Page 1

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Type MR105 Direct-Operated Pressure
Reducing Regulators
January 2015
TYPE MR105 DIRECT-OPERATED REGULATOR WITH
LOW-PRESSURE ACTUATOR
Figure 1. Type MR105 Direct-Operated Pressure Reducing Regulators
Contents
Introduction .................................................................. 2
Specifications .............................................................. 2
Features ......................................................................3
Principle of Operation .................................................. 4
Overpressure Protection.............................................. 4
Installation ................................................................... 6
Applications ................................................................. 6
Universal NACE Compliance....................................... 8
Capacity Information.................................................... 8
Ordering Information.................................................. 27
Ordering Guide ......................................................... 27
P1204P1205
TYPE MR105 DIRECT-OPERATED REGULATOR WITH
HIGH-PRESSURE ACTUATOR
Features
• Travel Indicator
• Large Flow
• Stability
• Fast Response
• Steel and Stainless Steel Constructions
Meet API 614 Requirements
• Available Constructions to Meet
NACE MR0175-2003 and NACE MR0103
Requirements for Sour Gas Service Capability
• Multiple Trim Materials Available
• ANSI/FCI 70-3-2004 Class VI Shutoff
• Multiple End Connection Options
• P
= P2 on High-Pressure Actuator
1
• Suitable for High-Temperature Applications
up to 250°F / 121°C
• Easy Access to Trim Parts
• Drain Valve
• Pressure-Loaded Actuator
• Bleed valve (for High-Pressure Actuator only)
www.fisherregulators.com
D103256X012
Page 2
Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Specications
The Specications section on this page provides the ratings and other specications for the Type MR105. The
following information is stamped on the nameplate fastened on the regulator at the factory: type; body size;
maximum inlet, outlet and differential pressure; maximum pressure above setpoint; maximum casing pressure;
maximum temperature; spring range; cage type; and trim and diaphragm material.
Body Sizes and End Connection Styles
See Table 1
Shutoff Classication per ANSI/FCI 70-3-2004
Class VI (Soft Seat)
Maximum Inlet, Outlet and Emergency Casing
Pressure
(1)
See Table 3
Outlet Pressure Ranges
(1)
5 to 300 psig / 0.34 to 20.7 bar; see Table 2
Maximum Setpoint
(1)
Low-Pressure Actuator: 43 psig / 3.0 bar
High-Pressure Actuator:
Downstream Control Line Connection Size
1/2 NPT
Maximum Pressure Over Setpoint to Avoid Internal
Parts Damage
Low-Pressure Actuator: 20 psig / 1.4 bar
High-Pressure Actuator: 120 psig / 8.3 bar
Spring Case Vent
Type Y602-12
Pressure-Loaded Spring Case Vent Connection
1/2 NPT
Approximate Weights
For Type MR105 with Low-Pressure Actuator
Nitrile (NBR) and Ethylene Propylene (EPDM)
Diaphragm: 300 psig / 20.7 bar
Fluorocarbon (FKM) Diaphragm:
150 psig / 10.3 bar
Construction Materials
For Type MR105 with High-Pressure Actuator
See Table 6
Maximum Differential Pressures
(1)
See Table 4
Flow and Sizing Coefcients
See Table 5
Temperature Capabilities
(1)
Nitrile (NBR): -20 to 180°F / -29 to 82°C
Fluorocarbon (FKM): 20 to 250°F / -7 to 121°C
Ethylene Propylene (EPDM)
(3)
: -20 to 225°F /
-29 to 107°C
(2)
Options
• Visual Travel Indicator
• Drain Valve
• Pressure-Loaded Actuator
• NACE Construction
• Bleed Valve (for High-Pressure Actuator Only)
• Ethylene Propylene (EPDM) Elastomer
Pressure Registration
External
1. The pressure/temperature limits in this Bulletin or any applicable standard limitation should not be exceeded.
2. Fluorocarbon (FKM) is limited to 200°F / 93°C in hot water.
3. Ethylene Propylene (EPDM) is limited to 20 to 250°F / -7 to 121°C when used with Low Pressure Actuator.
(1)
NPS 1 / DN 25: 86 lbs / 39 kg
NPS 2 / DN 50: 116 lbs / 53 kg
NPS 3 / DN 80: 165 lbs / 75 kg
NPS 4 / DN 100: 174 lbs / 79 kg
NPS 1 / DN 25: 76 lbs / 34 kg
NPS 2 / DN 50: 105 lbs / 48 kg
NPS 3 / DN 80: 155 lbs / 70 kg
NPS 4 / DN 100: 164 lbs / 74 kg
Trim Parts
Introduction
The Type MR105 regulators are direct-operated, pressure
reducing, high-capacity, multi-purpose regulators.
They are designed to handle pressures up to 400 psig /
27.6 bar and temperatures up to 250°F / 121°C.
This product provides a simple, fast, reliable and
economical way to control and reduce pressure in multi-
purpose applications suitable for different ow media
such as liquid, air and gas. Applications include lube oil
2
systems and any application where speed of response is
critical, minimum differential pressure is a concern or uid
is not free of impurities. Type MR105 regulator with a
low-pressure actuator can be set up to 43 psig / 3.0 bar
and the high-pressure actuator version can be set up
to 300 psig / 20.7 bar.
The units are available in 4 sizes, NPS 1 through 4 /
DN 25 through 100 and are available in several
end connection congurations to meet demands on
application requirements.
Page 3
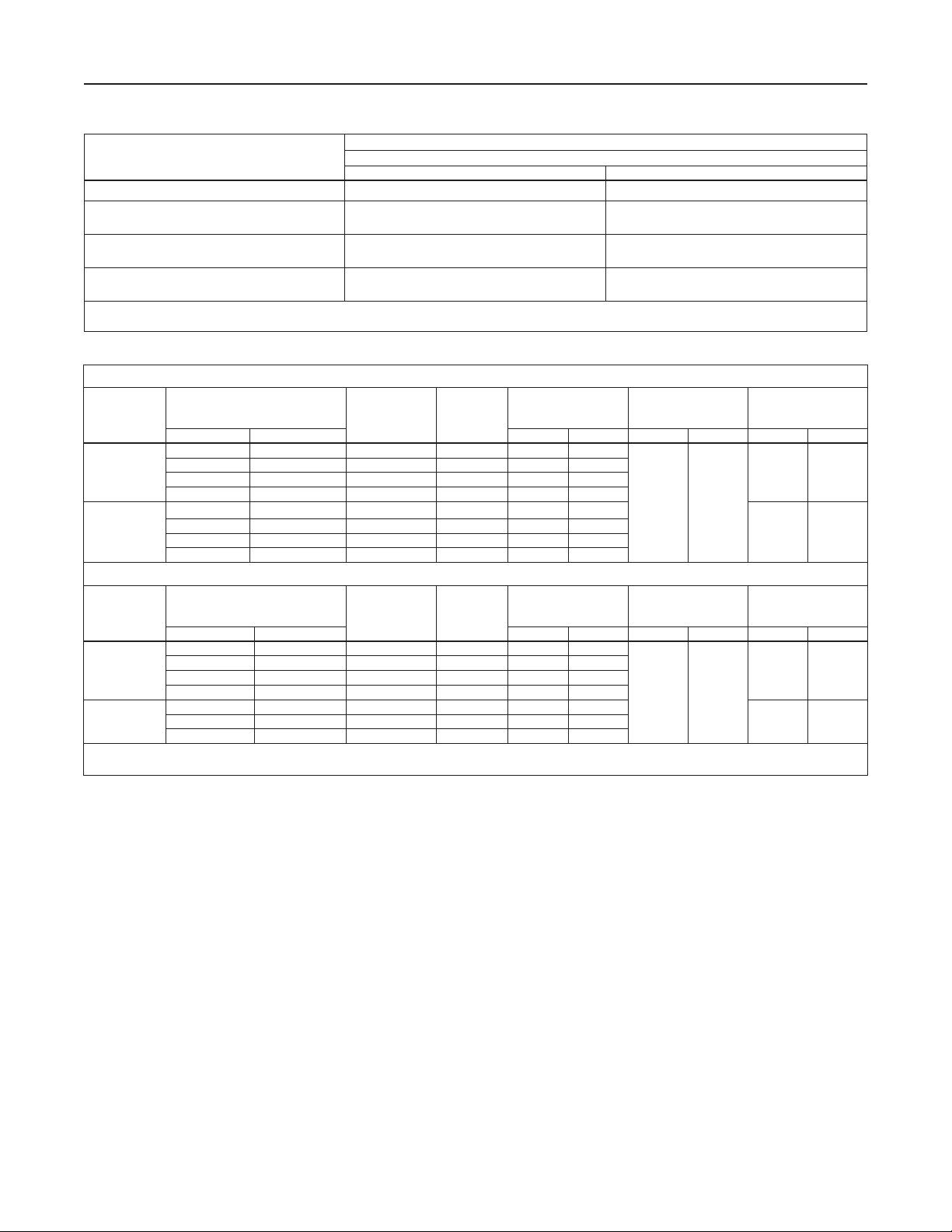
Table 1. Body Sizes and End Connection Styles
BODY MATERIAL
NPS 1 and 2 / DN 25 and 50 NPS 3 and 4 / DN 80 and 100
Cast Iron NPT, CL125 FF, CL250 RF CL125 FF, CL250 RF
WCC steel
CF8M Stainless steel
CF3M Stainless steel
1. Optional NACE construction available.
2. Constructions meet API 614 requirements.
(1)(2)
(1)(2)
(1)(2)
NPT, CL150 RF, CL300 RF, CL600 RF
or PN 16/25/40 RF
NPT, CL150 RF, CL300 RF, CL600 RF
or PN 16/25/40 RF
NPT, CL150 RF, CL300 RF, CL600 RF
or PN 16/25/40 RF
Table 2. Outlet Pressure Ranges
BODY SIZE, NPS 1 AND 2 / DN 25 AND 50
Actuator Type
Low Pressure
High Pressure
Actuator Type
Low Pressure
High Pressure
1. NPS 2 / DN 50 body size spring range is limited to 45 psig / 3.1 bar.
2. Maximum setpoint is limited to 150 psig / 10.3 bar for constructions with Fluorocarbon (FKM) diaphragm.
Spring Range
psig bar In. mm In. mm psig bar
5 to 12 0.34 to 0.83 GE42909X012 White 0.437 11.1
10 to 24 0.69 to 1.6 GE42910X012 Silver 0.500 12.7
14 to 32 0.96 to 2.2 GE42911X012 Orange 0.562 14.3
18 to 43 1.2 to 3.0 GE43002X012 Red 0.625 15.9
(1)
25 to 60
43 to 100 3.0 to 6.9 GE42909X012 White 0.437 11.1
75 to 175
110 to 300
Spring Range
psig bar In. mm In. mm psig bar
5 to 8 0.34 to 0.55 GE42909X012 White 0.437 11.1
8 to 20 0.55 to 1.4 GE42910X012 Silver 0.500 12.7
12 to 30 0.83 to 2.1 GE42911X012 Orange 0.562 14.3
18 to 39 1.2 to 2.7 GE43002X012 Red 0.625 15.9
39 to 72 2.7 to 5.0 GE42909X012 White 0.437 11.1
71 to 175
110 to 250
1.7 to 4.1
(2)
5.2 to 12.1
(2)
7.6 to 20.7
(2)
4.9 to 12.1
(2)
7.6 to 17.2
Spring Part
Number
(1)
GE42907X012 Green 0.375 9.52
(2)
GE42910X012 Silver 0.500 12.7
(2)
GE42911X012 Orange 0.562 14.3
BODY SIZE, NPS 3 AND 4 / DN 80 AND 100
Spring Part
Number
(2)
GE42910X012 Silver 0.500 12.7
(2)
GE42911X012 Orange 0.562 14.3
Spring Color
Code
Spring Color
Code
Bulletin 71.1:MR105
END CONNECTION STYLE
Body Size
CL150 RF, CL300 RF, CL600 RF
or PN 16 RF
CL150 RF, CL300 RF, CL600 RF
or PN 16 RF
CL150 RF, CL300 RF, CL600 RF
or PN 16 RF
Spring Wire Diameter Spring Free Length
9.70 246
Spring Wire Diameter Spring Free Length
9.70 246
Maximum Pressure
Over Setpoint to Avoid
Internal Parts Damage
20 1.4
120 8.3
Maximum Pressure
Over Setpoint to Avoid
Internal Parts Damage
20 1.4
120 8.3
Available in linear and quick opening trim cages for gas
and liquid applications, respectively. The cage-guided
metal plug provides superior control and stability.
The Type MR105 with steel or stainless steel body
construction has been designed to meet API 614 as
required by lube oil manufacturers.
Features
Travel Indicator—Travel indicator option provides
visual indication of the valve movement from the
closed to open position.
Large Flow—Able to pass large ow rates with
minimal offset from setpoint.
Stability—The Type MR105 regulator’s cage-guided
metal plug design provides superior control stability of
delivery pressure.
Fast Response—Direct-operated allows for fast
response to meet the most demanding pressure and
ow requirements.
Steel and Stainless Steel Constructions Meet
API 614 Requirements—Steel and Stainless steel
body constructions comply with the recommendations of
API Standard 614.
Available Constructions to Meet
NACE MR0175-2003 and NACE MR0103
Requirements for Sour Gas Service Capability—
Optional materials are available for applications
handling sour gases. These constructions comply
with the recommendations of NACE International
Standards MR0175 and MR0103.
Multiple Trim Materials Available—416, 316 and
316L Stainless steel options are available to meet
wider application requirements including demands on
lube oil and cooling water applications.
3
Page 4
Bulletin 71.1:MR105
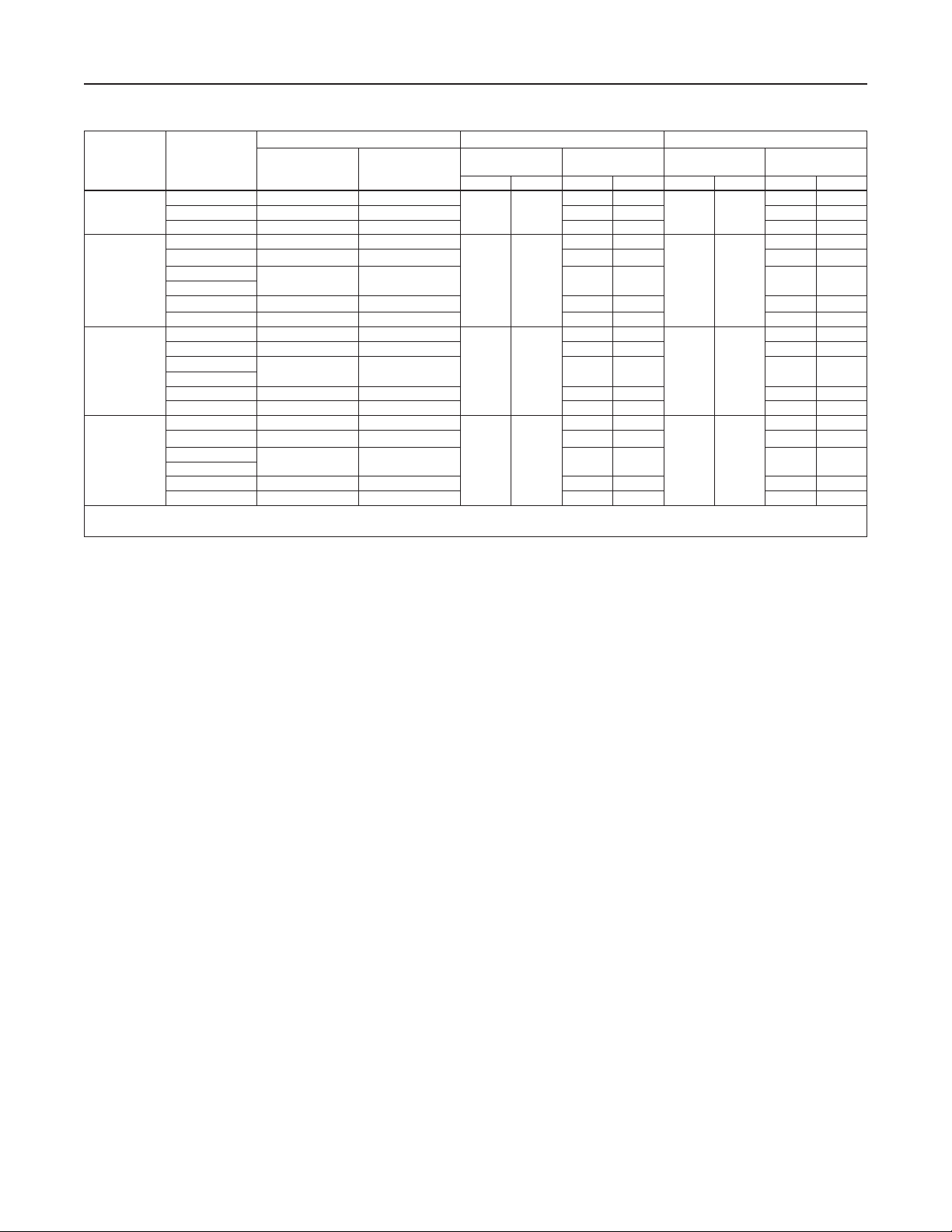
Table 3. Maximum Inlet, Outlet and Emergency Casing Pressures
BODY
MATERIAL
Cast Iron
WCC steel
CF8M
Stainless steel
CF3M
Stainless steel
1. Based on a maximum temperature of 250°F / 121°C.
2. Maximum outlet and emergency casing pressures for constructions with Fluorocarbon (FKM) diaphragm are limited to 230 psig / 15.8 bar or the body rating limit, whichever is lower.
END
CONNECTION
NPT 340 23.4
CL125 FF 175 12.1 175 12.1 175 12.1
CL250 RF 400 27.6 400 27.6 400 27.6
NPT 400 27.6
CL150 RF 245 16.9 245 16.9 245 16.9
CL300 RF
CL600 RF
PN 16 RF 245 16.9 245 16.9 245 16.9
PN 16/25/40 RF 400 27.6 400 27.6 400 27.6
NPT 400 27.6
CL150 RF 225 15.5 225 15.5 225 15.5
CL300 RF
CL600 RF
PN 16 RF 225 15.5 225 15.5 225 15.5
PN 16/25/40 RF 400 27.6 400 27.6 400 27.6
NPT 400 27.6
CL150 RF 185 12.7 185 12.7 185 12.7
CL300 RF
CL600 RF
PN 16 RF 185 12.7 185 12.7 185 12.7
PN 16/25/40 RF 400 27.6 400 27.6 400 27.6
MAXIMUM INLET PRESSURE MAXIMUM OUTLET PRESSURE MAXIMUM EMERGENCY CASING
psig bar
400 27.6 400 27.6 400 27.6
400 27.6 400 27.6 400 27.6
400 27.6 400 27.6 400 27.6
(1)
Low-Pressure
Actuator
psig bar psig bar psig bar psig bar
70 4.8
70 4.8
70 4.8
70 4.8
High-Pressure
340 23.4
400 27.6
400 27.6
400 27.6
Actuator
(2)
Low-Pressure
Actuator
70 4.8
70 4.8
70 4.8
70 4.8
High-Pressure
340 23.4
400 27.6
400 27.6
400 27.6
Actuator
(2)
ANSI/FCI 70-3-2004 Class VI Shutoff—Soft-seat
valve plug disks for tight shutoff.
Multiple End Connection Options—Type MR105 is
available in several end connection congurations to
meet demands on application requirements.
P1 = P2 on High-Pressure Actuator—Inlet pressure
rating equals outlet pressure rating on high-pressure
actuator constructions up to 400 psig / 27.6 bar.
Easy Drain—Feature allows you to drain the system
without expensive spool pieces saving you time
and space.
Easy Bleed—Feature allows you to purge the air
trapped underneath the diaphragm when the highpressure regulator is installed in the upright position,
which improves speed of response.
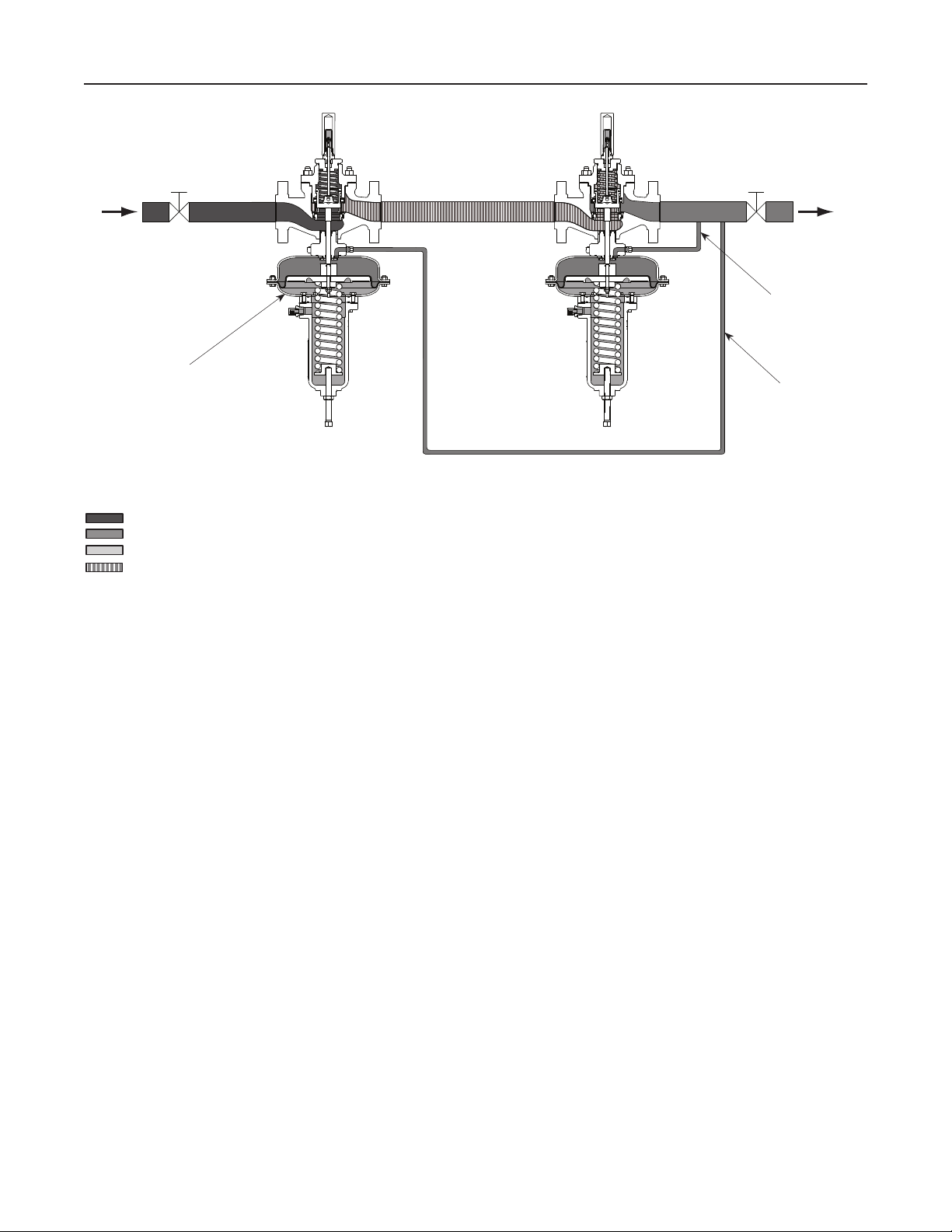
Principle of Operation
Refer to Figure 2. The Type MR105 is a direct-
operated pressure reducing regulator. Downstream
pressure is registered externally through a 1/2 NPT
control line tapped in the low-pressure actuator bonnet
or in the high-pressure actuator lower casing. When
downstream demand decreases, the pressure under
the actuator diaphragm increases. This pressure
overcomes the regulator setting (which is set by
the regulator control spring). Through the action of
the actuator stem and valve spring, the valve plug
moves closer to the seat ring and reduces ow. When
demand downstream increases, pressure under the
actuator diaphragm decreases. Spring force pushes
the actuator stem downward, the valve plug moves
away from the seat ring and the ow increases
downstream as the regulator opens in response to
the decreased pressure underneath the diaphragm.
The downward motion of the plug allows gas to ow
through the cage into the downstream system.
Increased downstream pressure permits the regulator
to close. The combination of valve spring force and
valve plug unbalance provides positive valve plug
shutoff against the port and upper seals.
Overpressure Protection
Type MR105 regulator with the low-pressure actuator
has outlet pressure ratings lower than the inlet
pressure ratings. Complete downstream overpressure
protection is needed if the actual inlet pressure
exceeds the outlet pressure rating.
Overpressuring any portion of a regulator or
associated equipment may cause personal injury,
leakage or property damage due to bursting
of pressure-containing parts or explosion of
accumulated gas. Provide appropriate pressurerelieving or pressure-limiting devices to ensure
4
Page 5
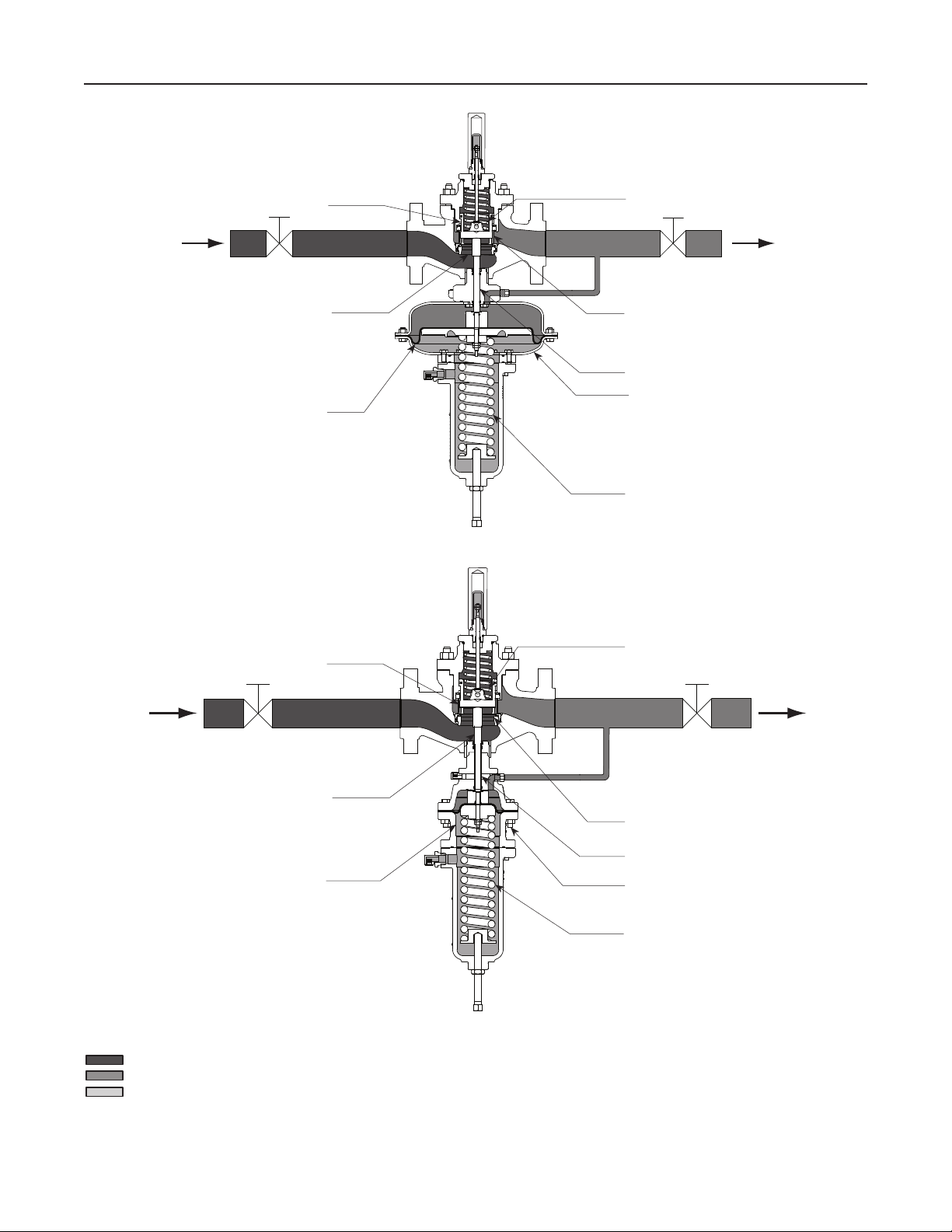
Bulletin 71.1:MR105
M1178
VALVE PLUG
SEAT RING
DIAPHRAGM
VALVE PLUG
VALVE SPRING
CAGE
ACTUATOR STEM
ACTUATOR
CONTROL SPRING
TYPE MR105 WITH LOW-PRESSURE ACTUATOR
VALVE SPRING
SEAT RING
DIAPHRAGM
M1181
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
Figure 2. Type MR105 Operational Schematic
CAGE
ACTUATOR STEM
ACTUATOR
CONTROL SPRING
TYPE MR105 WITH HIGH-PRESSURE ACTUATOR
5
Page 6

