Page 1

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Oxymitter DR
Hazardous Area In-Situ Oxygen Probe
Certified to: CENELEC EEXd IIB + H2 T3
CSA Class I, Division 1, Groups B, C, D
http://www.processanalytic.com
Page 2

ESSENTIAL INSTRUCTIONS
READ THIS PAGE BEFORE PROCEEDING!
Rosemount Analytical designs, manufactures and tests its products to meet many national and
international standards. Because these instruments are sophisticated technical products, you
MUST properly install, use, and maintain them to ensure they continue to operate within their
normal specifications. The following instructions MUST be adhered to and integrated into your
safety program when installing, using, and maintaining Rosemount Analytical products. Failure to
follow the proper instructions may cause any one of the following situations to occur: Loss of life;
personal injury; property damage; damage to this instrument; and warranty invalidation.
• Read all instructions prior to installing, operating, and servicing the product.
• If you do not understand any of the instructions, contact your Rosemount Analytical repre-
sentative for clarification.
• Follow all warnings, cautions, and instructions marked on and supplied with the product.
• Inform and educate your personnel in the proper installation, operation, and mainte-
nance of the product.
• Install your equipment as specified in the Installation Instructions of the appropriate In-
struction Manual and per applicable local and national codes. Connect all products to the
proper electrical and pressure sources.
• To ensure proper performance, use qualified personnel to install, operate, update, program,
and maintain the product.
• When replacement parts are required, ensure that qualified people use replacement parts
specified by Rosemount. Unauthorized parts and procedures can affect the product’s performance, place the safe operation of your process at risk, and VOID YOUR WARRANTY.
Look-alike substitutions may result in fire, electrical hazards, or improper operation.
• Ensure that all equipment doors are closed and protective covers are in place, except
when maintenance is being performed by qualified persons, to prevent electrical shock
and personal injury.
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice.
Emerson Process Management
Rosemount Analytical Inc.
Process Analytic Division
1201 N. Main St.
Orrville, OH 44667-0901
T (330) 682-9010
F (330) 684-4434
e-mail: gas.csc@EmersonProcess.com
http://www.processanalytic.com
Page 3

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PREFACE............................................................................................................................1
Definitions ............................................................................................................................1
Safety Instructions ..............................................................................................................2
1-0 DESCRIPTION AND SPECIFICATIONS........................................................................ 1-1
1-1 Component Checklist of Typical System (Package Contents) .................................. 1-1
1-2 System Overview............................................................................................................ 1-1
1-3 Probe Options................................................................................................................. 1-4
1-4 Specifications................................................................................................................... 1-6
2-0 INSTALLATION .............................................................................................................. 2-1
2-1 Mechanical Installation ................................................................................................... 2-1
2-2 Electrical Installation....................................................................................................... 2-7
2-3 Pneumatic Installation .................................................................................................... 2-8
2-4 System Setup .................................................................................................................. 2-9
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
3-0 STARTUP AND OPERATION ........................................................................................ 3-1
3-1 General ............................................................................................................................ 3-1
4-0 MAINTENANCE AND SERVICE .................................................................................. 4-1
4-1 Overview.......................................................................................................................... 4-1
4-2 Calibration........................................................................................................................ 4-1
4-3 Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR Replacement................................................................ 4-1
4-4 Terminal Block Replacement........................................................................................... 4-3
4-5 Entire Probe Replacement ............................................................................................ 4-4
4-6 Heater Strut Replacement ............................................................................................. 4-4
4-7 Cell Replacement ........................................................................................................... 4-5
4-8 Ceramic Diffusion Element Replacement..................................................................... 4-7
4-9 Termination Housing Wiring ............................................................................................ 4-9
5-0 TROUBLESHOOTING .................................................................................................... 5-1
5-1 Overview.......................................................................................................................... 5-1
5-2 Probe Troubleshooting ................................................................................................... 5-1
6-0 RETURN OF MATERIAL ................................................................................................ 6-1
6-1 Equipment Return........................................................................................................... 6-1
7-0 REPLACEMENT PARTS ................................................................................................ 7-1
8-0 OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES .......................................................................................... 8-1
9-0 APPENDICES ................................................................................................................. 9-1
10-0 INDEX............................................................................................................................ 10-1
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management i
Page 4

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Figure 1-1. Typical System Package ....................................................................................... 1-2
Figure 1-2. Typical System Installation .................................................................................... 1-3
Figure 1-3. Flame Arrestor Diffusion Assembly......................................................................... 1-4
Figure 1-4. Flame Arrestor Snubber Diffusion Assembly......................................................... 1-4
Figure 1-5. Abrasive Shield Assembly ..................................................................................... 1-5
Figure 2-1. Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR Installation ............................................................ 2-2
Figure 2-2. Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR with Abrasive Shield............................................. 2-3
Figure 2-3. Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR Adapter Plate Dimensions .................................. 2-4
Figure 2-4. Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR Adapter Plate Installation .................................... 2-5
Figure 2-5. Orienting the Optional Vee Deflector..................................................................... 2-6
Figure 2-6. Installation with Drip Loop and Insulation Removal ............................................... 2-6
Figure 2-7. Terminal Block ....................................................................................................... 2-8
Figure 2-8. Air Set, Plant Air Connection ................................................................................. 2-9
Figure 2-9. Temperature Controller Card Calibration Points ................................................. 2-10
Figure 2-10. Main PCB (Model 218A) EPROM Replacement ................................................. 2-11
Figure 2-11. Main PCB (Model TC200) EPROM Replacement ............................................... 2-13
Figure 2-12. Main PCB (Model 132) EPROM Replacement .................................................... 2-14
Figure 2-13. IFT 3000 Power Supply Board Jumper Configuration ......................................... 2-15
Figure 2-14. Heater Power Supply (HPS 3000) Jumper Configuration ................................... 2-15
Figure 2-15. DR Probe Wired to the ZA8C or A V8C Converter.............................................. 2-16
Figure 4-1. Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR Exploded View ..................................................... 4-2
Figure 4-2. Terminal Block ....................................................................................................... 4-3
Figure 4-3. Heater Strut Assembly ........................................................................................... 4-5
Figure 4-4. Cell Replacement Kit ............................................................................................. 4-6
Figure 4-5. Ceramic Diffusion Element Replacement.............................................................. 4-8
Figure 4-6. Termination Housing Connections......................................................................... 4-9
Figure 7-1. Cell Replacement Kit ............................................................................................. 7-2
Figure 7-2. Probe Disassembly Kit........................................................................................... 7-2
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1-1. Product Matrix ........................................................................................................ 1-7
Table 1-3. Calibration Components ........................................................................................ 1-8
Table 5-1. Fault Finding .......................................................................................................... 5-1
Table 7-1. Replacement Parts for Probe ................................................................................ 7-1
ii Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 5

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
PREFACE
The purpose of this manual is to provide information concerning the components, functions, installation and maintenance of the Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR.
Some sections may describe equipment not used in your configuration. The user should
become thoroughly familiar with the operation of this module before operating it. Read
this instruction manual completely.
DEFINITIONS
The following definitions apply to WARNINGS, CAUTIONS, and NOTES found throughout this
publication.
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Highlights an operation or maintenance
procedure, practice, condition, statement, etc. If not strictly observed, could
result in injury, death, or long-term
health hazards of personnel.
Highlights an essential operating procedure,
condition, or statement.
: EARTH (GROUND) TERMINAL
: PROTECTIVE CONDUCTOR TERMINAL
: RISK OF ELECTRICAL SHOCK
: WARNING: REFER TO INSTRUCTION BULLETIN
NOTE TO USERS
Highlights an operation or maintenance
procedure, practice, condition, statement, etc. If not strictly observed, could
result in damage to or destruction of
equipment, or loss of effectiveness.
NOTE
The number in the lower right corner of each illustration in this publication is a manual illustration number. It is not a part number, and is not related to the illustration in any technical
manner.
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management P-1
Page 6
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
FOR THE WIRING AND INSTALLATION
The following safety instructions apply specifically to all EU member states. They should
be strictly adhered to in order to assure compliance with the Low Voltage Directive. NonEU states should also comply with the following unless superseded by local or National
Standards.
1. Adequate earth connections should be made to all earthing points, internal and external,
where provided.
2. After installation or troubleshooting, all safety covers and safety grounds must be replaced.
The integrity of all earth terminals must be maintained at all times.
3. Mains supply cords should comply with the requirements of IEC227 or IEC245.
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
IMPORTANT
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
OF THIS APPARATUS
4. All wiring shall be suitable for use in an ambient temperature of greater than 75°C.
5. All cable glands used should be of such internal dimensions as to provide adequate cable
anchorage.
6. To ensure safe operation of this equipment, connection to the mains supply should only be
made through a circuit breaker which will disconnect all circuits carrying conductors during a
fault situation. The circuit breaker may also include a mechanically operated isolating switch.
If not, then another means of disconnecting the equipment from the supply must be provided
and clearly marked as such. Circuit breakers or switches must comply with a recognized
standard such as IEC947. All wiring must conform with any local standards.
7. Where equipment or covers are marked with the symbol to the right, hazard-
ous voltages are likely to be present beneath. These covers should only be
removed when power is removed from the equipment — and then only by
trained service personnel.
8. Where equipment or covers are marked with the symbol to the right, there is a
danger from hot surfaces beneath. These covers should only be removed by
trained service personnel when power is removed from the equipment. Certain surfaces may remain hot to the touch.
9. Where equipment or covers are marked with the symbol to the right, refer to
the Operator Manual for instructions.
10. All graphical symbols used in this product are from one or more of the follow-
ing standards: EN61010-1, IEC417, and ISO3864.
P-2 Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 7
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
CERAMIC FIBER PRODUCTS
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET
JULY 1, 1996
SECTION I. IDENTIFICATION
PRODUCT NAME
Ceramic Fiber Heaters, Molded Insulation Modules and Ceramic Fiber Radiant Heater Panels.
CHEMICAL FAMILY
Vitreous Aluminosilicate Fibers with Silicon Dioxide.
CHEMICAL NAME
N.A.
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
CHEMICAL FORMULA
N.A.
MANUFACTURER’S NAME AND ADDRESS
Watlow Columbia 573-474-9402
2101 Pennsylvania Drive 573-814-1300, ext. 5170
Columbia, MO 65202
HEALTH HAZARD SUMMARY
WARNING
• Possible cancer hazard based on tests with laboratory animals.
• May be irritating to skin, eyes and respiratory tract.
• May be harmful if inhaled.
• Cristobalite (crystalline silica) formed at high temperatures (above 1800ºF) can cause severe respiratory
disease.
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management P-3
Page 8

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
SECTION II. PHYSICAL DATA
APPEARANCE AND ODOR
Cream to white colored fiber shapes. With or without optional white to gray granular surface coating and/or optional
black surface coating.
SPECIFIC WEIGHT: 12-25 LB./CUBIC FOOT BOILING POINT: N.A.
VOLATILES (% BY WT.): N.A. WATER SOLUBILITY: N.A.
SECTION III. HAZARDOUS INGREDIENTS
MATERIAL, QUANTITY, AND THRESHOLD/EXPOSURE LIMIT VALUES
Aluminosilicate (vitreous) 99+ % 1 fiber/cc TWA
CAS. No. 142844-00-06 10 fibers/cc CL
Zirconium Silicate 0-10% 5 mg/cubic meter (TLV)
Black Surface Coating** 0 - 1% 5 mg/cubic meter (TLV)
Armorphous Silica/Silicon Dioxide 0-10% 20 mppcf (6 mg/cubic meter)
PEL (OSHA 1978) 3 gm cubic meter
(Respirable dust): 10 mg/cubic meter,
Intended TLV (ACGIH 1984-85)
**Composition is a trade secret.
SECTION IV. FIRE AND EXPLOSION DATA
FLASH POINT: NONE FLAMMABILITY LIMITS: N.A.
EXTINGUISHING MEDIA
Use extinguishing agent suitable for type of surrounding fire.
UNUSUAL FIRE AND EXPLOSION HAZARDS / SPECIAL FIRE FIGHTING PROCEDURES
N.A.
P-4 Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 9

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
January, 2002
SECTION V. HEALTH HAZARD DATA
THRESHOLD LIMIT VALUE
(See Section III)
EFFECTS OF OVER EXPOSURE
EYE
Avoid contact with eyes. Slightly to moderately irritating. Abrasive action may cause damage to outer surface of eye.
INHALATION
May cause respiratory tract irritation. Repeated or prolonged breathing of particles of respirable size may cause inflammation of the lung leading to chest pain, difficult breathing, coughing and possible fibrotic change in the lung (Pneumoconiosis). Pre-existing medical conditions may be aggravated by exposure: specifically, bronchial hyper-reactivity and
chronic bronchial or lung disease.
INGESTION
May cause gastrointestinal disturbances. Symptoms may include irritation and nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
SKIN
Slightly to moderate irritating. May cause irritation and inflammation due to mechanical reaction to sharp, broken ends
of fibers.
EXPOSURE TO USED CERAMIC FIBER PRODUCT
Product which has been in service at elevated temperatures (greater than 1800ºF/982ºC) may undergo partial conversion
to cristobalite, a form of crystalline silica which can cause severe respiratory disease (Pneumoconiosis). The amount of
cristobalite present will depend on the temperature and length of time in service. (See Section IX for permissible exposure levels).
SPECIAL TOXIC EFFECTS
The existing toxicology and epidemiology data bases for RCF’s are still preliminary. Information will be updated as
studies are completed and reviewed. The following is a review of the results to date:
EPIDEMIOLOGY
At this time there are no known published reports demonstrating negative health outcomes of workers exposed to refractory ceramic fiber (RCF). Epidemiologic investigations of RCF production workers are ongoing.
1) There is no evidence of any fibrotic lung disease (interstitial fibrosis) whatsoever on x-ray.
2) There is no evidence of any lung disease among those employees exposed to RCF that had never smoked.
3) A statistical “trend” was observed in the exposed population between the duration of exposure to RCF and a de-
crease in some measures of pulmonary function. These observations are clinically insignificant. In other words, if
these observations were made on an individual employee, the results would be interpreted as being within the normal range.
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management P-5
Page 10

