Page 1

Network Guide
Page 2

Copyright and Trademarks
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any
form or by any means, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of
Seiko Epson Corporation. No patent liability is assumed with respect to the use of the information contained herein.
Neither is any liability assumed for damages resulting from the use of the information contained herein.
Neither Seiko Epson Corporation nor its affiliates shall be liable to the purchaser of this product or third parties for
damages, losses, costs, or expenses incurred by purchaser or third parties as a result of: accident, misuse, or
abuse of this product or unauthorized modifications, repairs, or alterations to this product, or (excluding the U.S.)
failure to strictly comply with Seiko Epson Corporation’s operating and maintenance instructions.
Seiko Epson Corporation and its affiliates shall not be liable against any damages or problems arising from the use
of any options or any consumable products other than those designated as Original Epson Products or Epson
Approved Products by Seiko Epson Corporation.
Microsoft
EPSON is a registered trademark and Epson Exceed Your Vision is a registered logomark of Seiko Epson
Corporation.
This product includes software developed by the University of California, Berkeley, and its contributors.
Info-ZIP copyright and license
This is version 2005-Feb-10 of the Info-ZIP copyright and license. The definitive version of this document should
be available at ftp://ftp.info-zip.org/pub/infozip/license.html indefinitely.
Copyright © 1990-2005 Info-ZIP. All rights reserved.
For the purposes of this copyright and license, “Info-ZIP” is defined as the following set of individuals:
®
, Windows®, and Windows Vista® are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Mark Adler, John Bush, Karl Davis, Harald Denker, Jean-Michel Dubois, Jean-loup Gailly, Hunter
Goatley, Ed Gordon, Ian Gorman, Chris Herborth, Dirk Haase, Greg Hartwig, Robert Heath,
Jonathan Hudson, Paul Kienitz, David Kirschbaum, Johnny Lee, Onno van der Linden, Igor
Mandrichenko, Steve P. Miller, Sergio Monesi, Keith Owens, George Petrov, Greg Roelofs, Kai Uwe
Rommel, Steve Salisbury, Dave Smith, Steven M. Schweda, Christian Spieler, Cosmin Truta, Antoine
Verheijen, Paul von Behren, Rich Wales, Mike White
This software is provided “as is,” without warranty of any kind, express or implied. In no event shall Info-ZIP or its
contributors be held liable for any direct, indirect, incidental, special or consequential damages arising out of the
use of or inability to use this software.
Permission is granted to anyone to use this software for any purpose, including commercial applications, and to
alter it and redistribute it freely, subject to the following restrictions:
Copyright and Trademarks 2
Page 3

❏ Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, definition, disclaimer,
and this list of conditions.
❏ Redistributions in binary form (compiled executables) must reproduce the above copyright
notice, definition, disclaimer, and this list of conditions in documentation and/or other materials
provided with the distribution. The sole exception to this condition is redistribution of a standard
UnZipSFX binary (including SFXWiz) as part of a self-extracting archive; that is permitted without
inclusion of this license, as long as the normal SFX banner has not been removed from the binary
or disabled.
❏ Altered versions--including, but not limited to, ports to new operating systems, existing ports with
new graphical interfaces, and dynamic, shared, or static library versions--must be plainly
marked as such and must not be misrepresented as being the original source. Such altered
versions also must not be misrepresented as being Info-ZIP releases--including, but not limited to,
labeling of the altered versions with the names “Info-ZIP” (or any variation thereof, including, but
not limited to, different capitalizations), “Pocket UnZip,” “WiZ” or “MacZip” without the explicit
permission of Info-ZIP. Such altered versions are further prohibited from misrepresentative use of
the Zip-Bugs or Info-ZIP e-mail addresses or of the Info-ZIP URL(s).
❏ Info-ZIP retains the right to use the names “Info-ZIP,” “Zip,” “UnZip,” “UnZipSFX,” “WiZ,” “Pocket
UnZip,” “Pocket Zip,” and “MacZip” for its own source and binary releases.
General Notice: Other product names used herein are for identification purposes only and may be trademarks of
their respective owners. Epson disclaims any and all rights in those marks.
This information is subject to change without notice.
© 2009 Epson America, Inc. 3/09
Copyright and Trademarks 3
Page 4

Contents
Copyright and Trademarks
Safety Instructions
Warnings, Cautions, and Notes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Chapter 1 Introduction
About Your Printer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
About This Guide. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Operating Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Features of the Network Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Network Interface Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Status Light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Network Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
About the Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Terms and Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Chapter 2 How To
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Selecting a Printing Method for Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Printing Method Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Installing Components on Your Computer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
About Installing Components on Your Computer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Windows Vista . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Windows XP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Windows Server 2003 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Windows 2000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Macintosh. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Setting Up the Network Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Connecting the Network Interface to the Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Configuring the Network Interface for Windows. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Configuring the Network Interface for Macintosh . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Installing the Printer Driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
About Installing the Printer Driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Windows Vista . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Windows XP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Contents 4
Page 5

Windows Server 2003 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Windows 2000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Macintosh. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Chapter 3 Network Software
EpsonNet Config for Windows. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
About EpsonNet Config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Installing EpsonNet Config. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Accessing the EpsonNet Config User’s Guide. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
EpsonNet Config for Macintosh . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
About EpsonNet Config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Accessing the EpsonNet Config User’s Guide. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
EpsonNet Print. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
About EpsonNet Print . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Installing EpsonNet Print . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
For Windows Vista/XP/2000/Server 2003 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Configuring the Printer Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Chapter 4 Troubleshooting
General Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Cannot configure the network interface or cannot print from the network. . . . . . . . . . . 54
Cannot print even if you have assigned the IP address to the computer
and the printer.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Unable to start EpsonNet Config. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
The message “EpsonNet Config cannot be used because no network is installed.”
appears when you start EpsonNet Config. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
The message “Could not complete communicating configuration data”
appears when you send settings to the network interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
The Model Name and IP Address do not appear in the EpsonNet Config dialog box. . 55
Problems Specific to Your Network Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Windows 2000 Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Printing a Network Status Sheet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Contents 5
Page 6

Chapter 5 Tips for Administrators
Setting an IP Address on the Printer’s Control Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Network Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Universal Plug and Play. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Uninstalling Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Windows Vista . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Windows 2000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Windows XP/Server 2003 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Mac OS X. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Index
Contents 6
Page 7

Safety Instructions
Warnings, Cautions, and Notes
Warnings
must be followed carefully to avoid bodily injury.
w
Cautions
must be observed to avoid damage to your equipment.
c
Notes
contain important information and useful tips on the operation of your printer.
Safety Instructions 7
Page 8

