Page 1

www.eaglesonar.com
Pub. 988-0156-031
Fish-Finding & Depth-Sounding Sonars
Installation and Operation
Instructions
Page 2

Copyright © 2004 LEI-Eagle
All rights reserved.
®
FishMark
Eagle
®
is a registered trademark of LEI
and SeaFinder® are registered trademarks of LEI
Eagle Electronics may find it necessary to change or end our policies,
regulations, and special offers at any time. We reserve the right to do so
without notice. All features and specifications subject to change without
notice. All screens in this manual are simulated. On the cover:
SeaFinder
®
500CDF shown. Other models covered in the manual are
similar.
No part of this manual may be copied, reproduced, republished,
transmitted or distributed for any purpose, without prior written
consent of Eagle Electronics. Any unauthorized commercial
distribution of this manual is strictly prohibited.
For free owner's manuals and the most current information on
this product, its operation and accessories,
visit our web site:
www.eaglesonar.com
Eagle Electronics
P.O. Box 669
Catoosa, OK USA 74015
Printed in USA.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Section 1: Read Me First!................................................................1
Capabilities and Specifications ...........................................................2
How Sonar Works ................................................................................4
How to Use this Manual: Typographical Conventions.......................5
Section 2: Installation & Accessories...........................................7
Preparations.........................................................................................7
Transducer Installation.......................................................................7
Recommended Tools and Supplies ..................................................8
Selecting a Transducer Location.....................................................9
How low should you go?.................................................................10
Shoot-Thru-Hull vs. Transom Mounting ......................................11
Transom Transducer Assembly and Mounting ............................12
Trolling Motor Bracket Installation (single-frequency only) .......19
Transducer Orientation and Fish Arches .....................................20
Shoot-Thru-Hull Preparation........................................................22
Testing Determines Best Location................................................23
Shoot-Thru-Hull Installation ........................................................24
Speed/Temperature Sensors..............................................................26
Optional Speed Sensor Installation ..................................................27
Power Connections.............................................................................29
Mounting the Unit: Bracket, In-Dash or Portable ...........................31
Face Cover..........................................................................................35
Basic Sonar Operation ..................................................................37
Keyboard ............................................................................................37
Power/lights on and off ......................................................................38
Main Menu .........................................................................................39
Pages ..................................................................................................40
Basic Sonar Quick Reference ............................................................45
Sonar Operations ...............................................................................46
Fish Symbols vs. Full Sonar Chart ...............................................50
Other Free Training Aids ..............................................................50
Section 4: Sonar Options & Other Features.............................53
i
Page 4

ASP (Advanced Signal Processing)................................................53
Alarms ................................................................................................54
Depth Alarms .................................................................................55
Zone Alarm .....................................................................................56
Fish Alarm......................................................................................57
Backlight Level ..................................................................................58
Calibrate Speed..................................................................................59
Chart Speed........................................................................................60
ColorLine.........................................................................................61
ColorLine level: ..............................................................................61
Contrast..............................................................................................63
Depth Cursor......................................................................................63
Depth Range - Automatic ..................................................................64
Depth Range - Manual ......................................................................64
FasTrack .........................................................................................65
Fish I.D. (Fish Symbols & Depths) ................................................66
FishTrack ........................................................................................67
Frequency (Change Transducer Frequency) (SeaFinder CDF
only) ....................................................................................................68
To change the frequency setting to 50 kHz: .................................69
To change the frequency setting to 200 kHz: ...............................70
HyperScroll .....................................................................................70
Noise Rejection...................................................................................70
Overlay Data ......................................................................................70
Ping Speed & HyperScroll..............................................................73
To change Ping Speed: ...................................................................75
To adjust Sensitivity:.....................................................................75
To turn off HyperScroll:.................................................................75
Pop-up Help........................................................................................75
Reset Options .....................................................................................76
Reset Water Distance ........................................................................77
Set Keel Offset ...................................................................................77
Sensitivity & Auto Sensitivity...........................................................79
Automatic Sensitivity ....................................................................79
ii
Page 5

To turn Auto Sensitivity back on: .................................................81
Set Language .....................................................................................81
Software Version Information...........................................................81
Sonar Chart Mode..............................................................................82
Sonar Page & Sonar Chart Display Options ....................................82
Full Sonar Chart ............................................................................83
Split Zoom Sonar Chart.................................................................84
Digital Data/Chart .........................................................................84
Sonar Simulator.................................................................................86
Stop Chart ..........................................................................................87
Surface Clarity...................................................................................88
Transparency .....................................................................................90
Units of Measure................................................................................90
Zoom & Zoom Bar ..............................................................................91
Zoom Pan............................................................................................92
Section 5: Troubleshooting ..........................................................93
Section 6: Supplemental Material ..............................................97
iii
Page 6

Notes
iv
Page 7

Section 1: Read Me First!
How this manual can get you out on the water, fast!
Welcome to the exciting world of digital sonar! We know you're anxious
to begin finding fish, but we have a favor to ask. Before you grab your
unit and begin installing it, please give us a moment or two to explain
how our manual can help you get the best performance from your compact, wide-screen, fish finder.
First, we want to thank you for buying an Eagle sonar. Whether you're
a first time user or a professional fisherman, you'll discover that your
unit is easy to use, yet capable of handling demanding sonar tasks. You
won't find another sonar unit with this much power and this many features for this price!
Our goal for this book is to get you on the water fast, with a minimum
of fuss. Like you, we'd rather spend more time boating or fishing and
less time reading the manual!
So, we designed our book so that you don't have to read the whole thing
from front to back for the information you want. At the start (or end) of
each segment, we'll tell you what content is coming up next. If it's a
concept you're already familiar with, we'll show you how and where to
skip ahead for the next important topic. We've also made it easy to look
up any tips you may need from time to time. Here's how:
The manual is organized into 6 sections. This first section is an introduction to the sonar unit. It tells you the basics you need to know before
you can make the unit look below the surface to find some fish.
Section 2 will help you install your unit and the transducer. We'll also
tell you about some of the available accessories.
Section 3 covers Basic Sonar Operation. It will show you how easy it is
to run your sonar, right out of the box. This section features a one-page
Sonar Quick Reference. (If you've already jumped ahead and fig-
ured out how to install the unit yourself, and you just can't wait
1
Page 8

any longer, turn to the Quick Reference on page 45 and head
for the water with your sonar unit!)
After you've gained some experience with your sonar, you'll want to
check out Section 4, which discusses more advanced Sonar Options and
Other Features.
When you come to a sonar menu command on the unit's screen, you can
look it up in the manual by skimming over the table of contents, just flipping through Section 3 or scanning through the sonar options in Section 4.
If you're having difficulty with your sonar, you can find an answer to
the most common problems in Section 5, Sonar Troubleshooting.
Finally, in Section 6, we offer Supplemental Material, including a list of
warranty and customer service information.
Now, if you're into the fine details, glance over the next segment on specifications to see just how much sonar power your unit contains. It's important to us (and our power users), but, if you don't care how many watts of
power the unit has, skip ahead to important information on how sonar
works, on page 4.
Capabilities and Specifications: FishMark® 500C,
SeaFinder® 500CDF
General
Display:............................ 5.0" (12.7 cm) diagonal color TFT LCD; pro-
grammable to viewing preference.
Resolution:...................... 320 pixel x 240 pixel resolution; 76,800 total
pixels.
Backlighting:.................. Backlit screen and keypad with multiple
lighting levels for night use.
Input power:................... 10 to 15 volts DC.
Case size:......................... 5.4" H x 6.9" W x 3.4" D (13.8 x 17.6 x 8.6
cm); sealed and waterproof; suitable for
saltwater use.
2
Page 9

Back-up memory: .......... Built-in memory stores sonar records for
decades.
Languages:...................... 10; menu languages selectable by user.
Sonar
Frequency:...................... 50/200 kHz for SeaFinder 500CDF; 200 kHz
for FishMark 500C.
Transducers: .................. A dual-frequency Skimmer
transducer with
built-in temperature sensor is packed with
the SeaFinder 500CDF. It has 35°/12° cone
angles. A single-frequency Skimmer transducer with built-in temperature sensor is
packed with the FishMark 500C. It has a 20°
cone angle. Transducers operate at speeds up
to 70 mph (61 kts)
Watts: ............................... 1,500 watts peak-to-peak/188 watt RMS.
Sonar sounding
depth capability: ........... SeaFinder 500CDF: 1,500 feet (450 me-
ters). FishMark 500C: 800 feet (244 meters).
Actual capability depends on transducer configuration and installation, bottom composition and water conditions. All sonar units
typically read deeper in fresh water than in
salt water.
Depth display:................ Continuous display .
Audible alarms: ............. Deep/shallow/fish/zone.
Automatic ranging:....... Yes, with instant screen updates.
Auto bottom track:........ Yes.
Zoom bottom track: ...... Yes.
Split-screen zoom:......... Yes.
3
Page 10

Surface water temp: ..... Yes.
Speed/distance log: ....... Optional (requires optional speed sensor).
NOTICE!
The storage temperature range for your unit is from -4 degrees to +167
degrees Fahrenheit (-20 degrees to +75 degrees Celsius). Extended stor-
age in temperatures higher or lower than specified will damage the liquid crystal display in your unit. This type of damage is not covered by
the warranty. For more information, contact the factory's Customer
Service Department; phone numbers are listed on the last page.
How Sonar Works
Sonar has been around since the 1940s, so if you already know how it
works, skip ahead to the next segment on the typographical conventions
used in this manual. But, if you've never owned a sonar fish finder, this
segment will tell you the under water basics.
Sonar is an abbreviation for SOund NA
nology developed during World War II for tracking enemy submarines.
A sonar consists of a transmitter, transducer, receiver and display. In
simple terms, here's how it finds the bottom, or the fish:
The transmitter emits an electrical impulse, which the transducer converts into a sound wave and sends into the water. (The sound frequency
can't be heard by humans or fish.) The sound wave strikes an object
(fish, structure, bottom) and bounces back to the transducer, which
converts the sound back into an electrical signal.
The receiver amplifies this return signal, or echo, and sends it to the
display, where an image of the object appears on the scrolling sonar
chart. The sonar's microprocessor calculates the time lapse between the
transmitted signal and echo return to determine the distance to the
object. The whole process repeats itself several times each second.
vigation and Ranging, a tech-
4
Page 11

How to Use this Manual: Typographical Conventions
Many instructions are listed as numbered steps. The keypad and arrow
"keystrokes" appear as boldface type. So, if you're in a real hurry (or
just need a reminder), you can skim the instructions and pick out what
menu command to use by finding the boldface command text. The following paragraphs explain how to interpret the text formatting for
those commands and other instructions:
Arrow Keys
The arrow keys control a horizontal line depth cursor on the sonar
screen. The arrow keys also help you move around the menus so you
can execute different commands. They are represented by symbols like
these, which denote the down arrow key, the up arrow, the left arrow
and the right arrow: ↓ ↑ ← →.
Keyboard
The other keys perform a variety of functions. When the text refers to a
key to press, the key is shown in bold, sans serif type. For example, the
"Enter/Icons" key is shown as
Menu Commands
A menu command or a menu option will appear in small capital letters,
in a bold sans serif type like this:
are to select this command or option from a menu or take an action of
some kind with the menu item. Text that you may need to enter or file
names you need to select are show in italic type, such as data type.
Instructions = Menu Sequences
Most functions you perform with the sonar unit are described as a sequence of key strokes and selecting menu commands. We've written
them in a condensed manner for quick and easy reading.
ENT and the "Menu" key is shown as MENU.
DEPTH CURSOR. These indicate that you
5
Page 12

For example, instructions for turning on the Fish ID feature would
look like this:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
2. Press → or → ↓ to
FISH ID SYMBOLS|ENT|EXIT|EXIT.
MENU|↓ to SONAR FEATURES|ENT.
Translated into complete English, step 1 above would mean: "Start on
the Sonar Page. Press the Menu key then repeatedly press (or press and
hold) the down arrow key to scroll down the menu and select (highlight)
the Sonar Features menu command. Then press the Enter key."
Step 2 would mean: "Press the right arrow key (for dual-frequency
units) or press the right arrow key followed by the down arrow key (for
single-frequency units) to select (highlight) the Fish ID symbols command. Next, press the Enter key, then press the Exit key twice."
6
Page 13

Section 2: Installation & Accessories
Preparations
You can install the sonar system in some other order if you prefer, but
we recommend this installation sequence:
Caution:
You should read over this entire installation section before drilling any holes in your vessel!
1. Determine the approximate location for the sonar unit, so you can
plan how and where to route the cables for the transducer and power.
This will help you make sure you have enough cable length for the desired configuration.
2. Determine the approximate location for the transducer and its cable
route.
3. Determine the location of your battery or other power connection,
along with the power cable route.
4. Install the transducer and route the transducer cable to the sonar
unit.
5. Route the power cable from the unit's location to an appropriate
power source and connect it there.
6. Connect the transducer/power cable to the unit and mount the sonar
unit on the bracket.
Transducer Installation
These instructions will help you install your Skimmer
transom, on a trolling motor or inside a hull. These instructions cover
both single- and dual-frequency Skimmer transducers. Please read all
instructions before proceeding with any installation.
Your Skimmer transducer typically comes packaged with a one-piece
stainless steel bracket for mounting it to the transom of your boat. The
7
transducer on a
Page 14

