ELSA Cable User Manual
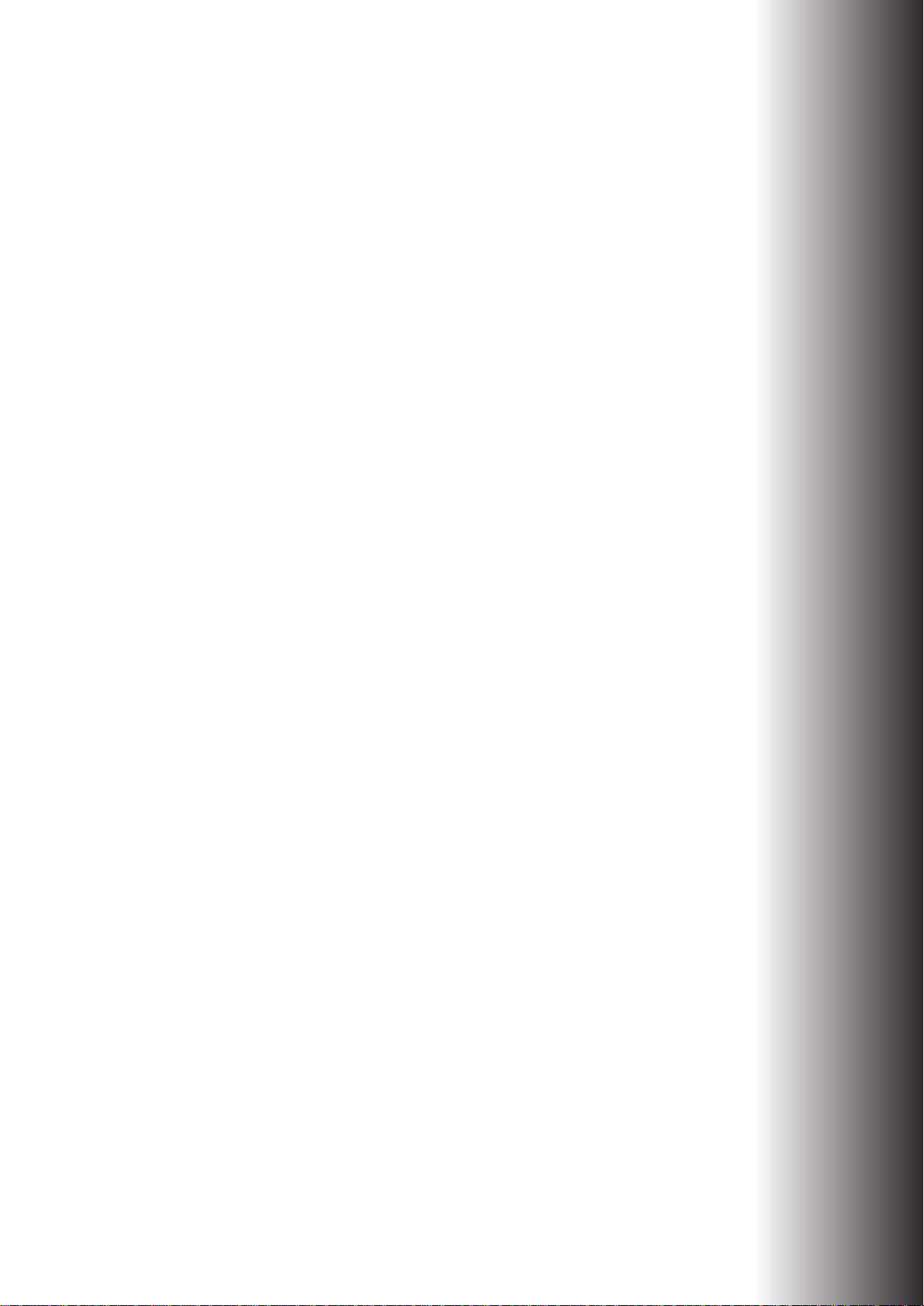
M
ELSA MicroLink
TM
Cable
Manual

© 1999 ELSA AG, Aachen (Germany)
While the information in this manual has been compiled with great care, it may not be deemed an
assurance of product characteristics. ELSA shall be liable only to the degree specified in the terms of
sale and delivery.
The reproduction and distribution of the documentation and software supplied with this product and the
use of its contents is subject to written authorization from ELSA. We reserve the right to make any
alterations that arise as the result of technical development.
ELSA is DIN EN ISO 9001 certified. The accredited TÜV CERT certification authority has confirmed ELSA
conformity to the worldwide ISO 9001 standard in certificate number 09 100 5069, issued on June 15,
1998.
Trademarks
Windows
®
, Windows NT® and Microsoft® are registered trademarks of Microsoft, Corp.
All other names mentioned may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners. The
ELSA logo is a registered trademark of ELSA AG.
Subject to change without notice. No liability for technical errors or omissions.
ELSA AG
Sonnenweg 11
52070 Aachen
Germany
ELSA, Inc.
2231 Calle De Luna
Santa Clara, CA 95054
USA
www.elsa.com
Aachen, October 1999
No. 20840/1099

Preface
Thank you for placing your trust in this ELSA product.
With the
Internet for you with unparalleled speeds and remain online permanently.
The highest quality standards in manufacturing and stringent quality control are the basis
for high product standards and consistent product quality.
This documentation contains the following chapters:
K Introducing the
K Installation and configuration
K Configuration modes
K Operating modes and functions
K Technical basics
K Technical reference
K Appendix
ELSA MicroLink Cable
ELSA MicroLink Cable
, you have chosen a modem that will open the door to the
Our online services (Internet server www.elsa.com) are available to you around the clock
should you have any queries regarding the topics discussed in this manual or require any
further support. In the Support file section under 'Know-How', you can find answers to
frequently asked questions (FAQs). The KnowledgeBase also contains a large pool of
information. Current drivers, firmware, tools and manuals can be downloaded at any
time.
The KnowledgeBase can also be found on the CD. Just open the file
\Misc\Support\MISC\ELSASIDE\index.htm.


Content
Content
V
Introducing the
The
ELSA MicroLink Cable
What does the unit look like?............................................................................ 1
Node or hub?...................................................................................................... 3
The highlights of the
Fast Internet....................................................................................................... 4
Internet at all times—always online ................................................................ 5
More than just Internet...................................................................................... 5
CE conformity and FCC radiation standard............................................................. 7
Installation and Configuration ....................................................................................9
First Steps............................................................................................................. 10
Quick Start: Quick configurations......................................................................... 11
Preparations..................................................................................................... 11
Configuration as a bridge ................................................................................ 11
Configuration as a router................................................................................. 13
Set up the workstation computers (Windows 95 or 98)....................................... 15
ELSA MicroLink Cable
takes the stage............................................................ 1
ELSA MicroLink Cable
..................................................................... 1
.......................................................... 4
English
Configuration modes ..................................................................................................17
The user-friendly method: inband......................................................................... 17
Requirements for inband configuration........................................................... 17
Alternatively: addresses can be managed by the DHCP server...................... 17
Starting inband configuration using
Start up inband configuration using telnet...................................................... 18
Configuration commands ..................................................................................... 19
What's happening on the line?............................................................................. 21
Trace Outputs................................................................................................... 21
New firmware with FirmSafe............................................................................... 22
This is how FirmSafe works............................................................................. 22
How to load new software.............................................................................. 23
Configuration using SNMP.............................................................................. 24
General............................................................................................................. 24
Accessing tables and parameters using SNMP.............................................. 25
The Management Information Base (MIB)...................................................... 27
Operating modes and functions ...............................................................................29
Security for your configuration............................................................................. 29
Password protection........................................................................................ 29
Login barring.................................................................................................... 29
Access control via TCP/IP................................................................................ 30
ELSA LANconfig
..................................... 18
ELSA Cable Modem

