Page 1

Quick Start Guide
00825-0200-4420, Rev FE
August 2015
Emerson™ Smart Wireless Gateway 1420
Page 2

Quick Start Guide
August 2015
NOTICE
This guide provides basic guidelines for the Smart Wireless Gateway. It does not provide
instructions for diagnostics, maintenance, service, or troubleshooting. Refer to the Smart
Wireless Gateway Reference Manual (document number 00809-0200-4420) for more
information and instructions. This guide and the manual are available electronically on
www.emersonprocess.com.
Explosions could result in death or serious injury.
Installation of this device in an explosive environment must be in accordance with the
appropriate local, national, and international standards, codes, and practices. Review the
Product Certifications section for any restrictions associated with a safe installation.
Avoid contact with the leads and terminals. High voltage may be present on leads can cause
electrical shock.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following
conditions:
This device may not cause harmful interference.
This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
This device must be installed to ensure a minimum antenna separation distance of 20 cm
from all persons.
Contents
Wireless considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
General considerations
Initial connection and configuration
Physical installation
Connect to the host system . . . . . . . . . . .16
2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
. . . . 5
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Software installation (optional) . . . . . . . .17
Verif y operations
Product specifications
Product Certifications
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Page 3

August 2015
Quick Start Guide
Wireless considerations
Power up sequence
The Smart Wireless Gateway (Gateway) should be installed and functioning
properly before power modules are installed in any wireless field devices. Wireless
field devices should also be powered up in order of proximity from the Smart
Wireless Gateway beginning with the closest. This will result in a simpler and
faster network installation.
Antenna position
The antenna should be positioned vertically, and be approximately 3-ft. (1 m)
from large structures or buildings to allow for clear communication to other
devices.
Mounting height
For optimal wireless coverage, the Gateway or remote antenna is ideally mounted
15- to 25-ft. (4,6 to 7,6 m) above ground or 6-ft. (2 m) above obstructions or
major infrastructure.
Gateway redundancy
If the wireless Gateway was ordered with redundancy (Gateway Redundancy code
RD), refer to Appendix D in the Smart Wireless Gateway Reference Manual
(document number 00809-0200-4420) for additional installation instructions.
3
Page 4

