Page 1
EPSON
24-PIN DOT MATRIX PRINTER
SERVICE MANUAL
EPSON DLQ-3000+
SEIKO EPSON CORPORATION
4008259
Page 2
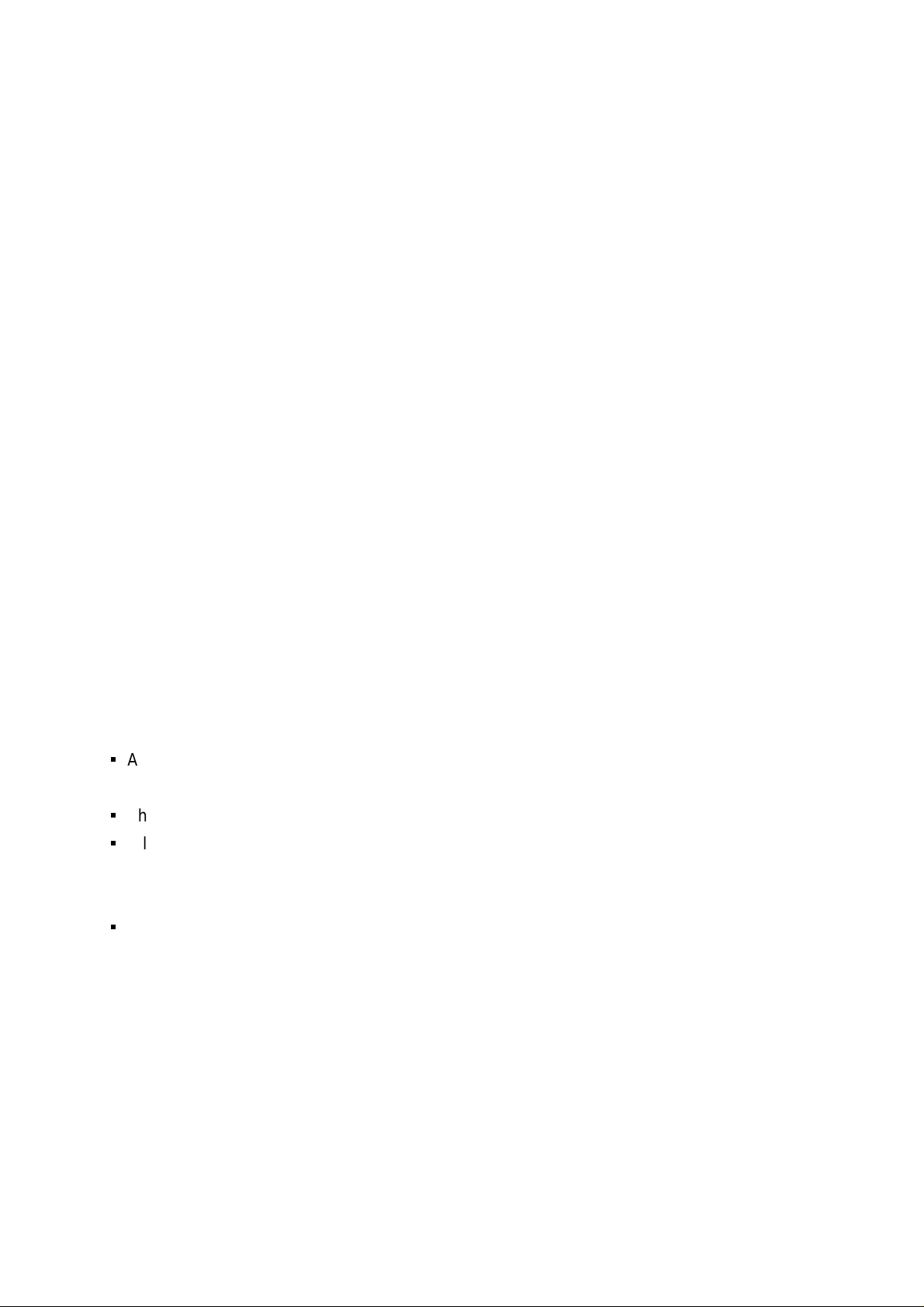
NOTICE
All rights reserved. Reproduction of any part of this manual in any form whatsoever
without SEIKO EPSON’s express written permission is forbidden.
The contents of this manual are subjects to change without notice.
All efforts have been made to ensure the accuracy of the contents of this manual.
However, should any errors be detected, SEIKO EPSON would greatly appreciate
being informed of them.
The above notwithstanding SEIKO EPSON can assume no responsibility for an y erro rs
in this manual or the consequences thereof.
EPSON is a registered trademark of SEIKO EPSON CORPORATION.
General Notice:
Other product names used herein are for identification purposes only and may be
trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
Copyright 1997 by SEIKO EPSON CORPORATION
Nagano, Japan
ii
Page 3

PRECAUTIONS
Precautionar y notations throughout the tex t are categorized rel ative t o 1) personal i njury and 2)
damage to equipment.
WARNING
CAUTION
The precautionary measures itemized below should always be observed when performing
repair/maintenance procedures.
Signals a precaution which, if ignored, could result in serious or fatal personal
injury. Great caution should be exercised in performing procedures preceded by
WARNING Headings.
Signals a precaution which, if ignored, could result in damage to equipment.
WARNING
1. ALWAYS DISCONNECT THE PRODUCT FROM BOTH THE POWER SOURCE AND
PERIPHERAL DEVICES PERFORMING ANY MAINTENANCE OR REPAIR PROCEDURES.
2. NO W ORK SHOULD BE PERFO RMED ON THE UNIT BY PERSONS UNF AMILIAR W ITH
BASIC SAFETY MEASURES AS DICTATED FOR ALL ELECTRONICS TECHNICIANS IN
THEIR LINE OF WORK.
3. WHEN PERFORMING TESTING AS DICTATED WITHIN THIS MANUAL. DO NOT
CONNECT THE UNIT TO A POWER SOURCE UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. WHEN
THE POWER SUPPLY CABLE MUST BE CONNECTED, USE EXTREME CAUTION IN
WORKING ON POWER SUPPLY AND OTHER ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS.
CAUTION
1. REPAIRS ON EPSON PRODUCT SHOULD BE PERFORMED ONLY BY EPSON
CERTIFIED REPAIR TECHNICIAN.
2. MAKE CERTAIN THAT THE SOURCE VOLTAGE IS THE SAME AS THE RATED VO LT AG E,
LISTED ON THE SERIAL NUMBER/RATING PLATE. IF THE EPSON PRODUCT HAS A
PRIMARY AC RATING DIFFERENT FROM AVAILABLE POWER SOURCE, DO NOT
CONNECT IT TO THE POWER SOURCE.
3. ALWAYS VERIFY THAT THE EPSON PRODUCT HAS BEEN DI SCONNECTED FROM T HE
POWER SOURCE BEFORE REMOVING OR REPLACING PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARDS
AND/OR INDIVIDUAL CHIPS.
4. IN ORDER TO PROTECT SENSITIVE MICROPROCESSORS AND CIRCUITRY, USE
STATIC DISCHARGE EQUIPMENT, SUCH AS ANTI-STATIC WRIST STRAPS, WHEN
ACCESSING INTERNAL COMPONENTS.
5. REPLACE MALFUNCTIONING COMPONENTS ONLY WITH THOSE COMPONENTS BY
THE MANUFACTURE; INTRODUCTION OF SECOND-SOURCE ICs OR OTHER
NONAPPROVED COMPONENTS MAY DAMAGE THE PRODUCT AND VOID ANY
APPLICABLE EPSON WARRANTY.
iii
Page 4

PREFACE
This manual describes functions, theory of electrical and mechanical operations, maintenance,
and repair of DLQ-3000+.
The instruct ions and procedur es incl uded herei n are i ntended for the ex peri ence repai r tec hnic ian,
and attention should be given to die precautions on the preceding page. The Chapters are
organized as follows:
CHAPTER 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Prov ides a general product ov erview, l ists specific ations, and illustrates the main components of
the printer.
CHAPTER 2. OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Describes the theory of printer operation.
CHAPTER 3. DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
Includes a step-by-step guide for product disassembly and assembly.
CHAPTER 4. ADJUSTMENT
Includes a step-by-step guide for adjustment.
CHAPTER 5. TROUBLESHOOTING
Provides EPSON-approved techniques for troubleshooting.
CHAPTER 6. MAINTENANCE
Describes preventive maintenance techniques and lists lubricants and adhesives required to
service the equipment.
APPENDIX
Describes connector pin assignments, circuit diagrams, circuit board component layout and
exploded diagram.
The contents of this manual are subject to change without notice.
iv
Page 5

REVISION SHEET
Revision Issued Data Contents
Rev. A August 21 1997 First Release
v
Page 6

TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
CHAPTER 2. OPERATING PRINCIPLES
CHAPTER 3. DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
CHAPTER 4. ADJUSTMENT
CHAPTER 5. TROUBLESHOOTING
CHAPTER 6. MAINTENANCE
APPENDIX
vi
Page 7

Chapter 1
Product Description
1.1 Features ..................................................................................................1-1
1.2 Consumables and Options....................................................................1-3
1.3 Hardware Specification..........................................................................1-4
1.3.1 printing Specification....................................................................1-4
1.3.2 Character Specifications and Control Codes.............................1-7
1.3.2.1 Coded Character Sets.........................................................1-7
1.3.2.2 Type Faces..........................................................................1-7
1.3.2.3 Rendition .............................................................................1-7
1.3.2.4 Combination of character tables and typefaces ..................1-8
1.3.2.5 Memory Size........................................................................1-9
1.3.2.6 Character Size.....................................................................1-9
1.3.2.7 Control Codes......................................................................1-9
1.3.3 Paper Feed Specification............................................................1-10
1.3.3.1 Friction Feed (Cut sheet)...................................................1-10
1.3.3.2 Tractor Feed (Continuous paper)......................................1-10
1.3.3.3 Paper Feed Speed and Accuracy......................................1-10
1.3.4 Paper Specification.....................................................................1-11
1.3.5 Printable Area..............................................................................1-17
1.3.6 Paper Thickness Detection ........................................................1-24
1.3.7 Ribbon Cartridge.........................................................................1-25
1.3.7.1 Monochrome ribbon cartridge............................................1-25
1.3.7.2 Color ribbon cartridge........................................................1-25
1.3.8 Input Data Buffer .........................................................................1-26
1.3.9 Electric Specifications................................................................1-26
1.3.10 Safety Approvals .......................................................................1-26
1.3.11 CE Marking.................................................................................1-26
1.3.12 Acoustic Noise...........................................................................1-27
1.3.13 Reliability....................................................................................1-27
1.3.14 Environmental Conditions........................................................1-27
Page 8

1.4 Interfaces ..............................................................................................1-28
1.4.1 Parallel Interface..........................................................................1-28
1.4.2 Serial Interface.............................................................................1-33
1.4.3 Optional Interface........................................................................1-34
1.4.4 Printer language..........................................................................1-35
1.4.5 Prevention Hosts from Data Transfer Time-out .......................1-36
1.4.6 Interface Selection ......................................................................1-36
1.5 Operation ..............................................................................................1-37
1.5.1 Control Panel...............................................................................1-37
1.5.1.1 Button Operations..............................................................1-37
1.5.1.2 Printer Status and LCD/LED Indicator Conditions.............1-39
1.5.1.3 Printer Status and Buzzer..................................................1-40
1.5.2 SelecType.....................................................................................1-41
1.5.2.1 SelecType Phase ..............................................................1-41
1.5.2.2 SelecType Operation.........................................................1-42
1.5.2.3 SelecType Option..............................................................1-43
1.5.3 Functions at Power On ...............................................................1-45
1.5.4 Bi-D Adjustment Mode................................................................1-46
1.5.5 Program Reload Mode................................................................1-46
1.5.6 Initialization..................................................................................1-47
1.5.6.1 Printer Initialization............................................................1-47
1.5.6.2 Initialize Defaults to the Standard......................................1-48
1.6 Main Components................................................................................1-49
1.6.1 C210MAIN Board.........................................................................1-49
1.6.2 C124PSB/PSE Board...................................................................1-50
1.6.3 Printer Mechanism......................................................................1-50
1.6.4 Housing........................................................................................1-51
Page 9

Product Description
1.1 Features
The DLQ 3000+, equipped with a Bi-directional parallel interface, is the most advanced
EPSON 24-pin impact-dot printer. It prints on continuous multi-part form as well as on single
sheet, which makes the printer highly usable in office environment . The main features of
this printer are:
Used in Network environment with parallel interface supported
Memory
CSF paper quantity sensor
Paper jam detection
Enhanced duplex printing
1 original plus 6 duplications in the copy mode
Wide printable area
70 line / A4 (0 mm can be set for the top and bottom margins at single print mode.)
Paper thickness detection function supported
Enables the auto and manual platen gap adjustment
Fonts
Bitmap fonts: 9 LQ and 1 draft typefaces
Scalable fonts: 4 typefaces
Bar-code fonts: 8 typefaces
Character tables
Standard version: 11 tables
NLSP version: 30 tables
Control codes
ESC/P2
IBM 2391 Plus Emulation
Input buffer
128 K byte
Interface
Bi-directional parallel interface (IEEE-1284 nibble mode supported)
Serial interface (EIA-232D)
Type-B interface level 2 (Optional)
Reliability
Total print volume: 9 million lines
Printhead life: 200 million strokes
Ribbon life: 6 million characters
Rev. A
1-1
Page 10
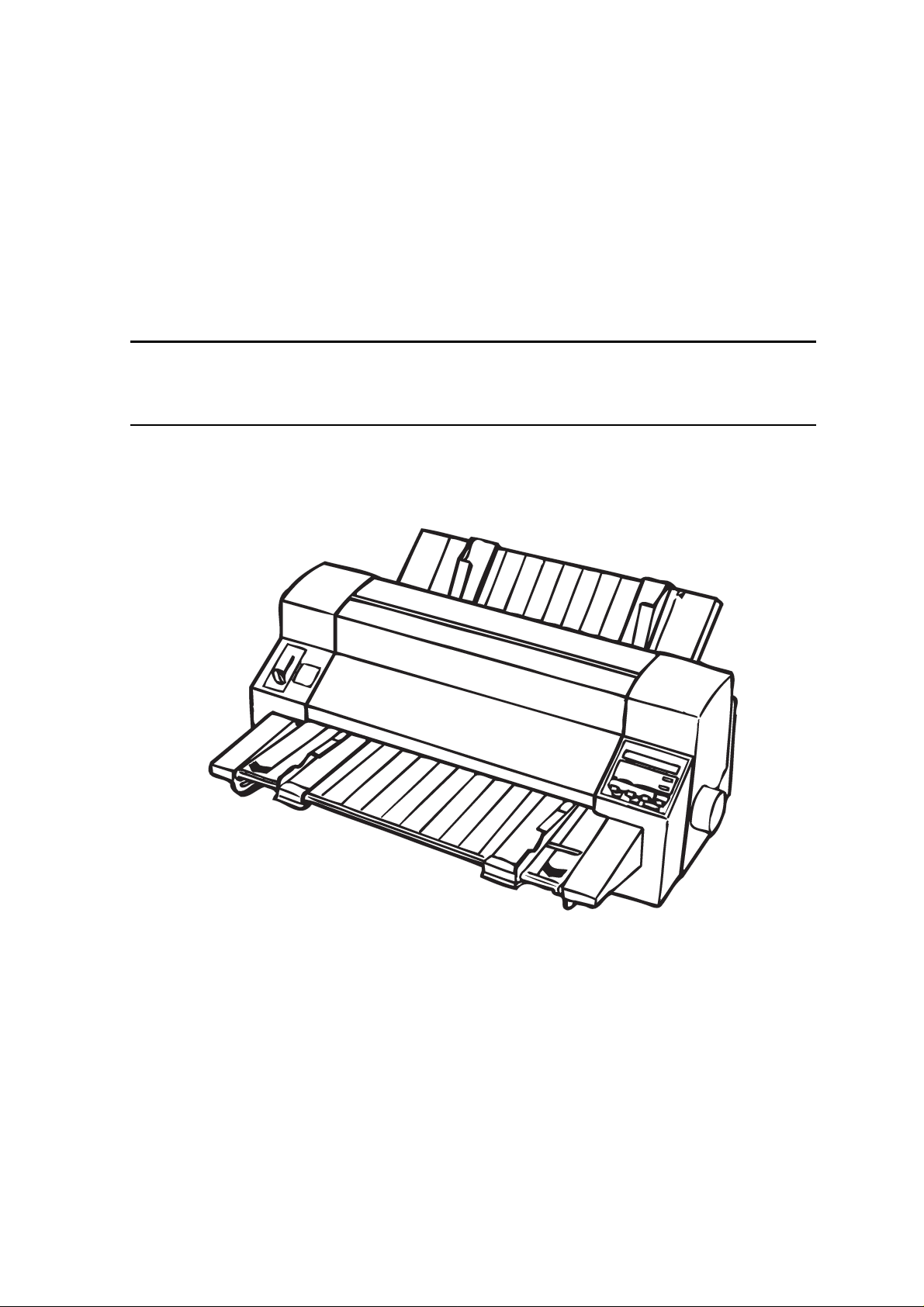
DLQ-3000+
Paper Thickness Adjust Lever
Printer Cover
Ribbon Cartridge
Rear Paper Guide
Power Switch
Left Guide Edge
Left Guide Edge Lock
Front Paper Guide
Printhead
Right Guide Edge Lock
Control Panel
Knob
Paper Bail
Right Guide Edge
Paper Support
Release Lever
1-2
Parallel Interface
Serial Interface
Tractor Unit
Figure 1-1. Exterior View of DLQ 3000+
Rev. A
Page 11
3
1.2 Consumables and Options
Table 1-1. Accessories and Options
Part Number Description
Consumable Supplies
S015066
S015067 Ribbon cartridge (Color)
Optional Equipment
C806830 Cut sheet feeder
C82307∗ / C82308∗
C82310∗ / C82311∗
C82312∗
C82313∗
C82314∗
C82315∗
C82331∗
C82345* IEEE-1284 parallel I/F card
C82346 Multi Protocol Ethernet I/F card
Accessory Equipment
Ribbon cartridge (Black)
32KB intelligent serial I/F card
32KB intelligent parallel I/F card
Localtalk™ card
32KB IEEE-488 I/F card
Coax I/F card
Twin-Ax I/F card
Ethernet I/F card
Power supply cable
Product Description
2
*
Note:
1. Asterisk at the end of the part numbers replaces the last digit of the part number,
which varies by the market.
2. Can be an accessory item according as market.
Rev. A
1-
Page 12
DLQ-3000+
1.3 Hardware Specification
1.3.1 printing Specification
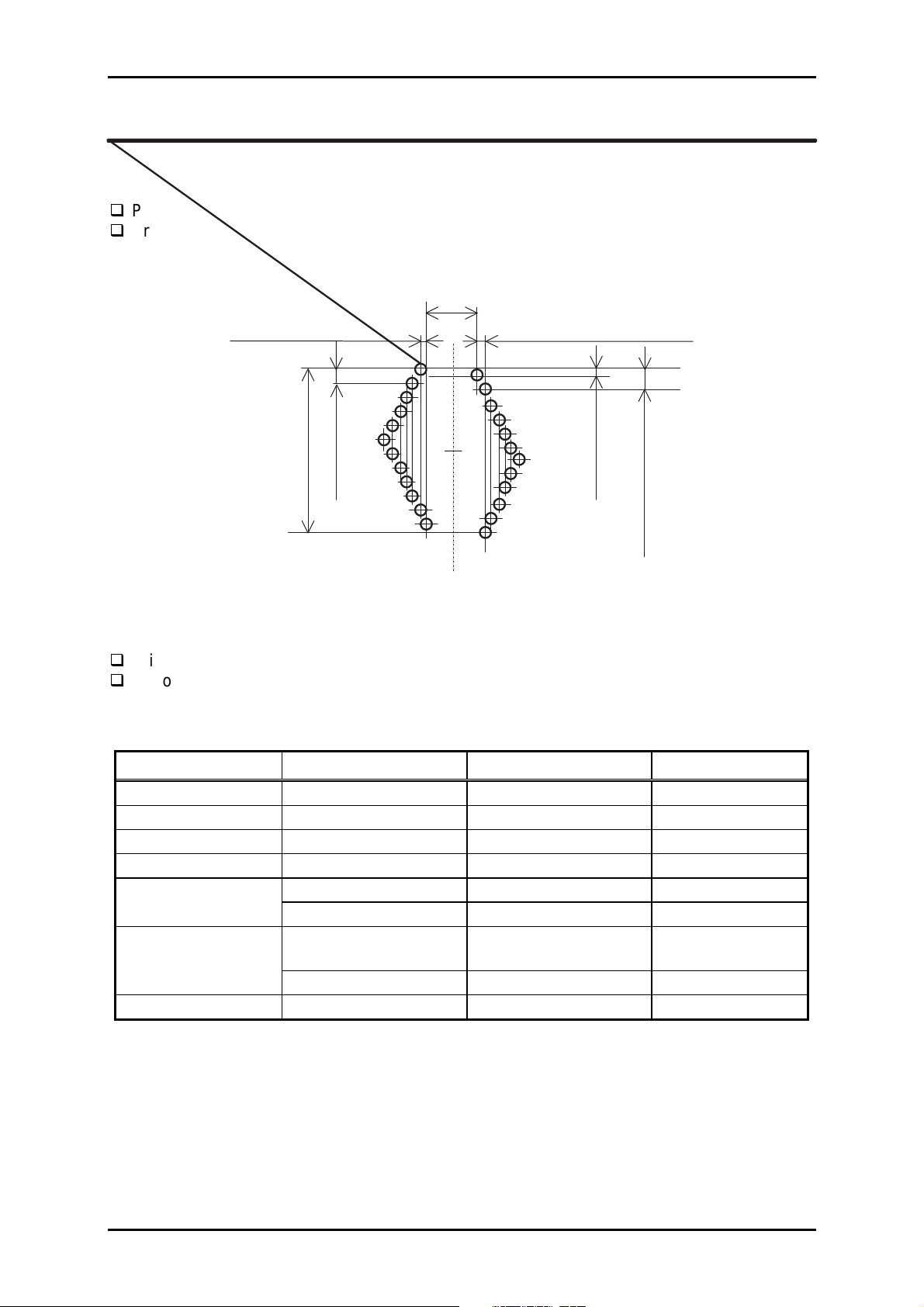
Print method Impact-dot matrix
Print pin arrangement 24-pin rhombus (See Figure 1-2.)
0.86 m m =1/30"+1/2160"
6x0.023m m (=1-1080")
#1 #2
3.25m m (=1/180"x23)
11x0.28m m (=1/90")
#23
6x0.023m m (=1-1080")
#24
0.14 m m (=1/180")
11x0.28m m (=1/90")
Figure 1-2. Pin Arrangement
Printing direction Bi-directional printing with logic seeking
Resolution See Table 1-2.
Table 1-2 .Printing Resolution
Printing Mode Horizontal Density Vertical Density Adjacent Dot Print
High speed draft 90 dpi 180 dpi No
Draft 120 dpi 180 dpi No
Draft condensed 240 dpi 180 dpi No
LQ 360 dpi 180 dpi No
8-pin bit image 60, 80, 90 or 120 dpi 60 dpi Yes
120 or 240 dpi 60 dpi No
24-pin bit image 60, 90, 120 or 180
180 dpi Yes
dpi
360 dpi 180 dpi No
Raster graphics 180 or 360 dpi 180 or 360 * dpi Yes
Note:When a color ribbon is installed, the printer can not print vertical 360 dpi graphics. In
that case, the printer changes vertical density to 180 dpi.
1-4
Rev. A
Page 13
Product Description
5
Printing speed See Table 1-3.
Table 1-3. Printing Speed
Printing Mode Character Size Maximum Printing Speed
Mode 0 Mode 1 Mode 2 Mode 3 Mode 4
High speed draft 10 cpi 444 444 160 160 240
10 cpi 360 333 240 120 180
Draft 12 cpi 432 400 288 144 216
15 cpi 540 500 360 180 270
Craft condensed 17 cpi 309 286 206 103 154
20 cpi 360 333 240 120 180
10 cpi 120 111 80 40 60
LQ 12 cpi 144 133 96 48 72
15 cpi 180 167 120 60 90
LQ condensed 17 cpi 206 190 137 68 103
20 cpi 240 222 160 80 120
Raster (360 dpi) 10 cpi 20 20 20 20 20
Printing Speed Mode Selection
This printer is designed to control the printing speed according to the power supply voltage
and printhead temperature. When the power supply voltage drops to the limit, the printer
stops printing, then resumes the job at a slower speed to print the remaining data for the
line. When the printhead temperature rises to the limit, the printer stops printing. Then it
resumes printing at a slower speed if the printhead temperature recovers to the specified
level. The printing speed mode is determined according to the flowchart shown in Page 1-6.
Rev. A
1-
Page 14
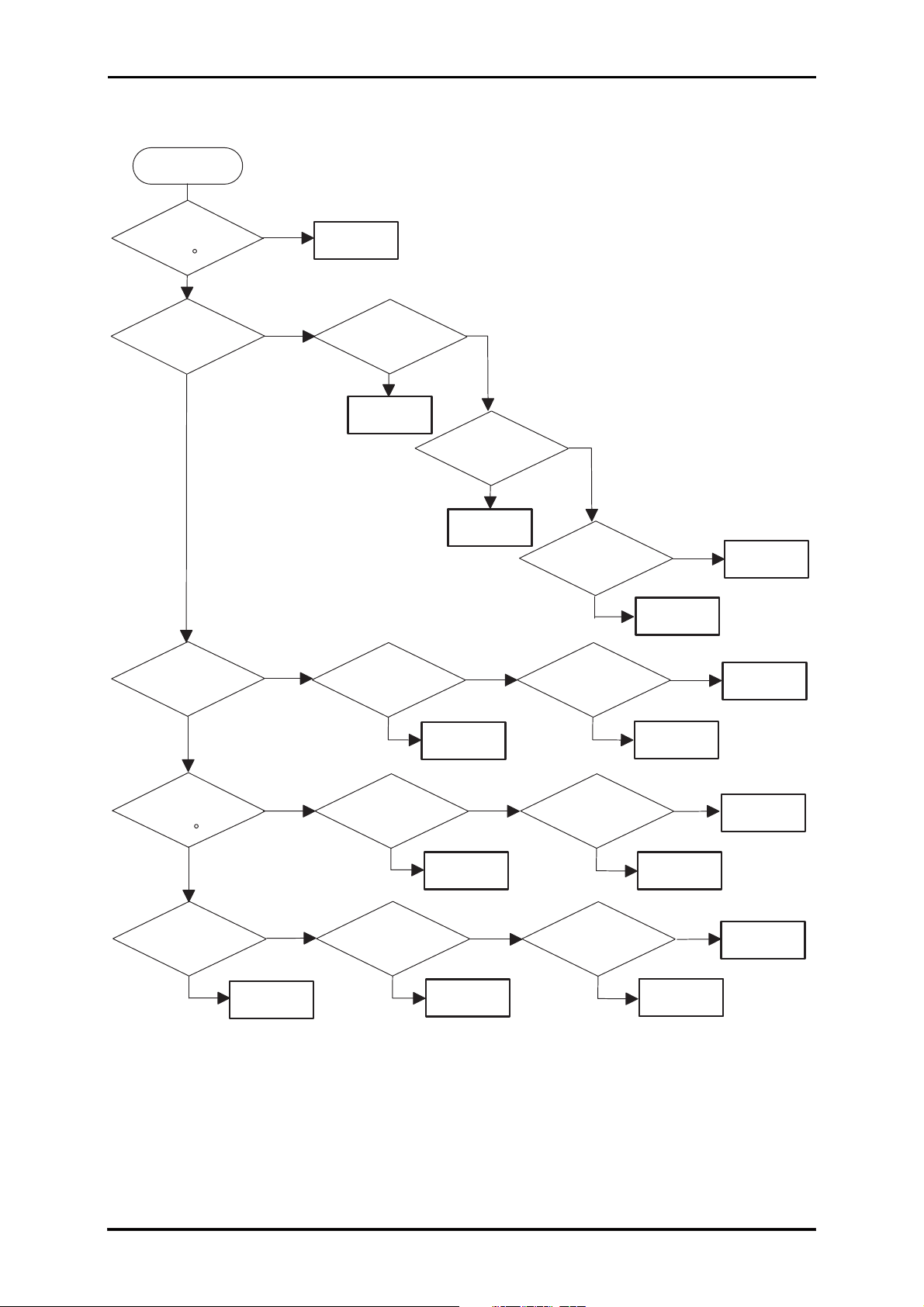
DLQ-3000+
START
Is th e
head tem perature
<
1 2 C ?
NO
P-Down* ?
NO
Is p rin t d u ty
>
5 0 % ?
=
YES
YES
NO
M ode 4
B lack color print?
NO
M ode 2
B lack color print?
YES
Is paper
thickness
>
0.19 m m ?
=
NO
M ode 2M ode 2
YES
YES
C opy 2 m ode?
NO
NO
Is paper
thickness
>
0.19 m m ?
=
YES
M ode 2M ode 2
YES
M ode 3
M ode 1
YES
Is the head
tem perature
>
3 8 C ?
=
YES
B lack color print?
NO
NO
YES
M ode 2
NO
B lack color print?
NO
Is paper
thickness
>
0.19 m m ?
=
NO
M ode 0
YES
M ode 0
YES
M ode 2
M ode 2
C opy 2 m ode?
NO
Is paper
thickness
>
0.19 m m ?
=
NO
NO
M ode 0
YES
M ode 1
M ode 0
YES
M ode 3
M ode 2M ode 2
P-D ow n : M eans that the line is the reprinted line after the pow er supply voltage drops. It is to prevent
the printhead and the printer m echanism from being driven under the im proper pow er
supply voltage.
Figure 1-3. Printing Speed Selection Mode
1-6
Rev. A
Page 15