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
PUMP 2
PUMP 1
FILTER 1
OIL TANK
M1202
Figure 3. Lube Oil Skid Diagram
TYPE MR108
BACKPRESSURE REGULATOR
that the limits in the Specications section are not
exceeded. Regulator operation within ratings does
not prevent the possibility of damage from external
sources or from debris in the pipeline. A regulator
should be inspected for damage periodically and after
any overpressure condition. Refer to the relief sizing
coefcients in the Specications and the Capacity
Information section to determine the required relief
valve capacity.
FILTER 2
TYPE MR105
PRESSURE REDUCING
REGULATOR
TO EQUIPMENT
BEARINGS, SEALS OR
SERVO-CONTROLS
Applications
Note
A linear cage is recommended for
applications where low ow stability
is a concern but it will limit the overall
capacity of the regulator.
Lube Oil Skids (Figure 3)
Installation
Vertical installation with the actuator installed directly
above or below the main valve is recommended but for
optimal performance the actuator should be installed
below the main valve. The use of a bleed valve is
recommended for liquid installations that require the
high pressure actuator to be mounted above the main
valve. The unit will operate in horizontal installations
with the actuator on the side, however, this could result
in premature wear of parts. Make sure that ow will
be in the same direction as that indicated by the body
arrow. Orientation of the two vents should always be
down. Vents may be rotated after regulator installation
so that the vent screens are down.
A control line must be installed to allow outlet pressure
to register on the actuator’s diaphragm. The size of the
control line is indicated in the Specications section,
and should be installed four to eight pipe diameter
downstream of the regulator and in an area of pipe that
is free of turbulence.
An instruction manual is provided with every regulator
shipped. Refer to this for detailed installation,
operation, adjustment and maintenance instructions.
Included is a complete listing of individual parts and
recommended spare parts.
Lube oil skids maintain oil ow to bearings, seals and
servo-controls on critical turbomachinery assets such as
air and gas compressors, steam turbines, power recovery
turbines and power generating equipment. These skids
are essential in keeping lube oil clean at all times and
ensure maximum service life for the equipment. Because
it is critical to maintain a constant ow and pressure of
oil to the equipment, it is normally equipped with two
pumps – the main pump and the auxiliary pump, which
will take over in case of main pump failure – and lters.
In normal condition, the skids operate in the
following manner:
• Lube oil is stored in the tank at atmospheric pressure.
• It is then fed to the main pump (Pump 1) which
pressurizes the lube oil.
• Oil then goes through a lter.
• After ltration, oil ow is split such that a fraction
is sent to a backpressure regulator to limit the supply
pressure to the pressure reducing regulator. 20%
of the pump rate ows through the backpressure
regulator, sending back oil to the oil tank.
• The pressure reducing regulator decreases the
pressure to a safe and allowable range. Flow
through this regulator is 80% of pump rate.
6
Page 7
SET HIGHER THAN
WORKER REGULATOR
Bulletin 71.1:MR105
WORKER CONTROL LINE
MONITOR CONTROL LINE
TYPE MR105
M1203
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
INTERMEDIATE PRESSURE
Figure 4. Type MR105 Monitor Regulator Operational Schematic
MONITOR REGULATOR
• Oil ows to large rotating equipment lubricating
bearings, e.g. turbines and compressors.
The loss of pressure or ow to the bearings or these
turbomachinery assets may shut down the equipment or
even the whole plant. Failure of the main pump or lter
results in the following upset operation:
• Auxiliary pump (Pump 2) and lter system is
brought into operation while main pump is
in operation.
• Auxiliary pump ramp up rate is one second.
• Auxiliary pump produces a pressure spike
that is beyond the limitations of the pressure
reducing regulator.
• The backpressure regulator relieves the excess
pressure back to the oil tank. Flow rate is 120% of
total pump rate.
Main pump can now be shut down to allow repair of
the system. High capacity direct-operated regulators
are recommended for this type of application where
speed of response is critical. The Type MR105 can
provide fast response to the pressure spikes as
described above while maintaining a constant delivery
pressure of oil to the bearing.
TYPE MR105
WORKER REGULATOR
Wide-Open Monitoring System
Refer to Figure 4. Monitoring system provides
overpressure protection by containment and therefore
does not vent to the atmosphere. It involves a specic
arrangement of two regulators in series which are
congured such that if one regulator fails wide open,
the other regulator assumes control to maintain
the downstream pressure at a set limit. During an
overpressure situation, monitoring systems keep the
customer on line. Testing is also relatively easy. To
perform a periodic test on a monitoring regulator, increase
the outlet set pressure of the worker regulator and watch
the outlet pressure gauge to determine if the monitor
regulator takes over at the appropriate outlet pressure.
In such systems, both regulators are sensing downstream
pressure. During normal operation of a wide-open monitor
conguration, one regulator (worker) is set at the desired
downstream pressure. The other regulator (monitor) is set
at a higher pressure and remains wide open. The lock-up
pressure will be the worker regulator lock-up pressure.
If the worker regulator fails open, the monitor regulator
controls the downstream pressure at its setpoint and the
lock-up pressure will be the monitor lock-up pressure.
7
Page 8