Quick Start Guide
General considerations
PC requirements
Operating system (optional software only)
Microsoft
Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2
Windows Server 2003 R2 Service Pack 2
Windows Server 2008 (Standard Edition), Service Pack 2
Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard Edition, Service Pack 1
Windows 7 Professional, Service Pack 1
Windows 7 Enterprise, Service Pack 1
Applications
Internet Explorer
Mozilla Firefox
.Net Framework 2.0 (for OPC proxy only)
Hard disk space
AMS
Gateway Setup CD: 250 MB
®
Windows™ XP Professional, Service Pack 3
®
6.0 or higher
®
1.5 or higher
®
Wireless Configurator: 1.5 GB
August 2015
4
Page 5
August 2015
+
+
+
S
S
S
S
N
d
N
d
d
Step 1: Initial connection and configuration
Quick Start Guide
DeltaV
™
ready
If the Gateway was ordered DeltaV Ready (Data Protocols Code 5), then skip to
Step 2: Physical installation, and connect the Gateway to a DeltaV 10.3 or newer
control network.
Initial connection and configuration
To configure the Smart Wireless Gateway, a local connection between a
PC/laptop and the Gateway needs to be established.
Powering the Gateway
Bench top power will be needed to power the Gateway by wiring a 24 VDC
(nominal) power source, with at least 250 mA, to the power terminals.
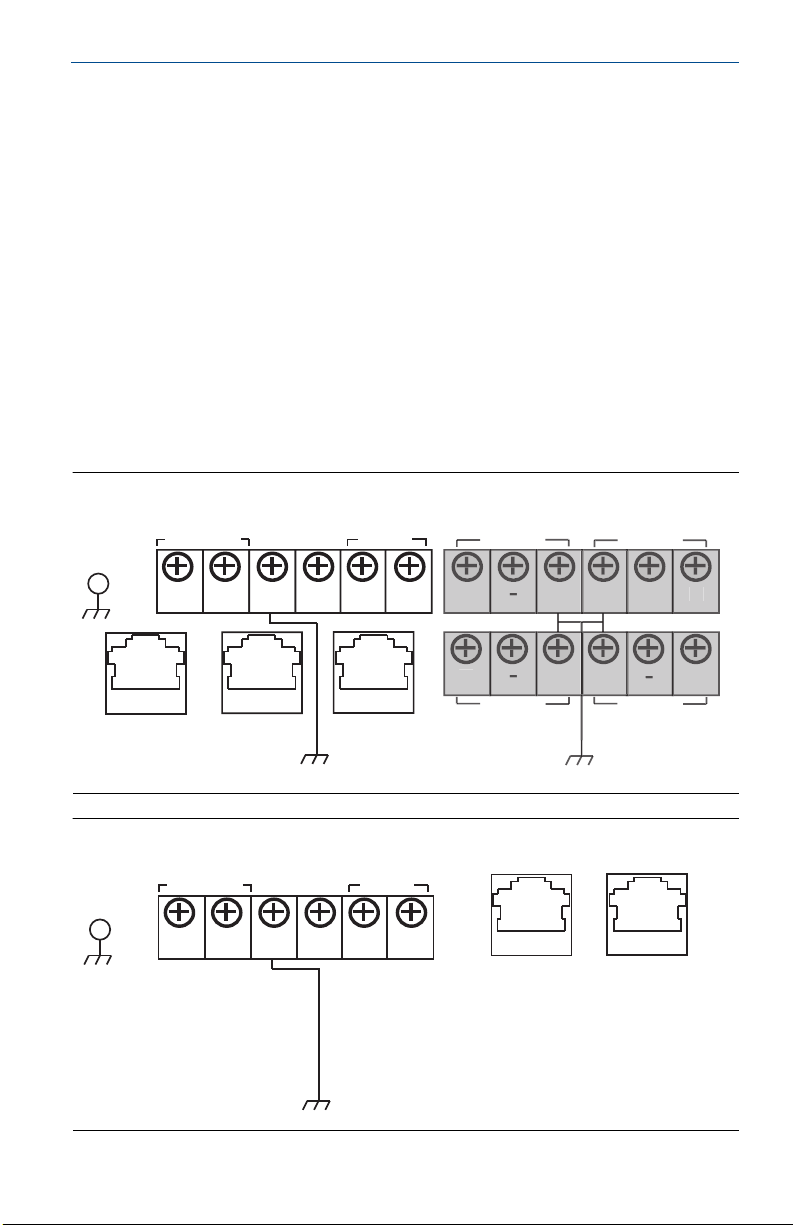
Figure 1. Legacy Gateway Terminal Block Diagram
Case
Ethernet 2
with Power
(Covered)
24 VDC
(nominal)
Power Input
+
-
Ethernet 2
(Secondary) (Primary)
Serial
®
Modbus
S
AB
ot Used
Not Use
+
Ethernet 1
ot Use
Not Use
-
Figure 2. Power over Ethernet (PoE) Terminal Block Diagram
24 VDC
(nominal)
Power Input
+
Case
S
-AB
Serial
Modbus
Ethernet 2
(Secondary) (Primary)
Ethernet 1
5
Page 6
Quick Start Guide
PoE PD on port 1
(Default jumpering for
production. Used for no
PoE also)
PoE PD on port 2
PoE PSE on port 1
PoE PSE on port 2
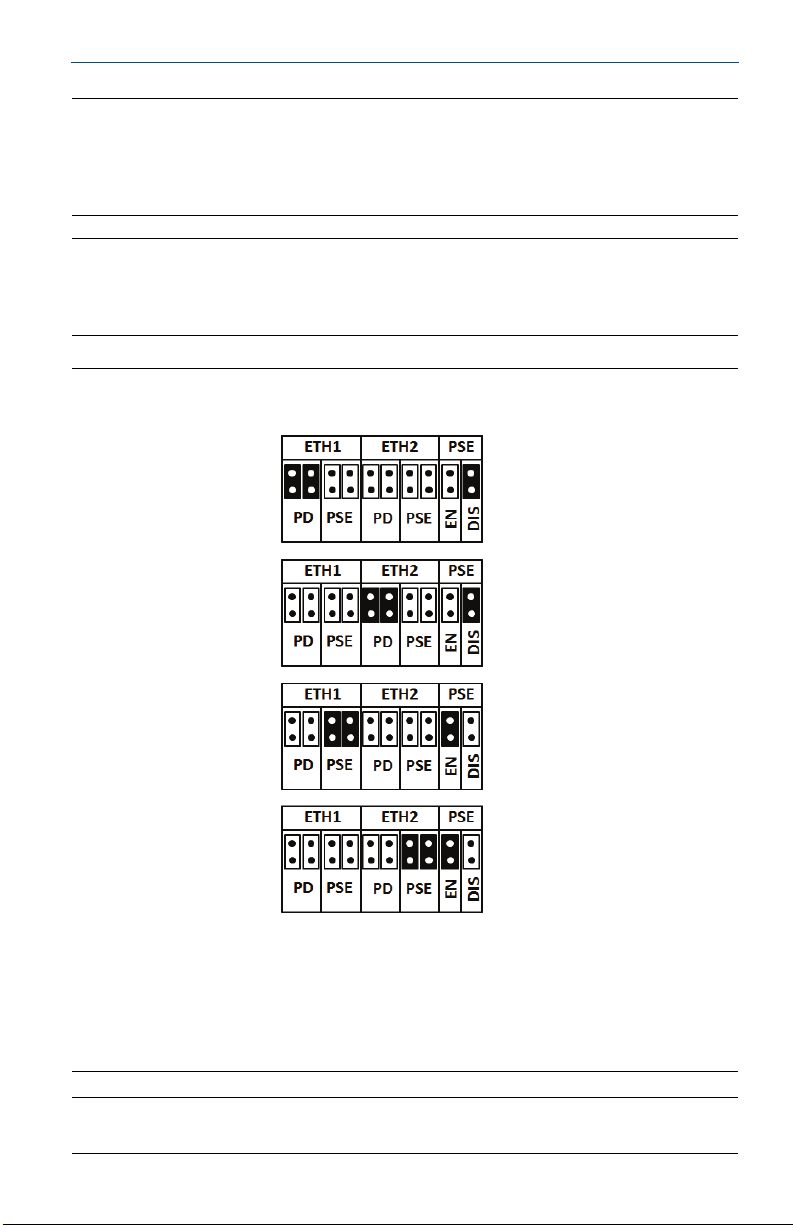
Black fill below indicates jumper.
August 2015
Note
Figure 1 depicts the terminal block of legacy Gateways prior to the introduction of PoE capabilities.
Figure 2 shows the terminal block arrangement of a PoE version of the Gateway. If the Gateway will
be powered via the standard 24 volt power input terminals, and no PSE is desired, it is not
necessary to change the default settings of the PoE jumper matrix.
Note
The Gateway enclosure case should always grounded in accordance with national and local
electrical codes. The most effective grounding method is a direct connection to earth ground with
minimal impedance.
Figure 3. 1420 PoE Jumpering Matrix (Located on 1420 Board)
Legend:
ETH1: Ethernet port 1 selected for PD or PSE
ETH2: Ethernet port 2 selected for PD or PSE
PD: Gateway derived its power off the Ethernet port selected
PSE: The Gateway is powered via the standard 24 volt power input terminals and provides power
via the selected Ethernet port to another device with a compatible PD port.
EN: Enabled; this enables the PSE operation
DIS: Disabled; this disables the PSE operation
Note
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection required when swapping PoE jumpers.
6
Page 7