7
1.3.2 Character Specifications and Control Codes
1.3.2.1 Coded Character Sets
ASCII international and Legal international character sets *
USA France Germany UK
Denmark 1 Sweden Italy Spain 1
Japan Norway Denmark 2 Spain 2
Latin America Korea Legal
Note: The codes for the international and legal characters are as follows:
23H, 24H, 40H, 5BH, 5CH, 5DH, 5EH, 60H, 7BH, 7CH, 7DH, 7EH
Standard version (11 character tables)
Italic table PC437 (US, Standard Europe)
PC850 (Multilingual) PC860 (Portuguese)
PC861 (Icelandic) PC863 (Canadian French)
PC865 (Nordic) Abicomp
BRASCII Roman 8
ISO Latin 1
NLSP version (30 character tables)
Italic table PC 437 (US, Standard Europe)
PC 850 (Multilingual) PC 437 (Greek)
PC 852 (East Europe) PC 853 (Turkish)
PC 855 (Cyrillic)PC 860 PC 857 ( Turkish)
PC 866 (Russian) PC 869 (Greek)
MAZOAWIA (Poland) Code MJK (CSFR)
ISO 8559-7 (Latin, Greek) ISO Latin 1T (Turkish)
Bulgaria (Bulgaria) PC 864 (Arabic)
Estonia PC 774 (LST 1283:1933)
ISO 8859-2 PC 866 LAT. (Latvian)
PC 860 (Portuguese) PC 861 (Icelandic)
PC 865 (Nordic) PCAPTEC (Arabic)
PC 708 (Arabic) PC 720 (Arabic)
PCAR864 (Arabic) Hebrew7 *
Hebrew8 *
1
PC862(Hebrew) *
Note 1: Theses character tables are not selected in the SelecType mode.
1
1
Product Description
1.3.2.2 Type Faces
Bitmap fonts (10 type faces)
Roman Sans Serif Courier Prestige
Script Script C OCR B
Orator Orator S Draft
Scalable fonts (4 type faces)
Roman Sans Serif Roman T Sans Serif H
Bar-code fonts (8 type faces)
EAN 13 EAN-8 Interleaved 2 of 5 UPC-A
UPC-E Code 39 Code 128 POSTNET
1.3.2.3 Rendition
ASCII
Double-width Double-height Condensed
Bolded Double-strike Italics
Super/subscript Outlined Shadowed
Underlined (Single, Double, Single-broken, Double-broken line)
Strike-through (Single, Double, Single-broken, Double-broken line)
Over-scored (Single, Double, Single-broken, Double-broken line)
Rev. A
1-
Page 16
DLQ-3000+
1.3.2.4 Combination of character tables and typefaces
Table 1-4. Character Tables and Type Faces
Character Tables Bitmap Fonts Scalable Fonts
Standard
version
NLSP
version
*
Italic table
1
PC 437 (US Stand ard Europe)
PC 850 (Multilingual)
PC 860 (Portuguese))
PC 861 (Icelandic)
PC 863 (Canadian-French)
PC 865 (Nordic)
BRASCII
Abicomp
Roman 8
ISO Latin 1
Italic table
1
*
PC 437 (US Stand ard Europe)
PC 850 (Multilingual)
PC 860 (Portuguese)
PC861 (Icelandic)
PC 865 (Nordic)
PC 864 (Arabic) EPSON Draft
PC 437 (Greek)
PC 852 (East Europe)
PC 853 (Turkish)
PC 855 (Cyrillic)
PC 857 (Turkish)
PC 866 (Russian)
PC 869 (Greek)
MAZOWIA ( P oland)
Code MJK (CSFR)
ISO 8859-7 (Lat in/Greek)
ISO Latin 1T (Turkish)
Bulgaria ( B ulgaria)
Estonia
PC 774 (LST 1283:1993)
ISO 8859-2
PC 866 LAT. (Latvian)
PCAPTEC (Arabic)
PC 708 (Arabic)
PC 720 (Arabic)
PCAR864 (Arabic)
EPSON Draft
EPSON Roman
EPSON Sans Serif
EPSON Courier
EPSON Prestige
EPSON Script
EPSON OCR-B
EPSON Orator
EPSON Orator-S
Epson Script C
EPSON Draft
EPSON Roman
EPSON Sans Serif
EPSON Courier
EPSON Prestige
EPSON Script
EPSON OCR-B
EPSON Orator
EPSON Orator-S
Epson Script C
EPSON Roman
EPSON Draft
EPSON Roman
EPSON Sans Serif
EPSON Courier
EPSON Prestige
EPSON Script
EPSON Draft (Arabic)
EPSON Naskh
(Roman)
EPSON Kufi (Sans Serif)
EPSON Roman
EPSON Sans Serif
EPSON Roman T
EPSON Sans Serif H
EPSON Roman
EPSON Sans Serif
EPSON Roman T
EPSON Sans Serif H
(Not supported)
(Not supported)
(Not supported)
Hebrew7 *
Hebrew8 *
PC862(Hebrew) *
2
2
2
EPSON Draft (Hebrew)
EPSON Miriam (Roman)
EPSON David
(Not supported)
(Courier)
Note:
1: ESC R command is effective on the character tables with bold weight.
2: These character tables are not selected in the SelecType mode.
1-8
Rev. A
Page 17
Product Description
9
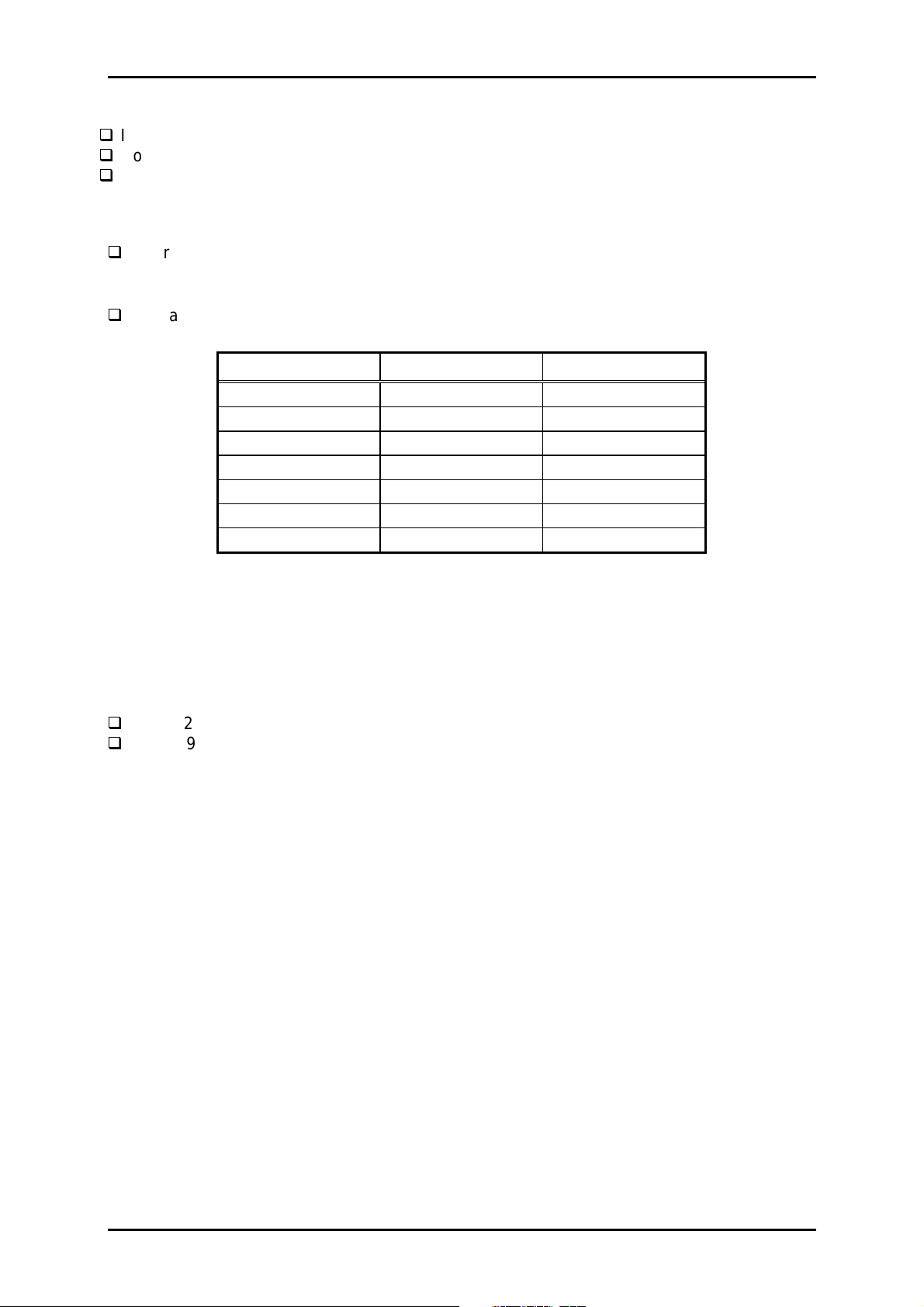
1.3.2.5 Memory Size
Input buffer 128 K byte or 1k byte
Download memory Approximately 10 K byte
CG ROM NLSP Version: 8 M bit, Standard Version: 4 M bit
1.3.2.6 Character Size
Character size
• Bit map font 10.5 point
• Scalable font 10.5 point
Character matrixes See Table 1-5.
Table 1-5. Character Matrixes
Character Horizontal Dots Vertical Dots
Draft 10 cpi 12 24
Draft 12 cpi 10 24
Draft 15 cpi 8 16
LQ 10 cpi 36 24
LQ 12 cpi 30 24
LQ 15 cpi 24 16
LQ proportional 48 (maximum) 24
Notes:
1. The character matrixes for high speed draft 10 cpi characters are made from the draft
12 cpi matrixes.
2. The character matrixes for 15 cpi character are also used for superscript and
subscript characters.
1.3.2.7 Control Codes
ESC/P2
IBM 2391 Plus Emulation
Rev. A
1-
Page 18