Chapter 1
Introduction
About Your Printer
Your printer has a built-in Ethernet interface and can connect anywhere on your network
using 10Base-T or 100Base-TX. The built-in Ethernet interface, which is called the network
interface in this manual, automatically selects the correct standard when it connects to a
network. In addition, it supports and automatically selects the IEEE 802.2, IEEE 802.3,
Ethernet II, and Ethernet SNAP network protocols.
Because the network interface supports multiple protocols and automatically detects
protocols on your network, you can print from Microsoft
applications.
Use the Software CD-ROM that came with the printer to easily configure the network
interface for use on the TCP/IP network and install the printer driver.
If you want to configure the network interface for protocols such as TCP/IP, AppleTalk®,
and SNMP, use EpsonNet Config, the configuration utility provided with your product, to
quickly and easily configure the network interface to use those protocols.
Note:
The EpsonNet Config utility configures the network interface to work only with protocols that exist
on your network. This does not imply that you can use all of the above-mentioned protocols on your
network or operating system. The protocols that the network interface can use may vary depending
on the operating system and the network configuration.
®
Windows® and Mac OS® X
About This Guide
This Network Guide contains information about using the printer on a network. It includes
how to set up the network interface, install the configuration software, and modify network
settings of your printer and computers.
For information about your printer, see your User’s Guide.
Note:
❏ To read the online guide, you must have Adobe
on your computer.
❏ This guide is written for network administrators, and many of the steps included here require
detailed network knowledge and administrator rights.
®
Reader® or Adobe Acrobat® Reader installed
Introduction 8
Page 9
❏ The term “network administrator” refers to the person responsible for maintaining the network.
“Administrator” is synonymous with “Supervisor” in this guide.
❏ The term “network interface” refers to the built-in Ethernet interface of the printer in this guide.
Operating Environment
The network interface supports the following environments.
OS Protocol
Windows Vista
Windows XP (Home,
Professional)
Windows 2000 (Professional)
Windows Server 2003
Mac OS X 10.5 Bonjour
®
TCP/IP (using LPR, Standard
TCP/IP Port, or EpsonNet
Print)
TCP/IP
Mac OS X 10.4 Bonjour
TCP/IP
AppleTalk
Mac OS X 10.3.9 Rendezvous
TCP/IP
AppleTalk
Features of the Network Interface
❏ Connects your Epson printer using a built-in Ethernet interface, which is called the
network interface in this manual, to the network.
❏ Supports multiple protocols.
❏ Supports both 10Base-T and 100Base-TX.
❏ Supports DHCP.
❏ Supports Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) that assigns an IP address
automatically to the network interface even if there is no DHCP server on the network.
❏ Supports the Dynamic DNS function.
Introduction 9
Page 10
❏ Supports SNMP and MIB.
❏ Supports SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol).
❏ Supports Bonjour on Mac OS X 10.4 or later.
❏ Supports Rendezvous on Mac OS X 10.3.9.
Network Interface Operation
Status Light
The indicator lights provide you with important information on the operations of the network
interface.
Status light Data light Network Status
Green Green Ready (10 M link)
Green Green (Flashing) Receiving packets (10 M link)
Orange Green Ready (100 M link)
Orange Green (Flashing) Receiving packets (100 M link)
Status light
Data light
The status light on the left side indicates whether the network interface is connected to
10Base-T or 100Base-TX. The light is orange when the connection is 100Base-TX, green
when the connection is 10Base-T.
The data light on the right side flashes when the host interface receives data.
If the light on the left side is solid green and the light on the right side is off, the connection
is disconnected.
Network Connector
RJ-45 connector: This connector is used to connect an Ethernet cable to a network. You
can use this cable for both 10Base-T and 100Base-TX.
Introduction 10
Page 11

Caution:
You must use a category-5 shielded twisted-pair cable to connect the network interface to a
c
network.
About the Software
The Software CD-ROM provided with your printer includes the following network software.
Note:
The software provided varies depending on your printer model.
❏ EpsonNet Config is a Windows-based configuration utility for administrators that allows
you to configure the network interface for various protocols such as TCP/IP and SNMP.
See “EpsonNet Config for Windows” on page 43.
❏ EpsonNet Config for Macintosh is a Macintosh-based configuration utility for
administrators that allows you to configure the network interface for TCP/IP, AppleTalk,
and IPP. See “EpsonNet Config for Macintosh” on page 44.
❏ EpsonNet Print is a utility that enables TCP/IP printing for Windows. (Windows
Vista/XP/2000/Server 2003 also support OS standard LPR printing.) See “EpsonNet
Print” on page 45.
Terms and Concepts
Configuration -- a prepared set of conditions for proper operation of a device. Configuring
the network interface is to prepare it to work with protocols available on a network.
DHCP -- a dynamic host configuration protocol. It is a protocol that assigns dynamic IP
addresses to devices on a network.
ftp -- a TCP/IP application protocol for file transfer
lpd -- a TCP/IP remote printing protocol application
Print queue -- a location where a print job is stored as a file, until the network interface
sends the job to the assigned printer
Protocol -- a rule that controls how data or information is exchanged through a network.
Computers and software cannot communicate with each other using different protocols.
TCP/IP -- Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, a layer of protocols that
provides communication between nodes on a network
Introduction 11
Page 12

Chapter 2
How To
Overview
This section describes the general procedure on how to set up the network interface for
use on a network.
1. Check the network interface operation.
Check the functions and operations of the network interface, such as status lights and
RJ-45 connector. See “Network Interface Operation” on page 10 for details.
2. Select a printing method.
Select a printing method appropriate for your network environment and operating
system. If you are not sure, see “Selecting a Printing Method for Windows” on page 13
for details.
3. Install the necessary components on your computer.
Make sure the necessary components (such as TCP/IP) are installed on the computer,
and network settings (such as IP address, subnet mask, etc.) of the computer is set.
See “About Installing Components on Your Computer” on page 14 for details.
4. Connect the network interface to the network.
Connect the network interface to the network. See “Connecting the Network Interface
to the Network” on page 21 for details.
5. Configure the network interface and install the printer driver on all the computers that
will use the printer.
See “Configuring the Network Interface for Windows” on page 22 or “Configuring the
Network Interface for Macintosh” on page 25 for details.
6. If necessary, configure the network settings of the network interface using EpsonNet
Config.
Configure the network interface for TCP/IP, MS Network, etc. using EpsonNet Config.
See “About EpsonNet Config” on page 43.
How To 12
Page 13

Selecting a Printing Method for Windows
Check if there is a Windows Vista/XP/Server 2003/2000 print server on your network, and
then use the suggestions below.
If a print server exists, set the printer to connect with LPR on the server and turn it into a
shared printer. Your clients can then print to this shared printer.
If no Windows print server exists, we recommend TCP/IP printing via LPR. This is the
method to use when you connect the printer to your network through the printer’s Ethernet
port. See “Windows Vista” on page 14, “Windows XP” on page 16, “Windows Server 2003”
on page 17, or “Windows 2000” on page 19.
Printing Method Features
This section describes features of the printing methods available for you to choose.
LPR (TCP/IP) printing for Ethernet connection
Advantages
❏ No computer as a network interface is required.
❏ No special utility for Windows Vista/XP/2000/Server 2003 is required.
❏ You can see the printer status using EPSON Status Monitor.
❏ For Windows Vista/XP/2000/Server 2003, you can create a print log using the event
viewer.
❏ You can print via a router.
Disadvantages
❏ You need to set up TCP/IP.
Microsoft Network Shared printing
Advantages
❏ Easy to set up.
❏ No computer as a network interface is required.
How To 13
Page 14