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Table 4. Maximum Differential Pressures
ACTUATOR TYPE
Low Pressure
High Pressure
BODY SIZE
NPS DN psid bar d psid bar d
1 25
2 50 200 13.6
3 80 225 15.5
4 100 225 15.5
1 25
2 50 200 13.6
3 80 225 15.5
4 100 250 17.2
Gas Service (Linear Cage) Liquid Service (Quick Opening Cage)
400 or maximum
inlet pressure,
whichever is lower
400 or maximum
inlet pressure,
whichever is lower
Table 5. Wide-Open Flow and IEC Sizing Coefficients
Body Size
NPS DN C
1 25 463 13.7 34.0 0.81 0.90 0.73 0.36
2 50 761 22.5 33.8 0.75 0.87 0.72 0.24
3 80 997 30.5 32.7 0.78 0.88 0.68 0.22
4 100 934 27.5 34.0 0.77 0.88 0.75 0.18
Body Size
NPS DN C
1 25 597 17.5 34.1 0.81 0.90 0.73 0.43
2 50 1740 48.2 36.1 0.81 0.90 0.82 0.34
3 80 3540 103.1 34.4 0.76 0.87 0.75 0.32
4 100 4300 135.9 31.6 0.72 0.85 0.65 0.30
Body Size
NPS DN C
2 50 1570 43.8 35.9 0.81 0.90 0.72 0.36
Wide-Open Flow Coefcient IEC Sizing Coefcient
Line Size Equals Body Size
g
Wide-Open Flow Coefcient IEC Sizing Coefcient
Line Size Equals Body Size
g
Wide-Open Flow Coefcient IEC Sizing Coefcient
Line Size Equals Body Size
g
C
v
C
v
REDUCED PORT QUICK OPENING CAGE
C
v
LINEAR CAGE
C
1
QUICK OPENING CAGE
C
1
C
1
MAXIMUM DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE
27.6 or maximum
inlet pressure,
whichever is lower
27.6 or maximum
inlet pressure,
whichever is lower
K
m
K
m
K
m
F
L
F
L
F
L
200 13.6
250 17.2
X
T
X
T
X
T
F
d
F
d
F
d
Universal NACE Compliance
Optional materials are available for applications
handling sour gases. These constructions comply with
the recommendations of NACE International Sour
Service Standards.
The manufacturing processes and materials used
by Emerson Process Management Regulator
Technologies, Inc. assure that all products specied
for sour gas service comply with the chemical,
physical and metallurgical requirements of NACE
MR0175 and/or NACE MR0103. Customers have
the responsibility to specify correct materials.
Environmental limitations may apply and shall be
determined by the user.
Capacity Information
Air Capacities
To determine wide-open ow capacity for relief valve
sizing, use one of the following equations:
For Critical Pressure Drops
Use this equation for critical pressure drops (absolute
outlet pressure equal to one-half or less than one-half
the absolute inlet pressure).
Q = P
1(abs)Cg
where,
Q = gas ow rate, SCFH
Cg = gas sizing coefcient
P1 = absolute inlet pressure, psia
For Non-Critical Pressure Drops
Use this equation for pressure drops lower than critical
(absolute outlet pressure greater than one-half of
absolute inlet pressure).
520
Q = CgP1SIN DEG
GT
3417
C
1
ΔP
P
1
8
Page 9

Table 6. Construction Materials
Bulletin 71.1:MR105
1. Powder coated.
where,
PART NAME STANDARD OPTIONAL
Body WCC steel
Body Flange WCC steel
Actuator Casings - Low Pressure AISI 1010 steel
Actuator Casings - High Pressure WCC steel
Internal Stiffener Plate AISI 1010 steel
Spring Case WCC steel CF3M/CF8M Stainless steel
Spring Case Spacer Zinc-Plated steel Stainless steel
Cage CF3M/CF8M (Quick Opening), CF8M (Linear) Stainless Steel
Valve Plug and Seat Ring 416 Stainless steel
Closing Spring Inconel® X750
Stem S17400 H1075 Stainless steel S20910 (Nitronic 50) Stainless steel
Lower Diaphragm Support S17400 H1075 Stainless steel
Diaphragm and Seals Nitrile (NBR) Fluorocarbon (FKM), Ethylene Propylene (EPDM)
Upper Diaphragm Plate Cast Iron
Control/Set Spring Steel Alloy
Spring Seats Zinc-Plated steel
Bolting
Adjusting Screw Zinc-Plated steel Stainless steel
SA194 Grade B7/NCF (Body to Bonnet),
SAE Grade 5/NCF (Actuator)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
Cast Iron, CF8M, CF3M Stainless steel
CF8M, CF3M Stainless steel
316/316L Stainless steel
CF3M/CF8M Stainless steel
316/316L Stainless steel
316, 316L,
S20910 (Nitronic 50) Stainless steel
(NPS 1 / DN 25 body size only)
(1)
Stainless steel
Maximum Allowable Pressure Drop for Liquid
Q = gas ow rate, SCFH
G = specic gravity of the gas
T = absolute temperature of gas
at inlet, °Rankine
Cg = gas sizing coefcient
P1 = absolute inlet pressure, psia
C1 = ow coefcient
ΔP = pressure drop across the regulator, psi
Then, if capacity is desired in normal cubic meters per hour
at 0°C and 1.01325 bar, multiply SCFH by 0.0268.
Liquid Capacities
To determine regulating capacities or to determine
wide-open capacities for relief sizing at any inlet
pressure, use the following equation.
Q = C
where,
Q = liquid ow rate, GPM
ΔP = pressure drop across the regulator, psi
CV = regulating or wide-open ow coefcient
G = specic gravity of the liquid
ΔP
v
G
Pressure drops in excess of allowable will result in
choked ow and possible cavitation damage.
Choked ow is the formation of vapor bubbles in
the liquid owstream causing a condition at the
vena contracta which tends to limit ow through
the regulator. The vena contracta is the minimum
cross-sectional area of the ow stream occurring just
downstream of the actual physical restriction.
Cavitation and ashing are physical changes in the
process uid. The change is from the liquid state to
the vapor state and results from the increase in uid
velocity at or just downstream of the greatest ow
restriction, normally the regulator orice.
To determine the maximum allowable pressure drop
for water:
ΔP
= Km (P1)
(allow)
where,
ΔP = Valve differential in psi
Km = Valve recovery coefcient from Table 5
P1 = Valve inlet pressure in psia
Inconel® is a mark owned by Special Metals Corporation.
9
Page 10

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Table 7. Typical Air CV Coefficient with Linear Cage - Setpoint Made at 10% Flow (for Type MR105 with Low-Pressure Actuator)
SPRING RANGE,
PART NUMBER
AND COLOR
5 to 12 psig /
0.34 to 0.83 bar
GE42909X012
White
10 to 24 psig /
0.69 to 1.6 bar
GE42910X012
Silver
14 to 32 psig /
0.96 to 2.2 bar
GE42911X012
Orange
18 to 43 psig /
1.2 to 3.0 bar
GE43002X012
Red
SET
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar 10% 20% 40% 10% 20% 40%
5 0.34
10 0.69
10 0.69
15 1.0
20 1.4
15 1.0
20 1.4
25 1.7
30 2.1
20 1.4
25 1.7
30 2.1
35 2.4
40 2.8
INLET
PRESSURE
25 1.7 2.58 3.69 7.51 2.97 4.52 9.08
75 5.2 2.55 4.02 8.50 3.52 4.50 9.04
150 10.3 2.78 3.98 8.95 3.24 4.97 10.3
250 17.2 2.05 3.24 8.50 3.14 4.81 10.5
25 1.7 2.56 6.04 13.6 4.66 9.56 20.3
75 5.2 3.96 7.72 13.7 4.63 8.68 21.9
150 10.3 3.64 6.80 13.7 3.89 8.39 21.8
250 17.2 3.84 8.45 13.7 4.34 8.26 20.4
25 1.7 2.57 4.88 10.9 3.75 6.47 13.1
75 5.2 2.82 5.05 11.3 3.38 6.06 12.8
150 10.3 2.80 5.01 11.6 3.56 6.15 14.3
250 17.2 3.25 5.12 12.7 3.46 6.48 14.3
25 1.7 3.67 7.36 13.7 4.64 9.99 21.6
75 5.2 3.81 7.38 13.7 5.03 9.36 22.1
150 10.3 3.91 7.77 13.7 5.13 9.84 22.1
250 17.2 3.84 7.85 13.7 4.53 9.84 21.5
50 3.4 4.68 10.4 13.7 5.98 12.3 22.5
75 5.2 4.48 9.64 13.7 5.71 11.9 22.5
150 10.3 4.76 11.0 13.7 4.83 10.5 22.5
250 17.2 4.89 10.1 13.7 5.92 13.6 22.5
25 1.7 2.95 5.58 12.1 4.27 7.34 16.5
75 5.2 2.81 5.54 12.1 3.67 6.49 15.4
150 10.3 2.86 5.18 11.7 4.05 7.50 16.4
250 17.2 3.01 5.77 13.3 3.87 7.08 18.3
25 1.7 3.87 7.67 13.2 4.77 10.4 19.8
75 5.2 3.42 6.69 13.7 4.51 8.77 21.9
150 10.3 3.52 6.99 13.7 5.15 9.67 22.0
250 17.2 3.73 7.26 13.7 4.34 8.94 21.8
50 3.4 4.68 9.18 13.7 5.12 11.1 22.3
75 5.2 3.73 8.46 13.7 4.83 11.9 22.3
150 10.3 4.05 8.79 13.7 5.2 11.4 22.5
250 17.2 4.06 9.73 13.7 4.78 10.9 22.5
50 3.4 5.18 11.1 13.7 5.77 13.8 22.3
75 5.2 4.99 11.2 13.7 6.33 14.1 22.5
150 10.3 4.78 11.1 13.7 6.23 14.5 22.4
250 17.2 5.53 12.7 13.7 5.29 13.6 22.5
50 3.4 2.69 5.46 11.2 3.74 7.43 15.5
75 5.2 2.59 5.13 11.1 4.66 6.60 15.3
150 10.3 3.03 5.36 11.9 4.19 7.44 16.2
250 17.2 2.83 5.03 12.0 4.06 7.00 16.8
50 3.4 3.18 6.49 13.0 4.97 8.82 20.4
75 5.2 3.67 6.90 13.7 4.11 8.98 20.6
150 10.3 3.22 6.73 13.7 4.80 8.97 21.0
250 17.2 3.46 6.66 13.7 4.59 8.76 20.3
50 3.4 4.41 8.24 13.7 4.77 10.9 21.5
75 5.2 4.18 8.24 13.7 5.82 10.2 22.1
150 10.3 3.96 8.30 13.7 5.89 10.9 22.0
250 17.2 3.79 7.89 13.7 5.04 10.7 22.1
50 3.4 4.70 9.42 13.7 5.93 12.5 21.9
75 5.2 4.64 9.11 13.7 6.19 13.1 22.3
150 10.3 4.44 9.42 13.7 6.28 12.9 22.4
250 17.2 4.41 9.14 13.7 5.69 12.5 22.5
50 3.4 5.34 11.1 13.7 6.31 15.2 21.7
75 5.2 4.55 10.5 13.7 7.17 14.8 22.1
150 10.3 4.52 11.0 13.7 5.53 12.1 22.5
250 17.2 5.11 11.0 13.7 6.29 14.9 22.5
NPS 1 / DN 25 Body NPS 2 / DN 50 Body
CV AT % DROOP
10
- continued -
Page 11

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Table 7. Typical Air CV Coefficient with Linear Cage - Setpoint Made at 10% Flow (for Type MR105
with Low-Pressure Actuator) (continued)
C
SPRING RANGE,
PART NUMBER
AND COLOR
5 to 8 psig /
0.34 to 0.55 bar
GE42909X012
White
8 to 20 psig /
0.55 to 1.4 bar
GE42910X012
Silver
12 to 30 psig /
0.83 to 2.1 bar
GE42911X012
Orange
18 to 39 psig /
1.2 to 2.7 bar
GE43002X012
Red
SET
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar 10% 20% 40% 10% 20% 40%
5 0.34
8 0.55
10 0.69
15 1.0
20 1.4
15 1.0
20 1.4
25 1.7
30 2.1
20 1.4
25 1.6
30 2.1
35 2.4
INLET
PRESSURE
25 1.7 4.96 6.90 12.2 4.72 6.55 10.0
75 5.2 4.63 6.63 12.2 4.47 6.02 10.6
150 10.3 4.43 6.60 11.3 4.24 6.06 10.8
250 17.2 3.97 5.81 11.1 4.39 5.97 10.6
25 1.7 6.47 10.5 21.7 5.58 8.64 17.5
75 5.2 5.72 9.35 20.2 5.23 8.25 16.8
150 10.3 5.22 8.82 19.1 5.32 9.08 17.1
250 17.2 5.50 9.05 20.1 4.55 7.95 17.2
25 1.7 5.54 9.22 17.6 4.08 7.67 15.0
75 5.2 5.79 8.79 17.3 4.75 7.29 15.1
150 10.3 5.28 8.07 16.9 4.58 6.95 13.8
250 17.2 5.18 8.34 17.4 4.13 6.69 13.9
25 1.7 7.06 13.2 29.1 5.78 11.0 23.9
75 5.2 7.06 12.9 29.1 6.06 10.6 23.3
150 10.3 6.33 11.9 28.0 5.45 9.91 23.0
250 17.2 6.68 12.3 27.7 5.28 9.73 23.0
50 3.4 6.51 13.7 30.5 7.20 13.7 25.3
75 5.2 8.53 16.8 30.5 7.75 13.9 24.8
150 10.3 8.19 16.7 30.5 6.71 13.1 27.1
250 17.2 8.41 16.8 30.5 8.00 13.2 27.4
25 1.7 5.84 9.95 20.4 4.79 7.80 17.0
75 5.2 5.71 9.19 19.9 5.00 8.10 16.3
150 10.3 5.39 9.13 19.5 5.10 8.29 17.1
250 17.2 5.51 9.10 19.9 5.05 8.28 17.2
25 1.7 7.94 14.2 28.1 5.15 9.96 22.6
75 5.2 6.68 12.0 27.7 6.54 11.2 24.5
150 10.3 6.36 11.4 27.6 6.20 10.8 24.4
250 17.2 5.72 10.9 26.9 5.37 9.58 22.7
50 3.4 9.28 15.8 30.5 6.78 12.8 25.3
75 5.2 7.34 14.6 30.5 6.60 13.3 25.2
150 10.3 5.83 12.4 30.5 6.76 13.0 25.3
250 17.2 8.30 15.9 30.5 6.30 12.3 25.5
50 3.4 9.98 17.3 30.5 7.54 16.3 25.1
75 5.2 10.3 19.6 30.5 8.23 16.7 25.2
150 10.3 8.45 16.8 30.5 7.94 16.1 25.2
250 17.2 8.39 18.2 30.5 7.87 16.0 25.4
50 3.4 5.86 9.73 20.3 4.63 7.98 16.7
75 5.2 5.77 9.40 20.6 4.94 8.54 16.8
150 10.3 5.46 9.05 19.9 5.00 8.25 17.1
250 17.2 5.89 9.60 20.4 5.30 8.59 18.0
50 3.4 7.28 12.7 26.5 6.02 10.3 22.8
75 5.2 6.87 12.1 27.1 6.06 10.4 22.4
150 10.3 5.26 9.59 23.1 6.02 10.3 23.3
250 17.2 6.59 11.6 26.7 5.67 10.2 23.5
50 3.4 6.57 13.0 30.5 6.42 11.9 25.8
75 5.2 8.02 14.6 30.2 6.64 12.1 26.1
150 10.3 7.09 13.6 29.7 6.49 12.2 25.5
250 17.2 7.25 13.5 30.5 6.87 12.5 26.8
50 3.4 10.6 17.5 30.5 7.45 14.2 26.3
75 5.2 7.36 14.8 30.5 7.97 15.2 26.3
150 10.3 7.05 14.5 30.5 7.27 14.3 26.6
250 17.2 7.89 16.0 30.5 7.25 15.0 26.7
NPS 3 / DN 80 Body NPS 4 / DN 100 Body
AT % DROOP
V
11
Page 12

