Page 1
Page 2
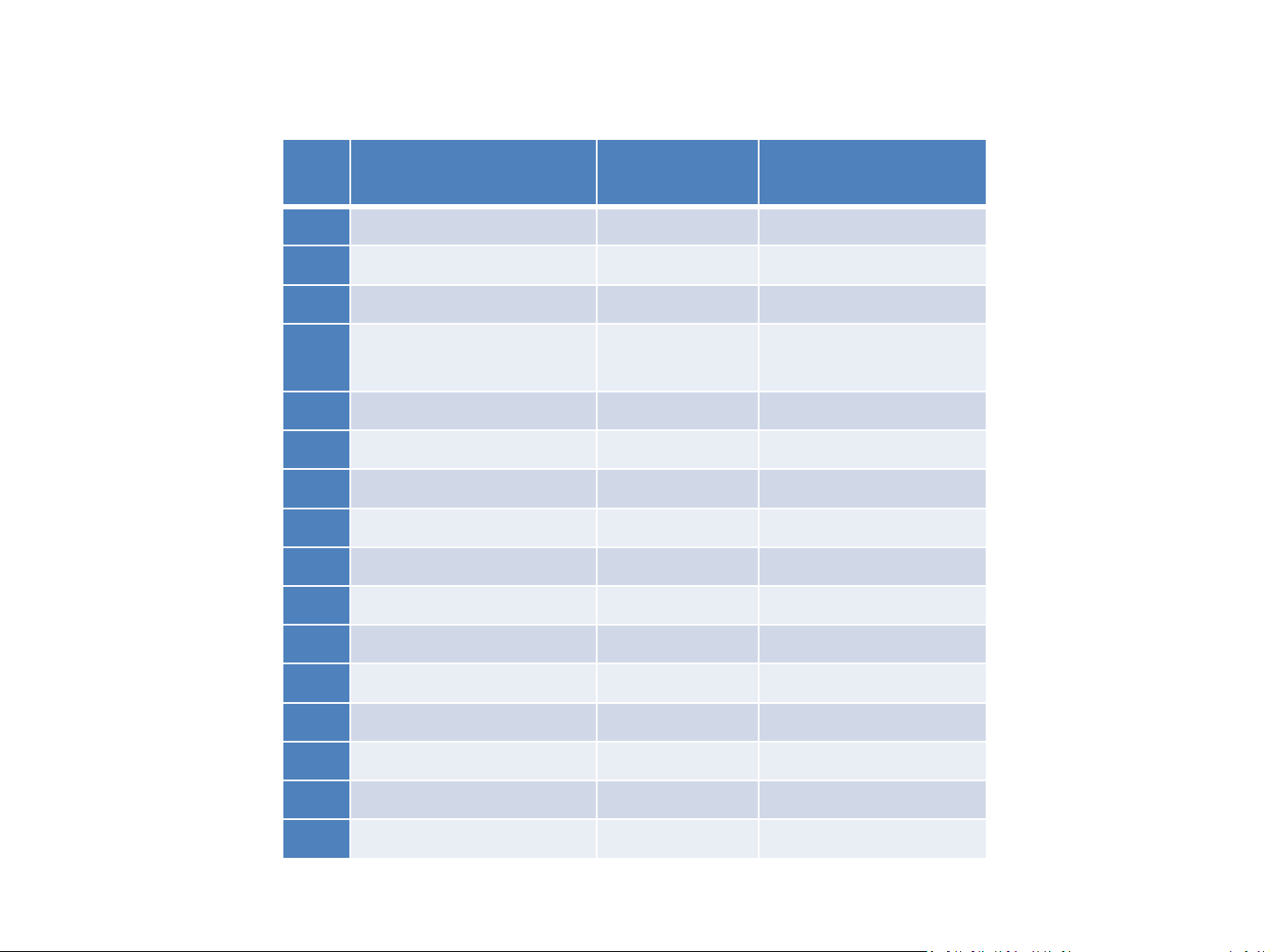
Parts List
Part
ID Part Name
2 2-snap 6SC02 2
3 3-snap 6SC03 1
5 5-snap 6SC05 2
B1
D1 LED red 6SCD1 1
D2 LED green 6SCD2 2
S1 Slide switch 6SCS1 1
U15 Gate 6SCU15 1
U16 Gate 6SCU16 1
Battery holder
(dual AA)
Mini base grid 6SCBGM 1
Jumper wire black 6SCJ1 1
Jumper wire red 6SCJ2 1
Number QTY
6SCB1 1
U17 Gate 6SCU17 1
U18 Gate 6SCU18 1
U19 Gate 6SCU19 1
U20 Gate 6SCU20 1
Page 3
Outline
1. Digital Signals
2. NOT Gate (Inverter)
3. AND Gate
4. OR Gate
5. NAND Gate
6. NOR Gate
7. Exclusive OR Gate
Warning: Shock Hazard – Never connect Snap Circuits® to the electrical outlets in your home in any way!
Warning: Choking Hazard – Small parts. Not for children under 3 years.
Warning: Always check your wiring before turning on a circuit. Never leave a circuit unattended while the batteries are installed. Never connect
additional batteries or other power sources to your circuits. Discard any cracked or broken parts.
Batteries:
• Use only 1.5V AA type, alkaline batteries.
• Insert batteries with correct polarity.
• Do not mix old and new batteries.
• Remove batteries when they are used up.
• Do not short circuit the battery terminals.
• Non-rechargeable batteries should not be recharged.
Rechargeable batteries should only be charged under adult
supervision, and should not be recharged while in the product.