❏ No special print utility is required.
Disadvantages
❏ Epson Status Monitor cannot be used.
❏ You cannot print via a router.
❏ It takes longer to start printing because more time is required to search for a network
printer.
Note:
Instructions for setting up Microsoft network shared printing are included in the printer User’s
Guide.
Installing Components on Your Computer
About Installing Components on Your Computer
Before configuring the network interface and printing from the computer, you need to install
the necessary components (such as TCP/IP) and assign an IP address and subnet mask
for your computer, depending on the printing method you want to use. See the section in
this chapter appropriate for your operating system.
Note:
❏ The Windows operating system CD-ROM may be required during the installation.
❏ When using TCP/IP for printing, you need to set the IP address, the subnet mask, and the
default gateway of the computer. These may be set automatically if your network uses DHCP.
Windows Vista
For Windows Vista, use the following procedure to install the necessary components.
1. Click Start, click Control Panel, and then click View network status and tasks or
double-click Network and Sharing Center.
2. Click View Status, and then click the Properties button.
Note:
If the User Account Control screen appears, click the Continue button.
How To 14
Page 15

3. Check if the following necessary components are in the list. If they are already installed,
go to the next chapter.
The following table lists the components required for configuring the network interface
with EpsonNet Config.
EpsonNet Config’s setting screens Necessary components
TCP/IP, SNMP (IP trap) Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
MS Network Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
The following table lists the components required for network printing.
Printing method Necessary components
LPR or Internet printing Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
4. If the necessary components are not in the list, click Install to install them, as described
below.
For LPR or Internet printing:
Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is installed by default. You cannot add or delete it.
5. For LPR or Internet printing:
Double-click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) on the Local Area Connection
Properties dialog box to open the Internet Protocols Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties
dialog box. Set the IP address and so on if necessary, then click OK.
6. Restart the computer.
How To 15
Page 16
The necessary components are now installed. Go to the section “Connecting the Network
Interface to the Network” on page 21.
Windows XP
For Windows XP, use the following procedure to install the necessary components.
1. Click Start, highlight Control Panel, and then click Network and Internet
Connections. Select Network Connections.
2. Under LAN or High-Speed Internet, click the Local Area Connection icon.
3. Under Network Tasks, click Change settings of this connection.
4. Check if the following necessary components are in the list. If they are already installed,
go to the next chapter.
The following table lists the components required for configuring the network interface
with EpsonNet Config.
EpsonNet Config’s setting screens Necessary components
TCP/IP, SNMP (IP trap) Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
MS Network Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
How To 16
Page 17
The following table lists the components required for network printing.
Printing method Necessary components
LPR Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Microsoft Network Shared printing TCP/IP client for Microsoft Networks
5. If the necessary components are not in the list, click Install to install them, as described
below.
For LPR:
Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is installed by default. You cannot add or delete it.
For Microsoft Network Shared printing:
Select Client and then click Add. Select Client for Microsoft Networks and then click
OK.
6. For LPR or Microsoft Network Shared printing:
Double-click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) on the Local Area Connection Properties
dialog box to open the Internet Protocols (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box. Set the IP
address and so on if necessary, then click OK.
7. Restart the computer.
The necessary components are now installed. Go to the section “Connecting the Network
Interface to the Network” on page 21.
Windows Server 2003
For Windows Server 2003, use the following procedure to install the necessary
components.
1. Click Start, point to Control Panel, and then select Network Connections. Click
Local Area Connections.
2. Click the Properties button.
How To 17
Page 18

3. Check if the following necessary components are in the list. If they are already installed,
go to the next chapter.
The following table lists the components required for configuring the network interface
with EpsonNet Config.
EpsonNet Config’s setting screens Necessary components
TCP/IP, SNMP (IP trap) Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
MS Network Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
The following table lists the components required for network printing.
Printing method Necessary components
LPR or Internet printing Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Microsoft Network Shared printing TCP/IP
Client for Microsoft Networks
4. If the necessary components are not in the list, click Install to install them, as described
below.
For LPR:
Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is installed by default. You cannot add or delete it.
For Microsoft Network Shared printing:
Select Client and then click Add. Select Client for Microsoft Networks and then click
OK.
How To 18
Page 19
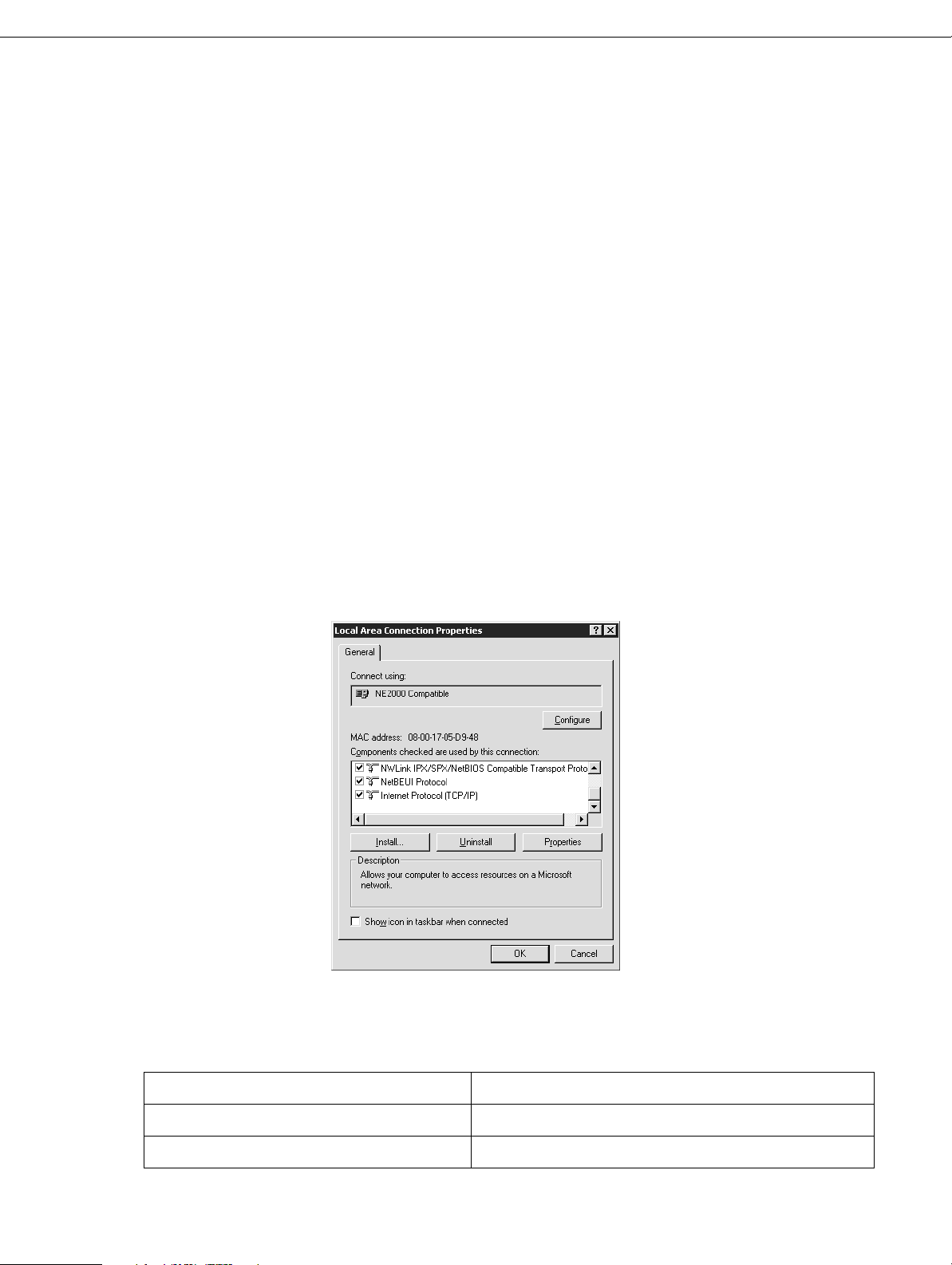
5. For LPR or Microsoft Network Shared printing:
Double-click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) on the Local Area Connection Properties
dialog box to open the Internet Protocols (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box. Set the IP
address and so on if necessary, then click OK.
6. Restart the computer.
The necessary components are now installed. Go to the section “Connecting the Network
Interface to the Network” on page 21.
Windows 2000
For Windows 2000, use the following procedure to install the necessary components.
1. Click Start, point to Settings, and then select Network and Dial-up Connections. The
Network and Dial-up Connections screen appears.
2. Right-click the desired network connection and then select Properties.
3. Check if the following necessary components are in the list. If they are already installed,
go to the next chapter.
The following table lists the components required for configuring the network interface
with EpsonNet Config.
EpsonNet Config’s setting screens Necessary components
TCP/IP or SNMP (IP trap) Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
MS Network Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
How To 19
Page 20