DLQ-3000+
1.3.3 Paper Feed Specification
1.3.3.1 Friction Feed (Cut sheet)
Paper Path
• Single sheet, envelopes Front and rear insertion (Manual/CSF insertion)
• Multi-part form Rear entry (Manual/CSF insertion)
Notes:
1. Set the release lever to “FRICTION”.
2. Do not load continuous paper (including folding paper).
3. Set the longer side of the envelope horizontally.
4. When setting No.6 envelope, align the left sheet edge guide with the marked position.
1.3.3.2 Tractor Feed (Continuous paper)
Paper Path
• Rear entry push tractor feed with paper parking function
Notes:
1. Set the release lever to “TRACTOR”.
2. Do not perform reverse feed for more than 1/6 inch.
3. Set the left and right sheet edge guides to the right and left ends of the front paper
guide, respectively.
1.3.3.3 Paper Feed Speed and Accuracy
Minimum feed length 1/360 inch (1/6, 1/8 or programmable with the
increment of 1/360 inch)
Feed speed
• 1/6 inch line feed 42 ms
• Continuous feed 6.0 IPS (inch/second)
0.152 MPS (m/second)
1-10
Rev. A
Page 19
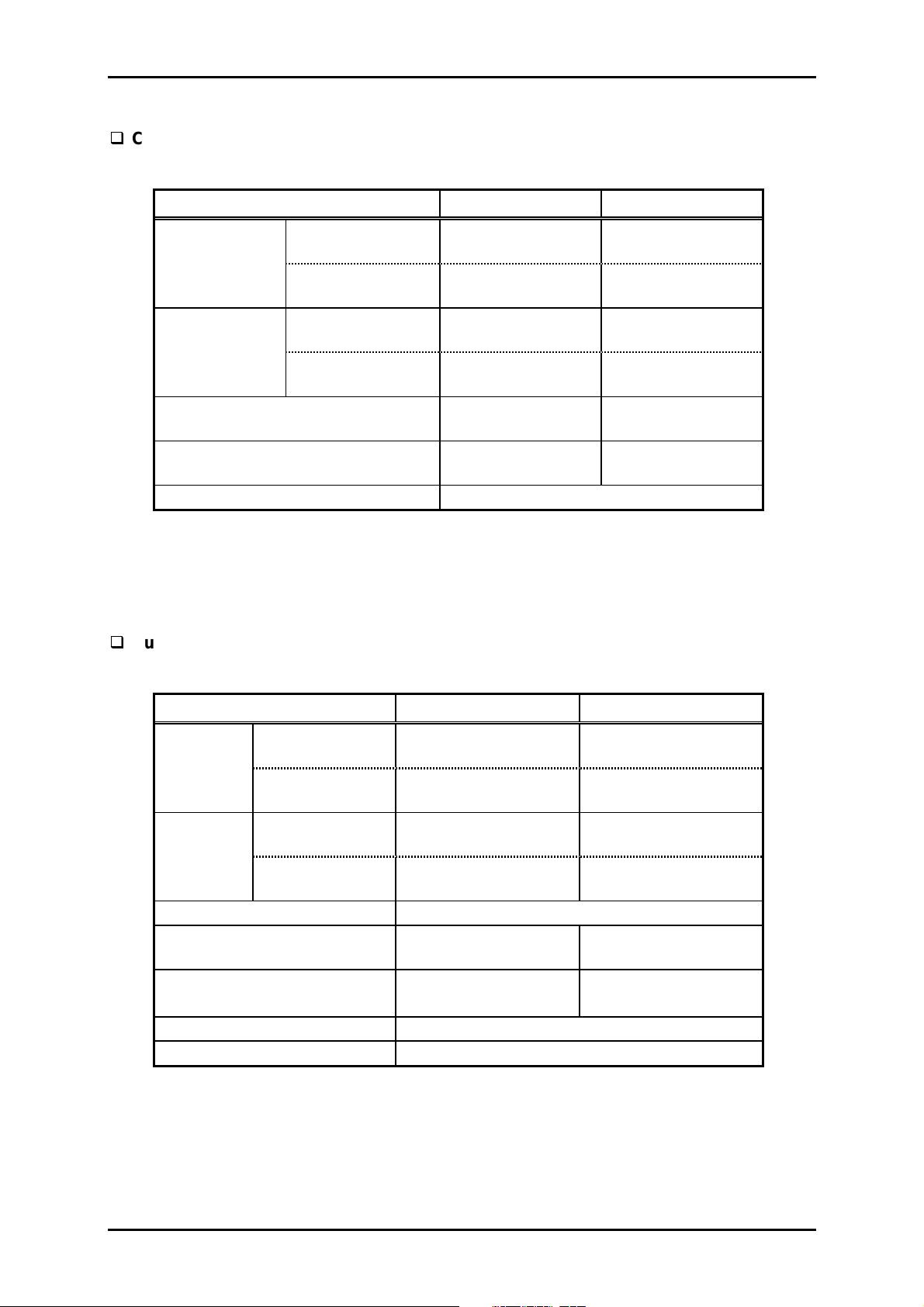
1.3.4 Paper Specification
Cut sheet (Single sheet)
Table 1-6. Cut sheet Specification : Single Sheet
Product Description
Minimum Maximum
Width
Length
Thickness
Weight
Manual insertion
CSF
Manual insertion
CSF
3.6 inch
92 mm
3.9 inch
100 mm
3.5 inch
92 mm
3.6 inch
92 mm
0.0025 inch
0.065 mm
52 g/m²
14 lb.
16.5 inch
420 mm
16.5 inch
420 mm
16.5 inch
420 mm
14.3 inch
364 mm
0.0047 inch
0.12 mm
105 g/m²
27 lb.
Quality Plain paper, Reclaimed paper
Notes:
1. Reclaimed paper can be used under condition of room temperatures only.
2. Ensure that the paper is not curled, folded or crumpled.
Cut sheet (Multi-part form)
Table 1-7. Cut sheet Specification : Multi-part Form
Minimum Maximum
Width
Length
Manual insertion
CSF
Manual insertion
CSF
3.6 inch
92 mm
3.9 inch
100 mm
3.5 inch
92 mm
3.6 inch
92 mm
16.5 inch
420 mm
16.5 inch
420 mm
16.5 inch
420 mm *
14.3 inch
364 mm *
1
1
Copies 1 original and 6 copies
Thickness
Weight
(I sheet of a multi-part form)
0.0047 inch
0.12 mm
40 g/m²
11 lb.
0.021 inch
0.53 mm
58 g/m²
15 lb.
Quality Carbon-less multi-part paper
Jointing Line glue (top, right and left side)
Notes:
1. Ensure that the paper is not curled, folded or crumpled.
2. The maximum length for the carbon-less multi-part paper is 297 mm with the left or
right side of the form line-glued.
3. CSF does not feed paper which is glued by the right or left side.
Rev. A
1-11
Page 20
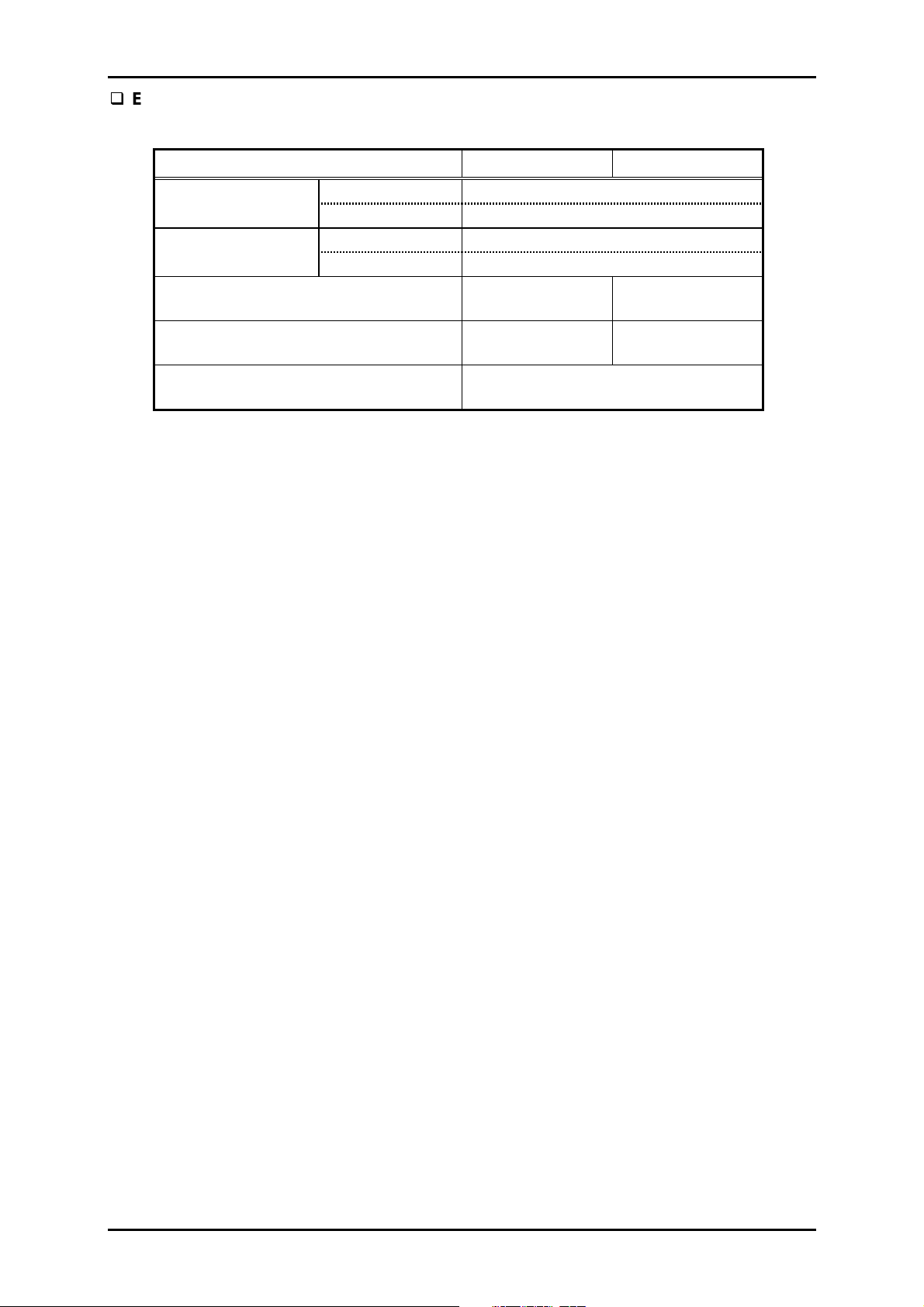
DLQ-3000+
Envelopes
Table 1-8. Envelope Specification
Minimum Maximum
Envelopes (No.6) Width 6.5 inch/165 mm
Length 3.6 inch/92 mm
Envelopes (No.10) Width 9.5 inch/241 mm
Length 4.1 inch/105 mm
Thickness
Weight
Quality
0.0063 inch
0.16 mm
45 g/m²
12 lb. /m²
Bond paper, Plain paper
Airmail paper without glue at a flap
0.021 inch
0.52 mm
91 g/m²
24 lb./m²
Notes:
1. Fold the flap of the envelope inside before loading at CSF or manual insertion.
2. Difference in thickness within the same printable area must be 0.0098 inch or less.
1-12
Rev. A
Page 21
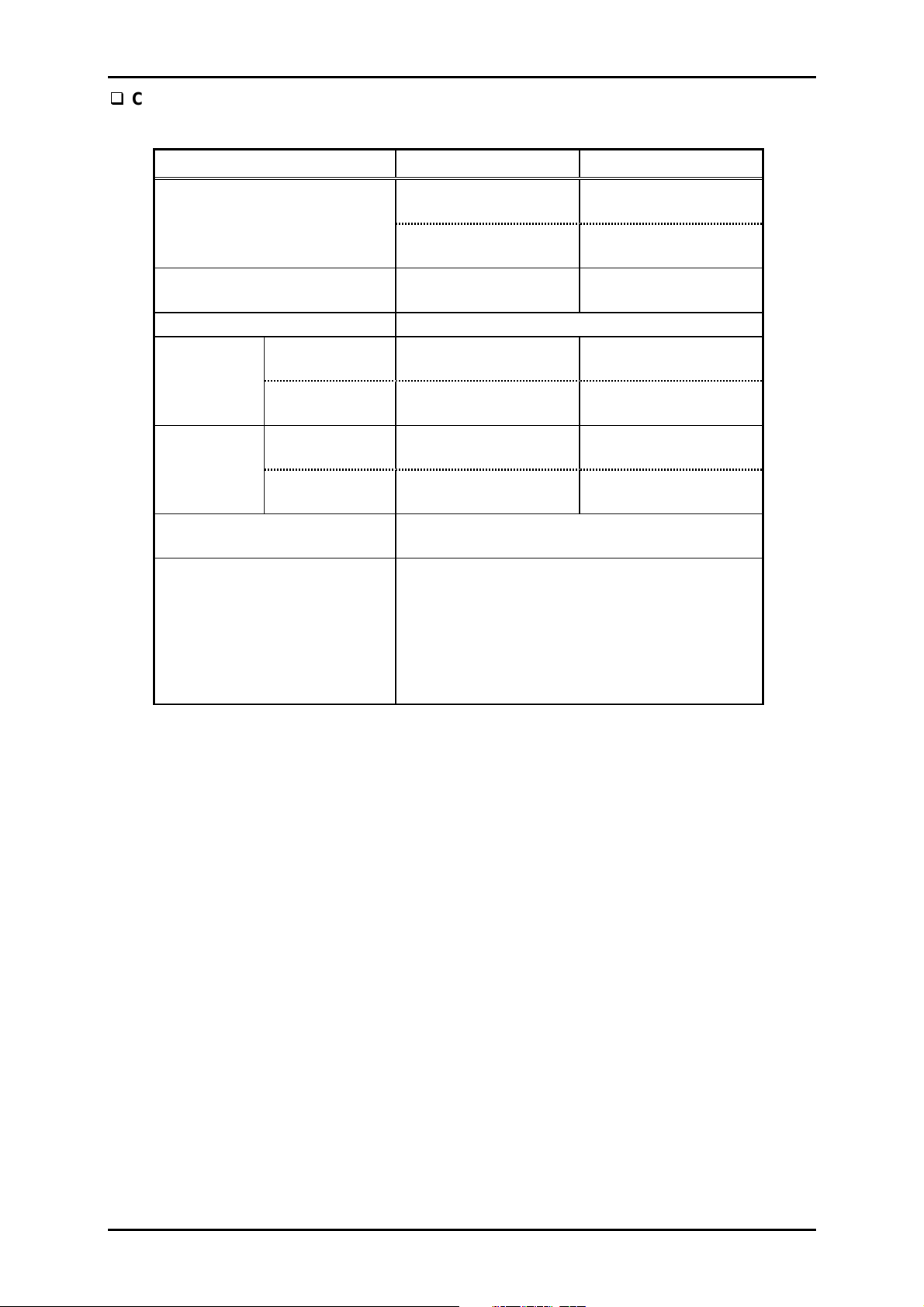
3
Continuous paper
Table 1-9. Continuous Paper Specification : Single Paper/Multi-Part Form
Product Description
Minimum Maximum
Length (1 page)
Total
Thickness
Weight
Quality
Jointing *
Width 4.0 inch
101.6 mm
4.0 inch
101.6 mm
3.5 inch
92 mm
Copies 1 original and 6 copies
Single sheet
1 sheet of
multi-part form
Cut sheet
1 sheet of
multi-part form
0.0025 inch
0.065 mm
0.0047 inch
0.12 mm
52.3 g/m²
14 lb.
40 g/m²
11 lb.
Plain paper, Reclaimed paper
Carbon-less multi-part form
Must be one of the followings:
1
- Point glue on the both sides
- Tape staple on the both sides
- Point glue on one side and tape staple on
the other side
Note: Do not use the paper which is glued by
the side or stapled.
16 inch
406.4 mm
22.0 inch
558.8 mm
16.4 inch
420 mm *
0.047 inch
0.12 mm
0.021 inch
0.53 mm
105 g/m²
27 lb.
58 g/m²
15 lb.
1
Rev. A
1-1
Page 22
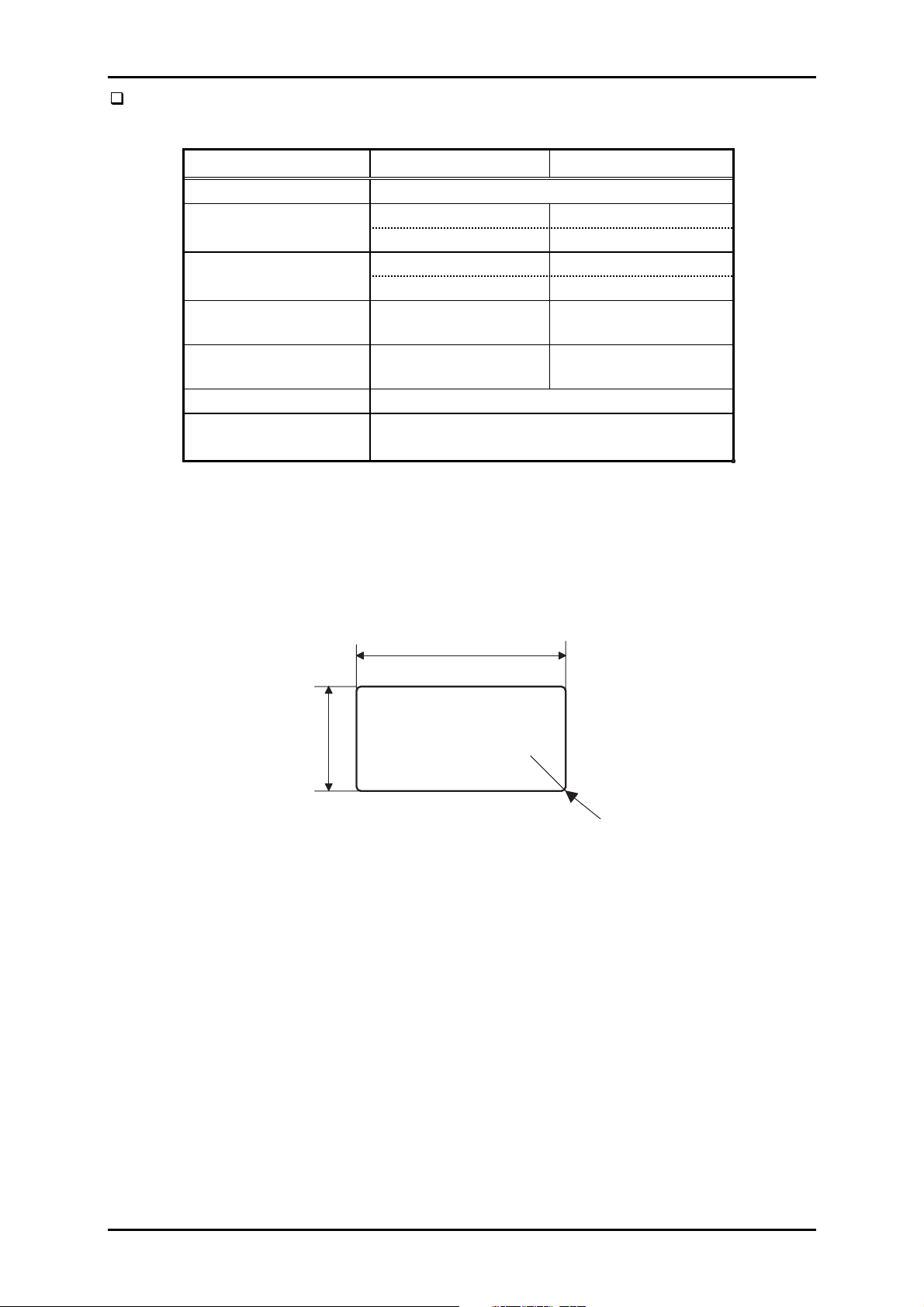
DLQ-3000+
Labels
Table 1-10. Label Specification
Minimum Maximum
Label size See Figure 1-4.
Base sheet width 4.0 inch 16.0 inch
101.6 mm 406.4 mm
Base sheet length 4.0 inch 22.0 inch
(1 page) 101.6 mm 559 mm
Base sheet thickness
Total thickness
0.0028 inch
0.07 mm
0.0063 inch
0.16 mm
0.0035 inch
0.09 mm
0.0075 inch
0.19 mm
Label weight 64 g/m²/17 lb.
Quality Plain paper or equivalent
The base sheet must be continuous paper.
Notes:
1. Use labels in the condition of the room temperature only.
2. Labels backed with the continuous base sheet can be used only.
3. When the label sheet whose base sheet is exposed around the labels, adjust the
platen gap manually to the portion covered with the label using PG adjust lever.
15/16 inch
(23.8mm or more)
2-1/2 inch
(63.5mm or more)
R 0.1inch (R 2.5m m or m ore)
Figure 1-4. Label Size
1-14
Rev. A
Page 23
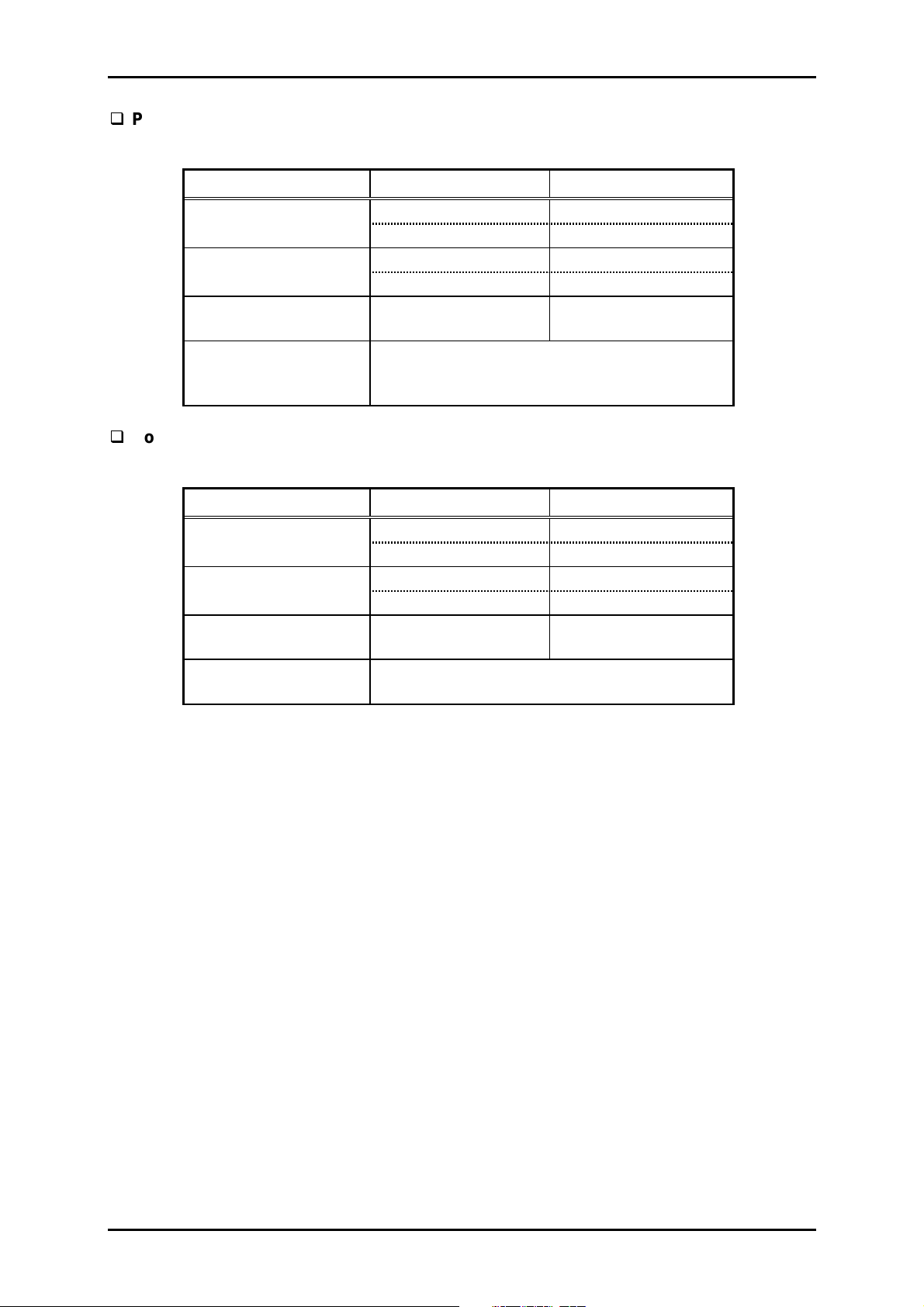
5
Pre-print paper
Table 1-11. Pre-Print Paper Specification
Width 4.0 inch 16.0 inch
Length 4.0 inch 22.0 inch
(1 page) 101.6 mm 559 mm
Total thickness
Quality
Continuous forms with labels
Table 1-12. Continuous Forms with Labels Specification
Product Description
Minimum Maximum
101.6 mm 406.4 mm
0.0025 inch
0.065 mm
The paper printed with the color which has
the reflective rate of less than 60 %, such as
black.
Minimum Maximum
0.047 inch
0.12 mm
Base sheet width 4.0 inch 16.0 inch
101.6 mm 406.4 mm
Base sheet length 4.0 inch 22.0 inch
(1 page) 101.6 mm 559 mm
Total thickness
Quality
–
–
Plain paper or equivalent
Airmail paper without glue at a flap
0.021 inch
0.53 mm
Note:
When using the continuous forms with labels, the label position must be registered
properly. It can be performed through the utility “Label Position Registering Utility”.
Rev. A
1-1
Page 24
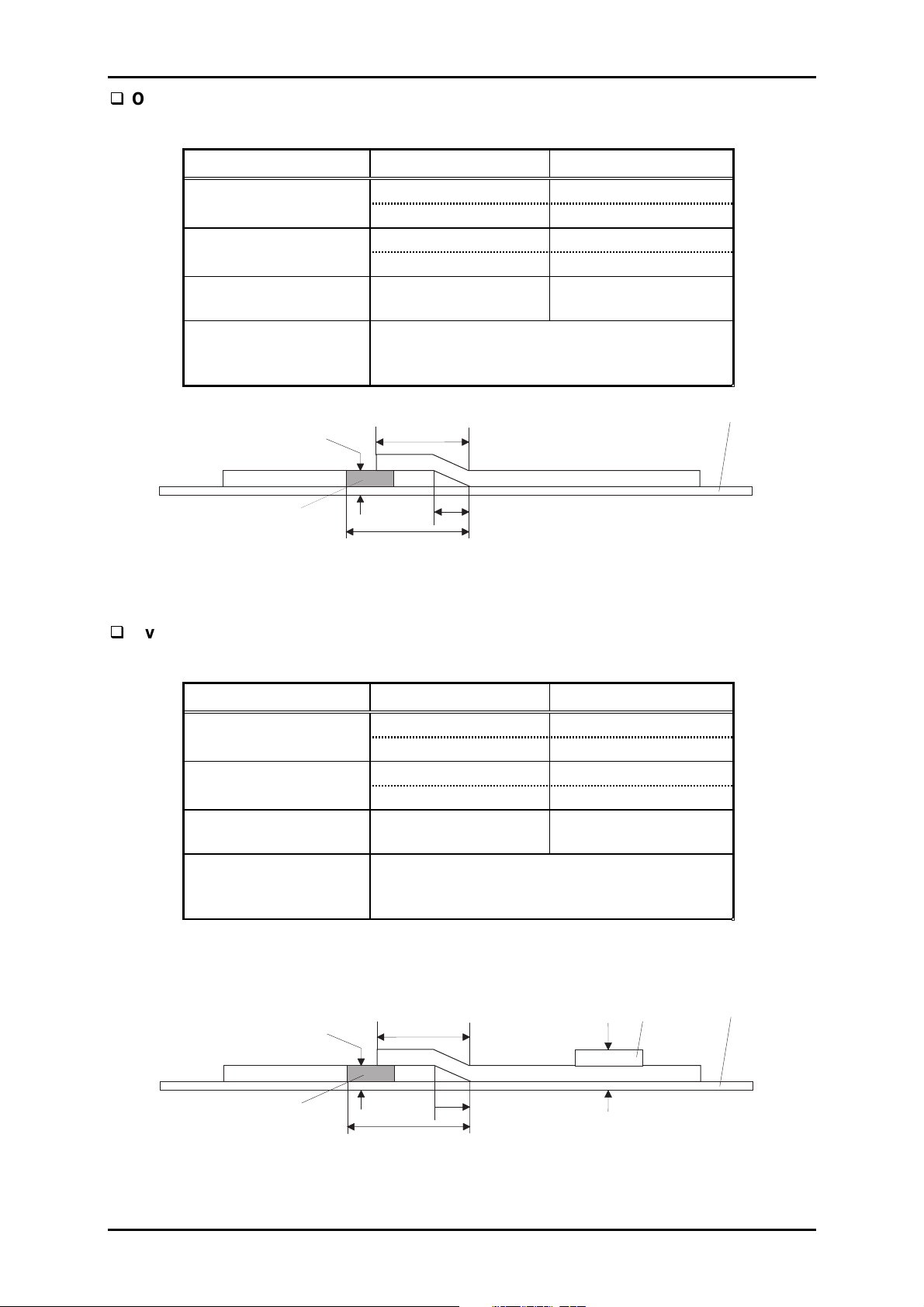
DLQ-3000+
Overlapping multi-part forms
Table 1-13. Overlapping Multi-Part Form Specification
Base sheet width 4.0 inch 16.0 inch
Base sheet length 4.0 inch 22.0 inch
(1 page) 101.6 mm 559 mm
Total thickness
Jointing
Minimum Maximum
101.6 mm 406.4 mm
–
–
0.026 inch
0.65 mm
Multi-part forms :Point glue
Joint for the base sheet and multi-part form
:Point glue
Total Thickness
Glue
Maximum 13.3 mm
Maximum 3.3 mm
Maximum 17 mm
Base Sheet
Figure 1-5. Overlapping multi-part Form Specification
Overlapping multi-part forms with labels
Table 1-14. Overlapping Multi-Part Form with Labels Specification
Minimum Maximum
Base sheet width 4.0 inch 16.0 inch
101.6 mm 406.4 mm
Base sheet length 4.0 inch 22.0 inch
(1 page) 101.6 mm 559 mm
Total thickness
–
–
0.026 inch
0.65 mm
Multi-part forms :Point glue
Jointing
Joint for the base sheet and multi-part form
:Point glue
Note: When using overlapping multi-part forms with labels, the label position must be
registered properly. It can be performed through the utility “Label Position
Registering Utility”.
1-16
Total Thickness
Glue
Maximum 13.3 mm
Maximum 17 mm
Label
Maximum 3.3 mm
Maximum 0.53 mm
Base Sheet
Figure 1-6. Overlapping multi-part Form with Labels Specification
Rev. A
Page 25
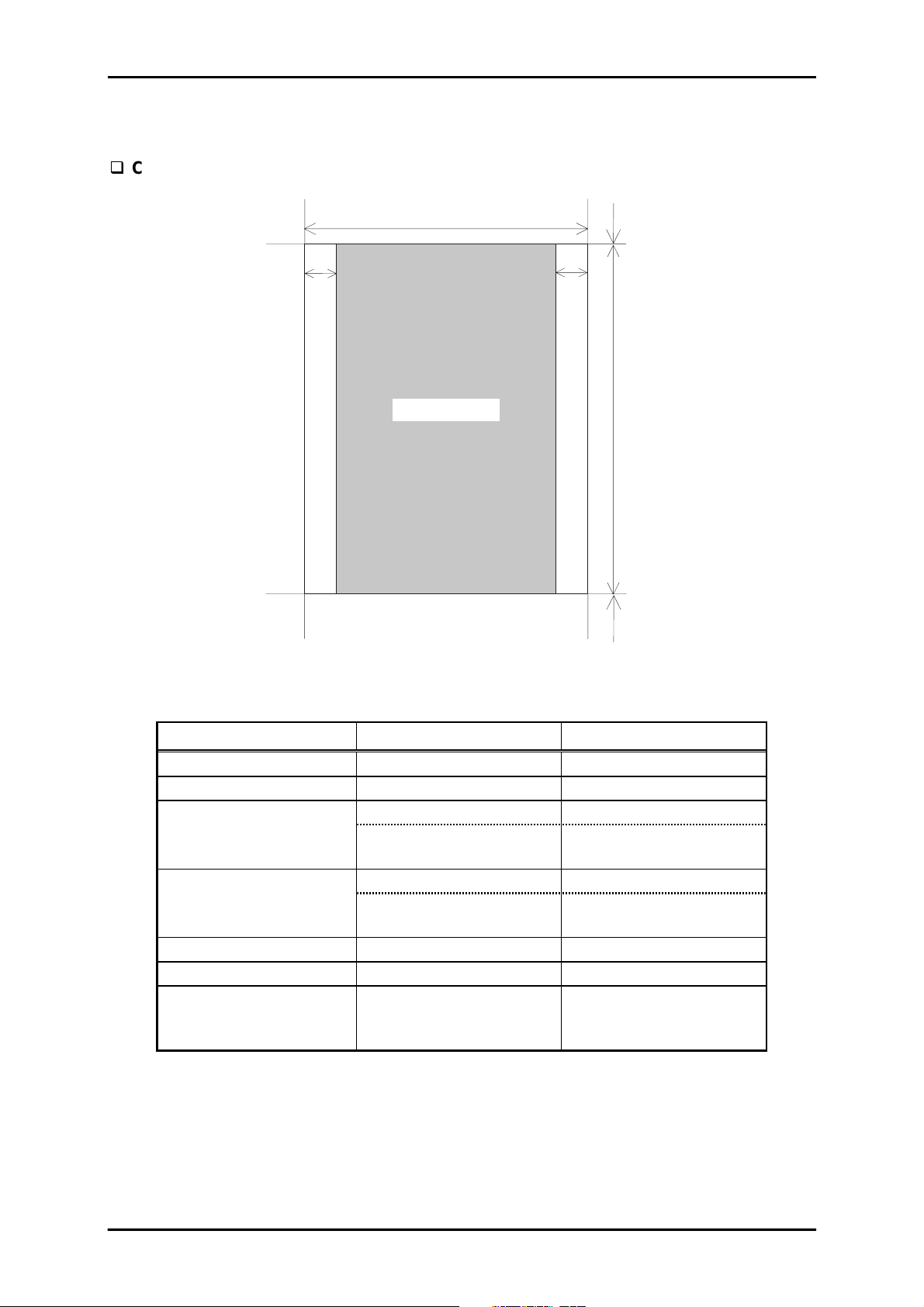
7
1.3.5 Printable Area
This section describes printable area for various types of paper.
Cut sheet
PW
Product Description
TM
LM
Printable A rea
RM
Figure 1-7. Printable Area for Cut Sheet
Table 1-15. Printing Area for Cut sheet
PL
BM
Single cut sheet Multi-part cut sheet
Paper width (PW) Refer to Section 1.3.4. Refer to Section 1.3.4.
Paper length (PL) Refer to Section 1.3.4. Refer to Section 1.3.4.
Left margin (LM) 3 mm (0.118”) or more 3 mm (0.118”) or more
[A3 landscape]
31 mm (1.22”) or more
[A3 landscape]
31 mm (1.22”) or more
Right margin (RM) 3 mm (0.118”) or more 3 mm (0.118”) or more
[A3 landscape]
20 mm (0.78”) or more
[A3 landscape]
20 mm (0.78”) or more
Top margin (TM) 0 mm (0”) or more 0 mm (0”) or more
Bottom margin (BM) 0 mm (0”) or more 0 mm (0”) or more
Width of printing area
Maximum 346 mm
(13.62”)
Maximum 346 mm
(13.62”)
(WPA)
Rev. A
1-1
Page 26
DLQ-3000+
Continuous paper
PW
LM
Perforation
Printable A rea
Perforation
RM
TM
PL
BM
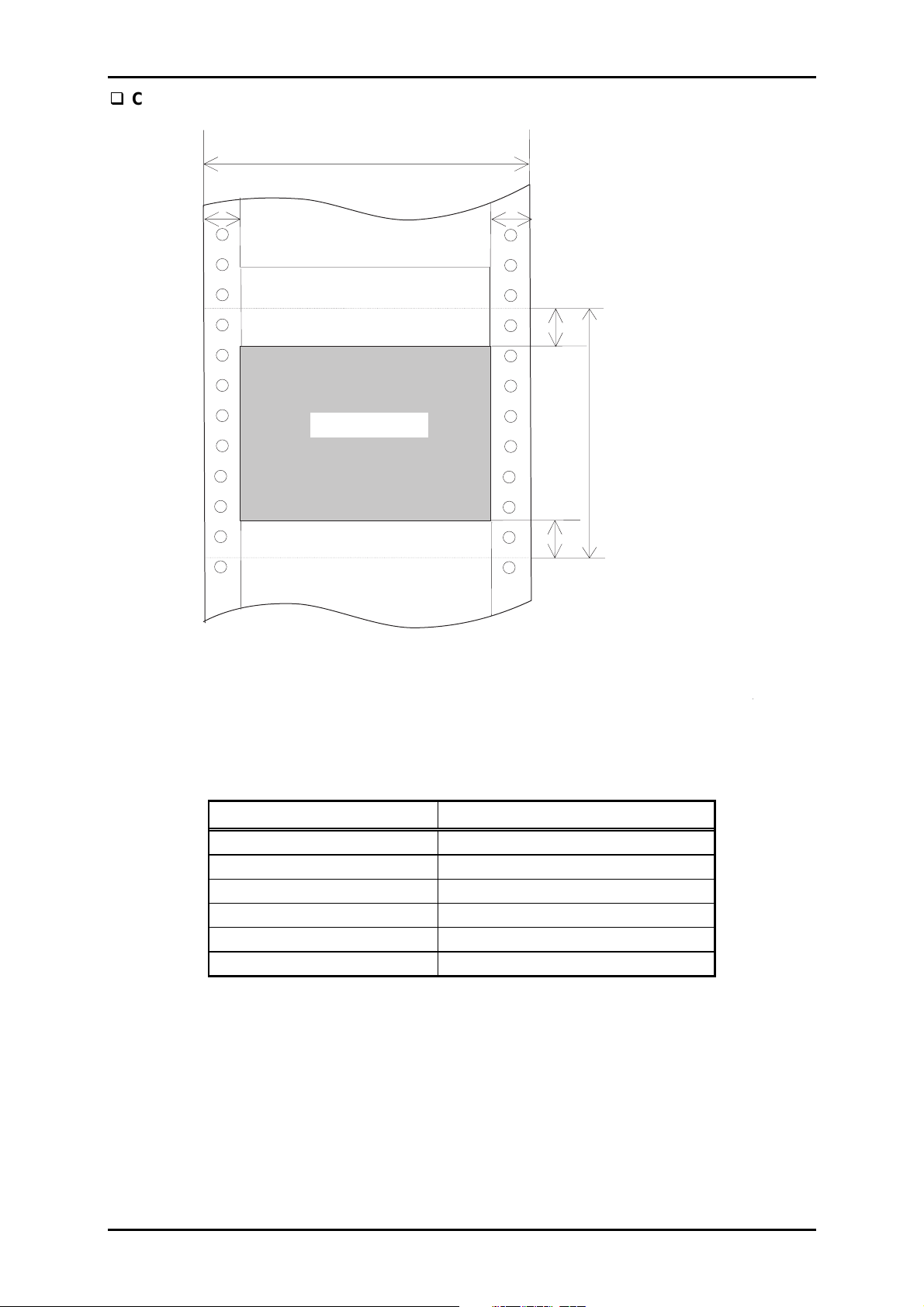
Figure 1-8. Printable Area for Continuous Paper
Continuous paper
Paper width (PW) Refer to Section 1.3.4.
Paper length (PL) Refer to Section 1.3.4.
Left margin (PM) 9 mm (0.354”) or more
Right margin (LM) 9 mm (0.354”) or more
Top margin (TM) 4.2 mm (0.165”) or more
Bottom margin (BM) 4.2 mm (0.165”) or more
Notes:
1. In the top 75 mm are, the paper feeding pitch may be irregular.
2. Forms-override printing is available for 2 lines after the paper end is detected.(Paper
feeding pitch is not guaranteed.) The end of the printable area is 4.2 m or more apart
from the bottom edge of the paper.
3. When the page width is 16 inches, note the followings:
• LM is 18 mm or more with the left tractor set at the farthest side toward the 136th
column.
• RM is 18 mm or more with the right tractor set at the farthest side toward the 1st
column.
1-18
Rev. A
Page 27
9
Product Description
Labels
LM
TM
TO L
LO L
Printable Area
BOL
ROL
P r in tin g p ro h ib ite d
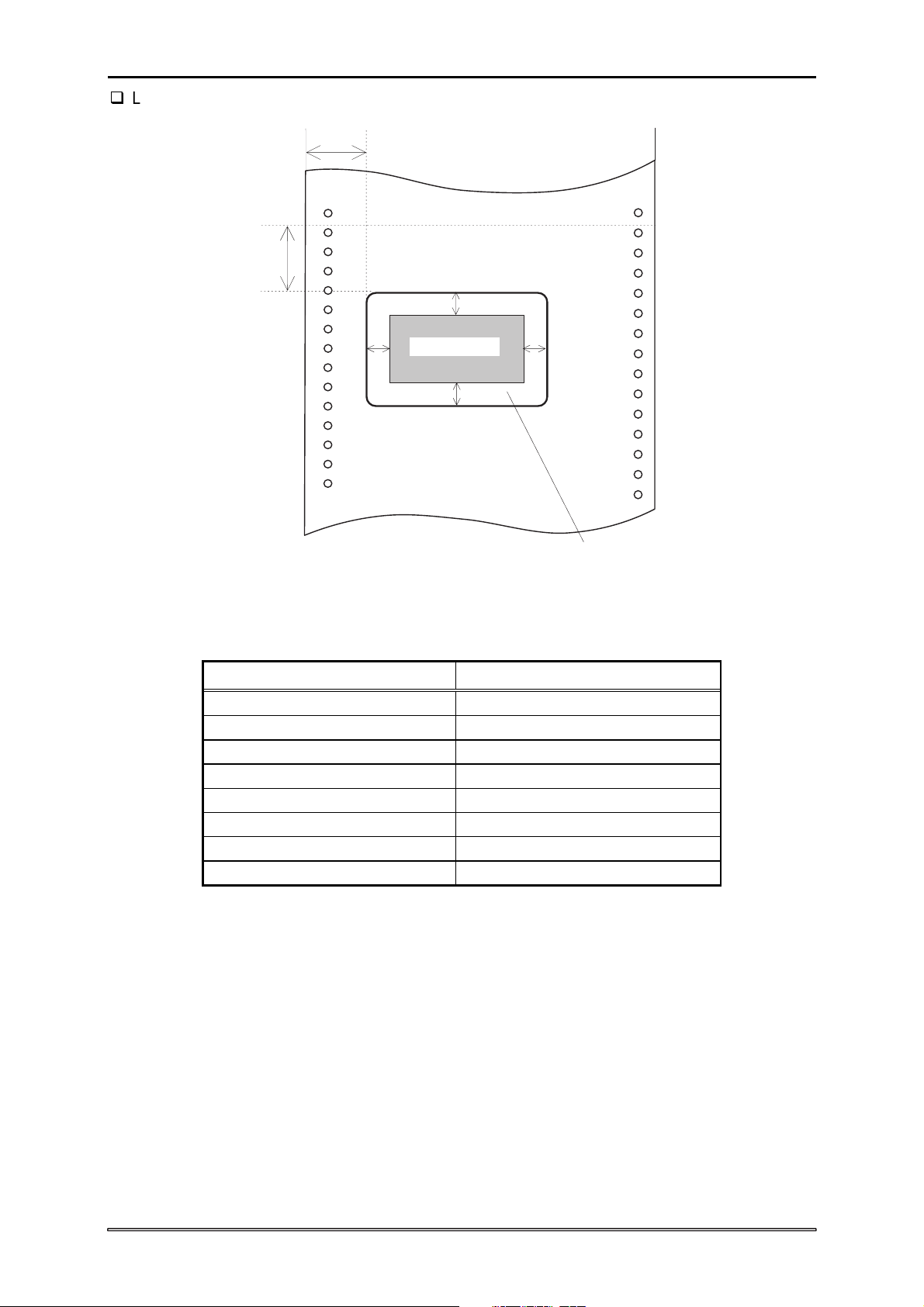
Figure 1-9. Printable Area for Labels
Table 1-16. Printable Area for Labels
Continuous paper
Paper width (PW) Refer to Section 1.3.4.
Paper length (PL) Refer to Section 1.3.4.
Left margin (LM) 12 mm (0.472”) or more
Top margin (TM) 1.2 mm (0.0472) or more
Left margin on label (LOL) 3 mm (0.118”) or more
Right margin on label (ROL) 3 mm (0.118”) or more
Top margin on label (TOL) 3 mm (0.118”) or more
Bottom margin on label (BOL) 3 mm (0.118”) or more
Notes:
1. Do not feed paper backward.
2. Use only the specified paper path for continuous paper.
3. The paper feeding pitch in the top 75 mm (2.9”) may be irregular.
Rev. A
1-1
Page 28
DLQ-3000+
Envelops
Print Direction
LM
(M anual insertion from the rear/C S F)
Printable Area
Print Direction
(M anual insertion form the front)
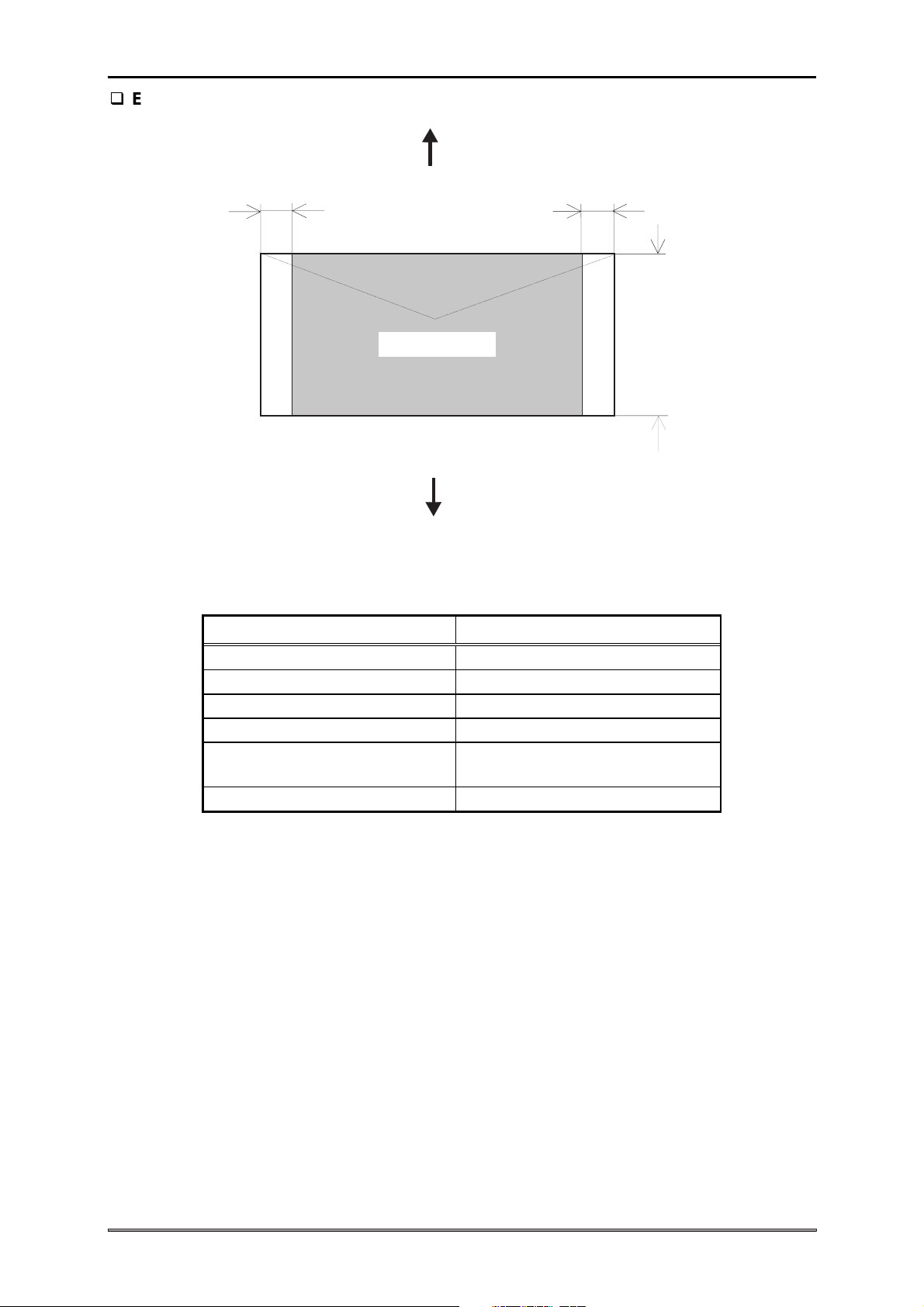
Figure 1-10. Printable Area for Envelopes
Table 1-17. Printable Area for Envelops
RM
TM
BM
Continuous paper
Paper width (PW) Refer to Section 1.3.4.
Paper length (PL) Refer to Section 1.3.4.
Left margin (LM) 3 mm(0.118”) or more
Right margin (RM) 3 mm(0.118”) or more
Top margin (TM)
0 mm (0”) or more *
Bottom margin (BM) 0 mm (0”) or more
Note 1: At CSF insertion:
4.2 mm (0.16”) or more
1
1-20
Rev. A
Page 29
Overlapping multi-part forms
Product Description
PW
TM
PL
LM B
LM
Printable A rea
: Printable A rea
RMB
RM
Perforation
BM
TM
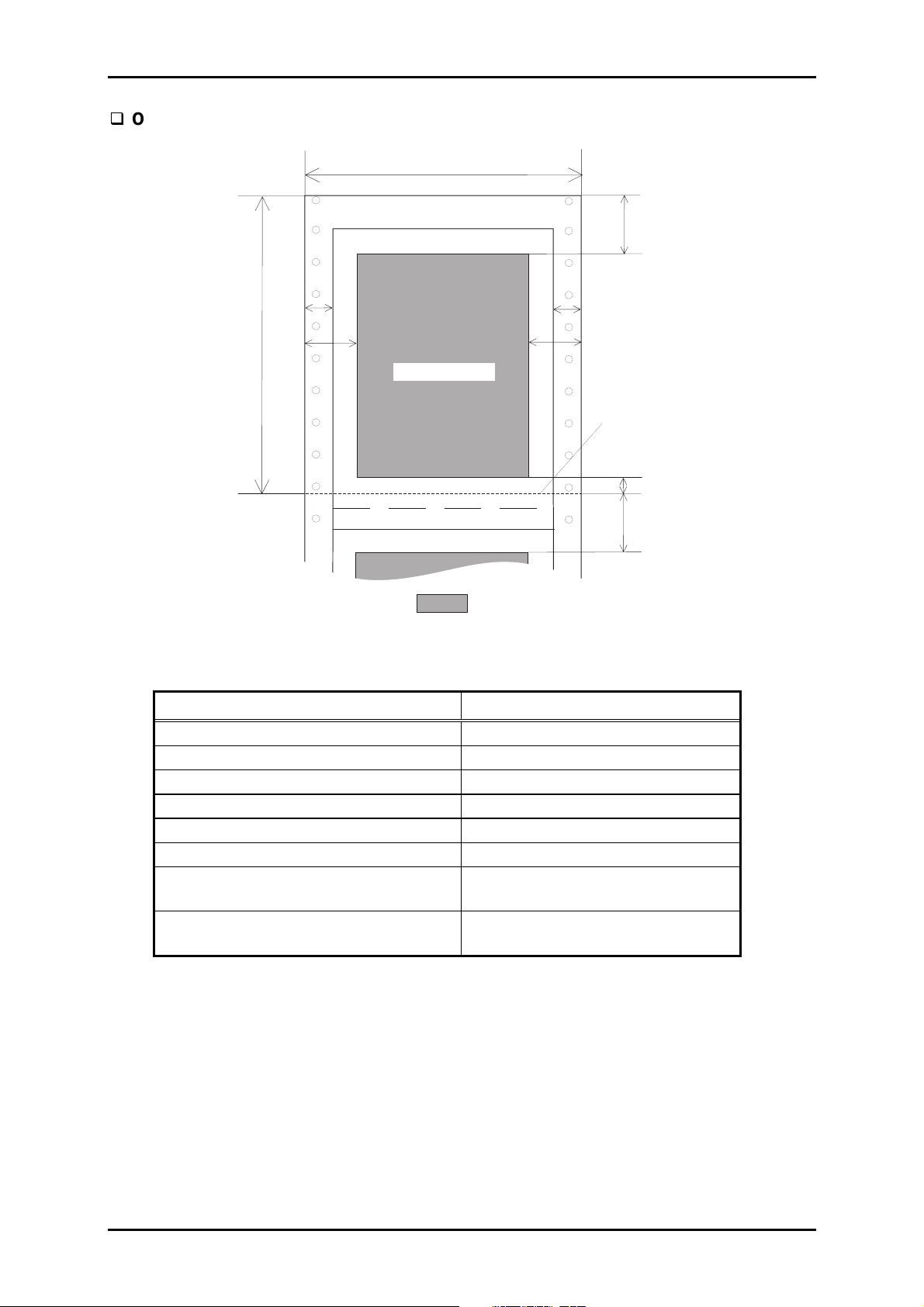
Figure 1-11. Printing Area for Overlapping Multi-part Forms
Table 1-18. Printing Area for Overlapping Multi-part Forms
Continuous paper
Paper width (PW) Refer to Section 1.3.4.
Paper length (PL) Refer to Section 1.3.4.
Left margin (LM) 19 mm (0.748”) or more
Right margin (RM) 19 mm (0.748”) or more
Top margin (TM) 21.2 mm (0.835”) or more
Bottom margin (BM) 4.2 mm (0.165”) or more
Left margin from the multi-part form to
13 mm (0.512”) ± 3 mm (0.118”)
the base sheet (LMB)
Right margin from the multi-part form
13 mm (0.512”) ± 3 mm (0.118”)
to the base sheet (RMB)
Notes:
1. Do not feed paper backward.
2. Use only the specified paper path for continuous paper.
3. The paper feeding pitch in the top 75 mm (2.9”) may be irregular.
4. Forms-override printing is available for 2 lines after the paper end is detected. The end of
the printable area is 4.2 mm or more apart from the bottom edge of the paper.
Rev. A
1-21
Page 30
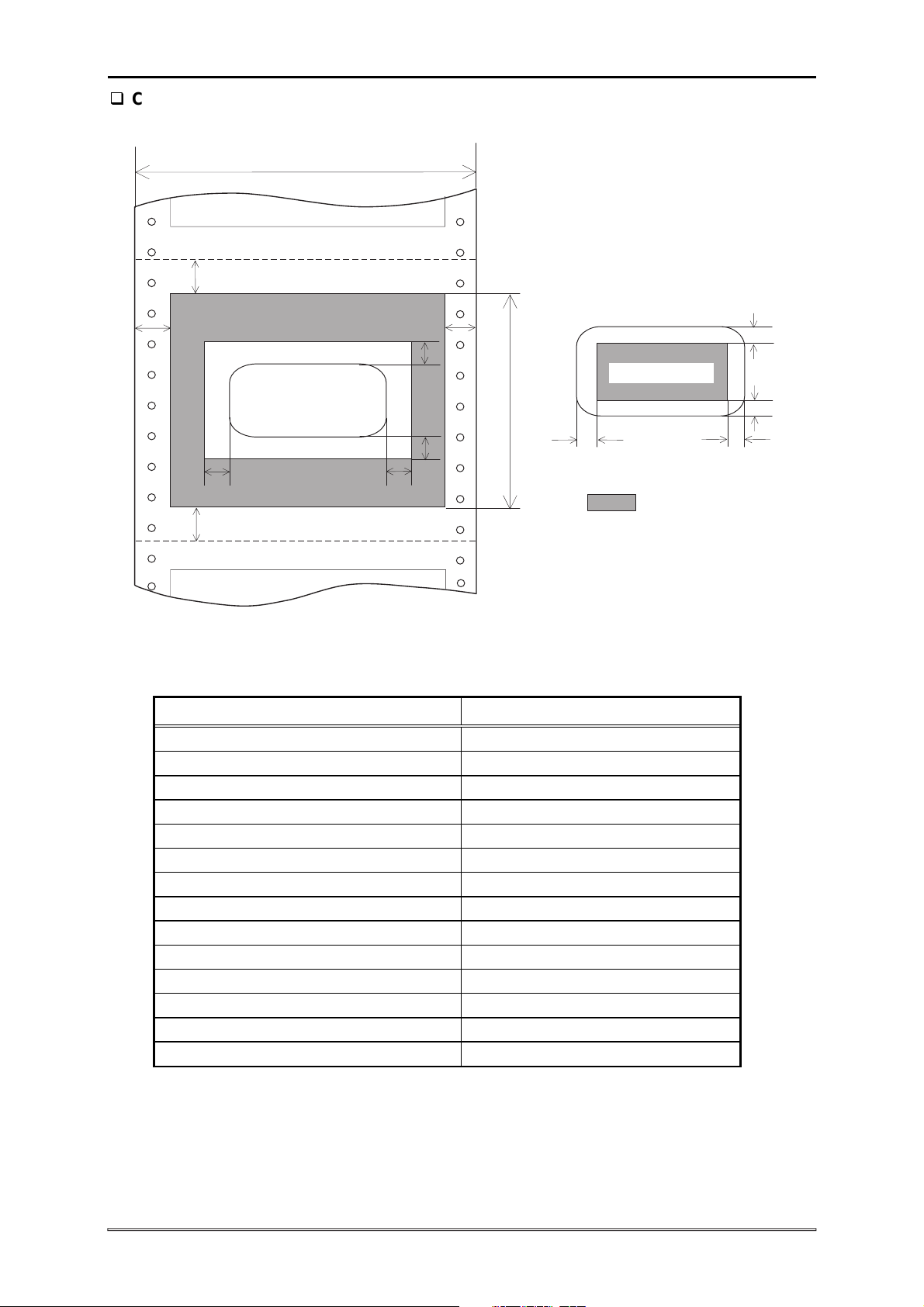
DLQ-3000+
Continuous forms with labels
PW
TM
LM
N on-printable Area
Label
LFL
BM
RFL
TFL
BFL
RM
Printable Area
PL
LO L
: P rintable Area
Figure 1-12. Printable Area for Continuous Forms with Labels
Table 1-19. Printable Area for Continuous Forms with Labels
Continuous paper
Paper width (PW) Refer to Section 1.3.4.
Paper length (PL) Refer to Section 1.3.4.
Left margin (LM) 9 mm (0.354”) or more
Right margin (RM) 9 mm (0.354”) or more
Top margin (TM) 4.2 mm (0.165”) or more
Bottom margin (BM) 4.2 mm (0.165”) or more
Left margin for label (LFL) 45 mm (1.77) or more
Right margin from label (RFL) 45 mm (1.77) or more
Top margin from label (TFL) 25 mm(0.984”) or more
Bottom margin from label (BFL) 25 mm(0.984”) or more
Left margin on label (LOL) 3 mm (0.118”) or more
Right margin on label (ROL) 3 mm (0.118”) or more
Top margin on label (TOL) 3 mm (0.118”) or more
Bottom margin on label (BOL) 3 mm (0.118”) or more
Notes:
1. Do not feed paper backward.
2. Use only the specified paper path for the continuous paper.
3. The paper feeding pitch in the top 75 mm (2.9”) may be irregular.
4. Forms-override printing is available for 20 lines after the paper end is detected.
(Paper feeding pitch is not guaranteed.) The end of the printable are is 4.2 mm or
more apart from the bottom edge of the paper.
TO L
BOL
ROL
1-22
Rev. A
Page 31