English
VI
Content
Security for your LAN............................................................................................ 30
Encryption ........................................................................................................ 31
TCP/IP packet filters ........................................................................................ 31
The hiding place—IP masquerading (NAT, PAT) ............................................ 31
IP routing............................................................................................................... 32
The IP routing table.......................................................................................... 32
Dynamic routing with IP RIP ............................................................................ 34
Local routing .................................................................................................... 35
IP masquerading (NAT, PAT)............................................................................ 36
DNS forwarding............................................................................................... 38
Bridging............................................................................................................ 39
Automatic address administration with DHCP..................................................... 40
The DHCP client............................................................................................... 41
The DHCP server.............................................................................................. 41
DHCP – 'on', 'off' or 'auto'?.............................................................................. 42
How are the addresses assigned?................................................................... 42
Technical basics .........................................................................................................47
Cable modem technology..................................................................................... 47
Standards......................................................................................................... 47
Access.............................................................................................................. 47
Registration in the cable network ................................................................... 48
Network technology.............................................................................................. 50
The network and its components .................................................................... 50
Connection modes ........................................................................................... 50
Kinds of networks............................................................................................ 52
IP addressing......................................................................................................... 52
IP routing and hierarchical IP addressing........................................................ 55
Expansion through local networks................................................................... 57
Appendix .......................................................................................................................63
Technical data ...................................................................................................... 63
Warranty conditions............................................................................................. 65
Declaration of conformity..................................................................................... 67
Description of the menu options ..............................................................................73
Status.................................................................................................................... 75
Status/Operating-time..................................................................................... 76
Status/Current-time......................................................................................... 76
Status/cable-statistics..................................................................................... 76
Status/LAN-statistics ...................................................................................... 77
Status/bridge statistics ................................................................................... 78
Status/TCP-IP-statistics................................................................................... 79
ELSA Cable Modem

Content
Status/IP-router-statistics ............................................................................... 83
Status/config statistics.................................................................................... 85
Status/Queue-statistics................................................................................... 85
Status/MCNS-statistics................................................................................... 87
Status/Init-status............................................................................................. 87
Status/DHCP-client-statistics.......................................................................... 88
Setup..................................................................................................................... 88
Setup/cable-module ........................................................................................ 89
Setup/LAN-module.......................................................................................... 89
Setup/bridge-module....................................................................................... 90
Setup/TCP-IP-module....................................................................................... 91
Setup/IP-router-module................................................................................... 94
Setup/SNMP-module..................................................................................... 101
Setup/DHCP-server-module........................................................................... 101
Setup/Config-module..................................................................................... 103
Firmware............................................................................................................. 104
Other................................................................................................................... 106
VII
English
ELSA Cable Modem

English
VIII
Content
ELSA Cable Modem

Introducing the ELSA MicroLink Cable
1
Introducing the
Internet access is the main application for the
cable network to which you have connected your modem may offer additional services or
regional information.
This chapter describes the display elements and connections of the modem, accessing
the Internet, and the characteristics and techniques that ensure fast, secure data
exchange.
The precise use of the
sections and with the aid of the examples in the 'Workshop'.
The term 'router', as used in the remainder of the manual, refers to the router functions
of our ELSA MicroLink Cable
The
This section introduces the unit's hardware. It covers the unit's display elements and
connection options.
ELSA MicroLink Cable
ELSA MicroLink Cable
.
ELSA MicroLink Cable
ELSA MicroLink Cable
's features will be explained in the following
takes the stage
. The operator of the
What does the unit look like?
We would first like to familiarize you with the device.
You will find a number of LEDs as display elements on the front panel.
ELSA MicroLink Cable

Introducing the ELSA MicroLink Cable
2
ON
Standby
Cable-Tx, -Rx,
-Sync, Reg’d
This LED flashes once when the power supply is switched on. After the self-test, either
an error is output by a flashing light code or the device starts and the LED remains lit.
Off Unit switched off, power supply plugged in
red 1 x short Boot procedure (test and load) started
red flashing Display of a boot error (flashing light code)
red Device ready for use
This LED shows that the unit is in stand-by mode. The
ELSA MicroLink Cable
is registered
with the cable network provider in this state, but there is no active connection to the local
network. In other words, no data can be exchanged between the Internet and the LAN
in this state.
ELSA MicroLink Cable
The
can be switched to this mode by configuring the function of
the power switch correspondingly and then actuating this switch on the rear of the unit.
These LEDs display the status of the interface to the cable network:
Blink codes
Cable-Tx yellow Data packet sent from the device to the Internet
Cable-Rx green Data packet received from the Internet
Cable-Sync green The device has found a channel on which it can communicate with the
cable network operator's headend.
Cable-Reg’d green The registration and all required negotiations between the unit and the
headend have been completed and the registration confirmed by the headend. The unit is ready to exchange data with the Internet in this state.
The Sync and Reg’d LEDs can display the various phases of the cable modem registration
through combined blink codes, thus offering configuration troubleshooting information.
The meanings of the specific blink codes:
SYNC REG'd What has been achieved so
far?
off off channel search with 64/256QAM chan-
1 pulse off QAM lock FEC lock
2 pulse off FEC lock TRC lock
on off TRC lock initial ranging
What is the modem trying to do?
nel
on 1 pulse initial ranging DHCP
on 2 pulse DHCP ToD
on 3 pulse ToD Configuration file
on 4 pulse Configuration file Registration
on on Registration
ELSA MicroLink Cable
Introducing the ELSA MicroLink Cable
3
LAN-Tx, -Rx,
LAN-Coll, -Link
These LEDs show the corresponding network controller status:
LAN -tx yellow Data packet sent from the device to the LAN
LAN-Rx green Data packet received from the LAN
LAN coll red Sending collision
LAN-Link green Connection to LAN is established and ready
Now turn the whole thing around and take a look at the rear. Beginning again on the lefthand side, you have:
ABC EFGD
1 Connector for the cable TV network (CATV)
2 Reset switch—performs a hardware reset
3 Factory Default button—the unit's factory defaults are restored after holding this
button for approx. 15 seconds
4 10Base-T network connection
5 Node/hub selector switch
6 Connection for power supply unit
7 On/standby switch
ELSA MicroLink Cable

Introducing the ELSA MicroLink Cable
4
Node or hub?
Please check the position of the Node/Hub switch when connecting the unit to the LAN:
K As the factory default, the switch is set to 'Node'. In this setting, the device acts as
a node on a network. It can, in this case, only be connected to a hub, not directly to
the network card of a computer.
K Set the switch to 'Hub' if you do not wish to connect the device to a hub but directly
to a workstation. In this setting the lines for sending and receiving the data are
crossed.
Look at the link status LED (Link) to check if the node/hub switch is set correctly.
Shared media:
Multiple users
share a single
“cable”
The highlights of the
The cable modem is a new Internet-access technology that is now competing with
conventional modems, Internet modems and small ISDN routers. To take maximum
advantage of your
in which cable modems have the technological edge.
ELSA MicroLink Cable
ELSA MicroLink Cable
, you should know the areas and characteristics
Fast Internet
Cable modems use a split transfer rate depending on the direction of the signals.
Downstream refers to the transfer of data from the network operator to the participant,
upstream is the opposite direction. This asymmetrical split is quite acceptable, since
users generally receive far more information from the Internet than they send to it.
Cable network
Up to 43 Mbps can be transferred downstream; upstream transfer speeds reach up to 10
Mbps.
This colossal performance is shared by up to 2000 users connected to the same cable
section, however. This is referred to as the use of a shared media.
Bandwidth:
Throughput,
transfer
capacity
The data flow in the cable network does not take place at a constantly high volume, but
in irregular intervals. Also, it's unlikely that all 2000 participants will be using the
network simultaneously, so the available bandwidth is certainly adequate to ensure the
fast transfer of data.
The cable network operators have the option of limiting the available bandwidth for
individual participants, or offering several channels with 43 Mbps each. Please contact
your network operator for further information on transfer rates and pricing models.
ELSA MicroLink Cable