August 2015
+ +
+
+
+
-
-
-
-
-A B
S S
S
S
S
24 V DC24 V DC
Power InputPower Input
ModbusModbus
Not UsedNot Used
Not UsedNot Used
Not UsedNot Used
Not UsedNot Used
CaseCase
S
POEPOE
P2P2 P1P1
A
B
Quick Start Guide
Note
Only one port and one mode of operation (PD or PSE) can be selected at a time; any other
combination of jumpers is invalid.
Note
IEEE 802.3af-2003 PoE standard provides up to 15.4 W of DC power (minimum 44 V DC and 350
mA) to each device. Only 12.95 W is assured to be available at the powered device as some power
is dissipated in the cable.
IEEE 802.3at-2009 PoE standard also known as “PoE+” or “PoE plus”, provides up to 25.5 W of
power. The 2009 standard prohibits a powered device from using all four pairs for power.
For more information on PoE and frequently asked questions, reference
document number 00870-0500-4420.
Establishing a connection
Note
For information on connecting a Windows 7 PC, see Technical Note (document number
00840-0900-4420).
1. Connect the PC/laptop to the Ethernet 1 (Primary) receptacle on the Gateway.
Figure 4. Gateway PC/Laptop Connection
A. PC/laptop
B. Ethernet 1 receptacle
Do not connect to the Ethernet 2 with power (covered) port. This port supplies power and
could damage the PC/laptop.
2. To establish the PC/laptop settings, navigate to Start>Settings>Network
Connections.
a. Select Local Area Connection.
b. Right click to select Properties.
7
Page 8

Quick Start Guide
August 2015
c. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), then select the Properties button.
Note
If the PC/laptop is from another network, record the current IP address and other settings so the
PC/laptop can be returned to the original network after the Gateway has been configured.
d. Select the Use the following IP address button.
e. In the IP address field, enter 192.168.1.12.
f. In the Subnet mask field, enter 255.255.255.0.
g. In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window, select OK.
h. In the Local Area Connection Properties window, select OK.
Note
Connecting to the Gateway's secondary Ethernet port requires different network settings. Refer to
Tab l e 1 for additional network settings.
8
Page 9