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
4) Pleural plaques (thickening along the chest wall) have been observed in a small number of employees who had a
long duration of employment. There are several occupational and non-occupational causes for pleural plaque. It
should be noted that plaques are not “pre-cancer” nor are they associated with any measurable effect on lung
function.
TOXICOLOGY
A number of studies on the health effects of inhalation exposure of rats and hamsters are available. Rats were exposed
to RCF in a series of life-time nose-only inhalation studies. The animals were exposed to 30, 16, 9, and 3 mg/m
corresponds with approximately 200, 150, 75, and 25 fibers/cc.
Animals exposed to 30 and 16 mg/m
posed to 9 mg/m
the response typically observed any time a material is inhaled into the deep lung. While a statistically significant increase in lung tumors was observed following exposure to the highest dose, there was no excess lung cancers at the
other doses. Two rats exposed to 30 mg/m
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) reviewed the carcinogenicity data on man-made vitreous fibers (including ceramic fiber, glasswool, rockwool, and slagwool) in 1987. IARC classified ceramic fiber, fibrous
glasswool and mineral wool (rockwool and slagwool) as possible human carcinogens (Group 2B).
3
had developed a mild parenchymal fibrosis; animals exposed to the lowest dose were found to have
3
were observed to have developed a pleural and parenchymal fibroses; animals ex-
3
and one rat exposed to 9 mg/m3 developed masotheliomas.
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
EMERGENCY FIRST AID PROCEDURES
3
, which
EYE CONTACT
Flush eyes immediately with large amounts of water for approximately 15 minutes. Eye lids should be held away from
the eyeball to insure thorough rinsing. Do not rub eyes. Get medical attention if irritation persists.
INHALATION
Remove person from source of exposure and move to fresh air. Some people may be sensitive to fiber induced irritation
of the respiratory tract. If symptoms such as shortness of breath, coughing, wheezing or chest pain develop, seek medical attention. If person experiences continued breathing difficulties, administer oxygen until medical assistance can be
rendered.
INGESTION
Do not induce vomiting. Get medical attention if irritation persists.
SKIN CONTACT
Do not rub or scratch exposed skin. Wash area of contact thoroughly with soap and water. Using a skin cream or lotion
after washing may be helpful. Get medical attention if irritation persists.
SECTION VI. REACTIVITY DATA
STABILITY/CONDITIONS TO AVOID
Stable under normal conditions of use.
HAZARDOUS POLYMERIZATION/CONDITIONS TO AVOID
N.A.
P-6 Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 11

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
January, 2002
INCOMPATIBILITY/MATERIALS TO AVOID
Incompatible with hydrofluoric acid and concentrated alkali.
HAZARDOUS DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS
N.A.
SECTION VII. SPILL OR LEAK PROCEDURES
STEPS TO BE TAKEN IF MATERIAL IS RELEASED OR SPILLED
Where possible, use vacuum suction with HEPA filters to clean up spilled material. Use dust suppressant where sweeping if necessary. Avoid clean up procedure which may result in water pollution. (Observe Special Protection Information Section VIII.)
WASTE DISPOSAL METHODS
The transportation, treatment, and disposal of this waste material must be conducted in compliance with all applicable
Federal, State, and Local regulations.
SECTION VIII. SPECIAL PROTECTION INFORMATION
RESPIRATORY PROTECTION
Use NIOSH or MSHA approved equipment when airborne exposure limits may be exceeded. NIOSH/MSHA approved
breathing equipment may be required for non-routine and emergency use. (See Section IX for suitable equipment).
Pending the results of long term health effects studies, engineering control of airborne fibers to the lowest levels attainable is advised.
VENTILATION
Ventilation should be used whenever possible to control or reduce airborne concentrations of fiber and dust. Carbon
monoxide, carbon dioxide, oxides of nitrogen, reactive hydrocarbons and a small amount of formaldehyde may accompany binder burn-off during first heat. Use adequate ventilation or other precautions to eliminate vapors resulting from
binder burn-off. Exposure to burn-off fumes may cause respiratory tract irritation, bronchial hyper-reactivity and asthmatic response.
SKIN PROTECTION
Wear gloves, hats and full body clothing to prevent skin contact. Use separate lockers for work clothes to prevent fiber
transfer to street clothes. Wash work clothes separately from other clothing and rinse washing machine thoroughly after
use.
EYE PROTECTION
Wear safety glasses or chemical worker’s goggles to prevent eye contact. Do not wear contact lenses when working
with this substance. Have eye baths readily available where eye contact can occur.
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management P-7
Page 12

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
SECTION IX. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS
PRECAUTIONS TO BE TAKEN IN HANDLING AND STORING
General cleanliness should be followed.
The Toxicology data indicate that ceramic fiber should be handled with caution. The handling practices described in this
MSDS must be strictly followed. In particular, when handling refractory ceramic fiber in any application, special caution should be taken to avoid unnecessary cutting and tearing of the material to minimize generation of airborne dust.
It is recommended that full body clothing be worn to reduce the potential for skin irritation. Washable or disposable
clothing may be used. Do not take unwashed work clothing home. Work clothes should be washed separately from
other clothing. Rinse washing machine thoroughly after use. If clothing is to be laundered by someone else, inform
launderer of proper procedure. Work clothes and street clothes should be kept separate to prevent contamination.
Product which has been in service at elevated temperatures (greater than 1800ºF/982ºC) may undergo partial conversion
to cristobalite, a form of crystalline silica. This reaction occurs at the furnace lining hot face. As a consequence, this
material becomes more friable; special caution must be taken to minimize generation of airborne dust. The amount of
cristobalite present will depend on the temperature and length in service.
IARC has recently reviewed the animal, human, and other relevant experimental data on silica in order to critically
evaluate and classify the cancer causing potential. Based on its review, IARC classified crystalline silica as a group 2A
carcinogen (probable human carcinogen).
The OSHA permissible exposure limit (PEL for cristobalite is 0.05 mg/m
value (TLV) for cristobalite is 0.05 mg/m
ment when airborne exposure limits may be exceeded. The minimum respiratory protection recommended for given airborne fiber or cristobalite concentrations are:
3
(respirable dust) (ACGIH 1991-92). Use NIOSH or MSHA approved equip-
3
(respirable dust). The ACGIH threshold limit
CONCENTRATION
0-1 fiber/cc or 0-0.05 mg/m3 cristobalite Optional disposable dust respirator (e.g. 3M 9970
(the OSHA PEL) or equivalent).
Up to 5 fibers/cc or up to 10 times the Half face, air-purifying respirator equipped with high
OSHA PEL for cristobalite efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter cartridges
(e.g. 3M 6000 series with 2040 filter or equivalent).
Up to 25 fibers/cc or 50 times the OSHA Full face, air-purifying respirator with high efficiency
PEL for cristobalite (2.5 mg/m
Greater than 25 fibers/cc or 50 times the Full face, positive pressure supplied air respirator
OSHA PEL for cristobalite (2.5 mg/m
If airborne fiber or cristobalite concentrations are not known, as minimum protection, use NIOSH/MSHA approved half
face, air-purifying respirator with HEPA filter cartridges.
3
) particulate air (HEPA) filter cartridges (e.g. 3M 7800S
with 7255 filters or equivalent) or powered air -purifying
respirator (PARR) equipped with HEPA filter cartridges
(e.g. 3M W3265S with W3267 filters or equivalent).
3
) (e.g. 3M 7800S with W9435 hose & W3196 low
pressure regulator kit connected to clean air supply
or equivalent).
P-8 Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 13

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
Insulation surface should be lightly sprayed with water before removal to suppress airborne dust. As water evaporates
during removal, additional water should be sprayed on surfaces as needed. Only enough water should be sprayed to
suppress dust so that water does not run onto the floor of the work area. To aid the wetting process, a surfactant can be
used.
After RCF removal is completed, dust-suppressing cleaning methods, such as wet sweeping or vacuuming, should be
used to clean the work area. If dry vacuuming is used, the vacuum must be equipped with HEPA filter. Air blowing or
dry sweeping should not be used. Dust-suppressing components can be used to clean up light dust.
Product packaging may contain product residue. Do not reuse except to reship or return Ceramic Fiber products to the
factory.
January, 2002
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management P-9
Page 14

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
For assistance with technical problems, please call the Customer Support Center (CSC). The
CSC is staffed 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
In addition to the CSC, you may also contact Field Watch. Field Watch coordinates Rosemount’s
field service throughout the U.S. and abroad.
Rosemount may also be reached via the Internet through e-mail and the World Wide Web:
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
Technical Support Hotline:
Phone: 1-800-433-6076
Phone: 1-800-654-RSMT (1-800-654-7768)
e-mail: GAS.CSC@frco.com
World Wide Web: www.processanalytic.com
P-10 Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 15