optional trolling motor mount uses a one-piece plastic bracket with an
adjustable strap. These are "kick-up" mounting brackets. They help
prevent damage if the transducer strikes an object while the boat is
moving. If the transducer does "kick-up," the bracket can easily be
pushed back into place without tools.
Read these instructions carefully before attempting the installation.
Determine which of the installation methods is right for your boat.
Remember, the transducer location and installation is the most
critical part of a sonar installation.
Recommended Tools and Supplies
If you prefer the option of routing the cable through the transom, you
will need a 5/8" drill bit. (If you intend to install an additional speed or
temp sensor and route its cable through the same hole in the transom,
you will need a 1" (25.4 mm) drill bit to accommodate all the cables.)
NOTE:
The following installation types also call for these recommended
tools and required supplies that you must provide (supplies listed
here are not included):
Single-frequency transom installations
Tools include: two adjustable wrenches, drill, #29 (0.136") drill bit, flathead screwdriver. Supplies: none.
Dual-frequency transom installations
Tools: two adjustable wrenches, drill, #20 (0.161") drill bit, flat-head
screwdriver. Supplies: four, 1" long, #12 stainless steel slotted wood
screws.
Single-frequency trolling motor installations
Tools: two adjustable wrenches, flat-head screwdriver. Supplies: plastic
cable ties.
Shoot-through hull installations
Tools: these will vary depending on your hull's composition. Consult
your boat dealer or manufacturer. Other tools are a wooden craft stick
8
Page 15
or similar tool for stirring and applying epoxy, and a paper plate or
Deadrise less than 10
piece of cardboard to mix the epoxy on. Supplies: rubbing alcohol, 100
grit sandpaper, specially formulated epoxy adhesive available from LEI
(see ordering information on the inside portion of the back cover). A
sandwich hull also requires polyester resin.
Selecting a Transducer Location
1. The location must be in the water at all times, at all operating speeds.
2. The transducer must be placed in a location that has a smooth flow of
water at all times. If the transducer is not placed in a smooth flow of
water, interference caused by bubbles and turbulence will show on the
sonar's display in the form of random lines or dots whenever the boat is
moving.
NOTE:
Some aluminum boats with strakes or ribs on the outside of the
hull create large amounts of turbulence at high speed. These boats
typically have large outboard motors capable of propelling the boat
at speeds faster than 35 mph. Typically, a good transom location on
aluminum boats is between the ribs closest to the engine.
3. The transducer should be installed with its face pointing straight
down, if possible. For shoot-thru applications: Many popular fishing
boat hulls have a flat keel pad that offers a good mounting surface. On
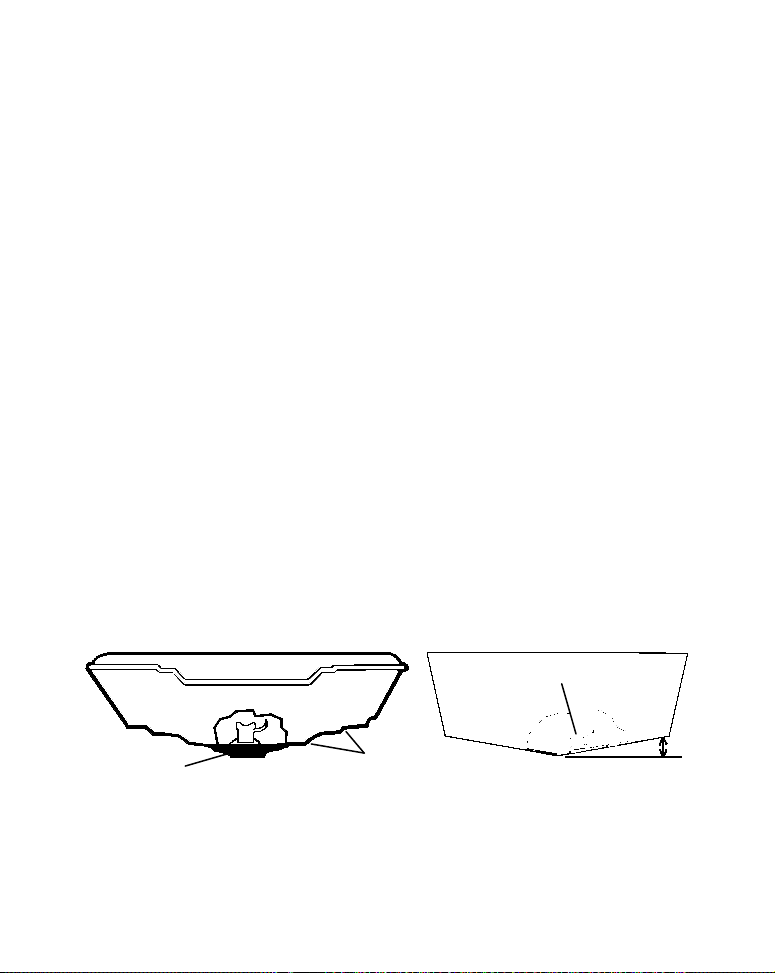
vee hulls, try to place the transducer where the deadrise is 10° or less.
°
Pad
Left, vee pad hull; right, vee hull. A pod style transducer is shown here,
but the principle is the same for Skimmers inside a hull.
Strakes
4. If the transducer is mounted on the transom, make sure it doesn't interfere with the trailer or hauling of the boat. Also, don't mount it
9
Page 16
closer than approximately one foot from the engine's lower unit. This
prevent the transducer from
location
will prevent cavitation (bubble) interference with propeller operation.
5. If possible, route the transducer cable away from other wiring on the
boat. Electrical noise from engine wiring, bilge pumps and aerators can
be displayed on the sonar's screen. Use caution when routing the transducer cable around these wires.
CAUTION: Clamp the transducer cable to transom near
the transducer. This will help
entering the boat if it is
knocked off at high speed.
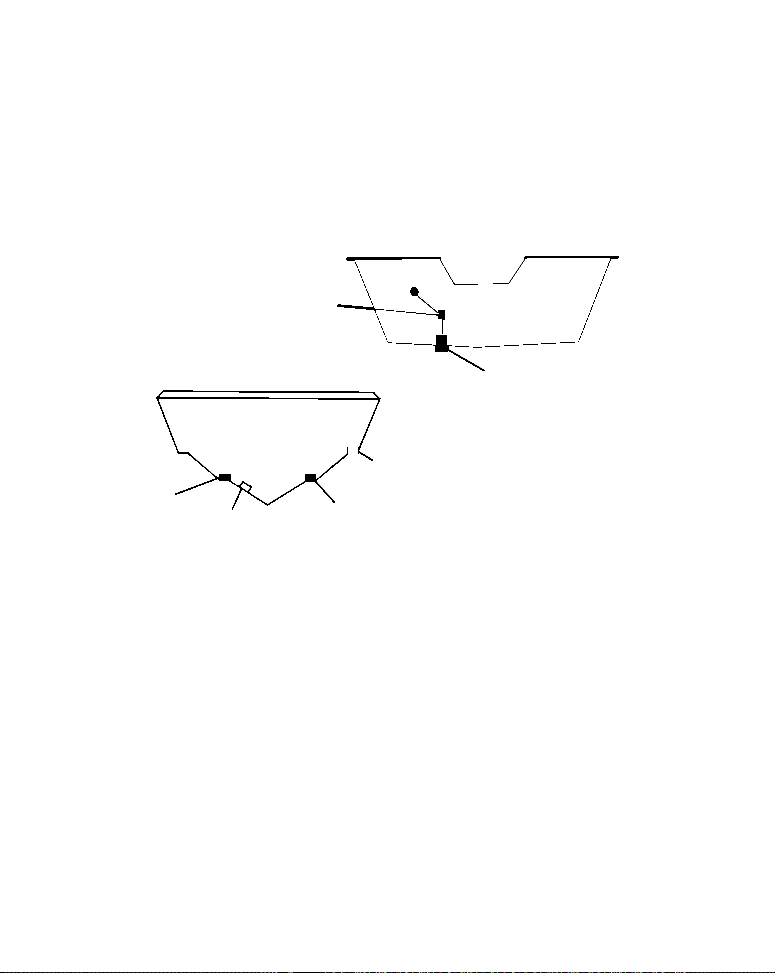
Poor location
Good
Good location
Poor angle
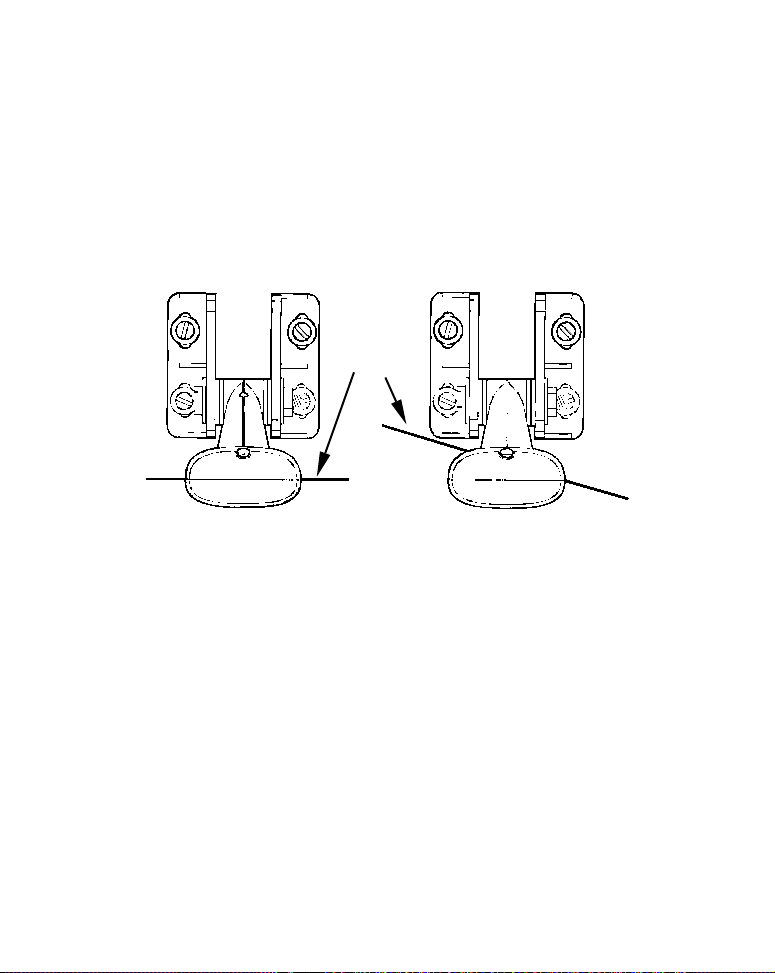
Good and poor transducer locations.
Good location
How low should you go?
For most situations, you should install your Skimmer transducer so
that its centerline is level with the bottom of the boat hull. This will
usually give you the best combination of smooth water flow and protection from bangs and bumps.
10
Page 17
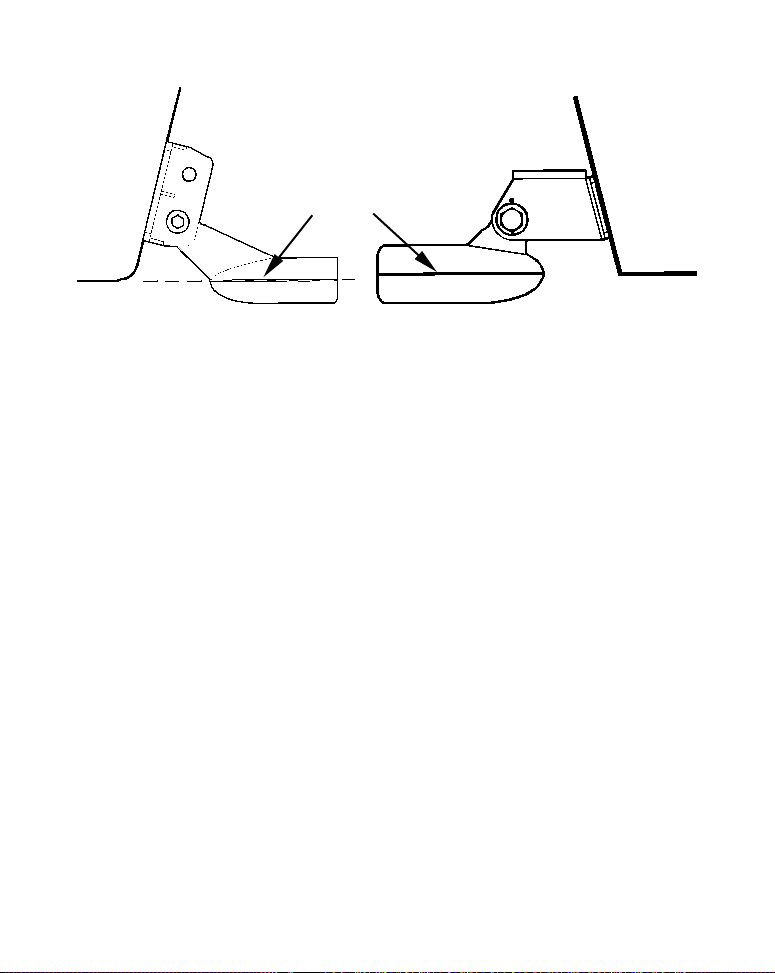
Transom
Transom
Transducer
centerline
Hull bottom
Align transducer centerline with hull bottom. A dual frequency trans-
ducer is shown at left and a single frequency transducer at right.
Hull bottom
However, there are times when you may need to adjust the transducer
slightly higher or lower. (The slots in the mounting brackets allow you
to loosen the screws and slide the transducer up or down.) If you frequently lose bottom signal lock while running at high speed, the transducer may be coming out of the water as you cross waves or wakes.
Move the transducer a little lower to help prevent this.
If you cruise or fish around lots of structure and cover, your transducer
may be frequently kicking up from object strikes. If you wish, you may
move the transducer a little higher for more protection.
There are two extremes you should avoid. Never let the edge of the
mounting bracket extend below the bottom of the hull. Never let the
bottom – the face – of the transducer rise above the bottom of the hull.
Shoot-Thru-Hull vs. Transom Mounting
In a shoot-thru-hull installation, the transducer is bonded to the inside
of the hull with epoxy. The sonar "ping" signal actually passes through
the hull and into the water. This differs from a bolt-thru-hull installation (often called simply "thru-hull"). In that case, a hole is cut in the
hull and a specially designed transducer is mounted through the hull
with a threaded shaft and nut. This puts the transducer in direct contact with the water.
11
Page 18