August 2015
Table 1. Default IP Addresses
Ethernet 1
Ethernet 2
Ethernet 1 (DeltaV Ready)
Ethernet 2 (DeltaV Ready)
Table 2. Subnet Settings
Subnet mask
Quick Start Guide
Gateway PC/laptop
192.168.1.10 192.168.1.12
192.168.2.10 192.168.2.12
10.5.255.254 10.5.255.200
10.9.255.254 10.9.255.200
Default
DeltaV
255.255.255.0
255.254.0.0
3. Disable proxies.
a. Open a standard web browser (Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, or
other).
b. Navigate to Tools>Internet Options>Connections>LAN Settings.
c. Uncheck the box under Proxy Server.
9
Page 10

Quick Start Guide
Configure the Smart Wireless Gateway
To complete initial configuration for the Gateway:
1. Access the default web page for the Gateway at https://192.168.1.10.
a. In the User name field, enter admin.
b. In the Password field, enter default.
Figure 5. Gateway Log In Screen
2. Navigate to System Settings>Gateway>Ethernet Communication to enter
the Network Settings.
a. Configure a static IP Address or set for DHCP and enter a Hostname.
b. Restart application at System Settings>Gateway>Backup And
Restore>Restart App.
3. Disconnect the power and Ethernet from the Gateway.
August 2015
10
Page 11

August 2015
Step 2: Physical installation
Pipe mount
Tools needed:
2-in. (51 mm) mounting pipe or mast
Two
For installing the Gateway with a pipe mount:
1. Insert one u-bolt around the pipe, through the top mounting holes of the
2. Use a
3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 for the second u-bolt and lower mounting holes.
5
/16-in. (7,9 mm) u-bolts supplied with Gateway
1
/2-in. socket-head wrench
Gateway enclosure, and through the washer plate.
1
/2-in. socket-head wrench to fasten the nuts to the u-bolt.
Quick Start Guide
Best practice
If the Gateway was ordered with output code 2, run a secondary Ethernet cable
when installing cable conduit from the Gateway to a convenient indoor location
to simplify future configuration changes.
11
Page 12

Quick Start Guide
Remote antenna (optional)
The remote antenna options provide flexibility for mounting the Gateway based
on wireless connectivity, lightning protection, and current work practices.
When installing remote mount antennas for the Smart Wireless Gateway, always use
established safety procedures to avoid falling or contact with high-power electrical
lines.
Install remote antenna components for the Smart Wireless Gateway in compliance with
local and national electrical codes and use best practices for lightning protection.
Before installing, consult with a local area electrical inspector, electrical officer, and
work area supervisor.
The Smart Wireless Gateway remote antenna option is specifically engineered to
provide installation flexibilit y while optimizing wireless performance and local spectrum
approvals. To maintain wireless performance and avoid non-compliance with spectrum
regulations, do not change the length of cable or the antenna type.
If the supplied remote mount antenna kit is not installed per these instructions,
Emerson Process Management is not responsible for wireless performance or
non-compliance with spectrum regulations.
The remote mount antenna kit includes coaxial sealant for the cable connections
for the lightning arrestor and antenna.
Find a location where the remote antenna has optimal wireless performance.
Ideally this will be 15- to 25-ft. (4,6 to 7,6 m) above the ground or 6-ft. (2 m)
above obstructions or major infrastructure. To install the remote antenna use one
of the following procedures:
August 2015
Installation of WL2/WN2 option (outdoor applications)
1. Mount the antenna on a 1.5- to 2-in. pipe mast using the supplied mounting
equipment.
2. Connect the lightning arrestor directly to the top of the Gateway.
3. Install the grounding lug, lock washer, and nut on top of the lightning arrestor.
4. Connect the antenna to the lightning arrestor using the supplied coaxial cable
ensuring the drip loop is not closer than 1-ft. (0,3m) from the lightning
arrestor.
5. Use the coaxial sealant to seal each connection between the wireless field
device, lightning arrestor, cable, and antenna.
6. Ensure the mounting mast, lightning arrestor, and Gateway are grounded
according to local/national electrical code.
7. Place any spare lengths of coaxial cable in 12-in. (0,3 m) coils.
12
Page 13