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Table 8. Typical Air CV Coefficient with Linear Cage - Setpoint Made at 10% Flow (for Type MR105 with High-Pressure Actuator)
SPRING RANGE,
PART NUMBER
AND COLOR
25 to 60 psig /
1.7 to 4.1 bar
GE42907X012
Green
25 to 45 psig /
1.7 to 3.1 bar
GE42907X012
Green
43 to 100 psig /
3.0 to 6.9 bar
GE42909X012
White
75 to 175 psig /
5.2 to 12.1 bar
GE42910X012
Silver
110 to 300 psig /
7.6 to 20.7 bar
GE42911X012
Orange
- Spring range is not available for the body size.
SET
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar 10% 20% 40% 10% 20% 40%
25 1.7
30 2.1
40 2.8
50 3.4
60 4.1
25 1.7
30 2.1
40 2.8
45 3.1
50 3.4
60 4.1
75 5.2
100 6.9
75 5.2
100 6.9
125 8.6
150 10.3
175 12.1
125 8.6
150 10.3
200 13.8
250 17.2
300 20.7 350 24.1 5.11 11.5 13.7 6.56 14.2 22.5
PRESSURE
50 3.4 2.01 2.74 5.26
75 5.2 2.10 3.13 5.83
150 10.3 2.17 3.24 6.30
250 17.2 2.00 2.99 7.61
50 3.4 2.17 3.47 6.61
75 5.2 2.73 3.64 7.13
150 10.3 2.33 3.66 8.14
250 17.2 2.28 3.72 10.1
50 3.4 2.48 4.14 8.86
75 5.2 2.82 4.64 9.73
150 10.3 2.50 4.34 10.6
250 17.2 2.72 4.89 13.6
75 5.2 2.77 5.11 11.6
150 10.3 3.01 5.55 13.6
250 17.2 3.07 6.03 13.7
75 5.2 3.10 5.69 13.7
150 10.3 3.62 6.83 13.7
250 17.2 3.50 7.21 13.7
50 3.4 3.17 4.27 6.43
75 5.2 2.74 3.77 6.24
150 10.3 3.18 4.01 6.81
250 17.2 2.95 3.89 6.64
50 3.4 2.96 4.15 7.35
75 5.2 3.37 4.44 8.00
150 10.3 3.30 4.62 8.10
250 17.2 3.09 4.35 7.74
50 3.4 3.41 5.39 9.80
75 5.2 3.86 5.66 10.8
150 10.3 3.44 5.31 10.5
250 17.2 3.60 5.46 10.4
75 5.2 3.71 5.86 11.6
150 10.3 3.67 5.63 11.3
250 17.2 3.92 6.01 12.4
75 5.2 2.48 4.05 8.07 3.46 5.05 9.51
150 10.3 2.61 4.12 9.19 3.35 4.99 9.34
250 17.2 2.49 4.07 10.8 3.30 5.12 9.71
75 5.2 2.71 4.63 10.1 3.75 5.94 11.6
150 10.3 2.77 4.85 10.9 3.71 5.75 11.3
250 17.2 2.75 5.01 13.3 3.69 5.81 11.7
100 6.9 2.71 5.21 12.2 4.21 6.84 14.9
150 10.3 3.33 6.23 13.7 4.24 7.29 15.4
250 17.2 3.15 5.93 13.7 3.89 6.84 14.8
150 10.3 3.64 7.53 13.7 4.16 8.26 20.0
250 17.2 3.57 7.50 13.7 4.37 8.73 21.0
100 6.9 2.60 4.35 9.01 3.50 5.02 9.72
250 17.2 2.59 4.17 9.72 3.76 5.63 10.1
150 10.3 2.71 5.14 11.5 3.62 6.13 13.2
250 17.2 3.00 5.46 12.7 4.17 6.72 14.2
200 13.8 3.34 6.50 13.7 4.13 7.88 17.7
300 20.7 3.50 6.63 13.7 4.45 8.13 18.5
200 13.8 3.94 7.93 13.7 4.90 9.21 21.8
300 20.7 3.90 8.06 13.7 4.98 9.43 21.8
200 13.8 4.06 8.86 13.7 5.34 11.0 22.1
300 20.7 4.55 9.82 13.7 5.70 11.3 22.5
150 10.3 2.38 4.55 9.87 3.52 5.89 12.3
250 17.2 2.94 5.07 11.2 3.86 6.56 12.9
200 13.8 2.97 5.58 12.7 4.10 7.14 15.3
300 20.7 3.08 5.85 13.6 4.37 7.33 16.3
250 17.2 3.82 7.75 13.7 4.94 9.20 21.3
300 20.7 4.23 8.35 13.7 5.62 10.5 22.1
300 20.7 3.90 9.76 13.7 5.66 11.4 22.5
350 24.1 5.06 10.2 13.7 6.75 13.7 22.5
12
INLET
CV AT % DROOP
NPS 1 / DN 25 Body NPS 2 / DN 50 Body
- continued -
Page 13

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Table 8. Typical Air CV Coefficient with Linear Cage - Setpoint Made at 10% Flow (for Type MR105
with High-Pressure Actuator) (continued)
SPRING RANGE,
PART NUMBER
AND COLOR
39 to 72 psig /
2.7 to 5.0 bar
GE42909X012
White
71 to 175 psig /
4.9 to 12.1 bar
GE42910X012
Silver
110 to 250 psig /
7.6 to 17.2 bar
GE42911X012
Orange
SET
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar 10% 20% 40% 10% 20% 40%
40 2.8
50 3.4
60 4.1
70 4.8
75 5.2
100 6.9
125 8.6
150 10.3
175 12.1
125 8.6
150 10.3
200 13.8
250 17.2
INLET
PRESSURE
75 5.2 3.57 4.93 7.96 3.48 4.79 7.68
150 10.3 4.00 5.45 8.86 3.82 5.20 8.44
250 17.2 3.87 5.22 8.48 3.68 4.97 8.08
75 5.2 4.00 5.46 9.98 3.93 5.34 9.68
150 10.3 3.91 5.49 10.0 3.75 5.25 9.57
250 17.2 3.89 5.50 9.74 3.70 5.24 9.28
75 5.2 4.35 6.74 12.4 4.30 6.63 12.1
150 10.3 3.96 6.06 11.8 3.82 5.82 11.3
250 17.2 4.54 6.52 12.3 4.32 6.21 11.7
100 6.9 4.24 6.85 14.0 4.17 6.71 13.6
150 10.3 4.52 7.11 14.0 4.38 6.86 13.4
250 17.2 4.51 6.90 14.0 4.30 6.57 13.4
100 6.9 4.22 6.23 11.4 4.16 6.11 11.0
150 10.3 4.53 6.56 11.8 4.39 6.35 11.4
250 17.2 4.30 6.21 11.0 4.11 5.92 10.5
150 10.3 3.56 6.26 13.4 3.49 6.11 13.0
250 17.2 4.76 7.42 14.5 4.58 7.11 13.8
200 13.8 5.49 9.09 19.5 5.37 8.84 18.8
300 20.7 5.36 8.78 18.7 5.16 8.42 17.8
200 13.8 5.80 10.3 23.4 5.71 10.1 22.7
300 20.7 5.91 10.3 22.7 5.72 9.97 21.7
200 13.8 4.86 9.89 26.3 4.82 9.74 25.6
300 20.7 6.86 12.4 28.4 6.68 12.0 27.3
150 10.3 4.40 7.06 14.3 4.35 6.95 13.9
250 17.2 4.56 6.81 13.5 4.41 6.57 12.9
200 13.8 5.08 8.27 17.4 5.00 8.10 16.9
300 20.7 4.16 7.07 15.2 4.03 6.82 14.6
250 17.2 6.42 11.1 24.4 6.33 10.9 23.7
300 20.7 6.83 11.5 25.1 6.69 11.2 24.3
300 20.7 7.58 13.5 29.6 7.49 13.3 27.5
350 24.1 8.40 15.1 29.5 8.24 14.7 27.5
NPS 3 / DN 80 Body NPS 4 / DN 100 Body
CV AT % DROOP
13
Page 14

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Table 9. Typical Water C
with Low-Pressure Actuator)
SPRING RANGE,
PART NUMBER
AND COLOR
5 to 12 psig /
0.34 to 0.83 bar
GE42909X012
White
10 to 24 psig /
0.69 to 1.6 bar
GE42910X012
Silver
14 to 32 psig /
0.96 to 2.2 bar
GE42911X012
Orange
18 to 43 psig /
1.2 to 3.0 bar
GE43002X012
Red
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar 10% 20% 40% 10% 20% 40% 10% 20% 40%
5 0.34
10 0.69
10 0.69
15 1.0
20 1.4
15 1.0
20 1.4
25 1.7
30 2.1
20 1.4
25 1.7
30 2.1
35 2.4
40 2.8
Coefficient with Quick Opening Cage - Setpoint Made at 10% Flow (for Type MR105
V
SET
INLET
PRESSURE
25 1.7
75 5.2
150 10.3
25 1.7
75 5.2
150 10.3
25 1.7
75 5.2
150 10.3
25 1.7
75 5.2
150 10.3
50 3.4
75 5.2
150 10.3
25 1.7
75 5.2
150 10.3
25 1.7
75 5.2
150 10.3
50 3.4
75 5.2
150 10.3
50 3.4
75 5.2
150 10.3
50 3.4
75 5.2
150 10.3
50 3.4
75 5.2
150 10.3
50 3.4
75 5.2
150 10.3
50 3.4
75 5.2
150 10.3
50 3.4
75 5.2
150 10.3 12.2 17.5 17.5 15.5 29.9 43.8 24.3 44.3 48.2
NPS 1 / DN 25 Body NPS 2 / DN 50 - Reduced Port NPS 2 / DN 50 Body
5.30 10.9 17.5 8.17 14.3 24.6 11.9 22.7 39.5
5.00 10.5 17.5 8.81 14.3 21.5 11.0 21.2 33.2
4.51 9.86 16.8 8.59 12.4 17.4 11.5 19.0 31.8
8.75 17.1 17.5 12.5 23.2 42.9 18.3 37.5 48.2
9.11 17.5 17.5 12.2 20.6 35.5 17.8 31.4 48.2
9.45 16.9 17.5 11.9 17.1 29.8 16.9 26.8 44.2
7.25 14.6 17.5 10.0 18.8 33.1 15.3 30.0 48.2
6.52 14.0 17.5 10.3 17.4 28.6 14.6 25.8 41.5
6.68 14.5 17.5 9.71 14.9 24.1 14.7 24.0 36.3
10.9 17.5 17.5 13.6 28.5 43.8 20.9 44.0 48.2
8.29 16.0 17.5 14.2 26.7 42.6 18.1 33.9 48.2
8.33 16.8 17.5 12.2 20.1 33.9 17.3 30.8 48.2
9.90 17.5 17.5 14.8 30.2 43.8 23.3 44.4 48.2
10.7 17.5 17.5 15.9 29.1 43.8 22.3 42.6 48.2
11.4 17.5 17.5 13.7 25.7 43.2 19.5 37.8 48.2
7.08 15.2 17.5 10.6 20.2 36.7 15.6 33.5 48.2
7.65 15.0 17.5 11.2 19.2 33.1 15.7 28.8 47.8
7.11 14.7 17.5 10.7 16.8 28.1 14.8 26.9 46.5
9.07 17.5 17.5 14.0 31.2 43.8 20.0 47.0 48.2
9.93 17.3 17.5 14.3 27.1 43.3 19.9 40.1 48.2
9.40 17.1 17.5 12.3 21.0 36.3 19.3 38.4 48.2
9.53 17.5 17.5 16.6 33.2 43.8 24.2 47.2 48.2
12.4 17.5 17.5 16.3 32.4 43.8 22.1 42.1 48.2
9.92 17.5 17.5 14.0 25.6 43.8 20.3 39.9 48.2
11.7 17.5 17.5 16.7 34.7 43.8 25.0 48.2 48.2
11.8 17.5 17.5 17.6 33.9 43.8 23.7 47.1 48.2
11.8 17.5 17.5 15.5 29.3 43.8 22.0 40.8 48.2
6.89 14.4 17.5 10.8 20.3 35.2 15.9 29.8 48.2
7.55 14.9 17.5 11.3 19.6 34.1 15.9 29.4 48.2
6.88 14.4 17.5 11.0 18.2 29.5 15.7 28.2 44.9
8.77 16.4 17.5 12.8 26.0 43.8 19.1 39.6 48.2
8.28 16.8 17.5 13.5 24.4 41.6 19.0 35.8 48.2
8.86 16.8 17.5 12.0 19.5 33.3 18.2 32.4 48.2
9.80 17.5 17.5 14.4 30.0 43.8 22.7 46.8 48.2
9.53 17.5 17.5 15.0 27.7 43.8 20.5 39.2 48.2
10.5 17.5 17.5 12.8 22.6 39.5 19.4 38.3 48.2
10.2 17.5 17.5 17.0 34.6 43.8 25.1 48.2 48.2
10.3 17.5 17.5 16.8 31.6 43.8 23.7 45.6 48.2
11.5 17.5 17.5 14.1 26.3 43.8 21.8 40.6 48.2
10.7 17.5 17.5 17.4 38.6 43.8 25.1 48.2 48.2
11.2 17.5 17.5 18.9 35.3 43.8 25.3 48.2 48.2
CV AT % DROOP
14
- continued -
Page 15