The following table lists the components required for network printing.
Printing method Necessary components
LPR Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Microsoft Network Shared printing Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Client for Microsoft Networks
4. If the necessary components are not in the list, click Install to install them, as described
below.
For LPR:
Select Protocol and then click Add. In the Select Network Protocol dialog box, select
Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and then click OK.
For Microsoft Network Shared printing:
To use Internet Protocol, see the description described earlier to install Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP).
Select Client and then click Add. Select Client for Microsoft Networks and then click
OK.
5. For LPR or Microsoft Network Shared printing:
Double-click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) on the Configuration menu to open the
TCP/IP Properties dialog box. Set the IP address and so on if necessary, then click OK.
6. Restart the computer.
The necessary components are now installed. Go to the section “Connecting the Network
Interface to the Network” on page 21.
Macintosh
To assign an IP address, subnet mask, etc. to your Macintosh, follow the steps below.
1. From the Apple menu, select System Preferences.
2. Open the Network control panel. Click the TCP/IP tab.
Note:
For Mac OS X 10.5, select Ethernet as the connecting method on the Network control panel,
select the method to assign the IP address from the Configure menu, and then assign the IP
address.
3. Select Built-in Ethernet from the Show pull-down menu.
4. Assign an IP address and other settings if necessary.
How To 20
Page 21

5. Click the Apply Now button to save any changes.
Go to the next section.
Setting Up the Network Interface
Connecting the Network Interface to the Network
Follow the instructions below to connect the network interface to the network. For more
information, see the Start Here sheet that came with your printer.
1. Make sure that your printer is turned off.
2. Connect one end of the network cable to the RJ-45 connector on the network interface,
and the other end to the network.
Caution:
❏ You must use a Category 5 shielded twisted-pair cable to connect the network
c
interface to prevent malfunction.
❏ Do not connect or disconnect the network cable when the printer is on.
❏ Do not connect the network interface and the computer directly. Be sure to use a HUB
to connect the network interface to the network.
Note:
You can use both 10Base-T and 100Base-TX. When you print a lot of data, we recommend you
use a higher speed with light network traffic.
3. Turn on your printer. After the status lights go off, print a network status sheet.
Caution:
After turning off the printer, wait until the status lights go off before turning it back on;
c
otherwise the network interface may not work correctly.
Note for Mac OS X 10.4 or later:
Since the printer supports Bonjour/Rendezvous and is on by default, you can use the printer on
a network just by connecting it to the network. If you want to disable the Bonjour/Rendezvous
setting, use the printer’s control panel. See “Setting an IP Address on the Printer’s Control
Panel” on page 39 for details.
Now, you can configure the network interface to use on the TCP/IP network and also install
the printer driver. See the next section.
How To 21
Page 22

Configuring the Network Interface for Windows
Configure the network interface for use on the TCP/IP network and install the printer driver
on your computer.
1. Insert the Software CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive.
With Windows Vista, if you see the AutoPlay window, click Run Epsetup.exe. When
you see the User Account screen, click Continue.
2. Click Easy Install.
3. Select Network.
Note:
If your printer is connected to your computer with a USB cable, select Local. Then follow the
on-screen instructions.
4. Click Install and follow the on-screen instructions.
Note:
If the Windows Security Alert window appears, click the Unblock button; otherwise the printer
is not listed on the screen of EpsonNet EasyInstall.
5. Select the printer and then click the Next button.
How To 22
Page 23

6. If you see the following screen, you can select a method for specifying the IP address.
If you select Automatic, DHCP becomes available and assigns an IP address
automatically. If you want to set the IP address manually, select Manual and then enter
the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway. Click the Next button.
Note:
It’s a good idea to write down the IP address for use when you set up additional computers.
7. Confirm the settings you have made, and then click the Next button.
8. Select the printer with its IP address you have just set, and then click the Next button
to install the printer driver.
How To 23
Page 24

9. Enter the printer name. If you want to print a test page, select the Print test page check
box. Click the Next button.
Note:
If the Windows Security Alert window appears, click the Unblock button.
10.Select the default printer, and then click the Next button.
11.Click the Finish button, and then follow the on-screen instructions to complete the
installation.
Now you can use the printer on the TCP/IP network.
How To 24
Page 25

Configuring the Network Interface for Macintosh
Configure the network interface for use on the TCP/IP network and install the printer driver
on your computer.
1. Insert the Software CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive.
The EPSON folder opens automatically.
2. Double-click the Mac OS X icon in the EPSON folder.
3. Make sure that all applications are closed, and then click Easy Install.
4. Select Network.
Note:
If your printer is connected to your computer with a USB cable, select Local, and then follow
the on-screen instructions.
5. Click Install, and then follow the on-screen instructions.
6. Select the printer and then click the Next button.
How To 25
Page 26

7. Select a method for specifying the IP address. If you select Automatic, DHCP
becomes available and assigns an IP address automatically. If you want to set the IP
address manually, select Manual and then enter the IP address, subnet mask, and
default gateway. Click the Next button.
Note:
It’s a good idea to write down the IP address for use when you set up additional computers.
8. Check the settings you have made, and then click the Next button.
How To 26
Page 27

9. Click the Finish button, and then follow the on-screen instructions to complete the
installation.
Follow the steps below to set up the printer.
Setting Up the Printer
Mac OS X 10.5
1. Open System Preferences.
2. Open Print & Fax.
3. Click the + button to add a new printer.
4. Select the desired printer model that is connected with Bonjour.
Note:
If your printer is not displayed with the desired connection, click More Printers, select the
desired connection from the drop-down list, and then select the printer model.
5. Click Add.
Now you can use the printer on the TCP/IP network.
Note:
If your product supports the scanning function, see the product’s User’s Guide to make the
settings.
How To 27
Page 28