August 2015
B
C
D
E
F
A
G
H
G
Figure 6. Installation of WL2/WN2 Option
Quick Start Guide
A. Control building
B. Remote antenna
C. Cable
D. Drip loop
E. Lightning arrestor
F. G atewa y
G. Ground
H. Earth
Installation of WL3/WL4 option (indoor to outdoor applications)
1. Mount the antenna on a 1.5- to 2-in. pipe mast using the supplied mounting
equipment.
2. Mount the lightning arrestor near the building egress.
3. Install the grounding lug, lock washer, and nut on top of the lightning arrestor.
4. Connect the antenna to the lightning arrestor using the supplied coaxial cable
ensuring the drip loop is not closer than 1-ft. (0,3m) from the lightning
arrestor.
5. Connect the lightning arrestor to the Gateway using the supplied coaxial
cable.
6. Use the coaxial sealant to seal each connection between the Gateway,
lightning arrestor, cable, and antenna.
7. Ensure the mounting mast, lightning arrestor, and Gateway are grounded
according to local/national electrical codes.
8. Place any spare lengths of coaxial cable in 12-in. (0,3 m) coils.
13
Page 14

Quick Start Guide
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
G
Figure 7. Installation of WL3/WL4 Option
August 2015
A. Control building
B. Remote antenna
C. Cable
D. Drip loop
E. Lightning arrestor
F. Ga te way
G. Ground
H. Earth
Note: Weather proofing is required!
The remote mount antenna kit includes coaxial sealant for the cable connections for the lightning
arrestor, antenna, and Gateway. The coaxial sealant must be applied to guarantee performance of
the wireless field network. See Figure 8 for details on applying weather proofing.
Figure 8. Applying Coaxial Sealant to Cable Connections
14
Page 15

August 2015
WL2
WL4
WL3
WN2
Table 3. Remote Antenna Kit Options
Quick Start Guide
Kit
option
WL2
WL3
WL4
WN2
F
Antenna Cable 1 Cable 2 Lightning arrestor
1
/2 Wavelength Dipole
Omni-Directional
+6 dB Gain
1
/2 Wavelength Dipole
Omni-Directional
+6 dB Gain
1
/2 Wavelength Dipole
Omni-Directional
+6 dB Gain
1
/2 Wavelength Dipole
Omni-Directional
+8 dB Gain
WL2
AA A A
B
G
50-ft. (15,2 m)
30-ft. (9,1 m)
40-ft. (12,2 m)
25-ft. (7,6 m)
WL3
D
LMR-400
LMR-400
LMR-400
LMR-400
E
N/A
20-ft. (6,1 m)
LMR-400
10-ft. (3,0 m)
LMR-400
N/A
WL4
C
D
HI
Head mount, jack to plug
Gas discharge tube
0.5 dB insertion loss
In-line, jack to jack
Gas discharge tube
0.5 dB insertion loss
In-line, jack to jack
Gas discharge tube
0.5 dB insertion loss
Head mount, jack to plug
Gas discharge tube
0.5 dB insertion loss
WN2
E
D
A. Antenna
B. 20-ft. (6, 1 m) cable
C. 10-ft. (3, 0 m) cable
D. Lightning arrestor
F. 50-ft. (15, 2 m) cable
G. 30-ft. (9, 1m) cable
H. 40-ft. (12, 2 m) cable
I. 25-ft. (7, 6m) cable
D
E. Interchangeable cables
Note
The coaxial cables on the remote antenna options WL3 and WL4 are interchangeable for
installation convenience.
15
Page 16

Quick Start Guide
+
S
SSS
N
d
N
d
d
+
-AB
24 VDC
(nominal)
Power Input
Serial
Modbus
Case
S
Ethernet 2
Ethernet 1
(Secondary) (Primary)
Step 3: Connect to the host system
1. Wire the Gateway’s Ethernet 1 (Primary) or Serial Output connection to the
Host System Network or Serial I/O.
2. For serial connections, connect A to A, B to B, making sure all terminations are
clean and secured to avoid wiring connection problems.
Figure 9. Legacy Gateway Terminal Block Diagram
24 VDC
(nominal)
Power Input
Serial
Modbus
ot Used
Not Use
August 2015
Case
Ethernet 2
with Power
(Covered)
+
S
-
Ethernet 2
(Secondary) (Primary)
AB
Ethernet 1
Figure 10. PoE Terminal Block Diagram
+
ot Use
-
Not Use
Do not connect the Host System to the Ethernet 2 with power (covered) port on the Smart
Wireless Gateway to avoid damaging the system.
Best practice
In accordance with Emerson WirelessHART® security guidelines, the Gateway
should be connected to the Host System via a LAN (Local Area Network) and not a
WAN (Wide Area Network).
16
Page 17