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Table 9. Typical Water C
with Low-Pressure Actuator) (continued)
SPRING RANGE,
PART NUMBER
AND COLOR
5 to 8 psig /
0.34 to 0.55 bar
GE42909X012
White
8 to 20 psig /
0.55 to 1.4 bar
GE42910X012
Silver
12 to 30 psig /
0.83 to 2.1 bar
GE42911X012
Orange
18 to 39 psig /
1.2 to 2.7 bar
GE43002X012
Red
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar 10% 20% 40% 10% 20% 40%
5 0.34
8 0.55
10 0.69
15 1.0
20 1.4
15 1.0
20 1.4
25 1.7
30 2.1
20 1.4
25 1.7
30 2.1
35 2.4
Coefficient with Quick Opening Cage - Setpoint Made at 10% Flow (for Type MR105
V
C
AT % DROOP
SET
INLET
PRESSURE
25 1.7 19.2 32.7 55.3 24.3 44.4 75.2
75 5.2 17.4 27.8 43.0 23.8 38.0 61.1
150 10.3 17.3 22.6 37.2 24.2 34.8 49.5
25 1.7 23.5 46.1 80.5 28.7 65.4 11 3
75 5.2 21.6 36.8 61.9 29.7 52.1 86.9
150 10.3 19.9 29.3 50.3 27.2 44.8 71.0
25 1.7 22.5 43.2 75.3 29.8 57.5 100
75 5.2 20.9 35.6 62.6 28.9 50.6 84.4
150 10.3 20.4 31.6 51.9 27.8 43.5 71.7
25 1.7 29.8 62.4 103 36.9 82.1 136
75 5.2 27.7 51.3 85.0 33.7 71.0 124
150 10.3 23.2 40.9 72.2 35.0 58.9 99.9
50 3.4 32.9 68.7 103 40.8 92.5 136
75 5.2 30.6 64.7 103 40.3 86.8 136
150 10.3 28.3 51.6 91.2 38.4 70.1 127
25 1.7 25.4 50.4 91.1 30.7 64.5 11 9
75 5.2 23.6 42.2 72.7 28.4 55.2 94.8
150 10.3 21.5 36.0 62.1 29.5 51.0 83.1
25 1.7 30.6 70.3 103 38.6 91.0 136
75 5.2 28.0 54.6 94.0 34.6 68.1 124
150 10.3 23.8 43.6 77.6 35.4 62.4 103
50 3.4 32.6 67.4 103 42.9 90.1 136
75 5.2 32.6 66.0 103 39.9 82.8 136
150 10.3 28.9 54.9 92.3 39.4 73.7 126
250 17.2 27.1 46.8 79.3 36.0 61.3 106.9
50 3.4 38.2 81.7 103 47.1 107 136
75 5.2 38.4 76.8 103 46.5 98.2 136
150 10.3 32.5 64.1 103 43.8 86.0 136
250 17.2 29.6 52.6 84.3 40.8 73.2 124.2
50 3.4 24.6 46.3 80.3 30.6 57.4 105
75 5.2 24.1 43.8 77.1 29.7 57.0 99.8
150 10.3 21.8 38.1 65.0 29.0 50.2 87.2
50 3.4 28.4 56.4 103 36.4 70.1 127
75 5.2 29.5 54.2 94.0 32.9 68.2 121
150 10.3 24.0 45.4 78.8 33.2 61.1 104
250 17.2 23.9 39.9 66.1 31.9 53.8 91.0
50 3.4 31.7 65.8 103 38.8 83.4 136
75 5.2 32.5 64.2 103 37.2 79.0 136
150 10.3 27.5 54.9 92.8 36.0 71.0 121
250 17.2 25.6 45.4 79.0 34.7 60.9 106.3
50 3.4 36.0 77.2 103 42.8 99.4 136
75 5.2 37.0 74.6 103 41.1 88.9 136
150 10.3 31.1 61.8 103 38.7 80.4 136
250 17.2 28.7 52.4 88.5 39.5 71.3 122
NPS 3 / DN 80 Body NPS 4 / DN 100 Body
V
15
Page 16

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Table 10. Typical Water C
Coefficient with Quick Opening Cage - Setpoint Made at 10% Flow (for Type MR105
V
with High-Pressure Actuator)
SPRING RANGE,
PART NUMBER
AND COLOR
25 to 60 psig /
1.7 to 4.1 bar
GE42907X012
Green
25 to 45 psig /
1.7 to 3.1 bar
GE42907X012
Green
43 to 100 psig /
3.0 to 6.9 bar
GE42909X012
White
75 to 175 psig /
5.2 to 12.1 bar
GE42910X012
Silver
110 to 300 psig /
7.6 to 20.7 bar
GE42911X012
Orange
- Spring range is not available for the body size.
SET
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar 10% 20% 40% 10% 20% 40% 10% 20% 40%
25 1.7
30 2.1
40 2.8
50 3.4
60 4.1
25 1.7
30 2.1
40 2.8
45 3.1
50 3.4
60 4.1
75 5.2
100 6.9
75 5.2
100 6.9
125 8.6
150 10.3
175 12.1
125 8.6
150 10.3
200 13.8
250 17.2
300 20.7 350 24.1 13.0 17.5 17.5 16.9 38.6 43.8 25.5 48.2 48.2
INLET
PRESSURE
50 3.4 4.39 8.73 15.5
75 5.2 4.83 9.38 16.4
150 10.3 4.87 11.7 17.5
250 17.2 4.10 17.5 17.5
50 3.4 4.80 10.0 17.3
75 5.2 5.34 10.8 17.5
150 10.3 5.59 14.0 17.5
250 17.2 5.33 17.5 17.5
50 3.4 5.88 13.2 17.5
75 5.2 7.05 13.7 17.5
150 10.3 7.68 16.8 17.5
250 17.2 9.43 17.5 17.5
75 5.2 7.30 15.3 17.5
150 10.3 9.17 17.5 17.5
250 17.2 15.9 17.5 17.5
75 5.2 8.07 17.1 17.5
150 10.3 10.9 17.5 17.5
250 17.2 15.8 17.5 17.5
50 3.4 7.25 12.1 19.6 9.73 16.2 28.9
75 5.2 8.14 12.8 19.5 11.2 17.8 27.9
150 10.3 7.35 11.3 17.3 10.3 16.0 24.8
50 3.4 7.30 13.3 23.4 10.2 18.9 33.7
75 5.2 8.66 14.1 22.9 12.3 20.4 32.6
150 10.3 7.48 12.4 20.5 11.0 18.3 29.5
50 3.4 8.82 17.7 31.9 13.4 27.6 48.2
75 5.2 10.9 18.4 30.8 15.4 26.8 45.4
150 10.3 8.71 15.2 26.0 13.9 23.0 39.8
75 5.2 8.68 16.9 31.2 13.1 25.4 46.6
150 10.3 9.27 16.1 29.4 12.6 24.8 43.0
75 5.2 6.02 12.4 17.5 8.40 15.9 28.6 11.9 23.6 43.0
150 10.3 6.73 13.8 17.5 8.78 15.2 26.3 13.1 23.4 41.5
250 17.2 8.03 17.5 17.5 8.45 13.9 23.2 11.9 20.4 37.4
75 5.2 6.76 14.4 17.5 9.60 19.0 35.0 13.5 28.0 48.2
150 10.3 7.76 15.6 17.5 9.80 17.1 30.7 15.3 27.9 48.2
250 17.2 8.36 17.5 17.5 8.93 15.6 26.6 13.9 25.7 46.8
100 6.9 7.89 16.2 17.5 9.82 20.9 39.5 15.3 32.5 48.2
250 17.2 12.4 17.5 17.5 10.2 18.1 32.6 15.5 29.7 48.2
150 10.3 10.1 17.5 17.5 11.9 24.7 43.8 17.0 38.7 48.2
250 17.2 13.0 17.5 17.5 13.0 23.5 43.1 19.1 40.0 48.2
100 6.9 5.79 12.5 17.5 8.07 15.8 29.6 11.9 24.5 45.1
250 17.2 6.22 13.9 17.5 9.18 15.6 26.2 12.4 22.1 41.6
150 10.3 7.23 15.2 17.5 9.30 18.7 35.9 14.7 29.8 48.2
250 17.2 8.54 16.7 17.5 11.1 19.5 34.0 15.7 28.1 48.2
200 13.8 8.66 17.4 17.5 11.1 22.4 40.8 16.6 33.9 48.2
300 20.7 10.9 17.5 17.5 12.1 22.0 39.6 16.7 35.5 48.2
200 13.8 9.92 17.5 17.5 12.8 26.5 43.8 19.0 40.5 48.2
300 20.7 11.9 17.5 17.5 14.4 26.1 43.8 21.7 43.3 48.2
200 13.8 10.6 17.5 17.5 14.4 33.5 43.8 21.0 48.2 48.2
300 20.7 12.4 17.5 17.5 15.7 29.8 43.8 24.5 48.2 48.2
150 10.3 6.53 14.7 17.5 9.47 19.7 37.2 13.6 29.7 48.2
250 17.2 7.68 15.0 17.5 11.1 19.3 33.2 16.2 30.0 48.2
200 13.8 7.44 15.7 17.5 10.3 21.4 41.1 15.1 33.4 48.2
300 20.7 9.65 17.5 17.5 12.1 21.5 38.5 17.6 35.1 48.2
250 17.2 9.44 17.5 17.5 12.5 27.4 43.8 19.0 42.3 48.2
300 20.7 11.7 17.5 17.5 15.8 29.4 43.8 23.6 46.5 48.2
300 20.7 11.2 17.5 17.5 14.3 32.3 43.8 22.7 48.2 48.2
350 24.1 14.1 17.5 17.5 18.3 35.5 43.8 28.4 48.2 48.2
CV AT % DROOP
NPS 1 / DN 25 Body NPS 2 / DN 50 - Reduced Port NPS 2 / DN 50 Body
16
- continued -
Page 17

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Table 10. Typical Water CV Coefficient with Quick Opening Cage - Setpoint Made at 10% Flow (for Type MR105
with High-Pressure Actuator) (continued)
SPRING RANGE,
PART NUMBER
AND COLOR
39 to 72 psig /
2.7 to 5.0 bar
GE42909X012
White
71 to 175 psig /
4.9 to 12.1 bar
GE42910X012
Silver
110 to 250 psig /
7.6 to 17.2 bar
GE42911X012
Orange
SET
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar 10% 20% 40% 10% 20% 40%
40 2.8
50 3.4
60 4.1
70 4.8
75 5.2
100 6.9
125 8.6
150 10.3
175 12.1
125 8.6
150 10.3
200 13.8
250 17.2
INLET
PRESSURE
75 5.2 16.2 26.6 42.4 19.5 33.1 53.1
150 10.3 16.6 24.6 36.0 21.7 33.4 47.9
250 17.2 15.3 20.9 29.6 20.7 28.3 38.0
75 5.2 17.3 31.2 51.5 23.4 42.5 70.0
150 10.3 18.6 28.5 43.2 24.4 39.2 56.8
250 17.2 16.0 23.4 34.8 21.9 31.6 44.7
75 5.2 18.8 37.1 64.0 26.0 50.1 87.3
150 10.3 20.5 32.8 50.6 26.6 43.5 65.4
250 17.2 16.9 26.4 39.6 22.7 34.6 51.0
100 6.9 20.2 39.2 67.4 26.5 51.4 87.9
150 10.3 22.7 37.6 59.4 30.2 50.8 78.0
250 17.2 18.4 29.5 45.3 24.3 39.2 58.4
100 6.9 18.8 34.8 60.0 24.4 46.0 77.1
150 10.3 21.8 35.2 55.3 29.1 47.9 71.8
250 17.2 17.5 28.1 42.8 23.8 38.2 55.8
150 10.3 20.8 37.8 67.4 26.6 51.1 86.2
250 17.2 21.1 35.0 55.5 28.2 46.7 71.3
200 13.8 22.2 41.5 73.1 28.3 55.0 92.2
300 20.7 22.9 38.2 65.5 30.4 50.8 81.0
200 13.8 25.2 51.3 92.5 32.7 68.6 118
300 20.7 26.3 45.7 76.4 35.5 62.7 93.6
200 13.8 29.6 64.4 103 37.4 83.3 136
300 20.7 30.1 55.2 90.1 40.0 71.8 114.5
150 10.3 21.1 41.8 74.0 26.3 55.1 95.2
250 17.2 22.5 37.8 60.1 30.4 49.7 80.5
200 13.8 23.4 44.7 78.4 28.5 56.6 98.4
300 20.7 24.4 41.4 65.1 31.4 53.3 89.4
250 17.2 26.7 54.8 95.2 32.4 69.4 123
300 20.7 32.3 57.9 94.7 39.1 73.5 119
300 20.7 28.9 64.2 103.1 36.0 81.6 136
350 24.1 36.9 67.9 103.1 47.9 92.5 135.9
NPS 3 / DN 80 Body NPS 4 / DN 100 Body
CV AT % DROOP
17
Page 18

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Table 11. Typical Air Capacities with Linear Cage - Setpoint Made at 10% Flow (for Type MR105 with Low-Pressure Actuator)
SPRING RANGE,
PART NUMBER
AND COLOR
5 to 12 psig /
0.34 to 0.83 bar
GE42909X012
White
10 to 24 psig /
0.69 to 1.6 bar
GE42910X012
Silver
14 to 32 psig /
0.96 to 2.2 bar
GE42911X012
Orange
18 to 43 psig /
1.2 to 3.0 bar
GE43002X012
Red
SET
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h
5 0.34
10 0.69
10 0.69
15 1.0
20 1.4
15 1.0
20 1.4
25 1.7
30 2.1
20 1.4
25 1.7
30 2.1
35 2.4
40 2.8
INLET
PRESSURE
25 1.7 3300 89 4800 130 9800 260 3800 100 5800 160 11,800 320
75 5.2 7700 210 12,200 330 25,800 690 10,600 280 13,600 360 27,300 730
150 10.3 15,500 420 22,200 600 50,000 1300 18,000 480 27,600 740 57,100 1500
250 17.2 18,400 490 29,100 780 76,400 2000 28,000 750 43,000 1200 93,800 2500
25 1.7 3100 84 7500 200 17,300 460 5700 150 11,800 320 25,700 690
75 5.2 12,000 320 23,400 630 41,600 1100 14,000 370 26,200 700 66,100 1800
150 10.3 20,300 540 38,000 1000 79,700 2100 21,600 580 46,600 1200 121,000 3200
250 17.2 34,500 930 76,000 2000 128,000 3400 38,800 1000 73,700 2000 182,000 4900
25 1.7 3100 84 6100 160 13,900 370 4600 120 8000 210 16,600 450
75 5.2 8600 230 15,300 410 34,200 920 10,200 270 18,300 490 38,500 1000
150 10.3 15,600 420 28,000 750 64,700 1700 19,700 530 34,200 920 79,300 2100
250 17.2 29,200 780 46,000 1200 114,000 3100 30,900 830 57,800 1500 127,000 3400
25 1.7 4000 110 8400 230 16,700 450 5100 140 11,400 310 26,200 700
75 5.2 11,600 310 22,400 600 43,200 1200 15,200 410 28,200 760 66,600 1800
150 10.3 21,900 590 43,400 1200 79,100 2100 28,500 760 54,600 1500 123,000 3300
250 17.2 34,500 920 70,500 1900 128,000 3400 40,400 1100 87,800 2400 192,000 5200
50 3.4 9800 260 21,900 590 30,600 820 12,500 330 26,000 700 48,200 1300
75 5.2 13,500 360 29,200 780 42,500 1100 17,100 460 35,900 960 68,000 1800
150 10.3 26,600 710 61,200 1600 79,400 2100 26,800 720 58,000 1600 125,000 3300
250 17.2 44,000 1200 90,800 2400 127,000 3400 52,800 1400 121,000 3200 202,000 5400
25 1.7 3300 87 6400 170 14,700 390 4700 130 8400 230 20,100 540
75 5.2 8500 230 16,800 450 36,800 990 11,100 300 19,600 520 46,400 1200
150 10.3 16,000 430 28,900 780 65,100 1700 22,500 600 41,600 1100 90,900 2400
250 17.2 27,000 720 51,800 1400 120,000 3200 34,500 920 63,200 1700 164,000 4400
25 1.7 3500 94 7700 210 15,100 400 4300 120 10,400 280 22,700 610
75 5.2 10,300 280 20,200 540 42,000 1100 13,500 360 26,400 710 66,000 1800
150 10.3 19,700 530 39,000 1000 77,900 2100 28,600 770 53,700 1400 122,000 3300
250 17.2 33,500 900 65,300 1700 127,000 3400 38,700 1000 79,800 2100 194,000 5200
50 3.4 9500 250 18,900 510 29,900 800 10,300 280 22,900 610 47,200 1300
75 5.2 11,200 300 25,500 680 43,000 1200 14,400 390 35,500 950 67,100 1800
150 10.3 22,600 610 49,100 1300 79,100 2100 28,900 770 63,400 1700 125,000 3400
250 17.2 36,400 980 87,500 2300 129,000 3400 42,700 1100 97,300 2600 202,000 5400
50 3.4 10,000 270 22,000 590 29,700 800 11,100 300 27,300 730 46,400 1200
75 5.2 14,700 390 33,200 890 42,300 1100 18,600 500 41,900 1100 67,800 1800
150 10.3 26,700 720 62,100 1700 78,900 2100 34,600 930 80,700 2200 125,000 3300
250 17.2 49,700 1300 114,000 3100 128,000 3400 47,200 1300 121,000 3300 202,000 5400
50 3.4 5600 150 11,600 310 24,100 640 7800 210 15,700 420 33,200 890
75 5.2 7800 210 15,500 420 33,600 900 14,000 370 19,900 530 46,300 1200
150 10.3 16,900 450 30,000 800 66,400 1800 23,200 620 41,300 1100 90,100 2400
250 17.2 25,400 680 45,200 1200 108,000 2900 36,300 970 62,500 1700 150,000 4000
50 3.4 6400 170 13,400 360 27,700 740 10,000 270 18,100 490 43,200 1200
75 5.2 11,000 290 20,700 560 41,600 1100 12,200 330 26,900 720 61,900 1700
150 10.3 18,000 480 37,600 1000 76,600 2100 26,600 710 49,800 1300 117,000 3100
250 17.2 31,100 830 59,800 1600 125,000 3300 41,000 1100 78,200 2100 181,000 4900
50 3.4 8500 230 16,400 440 29,800 800 9100 240 21,600 580 44,900 1200
75 5.2 12,300 330 24,500 660 42,600 1100 17,100 460 30,100 810 66,400 1800
150 10.3 22,100 590 46,400 1200 79,200 2100 32,700 880 60,600 1600 122,000 3300
250 17.2 34,000 910 70,900 1900 125,000 3300 45,000 1200 95,300 2600 198,000 5300
50 3.4 8400 230 17,900 480 28,600 770 10,600 280 23,600 630 44,700 1200
75 5.2 13,400 360 26,800 720 42,800 1100 17,800 480 38,300 1000 66,600 1800
150 10.3 24,800 660 52,600 1400 78,700 2100 34,900 930 71,800 1900 124,000 3300
250 17.2 39,700 1100 82,200 2200 124,000 3300 50,800 1400 112,000 3000 202,000 5400
50 3.4 8600 230 19,600 530 27,600 740 10,200 270 26,900 720 43,100 1200
75 5.2 12,800 340 30,300 810 42,500 1100 20,200 540 42,500 1100 65,500 1800
150 10.3 25,200 680 61,600 1700 79,700 2100 30,700 820 67,400 1800 125,000 3300
250 17.2 46,000 1200 99,300 2700 127,000 3400 56,200 1500 133,000 3600 204,000 5500
10% Droop 20% Droop 40% Droop 10% Droop 20% Droop 40% Droop
NPS 1 / DN 25 Body NPS 2 / DN 50 Body
CAPACITIES IN SCFH / Nm3/h OF AIR
- continued -
18
Page 19