• Do not mix alkaline, standard (carbon-zinc), or rechargeable
(nickel-cadmium) batteries.
• Do not connect batteries or battery holder in parallel.
• Never throw batteries in a fire or
attempt to open its outer casing.
• Batteries are harmful if swallowed,
so keep away from small children.
Page 4
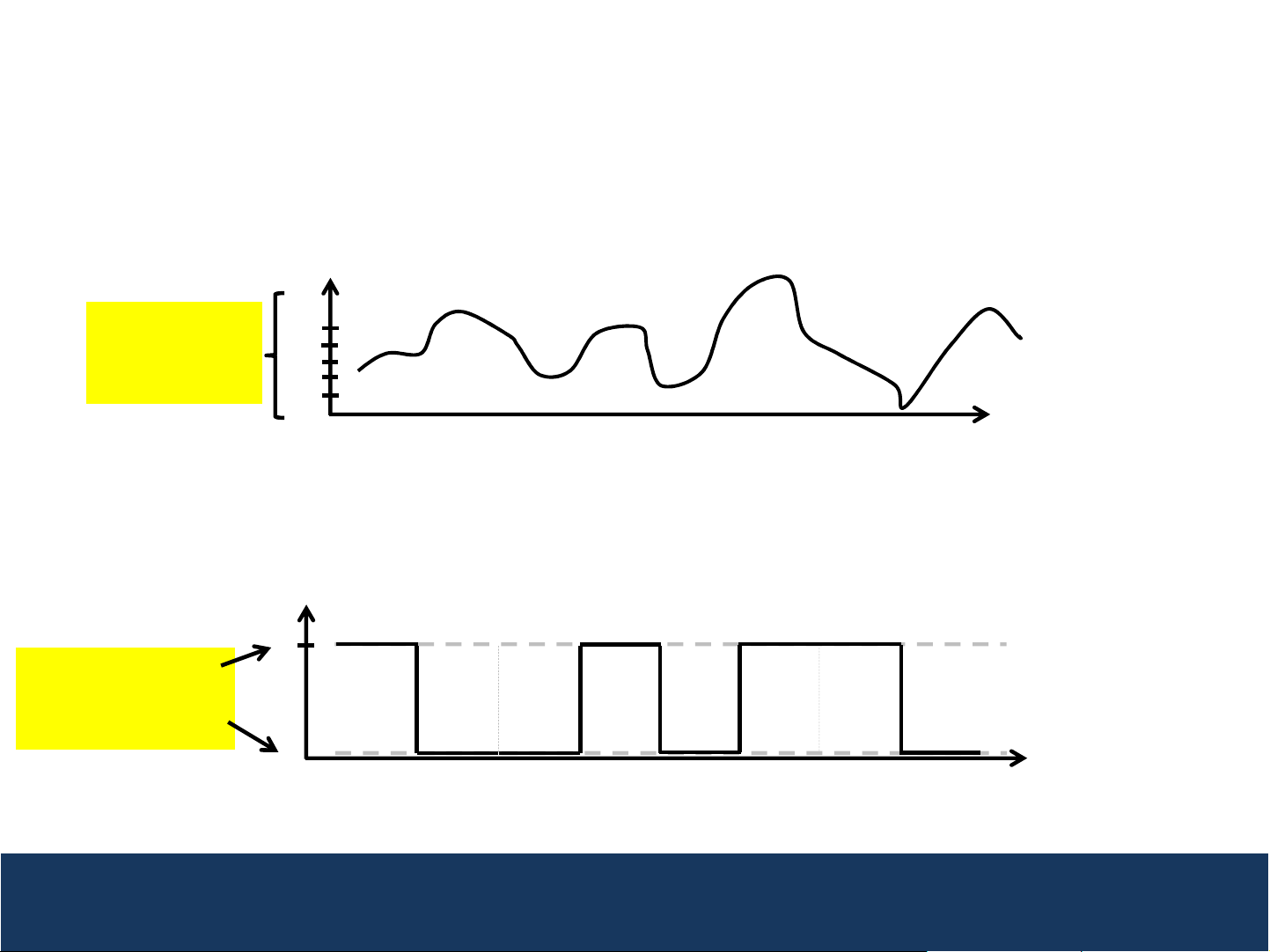
Analog vs. Digital Waveforms
Analog signals can take on a continuum of values while
Analog Waveform – can take on any voltage value
Voltage
Analog Signal
takes on a
Continuum of
Voltage values
5
4
3
2
1
0
Time
Digital Waveform – takes on discrete voltage values
Voltage
5
Example of Digital
Signal taking on two
discrete values
(0 Volts and 5 Volts)
0
Time
digital signals take on only discrete values
Page 5
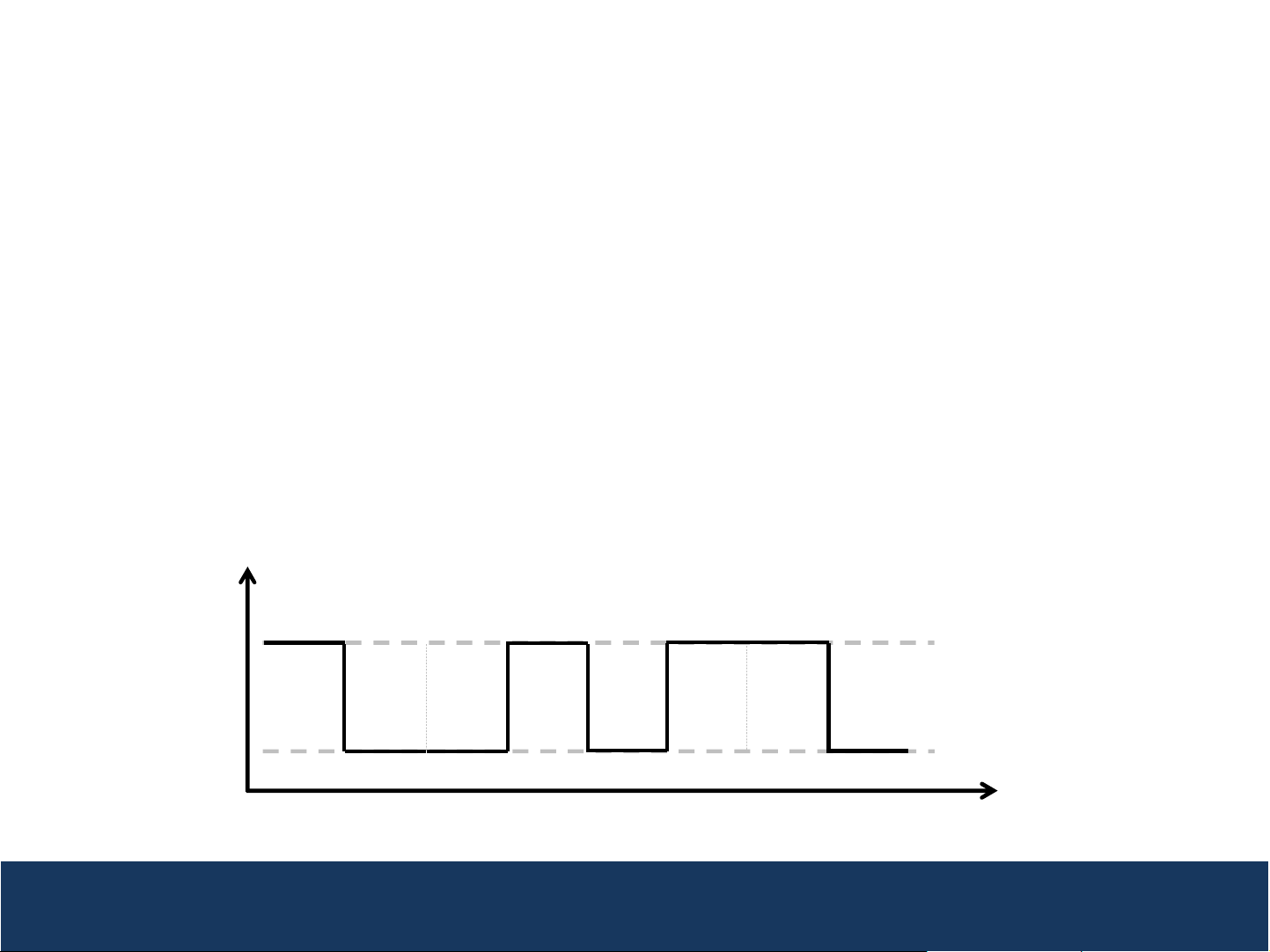
Digital Signals
Digital waveforms can be used to represent digital
signals (e.g. 0 or 1, true or false), for example
• 0 (false) – represented by 0 Volts
• 1 (true) – represented by a small voltage, e.g. 3 Volts
Example of Digital Waveform representing digital
signals
3V
0V
Digital signals are represented by a “high” state (1) or “true” state consisting of a small voltage
(e.g. 3V) and “low” state (0) or “false” state consisting of 0 Volts
True
1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0
False
False
True
False
True
True
False
Time
Page 6