Backbone
Introducing the ELSA MicroLink Cable
5
Backbone
direct
connection to
the Internet
:
The simple transfer rate between the network operator and participant does not by itself
determine the speed at which the Internet can be accessed. The network operator must
also forward data destined for the Internet to a backbone. The dimensioning of this
connection ultimately determines the speed at which you can surf. The backbone can
become a bottleneck if a large number of participants want to access Internet data
simultaneously and the network operator does not have an adequately dimensioned
connection to the Internet.
Internet at all times—always online
One of the biggest advantages of cable modem technology is the continuous availability
of the Internet. While “normal” Internet connections need to be established as required,
all cable modem users on a cable section can be permanently registered with the
headend. The multiport capabilities of the remote stations ensure that other participants
are not blocked due to a lack of connections. The advantages of this permanent Internet
connection:
K Immediate availability of all information
Your e-mail comes to you directly—not just when you pick it up. To view a Web
page, just open your browser and don't worry about connecting to your provider.
K Your own Internet server
Until now, running your own Internet server generally meant having an extremely
expensive leased line to the provider. Now you have one! If you would like to set
up your own Web server for your company, you can now do so and have it accessible
at all times via the cable modem at no additional cost.
More than just Internet
Together with the appropriate remote stations, cable modems form the connection
between network participants (private or business) and the network operator. Very high
throughputs—and thus very fast data transfers—can be realized using such a
connection. In addition to providing fast Internet access, this creates a number of other
interesting options for the evolution of network operators into information service
providers.
Regional content
Cable network operators generally have a local or regional orientation due to the
structure of the cable network. The headends that have to be additionally integrated into
the network with their restriction to around 2000 participants results in further area
limitations.
ELSA MicroLink Cable

6
Proxy
Introducing the ELSA MicroLink Cable
Network operators can take advantage of this structure to provide regional content in
addition to the Internet. This can be accomplished by setting up Web servers that do not
need to be accessible from the Internet. These can then be used for special information
services for network participants, such as the programs of local cinemas, regional news,
information for clubs and special-interest groups, and so on—essentially, everything
that is of interest to the regional cable network participants, but that might be
superfluous on the Web.
Proxy servers
The network operator can also use local servers to speed up access to the Internet.
These proxy servers are used for the intermediate storage of information from the
Internet.
: Stand-in
Every page requested from the Internet by participants in the local cable network section
is stored in this proxy server for a specific period of time. As a rule, the storage period
on the proxy server is determined by the cable network operator. If another participant
requests the same page, the proxy server can serve the page directly without having to
find it on the Internet first.
This is generally beneficial, for example by speeding up downloads considerably.
However, when calling up information subject to frequent changes such as stock prices,
accessing the current Web page is usually a must. In such a case the version of the page
stored on the proxy server can already be out of date or incorrect. If this could be relevant
to you, please check with your network operators whether they deploy proxy servers.
Clicking the Refresh button will download the current information directly from the
Internet, however.
ELSA MicroLink Cable

Introducing the ELSA MicroLink Cable
7
CE conformity and FCC radiation standard
CE
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits of the European
Council Directive on the approximation of the laws of the member states relating to
electromagnetic compatibility (89/336/EEC) according to EN 55022 class B and EN55024.
FCC
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device pursuant to Part 15 of the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Rules.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1 This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2 This device must accept any inteference received, including interference that may
cause undesired operation.
The FCC ID of this device is KJGMLCABLE.
CE and FCC
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against radio frequency
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy. It may interfere with radio communications if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions. However, there is no guarantee
that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
interference to radio or television reception (this can be determined by turning this
equipment off and on), the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or
more of the following measures:
K Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
K Increase the distance between this equipment and the receiver.
K Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit other than that to which the receiver
is connected.
K Consult your dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician.
K Caution: To comply with the limits for an FCC Class B computing device, always use
a shielded signal cable.
The Federal Communications Commission warns the user that changes or modifications
to the unit not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the
user's authority to operate the equipment.
ELSA MicroLink Cable

Introducing the ELSA MicroLink Cable
8
ELSA MicroLink Cable

Installation and configuration
Installation and configuration
9
The aim of this chapter is to get you online as quickly as possible. First please check that
the contents of the package are complete:
ELSA MicroLink Cable
K
K Power supply
K Twisted-pair LAN connector cable
K WAN connector cable (coaxial) or corresponding adapter
K Documentation
K CD containing
Computers to be connected to the Internet using this device must fulfill the following
requirements:
K Any operating system that supports the TCP/IP network protocol, such as Windows
95, Windows 98, Windows NT 4.0, OS/2, Linux, BeOS
K Windows 95, Windows 98 or Windows NT 4.0 and a CD-ROM drive on the computer
on which you would like to install the
K Ethernet network adapter
K TCP/IP network protocol installed and bound to the network adapter
ELSA LANconfig
and electronic documentation
ELSA LANconfig
configuration software.
English
First, we will show you how to connect your new
ELSA LANconfig
the
unit will then be ready to connect your computer or network to the Internet.
If this is all going too fast for you or you're not familiar with the technical terms, you can
also find further information in this documentation, such as detailed descriptions of the
unit and its functions, sample configurations, descriptions of the software, glossaries,
etc.
This unit is designed to be connected to the broadband cable TV network. The connection
is made using the supplied coaxial cable or the appropriate adapter.
configuration software and perform the initial configuration. The
ELSA MicroLink Cable
, how to install
ELSA MicroLink Cable

English
Installation and configuration
10
First Steps
Give it some power
1
First, give your device the power it needs through the power supply unit!
Onto the net
2
Connect the unit to your local network using the twisted pair cable. Please check the
position of the node/hub switch: 'Node' is the correct position when connecting the unit
to a network. Switch to 'Hub' when connecting the unit directly to a workstation.
The wire to the world
3
Connect the
adapter and a normal antenna cable. Data is transmitted through the cable TV network
in accordance with the MCNS (Multimedia Cable Network System)/DOCSIS standard.
ELSA MicroLink Cable
to the TV cable network using the coaxial cable or the
The connection to the cable TV network must provide a certain signal level. This value
will be checked by your cable network operator and adjusted as required.
And we're off
4
Switch the device on at the back. The 'Power' LED on the front panel lights up after a
short self-test. The 'LAN Link' LED indicates that the unit is correctly connected to the
LAN and that the Node/Hub switch is correctly set.
If this LED is not lit, change the position of the Node/Hub switch. If the LED still does not
light up, there may be a problem with the network adapter or the cabling.
Software installation
5
The
ELSA LANconfig
NT 4.0 may be used to configure the unit as required or to set it up for other applications.
Alternatively, you can perform the configuration via telnet from any other TCP/IP capable
computer (e.g. Linux, Solaris). Install the TCP/IP network protocol, followed by the
LANconfig
does not start up automatically after insertion of the CD, start Windows Explorer, click
on 'autorun.exe' on the
program.
on the computer that will be used to set up the device. If the setup program
configuration software for Windows 95, Windows 98 or Windows
ELSA MicroLink Cable
and follow the instructions in the install
ELSA
Configuring the
6
The first time
TCP/IP network and can immediately be configured.
When configuring the router with
quickly and conveniently guide you through the required settings.
ELSA MicroLink Cable
ELSA MicroLink Cable
ELSA LANconfig
is run, the new modem is automatically detected on the
ELSA LANconfig
, you can use the setup wizards to