August 2015
Twisted shielded pair cable is generally used to wire the serial connection, and it is
standard practice to ground the shield on the serial host side leaving the shield
floating on the Gateway side. Insulate the shield to avoid grounding issues.
Quick Start Guide
Power
Power the Gateway as directed in Step 1.
Step 4: Software installation (optional)
The 2-disk software pack contains the Security Setup Utility (only required for
secure host connections or OPC communications) and AMS Wireless
Configurator. The Security Setup Utility is located on Disk 1. To install the
software:
1. Exit/close all Windows programs, including any running in the background,
such as virus scan software.
2. Insert Disk 1 into the CD/DVD drive of the PC.
3. Follow the prompts.
AMS Wireless Configurator is located on Disk 2. To install the software:
1. Exit/close all Windows programs, including any running in the background,
such as virus scan software.
2. Insert Disk 2 into the CD/DVD drive of the PC.
3. Select Install from the menu when the AMS Wireless Configurator setup
begins.
4. Follow the prompts.
5. Allow AMS Wireless Configurator to reboot PC.
6. Do not remove the disk from the CD/DVD drive.
Note
Installation will resume automatically after login.
7. Follow the prompts.
Note
If the autorun function is disabled on the PC, or installation does not begin automatically, double
click D:\SETUP.EXE (where D is the CD/DVD drive on the PC) and select OK.
For more information about the Security Setup Utility and AMS Wireless
Configurator, see the Smart Wireless Gateway Reference Manual (document
number 00809-0200-4420).
17
Page 18

Quick Start Guide
Step 5: Verify operations
Operation is verified through the web interface by opening a web browser from
any PC on the host system network and entering the Gateway IP address or DHCP
host name in the address bar. If the Gateway has been connected and configured
properly, the security alert will be displayed followed by the log in screen.
Figure 11. Gateway Log In Screen
The Gateway is now ready to be integrated into the host system. If wireless field
devices were ordered with the Gateway, they were preconfigured with the same
network ID and join key information. Once the field devices are powered, they will
appear on the wireless network and communications can be verified under the
Explore tab using the web interface. The time needed for the network to form
depends on the number of devices.
August 2015
18
Page 19

August 2015
ge (
)
Product specifications
Input power
10.5 – 30 VDC (must be a Class 2 power supply)
Current draw
Operating current draw is based on 3.6 W average power consumption.
Momentary startup current draw up to twice operating current draw.
Maximum permissible current: 1A
250
Quick Start Guide
12
Operating
Region
Volta
24
30
VDC
PoE
Current (mA)
(1)
125
10.5
Input voltage
Normal Operation (no PSE or IEEE 802.3af): 10.5 – 30 VDC
PoE + PSE Operation (IEEE 802.3at): 17.5 – 30 VDC
PSE mode
50 V – 57 VDC Output (per IEEE 802.3at-2009)
25.5 W Maximum
Radio frequency power output from antenna
Maximum of 10 mW(10 dBm) EIRP
Maximum of 40 mW(16 dBm) EIRP forWN2 High Gain option
1. The current consumption is for Gateway operation only. If using PSE, calculations will need to be made to include the
device being powered.
19
Page 20

Quick Start Guide
Environmental
Operating temperature range
-40 to 140 °F (-40 to 70 °C)
Operating humidity range
10 – 90% relative humidity
Physical specifications
Weight
10 lb (4.54 kg)
Material of construction
Housing
Low-copper aluminum, NEMA® 4X
Paint
Polyurethane
August 2015
Cover gasket
Silicone Rubber
Antenna
Integrated Antenna: PBT/PC
Remote Antenna: Fiber Glass
Communication specifications
Isolated RS485
2-wire communication link for Modbus RTU multidrop connections
Baud Rate: 57600, 38400, 19200, or 9600
Protocol: Modbus RTU
Wiring: Single twisted shielded pair, 18 AWG
Wiring distance: up to 4,000-ft. (1,524 m)
20
Page 21

August 2015
Ethernet
10/1000base- TXEthernet communication port
™
Protocols: EtherNet/IP
Wiring: Cat5Eshielded cable
Wiring distance: 328-ft. (100 m)
Modbus TCP, OPC, HART-IP™, HTTPS (for Web Interface)
Modbus
Supports Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP with 32-bit floating point values,
integers, and scaled integers.
Modbus Registers are user-specified.
OPC
OPC server supports OPC DA v2, v3
Ethernet/IP
Supports Ethernet/IP protocol with 32-bit floating point values and integers.
Ethernet/IP assembly input-output instances are user configurable.
Ethernet/IP specifications are managed and distributed by ODVA.
Self-organizing network specifications
Quick Start Guide
Protocol
IEC 62591 (WirelessHART), 2.4 – 2.5 GHz DSSS
Maximum network size
100 wireless devices @ 8 sec or higher
50 wireless devices @ 4 sec
25 wireless devices @ 2 sec
12 wireless devices @ 1 sec
Supported device update rates
1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 seconds or 1 – 60 minutes
Network size/latency
100 Devices: less than 10 sec
50 Devices: less than 5 sec
Data reliability
> 99%
21
Page 22