Mac OS X 10.4 or below
1. Open the Applications folder.
2. Open the Utilities folder.
3. Open Printer Setup Utility, and then click Add.
4. For Mac OS X 10.4, select the printer model that is connected with Bonjour.
For Mac OS X 10.3, select Rendezvous from the drop-down list, and then select the
printer model from the list.
Note:
For Mac OS X 10.4, if your printer is not displayed with the desired connection, click More
Printers, select the desired connection from the drop-down list, and then select the printer
model.
5. Click Add.
Now you can use the printer on the TCP/IP network.
Installing the Printer Driver
About Installing the Printer Driver
To print to the network printer, you need to install the printer driver on all your network
computers. See the section in this chapter appropriate for your operating system.
Windows Vista
For Windows Vista, the printer driver installation procedure differs depending on the
printing method you prefer. Epson recommends printing with EpsonNet Print. See “For
Windows Vista/XP/2000/Server 2003” on page 46.
LPR printing
Note:
If you are using EpsonNet Print, the setup procedure is different. See “About EpsonNet Print” on
page 45 for details.
1. Click Start, Control Panel, and then Printer.
2. Click Add a printer to start the Add Printer wizard.
How To 28
Page 29

3. Click Add a local printer.
4. Select the Create a new port radio button, and then select Standard TCP/IP Port from
the list. Then click Next.
How To 29
Page 30

5. Enter the IP address of the network interface and then click Next. If you don’t know the
IP address, you can print a network status sheet. See “Printing a Network Status Sheet”
on page 56.
6. If an error occurs, the following dialog box appears. Select the Standard radio button
and then select EPSON Network Printer. Click Next.
7. Click Finish.
8. See the following section to install the printer driver.
Installing the printer driver
1. Insert the Software CD-ROM shipped with the printer.
2. Close the Epson Software Installation screen if it appears.
3. Click the Have Disk button. The Install From Disk dialog box appears.
4. Click Browse.
How To 30
Page 31

5. Select the CD-ROM drive for Drives, and double-click the WINVISTA_XP_2K folder.
Click Open.
6. Click OK in the Install From Disk dialog box.
7. Select the model name of the device, and then click Next.
Note:
If the Add Printer wizard prompts you to select either Keep existing driver or Replace existing
driver, be sure to select the Replace existing driver radio button.
8. Click Finish and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the setup.
Windows XP
For Windows XP, the printer driver installation procedure differs depending on the printing
method you prefer. Epson recommends printing with EpsonNet Print. See “For Windows
Vista/XP/2000/Server 2003” on page 46.
LPR printing
Note:
If you are using EpsonNet Print, the setup procedure is different. See “About EpsonNet Print” on
page 45 for details.
1. Click Start, click Control Panel, click Printers and Other Hardware, and then click
Printers and Faxes.
2. Under Printer Tasks, click Add a printer to start the Add Printer wizard, and then click
Next.
3. Click Local printer attached to this computer, clear the Automatically detect and
install my Plug and Play printer check box, and then click Next.
How To 31
Page 32

Note:
You must clear the Automatically detect and install my Plug and Play printer check box
because the printer is attached directly to the network, not to a Windows XP computer.
4. Select the Create a new port radio button, and then select Standard TCP/IP Port from
the list. Then click Next.
How To 32
Page 33

5. Enter the IP address of the network interface and then click Next. If you don’t know the
IP address, you can print a network status sheet. See “Printing a Network Status Sheet”
on page 56.
6. If an error occurs, the following dialog box appears. Select the Standard radio button
and then select EPSON Network Printer. Click Next.
7. Click Finish.
8. See the following section to install the printer driver.
Installing the printer driver
1. Insert the Software CD-ROM shipped with the printer.
2. Close the Software Installation screen if it appears.
3. Click the Have Disk button. The Install From Disk dialog box appears.
How To 33
Page 34

4. Click Browse.
5. Select the CD-ROM drive for Drives, and double-click the WINVISTA_XP_2K or
WINXP_2K folder. Click Open.
6. Click OK in the Install From Disk dialog box.
7. Select the model name of the printer, and then click Next.
Note:
If the Add Printer wizard prompts you to select either Keep existing driver or Replace existing
driver, be sure to select the Replace existing driver radio button.
8. Click Finish and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the setup.
Windows Server 2003
For Windows Server 2003, the printer driver installation procedure differs depending on the
printing method you prefer. Epson recommends printing with EpsonNet Print. See “For
Windows Vista/XP/2000/Server 2003” on page 46.
LPR printing
Note:
If you are using EpsonNet Print, the setup procedure is different. See “About EpsonNet Print” on
page 45 for details.
1. Click Start, and then select Printers and Faxes.
2. Double-click the Add Printer icon to start the Add Printer wizard, and then click Next.
3. Click Local printer attached to this computer, clear the Automatically detect and
install my Plug and Play printer check box, and then click Next.
How To 34
Page 35

Note:
You must clear the Automatically detect and install my Plug and Play printer check box
because the printer is attached directly to the network, not to a computer.
4. Select the Create a new port radio button, and then select Standard TCP/IP Port from
the list. Click Next.
5. When Add Standard TCP/IP Printer Port Wizard dialog box appears, click Next.
How To 35
Page 36

6. Enter the IP address of the network interface and then click Next. If you don’t know the
IP address, you can print a network status sheet. See “Printing a Network Status Sheet”
on page 56.
7. If an error occurs, the following dialog box appears. Select the Standard radio button
and then select EPSON Network Printer. Click Next.
8. Click Finish.
9. See the following section to install the printer driver.
Installing the printer driver
1. Insert the Software CD-ROM shipped with the printer.
2. Close the Software Installation screen if it appears.
3. Click the Have Disk button. The Install From Disk dialog box appears.
How To 36
Page 37

4. Click Browse.
5. Select the CD-ROM drive for Drives, and double-click the WINVISTA_XP_2K,
WINXP_2K, or WIN2000 folder. Click Open.
6. Click OK in the Install From Disk dialog box.
7. Select the model name of the printer, and then click Next.
Note:
If the Add Printer wizard prompts you to select either Keep existing driver or Replace existing
driver, be sure to select the Replace existing driver radio button.
8. Click Finish and then follow the on-screen instructions to complete the setup.
Windows 2000
For Windows 2000, the printer driver installation procedure differs depending on the
printing method you prefer. Epson recommends printing with EpsonNet Print. See “For
Windows Vista/XP/2000/Server 2003” on page 46.
LPR printing
Note:
If you are using EpsonNet Print, the setup procedure is different. See “About EpsonNet Print” on
page 45 for details.
1. Click Start, point to Settings, and then select Printers.
2. Double-click Add Printer to start the Add Printer wizard, and then click Next.
3. Click Local printer, clear the Automatically detect and install my Plug and Play
printer check box, and then click Next.
How To 37
Page 38

Note:
You must clear the Automatically detect and install my Plug and Play printer check box
because the printer is attached directly to the network, not to a Windows 2000 computer.
4. Select the Create a new port radio button, and then select Standard TCP/IP Port from
the list. Then click Next.
How To 38
Page 39

5. Enter the IP address of the network interface and then click Next. If you don’t know the
IP address, you can print a network status sheet. See “Printing a Network Status Sheet”
on page 56.
6. If an error occurs, the following dialog box appears. Select the Standard radio button
and then select EPSON Network Printer. Click Next.
7. Click Finish.
8. See the following section to install the printer driver.
Installing the printer driver
1. Insert the Software CD-ROM shipped with the printer.
2. Close the Software Installation screen if it appears.
3. Click the Have Disk button. The Install From Disk dialog box appears.
How To 39
Page 40