Installation and configuration
11
Quick Start: Quick configurations
We're sure that after you've installed the hardware and software, you'll want to get
going quickly without bothering with technical details. In the following sections, we'll
show you how to set up your
applications—without bothering with the whys and wherefores.
After the preparations that you should check in any case, we will introduce the
configuration of the unit as a bridge and IP router. Further information on the bridge and
router functions can be found in the 'Operating Modes' chapter.
ELSA MicroLink Cable
Preparations
The Internet is based on the TCP/IP network protocol. The individual devices in the
Internet (workstations, servers, routers, etc.) are identified using unique IP addresses. All
computers exchanging data on the Internet therefore must have the TCP/IP network
protocol installed and must be assigned a valid IP address.
quickly for the most common
English
IP addresses can either be manually entered, permanently for each computer, or assigned
automatically by a different computer, a so-called DHCP server. Your cable network
operator has such a DHCP server, and one is also contained in the
itself. For this quick-start, we prefer using the automatic assignment of an IP address by
a DHCP server. The cable network operator's DHCP server will be used when configuring
the unit as a bridge; in router mode the integrated DHCP server of the
will be used.
Cable
The following settings are required regardless of the operating mode you intend to use
with your
K Install the TCP/IP network protocol on all computers on the network.
K Activate the automatic assignment of IP addresses via DHCP for the workstations
Just how you do that will be explained in section 'How to set up the workstation
computers' towards the back of this chapter.
ELSA MicroLink Cable
(generally the default setting).
:
ELSA MicroLink Cable
ELSA MicroLink
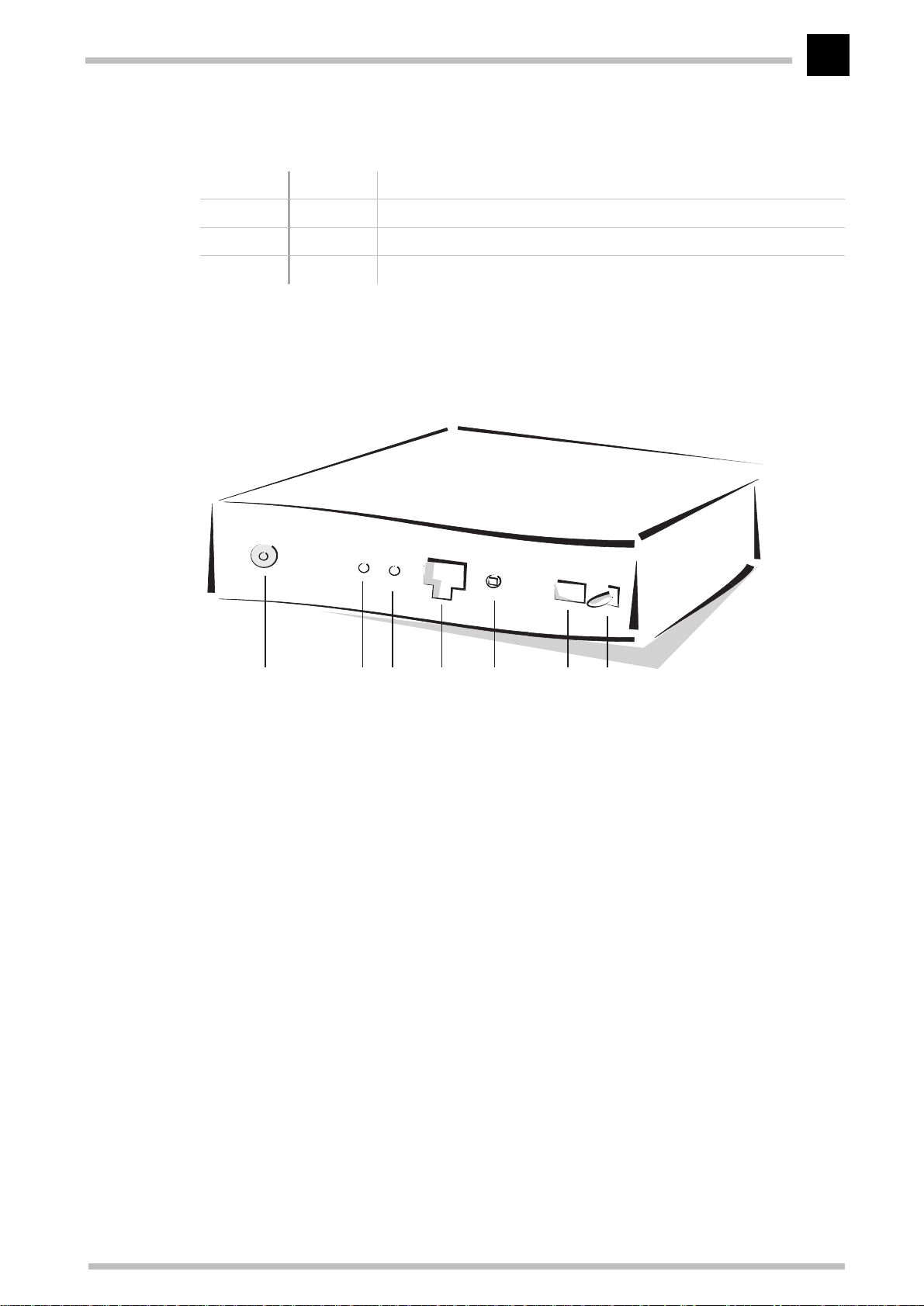
Configuration as a bridge
Bridge mode is the simplest configuration for the
the unit does not take IP addresses into consideration and transfers all data that is not
destined for workstations in the local network directly to the Internet. In the opposite
direction, all data coming from the Internet for a specific computer in the local network
is transferred (insofar as that computer has already sent data to the Internet). It's thus
not necessary to worry about the assignment of IP addresses. The computers in your
local network receive their IP addresses directly from the DHCP server of the cable
network operator.
ELSA MicroLink Cable
ELSA MicroLink Cable
. In this mode,
English
Installation and configuration
12
Internet
Computer workstation in
LAN
IP address assignment
MCNS/
DOCSIS
Server with
DHCP
Headend Cable TV net-
work
ELSA MicroLink Cable
as bridge
In this example, only one computer is connected to the Internet via the ELSA MicroLink
Cable. In principle however, several computers can be connected to the ELSA MicroLink
Cable, using a hub for example, if the network operator permits.
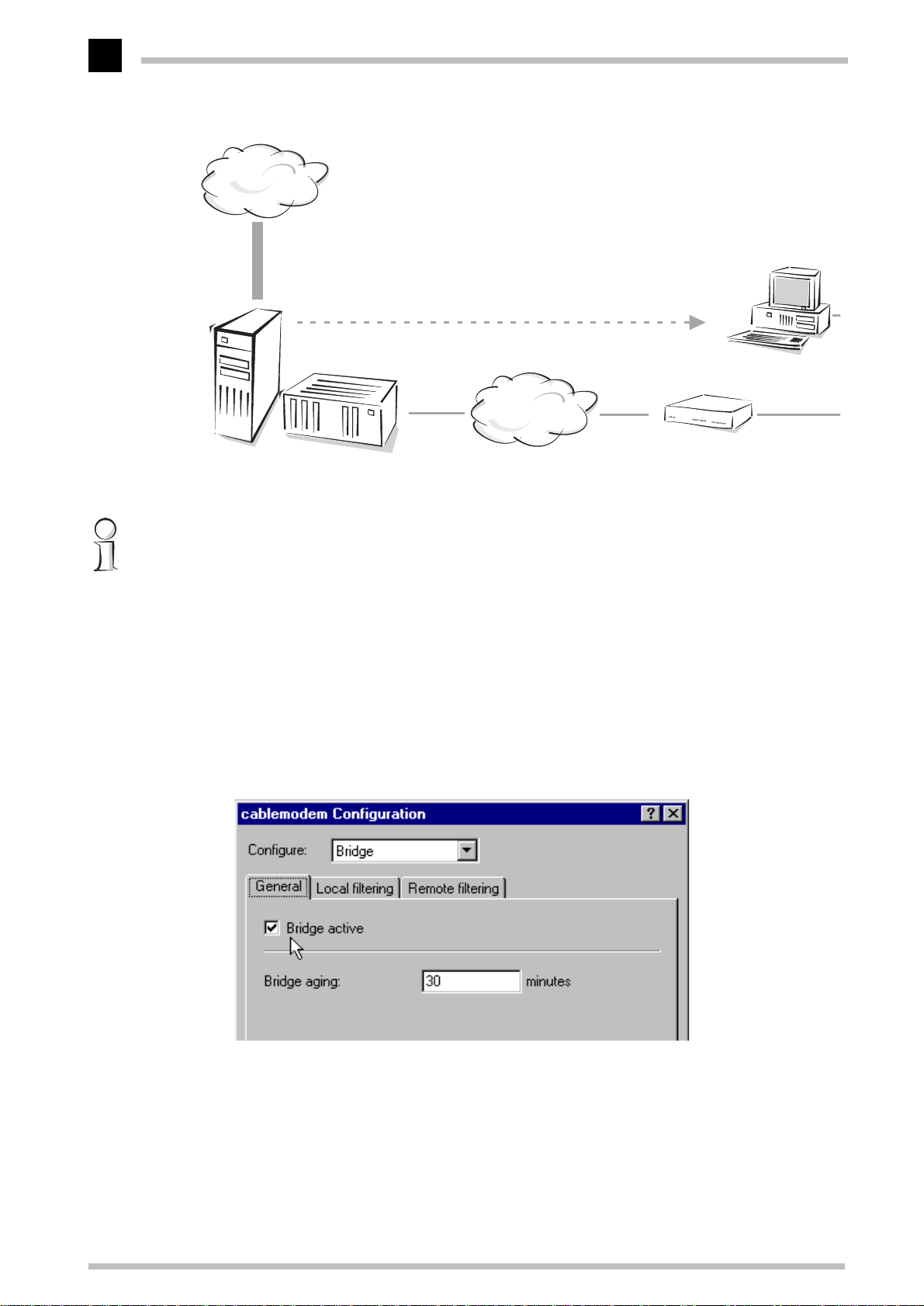
a Start up
LANconfig
ELSA LANconfig
.
b Click the entry for the
by clicking Start E Programs E ELSAlan E
ELSA MicroLink Cable
in the device list to open the
ELSA
configuration dialog. If an entry doesn't exist yet, create a new one using Device
E New. For the IP address, enter '10.0.0.254' or 'x.x.x.254', in which 'x.x.x' stands
for the addresses previously in use in your network, if applicable. Go to the 'Bridge'
section and activate the option 'Bridge' on the 'General' tab.
c Go to the 'TCP/IP' configuration section and on the 'Router' tab, disable the 'IP