3
Overlapping multi-part forms with labels
PW
Product Description
TM
PL
LM B
LM
Printable A rea
LFL
TFL
Label
BFL
RFL
RMB
RM
Perforation
LO L
BM
TM
Figure 1-13. Printable Area for Overlapping Multi-Part Forms with Labels
Table 1-20. Printable Area for Overlapping Multi-Part Forms
Continuous paper
Paper width (PW) Refer to Section 1.3.4.
Paper length (PL) Refer to Section 1.3.4.
Left margin (LM) 19 mm (0.748”) or more
Right margin (RM) 19 mm (0.748”) or more
Left margin from the multi-part forms
13 mm (0.552”) ± 3 mm (0.118”)
to the base sheet (LMB)
Right margin from the multi-part forms
13 mm (0.552”) ± 3 mm (0.118”)
to the base sheet (RMB)
Top margin (TM) 21.2 mm (0.835”) or more
Bottom margin (BM) 4.2 mm (0.165”) or more
Non-printable area (NA) 25.4 mm (1.0”) or more
Left margin from label (LFL) 45 mm (1.77”) or more
Right margin from label (RFL) 45 mm (1.77”) or more
Top margin from label (TFL) 25 mm(0.984”) or more
Bottom margin from label (BFL) 25 mm(0.984”) or more
Left margin on label (LOL) 3 mm (0.118”) or more
Right margin on label (ROL) 3 mm (0.118”) or more
Top margin on label (TOL) 3 mm (0.118”) or more
Bottom margin on label (BOL) 3 mm (0.118”) or more
Notes:
1. Do not feed paper backward.
2. The paper feeding pitch in the top 75 mm (2.9”) may be irregular.
ROL
TO L
Printable A rea
BOL
Label
: P rintable A rea
Rev. A
1-2
Page 32