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
1
DESCRIPTION AND SPECIFICATIONS
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
SECTION 1
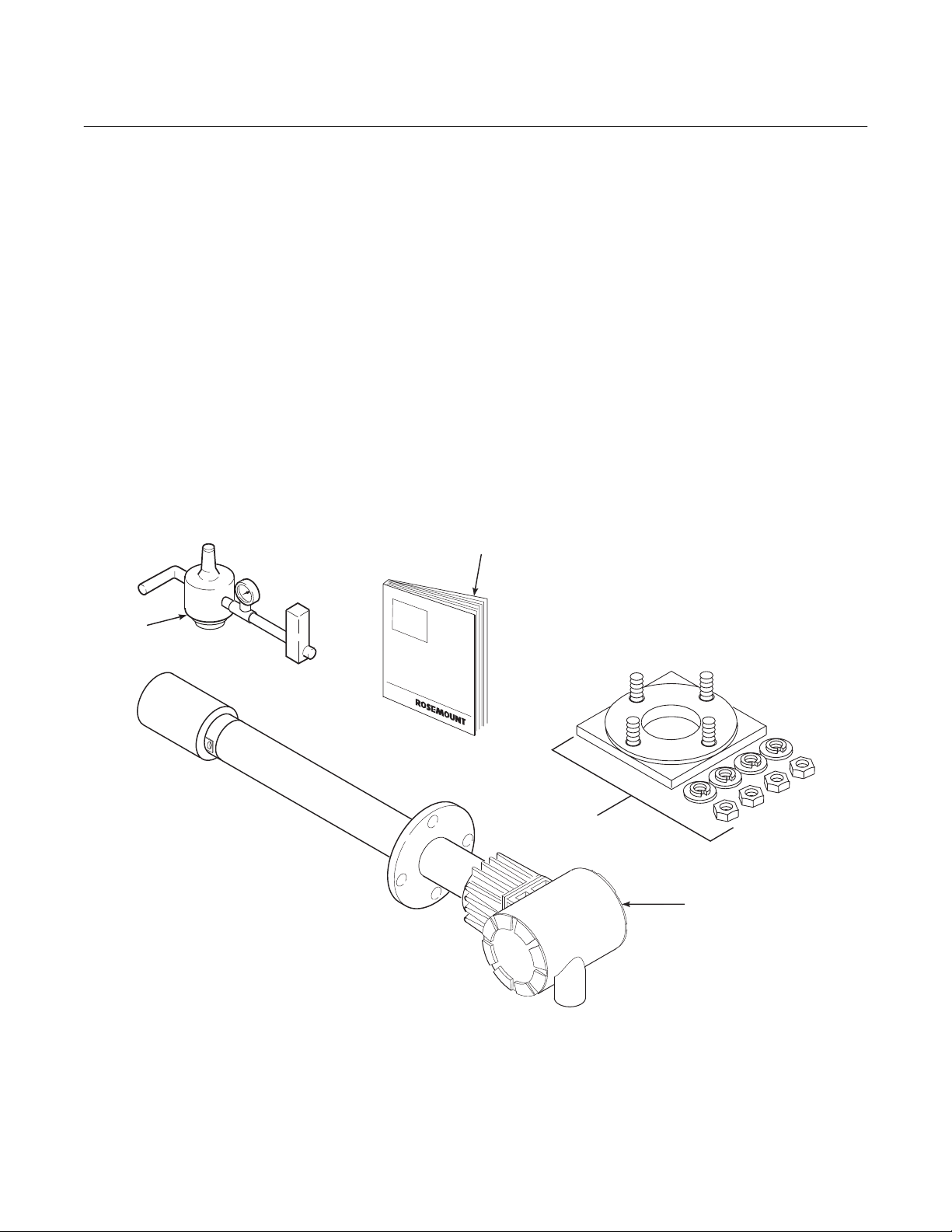
1-1 COMPONENT CHECKLIST OF TYPICAL
SYSTEM (PACKAGE CONTENTS)
A typical Rosemount Hazardous Area Oxymitter
DR In-Situ Oxygen Probe should contain the
items shown in Figure 1-1. Record the part number, serial number, and order number for each
component of your system in the table located on
the back cover of this manual.
The Oxymitter DR is offered in both
hazardous and general purpose configurations. The hazardous area version has the “EX” and CSA symbols
on the apparatus approval label. The
general purpose version does not
have an approval label. If you received
the general purpose version, ensure
you do not install it in a potentially explosive atmosphere.
Also, use the product matrix in Table 1-1 at the
end of this section to compare your order number against your unit. The first part of the matrix
defines the model. The last part defines the
various options and features of the Hazardous
Area Oxymitter DR. Ensure the features and
options specified by your order number are on
or included with the unit.
b. System Description
The Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR is designed to measure the net concentration of
oxygen in an industrial combustion process;
i.e., the oxygen remaining after all fuels have
been oxidized. The probe is permanently positioned within an exhaust duct or stack and
performs its task without the use of a sampling system.
The equipment measures oxygen percentage by reading the voltage developed across
a heated electrochemical cell, which consists
of a small yttria-stabilized, zirconia disc. Both
sides of the disc are coated with porous
metal electrodes. When operated at the
proper temperature, the millivolt output voltage of the cell is given by the following
Nernst equation:
EMF = KT log
Where:
1. P
is the partial pressure of the
2
oxygen in the measured gas on
one side of the cell.
2. P
is the partial pressure of the
1
oxygen in the reference air on
the opposite side of the cell.
3. T is the absolute temperature.
10(P1/P2
) + C
1-2 SYSTEM OVERVIEW
a. Scope
This Instruction Bulletin is designed to supply
details needed to install, start up, operate,
and maintain the Hazardous Area Oxymitter
DR. The Hazardous Area Direct Replacement Oxymitter can be interfaced to a number of different earlier model electronics
packages. These electronic packages are
not covered in this manual. For specification
information concerning calibration and operation of the system, refer to the Instruction
Bulletin applicable to your electronics.
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Description and Specifications 1-1
4. C is the cell constant.
5. K is an arithmetic constant.
When the cell is at operating temperature
and there are unequal oxygen concentrations across the cell, oxygen ions will travel
from the high oxygen partial pressure side to
the low oxygen partial pressure side of the
cell. The resulting logarithmic output voltage
is approximately 50 mV per decade. The
output is proportional to the inverse logarithm
of the oxygen concentration. Therefore, the
output signal increases as the oxygen concentration of the sample gas decreases. This
characteristic enables the Hazardous Area
Oxymitter DR to provide exceptional sensitivity at low oxygen concentrations.
Page 16
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
The Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR measures net oxygen concentration in the presence of all the products of combustion,
including water vapor. Therefore, it may be
considered an analysis on a “wet” basis. In
comparison with older methods, such as the
portable apparatus, which provides an
analysis on a “dry” gas basis, the “wet”
analysis will, in general, indicate a lower percentage of oxygen. The difference will be
proportional to the water content of the sampled gas stream.
c. System Configuration
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR units are
available in three length options, giving the
user the flexibility to use an in situ penetration appropriate to the size of the stack or
duct. The options on length are 457 mm
(18 in.), 0.91 m (3 ft), 1.83 m (6 ft).
Abrasive shields are offered for applications
where abrasive particulates are present.
Acid resistant cells are available for SO
2
and HCl environments. Bypass and probe
mounting jacket options are available for
process temperatures above 1300°F
(705°C).
d. System Features
1. The cell output voltage and sensitivity
increase as the oxygen concentration
decreases.
2. Field replaceable cell, heater, thermocouple, and diffusion element.
3. The Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR is
constructed of rugged 316L stainless
steel for all wetted parts.
1
4
2
3
1. Instruction Bulletin
2. Adapter Plate with Mounting Hardware and Gasket
3. Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
4. Reference Air Set
36220001
Figure 1-1. Typical System Package
1-2 Description and Specifications Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 17
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
1
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
e. Handling the Hazardous Area
Oxymitter DR
The Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR is
designed for industrial applications.
Treat each component of the system
with care to avoid physical damage.
Some probe components are made
from ceramics, which are susceptible
to shock when mishandled.
f. System Considerations
Prior to installing your Hazardous Area
Oxymitter DR, make sure you have all the
components necessary to make the system
installation. Ensure all the components are
properly integrated to make the system
functional.
NOTE
Retain the packaging in which the
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR arrived
from the factory in case any components are to be shipped to another
site. This packaging has been designed to protect the product.
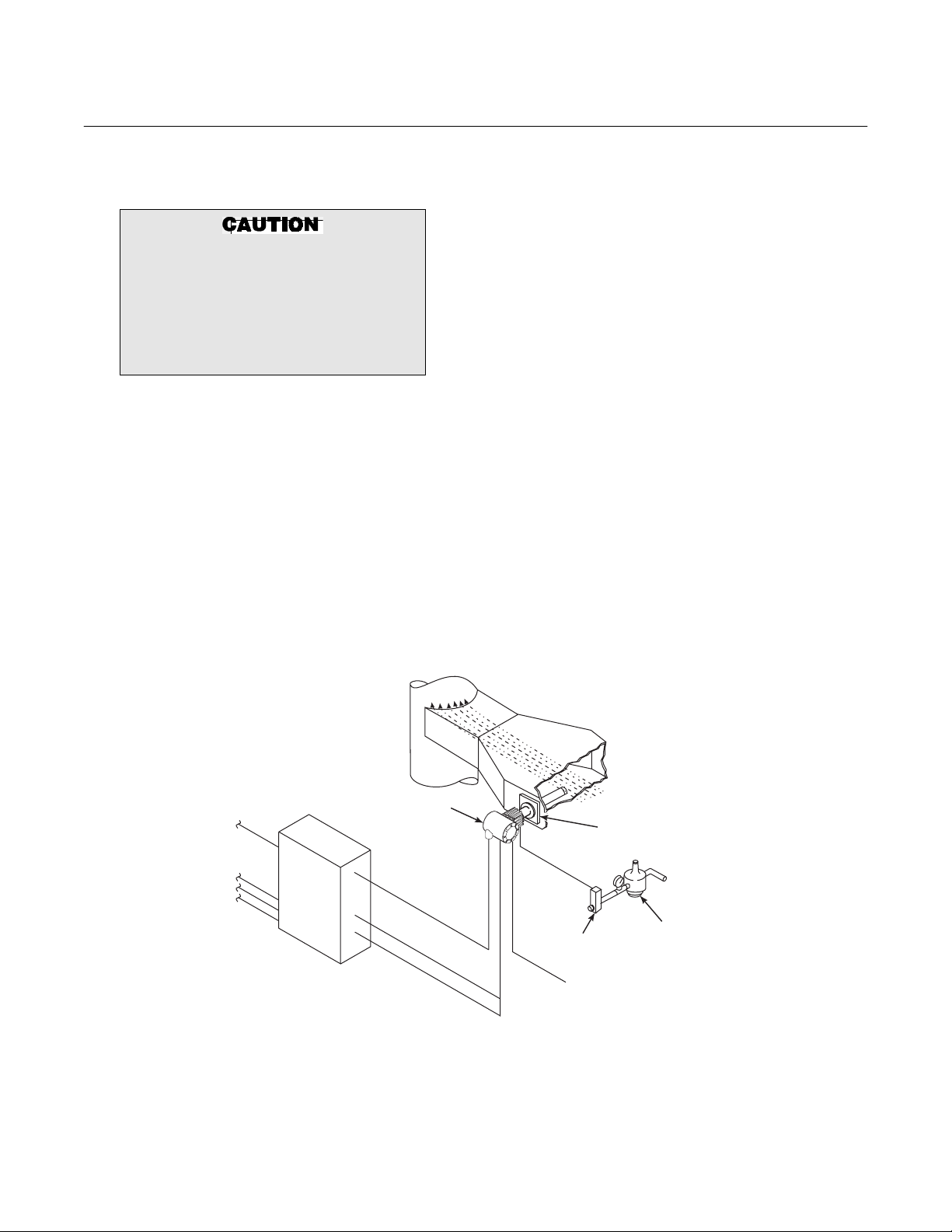
After verifying that you have all the components, select mounting locations and determine how each component will be placed in
terms of available line voltage, ambient
temperatures, environmental considerations, convenience, and serviceability. A
typical system installation is illustrated in
Figure 1-2.
Instrument air for reference is optional for
most applications. Ambient air will passively
diffuse into the inside of the probe in sufficient quantity for an accurate measurement.
Instrument air is required for applications
where the ambient air at the probe location
may not contain the typical 20.95% O
example would be an installation into a
positive pressure flue gas duct which has
many leaks into the surrounding air.
If the calibration gas bottles will be permanently connected, a blocking valve or check
valve is required next to the calibration fittings on the termination housing.
. An
2
4-20 mA
SIGNAL
AC POWER
OXYMITTER DR
EXISTING SIGNAL
CONDITIONING
ELECTRONICS
Figure 1-2. Typical System Installation
GASES
STACK
HEATER
POWER
OXYGEN
SIGNAL
THERMOCOUPLE
SIGNAL
DUCT
FLOWMETER
CALIBRATION
GAS
ADAPTER
PLATE
PRESSURE
REGULATOR
INSTRUMENT
AIR SUPPLY
(REFERENCE AIR)
36210004
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Description and Specifications 1-3
Page 18
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
This check valve or blocking valve is to
prevent breathing of the calibration gas line
and subsequent flue gas condensation and
corrosion.
g. Upgrading the Hazardous Area
Oxymitter DR
The Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR can
be easily upgraded to a full Oxymitter
4000 or 5000. This provides an economical upgrade path for users looking to preserve their probe investment upon the
eventual failure of the signal conditioning
electronics. Upgrading the Hazardous
Area Oxymitter DR to a full Oxymitter
4000 or 5000 requires only the addition of
a small electronics package to the existing termination housing of the Hazardous
Area Oxymitter DR probe. The converted
unit will be a full Oxymitter 4000 or 5000
Oxygen Transmitter with the capability of
providing a 4-20 mA oxygen signal without the need for an external signal conditioning electronics package. HART or
Fieldbus communications are provided
with the Oxymitter electronics. See Appendix A for upgrade information.
1-3 PROBE OPTIONS
a. Abrasive Shield Assembly
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
36220005
Figure 1-3. Flame Arrestor Diffusion Assembly
tures from igniting unburned fuel in the
stack. The ceramic diffusion assembly is
also available with a dust seal for use with
the abrasive shield assembly.
c. Flame Arrestor Snubber Diffusion
Assembly
The snubber diffusion assembly, Figure 14, is satisfactory for most applications.
This element is also available with a dust
seal for use with an abrasive shield.
The abrasive shield assembly, Figure 1-5,
is a stainless-steel tube that surrounds
the probe assembly. The shield protects
against particle abrasion and condensations, provides a guide for ease of
insertion, and acts as a position support,
especially for longer probes. The abrasive
shield assembly uses a modified diffusor
and vee deflector assembly, fitted with
dual dust seal packing.
b. Flame Arrestor Ceramic Diffusion
Assembly
The flame arrestor ceramic diffusion assembly, Figure 1-3, includes a set of baffles between the cell and the stack gases.
This keeps 816°C (1500°F) cell tempera-
1-4 Description and Specifications Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Figure 1-4. Flame Arrestor Snubber Diffusion
Assembly
36220006
Page 19
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
1
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
2
.187
.187
1
B
A
o
15
3.584
3.554
A
.45 MIN
VIEW A
o
90
ON INSIDE BREAK
FOR SMOOTH
ROUNDED EDGE ON
BOTH ENDS
OF CHAMFER
125
.187
6.00
SKIN CUT FACE FOR 90
o
B
VIEW B
o
22.5
0.75 THRU 4 PLS,
EQ SP ON 4.75 B.C.
NOTES:
16860033
1 WELD ON BOTH SIDES WITH EXPANDING
CHILL BLOCK.
2 BEFORE WELDING, BUTT ITEM 2 OR 4 WITH
ITEM 1 AS SHOWN.
.745
DIA ON A 7.50 DIA B.C. (REF)
.755
Figure 1-5. Abrasive Shield Assembly
NOTE
In highly abrasive applications, rotate the shield 90 degrees at normal
service intervals to present a new wear surface to the abrasive flow stream.
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Description and Specifications 1-5
Page 20

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
1-4 SPECIFICATIONS
Hazardous Area Certifications ............................ CENELEC EEXd IIB + H2 T3
Probe Lengths .................................................... 18 in. (457 mm)
Temperature Limits in Process
Measurement Area .................................. 0° to 704°C (32° to 1300°F)
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
CSA Class I, Division 1, Groups B, C, D
3 ft (0.91 m)
6 ft (1.83 m)
up to 1300°C (2400°F) with optional accessories
Resolution Sensitivity ......................................... 0.01% O
Sensing Cell Repeatability ................................. ±0.75% of O
transmitted signal
2
reading, or 0.05% O
2
2
System Response to Calibration Gas ................ Initial response in less than 3 seconds T90 in less than
8 seconds
Resolution Sensitivity ......................................... 0.01% of O
value
2
Mounting and Mounting Position ........................ Vertical or horizontal
Materials:
Probe ....................................................... Wetted or welded parts - 316L stainless steel
Non-wetted parts - 304 stainless steel, low-copper
aluminum
Termination Housing ............................... Low-copper aluminum
Calibration Gas Mixtures Recommended .......... 0.4% O
8% O2, Balance N
, Balance N
2
2
2
Calibration Gas Flow .......................................... 2.5 l/m (5 scfh)
Optional Reference Air ....................................... 1 l/m (2 scfh), clean, dry, instrument-quality air
(20.95% O
), regulated to 34 kPa (5 psi), Optional
2
Heater Voltage ................................................... 115 ±10% VAC, 50/60 Hz., 200VA
Thermocouple .................................................... Type K
Power Requirements:
Nominal ................................................... 175 W
Maximum ................................................. 500 W
Ambient Operating Temperature
(Junction Box) .......................................... 93°C (200°F) [71°C (160°F) max
for YEW replacement]
Fisher-Rosemount has satisfied all obligations coming from the European legislation to harmonize
the product requirements in Europe.
1-6 Description and Specifications Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 21

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
1
Table 1-1. Product Matrix
OXT4ACDR Explosion Proof Oxymitter DR In Situ Oxygen Transmitter
Explosion Proof Exchange Probe - Instruction Book
Code Sensing Probe Type
1 Ceramic Diffusion Element Probe (ANSI 3 in. 150 lbs)
2 Snubber Diffusion Element Probe (ANSI 3 in. 150 lbs)
3 Ceramic Diffusion Element Probe (DIN 2572) - 1/4 in. Tube Fittings
4 Snubber Diffusion Element Probe (DIN 2572) - 1/4 in. Tube Fittings
5 Ceramic Diffusion Element Probe (JIS)
6 Snubber Diffusion Element Probe (JIS)
Code Probe Assembly
0 18 in. (457 mm) Probe
1 18 in. (457 mm) Probe with 3 ft (0.91 m) Bypass
2 18 in. (457 mm) Probe with Abrasive Shield
3 3 ft (0.91 m) Probe
4 3 ft (0.91 m) Probe with Abrasive Shield
5 6 ft (1.83 m) Probe
6 6 ft (1.83 m) Probe with Abrasive Shield
(1)
(1)
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
(1)
Code Mounting Hardware - Stack Side
0 No Mounting Hardware (“0” must be chosen under “Mounting Hardware - Probe Side” below)
1 New Installation - Square weld plate with studs
2 Mounting to Model 218 Mounting Plate (with Model 218 Shield Removed)
3 Competitor’s Mount
(2)
Code Mounting Hardware - Probe Side
0 No Mounting Hardware
1 Probe Only (ANSI) (N. American Std.)
2 New Bypass or Abrasive Shield (ANSI)
4 Probe Only (DIN) (European Std.)
5 New Bypass or Abrasive Shield (DIN)
7 Probe Only (JIS) (Japanese Std.)
8 New Bypass or Abrasive Shield (JIS)
Code Filtered Customer Termination - NEMA 4X, IP66
11 Standard Filtered Termination
12 Transient Protected Filtered Termination
OXT4ADR 3 2 1 1 11 Example
HIGH SULFUR SERVICE
For high sulfur applications, please add an additional line item to your purchase order requesting high sulfur cell part number 4847B63G02 in
lieu of the standard ZrO
cell.
2
Cell replacement kits for high sulfur service are also available.
NOTES:
(1)
Recommended usages: High velocity particulates in flue stream, installation within 11.5 ft (3.5 m) of soot blowers or heavy salt cake buildup.
Applications: Pulverized coal, recovery boilers, lime kiln.
(2)
Where possible, specify SPS number; otherwise, provide details of the existing mounting plate as follows:
Plate with studs Bolt circle diameter, number, and arrangement of studs, stud thread, stud height above mounting plate.
Plate without studs Bolt circle diameter, number, and arrangement of holes, thread, depth of stud mounting plate with accessories.
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Description and Specifications 1-7
Page 22

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Part
Number Description
1A99119G01 Two disposable calibration gas bottles — 0.4%
1A99119G02 Two flow regulators for calibration gas bottles
1A99119G03 Bottle rack
*Calibration gas bottles cannot be shipped via airfreight.
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
Table 1-2. Calibration Components
and 8% O
, balance nitrogen — 550 liters each*
2
1-8 Description and Specifications Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 23