Router' option. Also deactivate the DHCP server of your
the 'DHCP Server' tab, as well as the 'IP Masquerading' function on the
'Masquerading' tab.
d Save the configuration with OK.
ELSA MicroLink Cable
ELSA MicroLink Cable
on
Installation and configuration
The
ELSA MicroLink Cable
is now ready for use in bridge mode. Open your Web browser,
and off you go into the Web with a whole new sensation of speed...
13
If you can only access the Internet with a single computer while using this configuration,
your cable network operator may have placed a limit on the maximum number of
connected computers. Either ask your network operator to increase the number, or
configure your ELSA MicroLink Cable as a router (with DHCP server and IP
masquerading).
If necessary, filters can be defined to restrict the exchange of data packets between the
local network and the Internet.
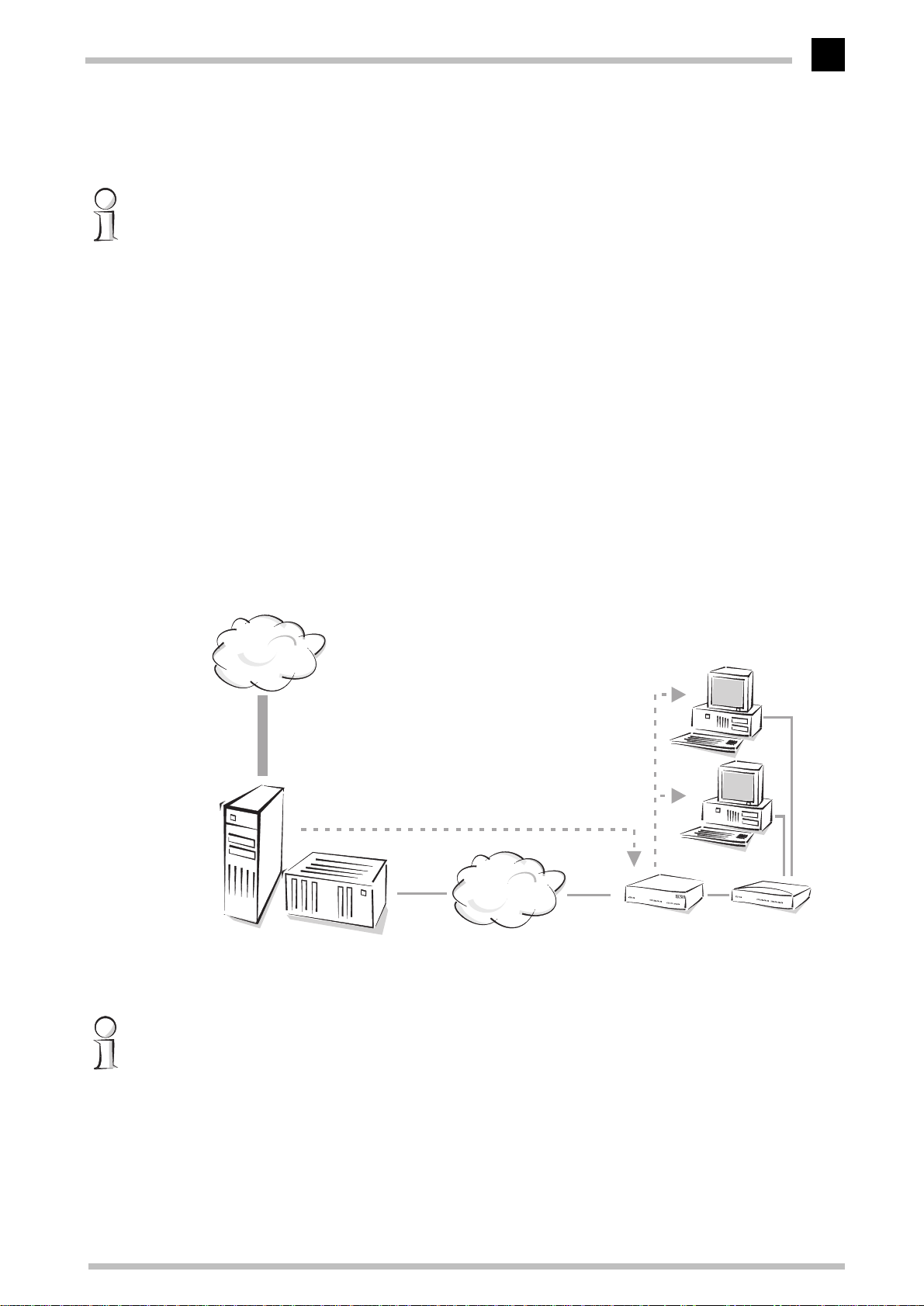
Configuration as a router
In addition to bridge mode, the
this mode, the
ELSA MicroLink Cable
computers exchanging data with the Internet. The exchange of data with the Internet can
thus be set up with much greater precision in this mode. The DHCP server and IP
masquerading functions will assist you with the administration of IP addresses in the
LAN.
Internet
ELSA MicroLink Cable
can also serve as an IP router. In
pays careful attention to the IP addresses of the
Computer workstation in
LAN
English
IP address assignment
IP address assignment
MCNS/
DOCSIS
Server with
DHCP
Headend Cable TV net-
work
ELSA MicroLink Cable
as router with DHCP server
Hub
In this example, several computers are connected to the ELSA MicroLink Cable, and thus
to the Internet, using a hub. In principle however, a single computer can also be
connected directly to the ELSA MicroLink Cable.
a Start up
LANconfig
ELSA LANconfig
.
by clicking Start E Programs E ELSAlan E
ELSA
ELSA MicroLink Cable
English
Installation and configuration
14
b In order for a device to be able to assign addresses to other devices on a TCP/IP
network, it first needs an IP address valid in the LAN itself (LAN-IP address). Click
the entry in the device list to open the configuration dialog. If an entry doesn't exist
yet, create a new one using Device E New. For the IP address, enter '10.0.0.254'
or 'x.x.x.254', in which 'x.x.x' stands for the addresses previously in use in your
network, if applicable. Switch to the 'TCP/IP' configuration section and on the
'General' tab, enter the LAN IP address and the associated netmask.
– If you have not used any IP addresses on your network so far, you can assign any
address you like from the address space reserved for private use, e.g. '10.0.0.1'
with the subnet mask '255.255.255.0'. You are thereby also defining the address
space that the DHCP server will use for the other devices on the network.
– If you have already configured IP addresses on the computers on the LAN,
allocate a free address to the device from the address space you used previously.
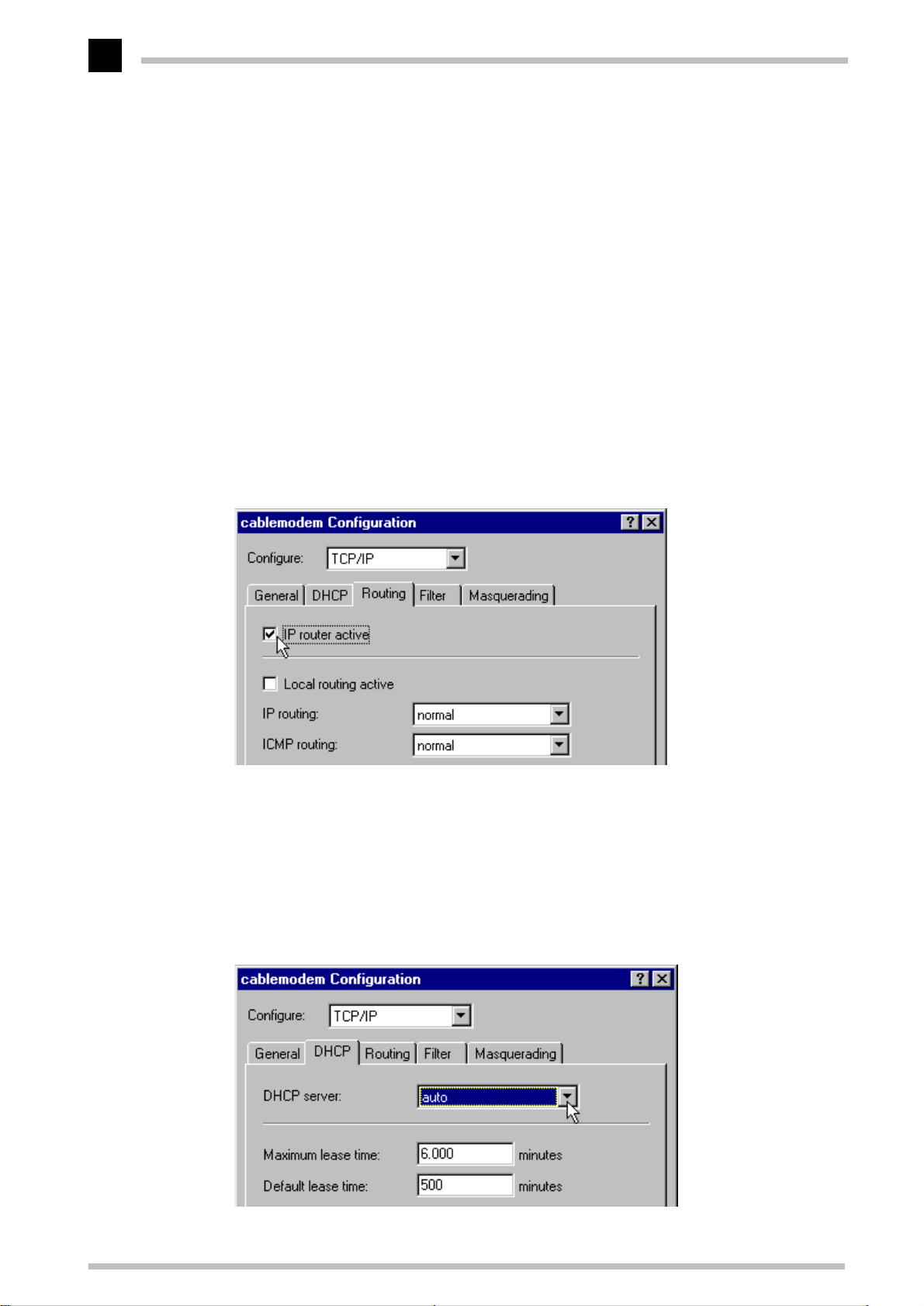
c On the 'Router' tab, enable the 'IP Router' option.
d On the 'Masquerading' tab, enable the 'IP Masquerading' function. This will conceal
the IP addresses in use in your local network from the Internet. This protects your
network from intruders and avoids conflicts with other networks that may be using
the same addresses internally (also see IP addressing and IP masquerading).
e Go to the 'DHCP' tab and set the DHCP server to Auto mode. This lets the unit handle
the local IP address administration by itself. The
the valid address pool by itself unless you specify otherwise.
ELSA MicroLink Cable
determines
ELSA MicroLink Cable