Logic Problem Statements
only if both inputs are true (batteries are not dead AND it’s the top of the hour).
Logic problems have outcomes (or outputs) that depend on events
(or inputs).
For example
• The cuckoo clock makes noise if the batteries are not dead AND it’s the top of
the hour.
• In this example, the output is “the cuckoo clock making noise” and the inputs
are “the batteries are not dead” and “it’s the top of the hour”.
Batteries not dead?
Top of the hour?
• Note that in this example, the output is true (cuckoo clock makes noise) if and
• You will see that this decision box can be represented by digital logic using an
AND gate, with the inputs and output being represented by digital signals.
You can think of digital logic gates as decision boxes that solve logic problems
Decision
Cuckoo clock makes noise?
Box
Page 7

Logic Gates
A digital logic gate is an Integrated Circuit (IC) device that
makes logical decisions based on various combinations of
digital signals presented to it’s inputs.
Digital logic gates can have more than one input signal,
but generally have a single output signal, just like the
decision box on the previous slide.
In the following slides, the input digital signals will be
represented by A and/or B and the output digital signal
will be represented by Q.
Input Digital
The next six slides will demonstrate how the output
Signals
Output Digital
Signal
digital signal is determined by the input digital signals for
various different digital logic gates (NOT gate, AND gate,
A
Digital Logic
OR gate, NAND gate, NOR gate, XOR gate).
B
Gate
Almost all modern electronics such as computers and cellphones use digital logic circuitry
Q
Page 8