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
2
INSTALLATION
The Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR and
probe abrasive shield are heavy. Use
proper lifting and carrying procedures
to avoid personal injury.
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
SECTION 2
4. The sensing point should be selected
so the process gas temperature falls
within a range of 0° to 704°C (32° to
1300°F). Figure 2-1 through Figure 2-4
provide mechanical installation references. The ambient temperature of the
termination housing must not exceed
65°C (149°F).
Before installing this equipment, read
the “Safety instructions for the wiring
and installation of this apparatus” at
the front of this Instruction Bulletin.
Failure to follow safety instructions
could result in serious injury or death.
2-1 MECHANICAL INSTALLATION
If the probe will be installed into an existing location, proceed to paragraph 2-1b.
a. Selecting Location
1. The location of the Hazardous Area
Oxymitter DR in the stack or flue is
most important for maximum accuracy
in the oxygen analyzing process. The
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR must be
positioned so the gas it measures is
representative of the process. Best results are normally obtained if the Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR is
positioned near the center of the duct
(40-60% insertion).
5. Ducts and stacks that operate under
negative pressure will draw air in
through any holes or torn seals, substantially affecting the oxygen reading.
Therefore, either make the necessary
repairs or install the Hazardous Area
Oxymitter DR upstream of any leakage.
6. Ensure the area is clear of internal and
external obstructions that will interfere
with installation and maintenance. Allow adequate clearance for removal of
the Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
(Figure 2-1).
b. Installation
1. Ensure all components are available to
install the Hazardous Area Oxymitter
DR. If equipped with the optional ceramic diffusion element, ensure it is not
damaged.
2. The Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
may be installed intact as it is received.
2. Longer ducts may require several Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR units since
the O
can vary due to stratification.
2
3. A point too near the wall of the duct, or
the inside radius of a bend, may not
provide a representative sample because of the very low flow conditions.
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Installation 2-1
An abrasive shield is recommended
for high velocity particulate in the flue
stream (such as those in coal-fired
boilers, kilns, and recovery boilers).
3. Weld or bolt adapter plate (Figure 2-4)
onto the duct.
NOTE
Page 24

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
EARTH
EXTERNAL
LABEL
APPROVED
CERTIFICATION
AMBIENT WEATHER CONDITIONS
INSULATE IF EXPOSED TO
803
DIM "B"
EARTH
REF.
GAS
E
V
I
-
L
A
E
R
T
E
I
H
P
U
S
C
O
M
T
A
E
V
I
S
O
O
M
T
A
E
V
I
S
O
R
-
I
C
G
N
I
N
R
A
L
S
G
N
I
N
R
A
L
N
E
H
W
W
-
T
P
H
X
E
G
I
T
N
I
P
-
E
E
K
500VA
5 Amps
R
TM
HART
SMART FAMILY
800-433-6076
Orrville,OH 44667-0901
Rosemount Analytical Inc.
R
TM
4-20 mA
85-264VAC 48-62 Hz
OXYMITTER 4000
SERIAL NO.
VOLTS: WATTS:
TAG NO.
OUTPUT: LINE FUSE:
E
V
I
-
L
A
E
R
T
E
I
H
P
U
C
R
-
I
C
N
E
H
W
W
-
T
P
H
X
E
G
I
T
N
I
P
-
E
E
K
EXTERNAL
EARTH
INTERNAL
3/4 NPT
ELEC CONN
REF AIR
CAL GAS
ANSI ( ) TUBE6.35 1/4
DIN 6.35 (1/4) TUBE
460
DIM "A"
PROBE
TABLE 2 INSTALLATION/REMOVAL
6 mm TUBEJIS
305
(12)
2174
(31.6)
(18.1)
18 IN.
1448
917
3 FT
(85.6)
(57.0)
1831
(36.1)
(72.1)
6 FT
PATTERNS; AND ARE NOT PRESSURE RATED.
THESE FLAT FACED FLANGES ARE
MANUFACTURED TO ANSI, DIN, & JIS BOLT
ALL DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS
WITH INCHES IN PARENTHESES UNLESS
OTHERWISE NOTED.
167
(6.58)
39
73
(1.55)
(2.89)
COVER REMOVAL & ACCESS
305
(12)
NOTES:
0.062 IN. THK GASKET
PROCESS FLOW MUST BE IN
THIS DIRECTION WITH RESPECT
TO DEFLECTOR 3534B48G01
CAL.
GAS
DIM "B"
343 (13.5)
REMOVAL ENVELOPE
BOTTOM VIEW
VENT
REF. AIR
66
(2.6)
WITH
DIM "A"
SNUBBER
76
(3.0)
DIFFUSER
210
DIN
(8.25)
18 (.71)
170
(6.69)
95 (3.8)
(GASKET INCLUDED)
ADD TO DIM “A”
FOR PROBE WITH
CERAMIC DIFFUSER
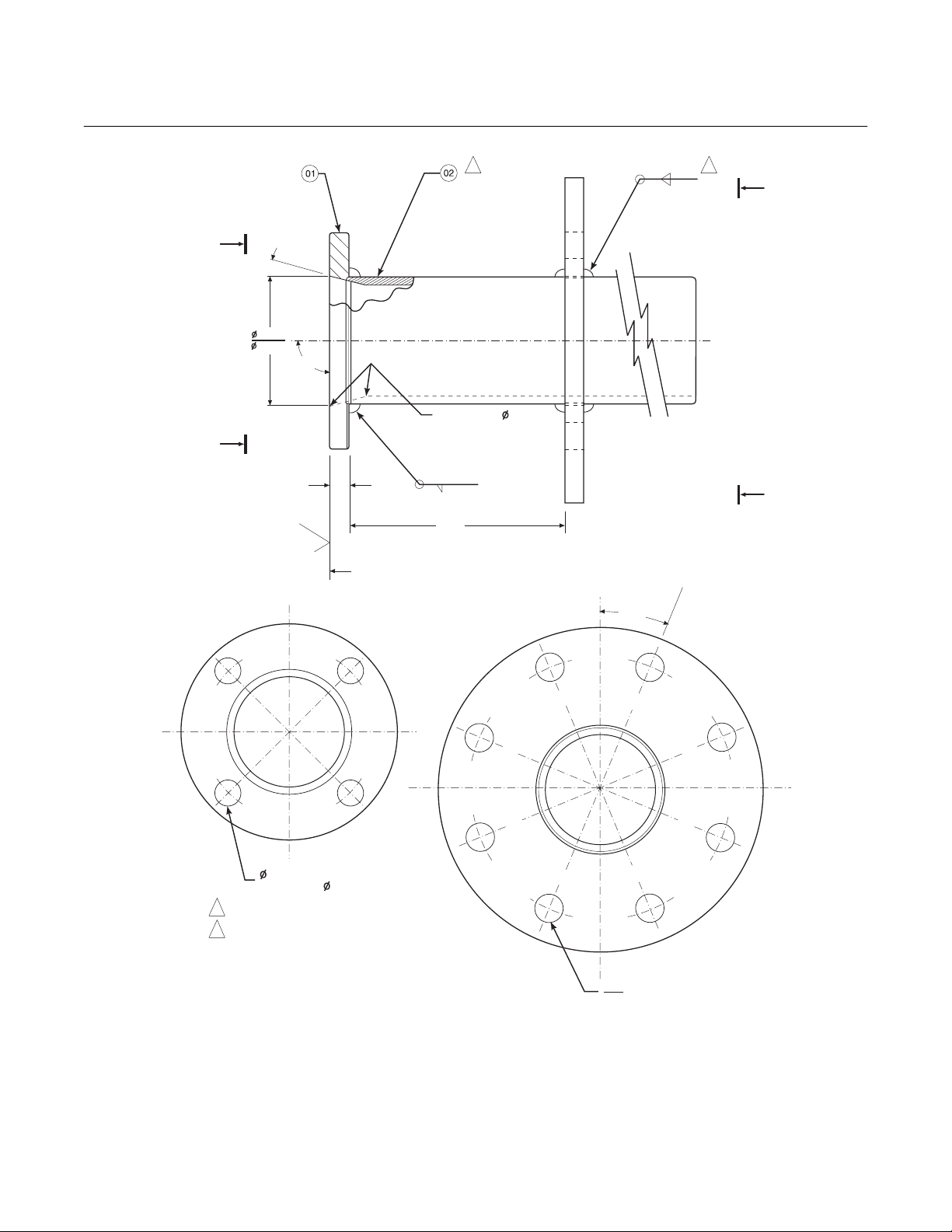
TABLE 1 MOUNTING FLANGE
ANSI
190
FLANGE
(7.5)
152.4
(6.00)
19 (.75)
HOLE DIA
DIA
(4) HOLES
EQ SP
ON BC
35910002
Figure 2-1. Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR Installation
2-2 Installation Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 25

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
2
E
R
E
H
P
S
O
M
-
T
G
A
N
I
N
E
R
V
A
I
W
S
O
-
L
P
X
E
343
(13.50)
"B"
VAL ENVELOPE
DIM
O
REM
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
E
V
I
-
L
A
T
I
U
C
R
I
C
N
E
H
W
T
H
G
I
T
N
I
P
-
E
E
K
3/4 NPT ELECTRICAL CONNECTION
1/4 IN. TUBE
1/4 IN. TUBE
6 mm TUBE
CAL.
GAS
CAL GAS*
*ADD CHECK VALVE IN CAL GAS LINE
ANSI
DIN
JIS
REF AIR
THESE FLAT FACED FLANGES ARE MANUFACTURED TO ANSI, DIN, & JIS BOLT
NOTES:
24
190
(0.94)
(9.25)
(9.25)
(9.00)
DIA
(7.48)
19
190
(0.75)
(7.48)
19
190
(0.75)
(7.50)
EQ SP
ON BC
HOLE
DIA
(8) HOLES
178
235
DIN
-3D39003
JIS
235
229
TABLE 4 ABRASIVE SHIELD
ANSI
FLANGE
FLANGE
(7.00)
INAL
NOM
91 (3.6) DIA
"A"
DIM
Y
BL
99
PATTERNS AND NOT PRESSURE RATED.
ALL DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS WITH INCHES IN PARENTHESES.
(3.9)
ASSEM
5
SNUBBER/DUST SEAL
(0.2)
SEAL ASSY
DIFFUSER/DUST
DEFLECTOR ASSY
VAL
O
TABLE 3 INSTALLATION/REM
"B"
DIM
DIM "A"
PROBE
912
387
1367
2287
(53.8)
(90.0)
(35.9)
843
1762
(69.4)
(33.2)
(15.3)
18 IN
3 FT
6 FT
35910003
Figure 2-2. Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR with Abrasive Shield
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Installation 2-3
Page 26

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
OXYMITTER 4000 WITH ABRASIVE SHIELD
TABLE VI. MOUNTING PLATE DIMENSIONS FOR HAZARDOUS AREA
JIS
DIN
ANSI
(in.)
"A"
MM
DIMENSIONS
235
235
229
(9.25)
(9.25)
(9.00)
125
100
121
"B"
(4.92)
(3.94)
(4.75)
DIA
M16x2
M20 x 2.5
0.625-11
"C"
THREAD
200
190
191
"D"
(7.89)
(7.48)
(7.50)
DIA B.C.
TO PROVIDE ADDITIONAL
CROSSHATCHED AREA IN
4 CORNERS MAY BE USED
o
22.5
WALL SURFACE.
OF PLATE TO OUTSIDE
HOLES FOR FIELD BOLTING
8 THREADED HOLES
EQUALLY SPACED ON
A
D DIA B.C.
ABRASIVE SHIELD
FLANGE O.D.
A
C
MOUNTING PLATE FOR
WITH ABRASIVE SHIELD
B
HAZARDOUS AREA OXYMITTER DR
MOUNTING PLATE OUTLINE
HAZARDOUS AREA OXYMITTER DR
TABLE V. MOUNTING PLATE DIMENSIONS FOR
DIN
ANSI
MM
(in.)
DIMENSIONS
216
197
"A"
(8.50)
(7.75)
M16x2
0.625-11
"B"
STUD SIZE
170.0
(6.69)
152.4
(6.00)
“C"
DIA B.C.
A
WITH INCHES IN PARENTHESES.
NOTE: DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS
82.6
C
(3.25) DIA
Figure 2-3. Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR Adapter Plate Dimensions
4 STUDS,
LOCKWASHERS AND
NUTS EQUALLY
SPACED ON
C DIA B.C.
B
MOUNTING PLATE FOR
HAZARDOUS AREA OXYMITTER DR
36220002
2-4 Installation Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 27

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
2
INSTALLATION FOR METAL
WALL STACK OR DUCT
CONSTRUCTION
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
INSTALLATION FOR MASONRY
WALL STACK CONSTRUCTION
MTG HOLES
SHOWN ROTATED
o
45 OUT OF
TRUE POSITION
WELD OR BOLT MOUNTING
PLATE TO METAL WALL
OF STACK OR DUCT.
JOINT MUST BE AIRTIGHT.
13 (0.50)
95 (3.75)
MIN DIA HOLE
IN WALL
STACK OR DUCT
METAL WALL
WITH ABRASIVE SHIELD
BOLT MOUNTING
PLATE TO OUTSIDE
WALL SURFACE
FIELD WELD
MOUNTING PLATE
MTG HOLES
SHOWN ROTATED
o
45 OUT OF
TRUE POSITION
JOINT MUST
BE AIRTIGHT
OUTSIDE WALL
SURFACE
NOTE: ALL MASONRY STACK WORK AND JOINTS EXCEPT
ADAPTOR PLATE NOT FURNISHED BY ROSEMOUNT.
PIPE TO
13 (0.50)
114 (4.50)
O.D. REF
PIPE 4.00 IN. SCHED 40
PIPE SLEEVE (NOT
BY ROSEMOUNT)
LENGTH BY CUSTOMER
MASONRY
STACK WALL
WITHOUT ABRASIVE SHIELD
82.5 (3.25)
WELD OR BOLT MOUNTING
PLATE TO METAL WALL
OF STACK OR DUCT.
JOINT MUST BE AIRTIGHT.
MIN DIA HOLE
IN WALL
STACK OR DUCT
METAL WALL
NOTE: DIMENSIONS IN MILLIMETERS WITH
BOLT MOUNTING
PLATE TO OUTSIDE
WALL SURFACE
JOINT MUST
BE AIRTIGHT
OUTSIDE WALL
SURFACE
INCHES IN PARENTHESES.
FIELD WELD
PIPE TO
MOUNTING PLATE
102 (4.0)
O.D. REF
PIPE 3.5 IN. SCHED 40
PIPE SLEEVE (NOT
BY ROSEMOUNT)
LENGTH BY CUSTOMER
MASONRY
STACK WALL
36220007
Figure 2-4. Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR Adapter Plate Installation
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Installation 2-5
Page 28