Typically, shoot-thru-hull installations give excellent high speed operation and good to excellent depth capability. There is no possibility of
transducer damage from floating objects, as there is with a transommounted transducer. A transducer mounted inside the hull can't be
knocked off when docking or loading on a trailer.
However, the shoot-thru-hull installation does have its drawbacks.
First, some loss of sensitivity does occur, even on the best hulls. This
varies from hull to hull, even from different installations on the same
hull. This is caused by differences in hull lay-up and construction.
Second, the transducer angle cannot be adjusted for the best fish arches
on your sonar display.
Lack of angle adjustment can be particularly troublesome on hulls that
sit with the bow high when at rest or at slow trolling speeds.
Third, a transducer CAN NOT shoot through wood and metal hulls.
Those hulls require either a transom mount or a thru-hull installation.
Fourth, if your Skimmer transducer has a built in temp sensor, it will
only show the temperature of the bilge, not the water surface temp.
Follow the testing procedures listed in the shoot-thru-hull installation
section at the end of this instruction booklet to determine if you can
satisfactorily shoot through the hull.
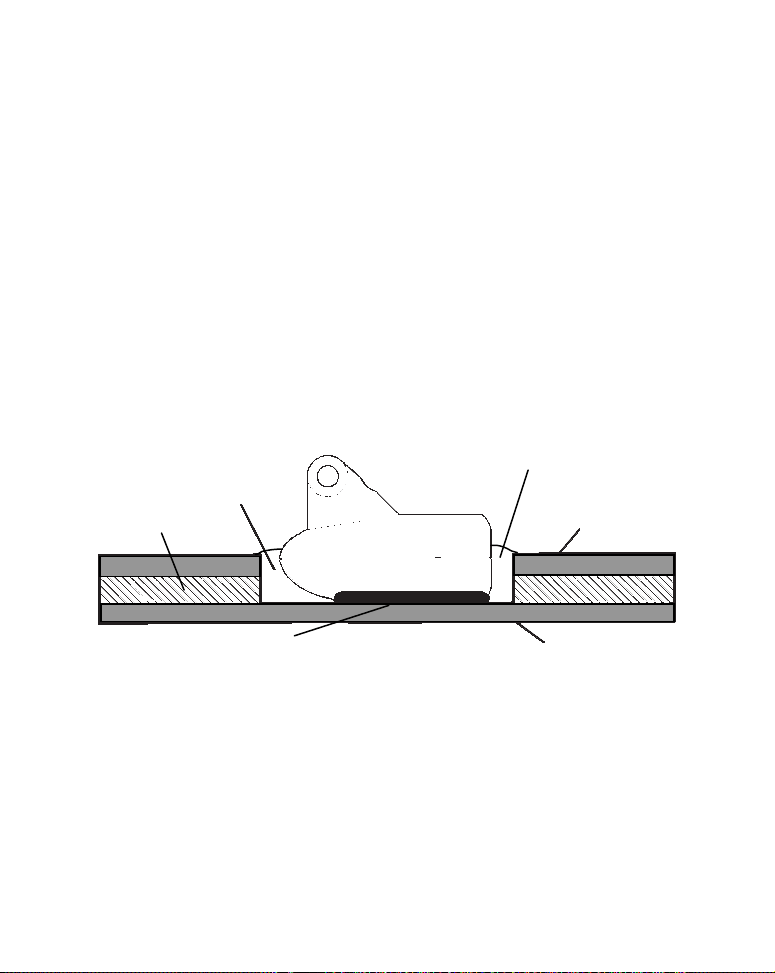
Transom Transducer Assembly and Mounting
The best way to install these transducers is to loosely assemble all of
the parts first, place the transducer's bracket against the transom and
see if you can move the transducer so that it's parallel with the ground.
The following instructions sometimes vary depending on the mounting
bracket that came with your transducer. Single frequency Skimmers
come with a one-piece stainless steel bracket, while dual frequency
Skimmers come with a two-piece plastic mounting bracket. Use the set
of instructions that fits your model.
12
Page 19
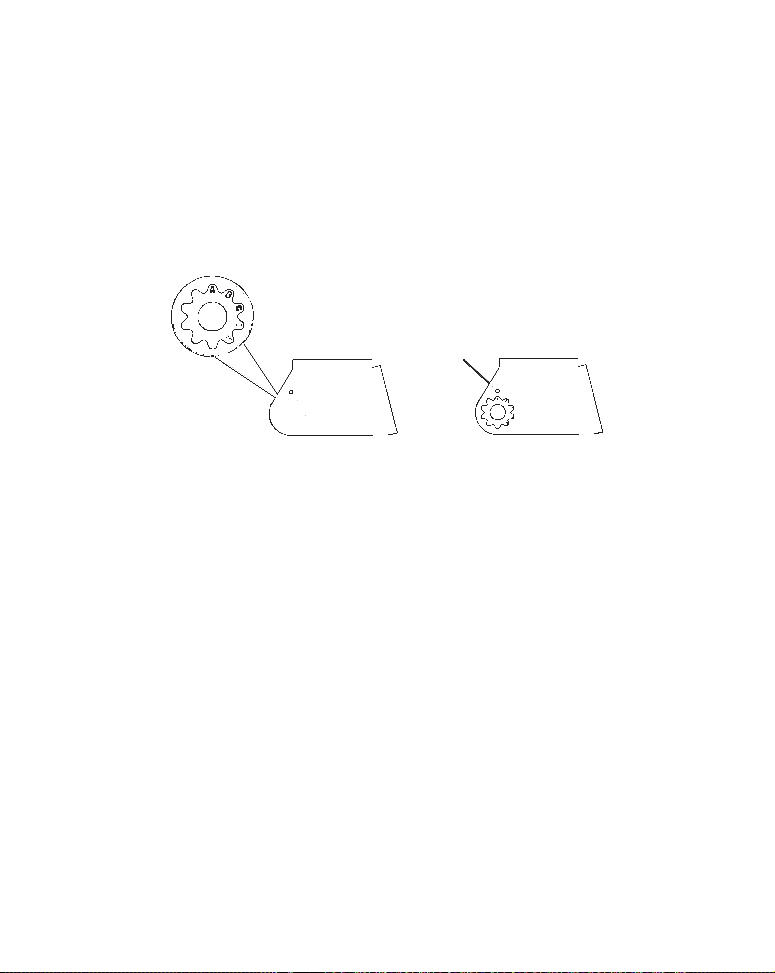
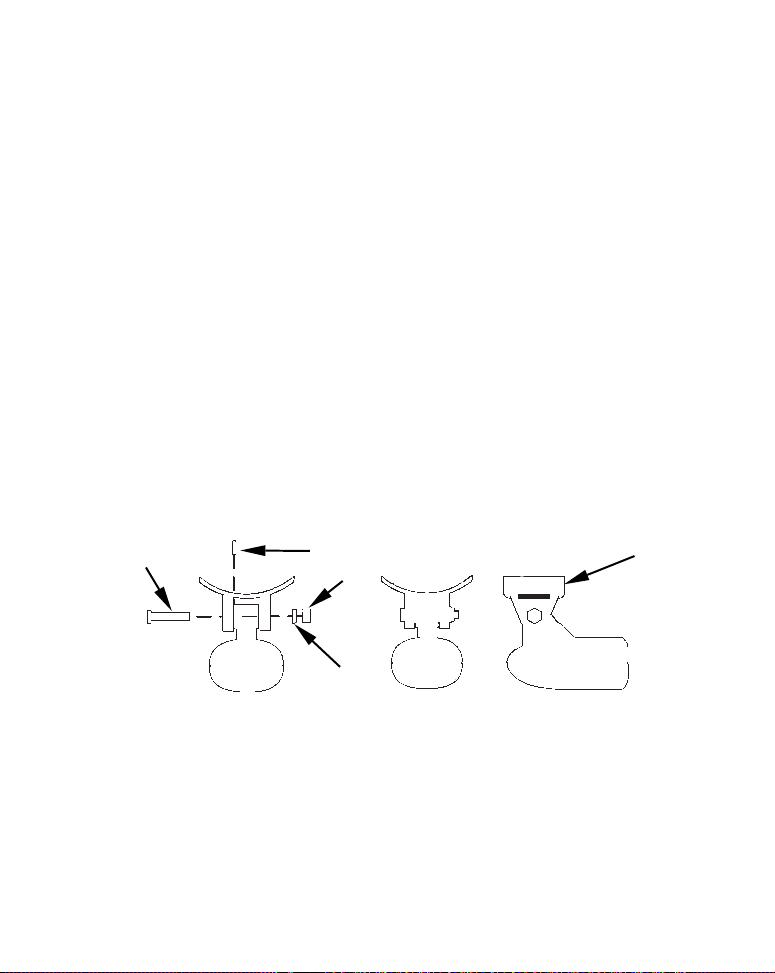
1. Assembling the bracket.
A. One-piece bracket: Press the two small plastic ratchets into the sides
of the metal bracket as shown in the following illustration. Notice there are
letters molded into each ratchet. Place each ratchet into the bracket with
the letter "A" aligned with the dot stamped into the metal bracket. This position sets the transducer's coarse angle adjustment for a 14° transom. Most
outboard and stern-drive transoms have a 14° angle.
Dot
Align plastic ratchets in bracket.
B. Two-piece bracket: Locate the four plastic ratchets in the transducer's hardware package. Press two ratchets into the sides of the plastic
bracket and two on either side of the transducer as shown in the following illustrations. Notice there are letters molded into each ratchet. Place
the ratchets into the bracket with the letter "A" aligned with the alignment mark molded into the bracket. Place the ratchets onto the transducer with the letter "A" aligned with the 12 o'clock position on the
transducer stem. These positions set the transducer's coarse angle adjustment for a 14° transom. Most outboard and stern-drive transoms
have a 14° angle.
13
Page 20
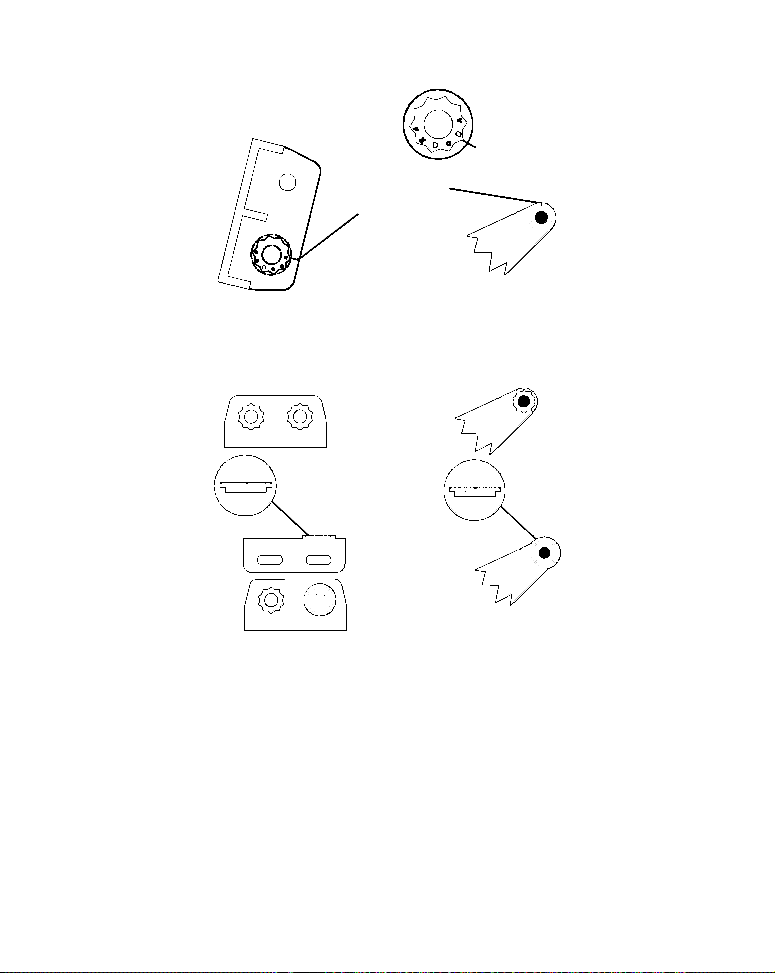
Alignment
ducer
positions
Alignment letters
Trans
bracket
Insert and align ratchets.
Transducer bracket
Ratchet
Add ratchets to bracket and transducer.
Transducer
Transducer
Ratchet
2. Aligning the transducer on the transom.
A. One-piece bracket: Slide the transducer between the two ratch-
ets. Temporarily slide the bolt though the transducer assembly and
hold it against the transom. Looking at the transducer from the side,
check to see if it will adjust so that its face is parallel to the ground.
If it does, then the "A" position is correct for your hull.
If the transducer's face isn't parallel with the ground, remove the
transducer and ratchets from the bracket. Place the ratchets into the
14
Page 21
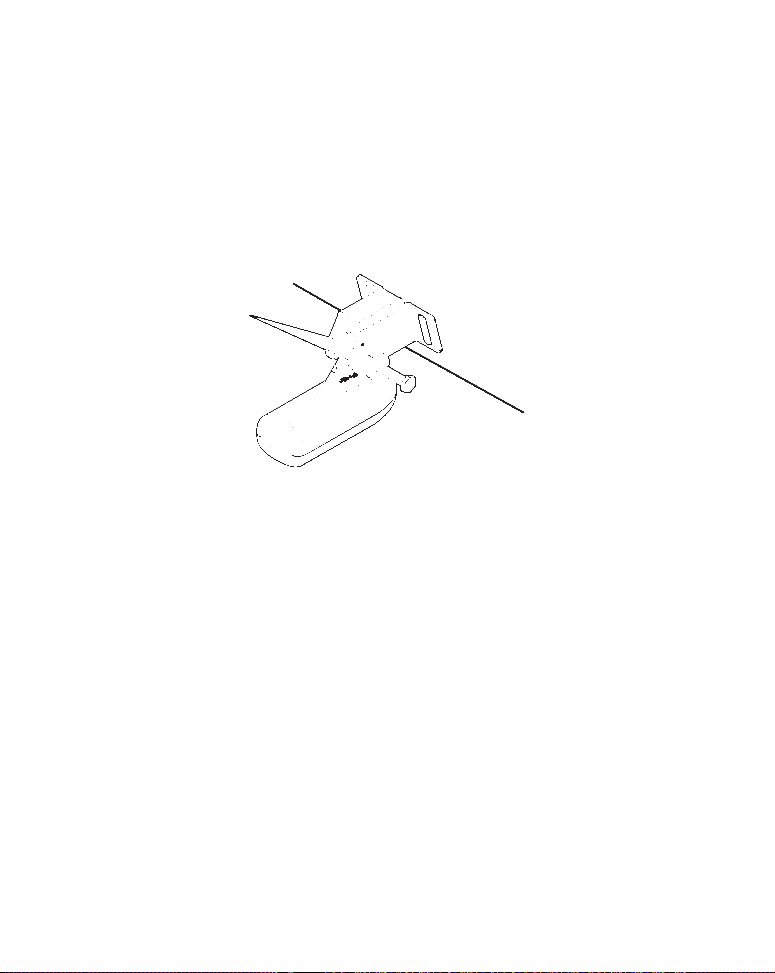
holes in the bracket with the letter "B" aligned with the dot stamped
in the bracket.
Reassemble the transducer and bracket and place them against the
transom. Again, check to see if you can move the transducer so it's parallel with the ground. If you can, then go to step 3A. If it doesn't, repeat
step 2A, but use a different alignment letter until you can place the
transducer on the transom correctly.
Ratchets
Insert bolt and check transducer position on transom.
B. Two-piece bracket: Assemble the transducer and bracket as
shown in the following figure. Temporarily slide the bolt though the
transducer assembly but don't tighten the nut at this time. Hold the
assembled transducer and bracket against the transom. Looking at the
transducer from the side, check to see if it will adjust so that its face is
parallel to the ground. If it does, then the "A" positions are correct for
your hull.
If the transducer's face isn't parallel with the ground, remove and
disassemble the transducer and ratchets. Place the ratchets into the
bracket holes with the letter "B" aligned with the bracket alignment
mark. Place them on the transducer aligned with the 12 o'clock position on the transducer stem.
Reassemble the transducer and bracket and place them against the
transom. Again, check to see if you can move the transducer so it's
15
Page 22
parallel with the ground. If you can, then go to step 3B. If it doesn't,
Flat washer
repeat step 2B, but use a different alignment letter until you can
place the transducer on the transom correctly.
Bolt
Flat washer
Assemble transducer and bracket.
Lock washer
Nut
3. Assembling the transducer.
A. One-piece bracket: Once you determine the correct position for the
ratchets, assemble the transducer as shown in the following figure.
Don't tighten the lock nut at this time.
Metal
Nut
Rubber
washers
Assemble transducer and bracket.
washer
Metal washer
Bolt
B. Two-piece bracket: Once you determine the correct position for the
ratchets, assemble the transducer as shown in the figure in step 2B.
Don't tighten the lock nut at this time.
4. Drilling mounting holes.
16
Page 23
Hold the transducer and bracket assembly against the transom. The
transducer should be roughly parallel to the ground. The transducer's centerline should be in line with the bottom of the hull. Don't
let the bracket extend below the hull!
Mark the center of each slot for the mounting screw pilot holes. You
will drill one hole in the center of each slot.
Drill the holes. For the one-piece bracket, use the #29 bit (for the #10
screws). For the two-piece bracket, use the #20 bit (for the #12
screws).
Transom
Transom
Position transducer mount on transom and mark mounting holes.
Side view shown at left and seen from above at right.
5. Attaching transducer to transom.
A. One-piece bracket: Remove the transducer from the bracket and reassemble it with the cable passing through the bracket over the bolt as
shown in the following figures.
For single-frequency Skimmer, route cable over bolt and through
bracket. Side view shown at left and seen from above at right.
17
Page 24
Both bracket types: Attach the transducer to the transom. Slide the
Flat-bottom hull
transducer up or down until it's aligned properly with the bottom of the
hull as shown in the preceding and following figures. Tighten the
bracket's mounting screws, sealing them with the caulking compound.
Adjust the transducer so that it's parallel to the ground and tighten the
nut until it touches the outer washer, then add 1/4 turn. Don't over
tighten the lock nut! If you do, the transducer won't "kick-up" if it
strikes an object in the water.
Bottom
of
hull
Deep-"vee" hull
Align transducer centerline with hull bottom and attach transducer to
transom. Rear view of dual-frequency Skimmer shown.
6. Route the transducer cable through or over the transom to the sonar
unit. Make sure to leave some slack in the cable at the transducer. If
possible, route the transducer cable away from other wiring on the boat.
Electrical noise from the engine's wiring, bilge pumps, VHF radio wires
and cables, and aerators can be picked up by the sonar. Use caution
when routing the transducer cable around these wires.
WARNING:
Clamp the transducer cable to the transom close to the
transducer. This can prevent the transducer from entering the boat if it is knocked off at high speed.
18
Page 25
If you need to drill a hole in the transom to pass the connector through,
Flat washer
the required hole size will be 5/8".
Caution:
If you drill a hole in the transom for the cable, make sure it is located above the waterline. After installation, be sure to seal the
hole with the same marine grade above- or below-waterline sealant used for the mounting screws.
7. Make a test run to determine the results. If the bottom is lost at
high speed, or if noise appears on the display, try sliding the transducer
bracket down. This puts the transducer deeper into the water, hopefully below the turbulence causing the noise. Don't allow the transducer
bracket to go below the bottom of the hull!
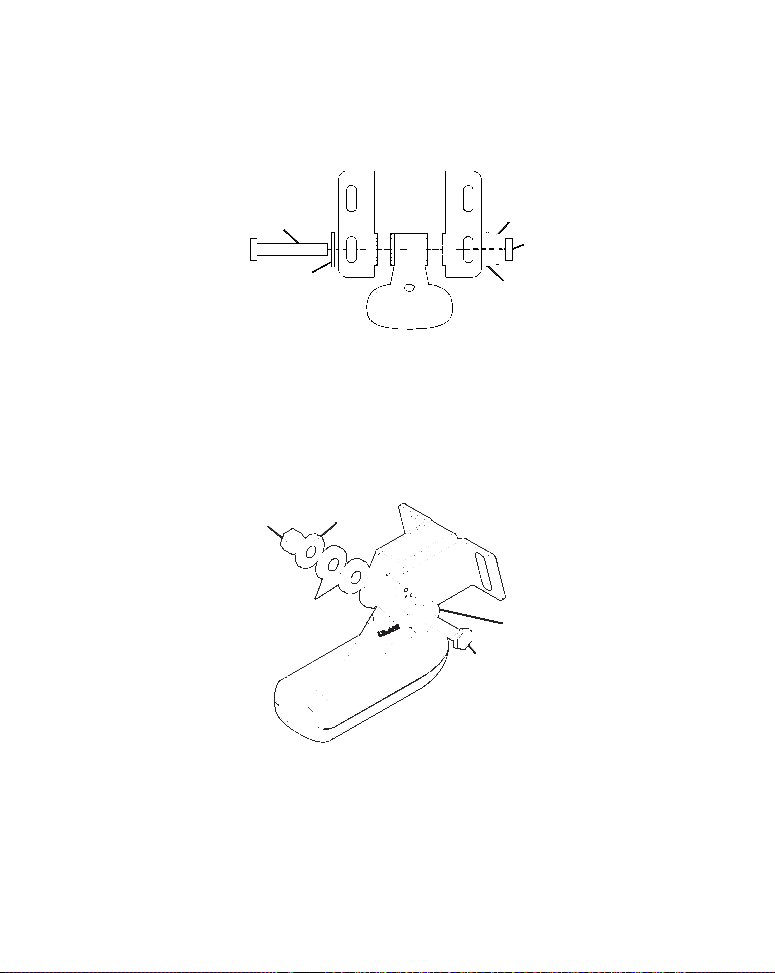
Trolling Motor Bracket Installation
(single-frequency only)
1. Attach the optional TMB-S bracket to the transducer as shown in the
following figure, using the hardware supplied with the transducer.
(Note: The internal tooth washer is supplied with the TMB-S.)
Bolt
Attach motor mounting bracket to transducer.
Internal tooth washer
Nut
2. Slide the adjustable strap supplied with the TMB-S through the slot
in the transducer bracket and wrap it around the trolling motor. Position the transducer to aim straight down when the motor is in the water. Tighten the strap securely.
3. Route the transducer cable alongside the trolling motor shaft. Use
plastic ties (not included) to attach the transducer cable to the trolling
19
TMB-S bracket
Page 26
motor shaft. Make sure there is enough slack in the cable for the motor
to turn freely. Route the cable to the sonar unit and the transducer is
ready for use.
Transducer mounted on trolling motor, side view.
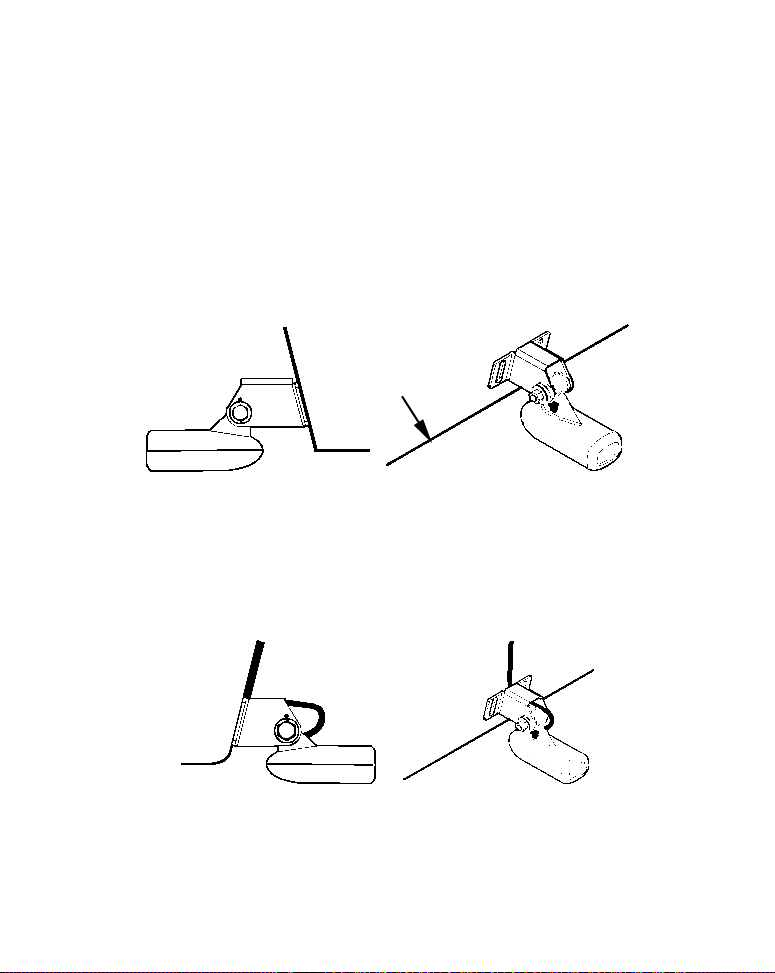
Transducer Orientation and Fish Arches
If you do not get good fish arches on your display, it could be because
the transducer is not parallel with the ground when the boat is at rest
in the water or at slow trolling speeds.
20
Page 27
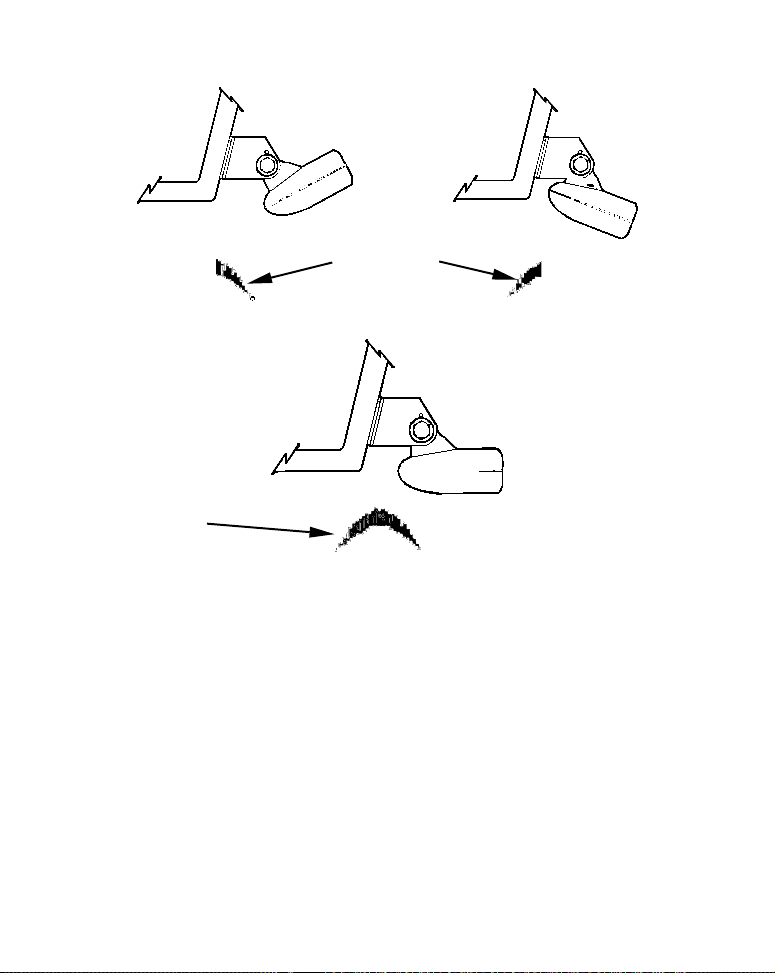
Partial fish arches
Transducer aimed
too far back
Full fish arch
Transducer angles and their effects on fish arches.
Proper transducer angle
Transducer aimed
too far forward
If the arch slopes up – but not back down – then the front of the transducer is too high and needs to be lowered. If only the back half of the
arch is printed, then the nose of the transducer is angled too far down
and needs to be raised.
NOTE:
Periodically wash the transducer's face with soap and water to remove any oil film. Oil and dirt on the face will reduce the sensitivity
or may even prevent operation.
21
Page 28
Shoot-Thru-Hull Preparation
Hulls With Flotation Materials
The transducer installation inside a fiberglass hull must be in an area
that does not have air bubbles in the resin or separated fiberglass layers. The sonar signal must pass through solid fiberglass. A successful
transducer installation can be made on hulls with flotation materials
(such as plywood, balsa wood or foam) between layers of fiberglass if
the material is removed from the chosen area. See the figure below.
WARNING:
Do not remove any material from your inner hull unless
you know the hull's composition. Careless grinding or
cutting on your hull can result in damage that could
sink your boat. Contact your boat dealer or manufacturer to confirm your hull specifications.
Fill with resin
Fill with resin
Flotation material
Inner hull
Epoxy to hull first
Epoxy the transducer to a solid portion of the hull.
Outer hull
For example, some (but not all) manufacturers use a layer of fiberglass,
then a core of balsa wood, finishing with an outer layer of fiberglass. Removing the inner layer of fiberglass and the balsa wood core exposes the
outer layer of fiberglass. The transducer can then be epoxied directly to
the outer layer of fiberglass. After the epoxy cures for 24 hours, fill the
remaining space with polyester resin. When the job is finished, the hull
is watertight and structurally sound. Remember, the sonar signal must
22
Page 29
pass through solid fiberglass. Any air bubbles in the fiberglass or the epoxy will reduce or eliminate the sonar signals.
Testing Determines Best Location
Ideally, the shoot-thru transducer should be installed as close to the
transom as possible, close to the centerline. This will give you the best
performance during high speed maneuvers.
Transducer location
(high speed)
Shoot-thru-hull transducer locations for
high speed or trolling speed operation.
Transducer location
(trolling speed)
To choose the proper location for shoot-thru-hull mounting, follow these
testing procedures: (You may need a helper to complete these steps.)
1. Anchor the boat in about 30 feet of water. Add a little water to the
sump of the boat. Plug the transducer into the sonar unit, turn it on, then
hold the transducer over the side of the boat in the water. Adjust the sensitivity and range controls until a second bottom echo is seen on the display. (You'll need to turn off Auto Sensitivity, Auto Depth Range and
ASP. Try a range setting that is two to three times the water depth. The
harder (more rocky) the bottom, the easier it will be to get a second bottom signal.) Don't touch the controls once they've been set.
2. Next, take the transducer out of the water and place it in the water
in the sump of the boat, face down. (The transducer face is shown in the
figure on the following page.) Notice how the signal strength decreases.
23
Page 30