4. Click Browse.
5. Select the CD-ROM drive and double-click the ENGLISH\WINVISTA_XP_2K, or
WINVISTA_XP folder. Click Open.
6. Click OK in the Install From Disk dialog box.
7. Select the model name of the printer, and then click Next.
Note:
If the Add Printer wizard prompts you to select either Keep existing driver or Replace existing
driver, be sure to select the Replace existing driver radio button.
8. Click Finish and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the setup.
Macintosh
Follow the steps below to set up a printer.
Note:
Make sure that the printer driver is installed on your Macintosh before following the steps below.
See the manual shipped with your printer for instructions on how to install the printer driver.
Mac OS X 10.5
Bonjour printing
1. Open System Preferences.
2. Open Print & Fax.
3. Click the + button to add a new printer.
4. Select the desired printer model that is connected with Bonjour.
5. Click Add.
TCP/IP printing
1. Open System Preferences.
2. Open Print & Fax.
3. Click the + button to add a new printer.
How To 40
Page 41

4. Click More Printers, select EPSON TCP/IP from the drop-down list, and then select the
printer model.
5. Click Add.
Mac OS X 10.4 or below
Bonjour/Rendezvous printing
1. Open the Applications folder.
2. Open the Utilities folder.
3. Open Printer Setup Utility, and then click Add.
4. For Mac OS X 10.4, select the printer model that is connected with Bonjour.
For Mac OS X 10.3, select Rendezvous from the drop-down list, and then select the
printer model from the list.
5. Click Add.
TCP/IP printing
1. Open the Applications folder.
2. Open the Utilities folder.
3. Open Printer Setup Utility, and then click Add.
4. For Mac OS X 10.4, click More Printers, select EPSON TCP/IP from the drop-down
list, and then select the printer model.
For Mac OS X 10.3, select EPSON TCP/IP from the drop-down list, and then select the
printer model from the list.
5. Click Add.
AppleTalk printing
1. Open the Applications folder.
2. Open the Utilities folder.
3. Open Printer Setup Utility, and then click Add.
How To 41
Page 42

4. For Mac OS X 10.4, click More Printers, select EPSON Apple Talk from the drop-
down list, select the zone, and then select the printer model.
For Mac OS X 10.3, select EPSON Apple Talk from the drop-down list, select the zone,
and then select the printer model.
5. Click Add.
How To 42
Page 43

Chapter 3
Network Software
This chapter explains how to use the network software provided with your printer.
Note:
The software provided varies depending on your printer model.
EpsonNet Config for Windows
About EpsonNet Config
EpsonNet Config is a Windows-based configuration software for administrators to
configure the network interface for TCP/IP, MS Network, and SNMP.
Note:
Be sure to use EpsonNet Config included on the Software CD-ROM shipped with this product.
System Requirements
The following table lists the system requirements of EpsonNet Config.
Operating systems Windows Vista
Windows XP Professional/Home Edition
Windows Server 2003
Windows 2000 Server/Professional
Hard disk drive space 49 MB
Installing EpsonNet Config
Follow the steps below to install EpsonNet Config on your computer to configure the
network interface.
Note:
If you add or delete protocols or services from your operating system after installing EpsonNet
Config, EpsonNet Config may not work correctly. If this happens, uninstall EpsonNet Config and
then install it again.
Network Software 43
Page 44

1. Make sure all the applications are closed, then insert the Software CD-ROM in the
CD-ROM drive.
2. Click Install Network Utility.
3. Click the icon located next to EpsonNet Config.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
Note:
If the Windows Security Alert window appears after you start EpsonNet Config, click the
Unblock button; otherwise the devices are not listed on the screen of EpsonNet Config.
Accessing the EpsonNet Config User’s Guide
The EpsonNet Config User’s Guide contains detailed information on EpsonNet Config.
Follow the steps below to access the EpsonNet Config User’s Guide.
1. Click Start, point to Programs or All Programs, select EpsonNet, and then select
EpsonNet Config V2. Click EpsonNet Config to start it.
2. From the Help menu, select EpsonNet Config Help.
The EpsonNet Config User’s Guide appears. By clicking the links on the left side of the
screen, you can get information on using EpsonNet Config.
EpsonNet Config for Macintosh
About EpsonNet Config
EpsonNet Config allows administrators to configure the network interface.
Note:
Be sure to use EpsonNet Config included on the software CD shipped with your printer.
Accessing the EpsonNet Config User’s Guide
The EpsonNet Config User’s Guide contains detailed information on EpsonNet Config.
Follow the steps below to access the EpsonNet Config User’s Guide.
Network Software 44
Page 45

1. Double-click the Macintosh HD icon. In the Applications folder, double-click the
EpsonNet folder, and then double-click the EpsonNet Config folder. Finally,
double-click the EpsonNet Config icon.
2. From the Help menu, select EpsonNet Config Help.
The EpsonNet Config User’s Guide appears. Click the links on the left side of the
screen to get information on using EpsonNet Config.
EpsonNet Print
About EpsonNet Print
EpsonNet Print is a utility program that provides peer to peer printing to Epson printers on
the TCP/IP network.
By using EpsonNet Print, you can find a printer located in the same segment or beyond a
router. You can select LPR standard printing, LPR enhanced printing, or High-speed
printing.
System Requirements
The following table lists the system requirements of EpsonNet Print.
Operating systems Windows Vista
Windows XP Home Edition/Professional (with Service Pack 1 or
higher)
Windows Server 2003
Windows 2000 (with Service Pack 4 or higher)
CPU Pentium
Memory 64 MB or more
Hard disk space 20 MB or more
Display 800 × 600 screen resolution, 256 color or more
®
II 400 MHz or better recommended
Network Software 45
Page 46

Installing EpsonNet Print
Follow the steps below to install EpsonNet Print. Be sure to install it on a computer
connected to the network.
Note:
If EpsonNet Direct Print (the older version of EpsonNet Print) is already installed on your computer,
you need to uninstall it before installing EpsonNet Print (the installation program will lead you
through uninstalling EpsonNet Direct Print 2).
1. Make sure all the applications are closed, then insert the Software CD-ROM in the
CD-ROM drive.
2. Click Install Network Utility.
3. Click the icon located next to EpsonNet Print.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
Your computer is now set up to print using LPR via EpsonNet Print. See the next section
to set up your printer.
For Windows Vista/XP/2000/Server 2003
Follow the steps below to add a port using the Add Printer Wizard.
❏ If you want to add a port for a printer with its IP address assigned automatically by the
DHCP server or router, see “Adding a port for a printer assigned with a dynamic IP
address,” below.
❏ If you want to add a port for a printer with its IP address assigned manually, see “Adding
a port for a printer assigned with a static IP address” on page 50.
Note:
❏ Be sure that the computer is connected to the network and TCP/IP is correctly set up.
❏ Be sure that the target Epson printer driver is installed on the computer.
❏ A valid IP address must be assigned to the printer.
Network Software 46
Page 47