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
4. If using the optional ceramic diffusion
element, the vee deflector must be correctly oriented. Before inserting the
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR, check
the direction of gas flow in the duct. Orient the vee deflector so the apex points
upstream toward the flow (Figure 2-5).
This may be done by loosening the
setscrews and rotating the vee deflector
to the desired position. Retighten the
setscrews.
5. In vertical installations, ensure the system cable drops vertically from the Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR and the
conduit is routed below the level of the
termination housing. This drip loop
minimizes the possibility that moisture
will damage the electrical connections
(Figure 2-6).
GAS FLOW
DIRECTION
VEE
DEFLECTOR
APEX
DIFFUSION
FILTER
ELEMENT
SETSCREW
DEFLECTOR
VEE
22220020
Figure 2-5. Orienting the Optional Vee Deflector
LINE
VOLTAG E
OXYGEN,
THERMOCOUPLE
SIGNAL
REPLACE INSULATION
AFTER INSTALLING
HAZARDOUS AREA
OXYMITTER DR
INSULATION
ADAPTER
Figure 2-6. Installation with Drip Loop and Insulation Removal
PLATE
E
V
I
-
L
A
E
R
T
E
I
H
P
S
O
-
M
T
G
A
N
I
N
E
R
V
A
I
W
S
O
L
P
U
C
R
I
C
N
E
H
-
X
E
W
T
H
G
I
T
N
I
P
-
E
E
K
DRIP
LOOP
CAL.
GAS
STACK OR DUCT
METAL WALL
36210007
2-6 Installation Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 29

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
2
6. If the system has an abrasive shield,
check the dust seal gaskets. The joints
in the two gaskets must be staggered
180°. Also, make sure the gaskets are
in the hub grooves as the Hazardous
Area Oxymitter DR slides into the 15°
chamfer in the abrasive shield.
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Disconnect and lock out power before
connecting the unit to the power
supply.
NOTE
If process temperatures will exceed
200°C (392°F), use anti-seize compound on stud threads to ease future
removal of Oxymitter DR.
7. Insert probe through the opening in the
mounting flange and bolt the unit to the
flange.
NOTE
To maintain CE compliance, ensure a
good connection exists between the
mounting plate studs or earthing
screws on termination housing and
earth.
8. Ensure the Hazardous Area Oxymitter
DR is properly earthed by way of both
internal and external points.
9. If insulation is being removed to access
the duct work for Hazardous Area
Oxymitter DR mounting, make sure the
insulation is replaced afterward (Figure
2-6).
Install all protective equipment covers
and safety ground leads after installation. Failure to install covers and
ground leads could result in serious
injury or death.
To meet the Safety Requirements of
IEC 1010 (EC requirement), and ensure
safe operation of this equipment, connection to the main electrical power
supply must be made through a circuit
breaker (min 10 A) which will disconnect all current-carrying conductors
during a fault situation. This circuit
breaker should also include a mechanically operated isolating switch. If
not, then another external means of
disconnecting the supply from the
equipment should be located close by.
Circuit breakers or switches must
comply with a recognized standard
such as IEC 947.
10. Ensure the installation does not obscure
the messages on either housing cover.
2-2 ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION
All wiring must conform to local and national
codes.
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Installation 2-7
The Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR and
probe abrasive shield are heavy. Use
proper lifting and carrying procedures
to avoid personal injury.
a. Remove screw (11, Figure 4-1), captive
washer (13), and cover lock (12). Remove
left housing cover (10).
Page 30

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
HEATER
POWER
THERMOCOUPLE
TYPE K
SIGNAL
OXYGEN
SIGNAL
LEFT SIDE OF
OXYMITTER DR
b. Connect Heater Power
Connect the heater power lines to the two
terminals indicated in (Figure 2-7).
c. Connect O
and Heater Thermocouple
2
Signals
TERMINAL
BLOCK
+
-
+
-
Figure 2-7. Terminal Block
Instrument Air (Reference Air): 68.95 kPag (10
psig) minimum, 1551.38 kPag (225 psig) maximum at 56.6 L/hr (2 scfh) maximum; less than
40 parts-per-million total hydrocarbons. Regulator outlet pressure should be set at 35 kPa
(5 psi).
HEATER POWER
PORT
GROUND
LUGS
SIGNAL
PORT
36210002
1. Oxygen Signal. Connect the oxygen
signal lines from the signal conditioning
electronics to the terminals shown in
Figure 2-7.
2. Heater Thermocouple Signal. Connect
the type K thermocouple signal lines
from the signal conditioning electronics
to the terminals indicated in Figure 2-7.
d. Install left housing cover (10, Figure 4-1)
and secure with cover lock (12), captive
washer (13), and screw (11).
2-3 PNEUMATIC INSTALLATION
If instrument air will be used as reference air
(see System Considerations, paragraph 1-2f),
connect the reference air set to the Hazardous
Area Oxymitter DR. The reference air set should
be installed in accordance with Figure 2-8.
NOTE
!
Upon completing installation, make
sure that the Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR is turned on and operating prior
to firing up the combustion process.
Damage can result from having a cold
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR exposed to the process gases.
During outages, and if possible, leave
all Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR units
running to prevent condensation and
premature aging from thermal cycling.
If the ducts will be washed down during outage, MAKE SURE to power
down the Hazardous Area Oxymitter
DR units and remove them from the
wash area.
2-8 Installation Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 31

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
2
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
4.81 (122.17)
FLOW SET
POINT KNOB
0.125-27 NPT FEMALE
OUTLET CONNECTION
1
0.250 OR 6 MM O.D.
TUBE COMPRESSION
FITTING
Rosemount Analytical Inc.
Orrville,OH 44667-0901
800-433-6076
TM
OXYMITTER DR
SERIAL NO.
TAG NO.
0.250 OR 6 MM O.D. TUBING
(SUPPLIED BY CUSTOMER)
2
OUTLET
1.19
(30.22)
DRAIN VALVE
10.0
(254)
REF
TO ELECTRONICS
3
REF AIR SET
263C152G01
3.12 (79.25) MAX
2.250 (57.15)
0.25-18 NPT FEMALE
INLET CONNECTION
2.0
(50.80)
1.50
(38.10)
1 FLOWMETER 0.2-2.0 SCFH 771B635H02
2 2" PRESSURE GAGE 0-15 PSIG 275431-006
3 COMBINATION FILTER-REG. 0-30 PSIG 4505C21G01
NOTE: DIMENSIONS ARE IN INCHES WITH
2 MOUNTING HOLES
3.19 (81.03) LG
THROUGH BODY FOR
0.312 (7.92) DIA BOLTS
INSTRUMENT AIR SUPPLY
10-225 PSIG MAX PRESSURE
MILLIMETERS IN PARENTHESES.
8.50
(215.90)
MAX
SCHEMATIC HOOKUP FOR REFERENCE AIR SUPPLY ON OXYMITTER DR PROBE HEAD.
Install all protective equipment covers
and safety ground leads before
equipment startup. Failure to install
covers and ground leads could result
in serious injury or death.
2-4 SYSTEM SETUP
a. Overview
This section covers the setup procedures
for the Oxymitter DR In-Situ Oxygen Probe.
The DR probe can be used with several
electronics packages including: Models 218,
218A, 225, 132 (analog and digital), TC200,
and ZA8C.
For Westinghouse Models 218, 225, and
132 (analog), refer to paragraph 2-4b. Addi-
36210008
Figure 2-8. Air Set, Plant Air Connection
tional information can be found in IB-106-
101.
For Westinghouse Model 218A, refer to
paragraph 2-4c. Additional information can
be found in IB-106-101A.
For Westinghouse Model TC200, refer to
paragraph 2-4d. Additional information can
be found in IB-107-020.
For Westinghouse Model 132 (digital), refer
to paragraph 2-4e. Additional information
can be found in IB-106-106A.
For Rosemount World Class 3000, refer to
paragraph 2-4f. Additional information can
be found in IB-106-300NFX.
For Yokogawa Model ZA8C, refer to paragraph 2-4g.
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Installation 2-9
Page 32

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
b. WESTINGHOUSE MODELS 218, 225,
AND 132 (ANALOG) ELECTRONICS
SETUP
Before beginning operation, it is important
that the probe heater setpoint of the existing
electronics be changed to support the Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR In-Situ Oxygen
Probe. The setpoint adjustment procedure
required for Models 218, 225, and 132
analog electronics is as follows:
1. Open electronics enclosure.
2. On temperature controller card, Figure
2-9, connect jumper wire from TP3 to
either Pin 2 or Pin 7.
3. Set voltmeter to read DC millivolts
(MV).
4. Attach voltmeter with positive (+) lead
on TP1 and negative (-) on either Pin 2
or 7.
TP3
5. Adjust potentiometer M110-1 to read -
322.3 millivolts nominal.
6. Remove voltmeter leads.
7. Remove jumper wire.
TP1
M110-1
NOTE
The voltage given above is for an ambient (machinery space) temperature
of 25°C (77°F). For each degree of ambient temperature above or below 25°C
(77°F), add or subtract 0.242 mV from
the nominal. Example: at 31°C (87°F),
the nominal voltage of -322.3 Mv
should be increased (made less negative) by 10 x 0.242 or 2.42 mV, making
the adjusted nominal -319.9 Mv.
PIN 2
(PSC)
23 567 1012
PIN 7 (PSC)
P0019
Figure 2-9. Temperature Controller Card
Calibration Points
2-10 Installation Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 33

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
2
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
c. WESTINGHOUSE MODEL 218A ELEC-
TRONICS SETUP
Before beginning operation, it is important
that the probe heater setpoint of the existing
electronics be changed to support the Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR probe. To convert the Model 218A Digital Electronics
Package for use with the DR probe, an
EPROM change is necessary. Remove
Main PCB and check back of board to identify unit as G02 or G04. The replacement
EPROM needed is as identified below:
G02 G04
United States 1M03192G01 1M02982G01
United Kingdom 1M03192G02 1M02982G02
Germany 1M03192G03 1M02982G03
France 1M03192G04 1M02982G04
Italy 1M03192G05 1M02982G05
NOTE
The replacement EPROM when using a
multiprobe averager unit is
1M02982G10.
To replace the EPROM, proceed as follows:
1. Shut off and lock out power to the
electronics package.
2. Open electronics enclosure.
3. On the Main PCB, Figure 2-10, locate
and remove old EPROM.
4. Replace with new EPROM.
5. Close electronics enclosure and power
up system.
EPROM
MAIN PCB
Figure 2-10. Main PCB (Model 218A) EPROM Replacement
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Installation 2-11
P0020
Page 34

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
d. WESTINGHOUSE MODEL TC200 VERI-
TRIM ELECTRONICS SETUP
Before beginning operation, it is important
that the probe heater setpoint of the existing
electronics be changed to support the Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR In-Situ Oxygen
Probe. To convert the Model TC200 Electronics Package for use with the DR probe,
an EPROM change is necessary. The replacement EPROM needed is part number
1M03154G02.
1. EPROM replacement. To replace the
EPROM, proceed as follows:
(a) Shut off and lock out power to the
electronics package.
(b) Open electronics enclosure.
(c) On the main PCB, Figure 2-11, lo-
cate and remove old EPROMs U11
and U12.
(d) Replace with new EPROMs (part
number 1M03154G02) being
careful to install U11 and U12 in
their proper locations.
2. Heater Setpoint Adjustment. The adjustment procedure required for the
Model TC200 Electronics Package is
as follows:
(a) Open keylocked enclosure to ac-
cess membrane keyboard.
(b) Put controller in PAR (parameter)
mode by depressing "LOCK" "▲"
"%O2" "INC" "ACK" in sequence.
(c) Depress "ACK" pushbutton to clear
display.
(d) Press "NUM" pushbutton.
(e) Using "INC", "DEC" buttons, dis-
play parameter 125.
(f) Press "VAL" button.
(g) Using "INC", "DEC" buttons,
change parameter 125 value to
15.4.
(h) Press "ENT" to save new value.
(e) Close electronics enclosure and
power up system.
2-12 Installation Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 35

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
2
DIS A/M
EPROMS
U11 AND U12
U12
U11
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Figure 2-11. Main PCB (Model TC200) EPROM Replacement
P0021
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Installation 2-13
Page 36

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
e. WESTINGHOUSE MODEL 132 DIGITAL
ELECTRONICS SETUP
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
To replace the EPROM, proceed as follows:
Before beginning operation, it is important
that the probe heater setpoint of the existing
electronics be changed to support the Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR In-Situ Oxygen
Probe. To convert the Model 132 Digital
Electronics Package for use with the DR
probe, an EPROM change is necessary.
The replacement EPROM needed is as
identified below:
United States IM03222G01
R38
TP1
EPROM
R8
U2
C48
U1
C37
LM8
03
P61
U7
C44
R27
XT1
C26
C27
C38
R38
C29
C28
04
R12
U6
U4
C30
C29
R26
P25
P36
CR25
C13
D12
O18
1
C46
P28
LED1
U9
R41
RP1
TP2
C24
D14
C23
D13
C14
D1
C16
D2
MAIN PCB
J1
08
R63
R62
R54
R53
U13
R48
C22
C21
C12
C13
C10
C34
M55
CR18
CR17
R48
C39
20
C31
U10
C43
C42
R42
CR15
CR16
CR24
R36
CR13
CR14
CR12
CR11
R37
R86
CR18
R68
U3
09
C41
R64
BR1
1. Shut off and lock out power to the
electronics package.
2. Open electronics enclosure.
3. On the Main PCB, Figure 2-12, locate
and remove old EPROM.
4. Replace with new EPROM.
5. Close electronics enclosure and power
up system.
TX2
C38
R56
CR19
C30
R44
R49
R47
U14
R43
R38
R61
P22
P29
C86
C10
U12
C16
U2
C32
TR1
TX1
C36
C11
R46
R48
P62
C7
C9
U11
C8
R6
C48
C4
C3 C8
C47
C1
C2
C3
R9
2001A
F2
2001A
CK1
F1
C7
I
R58
R57
R59
P68
U19
U17
R18
R16
R17
R19
U16
R11
R18
CR3
CR4
U18
R4
R5
CR1
CR2
CR21
CR22
08
A
28
28
R16
28
C46
CR7
CR6
CR8
CR5
28
28
LK2
28
R7
R6
R14
R23
R28
LK1
CR20
CR23
5A
F3
5A
F4
28
28
C17
R2
R1
R21
R13
R24
FIL1
R1
CR9
R81
ALARM
MTR-T/C CELL SKG STK-T/C ML-O/P
T83
C11
T82
OFF
N
L
HEATER
E
E
N
MAIN INPUT
L
T81
SW1
MOV1
MOV2
ON
P0022
Figure 2-12. Main PCB (Model 132) EPROM Replacement
2-14 Installation Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 37