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Table 11. Typical Air Capacities with Linear Cage - Setpoint Made at 10% Flow (for Type MR105
with Low-Pressure Actuator) (continued)
SPRING RANGE,
PART NUMBER
AND COLOR
5 to 8 psig /
0.34 to 0.55 bar
GE42909X012
White
8 to 20 psig /
0.55 to 1.4 bar
GE42910X012
Silver
12 to 30 psig /
0.83 to 2.1 bar
GE42911X012
Orange
18 to 39 psig /
1.2 to 2.7 bar
GE43002X012
Red
SET
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h
5 0.34
8 0.55
10 0.69
15 1.0
20 1.4
15 1.0
20 1.4
25 1.7
30 2.1
20 1.4
25 1.7
30 2.1
35 2.4
INLET
PRESSURE
25 1.7 6300 170 8700 230 15,600 420 6200 160 8600 230 13,300 360
75 5.2 13,600 360 19,400 520 35,900 960 13,800 370 18,500 500 32,800 880
150 10.3 23,900 640 35,600 950 61,100 1600 24,000 640 34,300 920 61,000 1600
250 17.2 34,400 920 50,400 1300 95,900 2600 40,000 1100 54,400 1500 97,000 2600
25 1.7 8000 210 13,000 350 27,300 730 7000 190 11,000 300 22,800 610
75 5.2 16,800 450 27,400 730 59,200 1600 16,100 430 25,400 680 51,700 1400
150 10.3 28,200 750 47,600 1300 103,000 2800 30,100 810 51,400 1400 97,100 2600
250 17.2 47,700 1300 78,500 2100 174,000 4700 41,500 1100 72,400 1900 156,000 4200
25 1.7 6600 180 11,200 300 22,000 590 5000 130 9600 260 19,300 520
75 5.2 17,000 450 25,800 690 50,800 1400 14,600 390 22,500 600 46,600 1200
150 10.3 28,500 760 43,500 1200 91,000 2400 25,900 690 39,300 1100 78,100 2100
250 17.2 44,900 1200 72,300 1900 151,000 4000 37,700 1000 61,000 1600 127,000 3400
25 1.7 7700 210 15,000 400 34,800 930 6400 170 12,700 340 29,400 790
75 5.2 20,700 560 37,800 1000 85,400 2300 18,600 500 32,500 870 71,700 1900
150 10.3 34,100 910 64,300 1700 151,000 4000 30,900 830 56,100 1500 130,000 3500
250 17.2 57,900 1600 106,000 2900 240,000 6400 48,100 1300 88,700 2400 210,000 5600
50 3.4 13,300 360 28,300 760 64,000 1700 15,200 410 29,200 780 55,100 1500
75 5.2 25,000 670 49,300 1300 91,000 2400 23,600 630 42,700 1100 76,100 2000
150 10.3 44,200 1200 90,300 2400 168,000 4500 38,000 1000 74,000 2000 154,000 4100
250 17.2 72,900 2000 145,000 3900 271,000 7300 72,800 2000 121,000 3200 250,000 6700
25 1.7 6400 170 11,300 300 24,500 660 5300 140 9000 240 20,900 560
75 5.2 16,700 450 27,000 720 58,400 1600 15,400 410 24,900 670 50,200 1300
150 10.3 29,100 780 49,200 1300 105,000 2800 28,900 770 47,000 1300 97,000 2600
250 17.2 47,800 1300 78,900 2100 173,000 4600 46,000 1200 75,400 2000 157,000 4200
25 1.7 7200 190 14,100 380 31,700 850 4700 130 10,100 270 26,100 700
75 5.2 19,600 520 35,300 940 81,300 2200 20,000 530 34,200 920 75,400 2000
150 10.3 34,300 920 61,600 1700 149,000 4000 35,100 940 61,400 1600 138,000 3700
250 17.2 49,600 1300 94,200 2500 234,000 6300 48,900 1300 87,200 2300 207,000 5600
50 3.4 18,400 490 32,000 860 63,900 1700 13,800 370 26,600 710 54,300 1500
75 5.2 21,400 570 42,600 1100 90,200 2400 19,900 530 40,500 1100 77,300 2100
150 10.3 31,500 840 66,900 1800 166,000 4400 38,300 1000 73,600 2000 143,000 3800
250 17.2 71,900 1900 138,000 3700 267,000 7200 57,400 1500 112,000 3000 232,000 6200
50 3.4 18,900 510 33,800 910 64,600 1700 14,600 390 32,600 870 52,900 1400
75 5.2 29,700 800 56,800 1500 89,800 2400 24,500 660 50,300 1300 76,800 2100
150 10.3 45,600 1200 90,500 2400 167,000 4500 44,900 1200 91,200 2400 143,000 3800
250 17.2 72,700 1900 158,000 4200 269,000 7200 71,700 1900 145,000 3900 231,000 6200
50 3.4 12,000 320 20,100 540 42,600 1100 9800 260 17,000 460 36,300 970
75 5.2 16,900 450 27,600 740 60,300 1600 15,100 400 26,100 700 51,600 1400
150 10.3 29,500 790 48,800 1300 107,000 2900 28,300 760 46,700 1300 96,600 2600
250 17.2 51,100 1400 83,200 2200 177,000 4700 48,300 1300 78,200 2100 164,000 4400
50 3.4 14,400 390 25,700 690 55,100 1500 12,200 330 21,400 570 48,900 1300
75 5.2 20,000 540 35,400 950 79,300 2100 18,300 490 31,600 850 68,800 1800
150 10.3 28,400 760 51,700 1400 125,000 3300 34,100 910 58,300 1600 132,000 3500
250 17.2 57,100 1500 100,000 2700 232,000 6200 51,600 1400 93,000 2500 214,000 5700
50 3.4 12,400 330 25,500 680 62,800 1700 12,400 330 23,900 640 54,400 1500
75 5.2 23,100 620 42,300 1100 88,300 2400 19,700 530 36,500 980 79,500 2100
150 10.3 38,200 1000 73,500 2000 160,000 4300 36,700 980 68,900 1800 145,000 3900
250 17.2 62,900 1700 117,000 3100 265,000 7100 62,600 1700 114,000 3100 244,000 6500
50 3.4 18,700 500 32,700 880 63,000 1700 13,400 360 27,100 730 54,300 1500
75 5.2 20,800 560 42,500 1100 90,300 2400 23,200 620 45,000 1200 79,900 2100
150 10.3 38,000 1000 78,400 2100 167,000 4500 41,100 1100 81,000 2200 151,000 4000
250 17.2 68,400 1800 139,000 3700 270,000 7200 66,000 1800 137,000 3700 244,000 6500
10% Droop 20% Droop 40% Droop 10% Droop 20% Droop 40% Droop
NPS 3 / DN 80 Body NPS 4 / DN 100 Body
CAPACITIES IN SCFH / Nm3/h OF AIR
19
Page 20

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Table 12. Typical Air Capacities with Linear Cage - Setpoint Made at 10% Flow (for Type MR105 with High-Pressure Actuator)
SPRING RANGE,
PART NUMBER
AND COLOR
25 to 60 psig /
1.7 to 4.1 bar
GE42907X012
Green
25 to 45 psig /
1.7 to 3.1 bar
GE42907X012
Green
43 to 100 psig /
3.0 to 6.9 bar
GE42909X012
White
75 to 175 psig /
5.2 to 12.1 bar
GE42910X012
Silver
110 to 300 psig /
7.6 to 20.7 bar
GE42911X012
Orange
- Spring range is not available for the body size.
SET
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h
25 1.7
30 2.1
40 2.8
50 3.4
60 4.1
25 1.7
30 2.1
40 2.8
45 3.1
50 3.4
60 4.1
75 5.2
100 6.9
75 5.2
100 6.9
125 8.6
150 10.3
175 12.1
125 8.6
150 10.3
200 13.8
250 17.2
300 20.7 350 24.1 46,800 1300 119,000 3200 171,000 4600 60,000 1600 146,000 3900 264,000 7100
INLET
PRESSURE
50 3.4 4100 110 5600 150 11,200 300
75 5.2 6300 170 9400 250 17,700 470
150 10.3 12,100 330 18,100 490 35,200 940
250 17.2 17,900 480 26,900 720 68,400 1800
50 3.4 4200 110 6900 190 13,800 370
75 5.2 8000 220 10,900 290 21,500 580
150 10.3 13,000 350 20,500 550 45,500 1200
250 17.2 20,500 550 33,500 900 91,000 2400
50 3.4 4000 110 7300 200 17,600 470
75 5.2 8000 210 13,400 360 29,000 780
150 10.3 14,000 370 24,200 650 59,000 1600
250 17.2 24,500 660 44,000 1200 122,000 3300
75 5.2 7300 190 14,000 380 33,800 910
150 10.3 16,700 450 30,900 830 76,000 2000
250 17.2 27,600 740 54,200 1500 129,000 3500
75 5.2 7200 190 14,400 390 38,900 1000
150 10.3 19,900 530 37,800 1000 80,400 2200
250 17.2 31,400 840 64,800 1700 129,000 3500
50 3.4 6400 170 8800 240 13,600 370
75 5.2 8100 220 11,300 300 18,800 500
150 10.3 17,700 470 22,300 600 37,800 1000
250 17.2 26,300 700 34,700 930 59,200 1600
50 3.4 5700 150 8200 220 15,300 410
75 5.2 9900 260 13,200 350 24,000 640
150 10.3 18,300 490 25,700 690 45,000 1200
250 17.2 27,600 740 38,800 1000 69,100 1900
50 3.4 5500 150 9500 260 19,400 520
75 5.2 10,800 290 16,300 440 31,900 860
150 10.3 19,100 510 29,500 790 58,400 1600
250 17.2 32,100 860 48,700 1300 93,200 2500
75 5.2 10,100 270 16,500 440 34,200 920
150 10.3 20,300 540 31,200 840 62,700 1700
250 17.2 35,000 940 53,600 1400 110,000 3000
75 5.2 6500 170 11,100 300 23,500 630 9000 240 13,800 370 27,600 740
150 10.3 14,500 390 23,000 620 51,300 1400 18,500 500 27,600 740 51,800 1400
250 17.2 22,400 600 36,600 980 97,300 2600 29,500 790 45,700 1200 86,600 2300
75 5.2 6300 170 11,700 310 28,500 760 8600 230 15,000 400 32,600 870
150 10.3 15,200 410 26,800 720 61,100 1600 20,300 540 31,600 850 62,400 1700
250 17.2 24,700 660 45,000 1200 120,000 3200 32,900 880 51,800 1400 104,000 2800
100 6.9 8600 230 17,700 470 45,000 1200 13,300 360 23,100 620 54,700 1500
150 10.3 17,800 480 33,900 910 76,000 2000 22,600 610 39,500 1100 85,100 2300
250 17.2 28,300 760 53,200 1400 129,000 3400 34,700 930 61,100 1600 132,000 3500
150 10.3 18,000 480 38,800 1000 78,200 2100 20,500 550 42,400 1100 108,000 2900
250 17.2 31,700 850 67,000 1800 130,000 3500 38,600 1000 77,600 2100 187,000 5000
100 6.9 8200 220 14,800 400 33,300 890 11,000 300 17,000 450 35,700 960
250 17.2 23,300 620 37,400 1000 87,400 2300 33,500 900 50,200 1300 90,400 2400
150 10.3 13,400 360 26,500 710 62,700 1700 17,800 480 31,500 840 71,200 1900
250 17.2 26,600 710 48,700 1300 114,000 3100 36,800 990 59,700 1600 127,000 3400
200 13.8 22,200 590 44,600 1200 99,700 2700 27,400 730 54,000 1400 126,000 3400
300 20.7 36,900 990 70,400 1900 154,000 4100 46,600 1200 85,800 2300 196,000 5200
200 13.8 23,900 640 51,400 1400 103,000 2700 29,600 790 59,500 1600 152,000 4100
300 20.7 40,300 1100 84,500 2300 154,000 4100 51,200 1400 98,400 2600 231,000 6200
200 13.8 21,000 560 52,300 1400 99,100 2700 27,600 740 64,600 1700 150,000 4000
300 20.7 45,600 1200 101,000 2700 153,000 4100 56,900 1500 115,000 3100 241,000 6500
150 10.3 10,000 270 21,200 570 51,700 1400 14,700 400 27,400 730 64,500 1700
250 17.2 25,500 680 44,600 1200 100,000 2700 33,400 890 57,500 1500 114,000 3100
200 13.8 18,000 480 36,200 970 89,300 2400 24,800 660 46,100 1200 107,000 2900
300 20.7 31,800 850 61,300 1600 145,000 3900 44,900 1200 76,500 2000 173,000 4600
250 17.2 27,300 730 60,200 1600 126,000 3400 35,100 940 71,300 1900 182,000 4900
300 20.7 40,400 1100 83,200 2200 151,000 4100 53,600 1400 105,000 2800 230,000 6200
300 20.7 31,800 850 88,300 2400 150,000 4000 46,100 1200 103,000 2800 228,000 6100
350 24.1 54,300 1500 115,000 3100 176,000 4700 72,200 1900 155,000 4200 275,000 7400
20
CAPACITIES IN SCFH / Nm3/h OF AIR
NPS 1 / DN 25 Body NPS 2 / DN 50 Body
10% Droop 20% Droop 40% Droop 10% Droop 20% Droop 40% Droop
- continued -
Page 21