DLQ-3000+
3. Forms-override printing is available for 20 lines after the paper end is detected.
(Paper feeding pitch is not guaranteed.) The end of the printable are is 4.2 mm or
more apart from the bottom edge of the paper
1.3.6 Paper Thickness Detection
This printer is equipped with the automatic paper thickness adjust function. When the paper
thickness lever is set to “Auto position”, the printer automatically measures thickness of
each paper loaded to set the proper PG (platen Gap) the detected thickness. PG is also
adjusted manually. See Table 1-21 which shows the adjust lever position and
corresponding paper thickness and platen gap.
Table 1-21. PG Adjust Lever
Adjust lever Paper thickness (inch) Paper thickness (mm) PG
position Maximum Minimum Maximum Minimum Inch mm
-1 0.0024 0.0043 0.06 0.11 0.0138 0.35
0 0.0024 0.0043 0.06 0.11 0.0154 0.39
1 0.0043 0.0059 0.11 0.15 0.0169 0.43
2 0.0059 0.0075 0.15 0.19 0.0181 0.46
3 0.0075 0.0098 0.19 0.25 0.0197 0.50
4 0.0098 0.0122 0.25 0.30 0.0217 0.55
5 0.0122 0.0146 0.30 0.36 0.0240 0.61
6 0.0146 0.0165 0.36 0.42 0.0264 0.67
7 0.0165 0.0185 0.42 0.46 0.0280 0.71
8 0.0185 0.0201 0.46 0.49 0.0291 0.74
9 0.0201 0.0217 0.49 0.53 0.0307 0.78
Notes: Switching to “Dark” in the copy mode is effective under the following conditions:
In the “Auto” mode: Paper thickness is 0.2 mm or more.
Manual adjustment: The lever is set to one of the positions in the range from
3 to 9.
1-24
Rev. A
Page 33

Product Description
5
1.3.7 Ribbon Cartridge
1.3.7.1 Monochrome ribbon cartridge
Color Black
Ribbon fabric Nylon 66
Ribbon dimension 25.5 mm (W) X 17 mm (L) X 1.5 mm (D)
ribbon thickness 0.128 mm ± 0.007 mm
Cartridge dimension 153 mm/6.0” (W) X 33 mm/1.3” (H) X 105 mm/4.1” (D)
Ribbon life * 6 million characters
Ribbon replacement Whole cartridge
Item No. S015066
∗ At 10 cpi printing in the LQ mode. (48 dots per character)
1.3.7.2 Color ribbon cartridge
Color Black Magenta, Cyan, Yellow
Ribbon fabric Nylon 66
Ribbon dimension 25.5 mm (W) X 17 mm (L) X 1.5 mm (D)
ribbon thickness 0.128 mm ± 0.007 mm
Cartridge dimension 153 mm/6.0” (W) X 33 mm/1.3” (H) X 105 mm/4.1” (D)
Ribbon life * Black: 1.5 million characters
Magenta 1.1 million characters
Cyan 1.1 million characters
Yellow 0.8 million characters
Ribbon replacement Whole cartridge
Item No. S015067
∗ At 10 cpi printing in the LQ mode. (48 dots per character)
Rev. A
1-2
Page 34

DLQ-3000+
1.3.8 Input Data Buffer
Approximately 128 K byte/1K byte
1.3.9 Electric Specifications
120 V version
Rated voltage AC 120 V
Input voltage range AC 103.5 to 132 V
Rated frequency renege 50 to 60 Hz
Input frequency range 49.5 to 60.5 Hz
Rated current 7 A (maximum)
Power consumption Approximately 60 W (ISO/IEC 10561 Letter pattern)
Insulation resistance 10 M ohms minute
Dielectric strength AC 1,000 V rms. for 1 minute or
220 - 240V version
Rated voltage AC 220 to 240 V
Input voltage range AC 198 to 264 V
Rated frequency renege 50 to 60 Hz
Input frequency range 49.5 to 60.5 Hz
Rated current 0.7 A (maximum)
Power consumption Approximately 60 W (ISO/IEC 10561 Letter pattern)
Insulation resistance 10 M ohms min.
Dielectric strength AC 1,500 Vrms. For 1 minute
Energy Star program compliant
(Between AC line and chassis, 500 VDC)
AC 1,200 V rms. for 1 second
(Between AC line and chassis)
Energy Star program compliant
(Between AC line and chassis, DC 500 V)
(Between AC line and chassis)
1.3.10 Safety Approvals
120 V version
Safety standards UL1950 with D3
EMI FCC part15 subpart B class B
220 - 240 V version
Safety standards EN 60950 (TÜV, NEMKO)
EMI EN 55022 (CISPR Pub.22) class B
1.3.11 CE Marking
220 - 240 V version
Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC EN60950
EMC Directive 89/336/EEC EN55022 class B
CSA22.2 No. 950 with D3
CSA C108.8 class B
AS/NZS 3548 class B
EN61000-3-2
EN61000-3-3
EN50082-1
IEC801-2
IEC801-3
IEC801-4
1-26
Rev. A
Page 35

Product Description
7
1.3.12 Acoustic Noise
Noise level Approximately 55 dB (A) (According to ISO 7779)
1.3.13 Reliability
Total print volume 9 million lines (excluding printhead)
Printhead life 200 million strokes/pin (Monochrome ribbon)
100 million strokes/pin (Color ribbon)
Ribbon life
• Fabric black ribbon life 6 million characters*
• Fabric color ribbon Black : 1.5 million characters*
Magenta: 1.1 million characters*
Cyan: 1.1 million characters*
Yellow: 0.8 million characters*
* 1 character is formed with 48 dots.
At 10-cpi printing (LQ mode)
1.3.14 Environmental Conditions
Table 1-22. Environmental Condition
Operating Non-operating
5 to 35 °C -30 to 65 °C
Temperature 15 to 35 °C *
15 to 25 °C *
10 to 80 % 5 to 85 %
Humidity *
3
10 to 80 % *
20 to 60 % *
Resistance to shock 0.25G, 10 to 55 Hz
(Directions: X,Y and Z)
Resistance to Vibration 1G, Within 1 ms
(Directions: X,Y and Z)
Notes:
1. When the optional film ribbon is used.
2. When the envelopes or labels are printed.
3. Without condensation
1
2
1
2
-20 to 40 °C *
5 to 85 % *
1
1
0.50G, 10 to 55 Hz
(Directions: X,Y and Z)
2G, Within 1 ms
(Directions: X,Y and Z)
Rev. A
1-2
Page 36

DLQ-3000+
1.4 Interfaces
The EPSON DLQ-3000+ is equipped with the parallel and Mac serial interfaces and a card
slot for an optional Type-B interface. This section provides information on each interface.
1.4.1 Parallel Interface
Forward Channel
Transmission mode 8 bit parallel, IEEE-1284 compatibility mode
Synchronization By /STROBE pulse
Handshaking By /BUSY and /ACKNLG signal
Signal level TTL compatible (IEEE-1284 level 1 device)
Adaptable connector 57-30360 (Amphenol) or equivalent
Table 1-23. Signal level of TTL Compatible (IEEE-1284 level 1 device)
Parameter Minimum Maximum Condition
VOH* - 5.5 V
VOL* -0.5 V IOH* - 0.32 mA VOH = 2.4 V
IOL* - 12 mA VOL = 0.4 V
CO - 50 pf
VIH - 2.0 V
VIL 0.8 V IIH - 0.32 mA VIH = 2.0 V
IIL - 12 mA VIL = 0.8 V
CI - 50 pf
∗ A LOW logic level on the Logic H signal is as follows:
2.0 V or less when the printer is powered off.
3.0 V or more when the printer is powered on.
The receiver provides an impedance equivalent to 7.5 K ohms to ground.
The BUSY signal is HIGH in the following cases:
During data entry
When the input data buffer is full.
While /INIT signal is at low level
During hardware initialization
During the signal /ERROR or PE is LOW or HIGH, respectively.
During the self-test printing mode.
During the default setting mode.
During the adjustment mode.
The /ERROR signal is LOW when one of the following errors has occurred:
Printer hardware error (fatal error)
Paper-out error
The PE signal is HIGH when the following error has occurred:
Paper-out error
1-28
Rev. A
Page 37

9
Table 1-24. Data Transmission Timing
Parameter Minimum Maximum
Product Description
tsetup 500 ns
thold 500 ns
tstb 500 ns
tready 0
tbusy
treply
tack 500 ns
tnbusy 0
tnext 0
tt-out *
tt-in *
1
2
Note:
1. Rise and fall time for output signals
2. Rise and fall time for input signal
DATA (n)
DATA
thold
500 ns
10 µs
120 ns
200 ns
DATA (n+1)
STOR BE
ts tb
tsetup
BUSY
tready
tbusy
ACKNLG
tre p ly
ta c k
tnbusy
Figure 1-14. Data Transmission Timing Chart
tnext
Rev. A
1-2
Page 38

DLQ-3000+
16,33,19-30
g
Table 1-25 shows the connector pin assignment and signals for forward channel of the
parallel interface.
Table 1-25. Connector Pin Assignments and Signals (Forward Channel)
Pin No. Signal Name
1
/STROBE
Return
GND Pin
19 I
I/O Description
The strobe pulse. Read-in of data is
performed at the falling edge of this
pulse.
The data 0 to data 7 signals
2-9
DATA 1- 8
20-27 I
represent data bits 0 to 7,
respectively. Each signal is at a HIGH
level when data is logical 1 and a
LOW level when data is logical 0.
This signal is a negative pulse
10
/ACKNLG
28 O
indicating that the printer can again
accept data.
11
12
13
14
BUSY
PE
SLCT
/AFXT
29 O
28 O
28 O
30 I Not used.
When this signal is at a HIGH level,
the printer is not ready to accept data.
When this signal is at a HIGH level,
the paper empty status is detected.
Always at a HIGH level when the
printer is powered on.
The falling edge of a negative pulse
31
/INIT
30 I
or a LOW signal on this line causes
the printer to initialize. Minimum 50 us
pulse is necessary.
32
36
18
35
/ERROR
/SLIN
Logic H
+5V
29 O
30 I Not used.
When the printer detects an error, this
signal goes LOW.
Pulled up to +5V via 3.9 K-ohm
O
resistor.
O Pulled up to +5V via 3.3 K-ohm
resistor.
15,34
Note)
17
Chassis GND
GND
NC
Chassis ground.
Si
nal ground.
Not connected.
1. */* at the beginning of a signal means active low.
2. The I/O column indicates the direction of the signal as viewed form the printer.
1-30
Rev. A
Page 39

Product Description
Reverse Channel
Transmission mode IEEE-1284 nibble mode
Adaptable connector Same as for the forward channel
Synchronization Refer to the IEEE-1284 specification
Handshaking Refer to the IEEE-1284 specification
Data transmission timing Ref e r to the IEEE-1284 specification
Signal level IEEE-1284 level 1 device
See the forward channel.
Table 1-26 shows the connector pin assignment and signals for reverse channel of the
parallel interface.
Table 1-26. Connector Pin Assignment and Signals (Reverse Channel)
Pin No. Signal Name
1 HostClk 19 I Clock signal from the host computer.
2-9 DATA 1-8 20-27 I
10 PtrClk 28 O Clock signal from the printer
11
12
13 Xflag/Data bit
14 HostBusy 30 I Busy signal from the host computer
31 /INIT 30 I Not used
32
36 1284-Active 30 I 1284 active signal.
18 Logic-H
35 +5V
17 Chassis GND
16,33,
19-30
15,34 NC
Note)
PtrBusy /
Data bit 3,7
AckDatareq /
Data Bit 2,6
1,5
/Data Avail /
Data bit 0,4
GND
Return
GND Pin
29 O
28 O
28 O
29 O
I/O Description
O
O
These signals represent parallel data
on bits 2 to 9. Each signal is High
when the data is logical 1 and LOW
when the data is logical 0.
Busy signal from the printer.
Data bit 3 or 7 in reverse channel.
Acknowledge request signal.
Data bit 2 or 6 in reverse channel.
X flag signal.
Data bit 1 or 5 in reverse channel.
Data available signal.
Data bit 0 or 4 in reverse channel.
Pulled up to +5V via 3.9 K-ohm
resistor.
Pulled up to +5V via 3.3 K-ohm
resistor.
Chassis ground for the printer.
Signal ground.
Not connected.
1. */* at the beginning of a signal means active low.
2. The I/O column indicates the direction of the signal as viewed form the printer.
Rev. A
1-31
Page 40

DLQ-3000+
Extensibility Request
The printer responds affirmatively when the extensibility request values are 00H or 04H,
as follows:
00H Request nibble mode reverse channel transfer.
04H Request device ID using nibble mode rev channel transfer
Device ID
The printer sends following device ID string upon request:
[00H] [3DH]
MFG EPSON;
CMD ESCPL2, PRPXL24, BDC;
MDL DLQ-3000+;
CLS PRINTER;
1-32
Rev. A
Page 41

Product Description
3
1.4.2 Serial Interface
Synchronization Asynchronous
Signal level EIA-232D
MARK (logical 1): -3 V to -25 V
SPACE (logical): +3 V to +25 V
Word format Start bit: 1 bit
Data bit: 8 bit
Parity bit: Odd, Even or Non
Stop bit: 1 bit
Baud rate 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600 or 19200 bps
Handshaking DTR signal and XON/XOFF
DTR = MARK, XOFF: Indicates that the printer cannot receive data.
DTR = SPACE, XON: Indicates that the printer is ready to receive data.
The DTR signal is MARK and XOFF code (DC3, 13H) is transmitted when the rest of
the input buffer becomes 256 byte. The DTR signal is SPACE and XON code (DC1,
11H) is transmitted when the rest of the input buffer becomes 256 byte.
Error handling Parity error is detected only.
(Overrun error and framing error are ignored.)
Connector 25-pin sub-miniature D-shell connector. (female)
Table 1-27. Connector Pin Assignment for Serial Interface
Pin No. Signal Name I/O Function Description
1 Chassis GND
2 TXD Out Transmits data
3 RXD In Receives data
4 RTS Out
7 Signal GND
11 REV Out Connected directly to the DTR signal.
20 DTR Out Data terminal ready
others NC
Chassis GND
Request to send. Always SPACE level
when the printer is powered on. Pulled
up to +12 V via 4.7 L ohm resistor.
Signal GND
Not used. Not connected.
Note: In and Out refers to the direction of the signal flow from the printer’s point of
view.
Rev. A
1-3
Page 42

DLQ-3000+
1.4.3 Optional Interface
The EPSON DLQ-3000+ supports an optional Type-B interface (Level 2) with the following
characteristics.
Reply message
Table 1-28. Reply Message
Reply message ESC/P2 IBM 2391 Plus
Main-type MT24p, PW136cl10cpi, PRG(W0xxxx)rev
Product name DLQ-3000+
Emulation type ESCPL2, PRPXL24, BDC
Entity type EPSONLQ2 EPSONPRPXL24
Reply for optional command
Table 1-29. Reply for Option Command
Option command No. command name Reply-A Reply-B
00h No Operation
01h Start Hard Ware Reset Accept Execute OK
02h Start Soft Ware Reset Reject
03h Send Main System Type Accept Execute OK
04h Send Name Data Reject
05h Inquire Name Data Accept Execute OK
06h Send Product Name Accept Execute OK
07h
08h Complete Buffered Data Accept Execute OK
09h Stop Procedure Reject
0Ah Return Buffered Data Reject
0Bh Send Entity Type Accept Execute OK
0Ch Send Status Accept Execute OK
0Dh Quit Procedure Reject
0Eh Inquire ASCII Message Reject
0Fh Send ASCII Message Accept Execute OK
10h - 13h (Reserved) Unknown
14h Inquire Emergency Message Accept Execute OK
15h Send Emergency Reply Accept Execute OK
16h - 1Fh (Reserved) Unknown
Send Soft Ware Emulation
Type
Accept
Execute OK
1-34
Rev. A
Page 43

Product Description
5
Supported Main Command and Sending Timing
Table 1-30. Supported Main Command and Sending Timing
Main Command Command name Sending Timing
01h Start Software Reset
02h Send option type
04h Send Name Data
07h
0Eh Inquire ASCII Message
14h Inquire Emergency Reply
15h Send Emergency Message
Emergency Command
Inquire Software Emulation
Name
/INIT signal on the standard parallel I/F
Type-B I/F option command : 01h
Panel Reset
Cold Start
Deciding the level of type-B I/F after
power on.
Type-B I/F option command : 05h
Changing software Emulation Type
Writing to DBIN register
Reply for Emergency command
Receive Emergency Command
Table 1-31. Emergency Command
Command No. Command name
0x00 Get device IC
0x01 Get all status
1.4.4 Printer language
ESC/P2
IBM 2391 Plus emulation
EPSON Remote
Rev. A
1-3
Page 44

DLQ-3000+
1.4.5 Prevention Hosts from Data Transfer Time-out
Generally, hosts abandon data transfer to peripherals when a peripheral is BUSY
continuously for dozens of seconds. To prevent this kind of time-out, the printer receives
data very slowly, several bytes par minute, even the printer is in a busy state. This
slowdown starts when the remainder of input buffer drops under several hundreds of bytes.
Finally, the printer is BUSY continuously when the input buffer is full.
1.4.6 Interface Selection
The EPSON DLQ-3000+ has three types of interfaces: Parallel, Serial, and optional Type-B.
Each interface can be selected manually by SelecType or automatically. Both modes are
selected thorough the default setting mode.
Manual selection
One of the 3 interfaces can be selected by SelecType.
Automatic selection mode (Enabled by SelecType)
When the printer is powered on, the printer is initialized to the idle state scanning which
interface receives data. Then the interface that receives data first is selected. When the
host stops data transfer and the printer is in stand-by state for the seconds specified by
SelecType, the printer is returned to the idle state. As long as the host sends data or the
printer interface is busy state, the selected interface is left as it is.
Interface selection and interface state
Interface selection and the corresponding interface states are as follows:
When an interface other than parallel interface is selected, the interface goes into
the BUSY state.
When an interface other than serial interface is selected, the interface sends XOFF
and sets the DTR signal MARK.
When an interface other than optional interface is selected, the printer sets
“OFFLINE” bit of MNSTS register to the optional interface.
When the printer is initialized and returned to the idle state:
• The parallel interface goes into ready state.
• The serial interface sends XON and sets the DTR SPACE and the printer
resets OFFLINE bit of MNSTS register to the optional interface.
Note: An interrupt signal such as /INIT signal on the parallel interface is not effective while
that interface is not selected.
Idle State
1-36
Selected State
Figure 1-15. Interface Selection
Non-selected State
Rev. A
Page 45

Product Description
7
1.5 Operation
This section describes the function of each button on the control panel and LED printer
status indicators.
1.5.1 Control Panel
The control panel for this printer consists of 10 non-lock type push buttons, 4 LED indicators
and 1 LCD. See Figure 1-16.
Power
Tear O ff
Font
1.5.1.1 Button Operations
Paper O ut
16-character LC D
S ele cT ype
Paper select
LF/FF
Pitch
Load/E ject
-----R e s e t-----
Pause
Figure 1-16. Control Panel
LCD: 16 characters
Power LEDs: Green
Paper Out LED: Red
Tear-off LED: Orange
Pause LED: Orange
Effectiveness
Basically, all button operations are always effective except for the following cases.
• During printing, only the
• The
•
Pause functions
• Press the
• Press the
Even if the
SelecType
Load/Eject
Pause
button is only effective during the printer is in the standby status.
and “
Pause
Pause
button to stop printing.
button again to resume printing.
button is pressed, the interface continues to receive data until the
Pause
Pause
button is effective.
” buttons are not effective during the SelecType mode.
input buffer is full and the CR moves to the ribbon changing position.
Reset function
Press the
Pause
Load/Eject
and
buttons simultaneously to initialize the printer. Refer to
Section 1.5.5.
Rev. A
1-3
Page 46

DLQ-3000+
Paper feed function
Table 1-32 shows the button operations and the corresponding paper feed functions
Table 1-32. Paper Feed Functions
Operations Function
Paper loaded Paper out
.
Press LF/FF
shortly. Tractor feed Line feed *¹ Load continuous paper
Press LF/FF for
a few seconds. Tractor feed Form feed *¹ Load continuous paper
Press. Friction feed Eject Load a sheet *².
Load/Eject
Press ↓.
Press ↑.
Insert a sheet to the manual
insertion slot. (Friction feed)
Friction feed Line feed Load a sheet *².
Friction feed Form feed Load a sheet *².
Tractor feed Paper park*¹ Load continuous paper
Friction feed Micro feed (forward) —
Tractor feed Micro feed (forward) *³ —
Friction feed Micro feed (backward) —
Tractor feed Micro feed (backward)*³ —
—
Load the inserted sheet.
*².
Notes)
1. When the printer is in the tear-off state, these functions are performed after returning
from the tear-off position.
2. Once a sheet is manually inserted, the printer enters manual insertion mode. While the
mode is active, even if data is remaining in the buffer, the printer goes into a paper-out
error state at each end of a sheet and waits for the next sheet to be inserted. CSF
insertion is enabled again by loading sheets into the CSF or by initializing the printer.
3. ↓↓ and ↑↑ buttons are used as described below:
Pressing the button continuously feeds paper forward*/backward* with a increment
•
of 1/180 inch.
Pressing the button continuously feeds paper forward*/backward* slowly.
•
When the printer is in the tear-off state, these buttons are used to adjust tear-off
•
position. The adjusted position is stored in the EEPROM.
* To feed forward or backward means toward the front or rear of the printer,
respectively.
Tear -off function
The printer has 2 types of tear-off functions; manual tear-off and auto tear-off. The
manual tea-off is performed by pressing the Tear Off button . The auto tear-off is
enabled by SelecType. These functions are same as for the conventional EPSON
printers.
Paper select function
Press the Paper Select button to select one of the following paper memory numbers.
• 0: All cases
• a(9): When the printer has the special paper information.
Note: The Paper Select button is only effective without any paper set.
1-38
Rev. A
Page 47

Product Description
9
1.5.1.2 Printer Status and LCD/LED Indicator Conditions
Table 1-33 shows the printer status and When the printer is in more than one status, the
printer indicates the prime status. If they have the same priority, the status occurs first is
indicated. The priority in the first column means that the status with the lower numbers have
higher priority.
Table 1-33. Printer Status and LCD/LED Indicator Conditions
Priority
1 Fatal error *
Printer State LCD message LED
Paper Out
1
Please turn off Blinks Blinks Blinks
Pause Tear-Off
2 Program reload mode Program Mode Off Off Off
3 Cover open error Cover Open On/Off *
4 Release lever operation
error *
2
Put Lever Back Blinks On On/Off
6
On On/Off
5 Paper jam error Paper Jam Blinks On On/Off
6 Paper out error *
7
Incomplete changing
paper path error *
8 Paper size error *
3
4
5
Paper Out On On On/Off
Wrong Paper Path Off On On/Off
Wrong Paper Size Off On On/Off
9 Eject error Pull Paper Out Blinks On On/Off
10 Printhead is overheated. Please Wait Off Blinks On/Off
11 Entry to SelecType 1 SelecType 1 Off Off Off
11 Entry to SelecType 2 SelecType 2 Off Off Off
12 Tear-off Cut the paper Off On/Off
13
Data is in buffer but the
printer is paused
Data in Buffer Off On Off
6
*
14 Pause Pause : #0 Off On Off
15 Bi-D adjustment Bi-d adjustment Off Off Off
15 Hex dump mode Hex dump Off Off O ff
15 Ordinary printing Printing : #0 Off Of f Off
15 Test printing Test Printing Off Off Off
15 Setting printing Setting Printing Off Off Off
16 Standby Ready : #0 Off Off O ff
Notes)
1. Fatal error occurs when the printer is under any of the following conditions:
• Power supply voltage is at an abnormal level.
• The printhead temperature is abnormal.
• Carriage does not move normally.
• Platen gap does not move normally.
• An error occurs while executing EEPROM commands or program reload mode.
• The printer control circuit does not work correctly.
2. This error occurs when the friction lever is not set to the appropriate position.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
On
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
Rev. A
1-3
Page 48