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
2
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
f. WORLD CLASS 3000 INTELLIGENT
FIELD TRANSMITTER SETUP
The DR probe operates with a 115 VAC
heater. Ensure that the voltage selection
jumpers in the IFT or HPS, if used, are set
CONFIGURATION
LINE VOLTAGE
SELECTION
100 V.A.C.
120 V.A.C.
220 V.A.C.
240 V.A.C.
JUMPER
(INSTALL)
JM3, JM7, JM2
JM8, JM7, JM1
JM6, JM5, JM2
JM6, JM5, JM1
Figure 2-13. IFT 3000 Power Supply Board Jumper Configuration
JUMPER
WORLD CLASS PROBE (44V)
REPLACEMENT" PROBE (115V)
REPLACEMENT PROBE (115V)
ALWAYS DISCONNECT LINE VOLTAGE
FROM INTELLIGENT FIELD TRANSMITTER
BEFORE CHANGING JUMPERS.
PROBE HEATER
VOLTAGE SELECTION
218 PROBE (115V)
WORLD CLASS "DIRECT
OR OXYMITTER DIRECT
properly. Refer to Figure 2-13 for IFT
jumper selection, and Figure 2-14 for HPS
jumper selection. For additional setup and
configuration information, refer to IB-106300NFX.
JUMPER
(INSTALL)
JM10
JM9
JM9
36210015
If incorrect heater voltage is selected, damage to the Oxymitter DR may occur. Refer to
IB-106-300NFX for additional configuration information. Always update the relevant labeling
to reflect the set voltage.
ALWAYS DISCONNECT LINE VOLTAGE
FROM HEATER POWER SUPPLY AND
ANALOG ELECTRONICS (IF USED)
BEFORE CHANGING JUMPERS.
HEATER
POWER
REMOTE
ON
ELECTRONICS
SELECTION
*ANALOG (EXISTING)
DIGITAL
(NEXT GENERATION)
JUMPER
REMOVE JM2
*INSTALL JM2
JUMPER
INSTALL JM3, JM6
REMOVE JM3, JM6
36210014
LINE VOLTAGE
SELECTION
1
100/120 V.A.C.
220/240 V.A.C.
PROBE HEATER
VOLTAGE SELECTION
WORLD CLASS PROBE
DIRECT REPLACEMENT
(44V)
218 PROBE (115V)
WORLD CLASS OR
DR OXYMITTER
NOTES:
1
JUMPER
CONFIGURATIONS
JUMPER
(INSTALL)
JM4, JM1
JM5
JUMPER
(INSTALL)
JM7
JM8
JM8
100 V.A.C. OPERATION REQUIRES TRANSFORMER PART
NUMBER 1M02961G02.
Figure 2-14. Heater Power Supply (HPS 3000) Jumper Configuration
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Installation 2-15
Page 38

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
g. THE YOKOGAWA ZA8C AND AV8C
CONVERTER ELECTRONICS SETUP
The Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR probe
can be wired to work with the Yokogawa®
ZA8C
OR
AV8C
TERMINAL
}
}
}
3+
4–
5+
6–
7+
8–
16
17
THERMOCOUPLE
32
ZA8C OR AV8C
GND
SHIELD
CELL
COLD
JUNCTION
PROBE
HEATER
ZA8C and AV8C Converters. Connect the
cabling from the ZA8C or AV8C terminal to
the probe terminal in the junction box as
shown in Figure 2-15.
COLD
JUNCTION
DEVICE
+
–
+
+
-
-
ZA8C
OR
AV8C
CONVERTER
HEATER AND SIGNAL CABLE
OXYMITTER DR PROBE
WITH ADAPTER FLANGE
NOTES: 1. HEATER TEMPERATURE SET TO 1380 F (750 C)
2.
THE GREATER MASS OF THE OXYMITTER DIRECT REPLACEMENT PROBE REQUIRES
LONGER TIME TO HEAT UP. UPON STARTUP, THE YOKOGAWA ELECTRONICS MAY
INDICATE AN ERROR BECAUSE THE PROBE HAS NOT REACHED TEMPERATURE SETPOINT
IN THE NORMAL TIME. REMOVE POWER FROM THE YOKOGAWA ELECTRONICS OR PROBE
MODULE TO CLEAR THE ERROR, AND RESTORE POWER. THIS PROCEDURE MAY HAVE TO
BE REPEATED A COUPLE OF TIMES BEFORE PROBE OPERATING TEMPERATURE IS REACHED.
oo
Figure 2-15. DR Probe Wired to the ZA8C or A V8C Converter
SHIELD
STACK WALL
EXISTING
MOUNTING
36210009
2-16 Installation Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 39

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
3
STARTUP AND OPERATION
Install all protective equipment covers
and safety ground leads before
equipment startup. Failure to install
covers and ground leads could result
in serious injury or death.
3-1 GENERAL
For startup and operation instructions, refer to
the Instruction Bulletin provided with your electronics package.
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
SECTION 3
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Startup and Operation 3-1
Page 40

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
3-2 Startup and Operation Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 41

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
4
MAINTENANCE AND SERVICE
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
SECTION 4
When working on this equipment on
the laboratory bench, be aware that
the probe, probe tube, and flame arrestor hub can be hot [up to 370°C
(698°F)] in the region of the probe
heater.
Install all protective equipment covers
and safety ground leads after equipment repair or service. Failure to install covers and ground leads could
result in serious injury or death.
4-1 OVERVIEW
This section identifies the calibration methods
available and provides the procedures to maintain and service the Hazardous Area Oxymitter
DR.
4-2 CALIBRATION
The Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR should be
calibrated when commissioned. Under normal
circumstances the probe will not require frequent calibration. When calibration is required,
follow the procedure described in the Instruction
Bulletin applicable to your electronics package.
It is recommended that the Hazardous
Area Oxymitter DR be removed from
the stack for all service activities.
Wear heat resistant gloves and clothing to remove probe from stack. Normal operating temperature of diffusor
and vee deflector are approximately
316 to 472°C (600 to 800°F). The unit
should be allowed to cool and be
taken to a clean work area. Failure to
comply may cause severe burns.
Disconnect and lock out power before
working on any electrical components.
There is voltage up to 115 VAC.
4-3 HAZARDOUS AREA OXYMITTER DR
REPLACEMENT
a. Remove.
1. Turn off power to the system.
2. Shut off the calibration gases at the
cylinders and the instrument air.
3. Disconnect the calibration gas and instrument air lines from the Hazardous
Area Oxymitter DR.
4. While facing the Hazardous Area
Oxymitter DR and looking at the
Rosemount label, remove screw (11,
Figure 4-1), captive washer (13) and
cover lock (12) securing left housing
cover (10). Remove the cover to expose the terminal block (Figure 4-2).
5. Loosen the screw on the heater terminal cover and slide the cover back to
access the heater terminals. Loosen
the heater terminal screws and remove
the leads. Loosen the ground lug
screws and remove the leads. Slide the
heater power leads out of the heater
power port.
6. Loosen the oxygen and heater thermocouple signal terminal screws. Remove
the leads from the terminals and slide
the wires out of the signal port.
7. Remove insulation to access the
mounting bolts. Unbolt the Hazardous
Area Oxymitter DR from the stack and
take it to a clean work area.
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Maintenance and Service 4-1
Page 42

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
Note: Not all parts shown.
28
31
5
6
4
2
13
12
11
3
14
15
1
27
22
23
24
25
22
23
24
25
7
Integral Electrical
Barrier/Feedthrough
16
22
23
17
24
9
8
10
11
1. Right Housing Cover
2. Connecting Cable - Heater
3. Connecting Cable - Signal
4. Termination Housing
5. Screw
12
6. Lock Washer
13
7. Cable Clamp
8. Terminal Block
9. Captive Screw
10. Left Housing Cover
11. Screw
12. Cover Lock
13. Captive Washer
14. Washer
15. Screw
16. Probe Tube Assembly
17. Gasket
18. Corrugated Seal
19. Cell and Flange Assembly
20. Retainer Screw
21. Flame Arrester with
Snubber Diffuser
22. Tube Nut
(Inside Finned Housing)
23. Capillary Breather Tube
24. Gas Port
25. Cap
26. Tube Nut
27. O-ring
28. Strut Pressure Clamp
29. Heater Strut Assembly
30. Tube Clamp
31. Silicon Tube
18
19
20
21
29
30
26
36220004
Figure 4-1. Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR Exploded View
4-2 Maintenance and Service Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 43

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
4
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
HEATER
POWER
+
THERMOCOUPLE
TYPE K
SIGNAL
OXYGEN
SIGNAL
LEFT SIDE OF
OXYMITTER DR
-
+
-
Figure 4-2. Terminal Block
8. Allow the unit to cool to a comfortable
working temperature.
TERMINAL
BLOCK
HEATER POWER
PORT
GROUND
LUGS
SIGNAL
PORT
36210002
6. Turn on the calibration gases at the
cylinders and turn on instrument air.
b. Install.
1. Bolt the Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
to the stack and install insulation.
2. Insert the oxygen and heater thermocouple signal leads in the signal port
and connect to the oxygen and heater
thermocouple screw terminals
(Figure 4-2).
3. Insert the heater power leads in the
heater power port and connect to the
heater screw terminals. Slide the
heater terminal cover over the terminal
connection and tighten the cover
screw.
4. Install left housing cover (10,
Figure 4-1) and ensure it is tight. Secure the cover using cover lock (11),
captive washer (13), and screw (12).
5. Connect the calibration gas and instrument air lines to the Hazardous
Area Oxymitter DR.
7. Restore power to the system.
Opening the termination housing will
cause the loss of ALL hazardous permits. Opening the termination housing
in hazardous areas may cause an explosion resulting in loss of property,
severe personal injury, or death. It
may be required to get a hot work
permit from your company safety officer before opening the electronic
housing.
4-4 TERMINAL BLOCK REPLACEMENT
Refer to Figure 4-2 and perform the following
procedure to replace the terminal block.
a. Loosen the mounting screws on the termi-
nal block and carefully lift the block out of
the housing.
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Maintenance and Service 4-3
Page 44