Installation and configuration
f Go then to the 'Bridge' section and deactivate the option 'Bridge' on the 'General'
tab.
15
g Save the configuration with OK.
ELSA MicroLink Cable
The
and off you go into the Web with a whole new sensation of speed...
is now ready for use in router mode. Open your Web browser,
If necessary, filters can be defined to restrict the exchange of data packets between the
local network and the Internet. This lets you define restrictions on the workstations that
can access the Internet, or on specific pages of the Internet that cannot be viewed.
Set up the workstation computers (Windows 95 or 98)
We will now briefly show you how the workstation computers must be set up (e.g. under
Windows 95 and Windows 98) to ensure problem-free communication between the
computers on the TCP/IP network and the router, if this has not already been done.
K TCP/IP installation
Install TCP/IP by clicking Start E Settings E Control Panel E Network E Add
E Protocol. Select 'Microsoft' under Manufacturers and 'TCP/IP' under Network
Protocols.
English
K Obtain IP addresses automatically (use DHCP)
Here's how to set individual workstations to automatically obtain an IP address:
Start E Settings E Control Panel E Network E TCP/IP E Properties E IP
Address E Obtain an IP address automatically . Delete any existing entries for
DNS servers and gateways on the 'Gateway' and 'DNS Configuration' tabs and
disable the 'DNS' option. When rebooting, the workstation will look for a DHCP
server in the network and will allow the server to assign it an IP address and a
netmask.
K Configuring fixed IP addresses (not using DHCP)
If you do not wish to use a DHCP server on your network you should configure fixed
IP addresses on your workstation computers: Start E Settings E Control Panel
E Network E TCP/IP E Properties E IP Address E Specify an IP address.
Allocate unique IP addresses, e.g. from a reserved address space. The workstations
can be assigned the addresses '10.1.1.2' to '10.1.1.253', for example, the
MicroLink Cable
Ensure that the address intended for the
available by opening a DOS box and entering the command
you do not receive a reply to this request the address is probably still unused.
the address '10.1.1.1', all with the netmask '255.255.255.0'.
ELSA MicroLink Cable
, i.e. '10.1.1.1', is
ping 10.1.1.1
ELSA
. If
ELSA MicroLink Cable
English
Installation and configuration
16
Assign fixed IP addresses in router mode with activated IP masquerading only.
Otherwise, address conflicts with other users in your cable network may result when
using router mode without IP masquerading, or bridge mode.
K Specifying the gateway and the DNS server (not necessary if using DHCP)
Enter the LAN IP address of the
the gateway and domain name server (DNS server) in the individual workstations:
Start E Settings E Control Panel E Network E TCP/IP E Properties E
Gateway and DNS Configuration. You must also specify a host name for the DNS
configuration. Use the name of the PC for reasons of consistency, which, for
example, could be the same as the user name.
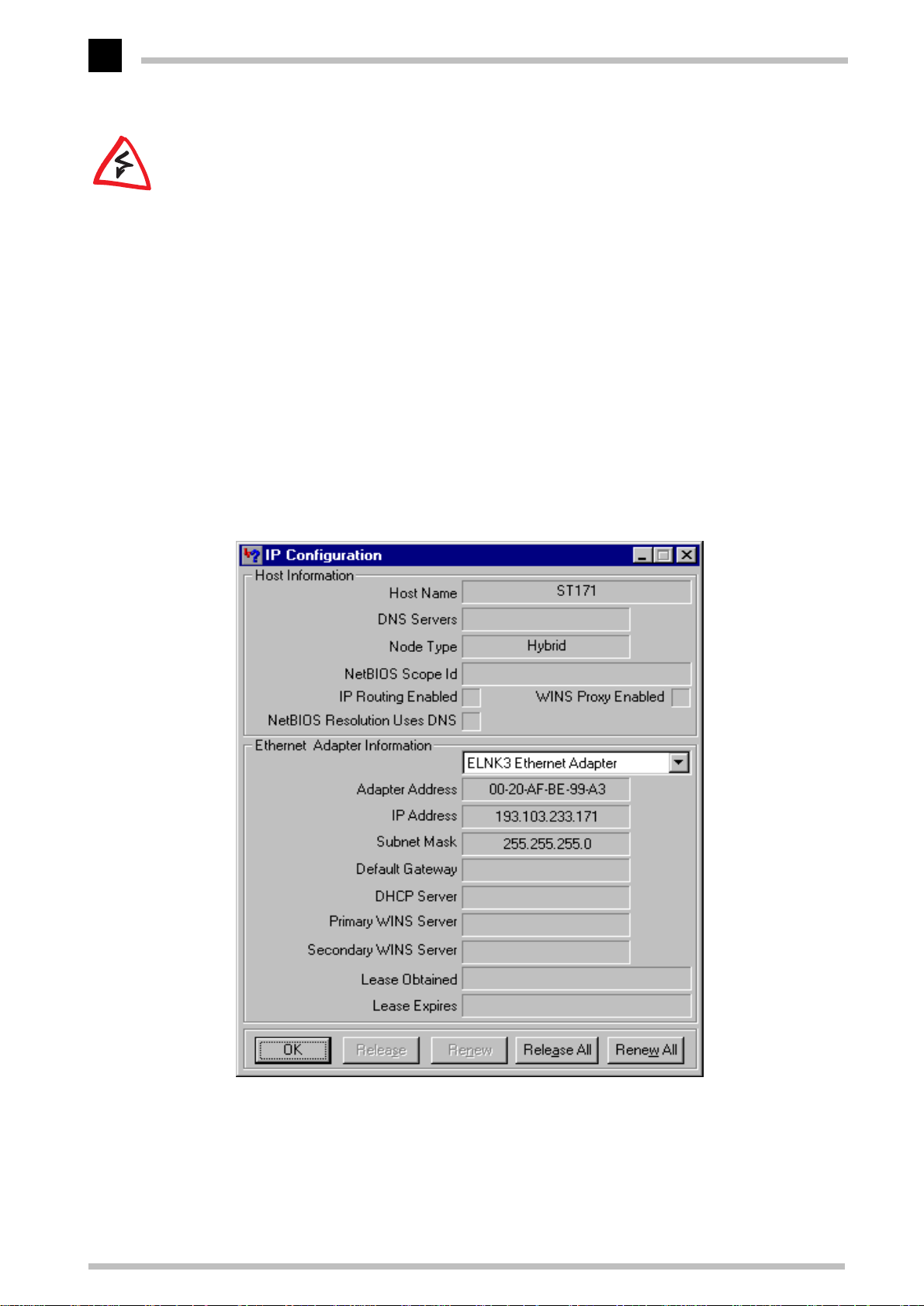
K Checking the IP configuration
Check the current IP configuration of the computer under Windows 95 or
Windows 98 by selecting Start E Run E winipcfg. Among other information, you
can see the IP address assigned to the computer by the DHCP server and the
addresses conveyed for the DNS server and gateway.
ELSA MicroLink Cable
in your own local network as
ELSA MicroLink Cable