The second bottom signal will probably disappear and the bottom signal
intensity will likely decrease.
3. Now move the transducer around to find the best location with the
strongest possible bottom signal. If you find a spot with an acceptable
bottom signal, mark the location and move on to step 4.
If you can't get an acceptable bottom signal, try turning up the sensitivity
by three or five keystrokes and then move the transducer around once
more. If you find a spot that works, mark it and move on to step 4.
If you have to turn up sensitivity by more than five keystrokes to get a
good signal, the transducer should be mounted on the outside of the
hull. This is especially true if you have to turn sensitivity all the way
up to get a decent bottom signal.
4. Most people can get good results by following steps 1 through 3, so this
step is optional. If you want to make an extra effort to be absolutely sure
that your selected location will work under all conditions, make a test run
with the boat on plane and observe the bottom signal. You'll need to figure
some way to prop the transducer into position while you make your test
run. (A brick or two might be sufficient to hold it in place.)
5. When you're satisfied with a location, mark it and proceed with the
installation.
Shoot-Thru-Hull Installation
If you are installing the transducer on a hull with floatation material
sandwiched within the hull, refer to the text "Hulls With Flotation Materials" beginning on page 22.
1. Make sure the area is clean, dry and free of oil or grease, then sand
both the inside surface of the hull and the face of the transducer with
100 grit sandpaper. The sanded hull area should be about 1-1/2 times
the diameter of the transducer. The surface of the hull must be flat so
the entire transducer face is in contact with the hull prior to bonding.
24
Page 31

After sanding, clean the hull and transducer with rubbing alcohol to
the bow of the boat.
remove any sanding debris.
Spread epoxy here
Sand this surface
(unit's face)
Orient the Skimmer
with the nose facing
To bow
Epoxy transducer to hull.
WARNING:
Use only the epoxy available from LEI. It has been formulated to work with these installation procedures.
Other epoxy types may be too thin or may not cure to the
right consistency for optimum transducer performance.
2. The epoxy consists of the epoxy itself and a hardener. Remove the
two compounds from the package and place them on the paper plate.
Thoroughly stir the two compounds together until the mixture has a
uniform color and consistency. Do not mix too fast or bubbles will form
in the epoxy. After mixing, you have 20 minutes to complete the installation before the epoxy becomes unworkable.
25
Page 32