Adding a port for a printer assigned with a dynamic IP address
1. For Windows Vista: Click Start, Control Panel, and then Printer. Click Add a printer
to start the Add Printer wizard.
For Windows XP: Click Start and then Printers and Faxes. Under Printer Tasks, click
Add a printer to start the Add Printer Wizard. Click Next.
For Windows Server 2003: Click Start and then Printers and Faxes. Double-click
Add Printer in the Printers folder to start the Add Printer Wizard. Click Next.
For Windows 2000: Click Start, point to Settings, and then select Printers.
Double-click Add Printer in the Printers folder to start the Add Printer Wizard. Click
Next.
2. For Windows Vista: Click Add a local printer. Select the Create a new port radio
button, and then select EpsonNet Print Port from the list. Click Next.
For Windows XP/Server 2003: Click Local printer attached to this computer, clear
the Automatically detect and install my Plug and Play printer check box, and then
click Next. Select the Create a new port radio button, and then select EpsonNet Print
Port from the list. Click Next.
Note:
If the following screen appears, click the Unblock button, and then click the Search Again
button to search the printers.
For Windows 2000: Click Local printer, clear the Automatically detect and install
my Plug and Play printer check box, and then click Next. Select the Create a new
port radio button, and then select EpsonNet Print Port from the list. Click Next.
Network Software 47
Page 48

3. Select the target printer, and then click Next.
Note:
❏ If the target printer is not in the list, click the Search Again button to search the printers
using new parameters.
❏ If you want to search printers in other segments, click the N/W Settings button. Select the
Specific Network Segments check box, and then enter the network address and subnet
mask of the network segment for the search. Then click the Add button. You can also
specify the time before declaring communication error.
Network Software 48
Page 49

4. Confirm the information about the printer’s port you want to configure, and then click
Finish.
Items Explanations
Port Type The following items are listed in the pull-down menu, and you can
select the port type you need.
IP Address (Auto): Configure the port automatically. If the IP
address of the printer is acquired automatically and the
computer and the printer are in the same segment, you can
select this port type.
IP Address (Manual): Use the printer’s IP Address for the port
name.
HostName (DNS): Use the printer’s host name registered in the
DNS server for the port name.
MS Network: Use the NetBIOS name registered in the printer for
the port name.
The port Information The following items are displayed:
- Port Name (If the port type is changed, the port name and the
host name or IP address are also changed.)
- Printer Model
- Host Name or IP Address
- Protocol
Finish button Register the port information to the system and close the Add
EpsonNet Print Port Wizard.
Back button Go back to the printer list window.
Cancel button Close the Add EpsonNet Print Port Wizard.
You need to install the printer driver. See “Installing the Printer Driver” on page 52.
Network Software 49
Page 50

Adding a port for a printer assigned with a static IP address
1. For Windows Vista: Click Start, Control Panel, and then Printer. Click Add a printer
to start the Add Printer wizard.
For Windows XP: Click Start and then Printers and Faxes. Under Printer Tasks, click
Add a printer to start the Add Printer Wizard. Click Next.
For Windows Server 2003: Click Start and then Printers and Faxes. Double-click
Add Printer in the Printers folder to start the Add Printer Wizard. Click Next.
For Windows 2000: Click Start, point to Settings, and then select Printers.
Double-click Add Printer in the Printers folder to start the Add Printer Wizard. Click
Next.
2. For Windows Vista: Click Add a local printer. Select the Create a new port radio
button, and then select EpsonNet Print Port from the list. Click Next.
For Windows XP/Server 2003: Click Local printer attached to this computer, clear
the Automatically detect and install my Plug and Play printer check box, and then
click Next. Select the Create a new port radio button, and then select EpsonNet Print
Port from the list. Click Next.
For Windows 2000: Click Local printer, clear the Automatically detect and install
my Plug and Play printer check box, and then click Next. Select the Create a new
port radio button, and then select EpsonNet Print Port from the list. Click Next.
3. Select Manual Setting from the list, and then click Next.
Network Software 50
Page 51

4. Enter the printer’s name and the port name is automatically entered to the Port Name
edit box. Then click Next.
5. Confirm the information about the printer’s port you want to configure, and then click
Finish.
Items Explanations
The port Information The following items are displayed:
- Port Name
- Host Name or IP Address
- Protocol
Finish button Register the port information to the system and close the Add
EpsonNet Print Port Wizard.
Back button Go back to the printer list window.
Cancel button Close the Add EpsonNet Print Port Wizard.
You need to install the printer driver. See the next section for instructions.
Network Software 51
Page 52

Installing the Printer Driver
Install the printer driver that comes with your printer.
1. Insert the Software CD-ROM shipped with the printer.
2. Close the EPSON Installation Program screen if it appears.
3. Click the Have Disk button. The Install From Disk dialog box appears.
4. Click Browse.
5. Select the CD-ROM drive for Drives, and double-click the appropriate folder for your
operating system. Click OK.
6. Click OK in the Install From Disk dialog box.
7. Select the model name of the printer, and then click Next.
Note:
If the Add Printer wizard asks you to select either Keep existing driver or Replace existing
driver, be sure to select the Replace existing driver radio button. Click Next.
8. Click Finish and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the setup.
The printer is now ready for peer-to-peer printing. To configure the printer port, see the next
section.
Configuring the Printer Port
Follow the steps below to configure the printer port. The printing speed differs depending
on your selection.
1. For Windows Vista:
Click Start, Control Panel, and then Printer.
For Windows XP/Server 2003:
Click Start and then Printers and Faxes.
For Windows 2000:
Click Start, point to Settings, and then select Printers.
2. Right-click the target printer, and then click Properties.
3. For Windows Vista/XP/Server 2003/2000:
Click the Ports tab, and then click the Configure Port button.
Network Software 52
Page 53

4. Make the appropriate settings for the desired port.
LPR enhanced printing:
Select the LPR Printing radio button, and then specify the queue name (up to 32
characters). LPR enhanced printing sends a print job to the target network printer
without spooling all of the print data. LPR enhanced printing is faster than LPR standard
printing.
LPR standard printing:
Select the Confirm file size check box, and then specify the queue name (up to 32
characters). Print data is spooled by the computer before being sent to the target
network printer.
Note:
When the print data size is 20 MB or more, we recommend that you use LPR enhanced printing.
High-speed printing:
Select the High-Speed Printing (RAW) radio button. The Epson high-speed printing
port sends a print job to the target network printer without spooling all of the print data.
High-Speed printing is faster than the other two printing methods.
5. Click OK.
If you select the High-Speed Printing (RAW) radio button and if the printer does not
support High-Speed printing, or if you fail to connect to the printer, an error message
appears. Follow the message to remedy the problem.
Network Software 53
Page 54

Chapter 4
Troubleshooting
General Problems
Cannot configure the network interface or cannot print from the network.
Cause What to do
The printer settings or network
settings may be wrong.
First, check to see if you can print a status sheet, as
described in “Printing a Network Status Sheet” on page
56. If you can print a status sheet, check the network
settings; otherwise, set the interface mode of the printer’s
control panel to Auto or Option.
Cannot print even if you have assigned the IP address to the computer and the printer.
Cause What to do
You have assigned an IP address to
the computer manually, but you
assigned the IP address to the
printer by Automatic Private IP
Addressing (APIPA).
Assign the printer’s IP address so that it belongs to the
same segment of the computer. Use EpsonNet Config
and the printer’s control panel.
Unable to start EpsonNet Config.
Cause What to do
You have added or deleted
protocols after installing EpsonNet
Config.
Uninstall EpsonNet Config and then reinstall it. See
“Uninstalling Software” on page 59 and “Installing
EpsonNet Config” on page 43.
Troubleshooting 54
Page 55