Configuration modes
Configuration modes
17
ELSA cable modems are always delivered with up-to-date software in which a number
of the settings have already been prepared for you.
It will nevertheless be necessary for you to add some information and configure them to
your specific needs. These settings are made as part of the configuration process.
This section will show you the programs and routes you can use to access the device and
set it up.
And, if the team at ELSA has produced firmware with new features, we will show you
how to load the new software.
The user-friendly method: inband
Using inband configuration allows any computer on the cable network or LAN to access
the router. However, this is only possible if the router permits it, as access from the
WAN or LAN can be restricted or completely blocked by the IP access list. Inband
configuration requires the use of either telnet (supplied with most operating systems) or
ELSA LANconfig
the
with your device. You can always obtain up-to-date releases from our online media.
configuration program for Windows.
ELSA LANconfig
is supplied
English
Requirements for inband configuration
TCP/IP or TFTP are used to make configurations using telnet or
TCP/IP protocol must therefore be installed on the computer being used and your cable
modem must be given an IP address which you will then use when addressing it.
A device that has not been configured yet will respond to the IP address
XXX.XXX.XXX.254, in which the Xs are placeholders for the network address in your LAN.
If the computers on your network have addresses such as 192.110.130.1, then you will
be able to address the router using 192.110.130.254.
If a computer with the address XXX.XXX.XXX.254 is already active on your network, shut
down the computer with this IP address before continuing. Give the device a new LAN
IP address as soon as you have established a connection to it, using ELSA LANconfig or
telnet.
ELSA LANconfig
. The
Alternatively: addresses can be managed by the DHCP server
If it is not absolutely essential that you configure the correct IP addresses manually, the
DHCP server can perform this task for you automatically. When using the DHCP server
you can have the IP addresses for all computers on the network assigned automatically
(see also chapter 'Automatic Address Administration with DHCP').
ELSA MicroLink Cable
Configuration modes
18
English
Starting inband configuration using
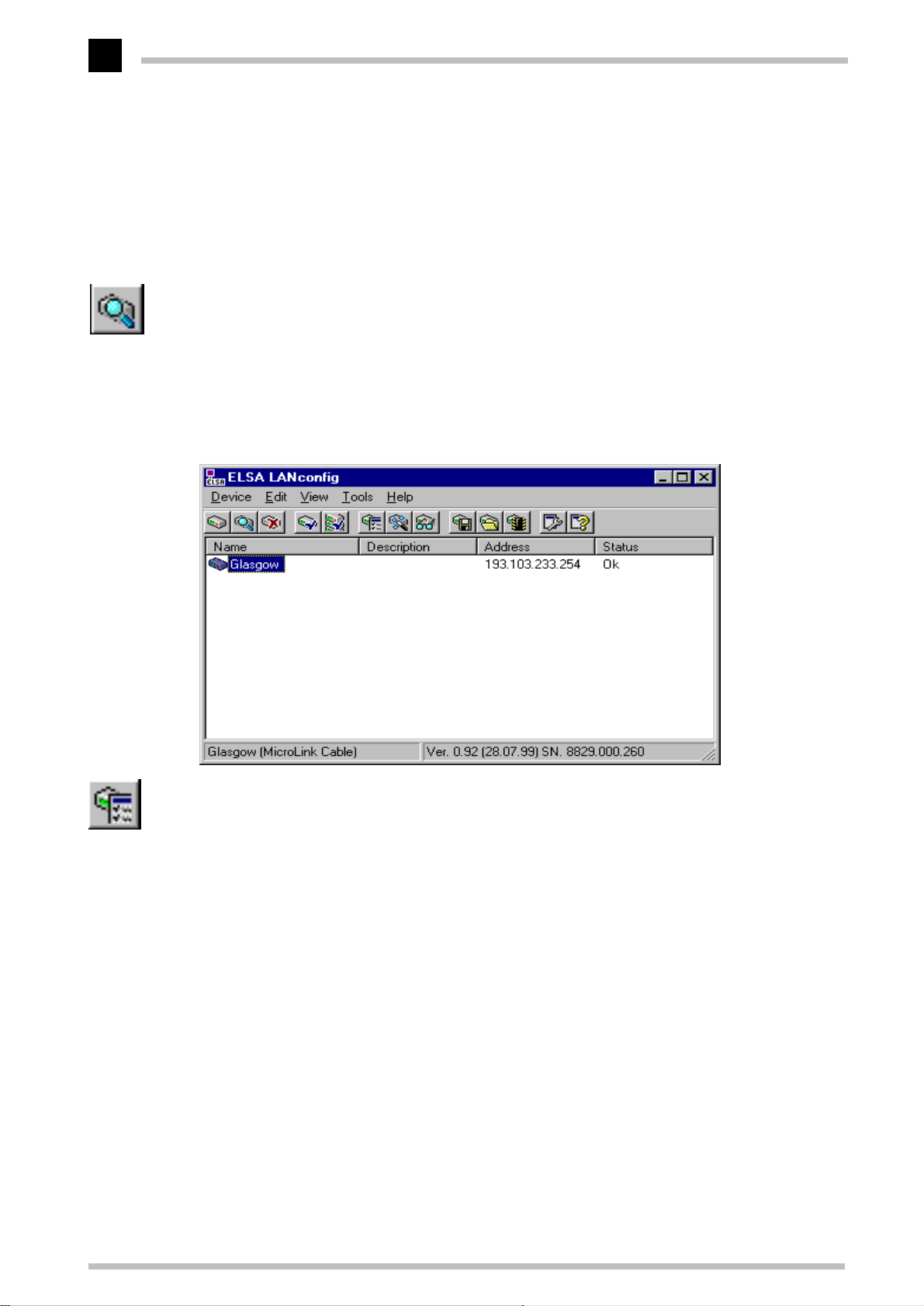
After the installation (double-click on 'autorun.exe') is complete, call up the
LANconfig
ELSA LANconfig
E
network for
Just click on the Find button or call up the command with Device E Find to initiate a
search for a new device manually.
to search. You will only need to specify the local area network if using the inband
solution, and then you're off.
Once
found, together with their names and a description if available, the IP address and its
status.
configuration tool, for example by clicking on Start E Programs E ELSAlan
in the Windows task bar.
ELSA MicroLink Cable
devices.
ELSA LANconfig
ELSA LANconfig
has finished its search, it displays a list of all the devices it has
ELSA LANconfig
ELSA LANconfig
will then prompt you for a location
searches the local area
ELSA
Double-clicking the entry for the highlighted device and then clicking the Configure
button or the Edit E Edit Configuration File option reads the device's current settings
and displays the general device information.
The remainder of the program's operation is essentially self-explanatory or covered in the
online help. You can click on the question mark top right in any window or right-click on
an unclear term at any time to call up context-sensitive help.
Start up inband configuration using telnet
Start inband configuration using telnet with the command from a DOS box:
telnet 10.1.80.125
Telnet will then establish a connection with the device using the IP address.
After the entry of the password (if you specified one to protect the settings) all
commands from the 'Configuration Commands' section are available.
ELSA MicroLink Cable
Configuration modes
19
Configuration commands
Enter commands and path specifications using the normal DOS or UNIX conventions if
you are using telnet or a terminal program to configure the device.
Enter a forward slash or backslash to separate the path specifications. You do not need
to write out commands and table entries in full; an unambiguous abbreviation will do.
The entries for the categories MENU, VALUE, TABLE, TABINFO, ACTION and INFO will
be displayed while configurations are made and may be modified. You can use the
following commands to do this:
This command ... ... means this ... ... for instance:
? or help Calls up help text -
English
dir, list, ll, ls <MENU>,
<VALUE> or <TABLE>
cd <MENU> or <TABLE> Switches to the MENU or TABLE
set <VALUE> This resets the VALUE. set IP-address 192.110.120.140 sets a
set <VALUE> ? Shows you which values can be
del <VALUE> Deletes a table row. del /se/wan/nam/AACHEN
do <ACTION>
(parameters)
passwd Allows a new password to be
Displays the contents of MENU,
VALUE or TABLE
specified
Insert a space between all
entries in table rows. An *
leaves the entry unchanged.
specified here
Executes the ACTION according
to any parameters specified,
specified. The old password, if
there is one, must be entered
first. The new password must
then be entered twice and confirmed each time with y.
dir/status/wan-statistics displays the
current WAN statistics
cd setup/tcp-ip-module (or cd se/tc
for short) switches to the TCP/IP module
new IP address
set /setup/name AACHEN assigns
the name 'AACHEN' to the device.
Deletes the entry for the remote station AACHEN.
do /firmware/firmware-upload starts
the upload of new firmware.
repeat <sec> <ACTION> Repeats the ACTION at an inter-
val of the number of seconds
specified. Any key can be used
to terminate the repetition.
time Sets the system time and date. time 24.12.1998 18:00:00
language <language> Sets the language for the cur-
rent configuration session.
exit, quit, x Configuration is terminated.
repeat 3 dir/status/wan-statistics
displays the current WAN statistics
every 3 seconds
Languages currently supported:
English (language english)
German (language deutsch)
ELSA MicroLink Cable