Spread a thin layer of epoxy (about 1/16" or 1.5 mm thick) on the face of
the transducer as shown in the previous figure. Make sure there are no
air pockets in the epoxy layer! Then, apply the remaining epoxy to the
sanded area on the hull.
3. Press the transducer into the epoxy, twisting and turning it to force
any air bubbles out from under the transducer face. Stop pressing when
you bottom out on the hull. When you're finished, the face of the transducer should be parallel with the hull, with a minimum amount of epoxy between the hull and transducer.
4. Apply a weight, such as a brick, to hold the transducer in place while
the epoxy cures. Be careful not to bump the transducer while the epoxy
is wet. Leave the weight in place for a minimum of three hours. Allow
the epoxy to cure for 24 hours before moving the boat.
5. After the epoxy has cured, route the cable to the sonar unit and it's
ready to use.
Speed/Temperature Sensors
This unit can accept as many as two temperature sensors, which can be
used to monitor the temperature of surface water, a live well or some
other location. These units can also accept an optional speed sensor for
showing speed and distance traveled. However, you can only use one accessory at a time. If you would like to use a speed sensor and a second
temperature sensor at the same time, you will need a combination device.
NOTE:
This unit is packed with a transducer containing a built-in temp sensor.
The SeaFinder package also includes a speed sensor. If you have a
FishMark 500C and want a speed sensor or additional temp sensor, see
the Accessory Ordering Information in the back of this manual.
If a second temp sensor is used, it must be the model TS-2U. This
model has a fixed electronic "address" which designates it as the second
of two temp sensors. Dual temperatures are only displayed on the Full
Chart page. The Large Digital page will only display the primary tem-
26
Page 33

perature sensor. See the following wiring diagram for temperature and
speed sensor combinations.
Sonar unit rear view
Accessory
socket
Temp
sensor
Speed sensor or
combo speed/
temp sensor.
Sonar unit with external temp sensor, external speed sensor, or combo
speed/temp sensor. The primary temperature sensor is built
into the transducer.
Power/transducer socket
Power/transducer
cable
Temp sensor built
into transducer.
3-amp fuse
Optional Speed Sensor Installation
All the units in this series can display speed and distance traveled, but
only the SeaFinder 500CDF comes packed with a speed sensor. If you
27
Page 34

wish to purchase an optional additional sensor for your unit, refer to
the accessory ordering information inside the back cover of this manual. The following instructions describe how to install the speed sensor.
Recommended tools for this job include: drill, 5/8" drill bit, 1/8" drill bit for
pilot holes, screwdriver. Required supplies for this job include: four #8
stainless steel wood screws (3/4" long), high quality, marine grade aboveor below-waterline caulking compound.
First find a location on the boat's transom where the water flow is smoothest. Don't mount the sensor behind strakes or ribs. These will disturb the
water flow to the speed sensor. Make sure the sensor will remain in the
water when the boat is on plane. Also make sure the location doesn't interfere with the boat's trailer. Typically, the sensor is mounted about one foot
to the side of the transom's centerline.
Once you've determined the proper location for the unit, place the sensor on the transom. The bottom of the bracket should be flush with the
hull's bottom. Using the sensor as a template, mark the hull for the
screws' pilot holes. Drill four 1/8" holes, one in each end of the slots.
Mount the sensor to the hull using #8 stainless steel wood screws (not
included). Use a high quality, marine grade above- or below-waterline
caulking compound to seal the screws. Make sure the sensor is flush
with the bottom of the hull and tighten the screws.
Good location
Stern view showing good location for mounting sensor on transom.
If the base of the transom has a radius, fill the gap between the transom and the sensor with the caulking compound. This will help ensure
a smooth water flow.
28
Page 35

Transom
Bottom of hull
Speed sensor mounting configuration:
side view (left) and rear view (right.)
Bottom of hull
Route the sensor's cable through or over the transom to the sonar unit.
If you need to drill a hole in the transom to pass the connector through,
the required hole size is 5/8".
Caution:
If you drill a hole in the transom for the cable, make sure it is located above the waterline. After installation, be sure to seal the
hole with the same marine grade above- or below-waterline sealant used for the screws.
The sensor is now ready for use. Connect the sensor to the accessory
socket on the back of your unit. If you have any questions concerning
the installation of the sensor, please contact your local boat dealer.
Power Connections
The unit works from a 12-volt battery system. For the best results, attach the power cable directly to the battery. You can attach the power
cable to an accessory or power buss, however you may have problems
with electrical interference. Therefore, it's safer to go ahead and attach
the power cable directly to the battery.
Caution:
When using the unit in a saltwater environment, we strongly recommend that you shut off the power supply to the power cable when
the unit is not in use. When the unit is turned off but still connected
to a power supply, electrolysis can occur in the power cable plug.
29
Page 36

This may result in corrosion of the plug body along with the electri-
3 amp fuse
cal contacts in the cable and the unit's power socket.
In saltwater environments we recommend you connect the power
cable to the auxiliary power switch included in most boat designs.
If that results in electrical interference, or if such a switch is not
available, we recommend connecting direct to the battery and installing an inline switch. This will let you shut off power to the
power cable when the unit is not in use. When you are not using
the unit, you should always shut off power to the power cable, especially when the power cable is disconnected from the unit.
If possible, keep the power cable away from other boat wiring, especially the engine's wires. This will provide the best isolation from electrical noise. If the cable is not long enough, splice #18 gauge wire onto
it. The power cable has two wires, red and black. Red is the positive
lead, black is negative or ground. Make sure to attach the in-line fuse
holder to the red lead as close to the power source as possible.
For example, if you have to extend the power cable to the battery or
power buss, attach one end of the fuse holder directly to the battery or
power buss. This will protect both the unit and the power cable in the
event of a short. It uses a 3-amp fuse.
To unit
Black wire
Power connections for the sonar unit.
Optional power off switch for
saltwater installations
12 volt
battery
Red wire with
30
Page 37

CAUTION:
Do not use this product without a 3-amp fuse wired into the power
cable! Failure to use a 3-amp fuse will void your warranty.
This unit has reverse polarity protection. No damage will occur if the
power wires are reversed. However, the unit will not work until the
wires are attached correctly.
An optional 8-foot, CA-4 external power cable with a cigarette lighter
adapter is available from Eagle.
Mounting the Unit: Bracket, In-Dash or Portable
You can install the sonar unit on the top of a dash with the supplied
gimbal bracket. It can also be installed in the dash or mounted on a
portable power supply.
If you use the supplied bracket, you may be interested in the optional
R-A-M
bracket mounting system. This converts the unit's gimbal
bracket to a swivel mount, which can be used on the dash or overhead
mounting positions. Installation instructions are supplied with the
R-A-M mounting kits.
Bracket Installation
Mount the unit in any convenient location, provided there is clearance
behind the unit when it's tilted for the best viewing angle. You should
also make sure there is enough room behind the unit to attach the
power and transducer cables. (A drawing on the next page shows the
dimensions of a gimbal-mounted sonar unit.)
Holes in the bracket's base allow wood screw or through-bolt mounting.
You may need to place a piece of plywood on the back side of thin fiberglass panels to reinforce the panel and secure the mounting hardware.
31
Page 38

Front
Install the gimbal bracket. Orient the bracket so the arms slope toward
the front of your unit.
Drill a 1-inch (25.4 mm) hole in the dash for the power and transducer
cables. The best location for this hole is immediately under the gimbal
bracket location. This way, the bracket can be installed so that it covers
the hole, holds the cables in position and results in a neat installation.
Some customers, however, prefer to mount the bracket to the side of the
cable hole — it's a matter of personal preference.
After drilling the hole, pass the transducer connector up through the
hole from under the dash. Pass the power cable's bare-wire end down
though the hole from the top.
If you wish, you can fill in the hole around the cables with a good marine caulking compound. (Some marine dealers stock cable hole covers
to conceal the opening.) No matter what type of installation you prefer,
be sure to leave enough slack in the cables to allow tilting or swiveling
the unit. If you choose to fill in the hole, be sure to position the cables
against the rear edge of the hole as you apply the fill material.
32
Page 39

137.9
[5.43]
173.9
[6.85]
72.9
[2.87]
23.4
[0.92]
157.9
[6.22]
Millimeter
[Inch]
Front view (left) and side view (right) showing dimensions of the
sonar unit when mounted on gimbal bracket.
56.9
[2.24]
Before positioning the bracket, be sure to hold the cables against the
rear edge of the hole. Then, slide the bracket over the hole and butt the
rear of the bracket base firmly against the cables, thus pinning them in
place against the side of the hole. Finally, fasten the bracket to the
dash. Attach the unit to the gimbal bracket using the supplied gimbal
knobs and washers.
In-Dash Installation
You can mount the unit in the dash with an optional FM-5 In-Dash
Adapter Kit. The kit includes mounting hardware, a template for cutting the hole and an instruction sheet, part 988-0147-43.
33
Page 40

ALWAYS VERIFY D
I
MENSIONS
146.5
[5.76]
Top
R 7.9
[0.31]
In-Dash
Template
Millimeters
[Inches]
113.5
[4.46]
In-dash mounting template for the sonar unit, showing
dimensions. NOTE: The figure above is not printed to scale. A scaled
template (FM-5 In-Dash Adapter Kit instructions) is available for free
download from our web site, www.eaglesonar.com.
Portable Installation
Like many Eagle products, this sonar unit is capable of portable operation by using the optional PPP-13 portable power pack. The power pack
and an optional portable transducer expand the uses for your sonar
unit. The PPP-13 makes it easy to use the unit on your boat or take it
to the dock, on a float tube, on an ice fishing trip or use it as a second
sonar in a friend's boat.
The PPP-13 Portable Power Pack can be used with eight "D" cell alkaline batteries or an optional sealed, rechargeable battery. For set-up directions, refer to the pack's instruction sheet, part 988-0147-601.
34
Page 41

"D" cell battery
Install batteries in power pack battery adapter.
Face Cover
Your unit comes with a white protective cover that snaps on and off the
front of the unit. This cover is intended for use when your unit and the
vehicle it's mounted in are idle.
WARNING:
When the unit is mounted in an unprotected area, such
as an open boat cockpit, the protective face cover must
be removed when the vehicle is moving at high speed.
This includes towing a boat on a trailer at highway
speeds. Otherwise, wind blast can pop off the cover.
35
Page 42

Notes
36
Page 43

Basic Sonar Operation
2
This section addresses the unit's most basic sonar operations. The instructions presented in Sec. 3 follow a chronological order. Sec. 4, Sonar
Options & Other Features, will discuss other more advanced functions
and utilities. Material in Sec. 4 is arranged in alphabetical order.
Before you turn on the sonar unit, it's a good idea to learn about the different keys, the Main Menu, the four Page screens and how they all
work together. BUT, if you just can't wait to get on the water, turn to
the one-page Quick Reference on page 45.
Keyboard
4
8
3
5
The SeaFinder 500CDF sonar unit, front view, showing
full sonar chart screen display and keyboard.
9
7
6
1
37
Page 44

1. PWR/LIGHT (Power & Light) – The PWR key turns the unit on and
off and activates the backlight.
2. PAGES – Pressing this and the ↑ and ↓ arrow keys switches the unit
between the three different page display options. (Full Sonar Chart,
Split Zoom Sonar Chart and Digital Data.)
3. MENU – Press this key to show the menus and submenus, which
allow you to select a command or adjust a feature.
4. ARROW KEYS – These keys are used to navigate through the
menus, make menu selections, move the chart cursor and enter data.
5. ENT (Enter) – This key allows you to save data, accept values or
execute menu commands.
6. EXIT – The Exit key lets you return to the previous screen, clear
data or clear a menu.
7. ALARM –The Alarm key is a shortcut to access the various sonar
alarms. Press this key once to open the Alarms menu.
8. ZOUT – (Zoom Out) – This key lets you zoom the screen out. This
key allows you to see the entire water column from surface to bottom.
9. ZIN – (Zoom In) – This key lets you zoom the screen in. This key enlarges fish signals and bottom detail.
Power/lights on and off
To turn on the unit, press PWR. As the unit powers up, the Full Sonar
Chart is displayed first.
To turn on the backlight, press
levels to select from. Repeatedly pressing
backlight settings and turn off the backlight.
PWR again. The unit has three backlight
PWR will cycle through the
38
Page 45

Turn off the unit by pressing and holding the
PWR key for 3 seconds.
Main Menu
The unit has a Main Menu, which contains some function commands and
some setup option commands. The instructions in this section will deal
only with sonar functions, the basic commands that make the unit show
sonar signals on your screen. This sonar unit will work fine right out of
the box with the factory default settings. But, if you want to learn about
the various sonar options, see Sec. 4, Sonar Options & Other Features.
You can access the Main Menu from any of the four Page screens by
pressing
display, press
"press the Menu key twice." See a full explanation of our instruction
text formatting on pages 5, "How to use this manual…".
MENU|MENU. To clear the menu screen and return to the page
EXIT. (Remember, our text style for "MENU|MENU" means
Main Menu.
The Main Menu commands and their functions are:
Screen command: changes the contrast or brightness of the display
screen.
39
Page 46

Sounds command: enables or disables the sounds for key strokes and
alarms and sets the alarm style.
Transparency command: adjust the level of transparency for dialogs.
Sonar Alarms command: turns sonar alarms on or off and changes
alarm thresholds.
Units of Measure command: changes the depth, speed, distance, or
temperature units of measure.
Set Keel Offset command: changes the depth offset of the keel from
the transducer.
Calibrate Water Speed command: calibrates the speed measurement.
Reset Water Distance command: resets the log of distance traveled to
zero.
Transducer Type command: sets the type of transducer connected to
the unit.
Sonar Simulator command: scrolls simulated data on the sonar chart.
Reset Options command: resets all options to factory default settings.
Popup Help command: turns popup help on or off.
Set Language command: chooses which language text appears in.
Software Information command: shows the product name and soft-
ware version.
Pages
The unit has three Page display options, accessed by pressing the PAGES
key. The list of display options appears in the following image.
40
Page 47

Pages Menu, showing Sonar display options.
All of the display options show the sonar chart in some format. This is a
"cross-section" view of the water column beneath the boat. The chart
moves across the screen, displaying sonar signal echoes that represent
fish, structure and the bottom.
The Pages Menu allows you to switch among the three chart display options. To access them, press
PAGES|↑ or ↓ to Option Name|EXIT.
The Sonar Page has its own menu, which is used for some advanced functions and for setting various options. (Sonar Options and other features
are discussed in Sec. 4.) To Access the Sonar Page menu, press
MENU.
41
Page 48

Sonar Page in split zoom sonar chart display mode.
Sonar chart digital data display option.
42
Page 49

Sonar Page Menu. Most of these functions are discussed in Sec. 4.
You can customize how the Sonar Page displays its pictures and other
data in many ways. Your unit also includes several special sonar features
and options that can help you better interpret the underwater scene.
We'll discuss all of those features and options in Sec. 4, but to show you
how easy this unit is to operate, the following page contains a simplified,
10-step quick reference that will cover most fish finding situations. The
quick reference describes how your unit will operate with all the sonar
features in their automatic modes, which are set at the factory.
43
Page 50

Digital data
overlay
(depth &
temperature)
Fish arches
Bottom signal
Surface signal
Surface clutter
Depth scale
In FasTrack, fish
arches show as
horizontal bars.
Sonar Page, showing full sonar chart mode.
44
Page 51

