NPN RD RESISTOR 3.3 K-OHM 1/4W 1
R10 NPN RD RESISTOR 120 OHM 1/4W 1
R11 NPN RD RESISTOR 330 K-OHM 1/4W 1 FOR US
NPN RD RESISTOR 680 K-OHM 1/4W 1 EXCEPT FOR US
R101 NPN RD RESISTOR 1 K-OHM 1/4W 1
R102 NPN RD RESISTOR 5.6 K-OHM 1/6W 2% 1
R103 NPN RD RESISTOR 1 K-OHM 1/6W 1
R104 NPN RN RESISTOR 5.6 K-OHM 1/6W 1% 1
R105 NPN RN RESISTOR 1470 OHM 1/6W 1
R106 NPN RN RESISTOR 1.5 K-OHM 3W 1
ZD1 NPN ZENER DIODE RD4.3EB3 1
ZD101 NPN ZENER DIODE RD6.2JSB2 1
ZD102 NPN ZENER DIODE RD39FB1-T 1
C1 NPN FILM CAPA. 0.22UF 250V 1
C2 NPN FILM CAPA. 0.1UF 275V 1 EXCEPT FOR US
C3-5 NPN CERA. CAPA. 2200PF 400V 3
C6 NPN CHEM. CAPA. 220UF 200V 1 FOR US
NPN CHEM. CAPA. 100UF 400V 1 EXCEPT FOR US
C7 NPN FILM CAPA. 0.01UF 630V 1
C8-9 NPN CERA. CAPA. 470PF 1KV 2 FOR US
NPN CERA. CAPA. 220PF 1KV 2 EXCEPT FOR US
C10 NPN FILM CAPA. 0.047UF 50V 1
C11 NPN FILM CAPA. 0.022UF 50V 1
C12 NPN FILM CAPA. 0.1UF 50V 1
C13-14 NPN FILM CAPA. 6800UF 50V 2 FOR US
NPN FILM CAPA. 0.022UF 50V 2 EXCEPT FOR US
C101 NPN CHEM. CAPA. 1000UF 10V 1
C102 NPN CHEM. CAPA. 470UF 10V 1
C103 NPN CHEM. CAPA. 4700UF 35V 1
C104 NPN CERA. CAPA. 0.01UF 250V 1
CN101 *2 NPN CABLE UNIT 04X135CC (D) 1
#2 NPN CABLE UNIT 04X135CC 1
D1 NPN FAST DIODE RU1P 1
D2 NPN FAST DIODE ERA22-02 1
D3 *2 NPN DIODE 1S1588 1
#2 NPN DIODE 1S2076A*A 1
D101 NPN SCHOTTKY DIODE SB140 1
D102 NPN FAST DIODE FMX-12S 1
DB1 NPN DIODE STACK D2SBA60 1
F1 09990080 FUSE 5TT2A-250V 1 FOR US
09990090 FUSE 215-1A-250V 1 EXCEPT FOR US
NPN FUSE HOLDER PFC5000 2
IC101 NPN IC-REG KIA7805PI 1
– 95 –
Page 100

DRWG.NO. REV. PARTS NO. PARTS NAME Q’TY REMARKS RANK
J10 *2 NPN BEADS INDUCTOR B01-RT 1 FOR US
#2 NPN BEADS INDUCTOR RH035047RT-Y7 1 FOR US
J11 *2 NPN BEADS INDUCTOR B01-RT 1
#2 NPN BEADS INDUCTOR RH035047RT-Y7 1
L1 NPN NOISE FILTER HR-24-183 1 FOR US
L1-2 *2 NPN NOISE FILTER LF-4D-183 2 EXCEPT FOR US
#2 NPN NOISE FILTER 64A-6001 2 EXCEPT FOR US
PC1 NPN OPTCOUPLER PC123FY2 1
Q1 NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC4546 1 FOR US
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC4234 1 EXCEPT FOR US
Q101 NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC1740SE 1
Q2 NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC2655 1
SW1 NPN SEESAW SWITCH T881SGSS9 1
T1 *2 NPN CONVERTER TRANSFORMER QBS-SDUS 1 FOR US
#2 NPN CONVERTER TRANSFORMER HAD US 1 FOR US
*2 NPN CONVERTER TRANSFORMER QBS-SDEC 1 EXCEPT FOR US
#2 NPN CONVERTER TRANSFORMER HAD EC 1 EXCEPT FOR US
W1-2 *2 NPN CABLE UNIT 01X160T (D) 2
#2 NPN CABLE UNIT 01X160T 2
- *2 NPN SCREW TAT 3-8 CT-FL 3
NPN WARNING SEAL ZBL-10 1
#2 NPN CAUTION SEAL UK POWER CORD 1 FOR UK
*2 NPN POWER CHASSIS HA-15 1
NPN RADIATION PLATE QBS-10 1
NPN FASTENER T18S 2 FOR AS,HK
NPN FASTENER T18S 3 EXCEPT FOR AS,HK
*2 NPN CORD SET EC-PN HA-10 1 FOR EC,LA
#2 NPN CORD SET EC-PN HA-10 1 FOR EC,LA,RU
NPN CORD SET US-PN HA-10 1 FOR US
NPN CORD SET UK-PN LC 1 FOR UK
*2 NPN CORD SET AS-PN LC 1 FOR AS
#2 NPN CORD SET AS-PN L=1.8M LC 1 FOR AS
*2 NPN CORD SET HK-PN QBA 1 FOR HK
#2 NPN CORD SET HK-PN SAA-1.8M 1 FOR HK
NPN SCREW TR 3-9 WS/WF 4
NPN HEAT RADIATION BD PUH23-35 1
* The fuse (F1) is the only part in the power supply unit that can be replaced.
– 96 –
 Loading...
Loading...