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Table 12. Typical Air Capacities with Linear Cage - Setpoint Made at 10% Flow (for Type MR105
with High-Pressure Actuator) (continued)
SPRING RANGE,
PART NUMBER
AND COLOR
39 to 72 psig /
2.7 to 5.0 bar
GE42909X012
White
71 to 175 psig /
4.9 to 12.1 bar
GE42910X012
Silver
110 to 250 psig /
7.6 to 17.2 bar
GE42911X012
Orange
SET
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h SCFH Nm3/h
40 2.8
50 3.4
60 4.1
70 4.8
75 5.2
100 6.9
125 8.6
150 10.3
175 12.1
125 8.6
150 10.3
200 13.8
250 17.2
INLET
PRESSURE
10% Droop 20% Droop 40% Droop 10% Droop 20% Droop 40% Droop
75 5.2 9900 270 13,900 370 23,100 620 11,200 300 14,500 390 23,200 620
150 10.3 21,600 580 29,400 790 47,800 1300 20,200 540 26,300 710 43,000 1200
250 17.2 33,500 900 45,300 1200 73,600 2000 33,600 900 44,000 1200 69,900 1900
75 5.2 10,300 280 14,700 390 28,400 760 9600 260 13,700 370 26,000 700
150 10.3 21,100 560 29,600 790 54,100 1500 22,300 600 31,300 840 53,100 1400
250 17.2 33,700 900 47,700 1300 84,500 2300 35,700 960 48,400 1300 83,600 2200
75 5.2 9900 270 16,800 450 34,300 920 9600 260 15,400 410 30,900 830
150 10.3 21,200 570 32,600 870 63,800 1700 22,400 600 33,600 900 60,900 1600
250 17.2 39,400 1100 56,500 1500 107,000 2900 37,900 1000 53,800 1400 100,000 2700
100 6.9 13,900 370 23,500 630 51,300 1400 14,300 380 22,700 610 47,500 1300
150 10.3 23,900 640 38,000 1000 75,600 2000 24,800 660 36,500 980 70,900 1900
250 17.2 39,100 1000 59,800 1600 122,000 3300 40,000 1100 60,700 1600 119,000 3200
100 6.9 13,200 350 20,800 560 41,100 1100 12,600 340 18,900 510 36,600 980
150 10.3 23,700 640 34,800 930 63,700 1700 23,000 620 31,300 840 58,400 1600
250 17.2 37,300 1000 53,900 1400 95,400 2600 37,300 1000 50,900 1400 93,000 2500
150 10.3 17,300 460 31,700 850 71,200 1900 22,500 600 35,200 940 71,200 1900
250 17.2 41,000 1100 64,200 1700 126,000 3400 40,000 1100 60,900 1600 116,000 3100
200 13.8 35,900 960 61,200 1600 136,000 3600 32,100 860 54,500 1500 119,000 3200
300 20.7 54,900 1500 90,300 2400 192,000 5200 49,800 1300 84,700 2300 179,000 4800
200 13.8 34,800 930 65,900 1800 161,000 4300 32,200 860 61,100 1600 145,000 3900
300 20.7 59,600 1600 105,000 2800 234,000 6300 61,100 1600 102,000 2700 225,000 6000
200 13.8 25,000 670 57,700 1500 175,000 4700 29,700 800 63,400 1700 165,000 4400
300 20.7 67,400 1800 124,000 3300 292,000 7800 60,500 1600 113,000 3000 258,000 6900
150 10.3 18,300 490 32,500 870 73,600 2000 11,900 320 15,100 400 52,300 1400
250 17.2 38,600 1000 58,400 1600 117,000 3100 31,600 850 39,700 1100 113,000 3000
200 13.8 30,400 820 52,800 1400 119,000 3200 26,600 710 43,700 1200 97,000 2600
300 20.7 42,000 1100 72,100 1900 157,000 4200 50,900 1400 80,100 2100 164,000 4400
250 17.2 45,300 1200 85,000 2300 205,000 5500 36,500 980 69,200 1900 170,000 4600
300 20.7 64,400 1700 112,000 3000 257,000 6900 57,800 1500 102,000 2700 227,000 6100
300 20.7 61,300 1600 121,000 3200 293,000 7900 51,200 1400 108,000 2900 264,000 7100
350 24.1 88,900 2400 168,000 4500 347,000 9300 80,600 2200 155,000 4200 319,000 8500
NPS 3 / DN 80 Body NPS 4 / DN 100 Body
CAPACITIES IN SCFH / Nm3/h OF AIR
21
Page 22

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Table 13. Typical Water Capacities with Quick Opening Cage - Setpoint Made at 10% Flow (for Type MR105
with Low-Pressure Actuator)
SPRING RANGE,
PART NUMBER
AND COLOR
5 to 12 psig /
0.34 to 0.83 bar
GE42909X012
White
10 to 24 psig /
0.69 to 1.6 bar
GE42910X012
Silver
14 to 32 psig /
0.96 to 2.2 bar
GE42911X012
Orange
18 to 43 psig /
1.2 to 3.0 bar
GE43002X012
Red
SET
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM
5 0.34
10 0.69
10 0.69
15 1.0
20 1.4
15 1.0
20 1.4
25 1.7
30 2.1
20 1.4
25 1.7
30 2.1
35 2.4
40 2.8
INLET
PRESSURE
25 1.7 24 91 44 170 72 270 37 140 58 220 100 380 54 200 92 350 160 610
75 5.2 42 160 79 300 130 500 74 280 11 0 410 160 620 92 350 160 610 250 950
150 10.3 52 200 110 400 180 690 99 370 140 510 190 720 130 500 210 780 350 1310
25 1.7 35 130 61 230 84 320 50 190 83 310 160 600 73 280 130 510 220 840
75 5.2 74 280 130 490 160 590 99 370 150 570 260 990 150 550 230 870 390 1460
150 10.3 110 410 180 680 210 790 140 520 180 690 320 1210 200 740 290 1080 470 1790
25 1.7 29 11 0 52 200 80 300 40 150 67 250 120 460 61 230 110 400 180 700
75 5.2 53 200 100 390 150 560 84 320 130 480 210 790 120 450 190 710 310 1150
150 10.3 77 290 160 590 200 770 110 420 160 600 260 980 170 640 260 970 390 1470
25 1.7 37 140 65 250 89 340 46 170 86 330 160 590 71 270 130 500 210 790
75 5.2 65 250 110 430 150 550 11 0 420 190 710 300 1150 140 540 240 900 380 1430
150 10.3 96 360 180 670 210 780 140 530 210 800 360 1360 200 760 320 1230 580 2200
50 3.4 56 210 95 360 110 430 84 320 150 580 260 1000 130 500 230 850 350 1310
75 5.2 81 310 130 500 150 560 120 450 200 750 330 1260 170 640 290 1090 430 1630
150 10.3 130 500 200 740 210 790 160 590 270 1000 450 1700 220 850 390 1480 700 2660
25 1.7 24 91 46 170 74 280 36 140 61 230 120 450 53 200 100 380 180 690
75 5.2 60 230 110 400 150 560 88 330 140 510 240 890 120 470 200 770 340 1290
150 10.3 82 310 150 580 200 770 120 470 180 670 300 1120 170 650 280 1070 490 1860
25 1.7 24 91 45 170 64 240 37 140 73 280 140 520 53 200 110 420 190 710
75 5.2 75 280 120 440 140 530 110 410 180 700 300 1130 150 570 270 1030 410 1560
150 10.3 11 0 410 180 670 210 790 140 530 220 820 380 1430 220 840 400 1500 610 2310
50 3.4 50 190 83 310 110 400 87 330 160 590 240 920 130 480 220 840 320 1200
75 5.2 90 340 120 450 140 530 120 450 210 800 320 1200 160 610 270 1040 420 1570
150 10.3 110 420 190 700 210 790 160 600 260 980 450 1700 230 870 410 1530 620 2350
50 3.4 56 210 90 340 110 410 80 300 150 560 240 920 120 450 210 810 330 1260
75 5.2 82 310 130 480 140 530 120 460 210 800 330 1230 160 620 290 111 0 440 1650
150 10.3 130 500 200 750 210 790 170 650 290 111 0 480 1830 240 920 410 1540 700 2660
50 3.4 39 150 73 280 110 420 61 230 100 390 180 700 90 340 150 570 270 1010
75 5.2 57 220 100 380 140 540 85 320 130 500 240 890 120 450 200 750 330 1260
150 10.3 79 300 150 560 200 760 130 480 190 710 310 1160 180 680 290 1100 470 1770
50 3.4 46 170 77 290 110 400 67 250 120 460 220 830 100 380 190 700 300 1130
75 5.2 60 230 11 0 410 150 580 98 370 160 600 280 1050 140 520 230 880 390 1470
150 10.3 100 380 170 650 210 790 140 510 200 750 340 1290 210 780 330 1250 550 2060
50 3.4 47 180 76 290 100 380 69 260 130 490 230 850 11 0 410 200 760 300 1150
75 5.2 66 250 110 420 150 580 100 390 170 650 290 1100 140 540 240 920 380 1450
150 10.3 120 440 180 690 210 790 140 540 230 850 400 1510 220 810 380 1450 580 2200
50 3.4 44 170 74 280 95 360 73 280 130 500 230 850 110 410 200 770 290 1100
75 5.2 68 260 110 420 140 550 11 0 420 190 710 300 1140 160 590 270 1020 400 1500
150 10.3 130 470 190 710 210 790 150 580 260 970 450 1690 240 900 400 1500 610 2300
50 3.4 40 150 71 270 96 360 65 250 130 490 220 830 94 360 170 660 290 111 0
75 5.2 70 260 110 430 140 510 120 450 200 750 310 1160 160 600 280 1040 420 1570
150 10.3 130 490 190 720 210 780 170 630 290 1090 480 1810 260 980 430 1610 630 2370
NPS 1 / DN 25 Body NPS 2 / DN 50 - Reduced Port NPS 2 / DN 50 Body
10% Droop 20% Droop 40% Droop 10% Droop 20% Droop 40% Droop 10% Droop 20% Droop 40% Droop
CAPACITIES IN GPM / LPM OF WATER
22
- continued -
Page 23

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Table 13. Typical Water Capacities with Quick Opening Cage - Setpoint Made at 10% Flow (for Type MR105
with Low-Pressure Actuator) (continued)
SPRING RANGE,
PART NUMBER
AND COLOR
5 to 8 psig /
0.34 to 0.55 bar
GE42909X012
White
8 to 20 psig /
0.55 to 1.4 bar
GE42910X012
Silver
12 to 30 psig /
0.83 to 2.1 bar
GE42911X012
Orange
18 to 39 psig /
1.2 to 2.7 bar
GE43002X012
Red
SET
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM
5 0.34
8 0.55
10 0.69
15 1.0
20 1.4
15 1.0
20 1.4
25 1.7
30 2.1
20 1.4
25 1.7
30 2.1
35 2.4
INLET
PRESSURE
25 1.7 87 330 130 480 220 830 110 420 170 640 290 1100
75 5.2 140 540 200 770 320 1190 190 720 270 1030 440 1650
150 10.3 190 730 240 900 390 1480 260 1000 360 1350 510 1920
25 1.7 99 370 170 640 300 1140 120 460 230 880 410 1550
75 5.2 180 670 260 1000 450 1680 240 900 360 1380 610 2310
150 10.3 220 840 300 1150 520 1980 300 1120 460 1720 720 2740
25 1.7 90 340 150 560 270 1010 120 450 190 730 350 1320
75 5.2 170 640 250 950 450 1680 230 880 350 1320 590 2220
150 10.3 230 860 330 1230 540 2040 300 1150 440 1660 730 2750
25 1.7 100 380 180 690 340 1300 130 470 230 890 460 1740
75 5.2 220 820 350 1320 590 2220 260 1000 470 1790 830 3150
150 10.3 260 980 420 1570 740 2790 380 1440 580 2210 1000 3770
50 3.4 190 700 340 1280 590 2210 230 870 440 1680 780 2960
75 5.2 230 870 420 1600 710 2680 300 1150 560 2100 970 3660
150 10.3 320 1190 520 1950 920 3470 420 1580 680 2590 1250 4740
25 1.7 86 330 150 560 280 1070 100 390 180 700 360 1370
75 5.2 190 700 290 1090 500 1900 220 840 370 1390 640 2410
150 10.3 240 910 370 1390 630 2400 320 1210 510 1920 830 3140
25 1.7 81 310 160 600 320 1220 100 390 200 760 420 1570
75 5.2 210 800 360 1360 630 2370 260 990 440 1650 810 3070
150 10.3 270 1000 440 1650 780 2960 390 1460 610 2310 1020 3850
50 3.4 170 650 310 1160 560 2110 230 850 400 1510 750 2840
75 5.2 240 890 420 1570 720 2730 290 1090 510 1930 920 3490
150 10.3 320 1220 540 2040 920 3460 430 1620 710 2680 1220 4630
250 17.2 380 1450 610 2320 1050 3960 500 1880 790 2970 1380 5210
50 3.4 180 690 340 1280 580 2200 230 860 430 1640 720 2730
75 5.2 270 1010 460 1750 750 2840 320 1220 580 2180 960 3630
150 10.3 360 1360 620 2340 1020 3850 480 1810 810 3070 1330 5050
250 17.2 420 1580 680 2590 1100 4170 560 2130 930 3520 1590 6000
50 3.4 140 530 230 860 410 1540 170 650 280 1040 520 1970
75 5.2 180 690 290 1090 510 1950 220 850 370 1380 650 2460
150 10.3 240 920 380 1440 650 2480 320 1200 490 1850 860 3240
50 3.4 150 560 260 970 490 1850 190 720 310 1180 590 2230
75 5.2 210 810 340 1290 610 2290 240 900 420 1590 760 2870
150 10.3 270 1010 450 1690 780 2960 360 1370 590 2220 1010 3800
250 17.2 340 1280 520 1980 870 3300 440 1670 690 2610 1170 4440
50 3.4 150 580 270 1030 520 1960 190 700 340 1280 660 2510
75 5.2 230 850 390 1460 680 2570 260 980 460 1760 860 3240
150 10.3 310 1150 530 2000 910 3430 390 1480 670 2530 1150 4350
250 17.2 360 1370 590 2230 1030 3910 480 1810 770 2930 1360 5140
50 3.4 160 590 290 1090 550 2090 180 700 360 1370 690 2620
75 5.2 240 920 430 1620 730 2750 270 1030 500 1880 920 3470
150 10.3 340 1280 590 2210 1000 3770 420 1590 740 2810 1280 4860
250 17.2 410 1540 670 2550 1150 4340 550 2070 900 3390 1540 5840
10% Droop 20% Droop 40% Droop 10% Droop 20% Droop 40% Droop
NPS 3 / DN 80 Body NPS 4 / DN 100 Body
CAPACITIES IN GPM / LPM OF WATER
23
Page 24