DLQ-3000+
3. Paper-out error occurs when the printer is under any of the following conditions:
• The printer does not load paper in spite of the attempt to load it.
• The printer finishes printing 1-page data on a sheet manually inserted.
• The end of the continuous paper has reached.
4. When the printer fails to change the paper path, this error occurs.
5. Paper size error occurs when the printer senses the condition that the currently loaded
paper size does not match the selected paper size.
6. It depends on the combination of the printer status.
1.5.1.3 Printer Status and Buzzer
The printer beeps to indicate several printer error status and failure operation. Printer status
and the corresponding beeper sounds are as described in Table 1-34.
Table 1-34. Printer Status and Buzzer
Printer status Beeper sound
Paper out error has occurred. – – –
Paper size error has occurred. – – –
Incomplete changing paper path error – – –
Eject error has occurred. – – –
Release lever operation error has occurred. — — — — —
Paper jam error has occurred. — — — — —
Fatal error has occurred. — — — — —
Illegal operation in SelecType –
Notes) The symbols “–“ and “—“ represent how a beep sounds.
“–“: Sounds 100 ms with the interval of 100 ms.
“—“: Sounds 500 ms with the interval of 100 ms.
1-40
Rev. A
Page 49

Product Description
1.5.2 SelecType
This printer provides SelecType function to change default settings.
1.5.2.1 SelecType Phase
See Figure 1-17 which shows the SelecType phase transitions. Boxes show printer states
or SelecType phases. The boxes with shadow involves button operations.
Printer State
Stand by state
SelecType
E n try to
SelecType 1
SelecType
E n try to
SelecType 2
SelecType
SelecType P hase
SelecType 1 p hase
FO NT
PITCH
FO NT
PITCH
SelecType 2 p hase
SelecType
in itn a liz a tio n *
D ata save phase
Font selection p hase
FO NT
Pitch selection phase
SelecType
SelecType
PITCH
SelecType
SelecType
Figure 1-17. SelecType Phase Transitions
Rev. A
1-41
Page 50

DLQ-3000+
1.5.2.2 SelecType Operation
SelecType 1 and 2 operations
Step 1. Selecting the feature
When the SelecType 1 or 2 starts, the first feature appears on the LCD. Scroll the
features by pressing the “↑” (next) or “↓” (previous) button until the desired feature
appears. Then press the “→” (enter) button, and the option menu for the selected
feature is displayed.
Step 2. Keeping/Changing the option
The current option marked with “*” for the menu appears. To keep the option as it is,
press the “←” button (escape) to return to the feature menu. To change the option,
press the “↑” (next) or “↓” (previous) button to scroll the option menu. Then press the
“→” (enter) button to fix the desired option. If the “Other” is selected, another option
menu appears. In this case, select the desirable option in the above mentioned way.
Step 3. Return to the previous menu
Press the “←” button (escape) to return to the previous menu. Pressing the button
several times to return to the SelecType 1 or 2 entry state.
Step 4. Exit
Press the “SelecType” button to exit the SelecType phase. With this operation, new
settings are automatically stored in the EEPROM and are effective until they are
changed again. This process is automatically followed by the SelecType initialization
phase and the printer returns to the stand-by status.
[Initializing all settings to the standard]
Select “Standard Setting” in the SelecType 2 menu. The message “Ready?” is
displayed. Then perform one of the followings:
To execute the initialization:
Press the “→” (enter) button. (All settings are reset to the standard and the printer
returns to the feature menu.
To return to the feature menu without executing the initialization
Press the “←” button (escape).
Press the “
Font and Pitch Select Operation
Step 1.
Displaying the current selection for the font/pitch
When the printer enters the Font/Pitch phase, the current option marked with “*”
appears.
SelecType
” button to exit the SelecType mode.
Step 2.
Step 3.
1-42
Changing the font/pitch
Press the “↑” (next) or “↓” (previous) button until the desired font/pitch appears.
Then press the “→” (enter) button to fix the selection. The selected font/pitch is
marked with “*” as the result.
Exit
Press the “SelecType” button to exit the Font/Pitch phase.
Rev. A
Page 51

Product Description
3
1.5.2.3 SelecType Option
Table 1-35 and Table 1-36 show the options available for the SelecType 1 and SelecType
2, Font and Pitch, respectively.
Table 1-35. SelecType 1 Option
Menu Option Note
T-margin Tractor
T-Margin Manual R
T-Margin Manual L
T-Margin CSF
Character Table
*8.5 mm
from 4.2 mm to 8.5 mm + 25.4 mm
*8.5 mm
from 0 mm to 8.5 mm + 25.4 mm
*8.5 mm
from 0 mm to 8.5 mm + 25.4 mm
*8.5 mm
from 0 mm to 8.5 mm + 25.4 mm
NLSP version
*PC437 PC437 Greek
PC850 PC852, PC853
PC855 PC857 PC864
PC866 PC869 ISO Latin 1T
Code MJK Bulgaria Estonia
ISO 8859-7 MAZOWIA
PC774 ISO 8859-2
PC866LAT PCAPTEC
PC 708 PC720 PCAR864
PC 860 PC865 PC861
USA – KOREA
Increment : 0.14 mm (1/180”)
Increment : 0.14 mm (1/180”)
Increment : 0.14 mm (1/180”)
Increment : 0.14 mm (1/180”)
Standard version
*PC437 PC850 PC860
PC861 PC863 PC865
Abicomp BRASCII ISO Latin 1
Roman 8 U.S.A – Korea
Page Tractor *11 inch 12 inch
8.5 inch 70/6 inch (A4)
Other (See the right column.)
Page CSF *A4 Letter
Other (See the right column.)
B-Margin Tractor
Line spacing *1/6 inch 1/8 inch At 1/6 inch spacing
Left-Margin
Right-Margin
Print Direction
*0.000 inch
From 0 to 1 inch
*0 columns
From 0 to 80 columns
*136 columns
From 1 to 136 columns
*Bi-directional Uni-directional
Auto
Option for “Other”:
xxx lines (from 24 to 132
lines at 1/6 line spacing)
Option for “Other”:
xxx lines (from 24 to *132
lines)
Increment: 1/180 inch
Note: The current options are marked with “*”.
Rev. A
1-4
Page 52

DLQ-3000+
Table 1-36. Options for SelecType 2, Font and Pitch
Menu Option Notes
SelecType 2
Language *English French
German Italian
Spanish Portuguese
Paper Type
Overlapping Form *Off On For continuous paper only
Intensity Mode *Normal Dark Use the copy mode only
Software *ESC/P2 IBM 2391 Plus
Auto CR (IBM) *Off On For IBM 2391 Plus emulation
A.G.M. (IBM) *Off On For IBM 2391 Plus emulation
Interface
I/F Time-out
Input Buffer *On Off
Baud Rate 300 BPS 600 BPS
Parity
Auto Tear-off *Off On
Auto LF *Off On
0 Slash *Off On
Buzzer *On Off
Standard Setting Ready?
*Normal Cards
Envelopes
*Auto Selection Parallel
RS-232C Option Slot
*10 sec.
From 1 to 255 seconds
1200 BPS 2400 BPS
4800 BPS 9600 BPS
*19200 BPS
*None Even
Odd
For cut sheet only
when the depth of multipart form printing is not
enough.
Font
*Roman Sans Serif Courier Prestige
Script OCR B Orator Orator S
Script C Roman T Sans Serif H Draft
H-Speed Draft
Pitch
*10 cpi 12 cpi 15 cpi 17 cpi 20 cpi
Proportional
Note: The current options are marked with “*”.
1-44
Rev. A
Page 53

Product Description
5
1.5.3 Functions at Power On
This printer has the following 7 service modes. To enter each mode, press specified button
(buttons) while holding down the Power switch.
Test Printing
• Button LQ mode:
Draft mode:
• Result Alphanumeric characters are printed continuously.
• Exit Press the
• Interface state All interfaces keep a busy state during the test printing.
Hex Dump Mode
• Buttons
• Result The printer prints the message “Hex Dump” and then starts printing
(period) is printed instead.
• Exit Press the
LF/FF
received data in the both hexadecimal code and corresponding
off the printer to exit the mode.
Pause
and
characters. If corresponding character does not exist, “.”
Pause
LF/FF
Load/Eject
button and turn the printer Off.
Load/Eject
button to print data remaining in buffer. Then turn
button with the power switch On.
button with the power switch On.
buttons with the power switch On.
Setting Printing
• Button
• Result Firmware version and user changeable default setting menu
• Exit When the printing is complete, the printed sheet or continuous paper
printer returns to the standby status.
• Interface State All the interfaces keeps a busy state during the printing.
SelecType
(SelecType menu) along with their options are printed with the
subtitles in the selected language.
button with the power switch On.
is ejected or fed to the tear-off position, respectively. Then the
Note: In each mode mentioned above, when the printer fails to load paper, the printer goes
into the Paper-out error status. In this case, insert a sheet and press the Load/Eject
button. (In the Hex Dump mode, the message “Hex Dump” is printed at first. Then the
printer waits for data.)
Bi-D adjustment (Refer to Section 1.5.4.)
• Button
Program Reload Mode (Refer to Section 1.5.5.)
• Buttons
EEPROM Clear
• Buttons
• Result Resets the printer to the standard factory setting, which is not always
Pause
Tear Off, LF/FF, Load/Eject
switch On.
SelecType, Paper Select
(This function is used only for emergency.)
button with the power switch On.
Pause
and
Pause
, and
On.
proper setting for each market.
buttons with the power
buttons with the power switch
Clear the driving line count for ribbon changing timing
• Button
• Result Clears the value for the driving line count stored in the EEPROM.
Rev. A
Paper Select
button with the power switch On.
1-4
Page 54

DLQ-3000+
1.5.4 Bi-D Adjustment Mode
This printer has the Bi-D adjustment mode which enables users to align vertical lines. Refer
to Table 1-37 and Figure 1-18.
Table 1-37. Bi-D Adjustment Item
Items Order
Draft mode 1
Bit Image (ESC ∗ 26H) mode
LQ mode 3
Start
Turn the printer on w hile
holding dow n "Pause" button.
The printer prints the guide for
Bi-D adjustm ent and the pattern
print for the draft m ode.
2
Press " " or " " button until the
LC D indicates the num ber for the
m ost closely aligned pattern.
: N e x t
: P revious
: E n te r
Fix the selected num ber by
pressing " " button, and the
printer prints the next pattern print.
Are all the adjustm ents
m ade?
Yes
T u rn th e p rin te r o ff.
End
Figure 1-18. Bi-D Adjustment Flowchart
No
1.5.5 Program Reload Mode
The printer has a 512-K byte Flash-EEPROM as a printer control software and a boot-strap
program storage. This Flash-EEPROM can erase all the data in itself at once electrically
and reprogram. Using this mode, the printer control software can be changed completely.
Refer to Chapter 3 for details.
1-46
Rev. A
Page 55

Product Description
7
1.5.6 Initialization
1.5.6.1 Printer Initialization
This printer has 5 initialization types: Power-on initialization, Operator initialization,
Initialization by the control panel operation, Software initialization and SelecType
initialization.
Power-on Initialization
Triggers
• Turning on the printer
• Cold reset command (Remote RS command)
Actions performed
• Initializes the printer mechanism.
• Clears input data buffer.
• Clears download character set.
• Clears print buffer.
• Sets default values.
Operator Initialization
Trigger
• The printer recognizes the /INIT signal (negative pulse) of parallel interface.
Actions Performed
• Clears input data buffer.
• Clears download character set.
• Clears print buffer.
• Sets default values.
Initialization by the control panel operation
Trigger
• Pressing the
Actions performed
• Clears input data buffer.
• Clears print buffer.
• Sets default values.
Pause
Load/Eject
and
Software Initialization
Trigger
• ESC @ commend
Actions Performed
• Clears print buffer.
• Sets default values.
SelecType Initialization
Trigger
• Exiting the SelecType mode
Actions Performed
• The printer settings are reset to the default except the download definition is
not cleared.
• The printer is put into the standby status.
buttons for 3 seconds.
Rev. A
1-4
Page 56

DLQ-3000+
1.5.6.2 Initialize Defaults to the Standard
The use changeable defaults can be initialized to the standard settings by SelecType. The
standard settings are shown in Table 1-38.
Table 1-38. Standard Settings
Items Standard settings
Font Roman
Pitch 10 cpi
Character Table PC437
Page Length Tractor 11 inch
CSF 132 lines
Line Spacing 1/6 inch
Top Margin Tractor 8.5 mm
Manual Rear 8.5 mm
Manual Front 8.5 mm
CSF 8.5 mm
Bottom Margin Tractor 0.0 mm
Left Margin 0 column
Right Margin 136 columns
Print Direction Bi-directional
Message Language English
Software ESC/P2
Interface Auto Selection
Interface Auto Selection Time-out 10 seconds
Input buffer ON
Serial interface Baud Rate 19200 bps
Parity None
Auto Tear-off Off
Auto LF Off
Auto CR (IBM 2391 PLUS) Off
AGM (IBM 2391 PLUS) Off
Over-lapping Forms Off
Paper Type (Cut sheet) Normal
Intensity Mode Normal
0 slash Off
Buzzer On
1-48
Rev. A
Page 57

9
1.6 Main Components
This printer is composed of the following components:
Printer mechanism
Main control board C210MAIN
PSB/PSE board C124 PSB/PSE
Control panel
Housings
1.6.1 C210MAIN Board
The C210MAIN consists of the followings:
CPU (H8/3033
CG-ROM
EEPROM
Flash-ROM/P-ROM for the program ROM
Gate array (E05B46)
DRAM
Drivers
Product Description
SDC03-V1
(PG M otor D river)
SLA5001
(Printhead D river)
2SA 1451
(Printhead D river)
SLA 7026M
(C R M otor D river)
M P 5302
(R ibbon M otor D river)
EEPRO M
SLA 7024M
(P F M o to r D riv e r)
CG-ROM
Flush R O M
(P R O G R A M )
DRAM
E05A88(G ATE ARRAY)
H 8/3003(C PU )
Figure 1-19. C210MAIN Board Component Layout
Rev. A
1-4
Page 58

DLQ-3000+
1.6.2 C124PSB/PSE Board
The electoral circuit board of this printer consists of 2 switching regulator circuits.
Fuse
Filter
Sw itching F E T
Transform er (T101)
TL494
(R egulator)
Transform er (T201)
Figure 1-20. C124PSB/PSE Board Component Layout
1.6.3 Printer Mechanism
The printer mechanism of this printer is composed of the followings:
CR motor
Ribbon motor
2 cooling fans
CR mechanism
PF motor
PG motor
Paper feed mechanism
1-50
Figure 1-21. Printer Mechanism
Rev. A
Page 59

1.6.4 Housing
This printer is composed of the following housings:
Bottom frame assembly
Upper housing assembly Rear shield cover
Printer cover assembly
Upper connector cover
Lower housing assembly
Rear cover
Product Description
U pper H ousing A ssem bly
Printer Cover Assem bly
Low er H ousing A ssem bly
R e a r S h ie ld C o v e r
U pper C onnector C over
Figure 1-22. Printer Housings
R ear C over
Bottom Fram e Assem bly
Rev. A
1-51
Page 60

Chapter 2
Operating Principle
2.1 Printer Mechanism Operating Principles.............................................2-1
2.1.1 Printing Mechanism......................................................................2-1
2.1.2 CR (Carriage) Mechanism ............................................................2-3
2.1.3 PG (Platen Gap) Adjustment Mechanism....................................2-4
2.1.4 Ribbon Feed/Ribbon Shift Mechanism........................................2-6
2.1.4.1 Ribbon Feed Mechanism.....................................................2-7
2.1.4.2 Ribbon Shift Mechanism......................................................2-7
2.1.5 Paper Feed Mechanism ................................................................2-9
2.1.5.1 Core of the Paper Feed Mechanism....................................2-9
2.1.5.2 Paper Feed Sensor Mechanism........................................2-10
2.1.5.3 Release Mechanism..........................................................2-12
2.2 Circuit Operating Principles................................................................2-13
2.2.1 Power Supply Voltage.................................................................2-13
2.2.2 Power Supply Circuit Operation ................................................2-14
2.3 Controller Circuit..................................................................................2-15
2.3.1 Interface Circuit...........................................................................2-18
2.3.2 Reset Circuit................................................................................2-19
2.3.3 Memory Back-up Circuit.............................................................2-20
2.3.4 Ribbon Motor Controller/Driver Circuit.....................................2-21
2.3.5 PF (Paper Feed) Motor Controller/Driver Circuit......................2-22
2.3.6 CR (Carriage) Motor Controller/Driver Circuit..........................2-23
2.3.6.1 Bi-D Adjustment Function..................................................2-25
2.3.6.2 Interlock Function..............................................................2-25
2.3.7 Printhead Controller/Driver Circuit............................................2-26
2.3.8 Control Panel Circuit...................................................................2-27
2.3.9 PG (Platen Gap) Motor Driver Circuit........................................2-28
2.3.10 Paper Thickness Detecting Circuit..........................................2-29
2.3.11 Paper Jam Sensor.....................................................................2-30
Page 61

2.3.12 Other Sensor Circuits...............................................................2-31
Page 62

Operating Principles
2.1 Printer M echanism Operating Princi pl es
This chapter describes the operating principles of the printer mechanism (M-5P60).
2.1.1 Printing Mechanism
Printhead
The printing mechanism of this printer is composed of the 24-pin impact dot printhead
and a ribbon mask. The printhead has 12 pin wires in each of 2 rows, which are aligned
in an rhombic layout. (See Figure 1-2 in Chapter 1.) Each wire has its own drive coil.
Actuating P late
Stopper
Actuating S pring
W ire R esetting S pring
H ead D riving C oil
Iron C ore
Paper
Dot W ire
Ink R ibbon
R ibbon M ask
Platen
Figure 2-1. Structure of the printhead
Printing process
1. The printing signal transmitted from controller circuit to the head driver circuit is
converted into the head drive voltage, which energizes a corresponding coil. The
energized coil then magnetizes the iron core.
2. The magnetized iron core draws the actuating plate which joins to the dot wire. This
movement rushes the wire toward the platen.
3. When the dot causes impact to the platen, it presses the ribbon to the paper, where a
dot prints.
4. When the coil energizing is terminated, the iron core, losing magnetic force, is
returned to the standby position by the bounce of the platen and tension of the
actuating spring.
The printing mechanism has an integrated thermistor to detect head temperatures. The
detected temperature is converted into an electrical signal and fed back to the controller
circuit. This information as well as paper thickness is used as a basis for determining
printhead driving mode to ensure high printing quality. It is particularly important to keep the
head temperature at a proper level constantly to minimize burning and deterioration of the
dot wires in the printhead, which are caused by the rise in the head temperatures due to
continuous printing. When the head temperature is below the specified level, the
appropriate driving mode is selected based on the detected temperature to keep the wires
respondent. (Refer to Section 1.3.1 in Chapter 1.) See Table 2-1 in Page 2-2 for the
printhead specification.
Rev. A
2-1
Page 63

DLQ-3000+
Table 2-1. Printhead Specification
Item Description
Printing method Impact dot printing
Number of wires 24 wires (14 wires on each of 2 rows in an rhombic
layout)
Wire diameter 0.20 mm
Head life Monochrome fabric ribbon: 200 million strokes / wire
Color ribbon: 100 million strokes / wire
Weight 180 g
Coil resistance
Response period
Drive voltage 31.5 to 38.5 V
Driving condition
Environmental condition Temperature: 5 to 55° C
Printhead drive method Flywheel type
8.19 ± 0.5 Ω (at 25° C)
Normal mode: 462 µs
•
Normal drive copy mode (when multi-part form or thick
paper is used.)
•
High duty condition (head temperature is high)
•
Cold mode (head temperature is low.)
Humidity: 10 to 85 %
2-2
Rev. A
Page 64

Operating Principles
3
2.1.2 CR (Carriage) Mechanism
The CR mechanism consists of the CR movement mechanism, external cooling fan, and
platen gap adjustment mechanism.
CR movement mechanism
The CR is supported by 2 CR guide shafts by its high and low ends. The stepping motor
used for the CR motor enables the CR to move to any positions. The motor also sends
torque to the timing belt pulley to drive the timing belt. The timing belt with one of the
edges fixed to the head carriage moves the head carriage along the carriage guide shaft
from right to left or vice versa according to the direction the CR motor rotates. Since the
length of the belt is affected by the change in temperature, belt tension spring is
attached to keep the belt with a constant tension. The HP sensor (Home Position sensor)
is located at the reference position (on the right side as seen from the front) in the printer
mechanism. Photo-coupler system used for the sensor detects the CR when the flag of
the CR crosses emission. It is only operated when the printer is turned on, and once it is
detected, CR movement is put under the open-loop control system. After the controller
circuit determines where to move the CR according to the received data, it converts the
distance to the position into the corresponding phase change pulse and outputs it to the
CR motor. If the CR home position is detected during printing or the printer initialization, it
indicates the status that the printer fails to detect the home position at a correct position
and an error occurs as a result. CR speed is controlled by the CR motor drive frequency
which depends on the printing data.
Belt Tension Spring
CR
Timing Belt
Platen
Printhead
Cooling Air
Flag
CR HP Sensor
Bushing
Timing Belt Pulley
External Cooling Fan
Figure 2-2. CR Mechanism
External cooling fans
This printer is equipped with 2 cooling fans. One, located at the left bottom of the printer,
eliminates excess heat from the circuit boards. The other one is externally attached to
the right side of the printer mechanism to blow the air directly to remove excess heat
from the printhead.
Table 2-2. External Cooling Fan Unit Specification
Type DC brush-less motor (ball bearing built in)
Power supply voltage
35 VDC ± 10 %
Consumption current 0.07 A or less
Rotating speed 3800 rpm or more
Rev. A
2-
Page 65

DLQ-3000+
2.1.3 PG (Platen Gap) Adjustment Mechanism
PG adjustment is made manually and automatically. In the manual PG adjustment mode,
the proper PG is originally set for the paper to be loaded by manually operating the PG
adjust lever located at the left front of the printer. On the other hand, the automatic PG
adjustment function lets the printer automatically measure the paper thickness and set the
proper PG for the thickness. This mode is activated by setting the PG adjust lever to the
automatic side. Figure 2-3 shows the PG adjustment mechanism.
Slit Disc Paper Thickness Sensor
PG Motor
Pinion Gear
CR Guide Shaft
Combination Gear
Sector Gear
PGHP Sensor
Platen
Printhead (CR Unit)
Ink Ribbon
Ribbon Mask
Paper
Figure 2-3. PG adjustment Mechanism
The PG adjustment mechanism located at the left top of the printer mechanism unit consists
of the PG motor, CR guide shaft, sectorial gear, combination gear, PG home position
sensor, and paper thickness sensor., After the PG is determined by the controller circuit
according to the paper thickness, the PG motor rotates corresponding amount. The torque
from the PG motor is transmitted via the motor pinion gear, combination gear and sectorial
gear to the CR guide shaft. Since the shaft is eccentric, the CR on the shaft moves from or
toward the platen as the shaft moves, depending on the direction the motor rotates. Seeing
from the left side of the printer mechanism, the clockwise or counterclockwise rotation of the
CR guide shaft narrows or widens the PG, respectively. The PG home position is detected
when the sectorial gear pushes the actuator on the PG home position sensor.
2-4
Rev. A
Page 66

Operating Principles
5
Manual PG adjustment function
This function allows the user to set the proper PG manually by setting the PG adjust
lever to one of the steps from -1 to 9. The selected step is converted into 4-bit data using
adjustment switches and the data is transferred to the controller circuit, where the PG is
determined based on the information.
Table 2-3. PG and PG Adjust Switch
PG lever Adjust switch condition Corresponding paper PG width Print mode
Steps #1 #2 #3 #4 Thickness (PT) (mm)
-1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Automatic
{{
{
−
{
−−−
{{{
−
{
−−
{{
−
{
−−−−
−−
{{
−
{
−−−
{
{
{
−
{
−
{
{
−
−
−
−
−−
−−
0.06=<PT<=0.11 0.35 Normal
0.06=<PT<=0.11 0.39 Normal
0.11<PT<=0.15 0.43 Normal
0.15<PT<=0.19 0.46 Normal
0.19<PT<=0.25 0.50 Copy 1/2
0.25<PT<=0.30 0.55 Copy 1/2
0.30<PT<=0.36 0.61 Copy 1/2
0.36<PT<=0.42 0.67 Copy 1/2
0.42<PT<=0.46 0.71 Copy 1/2
0.46<PT<=0.49 0.74 Copy 1/2
0.49<PT<=0.53 0.78 Copy 1/2
0.06=<PT<=0.53 Note 1 Note 2
Note)
1. PG width corresponds to the detected paper thickness.
2. Copy mode is used for paper with the thickness of 0.2 mm or more.
Automatic PG adjustment function
PG is automatically adjusted based on the paper thickness detected paper thickness
sensor which consists of the slit disc and the photo-electric transfer. Paper thickness is
detected in the following order:
1. PG home position is detected.
2. The gap between the platen surface and the printhead is measured by pressing
the printhead to the platen through the ribbon mask and ink ribbon.
3. The paper thickness is by pressing the printhead to the paper surface through the
ribbon mask and ink ribbon.
4. The printer sets the proper PG based on the measurement done in the step 2 and
3.
PG is determined for each paper loading action. When the CSF is used, this function is
activated when the printer is turned on. It is also performed when the paper quantity
sensor in the hopper is reset. However, no printing is performed during this operation.
(Refer to Section 2.3.10.)
Rev. A
2-
Page 67