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
b. Carefully align the new terminal block on
the pins so that it sits flat in the housing.
The round end of the terminal block should
be on the opposite side of the housing conduit ports and should not be able to rotate.
c. Tighten the three mounting screws and en-
sure the terminal block is secure in the
housing.
Opening the termination housing will
cause the loss of ALL hazardous permits. Opening the termination housing
in hazardous areas may cause an explosion resulting in loss of property,
severe personal injury, or death. It
may be required to get a hot work
permit from your company safety officer before opening the electronic
housing.
4-5 ENTIRE PROBE REPLACEMENT
Do not attempt to replace the probe until all
other possibilities for poor performance have
been considered. If probe replacement is
needed, see Table 7-1 for part numbers.
a. Follow the instructions in paragraph 4-3a to
remove the Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
from the stack or duct.
b. Remove four screws (15, Figure 4-1) and
washers (14). Separate the electrical connectors between the heater strut assembly
and the electrical barriers on the termination
housing. The probe and termination housing
can now be separated.
c. When installing the new probe, make sure
that o-ring (27) is in good condition. Connect the two electrical connectors between
the heater strut and the electrical barrier on
the termination housing. Make sure the
conduit port of the termination housing is on
the same side as the CAL and REF gas
ports.
e. Replace the housing cover (20) and ensure
it is tight.
f. Follow the instructions in paragraph 4-3b to
install the Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
into the stack or duct.
4-6 HEATER STRUT REPLACEMENT
This paragraph covers heater strut replacement.
Do not attempt to replace the heater strut until
all other possibilities for poor performance have
been considered. If heater strut replacement is
needed, order a replacement heater strut (Table
7-1).
Use heat resistant gloves and clothing
when removing probe. Do not attempt
to work on the probe until it has
cooled to room temperature. The
probe can be as hot as 800°F (427°C).
This can cause severe burns.
a. Follow the instructions in paragraph 4-3a to
remove the Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
from the stack or duct.
b. Remove four screws (15, Figure 4-1) and
washers (14). Separate the electrical connectors between the heater strut assembly
and the electrical barriers on the termination
housing. The probe and termination housing
can now be separated.
c. Once the probe and termination housing are
separated, spring tension releases and the
heater strut moves up. Carefully remove the
CAL and REF gas silicon tubes by pulling
them off the CAL and REF gas ports. Pull
the silicon tubes off the CAL and REF gas
lines.
d. Remove pressure clamp (28).
e. Remove tube nuts (26), and capillary
breather tubes (23) from the CAL, REF, and
VENT ports.
d. Install the four washers (14) and screws
(15) and tighten.
4-4 Maintenance and Service Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 45
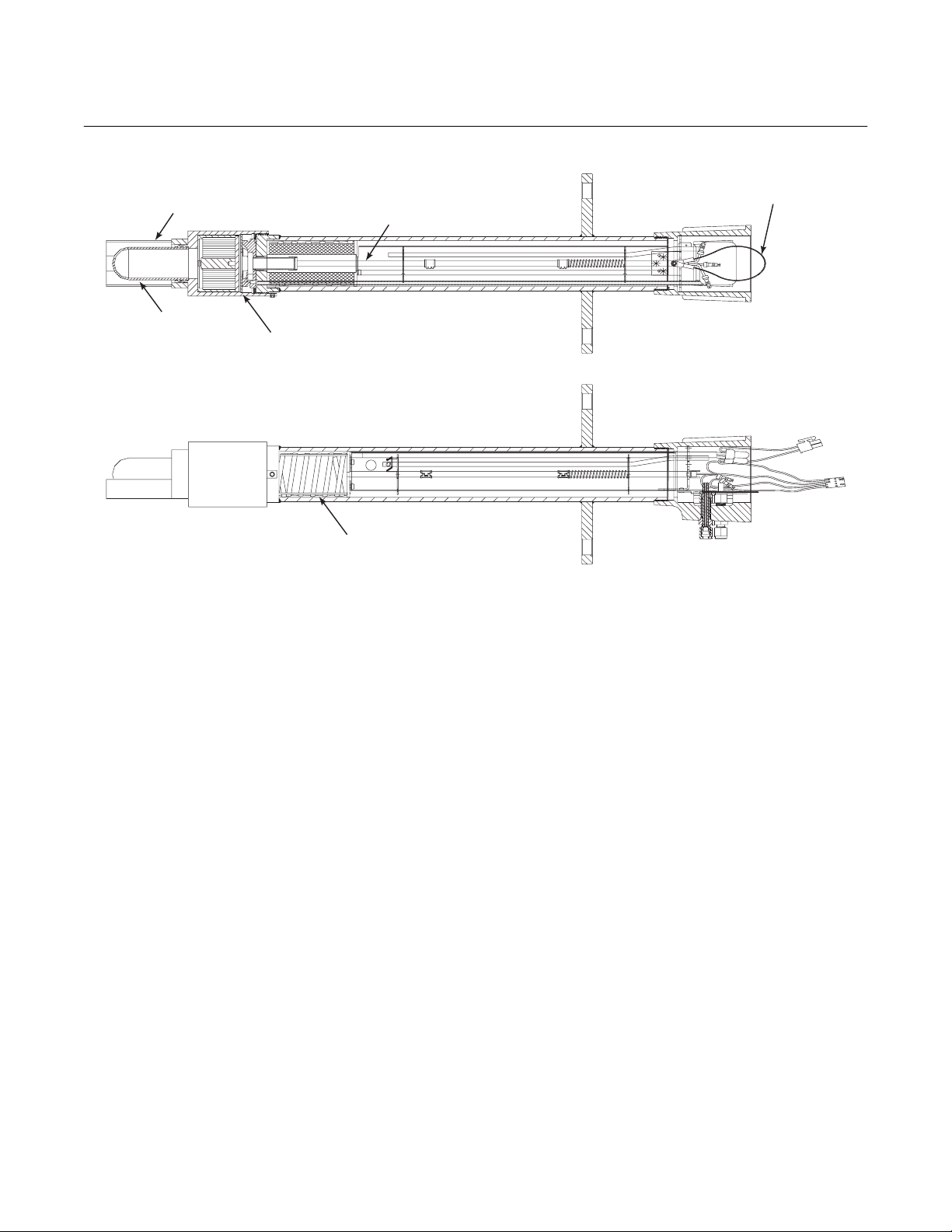
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
4
V-DE FL EC TOR
CERAMIC
DIFFUSER
ASSEMBLY
CELL FLANGE
CERAMIC SUPPORT ROD
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
WIRE
LOOP
HEATER
Figure 4-3. Heater Strut Assembly
f. Grasp the wire loop and carefully slide the
strut out of the probe tube (Figure 4-3).
g. When replacing the strut, align the slot on
the heater plate with the calibration gas line
in the probe tube. Slide the strut into the
probe tube. It will turn to align the hole on
the back plate of the strut with the calibration gas line. When the hole and the calibration gas line are aligned correctly, the
strut will slide in the rest of the way.
h. Push down on the back plate of the strut to
make sure you have spring tension and
then install the pressure clamp (28) on the
back plate.
i. Install capillary breather tubes (23) and tube
nuts (26) on the CAL, REF, and VENT
ports.
j. Replace the CAL and REF gas silicon
tubes.
k. Install the termination housing per the in-
27540007
structions in paragraph 4-5 steps c
through e.
l. Follow the instructions in paragraph 4-3b to
install the Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
into the stack or duct.
4-7 CELL REPLACEMENT
This paragraph covers oxygen sensing cell replacement. Do not attempt to replace the cell
until all other possibilities for poor performance
have been considered. If cell replacement is
needed, order the cell replacement kit
(Table 7-1).
The cell replacement kit (Figure 4-4) contains a
cell and flange assembly, corrugated seal,
setscrews, socket head cap screws, and antiseize compound. The items are carefully packaged to preserve precise surface finishes. Do
not remove items from the packaging until they
are ready to be used. Spanner wrenches and
hex wrenches needed for this procedure are
part of an available special tools kit (Table 7-1).
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Maintenance and Service 4-5
Page 46
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
PROBE TUBE
(NOT INCLUDED
IN KIT)
CORRUGATED
CALIBRATION GAS
PASSAGE
SEAL
CELL AND
FLANGE
ASSEMBLY
SOCKET HEAD
CAP SCREWS
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
The flame arrestor and flame arrestor
hub are among the critical components of this type of protection.
b. If the probe uses the standard diffusion
element, use a spanner wrench to remove
the diffusion element.
NOTE
To determine if the diffusion element
needs to be replaced, refer to paragraph 4-1.
22220028
Figure 4-4. Cell Replacement Kit
Use heat-resistant gloves and clothing
when removing the probe. Do not attempt to work on these components
until they have cooled to room temperature. Probe components can be as
hot as 427°C (800°F). This can cause
severe burns.
Disconnect and lock out power before
working on any electrical components.
There is voltage of up to 115 VAC.
Do not remove the cell unless certain
it needs to be replaced. Removal may
damage the cell and platinum pad. Go
through the complete troubleshooting
procedure to make sure the cell needs
to be replaced before removing it.
a. Follow the instructions in paragraph 4-3a to
remove the Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
from the stack or duct.
c. If equipped with the optional ceramic diffu-
sion assembly, remove and discard the
setscrews and remove the vee deflector
(Figure 4-5). Use spanner wrenches from
the probe disassembly kit (Table 7-1), to
turn the hub free from the retainer. Inspect
the diffusion element. If damaged, replace
the element.
d. Loosen the four socket head cap screws
from the cell and flange assembly and remove the assembly and the corrugated
seal. The cell flange has a notch that may
be used to gently pry the flange away from
the probe. Note that the contact pad inside
of the probe will sometimes fuse to the oxygen sensing cell. If the cell is fused to the
contact pad, push the cell assembly back
into the probe (against spring pressure) and
quickly twist the cell assembly. The cell and
contact pad should separate. If the contact
pad stays fused to the cell, a new
contact/thermocouple assembly must be installed. Disconnect the cell and the thermocouple wires at the probe electronics and
withdraw the cell with the wires still
attached.
e. Remove four screws (15, Figure 4-1) and
washers (14).
f. Separate the electrical connectors between
the heater strut and the termination housing.
4-6 Maintenance and Service Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 47

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
4
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
g. If the contact assembly is damaged, replace
the strut or the contact pad. Instructions for
replacing the contact pad are in the cell replacement kit.
h. Remove and discard the corrugated seal.
Clean the mating faces of the probe tube
and retainer. Remove burrs and raised
surfaces with a block of wood and crocus
cloth. Clean the threads on the retainer and
hub.
i. Rub a small amount of anti-seize compound
on both sides of the new corrugated seal.
j. Assemble the cell and flange assembly, cor-
rugated seal, and probe tube. Make sure
the calibration tube lines up with the calibration gas passage in each component.
Apply a small amount of anti-seize compound to the screw threads and use the
screws to secure assembly. Torque to
4 N·m (35 in-lbs).
k. Install the termination housing per the
instructions in paragraph 4-5 steps c
through e.
l. Apply anti-seize compound to the threads of
the cell assembly, hub, and setscrews. Reinstall the hub on the cell assembly. Using
pin spanner wrenches, torque to 14 N·m
(10 ft-lbs). If applicable, reinstall the vee deflector, orienting apex toward gas flow. Secure with the setscrews and anti-seize
compound. Torque to 2.8 N·m (25 in-lbs).
Set reference air flow at 56.6 l/hr (2 scfh).
After the Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR stabilizes, calibrate the unit. If new components
have been installed, repeat calibration after
24 hours of operation.
4-8 CERAMIC DIFFUSION ELEMENT
REPLACEMENT
NOTE
This refers to the ceramic diffusion
element only.
a. General
The diffusion element protects the cell from
particles in process gases. Normally, it does
not need to be replaced because the vee
deflector protects it from particulate erosion.
In severe environments, the filter may be
broken or subject to excessive erosion. Examine the ceramic diffusion element whenever removing the probe for any purpose.
Replace if damaged.
Damage to the ceramic diffusion element
may become apparent during calibration.
Compare probe response with previous response. A broken diffusion element will
cause a slower response to calibration gas.
Hex wrenches needed to remove setscrews
and socket head screws in the following
procedure are available as part of a Probe
Disassembly Kit, Table 7-1.
m. On systems equipped with an abrasive
shield, install the dust seal gaskets, with
joints 180° apart.
n. Reinstall the probe and gasket on the stack
flange.
o. Follow the instructions in paragraph 4-3b to
install the Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
into the stack or duct. If there is an abrasive
shield in the stack, make sure the dust seal
gaskets are in place as they enter the 15°
reducing cone.
p. Turn on power and monitor thermocouple
output. It should stabilize at 29.3+0.2 mV.
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Maintenance and Service 4-7
b. Replacement Procedure
1. Follow the instructions in paragraph
4-3a to remove the Hazardous Area
Oxymitter DR from the stack or duct.
2. Loosen setscrews, Figure 4-5, using
hex wrench from Probe Disassembly
Kit, Table 7-1, and remove vee deflector. Inspect setscrews. If damaged, replace with stainless setscrews coated
with anti-seize compound.
Page 48

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
M5-0.8 x 5 mm
LOCKING SET SCREW
(USE 2.5 mm HEX KEY)
THREADED
PROBE FLANGE
FLAME
ARRESTER
HUB
CEMENT
PORT
Figure 4-5. Ceramic Diffusion Element
Replacement
3. On systems equipped with abrasive
shield, remove dual dust seal gaskets.
4. Use spanner wrenches from Probe
Disassembly Kit, Table 7-1, to turn hub
free from retainer.
5. Put hub in vise. Break out old ceramic
diffusion element with chisel along cement line. Use a 9.5 mm (3/8 in.) pin
punch and clean fillet from the cement
port.
CEMENT
FILLET
SPANNER
WRENCH
CERAMIC
DIFFUSION
ELEMENT
M6-1 x 6 mm
SETSCREW
(USE 3 mm
HEX KEY)
VEE
DEFLECTOR
27540008
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
Do not get cement on ceramic diffusion element except where it touches
the hub. Any cement on ceramic diffusion element blocks airflow through
element. Wiping wet cement off of ceramic only forces cement into pores.
Also, do not get any cement onto the
flame arrestor element.
9. Thoroughly mix cement and insert tip
of squeeze bottle into cement port. Tilt
bottle and squeeze while simultaneously turning ceramic diffusion element
into seat. Do not get any cement on
upper part of ceramic diffusion element. Ensure complete penetration of
cement around 3 grooves in hub. Cement should extrude from opposite
hole. Wipe excess material back into
holes and wipe top fillet of cement to
form a uniform fillet. (A cotton swab is
useful for this.) Clean any excess cement from hub with water.
10. Allow filter to dry at room temperature
overnight or 1 to 2 hours at 93°C
(200°F).
11. Wipe a heavy layer of anti-seize compound onto the threads and mating
surfaces of the flame arrestor, diffusion
hub, and probe tube.
6. Break out remaining ceramic diffusion
element by tapping lightly around hub
with hammer. Clean grooves with
pointed tool if necessary.
7. Replace ceramic diffusion element using the ceramic diffusion element replacement kit in Table 7-1. This
consists of a diffusion element, cement, setscrews, anti-seize compound,
and instructions.
8. Test fit replacement ceramic diffusion
element to be sure seat is clean.
4-8 Maintenance and Service Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
12. Assemble flame arrestor and diffusion
hub with two pin spanner wrenches.
Torque to 14 N·m (10 ft-lbs). Secure
with hub retaining setscrew.
13. On systems equipped with abrasive
shield, install dust seal gaskets with
joints 180° apart.
14. Reinstall vee deflector, orienting apex
toward gas flow. Apply anti-seize compound to setscrews and tighten with
hex wrench.
15. Reinstall probe on stack flange.
Page 49

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
4
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
4-9 TERMINATION HOUSING WIRING
Under normal circumstances, the right termination housing should not need to be removed.
This side of the housing contains only two
jumper wires that connect the connectors from
the integral electrical barrier to pins in the
housing wall. If these jumpers should become
disconnected or need to be replaced, use the
diagram in Figure 4-6 to connect the jumpers.
HEATER (BLACK)
HEATER (BLACK)
OXYGEN CELL +
(ORANGE)
THERMOCOUPLE -
(YELLOW)
THERMOCOUPLE +
(RED)
OXYGEN CELL -
(GREEN)
36210011
Figure 4-6. Termination Housing Connections
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Maintenance and Service 4-9
Page 50

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
4-10 Maintenance and Service Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 51

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
5
TROUBLESHOOTING
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
SECTION 5
5-2 PROBE TROUBLESHOOTING
Install all protective equipment covers
and safety ground leads after troubleshooting. Failure to install covers and
ground leads could result in serious
injury or death.
5-1 OVERVIEW
Troubleshooting for the oxygen analyzer system
is broken down to the main component level. In
addition to the information in this section, instruction bulletins for individual models also discuss
troubleshooting.
For Models 218, 225, and 132 (analog), refer to
IB-106-101.
For Model 218A, refer to IB-106-101A.
For Model TC200, refer to IB-107-020.
For Model 132 (digital), refer to IB-106-106A.
For Yokogawa (YEW) ZA8C Converter, refer to
original converter documentation.
a. Probe Faults
Listed below are the five symptoms of probe
failure.
1. The system does not respond to
changes in the oxygen concentration.
2. The system responds to oxygen
changes but does not give the correct
indication.
3. The system does not give an acceptable indication of the value of the oxygen test gas being applied during calibration.
4. The probe takes a long time to return
to flue gas value after the calibration
gas is turned off.
5. The probe heater temperature is unstable.
b. Symptoms
Table 5-1 provides a guide to fault finding
for the above symptoms.
Table 5-1. Fault Finding
SYMPTOM CHECK FAULT REMEDY
1. No response to oxygen concentration
change when:
Heater is cold and
TC mV output is less
than setpoint
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Troubleshooting 5-1
Thermocouple continuity Thermocouple failure Replace thermocouple
or return probe to
Rosemount.
Cold heater resistance
should be 67 ohm to
77 ohm
Triac O/P to heater Failure of electronics Check electronics pack-
Heater failure Replace heater or return
probe to Rosemount.
age.
Page 52

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
SYMPTOM CHECK FAULT REMEDY
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
Table 5-1. Fault Finding (Continued)
Heater is hot and
T/C mV output is at
setpoint ±0.2 mV
2. System responds to
oxygen concentration changes but has
incorrect indication
Good response, with
incorrect indication
Recorder chart Recorder failure See Recorder Instruction
Manual.
Cell mV input to electronics and cell mV at
probe head
Recorder or remote
indicator
System calibration Calibration error Recalibrate system. Re-
No cell mV at probe
when test gas applied
Probe cell mV OK but no
input to electronics
Cell mV satisfactory both
at junction box and input
to electronics - failure of
electronics
Calibration error Recalibrate recorder or
Replace cell or return
probe to Rosemount.
Check out cable connection.
Check electronics package.
indicator. Reference Recorder Instruction Manual.
place cell if necessary.
3. Probe does not give
accurate indicationof
applied test gas
4. Probe takes a long
time to return to flue
gas value after
calibration gas is
turned off
5. Probe heater
temperature unstable
Probe mounting and
condition of duct
Cell mV input to electronics
Test gas input port Blocked port Clean port. If the flue
Ceramic diffusion element broken
Plugged diffusion element
Proper voltage heater is
installed
Air ingress into duct Stop air leaks or resite
probe.
Failure of electronics Check electronics pack-
age.
gas is condensing in the
test gas line, insulate the
back of the probe. Make
sure that the test gas
line is capped between
calibrations, or a check
valve is installed.
Diffusion element
cracked, broken, or
missing
Plugged diffusion element
Wrong heater Change heater to proper
Replace diffusion element.
Change diffusion element or snubber diffusion element.
voltage.
5-2 Troubleshooting Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 53