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Table 14. Typical Water Capacities with Quick Opening Cage - Setpoint Made at 10% Flow (for Type MR105
with High-Pressure Actuator)
SPRING
RANGE, PART
NUMBER
AND COLOR
25 to 60 psig /
1.7 to 4.1 bar
GE42907X012
Green
25 to 45 psig /
1.7 to 3.1 bar
GE42907X012
Green
43 to 100 psig /
3.0 to 6.9 bar
GE42909X012
White
75 to 175 psig /
5.2 to 12.1 bar
GE42910X012
Silver
110 to 300
psig /
7.6 to 20.7 bar
GE42911X012
Orange
- Spring range is not available for the body size.
SET
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM
25 1.7
30 2.1
40 2.8
50 3.4
60 4.1
25 1.7
30 2.1
40 2.8
45 3.1
50 3.4
60 4.1
75 5.2
100 6.9
75 5.2
100 6.9
125 8.6
150 10.3
175 12.1
125 8.6
150 10.3
200 13.8
250 17.2
300 20.7 350 24.1 120 440 170 660 190 730 150 570 310 1170 540 2040 230 860 480 1830 630 2390
INLET
PRESSURE
Droop
50 3.4 23 87 41 160 76 290
75 5.2 35 130 61 230 110 410
150 10.3 55 210 120 450 190 700
250 17.2 60 230 250 930 260 970
50 3.4 23 87 43 160 79 300
75 5.2 37 140 67 250 110 420
150 10.3 62 230 140 530 190 710
250 17.2 78 300 240 920 250 950
50 3.4 22 83 44 170 79 300
75 5.2 44 170 77 290 120 440
150 10.3 82 310 160 610 190 720
250 17.2 140 520 240 890 240 920
75 5.2 40 150 75 280 110 420
150 10.3 94 360 160 610 190 700
250 17.2 230 860 240 910 250 950
75 5.2 37 140 70 260 110 410
150 10.3 11 0 400 160 610 190 700
250 17.2 220 840 240 890 250 930
50 3.4 38 140 57 220 96 360 51 190 76 290 140 540
75 5.2 59 220 83 310 130 490 81 310 120 440 190 700
150 10.3 83 310 120 440 180 670 120 440 160 610 250 960
50 3.4 35 130 57 220 110 400 49 190 81 310 150 580
75 5.2 60 230 88 330 150 560 85 320 130 480 210 790
150 10.3 83 310 120 470 210 780 120 460 180 690 300 1130
50 3.4 33 120 59 220 120 460 50 190 92 350 180 700
75 5.2 68 260 100 390 180 690 96 360 150 570 270 1010
150 10.3 93 350 150 550 250 960 150 560 220 840 390 1470
75 5.2 51 190 89 340 180 660 77 290 130 510 260 990
150 10.3 97 370 150 570 280 1070 130 500 230 880 410 1560
75 5.2 33 120 61 230 110 400 46 170 78 300 150 580 65 250 120 440 230 860
150 10.3 69 260 130 480 180 680 90 340 140 530 250 940 130 510 220 820 390 1480
250 17.2 120 440 230 860 250 940 120 460 180 680 300 1150 170 650 260 1000 490 1840
75 5.2 31 120 59 220 100 380 44 170 78 300 160 620 62 230 120 440 240 910
150 10.3 76 290 140 520 180 670 96 360 150 570 280 1060 150 570 250 930 460 1730
250 17.2 120 440 230 860 240 920 130 470 200 740 340 1290 200 740 320 1230 600 2260
100 6.9 45 170 83 310 120 470 56 210 11 0 400 220 850 87 330 170 630 330 1260
250 17.2 170 640 230 860 240 910 140 520 220 830 400 1530 210 790 360 1370 670 2550
150 10.3 78 300 130 490 160 600 92 350 170 650 350 1310 130 500 270 1020 490 1850
250 17.2 160 620 210 810 230 890 170 620 270 1010 510 1910 240 920 460 1720 690 2590
100 6.9 33 120 64 240 110 430 46 170 81 310 170 640 68 260 130 470 260 970
250 17.2 84 320 170 640 240 890 120 470 190 720 330 1230 170 640 270 1020 520 1950
150 10.3 56 210 110 400 160 600 72 270 130 490 270 1020 110 430 210 780 410 1540
250 17.2 11 0 410 190 720 230 880 140 530 220 840 400 1510 200 750 320 1210 620 2340
200 13.8 81 310 150 550 190 710 100 390 190 710 370 1390 160 590 290 1080 550 2090
300 20.7 150 560 230 860 250 950 170 630 270 1030 500 1910 230 870 440 1650 700 2630
200 13.8 80 300 140 510 180 680 100 390 190 730 400 1510 150 580 290 1110 550 2070
300 20.7 150 580 220 830 240 920 190 700 300 1140 580 2180 280 1060 500 1890 700 2630
200 13.8 69 260 120 470 170 620 94 360 200 740 420 1590 140 520 280 1070 540 2050
300 20.7 150 560 210 780 240 890 190 710 320 1210 600 2280 290 111 0 520 1970 700 2630
150 10.3 40 150 81 310 140 540 58 220 110 410 240 890 83 310 160 620 360 1360
250 17.2 90 340 160 600 220 830 130 490 200 770 370 1390 190 720 320 1200 580 2180
200 13.8 60 230 110 430 170 650 83 310 160 590 330 1250 120 460 240 920 490 1850
300 20.7 120 470 200 760 240 920 160 590 250 940 470 1760 230 860 410 1530 690 2600
250 17.2 79 300 140 540 190 720 110 400 210 780 430 1640 160 600 320 1200 600 2270
300 20.7 130 480 190 710 230 860 170 650 290 1100 550 2070 260 980 460 1730 690 2620
300 20.7 97 370 160 600 210 780 120 470 250 950 530 1990 200 750 400 1510 650 2480
350 24.1 160 600 200 770 220 830 210 780 360 1350 580 2200 320 1200 530 2020 630 2380
CAPACITIES IN GPM / LPM OF WATER
NPS 1 / DN 25 Body NPS 2 / DN 50 - Reduced Port NPS 2 / DN 50 Body
10%
20%
Droop
40%
Droop
10%
Droop
20%
Droop
40%
Droop
10%
Droop
20%
Droop
40%
Droop
24
- continued -
Page 25

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Table 14. Typical Water Capacities with Quick Opening Cage - Setpoint Made at 10% Flow (for Type MR105
with High-Pressure Actuator) (continued)
CAPACITIES IN GPM / LPM OF WATER
SPRING RANGE,
PART NUMBER
AND COLOR
39 to 72 psig /
2.7 to 5.0 bar
GE42909X012
White
71 to 175 psig /
4.9 to 12.1 bar
GE42910X012
Silver
110 to 250 psig /
7.6 to 17.2 bar
GE42911X012
Orange
SET
PRESSURE
psig bar psig bar GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM GPM LPM
40 2.8
50 3.4
60 4.1
70 4.8
75 5.2
100 6.9
125 8.6
150 10.3
175 12.1
125 8.6
150 10.3
200 13.8
250 17.2
INLET
PRESSURE
75 5.2 100 380 140 550 240 910 120 460 180 660 300 1120
150 10.3 180 670 230 860 340 1290 230 880 300 1150 440 1670
250 17.2 220 820 270 1010 380 1440 290 1080 350 1330 480 1810
75 5.2 95 360 150 560 260 1000 130 480 200 750 350 1330
150 10.3 190 720 250 960 390 1490 250 950 340 1290 510 1920
250 17.2 230 860 290 1100 440 1660 300 1140 380 1450 550 2080
75 5.2 86 330 150 560 290 1090 120 450 190 730 380 1450
150 10.3 200 760 280 1060 440 1680 260 990 360 1370 560 2120
250 17.2 240 890 320 1210 490 1850 310 1180 410 1560 620 2330
100 6.9 120 470 210 780 390 1470 160 610 270 1000 490 1870
150 10.3 210 800 310 1150 500 1890 280 1070 400 1520 640 2430
250 17.2 250 950 350 1330 550 2080 330 1260 460 1720 690 2620
100 6.9 110 400 170 650 330 1250 140 530 220 840 410 1560
150 10.3 200 750 280 1050 460 1730 260 1000 370 1400 580 2190
250 17.2 240 900 330 1250 510 1940 320 1220 440 1660 650 2470
150 10.3 160 610 250 960 490 1850 210 780 340 1270 610 2320
250 17.2 270 1010 390 1460 630 2380 360 1350 500 1900 790 2990
200 13.8 210 790 340 1280 640 2400 270 1000 440 1650 780 2960
300 20.7 310 1180 460 1720 810 3050 420 1570 590 2240 970 3680
200 13.8 200 770 360 1360 720 2720 260 1000 470 1780 900 3400
300 20.7 340 1280 510 1930 890 3370 460 1730 680 2590 1070 4040
200 13.8 190 730 360 1380 770 2900 240 920 460 1740 960 3620
300 20.7 360 1360 570 2170 990 3750 480 1810 730 2760 1230 4660
150 10.3 130 490 220 840 450 1720 160 610 290 1080 570 2160
250 17.2 260 1000 390 1460 640 2420 360 1350 500 1870 840 3170
200 13.8 190 720 310 1180 610 2310 230 870 390 1460 750 2830
300 20.7 310 1180 460 1750 760 2870 400 1530 580 2200 1020 3860
250 17.2 220 840 400 1510 790 2970 270 1030 490 1870 990 3760
300 20.7 350 1340 550 2090 970 3690 430 1620 680 2590 1200 4540
300 20.7 250 950 480 1830 960 3640 310 1180 600 2270 1250 4720
350 24.1 410 1560 660 2500 1170 4410 540 2020 880 3320 1650 6240
10%
Droop
NPS 3 / DN 80 Body NPS 4 / DN 100 Body
20%
Droop
40%
Droop
10%
Droop
20%
Droop
40%
Droop
25
Page 26

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
R
(TRIM REMOVAL CLEARANCE)
A
G
1/4 NPT
PLUG OR
DRAIN VALVE
CONNECTION
R
(TRIM REMOVAL CLEARANCE)
G
A
1/4 NPT PLUG
OR DRAIN VALVE
CONNECTION
ERAA00135
D
19.5 /
494
13.1 /
333
AR (ACTUATOR REMOVAL CLEARANCE)
LOW-PRESSURE ACTUATOR
1/4 NPT
1/2 NPT
CONTROL LINE
CONNECTION
1/2 NPT
VENT
CONNECTION
1/8 NPT BLEED
VALVE (OPTIONAL)
ERAA00136
D
18.2 /
462
AR (ACTUATOR REMOVAL CLEARANCE)
HIGH-PRESSURE ACTUATOR
RT
(OPTIONAL
TRAVEL
INDICATOR)
3.4 /
85
4.4 /
111
1/4 NPT
1/2 NPT
CONTROL LINE
CONNECTION
1/2 NPT
VENT
CONNECTION
Figure 5. Type MR105 Dimensions
Table 15. Type MR105 Dimensions
BODY SIZE
CL125 FF/
CL150 RF
7.25 /
184
10.0 /
254
11.75 /
299
13.88 /
353
NPS DN
1 25
2 50
3 80 - - - -
4 100 - - - -
26
NPT
8.25 /
210
11.25 /
286
A
CL250 RF/
CL300 RF
7.75 /
197
10.50 /
267
12.50 /
318
14.50 /
368
CL600 RF
8.25 /
210
11.25 /
286
13.25 /
337
15.50 /
394
DIMENSION, In. / mm
PN
16/25/40 RF
7.62 /
194
10.25 /
260
12.48 /
317
13.78 /
350
AR
3.2 /
82
3.7 /
94
4.5 /
115
5.7 /
145
Low-
Pressure
Actuator
4.1 /
105
4.8 /
122
5.4 /
138
6.7 /
171
D
Pressure
Actuator
High-
5.5 /
140
6.2 /
158
6.8 /
173
8.1 /
206
IN. /
mm
G R RT
5.2 /
133
5.7 /
145
7.0 /
178
8.4 /
214
3.4 /
87
4.1 /
105
5.2 /
133
6.4 /
163
9.8 /
249
10.3 /
262
11.6 /
295
13.0 /
331
Page 27

Ordering Information
Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Use the Specications section on page 2 and
carefully review the description to the right of each
specication. Use this information to complete the
Ordering Guide
Body Size (Select One)
NPS 1 / DN 25
NPS 2 / DN 50
NPS 3 / DN 80
NPS 4 / DN 100
Actuator Type (Select One)
Low Pressure
High Pressure
Cage Type (Select One)
Linear (For Gas Service Only)
Quick Open (For Liquid Service Only)
Body Material and End Connection Style (Select One)
Cast Iron
NPT (1 or 2 NPT only)
CL125 FF
CL250 RF
WCC Steel
NPT (1 or 2 NPT only)
CL150 RF
CL300 RF
CL600 RF
PN 16 RF
PN 16/25/40 RF (NPS 1 or 2 / DN 25 or 50 only)
CF8M Stainless Steel
NPT (1 or 2 NPT only)
CL150 RF
CL300 RF
CL600 RF
PN 16 RF
PN 16/25/40 RF (NPS 1 or 2 / DN 25 or 50 only)
CF3M Stainless Steel
NPT (1 or 2 NPT only)
CL150 RF
CL300 RF
CL600 RF
PN 16 RF
PN 16/25/40 RF (NPS 1 or 2 / DN 25 or 50 only)
Diaphragm, O-rings and Seal Materials (Select One)
Nitrile (NBR)
Fluorocarbon (FKM)
Ethylene Propylene (EPDM)
Ordering Guide below. Specify the desired selection
wherever there is a choice to be made. Then send
the Ordering Guide to your local Sales Ofce.
Actuator Type and Outlet Pressure Range (Select One)
NPS 1 / DN 25
Low-Pressure Actuator
5 to 12 psig / 0.34 to 0.83 bar, White
10 to 24 psig / 0.69 to 1.6 bar, Silver
14 to 32 psig / 0.96 to 2.2 bar, Orange
18 to 43 psig / 1.2 to 3.0 bar, Red
High-Pressure Actuator
25 to 60 psig / 1.7 to 4.1 bar, Green
43 to 100 psig / 3.0 to 6.9 bar, White
75 to 175 psig / 5.2 to 12.1 bar, Silver
110 to 300 psig / 7.6 to 20.7 bar, Orange
(1)
(1)
NPS 2 / DN 50
Low-Pressure Actuator
5 to 12 psig / 0.34 to 0.83 bar, White
10 to 24 psig / 0.69 to 1.6 bar, Silver
14 to 32 psig / 0.96 to 2.2 bar, Orange
18 to 43 psig / 1.2 to 3.0 bar, Red
High-Pressure Actuator
25 to 45 psig / 1.7 to 3.1 bar, Green
43 to 100 psig / 3.0 to 6.9 bar, White
75 to 175 psig / 5.2 to 12.1 bar, Silver
110 to 300 psig / 7.6 to 20.7 bar, Orange
(1)
(1)
NPS 3 and 4 / DN 80 and 100
Low-Pressure Actuator
5 to 8 psig / 0.34 to 0.55 bar, White
8 to 20 psig / 0.55 to 1.4 bar, Silver
12 to 30 psig / 0.83 to 2.1 bar, Orange
18 to 39 psig / 1.2 to 2.7 bar, Red
High-Pressure Actuator
39 to 72 psig / 2.7 to 5.0 bar, White
71 to 175 psig / 4.9 to 12.1 bar, Silver
110 to 250 psig / 7.6 to 17.2 bar, Orange
(1)
(1)
Optional
Visual Travel Indicator
Drain Valve
Pressure-Loaded Actuator
NACE Construction
Bleed Valve (for High-Pressure Actuator Only)
- continued -
1. Maximum setpoint is limited to 150 psig / 10.3 bar for constructions with Fluorocarbon (FKM) diaphragm.
27
Page 28

Bulletin 71.1:MR105
Ordering Guide (continued)
Main Valve Replacement Parts Kit (Optional)
Yes, send one replacement parts kit to match
this order.
Actuator Replacement Parts Kit (Optional)
Yes, send one replacement parts kit to match
this order.
Wireless Position Monitor Mounting Kit (Optional)
Yes, send one mounting kit for mounting the
Topworx™ 4310 or the Fisher® 4320 wireless
position monitor.
Regulators Quick Order Guide
* * * Readily Available for Shipment
* * Allow Additional Time for Shipment
* Special Order, Constructed from Non-Stocked Parts. Consult
your local Sales Ofce for Availability.
Availability of the product being ordered is determined by the component with the
longest shipping time for the requested construction.
Specication Worksheet
Application:
Specic Use
Line Size
Fluid Type
Specic Gravity
Temperature
Does the Application Require Overpressure Protection?
Yes No
Pressure:
Maximum Inlet Pressure
Minimum Inlet Pressure
Differential Pressure
Set Pressure
Maximum Flow
Accuracy Requirements:
Less Than or Equal To:
5% 10% 20% 40%
Construction Material Requirements (if known):
Industrial Regulators
Emerson Process Management
Regulator Technologies, Inc.
USA - Headquarters
McKinney, Texas 75070 USA
Tel: +1 800 558 5853
Outside U.S. +1 972 548 3574
Asia-Pacic
Shanghai 201206, China
Tel: +86 21 2892 9000
Europe
Bologna 40013, Italy
Tel: +39 051 419 0611
Middle East and Africa
Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Tel: +971 4811 8100
For further information visit www.fisherregulators.com
The Emerson logo is a trademark and service mark of Emerson Electric Co. All other marks are the property of their prospective owners. Fisher is a mark owned by Fisher Controls International LLC,
a business of Emerson Process Management.
The contents of this publication are presented for informational purposes only, and while every effort has been made to ensure their accuracy, they are not to be construed as warranties or
guarantees, express or implied, regarding the products or services described herein or their use or applicability. We reserve the right to modify or improve the designs or specications of such
products at any time without notice.
Emerson Process Management Regulator Technologies, Inc. does not assume responsibility for the selection, use or maintenance of any product. Responsibility for proper selection, use and
maintenance of any Emerson Process Management Regulator Technologies, Inc. product remains solely with the purchaser.
Natural Gas Technologies
Emerson Process Management
Regulator Technologies, Inc.
USA - Headquarters
McKinney, Texas 75070 USA
Tel: +1 800 558 5853
Outside U.S. +1 972 548 3574
Asia-Pacic
Singapore 128461, Singapore
Tel: +65 6770 8337
Europe
Bologna 40013, Italy
Tel: +39 051 419 0611
Chartres 28008, France
Tel: +33 2 37 33 47 00
Middle East and Africa
Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Tel: +971 4811 8100
TESCOM
Emerson Process Management
Tescom Corporation
USA - Headquarters
Elk River, Minnesota 55330-2445, USA
Tels: +1 763 241 3238
+1 800 447 1250
Europe
Selmsdorf 23923, Germany
Tel: +49 38823 31 287
Asia-Pacic
Shanghai 201206, China
Tel: +86 21 2892 9499
©Emerson Process Management Regulator Technologies, Inc., 2010, 2015; All Rights Reserved
 Loading...
Loading...