Basic Sonar Quick Reference
1. Mount the transducer and unit. Connect the unit to electric power
and the transducer.
2. Launch your boat.
3. To turn on the unit, press and release
PWR key.
4. Head for your fishing grounds. Your unit automatically displays digital depth and surface water temperature in the corner of the screen.
The auto settings will track the bottom, displaying it in the lower portion of the screen. The full sonar chart will scroll from right to left,
showing you what's under the boat as you cruise across the water.
5. As you're watching the sonar returns, you can change the display by:
Zoom in to enlarge the chart for more detail: press
Zoom out to return to full chart mode: press
ZIN.
ZOUT.
6. If necessary, adjust sensitivity to improve chart readability. Press
MENU|ENT and the Sensitivity Menu will appear on the left of your
screen. Use ↑ and ↓ to change the setting.
Boosting sensitivity will show more information on your screen, which
may cause clutter. Reducing sensitivity will filter out some information,
but could omit important images. We recommend adjusting sensitivity
until the background is lightly "peppered" — that is, scattered dots appear, but individual objects (like fish arches or bottom structure) can be
easily picked out of the background.
7. Watch the display for the appearance of fish arches. When you see
arches, you've found fish! Stop the boat and get your lure or bait into
the water at the depth indicated on the sonar chart.
8. Gauge the fish depth by visually comparing the fish arches with the
depth scale on the right side of the screen, or get a more accurate
measure with the Depth Cursor. Press
MENU|↓ to DEPTH CURSOR|ENT.
45
Page 52

Press ↓ (or ↑) to align the cursor line with the fish arch. The exact
depth appears in a box at the right end of the cursor line. To clear the
cursor, press
9. If you are drifting at a very low speed or anchored, you are not moving fast enough for a fish to return the tell-tale fish arch signal. As you
drift over a fish, or as a fish swims through the transducer's signal
cone, the fish echo will appear as a straight line suspended between the
surface and the bottom.
EXIT.
10. To turn off the unit, press and hold
PWR key for three seconds.
Sonar Operations
As you can see from the quick reference on the previous page, basic operation
is pretty easy, right out of the box. If you are a sonar novice, try operating the
unit with the factory defaults until you get a feel for how it's working.
As you're learning the basics, there is one setting you might want to tinker
with from time to time — Sensitivity.
Sensitivity controls the unit's ability to pick up echoes. If you want to see
more detail, try increasing the sensitivity, a little at a time. There are situations when too much clutter appears on the screen. Decreasing the sensitivity
can reduce the clutter and show the strongest fish echoes, if fish are present.
As you change the sensitivity setting, you can see the difference on the chart
as it scrolls.
46
Page 53

Fig. 1 Fig. 2
Fig. 3 Fig. 4
These figures show results of different sensitivity levels on the same location. Fig. 1: Sensitivity at 88 percent, determined by Auto Sensitivity.
Typical of full auto mode. Fig. 2: Sensitivity set at 75 percent. Fig. 3: Sen-
sitivity set at 50 percent. Fig. 4: Sensitivity set at 100 percent.
You can change the sensitivity level whether you are in Auto Sensitivity
mode or Manual Sensitivity mode. The adjustment method works the
same in both modes, but it gives you slightly different results.
47
Page 54

Adjusting sensitivity in Auto Sensitivity Mode is similar to manually adjusting a car's speed with the accelerator pedal while cruise control is on.
You can tell the car to run faster, but when you let off the gas the cruise
control automatically keeps you from running slower than the minimum
speed setting. In the unit, auto mode will let you increase sensitivity to 100
percent, but the unit will limit your minimum setting. This prevents you
from turning sensitivity down too low to allow automatic bottom tracking.
When you change the setting with auto turned on, the unit will continue to
track the bottom and make minor adjustments to the sensitivity level,
with a bias toward the setting you selected.
Adjusting sensitivity in Manual Sensitivity Mode is similar to driving a
car without cruise control — you have complete manual control of the
car's speed. In the unit, manual mode allows you to set sensitivity at
100 percent (maximum) or zero percent (minimum.) Depending on water conditions, the bottom signal may completely disappear from the
screen when you reduce sensitivity to about 50 percent or less!
Try adjusting sensitivity in both auto and manual modes to see how
they work.
To adjust sensitivity:
1. Press
MENU|ENT.
2. The Sensitivity Control Bar appears. Press ↓ to decrease sensitivity;
press ↑ to increase sensitivity. When it's set at the desired level, press
EXIT. (When you reach the maximum or minimum limit, a tone sounds.)
48
Page 55

At left, Sonar Menu with Sensitivity command selected. At right, the
Sensitivity Control Bar.
NOTE:
If you want to change the sensitivity in Manual Mode, first turn off
Auto Sensitivity: from the Sonar Page, press
SENSITIVITY|ENT|↑ to SENSITIVITY|ENT. Press ↓ or ↑ to pick a different
sensitivity setting. When it's set at the desired level, press
MENU|↓ to AUTO
EXIT.
Important Tip:
While you are experimenting and learning, it's possible to scramble
the settings so that the sonar picture disappears from your screen.
If that happens, remember that it's easy to switch back to full
automatic operation by simply restoring the factory auto settings.
To Restore Factory Settings
1. Press MENU|MENU|↓ to RESET OPTIONS|ENT.
2. The unit asks if you want to reset all the options. Press ← to
YES|ENT. All options are reset, and the unit reverts back to the Full
Sonar Chart.
49
Page 56

Fish Symbols vs. Full Sonar Chart
You may have noticed in the quick reference that we used fish arches in
full sonar chart mode for our example, and not the popular Fish I.D.
fish symbol feature. Here's why.
Fish I.D. is an easier way for a sonar novice to recognize a fishy signal
return when he sees it. However, locating fish by symbol only has some
limitations.
Your sonar unit's microprocessor is remarkably powerful, but it can be
fooled. Some of the echoes calculated to be fish could be tree limbs or turtles! To see what's under your boat in maximum detail, we recommend
you turn off Fish I.D. and begin learning to interpret fish arches.
Fish I.D. is most handy when you're in another part of the boat or performing some task that prevents you from watching the sonar screen.
Then, you can turn on Fish I.D. and the audible fish alarm. When that
lunker swims under your boat, you'll hear it!
Fish I.D. can also be useful when you want to screen out some of the
sonar detail gathered by your unit. For example, in one case fisherman
in San Francisco Bay saw clouds of clutter in the water but no fish
arches. When a down rigger was pulled up, it brought up several small
jellyfish. The fisherman switched their sonar to Fish I.D., which
screened out the schools of jellyfish and clearly showed the game fish
there as fish symbols.
Other Free Training Aids
The sonar options section discusses Fish I.D., fish alarms and other features in greater detail. If you or a friend has Internet access, you can
also learn more about interpreting what you see on your sonar screen.
Visit our web site,
WWW.EAGLESONAR.COM. Be sure to check out the
free Sonar Tutorial, which includes animated illustrations and more
pictures of actual sonar returns, all described in detail. There's even a
"printer friendly" version of the tutorial available on our web site…it
makes a great supplement to this operation manual!
50
Page 57

For the ultimate training aid, be sure to download the free emulator
software for your unit. Aside from being just plain fun, this program
can help you learn both basic and advanced operations without burning
boat fuel! Eagle is one of the first sonar manufacturers to provide this
type of training tool for customers.
This PC application simulates the actual sonar unit on your computer.
You can run it from your computer keyboard or use your mouse to press
the virtual keys. Easy download and installation instructions are available on our web site.
Free training emulator is available for your unit on our web site.
51
Page 58

Notes
52
Page 59

Section 4: Sonar Options & Other Features
Material in this section is arranged in alphabetical order.
ASP (Advanced Signal Processing)
The ASP feature is a noise rejection system built into the sonar unit
that constantly evaluates the effects of boat speed, water conditions
and interference. This automatic feature gives you the best display possible under most conditions.
The ASP feature is an effective tool in combating noise. In sonar terms,
noise is any undesired signal. It is caused by electrical and mechanical
sources such as bilge pumps, engine ignition systems and wiring, air
bubbles passing over the face of the transducer, even vibration from the
engine. In all cases, noise can produce unwanted marks on the display.
The ASP feature has four settings — Off, Low, Medium and High. If
you have high noise levels, try using the "High" ASP setting. However,
if you are having trouble with noise, we suggest that you take steps to
find the interference source and fix it, rather than continually using the
unit with the high ASP setting.
There are times when you may want to turn the ASP feature off. This
allows you to view all incoming echoes before they are processed by the
ASP feature.
53
Page 60

At left, Sonar Menu with Sonar Features selected. In the Sonar
Features menu, Noise Rejection is selected with ASP in the default low
setting (center, dual-frequency menu; at right, single-frequency menu).
To change the ASP level:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to SONAR FEATURES|ENT.
2. Press ↓ to
3. Press ↓ or ↑ to select a setting, then press
4. To return to the previous page, press
NOISE REJECTION|ENT.
ENT.
EXIT|EXIT.
Alarms
This unit has three different types of sonar alarms. The first is the Fish
Alarm. It sounds when the Fish I.D. feature determines that an echo
is a fish.
Another alarm is the Zone Alarm, which consists of a bar on the side of
the screen. Any echo on the chart that appears inside this bar triggers
this alarm.
54
Page 61

The last alarm is the Depth Alarm, which has both a Shallow and a
Deep setting. This is useful as an anchor watch, a shallow water alert
or for navigation.
Depth Alarms
The depth alarms sound a tone when the bottom signal goes shallower
than the shallow alarm's setting or deeper than the deep alarm's setting. For example, if you set the shallow alarm to 10 feet, the alarm will
sound a tone if the bottom signal is less than 10 feet. It will continue to
sound until the bottom goes deeper than 10 feet.
The deep alarm works just the opposite. It sounds a warning tone if the
bottom depth goes deeper than the alarm's setting. Both depth alarms
work only off the digital bottom depth signals. No other targets will trip
these alarms. These alarms can be used at the same time or individually.
At left, Main Menu and Sonar Alarms command.
At right, the Sonar Alarms menu.
To adjust and turn on the shallow alarm:
1. Press ALARM|→ to SHALLOW ALARM DEPTH|ENT.
55
Page 62

2. Press ↑ or ↓ to change the first number, then press → to move the
cursor to the next number and repeat until the depth is correct, then
press
ENT.
3. Press ← to
4. To turn off the alarm, press
SHALLOW ALARM ENABLED|ENT|EXIT.
ALARM|ENT|EXIT.
To switch to a different depth setting, open the Sonar Alarms menu and
repeat the instructions in step 3 above.
To adjust and turn on the deep alarm:
1. Press ALARM|↓ to DEEP ALARM ENABLED|→ to DEEP ALARM DEPTH|ENT.
2. Press ↑ or ↓ to change the first number, then press → to move the
cursor to the next number and repeat until the depth is correct, then
press
ENT.
3. Press ← to
4. To turn off the alarm, press
ENABLED|ENT|EXIT.
DEEP ALARM ENABLED|ENT|EXIT.
ALARM|↓ to DEEP ALARM
To switch to a different depth setting, open the Sonar Alarms menu and
repeat the instructions in step 3 above.
Zone Alarm
The zone alarm is triggered when any echo passes inside the zone
alarm bar, shown on the right side of the screen.
To adjust and turn on the zone alarm:
1. Press ALARM|↓ to ZONE ALARM ENABLED|→ to ADJUST ZONE|ENT.
2. To set the upper boundary for the Zone Alarm, use ← or→ to select
UPPER, then press ↑ or ↓ to move the top of the bar to the desired depth.
3. To set the lower boundary for the Zone Alarm, use ← or→ to select
LOWER, then press ↑ or ↓ to move the bottom of the bar to the desired depth.
56
Page 63

At left, Sonar Alarms menu, with Adjust Zone command selected.
At right, Adjust Zone Alarm selection box, with Upper selected.
4. Press EXIT|← to ZONE ALARM ENABLED|ENT|EXIT. Now, any echo —
fish, bottom, structure — within the zone alarm's depth range will trigger the zone alarm.
5. To turn off the alarm, press
ENABLED|ENT|EXIT.
ALARM|↓ to ZONE ALARM
To switch to a different depth setting, open the Sonar Alarms menu and
repeat the instructions in steps 3 and 4 above.
Fish Alarm
Use the fish alarm for a distinctive audible alarm when fish or other
suspended objects are detected by the Fish I.D. feature (Fish I.D.
must be turned on for the Fish Alarm to work). A different tone sounds
for each fish symbol size shown on the display.
57
Page 64

Sonar Alarms menu with Fish Alarm selected. The check box to the left
is blank, indicating the alarm is turned off.
To turn the fish alarm on:
1. Press ALARM|↓ to FISH ALARM|ENT|EXIT.
2. To turn off the alarm, press
ALARM|↓ to FISH ALARM|ENT|EXIT.
Backlight Level
The unit defaults to the maximum backlight level. To adjust the display's backlight level:
Press
MENU|MENU|↓ to BACKLIGHT LEVEL|ENT. The BACKLIGHT LEVEL slider
bar appears. Press ↑ or ↓ to move the bar. At The lower end of the scale
backlighting is turned off; the upper end is maximum backlight level.
58
Page 65

The Backlight Level control bar appears automatically whenever you
turn on the unit.
Calibrate Speed
The speed sensor can be calibrated to compensate for inaccuracies. Before you change the setting, first calculate the percentage that the
speed is off. You will enter this percentage in a moment.
For example, if you figure the sensor is reading 10 percent faster than
actual speed, you will enter – 10 in the calibration window. If the sensor is reading 5 percent slower than true speed, you will enter + 5 in
the window.
When you make a run to compare your ground speed to speed sensor
speed, perform your test in relatively calm water free of current, if possible. (Unless, of course, you are taking the current speed into consideration when making your calculation.) After you have a correction figure, here's how to enter it:
1. Press
MENU|MENU|↓ to CALIBRATE WATER SPEED|ENT.
59
Page 66

2. Enter the number you calculated earlier: press ↑ or ↓ to change the
first character (+ or –), then press → to move the cursor to the next
number and repeat until the percentage is correct, then press
EXIT.
Chart Speed
The rate that echoes scroll across the screen is called the chart speed.
The default is maximum; we recommend that you leave the speed set
there for virtually all fishing conditions.
However, you might consider experimenting with chart speed when you
are stationary or drifting very slowly. You may sometimes achieve better images as you slow down the chart speed to match how fast you are
moving across the bottom.
If you are at anchor, ice fishing or fishing from a dock, experiment with
a chart speed around 50 percent. If you are drifting slowly, try a chart
speed around 75 percent. When you are stationary and a fish swims
through the sonar signal cone, the image appears on the screen as a
long line instead of a fish arch. Reducing the chart speed may result in
a shorter line that more closely resembles a regular fish return.
At left, Sonar Page menu with Chart Speed command selected.
At right, Chart Speed Control Bar.
60
Page 67