Quick Start Guide
Product Certifications
Rev 1.2
European Directive Information
A copy of the EC Declaration of Conformity can be found at the end of the Quick Start Guide.
The most recent revision of the EC Declaration of Conformity can be found at
www.rosemount.com.
Telecommunication Compliance
All wireless devices require certification to ensure they adhere to regulations regarding the
use of the RF spectrum. Nearly every country requires this type of product certification.
Emerson is working with governmental agencies around the world to supply fully compliant
products and remove the risk of violating country directives or laws governing wireless
device usage.
FCC and IC
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following
conditions: This device may not cause harmful interference. This device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation. This
device must be installed to ensure a minimum antenna separation distance of 20 cm from all
persons.
August 2015
Ordinary Location Certification
As standard, the transmitter has been examined and tested to determine that the design
meets the basic electrical, mechanical, and fire protection requirements by a nationally
recognized test laboratory (NRTL) as accredited by the Federal Occupational Safety and
Health Administration (OSHA).
Installing Equipment in North America
The US National Electrical Code (NEC) and the Canadian Electrical Code (CEC) permit the use
of Division marked equipment in Zones and Zone marked equipment in Divisions. The
markings must be suitable for the area classification, gas, and temperature class. This
information is clearly defined in the respective codes.
USA
N5 U.S.A. Division 2
Certificate: CSA 70010780
Standards: FM Class 3600 – 2011, FM Class 3611 – 2004, FM Class 3616 – 2011,
UL 50 - 11
Markings: NI CL 1, DIV 2, GP A, B, C, D T4; Suitable for use in CL II, III, DIV 2, GP F, G T4;
T4(-40 °C ≤ T
Nonincendive outputs to remote antenna
when connected per Rosemount drawing 01420-1011; Type 4X
Special Condition for Safe Use:
1. Explosion Hazard. Do not disconnect equipment when a flammable or combustible
atmosphere is present.
22
th
Ed, ANSI/ISA 61010-1 - 2012
≤ +60 °C);
a
Page 23

August 2015
Quick Start Guide
Canada
N6 Canada Division 2
Certificate: CSA 70010780
Standards: CAN/CSA C22.2 No. 0-M91 (R2001), CAN/CSA Std C22.2 No. 94-M91 (R2001),
CSA Std C22.2 No. 142-M1987, CSA Std C22.2 No. 213-M1987,
CSA C22.2 No. 61010-1 - 2012
Markings: Suitable for Class 1, Division 2, Groups A, B, C, and D, T4;
when connected per Rosemount drawing 01420-1011; Type 4X
Special Condition for Safe Use:
1. Explosion Hazard. Do not disconnect equipment when a flammable or combustible
atmosphere is present.
Europe
N1 ATE X Type n
Certificate: Baseefa07ATEX0056X
Standards: EN 60079-0: 2012, EN 60079-15: 2010
Markings: II 3 G Ex nA IIC T4 Gc, T4(-40 °C ≤ T
Special Conditions for Safe Use (X):
1. The equipment is not capable of withstanding the 500 V insulation test required by
clause 6.5.1 of EN 60079-15:2010. This must be taken into account when installing the
equipment.
2. The surface resistivity of the antenna is greater than 1GΩ. To avoid electrostatic charge
build-up, it must not be rubbed with a dry cloth or cleaned with solvents.
ND ATE X Dust
Certificate: Baseefa07ATEX0057X
Standards: EN 60079-0: 2012, EN 60079-31: 2009
Markings: II 3 D Ex tc IIIC T135 °C Dc, (-40 °C ≤ T
Special Condition for Safe Use (X):
1. The surface resistivity of the antenna is greater than 1GΩ. To avoid electrostatic charge
build-up, it must not be rubbed with a dry cloth or cleaned with solvents.
≤ +65 °C), V
a
≤ +65 °C)
a
MAX
= 28Vdc
International
N7 IECEx Type n
Certificate: IECEx BAS 07.0012X
Standards: IEC 60079-0: 2011, IEC 60079-15: 2010
Markings: Ex nA IIC T4 Gc, T4(-40 °C ≤ T
Special Conditions for Safe Use (X):
1. The apparatus is not capable of withstanding the 500 V electrical strength test as
defined in Clause 6.5.1 of IEC 60079-15:2012. This must be taken into account during
installation.
2. The surface resistivity of the antenna is greater than 1GΩ. To avoid electrostatic charge
build-up, it must not be rubbed with a dry cloth or cleaned with solvents.
≤ +65 °C), V
a
MAX
= 28Vdc
23
Page 24