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
6
RETURN OF MATERIAL
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
SECTION 6
6-1 EQUIPMENT RETURN
If factory repair of defective equipment is required, proceed as follows:
a. Secure a return authorization number from
a Rosemount Analytical Sales Office or representative before returning the equipment.
Equipment must be returned with complete
identification in accordance with Rosemount
instructions or it will not be accepted.
In no event will Rosemount be responsible
for equipment returned without proper
authorization and identification.
b. Carefully pack defective unit in a sturdy box
with sufficient shock absorbing material to
ensure that no additional damage will occur
during shipping.
c. In a cover letter, describe completely:
1. The symptoms from which it was determined that the equipment is faulty.
2. The environment in which the equipment has been operating (housing,
weather, vibration, dust, etc.).
3. Site from which equipment was
removed.
5. Complete shipping instructions for return of equipment.
6. Reference the return authorization
number.
d. Enclose a cover letter and purchase order
and ship the defective equipment according
to instructions provided in Rosemount Return Authorization, prepaid, to:
Rosemount Analytical Inc.
RMR Department
1201 N. Main Street
Orrville, Ohio 44667
If warranty service is requested, the defective unit will be carefully inspected and
tested at the factory. If failure was due to
conditions listed in the standard Rosemount
warranty, the defective unit will be repaired
or replaced at Rosemount's option, and an
operating unit will be returned to the customer in accordance with shipping instructions furnished in the cover letter.
For equipment no longer under warranty,
the equipment will be repaired at the factory
and returned as directed by the purchase
order and shipping instructions.
4. Whether warranty or nonwarranty
service is requested.
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Return of Material 6-1
Page 54

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
6-2 Return of Material Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 55

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
7
SECTION 7
REPLACEMENT PARTS
Table 7-1. Replacement Parts for Probe
Figure and Index No. Part Number Description
3D39496G06
3D39496G07
3D39496G08
3534B56G04
3534B56G05
3534B56G06
7-1 3535B44G01
7-1 3535B44G02
7-1 3535B44G03
7-1 3535B44G04 Cell Replacement Kit (No Inconel and Platinum Pad Assembly)
7-2 1L03825G01 Probe Disassembly Kit
1U05677G04 F/A Diffuser Hub Assembly (Snubber Diffusor)
1U05677G06 F/A Diffuser Hub Assembly (For use with Abrasive Shield)
6292A74G02 Ceramic Diffusion Element Replacement Kit
1N04966H02 Abrasive Shield Assembly (3 ft)
1N04966H03 Abrasive Shield Assembly (6 ft)
1M03241H01 90° Elbow for Bypass
4507C26G07 Bypass Gas Pickup Tube (3 ft)
4507C26G08 Bypass Gas Pickup Tube (6 ft)
4507C26G09 Bypass Gas Pickup Tube (9 ft)
263C152G01 Reference Gas Set
771B635H01 Calibration Gas Rotometer
1L03650H01 F/A Diffusion Hub Setscrew
1
V-Strut assembly includes contact and thermocouple assembly.
2
Contact and thermocouple assembly includes platinum pad and inconel wire
3
Cell replacement kit includes platinum pad and inconel wire.
1
V-Strut Assembly (18 in.)
1
V-Strut Assembly (3 ft)
1
V-Strut Assembly (6 ft.)
2
Contact and Thermocouple Assembly (18 in.)
2
Contact and Thermocouple Assembly (3 ft)
2
Contact and Thermocouple Assembly (6 ft)
3
Cell Replacement Kit (18 in.)
3
Cell Replacement Kit (3 ft)
3
Cell Replacement Kit (6 ft)
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
NOTE
The replacement parts listed above must be obtained only from the manufacturer or his agent.
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Replacement Parts 7-1
Page 56

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
GASKET
PROBE TUBE
(NOT INCLUDED
IN KIT)
CALIBRATION GAS
PASSAGE
ANSI
CORRUGATED
SEAL
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
CELL AND
FLANGE
ASSEMBLY
SOCKET HEAD
CAP SCREWS
WIRE AND
PAD ASSEMBLY
TEFLON
TUBING
ANTI-SEIZE
COMPOUND
22 GA.
WIRE
CLOSED END
CONNECTOR
SET SCREWS
Figure 7-1. Cell Replacement Kit
HEX KEYS
SPANNER
WRENCH
ANTI-SEIZE
COMPOUND
PHILIPS
SCREWDRIVER
WRENCH
35830009
TUBE INSERTION
TUBE
35830010
Figure 7-2. Probe Disassembly Kit
7-2 Replacement Parts Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 57

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
8
SECTION 8
OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES
BY-PASS PACKAGES
The specially designed Rosemount Analytical By-Pass Package
for oxygen analyzers has proven to withstand the high temperatures in process heaters while providing the same advantages
offered by the in situ sensor. Inconel or Kanthal steel tubes provide effective resistance to corrosion, and the package uses no
moving parts, air pumps, or other components common to other
sampling systems.
For more information, call Rosemount Analytical at
1-800-433-6076.
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
E
V
I
-
L
A
E
R
T
E
I
H
P
U
S
C
O
R
M
-
I
T
C
G
A
N
I
N
N
E
R
E
V
A
I
H
W
S
W
O
-
L
T
P
H
X
E
G
I
T
N
I
P
E
E
CAL.
GAS
26170024
O2 CALIBRATION GAS SEQUENCER
Rosemount Analytical’s O
Calibration Gas and Service Kits
2
have been carefully designed to provide a more convenient and
fully portable means of testing, calibrating, and servicing
Rosemount Analytical’s oxygen analyzers. These lightweight,
disposable gas cylinders eliminate the need to rent gas bottles.
For more information, call Rosemount Analytical at
1-800-433-6076.
26170021
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Optional Accessories 8-1
Page 58

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
8-2 Optional Accessories Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 59

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
9
SECTION 9
APPENDICES
APPENDIX A. UPDATING DR OXYMITTER TO FULL OXYMITTER
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Appendices 9-1
Page 60

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
9-2 Appendices Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 61

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
A
UPGRADING HAZARDOUS AREA OXYMITTER DR TO
FULL HAZARDOUS AREA OXYMITTER
A-1 UPGRADE PROCEDURE
Perform the following procedure to upgrade the
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR to a full Hazardous Area Oxymitter.
a. Remove power from the Oxymitter DR.
b. Remove the left and right covers from the
Oxymitter termination housing.
Instruction Manual
Appendix A
January, 2002
APPENDIX A
c. Remove and discard the two cable assem-
blies (1 and 2, Figure A-1) from the right
side of the termination housing.
d. Place the new Oxymitter electronic assem-
bly (3) near the right side of the termination
housing.
e. Plug the white connector with the two black
wires into the white socket on the bottom
power supply card.
f. Insert the electronics assembly into the ter-
mination housing. Ensure the black 4-wire
connector remains outside the housing and
in the slot provided in the top card of the
electronics assembly. The electronics assembly should seat on the bulkhead pins
easily. Do not force the assembly into place.
g. Plug the black 4-wire connector into the
black socket on the microprocessor card.
h. Tighten three screws (4) securing the elec-
tronics assembly into the termination housing.
2
1
D
DIA
I
A
C
CALIBRA
A
L
G
GNOSTIC
N
O
S
A
ALARMS
T
L
I
C
A
R
M
S
I
B
R
A
T
TION RECOMMENDED
I
O
N
T
TEST
E
P
POINTS
S
O
T
I
N
T
S
I
INC
N
C
I
INC
H
HIGH
N
IG
H
G
GAS
A
LO
S
G
GAS
D
DEC
E
C
D
DEC
H
HEA
E
A
T
TER
E
R
T
T/C
H
HEA
/
E
C
A
T
TER
C
CALIBRA
0
02 CELL
E
A
2
R
L
C
I
B
E
R
L
R
L
A
E
T
TION
C
I
O
O
N
M
M
E
N
D
0
02 CELL mV +
E
2
D
C
E
0
02 CELL mv
L
2
L
C
m
E
HEA
H
V
L
E
+
L
A
T
TER
m
E
H
HEA
v
R
E
-
A
T
T/C +
T
TER
/
C
E
R
+
C
T
T/C -
/
C
-
W
A
S
C
CAL
A
L
E
C
T
TEST GAS +
E
S
T
PRPR
G
A
O
OCESS -
S
C
+
E
S
%
% 02
S
-
0
2
4
1. Signal connecting cable
2. Heater connecting cable
3. Electronic assembly
4. Screw
Figure A-1. Component Replacement
3
36210017
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Appendices A-1
Page 62

Instruction Manual
Appendix A
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
i. In the left side of the termination housing,
place the new termination designation labels over the labels on the existing terminal
block. After placing the new labels, the terminal block should appear as shown in
Figure A-2.
j. The existing wiring from the Oxymitter to the
electronics may be reused. However, the
wires will be carrying new signals as noted
by the new labels. The 4-20 mA wires must
be removed from the old electronics and reterminated to the wires carrying the 4-20
mA O
signal to the control room.
2
k. The wires carrying the heater power must
be converted to carry AC power (90-250
AC TERMINAL
COVER
LINE VOLTAGE
(90 TO 250 VAC)
AC L1
AC N
VAC, 50/60 Hz) for the Oxymitter. The reterminations may be inside the old electronics housing, which will function as a
simple junction box. Alternatively, the old
electronics may be removed and replaced
with a smaller junction box.
l. Place the round error blink code and cali-
bration instructions label on the inside of the
right housing cover.
m. Install both housing covers.
n. Refer to the instruction bulletin provided
with your upgrade kit, IB-106-340C, for
startup and diagnostic information.
TERMINAL
BLOCK
AC LINE
VOLTAGE PORT
CALIBRATION HANDSHAKE
LOGIC I/O OR
4-20 mA
SIGNAL
LEFT SIDE OF
OXYMITTER 4000
Figure A-2. Terminal Block and Wiring
4-20
+
-
+
-
GROUND
LUGS
SIGNAL
PORT
36210016
A-2 Appendices Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 63

Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
10
INDEX
This index is an alphabetized listing of parts, terms, and procedures having to do with the Oxymitter DR In-Situ Oxygen Probe. Every item listed in this index refers to a location in the manual
by one or more page numbers.
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
SECTION 10
A
Abrasive Shield, 2-1, 2-3, 2-7
Absolute Temperature, 1-1
Adapter Plate, 1-2, 1-3, 2-1, 2-4, 2-5
Arithmetic Constant, 1-1
B
By-Pass Packages, 8-1
C
Calibration, 4-1
Calibration Gas, 1-3, 1-6, 2-2, 2-3, 4-1, 8-1
Calibration Gas Bottles, 1-8
Cell, 1-2, 4-5
Cell Constant, 1-1
Cell Replacement Kit, 7-2
Check Valve, 1-4
D
Diffusion Element, 1-2, 4-6, 4-8
Drip Loop, 2-6
E
Equipment Return, 6-1
H
Heater, 5-1
Heater Strut, 4-4
Heater Thermocouple, 1-2
I
Installation, Electrical, 2-7
Installation, Mechanical, 2-1
Installation, Pneumatic, 2-8
Instrument Air, 1-3, 2-8, 4-1
Insulation, 2-7, 4-1
M
Mounting, 1-6
N
Nernst Equation, 1-1
P
Packaging, 1-1
Partial Pressure, 1-1
Power Requirements, 1-6
Probe, 4-4, 7-1
Probe Disassembly Kit, 7-2
Probe Lengths, 1-2, 1-6
Process Temperature, 1-6
Product Matrix, 1-7
R
Reference Air, 1-3, 1-6, 2-2, 2-3
Reference Air Set, 1-2
Replacement Parts, Probe, 7-1
S
Specifications, 1-6
T
Terminal Block, 2-8, 4-1, 4-3
Thermocouple, Heater, 1-2
Troubleshooting, 5-1
V
Vee Deflector, 2-6
Z
Zirconia Disc, 1-1
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Index 10-1
Page 64

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
10-2 Index Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Page 65

WARRANTY
Rosemount warrants that the equipment manufactured and sold by it will, upon shipment, be free
of defects in workmanship or material. Should any failure to conform to this warranty become apparent during a period of one year after the date of shipment, Rosemount shall, upon prompt
written notice from the purchaser, correct such nonconformity by repair or replacement, F.O.B.
factory of the defective part or parts. Correction in the manner provided above shall constitute a
fulfillment of all liabilities of Rosemount with respect to the quality of the equipment.
THE FOREGOING WARRANTY IS EXCLUSIVE AND IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES OF QUALITY WHETHER WRITTEN, ORAL, OR IMPLIED (INCLUDING ANY
WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OF FITNESS FOR PURPOSE).
The remedy(ies) provided above shall be purchaser's sole remedy(ies) for any failure of
Rosemount to comply with the warranty provisions, whether claims by the purchaser are based
in contract or in tort (including negligence).
Rosemount does not warrant equipment against normal deterioration due to environment. Factors
such as corrosive gases and solid particulates can be detrimental and can create the need for repair or replacement as part of normal wear and tear during the warranty period.
Equipment supplied by Rosemount Analytical Inc. but not manufactured by it will be subject to the
same warranty as is extended to Rosemount by the original manufacturer.
At the time of installation it is important that the required services are supplied to the system and
that the electronic controller is set up at least to the point where it is controlling the sensor heater.
This will ensure, that should there be a delay between installation and full commissioning that the
sensor being supplied with ac power and reference air will not be subjected to component
deterioration.
3622/1-02
Page 66

Instruction Manual
IB-106-340CDR Original Issue
January, 2002
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
Hazardous Area Oxymitter DR
Emerson Process Management
Rosemount Analytical Inc.
Process Analytic Division
1201 N. Main St.
Orrville, OH 44667-0901
T (330) 682-9010
F (330) 684-4434
E gas.csc@emersonprocess.com
Part no.
Serial no.
Order no.
Fisher-Rosemount GmbH & Co.
Industriestrasse 1
63594 Hasselroth
Germany
T 49-6055-884 0
F 49-6055-884209
ASIA - PACIFIC
Fisher-Rosemount
Singapore Private Ltd.
1 Pandan Crescent
Singapore 128461
Republic of Singapore
T 65-777-8211
F 65-777-0947
http://www.processanalytic.com
© Rosemount Analytical Inc. 2002
EUROPE, MIDDLE EAST, AFRICA
Fisher-Rosemount Ltd.
Heath Place
Bognor Regis
West Sussex PO22 9SH
England
T 44-1243-863121
F 44-1243-845354
LATIN AMERICA
Fisher - Rosemount
Av. das Americas
3333 sala 1004
Rio de Janeiro, RJ
Brazil 22631-003
T 55-21-2431-1882
 Loading...
Loading...