If you do experiment with chart speed, remember to reset it to maximum when you resume trolling or moving across the water at higher
speed. To change chart speed:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to CHART SPEED|ENT.
2. The Chart Speed Control Bar appears. Press ↓ to decrease chart
speed; press ↑ to increase chart speed.
3. When it's set at the desired level, press
EXIT.
ColorLine
ColorLine lets you distinguish between strong and weak echoes. It
"paints" a brighter color on targets that are stronger than a preset
value. This allows you to tell the difference between a hard and soft
bottom. For example, a soft, muddy or weedy bottom returns a weaker
signal which is shown with a narrow, colored line (dark blue tinged
with red or a little yellow.) Since fish are among the weakest echoes,
they show up mostly as blue arches. A hard bottom or other relatively
hard target returns a strong signal which causes a wider brightly colored line (reddish yellow to bright yellow.)
If you have two signals of equal size, one with red to yellow color and
the other without, then the target with brighter color (yellow) is the
stronger signal. This helps distinguish weeds from trees on the bottom,
or fish from structure.
ColorLine is adjustable. Experiment with your unit to find the
ColorLine setting that's best for you. To adjust the ColorLine
level:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
2. The ColorLine Control Bar appears. Press ↓ to decrease ColorLine;
press ↑ to increase Colorline.
3. When it's set at the desired level, press
MENU|↓ to COLORLINE|ENT.
EXIT.
61
Page 68

At left, Sonar Page menu with ColorLine command selected.
At right, the ColorLine control bar.
Wider
ColorLine
Thin or no ColorLine
At left, little ColorLine indicates a soft bottom, probably sand or mud.
At right, the wider ColorLine indicates a harder, rocky bottom.
62
Page 69

Contrast
To adjust the display's contrast: Press MENU|MENU|ENT. The CONTRAST
slider bar appears. Press ↑ or ↓ to move the bar. The lower end of the
scale is minimum contrast; the upper end is maximum contrast.
Depth Cursor
The depth cursor consists of a horizontal line with a digital depth box on
the right side. The numbers inside the box show the depth of the cursor.
Cursor line
Depth box
At left, Sonar Page menu with Depth Cursor command selected. At
right, sonar chart with the depth cursor active. The school of fish is
31.91 feet deep.
The cursor can be moved to any location on the screen, letting you pinpoint the depth of a target.
1. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to DEPTH CURSOR|ENT.
2. The depth cursor appears. Press ↓ to lower the cursor line; press ↑ to
raise the cursor line.
3. To clear the depth cursor, press
EXIT.
63
Page 70

Depth Range - Automatic
When turned on for the first time, the bottom signal is automatically
placed in the lower half of the screen. This is called Auto Ranging and
is part of the automatic function. However, depending upon the bottom
depth and the current range, you can change the range to a different
depth. To do this:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to DEPTH RANGE|ENT.
At left, Sonar Page menu with Depth Range command selected. At
right, the Depth Range Control Scale.
2. The Depth Range Control Scale appears. Press ↑ or ↓ to select a different depth range. A blue bar highlights the selected range. The
lighter numbers cannot be selected.
3. When the new range is selected, press
EXIT to clear the menu.
Depth Range - Manual
You have complete control over the range when the unit is in the manual mode. There are 16 depth ranges, from 5 feet to 4,000 feet.
64
Page 71

To switch to Manual Depth Range:
1. First, turn off automatic depth range. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to AUTO DEPTH RANGE|ENT.
2. Press ↑ to
DEPTH RANGE|ENT and the Depth Range Control Scale appears.
3. Press ↓ or ↑ to select a different depth range. A horizontal black bar
highlights the selected range.
4. When the new range is selected, press
To turn Auto Depth Range on again:
EXIT to clear the menu.
From the Sonar Page, press MENU|↓ to AUTO DEPTH RANGE|ENT|EXIT.
NOTE:
The sonar's depth capability depends on the transducer installation, water and bottom conditions, and other factors.
FasTrack
This feature automatically converts all echoes to short horizontal lines
on the display's far right side. The graph on the rest of the screen continues to operate normally. FasTrack gives you a rapid update of conditions directly under the boat. This makes it useful for ice fishing, or
when you're fishing at anchor. When the boat is not moving, fish signals are long, drawn out lines on a normal chart display. FasTrack converts the graph to a vertical bar graph that, with practice, makes a useful addition to fishing at a stationary location.
65
Page 72

Surface clutter
Fish arches
Structure
In FasTrack, fish
arches show as
horizontal bars.
Bottom signal
ColorLine
Sonar Page showing FasTrack.
FasTrack
bar graph
Fish I.D. (Fish Symbols & Depths)
The Fish I.D. feature identifies targets that meet certain conditions as
fish. The microcomputer analyzes all echoes and eliminates surface
clutter, thermoclines, and other signals that are undesirable. In most
instances, remaining targets are fish. The Fish I.D. feature displays
fish symbols on the screen in place of the actual fish echoes.
There are several fish symbol sizes. These are used to designate the
relative size between targets. In other words, Fish I.D. displays a small
fish symbol when it thinks a target is a small fish, a medium fish symbol on a larger target and so on.
The sonar's microcomputer is sophisticated, but it can be fooled. It can't
distinguish between fish and other suspended objects such as trotlines,
turtles, submerged floats, air bubbles, etc. Individual tree limbs extending outwards from a group of limbs is the hardest object for the
Fish I.D. feature to distinguish from fish.
You may see fish symbols on the screen when actually, there are no
fish. The reverse is also true. The illustrations on the next page show
how Fish I.D. can actually miss fish that are present.
66
Page 73

Does that mean Fish I.D. is broken? No — the feature is simply interpreting sonar returns in a specific way to help take some of the work
out of reading the screen. Remember: Fish I.D. is one of the many tools
we provide so you can analyze your sonar returns for maximum fish
finding information. This and other features can help you successfully
"see" beneath the boat under varied water and fishing conditions. So,
practice with the unit in both the Fish I.D. mode and without to become
more familiar with the feature. The default for Fish I.D. is off.
Sonar Features menu with Fish I.D. Symbols selected (at left, dual-
frequency menu; at right, single-frequency menu). When the check box
to the left is checked, the feature is on.
To turn the Fish I.D. feature on:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
2. Press ↓ to
SYMBOLS|ENT|EXIT|EXIT.
MENU|↓ to SONAR FEATURES|ENT.
To turn off Fish I.D., repeat the instructions in step 2.
FishTrack
The FishTrack feature shows the depth of a fish symbol when it appears on the display. This lets you accurately gauge the depth of targets. This feature is available only when the Fish I.D. feature is on. The
default setting for FishTrack is off.
67
Page 74

To turn on FishTrack:
(Note: These instructions will turn on FishTrack and Fish I.D. at the
same time.)
1. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to SONAR FEATURES|ENT.
2. Press ↓ to
DEPTHS|ENT|EXIT|EXIT.
To turn off FishTrack, repeat the instructions in step 1. Turning off
FishTrack in this manner will not turn off Fish I.D. symbols.
Symbols with
FishTrack depths
Sonar Features menu with Fish I.D. Depths selected (at left, dual-
frequency menu; center, single-frequency menu). When the check box to
the left is checked, the feature is on. At right, Sonar Page showing Fish
I.D. symbols and FishTrack depths turned on.
Frequency (Change Transducer Frequency)
(SeaFinder CDF only)
The SeaFinder CDF transducer operates with both 200 kHz and 50
kHz. The 200 kHz frequency has a 12° cone angle and the 50 kHz frequency has a 35° cone angle.
68
Page 75

The default frequency is 200 kHz, which is best for use in shallow water
(about 300 feet or less). This frequency is the best choice for about 80
percent of the fresh and salt water sport fishing applications. When you
get into very deep salt water, 300 to 500 feet or deeper, the 50 kHz frequency is the best choice.
The 200 kHz transducer will give you better detail and definition, but
less depth penetration. The 50 kHz transducer will give you greater
depth penetration, but a little less detail and less definition. (Remember,
all sonar units typically read deeper in fresh water than in salt water.)
There is a common exception to these rules of thumb. Some fishermen
on freshwater lakes (or the ocean) using downriggers like to see them
on the sonar. In many of those cases, you'll see a 50 kHz transducer
frequency in use because the wider cone angle lets them watch the bait.
Sonar Features menu with a frequency of 200 kHz selected.
To change the frequency setting to 50 kHz:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
2. Press ↓ to
FISH DEPTHS|→ to 50 KHZ|ENT.
MENU|↓ to SONAR FEATURES|ENT.
69
Page 76

3. Press
To change the frequency setting to 200 kHz:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
2. Press ↓ to
3. Press
EXIT|EXIT to clear the menu.
MENU|↓ to SONAR FEATURES|ENT.
FISH SYMBOLS|→ to 200 KHZ|ENT.
EXIT|EXIT to clear the menu.
HyperScroll
See the entry on Ping Speed, which controls the HyperScroll feature.
Noise Rejection
See the entry on Advanced Signal Processing in this section.
Overlay Data
To change the digital data shown "floating" on top of the Sonar Page:
To select data for display:
1. Press MENU|↓ to OVERLAY DATA|ENT.
2. Press ↓ or ↑ to select Data Type|
ENT.
70
Page 77

Overlay Data command on the Sonar Menu, at left. Overlay Data
Shown selection menu, right. In this example, Depth will be displayed
in a large font.
When selected, the data type shifts to the top of the data list and a
check mark appears beside the data type. (If you wish, you may now
use ↓ or ↑ to select other Data Types for display.)
71
Page 78

Data list showing Water Speed selected to display on Sonar Page.
3. To return to the previous page, press EXIT.
To turn off displayed data:
1. Press MENU|↓ to OVERLAY DATA|ENT.
2. Press ↓ or ↑ to select Data Type|
ENT. The selected data type disappears
from the top of the list and reverts to its previous, unchecked position. (If
you wish, you may now use ↓ or ↑ to select other Data Types to turn off.)
3. To return to the previous page, press
To change displayed data font size:
EXIT.
1. Press MENU|↓ to OVERLAY DATA|ENT.
2. Press ↓ or ↑ to select Data Type|press → or ← to Data Size|
EXIT.
The selected data type will be displayed in the new size. (To change the
font size for another Data Type, press
ENT and repeat these steps, be-
ginning with step two above.)
3. To return to the previous page, press
EXIT.
72
Page 79

Tip:
If you wish, you can change the displayed data font size when you
select a data type:
1. From the Sonar page, press
MENU|↓ to OVERLAY DATA|ENT.
2. Press ↓ or ↑ to select Data Type|press → or ← to select Data
Size|
ENT.
The data will be shown in the new font size. To return to the previous page, press
Sonar Page with Overlay Data turned on. This example shows Depth,
EXIT.
Water Temperature and Water Speed.
NOTE:
Some data types can be displayed in only one font size. If that is the
case, the Data Size box will not be displayed for that data type.
Ping Speed & HyperScroll
Ping Speed controls the rate at which the transmitter and transducer
broadcast sonar sound waves — pings — into the water. The unit has a
default ping speed of 50 percent. At normal boating speeds, this auto-
73
Page 80

matically provides enough return echoes to refresh the screen and scroll
the chart at maximum chart speed.
However, when you are running at high speeds, or just want the fastest
possible screen update, you may want to use the HyperScroll feature.
When you change the Ping Speed to any setting greater than 50 percent, the unit automatically enters HyperScroll mode.
These faster ping rates allow you to maintain a high-detail picture on
the screen, and the screen refresh rate and chart scroll speed can keep
pace with the boat as it moves quickly over the bottom terrain.
When using HyperScroll, you may also need to manually decrease the
sensitivity for optimum performance. Depending on water depth and
other conditions, HyperScroll may cause a second bottom echo to return
to the transducer during the next ping cycle, or sounding. This can result
in a large amount of clutter appearing on the screen. If this occurs, just
decrease the sensitivity to a level that eliminates the clutter. When you
turn HyperScroll off, you can return to your original sensitivity level.
At left, Sonar Menu with Ping Speed command selected.
Ping Speed Control Bar, right, at default setting.
74
Page 81

To change Ping Speed:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to PING SPEED|ENT.
2. The Ping Speed Control Bar appears. Press ↑ to increase ping speed;
press ↓ to decrease speed. When it's set at the desired level, press
EXIT.
To adjust Sensitivity:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|ENT.
2. The Sensitivity Control Bar appears. Press ↓ to decrease sensitivity;
press ↑ to increase sensitivity. When it's set at the desired level, press
EXIT. (When you reach the maximum or minimum limit, a tone sounds.)
To turn off HyperScroll:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to PING SPEED|ENT.
2. The Ping Speed Control Bar appears. Press↓ to decrease ping speed
to 50 percent. When it's set at the desired level, press
EXIT.
When you boost ping speed and switch into HyperScroll, the width of
the FasTrack bar graph display doubles in width at the right side of the
screen. This allows you to better see the virtually instantaneous sonar
returns, just as you would on a flasher sonar unit. For more information on FasTrack, see its entry in this section.
Pop-up Help
Help is available for virtually all of the menu labels on this unit. By
highlighting a menu item and leaving it highlighted for a few seconds, a
"pop-up" message appears that describes the function of the menu item.
This feature is on by default.
To set up Popup Help: Press
option highlighted, press
ENT to check it (turn on) and uncheck it (turn
off). After the option is set, press
MENU|MENU|↓ to POPUP HELP. With the
EXIT to return to the page display.
75
Page 82

Example showing the Pop-up Help message for the Sensitivity com-
mand, located on the Sonar Menu.
Reset Options
This command is used to reset all features, options and settings to their
original factory defaults. This is useful when you have changed several
settings and want to return the unit to basic automatic operation.
1. Press
2. Press ← to
MENU|MENU|↓ to RESET OPTIONS|ENT.
YES|ENT.
3. All the menus are cleared and the unit reverts to the full sonar chart,
just as if you had turned it on for the first time. All options have been
returned to the factory settings.
76
Page 83

At left, Main Menu with Reset Options command selected. At right, the
Reset Options dialog box, with "Yes" selected.
Reset Water Distance
The sonar chart's Digital Data display option includes a box that shows
distance traveled, called Water Distance. This information is calculated
from an optional water speed sensor. The Water Distance window can
be reset to zero using the Reset Water Distance command.
Press
cleared and the water distance is reset to 0.00.
MENU|MENU|↓ to RESET WATER DISTANCE|ENT. The menus are
Screen Contrast and Backlight Level
See the separate entries in this section for Contrast and Backlight
Level.
Set Keel Offset
This unit measures water depth from the face of the transducer. Since
the transducer is installed below the water surface, the distance displayed by the digital depth, chart depth scale, chart cursor or fish symbols is not the exact water depth. If the transducer is 1 foot below the
77
Page 84

surface, and the screen shows the water depth as 30 feet, then the actual depth is 31 feet.
On sailboats or other large vessels with deep drafts, the distance between the transducer installation and the keel or lower engine unit can
be several feet. In those cases, an inexact depth reading could result in
grounding or striking underwater structure. The Keel Offset feature
eliminates the need for the navigator to mentally calculate how much
water is under his keel.
Keel Offset lets you calibrate the digital depth, chart depth scale, chart
cursor depth and fish symbol depth displayed on the screen. To calibrate
the depth indicators, first measure the distance from the face of the
transducer to the lowest part of the boat. In this example, we will use 3.5
feet. This will entered as a negative 3.5 feet, which makes the depth indicators perform as if the transducer's lower in the water than it really is.
1. Press
MENU|MENU|↓ to SET KEEL OFFSET|ENT.
2. The Keel Offset dialog box appears. Press ↓ to change the plus (+)
sign to a minus (–) sign.
3. Press → to the first number, then press ↑ to change the number to 3
4. Press → to the second number, then press ↑ to change the number to
5, then press
EXIT. The depth indicators now accurately show the depth
of water beneath the keel.
NOTE:
If knowing the exact depth of water beneath the keel is less important,
you can calibrate the depth indicators so that they show the actual water depth from surface to bottom. To do this, first measure the distance
from the face of the transducer up to the surface (the water line on the
boat). In this example, we will use 1.5 feet. This will be entered as a
positive 1.5 feet, which makes the depth indicators perform as if the
transducer's higher in the water than it really is.
1. Press
MENU|MENU|↓ to SET KEEL OFFSET|ENT.
78
Page 85