DLQ-3000+
2.1.4 Ribbon Feed/Ribbon Shift Mechanism
Ribbon feed/ribbon shift mechanism, located at the upper part of the CR, is composed of
the ribbon motor, ribbon wind-up mechanism inside the ribbon cartridge, ribbon shift
mechanism, and color ribbon cartridge sensor. The torque from the ribbon motor, the only
motor which drives these mechanisms, is transmitted to each mechanism by changing the
direction for rotating the motor, as described below:
Forward rotation (Clockwise): Color/Black ribbon shift
Backward rotation (Counterclockwise): Ribbon feed
A stepping motor used for the ribbon motor enables the CR to move to and stop at any
position. The color ribbon cartridge sensor detects which of color or black ribbon cartridge is
installed and switches the ribbon motor between the monochrome ribbon mode and color
ribbon mode according detected cartridge. The printer refers to the switch mode of the
sensor when the printer is turned on or resuming the operation after the cover open error is
detected. The motor is controlled by the open-loop system. While the motor is used fo r the
ribbon shift, the color home position sensor detects the reference position (black) to
manage the color ribbon shift. The motor drive speed and phase excitement mode changes
in accordance with printing modes such as copy mode, normal mode and color mode.
R ibbon B rake Spring
Ink Ribbon
R ibbon Feed R oller
R ibbon H old R oller
R ibbon D rive G ear
Figure 2-4. Ribbon Feed/Ribbon Shift Mechanism
Table 2-4. Color Ribbon Cartridge Sensor Specification
R ibbon C artridge
C olor R ibbon C artridge
Sensor
R ibbon Transm ission G ear Train
R ibbon P lanetary gear
CR/PF Pinion
R ibbon M otor
2-6
Detecting method Mechanical switch system
Rated voltage/current 5 to 10 mA/5 VDC ± 5%
Switch mode Monochrome ribbon mode : HIGH
Color ribbon mode: LOW
Rev. A
Page 68

Operating Principles
7
2.1.4.1 Ribbon Feed Mechanism
The ribbon feed mechanism is composed of the ribbon feed mechanism in the carriage,
ribbon motor and ribbon cartridge. When the ribbon motor rotates counterclockwise, the
ribbon drive pulley is driven to feed the ribbon. See Table 2-5 which shows how the torque
is differently transmitted via the gear train.
Table 2-5. Ribbon Motor Rotation and Torque Transmission
Rotational direction Torque transmission
C.C.W.
(for ribbon feed)
C.W.
(for ribbon shift)
Ribbon motor pinion → Ribbon planetary gear →
Ribbon transmission gear train →Ribbon drive gear
Ribbon motor pinion → Ribbon planetary gear →
Ribbon transmission gear (A) →Ribbon transmission gear (B) →
CS reduction gear → CS drive cam → CS drive lever
The endless ink ribbon in the ink cartridge is routed between the ribbon feed roller and the
ribbon hold roller. When the ribbon feed roller engaged with the ribbon drive gear is driven,
the ribbon between the rollers winds up. The ribbon brake spring is set at the exit in the
cartridge to wind the ribbon tightly.
2.1.4.2 Ribbon Shift Mechanism
The ribbon shift mechanism, which is composed of the ribbon motor, ribbon shift gear train
and color HP (Home Position) sensor, shifts the ribbon cartridge back and forth on CR unit.
Both black and color ribbons have the width of 1 inch. The black ribbon is entirely soaked
with the black ink, and the color ribbon is composed of 4 colored bands of black, red, blue
and yellow. When the color ribbon cartridge is installed on the CR, it is detected by the color
HP sensor, and the printer enters the color ribbon mode. With this mechanism, the color
print with 7 different colors is enabled. The printer shifts the color ribbon cartridge to the
black band position before shifting to another color each time the printer is turned on or the
cover open error is cleared. This is operated to avoid ribbon’s getting caught in the
printhead and resultant failure in ribbon shifting. The printer enters the monochrome ribbon
mode when the black ribbon is installed. In this mode, the printer shifts the cartridge with ¼
of the ribbon width under the following condition in order to lengthen the ribbon life:
• 10 cut sheets or 10 pages of continuous paper has been continuously printed
after the last shift.
• The release lever setting is changed.
• Continuous paper is loaded.
The cartridge positioning spring behind the cartridge, having the positioning pin at the top,
holds the ribbon cartridge firmly to act in the direction the CS drive lever is pressed down.
The ribbon motor sends torque to the CS drive lever, which shifts the cartridge between any
color bands, starting from the reference position, the position for the black belt. The
reference position is detected by the color HP sensor.
CR
C artridge P ositioning P in
C artridge P ositioning S pring
C olor R ibbon C artridge
Black
Cyan
M agenta
Yellow
C S D rive Lever
Figure 2-5. Ribbon Shift Mechanism
Rev. A
2-
Page 69

DLQ-3000+
Half-toning colors are created by printing a color on top of another, as shown in Table 2-6.
The printer prints the brighter color first to prevent the ribbon from being stained
.
Table 2-6. Coloring Sequence
Print color Print ribbon
First print Second print
Black Black
Magenta Magenta
Cyan Cyan
Yellow Yellow
Green Yellow Cyan
Orange Yellow Magenta
Violet Magenta Cyan
Ribbon Transmission Gear (B)
Ribbon Transmission Gear (A)
Ribbon Planetary Gear
Ribbon Planetary Gear
Ribbon Motor
−
−
−
−
CS Reduction Gear
CS Drive Lever
CS Drive Cam
Color HP Sensor
CS Drive Lever
Figure 2-6. Ribbon Shift Gear Train Mechanism
2-8
Rev. A
Page 70

Operating Principles
9
2.1.5 Paper Feed Mechanism
The paper feed mechanism consists of the platen roller, PF roller (Paper Feed roller), paper
eject roller, PF motor (Paper Feed motor), tractor unit, PEW sensor (Paper Width sensor),
front/rear paper sensor, release sensor, paper jam sensor, and paper shift mechanism.
2.1.5.1 Core of the Paper Feed Mechanism
This printer feeds paper by sliding it horizontally. Paper feed operation varies depending on
the release lever setting condition, as described below:
In the friction mode
Paper is held by the front paper bail and the for roller assemblies (2 upper and 2 lower
rollers) under the CR guide shaft.
• Feeding method: Front feeding (automatic), Rear feeding (manual), CSF
feeding
• Ejecting method: Front ejection
In the tractor mode
Switching the lever setting from the friction mode to the tractor mode puts the printer into
the tractor mode. In the tractor mode, the drive is disengaged from the rollers by the
release mechanism, and transmitted to the tractor side.
• Feeding method: Tractor
• Ejecting method: Front ejection
In the paper jam removal mode
Torque is disengaged from all the rollers in this mode. (See Section 2.1.5.3.) A stepping
motor is used for the PF motor, which enables the paper to move to and stop at any
position regardless of the direction. The motor is controlled by the controller circuit by the
open-loop system. It refers to the signals output from the sensors in the mechanism to
determine the amount to slide paper and the corresponding motor pulse. Torque sent
from the PF motor equally splits to the front and rear paper feed drive rollers via the 2
timing belts. If the belt tension is inappropriate (either too loose or too tense), the front
and rear rollers lose balance and paper jam is caused as the result. To balance the belt
tension with each other, reinstall the PF motor to the proper position. The PF motor is
fixed with 2 screws and the adjusting part such as the PF tension shaft. (See chapter 3
for detailed procedure.)
P r in te r M e c h a n is m F ra m e
Paper Bail R oller
Paper Feed D rive Roller
Sub P aper Feed R oller
A ssem bly
Tractor Transm ission G ear
Tractor
Paper Eject D rive Roller Assem bly
Platen
Paper Feed M otor
Figure 2-7. Core of the Paper Feed Mechanism
Rev. A
2-
Page 71

DLQ-3000+
2.1.5.2 Paper Feed Sensor Mechanism
The paper feed sensor mechanism is composed of the right/left PEW (Paper Width)
sensors, front/rear paper sensors and paper jam sensor. These sensors detect conditions
such as top and rear paper edge positions, paper width and paper jam. The paper feed
sensor mechanism monitors detected conditions and feeds back the information to the
CPU, which controls paper feeding. The feed-back timing for a read signal is selected by
the CPU depending on the movements of the paper feed and carriage motors. Figure 2-8
illustrates the paper feed sensor mechanism. Table 2-7 lists the paper feed sensor
functions.
Left P EW S ensor
Platen
Left P EW S ensor
Printhead
Front V iew
R ight PE W S ensor
M ask G uide
CR Motor
R ight PE W S ensor
Sub P aper Feed R oller Assem bly
Paper Jam Sensor
R ear P aper S ensor
M ask G uide
2-10
Printehad
Front P aper S ensor
Paper Eject D rive Roller A ssem bly
Top View
Figure 2-8. Paper Feed Sensor Mechanism
Rev. A
Page 72

Table 2-7. Functions of the Paper Feed Sensor
Sensor Detection Function
Operating Principles
Paper width measurement
(detects the left and right
paper edges)
Right/left PEW sensors Paper bottom detection
(detects the rear edge.)
Paper end detection Ensures the paper feed and paper
Left PEW sensor alone Leading edge detection at
loading paper
(detects the paper top.)
Front/Rear paper
sensors
Rear paper sensor
alone
Front paper sensor
alone
Paper jam sensor Paper jam detection Detects paper jam condition in the
Detects the leading/rear
edge of the paper.
Paper end detection Ensures the paper feed and paper
Detects the leading/rear
edges of the paper
Detects the leading edge of
the paper
Selects the left and right margins.
Depending on o the CR position,
one of the sensors is used.
If one of the sensors detects
paper, it is regarded “Paper is
loaded”. If both sensors don’t
detect paper, it is regarded “No
paper is loaded”.
eject action.
Determines the top margin.
Determines the top/bottom margin.
eject action.
Detects the leading edge and
printable area for the black-solid
print paper.
Performs front paper feeding.
front/rear paper feed direction.
Notes)
1. When the printer is powered on, if any of the right/left PEW sensor and front/rear paper
sensor detects paper, the printer does not detect the leading edge of the paper but the
paper end condition.
2. Left and right margin for cut sheet and continuous paper are switched by the release
sensor.
Black solid mode
This printer is equipped with the black solid print mode. In this mode, the printer prints
regardless of the reflection rate of the paper.
Paper jam detection
The paper jam sensor monitors a signal output for each step (1/216 inch per step). If the
output signal becomes the same as the one for power on time and the following signals
for the specified numbers of steps remain the same, the status is regarded as the paper
jam error, and the CPU indicates the paper jam error.
Rev. A
2-11
Page 73

DLQ-3000+
2.1.5.3 Release Mechanism
The release mechanism consists of the release lever, sub release lever, release lever link
and release sensor. It switches the paper path between cut sheet mode (including CSF
mode ), continuous paper mode and paper jam removal mode in accordance with the
release lever setting. It is performed by switching the torque from the PF motor and adding
/releasing pressure toward/from the rollers in the paper feed mechanism. The release lever
shifts the release lever link via the sub release lever to add friction to paper or to release
pressure from the paper.
Cut sheet mode
The torque from the PPF motor is transmitted to the PF mechanism side, where the
paper is fed with friction added by the sub paper loading roller assembly.
Continuous paper mode
The torque from the PF motor is transmitted to the tractor gear via the tractor gear train
to feed continuous paper. The sub paper loading rollers are used to hold and feed the
paper only.
Paper jam removal mode
To set the release lever to this mode releases the paper bail as well as the sub paper
loading rollers. In this full release condition, the jammed paper can be manually ejected
The release sensor detects whether the release mechanism is in the cut sheet mode or
continuous paper mode, and sends the information to the controller circuit.
Table 2-8. Release Mechanism Mode
Cut sheet
mode
Continuous
paper mode
Paper eject lever assembly Closed Open Open
Paper loading drive roller Closed Closed Open
Tractor transmission gear
and tractor gear condition
Disengaged Engaged Engaged
Release sensor state Open Closed Closed
Tractor Transmission Gear
Tractor Gear
Paper Feed Drive Roller
Sub Paper Feed Roller Assembly
Release Link Lever
Paper Bail Roller
Paper Eject Drive Roller Assembly
Paper jam
removal mode
Release Sensor
2-12
Sub Release Lever
Paper Jam Clear Mode
Figure 2-9. Release Mechanism
Friction Mode
Tractor Mode
Rev. A
Page 74

Operating Principles
3
2.2 Circuit Operating Principles
The power source of this printer is composed of the power switch, AC cable and C124
PSB/PSE board. It supplies DC voltage used to control the printer operation.
2.2.1 Power Supply Voltage
The electrical circuit of this printer uses an RCC (ringing choke converter) type switching
regulator, which outputs DC voltage required to operate the printer. DC voltage is divided
into 3 blocks: +35 VDC (CH. A), +35 VDC (CH. B) and +5 VDC, as listed below.
Table 2-9. DC Voltage Application
Voltage level Connector No. Application
+35 VDC ±
10%
+5 VDC ± 5%
CN2 CH. A
CH. B
CN3 Logic
• CR motor
• Printhead drive voltage
• Printhead
• Cooling fan motor
• PF motor
• Ribbon motor
• Vpp of the flush memory
• Hold voltage for the PF motor
• Hold voltage for the ribbon motor
• Serial I/F level converter
• Type-B I/F power supply voltage
• I/F power supply
Rev. A
2-1
Page 75

DLQ-3000+
2.2.2 Power Supply Circuit Operation
The AC power source is supplied to the PSB/PSE board via the AC cable, power switch and
fuse. The AC voltage is full-wave rectified using the diode bridge (DB1) and smoothed by
the condenser. The surge cut circuit by SCR reduces the rush current at power-on.
Over current protection circuit on the primary side
IC101 and IC201 detect the input voltage of the primary side. If the input voltage is
normal, the current does not flow into the shunt-regulator. However, if the over current
flows into the input voltage line, the shunt-regulator goes on and Q103 (Q203) goes on
and Q101 (Q201) goes off.
+35 VDC block
For the 35VDC block, the voltage is applied with AC/DC conversion between the primary
and secondary sides via coil T101 and T201. The amount of voltage and current output
to the secondary circuit is controlled at the gate by the on/off operation of the main
switching MOS FET (Q101 and Q201). Control is fed back to the Q101 and Q201 from
each protection circuit and controller circuit.
[+35 VDC line over current protection circuit]
If the voltage level for the +35 VDC line drops below +13 V, Q153 (Q253) and Q154 are
turned on by the detector circuit which consists of the R173 (R273) and R174 (R274),
then the PC102 goes on and the current cuts off as the result. At this time, the delay
circuit which consists of C157 and R154 makes the delay time. When the printer is
turned on, the protection circuit can not start operation since the delay circuit acts to
prevent the drivers on the main control board from rising before the +5 VDC lines rises
up.
+5 VDC block
The +5 V line is produced out of the stabilized and smoothed +35 V by the Regulator IC
TL494. Since the regulator internally has the stabilizing and smoothing circuit,
informa tion o n stab ilization is not f ed back to the primary side except f or t he inf ormation
on the over current protection circuit. When the output level of the +5 VDC is abnormally
high, the status is fed back to the primary side via the Zener diode (ZD153) and PC102,
then The gate for switching FET Q101 or Q201 is shortened to avoid abnormal operation
of the mechanism.
AC Power
Fuse
EMI Filter
Diode Bridge
Surge Cut
Smoothing
Circuit
Regulator IC
Constant Voltage
Circuit
Main Switching
Circuit
Main Switching
Circuit
Half-wave
Rectifier
Smoothing
Circuit
PC101
PC102
PC 201
Half-wave
Rectifier
Smoothing
Circuit
Figure 2-10. Power Circuit Block Diagram
+5 VDC
+35 VDC
(CH. B)
Protection Circuit
+35 VDC
(CH. A)
2-14
Rev. A
Page 76

Operating Principles
5
2.3 Controller Circuit
This section describes the controller circuit of this printer. This printer uses a 112-pin/QFPtype/16-bit microprocessor H8/3003 (IC16) for the CPU and drives it with the clock
frequency of 14.7 MHz. The control program is stored in the 1-Mbit Flash-ROM (IC15) or
PROM (IC18).The CPU receives the external reset signal and control the printer based on
the control program. When the Flash-ROM is in use, the control program can be transferred
by way of the parallel interface. DRAM is used as a work area and buffers. A non-volatile
memory EEPROM (IC23) stores information such as default values, customer data, total
printing amount value and PG adjustment value. The gate array E05B46 (IC25) controls the
following:
Clock Addresses Memory DRAM Parallel I/F
Type-B I/F Ports Motors Bitmap Printheads
It is also used for the PG measurement. The gate array E05A89 functions as the panel
interface controlled by the CPU. It is directly attached to the control panel circuit board to
simplify the circuits. See Table 2-10 which lists the main ICs and their functions.
Rev. A
2-1
Page 77

DLQ-3000+
Table 2-10. Main ICs and their Functions
IC Location Function
CPU (H8/3003 equivalent) IC16 The main CPU of the controller circuit
Gate Array (E05B46) IC25 Controls systems and peripheral devices.
Gate Array (E05A89) (built
in the panel circuit board.)
Flash-ROM IC15 Stores the control program.
PROM IC18
CG (8-Mbit MROM) IC21 Character generator
CG (4/8-Mbit MROM) IC24 Character generator
DRAM (HM514260 equivalent) IC26 Manages buffers and work area. (4Mbit)
EEPROM
(AT93C66 equivalent))
Reset IC (RST592D) IC22
Reset IC (RST594E) IC20
CR motor driver
(SLA7026)
PF motor driver
(SLA7024M)
Ribbon driver (MP5320) QM2
PG motor (SDC03-V1) QM1
Serial I/F transceiver IC
(MAX232CWE)
Shunt regulator (TL431) IC19
3-terminal regulator
(LM75L12)
−
IC23
IC7
IC6
IC14
IC17
Functions as the I/F between the control panel
and controller circuit.
Stores the control program when the Flash-ROM
is not equipped.
Stores values for default setting, customer data
and so on.
• Resets hardware
• Rests Flash-ROM (Recovery from the reset
condition is done for Flash-ROM prior to the
CPU and gate arrays.)
• Reset hardware
• Resets the CPU and gate arrays.
Drives the CR motor by constant current/uni-polar
drive.
Drives the PF motor by constant current/uni-polar
drive.
Drives the ribbon motor on the CR by constant
current/uni-polar drive.
Drives the PG motor by constant current/uni-polar
drive.
Transceiver circuit for the serial I/F
Produces the reference voltage (power supply for
the stabilizing the +5V) for the A/D converter.
Stabilizes 12V power supply voltage for head
pre-drive.
2-16
Rev. A
Page 78

Operating Principles
7
P a ra lle l I/F
Adjust Switch
External
C ooling Fan
Paper Thickness
Sensor
Type-B I/F
(O ptional)
S e ria l I/F
Printhead
H ead D river
G a te A rra y
E05B 46
(IC 25)
H ead
Therm istor
CG
Flash R O M
/P R O M
Reset IC
EEPRO M
DRAM
Reset IC
S yste m B us
C ontrol Panel
G a te A rra y
E05A 89
CPU
H 8/3003)
(IC 16)
C over O pen
Sensor
Color HP
S ensor
R ear P aper
Sensor
Front P aper
Sensor
L e ft/R ig h t P E W
Sensor
CR HP Sensor
R elease
S ensor
C SF Paper
Q uantity Sensor
C SF Sensor
CR Motor Driver
3-term inal
R egulator
+5 V S tabilizing
Circuit
P F M o to r D riv e r
+35 V
+35 (C H . A)
+12 V
+5 V
VU
R ibbon M otor
Driver
PPG M otor D river
Figure 2-11. Controller Circuit Block Diagram
PG H P Sensor
Paper Jam
Sensor
+35 V S ensor
In te rlo c k S w itc h
Rev. A
2-1
Page 79

DLQ-3000+
2.3.1 Interface Circuit
This section gives information on the parallel/serial interfaces of the DLQ-3000+.
Bi-directional parallel interface
The gate array E05B46 manages the IEEE-1284 nibble mode function using the internal
IFU (Interface Unit). It latches data from the host computer by the /STB signal and
automatically sends the BUSY signal. When the data is stored in the buffer, the gate
array clears the BUSY and sends /ACK back to the host computer.
Serial interface
Received data RXD sent from the host computer (i.e. RECEIVED DATA, which is also
applied to an optional interface.) is transferred to the CPU via the transceiver IC, and
then to the input buffer. The CPU directly outputs TXD data (TRANSMIT DATA). The codes
DC1/DC2 and DC3 are outputs when the input buffer is full, and DC1 is output when the
buffer memory recovers to the normal level. The signal REV (same as DTR:DATA
TERMINAL READY) is output to the port PC0 of the CPU to control the DTR. The printer
resumes printing when the CR code is received or the input buffer is full.
Type-B interface
Type-B interface is also controlled by the gate array E05B46.
System Bus
Type-B I/F
ADDRESS/DATA
HW R
RESET
READY
W RRDY
CMREQ
RDREQ
PARALELL I/F
PARALELL DATA
(D 0-7)
SLCT
AFXT
BUSY
RD
CE
IN H
STB
IN IT
ACK
PE
ERR
LH
G a te A rra y
E05B 46
CPU
ADDRESS /DATA
DTR RXT TXD
2-18
Transceiver IC
MAX202
REV DTR RXT TXD
S E R IA L I/F
Figure 2-12. Interface Circuit Block Diagram
Rev. A
Page 80

Operating Principles
9
2.3.2 Reset Circuit
The hardware reset circuit for this printer has 2 reset ICs: RST592D (IC22) and RST594E
(IC20). When the +5 v for logic line is unstable dew to power-on, it outputs the reset signal
until the +5 VDC line is stabilized to avoid abnormal operation of the printer. RST592D
monitors the Flash-ROM with the threshold voltage set at approximately 4.2 VDC. It outputs
the reset signal until the +5 VDC line is stabilized to 4.2 VDC. The Flash-ROM recovers
from the reset condition before the CPU and the gate arrays recover from the reset
condition. RST594E monitors the CPU and the gate arrays. The threshold voltage is set at
approximately 4.2 VDC. The reset signals is kept output until the +5 VDC line is 4.2 VDC.
Since the reset signal from the RST592D is sent to the manual reset terminal (MRST) in the
RST594E via the output port of the CPU, the Flash-ROM recovers from the reset condition
before the CPU and the gate arrays recover from the reset condition.
Flash-ROM
CPU
RP
+5V
+5V
Reset IC
PST592D
VOUT
VCC
Reset IC
PST594E
VCC
P61
RST
Figure 2-13. Reset Circuit Block Diagram
MRST
VOUT
System Bus
Gate Array
E05B46
RSTIN
Rev. A
2-1
Page 81

DLQ-3000+
2.3.3 Memory Back-up Circuit
When the printer power is turned off, mainly the following data is backed up in the
EEPROM AT93C66 (IC23).
Paper length, TOF, TEAR OFF, left and right margins, line spacing, pitch
selection, character code, character fonts, high speed print, print direction,
customer code
Interface setting
Values used for controlling the mechanism (condition for all the sensors)
Adjusted values used for controlling the mechanism (i.e. Bi-D adjustment, PG
adjustment and PG α value)
IPD ID for the boot strap program
The first operation date, accumulated print amount, accumulated power-on time
and timing for ribbon replacement
Data to be backed up is transferred by the gate array as serial data. At printer power off, the
gate array outputs the chip select signal ESC from port 126 and data to be backed-up is
sent to the EEPROM from port 124 (EDO) before the power supply voltage completely
drops. The data stored in the EEPROM is read by sending data to the EDI terminal in the
gate array when the printer is turned on. ECK is the clock signal for synchronization.
G a te A rra y
E05B 46
ECK
ECS
EDO
EDI
EEPRO M
AT93C 66
SK
CS
DI
DO
Figure 2-14.Memory Back-up Circuit Block Diagram
2-20
Rev. A
Page 82

Operating Principles
2.3.4 Ribbon Motor Controller/Driver Circuit
A PM-type stepping motor is used for the ribbon motor of this printer. It is driven by 1-1
phase or 2-2 phase excitation mode, based on the selected rotational speed. This motor
rotates in the both forward and backward directions and can stop at any position. Signal
PFA, /PFA, PFB and /PFB are output to drive each phase from the gate array (E05B46) via
the transistor array MP5302. Common voltage change signal (RF_R/H : Run/Hold) is output
from a port of the same gate array. To hold, both faces are driven simultaneously using the
5 VDC line. To switch between Run and Hold is operated by the signals RF_R/H output
from the gate array. While in the color ribbon mode, the printer switches mode between the
copy mode and normal mode according to the signal output from the paper thickness
sensor. See Table 2-11 for the ribbon motor drive term.
Table 2-11. Ribbon Motor Drive Term
Motor type 4 phases / 48-pole / PM-type stepping motor
Power supply voltage
Coil resistance
Drive frequency At color select:460, 600 pps
Excitation mode At color select:2-2 phase
Consumption current
(mA/motor)
Drive mode Constant current uni-polar drive (VPB line)
35 VDC ± 10%
76 Ω ± 10% (at 25°C per phase)
At ribbon feed:320, 640, 770 pps
At ribbon feed:2-2, 1-1 phase
1-fold speed (fabric ribbon):350 - 390
At color select
Copy mode: 550 or less
Normal mode: 400 or less
Gate Array
E05B46
RFA
RFA
RFB
RFB
RF-R/H
Transistor Array
MP5302
B1
B2
B3
B4
VPB(+35V)
EP
BP
C1
C2
C3
C4
+5V
CP
Figure 2-15. Ribbon Motor Driver circuit Block Diagram
RFA
RFA
RFB
RFB
RF COM
Rev. A
2-21
Page 83