NOT Gate (Inverter)
1
2
1
2
1
U15
2
1
2
1
2
2
0
Place parts labeled 1 on the grid
first and parts labeled 2 on second
Note: High electric currents can damage LEDs, so normally resistors
are placed in series with LEDs to protect them. Resistors aren’t
needed with your Snap Circuits® D1 & D2 LEDs, because they
already have internal resistors to protect them from incorrect
wiring. External resistors would be needed with the LEDs if you
were using your logic gates (U15-U20) to control other logic gates
along with the LEDs, because the low resistance of the LED and its
protection resistor could disrupt the operation of the logic gates
being controlled.
This circuit demonstrates how the NOT
Gate (U15) works. Connect one end of
the red jumper wire to the A input on
U15 and the loose end to either low
voltage (denoted as a “0”) or high
voltage (denoted as a “1”). If input A is
low (0, green LED off), then the Q output
on U15 will be high (1), and the red LED
(D1) will be on.
A
Q
The inversion of a state is often
represented with a bar over the
variable, so Q = A.
Input (A) Output (Q)
0 1
1 0
NOT gates are used in digital logic circuits to “invert a voltage level”. A high voltage level (1)
into the NOT gate becomes a low voltage level (0) at the output and vice versa.
Page 9

1
AND Gate
This circuit demonstrates how the AND Gate
(U16) works. Connect one end of the red and
1
2
2
1
U16
2
black jumper wires to the A & B inputs on U16
and the loose ends to either low voltage
(denoted as a “0”) or high voltage (denoted as
a “1”). If, and only if, both input A AND input
B are high (both 1s, both gree LEDs on), then
the Q output on U16 will be high (1), and the
red LED (D1) will be on.
A
Q
B
The output of an AND gate is often
0
1
2
1
2
2
2
represented as the product of the inputs,
so Q = AB.
Input (A) Input (B) Output (Q)
0 0 0
0 1 0
1 0 0
1 1 1
AND gates are used in digital logic circuits to perform a logical multiply. When one of the inputs is low (0),
the output is low (i.e. multiply by 0). The output will only be high (1) when both inputs are high.
Page 10