2. The Keel Offset dialog box appears with a plus (+) sign at the
front of the box.
3. Press → to the first number, then press ↑ to change the number
to 1.
4. Press → to the second number, them press ↑ to change the number to 5, then press
EXIT. The depth indicators now accurately show
the water depth from surface to bottom.
Sensitivity & Auto Sensitivity
The sensitivity controls the ability of the unit to pick up echoes. Sensitivity can be adjusted, because water conditions vary greatly. A low
sensitivity level (from zero to 50 percent) excludes much of the bottom
information, fish signals, and other target information.
High sensitivity levels let you see this detail, but it can also clutter the
screen with many undesired signals. Typically, the best sensitivity level
shows a good solid bottom signal with Grayline
ter.
Automatic Sensitivity
The default sensitivity mode is automatic. The unit bases the sensitivity level on water depth and conditions. When the unit is in the automatic mode, sensitivity is automatically adjusted to keep a solid bottom
signal displayed, plus a little more power. This gives it the capability to
show fish and other detail.
and some surface clut-
However, situations occur when it becomes necessary to increase or decrease the sensitivity. This typically happens when you wish to see
more detail, so an increase in sensitivity is indicated. Or, wave action
and boat wakes can create enough tiny air bubbles to clutter much of
the water column. In that case, a decrease in sensitivity is indicated to
reduce some of the clutter.
The control bar used to adjust sensitivity up or down is the same
whether the unit is in the automatic or manual mode. In automatic you
79
Page 86

can adjust sensitivity up to 100 percent but the unit will limit your
minimum setting. In auto, the unit will continue to make small adjustments, allowing for the setting you selected.
In manual mode, you have complete control over sensitivity, with the
ability to set it anywhere from zero to 100 percent. Once you select a
level in manual, the unit will continue to use that exact sensitivity setting until you change it or revert to auto mode.
To adjust sensitivity in auto mode:
1. Press
MENU|ENT.
2. The Sensitivity Control Bar appears. Press ↓ to decrease sensitivity;
press ↑ to increase sensitivity. When it's set at the desired level, press
EXIT. (When you reach the maximum or minimum limit, a tone sounds.)
At left, Sonar Menu with Sensitivity command selected. At right, the
Sensitivity Control Bar.
80
Page 87

To adjust sensitivity in manual mode:
1. First, turn off Auto Sensitivity: from the Sonar Page, press
to
AUTO SENSITIVITY|ENT.
2. Press ↑ to
SENSITIVITY|ENT and the Sensitivity Control Bar appears.
MENU|↓
Press ↓ or ↑ to pick a different sensitivity setting. When it's set at the
desired level, press
EXIT.
To turn Auto Sensitivity back on:
From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to AUTO SENSITIVITY|ENT|EXIT.
NOTE:
To return to the original factory setting for Auto Sensitivity, see the
entry in this section on Reset Options. If sensitivity is in manual
mode, the Reset Options command will switch back to Auto mode.
Tip:
For quicker sensitivity adjustments, try leaving the Sensitivity
Control Bar on the screen as the chart scrolls. You can see the
changes on the screen as you press the up or down arrows.
Set Language
This unit's menus are available in 10 languages: English, French, German, Spanish, Italian, Danish, Swedish, Russian, Dutch and Finnish.
To select a different language:
1. Press
2. Use ↓ or ↑ to select a different language and press
now appear in the language you selected.
MENU|MENU|↓ to SET LANGUAGE|ENT.
ENT. All menus
Software Version Information
From time to time, Lowrance updates the operating system software in
some of its products. These software upgrades are usually offered to
customers as free downloads from our web site, www.lowrance.com.
These upgrades make the unit perform better or introduce a new feature or function. You can find out what software version is running in
your sonar unit by using the Software Information command.
81
Page 88

1. Press
MENU|MENU|↓ to SOFTWARE INFO|ENT.
2. Read the information displayed on the screen.
3. To return to the last page displayed, press EXIT|EXIT.
Sonar Chart Mode
The default color scheme for the sonar chart is white background, but
we offer other variations to suit your viewing preferences. You can select the chart to be displayed in grayscale, reverse grayscale, blue background, Nightview, IceView, or bottom color tracking.
To change the chart mode color scheme:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
2. Press ↓ to
SONAR CHART MODE|ENT.
3. Press ↓ or ↑ to Mode Name|
4. Press
EXIT|EXIT to return to the Sonar Page.
MENU|↓ to SONAR FEATURES|ENT.
ENT.
Sonar Page & Sonar Chart Display Options
The Pages Menu offers three chart display options. To access them, press
PAGES ↑ or ↓ to Option Name|EXIT.
Pages Menu, showing sonar chart display options.
82
Page 89

Full Sonar Chart
This is the default mode used when the unit is turned on for the first
time or when it's reset to the factory defaults.
The bottom signal scrolls across the screen from right to left. Depth
scales on the right side of the screen aid in determining the depth of
targets. The line at the top of the screen represents the surface. The
bottom depth and surface temperature (if equipped with a temperature
sensor or a transducer with a temp sensor built in) show at the top left
corner of the screen.
The FasTrack™ display shows just to the right of the scale. This
changes all echoes into short horizontal bars, replicating a flasher sonar. The zoom bar on the far right shows the area that's zoomed when
the zoom is in use. (See the Zoom section for more information.)
Full Sonar Chart. The Overlay Data (depth and water temperature)
are set to different text sizes.
83
Page 90

Split Zoom Sonar Chart
A split chart shows the underwater world from the surface to the bottom on the right side of the screen. The left side shows an enlarged version of the right side. The zoom range shows at the bottom left corner of
the screen.
Split Zoom Sonar Chart. Image at left shows the left window zoomed to
2X. The right image shows the left window zoomed to 4X.
Digital Data/Chart
This mode shows the chart on the right side of the screen. The left side has
five large digital data boxes or windows containing (by default): Water
Depth; Water Temperature; Water Speed (from an optional speed sensor)
and Water Distance (distance traveled or log, it also requires a speed sensor).
84
Page 91

Digital Data/Chart
Customizing the Digital Data/Chart Screen
The Digital Data/Chart screen can be customized to show digital data
different from the defaults first shown. To customize this screen:
1. From the Sonar Page (in Digital Data mode), press
CUSTOMIZE|ENT.
MENU|↓ to
At left, the Sonar Menu showing the Customize command highlighted.
At right, the Water Temperature box is selected.
85
Page 92

2. The Water Temperature box title bar flashes, indicating the box contents can be changed. Press
Water Distance has been picked to replace Water Temperature in the
ENT|↑ or ↓ to select data type|ENT|EXIT.
top digital data box.
Tip:
You can customize other digital data boxes before returning to the
Sonar Page. After changing the first box by selecting the Data Type
and pressing Enter, use the ↓ key to select another box to change.
When the selected box title bar flashes, press
data type|
then press
ENT. Repeat these steps until you're finished customizing,
EXIT to return to the Sonar Page.
ENT|↑ or ↓ to select
Sonar Simulator
This unit has a built-in simulator that lets you run it as if you were on
the water. All sonar features and functions are useable. When in
simulator mode, the unit periodically will display “Simulated” at the
bottom of the Sonar Page. To use the simulator:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|MENU|↓ to SONAR SIMULATOR|ENT.
86
Page 93

Main Menu with Sonar Simulator command selected.
The Simulator is turned off (check box is unchecked).
NOTE:
If you turn on your unit before attaching a transducer, it may enter a
demo mode. The words "demo mode" flash on the bottom of the
screen and a sonar chart plays much like the simulator. Unlike the
simulator, the demo mode is for demonstration only, and will automatically stop as soon as you turn on the unit with a transducer attached. The simulator will continue to function normally.
Stop Chart
If you are running multiple units on a boat or using this unit in a car,
there are times when you may want to turn off the sonar. This command turns off the sonar and stops the chart from scrolling. Sonar restarts automatically each time you turn on your unit.
Press
MENU|↓ to STOP CHART|ENT|EXIT.
To turn on sonar and start the chart scrolling again, repeat the above step.
87
Page 94

Sonar Menu with Stop Chart command selected. The box is unchecked,
indicating that the chart is scrolling across the screen.
Surface Clarity
The markings extending downward from the zero line on the chart are
called "surface clutter." These markings are caused by wave action,
boat wakes, temperature inversion and more.
The surface clarity control reduces or eliminates surface clutter signals
from the display. It does this by changing the sensitivity of the receiver,
decreasing it near the surface and gradually increasing it as the depth
increases.
There are three levels of surface clarity available: low, medium, or high.
It can also be turned off. The default level is off.
To adjust the Surface Clarity level:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to SONAR FEATURES|ENT|ENT.
88
Page 95

Sonar Features menu with Surface Clarity selected (at left, dual-
frequency menu; at right, single-frequency menu).
2. Press ↓ or ↑ to select clarity level|EXIT|EXIT.
Surface clutter
In the illustration at left, Surface Clarity is turned off.
The right view shows Surface Clarity set at High.
89
Page 96

Transparency
Use the transparency menu to adjust the transparency of menu windows. A high transparency allows you to continue monitoring the sonar
chart while adjusting feature settings, though the text of the menus
may fade until it is unreadable. A low transparency will usually make
menu text easier to read, at the cost of watching your sonar returns.
Experiment with this feature until you find the right level of transparency for your eyes.
Main Menu with Transparency command selected.
To adjust Menu Transparency level:
Press
MENU|MENU|↓ to TRANSPARENCY|ENT. The TRANSPARENCY slider bar
appears. Press ↑ or ↓ to move the bar. The lower end of the scale makes
the menus opaque; the upper end is maximum transparency.
Units of Measure
This menu sets the speed and distance (statute or nautical miles, meters), depth (feet, fathoms, or meters) and temperature (degrees Fahrenheit or Celsius). To change the units:
Press
MENU|MENU|↓ to UNITS OF MEASURE|ENT.
90
Page 97

The Units of Measure Menu.
To set Units of Measure: Press ↓ to the desired units, then press ENT.
After all the options are set as desired, press EXIT|EXIT to return to the
page display.
Volume
This command adjusts the speaker volume, which controls the sound
levels for keystrokes and alarms. If you want to turn off all sounds, set
the volume to zero.
To adjust volume:
1. Press
2. The Volume Control Bar appears. Press ↓ to decrease the volume; press
↑ to increase the volume. When it's set at the desired level, press
MENU|MENU|↓ to VOLUME|ENT.
EXIT.
Zoom & Zoom Bar
"Zooming" the display is a common, fast and easy method used to enlarge small detail, fish signals and the bottom with its associated structure. This unit lets you zoom the display quickly and easily by pressing
the Zoom In key,
ZIN.
91
Page 98

Pressing
ZIN once doubles the size (2X) of all echoes on the screen.
Pressing it again quadruples the size of the echoes (4X). Press the Zoom
Out key,
ZOUT, to return the display to the normal mode.
At left, Sonar Page, normal view. Center, same view zoomed to 2X.
Right, same view zoomed to 4X
Zoom Pan
Your unit has the handy ability to quickly zoom in on any portion of the
water column with just the touch of an arrow key. The Zoom Pan feature
lets you rapidly move the zoomed area up and down to different depths.
By "pointing" your zoom at different portions of the chart as it scrolls,
you can get a good, close-up look at structure or cover below you.
To use Zoom Pan, switch to a manual depth Range setting (see page 64)
and turn on 2X or 4X Zoom. Then, simply press ↑ or
↓ to pan up and
down the water column.
92
Page 99

Section 5: Troubleshooting
If your unit is not working, or if you need technical help, please use the
following troubleshooting section before contacting the factory customer
service department. It may save you the trouble of returning your unit
for repair. For contact information, refer to the last page, just inside the
back cover of this manual.
Unit won't turn on:
1. Check the power cable's connection at the unit. Also check the wiring.
2. Make certain the power cable is wired properly. The red wire connects to the positive battery terminal, black to negative or ground.
3. Check the fuse.
4. Measure the battery voltage at the unit's power connector. It should
be at least 11 volts. If it isn't, the wiring to the unit is defective, the
battery terminals or wiring on the terminals are corroded, or the battery needs charging.
Unit operates only in demo mode:
1. The transducer has not yet been connected or has been disconnected.
To leave demo mode, make sure the transducer is securely connected
before turning the unit on.
Unit freezes, locks up, or operates erratically:
1. Electrical noise from the boat's motor, trolling motor, or an accessory
may be interfering with the sonar unit. Rerouting the power and transducer cables away from other electrical wiring on the boat may help.
Route the sonar unit's power cable directly to the battery instead of
through a fuse block or ignition switch
2. Inspect the transducer cable for breaks, cuts, or pinched wires.
3. Check both the transducer and power connectors. Make certain both
are securely plugged in to the unit.
93
Page 100

Weak bottom echo, digital readings erratic, or no fish signals:
1. Make sure the transducer is pointing straight down. Clean the face
of the transducer. Oil, dirt and fuel can cause a film to form on the
transducer, reducing its effectiveness. If the transducer is mounted
inside the hull, be sure it is shooting through only one layer of fiberglass and that it is securely bonded to the hull. When attaching a
transducer to the inside of a hull, ONLY use the epoxy available from
LEI (order information is inside the back cover). Do NOT use RTV
silicone rubber adhesive or any other type of epoxy. The LEI epoxy is
specially formulated so that it will cure properly for shoot-through
applications.
2. Electrical noise from the boat's motor can interfere with the sonar.
This causes the sonar to automatically increase its Discrimination or
noise rejection feature. This can cause the unit to eliminate weaker
signals such as fish or even structure from the display.
3. The water may be deeper than the sonar's ability to find the bottom. If
the sonar can't find the bottom signal while it's in the automatic mode, the
digital sonar display will flash continuously. It may change the range to
limits far greater than the water you are in. If this happens, place the unit
in the manual mode, then change the range to a realistic one, (for example,
0-100 feet) and increase the sensitivity. As you move into shallower water,
a bottom signal should appear.
4. Check the battery voltage. If the voltage drops, the unit's transmitter
power also drops, reducing its ability to find the bottom or targets.
Bottom echo disappears at high speeds or erratic digital reading or weak bottom echo while boat is moving
1. The transducer may be in turbulent water. It must be mounted in a
smooth flow of water in order for the sonar to work at all boat speeds.
Air bubbles in the water disrupt the sonar signals, interfering with its
ability to find the bottom or other targets. The technical term for this is
cavitation.
94
 Loading...
Loading...