DLQ-3000+
2.3.5 PF (Paper Feed) Motor Controller/Driver Circuit
Since this printer uses a hybrid-type stepping motor for the PF motor, it allows the paper to
move to and stop at any position, regardless of the direction for feeding paper. The motor is
driven by 1-2 phase with the open-loop system. Signals for 4 phases (PFA, /PFA, PFB and
/PFB) are output from the gate array E05B46 (IC25) driven by the motor drive IC SLA7024M
(IC6). To hold the motor, 2-2 phase is driven by the hold signal (PFIO) output from the same
gate array. See Table 2-12 which specifies the PF motor terms.
Table 2-12. PF Motor Drive Term
Motor type 4 phases / 200-pole / HB-type stepping motor
Power supply voltage
Coil resistance
Drive frequency
Driving mode Constant current uni-polar drive
Excitation mode 1-2 phase/2-2 phase (RUSH/HOLD)
Paper feed speed 42 m second (6 IPS intermittent drive)
Minimum step 0.07 mm (1/360”)/step
Consumption current
(mA/motor)
35 VDC ± 10%
5.0 Ω ± 10%
1430 − 7200 pps
6 IPS (1-2 phase): 1.3 A/phase
HOLD (2-2 phase): 0.35 A/phase
Gate Array
E05B46
PF A
PF_A
PF B
PF_B
PFIO
Motor Drive IC
SLA7024M(IC6)
VPB(+35V)
A
_A
B
_B
+5V
/TDA
/TDB
VPB(+35V)
+5V
+
GP
INA
IN-A
INB
IN-B
VSA
VSB
PFA
PFB
RSB
RSA
GND A
GND B
GP
Figure 2-16. PF Motor Drive Circuit Block Diagram
PF COM
PF A
PF_A
PF B
PF_B
GP
2-22
Rev. A
Page 84

Operating Principles
3
2.3.6 CR (Carriage) Motor Controller/Driver Circuit
The CR motor for this printer is a hybrid-type stepping motor, which enables the CR to move
to and stop at any position exactly, using both forward and backward rotation. It is
controlled by the open-loop system and driven by 1-2 phase, 2-2 phase or W1-2 phase (for
micro step), depending on the CR speed. This motor is controlled by the signals for 4
phases (PFA, /PFA, PFB and /PFB) output from the gate array E05B46 (IC25) via the drive
IC SLA7026M (IC7). The motor is also controlled by W1-2 phase for micro step. In this
mode, the micro step current set signals (/CASA1, 2 and CASA 1, 2) are output to divide
each set current for phase A and B into 4 steps with the range of 0 to 100 %. These 4 steps
are divided further into 8 steps, which varies depending on the combination with the
continuity timing.
Table 2-13. CR Motor Specification
Motor type 4 phases/200-pole/HB-type stepping motor
Power supply voltage
Coil resistance
Drive frequency 960 to 5760 pps
Consumption current 2-2 phase, 4-fold speed: 2.5 A/phase
Excitation mode 1-2 phase/2-2 phase/W1-2 phase drive
Note) Drive frequency and excitation mode vary with print speed.
35 VDC ± 10% (31.5 − 38.5 VDC)
1.1 Ω ± 10% (at 25°C/phase)
1-2 phase, 2/3-fold speed: 2.0A/ phase
W1-2 phase, 1-fold speed: 1.5A/ phase
Gate Array
E05B46
CR_A
CR_A
CR_B
CR_B
CAMA/B1-6
CAHDA/CAHDB
CASA1/CBSA1
CASA2/CBSA2
VPA(+35V)
+5V
+
GP
CR Motor Drive IC
SLA7026M
/INA
/IN_A
/INB
/IN_B
VSA
VSB
PFA
PFB
RSB
RSA
GND A
GND B
GP
_A
_B
/TDA
/TDB
VPA
A
B
+5V
Interlock
Switch
CR COM
CR COM
CR A
CR_A
CR B
CR_B
GP
Figure 2-17. CR Motor Drive Circuit Block Diagram
Rev. A
2-2
Page 85

DLQ-3000+
Note) : Applicable when the CR moves from 1st to 136th column direction.
Note) : Applicable when the CR moves from 1st to 136th column direction.
Table 2-14. 2-2 Phase Drive
Step No. Phase A Phase /A Phase B Phase /B
1On–On–
2On– –On
3–On–On
4 – On On –
Table 2-15. 1-2 Phase Drive
Step No. Phase A Phase /A Phase B Phase /B
1On–On–
2On–––
3On– –On
4–––On
5–On–On
6–On––
7 – On On –
8––On–
Table 2-16. W1-2 Phase Drive
Step No. Phase A Phase /A Phase B Phase /B
1 On (70.7%) – On (70.7%) –
2 On (43.1%) – On (100%) –
3 – – On (100%) –
4 – On (43.1%) On (100%) –
5 – On (70.7%) On (70.7%) –
6 – On (100%) On (43.1%) –
7 – On (100%) – –
8 – On (100%) – On (43.1%)
9 – On (70.7%) – On (70.7%)
10 – On (43.1%) – On (100%)
11 – – – On (100%)
12 On (43.1%) – – On (100%)
13 On (70.7%) – – On (70.7%)
14 On (100%) – – On (43.1%)
15 On (100%) – – –
16 On (100%) – On (43.1%) –
Note)
1. Applicable when the CR moves from 1st to 136th column direction.
2. Values shown in ( ) are current rates.
2-24
Rev. A
Page 86

Operating Principles
5
2.3.6.1 Bi-D Adjustment Function
Bi-D adjustment is performed to align dots vertically for the Bi-directional printing. This is
accomplished by delaying the print timing pulse on which the carriage moves from the 136th
column to the 1st, using the print timing pulse when the carriage moves from the 1st to
136th column as reference. Since print timing pulse varies according to the carriage speed,
the adjustment should be implemented for each speed mode. For this printer, the
adjustment can be made for the 4-fold, 2-fold and the default speeds.
2.3.6.2 Interlock Function
The mechanical cover open switch is serially connected to the common (VPA) on the CR
motor. When the printer cover is open, the interlock function acts so that the motor does not
rotate.
Rev. A
2-2
Page 87

DLQ-3000+
2.3.7 Printhead Controller/Driver Circuit
The printhead of this printer has 24 head coils (12X2 lines) driven by the constant current
coil driver circuit which consists of 2 transistors (PNP and NPN) and MOSFET. The
printhead is driven by the flat wheel system. The transistors turn on and off the head coil
voltages (VPA, VPB) according to the printing pulse A. MOSFET turns on and off the GP
according to the printing pulse B. If the 2 printing pulses are driven by different printing
timings, the head drive waveform shown bellow appears, since the printing pulse B controls
the drive waveform for the period of time “T” after the printing pulse A was driven. This is to
adjust the head drive waveform to avoid decline in respond speed at continuous printing.
VPA/VPB
(31.5~38.5V )
Print Pulse A
Print Pulse A
Print Pulse B
Head Coil
Print Pulse B
Head Coil Drive
Waveform
T
Figure 2-18. Printhead Drive Waveform
Data from the host computer is expanded into image data (CG data) and latched in the gate
array E05B46. The head data is allocated in the gate array. The latched data is processed
internally in the gate array and output while the signal NHPW/PHPW is active.
Table 2-17. Printhead Controller/Driver Circuit Specification
Head drive voltage
Responding
35 VDC ± 10%
462 seconds (2.16 KHz, normal mode, normal condition)
waveform
Drive current Peak time: 3.3 A (at 5°C, copy 2 mode)
VPA/VPB
CPU
E05B46
ADRESS/
DATA BUS
PHD01-14
HWR
LWR
NHD01-24
PreDriver
(QM3,4)
PreDriver
(IC1-4)
Printhead
Driver
Printhead
(Q6-33)
Printhead
Driver
(QM5-10)
2-26
Control Board
Figure 2-19. Printhead Controller/Driver Circuit Block Diagram
Rev. A
Page 88

Operating Principles
7
2.3.8 Control Panel Circuit
E05A89, the gate array for the control panel I/F, has the LCD driver, LED driver and panel
switch input circuit built in. The serial I/F is used for signal transmission between the control
panel and the main control board. The cover open sensor signal on the logic line is directly
sent to the main control board via the control panel board. If the printer cover is open, an
interlock switch function is activated for safety and puts the printer inactive state.
LC D
LCD Driver
C ontrol Board
DATA
RST
PNLTOM AIN
MAINTOPNL
SCK
+5V
GND
CASE O PEN
G a te A rra y
E05A 89
Switch
LED s
C over O pen Sensor
Figure 2-20. Control Panel Circuit Block Diagram
Rev. A
2-2
Page 89

DLQ-3000+
2.3.9 PG (Platen Gap) Motor Driver Circuit
Since a PM-type stepping motor is used for the PG motor, the motor can
rotate in the both forward and backward direction and stop anywhere. The torque from the
PG motor moves the CR guide shaft to obtain the proper PG. (Refer to Section 2.1.3.) The
motor is driven by 2-2 phase. Signals for 4 phases (PGA, PGAN, PGB and PGBN) are
output from the gate array E05B46 via the transistor array SDC03-V1. To hold the motor,
the hold signal (PGI) is output from the same gate array. Then the transistors 2SC3859
(Q4) and SHA03-V1 (Q3) are turned off to change the drive voltage from PBS (+35V) to the
5 VDC. See Table 2-18 for PG motor specification.
Table 2-18. PG Motor Specification
Motor type 4 phases/8-pole/PM-type stepping motor
Power supply voltage
Coil resistance
Consumption current
(per 1 phase)
Drive frequency 350 pps
Drive mode Constant current uni-polar drive
Excitation mode Uni-polar constant voltage drive, 2-2 phase drive
Rotational direction CW: Widens the PG
35 VDC ± 6%
250 ± 18Ω
Rush: 0.2 A on the average
Hold: 0.02A
CCW: Narrows the PG
PGA
PGB
PGC
PGD
PGCOM
Transistor Array
SDC03-V1
+5V
VPB
Q3
Q4
Figure 2-21. PG Motor Drive Circuit Block Diagram
Gate Array
E05b46
PGA
PGAN
PGB
PGBN
PGI
2-28
Rev. A
Page 90

Operating Principles
9
2.3.10 Paper Thickness Detecting Circuit
PG is detected by the paper thickness sensor which consists of the slit disc and the photoelectric transfer element. See Table 2-19 and Figure 2-22 for the paper thickness sensor
specification and paper thickness sensor circuit block diagram, respectively.
Table 2-19. Paper Thickness Sensor Specification
Detecting method Photo interrupt system
Power supply voltage
Outputs In 2 channels, TTL level
Minimum detecting thickness 0.008 mm
Detecting range 0 to 0.53 mm
+5V
PENCA
5 VDC ± 5%
Gate Array
E05B46
PENCA
PENCB
T
Paper Thickness Sensor
PENCB
PHA
Condition
Figure 2-22. Paper Thickness Sensor Circuit Block Diagram
To determine the paper thickness, the printer monitors the waveforms output from the PG
sensor, as shown in Figure 2-22. “T” output for PHD shows a period of time in which 2chanel pulses PENCA and PENCB change for 180°. The printer counts the different
numbers of pulses output while the printhead moves from PG home position to the platen
surface and surface of the loaded paper to determine the paper thickness which
corresponds to the difference between 2 values. The numbers of pulses are counted in the
following order:
1. After the printer power is turned on, the PG home position is detected.
2. Distance between the printhead and platen surface is measured
While the printhead is moving from the PG home position toward the platen surface,
the waveform stays at a constant level and when that status exceeds for specified
period of time, the printer assumes that the printhead has reached the platen. The
PG motor consequently stops rotating and the numbers of the pulses output during
this operation is counted and the value is fed back to the CPU.
3. The printhead returns to the stand-by position.
4. The distance between the PG home position and loaded paper surface is measured in
the same procedure.
Paper thickness is determined for each paper loaded. The last values for the platen position
and PG before power-off are stored in the EEPROM and are no lost if the printer power is
turned off.
Rev. A
2-2
Page 91

DLQ-3000+
2.3.11 Paper Jam Sensor
This printer is equipped with the paper jam sensor mechanism which consists of the
magnetized roller attached to the same shaft for the sub loading roller assembly and the
sensor (hall element) located beside the rear paper sensor. Having no contact with the
loading drive roller assembly, the magnetized roller rotates independently along paper.
Table 2-20 shows the paper jam sensor specification.
Table 2-20. Paper Jam Specification
Detecting element Hall element
Outputs In 1 channel, TTL level
Power supply voltage
5 VDC ± 5%
Paper Feed D rive R oller Assem bly
Paper
Paper Jam S ensor
(H all Sensor)
CPU
PJAM
M agnetized R oller
PA7
Figure 2-23. Paper Jam Sensor Block Diagram
The CPU reads the signal output directly from the paper jam sensor for each step (1/216
inch / step). If the current signal condition is the same as the previous one, it indicates the
status that the magnetized roller is not rotating, which is considered paper jam. When the
printer detects that condition continuously for the specified numbers of the output signals, it
indicates the paper jam error, and enters non-printing status. The paper jam signal
conditions for normal state and paper jam state are shown in Figure 2-24.
Previously detected condition
C urrently detected condition
N orm al Paper Feeding C ondition
Paper Jam C ondition
Figure 2-24. Paper Jam Sensor Signals
Paper jam detection starts after each paper loading motion regardless of the paper feed
direction. However, the sensor ignores the pulse output while the paper feed direction is
changed.
2-30
Rev. A
Page 92

Operating Principles
2.3.12 Other Sensor Circuits
This printer is equipped with other sensors to monitor printer condition in detailed.
Head thermistor
The head thermistor detects temperatures around the head and sends the information
with the analog signal to the CPU A/C converter using the internal resistance (16.5K Ω).
This information prevents worn-out and shorter life of the drive coils due to over duty
printing, and protects printhead during operation at low temperatures.
+35 VDC monitor
The CPU monitors head drive voltage by detecting the +35 VDC line with the internal A/D
converter. The printer changes the print mode according to the detected change in the
head drive voltage.
Cover open sensor
Cover open sensor, located at the top right of the upper housing, detects the printer
cover’s open/close condition. The output signal is reversed by the digital transistor and
input to the CPU interruption port via the filter circuit which consists of the resistor and
condenser.
Table 2-21. Cover Open Sensor Specification
Detecting method Mechanical switch
Power supply voltage
Detecting mode Cover open : LOW
5 VDC ± 5%
Cover closed : HIGH
Color HP (Home Position) sensor
Color HP sensor uses a photo interrupter system. When the home position for the color
ribbon cartridge is detected, the output signal is pulled up to 10 KΩ, then input to the
CPU port via the filter circuit which consists of the resistance and the condenser.
Table 2-22. Color HP Sensor Specification
Detecting method Photo interrupter system
Output system Open collector system
Resistance to voltage:30V or less
Sink current : 0.3 mA or less
Switch mode In the home position : LOW
Off the home position : HIGH
Note) After the printer is powered on or the cover open is detected, the printer refers to
the switching mode of this sensor.
Rear paper sensor
Rear paper sensor is located on the right side of the paper jam sensor. The output signal
is pulled up by 6.2 KΩ, then input to the CPU port via the filter circuit which consists of
the resistor and the condenser.
Table 2-23. Rear Paper Sensor Specification
Detecting method Mechanical switch (connector switch) system
Rated
current/voltage
Switch mode Paper detected : LOW
0.6 − 1.0mA, 5VDC ± 5%
No paper detected : HIGH
Rev. A
2-31
Page 93

DLQ-3000+
Front paper sensor
Front paper sensor detects TOF position as well as paper presence condition. It uses a
photo interrupter system. However, one end of the detecting lever is mechanically used
to detect the leading edge of the paper, and the other end is to cut in between the photo
interrupter sensor to detect paper. The output signal is pulled up to 10 KΩ, then input to
the CPU port via the filter circuit which consists of the resistor and the condenser.
Table 2-24. Front Paper Sensor Specification
Detecting method Photo interrupter systems
Output system Open collector system
Resistance to voltage:30V or less
Sink current : 0.3 mA or less
Detecting mode Paper detected : LOW
No paper detected : HIGH
Right/left PEW sensor
Right/left sensors are located on the left and right column direction with the CR on the
mask guide in between. They don’t only detect paper but the paper width so as to
determine the right and left margins. The output signal is output to the CPU A/D
converter.
Table 2-25. Right/left PEW Sensor Specification
Detecting method Photo micro sensor system
Output system Collector
Power supply voltage
CR home position sensor
The output signal for this sensor is pulled up to 10K Ω, then input to the CPU A/D
converter via the filter circuit which consists of the resistor and the condenser.
Table 2-26. CR Home Position Sensor Specification
Detecting method Photo coupler system
Output system Open collector system
Power supply voltage
Switching mode In the home position : LOW
Release sensor
The output signal for this sensor is pulled up to 6.2K Ω, then input to the CPU port via
the filter circuit which consists of the resistor and the condenser.
5 VDC ± 5%
Resistance to voltage:30V or less
Sink current : 0.3 mA or less
5 VDC ± 5%
Off the home position :HIGH
2-32
Table 2-27. Release Sensor Specification
Detecting method Leaf switch (mechanical) system
Rated current/voltage
Switch mode Cut sheet mode : Close
0.6 to 1.0mA, 5VDC ± 5%
Continuous paper mode : Open
Paper jam removal mode : Open
Rev. A
Page 94

Operating Principles
3
CSF sensor
CSF sensor uses terminals for the CSF paper quantity sensor. The output signal for this
sensor is pulled up to 10K Ω, then input to the CPU via the filter circuit which consists of
the resistor and the condenser.
Table 2-28. CSF Sensor Switch Mode
Switch mode CSF installed: LOW
No CSF installed: HIGH
CSF paper quantity sensor
CSF sensor, a potentiometer, is not attached to the printer but to the CSF. It monitors
paper quantity in the hopper and send the analog signal to the internal A/D converter of
the CPU.
PGHP (Platen Gap Home Position) sensor
The output signal for this sensor is pulled up to 390Ω, then input to the CPU port via the
filter circuit which consists of the resistor and the condenser.
Table 2-29. PGHP Sensor Specification
Detecting method Micro switch system
Power supply voltage
Switch mode In the home position: LOW
5 VDC ± 5%
Off the home position :HIGH
Rev. A
2-3
Page 95

Chapter 3
Disassembly and Assembly
3.1 Overview .................................................................................................3-1
3.1.1 Tools...............................................................................................3-1
3.1.2 Checks after Repair.......................................................................3-2
3.2 Disassembly and Assembly..................................................................3-3
3.2.1 Printhead Replacement ................................................................3-4
3.2.1.1 Printhead Removal..............................................................3-4
3.2.1.2 Ribbon Mask Removal........................................................3-5
3.2.2 Electrical Board Removal.............................................................3-6
3.2.2.1 Rear Cover Removal...........................................................3-6
3.2.2.2 C210 MAIN Board Removal................................................3-7
3.2.2.3 C124 PSB/PSE Board Removal .........................................3-9
3.2.3 Control Panel Removal...............................................................3-10
3.2.4 Adjust Switch Removal...............................................................3-10
3.2.5 Upper Housing Assembly Removal...........................................3-11
3.2.6 Printer Mechanism Removal......................................................3-12
3.2.6.1 Printer Mechanism Removal.............................................3-13
3.2.6.2 HP (Home Position) Sensor Assembly Removal..............3-14
3.2.6.3 Front Paper Sensor Removal............................................3-14
3.2.6.4 PF Sensor Assembly Removal..........................................3-15
3.2.6.5 PF Motor Assembly Removal............................................3-15
3.2.6.6 CR Motor Assembly Removal ...........................................3-16
3.2.6.7 CS (Color Shift) Motor Assembly Removal.......................3-17
3.2.6.8 Paper Eject Lever Assembly .............................................3-18
3.2.6.9 PG Motor Removal............................................................3-19
3.2.6.10 PG Sensor Removal........................................................3-19
3.2.6.11 PGHP Sensor Removal...................................................3-19
3.2.6.12 CR Removal....................................................................3-20
3.2.6.13 CS Board Assembly Removal.........................................3-23
3.2.6.14 PEW Sensor Assembly Removal....................................3-24
3.2.6.15 Color Ribbon Sensor Removal........................................3-25
Page 96

3.2.6.16 Platen Removal...............................................................3-26
3.2.6.17 Paper Jam Sensor / Rear Paper Sensor Removal..........3-28
3.2.7 Lower Housing Assembly Removal...........................................3-29
3.3 Reloading the Control Program..........................................................3-30
Page 97

Disassembly and Assembly
3.1 Overview
This chapter describes the procedures for disassembling and assembling the printer. Be
sure to read the precaution prior to disassembly and assembly.
WARNING
The temperature of the printhead can be very high during printing. Therefore,
always make sure that the printhead is cool enough to handle it.
Be sure to disconnect the AC power cable from the socket and disconnect the
interface cable prior to disassembling the printer.
CAUTION
Use only specified tools to keep the printer at its optimum condition.
Use only specified lubricants and adhesives.
Be sure to perform any specified adjustments.
Before disassembling, remove all options and accessories such as a sheet guide
and a ribbon cartridge.
3.1.1 Tools
Make sure you use the tools listed in Table 3-1 when disassembling and assembling the
printer.
Table 3-1. Tools
To ols Availability Part No.
Phillips screwdriver #2 Y B743800200
Box dri ver Y B741700200
Thickness gauge set Y B776702201
Round-nosed pliers Y B740400100
Nippers Y B740600100
Tweezers Y B741000100
ET holder Y B74800500
Note) Y: Available in the market.
Be sure to used specified types of screws when assembling the printer.
Table 3-2. Screw Types
Abbreviation Part name
CB Cross-recessed Bind head screw
CBB Cross-recessed Bind head B-tight screw
CBS Cross-recessed Bind head S-tight screw
CBB (P4) Cross-recessed Bind head B-tight sems screw
CP (P4) Cross-recessed Pan head sems screw
CC Cross-recessed Cup head screw
Rev. A
3-1
Page 98

DLQ-3000+
3.1.2 Checks after Repair
The check list shown below contains items to be checked after repairing the printer. Make
sure that you use the list to ensure that printer performance is up to the standard before
returning the printer to the customer.
Table 3-3. Check List after Repairing
Item Location Check points Check
Printing Printhead Are any dots missing?
Version up
Shipping
CR
mechanism Does the CR move smoothly?
Paper feed
mechanism
Paper paths Is paper selection smooth?
PG adjustment
mechanism
Self-test Is the test successful?
On-line test Is the test successful?
Printhead PG adjustment
Print Bi-D adjustment
Paper feed Belt tension adjustment
PG mechanism
Control program
—
—
Is the ribbon mask bent?
Noise Dust, Debris Lubrication
Is color shifting OK?
Is the CR motor overheated?
Is paper fed smoothly?
Noise Dust, Debris Lubrication
Is the PF motor overheated?
Is the platen damaged?
Are tractor teeth OK?
Is there any foreign matter lodged in
the paper paths?
Does the PG move smoothly when
measuring the PG.
Is the PG properly set?
PG motor backlash adjustment
The program version is .
Are the ribbon cartridge and
adjusting tools removed?
Are the accessories came with the
printer all packed?
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
Check Unnecessary
3-2
Rev. A
Page 99

Disassembly and Assembly
3
3.2 Disassembly and Assembly
This section describes how to disassemble the printer. Unless otherwise specified, no
assembly procedures are included, since it is usually performed by reversing the
disassembly procedures. Points to note at disassembling and assembling are described
under the heading WORK POINTS. Adjustments required after assembling are described
under the heading REQUIRED ADJUSTMENTS. Be sure to follow the instructions and perform
any necessary adjustments. The procedure for disassembling the main component is
shown below:
1) Printhead replacement
2) Rear cover removal
3) Electrical board removal
4) Control panel removal
5) Upper housing assembly removal
6) Printer mechanism disassembly
Refer to the exploded diagrams in Appendix for detailed part engagement and location.
Note) Perform “Control program reload” when C210 MAIN and sub boards are replaced.
START
Rear Cover Removal
C ontrol Panel R em oval
Adjust Switch Rem oval
U pper H ousing A ssem bly
Rem oval
Printer M echanism Disassem bly
Printhead R em oval
M ask R ibbon R em oval
Electrical C ircuit B oard
Rem oval
C 210 M AIN B oard
Rem oval
R eloading the C ontrol
Program
C 124 PSB/PSE Board
Rem oval
Low er H ousing A ssem bly
Rem oval
Figure 3-1. Disassembly Flowchart
Rev. A
3-
Page 100

DLQ-3000+
3.2.1 Printhead Replacement
3.2.1.1 Printhead Removal
You can remove the printhead without removing the upper housing assembly or printer
mechanism.
Step 1) Open the printer cover assembly, and remove 2 screws (CBS, 3X12) securing the
printhead.
Step 2) Lift up the printhead a little and release the head FFCs from the clips in the CR
assembly. Then disconnect the FFCs from the printhead.
Step 3) Remove the printhead from the CR assembly.
Head FFC
Printhead
CBS Screws (3X12)
Figure 3-2. Printhead Removal
CAUTION
Perform “Platen gap adjustment” after replacing the printhead.
When replacing the printhead, replace the ribbon mask along with the printhead.
3-4
Rev. A
 Loading...
Loading...