OR Gate
This circuit demonstrates how the OR Gate
(U17) works. Connect one end of the red
0
and black jumper wires to the A & B
inputs on U17 and the loose ends to either
low voltage (denoted as a “0”) or high
voltage (denoted as a “1”). If either input
A OR input B are high (1, either green LED
is on), then the Q output on U17 will be
1
1
2
2
1
U17
2
high (1), and the red LED (D1) will be on.
1
2
1
2
2
2
The output of an OR gate is often
A
B
represented as the sum of the inputs, so
Q = A+B.
Input (A) Input (B) Output (Q)
Q
0 0 0
0 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 1
OR gates are used in digital logic circuits to perform a logical add. When one of the inputs is high (1), the
output is high. The output will only be low (0) when both inputs are low.
Page 11

NAND Gate
This circuit demonstrates how the NAND Gate
0
1
1
2
(U18) works. Connect one end of the red and
black jumper wires to the A & B inputs on U18
and the loose ends to either low voltage
2
1
U18
2
(denoted as a “0”) or high voltage (denoted as a
“1”). If either input A OR input B are low (0,
either green LED is off), then the Q output on
U18 will be high (1), and the red LED (D1) will be
1
on. The output logic is exactly the opposite of
2
1
2
2
2
the AND gate, hence this gate is called the NOT
AND or NAND Gate
A
Q
B
Input (A) Input (B) Output (Q)
0 0 1
0 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 0
NAND gates are used in digital logic circuits to perform an inverted logical multiply. When one of the
inputs is low (0), the output is high. The output will only be low (0) when both inputs are high.
Page 12

NOR Gate
This circuit demonstrates how the NOR Gate
0
1
1
2
(U19) works. Connect one end of the red and
black jumper wires to the A & B inputs on U19
and the loose ends to either low voltage (denoted
2
U19
1
2
as a “0”) or high voltage (denoted as a “1”). If,
and only if, both input A AND input B are low (0,
both green LEDs are off), then the Q output on
U19 will be high (1), and the red LED (D1) will be
1
2
1
2
2
2
on. The output logic is exactly the opposite of the
OR gate, hence this gate is called the NOT OR or
NOR Gate
A
Q
B
Input (A) Input (B) Output (Q)
0 0 1
0 1 0
1 0 0
1 1 0
NOR gates are used in digital logic circuits to perform an inverted logical add. When one of the inputs is
high (1), the output is low. The output will only be high (1) when both inputs are low.
Page 13

Exclusive OR (XOR) Gate
0
1
1
2
OR (XOR) Gate (U20) works. Connect one
end of the red and black jumper wires to the
This circuit demonstrates how the Exclusive
2
1
U20
2
A & B inputs on U20 and the loose ends to
either low voltage (denoted as a “0”) or high
voltage (denoted as a “1”). If input A and
input B are exclusive (i.e. different, one
1
2
1
2
2
2
green LED is on and the other green LED is
off), then the Y output on U20 will be high
(1), and the red LED (D1) will be on.
A
B
Input (A) Input (B) Output (Q)
Q
0 0 0
0 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 0
XOR gates are used in digital logic circuits to perform a comparison. When the inputs are mutually exclusive
(i.e. different), then the output is high (1). When the inputs are the same, then the output is low (0).
Page 14

Quiz
1. The output will be LOW (0) for any case when one or more input is LOW (0) for a(n):
a) OR gate
b) NAND gate
c) AND gate
d) XOR gate
2. The output of a NOR gate is HIGH (1) if:
a) All inputs are HIGH (1)
b) Any input is HIGH (1)
c) Any Input is LOW (0)
d) All inputs are LOW (0)
3. Which of the following is true about a 2-input NAND gate:
a) If one of the inputs is HIGH (1), then the output is always the same as the opposite of the other input
b) There are 8 possible input combinations
c) The output is LOW (1) if any input is HIGH (1)
d) If one of the inputs is LOW (0), then the output is always the same as the other input
Page 15

Quiz Answers
1. The output will be LOW (0) for any case when one or more input is LOW (0) for a(n):
a) OR gate
b) NAND gate
c) AND gate
d) XOR gate
2. The output of a NOR gate is HIGH (1) if:
a) All inputs are HIGH (1)
b) Any input is HIGH (1)
c) Any Input is LOW (0)
d) All inputs are LOW (0)
3. Which of the following is true about a 2-input NAND gate:
a) If one of the inputs is HIGH (1), then the output is always the opposite of the other input
b) There are 8 possible input combinations
c) The output is LOW (1) if any input is HIGH (1)
d) If one of the inputs is LOW (0), then the output is always the same as the other input
Page 16

®
ELENCO
150 Carpenter Avenue
Wheeling, IL 60090
(847) 541-3800
Website: www.elenco.com
e-mail: elenco@elenco.com
 Loading...
Loading...