The message “EpsonNet Config cannot be used because no network is installed.” appears when you start EpsonNet Config.
Cause What to do
TCP/IP is not installed on the
computer.
TCP/IP is installed on the computer,
but its IP address is not set correctly.
Install the TCP/IP protocol.
Set a correct IP address for the computer.
The message “Could not complete communicating configuration data” appears when you send settings to the network interface.
Cause What to do
This may happen when using a
dial-up router.
Run Command Prompt from the computer on which
EpsonNet Config is installed, and then enter the following
command:
Format: >ROUTE_ADD_the IP address of the network
interface_ the IP address of the computer (the under bar
represents one space)
Example: >ROUTE ADD 192.168.192.168 22.33.44.55.
The Model Name and IP Address do not appear in the EpsonNet Config dialog box.
Cause What to do
If the valid IP address is not set, the
items indicated in the dialog box
mentioned above may not appear.
Set a valid IP address.
Refresh the status by selecting Refresh from the View
menu.
Increase the length of time before a timeout. To do this,
select Options from the Tool menu, and then select
Timeout. Note that doing so can cause EpsonNet Config
to run more slowly.
Troubleshooting 55
Page 56

Problems Specific to Your Network Environment
Windows 2000 Environment
A dial-up connection dialog box appears when printing with TCP/IP via
EpsonNet Print.
Cause What to do
You have selected a phone line or
modem (for Internet Explorer 4.0x)
for the Internet connection.
Printing ends normally after you cancel this dialog box,
but the message appears every time you print. Connect
to the Internet using a local area network or start a
dial-up network manually.
Printing a Network Status Sheet
Before you start configuring the network interface, be sure to print a network status sheet
that contains important information such as the current configuration and the MAC address
of the network interface.
To print a network status sheet, follow the steps below.
1. Press the r Right button on the printer’s control panel once to enter the Menu mode.
2. Press the d Down button until TEST PRINT appears on the LCD panel, then press
OK.
3. Press the d Down button until NETWORK SHEET appears.
4. Press the OK button.
5. Press the OK button again to print the network status sheet.
Note:
❏ You cannot print a status sheet in the following cases: the printer has started printing, it is
offline, or it is not ready to print.
❏ See the printer User’s Guide for more information on the printer’s control panel.
Troubleshooting 56
Page 57

Chapter 5
Tips for Administrators
Setting an IP Address on the Printer’s Control Panel
After connecting the printer to the network, you need to set the IP address for the network
interface.
To set the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway from the control panel, follow the
steps below.
1. Turn on your printer.
2. Press the r Right button on the printer’s control panel once to enter the Menu mode.
3. Press the d Down button until NETWORK SETTING appears.
4. Press the OK button, then press OK again to change the NETWORK SETUP. You can
use the following methods to get an IP address.
❏ Choose AUTO when getting the IP address from a DHCP server. The IP address is
automatically obtained from the DHCP server whenever the printer is reset or turned
on.
❏ Choose PANEL when setting the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway
using the printer’s control panel.
Note:
To use Auto, a DHCP server must be correctly configured on the network. See the online help
of your operating system for detailed instructions.
5. To set the IP address manually, press the Up or Down button until IP ADDRESS
appears, then press the OK button.
6. Press the l Left or r Right button to move the cursor and the u Up or d Down button
to change the number. Then press the OK button.
Note:
Repeat steps 5 and 6 to set the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
7. Press the + Cancel button to exit the Menu mode.
8. Turn off your printer and then turn it back on. Be sure to wait until the initialization is
complete.
Tips for Administrators 57
Page 58

9. Print a network status sheet to confirm the new IP address.
Note:
See the User’s Guide for more information about settings on the printer’s control panel.
Network Menu
These items are used to make network settings on the printer’s control panel.
Item Settings
NETWORK SETUP Panel, Auto, Init N/W set
IP ADDRESS 0.0.0.1 to 255.255.255.254
SUBNET MASK 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
DEFAULT
GATEWAY
BONJOUR On/Off
Note:
To activate the Network Menu settings, you must turn off the printer for more than five seconds and
then turn it back on.
0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
Universal Plug and Play
When you connect your printer to the network, an IP address is automatically assigned,
and the printer’s icon appears in the My Network Places folder.
Right-click the printer’s icon in the My Network Places folder and select Properties to see
information about the network interface.
To use this function, Universal Plug and Play must be installed.
Note:
Before using the Universal Plug and Play function, you must enable the Universal Plug and Play
function in EpsonNet Config. See the EpsonNet Config User’s Guide.
Tips for Administrators 58
Page 59

Uninstalling Software
Follow the steps below to uninstall the network software.
Windows Vista
1. Click Start, click Control Panel, and then click Uninstall a program.
2. Select the utility you want to uninstall, and then click the Uninstall/Change button.
3. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete uninstallation.
Windows 2000
1. Click Start, point to Settings, and then select Control Panel.
2. Double-click the Add/Remove Programs icon.
3. Select the utility you want to uninstall, and then click the Change/Remove button.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete uninstallation.
Windows XP/Server 2003
1. Click Start, click Control Panel, and then click Add or Remove Programs.
2. Click the Change or Remove Programs icon.
3. Select the utility you want to uninstall, and then click the Change/Remove button.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete uninstallation.
Mac OS X
1. Double-click the EpsonNet Config Installer icon.
2. Click the Continue button.
3. In the License dialog box, read the License Agreement, and then click the Accept
button.
Tips for Administrators 59
Page 60

4. Select Uninstall from the pull-down menu.
5. Click the Uninstall button.
6. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete uninstallation.
Note:
You can also uninstall EpsonNet Config by dragging the folder to the Trash.
Tips for Administrators 60
Page 61

Index
A
Administrator tips, 57 to 60
D
Data light, 10
DHCP
, 11, 23, 57
E
EpsonNet Config
Macintosh
Windows
EpsonNet EasyInstall
EpsonNet Print
, 44
, 43
, 22 to 24
, 45 to 53
G
Glossary, 11
I
Installation
EpsonNet Config
EpsonNet Print
printer driver
IP address
, 57
, 43
, 46
, 28 to 42
N
Network components, installing, 14 to 21
Network interface
configuring for Macintosh
configuring for Windows
connecting to network
lights
, 10
Network software, uninstalling
Network status sheet
, 25 to 28
, 22 to 24
, 21
, 59 to 60
, 56
O
Operating environment, 9
P
Printer driver
installing in Windows
installing on Macintosh
Problems, solving
Protocols
, 9
, 28 to 40
, 40 to 42
, 54 to 56
R
RJ-45 connector, 10
S
L
Lights, network interface, 10
LPR (TCP/IP) printing
description
setting up
, 13
, 28, 31, 34, 37
M
Macintosh
configuring network interface
installing printer driver
network settings
, 40 to 42
, 20 to 21
Microsoft Network Shared printing
, 25 to 28
, 13
Setting the IP address, 57
Software
description
uninstalling
Status light
, 11
, 59 to 60
, 10
T
TCP/IP
definition
printing in Windows
setting up on Macintosh
Troubleshooting
, 11
, 28, 31, 34, 37
, 54 to 56
, 20 to 21
Index 61
Page 62

U
Uninstalling network software, 59 to 60
Universal Plug and Play
Using the printer with
Macintosh
Windows 2000
, 40
, 37
Windows Server 2003
Windows Vista
Windows XP
, 28
, 31
, 58
, 34
Index 62
 Loading...
Loading...