Configuration modes
20
Text entries with spaces are only accepted if they are placed in quotation marks, e.g.
set/se/snmp/admin "The Administrator"
.
English
Text entries (individual and table values) can be deleted as follows:
set /se/snmp/admin ""
ELSA MicroLink Cable

What's happening on the line?
Configuration modes
21
Trace Outputs
Trace outputs may be used to monitor the internal processes in the cable modem during
or after configuration.
The trace outputs are slightly delayed behind the actual event, but are always in the
correct sequence. This will not usually hamper interpretation of the displays but should
be taken into consideration if making precise analyses.
How to start a trace
The command to call up a trace follows this syntax:
trace [code] [parameters]
The trace command, the code, the parameters and the combination commands are all
separated from each other by spaces. And what is lurking behind the code and
parameters?
This code ... ... in combination with the trace causes the following:
? Displays a help text
+ Switches on a trace output
English
- Switches off a trace output
# Switches between different trace outputs (toggle)
no code Displays the current status of the trace
This parameter ... ... brings up the following display for the trace:
Status Status messages for the connection
Error Error messages for the connection
IP router IP routing
IP-RIP IP Routing Information Protocol
ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol
ARP Address Resolution Protocol
Masquerade Processes in the masquerading module
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
This combination
command
... brings up the following display for the trace:
All All trace outputs
Display Status and error outputs
ELSA MicroLink Cable

Configuration modes
22
English
This combination
command
TCP-IP IP-Rt., IP-RIP, ICMP and ARP outputs
Time Displays the system time in front of the actual trace output
Source Includes a display of the protocol that has initiated the output in front of
... brings up the following display for the trace:
the trace.
Any appended parameters are processed from left to right. This means that it is possible
to call a parameter and then restrict it.
Examples
This code ... ... in combination with the trace causes the following:
trace Displays all protocols that can generate outputs during the configuration,
and the status of each output (ON or OFF)
trace + all Switches on all trace outputs
trace + all - icmp Switches on all trace outputs with the exception of the ICMP protocol
trace - time Switches off the system time output before the actual trace output.
You will find notes on the interpretation of trace outputs in the reference section of this
guide.
New firmware with FirmSafe
The software for the devices of ELSA is constantly being updated. We have fitted the
units with a flash ROM which makes child's play of updating the operating software so
that you can enjoy the benefits of new features and functions. No need to change the
EPROM, no need to open up the case: simply load the new release and you're away.
This is how FirmSafe works
FirmSafe makes the installation of the new software safe: The current firmware is not
simply overwritten but saved additionally in the device as a second firmware.
Only one of the firmware versions stored in the device can be active at any one time.
When new firmware is loaded the inactive firmware is overwritten. You can decide
which firmware version you want to activate after the upload:
K 'Immediate': The first option is to load the new firmware and activate it
immediately. The following situations can result:
– The new firmware is successfully loaded and then operates as desired.
Everything is then in order.
ELSA MicroLink Cable
 Loading...
Loading...