Quick Start Guide
NF IECEx Dust
Certificate: IECEx BAS 07.0013X
Standards: IEC 60079-0: 2011, IEC 60079-31: 2008
Markings: Ex tc IIIC T135 °C Dc, (-40 °C ≤ T
≤ +65 °C)
a
Special Condition for Safe Use (X):
1. The surface resistivity of the antenna is greater than 1GΩ. To avoid electrostatic charge
build-up, it must not be rubbed with a dry cloth or cleaned with solvents.
Brazil
N2 INMETRO Type n
Certificate: UL-BR 15.0350X
Standards: ABNT NBR IEC 60079-0:2008 + Errata 1:2011, IEC 60079-15:2012;
Markings: Ex nA IIC T4 Gc, T4(-40 °C ≤ T
≤ +65 °C)
a
Special Condition for Safe Use (X):
1. See certificate for special conditions.
China
N3 China Type n
Certificate: CNEx13.1929X
Standards: GB3836.1 – 2010, GB3836.8 - 2003
Markings: Ex nA nL IIC T4 Gc
Special Condition for Safe Use (X):
1. See certificate for special conditions.
August 2015
Japan
N4 TIIS Type n
Certificate: T64855
Markings: Ex nA nL IIC T4
EAC – Belarus, Kazakhstan, Russia
NM Technical Regulation Customs Union (EAC) Type n
Certificate: RU C-US.ГБ05.B.00578
Markings: 2Ex nA IIC T4 X;
T4(-40 °C ≤ T
IP66;
≤ +65 °C)
a
Combinations
KD Combination of N1, N5, and N6
24
Page 25

August 2015
Figure 12. Smart Wireless Gateway 1420 Declaration of Conformity
Quick Start Guide
25
Page 26

Quick Start Guide
August 2015
26
Page 27

August 2015
Quick Start Guide
27
Page 28

Global Headquarters
Emerson Process Management
6021 Innovation Blvd.
Shakopee, MN 55379, USA
+1 800 999 9307 or +1 952 906 8888
+1 952 949 7001
RFQ.RMD-RCC@EmersonProcess.com
North America Regional Office
Emerson Process Management
8200 Market Blvd.
Chanhassen, MN 55317, USA
+1 800 999 9307 or +1 952 906 8888
+1 952 949 7001
RMT-NA.RCCRFQ@Emerson.com
Latin America Regional Office
Emerson Process Management
1300 Concord Terrace, Suite 400
Sunrise, Florida, 33323, USA
+1 954 846 5030
+1 954 846 5121
RFQ.RMD-RCC@EmersonProcess.com
Europe Regional Office
Emerson Process Management Europe GmbH
Neuhofstrasse 19a P.O. Box 1046
CH 6340 Baar
Switzerland
+41 (0) 41 768 6111
+41 (0) 41 768 6300
RFQ.RMD-RCC@EmersonProcess.com
Asia Pacific Regional Office
Emerson Process Management Asia Pacific Pte Ltd
1 Pandan Crescent
Singapore 128461
+65 6777 8211
+65 6777 0947
Enquiries@AP.EmersonProcess.com
Middle East and Africa Regional Office
Emerson Process Management
Emerson FZE P.O. Box 17033,
Jebel Ali Free Zone - South 2
Dubai, United Arab Emirates
+971 4 8118100
+971 4 8865465
RFQ.RMTMEA@Emerson.com
*00825-0200-4420*
Quick Start Guide
00825-0200-4420, Rev FE
Standard Terms and Conditions of Sale can be found at:
www.rosemount.com\terms_of_sale.
AMS and the Emerson logo are re gistered trademarks and service marks of
Emerson Electric Co.
Rosemount and the Rosemount logotype are registered trademarks of
Rosemount Inc.
DeltaV is a trademark of Rosemount, Inc.
Microsoft and Internet Explorer are registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation in the United States and other countries.
Windows is a trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and
other countries.
Mozilla Firefox is a registered trademark of The Mozilla Foundation.
WirelessHART is a registered trademark of the FieldComm Group.
Modbus is a registered trademark of Modicon, Inc.
HART-IP is a trademark of the FieldComm Group.
EtherNet/IP is a trademark of ControlNet International under license by
ODVA.
NEMA is a registered trademark and service mark of the National Electrical
Manufacturers Association.
All other marks are the property of their respective owners.
© 2015 Rosemount Inc. All rights reserved.
August 2015
 Loading...
Loading...